Why Every Educator Needs to Teach Problem-Solving Skills
Strong problem-solving skills will help students be more resilient and will increase their academic and career success .

Want to learn more about how to measure and teach students’ higher-order skills, including problem solving, critical thinking, and written communication?
Problem-solving skills are essential in school, careers, and life.
Problem-solving skills are important for every student to master. They help individuals navigate everyday life and find solutions to complex issues and challenges. These skills are especially valuable in the workplace, where employees are often required to solve problems and make decisions quickly and effectively.
Problem-solving skills are also needed for students’ personal growth and development because they help individuals overcome obstacles and achieve their goals. By developing strong problem-solving skills, students can improve their overall quality of life and become more successful in their personal and professional endeavors.
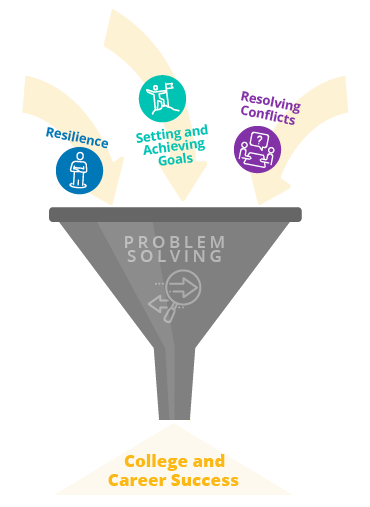
Problem-Solving Skills Help Students…
develop resilience.
Problem-solving skills are an integral part of resilience and the ability to persevere through challenges and adversity. To effectively work through and solve a problem, students must be able to think critically and creatively. Critical and creative thinking help students approach a problem objectively, analyze its components, and determine different ways to go about finding a solution.
This process in turn helps students build self-efficacy . When students are able to analyze and solve a problem, this increases their confidence, and they begin to realize the power they have to advocate for themselves and make meaningful change.
When students gain confidence in their ability to work through problems and attain their goals, they also begin to build a growth mindset . According to leading resilience researcher, Carol Dweck, “in a growth mindset, people believe that their most basic abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work—brains and talent are just the starting point. This view creates a love of learning and a resilience that is essential for great accomplishment.”
Set and Achieve Goals
Students who possess strong problem-solving skills are better equipped to set and achieve their goals. By learning how to identify problems, think critically, and develop solutions, students can become more self-sufficient and confident in their ability to achieve their goals. Additionally, problem-solving skills are used in virtually all fields, disciplines, and career paths, which makes them important for everyone. Building strong problem-solving skills will help students enhance their academic and career performance and become more competitive as they begin to seek full-time employment after graduation or pursue additional education and training.
Resolve Conflicts
In addition to increased social and emotional skills like self-efficacy and goal-setting, problem-solving skills teach students how to cooperate with others and work through disagreements and conflicts. Problem-solving promotes “thinking outside the box” and approaching a conflict by searching for different solutions. This is a very different (and more effective!) method than a more stagnant approach that focuses on placing blame or getting stuck on elements of a situation that can’t be changed.
While it’s natural to get frustrated or feel stuck when working through a conflict, students with strong problem-solving skills will be able to work through these obstacles, think more rationally, and address the situation with a more solution-oriented approach. These skills will be valuable for students in school, their careers, and throughout their lives.
Achieve Success
We are all faced with problems every day. Problems arise in our personal lives, in school and in our jobs, and in our interactions with others. Employers especially are looking for candidates with strong problem-solving skills. In today’s job market, most jobs require the ability to analyze and effectively resolve complex issues. Students with strong problem-solving skills will stand out from other applicants and will have a more desirable skill set.
In a recent opinion piece published by The Hechinger Report , Virgel Hammonds, Chief Learning Officer at KnowledgeWorks, stated “Our world presents increasingly complex challenges. Education must adapt so that it nurtures problem solvers and critical thinkers.” Yet, the “traditional K–12 education system leaves little room for students to engage in real-world problem-solving scenarios.” This is the reason that a growing number of K–12 school districts and higher education institutions are transforming their instructional approach to personalized and competency-based learning, which encourage students to make decisions, problem solve and think critically as they take ownership of and direct their educational journey.
Problem-Solving Skills Can Be Measured and Taught
Research shows that problem-solving skills can be measured and taught. One effective method is through performance-based assessments which require students to demonstrate or apply their knowledge and higher-order skills to create a response or product or do a task.
What Are Performance-Based Assessments?

With the No Child Left Behind Act (2002), the use of standardized testing became the primary way to measure student learning in the U.S. The legislative requirements of this act shifted the emphasis to standardized testing, and this led to a decline in nontraditional testing methods .
But many educators, policy makers, and parents have concerns with standardized tests. Some of the top issues include that they don’t provide feedback on how students can perform better, they don’t value creativity, they are not representative of diverse populations, and they can be disadvantageous to lower-income students.
While standardized tests are still the norm, U.S. Secretary of Education Miguel Cardona is encouraging states and districts to move away from traditional multiple choice and short response tests and instead use performance-based assessment, competency-based assessments, and other more authentic methods of measuring students abilities and skills rather than rote learning.
Performance-based assessments measure whether students can apply the skills and knowledge learned from a unit of study. Typically, a performance task challenges students to use their higher-order skills to complete a project or process. Tasks can range from an essay to a complex proposal or design.
Preview a Performance-Based Assessment
Want a closer look at how performance-based assessments work? Preview CAE’s K–12 and Higher Education assessments and see how CAE’s tools help students develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and written communication skills.
Performance-Based Assessments Help Students Build and Practice Problem-Solving Skills
In addition to effectively measuring students’ higher-order skills, including their problem-solving skills, performance-based assessments can help students practice and build these skills. Through the assessment process, students are given opportunities to practically apply their knowledge in real-world situations. By demonstrating their understanding of a topic, students are required to put what they’ve learned into practice through activities such as presentations, experiments, and simulations.
This type of problem-solving assessment tool requires students to analyze information and choose how to approach the presented problems. This process enhances their critical thinking skills and creativity, as well as their problem-solving skills. Unlike traditional assessments based on memorization or reciting facts, performance-based assessments focus on the students’ decisions and solutions, and through these tasks students learn to bridge the gap between theory and practice.
Performance-based assessments like CAE’s College and Career Readiness Assessment (CRA+) and Collegiate Learning Assessment (CLA+) provide students with in-depth reports that show them which higher-order skills they are strongest in and which they should continue to develop. This feedback helps students and their teachers plan instruction and supports to deepen their learning and improve their mastery of critical skills.

Explore CAE’s Problem-Solving Assessments
CAE offers performance-based assessments that measure student proficiency in higher-order skills including problem solving, critical thinking, and written communication.
- College and Career Readiness Assessment (CCRA+) for secondary education and
- Collegiate Learning Assessment (CLA+) for higher education.
Our solution also includes instructional materials, practice models, and professional development.
We can help you create a program to build students’ problem-solving skills that includes:
- Measuring students’ problem-solving skills through a performance-based assessment
- Using the problem-solving assessment data to inform instruction and tailor interventions
- Teaching students problem-solving skills and providing practice opportunities in real-life scenarios
- Supporting educators with quality professional development
Get started with our problem-solving assessment tools to measure and build students’ problem-solving skills today! These skills will be invaluable to students now and in the future.

Ready to Get Started?
Learn more about cae’s suite of products and let’s get started measuring and teaching students important higher-order skills like problem solving..
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Open access
- Published: 11 January 2023
The effectiveness of collaborative problem solving in promoting students’ critical thinking: A meta-analysis based on empirical literature
- Enwei Xu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6424-8169 1 ,
- Wei Wang 1 &
- Qingxia Wang 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 10 , Article number: 16 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
14k Accesses
13 Citations
3 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Science, technology and society
Collaborative problem-solving has been widely embraced in the classroom instruction of critical thinking, which is regarded as the core of curriculum reform based on key competencies in the field of education as well as a key competence for learners in the 21st century. However, the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking remains uncertain. This current research presents the major findings of a meta-analysis of 36 pieces of the literature revealed in worldwide educational periodicals during the 21st century to identify the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking and to determine, based on evidence, whether and to what extent collaborative problem solving can result in a rise or decrease in critical thinking. The findings show that (1) collaborative problem solving is an effective teaching approach to foster students’ critical thinking, with a significant overall effect size (ES = 0.82, z = 12.78, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.69, 0.95]); (2) in respect to the dimensions of critical thinking, collaborative problem solving can significantly and successfully enhance students’ attitudinal tendencies (ES = 1.17, z = 7.62, P < 0.01, 95% CI[0.87, 1.47]); nevertheless, it falls short in terms of improving students’ cognitive skills, having only an upper-middle impact (ES = 0.70, z = 11.55, P < 0.01, 95% CI[0.58, 0.82]); and (3) the teaching type (chi 2 = 7.20, P < 0.05), intervention duration (chi 2 = 12.18, P < 0.01), subject area (chi 2 = 13.36, P < 0.05), group size (chi 2 = 8.77, P < 0.05), and learning scaffold (chi 2 = 9.03, P < 0.01) all have an impact on critical thinking, and they can be viewed as important moderating factors that affect how critical thinking develops. On the basis of these results, recommendations are made for further study and instruction to better support students’ critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving.
Similar content being viewed by others
Fostering twenty-first century skills among primary school students through math project-based learning
A meta-analysis to gauge the impact of pedagogies employed in mixed-ability high school biology classrooms

A guide to critical thinking: implications for dental education
Introduction.
Although critical thinking has a long history in research, the concept of critical thinking, which is regarded as an essential competence for learners in the 21st century, has recently attracted more attention from researchers and teaching practitioners (National Research Council, 2012 ). Critical thinking should be the core of curriculum reform based on key competencies in the field of education (Peng and Deng, 2017 ) because students with critical thinking can not only understand the meaning of knowledge but also effectively solve practical problems in real life even after knowledge is forgotten (Kek and Huijser, 2011 ). The definition of critical thinking is not universal (Ennis, 1989 ; Castle, 2009 ; Niu et al., 2013 ). In general, the definition of critical thinking is a self-aware and self-regulated thought process (Facione, 1990 ; Niu et al., 2013 ). It refers to the cognitive skills needed to interpret, analyze, synthesize, reason, and evaluate information as well as the attitudinal tendency to apply these abilities (Halpern, 2001 ). The view that critical thinking can be taught and learned through curriculum teaching has been widely supported by many researchers (e.g., Kuncel, 2011 ; Leng and Lu, 2020 ), leading to educators’ efforts to foster it among students. In the field of teaching practice, there are three types of courses for teaching critical thinking (Ennis, 1989 ). The first is an independent curriculum in which critical thinking is taught and cultivated without involving the knowledge of specific disciplines; the second is an integrated curriculum in which critical thinking is integrated into the teaching of other disciplines as a clear teaching goal; and the third is a mixed curriculum in which critical thinking is taught in parallel to the teaching of other disciplines for mixed teaching training. Furthermore, numerous measuring tools have been developed by researchers and educators to measure critical thinking in the context of teaching practice. These include standardized measurement tools, such as WGCTA, CCTST, CCTT, and CCTDI, which have been verified by repeated experiments and are considered effective and reliable by international scholars (Facione and Facione, 1992 ). In short, descriptions of critical thinking, including its two dimensions of attitudinal tendency and cognitive skills, different types of teaching courses, and standardized measurement tools provide a complex normative framework for understanding, teaching, and evaluating critical thinking.
Cultivating critical thinking in curriculum teaching can start with a problem, and one of the most popular critical thinking instructional approaches is problem-based learning (Liu et al., 2020 ). Duch et al. ( 2001 ) noted that problem-based learning in group collaboration is progressive active learning, which can improve students’ critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Collaborative problem-solving is the organic integration of collaborative learning and problem-based learning, which takes learners as the center of the learning process and uses problems with poor structure in real-world situations as the starting point for the learning process (Liang et al., 2017 ). Students learn the knowledge needed to solve problems in a collaborative group, reach a consensus on problems in the field, and form solutions through social cooperation methods, such as dialogue, interpretation, questioning, debate, negotiation, and reflection, thus promoting the development of learners’ domain knowledge and critical thinking (Cindy, 2004 ; Liang et al., 2017 ).
Collaborative problem-solving has been widely used in the teaching practice of critical thinking, and several studies have attempted to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis of the empirical literature on critical thinking from various perspectives. However, little attention has been paid to the impact of collaborative problem-solving on critical thinking. Therefore, the best approach for developing and enhancing critical thinking throughout collaborative problem-solving is to examine how to implement critical thinking instruction; however, this issue is still unexplored, which means that many teachers are incapable of better instructing critical thinking (Leng and Lu, 2020 ; Niu et al., 2013 ). For example, Huber ( 2016 ) provided the meta-analysis findings of 71 publications on gaining critical thinking over various time frames in college with the aim of determining whether critical thinking was truly teachable. These authors found that learners significantly improve their critical thinking while in college and that critical thinking differs with factors such as teaching strategies, intervention duration, subject area, and teaching type. The usefulness of collaborative problem-solving in fostering students’ critical thinking, however, was not determined by this study, nor did it reveal whether there existed significant variations among the different elements. A meta-analysis of 31 pieces of educational literature was conducted by Liu et al. ( 2020 ) to assess the impact of problem-solving on college students’ critical thinking. These authors found that problem-solving could promote the development of critical thinking among college students and proposed establishing a reasonable group structure for problem-solving in a follow-up study to improve students’ critical thinking. Additionally, previous empirical studies have reached inconclusive and even contradictory conclusions about whether and to what extent collaborative problem-solving increases or decreases critical thinking levels. As an illustration, Yang et al. ( 2008 ) carried out an experiment on the integrated curriculum teaching of college students based on a web bulletin board with the goal of fostering participants’ critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving. These authors’ research revealed that through sharing, debating, examining, and reflecting on various experiences and ideas, collaborative problem-solving can considerably enhance students’ critical thinking in real-life problem situations. In contrast, collaborative problem-solving had a positive impact on learners’ interaction and could improve learning interest and motivation but could not significantly improve students’ critical thinking when compared to traditional classroom teaching, according to research by Naber and Wyatt ( 2014 ) and Sendag and Odabasi ( 2009 ) on undergraduate and high school students, respectively.
The above studies show that there is inconsistency regarding the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking. Therefore, it is essential to conduct a thorough and trustworthy review to detect and decide whether and to what degree collaborative problem-solving can result in a rise or decrease in critical thinking. Meta-analysis is a quantitative analysis approach that is utilized to examine quantitative data from various separate studies that are all focused on the same research topic. This approach characterizes the effectiveness of its impact by averaging the effect sizes of numerous qualitative studies in an effort to reduce the uncertainty brought on by independent research and produce more conclusive findings (Lipsey and Wilson, 2001 ).
This paper used a meta-analytic approach and carried out a meta-analysis to examine the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking in order to make a contribution to both research and practice. The following research questions were addressed by this meta-analysis:
What is the overall effect size of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking and its impact on the two dimensions of critical thinking (i.e., attitudinal tendency and cognitive skills)?
How are the disparities between the study conclusions impacted by various moderating variables if the impacts of various experimental designs in the included studies are heterogeneous?
This research followed the strict procedures (e.g., database searching, identification, screening, eligibility, merging, duplicate removal, and analysis of included studies) of Cooper’s ( 2010 ) proposed meta-analysis approach for examining quantitative data from various separate studies that are all focused on the same research topic. The relevant empirical research that appeared in worldwide educational periodicals within the 21st century was subjected to this meta-analysis using Rev-Man 5.4. The consistency of the data extracted separately by two researchers was tested using Cohen’s kappa coefficient, and a publication bias test and a heterogeneity test were run on the sample data to ascertain the quality of this meta-analysis.
Data sources and search strategies
There were three stages to the data collection process for this meta-analysis, as shown in Fig. 1 , which shows the number of articles included and eliminated during the selection process based on the statement and study eligibility criteria.
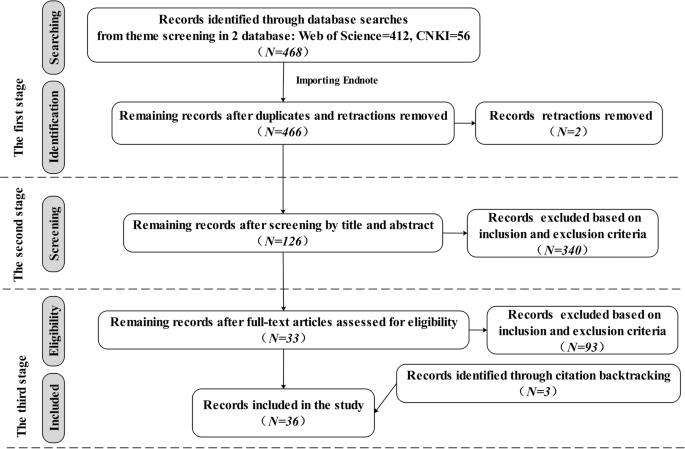
This flowchart shows the number of records identified, included and excluded in the article.
First, the databases used to systematically search for relevant articles were the journal papers of the Web of Science Core Collection and the Chinese Core source journal, as well as the Chinese Social Science Citation Index (CSSCI) source journal papers included in CNKI. These databases were selected because they are credible platforms that are sources of scholarly and peer-reviewed information with advanced search tools and contain literature relevant to the subject of our topic from reliable researchers and experts. The search string with the Boolean operator used in the Web of Science was “TS = (((“critical thinking” or “ct” and “pretest” or “posttest”) or (“critical thinking” or “ct” and “control group” or “quasi experiment” or “experiment”)) and (“collaboration” or “collaborative learning” or “CSCL”) and (“problem solving” or “problem-based learning” or “PBL”))”. The research area was “Education Educational Research”, and the search period was “January 1, 2000, to December 30, 2021”. A total of 412 papers were obtained. The search string with the Boolean operator used in the CNKI was “SU = (‘critical thinking’*‘collaboration’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘collaborative learning’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘CSCL’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘problem solving’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘problem-based learning’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘PBL’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘problem oriented’) AND FT = (‘experiment’ + ‘quasi experiment’ + ‘pretest’ + ‘posttest’ + ‘empirical study’)” (translated into Chinese when searching). A total of 56 studies were found throughout the search period of “January 2000 to December 2021”. From the databases, all duplicates and retractions were eliminated before exporting the references into Endnote, a program for managing bibliographic references. In all, 466 studies were found.
Second, the studies that matched the inclusion and exclusion criteria for the meta-analysis were chosen by two researchers after they had reviewed the abstracts and titles of the gathered articles, yielding a total of 126 studies.
Third, two researchers thoroughly reviewed each included article’s whole text in accordance with the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Meanwhile, a snowball search was performed using the references and citations of the included articles to ensure complete coverage of the articles. Ultimately, 36 articles were kept.
Two researchers worked together to carry out this entire process, and a consensus rate of almost 94.7% was reached after discussion and negotiation to clarify any emerging differences.
Eligibility criteria
Since not all the retrieved studies matched the criteria for this meta-analysis, eligibility criteria for both inclusion and exclusion were developed as follows:
The publication language of the included studies was limited to English and Chinese, and the full text could be obtained. Articles that did not meet the publication language and articles not published between 2000 and 2021 were excluded.
The research design of the included studies must be empirical and quantitative studies that can assess the effect of collaborative problem-solving on the development of critical thinking. Articles that could not identify the causal mechanisms by which collaborative problem-solving affects critical thinking, such as review articles and theoretical articles, were excluded.
The research method of the included studies must feature a randomized control experiment or a quasi-experiment, or a natural experiment, which have a higher degree of internal validity with strong experimental designs and can all plausibly provide evidence that critical thinking and collaborative problem-solving are causally related. Articles with non-experimental research methods, such as purely correlational or observational studies, were excluded.
The participants of the included studies were only students in school, including K-12 students and college students. Articles in which the participants were non-school students, such as social workers or adult learners, were excluded.
The research results of the included studies must mention definite signs that may be utilized to gauge critical thinking’s impact (e.g., sample size, mean value, or standard deviation). Articles that lacked specific measurement indicators for critical thinking and could not calculate the effect size were excluded.
Data coding design
In order to perform a meta-analysis, it is necessary to collect the most important information from the articles, codify that information’s properties, and convert descriptive data into quantitative data. Therefore, this study designed a data coding template (see Table 1 ). Ultimately, 16 coding fields were retained.
The designed data-coding template consisted of three pieces of information. Basic information about the papers was included in the descriptive information: the publishing year, author, serial number, and title of the paper.
The variable information for the experimental design had three variables: the independent variable (instruction method), the dependent variable (critical thinking), and the moderating variable (learning stage, teaching type, intervention duration, learning scaffold, group size, measuring tool, and subject area). Depending on the topic of this study, the intervention strategy, as the independent variable, was coded into collaborative and non-collaborative problem-solving. The dependent variable, critical thinking, was coded as a cognitive skill and an attitudinal tendency. And seven moderating variables were created by grouping and combining the experimental design variables discovered within the 36 studies (see Table 1 ), where learning stages were encoded as higher education, high school, middle school, and primary school or lower; teaching types were encoded as mixed courses, integrated courses, and independent courses; intervention durations were encoded as 0–1 weeks, 1–4 weeks, 4–12 weeks, and more than 12 weeks; group sizes were encoded as 2–3 persons, 4–6 persons, 7–10 persons, and more than 10 persons; learning scaffolds were encoded as teacher-supported learning scaffold, technique-supported learning scaffold, and resource-supported learning scaffold; measuring tools were encoded as standardized measurement tools (e.g., WGCTA, CCTT, CCTST, and CCTDI) and self-adapting measurement tools (e.g., modified or made by researchers); and subject areas were encoded according to the specific subjects used in the 36 included studies.
The data information contained three metrics for measuring critical thinking: sample size, average value, and standard deviation. It is vital to remember that studies with various experimental designs frequently adopt various formulas to determine the effect size. And this paper used Morris’ proposed standardized mean difference (SMD) calculation formula ( 2008 , p. 369; see Supplementary Table S3 ).
Procedure for extracting and coding data
According to the data coding template (see Table 1 ), the 36 papers’ information was retrieved by two researchers, who then entered them into Excel (see Supplementary Table S1 ). The results of each study were extracted separately in the data extraction procedure if an article contained numerous studies on critical thinking, or if a study assessed different critical thinking dimensions. For instance, Tiwari et al. ( 2010 ) used four time points, which were viewed as numerous different studies, to examine the outcomes of critical thinking, and Chen ( 2013 ) included the two outcome variables of attitudinal tendency and cognitive skills, which were regarded as two studies. After discussion and negotiation during data extraction, the two researchers’ consistency test coefficients were roughly 93.27%. Supplementary Table S2 details the key characteristics of the 36 included articles with 79 effect quantities, including descriptive information (e.g., the publishing year, author, serial number, and title of the paper), variable information (e.g., independent variables, dependent variables, and moderating variables), and data information (e.g., mean values, standard deviations, and sample size). Following that, testing for publication bias and heterogeneity was done on the sample data using the Rev-Man 5.4 software, and then the test results were used to conduct a meta-analysis.
Publication bias test
When the sample of studies included in a meta-analysis does not accurately reflect the general status of research on the relevant subject, publication bias is said to be exhibited in this research. The reliability and accuracy of the meta-analysis may be impacted by publication bias. Due to this, the meta-analysis needs to check the sample data for publication bias (Stewart et al., 2006 ). A popular method to check for publication bias is the funnel plot; and it is unlikely that there will be publishing bias when the data are equally dispersed on either side of the average effect size and targeted within the higher region. The data are equally dispersed within the higher portion of the efficient zone, consistent with the funnel plot connected with this analysis (see Fig. 2 ), indicating that publication bias is unlikely in this situation.
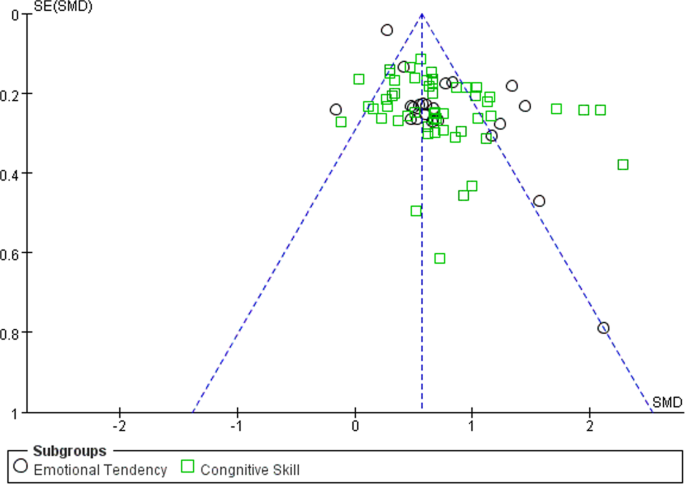
This funnel plot shows the result of publication bias of 79 effect quantities across 36 studies.
Heterogeneity test
To select the appropriate effect models for the meta-analysis, one might use the results of a heterogeneity test on the data effect sizes. In a meta-analysis, it is common practice to gauge the degree of data heterogeneity using the I 2 value, and I 2 ≥ 50% is typically understood to denote medium-high heterogeneity, which calls for the adoption of a random effect model; if not, a fixed effect model ought to be applied (Lipsey and Wilson, 2001 ). The findings of the heterogeneity test in this paper (see Table 2 ) revealed that I 2 was 86% and displayed significant heterogeneity ( P < 0.01). To ensure accuracy and reliability, the overall effect size ought to be calculated utilizing the random effect model.
The analysis of the overall effect size
This meta-analysis utilized a random effect model to examine 79 effect quantities from 36 studies after eliminating heterogeneity. In accordance with Cohen’s criterion (Cohen, 1992 ), it is abundantly clear from the analysis results, which are shown in the forest plot of the overall effect (see Fig. 3 ), that the cumulative impact size of cooperative problem-solving is 0.82, which is statistically significant ( z = 12.78, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.69, 0.95]), and can encourage learners to practice critical thinking.
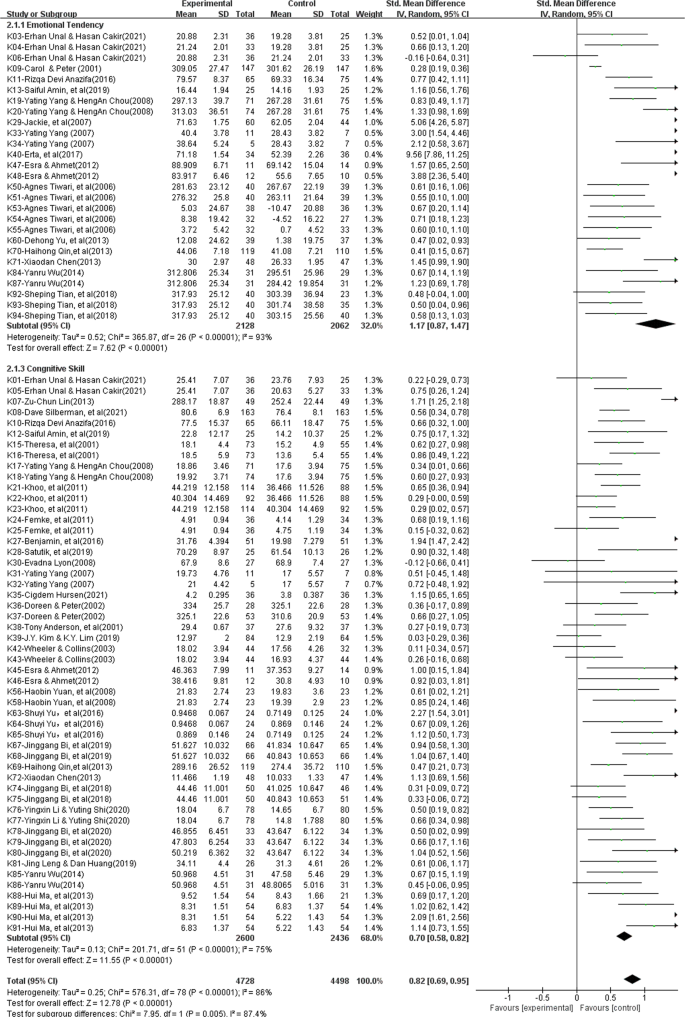
This forest plot shows the analysis result of the overall effect size across 36 studies.
In addition, this study examined two distinct dimensions of critical thinking to better understand the precise contributions that collaborative problem-solving makes to the growth of critical thinking. The findings (see Table 3 ) indicate that collaborative problem-solving improves cognitive skills (ES = 0.70) and attitudinal tendency (ES = 1.17), with significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 7.95, P < 0.01). Although collaborative problem-solving improves both dimensions of critical thinking, it is essential to point out that the improvements in students’ attitudinal tendency are much more pronounced and have a significant comprehensive effect (ES = 1.17, z = 7.62, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.87, 1.47]), whereas gains in learners’ cognitive skill are slightly improved and are just above average. (ES = 0.70, z = 11.55, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.58, 0.82]).
The analysis of moderator effect size
The whole forest plot’s 79 effect quantities underwent a two-tailed test, which revealed significant heterogeneity ( I 2 = 86%, z = 12.78, P < 0.01), indicating differences between various effect sizes that may have been influenced by moderating factors other than sampling error. Therefore, exploring possible moderating factors that might produce considerable heterogeneity was done using subgroup analysis, such as the learning stage, learning scaffold, teaching type, group size, duration of the intervention, measuring tool, and the subject area included in the 36 experimental designs, in order to further explore the key factors that influence critical thinking. The findings (see Table 4 ) indicate that various moderating factors have advantageous effects on critical thinking. In this situation, the subject area (chi 2 = 13.36, P < 0.05), group size (chi 2 = 8.77, P < 0.05), intervention duration (chi 2 = 12.18, P < 0.01), learning scaffold (chi 2 = 9.03, P < 0.01), and teaching type (chi 2 = 7.20, P < 0.05) are all significant moderators that can be applied to support the cultivation of critical thinking. However, since the learning stage and the measuring tools did not significantly differ among intergroup (chi 2 = 3.15, P = 0.21 > 0.05, and chi 2 = 0.08, P = 0.78 > 0.05), we are unable to explain why these two factors are crucial in supporting the cultivation of critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving. These are the precise outcomes, as follows:
Various learning stages influenced critical thinking positively, without significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 3.15, P = 0.21 > 0.05). High school was first on the list of effect sizes (ES = 1.36, P < 0.01), then higher education (ES = 0.78, P < 0.01), and middle school (ES = 0.73, P < 0.01). These results show that, despite the learning stage’s beneficial influence on cultivating learners’ critical thinking, we are unable to explain why it is essential for cultivating critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving.
Different teaching types had varying degrees of positive impact on critical thinking, with significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 7.20, P < 0.05). The effect size was ranked as follows: mixed courses (ES = 1.34, P < 0.01), integrated courses (ES = 0.81, P < 0.01), and independent courses (ES = 0.27, P < 0.01). These results indicate that the most effective approach to cultivate critical thinking utilizing collaborative problem solving is through the teaching type of mixed courses.
Various intervention durations significantly improved critical thinking, and there were significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 12.18, P < 0.01). The effect sizes related to this variable showed a tendency to increase with longer intervention durations. The improvement in critical thinking reached a significant level (ES = 0.85, P < 0.01) after more than 12 weeks of training. These findings indicate that the intervention duration and critical thinking’s impact are positively correlated, with a longer intervention duration having a greater effect.
Different learning scaffolds influenced critical thinking positively, with significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 9.03, P < 0.01). The resource-supported learning scaffold (ES = 0.69, P < 0.01) acquired a medium-to-higher level of impact, the technique-supported learning scaffold (ES = 0.63, P < 0.01) also attained a medium-to-higher level of impact, and the teacher-supported learning scaffold (ES = 0.92, P < 0.01) displayed a high level of significant impact. These results show that the learning scaffold with teacher support has the greatest impact on cultivating critical thinking.
Various group sizes influenced critical thinking positively, and the intergroup differences were statistically significant (chi 2 = 8.77, P < 0.05). Critical thinking showed a general declining trend with increasing group size. The overall effect size of 2–3 people in this situation was the biggest (ES = 0.99, P < 0.01), and when the group size was greater than 7 people, the improvement in critical thinking was at the lower-middle level (ES < 0.5, P < 0.01). These results show that the impact on critical thinking is positively connected with group size, and as group size grows, so does the overall impact.
Various measuring tools influenced critical thinking positively, with significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 0.08, P = 0.78 > 0.05). In this situation, the self-adapting measurement tools obtained an upper-medium level of effect (ES = 0.78), whereas the complete effect size of the standardized measurement tools was the largest, achieving a significant level of effect (ES = 0.84, P < 0.01). These results show that, despite the beneficial influence of the measuring tool on cultivating critical thinking, we are unable to explain why it is crucial in fostering the growth of critical thinking by utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
Different subject areas had a greater impact on critical thinking, and the intergroup differences were statistically significant (chi 2 = 13.36, P < 0.05). Mathematics had the greatest overall impact, achieving a significant level of effect (ES = 1.68, P < 0.01), followed by science (ES = 1.25, P < 0.01) and medical science (ES = 0.87, P < 0.01), both of which also achieved a significant level of effect. Programming technology was the least effective (ES = 0.39, P < 0.01), only having a medium-low degree of effect compared to education (ES = 0.72, P < 0.01) and other fields (such as language, art, and social sciences) (ES = 0.58, P < 0.01). These results suggest that scientific fields (e.g., mathematics, science) may be the most effective subject areas for cultivating critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
The effectiveness of collaborative problem solving with regard to teaching critical thinking
According to this meta-analysis, using collaborative problem-solving as an intervention strategy in critical thinking teaching has a considerable amount of impact on cultivating learners’ critical thinking as a whole and has a favorable promotional effect on the two dimensions of critical thinking. According to certain studies, collaborative problem solving, the most frequently used critical thinking teaching strategy in curriculum instruction can considerably enhance students’ critical thinking (e.g., Liang et al., 2017 ; Liu et al., 2020 ; Cindy, 2004 ). This meta-analysis provides convergent data support for the above research views. Thus, the findings of this meta-analysis not only effectively address the first research query regarding the overall effect of cultivating critical thinking and its impact on the two dimensions of critical thinking (i.e., attitudinal tendency and cognitive skills) utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving, but also enhance our confidence in cultivating critical thinking by using collaborative problem-solving intervention approach in the context of classroom teaching.
Furthermore, the associated improvements in attitudinal tendency are much stronger, but the corresponding improvements in cognitive skill are only marginally better. According to certain studies, cognitive skill differs from the attitudinal tendency in classroom instruction; the cultivation and development of the former as a key ability is a process of gradual accumulation, while the latter as an attitude is affected by the context of the teaching situation (e.g., a novel and exciting teaching approach, challenging and rewarding tasks) (Halpern, 2001 ; Wei and Hong, 2022 ). Collaborative problem-solving as a teaching approach is exciting and interesting, as well as rewarding and challenging; because it takes the learners as the focus and examines problems with poor structure in real situations, and it can inspire students to fully realize their potential for problem-solving, which will significantly improve their attitudinal tendency toward solving problems (Liu et al., 2020 ). Similar to how collaborative problem-solving influences attitudinal tendency, attitudinal tendency impacts cognitive skill when attempting to solve a problem (Liu et al., 2020 ; Zhang et al., 2022 ), and stronger attitudinal tendencies are associated with improved learning achievement and cognitive ability in students (Sison, 2008 ; Zhang et al., 2022 ). It can be seen that the two specific dimensions of critical thinking as well as critical thinking as a whole are affected by collaborative problem-solving, and this study illuminates the nuanced links between cognitive skills and attitudinal tendencies with regard to these two dimensions of critical thinking. To fully develop students’ capacity for critical thinking, future empirical research should pay closer attention to cognitive skills.
The moderating effects of collaborative problem solving with regard to teaching critical thinking
In order to further explore the key factors that influence critical thinking, exploring possible moderating effects that might produce considerable heterogeneity was done using subgroup analysis. The findings show that the moderating factors, such as the teaching type, learning stage, group size, learning scaffold, duration of the intervention, measuring tool, and the subject area included in the 36 experimental designs, could all support the cultivation of collaborative problem-solving in critical thinking. Among them, the effect size differences between the learning stage and measuring tool are not significant, which does not explain why these two factors are crucial in supporting the cultivation of critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
In terms of the learning stage, various learning stages influenced critical thinking positively without significant intergroup differences, indicating that we are unable to explain why it is crucial in fostering the growth of critical thinking.
Although high education accounts for 70.89% of all empirical studies performed by researchers, high school may be the appropriate learning stage to foster students’ critical thinking by utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving since it has the largest overall effect size. This phenomenon may be related to student’s cognitive development, which needs to be further studied in follow-up research.
With regard to teaching type, mixed course teaching may be the best teaching method to cultivate students’ critical thinking. Relevant studies have shown that in the actual teaching process if students are trained in thinking methods alone, the methods they learn are isolated and divorced from subject knowledge, which is not conducive to their transfer of thinking methods; therefore, if students’ thinking is trained only in subject teaching without systematic method training, it is challenging to apply to real-world circumstances (Ruggiero, 2012 ; Hu and Liu, 2015 ). Teaching critical thinking as mixed course teaching in parallel to other subject teachings can achieve the best effect on learners’ critical thinking, and explicit critical thinking instruction is more effective than less explicit critical thinking instruction (Bensley and Spero, 2014 ).
In terms of the intervention duration, with longer intervention times, the overall effect size shows an upward tendency. Thus, the intervention duration and critical thinking’s impact are positively correlated. Critical thinking, as a key competency for students in the 21st century, is difficult to get a meaningful improvement in a brief intervention duration. Instead, it could be developed over a lengthy period of time through consistent teaching and the progressive accumulation of knowledge (Halpern, 2001 ; Hu and Liu, 2015 ). Therefore, future empirical studies ought to take these restrictions into account throughout a longer period of critical thinking instruction.
With regard to group size, a group size of 2–3 persons has the highest effect size, and the comprehensive effect size decreases with increasing group size in general. This outcome is in line with some research findings; as an example, a group composed of two to four members is most appropriate for collaborative learning (Schellens and Valcke, 2006 ). However, the meta-analysis results also indicate that once the group size exceeds 7 people, small groups cannot produce better interaction and performance than large groups. This may be because the learning scaffolds of technique support, resource support, and teacher support improve the frequency and effectiveness of interaction among group members, and a collaborative group with more members may increase the diversity of views, which is helpful to cultivate critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
With regard to the learning scaffold, the three different kinds of learning scaffolds can all enhance critical thinking. Among them, the teacher-supported learning scaffold has the largest overall effect size, demonstrating the interdependence of effective learning scaffolds and collaborative problem-solving. This outcome is in line with some research findings; as an example, a successful strategy is to encourage learners to collaborate, come up with solutions, and develop critical thinking skills by using learning scaffolds (Reiser, 2004 ; Xu et al., 2022 ); learning scaffolds can lower task complexity and unpleasant feelings while also enticing students to engage in learning activities (Wood et al., 2006 ); learning scaffolds are designed to assist students in using learning approaches more successfully to adapt the collaborative problem-solving process, and the teacher-supported learning scaffolds have the greatest influence on critical thinking in this process because they are more targeted, informative, and timely (Xu et al., 2022 ).
With respect to the measuring tool, despite the fact that standardized measurement tools (such as the WGCTA, CCTT, and CCTST) have been acknowledged as trustworthy and effective by worldwide experts, only 54.43% of the research included in this meta-analysis adopted them for assessment, and the results indicated no intergroup differences. These results suggest that not all teaching circumstances are appropriate for measuring critical thinking using standardized measurement tools. “The measuring tools for measuring thinking ability have limits in assessing learners in educational situations and should be adapted appropriately to accurately assess the changes in learners’ critical thinking.”, according to Simpson and Courtney ( 2002 , p. 91). As a result, in order to more fully and precisely gauge how learners’ critical thinking has evolved, we must properly modify standardized measuring tools based on collaborative problem-solving learning contexts.
With regard to the subject area, the comprehensive effect size of science departments (e.g., mathematics, science, medical science) is larger than that of language arts and social sciences. Some recent international education reforms have noted that critical thinking is a basic part of scientific literacy. Students with scientific literacy can prove the rationality of their judgment according to accurate evidence and reasonable standards when they face challenges or poorly structured problems (Kyndt et al., 2013 ), which makes critical thinking crucial for developing scientific understanding and applying this understanding to practical problem solving for problems related to science, technology, and society (Yore et al., 2007 ).
Suggestions for critical thinking teaching
Other than those stated in the discussion above, the following suggestions are offered for critical thinking instruction utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
First, teachers should put a special emphasis on the two core elements, which are collaboration and problem-solving, to design real problems based on collaborative situations. This meta-analysis provides evidence to support the view that collaborative problem-solving has a strong synergistic effect on promoting students’ critical thinking. Asking questions about real situations and allowing learners to take part in critical discussions on real problems during class instruction are key ways to teach critical thinking rather than simply reading speculative articles without practice (Mulnix, 2012 ). Furthermore, the improvement of students’ critical thinking is realized through cognitive conflict with other learners in the problem situation (Yang et al., 2008 ). Consequently, it is essential for teachers to put a special emphasis on the two core elements, which are collaboration and problem-solving, and design real problems and encourage students to discuss, negotiate, and argue based on collaborative problem-solving situations.
Second, teachers should design and implement mixed courses to cultivate learners’ critical thinking, utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving. Critical thinking can be taught through curriculum instruction (Kuncel, 2011 ; Leng and Lu, 2020 ), with the goal of cultivating learners’ critical thinking for flexible transfer and application in real problem-solving situations. This meta-analysis shows that mixed course teaching has a highly substantial impact on the cultivation and promotion of learners’ critical thinking. Therefore, teachers should design and implement mixed course teaching with real collaborative problem-solving situations in combination with the knowledge content of specific disciplines in conventional teaching, teach methods and strategies of critical thinking based on poorly structured problems to help students master critical thinking, and provide practical activities in which students can interact with each other to develop knowledge construction and critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
Third, teachers should be more trained in critical thinking, particularly preservice teachers, and they also should be conscious of the ways in which teachers’ support for learning scaffolds can promote critical thinking. The learning scaffold supported by teachers had the greatest impact on learners’ critical thinking, in addition to being more directive, targeted, and timely (Wood et al., 2006 ). Critical thinking can only be effectively taught when teachers recognize the significance of critical thinking for students’ growth and use the proper approaches while designing instructional activities (Forawi, 2016 ). Therefore, with the intention of enabling teachers to create learning scaffolds to cultivate learners’ critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem solving, it is essential to concentrate on the teacher-supported learning scaffolds and enhance the instruction for teaching critical thinking to teachers, especially preservice teachers.
Implications and limitations
There are certain limitations in this meta-analysis, but future research can correct them. First, the search languages were restricted to English and Chinese, so it is possible that pertinent studies that were written in other languages were overlooked, resulting in an inadequate number of articles for review. Second, these data provided by the included studies are partially missing, such as whether teachers were trained in the theory and practice of critical thinking, the average age and gender of learners, and the differences in critical thinking among learners of various ages and genders. Third, as is typical for review articles, more studies were released while this meta-analysis was being done; therefore, it had a time limit. With the development of relevant research, future studies focusing on these issues are highly relevant and needed.
Conclusions
The subject of the magnitude of collaborative problem-solving’s impact on fostering students’ critical thinking, which received scant attention from other studies, was successfully addressed by this study. The question of the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking was addressed in this study, which addressed a topic that had gotten little attention in earlier research. The following conclusions can be made:
Regarding the results obtained, collaborative problem solving is an effective teaching approach to foster learners’ critical thinking, with a significant overall effect size (ES = 0.82, z = 12.78, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.69, 0.95]). With respect to the dimensions of critical thinking, collaborative problem-solving can significantly and effectively improve students’ attitudinal tendency, and the comprehensive effect is significant (ES = 1.17, z = 7.62, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.87, 1.47]); nevertheless, it falls short in terms of improving students’ cognitive skills, having only an upper-middle impact (ES = 0.70, z = 11.55, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.58, 0.82]).
As demonstrated by both the results and the discussion, there are varying degrees of beneficial effects on students’ critical thinking from all seven moderating factors, which were found across 36 studies. In this context, the teaching type (chi 2 = 7.20, P < 0.05), intervention duration (chi 2 = 12.18, P < 0.01), subject area (chi 2 = 13.36, P < 0.05), group size (chi 2 = 8.77, P < 0.05), and learning scaffold (chi 2 = 9.03, P < 0.01) all have a positive impact on critical thinking, and they can be viewed as important moderating factors that affect how critical thinking develops. Since the learning stage (chi 2 = 3.15, P = 0.21 > 0.05) and measuring tools (chi 2 = 0.08, P = 0.78 > 0.05) did not demonstrate any significant intergroup differences, we are unable to explain why these two factors are crucial in supporting the cultivation of critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included within the article and its supplementary information files, and the supplementary information files are available in the Dataverse repository: https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/IPFJO6 .
Bensley DA, Spero RA (2014) Improving critical thinking skills and meta-cognitive monitoring through direct infusion. Think Skills Creat 12:55–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2014.02.001
Article Google Scholar
Castle A (2009) Defining and assessing critical thinking skills for student radiographers. Radiography 15(1):70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radi.2007.10.007
Chen XD (2013) An empirical study on the influence of PBL teaching model on critical thinking ability of non-English majors. J PLA Foreign Lang College 36 (04):68–72
Google Scholar
Cohen A (1992) Antecedents of organizational commitment across occupational groups: a meta-analysis. J Organ Behav. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.4030130602
Cooper H (2010) Research synthesis and meta-analysis: a step-by-step approach, 4th edn. Sage, London, England
Cindy HS (2004) Problem-based learning: what and how do students learn? Educ Psychol Rev 51(1):31–39
Duch BJ, Gron SD, Allen DE (2001) The power of problem-based learning: a practical “how to” for teaching undergraduate courses in any discipline. Stylus Educ Sci 2:190–198
Ennis RH (1989) Critical thinking and subject specificity: clarification and needed research. Educ Res 18(3):4–10. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189x018003004
Facione PA (1990) Critical thinking: a statement of expert consensus for purposes of educational assessment and instruction. Research findings and recommendations. Eric document reproduction service. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ed315423
Facione PA, Facione NC (1992) The California Critical Thinking Dispositions Inventory (CCTDI) and the CCTDI test manual. California Academic Press, Millbrae, CA
Forawi SA (2016) Standard-based science education and critical thinking. Think Skills Creat 20:52–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2016.02.005
Halpern DF (2001) Assessing the effectiveness of critical thinking instruction. J Gen Educ 50(4):270–286. https://doi.org/10.2307/27797889
Hu WP, Liu J (2015) Cultivation of pupils’ thinking ability: a five-year follow-up study. Psychol Behav Res 13(05):648–654. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-0628.2015.05.010
Huber K (2016) Does college teach critical thinking? A meta-analysis. Rev Educ Res 86(2):431–468. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654315605917
Kek MYCA, Huijser H (2011) The power of problem-based learning in developing critical thinking skills: preparing students for tomorrow’s digital futures in today’s classrooms. High Educ Res Dev 30(3):329–341. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2010.501074
Kuncel NR (2011) Measurement and meaning of critical thinking (Research report for the NRC 21st Century Skills Workshop). National Research Council, Washington, DC
Kyndt E, Raes E, Lismont B, Timmers F, Cascallar E, Dochy F (2013) A meta-analysis of the effects of face-to-face cooperative learning. Do recent studies falsify or verify earlier findings? Educ Res Rev 10(2):133–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2013.02.002
Leng J, Lu XX (2020) Is critical thinking really teachable?—A meta-analysis based on 79 experimental or quasi experimental studies. Open Educ Res 26(06):110–118. https://doi.org/10.13966/j.cnki.kfjyyj.2020.06.011
Liang YZ, Zhu K, Zhao CL (2017) An empirical study on the depth of interaction promoted by collaborative problem solving learning activities. J E-educ Res 38(10):87–92. https://doi.org/10.13811/j.cnki.eer.2017.10.014
Lipsey M, Wilson D (2001) Practical meta-analysis. International Educational and Professional, London, pp. 92–160
Liu Z, Wu W, Jiang Q (2020) A study on the influence of problem based learning on college students’ critical thinking-based on a meta-analysis of 31 studies. Explor High Educ 03:43–49
Morris SB (2008) Estimating effect sizes from pretest-posttest-control group designs. Organ Res Methods 11(2):364–386. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428106291059
Article ADS Google Scholar
Mulnix JW (2012) Thinking critically about critical thinking. Educ Philos Theory 44(5):464–479. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-5812.2010.00673.x
Naber J, Wyatt TH (2014) The effect of reflective writing interventions on the critical thinking skills and dispositions of baccalaureate nursing students. Nurse Educ Today 34(1):67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2013.04.002
National Research Council (2012) Education for life and work: developing transferable knowledge and skills in the 21st century. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC
Niu L, Behar HLS, Garvan CW (2013) Do instructional interventions influence college students’ critical thinking skills? A meta-analysis. Educ Res Rev 9(12):114–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2012.12.002
Peng ZM, Deng L (2017) Towards the core of education reform: cultivating critical thinking skills as the core of skills in the 21st century. Res Educ Dev 24:57–63. https://doi.org/10.14121/j.cnki.1008-3855.2017.24.011
Reiser BJ (2004) Scaffolding complex learning: the mechanisms of structuring and problematizing student work. J Learn Sci 13(3):273–304. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327809jls1303_2
Ruggiero VR (2012) The art of thinking: a guide to critical and creative thought, 4th edn. Harper Collins College Publishers, New York
Schellens T, Valcke M (2006) Fostering knowledge construction in university students through asynchronous discussion groups. Comput Educ 46(4):349–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2004.07.010
Sendag S, Odabasi HF (2009) Effects of an online problem based learning course on content knowledge acquisition and critical thinking skills. Comput Educ 53(1):132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2009.01.008
Sison R (2008) Investigating Pair Programming in a Software Engineering Course in an Asian Setting. 2008 15th Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference, pp. 325–331. https://doi.org/10.1109/APSEC.2008.61
Simpson E, Courtney M (2002) Critical thinking in nursing education: literature review. Mary Courtney 8(2):89–98
Stewart L, Tierney J, Burdett S (2006) Do systematic reviews based on individual patient data offer a means of circumventing biases associated with trial publications? Publication bias in meta-analysis. John Wiley and Sons Inc, New York, pp. 261–286
Tiwari A, Lai P, So M, Yuen K (2010) A comparison of the effects of problem-based learning and lecturing on the development of students’ critical thinking. Med Educ 40(6):547–554. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2929.2006.02481.x
Wood D, Bruner JS, Ross G (2006) The role of tutoring in problem solving. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 17(2):89–100. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.1976.tb00381.x
Wei T, Hong S (2022) The meaning and realization of teachable critical thinking. Educ Theory Practice 10:51–57
Xu EW, Wang W, Wang QX (2022) A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of programming teaching in promoting K-12 students’ computational thinking. Educ Inf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11445-2
Yang YC, Newby T, Bill R (2008) Facilitating interactions through structured web-based bulletin boards: a quasi-experimental study on promoting learners’ critical thinking skills. Comput Educ 50(4):1572–1585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2007.04.006
Yore LD, Pimm D, Tuan HL (2007) The literacy component of mathematical and scientific literacy. Int J Sci Math Educ 5(4):559–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-007-9089-4
Zhang T, Zhang S, Gao QQ, Wang JH (2022) Research on the development of learners’ critical thinking in online peer review. Audio Visual Educ Res 6:53–60. https://doi.org/10.13811/j.cnki.eer.2022.06.08
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the graduate scientific research and innovation project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region named “Research on in-depth learning of high school information technology courses for the cultivation of computing thinking” (No. XJ2022G190) and the independent innovation fund project for doctoral students of the College of Educational Science of Xinjiang Normal University named “Research on project-based teaching of high school information technology courses from the perspective of discipline core literacy” (No. XJNUJKYA2003).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Educational Science, Xinjiang Normal University, 830017, Urumqi, Xinjiang, China
Enwei Xu, Wei Wang & Qingxia Wang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Enwei Xu or Wei Wang .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Additional information.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary tables, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Xu, E., Wang, W. & Wang, Q. The effectiveness of collaborative problem solving in promoting students’ critical thinking: A meta-analysis based on empirical literature. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 10 , 16 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01508-1
Download citation
Received : 07 August 2022
Accepted : 04 January 2023
Published : 11 January 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01508-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Impacts of online collaborative learning on students’ intercultural communication apprehension and intercultural communicative competence.
- Hoa Thi Hoang Chau
- Hung Phu Bui
- Quynh Thi Huong Dinh
Education and Information Technologies (2024)
Exploring the effects of digital technology on deep learning: a meta-analysis
Sustainable electricity generation and farm-grid utilization from photovoltaic aquaculture: a bibliometric analysis.
- A. A. Amusa
- M. Alhassan
International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Teaching problem solving: Let students get ‘stuck’ and ‘unstuck’
Subscribe to the center for universal education bulletin, kate mills and km kate mills literacy interventionist - red bank primary school helyn kim helyn kim former brookings expert @helyn_kim.
October 31, 2017
This is the second in a six-part blog series on teaching 21st century skills , including problem solving , metacognition , critical thinking , and collaboration , in classrooms.
In the real world, students encounter problems that are complex, not well defined, and lack a clear solution and approach. They need to be able to identify and apply different strategies to solve these problems. However, problem solving skills do not necessarily develop naturally; they need to be explicitly taught in a way that can be transferred across multiple settings and contexts.
Here’s what Kate Mills, who taught 4 th grade for 10 years at Knollwood School in New Jersey and is now a Literacy Interventionist at Red Bank Primary School, has to say about creating a classroom culture of problem solvers:
Helping my students grow to be people who will be successful outside of the classroom is equally as important as teaching the curriculum. From the first day of school, I intentionally choose language and activities that help to create a classroom culture of problem solvers. I want to produce students who are able to think about achieving a particular goal and manage their mental processes . This is known as metacognition , and research shows that metacognitive skills help students become better problem solvers.
I begin by “normalizing trouble” in the classroom. Peter H. Johnston teaches the importance of normalizing struggle , of naming it, acknowledging it, and calling it what it is: a sign that we’re growing. The goal is for the students to accept challenge and failure as a chance to grow and do better.
I look for every chance to share problems and highlight how the students— not the teachers— worked through those problems. There is, of course, coaching along the way. For example, a science class that is arguing over whose turn it is to build a vehicle will most likely need a teacher to help them find a way to the balance the work in an equitable way. Afterwards, I make it a point to turn it back to the class and say, “Do you see how you …” By naming what it is they did to solve the problem , students can be more independent and productive as they apply and adapt their thinking when engaging in future complex tasks.
After a few weeks, most of the class understands that the teachers aren’t there to solve problems for the students, but to support them in solving the problems themselves. With that important part of our classroom culture established, we can move to focusing on the strategies that students might need.
Here’s one way I do this in the classroom:
I show the broken escalator video to the class. Since my students are fourth graders, they think it’s hilarious and immediately start exclaiming, “Just get off! Walk!”
When the video is over, I say, “Many of us, probably all of us, are like the man in the video yelling for help when we get stuck. When we get stuck, we stop and immediately say ‘Help!’ instead of embracing the challenge and trying new ways to work through it.” I often introduce this lesson during math class, but it can apply to any area of our lives, and I can refer to the experience and conversation we had during any part of our day.
Research shows that just because students know the strategies does not mean they will engage in the appropriate strategies. Therefore, I try to provide opportunities where students can explicitly practice learning how, when, and why to use which strategies effectively so that they can become self-directed learners.
For example, I give students a math problem that will make many of them feel “stuck”. I will say, “Your job is to get yourselves stuck—or to allow yourselves to get stuck on this problem—and then work through it, being mindful of how you’re getting yourselves unstuck.” As students work, I check-in to help them name their process: “How did you get yourself unstuck?” or “What was your first step? What are you doing now? What might you try next?” As students talk about their process, I’ll add to a list of strategies that students are using and, if they are struggling, help students name a specific process. For instance, if a student says he wrote the information from the math problem down and points to a chart, I will say: “Oh that’s interesting. You pulled the important information from the problem out and organized it into a chart.” In this way, I am giving him the language to match what he did, so that he now has a strategy he could use in other times of struggle.
The charts grow with us over time and are something that we refer to when students are stuck or struggling. They become a resource for students and a way for them to talk about their process when they are reflecting on and monitoring what did or did not work.
For me, as a teacher, it is important that I create a classroom environment in which students are problem solvers. This helps tie struggles to strategies so that the students will not only see value in working harder but in working smarter by trying new and different strategies and revising their process. In doing so, they will more successful the next time around.
Related Content
Esther Care, Helyn Kim, Alvin Vista
October 17, 2017
David Owen, Alvin Vista
November 15, 2017
Loren Clarke, Esther Care
December 5, 2017
Global Education K-12 Education
Global Economy and Development
Center for Universal Education
Sopiko Beriashvili, Michael Trucano
April 26, 2024
Richard V. Reeves, Ember Smith
Michael Trucano, Sopiko Beriashvili
April 25, 2024
- Author Rights
- Diversity, Equity & Inclusion

- JOLE 2023 Special Issue
- Editorial Staff
- 20th Anniversary Issue
- The Development of Problem-Solving Skills for Aspiring Educational Leaders
Jeremy D. Visone 10.12806/V17/I4/R3
Introduction
Solving problems is a quintessential aspect of the role of an educational leader. In particular, building leaders, such as principals, assistant principals, and deans of students, are frequently beset by situations that are complex, unique, and open-ended. There are often many possible pathways to resolve the situations, and an astute educational leader needs to consider many factors and constituencies before determining a plan of action. The realm of problem solving might include student misconduct, personnel matters, parental complaints, school culture, instructional leadership, as well as many other aspects of educational administration. Much consideration has been given to the development of problem-solving skills for educational leaders. This study was designed to answer the following research question: “How do aspiring educational leaders’ problem solving skills, as well as perceptions of their problem-solving skills, develop during a year-long graduate course sequence focused on school-level leadership that includes the presentation of real-world scenarios?” This mixed-methods study extends research about the development of problem-solving skills conducted with acting administrators (Leithwood & Steinbach, 1992, 1995).
The Nature of Problems
Before examining how educational leaders can process and solve problems effectively, it is worth considering the nature of problems. Allison (1996) posited simply that problems are situations that require thought and/or actions. Further, there are different types of problems presented to educational leaders. First, there are well-structured problems , which can be defined as those with clear goals and relatively prescribed resolution pathways, including an easy way of determining whether goals were met (Allison, 1996).
Conversely, ill-structured problems are those with more open-ended profiles, whereby the goals, resolution pathways, or evidence of success are not necessarily clear. These types of problems could also be considered unstructured (Leithwood & Steinbach, 1995) or open-design (Allison, 1996). Many of the problems presented to educational leaders are unstructured problems. For example, a principal must decide how to discipline children who misbehave, taking into consideration their disciplinary history, rules and protocols of the school, and other contextual factors; determine how best to raise student achievement (Duke, 2014); and resolve personnel disputes among staff members. None of these problems point to singular solutions that can be identified as “right” or “wrong.” Surely there are responses that are less desirable than others (i.e. suspension or recommendation for expulsion for minor infractions), but, with justification and context, many possible solutions exist.
Problem-Solving Perspectives and Models
Various authors have shared perspectives about effective problem solving. Marzano, Waters, and McNulty (2005) outlined the “21 Responsibilities of the School Leader.” These responsibilities are highly correlated with student achievement based upon the authors’ meta- analysis of 69 studies about leadership’s effect on student achievement. The most highly correlated of the responsibilities was situational awareness , which refers to understanding the school deeply enough to anticipate what might go wrong from day-to-day, navigate the individuals and groups within the school, and recognize issues that might surface at a later time (Marzano et al., 2005). Though the authors discuss the utility of situational awareness for long- term, large-scale decision making, in order for an educational leader to effectively solve the daily problems that come her way, she must again have a sense of situational awareness, lest she make seemingly smaller-scale decisions that will lead to large-scale problems later.
Other authors have focused on problems that can be considered more aligned with the daily work of educational leaders. Considering the problem-type classification dichotomies of Allison (1996) and Leithwood and Steinbach (1995), problems that educational leaders face on a daily basis can be identified as either well-structured or unstructured. Various authors have developed problem-solving models focused on unstructured problems (Bolman & Deal, 2008; Leithwood & Steinbach, 1995; Simon, 1993), and these models will be explored next.
Simon (1993) outlined three phases of the decision-making process. The first is to find problems that need attention. Though many problems of educational leaders are presented directly to them via, for example, an adult referring a child for discipline, a parent registering a complaint about a staff member, or a staff member describing a grievance with a colleague, there is a corollary skill of identifying what problems—of the many that come across one’s desk— require immediate attention, or ultimately, any attention, at all. Second, Simon identified “designing possible courses of action” (p. 395). Finally, educational leaders must evaluate the quality of their decisions. From this point of having selected a viable and positively evaluated potential solution pathway, implementation takes place.
Bolman and Deal (2008) outlined a model of reframing problems using four different frames, through which problems of practice can be viewed. These frames provide leaders with a more complete set of perspectives than they would likely utilize on their own. The structural frame represents the procedural and systems-oriented aspects of an organization. Within this frame, a leader might ask whether there is a supervisory relationship involved in a problem, if a protocol exists to solve such a problem, or what efficiencies or logical processes can help steer a leader toward a resolution that meets organizational goals. The human resource frame refers to the needs of individuals within the organization. A leader might try to solve a problem of practice with the needs of constituents in mind, considering the development of employees and the balance between their satisfaction and intellectual stimulation and the organization’s needs. The political frame includes the often competing interests among individuals and groups within the organization, whereby alliances and negotiations are needed to navigate the potential minefield of many groups’ overlapping aims. From the political frame, a leader could consider what the interpersonal costs will be for the leader and organization among different constituent groups, based upon which alternatives are selected. Last, the symbolic frame includes elements of meaning within an organization, such as traditions, unspoken rules, and myths. A leader may need to consider this frame when proposing a solution that might interfere with a long-standing organizational tradition.
Bolman and Deal (2008) identified the political and symbolic frames as weaknesses in most leaders’ consideration of problems of practice, and the weakness in recognizing political aspects of decision making for educational leaders was corroborated by Johnson and Kruse (2009). An implication for leadership preparation is to instruct students in the considerations of these frames and promote their utility when examining problems.
Authors have noted that experts use different processes than novice problem solvers (Simon, 1993; VanLehn, 1991). An application of this would be Simon’s (1993) assertion that experts can rely on their extensive experience to remember solutions to many problems, without having to rely on an extensive analytical process. Further, they may not even consider a “problem” identified by a novice a problem, at all. With respect to educational leaders, Leithwood and Steinbach (1992, 1995) outlined a set of competencies possessed by expert principals, when compared to their typical counterparts. Expert principals were better at identifying the nature of problems; possessing a sense of priority, difficulty, how to proceed, and connectedness to prior situations; setting meaningful goals for problem solving, such as seeking goals that are student-centered and knowledge-focused; using guiding principles and long-term purposes when determining the best courses of action; seeing fewer obstacles and constraints when presented with problems; outlining detailed plans for action that include gathering extensive information to inform decisions along the plan’s pathway; and responding with confidence and calm to problem solving. Next, I will examine how problem-solving skills are developed.
Preparation for Educational Leadership Problem Solving
How can the preparation of leaders move candidates toward the competencies of expert principals? After all, leading a school has been shown to be a remarkably complex enterprise (Hallinger & McCary, 1990; Leithwood & Steinbach, 1992), especially if the school is one where student achievement is below expectations (Duke, 2014), and the framing of problems by educational leaders has been espoused as a critically important enterprise (Bolman & Deal, 2008; Dimmock, 1996; Johnson & Kruse, 2009; Leithwood & Steinbach, 1992, 1995; Myran & Sutherland, 2016). In other disciplines, such as business management, simulations and case studies are used to foster problem-solving skills for aspiring leaders (Rochford & Borchert, 2011; Salas, Wildman, & Piccolo, 2009), and attention to problem-solving skills has been identified as an essential curricular component in the training of journalism and mass communication students (Bronstein & Fitzpatrick, 2015). Could such real-world problem solving methodologies be effective in the preparation of educational leaders? In a seminal study about problem solving for educational leaders, Leithwood and Steinbach (1992, 1995) sought to determine if effective problem-solving expertise could be explicitly taught, and, if so, could teaching problem- processing expertise be helpful in moving novices toward expert competence? Over the course of four months and four separate learning sessions, participants in the control group were explicitly taught subskills within six problem-solving components: interpretation of the problem for priority, perceived difficulty, data needed for further action, and anecdotes of prior experience that can inform action; goals for solving the problem; large-scale principles that guide decision making; barriers or obstacles that need to be overcome; possible courses of action; and the confidence of the leader to solve the problem. The authors asserted that providing conditions to participants that included models of effective problem-solving, feedback, increasingly complex problem-solving demands, frequent opportunities for practice, group problem-solving, individual reflection, authentic problems, and help to stimulate metacognition and reflection would result in educational leaders improving their problem-solving skills.
The authors used two experts’ ratings of participants’ problem-solving for both process (their methods of attacking the problem) and product (their solutions) using a 0-3 scale in a pretest-posttest design. They found significant increases in some problem-solving skills (problem interpretation, goal setting, and identification of barriers or obstacles that need to be overcome) after explicit instruction (Leithwood & Steinbach, 1992, 1995). They recommended conducting more research on the preparation of educational leaders, with particular respect to approaches that would improve the aspiring leaders’ problem-solving skills.
Solving problems for practicing principals could be described as constructivist, since most principals do solve problems within a social context of other stakeholders, such as teachers, parents, and students (Leithwood & Steinbach, 1992). Thus, some authors have examined providing opportunities for novice or aspiring leaders to construct meaning from novel scenarios using the benefits of, for example, others’ point of view, expert modeling, simulations, and prior knowledge (Duke, 2014; Leithwood & Steinbach, 1992, 1995; Myran & Sutherland, 2016; Shapira-Lishchinsky, 2015). Such collaborative inquiry has been effective for teachers, as well (DeLuca, Bolden, & Chan, 2017). Such learning can be considered consistent with the ideas of other social constructivist theorists (Berger & Luckmann, 1966; Vygotsky, 1978) as well, since individuals are working together to construct meaning, and they are pushing into areas of uncertainty and lack of expertise.
Shapira-Lishchinsky (2015) added some intriguing findings and recommendations to those of Leithwood and Steinbach (1992, 1995). In this study, 50 teachers with various leadership roles in their schools were presented regularly with ethical dilemmas during their coursework. Participants either interacted with the dilemmas as members of a role play or by observing those chosen. When the role play was completed, the entire group debriefed and discussed the ethical dilemmas and role-playing participants’ treatment of the issues. This method was shown, through qualitative analysis of participants’ discussions during the simulations, to produce rich dialogue and allow for a safe and controlled treatment of difficult issues. As such, the use of simulations was presented as a viable means through which to prepare aspiring educational leaders. Further, the author suggested the use of further studies with simulation-based learning that seek to gain information about aspiring leaders’ self-efficacy and psychological empowerment. A notable example of project-based scenarios in a virtual collaboration environment to prepare educational leaders is the work of Howard, McClannon, and Wallace (2014). Shapira-Lishchinsky (2015) also recommended similar research in other developed countries to observe the utility of the approaches of simulation and social constructivism to examine them for a wider and diverse aspiring administrator candidate pool.
Further, in an extensive review of prior research studies on the subject, Hallinger and Bridges (2017) noted that Problem-Based Learning (PBL), though applied successfully in other professions and written about extensively (Hallinger & Bridges, 1993, 2017; Stentoft, 2017), was relatively unheralded in the preparation of educational leaders. According to the authors, characteristics of PBL included problems replacing theory as the organization of course content, student-led group work, creation of simulated products by students, increased student ownership over learning, and feedback along the way from professors. Their review noted that PBL had positive aspects for participants, such as increased motivation, real-world connections, and positive pressure that resulted from working with a team. However, participants also expressed concerns about time constraints, lack of structure, and interpersonal dynamics within their teams. There were positive effects found on aspiring leaders’ problem-solving skill development with PBL (Copland, 2000; Hallinger & Bridges, 2017). Though PBL is much more prescribed than the scenarios strategy described in the Methods section below, the applicability of real-world problems to the preparation of educational leaders is summarized well by Copland (2000):
[I]nstructional practices that activate prior knowledge and situate learning in contexts similar to those encountered in practice are associated with the development of students’ ability to understand and frame problems. Moreover, the incorporation of debriefing techniques that encourage students’ elaboration of knowledge and reflection on learning appear to help students solidify a way of thinking about problems. (p. 604)
This study involved a one-group pretest-posttest design. No control group was assigned, as the pedagogical strategy in question—the use of real-world scenarios to build problem-solving skill for aspiring educational leaders—is integral to the school’s curriculum that prepares leaders, and, therefore, it is unethical to deny to student participants (Gay & Airasian, 2003). Thus, all participants were provided instruction with the use of real-world scenarios.
Participants. Graduate students at a regional, comprehensive public university in the Northeast obtaining a 6 th -year degree (equivalent to a second master’s degree) in educational leadership and preparing for certification as educational administrators served as participants. Specifically, students in three sections of the same full-year, two-course sequence, entitled “School Leadership I and II” were invited to participate. This particular course was selected from the degree course sequence, as it deals most directly with the problem-solving nature and daily work of school administrators. Some key outcomes of the course include students using data to drive school improvement action plans, communicating effectively with a variety of stakeholders, creating a safe and caring school climate, creating and maintaining a strategic and viable school budget, articulating all the steps in a hiring process for teachers and administrators, and leading with cultural proficiency.
The three sections were taught by two different professors. The professors used real- world scenarios in at least half of their class meetings throughout the year, or in approximately 15 classes throughout the year. During these classes, students were presented with realistic situations that have occurred, or could occur, in actual public schools. Students worked with their classmates to determine potential solutions to the problems and then discussed their responses as a whole class under the direction of their professor, a master practitioner. Both professors were active school administrators, with more than 25 years combined educational leadership experience in public schools. It should be noted that the scenario presentation and discussions took place during the class sessions, only. These were not presented for homework or in online forums.
Of the 44 students in these three sections, 37 volunteered to participate at some point in the data collection sequence, but not all students in the pretest session attended the posttest session months later and vice versa. As a result, only 20 students’ data were used for the matched pairs analysis. All 37 participants were certified professional educators in public schools in Connecticut. The participants’ professional roles varied and included classroom teachers, instructional coaches, related service personnel, unified arts teachers, as well as other non- administrative educational roles. Characteristics of participants in the overall and matched pairs groups can be found in Table 1.
Table 1 Participant Characteristics
Procedure. Participants’ data were compared between a fall of 2016 baseline data collection period and a spring of 2017 posttest data collection period. During the fall data collection period, participants were randomly assigned one of two versions of a Google Forms survey. After items about participant characteristics, the survey consisted of 11 items designed to elicit quantitative and qualitative data about participants’ perceptions of their problem-solving abilities, as well as their ability to address real-world problems faced by educational leaders. The participants were asked to rate their perception of their situational awareness, flexibility, and problem solving ability on a 10-point (1-10) Likert scale, following operational definitions of the terms (Marzano, Waters, & McNulty, 2005; Winter, 1982). They were asked, for each construct, to write open-ended responses to justify their numerical rating. They were then asked to write what they perceived they still needed to improve their problem-solving skills. The final four items included two real-world, unstructured, problem-based scenarios for which participants were asked to create plans of action. They were also asked to rate their problem-solving confidence with respect to their proposed action plans for each scenario on a 4-point (0-3) Likert scale.
During the spring data collection period, participants accessed the opposite version of the Google Forms survey from the one they completed in the fall. All items were identical on the two survey versions, except the scenarios, which were different on each survey version. The use of two versions was to ensure that any differences in perceived or actual difficulty among the four scenarios provided would not alter results based upon the timing of participant access (Leithwood & Steinbach, 1995). In order to link participants’ fall and spring data in a confidential manner, participants created a unique, six-digit alphanumeric code.
A focus group interview followed each spring data collection session. The interviews were recorded to allow for accurate transcription. The list of standard interview questions can be found in Table 2. This interview protocol was designed to elicit qualitative data with respect to aspiring educational leaders’ perceptions about their developing problem-solving abilities.
Table 2 Focus Group Interview Questions ___________________________________________________________________________________________
Please describe the development of your problem-solving skills as an aspiring educational leader over the course of this school year. In what ways have you improved your skills? Be as specific as you can.
What has been helpful to you (i.e. coursework, readings, experiences, etc.) in this development of your problem-solving skills? Why?
What do you believe you still need for the development in your problem-solving skills as an aspiring educational leader?
Discuss your perception of your ability to problem solve as an aspiring educational leader. How has this changed from the beginning of this school year? Why?
Please add anything else you perceive is relevant to this conversation about the development of your problem-solving skills as an aspiring educational leader.
___________________________________________________________________________________________
Data Analysis.
Quantitative data . Data were obtained from participants’ responses to Likert-scale items relating to their confidence levels with respect to aspects of problem solving, as well as from the rating of participants’ responses to the given scenarios against a rubric. The educational leadership problem-solving rubric chosen (Leithwood & Steinbach, 1995) was used with permission, and it reflects the authors’ work with explicitly teaching practicing educational leaders components of problem solving. The adapted rubric can be found in Figure 1. Through the use of this rubric, each individual response by a participant to a presented scenario was assigned a score from 0-15. It should be noted that affect data (representing the final 3 possible points on the 18-point rubric) were obtained via participants’ self-reporting their confidence with respect to their proposed plans of action. To align with the rubric, participants self-assessed their confidence through this item with a 0-3 scale.
0 = No Use of the Subskill 1 = There is Some Indication of Use of the Subskill 2 = The Subskill is Present to Some Degree 3 = The Subskill is Present to a Marked Degree; This is a Fine Example of this Subskill
Figure 1. Problem-solving model for unstructured problems. Adapted from “Expert Problem Solving: Evidence from School and District Leaders,” by K. Leithwood and R. Steinbach, pp. 284-285. Copyright 1995 by the State University of New York Press.
I compared Likert-scale items and rubric scores via descriptive statistics and rubric scores also via a paired sample t -test and Cohen’s d , all using the software program IBM SPSS. I did not compare the Likert-scale items about situational awareness, flexibility, and problem solving ability with t -tests or Cohen’s d , since these items did not represent a validated instrument. They were only single items based upon participants’ ratings compared to literature-based definitions. However, the value of the comparison of means from fall to spring was triangulated with qualitative results to provide meaning. For example, to say that participants’ self-assessment ratings for perceived problem-solving abilities increased, I examined both the mean difference for items from fall to spring and what participants shared throughout the qualitative survey items and focus group interviews.
Prior to scoring participants’ responses to the scenarios using the rubric, and in an effort to maximize the content validity of the rubric scores, I calibrated my use of the rubric with two experts from the field. Two celebrated principals, representing more than 45 combined years of experience in school-level administration, collaboratively and comparatively scored participant responses. Prior to scoring, the team worked collaboratively to construct appropriate and comprehensive exemplar responses to the four problem-solving scenarios. Then the team blindly scored fall pretest scenario responses using the Leithwood and Steinbach (1995) rubric, and upon comparing scores, the interrater reliability correlation coefficient was .941, indicating a high degree of agreement throughout the team.
Qualitative data. These data were obtained from open-ended items on the survey, including participants’ responses to the given scenarios, as well as the focus group interview transcripts. I analyzed qualitative data consistent with the grounded theory principles of Strauss and Corbin (1998) and the constant comparative methods of Glaser (1965), including a period of open coding of results, leading to axial coding to determine the codes’ dimensions and relationships between categories and their subcategories, and selective coding to arrive at themes. Throughout the entire data analysis process, I repeatedly returned to raw data to determine the applicability of emergent codes to previously analyzed data. Some categorical codes based upon the review of literature were included in the initial coding process. These codes were derived from the existing theoretical problem-solving models of Bolman and Deal (2008) and Leithwood and Steinbach (1995). These codes included modeling , relationships , and best for kids . Open codes that emerged from the participants’ responses included experience , personality traits , current job/role , and team . Axial coding revealed, for example, that current jobs or roles cited, intuitively, provided both sufficient building-wide perspective and situational memory (i.e. for special education teachers and school counselors) and insufficient experiences (i.e. for classroom teachers) to solve the given problems with confidence. From such understandings of the codes, categories, and their dimensions, themes were developed.
Quantitative Results. First, participants’ overall, aggregate responses (not matched pairs) were compared from the fall to spring, descriptively. These findings are outlined in Table 3. As is seen in the table, each item saw a modest increase over the course of the year. Participant perceptions of their problem-solving abilities across the three constructs presented (situational awareness, flexibility, and problem solving) did increase over the course of the year, as did the average group score for the problem-solving scenarios. However, due to participant differences in the two data collection periods, these aggregate averages do not represent a matched-pair dataset.
Table 3 Fall to Spring Comparison of Likert-Scale and Rubric-Scored Items
a These problem-solving dimensions from literature were rated by participants on a scale from 1- 10. b Participants received a rubric score for each scenario between 0-18. Participants’ two scenario scores for each data collection period (fall, spring) were averaged to arrive at the scores represented here.
In order to determine the statistical significance of the increase in participants’ problem- solving rubric scores, a paired-samples t -test was applied to the fall ( M = 9.15; SD = 2.1) and spring ( M = 9.25; SD = 2.3) averages. Recall that 20 participants had valid surveys for both the fall and spring. The t -test ( t = -.153; df = 19; p = .880) revealed no statistically significant change from fall to spring, despite the minor increase (0.10). I applied Cohen’s d to calculate the effect size. The small sample size ( n = 20) for the paired-sample t -test may have contributed to the lack of statistical significance. However, standard deviations were also relatively small, so the question of effect size was of particular importance. Cohen’s d was 0.05, which is also very small, indicating that little change—really no improvement, from a statistical standpoint—in participants’ ability to create viable action plans to solve real-world problems occurred throughout the year. However, the participants’ perceptions of their problem-solving abilities did increase, as evidenced by the increases in the paired-samples perception means shown in Table 3, though these data were only examined descriptively (from a quantitative perspective) due to the fact that these questions were individual items that are not part of a validated instrument.
Qualitative Results. Participant responses to open-ended items on the questionnaire, responses to the scenarios, and oral responses to focus group interview questions served as sources of qualitative data. Since the responses to the scenarios were focused on participant competence with problem solving, as measured by the aforementioned rubric (Leithwood & Steinbach, 1995), these data were examined separately from data collected from the other two sources.
Responses to scenarios. As noted, participants’ rubric ratings for the scenarios did not display a statistically significant increase from fall to spring. As such, this outline will not focus upon changes in responses from fall to spring. Rather, I examined the responses, overall, through the lens of the Leithwood and Steinbach (1995) problem-solving framework indicators against which they were rated. Participants typically had outlined reasonable, appropriate, and logical solution processes. For example, in a potential bullying case scenario, two different participants offered, “I would speak to the other [students] individually if they have said or done anything mean to other student [ sic ] and be clear that it is not tolerable and will result in major consequences” and “I would initiate an investigation into the situation beginning with [an] interview with the four girls.” These responses reflect actions that the consulted experts anticipated from participants and deemed as logical and needed interventions. However, these two participants omitted other needed steps, such as addressing the bullied student’s mental health needs, based upon her mother’s report of suicidal ideations. Accordingly, participants earned points for reasonable and logical responses very consistently, yet, few full-credit responses were observed.
Problem interpretation scores were much more varied. For this indicator, some participants were able to identify many, if not all, the major issues in the scenarios that needed attention. For example, for a scenario where two teachers were not interacting professionally toward each other, many participants correctly identified that this particular scenario could include elements of sexual harassment, professionalism, teaching competence, and personality conflict. However, many other participants missed at least two of these key elements of the problem, leaving their solution processes incomplete. The categories of (a) goals and (b) principles and values also displayed a similarly wide distribution of response ratings.
One category, constraints, presented consistent difficulty for the participants. Ratings were routinely 0 and 1. Participants could not consistently report what barriers or obstacles would need addressing prior to success with their proposed solutions. To be clear, it was not a matter of participants listing invalid or unrealistic barriers or obstacles; rather, the participants were typically omitting constraints altogether from their responses. For example, for a scenario involving staff members arriving late and unprepared to data team meetings, many participants did not identify that a school culture of not valuing data-driven decision making or lack of norms for data team work could be constraints that the principal could likely face prior to reaching a successful resolution.
Responses to open-ended items. When asked for rationale regarding their ratings for situational awareness, flexibility, and problem solving, participants provided open-ended responses. These responses revealed patterns worth considering, and, again, this discussion will consider, in aggregate, responses made in both the pre- and post- data collection periods, again due to the similarities in responses between the two data collection periods. The most frequently observed code (112 incidences) was experience . Closely related were the codes current job/role (50 incidences). Together, these codes typically represented a theme that participants were linking their confidence with respect to problem solving with their exposure (or lack thereof) in their professional work. For example, a participant reported, “As a school counselor, I have a lot of contact with many stakeholders in the school -admin [ sic ], parents, teachers, staff, etc. I feel that I have a pretty good handle on the systemic issues.” This example is one of many where individuals working in counseling, instructional coaching, special education, and other support roles expressed their advanced levels of perspective based upon their regular contact with many stakeholders, including administrators. Thus, they felt they had more prior knowledge and situational memory about problems in their schools.
However, this category of codes also included those, mostly classroom or unified arts teachers, who expressed that their relative lack of experiences outside their own classrooms limited their perspective for larger-scale problem solving. One teacher succinctly summarized this sentiment, “I have limited experience in being part of situations outside of my classroom.” Another focused on the general problem solving skill in her classroom not necessarily translating to confidence with problem solving at the school level: “I feel that I have a high situational awareness as a teacher in the classroom, but as I move through these leadership programs I find that I struggle to take the perspective of a leader.” These experiences were presented in opposition to their book learning or university training. There were a number of instances (65 combined) of references to the value of readings, class discussions, group work, scenarios presented, research, and coursework in the spring survey. When asked what the participants need more, again, experience was referenced often. One participant summarized this concept, “I think that I, personally, need more experience in the day-to-day . . . setting.” Another specifically separated experiences from scenario work, “[T]here is [ sic ] some things you can not [ sic ] learn from merely discussing a ‘what if” scenario. A seasoned administrator learns problem solving skills on the job.”
Another frequently cited code was personality traits (63 incidences), which involved participants linking elements of their own personalities to their perceived abilities to process problems, almost exclusively from an assets perspective. Examples of traits identified by participants as potentially helpful in problem solving included: open-mindedness, affinity for working with others, not being judgmental, approachability, listening skills, and flexibility. One teacher exemplified this general approach by indicating, “I feel that I am a good listener in regards to inviting opinions. I enjoy learning through cooperation and am always willing to adapt my teaching to fit needs of the learners.” However, rare statements of personality traits interfering with problem solving included, “I find it hard to trust others [ sic ] abilities” and “my personal thoughts and biases.”
Another important category of the participant responses involved connections with others. First, there were many references to relationships (27 incidences), mostly from the perspective that building positive relationships leads to greater problem-solving ability, as the aspiring leader knows stakeholders better and can rely on them due to the history of positive interactions. One participant framed this idea from a deficit perspective, “Not knowing all the outlying relationships among staff members makes situational awareness difficult.” Another identified that established positive relationships are already helpful to an aspiring leader, “I have strong rapport with fellow staff members and administrators in my building.” In a related way, many instances of the code team were identified (29). These references overwhelmingly identified that solving problems within a team context is helpful. One participant stated, “I often team with people to discuss possible solutions,” while another elaborated,
I recognize that sometimes problems may arise for which I am not the most qualified or may not have the best answer. I realize that I may need to rely on others or seek out help/opinions to ensure that I make the appropriate decision.
Overall, participants recognized that problem-solving for leaders does not typically occur in a vacuum.
Responses to focus group interview questions. As with the open-ended responses, patterns were evident in the interview responses, and many of these findings were supportive of the aforementioned themes. First, participants frequently referenced the power of group work to help build their understanding about problems and possible solutions. One participant stated, “hearing other people talk and realizing other concerns that you may not have thought of . . . even as a teacher sometimes, you look at it this way, and someone else says to see it this way.” Another added, “seeing it from a variety of persons [ sic ] point of views. How one person was looking at it, and how another person was looking at it was really helpful.” Also, the participants noted the quality of the discussion was a direct result of “professors who have had real-life experience” as practicing educational leaders, so they could add more realistic feedback and insight to the discussions.
Perhaps most notable in the participant responses during the focus groups was the emphasis on the value of real-world scenarios for the students. These were referenced, without prompting, in all three focus groups by many participants. Answers to the question about what has been most helpful in the development of their problem-solving skills included, “I think the real-world application we are doing,” “I think being presented with all the scenarios,” and “[the professor] brought a lot of real situations.”
With respect to what participants believed they still needed to become better and more confident problem solvers, two patterns emerged. First, students recognized that they have much more to learn, especially with respect to policy and law. It is noteworthy that, with few exceptions, these students had not taken the policy or law courses in the program, and they had not yet completed their administrative internships. Some students actually reported rating themselves as less capable problem solvers in the spring because they now understood more clearly what they lacked in knowledge. One student exemplified this sentiment, “I might have graded myself higher in the fall than I did now . . . [I now can] self identify areas I could improve in that I was not as aware of.” Less confidence in the spring was a minority opinion, however. In a more typical response, another participant stated, “I feel much more prepared for that than I did at the beginning of the year.”
Overall, the most frequently discussed future need identified was experience, either through the administrative internship or work as a formal school administrator. Several students summarized this idea, “That real-world experience to have to deal with it without being able to talk to 8 other people before having to deal with it . . . until you are the person . . . you don’t know” and “They tell you all they want. You don’t know it until you are in it.” Overall, most participants perceived themselves to have grown as problem solvers, but they overwhelmingly recognized that they needed more learning and experience to become confident and effective problem solvers.
This study continues a research pathway about the development of problem-solving skills for administrators by focusing on their preparation. The participants did not see a significant increase in their problem-solving skills over the year-long course in educational leadership.
Whereas, this finding is not consistent with the findings of others who focused on the development of problem-solving skills for school leaders (Leithwood & Steinbach, 1995; Shapira-Lishchinsky, 2015), nor is it consistent with PBL research about the benefits of that approach for aspiring educational leaders (Copland, 2000; Hallinger & Bridges, 2017), it is important to note that the participants in this study were at a different point in their careers. First, they were aspirants, as opposed to practicing leaders. Also, the studied intervention (scenarios) was not the same or nearly as comprehensive as the prescriptive PBL approach. Further, unlike the participants in either the practicing leader or PBL studies, because these individuals had not yet had their internship experiences, they had no practical work as educational leaders. This theme of lacking practical experience was observed in both open-ended responses and focus group interviews, with participants pointing to their upcoming internship experiences, or even their eventual work as administrators, as a key missing piece of their preparation.
Despite the participants’ lack of real gains across the year of preparation in their problem- solving scores, the participants did, generally, report an increase in their confidence in problem solving, which they attributed to a number of factors. The first was the theme of real-world context. This finding was consistent with others who have advocated for teaching problem solving through real-world scenarios (Duke, 2014; Leithwood & Steinbach, 1992, 1995; Myran & Sutherland, 2016; Shapira-Lishchinsky, 2015). This study further adds to this conversation, not only a corroboration of the importance of this method (at least in aspiring leaders’ minds), but also that participants specifically recognized their professors’ experiences as school administrators as important for providing examples, context, and credibility to the work in the classroom.
In addition to the scenario approach, the participants also recognized the importance of learning from one another. In addition to the experiences of their practitioner-professors, many participants espoused the value of hearing the diverse perspectives of other students. The use of peer discussion was also an element of instruction in the referenced studies (Leithwood & Steinbach, 1995; Shapira-Lishchinsky, 2015), corroborating the power of aspiring leaders learning from one another and supporting existing literature about the social nature of problem solving (Berger & Luckmann, 1966; Leithwood & Steinbach, 1992; Vygotsky, 1978).
Finally, the ultimate theme identified through this study is the need for real-world experience in the field as an administrator or intern. It is simply not enough to learn about problem solving or learn the background knowledge needed to solve problems, even when the problems presented are real-world in nature. Scenarios are not enough for aspiring leaders to perceive their problem-solving abilities to be adequate or for their actual problem-solving abilities to improve. They need to be, as some of the participants reasoned, in positions of actual responsibility, where the weight of their decisions will have tangible impacts on stakeholders, including students.
The study of participants’ responses to the scenarios connected to the Four Frames model of Bolman and Deal (2008). The element for which participants received the consistently highest scores was identifying solution processes. This area might most logically be connected to the structural and human resource frames, as solutions typically involve working to meet individuals’ needs, as is necessary in the human resource frame, and attending to protocols and procedures, which is the essence of the structural frame. As identified above, the political and symbolic frames have been cited by the authors as the most underdeveloped by educational leaders, and this assertion is corroborated by the finding in this study that participants struggled the most with identifying constraints, which can sometimes arise from an understanding of the competing personal interests in an organization (political frame) and the underlying meaning behind aspects of an organization (symbolic frame), such as unspoken rules and traditions. The lack of success identifying constraints is also consistent with participants’ statements that they needed actual experiences in leadership roles, during which they would likely encounter, firsthand, the types of constraints they were unable to articulate for the given scenarios. Simply, they had not yet “lived” these types of obstacles.
The study includes several notable limitations. First, the study’s size is limited, particularly with only 20 participants’ data available for the matched pairs analysis. Further, this study was conducted at one university, within one particular certification program, and over three sections of one course, which represented about one-half of the time students spend in the program. It is likely that more gains in problem-solving ability and confidence would have been observed if this study was continued through the internship year. Also, the study did not include a control group. The lack of an experimental design limits the power of conclusions about causality. However, this limitation is mitigated by two factors. First, the results did not indicate a statistically significant improvement, so there is not a need to attribute a gain score to a particular variable (i.e. use of scenarios), anyway, and, second, the qualitative results did reveal the perceived value for participants in the use of scenarios, without any prompting of the researcher. Finally, the participant pool was not particularly diverse, though this fact is not particularly unusual for the selected university, in general, representing a contemporary challenge the university’s state is facing to educate its increasingly diverse student population, with a teaching and administrative workforce that is predominantly White.
The findings in this study invite further research. In addressing some of the limitations identified here, expanding this study to include aspiring administrators across other institutions representing different areas of the United States and other developed countries, would provide a more generalizable set of results. Further, studying the development of problem-solving skills during the administrative internship experience would also add to the work outlined here by considering the practical experience of participants.
In short, this study illustrates for those who prepare educational leaders the value of using scenarios in increasing aspiring leaders’ confidence and knowledge. However, intuitively, scenarios alone are not enough to engender significant change in their actual problem-solving abilities. Whereas, real-world context is important to the development of aspiring educational leaders’ problem-solving skills, the best context is likely to be the real work of administration.
Allison, D. J. (1996). Problem finding, classification and interpretation: In search of a theory of administrative problem processing. In K. Leithwood, J. Chapman, D. Corson, P. Hallinger, & A. Hart (Eds.), International handbook of educational leadership and administration (pp. 477–549). Norwell, MA: Kluwer Academic.
Berger, P. L., & Luckmann, T. (1966). The social construction of reality . Garden City, NJ: Doubleday.
Bolman, L. G., & Deal, T. E. (2008). Re-framing organizations: Artistry, choice and leadership (4th ed.). San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
Bronstein, C., & Fitzpatrick, K. R. (2015). Preparing tomorrow’s leaders: Integrating leadership development in journalism and mass communication education. Journalism & Mass Communication Educator, 70 (1), 75–88. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077695814566199
Copland, M. A. (2000). Problem-based learning and prospective principals’ problem-framing ability. Educational Administration Quarterly , 36 , 585–607.
Deluca, C., Bolden, B., & Chan, J. (2017). Systemic professional learning through collaborative inquiry: Examining teachers’ perspectives. Teaching and Teacher Education , 67 , 67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2017.05.014
Dimmock, C. (1996). Dilemmas for school leaders and administrators in restructuring. In K. Leithwood, J. Chapman, D. Corson, P. Hallinger, & A. Hart (Eds.), International Handbook of Educational Leadership and Administration (pp. 135–170). Norwell, MA: Kluwer Academic.
Duke, D. L. (2014). A bold approach to developing leaders for low-performing schools. Management in Education, 28 (3), 80–85. https://doi.org/10.1177/0892020614537665
Gay, L. R., & Airasian, P. (2003). Educational research: Competancies for analysis and applications (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education.
Glaser, B. G. (1965). The constant comparative method of qualitative analysis. Social Problems, 12 (4), 436-445.
Hallinger, P., & Bridges, E. (1993). Problem-based learning in medical and managerial education. In P. Hallinger, K. Leithwood, & J. Murphy (Eds.), Cognitive perspectives on educational leadership (pp. 253–267). New York: Teachers’ College Press.
Hallinger, P., & Bridges, E. M. (2017). A systematic review of research on the use of problem- based learning in the preparation and development of school leaders. Educational Administration Quarterly . 53(2), 255-288. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013161X16659347
Hallinger, P., & McCary, C. E. (1990). Developing the strategic thinking of instructional leaders. Elementary School Journal , 91 (2), 89–108.
Howard, B. B., McClannon, T. W., & Wallace, P. R. (2014). Collaboration through role play among graduate students in educational leadership in distance learning. American Journal of Distance Education , 28 (1), 51–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/08923647.2014.868665
Johnson, B. L., & Kruse, S. D. (2009). Decision making for educational leaders: Underexamined dimensions and issues . Albany, NY: State University of New York Press.
Leithwood, K., & Steinbach, R. (1992). Improving the problem-solving expertise of school administrators: Theory and practice. Education and Urban Society , 24 (3), 317–345. Retrieved from https://journals.sagepub.com.ccsu.idm.oclc.org/doi/pdf/10.1177/0013124592024003003
Leithwood, K., & Steinbach, R. (1995). Expert problem solving: Evidence from school and district leaders . Albany, NY: State University of New York Press.
Marzano, R. J., Waters, T., & McNulty, B. A. (2005). School leadership that works: From research to results . Denver, CO: ASCD.
Myran, S., & Sutherland, I. (2016). Problem posing in leadership education: Using case study to foster more effective problem solving. Journal of Cases in Educational Leadership , 19 (4), 57–71. https://doi.org/10.1177/1555458916664763
Rochford, L., & Borchert, P. S. (2011). Assessing higher level learning: Developing rubrics for case analysis. Journal of Education for Business , 86 , 258–265. https://doi.org/10.1080/08832323.2010.512319
Salas, E., Wildman, J. L., & Piccolo, R. F. (2009). Using simulation based training to enhance management education. Academy of Management Learning & Education , 8 (4), 559–573. https://doi.org/10.5465/AMLE.2009.47785474
Shapira-Lishchinsky, O. (2015). Simulation-based constructivist approach for education leaders. Educational Management Administration & Leadership , 43 (6), 972–988. https://doi.org/10.1177/1741143214543203
Simon, H. A. (1993). Decision making: Rational, nonrational, and irrational. Educational Administration Quarterly , 29 (3), 392–411. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013161X93029003009
Stentoft, D. (2017). From saying to doing interdisciplinary learning: Is problem-based learning the answer? Active Learning in Higher Education , 18 (1), 51–61. https://doi.org/10.1177/1469787417693510
Strauss, A., & Corbin, J. (1998). Basics of qualitative research (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
VanLehn, K. (1991). Rule acquisition events in the discovery of problem-solving strategies. Cognitive Science , 15 (1), 1–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/0364-0213(91)80012-T
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Winter, R. (1982). Dilemma analysis: A contribution to methodology for action research. Cambridge Journal of Education, 12 (3), 166-173.
Author Biography
Dr. Jeremy Visone is an Assistant Professor of Educational Leadership, Policy, & Instructional Technology. Until 2016, he worked as an administrator at both the elementary and secondary levels, most recently at Anna Reynolds Elementary School, a National Blue Ribbon School in 2016. Dr. Visone can be reached at [email protected] .
Center for Teaching
Teaching problem solving.
Print Version
Tips and Techniques
Expert vs. novice problem solvers, communicate.
- Have students identify specific problems, difficulties, or confusions . Don’t waste time working through problems that students already understand.
- If students are unable to articulate their concerns, determine where they are having trouble by asking them to identify the specific concepts or principles associated with the problem.
- In a one-on-one tutoring session, ask the student to work his/her problem out loud . This slows down the thinking process, making it more accurate and allowing you to access understanding.
- When working with larger groups you can ask students to provide a written “two-column solution.” Have students write up their solution to a problem by putting all their calculations in one column and all of their reasoning (in complete sentences) in the other column. This helps them to think critically about their own problem solving and helps you to more easily identify where they may be having problems. Two-Column Solution (Math) Two-Column Solution (Physics)
Encourage Independence
- Model the problem solving process rather than just giving students the answer. As you work through the problem, consider how a novice might struggle with the concepts and make your thinking clear
- Have students work through problems on their own. Ask directing questions or give helpful suggestions, but provide only minimal assistance and only when needed to overcome obstacles.
- Don’t fear group work ! Students can frequently help each other, and talking about a problem helps them think more critically about the steps needed to solve the problem. Additionally, group work helps students realize that problems often have multiple solution strategies, some that might be more effective than others
Be sensitive
- Frequently, when working problems, students are unsure of themselves. This lack of confidence may hamper their learning. It is important to recognize this when students come to us for help, and to give each student some feeling of mastery. Do this by providing positive reinforcement to let students know when they have mastered a new concept or skill.
Encourage Thoroughness and Patience
- Try to communicate that the process is more important than the answer so that the student learns that it is OK to not have an instant solution. This is learned through your acceptance of his/her pace of doing things, through your refusal to let anxiety pressure you into giving the right answer, and through your example of problem solving through a step-by step process.
Experts (teachers) in a particular field are often so fluent in solving problems from that field that they can find it difficult to articulate the problem solving principles and strategies they use to novices (students) in their field because these principles and strategies are second nature to the expert. To teach students problem solving skills, a teacher should be aware of principles and strategies of good problem solving in his or her discipline .
The mathematician George Polya captured the problem solving principles and strategies he used in his discipline in the book How to Solve It: A New Aspect of Mathematical Method (Princeton University Press, 1957). The book includes a summary of Polya’s problem solving heuristic as well as advice on the teaching of problem solving.

Teaching Guides
- Online Course Development Resources
- Principles & Frameworks
- Pedagogies & Strategies
- Reflecting & Assessing
- Challenges & Opportunities
- Populations & Contexts
Quick Links
- Services for Departments and Schools
- Examples of Online Instructional Modules
Problems and Problem Solving
What is a problem?
In common language, a problem is an unpleasant situation, a difficulty.
But in education the first definition in Webster's Dictionary — "a question raised for inquiry, consideration, or solution" — is a common meaning.
More generally in education, it's useful to define problem broadly — as any situation, in any area of life, where you have an opportunity to make a difference, to make things better — so problem solving is converting an actual current state into a desired future state that is better, so you have "made things better." Whenever you are thinking creatively-and-critically about ways to increase the quality of life (or to avoid a decrease in quality) for yourself and/or for others, you are actively involved in problem solving. Defined in this way, problem solving includes almost everything you do in life.
Problem-Solving Skills — Creative and Critical
An important goal of education is helping students learn how to think more productively while solving problems, by combining creative thinking (to generate ideas) and critical thinking (to evaluate ideas) with accurate knowledge (about the truth of reality). Both modes of thinking (creative & critical) are essential for a well-rounded productive thinker, according to experts in both fields:
Richard Paul (a prominent advocate of CRITICAL THINKING ) says, "Alternative solutions are often not given, they must be generated or thought-up. Critical thinkers must be creative thinkers as well, generating possible solutions in order to find the best one. Very often a problem persists, not because we can't tell which available solution is best, but because the best solution has not yet been made available — no one has thought of it yet."
Patrick Hillis & Gerard Puccio (who focus on CREATIVE THINKING ) describe the combining of creative generation with critical evaluation in a strategy of creative-and-critical Problem Solving that "contains many tools which can be used interchangeably within any of the stages. These tools are selected according to the needs of the task and are either divergent (i.e., used to generate options) or convergent (i.e., used to evaluate options)."
Creative Thinking can be motivated and guided by Creative Thinking: One of the interactions between creative thinking and critical thinking occurs when we use critical Evaluation to motivate and guide creative Generation in a critical - and - creative process of Guided Generation that is Guided Creativity . In my links-page for CREATIVITY you can explore this process in three stages, to better understand how a process of Guided Creativity — explored & recognized by you in Part 1 and then described by me in Part 2 — could be used (as illustrated in Part 3 ) to improve “the party atmosphere” during a dinner you'll be hosting, by improving a relationship.
Education for Problem Solving
By using broad definitions for problem solving and education, we can show students how they already are using productive thinking to solve problems many times every day, whenever they try to “make things better” in some way..
Problem Solving: a problem is an opportunity , in any area of life, to make things better. Whenever a decision-and-action helps you “ make it better ” — when you convert an actual state (in the past) into a more desirable actual state (in the present and/or future) — you are problem solving, and this includes almost everything you do in life, in all areas of life. { You can make things better if you increase quality for any aspect of life, or you maintain quality by reducing a potential decrease of quality. } / design thinking ( when it's broadly defined ) is the productive problem-solving thinking we use to solve problems. We can design (i.e. find, invent, or improve ) a better product, activity, relationship, and/or strategy (in General Design ) and/or (in Science-Design ) explanatory theory. { The editor of this links-page ( Craig Rusbult ) describes problem solving in all areas of life .}
note: To help you decide whether to click a link or avoid it, links highlighted with green or purple go to pages I've written, in my website about Education for Problem Solving or in this website for THINKING SKILLS ( CREATIVE and CRITICAL ) we use to SOLVE PROBLEMS .
Education: In another broad definition, education is learning from life-experiences, learning how to improve, to become more effective in making things better. For example, Maya Angelou – describing an essential difference between past and present – says "I did then what I knew how to do. Now that I know better, I do better, " where improved problem solving skills (when "do better" leads to being able to more effectively "make things better") has been a beneficial result of education, of "knowing better" due to learning from life-experiences.
Growth: One of the best ways to learn more effectively is by developing-and-using a better growth mindset so — when you ask yourself “how well am I doing in this area of life?” and honestly self-answer “not well enough” — instead of thinking “not ever” you are thinking “not yet” because you know that your past performance isn't your future performance; and you are confident that in this area of life (and in other areas) you can “grow” by improving your understandings-and-skills, when you invest intelligent effort in your self-education and self-improving. And you can "be an educator" by supporting the self-improving of other people by helping them improve their own growth mindsets. { resources for Growth Mindset }
Growth in Problem-Solving Skills: A main goal of this page is to help educators help students improve their skill in solving problems — by improving their ability to think productively (to more effectively combine creative thinking with critical thinking and accurate knowledge ) — in all areas of their everyday living. {resources: growth mindset for problem solving that is creative-and-critical }
How? You can improve your Education for Problem Solving by creatively-and-critically using general principles & strategies (like those described above & below, and elsewhere) and adapting them to specific situations, customizing them for your students (for their ages, abilities, experiences,...) and teachers, for your community and educational goals.
Promote Productive Thinking:

Build Educational Bridges:
When we show students how they use a similar problem-solving process (with design thinking ) for almost everything they do in life , we can design a wide range of activities that let us build two-way educational bridges:
• from Life into School, building on the experiences of students, to improve confidence: When we help students recognize how they have been using a problem-solving process of design thinking in a wide range of problem-solving situations,... then during a classroom design activity they can think “I have done this before (during design-in-life ) so I can do it again (for design-in-school )” to increase their confidence about learning. They will become more confident that they can (and will) improve the design-thinking skills they have been using (and will be using) to solve problems in life and in school.
• from School into Life, appealing to the hopes of students, to improve motivation: We can show each student how they will be using design thinking for "almost everything they do" in their future life (in their future whole-life, inside & outside school) so the design-thinking skills they are improving in school will transfer from school into life and will help them achieve their personal goals for life . When students want to learn in school because they are learning for life, this will increase their motivations to learn.
Improve Educational Equity:
When we build these bridges (past-to-present from Life into School , and present-to-future from School into Life ) we can improve transfers of learning — in time (past-to-present & present-to-future) and between areas (in school-life & whole-life) for whole-person education — and transitions in attitudes to improve a student's confidence & motivations. This will promote diversity and equity in education by increasing confidence & motivation for a wider range of students, and providing a wider variety of opportunities for learning in school, and for success in school. We want to “open up the options” for all students, so they will say “yes, I can do this” for a wider variety of career-and-life options, in areas of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Math) and non-STEM .
This will help us improve diversity-and-equity in education by increasing confidence & motivations for a wider range of students, and providing a wider variety of opportunities for learning in school, and success in school.
Design Curriculum & Instruction:

• DEFINE GOALS for desired outcomes, for ideas-and-skills we want students to learn,
• DESIGN INSTRUCTION with learning activities (and associated teaching activities ) that will provide opportunities for experience with these ideas & skills, and help students learn more from their experiences. {more about Defining Goals and Designing Instruction } {one valuable activity is using a process-of-inquiry to learn principles-for-inquiry }
Problem-Solving Process for Science and Design
We'll look at problem-solving process for science (below) and design ( later ) separately, and for science-and-design together., problem-solving process for science, is there a “scientific method” we have reasons to say....
NO, because there is not a rigid sequence of steps that is used in the same way by all scientists, in all areas of science, at all times, but also...
YES, because expert scientists (and designers) tend to be more effective when they use flexible strategies — analogous to the flexible goal-directed improvising of a hockey player, but not the rigid choreography of a figure skater — to coordinate their thinking-and-actions in productive ways, so they can solve problems more effectively.
Below are some models that can help students understand and do the process of science. We'll begin with simplicity, before moving on to models that are more complex so they can describe the process more completely-and-accurately.
A simple model of science is PHEOC (Problem, Hypothesis, Experiment, Observe, Conclude). When PHEOC, or a similar model, is presented — or is misinterpreted — as a rigid sequence of fixed steps, this can lead to misunderstandings of science, because the real-world process of science is flexible. An assumption that “model = rigidity” is a common criticism of all models-for-process, but this unfortunate stereotype of "rigidity" is not logically justifiable because all models emphasize the flexibility of problem-solving process in real life, and (ideally) in the classroom. If a “step by step” model (like PHEOC or its variations) is interpreted properly and is used wisely, the model can be reasonably accurate and educationally useful. For example,...
A model that is even simpler — the 3-step POE (Predict, Observe, Learn) — has the essentials of scientific logic, and is useful for classroom instruction.
Science Buddies has Steps of the Scientific Method with a flowchart showing options for flexibility of timing. They say, "Even though we show the scientific method as a series of steps, keep in mind that new information or thinking might cause a scientist to back up and repeat steps at any point during the process. A process like the scientific method that involves such backing up and repeating is called an iterative process." And they compare Scientific Method with Engineering Design Process .
Lynn Fancher explains - in The Great SM - that "while science can be done (and often is) following different kinds of protocols, the [typical simplified] description of the scientific method includes some very important features that should lead to understanding some very basic aspects of all scientific practice," including Induction & Deduction and more.
From thoughtco.com, many thoughts to explore in a big website .
Other models for the problem solving process of science are more complex, so they can be more thorough — by including a wider range of factors that actually occur in real-life science, that influence the process of science when it's done by scientists who work as individuals and also as members of their research groups & larger communities — and thus more accurate. For example,
Understanding Science (developed at U.C. Berkeley - about ) describes a broad range of science-influencers, * beyond the core of science: relating evidence and ideas . Because "the process of science is exciting" they want to "give users an inside look at the general principles, methods, and motivations that underlie all of science." You can begin learning in their homepage (with US 101, For Teachers, Resource Library,...) and an interactive flowchart for "How Science Works" that lets you explore with mouse-overs and clicking.
* These factors affect the process of science, and occasionally (at least in the short run) the results of science. To learn more about science-influencers,...
Knowledge Building (developed by Bereiter & Scardamalia, links - history ) describes a human process of socially constructing knowledge.
The Ethics of Science by Henry Bauer — author of Scientific Literacy and the Myth of the Scientific Method (click "look inside") — examines The Knowledge Filter and a Puzzle and Filter Model of "how science really works."
[[ i.o.u. - soon, in mid-June 2021, I'll fix the links in this paragraph.]] Another model that includes a wide range of factors (empirical, social, conceptual) is Integrated Scientific Method by Craig Rusbult, editor of this links-page . Part of my PhD work was developing this model of science, in a unifying synthesis of ideas from scholars in many fields, from scientists, philosophers, historians, sociologists, psychologists, educators, and myself. The model is described in two brief outlines ( early & later ), more thoroughly, in a Basic Overview (with introduction, two visual/verbal representations, and summaries for 9 aspects of Science Process ) and a Detailed Overview (examining the 9 aspects more deeply, with illustrations from history & philosophy of science), and even more deeply in my PhD dissertation (with links to the full text, plus a “world record” Table of Contents, references, a visual history of my diagrams for Science Process & Design Process, and using my integrative model for [[ integrative analysis of instruction ). / Later, I developed a model for the basic logic-and-actions of Science Process in the context of a [[ more general Design Process .
Problem-Solving Process for Design
Because "designing" covers a wide range of activities, we'll look at three kinds of designing..
Engineering Design Process: As with Scientific Method,
a basic process of Engineering Design can be outlined in a brief models-with-steps – 5 5 in cycle 7 in cycle 8 10 3 & 11 . {these pages are produced by ==[later, I'll list their names]}
and it can be examined in more depth: here & here and in some of the models-with-steps (5... 3 & 11), and later .
Problem-Solving Process: also has models-with-steps ( 4 4 5 6 7 ) * and models-without-steps (like the editor's model for Design-Thinking Process ) to describe creative-and-critical thinking strategies that are similar to Engineering Design Process, and are used in a wider range of life — for all problem-solving situations (and these include almost everything we do in life) — not just for engineering. { * these pages are produced by ==}
Design-Thinking Process: uses a similar creative-and-critical process, * but with a focus on human - centered problems & solutions & solving - process and a stronger emphasis on using empathy . (and creativity )
* how similar? This depends on whether we define Design Thinking in ways that are narrow or broad. {the wide scope of problem-solving design thinking } {why do I think broad definitions (for objectives & process) are educationally useful ?}
Education for Design Thinking (at Stanford's Design School and beyond)
Problem Solving in Our Schools:
Improving education for problem solving, educators should want to design instruction that will help students improve their thinking skills. an effective strategy for doing this is..., goal-directed designing of curriculum & instruction.
When we are trying to solve a problem (to “make things better”) by improving our education for problem solving, a useful two-part process is to...
1. Define GOALS for desired outcomes, for the ideas-and-skills we want students to learn;
2. Design INSTRUCTION with Learning Activities that will provide opportunities for experience with these ideas & skills, and will help students learn more from their experiences.
Basically, the first part ( Define Goals ) is deciding WHAT to Teach , and the second part ( Design Instruction ) is deciding HOW to Teach .
But before looking at WHAT and HOW , here are some ways to combine them with...
Strategies for Goal-Directed Designing of WHAT-and-HOW.
Understanding by Design ( UbD ) is a team of experts in goal-directed designing,
as described in an overview of Understanding by Design from Vanderbilt U.
Wikipedia describes two key features of UbD: "In backward design, the teacher starts with classroom outcomes [#1 in Goal-Directed Designing above ] and then [#2] plans the curriculum, * choosing activities and materials that help determine student ability and foster student learning," and "The goal of Teaching for Understanding is to give students the tools to take what they know, and what they will eventually know, and make a mindful connection between the ideas. ... Transferability of skills is at the heart of the technique. Jay McTighe and Grant Wiggin's technique. If a student is able to transfer the skills they learn in the classroom to unfamiliar situations, whether academic or non-academic, they are said to truly understand."
* UbD "offers a planning process and structure to guide curriculum, assessment, and instruction. Its two key ideas are contained in the title: 1) focus on teaching and assessing for understanding and learning transfer, and 2) design curriculum “backward” from those ends."
ASCD – the Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (specializing in educational leadership ) – has a resources-page for Understanding by Design that includes links to The UbD Framework and Teaching for Meaning and Understanding: A Summary of Underlying Theory and Research plus sections for online articles and books — like Understanding by Design ( by Grant Wiggins & Jay McTighe with free intro & U U ) and Upgrade Your Teaching: Understanding by Design Meets Neuroscience ( about How the Brain Learns Best by Jay McTighe & Judy Willis who did a fascinating ASCD Webinar ) and other books — plus DVDs and videos (e.g. overview - summary ) & more .
Other techniques include Integrative Analysis of Instruction and Goal-Directed Aesop's Activities .
In two steps for a goal-directed designing of education , you:
1) Define GOALS (for WHAT you want students to improve) ;
2) Design INSTRUCTION (for HOW to achieve these Goals) .
Although the sections below are mainly about 1. WHAT to Teach (by defining Goals ) and 2. HOW to Teach (by designing Instruction ) there is lots of overlapping, so you will find some "how" in the WHAT, and lots of "what" in the HOW.
P ERSONAL Skills (for Thinking about Self)
A very useful personal skill is developing-and-using a...
Growth Mindset: If self-education is broadly defined as learning from your experiences, better self-education is learning more effectively by learning more from experience, and getting more experiences. One of the best ways to learn more effectively is by developing a better growth mindset so — when you ask yourself “how well am I doing in this area of life?” and honestly answer “not well enough” — you are thinking “not yet” (instead of “not ever”) because you are confident that in this area of life (as in most areas, including those that are most important) you can “grow” by improving your skills, when you invest intelligent effort in your self-education. And you can support the self-education of other people by helping them improve their own growth mindsets. Carol Dweck Revisits the Growth Mindset and (also by Dweck) a video, Increasing Educational Equity and Opportunity . 3 Ways Educators Can Promote A Growth Mindset by Dan LaSalle, for Teach for America. Growth Mindset: A Driving Philosophy, Not Just a Tool by David Hochheiser, for Edutopia. Growth Mindset, Educational Equity, and Inclusive Excellence by Kris Slowinski who links to 5 videos . What’s Missing from the Conversation: The Growth Mindset in Cultural Competency by Rosetta Lee. YouTube video search-pages for [ growth mindset ] & [ mindset in education ] & [ educational equity mindset ].
also: Growth Mindset for Creativity
Self-Perception -- [[a note to myself: accurate understanding/evaluation of self + confidence in ability to improve/grow ]]
M ETA C OGNITIVE Skills (for Solving Problems)
What is metacognition? Thinking is cognition. When you observe your thinking and think about your thinking (maybe asking “how can I think more effectively?”) this is meta- cognition, which is cognition about cognition. To learn more about metacognition — what it is, why it's valuable, and how to use it more effectively — some useful web-resources are:
a comprehensive introductory overview by Nancy Chick, for Vanderbilt U.
my links-section has descriptions of (and links to) pages by other authors: Jennifer Livingston, How People Learn, Marsha Lovett, Carleton College, Johan Lehrer, Rick Sheets, William Peirce, and Steven Shannon, plus links for Self-Efficacy with a Growth Mindset , and more about metacognition.
my summaries about the value of combining cognition-and-metacognition and regulating it for Thinking Strategies (of many kinds ) to improve Performing and/or Learning by Learning More from Experience with a process that is similar to...
the Strategies for Self-Regulated Learning developed by other educators.
videos — search youtube for [ metacognition ] and [ metacognitive strategies ] and [ metacognition in education ].
And in other parts of this links-page,
As one part of guiding students during an inquiry activity a teacher can stimulate their metacognition by helping them reflect on their experiences.
While solving problems, almost always it's useful to think with empathy and also with metacognitive self-empathy by asking “what do they want?” and “what do I want?” and aiming for a win-win solution.
P ROCESS -C OORDINATING Skills (for Solving Problems)
THINKING SKILLS and THINKING PROCESS: When educators develop strategies to improve the problem solving abilities of students, usually their focus is on thinking skills. But thinking process is also important.
Therefore, it's useful to define thinking skills broadly, to include thinking that leads to decisions-about-actions, and actions:
thinking → action-decisions → actions
[[ I.O.U. -- later, in mid-June 2021, the ideas below will be developed -- and i'll connect it with Metacognitive Skills because we use Metacognition to Coordinate Process.
[[ here are some ideas that eventually will be in this section:
Collaborative Problem Solving [[ this major new section will link to creative.htm# collaborative-creativity (with a brief summary of ideas from there) and expand these ideas to include general principles and "coordinating the collaboration" by deciding who will do what, when, with some individual "doing" and some together "doing" ]]
actions can be mental and/or physical (e.g. actualizing Experimental Design to do a Physical Experiment, or actualizing an Option-for-Action into actually doing the Action
[[a note to myself: educational goals: we should help students improve their ability to combine their thinking skills — their creative Generating of Options and critical Generating of Options, plus using their Knowledge-of-Ideas that includes content-area knowledge plus the Empathy that is emphasized in Design Thinking — into an effective thinking process .
[[ Strategies for Coordinating: students can do this by skillfully Coordinating their Problem-Solving Actions (by using their Conditional Knowledge ) into an effective Problem-Solving Process.
[[ During a process of design, you coordinate your thinking-and-actions by making action decisions about “what to do next.” How? When you are "skillfully Coordinating..." you combine cognitive/metacognitive awareness (of your current problem-solving process) with (by knowing, for each skill, what it lets you accomplish, and the conditions in which it will be useful).
[[ a little more about problem-solving process
[[ here are more ideas that might be used here:
Sometimes tenacious hard work is needed, and perseverance is rewarded. Or it may be wise to be flexible – to recognize that what you've been doing may not be the best approach, so it's time to try something new – and when you dig in a new location your flexibility pays off.
Perseverance and flexibility are contrasting virtues. When you aim for an optimal balancing of this complementary pair, self-awareness by “knowing yourself” is useful. Have you noticed a personal tendency to err on the side of either too much perseverance or not enough? Do you tend to be overly rigid, or too flexible?
Making a wise decision about perseverance — when you ask, “Do I want to continue in the same direction, or change course?” * — is more likely when you have an aware understanding of your situation, your actions, the results, and your goals. Comparing results with goals is a Quality Check, providing valuable feedback that you can use as a “compass” to help you move in a useful direction. When you look for signs of progress toward your goals in the direction you're moving, you may have a feeling, based on logic and experience, that your strategy for coordinating the process of problem solving isn't working well, and it probably never will. Or you may feel that the goal is almost in sight and you'll soon reach it.
- How I didn't Learn to Ski (and then did) with Persevering plus Flexible Insight -
PRINCIPLES for PROBLEM SOLVING
Should we explicitly teach principles for thinking, can we use a process of inquiry to teach principles for inquiry, should we use a “model” for problem-solving process.
combining models?
What are the benefits of infusion and separate programs?
Principles & Strategies & Models ?
Should we explicitly teach “principles” for thinking?
Using evidence and logic — based on what we know about the ways people think and learn — we should expect a well-designed combination of “experience + reflection + principles” to be more educationally effective than experience by itself, to help students improve their creative-and-critical thinking skills and whole-process skills in solving problems (for design-inquiry) and answering questions (for science-inquiry).
Can we use a process-of-inquiry to teach principles-for-inquiry?

* In a typical sequence of ERP, students first get Experiences by doing a design activity. During an activity and afterward, they can do Reflections (by thinking about their experiences) and this will help them recognize Principles for doing Design-Thinking Process that is Problem-Solving Process. { design thinking is problem-solving thinking }
During reflections & discussions, typically students are not discovering new thoughts & actions. Instead they are recognizing that during a process of design they are using skills they already know because they already have been using Design Thinking to do almost everything in their life . A teacher can facilitate these recognitions by guiding students with questions about what they are doing now, and what they have done in the past, and how these experiences are similar, but also are different in some ways. When students remember (their prior experience) and recognize (the process they did use, and are using), they can formulate principles for their process of design thinking. But when they formulate principles for their process of problem solving, they are just making their own experience-based prior knowledge — of how they have been solving problems, and are now solving problems — more explicit and organized.
If we help students "make their own experience-based prior knowledge... more explicit and organized" by showing them how their knowledge can be organized into a model for problem-solving process, will this help them improve their problem-solving abilities?
IOU - This mega-section will continue being developed in mid-June 2021.
[[a note to myself: thinking skills and thinking process — What is the difference? - Experience + Reflection + Principles - coordination-decisions
[[are the following links specifically for this section about "experience + principles"? maybe not because these seem to be about principles, not whether to teach principles.]]
An excellent overview is Teaching Thinking Skills by Kathleen Cotton. (the second half of her page is a comprehensive bibliography)
This article is part of The School Improvement Research Series (available from Education Northwest and ERIC ) where you can find many useful articles about thinking skills & other topics, by Cotton & other authors. [[a note to myself: it still is excellent, even though it's fairly old, written in 1991 -- soon, I will search to find more-recent overviews ]]
Another useful page — What Is a Thinking Curriculum ? (by Fennimore & Tinzmann) — begins with principles and then moves into applications in Language Arts, Mathematics, Sciences, and Social Sciences.
My links-page for Teaching-Strategies that promote Active Learning explores a variety of ideas about strategies for teaching (based on principles of constructivism, meaningful reception,...) in ways that are intended to stimulate active learning and improve thinking skills. Later, a continuing exploration of the web will reveal more web-pages with useful “thinking skills & problem solving” ideas (especially for K-12 students & teachers) and I'll share these with you, here and in TEACHING ACTIVITIES .
Of course, thinking skills are not just for scholars and schoolwork, as emphasized in an ERIC Digest , Higher Order Thinking Skills in Vocational Education . And you can get information about 23 ==Programs that Work from the U.S. Dept of Education.
goals can include improving affective factors & character == e.g. helping students learn how to develop & use use non-violent solutions for social problems .
INFUSION and/or SEPARATE PROGRAMS?
In education for problem solving, one unresolved question is "What are the benefits of infusion, or separate programs? " What is the difference?
With infusion , thinking skills are closely integrated with content instruction in a subject area, in a "regular" course.
In separate programs , independent from content-courses, the explicit focus of a course is to help students improve their thinking skills.
In her overview of the field, Kathleen Cotton says,
Of the demonstrably effective programs, about half are of the infused variety, and the other half are taught separately from the regular curriculum. ... The strong support that exists for both approaches... indicates that either approach can be effective. Freseman represents what is perhaps a means of reconciling these differences [between enthusiastic advocates of each approach] when he writes, at the conclusion of his 1990 study: “Thinking skills need to be taught directly before they are applied to the content areas. ... I consider the concept of teaching thinking skills directly to be of value especially when there follows an immediate application to the content area.”
For principles and examples of infusion , check the National Center for Teaching Thinking which lets you see == What is Infusion? (an introduction to the art of infusing thinking skills into content instruction), and == sample lessons (for different subjects, grade levels, and thinking skills). -- resources from teach-think-org -- [also, lessons designed to infuse Critical and Creative Thinking into content instruction]
Infusing Teaching Thinking Into Subject-Area Instruction (by Robert Swarz & David Perkins) - and more about the book
And we can help students improve their problem-solving skills with teaching strategies that provide structure for instruction and strategies for thinking . ==[use structure+strategies only in edu-section?
Adobe [in creative]
MORE about Teaching Principles for Problem Solving
[[ i.o.u. -- this section is an "overlap" between #1 (Goals) and #2 (Methods) so... maybe i'll put it in-between them? -- i'll decide soon, maybe during mid-June 2021 ]]
Two Kinds of Inquiry Activities (for Science and Design )
To more effectively help students improve their problem-solving skills, teachers can provide opportunities for students to be actively involved in solving problems, with inquiry activities . What happens during inquiry? Opportunities for inquiry occur whenever a gap in knowledge — in conceptual knowledge (so students don't understand) or procedural knowledge (so they don't know what to do, or how) — stimulates action (mental and/or physical) and students are allowed to think-do-learn.
Students can be challenged to solve two kinds of problems during two kinds of inquiry activity:
during Science-Inquiry they try to improve their understanding, by asking problem-questions and seeking answers. During their process of solving problems, they are using Science-Design , aka Science , to design a better explanatory theory.
during Design-Inquiry they try to improve some other aspect(s) of life, by defining problem-projects and seeking solutions. During their process of solving problems, they are using General Design (which includes Engineering and more) to design a better product, activity, or strategy.
But... whether the main objective is for Science-Design or General Design, a skilled designer will be flexible, will do whatever will help them solve the problem(s). Therefore a “scientist” sometimes does engineering, and an “engineer” sometimes does science. A teacher can help students recognize how-and-why they also do these “ crossover actions ” during an activity for Science Inquiry or Design Inquiry. Due to these connections, we can build transfer-bridges between the two kinds of inquiry , and combine both to develop “hybrid activities” for Science-and-Design Inquiry.
Goal-Priorities: There are two kinds of inquiry, so (re: Goals for What to Learn) what emphasis do we want to place on activities for Science -Inquiry and Design -Inquiry? (in the limited amount of classroom time that teachers can use for Inquiry Activities)
Two Kinds of Improving (for Performing and Learning )
Goal-Priorities: There are two kinds of improving, so (re: Goals for What to Learn) what emphasis do we want to place on better Performing (now) and Learning (for later)?
When defining goals for education, we ask “How important is improving the quality of performing now, and (by learning now ) of performing later ?” For example, a basketball team (coach & players) will have a different emphasis in an early-season practice (when their main goal is learning well) and end-of-season championship game (when their main goal is performing well). {we can try to optimize the “total value” of performing/learning/enjoying for short-term fun plus long-term satisfactions }
SCIENCE (to use-learn-teach Skills for Problem Solving )
Problem-solving skills used for science.
This section supplements models for Scientific Method that "begin with simplicity, before moving on to models that are more complex so they can describe the process more completely-and-accurately. " On the spectrum of simplicity → complexity , one of the simplest models is...
POE (Predict, Observe, Learn) to give students practice with the basic scientific logic we use to evaluate an explanatory theory about “what happens, how, and why.” POE is often used for classroom instruction — with interactive lectures [iou - their website is temporarily being "restored"] & in other ways — and research has shown it to be effective. A common goal of instruction-with-POE is to improve the conceptual knowledge of students, especially to promote conceptual change their alternative concepts to scientific concepts. But students also improve their procedural knowledge for what the process of science is, and how to do the process. { more – What's missing from POE ( experimental skills ) w hen students use it for evidence-based argumentation and Ecologies - Educational & Conceptual }
Dany Adams (at Smith College) explicitly teaches critical thinking skills – and thus experiment-using skills – in the context of scientific method.
Science Buddies has models for Scientific Method (and for Engineering Design Process ) and offers Detailed Help that is useful for “thinking skills” education. ==[DetH]
Next Generation Science Standards ( NGSS ) emphasizes the importance of designing curriculum & instruction for Three Dimensional Learning with productive interactions between problem-solving Practices (for Science & Engineering ) and Crosscutting Concepts and Disciplinary Core Ideas.
Science: A Process Approach ( SAPA ) was a curriculum program earlier, beginning in the 1960s. Michael Padilla explains how SAPA defined The Science Process Skills as "a set of broadly transferable abilities, appropriate to many science disciplines and reflective of the behavior of scientists. SAPA categorized process skills into two types, basic and integrated. The basic (simpler) process skills provide a foundation for learning the integrated (more complex) skills." Also, What the Research Says About Science Process Skills by Karen Ostlund; and Students' Understanding of the Procedures of Scientific Enquiry by Robin Millar, who examines several approaches and concludes (re: SAPA) that "The process approach is not, therefore, a sound basis for curriculum planning, nor does the analysis on which it is based provide a productive framework for research." But I think parts of it can be used creatively for effective instruction. { more about SAPA }
ENGINEERING (to use-learn-teach Skills for Problem Solving )
Problem-solving skills used for engineering.
Engineering is Elementary ( E i E ) develops activities for students in grades K-8. To get a feeling for the excitement they want to share with teachers & students, watch an "about EiE" video and explore their website . To develop its curriculum products, EiE uses research-based Design Principles and works closely with teachers to get field-testing feedback, in a rigorous process of educational design . During instruction, teachers use a simple 5-phase flexible model of engineering design process "to guide students through our engineering design challenges... using terms [ Ask, Imagine, Plan, Create, Improve ] children can understand." {plus other websites about EiE }
Project Lead the Way ( PLTW ), another major developer of k-12 curriculum & instruction for engineering and other areas, has a website you can explore to learn about their educational philosophy & programs (at many schools ) & resources and more. And you can web-search for other websites about PLTW.
Science Buddies , at level of k-12, has tips for science & engineering .
EPICS ( home - about ), at college level, is an engineering program using EPICS Design Process with a framework supplemented by sophisticated strategies from real-world engineering. EPICS began at Purdue University and is now used at ( 29 schools) (and more with IUCCE ) including Purdue, Princeton, Notre Dame, Texas A&M, Arizona State, UC San Diego, Drexel, and Butler.
DESIGN THINKING (to use-learn-teach Skills for Problem Solving )
Design Thinking emphasizes the importance of using empathy to solve human-centered problems.
Stanford Institute of Design ( d.school ) is an innovative pioneer in teaching a process of human-centered design thinking that is creative-and-critical with empathy . In their Design Thinking Bootleg – that's an updated version of their Bootcamp Bootleg – they share a wide variety of attitudes & techniques — about brainstorming and much more — to stimulate productive design thinking with the objective of solving real-world problems. {their first pioneer was David Kelley }
The d.school wants to "help prepare a generation of students to rise with the challenges of our times." This goal is shared by many other educators, in k-12 and colleges, who are excited about design thinking. Although d.school operates at college level, they (d.school + IDEO ) are active in K-12 education as in their website about Design Thinking in Schools ( FAQ - resources ) that "is a directory [with brief descriptions] of schools and programs that use design thinking in the curriculum for K12 students... design thinking is a powerful way for today’s students to learn, and it’s being implemented by educators all around the world." { more about Education for Design Thinking in California & Atlanta & Pittsburgh & elsewhere} [[a note to myself: @ ws and maybe my broad-definition page]]
On twitter, # DTk12 chat is an online community of enthusiastic educators who are excited about Design Thinking ( DT ) for K-12 Education, so they host a weekly twitter chat (W 9-10 ET) and are twitter-active informally 24/7.
PROBLEM-BASED LEARNING (to use-learn-teach Skills for Problem Solving )
Problem-Based Learning ( PBL ? ) is a way to improve motivation, thinking, and learning. You can learn more from:
overviews of PBL from U of WA & Learning-Theories.com ;
and (in ERIC Digests) using PBL for science & math plus a longer introduction - challenges for students & teachers (we never said it would be easy!) ;
a deeper examination by John Savery (in PDF & [without abstract] web-page );
Most Popular Papers from The Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-based Learning ( about IJPBL ).
videos about PBL by Edutopia (9:26) and others ;
a search in ACSD for [problem-based learning] → a comprehensive links-page for Problem-Based Learning and an ACSD-book about...
Problems as Possibilities by Linda Torp and Sara Sage: Table of Contents - Introduction (for 2nd Edition) - samples from the first & last chapters - PBL Resources (including WeSites in Part IV) .
PBL in Schools:
Samford University uses PBL (and other activities) for Transformational Learning that "emphasizes the whole person, ... helps students grow physically, mentally, and spiritually, and encourages them to value public service as well as personal gain."
In high school education, Problem-Based Learning Design Institute from Illinois Math & Science Academy ( about ); they used to have an impressive PBL Network ( sitemap & web-resources from 2013, and 9-23-2013 story about Kent, WA ) that has mysteriously disappeared. https://www.imsa.edu/academics/inquiry/resources/ research_ethics
Vanderbilt U has Service Learning thru Community Engagement with Challenges and Opportunities and tips for Teaching Step by Step & Best Practices and Resource-Links for many programs, organizations, articles, and more.
What is PBL? The answer is " Problem-Based Learning and/or Project-Based Learning " because both meanings are commonly used. Here are 3 pages (+ Wikipedia) that compare PBL with PBL, examine similarities & differences, consider definitions:
John Larmer says "we [at Buck Institute for Education which uses Project Based Learning ] decided to call problem-based learning a subset of project-based learning [with these definitions, ProblemBL is a narrower category, so all ProblemBL is ProjectBL, but not vice versa] – that is, one of the ways a teacher could frame a project is to solve a problem, " and concludes that "the semantics aren't worth worrying about, at least not for very long. The two PBLs are really two sides of the same coin. ... The bottom line is the same: both PBLs can powerfully engage and effectively teach your students!" Chris Campbell concludes, "it is probably the importance of conducting active learning with students that is worthy and not the actual name of the task. Both problem-based and project-based learning have their place in today’s classroom and can promote 21st Century learning." Jan Schwartz says "there is admittedly a blurring of lines between these two approaches to education, but there are differences." Wikipedia has Problem-Based Learning (with "both" in P5BL ) and Project-Based Learning .
i.o.u. - If you're wondering "What can I do in my classroom today ?", eventually (maybe in June 2021) there will be a section for "thinking skills activities" in this page, and in the area for TEACHING ACTIVITIES .


Problem Solving in Education: A Global Imperative

Pedagogical Shifts
Essential lessons, leadership challenges and opportunities.
Jamaludin, A., & Hung, D. W. L. (2016). Digital "learning trails": Scaling technology-facilitated curricular innovation in schools with a rhizomatic lens. Journal of Educational Change , 17 (3), 355–377.
Kahneman, D. (2011). Thinking, fast and slow . New York: Farrar, Strauss, & Giroux.
National Academy of Sciences. (2010). Rising above the gathering storm, revisited: Rapidly approaching category 5. Washington, DC: National Academies Press.
McNeill, K. L., González-Howard, M., Katsh-Singer, R., & Loper, S. (2017). Moving beyond pseudoargumentation: Teachers' enactments of an educative science curriculum focused on argumentation. Science Education , 101 (3), 426–457.
Ng, P. T. (2017). Learning from Singapore: The power of paradoxes . New York: Routledge.
OECD. (2012). PISA 2012 results: Creative problem solving. Paris: OECD.
Patchen, A. K., Zhang, L., & Barnett, M. (2017). Growing plants and scientists: Fostering positive attitudes toward science among all participants in an afterschool hydroponics program. Journal of Science and Educational Technology , 26 (3), 279–294.
Prensky, M. R. (2012). From digital natives to digital wisdom: Hopeful essays for 21st century learning. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin.
Shirley, D. (2016). The new imperatives of educational change: Achievement with integrity . New York: Routledge.
• 1 Read more about the Jurong Secondary School project .

He has conducted in-depth studies about school innovations in England, Germany, Canada, and South Korea. Shirley has been a visiting professor at Harvard University in the United States, Venice International University in Italy, the National Institute of Education in Singapore, the University of Barcelona in Spain, and the University of Stavanger in Norway. He is a fellow of the Royal Society of Arts. Shirley’s previous book is The New Imperatives of Educational Change: Achievement with Integrity .

Pak Tee Ng is Associate Dean, Leadership Learning at the National Institute of Education of Nanyang Technological University in Singapore and the author of Learning from Singapore: The Power of Paradoxes (Routledge, 2017).

ASCD is a community dedicated to educators' professional growth and well-being.
Let us help you put your vision into action., related articles.
For STEM Education, the Time Is Now

How to Signal “STEM Is For You”?

STEM Doesn’t Have to Be Rocket Science
How to Start with STEM
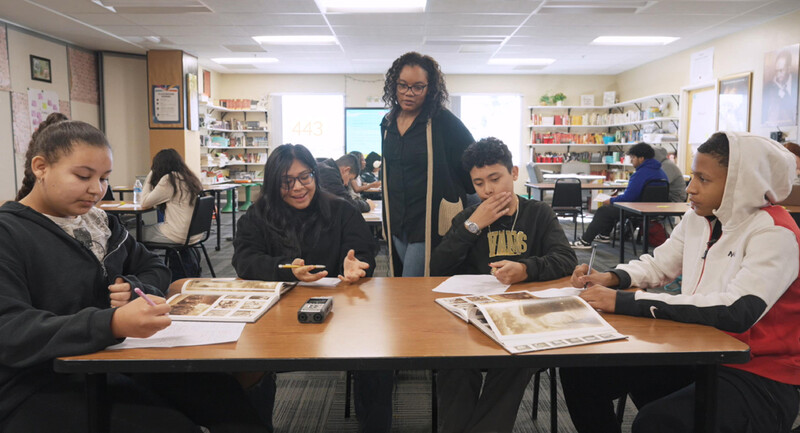

Picture Books Aren’t Just for the Youngest Students
From our issue.

To process a transaction with a Purchase Order please send to [email protected]
Benefits of Problem-Solving in the K-12 Classroom
Posted October 5, 2022 by Miranda Marshall

From solving complex algebra problems to investigating scientific theories, to making inferences about written texts, problem-solving is central to every subject explored in school. Even beyond the classroom, problem-solving is ranked among the most important skills for students to demonstrate on their resumes, with 82.9% of employers considering it a highly valued attribute. On an even broader scale, students who learn how to apply their problem-solving skills to the issues they notice in their communities – or even globally – have the tools they need to change the future and leave a lasting impact on the world around them.
Problem-solving can be taught in any content area and can even combine cross-curricular concepts to connect learning from all subjects. On top of building transferrable skills for higher education and beyond, read on to learn more about five amazing benefits students will gain from the inclusion of problem-based learning in their education:
- Problem-solving is inherently student-centered.
Student-centered learning refers to methods of teaching that recognize and cater to students’ individual needs. Students learn at varying paces, have their own unique strengths, and even further, have their own interests and motivations – and a student-centered approach recognizes this diversity within classrooms by giving students some degree of control over their learning and making them active participants in the learning process.
Incorporating problem-solving into your curriculum is a great way to make learning more student-centered, as it requires students to engage with topics by asking questions and thinking critically about explanations and solutions, rather than expecting them to absorb information in a lecture format or through wrote memorization.
- Increases confidence and achievement across all school subjects.
As with any skill, the more students practice problem-solving, the more comfortable they become with the type of critical and analytical thinking that will carry over into other areas of their academic careers. By learning how to approach concepts they are unfamiliar with or questions they do not know the answers to, students develop a greater sense of self-confidence in their ability to apply problem-solving techniques to other subject areas, and even outside of school in their day-to-day lives.
The goal in teaching problem-solving is for it to become second nature, and for students to routinely express their curiosity, explore innovative solutions, and analyze the world around them to draw their own conclusions.
- Encourages collaboration and teamwork.
Since problem-solving often involves working cooperatively in teams, students build a number of important interpersonal skills alongside problem-solving skills. Effective teamwork requires clear communication, a sense of personal responsibility, empathy and understanding for teammates, and goal setting and organization – all of which are important throughout higher education and in the workplace as well.
- Increases metacognitive skills.
Metacognition is often described as “thinking about thinking” because it refers to a person’s ability to analyze and understand their own thought processes. When making decisions, metacognition allows problem-solvers to consider the outcomes of multiple plans of action and determine which one will yield the best results.
Higher metacognitive skills have also widely been linked to improved learning outcomes and improved studying strategies. Metacognitive students are able to reflect on their learning experiences to understand themselves and the world around them better.
- Helps with long-term knowledge retention.
Students who learn problem-solving skills may see an improved ability to retain and recall information. Specifically, being asked to explain how they reached their conclusions at the time of learning, by sharing their ideas and facts they have researched, helps reinforce their understanding of the subject matter.
Problem-solving scenarios in which students participate in small-group discussions can be especially beneficial, as this discussion gives students the opportunity to both ask and answer questions about the new concepts they’re exploring.
At all grade levels, students can see tremendous gains in their academic performance and emotional intelligence when problem-solving is thoughtfully planned into their learning.
Interested in helping your students build problem-solving skills, but aren’t sure where to start? Future Problem Solving Problem International (FPSPI) is an amazing academic competition for students of all ages, all around the world, that includes helpful resources for educators to implement in their own classrooms!
Learn more about this year’s competition season from this recorded webinar: https://youtu.be/AbeKQ8_Sm8U and/or email [email protected] to get started!
Signup Newsletter
Sign me up for the newsletter!

The Institute of Competition Sciences (ICS) was founded in 2012 to help transform learning into an exciting challenge for all students. We exist to support students in realizing the full potential of their future.
Quick Links
- Competitions
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Connect with us on social media

Copyright © 2024 Institute of Competition Sciences. All rights reserved.

MSU Extension
Problem-solving skills are an important factor in academic success.
Elizabeth Gutierrez, Michigan State University Extension - May 11, 2012
Updated from an original article written by [email protected]..
Parents and caregivers can ensure their children's success by teaching and modeling effective problem-solving at home.

Helping your child learn how to problem solve is a critical skill for school readiness. Parents and caregivers are a child’s first and most important teacher; therefore, modeling good problem solving skills is very important. Children learn by watching parents and caregivers handle different situations and solve problems. If a parent handles problems by yelling, throwing things, hitting, grabbing or using other unacceptable strategies, a child will learn to do the same thing.
Often, adults will prevent their children from seeing all conflicts or disagreements. Remember, it is important for children to see adults negotiate differences, compromise and resolve conflicts. Learning to negotiate differences in a constructive way and allowing children to see how this is done is very effective and important. If parent and caregivers handle these situations privately, there is no example for the child/children to learn from.
Children can learn how to be assertive verbally as a result of seeing and listening to how adults resolve conflict. Another simple way a child can learn how to be assertive verbally is by role-playing with puppets and through pretend play with an adult. When using these techniques, it is important to help your child think of constructive ways to respond to different situations. By using puppets and role-play, your child can also learn about how others may feel in specific situations. When using these techniques, it is important not to criticize or label the child for past misbehavior.
There are some basic steps to problem solving from Incredible Years :
- Identify the problem.
- List the possible solutions or courses of action.
- Weigh the possible solutions.
- Choose a solution to try.
- Put the solution into practice.
- Evaluate the solution.
Using effective problem solving techniques will help children avoid conflict with others in a school setting and in their everyday lives. It will also strengthen children’s beginning empathy skills and help them learn more positive attributions about another person’s intentions. Effective problem solving skills is essential for academic and social success.
For more articles on child development, academic success, parenting and life skill development, please visit the Michigan State University Extension website.
This article was published by Michigan State University Extension . For more information, visit https://extension.msu.edu . To have a digest of information delivered straight to your email inbox, visit https://extension.msu.edu/newsletters . To contact an expert in your area, visit https://extension.msu.edu/experts , or call 888-MSUE4MI (888-678-3464).
Did you find this article useful?

Ready to grow with 4-H? Sign up today!
new - method size: 3 - Random key: 0, method: tagSpecific - key: 0
You Might Also Be Interested In

AC3 Podcast episode 3
Published on June 30, 2021

MIFruitcast: Meet the Educators
Published on January 18, 2024
MIFruitcast: Biological Controls with Jackie Perkins
Published on December 1, 2023

MSU Dairy Virtual Coffee Break: Fresh Research on Milk fever
Published on April 7, 2021

MI Community Minutes: Sustainability Efforts in Local Government with City of Holland's Dan Broersma
Published on January 24, 2022
MSU Dairy Virtual Coffee Break: Feed management 101
- child & family development
- early childhood development
- msu extension
- social and emotional development
- child & family development,
- early childhood development,
- msu extension,

Explained: Importance of critical thinking, problem-solving skills in curriculum
F uture careers are no longer about domain expertise or technical skills. Rather, critical thinking and problem-solving skills in employees are on the wish list of every big organization today. Even curriculums and pedagogies across the globe and within India are now requiring skilled workers who are able to think critically and are analytical.
The reason for this shift in perspective is very simple.
These skills provide a staunch foundation for comprehensive learning that extends beyond books or the four walls of the classroom. In a nutshell, critical thinking and problem-solving skills are a part of '21st Century Skills' that can help unlock valuable learning for life.
Over the years, the education system has been moving away from the system of rote and other conventional teaching and learning parameters.
They are aligning their curriculums to the changing scenario which is becoming more tech-driven and demands a fusion of critical skills, life skills, values, and domain expertise. There's no set formula for success.
Rather, there's a defined need for humans to be more creative, innovative, adaptive, agile, risk-taking, and have a problem-solving mindset.
In today's scenario, critical thinking and problem-solving skills have become more important because they open the human mind to multiple possibilities, solutions, and a mindset that is interdisciplinary in nature.
Therefore, many schools and educational institutions are deploying AI and immersive learning experiences via gaming, and AR-VR technologies to give a more realistic and hands-on learning experience to their students that hone these abilities and help them overcome any doubt or fear.
ADVANTAGES OF CRITICAL THINKING AND PROBLEM-SOLVING IN CURRICULUM
Ability to relate to the real world: Instead of theoretical knowledge, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills encourage students to look at their immediate and extended environment through a spirit of questioning, curiosity, and learning. When the curriculum presents students with real-world problems, the learning is immense.
Confidence, agility & collaboration : Critical thinking and problem-solving skills boost self-belief and confidence as students examine, re-examine, and sometimes fail or succeed while attempting to do something.
They are able to understand where they may have gone wrong, attempt new approaches, ask their peers for feedback and even seek their opinion, work together as a team, and learn to face any challenge by responding to it.
Willingness to try new things: When problem-solving skills and critical thinking are encouraged by teachers, they set a robust foundation for young learners to experiment, think out of the box, and be more innovative and creative besides looking for new ways to upskill.
It's important to understand that merely introducing these skills into the curriculum is not enough. Schools and educational institutions must have upskilling workshops and conduct special training for teachers so as to ensure that they are skilled and familiarized with new teaching and learning techniques and new-age concepts that can be used in the classrooms via assignments and projects.
Critical thinking and problem-solving skills are two of the most sought-after skills. Hence, schools should emphasise the upskilling of students as a part of the academic curriculum.
The article is authored by Dr Tassos Anastasiades, Principal- IB, Genesis Global School, Noida.
Watch Live TV in English
Watch Live TV in Hindi


Improving Problem Solving Skills
- January 15, 2021

“All life is problem solving.” – Karl Popper.
I am starting this article with the words of a wise man who defined perfectly what life has to offer. Having to deal with problems is part of our existence. From the day we are born until the day we die, problems are our fellow travelers in our journey of life. They are key factors in our upbringing throughout our lifetime. If there were no problems, there would be no development of skills, or character, or progress toward a better future. Someone defined problems as a gift: without them we wouldn’t grow, while another one defined problems not as stop signs, but as guidelines. Facing a certain problem and reaching its solution successfully will lead to other challenges. People approach their problems differently. Some consider them obstacles in their life. I believe that whenever you see your problems like this, you only have made yourself a victim. Having such an approach will not lead to positive solutions, but only failures. When others see them as an opportunity to take advantage of their achievements,we find that life has to offer for every problem, an opportunity with its solution, and new challenges for the next generations. I think it’s part of growing up. The history of evolution of humanity up to the progress humans have reached today is nothing but a chain reaction of problem solving.
Solutions and problem solving skills
In order to give the best solutions to our problems, we must first develop in ourselves the necessary skills. Not all the problems are the same, but in general; they all require certain skills which are used for most problems. Critical thinking is a valuable asset. It enables us to correctly assess a situation and come up with a logical solution. The most important aspect of critical thinking is analytical thinking. It implies gathering information, intercepting, and evaluating. Communication skills enable us to cooperate with other coworkers during the critical thinking process, reaching the best solutions for the problem. Creative thinking implies being able to discover certain patterns of information and make abstract connections between seemingly unrelated data, whereas the ability to solve problems can help us correctly analyze a problem and work on implementing solutions for it.

Five phases of problem solving
Different problem solvers have different approaches, but all aim toward the best solution and results. For example, Rafis Abazov explains in one of his articles how to improve your problem-solving skills. He is a university professor who speaks to his students in a plain and short form. He breaks down the solutions in five phases:
1. Identify the problem. His definition of problems solving skills is simple. It is the ability to identify the nature of a problem, deconstruct it (break it down) and develop an effective set of actions to address the challenges related to it. He quotes Albert Einstein, who once said: “The formulation of the problem is often more essential than its solution, which may be merely a mat- ter of mathematical or experimental skill.”
2. Define the main elements of the problem. The next step is the ability to break down the problem into small manageable parts by defining the main elements of the problem. It is an essential psychological and managerial skill. Instead of facing an enormous problem, break it down in smaller elements. It makes it easier to solve. For example, here is one way to break tasks down.
- Look at the big picture. Understand what the result will look like.
- Examine the parts of the task. Do it step by step, because it will not happen immediately through magic
- Think of the order of the pieces: which comes first, second, third etc.
- Create a timeline for your tasks. The deadline will make you more focused for each task.
- Have a plan to stay on track. Put the time you will spend on the project into your schedule.
- Complete the task early enough to make a final review.
3. Examine possible solutions. It is very tricky as on the surface: it might look like the reaching of the goal is close. Finding simplistic ways can not give the same result as finding the most effective ways and turn them to opportunities to make a strong success story.
4. Act on resolving the problem. Developing a step-by-step execution plan and acting effectively and decisively is the final touch. It doesn’t matter how effectively students identify the problem with its constituents and look for possible solutions; all that matters is the ability to perform concrete steps to execute the plan.
5. Look for lessons to learn. After all is done, it is crucial to reflect upon the solved problem, try to evaluate the entire process and formulate the lessons to be learned for the next project. Reflection is essential in order to learn from problem solving.

Education is one of the most important things in the world. In schools, people learn from an early age to face problems and look for their solutions. But most schools teach their students to memorize facts, formulas and functions without any applicability to the challenges in real life they will face later. Instead, they need challenges; problems which focus on real-world scenarios. They need a chance to understand the world they are entering and be prepared for it. In the real world, students will not have nice problems, but complex ones. Since the challenges of the real world will not be simple, the problems meant to prepare students for this world should not be either. Students need to apply what they have learned in school later on in life. For example, in English class, students read The Giver by Lois Lowry and analyzed whether the society in the book was ethical. Students need to understand what ethical means and how it’s applicable in real situations. It is important to teach students how to grapple. It’s more powerful than perseverance. Grapple is like perseverance, but beyond that. It means trying again and again, even after having failed. Grappling is working hard to make sure you understand the problem fully, and then using every resource at your fingertips to solve it.
Teachers need to put more importance on student understanding than on getting the right answer. They also need a more practical view of the world. Students must have an introduction of the society they live in and its benefits and drawbacks. It will enable them to come out with incredible problem-solving skills and the ability to look at any problem and have a thousand ways to solve it in their minds already because they didn’t just memorize functions and periodic tables. They understand why and they work to understand how to solve a problem instead of just getting the answer.
References:
“6 Examples of Critical Thinking Skills.” Indeed Career Guide. Indeed. Accessed November 2020. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/critical-thinking-examples.
“Break Large Tasks down into Smaller, More Manageable Pieces.” UGA Today, May 27, 2020. https://news.uga.edu/break-large-tasks-down-into-smaller-more-manageable-pieces/.
“How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills.” Top Universities, June 23, 2016. https://www.topuniversities.com/blog/how-improve-your-problem-solving-skills.
Pelletiere, Anna. “4 Tips on Teaching Problem Solving (From a Student).” Edutopia. George Lucas Educational Foundation, November 1, 2016. https://www.edutopia.org/blog/4-tips-teaching-problem-solving-from-student-anna-pelletiere.
“Problem Solving Quotes: LeadingThoughts – Quotes on Problem Solving.” Problem Solving Quotes | LeadingThoughts – Quotes on Problem Solving – LeadershipNow.com. Accessed November 2020. https://www.leadershipnow.com/probsolvingquotes.html.
“Problems and Problem Solving Quotes from Decision-Making-Solutions.com.” Making. Accessed November 2020. https://www.decision-making-solutions.com/problem_solving_quotes.html.
Share this:
Most Recent Posts

A Student’s Guide To Preparing Yourself Financially For College

The Importance of Eye Health in the Workplace

Why Do Some U.S. Public Schools Fail?

How to Write Unique Assignments? Tips for Students

Homeschooling Helps Introverted Students Thrive

Why Schools Need to Invest in a Teacher Evaluation Software Service

Related Posts
Regardless of the field or industry you work in, you will want your workplace to be productive and efficient. As such, a previous post listing
Introverted students often face hardships when interacting with their classmates; they can be bullied for being shy. Many parents feel administrators do not discipline bullies
Within the large field of educational technology, teacher assessment software is a crucial component that, when integrated into the curriculum, can reinforce the contemporary learning
Vision And Better Academic Performance: The Surprising Link
Eye conditions and vision issues have been increasing among the youth at an alarming rate. Other than genetic factors, the tumultuous events of the past

How to Lead a New Company to Success
Running a business in the United States is daunting, with 18 percent of small businesses failing within their first year. Taking over the helm of
The Future of Education
The future is uncertain, and we cannot predict what will happen. In the digital age, personal devices make the access and the transfer of information

Unlock New Horizons in Your Coaching Career with Online Certification
Maintaining relevance and competitiveness is essential for professional advancement in the ever-evolving coaching field. One effective method to perform this is by enrolling in online

Exploring Binary Converter Apps: Enhancing Digital Literacy in the Modern Age
Digital literacy is no longer a luxury but an essential necessity of the rapidly evolving and tech-centric world we are living in. Understanding binary codes
Problem-Solving Method in Teaching
The problem-solving method is a highly effective teaching strategy that is designed to help students develop critical thinking skills and problem-solving abilities . It involves providing students with real-world problems and challenges that require them to apply their knowledge, skills, and creativity to find solutions. This method encourages active learning, promotes collaboration, and allows students to take ownership of their learning.
Table of Contents
Definition of problem-solving method.
Problem-solving is a process of identifying, analyzing, and resolving problems. The problem-solving method in teaching involves providing students with real-world problems that they must solve through collaboration and critical thinking. This method encourages students to apply their knowledge and creativity to develop solutions that are effective and practical.
Meaning of Problem-Solving Method
The meaning and Definition of problem-solving are given by different Scholars. These are-
Woodworth and Marquis(1948) : Problem-solving behavior occurs in novel or difficult situations in which a solution is not obtainable by the habitual methods of applying concepts and principles derived from past experience in very similar situations.
Skinner (1968): Problem-solving is a process of overcoming difficulties that appear to interfere with the attainment of a goal. It is the procedure of making adjustments in spite of interference
Benefits of Problem-Solving Method
The problem-solving method has several benefits for both students and teachers. These benefits include:
- Encourages active learning: The problem-solving method encourages students to actively participate in their own learning by engaging them in real-world problems that require critical thinking and collaboration
- Promotes collaboration: Problem-solving requires students to work together to find solutions. This promotes teamwork, communication, and cooperation.
- Builds critical thinking skills: The problem-solving method helps students develop critical thinking skills by providing them with opportunities to analyze and evaluate problems
- Increases motivation: When students are engaged in solving real-world problems, they are more motivated to learn and apply their knowledge.
- Enhances creativity: The problem-solving method encourages students to be creative in finding solutions to problems.
Steps in Problem-Solving Method
The problem-solving method involves several steps that teachers can use to guide their students. These steps include
- Identifying the problem: The first step in problem-solving is identifying the problem that needs to be solved. Teachers can present students with a real-world problem or challenge that requires critical thinking and collaboration.
- Analyzing the problem: Once the problem is identified, students should analyze it to determine its scope and underlying causes.
- Generating solutions: After analyzing the problem, students should generate possible solutions. This step requires creativity and critical thinking.
- Evaluating solutions: The next step is to evaluate each solution based on its effectiveness and practicality
- Selecting the best solution: The final step is to select the best solution and implement it.
Verification of the concluded solution or Hypothesis
The solution arrived at or the conclusion drawn must be further verified by utilizing it in solving various other likewise problems. In case, the derived solution helps in solving these problems, then and only then if one is free to agree with his finding regarding the solution. The verified solution may then become a useful product of his problem-solving behavior that can be utilized in solving further problems. The above steps can be utilized in solving various problems thereby fostering creative thinking ability in an individual.
The problem-solving method is an effective teaching strategy that promotes critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration. It provides students with real-world problems that require them to apply their knowledge and skills to find solutions. By using the problem-solving method, teachers can help their students develop the skills they need to succeed in school and in life.
- Jonassen, D. (2011). Learning to solve problems: A handbook for designing problem-solving learning environments. Routledge.
- Hmelo-Silver, C. E. (2004). Problem-based learning: What and how do students learn? Educational Psychology Review, 16(3), 235-266.
- Mergendoller, J. R., Maxwell, N. L., & Bellisimo, Y. (2006). The effectiveness of problem-based instruction: A comparative study of instructional methods and student characteristics. Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-based Learning, 1(2), 49-69.
- Richey, R. C., Klein, J. D., & Tracey, M. W. (2011). The instructional design knowledge base: Theory, research, and practice. Routledge.
- Savery, J. R., & Duffy, T. M. (2001). Problem-based learning: An instructional model and its constructivist framework. CRLT Technical Report No. 16-01, University of Michigan. Wojcikowski, J. (2013). Solving real-world problems through problem-based learning. College Teaching, 61(4), 153-156

Problem-Solving in Mathematics Education
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2020
- Cite this reference work entry

- Manuel Santos-Trigo 2
1247 Accesses
8 Citations
Introduction
Problem-solving approaches appear in all human endeavors. In mathematics, activities such as posing or defining problems and looking for different ways to solve them are central to the development of the discipline. In mathematics education, the systematic study of what the process of formulating and solving problems entails and the ways to structure problem-solving approaches to learn mathematics has been part of the research agenda in mathematics education. How have research and practicing problem-solving approaches changed and evolved in mathematics education, and what themes are currently investigated? Two communities have significantly contributed to the characterization and development of the research and practicing agenda in mathematical problem-solving: mathematicians who recognize that the process of formulating, representing, and solving problems is essential in the development of mathematical knowledge (Polya 1945 ; Hadamard 1945 ; Halmos 1980 ) and mathematics...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Artigue M, Houdement C (2007) Problem solving in France: didactic and curricular perspectives. ZDM Int J Math Educ 39(5–6):365–382
Article Google Scholar
Cai J, Nie B (2007) Problem solving in Chinese mathematics education: research and practice. ZDM Int J Math Educ 39(5–6):459–473
Common Core State Standards for Mathematics (CCSS) (2010) Common Core State Standards initiative. http://www.corestandards.org/
Devlin K (2002) The millennium problems. The seven greatest unsolved mathematical puzzles of our time. Granta Publications, London
Google Scholar
Dick TP, Hollebrands K (2011) Focus in high school mathematics: technology to support reasoning and sense making. The National Council of Teachers of Mathematics, Reston
Doorman M, Drijvers P, Dekker T, Van den Heuvel-Panhuizen M, de Lange J, Wijers M (2007) Problem solving as a challenge for mathematics education in the Netherlands. ZDM Int J Math Educ 39(5–6):405–418
English LD, Gainsburg J (2016) Problem solving in a 21st-century mathematics curriculum. In: English LD, Kirshner D (eds) Handbook of international research in mathematics education. Routledge, New York, pp 313–335
Hadamard J (1945) An essay on the psychology of invention in the mathematical field. Dover Publications, New York
Halmos PR (1980) The heart of mathematics. Am Math Mon 87(7):519–524
Halmos PR (1994) What is teaching. Am Math Mon 101(9):848–854
Hilbert D (1902) Mathematical problems. Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society, 8:437–479
Hoyles C, Lagrange J-B (eds) (2010) Mathematics education and technology: rethinking the terrain. The 17th ICMI study. Springer, New York
Krutestkii VA (1976) The psychology of mathematical abilities in school children. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Lester FK, Kehle PE (1994) From problem solving to modeling: The evolution of thinking about research on complex mathematical activity. In: Lesh R, Doerr HM (ed) Beyond constructivism: Models and modeling perspectives on mathematics problem solving, learning, and teaching. Mahawah: New Jersey, pp 501–517
Lesh R, Zawojewski JS (2007) Problem solving and modeling. In: Lester FK Jr (ed) The second handbook of research on mathematics teaching and learning. National Council of Teachers of Mathematics. Information Age Publishing, Charlotte, pp 763–804
Lester F, Kehle PE (2003) From problem solving to modeling: the evolution of thinking about research on complex mathematical activity. In: Lesh R, Doerr H (eds) Beyond constructivism: models and modeling perspectives on mathematics problem solving, learning and teaching. Lawrence Erlbaum, Mahwah, pp 501–518
Liljedahl P, Santos-Trigo M (2019) Mathematical problem solving. Current themes, trends and research, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-10472-6 Cham, Switzerland: Springer
NCTM (1989) Curriculum and evaluation standards for school mathematics. NCTM, Reston
NCTM (2000) Principles and standards for school mathematics. National Council of Teachers of Mathematics, Reston
NCTM (2009) Focus in high school mathematics. Reasoning and sense making. NCTM, Reston
Perkins DN, Simmons R (1988) Patterns of misunderstanding: An integrative model of science, math, and programming. Rev of Edu Res 58(3):303–326
Polya G (1945) How to solve it. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Book Google Scholar
Santos-Trigo M (2007) Mathematical problem solving: an evolving research and practice domain. ZDM Int J Math Educ 39(5, 6):523–536
Santos-Trigo M, Reyes-Martínez I (2018) High school prospective teachers’ problem-solving reasoning that involves the coordinated use of digital technologies. Int J Math Educ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2018.1489075
Santos-Trigo M, Reyes-Rodriguez, A (2016) The use of digital technology in finding multiple paths to solve and extend an equilateral triangle task, International. Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology 47:1:58–81. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2015.1049228
Schoenfeld AH (1985) Mathematical problem solving. Academic, New York
Schoenfeld AH (1992) Learning to think mathematically: problem solving, metacognition, and sense making in mathematics. In: Grows DA (ed) Handbook of research on mathematics teaching and learning. Macmillan, New York, pp 334–370
Schoenfeld AH (2015) How we think: a theory of human decision-making, with a focus on teaching. In: Cho SJ (ed) The proceedings of the 12th international congress on mathematical education. Springer, Cham, pp 229–243. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12688-3_16
Chapter Google Scholar
Selden J, Mason A, Selden A (1989) Can average calculus students solve nonroutine problems? J Math Behav 8:45–50
Wertheimer M (1945) Productive thinking. Harper, New York
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Research and Advanced Studies, Mathematics Education Department, Cinvestav-IPN, Mexico City, Mexico
Manuel Santos-Trigo
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Manuel Santos-Trigo .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Education, Centre for Mathematics Education, London South Bank University, London, UK
Stephen Lerman
Section Editor information
Department of Science Teaching, The Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel
Ruhama Even
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Santos-Trigo, M. (2020). Problem-Solving in Mathematics Education. In: Lerman, S. (eds) Encyclopedia of Mathematics Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15789-0_129
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15789-0_129
Published : 23 February 2020
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-15788-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-15789-0
eBook Packages : Education Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Education
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
The Importance of Problem Solving and How to Teach it to Kids

FamilyEducation Editorial Staff
Teach your kids to be brilliant problem solvers so they can shine.
We get so lost as parents with all the demands to do more for our children—get better grades, excel at extracurricular activities, have good relationships—that we may be overlooking one of the essential skills they need: problem-solving.
More: A Parent’s Guide to Conscious Discipline
In a Harvard Business Review study about the skills that influence a leader's success, problem-solving ranked third out of 16.
Whether you want your child to get into an Ivy League school, have great relationships, or to be able to take care of the thousands of frustrating tasks that come with adulting, don't miss this significant super-power that helps them succeed.
Our kids face challenges daily when it comes to navigating sibling conflict, a tough math question, or negative peer pressure. Our job as parents or teachers is not to solve everything for them —it is to teach them how to solve things themselves. Using their brains in this way is the crucial ability needed to become confident, smart, and successful individuals.
And the bonus for you is this: instead of giving up or getting frustrated when they encounter a challenge, kids with problem-solving skills manage their emotions, think creatively and learn persistence.
With my children (I have eight), they often pushed back on me for turning the situation back on them to solve, but with some gentle nudging, the application of many tools, and some intriguing conversations, my kids are unbeatable.
Here are some of the best, research-based practices to help your child learn problem-solving so they can build smarter brains and shine in the world:
Don’t have time to read now? Pin it for later:
1. Model Effective Problem-Solving

When you encounter a challenge, think out loud about your mental processes to solve difficulties. Showing your children how you address issues can be done numerous times a day with the tangible and intangible obstacles we all face.
2. Ask for Advice

Ask your kids for advice when you are struggling with something. Your authenticity teaches them that it's common to make mistakes and face challenges.
When you let them know that their ideas are valued, they'll gain the confidence to attempt solving problems on their own.
3. Don't Provide The Answer—Ask More Questions

By not providing a solution, you are helping them to strengthen their mental muscles to come up with their ideas.
At the same time, the task may be too big for them to cognitively understand. Break it down into small steps, and either offer multiple solutions from which they can choose, or ask them leading questions that help them reach the answers themselves.
4. Be Open-Minded

This particular point is critical in building healthy relationships. Reliable partners can hold their values and opinions while also seeing the other's perspective. And then integrate disparate views into a solution.
Teach them to continually ask, "What is left out of my understanding here?"
High-performing teams in business strive for diversity—new points of view and fresh perspectives to allow for more creative solutions. Children need to be able to assess a problem outside of immediate, apparent details, and be open to taking risks to find a better, more innovative approach. Be willing to take on a new perspective.
5. Go Out and Play

It may seem counter-intuitive, but problems get solved during play according to research.
See why independent play is vital for raising empowered children here .
Have you ever banged around an idea in your head with no solution? If so, it's time to get out of your mind and out to play.
Tech companies understand this strategy (I know, I worked at one), by supplying refreshing snacks and ping pong tables and napping pods. And while they have deadlines to meet, they don't micromanage the thinking of their employees.
Offer many activities that will take your child’s mind off of the problem so they can refuel and approach things from a fresh perspective.
Let them see you fail, learn, and try again. Show your child a willingness to make mistakes. When they are solving something, as tricky as it may be, allow your child to struggle, sometimes fail and ultimately learn from experiencing consequences.
Problems are a part of life. They grow us to reach our highest potential. Every problem is there not to make your child miserable, but to lead them closer to their dreams.
Tami Green, America’s most respected life coach, has received magical endorsements by experts from Baylor University and the past president of the American Psychiatric Association. She received her coaching certification from Oprah's enchanting life coach, Dr. Martha Beck. She is a brilliant coach who has helped thousands achieve an exhilarated life through her coaching, classes, and conferences. To see more tips like these, visit her website and join her self-help community here .
About FamilyEducation's Editorial Team
Subscribe to family education.
Your partner in parenting from baby name inspiration to college planning.
The Higher Education Review

- Engineering
- Jobs and Careers
- Media and Mass Communication
- Education Consultancy
- Universities
- Magazine April ›› 2020 ›› Special issue
The Importance Of Problem Solving Skills and How To Develop Them
Author : Akhil Shahani , Managing Director , The Shahani Group
.png)
Download now complete list of Top Private Engineering Colleges
What is problem solving and why is it important

By Wayne Stottler , Kepner-Tregoe
- Problem Solving & Decision Making Over time, developing and refining problem solving skills provides the ability to solve increasingly complex problems Learn More
For over 60 years, Kepner-Tregoe has been helping companies across industries and geographies to develop and mature their problem-solving capabilities through KT’s industry leading approach to training and the implementation of best practice processes. Considering that problem solving is a part of almost every person’s daily life (both at home and in the workplace), it is surprising how often we are asked to explain what problem solving is and why it is important.
Problem solving is at the core of human evolution. It is the methods we use to understand what is happening in our environment, identify things we want to change and then figure out the things that need to be done to create the desired outcome. Problem solving is the source of all new inventions, social and cultural evolution, and the basis for market based economies. It is the basis for continuous improvement, communication and learning.
If this problem-solving thing is so important to daily life, what is it?
Problem-solving is the process of observing what is going on in your environment; identifying things that could be changed or improved; diagnosing why the current state is the way it is and the factors and forces that influence it; developing approaches and alternatives to influence change; making decisions about which alternative to select; taking action to implement the changes; and observing impact of those actions in the environment.
Each step in the problem-solving process employs skills and methods that contribute to the overall effectiveness of influencing change and determine the level of problem complexity that can be addressed. Humans learn how to solve simple problems from a very early age (learning to eat, make coordinated movements and communicate) – and as a person goes through life problem-solving skills are refined, matured and become more sophisticated (enabling them to solve more difficult problems).
Problem-solving is important both to individuals and organizations because it enables us to exert control over our environment.
Fixing things that are broken
Some things wear out and break over time, others are flawed from day-1. Personal and business environments are full of things, activities, interactions and processes that are broken or not operating in the way they are desired to work. Problem-solving gives us a mechanism for identifying these things, figuring out why they are broken and determining a course of action to fix them.
Addressing risk
Humans have learned to identify trends and developed an awareness of cause-and-effect relationships in their environment. These skills not only enable us to fix things when they break but also anticipate what may happen in the future (based on past-experience and current events). Problem-solving can be applied to the anticipated future events and used to enable action in the present to influence the likelihood of the event occurring and/or alter the impact if the event does occur.
Improving performance
Individuals and organizations do not exist in isolation in the environment. There is a complex and ever-changing web of relationships that exist and as a result, the actions of one person will often have either a direct impact on others or an indirect impact by changing the environment dynamics. These interdependencies enable humans to work together to solve more complex problems but they also create a force that requires everyone to continuously improve performance to adapt to improvements by others. Problem-solving helps us understand relationships and implement the changes and improvements needed to compete and survive in a continually changing environment.
Seizing opportunity
Problem solving isn’t just about responding to (and fixing) the environment that exists today. It is also about innovating, creating new things and changing the environment to be more desirable. Problem-solving enables us to identify and exploit opportunities in the environment and exert (some level of) control over the future.
Problem solving skills and the problem-solving process are a critical part of daily life both as individuals and organizations. Developing and refining these skills through training, practice and learning can provide the ability to solve problems more effectively and over time address problems with a greater degree of complexity and difficulty. View KT’s Problem Solving workshop known to be the gold standard for over 60 years.

We are experts in:
For inquiries, details, or a proposal!
Subscribe to the KT Newsletter
Environmental Education, Reading and Fun: Community Event Incorporates Them All

The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service is committed to creating a lasting base of environmental literacy, stewardship, and problem-solving skills for today's youth. One way the service works towards this goal is by participating in community events where environmental education can be promoted. Wolf Creek National Fish Hatchery is always excited for opportunities in the community to provide such encounters.
Marsha Hart, Environmental Education and Outreach Specialist at Wolf Creek National Fish Hatchery, attended the local “Read Across Russell County” event held at the Russell County Public Library on March 14, 2024. Wolf Creek NFH, along with other community partners, created an atmosphere where children and youth could have fun while reading and learning about various topics.

Wolf Creek NFH set up to focus on pollination including topics such as what are pollinators, what is the process of pollination, the importance of pollination, and what can be done to help pollinators. To incorporate reading and fun, participants would spin a large wheel that would land on a question or topic about pollination for them to read aloud, and then answer or discuss the topic. It was wonderful to hear children share what they already know about pollinators, and be eager to learn more! Parents also joined in on the fun, with some telling of flowers they plant that attract pollinators and others telling about enjoying watching butterflies as they move from flower to flower.
The event was a success, with over 450 in attendance. Events like this provide the opportunity for us to join in community partnerships, and engage children and youth in environmental literacy.
Latest Stories

You are exiting the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service website
You are being directed to
We do not guarantee that the websites we link to comply with Section 508 (Accessibility Requirements) of the Rehabilitation Act. Links also do not constitute endorsement, recommendation, or favoring by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
- Apply to UMaine
Center for Undergraduate Research

CUGR Announces Summer 2024 EPIC Fellowship Awardees
The University of Maine’s Center for Undergraduate Research (CUGR) is pleased to announce Summer 2024 EPIC fellowship winners.
Experiential Programs Innovation Central (EPIC) aspires to provide integrated experiential learning and high-impact, student-centered education opportunities through hands-on exposure to research practices, emerging technologies, design thinking, interdisciplinary experiences, and innovative problem-solving.
Students interested in pursuing any CUGR fellowship are encouraged to enroll in the EPIC course, INT 125, to support their preparation for undergraduate research beyond the classroom in any discipline. To learn more, visit umaine.edu/epic.
Recipients of the EPIC fellowship will receive $4,000 to put towards their research and experiential learning project.
This year’s recipients are:
- Robert Atwater , Engineering Physics, “Characterizing the Effects of Defect Doping on BaTiO3,” advised by Nicholas Bingham
- Jenna Cox , Psychology, “The Friendship Machine: Fast Friends And Its Effects Across Time In a University Setting,” advised by Jordan LaBouff
- Katie Davison , Communication Sciences and Disorders and Sociology, “Exploring Social-Communication, Health, and Educational Experiences of Children with Brain Injury,” advised by Jessica Riccardi
- Myles Harrison , Finance and Financial Economics, “A Maine Equity Index: How Have Maine Stocks Fared Over Time? Performance and Characteristics,” advised by Sebastian Lobe
- Matthew Patterson , New Media and Computer Science, “Our ClassXRoom,” advised by Justin Dimmel
- Arrow Smith , Anthropology and English, “Anonymity in Public Space Graffiti: Gender Differences in Public Restrooms across The University of Maine,” advised by Heather Falconer

- Colleges & Degrees
- Academic Calendar
- International Education
- Graduate Studies
- Accreditation
- Tuition and Fees
- Parking & Maps
- Careers with CSULB
- Alumni Home
- Alumni Volunteering
- Alumni Giving
Campus Life
- Centers & Organizations
- Commencement
- Student Life
- Office of the President
- Office of the Provost
- Administration & Finance
- Student Affairs
- University Relations & Development
- Information Technology
- Beach Shops
- Campus Directory
- Enrollment Services
- Financial Aid
- Schedule of Classes
- Student Records
- 49er Foundation
- Research Foundation

1250 BELLFLOWER BOULEVARD LONG BEACH, CALIFORNIA 90840 562.985.4111
David Teubner 2024 Distinguished Faculty Teaching Award Recipient
Associate Professor David Teubner is the 2024 recipient of the CSULB Distinguished Faculty Teaching Award. Dave has been an influential leader in the Design Department and a dedicated leader in the Industrial Design program. He is passionate about design and has worked in the field since 1980 in animation, film production, advertising, and industrial design. Dave instills design thinking and problem-solving in all his courses, the use of technology, and is now incorporating AI into his curriculum.
The University Achievement Awards were held on Wednesday, April 24, 2024, at The Pointe on CSULB campus with Dr. Karyn Scissum Gunn, Provost & Senior Vice President; Simon Kim, AVP, Research and Development; and Pei-Fang Hung, Chair, Academic Senate presiding. Our sincere congratulations go to Associate Professor David Teubner on receiving the prestigious award. For the full story: https://www.csulb.edu/office-of-the-provost/university-achievement-awards


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Problem-solving skills are important for every student to master. They help individuals navigate everyday life and find solutions to complex issues and challenges. ... Education must adapt so that it nurtures problem solvers and critical thinkers." Yet, the "traditional K-12 education system leaves little room for students to engage in ...
Collaborative problem-solving has been widely embraced in the classroom instruction of critical thinking, which is regarded as the core of curriculum reform based on key competencies in the field ...
Educational leaders' effectiveness in solving problems is vital to school and system-level efforts to address macrosystem problems of educational inequity and social injustice. Leaders' problem-solving conversation attempts are typically influenced by three types of beliefs—beliefs about the nature of the problem, about what causes it, and about how to solve it. Effective problem solving ...
Understanding pedagogical problem solving is important because part of education is to teach learners to solve conceptual and pedagogical problems themselves, and part of Initial Teacher Education is to teach teachers how to analyse and solve pedagogical problems. ... Research in Science & Technological Education, 1-22. doi:10.1080/02635143. ...
By naming what it is they did to solve the problem, students can be more independent and productive as they apply and adapt their thinking when engaging in future complex tasks. After a few weeks ...
Introduction Solving problems is a quintessential aspect of the role of an educational leader. In particular, building leaders, such as principals, assistant principals, and deans of students, are frequently beset by situations that are complex, unique, and open-ended. There are often many possible pathways to resolve the situations, and an astute educational leader needs to…
Problem solving is a necessary skill in all disciplines and one that the Sheridan Center is focusing on as part of the Brown Learning Collaborative, which provides students the opportunity to achieve new levels of excellence in six key skills traditionally honed in a liberal arts education - critical reading, writing, research, data ...
Make students articulate their problem solving process . In a one-on-one tutoring session, ask the student to work his/her problem out loud. This slows down the thinking process, making it more accurate and allowing you to access understanding. When working with larger groups you can ask students to provide a written "two-column solution.".
Problem-Solving Skills — Creative and Critical. An important goal of education is helping students learn how to think more productively while solving problems, by combining creative thinking (to generate ideas) and critical thinking (to evaluate ideas) with accurate knowledge (about the truth of reality). Both modes of thinking (creative & critical) are essential for a well-rounded ...
Problem solving is a new global imperative of educational change (Shirley, 2016). We stand today on the edge of a true international renaissance, unlike anything ever achieved in history. New technologies, higher levels of education, better health care, increasing life expectancy, and the interdependence of our economies are bringing humanity ...
From solving complex algebra problems to investigating scientific theories, to making inferences about written texts, problem-solving is central to every subject explored in school. Even beyond the classroom, problem-solving is ranked among the most important skills for students to demonstrate on their resumes, with 82.9% of employers ...
Evaluate the solution. Using effective problem solving techniques will help children avoid conflict with others in a school setting and in their everyday lives. It will also strengthen children's beginning empathy skills and help them learn more positive attributions about another person's intentions. Effective problem solving skills is ...
If you really want to build critical thinking skills in your students, problem-solving is a great way to start. But the problem is, problem-solving is not announcing to your students, "Hey kids, try this problem: 391 x 17.". First of all, that's not a problem. It's an expression, specifically a numerical expression. Expressions get ...
In a nutshell, critical thinking and problem-solving skills are a part of '21st Century Skills' that can help unlock valuable learning for life. Over the years, the education system has been ...
Singer et al. ( 2013) provides a broad view about problem posing that links problem posing experiences to general mathematics education; to the development of abilities, attitudes and creativity; and also to its interrelation with problem solving, and studies on when and how problem-solving sessions should take place.
3. Examine possible solutions. It is very tricky as on the surface: it might look like the reaching of the goal is close. Finding simplistic ways can not give the same result as finding the most effective ways and turn them to opportunities to make a strong success story. 4. Act on resolving the problem.
Problem solving plays an important role in mathematics and should have a prominent role in the mathematics education of K-12 students. However, knowing how to incorporate problem solving meaningfully into the mathematics curriculum is not necessarily obvious to mathematics teachers. (The term "problem solving" refers to mathematical tasks that ...
Problem solving is important in child development because confident, capable children usually grow into confident, capable adults. <. If students practice problem solving consistently, they can develop greater situational and social awareness. Additionally, they learn to manage time and develop patience. As students mature, problems they face ...
The problem-solving method is an effective teaching strategy that promotes critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration. It provides students with real-world problems that require them to apply their knowledge and skills to find solutions. By using the problem-solving method, teachers can help their students develop the skills they need to ...
Introduction. Problem-solving approaches appear in all human endeavors. In mathematics, activities such as posing or defining problems and looking for different ways to solve them are central to the development of the discipline. In mathematics education, the systematic study of what the process of formulating and solving problems entails and ...
Show your child a willingness to make mistakes. When they are solving something, as tricky as it may be, allow your child to struggle, sometimes fail and ultimately learn from experiencing consequences. Problems are a part of life. They grow us to reach our highest potential. Every problem is there not to make your child miserable, but to lead ...
How successful your choice will be is highly dependent on your problem solving skills. The Four Stages of Problem Solving You do not need to be highly intelligent to be a good problem solver. Developing these capabilities requires practice and discipline. A starting point would be to understand the four main stages of solving a problem.
The importance of problem-solving abilities is emphasized by Aydoğdu & Ayaz (2008) which states that problem-solving abilities can be a way for students to build ideas about Mathematics and can ...
Problem-solving enables us to identify and exploit opportunities in the environment and exert (some level of) control over the future. Problem solving skills and the problem-solving process are a critical part of daily life both as individuals and organizations. Developing and refining these skills through training, practice and learning can ...
The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service is committed to creating a lasting base of environmental literacy, stewardship, and problem-solving skills for today's youth. One way the service works towards this goal is by participating in community events where environmental education can be promoted. Wolf Creek National Fish Hatchery is always excited for opportunities in the community to provide such ...
The University of Maine's Center for Undergraduate Research (CUGR) is pleased to announce Summer 2024 EPIC fellowship winners. Experiential Programs Innovation Central (EPIC) aspires to provide integrated experiential learning and high-impact, student-centered education opportunities through hands-on exposure to research practices, emerging technologies, design thinking, interdisciplinary ...
Associate Professor David Teubner is the 2024 recipient of the CSULB Distinguished Faculty Teaching Award. Dave has been an influential leader in the Design Department and a dedicated leader in the Industrial Design program. He is passionate about design and has worked in the field since 1980 in animation, film production, advertising, and industrial design. Dave instills design thinking and ...