Appointments at Mayo Clinic
- Pregnancy week by week
- Fetal presentation before birth
The way a baby is positioned in the uterus just before birth can have a big effect on labor and delivery. This positioning is called fetal presentation.
Babies twist, stretch and tumble quite a bit during pregnancy. Before labor starts, however, they usually come to rest in a way that allows them to be delivered through the birth canal headfirst. This position is called cephalic presentation. But there are other ways a baby may settle just before labor begins.
Following are some of the possible ways a baby may be positioned at the end of pregnancy.

Head down, face down
When a baby is head down, face down, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput anterior position. This the most common position for a baby to be born in. With the face down and turned slightly to the side, the smallest part of the baby's head leads the way through the birth canal. It is the easiest way for a baby to be born.
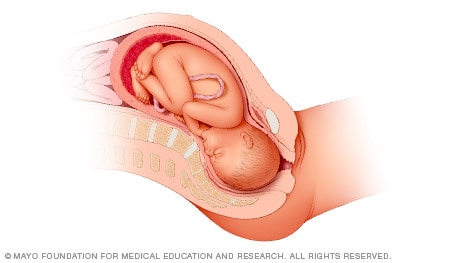
Head down, face up
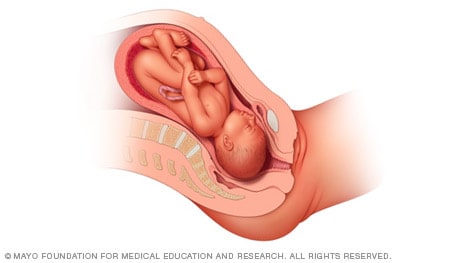
When a baby is head down, face up, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput posterior position. In this position, it might be harder for a baby's head to go under the pubic bone during delivery. That can make labor take longer.
Most babies who begin labor in this position eventually turn to be face down. If that doesn't happen, and the second stage of labor is taking a long time, a member of the health care team may reach through the vagina to help the baby turn. This is called manual rotation.
In some cases, a baby can be born in the head-down, face-up position. Use of forceps or a vacuum device to help with delivery is more common when a baby is in this position than in the head-down, face-down position. In some cases, a C-section delivery may be needed.
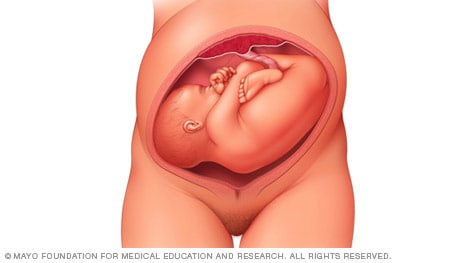
Frank breech
When a baby's feet or buttocks are in place to come out first during birth, it's called a breech presentation. This happens in about 3% to 4% of babies close to the time of birth. The baby shown below is in a frank breech presentation. That's when the knees aren't bent, and the feet are close to the baby's head. This is the most common type of breech presentation.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a frank breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Most babies in a frank breech position are born by planned C-section.

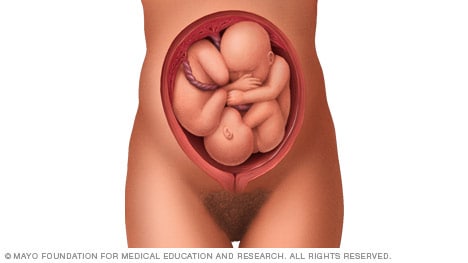
Complete and incomplete breech
A complete breech presentation, as shown below, is when the baby has both knees bent and both legs pulled close to the body. In an incomplete breech, one or both of the legs are not pulled close to the body, and one or both of the feet or knees are below the baby's buttocks. If a baby is in either of these positions, you might feel kicking in the lower part of your belly.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a complete or incomplete breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies in a complete or incomplete breech position are born by planned C-section.

When a baby is sideways — lying horizontal across the uterus, rather than vertical — it's called a transverse lie. In this position, the baby's back might be:
- Down, with the back facing the birth canal.
- Sideways, with one shoulder pointing toward the birth canal.
- Up, with the hands and feet facing the birth canal.
Although many babies are sideways early in pregnancy, few stay this way when labor begins.
If your baby is in a transverse lie during week 37 of your pregnancy, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of your health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a transverse lie, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies who are in a transverse lie are born by C-section.
If you're pregnant with twins and only the twin that's lower in the uterus is head down, as shown below, your health care provider may first deliver that baby vaginally.
Then, in some cases, your health care team may suggest delivering the second twin in the breech position. Or they may try to move the second twin into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
Your health care team may suggest delivery by C-section for the second twin if:
- An attempt to deliver the baby in the breech position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to have the baby delivered vaginally in the breech position.
- An attempt to move the baby into a head-down position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to move the baby to a head-down position.
In some cases, your health care team may advise that you have both twins delivered by C-section. That might happen if the lower twin is not head down, the second twin has low or high birth weight as compared to the first twin, or if preterm labor starts.
- Landon MB, et al., eds. Normal labor and delivery. In: Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Holcroft Argani C, et al. Occiput posterior position. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Frequently asked questions: If your baby is breech. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/if-your-baby-is-breech. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Hofmeyr GJ. Overview of breech presentation. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Strauss RA, et al. Transverse fetal lie. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Chasen ST, et al. Twin pregnancy: Labor and delivery. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Cohen R, et al. Is vaginal delivery of a breech second twin safe? A comparison between delivery of vertex and non-vertex second twins. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine. 2021; doi:10.1080/14767058.2021.2005569.
- Marnach ML (expert opinion). Mayo Clinic. May 31, 2023.
Products and Services
- A Book: Obstetricks
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to a Healthy Pregnancy
- 3rd trimester pregnancy
- Fetal development: The 3rd trimester
- Overdue pregnancy
- Pregnancy due date calculator
- Prenatal care: 3rd trimester
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
- Healthy Lifestyle
Make twice the impact
Your gift can go twice as far to advance cancer research and care!

Fetal Presentation: Baby’s First Pose

Share this post

Occiput Anterior
Occiput posterior, transverse position, complete breech, frank breech, changing fetal presentation, baby positions.
The position in which your baby develops is called the “fetal presentation.” During most of your pregnancy, the baby will be curled up in a ball – that’s why we call it the “fetal position.” The baby might flip around over the course of development, which is why you can sometimes feel a foot poking into your side or an elbow prodding your bellybutton. As you get closer to delivery, the baby will change positions and move lower in your uterus in preparation. Over the last part of your pregnancy, your doctor or medical care provider will monitor the baby’s position to keep an eye out for any potential problems.
In the occiput anterior position, the baby is pointed headfirst toward the birth canal and is facing down – toward your back. This is the easiest possible position for delivery because it allows the crown of the baby’s head to pass through first, followed by the shoulders and the rest of the body. The crown of the head is the narrowest part, so it can lead the way for the rest of the head.
The baby’s head will move slowly downward as you get closer to delivery until it “engages” with your pelvis. At that point, the baby’s head will fit snugly and won’t be able to wobble around. That’s exactly where you want to be just before labor. The occiput anterior position causes the least stress on your little one and the easiest labor for you.
In the occiput posterior position, the baby is pointed headfirst toward the birth canal but is facing upward, toward your stomach. This can trap the baby’s head under your pubic bone, making it harder to get out through the birth canal. In most cases, a baby in the occiput posterior position will either turn around naturally during the course of labor or your doctor or midwife may help it along manually or with forceps.
In a transverse position, the baby is sideways across the birth canal rather than head- or feet-first. It’s rare for a baby to stay in this position all the way up to delivery, but your doctor may attempt to gently push on your abdomen until the baby is in a more favorable fetal presentation. If you go into labor while the baby is in a transverse position, your medical care provider will likely recommend a c-section to avoid stressing or injuring the baby.
Breech Presentation
If the baby’s legs or buttocks are leading the way instead of the head, it’s called a breech presentation. It’s much harder to deliver in this position – the baby’s limbs are unlikely to line up all in the right direction and the birth canal likely won’t be stretched enough to allow the head to pass. Breech presentation used to be extremely dangerous for mothers and children both, and it’s still not easy, but medical intervention can help.
Sometimes, the baby will turn around and you’ll be able to deliver vaginally. Most healthcare providers, however, recommend a cesarean section for all breech babies because of the risks of serious injury to both mother and child in a breech vaginal delivery.
A complete breech position refers to the baby being upside down for delivery – feet first and head up. The baby’s legs are folded up and the feet are near the buttocks.
In a frank breech position, the baby’s legs are extended and the baby’s buttocks are closest to the birth canal. This is the most common breech presentation .
By late in your pregnancy, your baby can already move around – you’re probably feeling those kicks! Unfortunately, your little one doesn’t necessarily know how to aim for the birth canal. If the baby isn’t in the occiput anterior position by about 32 weeks, your doctor or midwife will typically recommend trying adjust the fetal presentation. They’ll use monitors to keep an eye on the baby and watch for signs of stress as they push and lift on your belly to coax your little one into the right spot. Your doctor may also advise you to try certain exercises at home to encourage the baby to move into the proper position. For example, getting on your hands and knees for a few minutes every day can help bring the baby around. You can also put cushions on your chairs to make sure your hips are always elevated, which can help move things into the right place. It’s important to start working on the proper fetal position early, as it becomes much harder to adjust after about 37 weeks when there’s less room to move around.
In many cases, the baby will eventually line up properly before delivery. Sometimes, however, the baby is still in the wrong spot by the time you go into labor. Your doctor or midwife may be able to move the baby during labor using forceps or ventouse . If that’s not possible, it’s generally safer for you and the baby if you deliver by c-section.
Image Credit and License
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Stages of Pregnancy
- Foods to Avoid
- Medicines to Avoid
- Pregnancy Road Map
Birth Injuries
- Cerebral Palsy
- Brachial Plexus Injuries & Erb’s Palsy
- Brain Damage
- Meconium Aspiration
- Bone Fractures
- Nerve Damage
Newborn Care
- Baby Development
Legal Issues
- Birth Injury vs. Birth Defect
- Birth Injury Lawsuits
- Proving Your Case
- Elements Of A Case

- Email Address *
- Phone Number *
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
- Trying to Conceive
- Signs & Symptoms
- Pregnancy Tests
- Fertility Testing
- Fertility Treatment
- Weeks & Trimesters
- Staying Healthy
- Preparing for Baby
- Complications & Concerns
- Pregnancy Loss
- Breastfeeding
- School-Aged Kids
- Raising Kids
- Personal Stories
- Everyday Wellness
- Safety & First Aid
- Immunizations
- Food & Nutrition
- Active Play
- Pregnancy Products
- Nursery & Sleep Products
- Nursing & Feeding Products
- Clothing & Accessories
- Toys & Gifts
- Ovulation Calculator
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- How to Talk About Postpartum Depression
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
Fetal Positions for Labor and Birth
Knowing your baby's position can you help ease pain and speed up labor
In the last weeks of pregnancy , determining your baby's position can help you manage pain and discomfort. Knowing your baby's position during early labor can help you adjust your own position during labor and possibly even speed up the process.
Right or Left Occiput Anterior
Illustration by JR Bee, Verywell
Looking at where the baby's head is in the birth canal helps determine the fetal position.The front of a baby's head is referred to as the anterior portion and the back is the posterior portion. There are two different positions called occiput anterior (OA) positions that may occur.
The left occiput anterior (LOA) position is the most common in labor. In this position, the baby's head is slightly off-center in the pelvis with the back of the head toward the mother's left thigh.
The right occiput anterior (ROA) presentation is also common in labor. In this position, the back of the baby is slightly off-center in the pelvis with the back of the head toward the mother's right thigh.
In general, OA positions do not lead to problems or additional pain during labor or birth.
Right or Left Occiput Transverse
Illustration by JR Bee, Verywell
When facing out toward the mother's right thigh, the baby is said to be left occiput transverse (LOT). This position is halfway between a posterior and anterior position. If the baby was previously in a posterior position (in either direction), the LOT position indicates positive movement toward an anterior position.
When the baby is facing outward toward the mother's left thigh, the baby is said to be right occiput transverse (ROT). Like the previous presentation, ROT is halfway between a posterior and anterior position. If the baby was previously in a posterior position, ROT is a sign the baby is making a positive move toward an anterior position.
When a baby is in the left occiput transverse position (LOT) or right occiput transverse (ROT) position during labor, it may lead to more pain and a slower progression.
Tips to Reduce Discomfort
There are several labor positions a mother can try to alleviate pain and encourage the baby to continue rotating toward an anterior position, including:
- Pelvic tilts
- Standing and swaying
A doula , labor nurse, midwife , or doctor may have other suggestions for positions.
Right or Left Occiput Posterior
When facing forward, the baby is in the occiput posterior position. If the baby is facing forward and slightly to the left (looking toward the mother's right thigh) it is in the left occiput posterior (LOP) position. This presentation can lead to more back pain (sometimes referred to as " back labor ") and slow progression of labor.
In the right occiput posterior position (ROP), the baby is facing forward and slightly to the right (looking toward the mother's left thigh). This presentation may slow labor and cause more pain.
To help prevent or decrease pain during labor and encourage the baby to move into a better position for delivery, mothers can try a variety of positions, including:
- Hands and knees
- Pelvic rocking
Mothers may try other comfort measures, including:
- Bathtub or shower (water)
- Counter pressure
- Movement (swaying, dancing, sitting on a birth ball )
- Rice socks (heat packs)
How a Doctor Determines Baby's Position
Leopold's maneuvers are a series of hands-on examinations your doctor or midwife will use to help determine your baby's position. During the third trimester , the assessment will be done at most of your prenatal visits. Knowing the baby's position before labor begins can help you prepare for labor and delivery.
Once labor begins, a nurse, doctor, or midwife will be able to get a more accurate sense of your baby's position by performing a vaginal exam. When your cervix is dilated enough, the practitioner will insert their fingers into the vagina and feel for the suture lines of the baby's skull as it moves down in the birth canal. It's important to ensure the baby is head down and moving in the right direction.
Labor and delivery may be more complicated if the baby is not in a head-down position, such as in the case of a breech presentation.
How You Can Determine Baby's Position
While exams by health practitioners are an important part of your care, from the prenatal period through labor and delivery, often the best person to assess a baby's position in the pelvis is you. Mothers should pay close attention to how the baby moves and where different movements are felt.
A technique called belly mapping can help mothers ask questions of themselves to assess their baby's movement and get a sense of the position they are in as labor approaches.
For example, the position of your baby's legs can be determined by asking questions about the location and strength of the kicking you feel. The spots where you feel the strongest kicks are most likely where your baby's feet are.
Other landmarks you can feel for include a large, flat plane, which is most likely your baby's back. Sometimes you can feel the baby arching his or her back.
At the top or bottom of the flat plane, you may feel either a hard, round shape (most likely your baby's head) or a soft curve (most likely to be your baby's bottom).
Guittier M, Othenin-Girard V, de Gasquet B, Irion O, Boulvain M. Maternal positioning to correct occiput posterior fetal position during the first stage of labour: a randomised controlled trial . BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology . 2016;123(13):2199-2207. doi:10.1111/1471-0528.13855
Gizzo S, Di Gangi S, Noventa M, Bacile V, Zambon A, Nardelli G. Women’s Choice of Positions during Labour: Return to the Past or a Modern Way to Give Birth? A Cohort Study in Italy . Biomed Res Int . 2014;2014:1-7. doi:10.1155/2014/638093
Ahmad A, Webb S, Early B, Sitch A, Khan K, MacArthur C. Association between fetal position at onset of labor and mode of delivery: a prospective cohort study . Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology . 2014;43(2):176-182. doi:10.1002/uog.13189
Nishikawa M, Sakakibara H. Effect of nursing intervention program using abdominal palpation of Leopold’s maneuvers on maternal-fetal attachment . Reprod Health . 2013;10(1). doi:10.1186/1742-4755-10-12
Choi S, Park Y, Lee D, Ko H, Park I, Shin J. Sonographic assessment of fetal occiput position during labor for the prediction of labor dystocia and perinatal outcomes . The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine . 2016;29(24):3988-3992. doi:10.3109/14767058.2016.1152250
Bamberg C, Deprest J, Sindhwani N et al. Evaluating fetal head dimension changes during labor using open magnetic resonance imaging . J Perinat Med . 2017;45(3). doi:10.1515/jpm-2016-0005
Gabbe S, Niebyl J, Simpson J et al. Obstetrics . Philadelphia, Pa.: Elsevier; 2012.
By Robin Elise Weiss, PhD, MPH Robin Elise Weiss, PhD, MPH is a professor, author, childbirth and postpartum educator, certified doula, and lactation counselor.

- Mammary Glands
- Fallopian Tubes
- Supporting Ligaments
- Reproductive System
- Gametogenesis
- Placental Development
- Maternal Adaptations
- Menstrual Cycle
- Antenatal Care
- Small for Gestational Age
- Large for Gestational Age
- RBC Isoimmunisation
- Prematurity
- Prolonged Pregnancy
- Multiple Pregnancy
- Miscarriage
- Recurrent Miscarriage
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
- Breech Presentation
- Abnormal lie, Malpresentation and Malposition
- Oligohydramnios
- Polyhydramnios
- Placenta Praevia
- Placental Abruption
- Pre-Eclampsia
- Gestational Diabetes
- Headaches in Pregnancy
- Haematological
- Obstetric Cholestasis
- Thyroid Disease in Pregnancy
- Epilepsy in Pregnancy
- Induction of Labour
- Operative Vaginal Delivery
- Prelabour Rupture of Membranes
- Caesarean Section
- Shoulder Dystocia
- Cord Prolapse
- Uterine Rupture
- Amniotic Fluid Embolism
- Primary PPH
- Secondary PPH
- Psychiatric Disease
- Postpartum Contraception
- Breastfeeding Problems
- Primary Dysmenorrhoea
- Amenorrhoea and Oligomenorrhoea
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
- Endometriosis
- Endometrial Cancer
- Adenomyosis
- Cervical Polyps
- Cervical Ectropion
- Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia + Cervical Screening
- Cervical Cancer
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Ovarian Cysts & Tumours
- Urinary Incontinence
- Genitourinary Prolapses
- Bartholin's Cyst
- Lichen Sclerosus
- Vulval Carcinoma
- Introduction to Infertility
- Female Factor Infertility
- Male Factor Infertility
- Female Genital Mutilation
- Barrier Contraception
- Combined Hormonal
- Progesterone Only Hormonal
- Intrauterine System & Device
- Emergency Contraception
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- Genital Warts
- Genital Herpes
- Trichomonas Vaginalis
- Bacterial Vaginosis
- Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
- Obstetric History
- Gynaecological History
- Sexual History
- Obstetric Examination
- Speculum Examination
- Bimanual Examination
- Amniocentesis
- Chorionic Villus Sampling
- Hysterectomy
- Endometrial Ablation
- Tension-Free Vaginal Tape
- Contraceptive Implant
- Fitting an IUS or IUD
Abnormal Fetal lie, Malpresentation and Malposition
Original Author(s): Anna Mcclune Last updated: 1st December 2018 Revisions: 12
- 1 Definitions
- 2 Risk Factors
- 3.2 Presentation
- 3.3 Position
- 4 Investigations
- 5.1 Abnormal Fetal Lie
- 5.2 Malpresentation
- 5.3 Malposition
The lie, presentation and position of a fetus are important during labour and delivery.
In this article, we will look at the risk factors, examination and management of abnormal fetal lie, malpresentation and malposition.
Definitions
- Longitudinal, transverse or oblique
- Cephalic vertex presentation is the most common and is considered the safest
- Other presentations include breech, shoulder, face and brow
- Usually the fetal head engages in the occipito-anterior position (the fetal occiput facing anteriorly) – this is ideal for birth
- Other positions include occipito-posterior and occipito-transverse.
Note: Breech presentation is the most common malpresentation, and is covered in detail here .
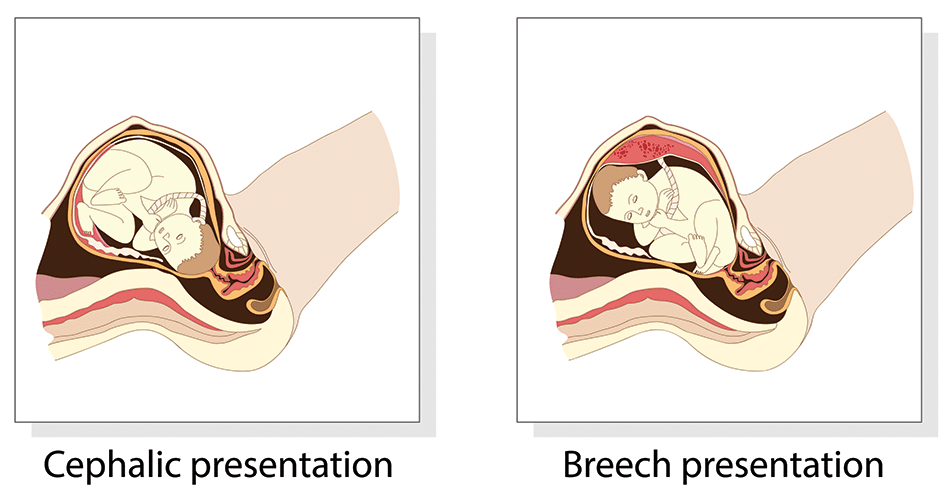
Fig 1 – The two most common fetal presentations: cephalic and breech.
Risk Factors
The risk factors for abnormal fetal lie, malpresentation and malposition include:
- Multiple pregnancy
- Uterine abnormalities (e.g fibroids, partial septate uterus)
- Fetal abnormalities
- Placenta praevia
- Primiparity
Identifying Fetal Lie, Presentation and Position
The fetal lie and presentation can usually be identified via abdominal examination. The fetal position is ascertained by vaginal examination.
For more information on the obstetric examination, see here .
- Face the patient’s head
- Place your hands on either side of the uterus and gently apply pressure; one side will feel fuller and firmer – this is the back, and fetal limbs may feel ‘knobbly’ on the opposite side
Presentation
- Palpate the lower uterus (above the symphysis pubis) with the fingers of both hands; the head feels hard and round (cephalic) and the bottom feels soft and triangular (breech)
- You may be able to gently push the fetal head from side to side
The fetal lie and presentation may not be possible to identify if the mother has a high BMI, if she has not emptied her bladder, if the fetus is small or if there is polyhydramnios .
During labour, vaginal examination is used to assess the position of the fetal head (in a cephalic vertex presentation). The landmarks of the fetal head, including the anterior and posterior fontanelles, indicate the position.
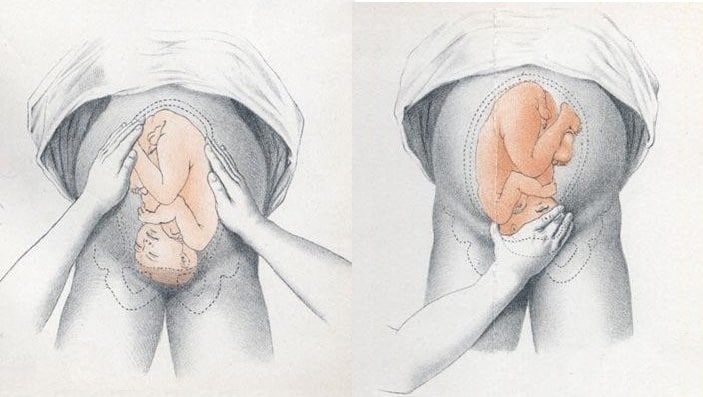
Fig 2 – Assessing fetal lie and presentation.
Investigations
Any suspected abnormal fetal lie or malpresentation should be confirmed by an ultrasound scan . This could also demonstrate predisposing uterine or fetal abnormalities.
Abnormal Fetal Lie
If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted – ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation.
ECV is the manipulation of the fetus to a cephalic presentation through the maternal abdomen.
It has an approximate success rate of 50% in primiparous women and 60% in multiparous women. Only 8% of breech presentations will spontaneously revert to cephalic in primiparous women over 36 weeks gestation.
Complications of ECV are rare but include fetal distress , premature rupture of membranes, antepartum haemorrhage (APH) and placental abruption. The risk of an emergency caesarean section (C-section) within 24 hours is around 1 in 200.
ECV is contraindicated in women with a recent APH, ruptured membranes, uterine abnormalities or a previous C-section .
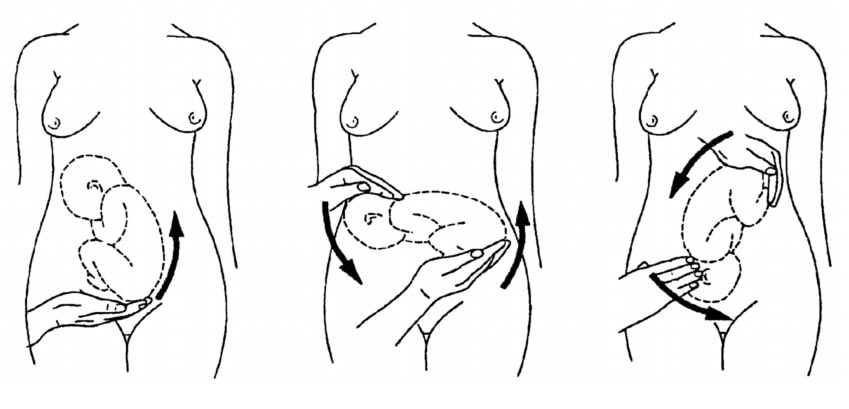
Fig 3 – External cephalic version.
Malpresentation
The management of malpresentation is dependent on the presentation.
- Breech – attempt ECV before labour, vaginal breech delivery or C-section
- Brow – a C-section is necessary
- If the chin is anterior (mento-anterior) a normal labour is possible; however, it is likely to be prolonged and there is an increased risk of a C-section being required
- If the chin is posterior (mento-posterior) then a C-section is necessary
- Shoulder – a C-section is necessary
Malposition
90% of malpositions spontaneously rotate to occipito-anterior as labour progresses. If the fetal head does not rotate, rotation and operative vaginal delivery can be attempted. Alternatively a C-section can be performed.
- Usually the fetal head engages in the occipito-anterior position (the fetal occiput facing anteriorly) - this is ideal for birth
If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted - ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation.
- Breech - attempt ECV before labour, vaginal breech delivery or C-section
Found an error? Is our article missing some key information? Make the changes yourself here!
Once you've finished editing, click 'Submit for Review', and your changes will be reviewed by our team before publishing on the site.
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site and to show you relevant advertising. To find out more, read our privacy policy .
Privacy Overview

- Pregnancy Classes

Breech Births
In the last weeks of pregnancy, a baby usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation. A breech presentation occurs when the baby’s buttocks, feet, or both are positioned to come out first during birth. This happens in 3–4% of full-term births.
What are the different types of breech birth presentations?
- Complete breech: Here, the buttocks are pointing downward with the legs folded at the knees and feet near the buttocks.
- Frank breech: In this position, the baby’s buttocks are aimed at the birth canal with its legs sticking straight up in front of his or her body and the feet near the head.
- Footling breech: In this position, one or both of the baby’s feet point downward and will deliver before the rest of the body.
What causes a breech presentation?
The causes of breech presentations are not fully understood. However, the data show that breech birth is more common when:
- You have been pregnant before
- In pregnancies of multiples
- When there is a history of premature delivery
- When the uterus has too much or too little amniotic fluid
- When there is an abnormally shaped uterus or a uterus with abnormal growths, such as fibroids
- The placenta covers all or part of the opening of the uterus placenta previa
How is a breech presentation diagnosed?
A few weeks prior to the due date, the health care provider will place her hands on the mother’s lower abdomen to locate the baby’s head, back, and buttocks. If it appears that the baby might be in a breech position, they can use ultrasound or pelvic exam to confirm the position. Special x-rays can also be used to determine the baby’s position and the size of the pelvis to determine if a vaginal delivery of a breech baby can be safely attempted.
Can a breech presentation mean something is wrong?
Even though most breech babies are born healthy, there is a slightly elevated risk for certain problems. Birth defects are slightly more common in breech babies and the defect might be the reason that the baby failed to move into the right position prior to delivery.
Can a breech presentation be changed?
It is preferable to try to turn a breech baby between the 32nd and 37th weeks of pregnancy . The methods of turning a baby will vary and the success rate for each method can also vary. It is best to discuss the options with the health care provider to see which method she recommends.
Medical Techniques
External Cephalic Version (EVC) is a non-surgical technique to move the baby in the uterus. In this procedure, a medication is given to help relax the uterus. There might also be the use of an ultrasound to determine the position of the baby, the location of the placenta and the amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus.
Gentle pushing on the lower abdomen can turn the baby into the head-down position. Throughout the external version the baby’s heartbeat will be closely monitored so that if a problem develops, the health care provider will immediately stop the procedure. ECV usually is done near a delivery room so if a problem occurs, a cesarean delivery can be performed quickly. The external version has a high success rate and can be considered if you have had a previous cesarean delivery.
ECV will not be tried if:
- You are carrying more than one fetus
- There are concerns about the health of the fetus
- You have certain abnormalities of the reproductive system
- The placenta is in the wrong place
- The placenta has come away from the wall of the uterus ( placental abruption )
Complications of EVC include:
- Prelabor rupture of membranes
- Changes in the fetus’s heart rate
- Placental abruption
- Preterm labor
Vaginal delivery versus cesarean for breech birth?
Most health care providers do not believe in attempting a vaginal delivery for a breech position. However, some will delay making a final decision until the woman is in labor. The following conditions are considered necessary in order to attempt a vaginal birth:
- The baby is full-term and in the frank breech presentation
- The baby does not show signs of distress while its heart rate is closely monitored.
- The process of labor is smooth and steady with the cervix widening as the baby descends.
- The health care provider estimates that the baby is not too big or the mother’s pelvis too narrow for the baby to pass safely through the birth canal.
- Anesthesia is available and a cesarean delivery possible on short notice
What are the risks and complications of a vaginal delivery?
In a breech birth, the baby’s head is the last part of its body to emerge making it more difficult to ease it through the birth canal. Sometimes forceps are used to guide the baby’s head out of the birth canal. Another potential problem is cord prolapse . In this situation the umbilical cord is squeezed as the baby moves toward the birth canal, thus slowing the baby’s supply of oxygen and blood. In a vaginal breech delivery, electronic fetal monitoring will be used to monitor the baby’s heartbeat throughout the course of labor. Cesarean delivery may be an option if signs develop that the baby may be in distress.
When is a cesarean delivery used with a breech presentation?
Most health care providers recommend a cesarean delivery for all babies in a breech position, especially babies that are premature. Since premature babies are small and more fragile, and because the head of a premature baby is relatively larger in proportion to its body, the baby is unlikely to stretch the cervix as much as a full-term baby. This means that there might be less room for the head to emerge.
Want to Know More?
- Creating Your Birth Plan
- Labor & Birth Terms to Know
- Cesarean Birth After Care
Compiled using information from the following sources:
- ACOG: If Your Baby is Breech
- William’s Obstetrics Twenty-Second Ed. Cunningham, F. Gary, et al, Ch. 24.
- Danforth’s Obstetrics and Gynecology Ninth Ed. Scott, James R., et al, Ch. 21.
BLOG CATEGORIES
- Can I get pregnant if… ? 3
- Child Adoption 19
- Fertility 54
- Pregnancy Loss 11
- Breastfeeding 29
- Changes In Your Body 5
- Cord Blood 4
- Genetic Disorders & Birth Defects 17
- Health & Nutrition 2
- Is it Safe While Pregnant 54
- Labor and Birth 65
- Multiple Births 10
- Planning and Preparing 24
- Pregnancy Complications 68
- Pregnancy Concerns 62
- Pregnancy Health and Wellness 149
- Pregnancy Products & Tests 8
- Pregnancy Supplements & Medications 14
- The First Year 41
- Week by Week Newsletter 40
- Your Developing Baby 16
- Options for Unplanned Pregnancy 18
- Paternity Tests 2
- Pregnancy Symptoms 5
- Prenatal Testing 16
- The Bumpy Truth Blog 7
- Uncategorized 4
- Abstinence 3
- Birth Control Pills, Patches & Devices 21
- Women's Health 34
- Thank You for Your Donation
- Unplanned Pregnancy
- Getting Pregnant
- Healthy Pregnancy
- Privacy Policy
Share this post:
Similar post.

Episiotomy: Advantages & Complications

Retained Placenta

What is Dilation in Pregnancy?
Track your baby’s development, subscribe to our week-by-week pregnancy newsletter.
- The Bumpy Truth Blog
- Fertility Products Resource Guide
Pregnancy Tools
- Ovulation Calendar
- Baby Names Directory
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Quiz
Pregnancy Journeys
- Partner With Us
- Corporate Sponsors
Twin fetal presentation – also known as the position of your babies in the womb – dictates whether you'll have a vaginal or c-section birth. Toward the end of pregnancy, most twins will move in the head-down position (vertex), but there's a risk that the second twin will change position after the first twin is born. While there are options to change the second twin's position, this can increase the risk of c-section and other health issues. Learn about the six possible twin fetal presentations: vertex-vertex, vertex-breech, breech-breech, vertex-transverse, breech-transverse, and transverse-transverse – and how they'll impact your delivery and risks for complications.
What is fetal presentation and what does it mean for your twins?
As your due date approaches, you might be wondering how your twins are currently positioned in the womb, also known as the fetal presentation, and what that means for your delivery. Throughout your pregnancy, your twin babies will move in the uterus, but sometime during the third trimester – usually between 32 and 36 weeks – their fetal presentation changes as they prepare to go down the birth canal.
The good news is that at most twin births, both babies are head-down (vertex), which means you can have a vaginal delivery. In fact, nearly 40 percent of twins are delivered vaginally.
But if one baby has feet or bottom first (breech) or is sideways (transverse), your doctor might deliver the lower twin vaginally and then try to rotate the other twin so that they face head-down (also called external cephalic version or internal podalic version) and can be delivered vaginally. But if that doesn't work, there's still a chance that your doctor will be able to deliver the second twin feet first vaginally via breech extraction (delivering the breech baby feet or butt first through the vagina).
That said, a breech extraction depends on a variety of factors – including how experienced your doctor is in the procedure and how much the second twin weighs. Studies show that the higher rate of vaginal births among nonvertex second twins is associated with labor induction and more experienced doctors, suggesting that proper delivery planning may increase your chances of a vaginal birth .
That said, you shouldn't totally rule out a Cesarean delivery with twins . If the first twin is breech or neither of the twins are head-down, then you'll most likely have a Cesarean delivery.
Research also shows that twin babies who are born at less than 34 weeks and have moms with multiple children are associated with intrapartum presentation change (when the fetal presentation of the second twin changes from head-down to feet first after the delivery of the first twin) of the second twin. Women who have intrapartum presentation change are more likely to undergo a Cesarean delivery for their second twin.
Here's a breakdown of the different fetal presentations for twin births and how they will affect your delivery.
Head down, head down (vertex, vertex)
This fetal presentation is the most promising for a vaginal delivery because both twins are head-down. Twins can change positions, but if they're head-down at 28 weeks, they're likely to stay that way.
When delivering twins vaginally, there is a risk that the second twin will change position after the delivery of the first. Research shows that second twins change positions in 20 percent of planned vaginal deliveries. If this happens, your doctor may try to rotate the second twin so it faces head-down or consider a breech extraction. But if neither of these work or are an option, then a Cesarean delivery is likely.
In vertex-vertex pairs, the rate of Cesarean delivery for the second twin after a vaginal delivery of the first one is 16.9 percent.
Like all vaginal deliveries, there's also a chance you'll have an assisted birth, where forceps or a vacuum are needed to help deliver your twins.
Head down, bottom down (vertex, breech)
When the first twin's (the lower one) head is down, but the second twin isn't, your doctor may attempt a vaginal delivery by changing the baby's position or doing breech extraction, which isn't possible if the second twin weighs much more than the first twin.
The rates of emergency C-section deliveries for the second twin after a vaginal delivery of the first twin are higher in second twins who have a very low birth weight. Small babies may not tolerate labor as well.
Head down, sideways (vertex, transverse)
If one twin is lying sideways or diagonally (oblique), there's a chance the baby may shift position as your labor progresses, or your doctor may try to turn the baby head-down via external cephalic version or internal podalic version (changing position in the uterus), which means you may be able to deliver both vaginally.
Bottom down, bottom down (breech, breech)
When both twins are breech, a planned C-section is recommended because your doctor isn't able to turn the fetuses. Studies also show that there are fewer negative neonatal outcomes for planned C-sections than planned vaginal births in breech babies.
As with any C-section, the risks for a planned one with twins include infection, loss of blood, blood clots, injury to the bowel or bladder, a weak uterine wall, placenta abnormalities in future pregnancies and fetal injury.
Bottom down, sideways (breech, transverse)
When the twin lowest in your uterus is breech or transverse (which happens in 25 percent of cases), you'll need to have a c-section.
Sideways, sideways (transverse, transverse)
This fetal presentation is rare with less than 1 percent of cases. If both babies are lying horizontally, you'll almost definitely have a C-section.
Learn more:
- Twin fetal development month by month
- Your likelihood of having twins or more
- When and how to find out if you’re carrying twins or more
Was this article helpful?
32 weeks pregnant with twins

28 weeks pregnant with twins

36 weeks pregnant with twins

24 weeks pregnant with twins

BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies .
Cleveland Clinic. Fetal Positions for Birth: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/9677-fetal-positions-for-birth Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Mayo Clinic. Fetal Presentation Before Birth: https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/multimedia/fetal-positions/sls-20076615?s=7 Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
NHS. Giving Birth to Twins or More: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29016498/ Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Science Direct. Breech Extraction: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/breech-extraction Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Obstetrics & Gynecology. Clinical Factors Associated With Presentation Change of the Second Twin After Vaginal Delivery of the First Twin https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29016498/ Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Fetal presentation and successful twin vaginal delivery: https://www.ajog.org/article/S0002-9378(04)00482-X/fulltext [Accessed July 2021]
The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine. Changes in fetal presentation in twin pregnancies https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/14767050400028592 Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Reviews in Obstetrics & Gynecology. An Evidence-Based Approach to Determining Route of Delivery for Twin Gestations https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3252881/ Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Nature. Neonatal mortality and morbidity in vertex–vertex second twins according to mode of delivery and birth weight: https://www.nature.com/articles/7211408 Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Cochrane. Planned cesarean for a twin pregnancy: https://www.cochrane.org/CD006553/PREG_planned-caesarean-section-twin-pregnancy Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Kids Health. What Is the Apgar Score?: https://www.kidshealth.org/Nemours/en/parents/apgar0.html Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology. Neonatal mortality in second twin according to cause of death, gestational age, and mode of delivery https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15467540/ Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Lancet. Planned cesarean section versus planned vaginal birth for breech presentation at term: a randomised multicentre trial. Term Breech Trial Collaborative Group https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11052579/ Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Cleveland Clinic. Cesarean Birth (C-Section): https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/7246-cesarean-birth-c-section Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
St. Jude Medical Staff. Delivery of Twin Gestation: http://www.sjmedstaff.org/documents/Delivery-of-twins.pdf Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]

Where to go next

Need to talk? Call 1800 882 436. It's a free call with a maternal child health nurse. *call charges may apply from your mobile
Is it an emergency? Dial 000 If you need urgent medical help, call triple zero immediately.
Share via email
There is a total of 5 error s on this form, details are below.
- Please enter your name
- Please enter your email
- Your email is invalid. Please check and try again
- Please enter recipient's email
- Recipient's email is invalid. Please check and try again
- Agree to Terms required
Error: This is required
Error: Not a valid value
Malpresentation
8-minute read
If you feel your waters break and you have been told that your baby is not in a head-first position, seek medical help immediately .
- Malpresentation is when your baby is not facing head-first down the birth canal as birth approaches.
- The most common type of malpresentation is breech — when your baby’s bottom or feet are facing downwards.
- A procedure called external cephalic version can sometimes turn a breech baby into a head-first position at 36 weeks.
- Most babies with malpresentation are born by caesarean, but you may be able to have a vaginal birth if your baby is breech.
- There is a serious risk of cord prolapse if your waters break and your baby is not head-first.
What are presentation and malpresentation?
‘Presentation’ describes how your baby is facing down the birth canal. The ‘presenting part’ is the part of your baby’s body that is against the cervix .
The ideal presentation is head-first, with the crown (top) of the baby’s head against the cervix, with the chin tucked into the baby’s chest. This is called ‘vertex presentation’.
If your baby is in any other position, it’s called ‘malpresentation’. Malpresentation can mean your baby’s face, brow, buttocks, foot, back, shoulder, arms or legs or the umbilical cord are against the cervix.
It’s safest for your baby’s head to come out first. If any other body part goes down the birth canal first, the risks to you and your baby may be higher. Malpresentation increases the chance that you will have a more complex vaginal birth or a caesarean.
If my baby is not head-first, what position could they be in?
Malpresentation is caused by your baby’s position (‘lie’). There are different types of malpresentation.
Breech presentation
This is when your baby is lying with their bottom or feet facing down. Sometimes one foot may enter the birth canal first (called a ‘footling presentation’).
Breech presentation is the most common type of malpresentation.
Face presentation
This is when your baby is head-first but stretching their neck, with their face against the cervix.
Transverse lie
This is when your baby is lying sideways. Their back, shoulders, arms or legs may be the first to enter the birth canal.
Oblique lie
This is when your baby is lying diagonally. No particular part of their body is against the cervix.
Unstable lie
This is when your baby continually changes their position after 36 weeks of pregnancy.
Cord presentation
This is when the umbilical cord is against the cervix, between your baby and the birth canal. It can happen in any situation where your baby’s presenting part is not sitting snugly in your pelvis. It can become an emergency if it leads to cord prolapse (when the cord is born before your baby, potentially reducing placental blood flow to your baby).
What is malposition?
If your baby is lying head-first, the best position for labour is when their face is towards your back.
If your baby is facing the front of your body (posterior position) or facing your side (transverse position) this is called malposition. Transverse position is not the same as transverse lie. A transverse position means your labour may take a bit longer and you might feel more pain in your back. Often your baby will move into a better position before or during labour.
Why might my baby be in the wrong position?
Malpresentation may be caused by:
- a low-lying placenta
- too much or too little amniotic fluid
- many previous pregnancies, making the muscles of the uterus less stable
- carrying twins or more
Often no cause is found.
Is it likely that my baby will be in the wrong position?
Many babies are in a breech position during pregnancy. They usually turn head-first as pregnancy progresses, and more than 9 in 10 babies in Australia have a vertex presentation (ideal presentation, head-first) at birth.
You are more likely to have a malpresentation if:
- this is your first baby
- you are over 40 years old
- you've had a previous breech baby
- you go into labour prematurely
How is malpresentation diagnosed?
Malpresentation is normally diagnosed when your doctor or midwife examines you, from 36 weeks of pregnancy. If it’s not clear, it can be confirmed with an ultrasound.
Can my baby’s position be changed?
If you are 36 weeks pregnant , it may be possible to gently turn your baby into a head-first position. This is done by an obstetrician using a technique called external cephalic version (ECV).
Some people try different postures or acupuncture to correct malpresentation, but there isn’t reliable evidence that either of these work.
Will I need a caesarean if my baby has a malpresentation?
Most babies with a malpresentation close to birth are born by caesarean . You may be able to have a vaginal birth with a breech baby, but you will need to go to a hospital that can offer you and your baby specialised care.
If your baby is breech, an elective (planned) caesarean is safer for your baby than a vaginal birth in the short term. However, in the longer term their health will be similar, on average, regardless of how they were born.
A vaginal birth is safer for you than an elective caesarean. However, about 4 in 10 people planning a vaginal breech birth end up needing an emergency caesarean . If this happens to you, the risk of complications will be higher.
Your doctor can talk to you about your options. Whether it’s safe for you to try a vaginal birth will depend on many factors. These include how big your baby is, the position of your baby, the structure of your pelvis and whether you’ve had a caesarean in the past.
What are the risks if I have my baby when it’s not head-first?
If your waters break when your baby is not head-first, there is a risk of cord prolapse. This is an emergency.

Vaginal breech birth
Risks to your baby can include:
- Erb’s palsy
- fractures, dislocations or other injuries
- bleeding in your baby’s brain
- low Apgar scores
- their head getting stuck – this is an emergency
Risks to you include:
- blood loss or blood clots
- infection in the wound
- problems with the anaesthetic
- damage to other organs nearby, such as your bladder
- a higher chance of problems in future pregnancies
- a longer recovery time than after a vaginal birth
Risks to your baby include:
- trouble with breathing — this is temporary
- getting a small cut during the surgery
Will I have a malpresentation in my future pregnancies?
If you had a malpresentation in one pregnancy, you have a higher chance of it happening again, but it won’t necessarily happen in future pregnancies. If you’re worried, it may help to talk to your doctor or midwife so they can explain what happened.

Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call . Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content .
Last reviewed: July 2022
Related pages
Labour complications.
- Interventions during labour
- Giving birth - stages of labour
Breech pregnancy
Search our site for.
- Caesarean Section
- Foetal Version
Need more information?
Top results
When a baby is positioned bottom-down late in pregnancy, this is called the breech position. Find out about 3 main types and safe birthing options.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website

Breech Presentation at the End of your Pregnancy
Breech presentation occurs when your baby is lying bottom first or feet first in the uterus (womb) rather than the usual head first position. In early pregnancy, a breech position is very common.
Read more on RANZCOG - Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists website

Breech presentation and turning the baby
In preparation for a safe birth, your health team will need to turn your baby if it is in a bottom first ‘breech’ position.
Read more on WA Health website

External Cephalic Version for Breech Presentation - Pregnancy and the first five years
This information brochure provides information about an External Cephalic Version (ECV) for breech presentation
Read more on NSW Health website

Presentation and position of baby through pregnancy and at birth
Presentation and position refer to where your baby’s head and body is in relation to your birth canal. Learn why it’s important for labour and birth.
Even if you’re healthy and well prepared for childbirth, there’s always a chance of unexpected problems. Learn more about labour complications.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Call us and speak to a Maternal Child Health Nurse for personal advice and guidance.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Government Accredited with over 140 information partners
We are a government-funded service, providing quality, approved health information and advice

Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
© 2024 Healthdirect Australia Limited
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
- Infants & Toddlers
- Mental Health
- Weight Management
- Orthopedics & Spine
- Brain & Memory
- Breakthroughs
- Cold & Flu
- Ear, Nose & Throat
- Heart & Vascular
- Men’s Health
- Women’s Health

A trimester-by-trimester guide to pregnancy
By: My Vanderbilt Health
April 24, 2024
Learn how each stage of pregnancy can affect you physically — and how your medical team will be working to care for you and your growing baby.
While everyone’s experience will be different, there are some common changes you can expect throughout the stages of pregnancy.
Pregnancies last around 40 weeks, counting from the first day of your last menstrual period. Here’s what you can expect during each of your three trimesters.
First Trimester (Weeks 0-13)
The earliest symptoms of pregnancy include breast tenderness, mood changes and a missed period. By the second month, you may feel sick to your stomach and fatigued. During this stage of the pregnancy, your belly and breasts will grow and your clothes may start to feel tight. You may also experience headaches, dizziness, heartburn or constipation.
“The most common reasons people seek care during the first trimester are nausea, vomiting, spotting and bleeding,” said Dr. Jody L. Stonehocker, an obstetrician with Vanderbilt Women’s Health .
“I tell patients that if they’re experiencing bleeding, they should come in to get checked out,” said Stonehocker . “It doesn’t necessarily mean anything is wrong, but, especially if they haven’t had an ultrasound yet, we want to rule out ectopic pregnancy .”
First trimester tests include:
- A blood draw to scan for anemia, blood type, HIV and other conditions
- Urine samples
- Pelvic exam
- An ultrasound to confirm pregnancy, verify gestational age and determine if you’re carrying multiples
- The option to receive non-invasive prenatal testing , a blood test that screens for Down syndrome and other chromosomal conditions — and also allows you to find out the baby’s sex
Though you’ll see a provider regularly throughout pregnancy — appointments start out every 6 weeks and gradually become more frequent — don’t neglect the other aspects of your health.
Though you’ll see a provider regularly throughout pregnancy — appointments start out every 6 weeks and gradually become more frequent — don’t neglect the other aspects of your health. You can (and should!) go to your regular dental cleanings, and low-impact exercise like walking or yoga can improve your overall health.
Second Trimester (Weeks 14-27)
In the second trimester, you’ll start to feel your baby move. You’ll also feel more pressure on your bladder, stomach and other organs and may see a dark line emerge on your belly, called the linea nigra. You will also start gaining weight at a more regular pace — around 1 pound a week until you give birth. If you prefer not to track your weight, you can discuss modifications with your provider, like standing away from the scale’s display during appointments.
Second trimester tests include:
- Urine tests
- 20-week ultrasound to see the size, position and number of babies, check for physical issues and see the sex of the baby
- Blood sugar test to check for gestational diabetes
Third Trimester (Week 28-Birth)
As your baby grows, you may feel short of breath as your organs become more cramped. Your breasts will continue to grow, and milk may leak from your nipples. You will also start to feel minor contractions called Braxton-Hicks contractions . Also known as “false labor,” Braxton-Hicks contractions tend to be irregular and do not get stronger over time.
Third trimester tests include:
- Repeat testing for anemia, HIV and other conditions
- A swab for Group B streptococcus, a type of bacteria. If you’re positive, your obstetric care team will give you medicine during labor to lower the chance that your baby gets the bacteria.
In this stage of pregnancy, you should think through your birth plan so you can express your labor and postpartum preferences to your birthing partner and care team. This is also a great time to take any childbirth or breastfeeding classes, such as those offered by Vanderbilt Health .

Expert care for you and your baby
Each pregnancy and delivery is unique and yours should be too. Learn more about how Vanderbilt Health’s obstetrics and maternal fetal medicine teams bring together nationally ranked expertise and personalized care from your first prenatal visit to delivery and beyond.
To learn more, call 615-343-5700 or schedule an appointment online .
Related Articles
Making the most of your prenatal care
Early and continuous prenatal care can set you up for a supportive partnership with your health care provider throughout your pregnancy. Learn what to expect at your appointments.

Discomfort during pregnancy: 12 common symptoms
Does your pregnancy “glow” sometimes feel more like a pregnancy “ouch?” Rest assured — you’re not alone. Our expert outlines the common discomforts of pregnancy and what to do about them.

What is an amniocentesis?
What to expect with this pregnancy screening procedure.
Sign up for updates on My Vanderbilt Health
Abortion now illegal after 6 weeks in Florida, with few exceptions. Here's what that means

As of Wednesday, May 1, most abortions in Florida after six weeks will be illegal.
The state's previous 15-week ban passed in 2022 went into effect a month ago, when the state Supreme Court overruled a 34-year-old decision that said a privacy provision in the state constitution protected a woman’s right to terminate a pregnancy. But that ruling also triggered a more restrictive 6-week ban passed by the Florida Legislature last year to go into effect 30 days later.
That means Florida is no longer the southern state with the least restrictive abortion laws. Floridians needing or wanting abortions after six weeks of pregnancy would need to travel to North Carolina, where the limit is 12 weeks, or up to Virginia where there are no laws banning abortion.
Previously Florida was the destination for people in the South with little or no access to abortion services, more than 25,000 in the last five years, according to the nonprofit site KFF Health News .
Abortion is currently banned in 14 states, limited to gestational periods between six and 12 weeks in five, between 15 and 22 weeks in 6 more, and has no bans in 25 states and Washington, D.C. according to nonprofit KFF. Many GOP-led states rushed to enact abortion bans after the U.S. Supreme Court struck down Roe v. Wade in 2022.
Prep for the polls: See who is running for president and compare where they stand on key issues in our Voter Guide
However, the Florida Supreme Court also ruled that a proposed constitutional amendment about abortion could go on the November ballot this year. If voters approve it, Florida's abortion laws would go back to more or less what they were when Roe v. Wade was still in force.
Florida abortion rulings: A win for both sides, but voters have last say with Amendment 4
What are Florida's abortion laws?
As of May 1, all abortions (with a few exceptions) are illegal in the state of Florida after a "physician determines the gestational age of the fetus is more than 6 weeks," a time when many pregnant people don't yet know they're pregnant.
People may have as little as two weeks after missing a period to find out and get both appointments at the state's overworked clinics, which leaves an extremely narrow window for a pregnant person in a potentially traumatic situation to take action. The state also requires a 24-hour waiting period so patients will need to fit two appointments before the legal deadline
However, while the law reduces the amount of time pregnant people have to get an abortion, it does provide some exemptions for rape and incest that the 15-week ban lacked, something that drew criticism even from some supporters.
How many people got abortions in 2023? New report finds increase despite bans
When do most people find out they're pregnant?
According to a 2021 study from ANSIRH (Advancing New Standards in Reproductive Health) at the University of California San Francisco, about one in three people confirm their pregnancies after six weeks, and one in five after seven weeks.
"Later confirmation of pregnancy is even higher among young people, people of color, and those living with food insecurity," the study's summary said, "suggesting that gestational bans on abortion in the first trimester will disproportionally hurt these populations."
Does Florida's 6-week abortion law include exemptions for danger to the mother?
Yes, but only for extreme cases. Two physicians must certify, in writing, that in their judgment an abortion is necessary "to save the pregnant woman’s life or avert a serious risk of substantial and irreversible physical impairment of a major bodily function." One physician may certify it if another is unavailable at the time.
This requires physicians willing to risk possible fines, loss of license and even imprisonment by going on record against oversight committees and the state. Attempts by Democrats to clarify the conditions under which a physician may make that call without risking their medical license were struck down.
Does the 6-week abortion ban in Florida include exemptions for a fetus that has died or is going to die?
Yes. If two physicians have certified in writing that in reasonable medical judgment, the fetus has a fatal fetal abnormality, the pregnancy may be terminated.
However, the law now contains new language requiring that the pregnancy must not have "progressed to the third trimester," which could be interpreted to mean that abortions for fatal fetal abnormalities are banned after 27 weeks.
Does the 6-week abortion ban in Florida include exemptions for rape or incest?
Abortions are permitted in the case of rape, incest or human trafficking but only up to 15 weeks, and only if the pregnant person has copies of "a restraining order, police report, medical record, or other court order or documentation" to provide evidence that they are a victim of rape or incest.
If the pregnant person is a minor, the physician must report the incident of rape or incest to the central abuse hotline.
Abortion rights battle: Abortion rights inspire these young voters like no other issue. How they're fighting ahead of 2024.
Does the 6-week abortion ban in Florida ban abortion pills?
Abortion pills are banned unless they are administered by a licensed doctor in person.
So-called "abortion pills" — actually two pills, mifepristone and misoprostol , taken up to 48 hours apart — which cause a person’s cervix to dilate and their uterus to contract, emptying the embryo from the person’s uterus, have dramatically risen in popularity in the last few years both for the relative convenience compared to surgical abortions and to get around abortion bans. Access to them has been challenged and will be decided by the U.S. Supreme Court .
The new law clearly states that abortions may only be performed by a physician in the same room. Telehealth sessions are specifically banned.
Can I go to jail for getting an abortion after 6 weeks in Florida?
Florida law prohibits anyone from willfully performing or actively helping someone get an abortion outside of the six-week gestational period or the legal exemptions. Doing so is considered a third-degree felony, punishable by fines and imprisonment of five years. It is unclear if the pregnant person is also liable.
What were Florida's abortion laws before?
Before the 15-week ban, the Roe v. Wade standard had applied across the country for decades. Abortions were legal:
- To the end of the first trimester (up to 12 weeks) for any reason
- During the second trimester (up to 24 weeks) to protect the health of the pregnant person
- During the third trimester if necessary to preserve the pregnant person's life or health
A full-term pregnancy is considered to be 39-40 weeks .
Protection for abortion travelers: Biden's new HIPAA rule shields medical records for out-of-state abortions
What would Amendment 4, Florida's abortion amendment do?
The proposed amendment submitted by Floridians Protecting Freedom that will appear on November's ballot reads:
“No law shall prohibit, penalize, delay, or restrict abortion before viability or when necessary to protect the patient’s health, as determined by the patient’s healthcare provider. This amendment does not change the Legislature’s constitutional authority to require notification to a parent or guardian before a minor has an abortion.”
Fetal viability has been put at about 24 weeks.
For the amendment to pass it must win by a supermajority, or at least 60% of the vote. According to an exclusive USA TODAY/Ipsos poll of more than 1,000 Floridians, half said they would vote in favor.

- Weill Cornell Medicine
Wayfinder menu

Pregnancy Cytokine Levels Impact Fetal Brain Development and Offspring Behavior
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine have discovered in a preclinical model that cytokines, proteins that control immune response, circulating in maternal blood during pregnancy may mitigate an offspring's risk for psychiatric conditions. The findings are surprising because circulating maternal cytokines are at such low levels that they were not implicated in fetal brain development and offspring behavior before.
The study published online in Brain, Behavior, and Immunity on Feb. 29, reported that cytokine XCL1 produced by maternal immune cells can function as a pregnancy hormone and is required for the proper development of placenta and male offspring fear behavior. These results support epidemiological studies which have long suggested a link between human maternal infection and inflammation during pregnancy and offspring developing psychiatric disorders later life.
“Using mouse models, we found that circulating XCL1 normally remained at the same low pre-pregnancy level throughout gestation except for a short rise and fall in the middle period,” said corresponding author Dr. Miklos Toth , professor of pharmacology at Weill Cornell Medicine. “This temporary rise is essential for the proper development of the placenta and offspring emotional behavior.” First author Dr. Rosa Chen was a graduate student in the Toth lab during the study, which was a collaboration with Dr. Heidi Stuhlmann , acting chair of Biochemistry and also of Cell and Developmental Biology and the Harvey Klein Professor of Biomedical Sciences, Cell and Developmental Biology at Weill Cornell Medicine.
When this spike in XCL1 in maternal blood was blocked genetically or neutralized by anti-XCL1 antibodies, the researchers found increased production of factors associated with tissue damage in the fetal placenta which led to increased innate anxiety and stress reactions in male mouse offspring. The researchers also found a neuronal abnormality in the developing brains of these offspring, specifically in the ventral hippocampus, a region that has been linked to anxiety and anxious behavior.
The immune and neuronal abnormalities observed when the cytokine spike was blocked were normalized by adulthood, suggesting that the adult anxious behavior of the offspring could be related to the early-life proinflammatory state caused by the absence of elevated XCL1.
Dr. Toth will explore other chemokines that may regulate placenta development and impact offspring emotional behavior. The team plans to collaborate with researchers who have access to blood samples from pregnant women to see if the profile of XCL1, a protein also found in humans, corresponds to the observations in mouse models.
This study was support by the National Institute of Mental Health, a part of the National Institutes of Health, grant R01MH113124 and 1R01MH117004.
Our Resources
- Shared Resources
- Funding Opportunities
- Research Opportunities
- Cancer Clinical Trials
- Member Resources
Our Researchers

- Alzheimer's disease & dementia
- Arthritis & Rheumatism
- Attention deficit disorders
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Biomedical technology
- Diseases, Conditions, Syndromes
- Endocrinology & Metabolism
- Gastroenterology
- Gerontology & Geriatrics
- Health informatics
- Inflammatory disorders
- Medical economics
- Medical research
- Medications
- Neuroscience
- Obstetrics & gynaecology
- Oncology & Cancer
- Ophthalmology
- Overweight & Obesity
- Parkinson's & Movement disorders
- Psychology & Psychiatry
- Radiology & Imaging
- Sleep disorders
- Sports medicine & Kinesiology
- Vaccination
- Breast cancer
- Cardiovascular disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Colon cancer
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
- Lung cancer
- Multiple sclerosis
- Myocardial infarction
- Ovarian cancer
- Post traumatic stress disorder
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Schizophrenia
- Skin cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Full List »
share this!
April 26, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
Researchers find pregnancy cytokine levels impact fetal brain development and offspring behavior
by Weill Cornell Medical College
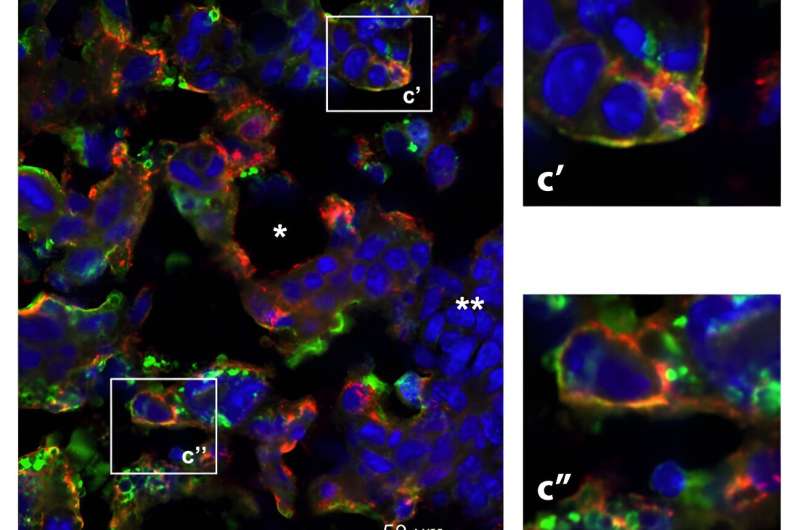
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine have discovered in a preclinical model that cytokines, proteins that control immune response, circulating in maternal blood during pregnancy may mitigate an offspring's risk for psychiatric conditions. The findings are surprising because circulating maternal cytokines are at such low levels that they were not implicated in fetal brain development and offspring behavior before.
The study published online in Brain, Behavior, and Immunity on Feb 29, reported that cytokine XCL1 produced by maternal immune cells can function as a pregnancy hormone and is required for the proper development of placenta and male offspring fear behavior. These results support epidemiological studies which have long suggested a link between human maternal infection and inflammation during pregnancy and offspring developing psychiatric disorders later life.
"Using mouse models, we found that circulating XCL1 normally remained at the same low pre-pregnancy level throughout gestation except for a short rise and fall in the middle period," said corresponding author Dr. Miklos Toth, professor of pharmacology at Weill Cornell Medicine. "This temporary rise is essential for the proper development of the placenta and offspring emotional behavior."
First author Dr. Rosa Chen was a graduate student in the Toth lab during the study, which was a collaboration with Dr. Heidi Stuhlmann, acting chair of Biochemistry and also of Cell and Developmental Biology and the Harvey Klein Professor of Biomedical Sciences, Cell and Developmental Biology at Weill Cornell Medicine.
When this spike in XCL1 in maternal blood was blocked genetically or neutralized by anti-XCL1 antibodies, the researchers found increased production of factors associated with tissue damage in the fetal placenta which led to increased innate anxiety and stress reactions in male mouse offspring. The researchers also found a neuronal abnormality in the developing brains of these offspring, specifically in the ventral hippocampus, a region that has been linked to anxiety and anxious behavior.
The immune and neuronal abnormalities observed when the cytokine spike was blocked were normalized by adulthood, suggesting that the adult anxious behavior of the offspring could be related to the early life proinflammatory state caused by the absence of elevated XCL1.
Dr. Toth will explore other chemokines that may regulate placenta development and impact offspring emotional behavior. The team plans to collaborate with researchers who have access to blood samples from pregnant women to see if the profile of XCL1, a protein also found in humans, corresponds to the observations in mouse models.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Study finds young adults reduced drinking during and after pandemic
58 minutes ago

Study reveals hidden diversity of innate immune cells
A new form of mpox that may spread more easily found in Congo's biggest outbreak
2 hours ago

New study supports psilocybin's potential as an antidepressant
11 hours ago

Global study reveals stark differences between females and males in disease burden causes

Researcher discusses mechanism behind a birth defect affecting brain size
12 hours ago

Study indicates that cancer patients gain important benefits from genome-matched treatments
13 hours ago

Machine learning tool identifies rare, undiagnosed immune disorders through patients' electronic health records
New technique improves T cell-based immunotherapies for solid tumors
14 hours ago
Unraveling the roles of non-coding DNA explains childhood cancer's resistance to chemotherapy
Related stories.

Metformin during pregnancy impacts offspring brain development, finds study
Mar 18, 2024
Study shows maternal microbiota can affect fetal development
Oct 20, 2023

New study explores infection effect on fetal brain development
Jul 21, 2022
Study shows offspring response to maternal diet and male hormone
Mar 22, 2018

Antidepressant use, infection during pregnancy linked to neurodevelopmental disorders
Dec 20, 2022

Administering opioids to pregnant mice alters behavior and gene expression in offspring
Jul 26, 2021
Recommended for you
Experimental vaccine targets portions of the flu virus that don't change
15 hours ago
New mRNA cancer vaccine triggers fierce immune response to fight malignant brain tumor
18 hours ago
Scientists identify new brain circuit in mice that controls body's inflammatory reactions
Researchers find difference in pancreatic cancer cells, offering new hope for immunotherapy effectiveness
20 hours ago
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

Sign up for the Health News Florida newsletter
Why is a 6-week abortion ban nearly a total ban it's about how we date a pregnancy.

Florida's abortion ban after six-weeks gestation is in effect as of May 1. That means the time a person has to decide whether or not to have an abortion in Florida is – at most – two weeks.
It has to do with how the medical community dates a pregnancy. Here's the deal:
- A pregnancy is measured from the first day of a woman's last menstrual period , or LMP.
- For the first two of those six weeks – before ovulation – there is no pregnancy.
- Ovulation, sexual intercourse and conception have to happen, generally, about two weeks after the first day of the LMP.
- There's about a week between when an egg is fertilized and when it implants in the uterus.
- It takes another week before there's enough of a specialized pregnancy hormone in someone's urine for a home pregnancy test to turn positive. That's also about the time that a missed period might clue a woman in that she might be pregnant.
- All of the above is true for people with regular menstrual cycles. For the many women with irregular cycles, it can take longer to diagnose a pregnancy.
So, a six-week limit on abortion is really a limit of four weeks after conception, and one or two weeks after a person learns they are pregnant. There are lots of variations in these biological norms from person-to-person and even from month-to-month.
Florida's six-week ban has exceptions if the pregnant patient's life or a "major bodily function" is in jeopardy, in cases of rape, or if the fetus has a "fatal fetal abnormality."
The six-week limit on abortion is not common – it is in effect in South Carolina and Georgia, at the moment. Many more states have full abortion bans .
The first six-week ban went into effect before Roe v. Wade was overturned in September 2021 in Texas. That was a ban on abortion after a "heartbeat" could be detected. Physicians have pointed out that there is no fetal heart at six-weeks gestation, but cardiac activity begins at that stage of development.
Copyright 2024 NPR


What Is a Subchorionic Hemorrhage in Pregnancy?
S ubchorionic hematomas can cause bleeding in pregnancy, but they aren't always cause for concern. Here’s what you need to know about them.
At 12 weeks pregnant, when many people are preparing to share their big news, I was keeping mine a closely guarded secret. Each time I went to the bathroom, the familiar pangs of anxiety returned as I wondered time and time again, was this bleed different? Was this the bleed that meant I was losing my baby?
Each time my baby was fine. I wasn't miscarrying; I was experiencing symptoms of a subchorionic hematoma, also referred to as subchorionic hemorrhage and subchorionic bleeding.
Subchorionic hematomas are an anomaly usually associated with persistent bleeding that starts in the first trimester. In my (rather extreme) case, it meant that I bled from weeks 6 to 27—sometimes with medium-sized clots the size of my palm—and I was in and out of hospital for much of my pregnancy.
But despite the dramatic presentation, experts say subchorionic hematomas are relatively common and often don't care serious issues in pregnancy.
What Causes a Subchorionic Hematoma?
A subchorionic hematoma or subchorionic hemorrhage occurs when blood collects between the wall of the uterus and the membrane sac that surrounds the fetus.
"This typically results from a partial detachment of the membrane, known as the chorion, from the wall of the uterus," explains Robin Kalish , M.D., FACOG, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist and director of clinical maternal-fetal medicine at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City.
While the exact cause of the separation is usually unknown, there is an upside: "Most pregnancies with a subchorionic hematoma will have normal outcomes," adds Dr. Kalish.
Risk Factors for a Subchorionic Hematoma
While it's often unclear what causes a subchorionic hematoma, certain modifiable risk factors could contribute to a hematoma growing, says Mackenzie Naert, M.D. , a clinical fellow in obstetrics and gynecology at Brigham and Women's and Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
One of those factors is being on blood thinners. "In certain cases, a patient and physician may decide to hold the blood thinners for a patient with a hematoma,” says Dr. Naert.
Here are some other factors that can put a patient at risk for a subchorionic hematoma:
- Uterine malformation
- History of recurrent pregnancy loss
- Pelvic infections
- IVF pregnancies
Still, many patients with a subchorionic hematoma will have no risk factors, and they'll never know the cause. I didn't discover what caused my subchorionic hematoma, and by the time it eventually resolved, it was rarely discussed again.
“Overall, it isn't necessary or possible to identify a cause of the hematoma since there is not much to do other than monitor for any bleeding,” explains Dr. Naert.
How Common Is a Subchorionic Hematoma?
Vaginal bleeding can happen in all stages of pregnancy and affects up to 25% of pregnant people in the first trimester. Subchorionic hematomas are the most common cause of bleeding from 10 to 20 weeks, contributing to about 11% of all cases.
"Subchorionic hematomas are quite common and are probably more widely experienced than people expect," says Dr. Kalish.
Subchorionic Hematoma Pregnancy Symptoms
Bleeding is a common symptom of subchorionic hematoma and can range from light spotting to heavy. Bleeding was the first symptom I had at around 6 weeks. It intensified at week 12 and continued until week 27.
While some pregnant people will experience spontaneous bleeding like me, others may also experience cramps or have no symptoms at all.
How Is a Subchorionic Hematoma Diagnosed?
The first step in diagnosing a subchorionic hematoma is usually an ultrasound, which can indicate the size and location of the bleed. All bleeding should be investigated to rule out miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or an infection.
How Serious Is a Subchorionic Hemorrhage?
The data is mixed, but generally speaking, subchorionic hematomas shouldn't cause too much concern. Even where risks may be associated, many pregnant people will go on to deliver healthy babies regardless of their symptoms.
With that said, one study found a subchorionic hematoma could carry an increased risk of adverse outcomes, including early pregnancy loss, fetal growth restriction, placental abruption, or preterm delivery. But other research hasn’t found a clear correlation between subchorionic hematomas and negative outcomes.
Experts say size could play a role in the impact of subchorionic hematomas. Dr. Kalish considers a small subchorionic hematoma as a bleed that encompasses less than 20% of the pregnancy sac, while a larger one could involve more than 50%. "While larger subchorionic hematoma are associated with a higher risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes, ongoing bleeding–especially when heavy and associated with cramping or pain–is more worrisome than the subchorionic hematoma size alone," she says.
Can a Subchorionic Hemorrhage Cause a Miscarriage?
While some research has found a connection between subchorionic hematoma and miscarriage, the evidence isn’t clear.
In her 2019 research of the correlation, Dr. Naert found reassuring results. "Historically, people have thought that subchorionic hematomas were associated with a higher risk of miscarriage but our study did not find this," she explains. "Certainly there is still a lot we may not know about hematomas, but with the current data, I feel confident reassuring patients that the subchorionic hematoma itself does not increase the risk of miscarriage."
Treating a Subchorionic Hematoma
Once a subchorionic hematoma is diagnosed, there's typically not much that can be done besides ongoing monitoring and follow-up appointments with your health care provider. Most subchorionic hematomas will resolve on their own, like mine eventually did—and today I have a beautiful, healthy (and very cheeky!) child.
There's various information available around home remedies like bed rest, and even drinking pomegranate juice. However, generally speaking, none of these are backed by science. "There is nothing anyone can do with subchorionic hematomas to help it go away or improve," explains Dr. Naert.
A provider may suggest avoiding sexual intercourse. “But not because the subchorionic hematoma is caused or worsened by intercourse,” says Dr. Naert. “Intercourse during pregnancy can cause bleeding from the cervix even in the absence of a hematoma and this bleeding can blur the picture.”
As for bed rest, she says that can actually increase the risk of blood clots. And heavy lifting should be avoided throughout all trimesters, both for patients with and without subchorionic hematomas.
The best thing you can do is stay connected with your health care provider who will continue to monitor you and your fetus throughout your pregnancy.
Always call your medical provider for any bleeding you experience during pregnancy. If a subchorionic hematoma is diagnosed, it’s important to look out for signs that may require medical attention like these below:
- You have new or increased vaginal bleeding
- You feel dizzy, light-headed, or like you might faint
- You feel increased pain in the pelvic area or belly
- You have a fever (100.4 F or greater)
- You believe you passed tissue (save any tissue you pass if you’re able to)
The Bottom Line
Subchorionic hematomas can cause light to heavy bleeding during pregnancy. While most pregnancies will have normal outcomes, vaginal bleeding is always a reason to connect with your medical provider.
It’s important for pregnant people to know they did nothing wrong. "For patients with bleeding early in pregnancy, I reassure them that there was nothing they did to cause the bleeding, and similarly nothing they can do to stop it,” explains Dr. Naert. “It just takes time to know the significance of the bleeding and, in the majority of cases, the pregnancy will be fine."
For more Parents news, make sure to sign up for our newsletter!
Read the original article on Parents .

Sponsored by the Asper Foundation and Reichman University

- Environment
- News Briefs
Creator Of Pregnancy Monitor ‘Belt’ Merges With US Company

The Israeli developer of a belt-like device that monitors the health of both a pregnant woman and her fetus has merged with a US firm to create a new combined company.
Nuvo ’s FDA-cleared device INVU is worn around the belly of the expectant mother and uses central and acoustic sensors to measure fetal movements, fetal heart rate and maternal heart rate.
The Tel Aviv-based company has merged with California-headquartered LAMF Global Ventures , and the new entity will retain the Nuvo name and existing operational and management structure. It will also be publicly traded on the NASDAQ Stock Market as NUVO, beginning May 2.
Nuvo CEO Rice Powell will become the head of the combined company,
The device is in use in both Israel and the United States, and the company is planning to expand into Europe this year, having filed a request for European Union approval in March 2023.
“Nuvo is committed to solving the inherent problems of a broken pregnancy care system by enabling access to quality care with advanced remote monitoring technology,” said Powell.
“Becoming a public company provides us with the resources to redefine pregnancy care and address health disparities by ensuring that all expectant mothers can receive timely and accurate care, regardless of their background or location,” he said.
Related posts

New Cybersecurity Platform Protecting Vendor Supply Chains

Car Inspection Platform UVeye Wins Prestigious US Automotive Award

US Chip Giant Nvidia Snaps Up 2 Israeli AI Startups In Same Week

Elbit Sells Air Defense System To Foreign Client For $50M
Facebook comments.

Weekly Newsletter
Subscribe to our free weekly round-up of the top tech stories from israel.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Abortion in Florida will be limited to the first 6 weeks of pregnancy starting May 1
Regan McCarthy
As Florida's six-week ban on abortions is set to take effect May 1, abortion providers and adoption services are trying to get ready.
Copyright © 2024 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.

COMMENTS
This positioning is called fetal presentation. Babies twist, stretch and tumble quite a bit during pregnancy. Before labor starts, however, they usually come to rest in a way that allows them to be delivered through the birth canal headfirst. This position is called cephalic presentation.
Fetal presentation, or how your baby is situated in your womb at birth, is determined by the body part that's positioned to come out first, and it can affect the way you deliver. ... Like the transverse lie, this position is more common earlier in pregnancy, and it's likely your provider will intervene if your baby is still in the oblique lie ...
Possible fetal positions can include: Occiput or cephalic anterior: This is the best fetal position for childbirth. It means the fetus is head down, facing the birth parent's spine (facing backward). Its chin is tucked towards its chest. The fetus will also be slightly off-center, with the back of its head facing the right or left.
Toward the end of pregnancy, the fetus moves into position for delivery. Normally, the presentation is vertex (head first), and the position is occiput anterior (facing toward the pregnant person's spine) and with the face and body angled to one side and the neck flexed. Variations in fetal presentations include face, brow, breech, and shoulder.
Fetal lie: Relation of the fetus to the long axis of the uterus; longitudinal, oblique, or transverse. Normal fetal lie is longitudinal, normal presentation is vertex, and occiput anterior is the most common position. Abnormal fetal lie, presentation, or position may occur with. Fetopelvic disproportion (fetus too large for the pelvic inlet)
The position in which your baby develops is called the "fetal presentation.". During most of your pregnancy, the baby will be curled up in a ball - that's why we call it the "fetal position.". The baby might flip around over the course of development, which is why you can sometimes feel a foot poking into your side or an elbow ...
The vertex presentation describes the orientation a fetus should be in for a safe vaginal delivery. It becomes important as you near your due date because it tells your pregnancy care provider how they may need to deliver your baby. Vertex means "crown of the head.". This means that the crown of the fetus's head is presenting towards the ...
During routine prenatal care, clinicians assess fetal lie and presentation with physical examination in the late third trimester. Ultrasonography can also be done. If breech presentation is detected, external cephalic version can sometimes move the fetus to vertex presentation before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks.
Breech Presentations. Breech presentation happens when your little one's feet or buttocks are in position to be delivered first, and make up just under 5 percent of all pregnancies. Your provider will likely order an ultrasound toward the end of your pregnancy if they suspect your baby is in a breech position.
If your baby is headfirst, the 3 main types of presentation are: anterior - when the back of your baby's head is at the front of your belly. lateral - when the back of your baby's head is facing your side. posterior - when the back of your baby's head is towards your back. Top row: 'right anterior — left anterior'.
There are several labor positions a mother can try to alleviate pain and encourage the baby to continue rotating toward an anterior position, including: Lunging. Pelvic tilts. Standing and swaying. A doula, labor nurse, midwife, or doctor may have other suggestions for positions.
Presentation of twins in Der Rosengarten ("The Rose Garden"), a standard medical text for midwives published in 1513. In obstetrics, the presentation of a fetus about to be born specifies which anatomical part of the fetus is leading, that is, is closest to the pelvic inlet of the birth canal. According to the leading part, this is identified as a cephalic, breech, or shoulder presentation.
Abnormal Fetal Lie. If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted - ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation. ECV is the manipulation of the fetus to a cephalic presentation through the maternal abdomen. It has an approximate success rate of 50% in primiparous women and 60% in multiparous women.
Breech Births. In the last weeks of pregnancy, a baby usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation. A breech presentation occurs when the baby's buttocks, feet, or both are positioned to come out first during birth. This happens in 3-4% of full-term births.
Introduction. Cephalic presentation is the most physiologic and frequent fetal presentation and is associated with the highest rate of successful vaginal delivery as well as with the lowest frequency of complications 1.Studies on the frequency of breech presentation by gestational age (GA) were published more than 20 years ago 2, 3, and it has been known that the prevalence of breech ...
Compound presentation is a fetal presentation in which an extremity presents alongside the part of the fetus closest to the birth canal. The majority of compound presentations consist of a fetal hand or arm presenting with the head [ 1 ]. This topic will review the pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management of this ...
Fetal position reflects the orientation of the fetal head or butt within the birth canal. The bones of the fetal scalp are soft and meet at "suture lines." Over the forehead, where the bones meet, is a gap, called the "anterior fontanel," or "soft spot." This will close as the baby grows during the 1st year of life, but at birth, it is open.
Twin fetal presentation - also known as the position of your babies in the womb - dictates whether you'll have a vaginal or c-section birth. Toward the end of pregnancy, most twins will move in the head-down position (vertex), but there's a risk that the second twin will change position after the first twin is born.
Fetal presentation is a reference to the part of the fetus that is overlying the maternal pelvic inlet. The most common relationship between fetus and mother is the longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation. A breech fetus also is a longitudinal lie, with the fetal buttocks as the presenting part. ... As pregnancy proceeds to term, most fetuses ...
Malpresentation can mean your baby's face, brow, buttocks, foot, back, shoulder, arms or legs or the umbilical cord are against the cervix. It's safest for your baby's head to come out first. If any other body part goes down the birth canal first, the risks to you and your baby may be higher. Malpresentation increases the chance that you ...
Each pregnancy and delivery is unique and yours should be too. Learn more about how Vanderbilt Health's obstetrics and maternal fetal medicine teams bring together nationally ranked expertise and personalized care from your first prenatal visit to delivery and beyond. To learn more, call 615-343-5700 or schedule an appointment online. Learn More
"Later confirmation of pregnancy is even higher among young people, people of color, and those living with food insecurity," the study's summary said, "suggesting that gestational bans on abortion ...
A pregnancy is measured from the first day of a woman's last menstrual period, or LMP. For the first two of those six weeks - before ovulation - there is no pregnancy. ... or if the fetus has ...
"Using mouse models, we found that circulating XCL1 normally remained at the same low pre-pregnancy level throughout gestation except for a short rise and fall in the middle period," said corresponding author Dr. Miklos Toth, professor of pharmacology at Weill Cornell Medicine. "This temporary rise is essential for the proper development ...
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine have discovered in a preclinical model that cytokines, proteins that control immune response, circulating in maternal blood during pregnancy may mitigate an ...
Florida's six-week ban has exceptions if the pregnant patient's life or a "major bodily function" is in jeopardy, in cases of rape, or if the fetus has a "fatal fetal abnormality." The six-week limit on abortion is not common - it is in effect in South Carolina and Georgia, at the moment. Many more states have full abortion bans.
With that said, one study found a subchorionic hematoma could carry an increased risk of adverse outcomes, including early pregnancy loss, fetal growth restriction, placental abruption, or preterm ...
During pregnancy, the fetus can be positioned in many different ways inside the mother's uterus. The fetus may be head up or down or facing the mother's back or front. At first, the fetus can move around easily or shift position as the mother moves. Toward the end of the pregnancy the fetus is larger, has less room to move, and stays in one ...
The Israeli developer of a belt-like device that monitors the health of both a pregnant woman and her fetus has merged with a US firm to create a new combined company. Nuvo 's FDA-cleared device INVU is worn around the belly of the expectant mother and uses central and acoustic sensors to measure fetal movements, fetal heart rate and ...
MCCARTHY: The six-week ban will allow exceptions for rape or fatal fetal abnormalities. And like the current 15-week ban, it allows abortions in order to save the life of the pregnant person.