- Privacy Policy

Home » Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
Table of Contents

Survey Research
Definition:
Survey Research is a quantitative research method that involves collecting standardized data from a sample of individuals or groups through the use of structured questionnaires or interviews. The data collected is then analyzed statistically to identify patterns and relationships between variables, and to draw conclusions about the population being studied.
Survey research can be used to answer a variety of questions, including:
- What are people’s opinions about a certain topic?
- What are people’s experiences with a certain product or service?
- What are people’s beliefs about a certain issue?
Survey Research Methods
Survey Research Methods are as follows:
- Telephone surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents over the phone, often used in market research or political polling.
- Face-to-face surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents in person, often used in social or health research.
- Mail surveys: A survey research method where questionnaires are sent to respondents through mail, often used in customer satisfaction or opinion surveys.
- Online surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents through online platforms, often used in market research or customer feedback.
- Email surveys: A survey research method where questionnaires are sent to respondents through email, often used in customer satisfaction or opinion surveys.
- Mixed-mode surveys: A survey research method that combines two or more survey modes, often used to increase response rates or reach diverse populations.
- Computer-assisted surveys: A survey research method that uses computer technology to administer or collect survey data, often used in large-scale surveys or data collection.
- Interactive voice response surveys: A survey research method where respondents answer questions through a touch-tone telephone system, often used in automated customer satisfaction or opinion surveys.
- Mobile surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents through mobile devices, often used in market research or customer feedback.
- Group-administered surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to a group of respondents simultaneously, often used in education or training evaluation.
- Web-intercept surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to website visitors, often used in website or user experience research.
- In-app surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to users of a mobile application, often used in mobile app or user experience research.
- Social media surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents through social media platforms, often used in social media or brand awareness research.
- SMS surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents through text messaging, often used in customer feedback or opinion surveys.
- IVR surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents through an interactive voice response system, often used in automated customer feedback or opinion surveys.
- Mixed-method surveys: A survey research method that combines both qualitative and quantitative data collection methods, often used in exploratory or mixed-method research.
- Drop-off surveys: A survey research method where respondents are provided with a survey questionnaire and asked to return it at a later time or through a designated drop-off location.
- Intercept surveys: A survey research method where respondents are approached in public places and asked to participate in a survey, often used in market research or customer feedback.
- Hybrid surveys: A survey research method that combines two or more survey modes, data sources, or research methods, often used in complex or multi-dimensional research questions.
Types of Survey Research
There are several types of survey research that can be used to collect data from a sample of individuals or groups. following are Types of Survey Research:
- Cross-sectional survey: A type of survey research that gathers data from a sample of individuals at a specific point in time, providing a snapshot of the population being studied.
- Longitudinal survey: A type of survey research that gathers data from the same sample of individuals over an extended period of time, allowing researchers to track changes or trends in the population being studied.
- Panel survey: A type of longitudinal survey research that tracks the same sample of individuals over time, typically collecting data at multiple points in time.
- Epidemiological survey: A type of survey research that studies the distribution and determinants of health and disease in a population, often used to identify risk factors and inform public health interventions.
- Observational survey: A type of survey research that collects data through direct observation of individuals or groups, often used in behavioral or social research.
- Correlational survey: A type of survey research that measures the degree of association or relationship between two or more variables, often used to identify patterns or trends in data.
- Experimental survey: A type of survey research that involves manipulating one or more variables to observe the effect on an outcome, often used to test causal hypotheses.
- Descriptive survey: A type of survey research that describes the characteristics or attributes of a population or phenomenon, often used in exploratory research or to summarize existing data.
- Diagnostic survey: A type of survey research that assesses the current state or condition of an individual or system, often used in health or organizational research.
- Explanatory survey: A type of survey research that seeks to explain or understand the causes or mechanisms behind a phenomenon, often used in social or psychological research.
- Process evaluation survey: A type of survey research that measures the implementation and outcomes of a program or intervention, often used in program evaluation or quality improvement.
- Impact evaluation survey: A type of survey research that assesses the effectiveness or impact of a program or intervention, often used to inform policy or decision-making.
- Customer satisfaction survey: A type of survey research that measures the satisfaction or dissatisfaction of customers with a product, service, or experience, often used in marketing or customer service research.
- Market research survey: A type of survey research that collects data on consumer preferences, behaviors, or attitudes, often used in market research or product development.
- Public opinion survey: A type of survey research that measures the attitudes, beliefs, or opinions of a population on a specific issue or topic, often used in political or social research.
- Behavioral survey: A type of survey research that measures actual behavior or actions of individuals, often used in health or social research.
- Attitude survey: A type of survey research that measures the attitudes, beliefs, or opinions of individuals, often used in social or psychological research.
- Opinion poll: A type of survey research that measures the opinions or preferences of a population on a specific issue or topic, often used in political or media research.
- Ad hoc survey: A type of survey research that is conducted for a specific purpose or research question, often used in exploratory research or to answer a specific research question.
Types Based on Methodology
Based on Methodology Survey are divided into two Types:
Quantitative Survey Research
Qualitative survey research.
Quantitative survey research is a method of collecting numerical data from a sample of participants through the use of standardized surveys or questionnaires. The purpose of quantitative survey research is to gather empirical evidence that can be analyzed statistically to draw conclusions about a particular population or phenomenon.
In quantitative survey research, the questions are structured and pre-determined, often utilizing closed-ended questions, where participants are given a limited set of response options to choose from. This approach allows for efficient data collection and analysis, as well as the ability to generalize the findings to a larger population.
Quantitative survey research is often used in market research, social sciences, public health, and other fields where numerical data is needed to make informed decisions and recommendations.
Qualitative survey research is a method of collecting non-numerical data from a sample of participants through the use of open-ended questions or semi-structured interviews. The purpose of qualitative survey research is to gain a deeper understanding of the experiences, perceptions, and attitudes of participants towards a particular phenomenon or topic.
In qualitative survey research, the questions are open-ended, allowing participants to share their thoughts and experiences in their own words. This approach allows for a rich and nuanced understanding of the topic being studied, and can provide insights that are difficult to capture through quantitative methods alone.
Qualitative survey research is often used in social sciences, education, psychology, and other fields where a deeper understanding of human experiences and perceptions is needed to inform policy, practice, or theory.
Data Analysis Methods
There are several Survey Research Data Analysis Methods that researchers may use, including:
- Descriptive statistics: This method is used to summarize and describe the basic features of the survey data, such as the mean, median, mode, and standard deviation. These statistics can help researchers understand the distribution of responses and identify any trends or patterns.
- Inferential statistics: This method is used to make inferences about the larger population based on the data collected in the survey. Common inferential statistical methods include hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and correlation analysis.
- Factor analysis: This method is used to identify underlying factors or dimensions in the survey data. This can help researchers simplify the data and identify patterns and relationships that may not be immediately apparent.
- Cluster analysis: This method is used to group similar respondents together based on their survey responses. This can help researchers identify subgroups within the larger population and understand how different groups may differ in their attitudes, behaviors, or preferences.
- Structural equation modeling: This method is used to test complex relationships between variables in the survey data. It can help researchers understand how different variables may be related to one another and how they may influence one another.
- Content analysis: This method is used to analyze open-ended responses in the survey data. Researchers may use software to identify themes or categories in the responses, or they may manually review and code the responses.
- Text mining: This method is used to analyze text-based survey data, such as responses to open-ended questions. Researchers may use software to identify patterns and themes in the text, or they may manually review and code the text.
Applications of Survey Research
Here are some common applications of survey research:
- Market Research: Companies use survey research to gather insights about customer needs, preferences, and behavior. These insights are used to create marketing strategies and develop new products.
- Public Opinion Research: Governments and political parties use survey research to understand public opinion on various issues. This information is used to develop policies and make decisions.
- Social Research: Survey research is used in social research to study social trends, attitudes, and behavior. Researchers use survey data to explore topics such as education, health, and social inequality.
- Academic Research: Survey research is used in academic research to study various phenomena. Researchers use survey data to test theories, explore relationships between variables, and draw conclusions.
- Customer Satisfaction Research: Companies use survey research to gather information about customer satisfaction with their products and services. This information is used to improve customer experience and retention.
- Employee Surveys: Employers use survey research to gather feedback from employees about their job satisfaction, working conditions, and organizational culture. This information is used to improve employee retention and productivity.
- Health Research: Survey research is used in health research to study topics such as disease prevalence, health behaviors, and healthcare access. Researchers use survey data to develop interventions and improve healthcare outcomes.
Examples of Survey Research
Here are some real-time examples of survey research:
- COVID-19 Pandemic Surveys: Since the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, surveys have been conducted to gather information about public attitudes, behaviors, and perceptions related to the pandemic. Governments and healthcare organizations have used this data to develop public health strategies and messaging.
- Political Polls During Elections: During election seasons, surveys are used to measure public opinion on political candidates, policies, and issues in real-time. This information is used by political parties to develop campaign strategies and make decisions.
- Customer Feedback Surveys: Companies often use real-time customer feedback surveys to gather insights about customer experience and satisfaction. This information is used to improve products and services quickly.
- Event Surveys: Organizers of events such as conferences and trade shows often use surveys to gather feedback from attendees in real-time. This information can be used to improve future events and make adjustments during the current event.
- Website and App Surveys: Website and app owners use surveys to gather real-time feedback from users about the functionality, user experience, and overall satisfaction with their platforms. This feedback can be used to improve the user experience and retain customers.
- Employee Pulse Surveys: Employers use real-time pulse surveys to gather feedback from employees about their work experience and overall job satisfaction. This feedback is used to make changes in real-time to improve employee retention and productivity.
Survey Sample
Purpose of survey research.
The purpose of survey research is to gather data and insights from a representative sample of individuals. Survey research allows researchers to collect data quickly and efficiently from a large number of people, making it a valuable tool for understanding attitudes, behaviors, and preferences.
Here are some common purposes of survey research:
- Descriptive Research: Survey research is often used to describe characteristics of a population or a phenomenon. For example, a survey could be used to describe the characteristics of a particular demographic group, such as age, gender, or income.
- Exploratory Research: Survey research can be used to explore new topics or areas of research. Exploratory surveys are often used to generate hypotheses or identify potential relationships between variables.
- Explanatory Research: Survey research can be used to explain relationships between variables. For example, a survey could be used to determine whether there is a relationship between educational attainment and income.
- Evaluation Research: Survey research can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of a program or intervention. For example, a survey could be used to evaluate the impact of a health education program on behavior change.
- Monitoring Research: Survey research can be used to monitor trends or changes over time. For example, a survey could be used to monitor changes in attitudes towards climate change or political candidates over time.
When to use Survey Research
there are certain circumstances where survey research is particularly appropriate. Here are some situations where survey research may be useful:
- When the research question involves attitudes, beliefs, or opinions: Survey research is particularly useful for understanding attitudes, beliefs, and opinions on a particular topic. For example, a survey could be used to understand public opinion on a political issue.
- When the research question involves behaviors or experiences: Survey research can also be useful for understanding behaviors and experiences. For example, a survey could be used to understand the prevalence of a particular health behavior.
- When a large sample size is needed: Survey research allows researchers to collect data from a large number of people quickly and efficiently. This makes it a useful method when a large sample size is needed to ensure statistical validity.
- When the research question is time-sensitive: Survey research can be conducted quickly, which makes it a useful method when the research question is time-sensitive. For example, a survey could be used to understand public opinion on a breaking news story.
- When the research question involves a geographically dispersed population: Survey research can be conducted online, which makes it a useful method when the population of interest is geographically dispersed.
How to Conduct Survey Research
Conducting survey research involves several steps that need to be carefully planned and executed. Here is a general overview of the process:
- Define the research question: The first step in conducting survey research is to clearly define the research question. The research question should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the population of interest.
- Develop a survey instrument : The next step is to develop a survey instrument. This can be done using various methods, such as online survey tools or paper surveys. The survey instrument should be designed to elicit the information needed to answer the research question, and should be pre-tested with a small sample of individuals.
- Select a sample : The sample is the group of individuals who will be invited to participate in the survey. The sample should be representative of the population of interest, and the size of the sample should be sufficient to ensure statistical validity.
- Administer the survey: The survey can be administered in various ways, such as online, by mail, or in person. The method of administration should be chosen based on the population of interest and the research question.
- Analyze the data: Once the survey data is collected, it needs to be analyzed. This involves summarizing the data using statistical methods, such as frequency distributions or regression analysis.
- Draw conclusions: The final step is to draw conclusions based on the data analysis. This involves interpreting the results and answering the research question.
Advantages of Survey Research
There are several advantages to using survey research, including:
- Efficient data collection: Survey research allows researchers to collect data quickly and efficiently from a large number of people. This makes it a useful method for gathering information on a wide range of topics.
- Standardized data collection: Surveys are typically standardized, which means that all participants receive the same questions in the same order. This ensures that the data collected is consistent and reliable.
- Cost-effective: Surveys can be conducted online, by mail, or in person, which makes them a cost-effective method of data collection.
- Anonymity: Participants can remain anonymous when responding to a survey. This can encourage participants to be more honest and open in their responses.
- Easy comparison: Surveys allow for easy comparison of data between different groups or over time. This makes it possible to identify trends and patterns in the data.
- Versatility: Surveys can be used to collect data on a wide range of topics, including attitudes, beliefs, behaviors, and preferences.
Limitations of Survey Research
Here are some of the main limitations of survey research:
- Limited depth: Surveys are typically designed to collect quantitative data, which means that they do not provide much depth or detail about people’s experiences or opinions. This can limit the insights that can be gained from the data.
- Potential for bias: Surveys can be affected by various biases, including selection bias, response bias, and social desirability bias. These biases can distort the results and make them less accurate.
- L imited validity: Surveys are only as valid as the questions they ask. If the questions are poorly designed or ambiguous, the results may not accurately reflect the respondents’ attitudes or behaviors.
- Limited generalizability : Survey results are only generalizable to the population from which the sample was drawn. If the sample is not representative of the population, the results may not be generalizable to the larger population.
- Limited ability to capture context: Surveys typically do not capture the context in which attitudes or behaviors occur. This can make it difficult to understand the reasons behind the responses.
- Limited ability to capture complex phenomena: Surveys are not well-suited to capture complex phenomena, such as emotions or the dynamics of interpersonal relationships.
Following is an example of a Survey Sample:
Welcome to our Survey Research Page! We value your opinions and appreciate your participation in this survey. Please answer the questions below as honestly and thoroughly as possible.
1. What is your age?
- A) Under 18
- G) 65 or older
2. What is your highest level of education completed?
- A) Less than high school
- B) High school or equivalent
- C) Some college or technical school
- D) Bachelor’s degree
- E) Graduate or professional degree
3. What is your current employment status?
- A) Employed full-time
- B) Employed part-time
- C) Self-employed
- D) Unemployed
4. How often do you use the internet per day?
- A) Less than 1 hour
- B) 1-3 hours
- C) 3-5 hours
- D) 5-7 hours
- E) More than 7 hours
5. How often do you engage in social media per day?
6. Have you ever participated in a survey research study before?
7. If you have participated in a survey research study before, how was your experience?
- A) Excellent
- E) Very poor
8. What are some of the topics that you would be interested in participating in a survey research study about?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
9. How often would you be willing to participate in survey research studies?
- A) Once a week
- B) Once a month
- C) Once every 6 months
- D) Once a year
10. Any additional comments or suggestions?
Thank you for taking the time to complete this survey. Your feedback is important to us and will help us improve our survey research efforts.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Survey Research: Definition, Examples and Methods

Survey Research is a quantitative research method used for collecting data from a set of respondents. It has been perhaps one of the most used methodologies in the industry for several years due to the multiple benefits and advantages that it has when collecting and analyzing data.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Research
In this article, you will learn everything about survey research, such as types, methods, and examples.
Survey Research Definition
Survey Research is defined as the process of conducting research using surveys that researchers send to survey respondents. The data collected from surveys is then statistically analyzed to draw meaningful research conclusions. In the 21st century, every organization’s eager to understand what their customers think about their products or services and make better business decisions. Researchers can conduct research in multiple ways, but surveys are proven to be one of the most effective and trustworthy research methods. An online survey is a method for extracting information about a significant business matter from an individual or a group of individuals. It consists of structured survey questions that motivate the participants to respond. Creditable survey research can give these businesses access to a vast information bank. Organizations in media, other companies, and even governments rely on survey research to obtain accurate data.
The traditional definition of survey research is a quantitative method for collecting information from a pool of respondents by asking multiple survey questions. This research type includes the recruitment of individuals collection, and analysis of data. It’s useful for researchers who aim to communicate new features or trends to their respondents.
LEARN ABOUT: Level of Analysis Generally, it’s the primary step towards obtaining quick information about mainstream topics and conducting more rigorous and detailed quantitative research methods like surveys/polls or qualitative research methods like focus groups/on-call interviews can follow. There are many situations where researchers can conduct research using a blend of both qualitative and quantitative strategies.
LEARN ABOUT: Survey Sampling
Survey Research Methods
Survey research methods can be derived based on two critical factors: Survey research tool and time involved in conducting research. There are three main survey research methods, divided based on the medium of conducting survey research:
- Online/ Email: Online survey research is one of the most popular survey research methods today. The survey cost involved in online survey research is extremely minimal, and the responses gathered are highly accurate.
- Phone: Survey research conducted over the telephone ( CATI survey ) can be useful in collecting data from a more extensive section of the target population. There are chances that the money invested in phone surveys will be higher than other mediums, and the time required will be higher.
- Face-to-face: Researchers conduct face-to-face in-depth interviews in situations where there is a complicated problem to solve. The response rate for this method is the highest, but it can be costly.
Further, based on the time taken, survey research can be classified into two methods:
- Longitudinal survey research: Longitudinal survey research involves conducting survey research over a continuum of time and spread across years and decades. The data collected using this survey research method from one time period to another is qualitative or quantitative. Respondent behavior, preferences, and attitudes are continuously observed over time to analyze reasons for a change in behavior or preferences. For example, suppose a researcher intends to learn about the eating habits of teenagers. In that case, he/she will follow a sample of teenagers over a considerable period to ensure that the collected information is reliable. Often, cross-sectional survey research follows a longitudinal study .
- Cross-sectional survey research: Researchers conduct a cross-sectional survey to collect insights from a target audience at a particular time interval. This survey research method is implemented in various sectors such as retail, education, healthcare, SME businesses, etc. Cross-sectional studies can either be descriptive or analytical. It is quick and helps researchers collect information in a brief period. Researchers rely on the cross-sectional survey research method in situations where descriptive analysis of a subject is required.
Survey research also is bifurcated according to the sampling methods used to form samples for research: Probability and Non-probability sampling. Every individual in a population should be considered equally to be a part of the survey research sample. Probability sampling is a sampling method in which the researcher chooses the elements based on probability theory. The are various probability research methods, such as simple random sampling , systematic sampling, cluster sampling, stratified random sampling, etc. Non-probability sampling is a sampling method where the researcher uses his/her knowledge and experience to form samples.
LEARN ABOUT: Survey Sample Sizes
The various non-probability sampling techniques are :
- Convenience sampling
- Snowball sampling
- Consecutive sampling
- Judgemental sampling
- Quota sampling
Process of implementing survey research methods:
- Decide survey questions: Brainstorm and put together valid survey questions that are grammatically and logically appropriate. Understanding the objective and expected outcomes of the survey helps a lot. There are many surveys where details of responses are not as important as gaining insights about what customers prefer from the provided options. In such situations, a researcher can include multiple-choice questions or closed-ended questions . Whereas, if researchers need to obtain details about specific issues, they can consist of open-ended questions in the questionnaire. Ideally, the surveys should include a smart balance of open-ended and closed-ended questions. Use survey questions like Likert Scale , Semantic Scale, Net Promoter Score question, etc., to avoid fence-sitting.
LEARN ABOUT: System Usability Scale
- Finalize a target audience: Send out relevant surveys as per the target audience and filter out irrelevant questions as per the requirement. The survey research will be instrumental in case the target population decides on a sample. This way, results can be according to the desired market and be generalized to the entire population.
LEARN ABOUT: Testimonial Questions
- Send out surveys via decided mediums: Distribute the surveys to the target audience and patiently wait for the feedback and comments- this is the most crucial step of the survey research. The survey needs to be scheduled, keeping in mind the nature of the target audience and its regions. Surveys can be conducted via email, embedded in a website, shared via social media, etc., to gain maximum responses.
- Analyze survey results: Analyze the feedback in real-time and identify patterns in the responses which might lead to a much-needed breakthrough for your organization. GAP, TURF Analysis , Conjoint analysis, Cross tabulation, and many such survey feedback analysis methods can be used to spot and shed light on respondent behavior. Researchers can use the results to implement corrective measures to improve customer/employee satisfaction.
Reasons to conduct survey research
The most crucial and integral reason for conducting market research using surveys is that you can collect answers regarding specific, essential questions. You can ask these questions in multiple survey formats as per the target audience and the intent of the survey. Before designing a study, every organization must figure out the objective of carrying this out so that the study can be structured, planned, and executed to perfection.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
Questions that need to be on your mind while designing a survey are:
- What is the primary aim of conducting the survey?
- How do you plan to utilize the collected survey data?
- What type of decisions do you plan to take based on the points mentioned above?
There are three critical reasons why an organization must conduct survey research.
- Understand respondent behavior to get solutions to your queries: If you’ve carefully curated a survey, the respondents will provide insights about what they like about your organization as well as suggestions for improvement. To motivate them to respond, you must be very vocal about how secure their responses will be and how you will utilize the answers. This will push them to be 100% honest about their feedback, opinions, and comments. Online surveys or mobile surveys have proved their privacy, and due to this, more and more respondents feel free to put forth their feedback through these mediums.
- Present a medium for discussion: A survey can be the perfect platform for respondents to provide criticism or applause for an organization. Important topics like product quality or quality of customer service etc., can be put on the table for discussion. A way you can do it is by including open-ended questions where the respondents can write their thoughts. This will make it easy for you to correlate your survey to what you intend to do with your product or service.
- Strategy for never-ending improvements: An organization can establish the target audience’s attributes from the pilot phase of survey research . Researchers can use the criticism and feedback received from this survey to improve the product/services. Once the company successfully makes the improvements, it can send out another survey to measure the change in feedback keeping the pilot phase the benchmark. By doing this activity, the organization can track what was effectively improved and what still needs improvement.
Survey Research Scales
There are four main scales for the measurement of variables:
- Nominal Scale: A nominal scale associates numbers with variables for mere naming or labeling, and the numbers usually have no other relevance. It is the most basic of the four levels of measurement.
- Ordinal Scale: The ordinal scale has an innate order within the variables along with labels. It establishes the rank between the variables of a scale but not the difference value between the variables.
- Interval Scale: The interval scale is a step ahead in comparison to the other two scales. Along with establishing a rank and name of variables, the scale also makes known the difference between the two variables. The only drawback is that there is no fixed start point of the scale, i.e., the actual zero value is absent.
- Ratio Scale: The ratio scale is the most advanced measurement scale, which has variables that are labeled in order and have a calculated difference between variables. In addition to what interval scale orders, this scale has a fixed starting point, i.e., the actual zero value is present.
Benefits of survey research
In case survey research is used for all the right purposes and is implemented properly, marketers can benefit by gaining useful, trustworthy data that they can use to better the ROI of the organization.
Other benefits of survey research are:
- Minimum investment: Mobile surveys and online surveys have minimal finance invested per respondent. Even with the gifts and other incentives provided to the people who participate in the study, online surveys are extremely economical compared to paper-based surveys.
- Versatile sources for response collection: You can conduct surveys via various mediums like online and mobile surveys. You can further classify them into qualitative mediums like focus groups , and interviews and quantitative mediums like customer-centric surveys. Due to the offline survey response collection option, researchers can conduct surveys in remote areas with limited internet connectivity. This can make data collection and analysis more convenient and extensive.
- Reliable for respondents: Surveys are extremely secure as the respondent details and responses are kept safeguarded. This anonymity makes respondents answer the survey questions candidly and with absolute honesty. An organization seeking to receive explicit responses for its survey research must mention that it will be confidential.
Survey research design
Researchers implement a survey research design in cases where there is a limited cost involved and there is a need to access details easily. This method is often used by small and large organizations to understand and analyze new trends, market demands, and opinions. Collecting information through tactfully designed survey research can be much more effective and productive than a casually conducted survey.
There are five stages of survey research design:
- Decide an aim of the research: There can be multiple reasons for a researcher to conduct a survey, but they need to decide a purpose for the research. This is the primary stage of survey research as it can mold the entire path of a survey, impacting its results.
- Filter the sample from target population: Who to target? is an essential question that a researcher should answer and keep in mind while conducting research. The precision of the results is driven by who the members of a sample are and how useful their opinions are. The quality of respondents in a sample is essential for the results received for research and not the quantity. If a researcher seeks to understand whether a product feature will work well with their target market, he/she can conduct survey research with a group of market experts for that product or technology.
- Zero-in on a survey method: Many qualitative and quantitative research methods can be discussed and decided. Focus groups, online interviews, surveys, polls, questionnaires, etc. can be carried out with a pre-decided sample of individuals.
- Design the questionnaire: What will the content of the survey be? A researcher is required to answer this question to be able to design it effectively. What will the content of the cover letter be? Or what are the survey questions of this questionnaire? Understand the target market thoroughly to create a questionnaire that targets a sample to gain insights about a survey research topic.
- Send out surveys and analyze results: Once the researcher decides on which questions to include in a study, they can send it across to the selected sample . Answers obtained from this survey can be analyzed to make product-related or marketing-related decisions.
Survey examples: 10 tips to design the perfect research survey
Picking the right survey design can be the key to gaining the information you need to make crucial decisions for all your research. It is essential to choose the right topic, choose the right question types, and pick a corresponding design. If this is your first time creating a survey, it can seem like an intimidating task. But with QuestionPro, each step of the process is made simple and easy.
Below are 10 Tips To Design The Perfect Research Survey:
- Set your SMART goals: Before conducting any market research or creating a particular plan, set your SMART Goals . What is that you want to achieve with the survey? How will you measure it promptly, and what are the results you are expecting?
- Choose the right questions: Designing a survey can be a tricky task. Asking the right questions may help you get the answers you are looking for and ease the task of analyzing. So, always choose those specific questions – relevant to your research.
- Begin your survey with a generalized question: Preferably, start your survey with a general question to understand whether the respondent uses the product or not. That also provides an excellent base and intro for your survey.
- Enhance your survey: Choose the best, most relevant, 15-20 questions. Frame each question as a different question type based on the kind of answer you would like to gather from each. Create a survey using different types of questions such as multiple-choice, rating scale, open-ended, etc. Look at more survey examples and four measurement scales every researcher should remember.
- Prepare yes/no questions: You may also want to use yes/no questions to separate people or branch them into groups of those who “have purchased” and those who “have not yet purchased” your products or services. Once you separate them, you can ask them different questions.
- Test all electronic devices: It becomes effortless to distribute your surveys if respondents can answer them on different electronic devices like mobiles, tablets, etc. Once you have created your survey, it’s time to TEST. You can also make any corrections if needed at this stage.
- Distribute your survey: Once your survey is ready, it is time to share and distribute it to the right audience. You can share handouts and share them via email, social media, and other industry-related offline/online communities.
- Collect and analyze responses: After distributing your survey, it is time to gather all responses. Make sure you store your results in a particular document or an Excel sheet with all the necessary categories mentioned so that you don’t lose your data. Remember, this is the most crucial stage. Segregate your responses based on demographics, psychographics, and behavior. This is because, as a researcher, you must know where your responses are coming from. It will help you to analyze, predict decisions, and help write the summary report.
- Prepare your summary report: Now is the time to share your analysis. At this stage, you should mention all the responses gathered from a survey in a fixed format. Also, the reader/customer must get clarity about your goal, which you were trying to gain from the study. Questions such as – whether the product or service has been used/preferred or not. Do respondents prefer some other product to another? Any recommendations?
Having a tool that helps you carry out all the necessary steps to carry out this type of study is a vital part of any project. At QuestionPro, we have helped more than 10,000 clients around the world to carry out data collection in a simple and effective way, in addition to offering a wide range of solutions to take advantage of this data in the best possible way.
From dashboards, advanced analysis tools, automation, and dedicated functions, in QuestionPro, you will find everything you need to execute your research projects effectively. Uncover insights that matter the most!
MORE LIKE THIS

Top 20 Employee Engagement Software Solutions
May 3, 2024

15 Best Customer Experience Software of 2024
May 2, 2024

Journey Orchestration Platforms: Top 11 Platforms in 2024

Top 12 Employee Pulse Survey Tools Unlocking Insights in 2024
May 1, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9 Survey research
Survey research is a research method involving the use of standardised questionnaires or interviews to collect data about people and their preferences, thoughts, and behaviours in a systematic manner. Although census surveys were conducted as early as Ancient Egypt, survey as a formal research method was pioneered in the 1930–40s by sociologist Paul Lazarsfeld to examine the effects of the radio on political opinion formation of the United States. This method has since become a very popular method for quantitative research in the social sciences.
The survey method can be used for descriptive, exploratory, or explanatory research. This method is best suited for studies that have individual people as the unit of analysis. Although other units of analysis, such as groups, organisations or dyads—pairs of organisations, such as buyers and sellers—are also studied using surveys, such studies often use a specific person from each unit as a ‘key informant’ or a ‘proxy’ for that unit. Consequently, such surveys may be subject to respondent bias if the chosen informant does not have adequate knowledge or has a biased opinion about the phenomenon of interest. For instance, Chief Executive Officers may not adequately know employees’ perceptions or teamwork in their own companies, and may therefore be the wrong informant for studies of team dynamics or employee self-esteem.
Survey research has several inherent strengths compared to other research methods. First, surveys are an excellent vehicle for measuring a wide variety of unobservable data, such as people’s preferences (e.g., political orientation), traits (e.g., self-esteem), attitudes (e.g., toward immigrants), beliefs (e.g., about a new law), behaviours (e.g., smoking or drinking habits), or factual information (e.g., income). Second, survey research is also ideally suited for remotely collecting data about a population that is too large to observe directly. A large area—such as an entire country—can be covered by postal, email, or telephone surveys using meticulous sampling to ensure that the population is adequately represented in a small sample. Third, due to their unobtrusive nature and the ability to respond at one’s convenience, questionnaire surveys are preferred by some respondents. Fourth, interviews may be the only way of reaching certain population groups such as the homeless or illegal immigrants for which there is no sampling frame available. Fifth, large sample surveys may allow detection of small effects even while analysing multiple variables, and depending on the survey design, may also allow comparative analysis of population subgroups (i.e., within-group and between-group analysis). Sixth, survey research is more economical in terms of researcher time, effort and cost than other methods such as experimental research and case research. At the same time, survey research also has some unique disadvantages. It is subject to a large number of biases such as non-response bias, sampling bias, social desirability bias, and recall bias, as discussed at the end of this chapter.
Depending on how the data is collected, survey research can be divided into two broad categories: questionnaire surveys (which may be postal, group-administered, or online surveys), and interview surveys (which may be personal, telephone, or focus group interviews). Questionnaires are instruments that are completed in writing by respondents, while interviews are completed by the interviewer based on verbal responses provided by respondents. As discussed below, each type has its own strengths and weaknesses in terms of their costs, coverage of the target population, and researcher’s flexibility in asking questions.
Questionnaire surveys
Invented by Sir Francis Galton, a questionnaire is a research instrument consisting of a set of questions (items) intended to capture responses from respondents in a standardised manner. Questions may be unstructured or structured. Unstructured questions ask respondents to provide a response in their own words, while structured questions ask respondents to select an answer from a given set of choices. Subjects’ responses to individual questions (items) on a structured questionnaire may be aggregated into a composite scale or index for statistical analysis. Questions should be designed in such a way that respondents are able to read, understand, and respond to them in a meaningful way, and hence the survey method may not be appropriate or practical for certain demographic groups such as children or the illiterate.
Most questionnaire surveys tend to be self-administered postal surveys , where the same questionnaire is posted to a large number of people, and willing respondents can complete the survey at their convenience and return it in prepaid envelopes. Postal surveys are advantageous in that they are unobtrusive and inexpensive to administer, since bulk postage is cheap in most countries. However, response rates from postal surveys tend to be quite low since most people ignore survey requests. There may also be long delays (several months) in respondents’ completing and returning the survey, or they may even simply lose it. Hence, the researcher must continuously monitor responses as they are being returned, track and send non-respondents repeated reminders (two or three reminders at intervals of one to one and a half months is ideal). Questionnaire surveys are also not well-suited for issues that require clarification on the part of the respondent or those that require detailed written responses. Longitudinal designs can be used to survey the same set of respondents at different times, but response rates tend to fall precipitously from one survey to the next.
A second type of survey is a group-administered questionnaire . A sample of respondents is brought together at a common place and time, and each respondent is asked to complete the survey questionnaire while in that room. Respondents enter their responses independently without interacting with one another. This format is convenient for the researcher, and a high response rate is assured. If respondents do not understand any specific question, they can ask for clarification. In many organisations, it is relatively easy to assemble a group of employees in a conference room or lunch room, especially if the survey is approved by corporate executives.
A more recent type of questionnaire survey is an online or web survey. These surveys are administered over the Internet using interactive forms. Respondents may receive an email request for participation in the survey with a link to a website where the survey may be completed. Alternatively, the survey may be embedded into an email, and can be completed and returned via email. These surveys are very inexpensive to administer, results are instantly recorded in an online database, and the survey can be easily modified if needed. However, if the survey website is not password-protected or designed to prevent multiple submissions, the responses can be easily compromised. Furthermore, sampling bias may be a significant issue since the survey cannot reach people who do not have computer or Internet access, such as many of the poor, senior, and minority groups, and the respondent sample is skewed toward a younger demographic who are online much of the time and have the time and ability to complete such surveys. Computing the response rate may be problematic if the survey link is posted on LISTSERVs or bulletin boards instead of being emailed directly to targeted respondents. For these reasons, many researchers prefer dual-media surveys (e.g., postal survey and online survey), allowing respondents to select their preferred method of response.
Constructing a survey questionnaire is an art. Numerous decisions must be made about the content of questions, their wording, format, and sequencing, all of which can have important consequences for the survey responses.
Response formats. Survey questions may be structured or unstructured. Responses to structured questions are captured using one of the following response formats:
Dichotomous response , where respondents are asked to select one of two possible choices, such as true/false, yes/no, or agree/disagree. An example of such a question is: Do you think that the death penalty is justified under some circumstances? (circle one): yes / no.
Nominal response , where respondents are presented with more than two unordered options, such as: What is your industry of employment?: manufacturing / consumer services / retail / education / healthcare / tourism and hospitality / other.
Ordinal response , where respondents have more than two ordered options, such as: What is your highest level of education?: high school / bachelor’s degree / postgraduate degree.
Interval-level response , where respondents are presented with a 5-point or 7-point Likert scale, semantic differential scale, or Guttman scale. Each of these scale types were discussed in a previous chapter.
Continuous response , where respondents enter a continuous (ratio-scaled) value with a meaningful zero point, such as their age or tenure in a firm. These responses generally tend to be of the fill-in-the blanks type.
Question content and wording. Responses obtained in survey research are very sensitive to the types of questions asked. Poorly framed or ambiguous questions will likely result in meaningless responses with very little value. Dillman (1978) [1] recommends several rules for creating good survey questions. Every single question in a survey should be carefully scrutinised for the following issues:
Is the question clear and understandable ?: Survey questions should be stated in very simple language, preferably in active voice, and without complicated words or jargon that may not be understood by a typical respondent. All questions in the questionnaire should be worded in a similar manner to make it easy for respondents to read and understand them. The only exception is if your survey is targeted at a specialised group of respondents, such as doctors, lawyers and researchers, who use such jargon in their everyday environment. Is the question worded in a negative manner ?: Negatively worded questions such as ‘Should your local government not raise taxes?’ tend to confuse many respondents and lead to inaccurate responses. Double-negatives should be avoided when designing survey questions.
Is the question ambiguous ?: Survey questions should not use words or expressions that may be interpreted differently by different respondents (e.g., words like ‘any’ or ‘just’). For instance, if you ask a respondent, ‘What is your annual income?’, it is unclear whether you are referring to salary/wages, or also dividend, rental, and other income, whether you are referring to personal income, family income (including spouse’s wages), or personal and business income. Different interpretation by different respondents will lead to incomparable responses that cannot be interpreted correctly.
Does the question have biased or value-laden words ?: Bias refers to any property of a question that encourages subjects to answer in a certain way. Kenneth Rasinky (1989) [2] examined several studies on people’s attitude toward government spending, and observed that respondents tend to indicate stronger support for ‘assistance to the poor’ and less for ‘welfare’, even though both terms had the same meaning. In this study, more support was also observed for ‘halting rising crime rate’ and less for ‘law enforcement’, more for ‘solving problems of big cities’ and less for ‘assistance to big cities’, and more for ‘dealing with drug addiction’ and less for ‘drug rehabilitation’. A biased language or tone tends to skew observed responses. It is often difficult to anticipate in advance the biasing wording, but to the greatest extent possible, survey questions should be carefully scrutinised to avoid biased language.
Is the question double-barrelled ?: Double-barrelled questions are those that can have multiple answers. For example, ‘Are you satisfied with the hardware and software provided for your work?’. In this example, how should a respondent answer if they are satisfied with the hardware, but not with the software, or vice versa? It is always advisable to separate double-barrelled questions into separate questions: ‘Are you satisfied with the hardware provided for your work?’, and ’Are you satisfied with the software provided for your work?’. Another example: ‘Does your family favour public television?’. Some people may favour public TV for themselves, but favour certain cable TV programs such as Sesame Street for their children.
Is the question too general ?: Sometimes, questions that are too general may not accurately convey respondents’ perceptions. If you asked someone how they liked a certain book and provided a response scale ranging from ‘not at all’ to ‘extremely well’, if that person selected ‘extremely well’, what do they mean? Instead, ask more specific behavioural questions, such as, ‘Will you recommend this book to others, or do you plan to read other books by the same author?’. Likewise, instead of asking, ‘How big is your firm?’ (which may be interpreted differently by respondents), ask, ‘How many people work for your firm?’, and/or ‘What is the annual revenue of your firm?’, which are both measures of firm size.
Is the question too detailed ?: Avoid unnecessarily detailed questions that serve no specific research purpose. For instance, do you need the age of each child in a household, or is just the number of children in the household acceptable? However, if unsure, it is better to err on the side of details than generality.
Is the question presumptuous ?: If you ask, ‘What do you see as the benefits of a tax cut?’, you are presuming that the respondent sees the tax cut as beneficial. Many people may not view tax cuts as being beneficial, because tax cuts generally lead to lesser funding for public schools, larger class sizes, and fewer public services such as police, ambulance, and fire services. Avoid questions with built-in presumptions.
Is the question imaginary ?: A popular question in many television game shows is, ‘If you win a million dollars on this show, how will you spend it?’. Most respondents have never been faced with such an amount of money before and have never thought about it—they may not even know that after taxes, they will get only about $640,000 or so in the United States, and in many cases, that amount is spread over a 20-year period—and so their answers tend to be quite random, such as take a tour around the world, buy a restaurant or bar, spend on education, save for retirement, help parents or children, or have a lavish wedding. Imaginary questions have imaginary answers, which cannot be used for making scientific inferences.
Do respondents have the information needed to correctly answer the question ?: Oftentimes, we assume that subjects have the necessary information to answer a question, when in reality, they do not. Even if a response is obtained, these responses tend to be inaccurate given the subjects’ lack of knowledge about the question being asked. For instance, we should not ask the CEO of a company about day-to-day operational details that they may not be aware of, or ask teachers about how much their students are learning, or ask high-schoolers, ‘Do you think the US Government acted appropriately in the Bay of Pigs crisis?’.
Question sequencing. In general, questions should flow logically from one to the next. To achieve the best response rates, questions should flow from the least sensitive to the most sensitive, from the factual and behavioural to the attitudinal, and from the more general to the more specific. Some general rules for question sequencing:
Start with easy non-threatening questions that can be easily recalled. Good options are demographics (age, gender, education level) for individual-level surveys and firmographics (employee count, annual revenues, industry) for firm-level surveys.
Never start with an open ended question.
If following a historical sequence of events, follow a chronological order from earliest to latest.
Ask about one topic at a time. When switching topics, use a transition, such as, ‘The next section examines your opinions about…’
Use filter or contingency questions as needed, such as, ‘If you answered “yes” to question 5, please proceed to Section 2. If you answered “no” go to Section 3′.
Other golden rules . Do unto your respondents what you would have them do unto you. Be attentive and appreciative of respondents’ time, attention, trust, and confidentiality of personal information. Always practice the following strategies for all survey research:
People’s time is valuable. Be respectful of their time. Keep your survey as short as possible and limit it to what is absolutely necessary. Respondents do not like spending more than 10-15 minutes on any survey, no matter how important it is. Longer surveys tend to dramatically lower response rates.
Always assure respondents about the confidentiality of their responses, and how you will use their data (e.g., for academic research) and how the results will be reported (usually, in the aggregate).
For organisational surveys, assure respondents that you will send them a copy of the final results, and make sure that you follow up with your promise.
Thank your respondents for their participation in your study.
Finally, always pretest your questionnaire, at least using a convenience sample, before administering it to respondents in a field setting. Such pretesting may uncover ambiguity, lack of clarity, or biases in question wording, which should be eliminated before administering to the intended sample.
Interview survey
Interviews are a more personalised data collection method than questionnaires, and are conducted by trained interviewers using the same research protocol as questionnaire surveys (i.e., a standardised set of questions). However, unlike a questionnaire, the interview script may contain special instructions for the interviewer that are not seen by respondents, and may include space for the interviewer to record personal observations and comments. In addition, unlike postal surveys, the interviewer has the opportunity to clarify any issues raised by the respondent or ask probing or follow-up questions. However, interviews are time-consuming and resource-intensive. Interviewers need special interviewing skills as they are considered to be part of the measurement instrument, and must proactively strive not to artificially bias the observed responses.
The most typical form of interview is a personal or face-to-face interview , where the interviewer works directly with the respondent to ask questions and record their responses. Personal interviews may be conducted at the respondent’s home or office location. This approach may even be favoured by some respondents, while others may feel uncomfortable allowing a stranger into their homes. However, skilled interviewers can persuade respondents to co-operate, dramatically improving response rates.
A variation of the personal interview is a group interview, also called a focus group . In this technique, a small group of respondents (usually 6–10 respondents) are interviewed together in a common location. The interviewer is essentially a facilitator whose job is to lead the discussion, and ensure that every person has an opportunity to respond. Focus groups allow deeper examination of complex issues than other forms of survey research, because when people hear others talk, it often triggers responses or ideas that they did not think about before. However, focus group discussion may be dominated by a dominant personality, and some individuals may be reluctant to voice their opinions in front of their peers or superiors, especially while dealing with a sensitive issue such as employee underperformance or office politics. Because of their small sample size, focus groups are usually used for exploratory research rather than descriptive or explanatory research.
A third type of interview survey is a telephone interview . In this technique, interviewers contact potential respondents over the phone, typically based on a random selection of people from a telephone directory, to ask a standard set of survey questions. A more recent and technologically advanced approach is computer-assisted telephone interviewing (CATI). This is increasing being used by academic, government, and commercial survey researchers. Here the interviewer is a telephone operator who is guided through the interview process by a computer program displaying instructions and questions to be asked. The system also selects respondents randomly using a random digit dialling technique, and records responses using voice capture technology. Once respondents are on the phone, higher response rates can be obtained. This technique is not ideal for rural areas where telephone density is low, and also cannot be used for communicating non-audio information such as graphics or product demonstrations.
Role of interviewer. The interviewer has a complex and multi-faceted role in the interview process, which includes the following tasks:
Prepare for the interview: Since the interviewer is in the forefront of the data collection effort, the quality of data collected depends heavily on how well the interviewer is trained to do the job. The interviewer must be trained in the interview process and the survey method, and also be familiar with the purpose of the study, how responses will be stored and used, and sources of interviewer bias. They should also rehearse and time the interview prior to the formal study.
Locate and enlist the co-operation of respondents: Particularly in personal, in-home surveys, the interviewer must locate specific addresses, and work around respondents’ schedules at sometimes undesirable times such as during weekends. They should also be like a salesperson, selling the idea of participating in the study.
Motivate respondents: Respondents often feed off the motivation of the interviewer. If the interviewer is disinterested or inattentive, respondents will not be motivated to provide useful or informative responses either. The interviewer must demonstrate enthusiasm about the study, communicate the importance of the research to respondents, and be attentive to respondents’ needs throughout the interview.
Clarify any confusion or concerns: Interviewers must be able to think on their feet and address unanticipated concerns or objections raised by respondents to the respondents’ satisfaction. Additionally, they should ask probing questions as necessary even if such questions are not in the script.
Observe quality of response: The interviewer is in the best position to judge the quality of information collected, and may supplement responses obtained using personal observations of gestures or body language as appropriate.
Conducting the interview. Before the interview, the interviewer should prepare a kit to carry to the interview session, consisting of a cover letter from the principal investigator or sponsor, adequate copies of the survey instrument, photo identification, and a telephone number for respondents to call to verify the interviewer’s authenticity. The interviewer should also try to call respondents ahead of time to set up an appointment if possible. To start the interview, they should speak in an imperative and confident tone, such as, ‘I’d like to take a few minutes of your time to interview you for a very important study’, instead of, ‘May I come in to do an interview?’. They should introduce themself, present personal credentials, explain the purpose of the study in one to two sentences, and assure respondents that their participation is voluntary, and their comments are confidential, all in less than a minute. No big words or jargon should be used, and no details should be provided unless specifically requested. If the interviewer wishes to record the interview, they should ask for respondents’ explicit permission before doing so. Even if the interview is recorded, the interviewer must take notes on key issues, probes, or verbatim phrases
During the interview, the interviewer should follow the questionnaire script and ask questions exactly as written, and not change the words to make the question sound friendlier. They should also not change the order of questions or skip any question that may have been answered earlier. Any issues with the questions should be discussed during rehearsal prior to the actual interview sessions. The interviewer should not finish the respondent’s sentences. If the respondent gives a brief cursory answer, the interviewer should probe the respondent to elicit a more thoughtful, thorough response. Some useful probing techniques are:
The silent probe: Just pausing and waiting without going into the next question may suggest to respondents that the interviewer is waiting for more detailed response.
Overt encouragement: An occasional ‘uh-huh’ or ‘okay’ may encourage the respondent to go into greater details. However, the interviewer must not express approval or disapproval of what the respondent says.
Ask for elaboration: Such as, ‘Can you elaborate on that?’ or ‘A minute ago, you were talking about an experience you had in high school. Can you tell me more about that?’.
Reflection: The interviewer can try the psychotherapist’s trick of repeating what the respondent said. For instance, ‘What I’m hearing is that you found that experience very traumatic’ and then pause and wait for the respondent to elaborate.
After the interview is completed, the interviewer should thank respondents for their time, tell them when to expect the results, and not leave hastily. Immediately after leaving, they should write down any notes or key observations that may help interpret the respondent’s comments better.
Biases in survey research
Despite all of its strengths and advantages, survey research is often tainted with systematic biases that may invalidate some of the inferences derived from such surveys. Five such biases are the non-response bias, sampling bias, social desirability bias, recall bias, and common method bias.
Non-response bias. Survey research is generally notorious for its low response rates. A response rate of 15-20 per cent is typical in a postal survey, even after two or three reminders. If the majority of the targeted respondents fail to respond to a survey, this may indicate a systematic reason for the low response rate, which may in turn raise questions about the validity of the study’s results. For instance, dissatisfied customers tend to be more vocal about their experience than satisfied customers, and are therefore more likely to respond to questionnaire surveys or interview requests than satisfied customers. Hence, any respondent sample is likely to have a higher proportion of dissatisfied customers than the underlying population from which it is drawn. In this instance, not only will the results lack generalisability, but the observed outcomes may also be an artefact of the biased sample. Several strategies may be employed to improve response rates:
Advance notification: Sending a short letter to the targeted respondents soliciting their participation in an upcoming survey can prepare them in advance and improve their propensity to respond. The letter should state the purpose and importance of the study, mode of data collection (e.g., via a phone call, a survey form in the mail, etc.), and appreciation for their co-operation. A variation of this technique may be to ask the respondent to return a prepaid postcard indicating whether or not they are willing to participate in the study.
Relevance of content: People are more likely to respond to surveys examining issues of relevance or importance to them.
Respondent-friendly questionnaire: Shorter survey questionnaires tend to elicit higher response rates than longer questionnaires. Furthermore, questions that are clear, non-offensive, and easy to respond tend to attract higher response rates.
Endorsement: For organisational surveys, it helps to gain endorsement from a senior executive attesting to the importance of the study to the organisation. Such endorsement can be in the form of a cover letter or a letter of introduction, which can improve the researcher’s credibility in the eyes of the respondents.
Follow-up requests: Multiple follow-up requests may coax some non-respondents to respond, even if their responses are late.
Interviewer training: Response rates for interviews can be improved with skilled interviewers trained in how to request interviews, use computerised dialling techniques to identify potential respondents, and schedule call-backs for respondents who could not be reached.
Incentives : Incentives in the form of cash or gift cards, giveaways such as pens or stress balls, entry into a lottery, draw or contest, discount coupons, promise of contribution to charity, and so forth may increase response rates.
Non-monetary incentives: Businesses, in particular, are more prone to respond to non-monetary incentives than financial incentives. An example of such a non-monetary incentive is a benchmarking report comparing the business’s individual response against the aggregate of all responses to a survey.
Confidentiality and privacy: Finally, assurances that respondents’ private data or responses will not fall into the hands of any third party may help improve response rates
Sampling bias. Telephone surveys conducted by calling a random sample of publicly available telephone numbers will systematically exclude people with unlisted telephone numbers, mobile phone numbers, and people who are unable to answer the phone when the survey is being conducted—for instance, if they are at work—and will include a disproportionate number of respondents who have landline telephone services with listed phone numbers and people who are home during the day, such as the unemployed, the disabled, and the elderly. Likewise, online surveys tend to include a disproportionate number of students and younger people who are constantly on the Internet, and systematically exclude people with limited or no access to computers or the Internet, such as the poor and the elderly. Similarly, questionnaire surveys tend to exclude children and the illiterate, who are unable to read, understand, or meaningfully respond to the questionnaire. A different kind of sampling bias relates to sampling the wrong population, such as asking teachers (or parents) about their students’ (or children’s) academic learning, or asking CEOs about operational details in their company. Such biases make the respondent sample unrepresentative of the intended population and hurt generalisability claims about inferences drawn from the biased sample.
Social desirability bias . Many respondents tend to avoid negative opinions or embarrassing comments about themselves, their employers, family, or friends. With negative questions such as, ‘Do you think that your project team is dysfunctional?’, ‘Is there a lot of office politics in your workplace?’, ‘Or have you ever illegally downloaded music files from the Internet?’, the researcher may not get truthful responses. This tendency among respondents to ‘spin the truth’ in order to portray themselves in a socially desirable manner is called the ‘social desirability bias’, which hurts the validity of responses obtained from survey research. There is practically no way of overcoming the social desirability bias in a questionnaire survey, but in an interview setting, an astute interviewer may be able to spot inconsistent answers and ask probing questions or use personal observations to supplement respondents’ comments.
Recall bias. Responses to survey questions often depend on subjects’ motivation, memory, and ability to respond. Particularly when dealing with events that happened in the distant past, respondents may not adequately remember their own motivations or behaviours, or perhaps their memory of such events may have evolved with time and no longer be retrievable. For instance, if a respondent is asked to describe his/her utilisation of computer technology one year ago, or even memorable childhood events like birthdays, their response may not be accurate due to difficulties with recall. One possible way of overcoming the recall bias is by anchoring the respondent’s memory in specific events as they happened, rather than asking them to recall their perceptions and motivations from memory.
Common method bias. Common method bias refers to the amount of spurious covariance shared between independent and dependent variables that are measured at the same point in time, such as in a cross-sectional survey, using the same instrument, such as a questionnaire. In such cases, the phenomenon under investigation may not be adequately separated from measurement artefacts. Standard statistical tests are available to test for common method bias, such as Harmon’s single-factor test (Podsakoff, MacKenzie, Lee & Podsakoff, 2003), [3] Lindell and Whitney’s (2001) [4] market variable technique, and so forth. This bias can potentially be avoided if the independent and dependent variables are measured at different points in time using a longitudinal survey design, or if these variables are measured using different methods, such as computerised recording of dependent variable versus questionnaire-based self-rating of independent variables.
- Dillman, D. (1978). Mail and telephone surveys: The total design method . New York: Wiley. ↵
- Rasikski, K. (1989). The effect of question wording on public support for government spending. Public Opinion Quarterly , 53(3), 388–394. ↵
- Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J.-Y., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology , 88(5), 879–903. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879. ↵
- Lindell, M. K., & Whitney, D. J. (2001). Accounting for common method variance in cross-sectional research designs. Journal of Applied Psychology , 86(1), 114–121. ↵
Social Science Research: Principles, Methods and Practices (Revised edition) Copyright © 2019 by Anol Bhattacherjee is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Doing Survey Research | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Doing Survey Research | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Survey research means collecting information about a group of people by asking them questions and analysing the results. To conduct an effective survey, follow these six steps:
- Determine who will participate in the survey
- Decide the type of survey (mail, online, or in-person)
- Design the survey questions and layout
- Distribute the survey
- Analyse the responses
- Write up the results
Surveys are a flexible method of data collection that can be used in many different types of research .
Table of contents
What are surveys used for, step 1: define the population and sample, step 2: decide on the type of survey, step 3: design the survey questions, step 4: distribute the survey and collect responses, step 5: analyse the survey results, step 6: write up the survey results, frequently asked questions about surveys.
Surveys are used as a method of gathering data in many different fields. They are a good choice when you want to find out about the characteristics, preferences, opinions, or beliefs of a group of people.
Common uses of survey research include:
- Social research: Investigating the experiences and characteristics of different social groups
- Market research: Finding out what customers think about products, services, and companies
- Health research: Collecting data from patients about symptoms and treatments
- Politics: Measuring public opinion about parties and policies
- Psychology: Researching personality traits, preferences, and behaviours
Surveys can be used in both cross-sectional studies , where you collect data just once, and longitudinal studies , where you survey the same sample several times over an extended period.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Before you start conducting survey research, you should already have a clear research question that defines what you want to find out. Based on this question, you need to determine exactly who you will target to participate in the survey.
Populations
The target population is the specific group of people that you want to find out about. This group can be very broad or relatively narrow. For example:
- The population of Brazil
- University students in the UK
- Second-generation immigrants in the Netherlands
- Customers of a specific company aged 18 to 24
- British transgender women over the age of 50
Your survey should aim to produce results that can be generalised to the whole population. That means you need to carefully define exactly who you want to draw conclusions about.
It’s rarely possible to survey the entire population of your research – it would be very difficult to get a response from every person in Brazil or every university student in the UK. Instead, you will usually survey a sample from the population.
The sample size depends on how big the population is. You can use an online sample calculator to work out how many responses you need.
There are many sampling methods that allow you to generalise to broad populations. In general, though, the sample should aim to be representative of the population as a whole. The larger and more representative your sample, the more valid your conclusions.
There are two main types of survey:
- A questionnaire , where a list of questions is distributed by post, online, or in person, and respondents fill it out themselves
- An interview , where the researcher asks a set of questions by phone or in person and records the responses
Which type you choose depends on the sample size and location, as well as the focus of the research.
Questionnaires
Sending out a paper survey by post is a common method of gathering demographic information (for example, in a government census of the population).
- You can easily access a large sample.
- You have some control over who is included in the sample (e.g., residents of a specific region).
- The response rate is often low.
Online surveys are a popular choice for students doing dissertation research , due to the low cost and flexibility of this method. There are many online tools available for constructing surveys, such as SurveyMonkey and Google Forms .
- You can quickly access a large sample without constraints on time or location.
- The data is easy to process and analyse.
- The anonymity and accessibility of online surveys mean you have less control over who responds.
If your research focuses on a specific location, you can distribute a written questionnaire to be completed by respondents on the spot. For example, you could approach the customers of a shopping centre or ask all students to complete a questionnaire at the end of a class.
- You can screen respondents to make sure only people in the target population are included in the sample.
- You can collect time- and location-specific data (e.g., the opinions of a shop’s weekday customers).
- The sample size will be smaller, so this method is less suitable for collecting data on broad populations.
Oral interviews are a useful method for smaller sample sizes. They allow you to gather more in-depth information on people’s opinions and preferences. You can conduct interviews by phone or in person.
- You have personal contact with respondents, so you know exactly who will be included in the sample in advance.
- You can clarify questions and ask for follow-up information when necessary.
- The lack of anonymity may cause respondents to answer less honestly, and there is more risk of researcher bias.
Like questionnaires, interviews can be used to collect quantitative data : the researcher records each response as a category or rating and statistically analyses the results. But they are more commonly used to collect qualitative data : the interviewees’ full responses are transcribed and analysed individually to gain a richer understanding of their opinions and feelings.
Next, you need to decide which questions you will ask and how you will ask them. It’s important to consider:
- The type of questions
- The content of the questions
- The phrasing of the questions
- The ordering and layout of the survey
Open-ended vs closed-ended questions
There are two main forms of survey questions: open-ended and closed-ended. Many surveys use a combination of both.
Closed-ended questions give the respondent a predetermined set of answers to choose from. A closed-ended question can include:
- A binary answer (e.g., yes/no or agree/disagree )
- A scale (e.g., a Likert scale with five points ranging from strongly agree to strongly disagree )
- A list of options with a single answer possible (e.g., age categories)
- A list of options with multiple answers possible (e.g., leisure interests)
Closed-ended questions are best for quantitative research . They provide you with numerical data that can be statistically analysed to find patterns, trends, and correlations .
Open-ended questions are best for qualitative research. This type of question has no predetermined answers to choose from. Instead, the respondent answers in their own words.
Open questions are most common in interviews, but you can also use them in questionnaires. They are often useful as follow-up questions to ask for more detailed explanations of responses to the closed questions.
The content of the survey questions
To ensure the validity and reliability of your results, you need to carefully consider each question in the survey. All questions should be narrowly focused with enough context for the respondent to answer accurately. Avoid questions that are not directly relevant to the survey’s purpose.
When constructing closed-ended questions, ensure that the options cover all possibilities. If you include a list of options that isn’t exhaustive, you can add an ‘other’ field.
Phrasing the survey questions
In terms of language, the survey questions should be as clear and precise as possible. Tailor the questions to your target population, keeping in mind their level of knowledge of the topic.
Use language that respondents will easily understand, and avoid words with vague or ambiguous meanings. Make sure your questions are phrased neutrally, with no bias towards one answer or another.
Ordering the survey questions
The questions should be arranged in a logical order. Start with easy, non-sensitive, closed-ended questions that will encourage the respondent to continue.
If the survey covers several different topics or themes, group together related questions. You can divide a questionnaire into sections to help respondents understand what is being asked in each part.
If a question refers back to or depends on the answer to a previous question, they should be placed directly next to one another.
Before you start, create a clear plan for where, when, how, and with whom you will conduct the survey. Determine in advance how many responses you require and how you will gain access to the sample.
When you are satisfied that you have created a strong research design suitable for answering your research questions, you can conduct the survey through your method of choice – by post, online, or in person.
There are many methods of analysing the results of your survey. First you have to process the data, usually with the help of a computer program to sort all the responses. You should also cleanse the data by removing incomplete or incorrectly completed responses.
If you asked open-ended questions, you will have to code the responses by assigning labels to each response and organising them into categories or themes. You can also use more qualitative methods, such as thematic analysis , which is especially suitable for analysing interviews.
Statistical analysis is usually conducted using programs like SPSS or Stata. The same set of survey data can be subject to many analyses.
Finally, when you have collected and analysed all the necessary data, you will write it up as part of your thesis, dissertation , or research paper .
In the methodology section, you describe exactly how you conducted the survey. You should explain the types of questions you used, the sampling method, when and where the survey took place, and the response rate. You can include the full questionnaire as an appendix and refer to it in the text if relevant.
Then introduce the analysis by describing how you prepared the data and the statistical methods you used to analyse it. In the results section, you summarise the key results from your analysis.
A Likert scale is a rating scale that quantitatively assesses opinions, attitudes, or behaviours. It is made up of four or more questions that measure a single attitude or trait when response scores are combined.
To use a Likert scale in a survey , you present participants with Likert-type questions or statements, and a continuum of items, usually with five or seven possible responses, to capture their degree of agreement.
Individual Likert-type questions are generally considered ordinal data , because the items have clear rank order, but don’t have an even distribution.
Overall Likert scale scores are sometimes treated as interval data. These scores are considered to have directionality and even spacing between them.
The type of data determines what statistical tests you should use to analyse your data.
A questionnaire is a data collection tool or instrument, while a survey is an overarching research method that involves collecting and analysing data from people using questionnaires.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). Doing Survey Research | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/surveys/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, qualitative vs quantitative research | examples & methods, construct validity | definition, types, & examples, what is a likert scale | guide & examples.
Table of Contents
Ai, ethics & human agency, collaboration, information literacy, writing process, survey research, develop knowledge that is otherwise unavailable by developing an effective survey..
Surveys are a series of questions, which are usually presented in questionnaire format. Surveys can be distributed face-to-face, over the phone, or over the Internet.
Developing, Designing, and Distributing Surveys
Surveys are usually developed to obtain information that is otherwise unavailable. For example, suppose you feel that nationwide statistics on college-age drinking or cheating fail to adequately represent life on your campus. You could then develop a survey to demonstrate (or not demonstrate) your point of view.
Note: This section presents detailed instructions for developing, designing, and distributing surveys. Because English teachers are primarily concerned with how your survey is written, they may encourage you not to worry about some of the design issues addressed below, such as census, random, and stratified census sampling procedures
Determine your survey design by creating questions with your purpose and audience in mind.
To develop a credible survey, you must first organize a systematic approach to your study. This involves insuring your study sample actually represents the population of interest. For example, if you were conducting a survey of whether or not college students ever plagiarized or cheated on a test, you would not want to submit your survey to teachers or parents; you would want to hear from college students. A well-designed survey will reduce the chances of this type of misuse of the data.
Ask the Right Questions
Surveys most commonly take the form of a questionnaire. However, a questionnaire is not just a collection of questions, it is a set of questions focused on a particular objective or set of objectives. Defining objectives simply demonstrates you know what you are doing before you do it. If you have selected a topic like “The education of the 20-year-old,” you would most likely need to narrow the topic before designing your survey. One way to narrow the topic is to consider the when question. When does the education of the 20-year-old interest us? It could be cave people, residents of Europe during the plagues, or some time in the 20th century. Take your choice, but the application of a single survey to cover all the periods of time is highly unlikely.
Limit the Survey
Limit your focus by restricting a geographical region. You may want to survey 20-year-olds who live within 1,000 miles of the North Pole, or only those who live in Palaski County, Missouri. By establishing a geographical target population you can expect reasonable closure. If you wanted to interview all the subjects in your original category (the education of 20-year-olds), you may never get around to writing your report. Another factor that influences your survey is the extent to which you want to examine your population. Do you want to look at all the 20-year-old-students or can you focus on a specific subgroup (such as 20-year-old-students in trade schools or 2-year vs. 4-year colleges or, perhaps, the 20-year-old-students who are self-directed learners attending no formal institution)? What do you want to know about these people anyway? Are you interested in how they learn, why they learn, what they learn or perhaps, how much they spend?
Define Objectives
Ask yourself: What am I going to do with the information once it is revealed? You may plan to simply report your findings, make comparisons with other information or take the results of your survey to support or reject a whole new social theory. All these considerations should be met before beginning your survey research. A well-defined set of objectives eases the burden on the researcher.
Create a Survey Instrument
Learn to write effective survey questions..
After defining the population, surveyors need to create an instrument if a proven survey instrument does not exist. As discussed in more detail below, survey creation parallels the computer axiom “GIGO”–Garbage In—Garbage Out. A well-designed, accurate survey is an excellent way for researchers to gather information or data about a particular subject of interest. When prepared in an unprofessional manner, surveys can also become an inaccurate, misused, misunderstood conveyer of misinformation. If a researcher has developed an idea or hypothesis and seeks information only to prove that the idea is correct, the process, the ethics, the motivation, and the very essence of the researcher are worthy of rigorous challenge and should, most likely, be rejected.
Writing Survey Questions
A survey is more than a list of questions. Not only should each question relate to a specific part of your objectives, but each question should be written in a concise and precise manner, and the survey population must be able to understand what is being asked.
There are four common question formats, as discussed in detail below.
Demographic Questions
Demographic questions attempt to identify the characteristics of the population or sample completing the survey.
Your English instructors do not expect you to generalize from a small sample to a larger population, so your sample does not need to reflect characteristics in the overall population. However, you will need to talk meaningfully about your sample, so you will want to describe the characteristics of your respondents as specifically as possible. The kinds of characteristics you should identify are determined largely by the purpose of your research. Gender, income, age, and level of education are examples of the sort of demographic characteristics that you may want to account for in your survey.
Demographic Example:
Circle One : Male or Female?
Closed Questions
With the closed question, the survey provides responses and the subject selects the one that is most appropriate. When constructing closed questions, you need to provide choices that will allow you to make meaningful interpretations.
Closed questions allow the researcher to deal with the responses in a more efficient manner than open ended questions. Both forms of questions can produce similar information.
Closed Question Example:
How often do you study?
a. less than 6 hours a week
b. 6-10 hours a week
b. 11-15 hours a week
c. more than 15 hours a week
The closed question allows for greater uniformity of response, and the categories can be easily matched to the areas of interest by the researcher. Whether you select one type or a combination of questions for your survey, each question must be clear, unambiguous, and relate to a specific item in your objectives.
A common error is to create a double-barreled question such as, “Do you walk to school or carry your lunch?” Clearly, this question is attempting to ask two different things and a simple yes or no response won’t really answer the question. The original question should be rewritten as two questions: “Do you walk to school?” “Do you carry your lunch?” Now the respondent can provide you useful data.
Rank-Ordered Questions
When your library research has informed you that your audience is likely to be concerned about several issues, you can determine which concern is most troubling by asking a rank-ordered question. Essentially, as illustrated by the following example, the rank-order question presents respondents with several alternatives and requests that they rank them according to priority:
Rank-Ordered Question:
Please rank your five most important reasons for not contributing to our company’s blood drives. Put a #1 by your most important concern, a #2 by your second most important concern, and so forth.
_____ Lack of time _____ Lack of awareness of former blood drives _____ Perception that the blood bank has plenty of blood _____ Concern about possible pain _____ Concern about infection _____ Concern about fainting _____ Concern about vomiting _____ Concern about bruising _____ Concern about being infected with AIDS _____ Belief company should provide some compensation
Open Questions
An open question requires respondents to answer in their own words, like a short-answer or essay type response. Open questions allow for free-flowing responses and are less restrictive than the closed questions. If you are going to use an open-ended question format for mailed surveys, don’t expect a high response rate. People seem more inclined to circle or mark a response than to write a lengthy response.
Open Question Example:
(Ans)_________________________________
Because open-ended commentaries can enrich your interpretation of the statistics, you would be wise to include a few such questions in all surveys that you conduct. One generic question that you might find useful is “What important item(s) has/have been left out of this survey?” However, because they are difficult to tabulate and because they require time on the part of your respondents, be sure to limit the number of open-ended questions you ask.
How Many Questions?
Of course, when you are freewriting possible questions, you should attempt to generate as many questions as possible. You might also ask friends and colleagues what questions they would ask if pursuing your topic. Consider using questions that other researchers have asked, and base additional questions on the sources you have consulted to develop an informed survey. Ultimately, however, you will need to limit the questions so that you have a better chance of getting the surveys back. Before submitting your survey to your targeted sample, ask a few people to take it and time how long it takes them to complete it. Many people are willing to give 15 minutes to a survey, yet find a survey that takes more than 30 minutes intolerable.
Formatting Guidelines
Your questionnaire should be prepared so that someone will read it and respond. Try to make this process as easy as possible for the respondent. Make the questionnaire look like a questionnaire. Have it neatly organized, with questions in a logical sequence, numbering each question and page. If you mix open-and closed-ended questions, put the open-ended questions at the end of the questionnaire. An open-ended response is more threatening than a “select a, b, c, or d” response. Keep your questionnaire focused and as short as possible. Each page added reduces the number of potential respondents who will complete the survey.
Sample the Population
Understand the basics of census and random sampling techniques..
A critical step in survey research involves sampling the population. Now that you have narrowed your objectives to something achievable, who are you going to sample? For many, this is a rather simple step: Ask the people who are able to answer your questions! If you want to learn about the educational perceptions of 20-year-olds, ask them. If you want to learn about the parental perceptions of the education of 20-year-olds, ask the parents.
Since data collection involving humans can raise legal, ethical, and moral issues, if you chose to survey the 20-year-olds on a particular college campus, find out what procedures are required before distributing your questionnaire or conducting interviews (see Informed Consent).
- Surveys and questionnaires may be presented:
- In paper format.
- Over the phone.
- Face to face.
- Online, perhaps with results viewable in real time.
Census Sample
A researcher may elect to include all the subjects within the population of interest, otherwise known as a census sample. If one is investigating a particular group of people, such as students enrolled in Composition 1 at 8:00 on Monday morning at a particular university, one would survey all the members of the class. The investigation of all the class members is referred to as a census sample.
Random Sample
If you are seeking information about a statewide issue, you would not attempt to interview everyone in the state. Information is still available if you use a technique that allows a sample from the population of interest to represent the population as a whole. A common technique is to employ the random sample. Random sampling implies that each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected in the sample from the population. As a general rule, the higher the sample size the higher the representativeness. The more representativeness you have in the sample, the more it tends to “look like” the population you are studying. Further study in sampling techniques will show how sample size can be determined to afford the researcher a particular level of confidence in the research outcomes.
Random Sample Techniques
Simple random samples may be made using a variety of techniques. One of the most common techniques is the use of a random number table (see Table 1). If you wanted to select 15 people from a classroom of 60 students, begin by obtaining a class roster of all the students. Assign each student a number from 1 – 60. Now we can use the table. Select a row and column. Any row/ column can serve as a starting point. For instance, if you select row 5, column 7 as your starting point, look at the first two digits (34). This number falls within your population range (1 – 60) and therefore can be used as the first of your required 15 people to be selected. Continue down the column. The next number is 68, but that is outside your range, so you should simply skip it and go to the next number, which is 47. When column 7 is exhausted, go to columns 8, 9, and 10 and if you haven’t accomplished your sample of 15, go to column 1 and continue. Note that column 9, rows 2 and 4 repeat the number 60. Since you have selected 60 the first time, simply skip the second and subsequent times. Using this technique, the 15 people from your class size of 60 are represented by numbers 34, 47, 32, 29, 33, 08, 25, 05, 41, 60, 03, 38, 16, 15, and 28. You have just accomplished a simple random sample. As with many things, once you become familiar with the technique, it is often easier to accomplish than to explain.
Table 1—TABLE OF RANDOM NUMBERS
Stratified-Random Sample
Another method of random sampling is called a stratified-random sample . For instance, one may look at the national census for a particular city or state. By applying percentages of age, ethnicity, or gender within the survey design, the researcher is able to gain representativeness within the survey. If the population of a city under study has a population that is 10% Afro-American, 10% Hispanic, 70% Caucasian, and 10% of other ethnic origins, then the researcher would insure the sample of the population contained 10% Afro-American, 10% Hispanic, and so on. The key to random-stratified sampling is to place the population into various categories, called strata, such as age, gender, ethnicity, income, etc. Then select individuals at random from each category. This technique can be used to identify a highly representative sample using a smaller sample size than a purely random sample.
Transmit the Survey
For the mailed survey there are several tactics you can employ to increase the response rate. Write a letter of transmittal stating the purpose and importance of the study, the reason why the individual was selected to participate, insurance of confidentiality, and an offer of thanks for the individual’s participation. If a separate letter is not appropriate, then consider a survey coversheet that contains similar information. Another technique is to send out a mailing informing intended participants that a questionnaire is forthcoming. Advance notification informing individuals they have been selected for your survey may also spark supportive interest.
Sending the Survey and Following Up
Always pick a date for respondents to reply, and be sure that date is at least a few weeks after the survey is mailed. Otherwise you’ll spend most of your time waiting for a response that will never come. About two weeks after your initial mailing, send a follow-up letter. In the letter thank those who have responded and indicate the necessity of obtaining outstanding surveys. Sometimes a statement like “If you have lost the original survey, please contact (researcher’s name, address, phone/fax number) and a new survey will be sent immediately” may also be helpful.
How many follow-ups are required?
That number is up to the researcher. If you can complete your research with a 20% response rate and your sample represents the population from which it is drawn, then don’t follow up. Do be prepared to explain in your report why you stopped. Some researchers will attempt as many as three times to gain subject participation. Given that you have had a particular number of responses now, ask yourself, “Would my results be different if everyone responded?” If you had a 90% initial response, it is unlikely that the remaining 10% would disrupt your findings. If the initial response was only 10%, then you have a considerable amount of work ahead of you.

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...

Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Speech & Writing

- Writing Center
- Current Students
- Online Only Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Parents & Family
- Alumni & Friends
- Community & Business
- Student Life
- Video Introduction
- Become a Writing Assistant
- All Writers
- Graduate Students
- ELL Students
- Campus and Community
- Testimonials
- Encouraging Writing Center Use
- Incentives and Requirements
- Open Educational Resources
- How We Help
- Get to Know Us
- Conversation Partners Program
- Workshop Series
- Professors Talk Writing
- Computer Lab
- Starting a Writing Center
- A Note to Instructors
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review
- Research Proposal
- Argument Essay
- Rhetorical Analysis
Introduction to Primary Research: Observations, Surveys, and Interviews

Primary Research: Definitions and Overview
How research is defined varies widely from field to field, and as you progress through your college career, your coursework will teach you much more about what it means to be a researcher within your field.* For example, engineers, who focus on applying scientific knowledge to develop designs, processes, and objects, conduct research using simulations, mathematical models, and a variety of tests to see how well their designs work. Sociologists conduct research using surveys, interviews, observations, and statistical analysis to better understand people, societies, and cultures. Graphic designers conduct research through locating images for reference for their artwork and engaging in background research on clients and companies to best serve their needs. Historians conduct research by examining archival materials—newspapers, journals, letters, and other surviving texts—and through conducting oral history interviews. Research is not limited to what has already been written or found at the library, also known as secondary research. Rather, individuals conducting research are producing the articles and reports found in a library database or in a book. Primary research, the focus of this essay, is research that is collected firsthand rather than found in a book, database, or journal.
Primary research is often based on principles of the scientific method, a theory of investigation first developed by John Stuart Mill in the nineteenth century in his book Philosophy of the Scientific Method . Although the application of the scientific method varies from field to field, the general principles of the scientific method allow researchers to learn more about the world and observable phenomena. Using the scientific method, researchers develop research questions or hypotheses and collect data on events, objects, or people that is measurable, observable, and replicable. The ultimate goal in conducting primary research is to learn about something new that can be confirmed by others and to eliminate our own biases in the process.
Essay Overview and Student Examples
The essay begins by providing an overview of ethical considerations when conducting primary research, and then covers the stages that you will go through in your primary research: planning, collecting, analyzing, and writing. After the four stages comes an introduction to three common ways of conducting primary research in first year writing classes:
Observations . Observing and measuring the world around you, including observations of people and other measurable events.
Interviews . Asking participants questions in a one-on-one or small group setting.
Surveys . Asking participants about their opinions and behaviors through a short questionnaire.
In addition, we will be examining two student projects that used substantial portions of primary research:
Derek Laan, a nutrition major at Purdue University, wanted to learn more about student eating habits on campus. His primary re-search included observations of the campus food courts, student behavior while in the food courts, and a survey of students’ daily food intake. His secondary research included looking at national student eating trends on college campuses, information from the United States Food and Drug Administration, and books on healthy eating.
Jared Schwab, an agricultural and biological engineering major at Purdue, was interested in learning more about how writing and communication took place in his field. His primary research included interviewing a professional engineer and a student who was a senior majoring in engineering. His secondary research included examining journals, books, professional organizations, and writing guides within the field of engineering.
Ethics of Primary Research
Both projects listed above included primary research on human participants; therefore, Derek and Jared both had to consider research ethics throughout their primary research process. As Earl Babbie writes in The Practice of Social Research , throughout the early and middle parts of the twentieth century researchers took advantage of participants and treated them unethically. During World War II, Nazi doctors performed heinous experiments on prisoners without their consent, while in the U.S., a number of medical and psychological experiments on caused patients undue mental and physical trauma and, in some cases, death. Because of these and other similar events, many nations have established ethical laws and guidelines for researchers who work with human participants. In the United States, the guidelines for the ethical treatment of human research participants are described in The Belmont Report , released in 1979. Today, universities have Institutional Review Boards (or IRBs) that oversee research. Students conducting research as part of a class may not need permission from the university’s IRB, although they still need to ensure that they follow ethical guidelines in research. The following provides a brief overview of ethical considerations:
- Voluntary participation . The Belmont Report suggests that, in most cases, you need to get permission from people before you involve them in any primary research you are conducting. If you are doing a survey or interview, your participants must first agree to fill out your survey or to be interviewed. Consent for observations can be more complicated, and is dis-cussed later in the essay.
Confidentiality and anonymity . Your participants may reveal embarrassing or potentially damaging information such as racist comments or unconventional behavior. In these cases, you should keep your participants’ identities anonymous when writing your results. An easy way to do this is to create a “pseudonym” (or false name) for them so that their identity is protected.
Researcher bias . There is little point in collecting data and learning about something if you already think you know the answer! Bias might be present in the way you ask questions, the way you take notes, or the conclusions you draw from the data you collect.
The above are only three of many considerations when involving human participants in your primary research. For a complete under-standing of ethical considerations please refer to The Belmont Report .
Now that we have considered the ethical implications of research, we will examine how to formulate research questions and plan your primary research project.
Planning Your Primary Research Project
The primary research process is quite similar to the writing process, and you can draw upon your knowledge of the writing process to understand the steps involved in a primary research project. Just like in the writing process, a successful primary research project begins with careful planning and background research. This section first describes how to create a research timeline to help plan your research. It then walks you through the planning stages by examining when primary research is useful or appropriate for your first year composition course, narrowing down a topic, and developing research questions.
The Research Timeline
When you begin to conduct any kind of primary research, creating a timeline will help keep you on task. Because students conducting primary research usually focus on the collection of data itself, they often overlook the equally important areas of planning (invention), analyzing data, and writing. To help manage your time, you should create a research timeline, such as the sample timeline presented here.
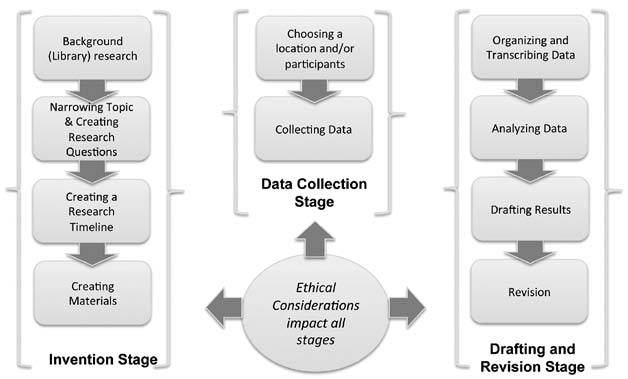
When Primary Research Is Useful or Appropriate
In Evaluating Scientific Research: Separating Fact from Fiction , Fred Leavitt explains that primary research is useful for questions that can be answered through asking others and direct observation. For first year writing courses, primary research is particularly useful when you want to learn about a problem that does not have a wealth of published information. This may be because the problem is a recent event or it is something not commonly studied. For example, if you are writing a paper on a new political issue, such as changes in tax laws or healthcare, you might not be able to find a wealth of peer-reviewed research because the issue is only several weeks old. You may find it necessary to collect some of your own data on the issue to supplement what you found at the library. Primary research is also useful when you are studying a local problem or learning how a larger issue plays out at the local level. Although you might be able to find information on national statistics for healthy eating, whether or not those statistics are representative of your college campus is something that you can learn through primary research.
However, not all research questions and topics are appropriate for primary research. As Fred Leavitt writes, questions of an ethical, philosophical, or metaphysical nature are not appropriate because these questions are not testable or observable. For example, the question “Does an afterlife exist?” is not a question that can be answered with primary research. However, the question “How many people in my community believe in an afterlife?” is something that primary research can answer.
Narrowing Your Topic
Just like the writing process, you should start your primary research process with secondary (library) research to learn more about what is already known and what gaps you need to fill with your own data. As you learn more about the topic, you can narrow down your interest area and eventually develop a research question or hypothesis, just as you would with a secondary research paper.
Developing Research Questions or Hypotheses
As John Stuart Mill describes, primary research can use both inductive and deductive approaches, and the type approach is usually based on the field of inquiry. Some fields use deductive reasoning , where researchers start with a hypothesis or general conclusion and then collect specific data to support or refute their hypothesis. Other fields use inductive reasoning , where researchers start with a question and collect information that eventually leads to a conclusion.
Once you have spent some time reviewing the secondary research on your topic, you are ready to write a primary research question or hypothesis. A research question or hypothesis should be something that is specific, narrow, and discoverable through primary research methods. Just like a thesis statement for a paper, if your research question or hypothesis is too broad, your research will be unfocused and your data will be difficult to analyze and write about. Here is a set of sample research questions:
Poor Research Question : What do college students think of politics and the economy?
Revised Research Question : What do students at Purdue University believe about the current economic crisis in terms of economic recoverability?
The poor research question is unspecific as to what group of students the researcher is interested in—i.e. students in the U.S.? In a particular state? At their university? The poor research question was also too broad; terms like “politics” and the “economy” cover too much ground for a single project. The revised question narrows down the topic to students at a particular university and focuses on a specific issue related to the economy: economic recoverability. The research question could also be rephrased as a testable hypothesis using deductive reasoning: “Purdue University college students are well informed about economic recoverability plans.” Because they were approaching their projects in an exploratory, inductive manner, both Derek and Jared chose to ask research questions:
Derek: Are students’ eating habits at Purdue University healthy or unhealthy? What are the causes of students’ eating behavior?
Jared: What are the major features of writing and communication in agricultural and biological engineering? What are the major controversies?
A final step in working with a research question or hypothesis is determining what key terms you are using and how you will define them. Before conducting his research, Derek had to define the terms “healthy” and “unhealthy”; for this, he used the USDA’s Food Pyramid as a guide. Similarly, part of what Jared focused on in his interviews was learning more about how agricultural and biological engineers defined terms like “writing” and “communication.” Derek and Jared thought carefully about the terms within their research questions and how these terms might be measured.
Choosing a Data Collection Method
Once you have formulated a research question or hypothesis, you will need to make decisions about what kind of data you can collect that will best address your research topic. Derek chose to examine eating habits by observing both what students ate at lunch and surveying students about eating behavior. Jared decided that in-depth interviews with experienced individuals in his field would provide him with the best information.
To choose a data collection method for your research question, read through the next sections on observations, interviews, and surveys.
Observations
Observations have lead to some of the most important scientific discoveries in human history. Charles Darwin used observations of the animal and marine life at the Galapagos Islands to help him formulate his theory of evolution that he describes in On the Origin of Species . Today, social scientists, natural scientists, engineers, computer scientists, educational researchers, and many others use observations as a primary research method.
Observations can be conducted on nearly any subject matter, and the kinds of observations you will do depend on your research question. You might observe traffic or parking patterns on campus to get a sense of what improvements could be made. You might observe clouds, plants, or other natural phenomena. If you choose to observe people, you will have several additional considerations including the manner in which you will observe them and gain their consent.
If you are observing people, you can choose between two common ways to observe: participant observation and unobtrusive observation. Participant observation is a common method within ethnographic research in sociology and anthropology. In this kind of observation, a researcher may interact with participants and become part of their community. Margaret Mead, a famous anthropologist, spent extended periods of time living in, and interacting with, communities that she studied. Conversely, in unobtrusive observation, you do not interact with participants but rather simply record their behavior. Although in most circumstances people must volunteer to be participants in research, in some cases it is acceptable to not let participants know you are observing them. In places that people perceive as public, such as a campus food court or a shopping mall, people do not expect privacy, and so it is generally acceptable to observe without participant consent. In places that people perceive as private, which can include a church, home, classroom, or even an intimate conversation at a restaurant, participant consent should be sought.
The second issue about participant consent in terms of unobtrusive observation is whether or not getting consent is feasible for the study. If you are observing people in a busy airport, bus station, or campus food court, getting participant consent may be next to impossible. In Derek’s study of student eating habits on campus, he went to the campus food courts during meal times and observed students purchasing food. Obtaining participant consent for his observations would have been next to impossible because hundreds of students were coming through the food court during meal times. Since Derek’s research was in a place that participants would perceive as public, it was not practical to get their consent, and since his data was anonymous, he did not violate their privacy.
Eliminating Bias in Your Observation Notes
The ethical concern of being unbiased is important in recording your observations. You need to be aware of the difference between an observation (recording exactly what you see) and an interpretation (making assumptions and judgments about what you see). When you observe, you should focus first on only the events that are directly observable. Consider the following two example entries in an observation log:
- The student sitting in the dining hall enjoys his greasy, oil-soaked pizza. He is clearly oblivious of the calorie content and damage it may do to his body.
- The student sits in the dining hall. As he eats his piece of pizza, which drips oil, he says to a friend, “This pizza is good.”
The first entry is biased and demonstrates judgment about the event. First, the observer makes assumptions about the internal state of the student when she writes “enjoys” and “clearly oblivious to the calorie content.” From an observer’s standpoint, there is no way of ascertaining what the student may or may not know about pizza’s nutritional value nor how much the student enjoys the pizza. The second entry provides only the details and facts that are observable.
To avoid bias in your observations, you can use something called a “double-entry notebook.” This is a type of observation log that encourages you to separate your observations (the facts) from your feelings and judgments about the facts.
- Observations Thoughts
- The student sits in the dining hall. As he eats his piece of pizza, which drips oil, he says to a friend, "this pizza is good." It seems like the student really enjoys the high-calorie-content pizza.
- I observed cash register #1 for 15 minutes. During that time, 22 students paid for meals. Of those 22 students, 15 grabbed a candy bar or granola bar. 3 of the 22 students had a piece of fruit on their plate Fruit is less accessible than candy bars (it is further back in the dining court). Is this why more students are reaching for candy bars?
Figure 3: Two sample entries from a double-entry notebook.
Observations are only one strategy in collecting primary research. You may also want to ask people directly about their behaviors, beliefs, or attitudes—and for this you will need to use surveys or interviews.
Surveys and Interviews: Question Creation
Sometimes it is very difficult for a researcher to gain all of the necessary information through observations alone. Along with his observations of the dining halls, Derek wanted to know what students ate in a typical day, and so he used a survey to have them keep track of their eating habits. Likewise, Jared wanted to learn about writing and communication in engineering and decided to draw upon expert knowledge by asking experienced individuals within the field.
Interviews and surveys are two ways that you can gather information about people’s beliefs or behaviors. With these methods, the information you collect is not first-hand (like an observation) but rather “self-reported” data, or data collected in an indirect manner. William Shadish, Thomas Cook, and Donald Campbell argued that people are inherently biased about how they see the world and may report their own actions in a more favorable way than they may actually behave. Despite the issues in self-reported data, surveys and interviews are an excellent way to gather data for your primary research project.
Survey or Interview?
How do you choose between conducting a survey or an interview? It depends on what kind of information you are looking for. You should use surveys if you want to learn about a general trend in people’s opinions, experiences, and behavior. Surveys are particularly useful to find small amounts of information from a wider selection of people in the hopes of making a general claim. Interviews are best used when you want to learn detailed information from a few specific people. Interviews are also particularly useful if you want to interview experts about their opinions, as Jared did. In sum, use interviews to gain de-tails from a few people, and surveys to learn general patterns from many people.
Writing Good Questions
One of the greatest challenges in conducting surveys and interviews is writing good questions. As a researcher, you are always trying to eliminate bias, and the questions you ask need to be unbiased and clear. Here are some suggestions on writing good questions:
Ask about One Thing at a Time
A poorly written question can contain multiple questions, which can confuse participants or lead them to answer only part of the question you are asking. This is called a “double-barreled question” in journalism. The following questions are taken from Jared’s research:
Poor question: What kinds of problems are being faced in the field today and where do you see the search for solutions to these problems going?
Revised question #1: What kinds of problems are being faced in the field today?
Revised question #2: Where do you see the search for solutions to these problems going?
Avoid Leading Questions
A leading question is one where you prompt the participant to respond in a particular way, which can create bias in the answers given:
Leading question: The economy is clearly in a crisis, wouldn’t you agree?
Revised question: Do you believe the economy is currently in a crisis? Why or why not?
Understand When to Use Open and Closed Questions
Closed questions, or questions that have yes/no or other limited responses, should be used in surveys. However, avoid these kinds of questions in interviews because they discourage the interviewee from going into depth. The question sample above, “Do you believe the economy currently is in a crisis?” could be answered with a simple yes or no, which could keep a participant from talking more about the issue. The “why or why not?” portion of the question asks the participant to elaborate. On a survey, the question “Do you believe the economy currently is in a crisis?” is a useful question because you can easily count the number of yes and no answers and make a general claim about participant responses.
Write Clear Questions
When you write questions, make sure they are clear, concise, and to the point. Questions that are too long, use unfamiliar vocabulary, or are unclear may confuse participants and you will not get quality responses.
Now that question creation has been addressed, we will next examine specific considerations for interviews and surveys.
Interviews, or question and answer sessions with one or more people, are an excellent way to learn in-depth information from a person for your primary research project. This section presents information on how to conduct a successful interview, including choosing the right person, ways of interviewing, recording your interview, interview locations, and transcribing your interview.
Choosing the Right Person
One of the keys to a successful interview is choosing the right person to interview. Think about whom you would like to interview and whom you might know. Do not be afraid to ask people you do not know for interviews. When asking, simply tell them what the interview will be about, what the interview is for, and how much time it will take. Jared used his Purdue University connection to locate both of the individuals that he ended up interviewing—an advanced Purdue student and a Purdue alum working in an Engineering firm.
Face-to-Face and Virtual Interviews
When interviewing, you have a choice of conducting a traditional, face-to-face interview or an interview using technology over the Internet. Face-to-face interviews have the strength that you can ask follow-up questions and use non-verbal communication to your advantage. Individuals are able to say much more in a face-to-face interview than in an email, so you will get more information from a face-to-face interview. However, the Internet provides a host of new possibilities when it comes to interviewing people at a distance. You may choose to do an email interview, where you send questions and ask the person to respond. You may also choose to use a video or audio conferencing program to talk with the person virtually. If you are choosing any Internet-based option, make sure you have a way of recording the interview. You may also use a chat or instant messaging program to interview your participant—the benefit of this is that you can ask follow-up questions during the interview and the interview is already transcribed for you. Because one of his interviewees lived several hours away, Jared chose to interview the Purdue student face-to-face and the Purdue alum via email.
Finding a Suitable Location
If you are conducting an in-person interview, it is essential that you find a quiet place for your interview. Many universities have quiet study rooms that can be reserved (often found in the university library). Do not try to interview someone in a coffee shop, dining hall, or other loud area, as it is difficult to focus and get a clear recording.
Recording Interviews
One way of eliminating bias in your research is to record your interviews rather than rely on your memory. Recording interviews allows you to directly quote the individual and re-read the interview when you are writing. It is recommended that you have two recording devices for the interview in case one recording device fails. Most computers, MP3 players, and even cell phones come with recording equipment built in. Many universities also offer equipment that students can check out and use, including computers and recorders. Before you record any interview, be sure that you have permission from your participant.
Transcribing Your Interview
Once your interview is over, you will need to transcribe your interview to prepare it for analysis. The term transcribing means creating a written record that is exactly what was said—i.e. typing up your interviews. If you have conducted an email or chat interview, you already have a transcription and can move on to your analysis stage.
Other than the fact that they both involve asking people questions, interviews and surveys are quite different data collection methods. Creating a survey may seem easy at first, but developing a quality survey can be quite challenging. When conducting a survey, you need to focus on the following areas: survey creation, survey testing, survey sampling, and distributing your survey.
Survey Creation: Length and Types of Questions
One of the keys to creating a successful survey is to keep your survey short and focused. Participants are unlikely to fill out a survey that is lengthy, and you’ll have a more difficult time during your analysis if your survey contains too many questions. In most cases, you want your survey to be something that can be filled out within a few minutes. The target length of the survey also depends on how you will distribute the survey. If you are giving your survey to other students in your dorm or classes, they will have more time to complete the survey. Therefore, five to ten minutes to complete the survey is reasonable. If you are asking students as they are walking to class to fill out your survey, keep it limited to several questions that can be answered in thirty seconds or less. Derek’s survey took about ten minutes and asked students to describe what they ate for a day, along with some demographic information like class level and gender.
Use closed questions to your advantage when creating your survey. A closed question is any set of questions that gives a limited amount of choices (yes/no, a 1–5 scale, choose the statement that best describes you). When creating closed questions, be sure that you are accounting for all reasonable answers in your question creation. For example, asking someone “Do you believe you eat healthy?” and providing them only “yes” and “no” options means that a “neutral” or “undecided” option does not exist, even though the survey respondent may not feel strongly either way. Therefore, on closed questions you may find it helpful to include an “other” category where participants can fill in an answer. It is also a good idea to have a few open-ended questions where participants can elaborate on certain points or earlier responses. How-ever, open-ended questions take much longer to fill out than closed questions.
Survey Creation: Testing Your Survey
To make sure your survey is an appropriate length and that your questions are clear, you can “pilot test” your survey. Prior to administering your survey on a larger scale, ask several classmates or friends to fill it out and give you feedback on the survey. Keep track of how long the survey takes to complete. Ask them if the questions are clear and make sense. Look at their answers to see if the answers match what you wanted to learn. You can revise your survey questions and the length of your survey as necessary.
Sampling and Access to Survey Populations
“Sampling” is a term used within survey research to describe the subset of people that are included in your study. Derek’s first research question was: “Are students’ eating habits at Purdue University healthy or unhealthy?” Because it was impossible for Derek to survey all 38,000 students on Purdue’s campus, he had to choose a representative sample of students. Derek chose to survey students who lived in the dorms because of the wide variety of student class levels and majors in the dorms and his easy access to this group. By making this choice, however, he did not account for commuter students, graduate students, or those who live off campus. As Derek’s case demonstrates, it is very challenging to get a truly representative sample.
Part of the reason that sampling is a challenge is that you may find difficulty in finding enough people to take your survey. In thinking about how get people to take your survey, consider both your everyday surroundings and also technological solutions. Derek had access to many students in the dorms, but he also considered surveying students in his classes in order to reach as many people as possible. Another possibility is to conduct an online survey. Online surveys greatly increase your access to different kinds of people from across the globe, but may decrease your chances of having a high survey response rate. An email or private message survey request is more likely to be ignored due to the impersonal quality and high volume of emails most people receive.
Analyzing and Writing About Primary Research
Once you collect primary research data, you will need to analyze what you have found so that you can write about it. The purpose of analyzing your data is to look at what you collected (survey responses, interview answers to questions, observations) and to create a cohesive, systematic interpretation to help answer your research question or examine the validity of your hypothesis.
When you are analyzing and presenting your findings, remember to work to eliminate bias by being truthful and as accurate as possible about what you found, even if it differs from what you expected to find. You should see your data as sources of information, just like sources you find in the library, and you should work to represent them accurately.
The following are suggestions for analyzing different types of data.
If you’ve counted anything you were observing, you can simply add up what you counted and report the results. If you’ve collected descriptions using a double-entry notebook, you might work to write thick descriptions of what you observed into your writing. This could include descriptions of the scene, behaviors you observed, and your overall conclusions about events. Be sure that your readers are clear on what were your actual observations versus your thoughts or interpretations of those observations.
If you’ve interviewed one or two people, then you can use your summary, paraphrasing, and quotation skills to help you accurately describe what was said in the interview. Just like in secondary research when working with sources, you should introduce your interviewees and choose clear and relevant quotes from the interviews to use in your writing. An easy way to find the important information in an interview is to print out your transcription and take a highlighter and mark the important parts that you might use in your paper. If you have conducted a large number of interviews, it will be helpful for you to create a spreadsheet of responses to each question and compare the responses, choosing representative answers for each area you want to describe.
Surveys can contain quantitative (numerical) and qualitative (written answers/descriptions) data. Quantitative data can be analyzed using a spreadsheet program like Microsoft Excel to calculate the mean (average) answer or to calculate the percentage of people who responded in a certain way. You can display this information in a chart or a graph and also describe it in writing in your paper. If you have qualitative responses, you might choose to group them into categories and/or you may choose to quote several representative responses.
Writing about Primary Research
In formal research writing in a variety of fields, it is common for research to be presented in the following format: introduction/background; methods; results; discussions; conclusion. Not all first year writing classes will require such an organizational structure, although it is likely that you will be required to present many of these elements in your paper. Because of this, the next section examines each of these in depth.
Introduction (Review of Literature)
The purpose of an introduction and review of literature in a research paper is to provide readers with information that helps them under-stand the context, purpose, and relevancy of your research. The introduction is where you provide most of your background (library) research that you did earlier in the process. You can include articles, statistics, research studies, and quotes that are pertinent to the issues at hand. A second purpose in an introduction is to establish your own credibility (ethos) as a writer by showing that you have researched your topic thoroughly. This kind of background discussion is required in nearly every field of inquiry when presenting research in oral or written formats.
Derek provided information from the Food and Drug Administration on healthy eating and national statistics about eating habits as part of his background information. He also made the case for healthy eating on campus to show relevancy:
Currently Americans are more overweight than ever. This is coming at a huge cost to the economy and government. If current trends in increasing rates of overweight and obesity continue it is likely that this generation will be the first one to live shorter lives than their parents did. Looking at the habits of university students is a good way to see how a new generation behaves when they are living out on their own for the first time.
Describing What You Did (Methods)
When writing, you need to provide enough information to your readers about your primary research process for them to understand what you collected and how you collected it. In formal research papers, this is often called a methods section. Providing information on your study methods also adds to your credibility as a writer. For surveys, your methods would include describing who you surveyed, how many surveys you collected, decisions you made about your survey sample, and relevant demographic information about your participants (age, class level, major). For interviews, introduce whom you interviewed and any other relevant information about interviewees such as their career or expertise area. For observations, list the locations and times you observed and how you recorded your observations (i.e. double-entry notebook). For all data types, you should describe how you analyzed your data.
The following is a sample from Jared about his participants:
In order to gain a better understanding of the discourse community in environmental and resource engineering, I interviewed Anne Dare, a senior in environmental and natural resource engineering, and Alyson Keaton an alumnus of Purdue University. Alyson is a current employee of the Natural Resource Conservation Service (NRCS), which is a division of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).
Here is a sample from Derek’s methods section:
I conducted a survey so that I could find out what students at Purdue actually eat on a typical day. I handed out surveys asking students to record what they ate for a day . . . I received 29 back and averaged the results based on average number of servings from each food group on the old food guide pyramid. The group included students from the freshman to the graduate level and had 8 women and 21 men respond.
Describing Your Study Findings (Results)
In a formal research paper, the results section is where you describe what you found. The results section can include charts, graphs, lists, direct quotes, and overviews of findings. Readers find it helpful if you are able to provide the information in different formats. For example, if you have any kind of numbers or percentages, you can talk about them in your written description and then present a graph or chart showing them visually. You should provide specific details as supporting evidence to back up your findings. These details can be in the form of direct quotations, numbers, or observations.
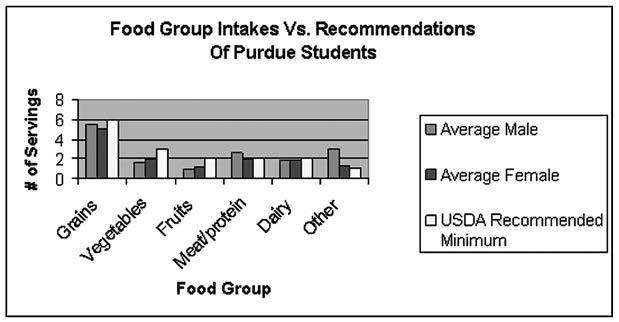
Jared describes some of his interview results:
Alyson also mentioned the need for phone conversation. She stated, “The phone is a large part of my job. I am communicating with other NRCS offices daily to find out the status of our jobs.” She needs to be in constant contact in order to insure that everything is running smoothly. This is common with those overseeing projects. In these cases, the wait for a response to an email or a memo can be too long to be effective.
Interpreting What You Learned (Discussion)
In formal research papers, the discussion section presents your own interpretation of your results. This may include what you think the results mean or how they are useful to your larger argument. If you are making a proposal for change or a call to action, this is where you make it. For example, in Derek’s project about healthy eating on campus, Derek used his primary research on students’ unhealthy eating and observations of the food courts to argue that the campus food courts needed serious changes. Derek writes, “Make healthy food options the most accessible in every dining hall while making unhealthy foods the least. Put nutrition facts for everything that is served in the dining halls near the food so that students can make more informed decisions on what to eat.”
Jared used the individuals he interviewed as informants that helped him learn more about writing in agricultural and biological engineering. He integrated the interviews he conducted with secondary research to form a complete picture of writing and communication in agricultural and biological engineering. He concludes:
Writing takes so many forms, and it is important to know about all these forms in one way or another. The more forms of writing you can achieve, the more flexible you can be. This ability to be flexible can make all the difference in writing when you are dealing with a field as complex as engineering.
Primary Research and Works Cited or References Pages
The last part of presenting your primary research project is a works cited or references page. In general, since you are working with data you collected yourself, there is no source to cite an external source. Your methods section should describe in detail to the readers how and where the data presented was obtained. However, if you are working with interviews, you can cite these as “personal communication.” The MLA and APA handbooks both provide clear listings of how to cite personal communication in a works cited/references page.
This essay has presented an overview to three commonly used methods of primary research in first year writing courses: observations, interviews, and surveys. By using these methods, you can learn more about the world around you and craft meaningful written discussions of your findings.
- Primary research techniques show up in more places than just first year writing courses. Where else might interviews, surveys, or observations be used? Where have you seen them used?
- The chapter provides a brief discussion of the ethical considerations of research. Can you think of any additional ethical considerations when conducting primary research? Can you think of ethical considerations unique to your own research project?
- Primary research is most useful for first year writing students if it is based in your local community or campus. What are some current issues on your campus or in your community that could be investigated using primary research methods?
- In groups or as a class, make a list of potential primary research topics. After each topic on the list, consider what method of inquiry (observation, interview, or survey) you would use to study the topic and answer why that method is a good choice.
Suggested Resources
For more information on the primary methods of inquiry described here, please see the following sources:
Works Cited
This essay was written by Dana Lynn Driscoll and was published as a chapter in Writing Spaces: Readings on Writing , Volume 2, a peer-reviewed open textbook series for the writing classroom. This work is licensed under the Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0) . Please keep this information on this material if you use, adapt, and/or share it.
Contact Info
Kennesaw Campus 1000 Chastain Road Kennesaw, GA 30144
Marietta Campus 1100 South Marietta Pkwy Marietta, GA 30060
Campus Maps
Phone 470-KSU-INFO (470-578-4636)
kennesaw.edu/info
Media Resources
Resources For
Related Links
- Financial Aid
- Degrees, Majors & Programs
- Job Opportunities
- Campus Security
- Global Education
- Sustainability
- Accessibility
470-KSU-INFO (470-578-4636)
© 2024 Kennesaw State University. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Statement
- Accreditation
- Emergency Information
- Report a Concern
- Open Records
- Human Trafficking Notice

Survey Method
The essence of survey method can be explained as “questioning individuals on a topic or topics and then describing their responses” [1] . In business studies survey method of primary data collection is used in order to test concepts, reflect attitude of people, establish the level of customer satisfaction, conduct segmentation research and a set of other purposes. Survey method can be used in both, quantitative , as well as, qualitative studies.
Survey method pursues two main purposes:
- Describing certain aspects or characteristics of population and/or
- Testing hypotheses about nature of relationships within a population.
Survey method can be broadly divided into three categories: mail survey, telephone survey and personal interview. The descriptions of each of these methods are briefly explained on the following table [2] :
Major survey methods and their descriptions
Alternatively, from the viewpoint of practicality, the most popular variations of surveys include questionnaires , interviews and documentation review. The main advantages and disadvantages associated with these primary data collection methods are explained by Denscombe (2010) [3] in the following manner:
Advantages and disadvantages of survey data collection methods
Advantages of Survey Method
- Surveys can be conducted faster and cheaper compared to other methods of primary data collection such as observation and experiments
- Primary data gathered through surveys are relatively easy to analyse
Disadvantages of Survey Method
- In some cases, unwillingness or inability of respondents to provide information
- Human bias of respondents, i.e. respondents providing inaccurate information
- Differences in understanding: it is difficult to formulate questions in such a way that it will mean exactly same thing to each respondent
My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step assistance offers practical assistance to complete a dissertation with minimum or no stress. The e-book covers all stages of writing a dissertation starting from the selection to the research area to submitting the completed version of the work within the deadline.

[1] Jackson, S.L. (2011) “Research Methods and Statistics: A Critical Approach”, 4 th edition, Cengage Learning, p.17
[2] Source: Jackson, S.L. (2011) “Research Methods and Statistics: A Critical Approach”, 4 th edition, Cengage Learning
[3] Denscombe, M. (2010) “The Good Research Guide for Small-Scale Social Research Projects” fourth edition, Butterworth-Heinemann
How to Write a Survey Paper: Brief Overview

Every student wishes there was a shortcut to learning about a subject. Writing a survey paper can be an effective tool for synthesizing and consolidating information on a particular topic to gain mastery over it.
There are several techniques and best practices for writing a successful survey paper. Our team is ready to guide you through the writing process and teach you how to write a paper that will benefit your academic and professional career.
What is a Survey Paper
A survey paper is a type of academic writing that aims to give readers a comprehensive understanding of the current state of research on a particular topic. By synthesizing and analyzing already existing research, a survey paper provides good shortcuts highlighting meaningful achievements and recent advances in the field and shows the gaps where further research might be needed.
The survey paper format includes an introduction that defines the scope of the research domain, followed by a thorough literature review section that summarizes and critiques existing research while showcasing areas for further research. A good survey paper must also provide an overview of commonly used methodologies, approaches, key terms, and recent trends in the field and a clear summary that synthesizes the main findings presented.
Our essay writing service team not only provides the best survey paper example but can also write a custom academic paper based on your specific requirements and needs.
How to Write a Survey Paper: Important Steps
If you have your head in your hands, wondering how to write a survey paper, you must be new here. Luckily, our team of experts got you! Below you will find the steps that will guide you to the best approach to writing a successful survey paper. No more worries about how to research a topic . Let's dive in!

Obviously, the first step is to choose a topic that is both interesting to you and relevant to a large audience. If you are struggling with topic selection, go for only the ones that have the most literature to compose a comprehensive research paper.
Once you have selected your topic, define the scope of your survey paper and the specific research questions that will guide your literature review. This will help you establish boundaries and ensure that your paper is focused and well-structured.
Next, start collecting existing research on your topic through various academic databases and literature reviews. Make sure you are up to date with recent discoveries and advances. Before selecting any work for the survey, make sure the database is credible. Determine what sources are considered trustworthy and reputable within the specific domain.
Continue survey paper writing by selecting the most relevant and significant research pieces to include in your literature overview. Make sure to methodically analyze each source and critically evaluate its relevance, rigor, validity, and contribution to the field.
At this point, you have already undertaken half of the job. Maybe even more since collecting and analyzing the literature is often the most challenging part of writing a survey paper. Now it's time to organize and structure your paper. Follow the well-established outline, give a thorough review, and compose compelling body paragraphs. Don't forget to include detailed methodology and highlight key findings and revolutionary ideas.
Finish off your writing with a powerful conclusion that not only summarizes the key arguments but also indicates future research directions.
Feeling Overwhelmed by All the College Essays?
Our expert writers will ensure that you submit top-quality papers without missing any deadlines!
Survey Paper Outline
The following is a general outline of a survey paper.
- Introduction - with background information on the topic and research questions
- Literature Overview - including relevant research studies and their analysis
- Methodologies and Approaches - detailing the methods used to collect and analyze data in the literature overview
- Findings and Trends - summarizing the key findings and trends from the literature review
- Challenges and Gaps - highlighting the limitations of studies reviewed
- Future Research Direction - exploring future research opportunities and recommendations
- Conclusion - a summary of the research conducted and its significance, along with suggestions for further work in this area.
- References - a list of all the sources cited in the paper, including academic articles and reports.
You can always customize this outline to fit your paper's specific requirements, but none of the components can be eliminated. Our custom essay writer
Further, we can explore survey paper example formats to get a better understanding of what a well-written survey paper looks like. Our custom essay writer can assist in crafting a plagiarism-free essay tailored to meet your unique needs.
Survey Paper Format
Having a basic understanding of an outline for a survey paper is just the beginning. To excel in survey paper writing, it's important to become proficient in academic essay formatting techniques. Have the following as a rule of thumb: make sure each section relates to the others and that the flow of your paper is logical and readable.
Title - You need to come up with a clear and concise title that reflects the main objective of your research question.
Survey paper example title: 'The analysis of recommender systems in E-commerce.'
Abstract - Here, you should state the purpose of your research and summarize key findings in a brief paragraph. The abstract is a shortcut to the paper, so make sure it's informative.
Introduction - This section is a crucial element of an academic essay and should be intriguing and provide background information on the topic, feeding the readers' curiosity.
Literature with benefits and limitations - This section dives into the existing literature on the research question, including relevant studies and their analyses. When reviewing the literature, it is important to highlight both benefits and limitations of existing studies to identify gaps for future research.
Result analysis - In this section, you should present and analyze the results of your survey paper. Make sure to include statistical data, graphs, and charts to support your conclusions.
Conclusion - Just like in any other thesis writing, here you need to sum up the key findings of your survey paper. How it helped advance the research topic, what limitations need to be addressed, and important implications for future research.
Future Research Direction - You can either give this a separate section or include it in a conclusion, but you can never overlook the importance of a future research direction. Distinctly point out areas of limitations and suggest possible avenues for future research.
References - Finally, be sure to include a list of all the sources/references you've used in your research. Without a list of references, your work will lose all its credibility and can no longer be beneficial to other researchers.
Writing a Good Survey Paper: Helpful Tips
After mastering the basics of how to write a good survey paper, there are a few tips to keep in mind. They will help you advance your writing and ensure your survey paper stands out among others.

Select Only Relevant Literature
When conducting research, one can easily get carried away and start hoarding all available literature, which may not necessarily be relevant to your research question. Make sure to stay within the scope of your topic. Clearly articulate your research question, and then select only literature that directly addresses the research question. A few initial readings might not reveal the relevance, so you need a systematic review and filter of the literature that is directly related to the research question.
Use Various Sources and Be Up-to-Date
Our team suggests only using up-to-date material that was published within the last 5 years. Additional sources may be used if they contribute significantly to the research question, but it is important to prioritize current literature.
Use more than 10 research papers. Though narrowing your pool of references to only relevant literature is important, it's also crucial that you have a sufficient number of sources.
Rely on Reputable Sources
Writing a survey paper is a challenge. Don't forget that it is quality over quantity. Be sure to choose reputable sources that have been peer-reviewed and are recognized within your field of research. Having a large number of various research papers does not mean that your survey paper is of high quality.
Construct a Concise Research Question
Having a short and to-the-point research question not only helps the audience understand the direction of your paper but also helps you stay focused on a clear goal. With a clear research question, you will have an easier time selecting the relevant literature, avoiding unnecessary information, and maintaining the structure of your paper.
Use an Appropriate Format
The scholarly world appreciates when researchers follow a standard format when presenting their survey papers. Therefore, it is important to use a suitable and consistent format that adheres to the guidelines provided by your academic institution or field.
Our paper survey template offers a clear structure that can aid in organizing your thoughts and sources, as well as ensuring that you cover all the necessary components of a survey paper.
Don't forget to use appropriate heading, font, spacing, margins, and referencing style. If there is a strict word limit, be sure to adhere to it and use concise wording.
Use Logical Sequence
A survey paper is different from a regular research paper. Every element of the essay needs to relate to the research question and tie into the overall objective of the paper.
Writing research papers takes a lot of effort and attention to detail. You will have to revise, edit and proofread your work several times. If you are struggling with any aspect of the writing process, just say, ' Write my research paper for me ,' and our team of tireless writers will be happy to assist you.
Starting Point: Survey Paper Example Topics
Learning how to write a survey paper is important, but it is only one aspect of the process.
Now you need a powerful research question. To help get you started, we have compiled a list of survey paper example topics that may inspire you.
- Survey of Evolution and Challenges of Electronic Search Engines
- A Comprehensive Survey Paper on Machine Learning Algorithms
- Survey of Leaf Image Analysis for Plant Species Recognition
- Advances in Natural Language Processing for Sentiment Analysis
- Emerging Trends in Cybersecurity Threat Detection
- A Comprehensive Survey of Techniques in Big Data Analytics in Healthcare
- A Survey of Advances in Digital Art and Virtual Reality
- A Systematic Review of the Impact of Social Media Marketing Strategies on Consumer Behavior
- A Survey of AI Systems in Artistic Expression
- Exploring New Research Methods and Ethical Considerations in Anthropology
- Exploring Data-driven Approaches for Performance Analysis and Decision Making in Sports
- A Survey of Benefits of Optimizing Performance through Diet and Supplementation
- A Critical Review of Existing Research on The Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity Conservation Strategies
- Investigating the Future of Blockchain Technology for Secure Data Sharing
- A Critical Review of the Literature on Mental Health and Innovation in the Workplace
Final Thoughts
Next time you are asked to write a survey paper, remember it is not just following an iterative process of gathering and summarizing existing research; it requires a deep understanding of the subject matter as well as critical analysis skills. Creative thinking and innovative approaches also play a key role in producing high-quality survey papers.
Our expert writers can help you navigate the complex process of writing a survey paper, from topic selection to data analysis and interpretation.
Finding It Difficult to Write a Survey Paper?
Our essay writing service offers plagiarism-free papers tailored to your specific needs.
Are you looking for advice on how to create an engaging and informative survey paper? This frequently asked questions (FAQ) section offers valuable responses to common inquiries that researchers frequently come across when writing a survey paper. Let's delve into it!
What is Survey Paper in Ph.D.?
What is the difference between survey paper and literature review paper, related articles.
%20(1).webp)
Survey Method essay
Surveys are one of the most popular methods to collect primary data from the informed sources of data. As Denscombe (1998) stated, the purpose of a survey is “to get a detailed and comprehensive view about the data obtained, which will be used for mapping”. There are three main characteristics in survey method which are pointed out by Denscombe (1998) as follows: ? Wide and inclusive coverage ? At a specific point in time ? Empirical research
The popularity of the surveys method is established due to the fact that it provides a quantitative or numeric description of some fraction of the population, that is, the sample, by asking question (Creswell, 1994; Neuman, 2000; Fink, 1995). Under surveys it is possible to make a generalisation of the results obtained as the surveys allow a large number of respondents to participate in the survey (Davis, 1996). However, there is a low-response bias because many people do not wish to participate in the survey (Aaker, Kumar & Day, 1995).
In order to get a clear indication of the systems, procedures and practices of Talent Management, the survey method had been chosen for the collection of more information with the object of describing, comparing or explaining the knowledge, attitude or behavior of the subjects and thereby to arrive at some definite conclusion for the research question. Mail survey will be used to collect a data set from a sample population of music listeners who are most likely in a position to provide the best information available in respect of the impact of the internet on the music in general and the Indian Punjabi music in particular in this research.
According to Robert et al. (2001) mail questionnaires are advantageous when responses for many questions have to be obtained from a sample that is geographically dispersed. As this research will collect data from senior HR Professional across the United Kingdom, mail questionnaire is the most appropriate way to conduct this research. Table 3. 2 shows the main advantages and disadvantages in the mail survey which will be considered in this research.
Related essays:
- General Observation essay
- What can the NPO change in its radio content to increase its reach of the Turkish and Moroccan-Dutch? essay
- Homeless Mentally Ill Individuals Share How They See Their Future in essay
- TABLE OF CONTENTS essay
With the mail surveys, one disadvantage in the research is that a letter, to encourage completion the survey by explaining why they are selected, the importance of the investigation, and how the results will benefit them with confidentiality guarantee in this research has to be sent to the samples for maximising the response rate. In order to pursue this research study it was necessary to select a target population. For the current research the population covers music listeners especially who mostly use internet or listening as well as purchasing music product.
The sample population required for the survey has been selected by communicating through friends and acquaintances. Moreover some music shops were also contacted to collect the email ids of their regular purchasers. By writing to the online music shops also some more customers’ ids were collected. On collection of all the required information on the samples the information on the potential target population was then stratified by the various demographic parameters to arrive at an appropriate random sample population.
The target population was then randomly chosen to reduce the sample size down to 150 different individuals. This approach was necessary for brevity as well as to have an effective follow up with the samples for collection of information on the impact of the internet on the music industry. It was decided to collect the primary data through a self-administered questionnaire distributed to the selected sample population in this research. A questionnaire is a document containing questions and other types of items designed to solicit information appropriate for analysis.
This involved drawing on existing research in the area of impact of internet on the music industry research to identify aspects relevant to the current research. Questionnaires are the instrument of choice for many researchers working in various fields, theoretical traditions and research designs (Creswell 2003, Bryman 2004), no doubt because they are seen as the most appropriate tool to obtain systematic and comparable data from a large number of individuals and analyze it economically (De Witte and van Muijen 1999, Fogelman 2002).
The following section will describe and explain the format, structure and content of the questionnaire. Based on the observations gathered from the literature available in respect of the impact of internet on the music industry, the questionnaire was constructed to collect the information and data from music listeners who are also users of internet. The purpose of the questionnaire was to find out the level and extent of usage of internet for listening to music as well as for purchase of music products.
It was also necessary to find out the interest of the samples in various genres of music and their knowledge on the P2P file sharing. The questions have been constructed as closed end questions giving different options to the respondents to express their opinion about particular issues numerically indicating the degree of availability and intensity of the efforts. The first section of the questionnaire is devoted to the demographic information about the participating individuals. The information about the age, marital status, employment and current income are some of the questions included in this section.
This basic information was collected to tabulate and present the information pertaining to the demography of the participants. This gives the reader an idea about the homogeneity of the sample to represent the bulk of the informants. The second part of the questionnaire is devoted to find out the level of interest of the samples on music. The questions were framed accordingly to gather information on the interest of he samples on the music in general. Here again the questions were framed as closed ones to make the job of the respondents easier.
The third section of the questionnaire deals with the knowledge and usage of the internet by the samples. Relevant questions on the time the samples spend on the internet and also the purposes for which they use internet have been framed. The fourth section relates to the information on the purchase of music by the samples. The last section of the questionnaire contains questions to assess the awareness of the samples on the existence of piracy in the music industry. The results obtained were tabulated and analysed and the findings and analysis are presented in the next Chapter.
The Psychometric Survey Method Concept Essay
Introduction, support for psychometric surveys in linking creativity and personality types, weaknesses of psychometric surveys in linking creativity with personality types, reference list.
Psychometric surveys have been used to assess people’s emotional and intellectual capabilities for many decades now (Cripps 2017). These tests are categorised into different types, depending on the kind of choices given to respondents when answering psychology-based questions. Based on their relative success in psychology, companies have used them in employee recruitment processes to understand personality types and explore their alignment to different job categories (Cripps 2017).
However, there is doubt regarding how well these tests could measure human creativity using personality traits (Cripps 2017). Based on this challenge, this paper critically assesses the use of psychometric surveys to explain people’s creativity using their personality types.
Furr and Bacharach (2013) say that psychometric tests can be reliably used to assess creativity; however, they caution users to assess three issues (nature of reliability, the importance of “norming,” and their validity) when using such tests. Support for psychometric tests in measuring creativity possibly draws its roots in the works of J.P. Guilford, who used the survey to show the difference between intelligence quotient (IQ) tests and creativity (Carlson 2015; Cripps 2017).
His study was premised on the factor analytic technique as an approach for assessing creative indices underpinning people’s success in life (Carlson 2015; Cripps 2017). The approach helped him to come up with two types of thought processes – convergent and divergent thinking (Carlson 2015). Divergent thinking measures were associated with creativity, while convergent thinking was linked with the production of one-worded answers meant to fit specific standardised criteria of assessment (Carlson 2015).
Similar to other methods of psychological assessments, psychometric surveys have specific criteria that researchers should meet before accurately measuring a construct of interest. According to Riding and Rayner (2013), there are four main psychometric requirements for assessing creativity and they include reliability, construct validity, predictive validity and respondents’ honesty. Psychometric surveys are known to use two methods for assessing personality and creativity – personality approach and cognitive approach (Ness, Kaye & Stenner 2016).
The personality approach links creativity with personality as an individual difference variable. The California Psychological Inventory and Myers Briggs Types Indicator are some tests that belong to this category of assessments (Ness, Kaye & Stenner 2016). Comparatively, the cognitive approach to creative thinking considers logic and rationality as important tenets of creativity assessments (Ness, Kaye & Stenner 2016).
The merits of psychometric tests in linking creativity to personality types are associated with the success of different personality tests such as the HEXACO-PI-R and NEO-PI-R models. The HEXACO-PI-R test measures creativity and personality using six attributes. The first three focus on people’s tendency to be honest, conscious and emotionally stable (Bernasco, Elffers & van Gelder 2017). The last three focus on their extraversion, agreeableness and openness to experience (Bernasco et al. 2017).
Results that relate to “openness to experience” and conscientiousness have provided good measures for assessing creativity (Bernasco, Elffers & van Gelder 2017). The NEO-PI-R test also uses a similar metric in assessing creativity because, although it is a 240-item questionnaire, it uses the “openness” tenet of personality tests to measure creativity (Ashton 2013).
The success of psychometric surveys in measuring creativity and personality is founded on several theories. One of them is the classical test theory, which presupposes that a person’s psychometric results are products of error and true scores (Johnson 2014). Another one is the item test theory, which investigates the relationship between a person’s performance on a test item and the expected or “mainstream” results.
Here, the theory presupposes that each item of measurement does not have the same level of difficulty (van der Linden & Hambleton 2013). The item test theory is linked with the Rasch model for measurement, which also forms part of the wider body of theories linking psychometric test surveys to creativity (Wu, Tam & Jen 2017). It strives to create measurements from categorical data by balancing a respondent’s creativity and personality traits with the difficulty of the item being measured (Ness, Kaye & Stenner 2016).
Collectively, these theories support the success of psychometric surveys in understanding creativity through personality types because they endear to improve its reliability and validity. Additionally, Price (2016), McCoach, Gable and Madura (2013) say that psychometric tests score high above the reliability index of 0.7 on the Cronbach alpha scale, meaning that they are “highly reliable” tests for measuring creativity and personality.
Critics of psychometric testing draw attention to social desirability as one of its key weaknesses in linking creativity and personality (Ness, Kaye & Stenner 2016). This flaw is commonly observed among studies, which have participants who feel that the tests “judge” them (Ness, Kaye & Stenner 2016). Consequently, they may feel the need to respond in a manner that disapproves this notion, as opposed to being truthful about their responses.
This weakness could manifest in two ways – self-deception and impression management. In self-deception, participants tend to underrate their weaknesses and magnify their strengths (Ness, Kaye & Stenner 2016). Comparatively, in impression management, they may “act nicely” to minimise the probability of social disapproval (Ness, Kaye & Stenner 2016).
Psychometric tests have also been linked to weaknesses relating to the presence of extraneous variables, such as weather and mood of the participants, in research studies (Ness, Kaye & Stenner 2016). For example, informants could provide inaccurate findings when the surveys are administered in hot temperatures because of low attention levels, vigilance and reaction times. This way, it is difficult to find a reliable measure for personality types or creativity Gulliksen (2013) also suggests that cultural bias could affect how questions are formulated in psychometric surveys, thereby undermining the probability of using personality types to assess creativity levels.
Lastly, psychometric surveys have also been criticised for their inability to measure multilingual creative advantages that may appear as personality traits (Fulcher & Davidson 2013). Therefore, alternative tests such as the Lifetime Creativity Scale and the Creative Personality Scale have been mentioned as replacements for measuring these attributes (Fulcher & Davidson 2013).
The weaknesses of psychometric surveys in improving people’s understanding of creativity through personality types centre on the probability that respondents could provide fake results (Ness, Kaye & Stenner 2016). However, the normal distribution of test scores could mitigate this problem. Indeed, most psychometric tests have an inbuilt mechanism for measuring how a person’s creativity and personality scores compare to the norm (Kolen & Brennan 2014). Therefore, researchers can still assess personalities and creativity objectively and within a contextualised but in-depth manner.
Proper questionnaire designs could also address this weakness because they shape respondents’ views (Ness, Kaye & Stenner 2016). In light of this discussion, Kline (2013) suggests that the questions posed in psychometric tests should be pre-tested under typical conditions to evaluate how best they measure creativity using personality traits. Additionally, Loewenthal and Lewis (2015) caution that the findings of psychometric tests, especially when measuring creativity and personality should be contextualised within a specified set of data because creativity is not a standardised variable.
For example, it is difficult to analyse creativity in isolation because it needs to be categorised or normalised across a larger group of test scores to provide a reliable comparison (Ness, Kaye & Stenner 2016). Psychometric surveys normalise data across a large representative sample of responses, thereby providing a reliable sample of creativity (Ness, Kaye & Stenner 2016). For example, people who score 90% on the extroversion scale should understand the score to mean that they are 90% more extroverted than the group of respondents where the normal distribution occurred.
Based on the above views, questions asked in psychometric surveys help us to understand creativity as a normalised variable (Urbina 2014). Here, it is important to develop personality-identifying questions within the constructs they are supposed to measure. For example, if creativity is assessed without considering the role of time, which often influences associated processes, an erroneous result may be obtained. Ness, Kaye and Stenner (2016) also highlight the importance of factoring in the response style of the target population in answering research questions and interpreting test scores.
According to the findings highlighted in this paper, psychometric tests are some of the most popular assessment techniques for measuring personality types and creativity. Consequently, they have a record of success in this regard. Broadly, the success of the psychometric survey in measuring these two human attributes stems from its objectivity. In other words, the test has helped researchers to measure creativity in almost a similar manner as techniques adopted in the natural sciences. Its inherent weaknesses are premised on its vulnerability to social desirability weaknesses and the effects of extraneous variables on test scores.
However, these weaknesses are not unique to the technique because other personality assessment techniques have the same challenge. Nonetheless, the evidences gathered in this study show that these tests improve people’s understanding of creativity as a normalised variable. Stated differently, its helps in portraying creativity as a subjective human trait that can be explained using personality types.
Ashton, MC 2013, Individual differences and personality , 2nd edn, Academic Press, London.
Bernasco, W, Elffers, E & van Gelder, J 2017, The Oxford handbook of offender decision-making , Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Carlson, AL (ed.) 2015, Genius on television: essays on small screen depictions of big minds, McFarland, London.
Cripps, B (ed.) 2017, Psychometric testing: critical perspectives , John Wiley & Sons, London.
Fulcher, G & Davidson, F 2013, The Routledge handbook of language testing , Routledge, London.
Furr, RM & Bacharach, VR 2013, Psychometrics: an introduction , 2nd edn, SAGE, London.
Gulliksen, H 2013, Theory of mental tests , Routledge, London.
Johnson, TP (ed.) 2014, Handbook of health survey methods , John Wiley & Sons, London.
Kline, P 2013, Handbook of psychological testing , 2nd edn, Routledge, London.
Kolen, MJ & Brennan, RL 2014, Test equating, scaling and linking: methods and practices, 3rd edn , Springer Science & Business Media, London.
Loewenthal, K & Lewis, CA 2015, An Introduction to psychological tests and scales, 2nd edn , Psychology Press, London.
McCoach, DB, Gable, RK & Madura, JP 2013, Instrument development in the affective domain: school and corporate applications, 3rd edn, Springer Science & Business Media, London.
Ness, H, Kaye, H & Stenner, P (eds) 2016, DE300- investigating psychology 3 , 1st edn, The Open University, Milton Keynes.
Price, LR 2016, Psychometric methods: theory into practice , Guilford Publications, London.
Riding, R & Rayner, S 2013, Cognitive styles and learning strategies: understanding style differences in learning and behaviour , 3rd edn, Routledge, London.
Urbina, S 2014, Essentials of psychological testing , John Wiley & Sons, London.
van der Linden, WJ & Hambleton, RK 2013, Handbook of modern item response theory, 3rd edn, Springer Science & Business Media, London.
Wu, M, Tam, HP & Jen, T 2017, Educational measurement for applied researchers: theory into practice, Springer, London.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 6). The Psychometric Survey Method Concept. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-psychometric-survey-method-concept/
"The Psychometric Survey Method Concept." IvyPanda , 6 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/the-psychometric-survey-method-concept/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'The Psychometric Survey Method Concept'. 6 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "The Psychometric Survey Method Concept." February 6, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-psychometric-survey-method-concept/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Psychometric Survey Method Concept." February 6, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-psychometric-survey-method-concept/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Psychometric Survey Method Concept." February 6, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-psychometric-survey-method-concept/.
- The NEO-PI-R Questionnaire for Personality Testing
- The Applications of a Psychometric Approach in the Study of Personality
- Psychometric and Personality Testing in Companies
- The concept of psychometric testing
- Psychometric Tests in Human Resources Management
- The Relationship Between Personality and Infidelity Among Millennials
- Psychometric Testing in the Employee Selection Process
- T he Role of Confidentiality in Psychometric and Educational Testing
- Personality, Intelligence, and Creativity
- Psychological Testing of Intellectual Disabilities
- Relationship of Identity, Intimacy and Midlife Well-Being
- Psychology: Chewing Gum' Negative Effects
- Multitasking Person in Modern Life
- The Main Features of Multitasking
- Social Psychology Principles in American Movies
- Search Menu
- Advance articles
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- Why Submit?
- About Journal of Survey Statistics and Methodology
- About the American Association for Public Opinion Research
- About the American Statistical Association
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Editors-in-Chief
Kristen Olson
Katherine Jenny Thompson
Editorial board
Why Submit to JSSAM ?
The Journal of Survey Statistics and Methodology is an international, high-impact journal sponsored by the American Association for Public Opinion Research (AAPOR) and the American Statistical Association. Published since 2013, the journal has quickly become a trusted source for a wide range of high quality research in the field.
Latest articles
Latest posts on x.

Virtual Issues
These specially curated, themed collections from JSSAM feature a selection of papers previously published in the journal.
Browse all virtual issues

Email alerts
Register to receive table of contents email alerts as soon as new issues of Journal of Survey Statistics and Methodology are published online.

Publish in JSSAM
Want to publish in Journal of Survey Statistics and Methodology ? The journal publishes articles on statistical and methodological issues for sample surveys, censuses, administrative record systems, and other related data.
View instructions to authors
Related Titles
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 2325-0992
- Copyright © 2024 American Association for Public Opinion Research
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

20 Advantages and Disadvantages of Survey Research
Survey research is a critical component of measurement and applied social research. It is a broad area that encompasses many procedures that involve asking questions to specific respondents.
A survey can be anything from a short feedback form to intensive, in-depth interviews that attempt to gather specific data about situations, events, or circumstances. Although there are several methods of application that researchers can apply using this tool, you can divide surveys into two generic categories: interviews and questionnaires.
Innovations in this area in recent years allow for advanced software solutions to provide more data to researchers because of the availability of online and mobile surveys. That means the people who are in the most challenging places to reach can still provide feedback on critical ideas, services, or solutions.
Several survey research advantages and disadvantages exist, so reviewing each critical point is necessary to determine if there is value in using this approach for your next project.
List of the Advantages of Survey Research
1. It is an inexpensive method of conducting research. Surveys are one of the most inexpensive methods of gathering quantitative data that is currently available. Some questionnaires can be self-administered, making it a possibility to avoid in-person interviews. That means you have access to a massive level of information from a large demographic in a relatively short time. You can place this option on your website, email it to individuals, or post it on social media profile.
Some of these methods have no financial cost at all, relying on personal efforts to post and collect the information. Robust targeting is necessary to ensure that the highest possible response rate becomes available to create a more accurate result.
2. Surveys are a practical solution for data gathering. Surveys or a practical way to gather information about something specific. You can target them to a demographic of your choice or manage them in several different ways. It is up to you to determine what questions get asked and in what format. You can use polls, questionnaires, quizzes, open-ended questions, and multiple-choice to collect info in real-time situations so that the feedback is immediately useful.
3. It is a fast way to get the results that you need. Surveys provide fast and comfortable results because of today’s mobile and online tools. It is not unusual for this method of data collection to generate results in as little as one day, and sometimes it can be even less than that depending on the scale and reach of your questions. You no longer need to wait for another company to deliver the solutions that you need because these questionnaires give you insights immediately. That means you can start making decisions in the shortest amount of time possible.
4. Surveys provide opportunities for scalability. A well-constructed survey allows you to gather data from an audience of any size. You can distribute your questions to anyone in the world today because of the reach of the Internet. All you need to do is send them a link to the page where you solicit information from them. This process can be done automatically, allowing companies to increase the efficiency of their customer onboarding processes.
Marketers can also use surveys as a way to create lead nurturing campaigns. Scientific research gains a benefit through this process as well because it can generate social insights at a personal level that other methods are unable to achieve.
5. It allows for data to come from multiple sources at once. When you construct a survey to meet the needs of a demographic, then you have the ability to use multiple data points collected from various geographic locations. There are fewer barriers in place today with this method than ever before because of the online access we have around the world.
Some challenges do exist because of this benefit, namely because of the cultural differences that exist between different countries. If you conduct a global survey, then you will want to review all of the questions to ensure that an offense is not unintentionally given.
6. Surveys give you the opportunity to compare results. After researchers quantify the information collected from surveys, the data can be used to compare and contrast the results from other research efforts. This benefit makes it possible to use the info to measure change. That means a questionnaire that goes out every month or each year becomes more valuable over time.
When you can gather a significant amount of data, then the picture you are trying to interpret will become much clearer. Surveys provide the capability of generating new strategies or identifying new trends to create more opportunities.
7. It offers a straightforward analysis and visualization of the data. Most surveys are quantitative by design. This process allows for the advantage of a straightforward analysis process so that the results can be quickly visualized. That means a data scientist doesn’t need to be available to start the work of interpreting the results. You can take advantage of third-party software tools that can turn this info into usable reports, charts, and tables to facilitate the presentation efforts.
8. Survey respondents can stay anonymous with this research approach. If you choose to use online or email surveys, then there is a fantastic opportunity to allow respondents to remain anonymous. Complete invisibility is also possible with postal questionnaires, allowing researchers to maximize the levels of comfort available to the individuals who offer answers. Even a phone conversation doesn’t require a face-to-face meeting, creating this unique benefit.
When people have confidence in the idea that their responses will not be directly associated with their reputation, then researchers have an opportunity to collect information with greater accuracy.
9. It is a research tool with fewer time constraints. Surveys have fewer time limits associated with them when compared to other research methods. There is no one on the other end of an email or postal questionnaire that wants an immediate answer. That means a respondent can take additional time to complete each answer in the most comfortable way possible. This benefit is another way to encourage more honesty within the results since having a researcher presence can often lead to socially desirable answers.
10. Surveys can cover every component of any topic. Another critical advantage that surveys provide is the ability to ask as many questions as you want. There is a benefit in keeping an individual questionnaire short because a respondent may find a lengthy process to be frustrating. The best results typically come when you can create an experience that involves 10 or fewer questions.
Since this is a low-cost solution for gathering data, there is no harm in creating multiple surveys that have an easy mode of delivery. This benefit gives you the option to cover as many sub-topics as possible so that you can build a complete profile of almost any subject matter.
List of the Disadvantages of Survey Research
1. There is always a risk that people will provide dishonest answers. The risk of receiving a dishonest answer is lower when you use anonymous surveys, but it does not disappear entirely. Some people want to help researchers come to whatever specific conclusion they think the process is pursuing. There is also a level of social desirability bias that creeps into the data based on the interactions that respondents have with questionnaires. You can avoid some of this disadvantage by assuring individuals that their privacy is a top priority and that the process you use prevents personal information leaks, but you can’t stop this problem 100% of the time.
2. You might discover that some questions don’t get answers. If you decide to use a survey to gather information, then there is a risk that some questions will be left unanswered or ignored. If some questions are not required, then respondents might choose not to answer them. An easy way to get around this disadvantage is to use an online solution that makes answering questions a required component of each step. Then make sure that your survey stays short and to the point to avoid having people abandon the process altogether.
3. There can be differences in how people understand the survey questions. There can be a lot of information that gets lost in translation when researchers opt to use a survey instead of other research methods. When there is not someone available to explain a questionnaire entirely, then the results can be somewhat subjective. You must give everyone an opportunity to have some understanding of the process so that you can encourage accurate answers.
It is not unusual to have respondents struggle to grasp the meaning of some questions, even though the text might seem clear to the people who created it. Whenever miscommunication is part of the survey process, the results will skew in unintended directions. The only way to avoid this problem is to make the questions as simple as possible.
4. Surveys struggle to convey emotions with the achievable results. A survey does not do a good job of capturing a person’s emotional response to the questions then counter. The only way to gather this information is to have an in-person interview with every respondent. Facial expressions and other forms of body language can add subtlety to a conversation that isn’t possible when someone is filling out an online questionnaire.
Some researchers get stuck trying to interpret feelings in the data they receive. A sliding-scale response that includes various levels of agreement or disagreement can try to replicate the concept of emotion, but it isn’t quite the same as being in the same room as someone. Assertion and strength will always be better information-gathering tools than multiple-choice questions.
5. Some answers can be challenging to classify. Surveys produce a lot of data because of their nature. You can tabulate multiple-choice questions, graph agreement or disagreement in specific areas, or create open-ended questions that can be challenging to analyze. Individualized answers can create a lot of useful information, but they can also provide you with data that cannot be quantified. If you incorporate several questions of this nature into a questionnaire, then it will take a long time to analyze what you received.
Only 10% of the questions on the survey should have an open-ended structure. If the questions are confusing or bothersome, then you might find that the information you must manually review is mostly meaningless.
6. You must remove someone with a hidden agenda as soon as possible. Respondent bias can be a problem in any research type. Participants in your survey could have an interest in your idea, service, or product. Others might find themselves being influenced to participate because of the subject material found in your questionnaire. These issues can lead to inaccurate data gathering because it generates an imbalance of respondents who either see the process as overly positive or negative.
This disadvantage of survey research can be avoided by using effective pre-screening tools that use indirect questions that identify this bias.
7. Surveys don’t provide the same level of personalization. Any marketing effort will feel impersonal unless you take the time to customize the process. Because the information you want to collect on a questionnaire is generic by nature, it can be challenging to generate any interest in this activity because there is no value promised to the respondent. Some people can be put off by the idea of filling out a generic form, leading them to abandon the process.
This issue is especially difficult when your survey is taken voluntarily online, regardless of an email subscription or recent purchase.
8. Some respondents will choose answers before reading the questions. Every researcher hopes that respondents will provide conscientious responses to the questions offered in a survey. The problem here is that there is no way to know if the person filling out the questionnaire really understood the content provided to them. You don’t even have a guarantee that the individual read the question thoroughly before offering a response.
There are times when answers are chosen before someone fully reads the question and all of the answers. Some respondents skip through questions or make instant choices without reading the content at all. Because you have no way to know when this issue occurs, there will always be a measure of error in the collected data.
9. Accessibility issues can impact some surveys. A lack of accessibility is always a threat that researchers face when using surveys. This option might be unsuitable for individuals who have a visual or hearing impairment. Literacy is often necessary to complete this process. These issues should come under consideration during the planning stages of the research project to avoid this potential disadvantage. Then make the effort to choose a platform that has the accessibility options you need already built into it.
10. Survey fatigue can be a real issue that some respondents face. There are two issues that manifest themselves because of this disadvantage. The first problem occurs before someone even encounters your questionnaire. Because they feel overwhelmed by the growing number of requests for information, a respondent is automatically less inclined to participate in a research project. That results in a lower overall response rate.
Then there is the problem of fatigue that happens while taking a survey. This issue occurs when someone feels like the questionnaire is too long or contains questions that seem irrelevant. You can tell when this problem happens because a low completion rate is the result. Try to make the process as easy as possible to avoid the issues with this disadvantage.
Surveys sometimes have a poor reputation. Researchers have seen response rates decline because this method of data gathering has become unpopular since the 1990s. Part of the reason for this perception is due to the fact that everyone tries to use it online since it is a low-cost way to collect information for decision-making purposes.
That’s why researchers are moving toward a rewards-based system to encourage higher participation and completion rates. The most obvious way to facilitate this behavior is to offer something tangible, such as a gift card or a contest entry. You can generate more responses by creating an anonymous process that encourages direct and honest answers.
These survey research advantages and disadvantages prove that this process isn’t as easy as it might see from the outside. Until you sit down to start writing the questions, you may not entirely know where you want to take this data collection effort. By incorporating the critical points above, you can begin to craft questions in a way that encourages the completion of the activity.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
U.S. Surveys
Pew Research Center has deep roots in U.S. public opinion research. Launched initially as a project focused primarily on U.S. policy and politics in the early 1990s, the Center has grown over time to study a wide range of topics vital to explaining America to itself and to the world. Our hallmarks: a rigorous approach to methodological quality, complete transparency as to our methods, and a commitment to exploring and evaluating ongoing developments in data collection. Learn more about how we conduct our domestic surveys here .
The American Trends Panel

Try our email course on polling
Want to know more about polling? Take your knowledge to the next level with a short email mini-course from Pew Research Center. Sign up now .
From the 1980s until relatively recently, most national polling organizations conducted surveys by telephone, relying on live interviewers to call randomly selected Americans across the country. Then came the internet. While it took survey researchers some time to adapt to the idea of online surveys, a quick look at the public polls on an issue like presidential approval reveals a landscape now dominated by online polls rather than phone polls.
Most of our U.S. surveys are conducted on the American Trends Panel (ATP), Pew Research Center’s national survey panel of over 10,000 randomly selected U.S. adults. ATP participants are recruited offline using random sampling from the U.S. Postal Service’s residential address file. Survey length is capped at 15 minutes, and respondents are reimbursed for their time. Respondents complete the surveys online using smartphones, tablets or desktop devices. We provide tablets and data plans to adults without home internet. Learn more about how people in the U.S. take Pew Research Center surveys.

Methods 101
Our video series helps explain the fundamental concepts of survey research including random sampling , question wording , mode effects , non probability surveys and how polling is done around. the world.
The Center also conducts custom surveys of special populations (e.g., Muslim Americans , Jewish Americans , Black Americans , Hispanic Americans , teenagers ) that are not readily studied using national, general population sampling. The Center’s survey research is sometimes paired with demographic or organic data to provide new insights. In addition to our U.S. survey research, you can also read more details on our international survey research , our demographic research and our data science methods.
Our survey researchers are committed to contributing to the larger community of survey research professionals, and are active in AAPOR and is a charter member of the American Association of Public Opinion Research (AAPOR) Transparency Initiative .
Frequently asked questions about surveys
- Why am I never asked to take a poll?
- Can I volunteer to be polled?
- Why should I participate in surveys?
- What good are polls?
- Do pollsters have a code of ethics? If so, what is in the code?
- How are your surveys different from market research?
- Do you survey Asian Americans?
- How are people selected for your polls?
- Do people lie to pollsters?
- Do people really have opinions on all of those questions?
- How can I tell a high-quality poll from a lower-quality one?
Reports on the state of polling
- Key Things to Know about Election Polling in the United States
- A Field Guide to Polling: 2020 Edition
- Confronting 2016 and 2020 Polling Limitations
- What 2020’s Election Poll Errors Tell Us About the Accuracy of Issue Polling
- Q&A: After misses in 2016 and 2020, does polling need to be fixed again? What our survey experts say
- Understanding how 2020 election polls performed and what it might mean for other kinds of survey work
- Can We Still Trust Polls?
- Political Polls and the 2016 Election
- Flashpoints in Polling: 2016
Sign up for our Methods newsletter
The latest on survey methods, data science and more, delivered quarterly.
OTHER RESEARCH METHODS
Sign up for our weekly newsletter.
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
An official website of the United States government
- Research @ BEA
Studies on the Value of Data
The U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis has undertaken a series of studies that present methods for quantifying the value of simple data that can be differentiated from the complex data created by highly skilled workers that was studied in Calderón and Rassier 2022 . Preliminary studies in this series focus on tax data, individual credit data, and driving data. Additional examples include medical records, educational transcripts, business financial records, customer data, equipment maintenance histories, social media profiles, tourist maps, and many more. If new case studies under this topic are released, they will be added to the listing below.
- Capitalizing Data: Case Studies of Driving Records and Vehicle Insurance Claims | April 2024
- Private Funding of “Free” Data: A Theoretical Framework | April 2024
- Capitalizing Data: Case Studies of Tax Forms and Individual Credit Reports | June 2023
Rachel Soloveichik
JEL Code(s) E01 Published April 2024
An official website of the United States government, Department of Justice.
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
National Crime Victimization Survey: Prevalence Estimation Methods
This report evaluates the current method for estimating prevalence rates using the National Crime Victimization Survey (NCVS). Because the NCVS was designed to produce victimization rates and uses a rotating panel, its data structure contributes to challenges with estimating prevalence rates. Several alternative methods were compared to determine whether any would overcome the limitations of the current method. Additionally, detailed examples were developed to illustrate how each method could be operationalized and what the resulting estimates would look like. See the accompanying report by the Bureau of Justice Statistics, A New Measure of Prevalence for the National Crime Victimization Survey .
Additional Details
- Full report, (PDF 1.5M)
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Business and industry
Economic activity and social change in the UK, real-time indicators: 2 May 2024
Early data on the UK economy and society. These faster indicators are created using rapid response surveys, novel data sources and innovative methods. These are official statistics in development.
https://www.ons.gov.uk/releases/economicactivityandsocialchangeintheukrealtimeindicators2may2024
Official statistics are produced impartially and free from political influence.
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
Can you trust 2024 election polls on Donald Trump and Joe Biden? Here's how to cut through the noise.

Love them or hate them, political polls aren’t going anywhere. As the 2024 presidential election kicks into high gear, the internet will be flooded with surveys tracking the horserace between President Joe Biden and former President Donald Trump.
Keeping track of the numbers can be daunting: Who's ahead in national polls? Who's ahead in state-level surveys? Figuring out which numbers to pay attention to – and whether any of it actually matters – can be even more challenging.
Luckily, the USA TODAY Network has got you covered. Here’s a refresher on why polls matter, whether you can trust them and what to look out for this year.
What do polls tell us about the election?
Think of polls as quick snapshots rather than crystal ball readings.
Prep for the polls: See who is running for president and compare where they stand on key issues in our Voter Guide
They don’t necessarily predict the results of an election. Rather, they’re used to gauge how people feel about a race during a specific period. Pollsters may ask questions about the future, but surveys have more to say about the voters' current temperature.
Polls also tend to have a short shelf life. Public opinion can shift quickly, meaning that the results of polls are often only a reliable measure of the state of a race during the time they were taken.
A survey taken two months ago won’t reflect the state of a race today, and a poll fielded tomorrow won’t tell us who is going to win the presidential election in November.
However, that doesn't mean polls captured at the beginning of a campaign cycle don't matter. The insights from early polls tease out the major issues voters are thinking about that could shape the race. They also help trace the trendlines of how a candidate is performing – whether they’re gaining traction, stagnating or losing support.
Pollster John Zogby likened the importance of looking at early polling to checking benchmarks while trying to reach an exercise goal.
“Am I going to get on the scale the day before to see how I did?” said Zogby. “No, I get on the scale every so often to say what am I doing? How am I doing? What am I doing right?”
Conducting polls early in a race and often throughout the course of an election allows political scientists, journalists and the public to track trends and spot major inflection points in campaigns.
Beware of two-candidate polls
Not all polls are built the same. The way a survey is designed, from how questions are worded to the demographics of the participants chosen, can influence the accuracy of its results.
David Paleologos , director of the Suffolk University Political Research Center, said political polls are most accurate when they replicate as closely as possible the questions and options voters will see on their ballot.
For instance, he said that polls on the 2024 presidential election should include choices beyond the two major party candidates – Trump and Biden – because most ballots will contain third-party and independent candidates who will garner some support.
“If the polls only show a binary choice, between Trump or Biden, you're not getting the full picture,” Paleologos said.
He pointed to close margins in critical swing states, including Wisconsin, Arizona and Georgia, during the 2020 election as an example. Trump lost in those states by fewer votes than Libertarian Party candidate Jo Jorgensen received.
If Jorgensen had not been in the race, the results in those battlegrounds, and possibly the outcome of the election nationally, could have looked markedly different, Paleologos said.
The Libertarian Party hasn’t yet chosen its candidate for the 2024 election. But early polls that include the party and other independent candidates as options are likely to more accurately show how disaffected voters are looking at their options, he explained.
Suffolk University and USA TODAY have a partnership collecting polling data and insights.
Who's being polled?
Another factor that can impact a poll’s accuracy is the sample population surveyed. Polls randomly select a small sample of people designed to represent the broader views and attitudes of a larger population. But every organization uses different methodologies to create their samples.
For instance, some election polls take the temperature of the general population, while others only include active voters or likely voters. They also may weigh demographic information, such as the ratio of Democrats to Republicans, differently.
In the 2024 race, Zogby, author of the forthcoming book "Beyond the Horse Race: How to Read Polls and Why We Should," suggested that the most accurate polls include only likely voters, the pool of people already planning to cast a ballot in November.
“A likely voter today may not be a likely voter on October 31,” Zogby said, but capturing these voters allows political scientists to better understand the Americans who will choose the next president.
Should I pay attention to national polls or state surveys?
Pollsters were lambasted in 2016 for projecting that then-Democratic nominee Hillary Clinton would win the election over Trump.
But national polls , which are supposed to reflect the popular vote across all states, were technically right. Overall, Clinton won nearly 2.9 million more votes than Trump.
So, what went wrong? Many analysts overstated Clinton’s lead in national polls, and few organizations conducted state-specific polls in former Democratic strongholds, such as Wisconsin, Michigan and Pennsylvania, that Trump was able to capture. His wins in those states ultimately landed him the electoral college victory.
That’s not to say that national polls are inferior to state polls, but you should think of them differently.
“National polls are more valuable to understand what the issues are impacting likely voters,” Paleologos said, while state polls better represent the horserace.
He and other polling experts told USA TODAY that Biden needs to lead Trump by three to four percentage points in a national poll to be tied with the Republican in the electoral college . That's because large liberal-leaning states like California and New York tend to tilt the results of national polls in Democrats’ favor, whereas the "electoral college these days skews Republican," Zogby said.
In other words, a national poll showing Biden and Trump tied would tell a similar story to a swing state poll that shows Trump leading Biden by a few points. But generally, experts warn against comparing national and state surveys, which are built off of different methodologies, against one another.
Can you trust the polls?
Mostly. Because polls are analyzing a myriad of shifting factors, they'll always have some level of uncertainty baked in, regardless of the specific election. Organizations also don’t collaborate on what states they plan to poll, or when, which means there’s always potential for blind spots, like in 2016.
Some political observers rely on poll averages, such as a tally from Real Clear Politics. These are generally reliable, but they can miss trends.
But when interpreted properly, polls often provide an accurate portrait of the state of an election.
“There are folks that will say, ‘Oh, you missed the election by two points,’” Zogby said. "Well, two points – that showed the ballpark of what was going to happen.”
And the more polls there are, the easier it is to evaluate the race.

COMMENTS
Survey research means collecting information about a group of people by asking them questions and analyzing the results. To conduct an effective survey, follow these six steps: Determine who will participate in the survey. Decide the type of survey (mail, online, or in-person) Design the survey questions and layout.
Survey Research. Definition: Survey Research is a quantitative research method that involves collecting standardized data from a sample of individuals or groups through the use of structured questionnaires or interviews. The data collected is then analyzed statistically to identify patterns and relationships between variables, and to draw conclusions about the population being studied.
Survey research is defined as "the collection of information from a sample of individuals through their responses to questions" ( Check & Schutt, 2012, p. 160 ). This type of research allows for a variety of methods to recruit participants, collect data, and utilize various methods of instrumentation. Survey research can use quantitative ...
An online survey is a method for extracting information about a significant business matter from an individual or a group of individuals. It consists of structured survey questions that motivate the participants to respond. Creditable survey research can give these businesses access to a vast information bank. Organizations in media, other ...
Survey research is a research method involving the use of standardised questionnaires or interviews to collect data about people and their preferences, thoughts, and behaviours in a systematic manner. Although census surveys were conducted as early as Ancient Egypt, survey as a formal research method was pioneered in the 1930-40s by sociologist Paul Lazarsfeld to examine the effects of the ...
Survey research means collecting information about a group of people by asking them questions and analysing the results. To conduct an effective survey, follow these six steps: Determine who will participate in the survey. Decide the type of survey (mail, online, or in-person) Design the survey questions and layout. Distribute the survey.
Survey research is defined as. "the collection of information from. a sample of individuals through their. responses to questions" (Check &. Schutt, 2012, p. 160). This type of r e -. search ...
Surveys can also be used to assess needs, evaluate demand, and examine impact (Salant & Dillman, 1994, p. 2). The term . survey instrument. is often used to distinguish the survey tool from the survey research that it is designed to support. 1.1 Survey Strengths . Surveys are capable of obtaining information from large samples of the population ...
Develop knowledge that is otherwise unavailable by developing an effective survey. Surveys are a series of questions, which are usually presented in questionnaire format. Surveys can be distributed face-to-face, over the phone, or over the Internet. Developing, Designing, and Distributing Surveys Surveys are usually developed to obtain information that is otherwise unavailable. For example ...
data essay Feb 12, 2024. ... The latest on survey methods, data science and more, delivered quarterly. Sign Up. All. Survey Methods. Publications. Filtering by: Reset; short read Mar 5, 2024. Online opt-in polls can produce misleading results, especially for young people and Hispanic adults.
In formal research papers, this is often called a methods section. Providing information on your study methods also adds to your credibility as a writer. For surveys, your methods would include describing who you surveyed, how many surveys you collected, decisions you made about your survey sample, and relevant demographic information about ...
Questionnaires vs. surveys. A survey is a research method where you collect and analyze data from a group of people. A questionnaire is a specific tool or instrument for collecting the data.. Designing a questionnaire means creating valid and reliable questions that address your research objectives, placing them in a useful order, and selecting an appropriate method for administration.
The essence of survey method can be explained as "questioning individuals on a topic or topics and then describing their responses".In business studies survey method of primary data collection is used in order to test concepts, reflect attitude of people, establish the level of customer satisfaction, conduct segmentation research and a set of other purposes.
Before selecting any work for the survey, make sure the database is credible. Determine what sources are considered trustworthy and reputable within the specific domain. Continue survey paper writing by selecting the most relevant and significant research pieces to include in your literature overview.
The main heading of "Methods" should be centered, boldfaced, and capitalized. Subheadings within this section are left-aligned, boldfaced, and in title case. You can also add lower level headings within these subsections, as long as they follow APA heading styles. To structure your methods section, you can use the subheadings of ...
Surveys are one of the most popular methods to collect primary data from the informed sources of data. As Denscombe (1998) stated, the purpose of a survey is "to get a detailed and comprehensive view about the data obtained, which will be used for mapping". There are three main characteristics in survey method which are … Survey Method essay Read More »
Psychometric surveys are known to use two methods for assessing personality and creativity - personality approach and cognitive approach (Ness, Kaye & Stenner 2016). The personality approach links creativity with personality as an individual difference variable. The California Psychological Inventory and Myers Briggs Types Indicator are some ...
The survey technique is the most widely used method in social science and also the most relevant to this study. It typically involves cross-sectional and longitudinal studies using questionnaires or interviews to collect large amount of data. Table 3.1 collates the advantages and disadvantages of these three survey methods.
Why Submit to JSSAM?. The Journal of Survey Statistics and Methodology is an international, high-impact journal sponsored by the American Association for Public Opinion Research (AAPOR) and the American Statistical Association.Published since 2013, the journal has quickly become a trusted source for a wide range of high quality research in the field.
List of the Advantages of Survey Research. 1. It is an inexpensive method of conducting research. Surveys are one of the most inexpensive methods of gathering quantitative data that is currently available. Some questionnaires can be self-administered, making it a possibility to avoid in-person interviews.
2016: Through-Course and End-of-Course Assessments. Download sample Academic Papers along with scoring guidelines and scoring distributions. If you are using assistive technology and need help accessing these PDFs in another format, contact Services for Students with Disabilities at 212-713-8333 or by email at [email protected].
However, at this point, the Center has switched almost completely to conducting its U.S. surveys online using the ATP. Panel members are recruited offline, and survey questionnaires are taken via self-administered online surveys. Those who don't have internet access can take our surveys on internet-enabled tablets we provide to them ...
Pew Research Center has deep roots in U.S. public opinion research. Launched initially as a project focused primarily on U.S. policy and politics in the early 1990s, the Center has grown over time to study a wide range of topics vital to explaining America to itself and to the world.Our hallmarks: a rigorous approach to methodological quality, complete transparency as to our methods, and a ...
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyze data (for example, experiments, surveys, and statistical tests). In shorter scientific papers, where the aim is to report the findings of a specific study, you might simply describe what you did in a methods section .
The U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis has undertaken a series of studies that present methods for quantifying the value of simple data that can be differentiated from the complex data created by highly skilled workers that was studied in Calderón and Rassier 2022. Preliminary studies in this series focus on tax data, individual credit data, and driving data.
This report evaluates the current method for estimating prevalence rates using the National Crime Victimization Survey (NCVS). Because the NCVS was designed to produce victimization rates and uses a rotating panel, its data structure contributes to challenges with estimating prevalence rates.
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations, theses, and research papers. Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research.
Early data on the UK economy and society. These faster indicators are created using rapid response surveys, novel data sources and innovative methods. These are official statistics in development.
As the 2024 presidential election kicks into high gear, the internet will be flooded with surveys tracking the horserace between President Joe Biden and former President Donald Trump.
In recent years, generative artificial intelligence models, represented by Large Language Models (LLMs) and Diffusion Models (DMs), have revolutionized content production methods. These artificial intelligence-generated content (AIGC) have become deeply embedded in various aspects of daily life and work, spanning texts, images, videos, and audio. The authenticity of AI-generated content is ...