Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples

How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Shona McCombes .
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more variables . An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls. A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Step 1: ask a question.
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2: Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalise more complex constructs.
Step 3: Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
Step 4: Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
Step 6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
A hypothesis is not just a guess. It should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, May 06). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/hypothesis-writing/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, operationalisation | a guide with examples, pros & cons, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Research Hypothesis: Good & Bad Examples
What is a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis is an attempt at explaining a phenomenon or the relationships between phenomena/variables in the real world. Hypotheses are sometimes called “educated guesses”, but they are in fact (or let’s say they should be) based on previous observations, existing theories, scientific evidence, and logic. A research hypothesis is also not a prediction—rather, predictions are ( should be) based on clearly formulated hypotheses. For example, “We tested the hypothesis that KLF2 knockout mice would show deficiencies in heart development” is an assumption or prediction, not a hypothesis.
The research hypothesis at the basis of this prediction is “the product of the KLF2 gene is involved in the development of the cardiovascular system in mice”—and this hypothesis is probably (hopefully) based on a clear observation, such as that mice with low levels of Kruppel-like factor 2 (which KLF2 codes for) seem to have heart problems. From this hypothesis, you can derive the idea that a mouse in which this particular gene does not function cannot develop a normal cardiovascular system, and then make the prediction that we started with.
What is the difference between a hypothesis and a prediction?
You might think that these are very subtle differences, and you will certainly come across many publications that do not contain an actual hypothesis or do not make these distinctions correctly. But considering that the formulation and testing of hypotheses is an integral part of the scientific method, it is good to be aware of the concepts underlying this approach. The two hallmarks of a scientific hypothesis are falsifiability (an evaluation standard that was introduced by the philosopher of science Karl Popper in 1934) and testability —if you cannot use experiments or data to decide whether an idea is true or false, then it is not a hypothesis (or at least a very bad one).
So, in a nutshell, you (1) look at existing evidence/theories, (2) come up with a hypothesis, (3) make a prediction that allows you to (4) design an experiment or data analysis to test it, and (5) come to a conclusion. Of course, not all studies have hypotheses (there is also exploratory or hypothesis-generating research), and you do not necessarily have to state your hypothesis as such in your paper.
But for the sake of understanding the principles of the scientific method, let’s first take a closer look at the different types of hypotheses that research articles refer to and then give you a step-by-step guide for how to formulate a strong hypothesis for your own paper.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Hypotheses can be simple , which means they describe the relationship between one single independent variable (the one you observe variations in or plan to manipulate) and one single dependent variable (the one you expect to be affected by the variations/manipulation). If there are more variables on either side, you are dealing with a complex hypothesis. You can also distinguish hypotheses according to the kind of relationship between the variables you are interested in (e.g., causal or associative ). But apart from these variations, we are usually interested in what is called the “alternative hypothesis” and, in contrast to that, the “null hypothesis”. If you think these two should be listed the other way round, then you are right, logically speaking—the alternative should surely come second. However, since this is the hypothesis we (as researchers) are usually interested in, let’s start from there.
Alternative Hypothesis
If you predict a relationship between two variables in your study, then the research hypothesis that you formulate to describe that relationship is your alternative hypothesis (usually H1 in statistical terms). The goal of your hypothesis testing is thus to demonstrate that there is sufficient evidence that supports the alternative hypothesis, rather than evidence for the possibility that there is no such relationship. The alternative hypothesis is usually the research hypothesis of a study and is based on the literature, previous observations, and widely known theories.
Null Hypothesis
The hypothesis that describes the other possible outcome, that is, that your variables are not related, is the null hypothesis ( H0 ). Based on your findings, you choose between the two hypotheses—usually that means that if your prediction was correct, you reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative. Make sure, however, that you are not getting lost at this step of the thinking process: If your prediction is that there will be no difference or change, then you are trying to find support for the null hypothesis and reject H1.
Directional Hypothesis
While the null hypothesis is obviously “static”, the alternative hypothesis can specify a direction for the observed relationship between variables—for example, that mice with higher expression levels of a certain protein are more active than those with lower levels. This is then called a one-tailed hypothesis.
Another example for a directional one-tailed alternative hypothesis would be that
H1: Attending private classes before important exams has a positive effect on performance.
Your null hypothesis would then be that
H0: Attending private classes before important exams has no/a negative effect on performance.
Nondirectional Hypothesis
A nondirectional hypothesis does not specify the direction of the potentially observed effect, only that there is a relationship between the studied variables—this is called a two-tailed hypothesis. For instance, if you are studying a new drug that has shown some effects on pathways involved in a certain condition (e.g., anxiety) in vitro in the lab, but you can’t say for sure whether it will have the same effects in an animal model or maybe induce other/side effects that you can’t predict and potentially increase anxiety levels instead, you could state the two hypotheses like this:
H1: The only lab-tested drug (somehow) affects anxiety levels in an anxiety mouse model.
You then test this nondirectional alternative hypothesis against the null hypothesis:
H0: The only lab-tested drug has no effect on anxiety levels in an anxiety mouse model.
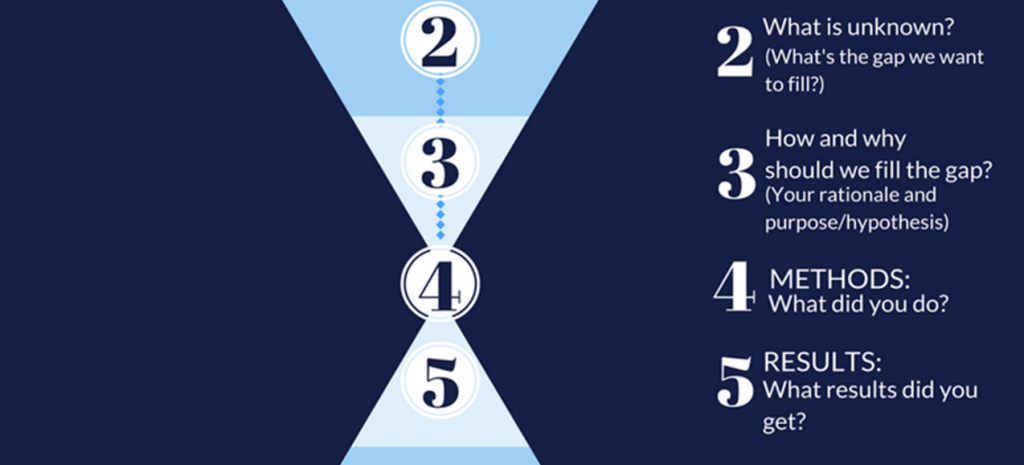
How to Write a Hypothesis for a Research Paper
Now that we understand the important distinctions between different kinds of research hypotheses, let’s look at a simple process of how to write a hypothesis.
Writing a Hypothesis Step:1
Ask a question, based on earlier research. Research always starts with a question, but one that takes into account what is already known about a topic or phenomenon. For example, if you are interested in whether people who have pets are happier than those who don’t, do a literature search and find out what has already been demonstrated. You will probably realize that yes, there is quite a bit of research that shows a relationship between happiness and owning a pet—and even studies that show that owning a dog is more beneficial than owning a cat ! Let’s say you are so intrigued by this finding that you wonder:
What is it that makes dog owners even happier than cat owners?
Let’s move on to Step 2 and find an answer to that question.
Writing a Hypothesis Step 2:
Formulate a strong hypothesis by answering your own question. Again, you don’t want to make things up, take unicorns into account, or repeat/ignore what has already been done. Looking at the dog-vs-cat papers your literature search returned, you see that most studies are based on self-report questionnaires on personality traits, mental health, and life satisfaction. What you don’t find is any data on actual (mental or physical) health measures, and no experiments. You therefore decide to make a bold claim come up with the carefully thought-through hypothesis that it’s maybe the lifestyle of the dog owners, which includes walking their dog several times per day, engaging in fun and healthy activities such as agility competitions, and taking them on trips, that gives them that extra boost in happiness. You could therefore answer your question in the following way:
Dog owners are happier than cat owners because of the dog-related activities they engage in.
Now you have to verify that your hypothesis fulfills the two requirements we introduced at the beginning of this resource article: falsifiability and testability . If it can’t be wrong and can’t be tested, it’s not a hypothesis. We are lucky, however, because yes, we can test whether owning a dog but not engaging in any of those activities leads to lower levels of happiness or well-being than owning a dog and playing and running around with them or taking them on trips.
Writing a Hypothesis Step 3:
Make your predictions and define your variables. We have verified that we can test our hypothesis, but now we have to define all the relevant variables, design our experiment or data analysis, and make precise predictions. You could, for example, decide to study dog owners (not surprising at this point), let them fill in questionnaires about their lifestyle as well as their life satisfaction (as other studies did), and then compare two groups of active and inactive dog owners. Alternatively, if you want to go beyond the data that earlier studies produced and analyzed and directly manipulate the activity level of your dog owners to study the effect of that manipulation, you could invite them to your lab, select groups of participants with similar lifestyles, make them change their lifestyle (e.g., couch potato dog owners start agility classes, very active ones have to refrain from any fun activities for a certain period of time) and assess their happiness levels before and after the intervention. In both cases, your independent variable would be “ level of engagement in fun activities with dog” and your dependent variable would be happiness or well-being .
Examples of a Good and Bad Hypothesis
Let’s look at a few examples of good and bad hypotheses to get you started.
Good Hypothesis Examples
Bad hypothesis examples, tips for writing a research hypothesis.
If you understood the distinction between a hypothesis and a prediction we made at the beginning of this article, then you will have no problem formulating your hypotheses and predictions correctly. To refresh your memory: We have to (1) look at existing evidence, (2) come up with a hypothesis, (3) make a prediction, and (4) design an experiment. For example, you could summarize your dog/happiness study like this:
(1) While research suggests that dog owners are happier than cat owners, there are no reports on what factors drive this difference. (2) We hypothesized that it is the fun activities that many dog owners (but very few cat owners) engage in with their pets that increases their happiness levels. (3) We thus predicted that preventing very active dog owners from engaging in such activities for some time and making very inactive dog owners take up such activities would lead to an increase and decrease in their overall self-ratings of happiness, respectively. (4) To test this, we invited dog owners into our lab, assessed their mental and emotional well-being through questionnaires, and then assigned them to an “active” and an “inactive” group, depending on…
Note that you use “we hypothesize” only for your hypothesis, not for your experimental prediction, and “would” or “if – then” only for your prediction, not your hypothesis. A hypothesis that states that something “would” affect something else sounds as if you don’t have enough confidence to make a clear statement—in which case you can’t expect your readers to believe in your research either. Write in the present tense, don’t use modal verbs that express varying degrees of certainty (such as may, might, or could ), and remember that you are not drawing a conclusion while trying not to exaggerate but making a clear statement that you then, in a way, try to disprove . And if that happens, that is not something to fear but an important part of the scientific process.
Similarly, don’t use “we hypothesize” when you explain the implications of your research or make predictions in the conclusion section of your manuscript, since these are clearly not hypotheses in the true sense of the word. As we said earlier, you will find that many authors of academic articles do not seem to care too much about these rather subtle distinctions, but thinking very clearly about your own research will not only help you write better but also ensure that even that infamous Reviewer 2 will find fewer reasons to nitpick about your manuscript.
Perfect Your Manuscript With Professional Editing
Now that you know how to write a strong research hypothesis for your research paper, you might be interested in our free AI proofreader , Wordvice AI, which finds and fixes errors in grammar, punctuation, and word choice in academic texts. Or if you are interested in human proofreading , check out our English editing services , including research paper editing and manuscript editing .
On the Wordvice academic resources website , you can also find many more articles and other resources that can help you with writing the other parts of your research paper , with making a research paper outline before you put everything together, or with writing an effective cover letter once you are ready to submit.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Definition, Format, Examples, and Tips
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amy Morin, LCSW, is a psychotherapist and international bestselling author. Her books, including "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do," have been translated into more than 40 languages. Her TEDx talk, "The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong," is one of the most viewed talks of all time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/VW-MIND-Amy-2b338105f1ee493f94d7e333e410fa76.jpg)
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis.
- Operationalization
Hypothesis Types
Hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process.
Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance. The hypothesis might be: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
At a Glance
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.
The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. At this point, researchers then begin to develop a testable hypothesis.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore numerous factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk adage that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
How to Formulate a Good Hypothesis
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
The Importance of Operational Definitions
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
Operational definitions are specific definitions for all relevant factors in a study. This process helps make vague or ambiguous concepts detailed and measurable.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in various ways. Clearly defining these variables and how they are measured helps ensure that other researchers can replicate your results.
Replicability
One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable.
Replication means repeating an experiment in the same way to produce the same results. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. For example, how would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
To measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming others. The researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness in this situation.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative population sample and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have higher reading scores than students who do not receive the intervention."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "There is no difference in anxiety levels between people who take St. John's wort supplements and those who do not."
- "There is no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
- "There is no difference in aggression levels between children who play first-person shooter games and those who do not."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "People who take St. John's wort supplements will have less anxiety than those who do not."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
- "Children who play first-person shooter games will show higher levels of aggression than children who do not."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when conducting an experiment is difficult or impossible. These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can examine how the variables are related. This research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
The Craft of Writing a Strong Hypothesis

Table of Contents
Writing a hypothesis is one of the essential elements of a scientific research paper. It needs to be to the point, clearly communicating what your research is trying to accomplish. A blurry, drawn-out, or complexly-structured hypothesis can confuse your readers. Or worse, the editor and peer reviewers.
A captivating hypothesis is not too intricate. This blog will take you through the process so that, by the end of it, you have a better idea of how to convey your research paper's intent in just one sentence.
What is a Hypothesis?
The first step in your scientific endeavor, a hypothesis, is a strong, concise statement that forms the basis of your research. It is not the same as a thesis statement , which is a brief summary of your research paper .
The sole purpose of a hypothesis is to predict your paper's findings, data, and conclusion. It comes from a place of curiosity and intuition . When you write a hypothesis, you're essentially making an educated guess based on scientific prejudices and evidence, which is further proven or disproven through the scientific method.
The reason for undertaking research is to observe a specific phenomenon. A hypothesis, therefore, lays out what the said phenomenon is. And it does so through two variables, an independent and dependent variable.
The independent variable is the cause behind the observation, while the dependent variable is the effect of the cause. A good example of this is “mixing red and blue forms purple.” In this hypothesis, mixing red and blue is the independent variable as you're combining the two colors at your own will. The formation of purple is the dependent variable as, in this case, it is conditional to the independent variable.
Different Types of Hypotheses

Types of hypotheses
Some would stand by the notion that there are only two types of hypotheses: a Null hypothesis and an Alternative hypothesis. While that may have some truth to it, it would be better to fully distinguish the most common forms as these terms come up so often, which might leave you out of context.
Apart from Null and Alternative, there are Complex, Simple, Directional, Non-Directional, Statistical, and Associative and casual hypotheses. They don't necessarily have to be exclusive, as one hypothesis can tick many boxes, but knowing the distinctions between them will make it easier for you to construct your own.
1. Null hypothesis
A null hypothesis proposes no relationship between two variables. Denoted by H 0 , it is a negative statement like “Attending physiotherapy sessions does not affect athletes' on-field performance.” Here, the author claims physiotherapy sessions have no effect on on-field performances. Even if there is, it's only a coincidence.
2. Alternative hypothesis
Considered to be the opposite of a null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis is donated as H1 or Ha. It explicitly states that the dependent variable affects the independent variable. A good alternative hypothesis example is “Attending physiotherapy sessions improves athletes' on-field performance.” or “Water evaporates at 100 °C. ” The alternative hypothesis further branches into directional and non-directional.
- Directional hypothesis: A hypothesis that states the result would be either positive or negative is called directional hypothesis. It accompanies H1 with either the ‘<' or ‘>' sign.
- Non-directional hypothesis: A non-directional hypothesis only claims an effect on the dependent variable. It does not clarify whether the result would be positive or negative. The sign for a non-directional hypothesis is ‘≠.'
3. Simple hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, “Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking.
4. Complex hypothesis
In contrast to a simple hypothesis, a complex hypothesis implies the relationship between multiple independent and dependent variables. For instance, “Individuals who eat more fruits tend to have higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.” The independent variable is eating more fruits, while the dependent variables are higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.
5. Associative and casual hypothesis
Associative and casual hypotheses don't exhibit how many variables there will be. They define the relationship between the variables. In an associative hypothesis, changing any one variable, dependent or independent, affects others. In a casual hypothesis, the independent variable directly affects the dependent.
6. Empirical hypothesis
Also referred to as the working hypothesis, an empirical hypothesis claims a theory's validation via experiments and observation. This way, the statement appears justifiable and different from a wild guess.
Say, the hypothesis is “Women who take iron tablets face a lesser risk of anemia than those who take vitamin B12.” This is an example of an empirical hypothesis where the researcher the statement after assessing a group of women who take iron tablets and charting the findings.
7. Statistical hypothesis
The point of a statistical hypothesis is to test an already existing hypothesis by studying a population sample. Hypothesis like “44% of the Indian population belong in the age group of 22-27.” leverage evidence to prove or disprove a particular statement.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
Writing a hypothesis is essential as it can make or break your research for you. That includes your chances of getting published in a journal. So when you're designing one, keep an eye out for these pointers:
- A research hypothesis has to be simple yet clear to look justifiable enough.
- It has to be testable — your research would be rendered pointless if too far-fetched into reality or limited by technology.
- It has to be precise about the results —what you are trying to do and achieve through it should come out in your hypothesis.
- A research hypothesis should be self-explanatory, leaving no doubt in the reader's mind.
- If you are developing a relational hypothesis, you need to include the variables and establish an appropriate relationship among them.
- A hypothesis must keep and reflect the scope for further investigations and experiments.
Separating a Hypothesis from a Prediction
Outside of academia, hypothesis and prediction are often used interchangeably. In research writing, this is not only confusing but also incorrect. And although a hypothesis and prediction are guesses at their core, there are many differences between them.
A hypothesis is an educated guess or even a testable prediction validated through research. It aims to analyze the gathered evidence and facts to define a relationship between variables and put forth a logical explanation behind the nature of events.
Predictions are assumptions or expected outcomes made without any backing evidence. They are more fictionally inclined regardless of where they originate from.
For this reason, a hypothesis holds much more weight than a prediction. It sticks to the scientific method rather than pure guesswork. "Planets revolve around the Sun." is an example of a hypothesis as it is previous knowledge and observed trends. Additionally, we can test it through the scientific method.
Whereas "COVID-19 will be eradicated by 2030." is a prediction. Even though it results from past trends, we can't prove or disprove it. So, the only way this gets validated is to wait and watch if COVID-19 cases end by 2030.
Finally, How to Write a Hypothesis

Quick tips on writing a hypothesis
1. Be clear about your research question
A hypothesis should instantly address the research question or the problem statement. To do so, you need to ask a question. Understand the constraints of your undertaken research topic and then formulate a simple and topic-centric problem. Only after that can you develop a hypothesis and further test for evidence.
2. Carry out a recce
Once you have your research's foundation laid out, it would be best to conduct preliminary research. Go through previous theories, academic papers, data, and experiments before you start curating your research hypothesis. It will give you an idea of your hypothesis's viability or originality.
Making use of references from relevant research papers helps draft a good research hypothesis. SciSpace Discover offers a repository of over 270 million research papers to browse through and gain a deeper understanding of related studies on a particular topic. Additionally, you can use SciSpace Copilot , your AI research assistant, for reading any lengthy research paper and getting a more summarized context of it. A hypothesis can be formed after evaluating many such summarized research papers. Copilot also offers explanations for theories and equations, explains paper in simplified version, allows you to highlight any text in the paper or clip math equations and tables and provides a deeper, clear understanding of what is being said. This can improve the hypothesis by helping you identify potential research gaps.
3. Create a 3-dimensional hypothesis
Variables are an essential part of any reasonable hypothesis. So, identify your independent and dependent variable(s) and form a correlation between them. The ideal way to do this is to write the hypothetical assumption in the ‘if-then' form. If you use this form, make sure that you state the predefined relationship between the variables.
In another way, you can choose to present your hypothesis as a comparison between two variables. Here, you must specify the difference you expect to observe in the results.
4. Write the first draft
Now that everything is in place, it's time to write your hypothesis. For starters, create the first draft. In this version, write what you expect to find from your research.
Clearly separate your independent and dependent variables and the link between them. Don't fixate on syntax at this stage. The goal is to ensure your hypothesis addresses the issue.
5. Proof your hypothesis
After preparing the first draft of your hypothesis, you need to inspect it thoroughly. It should tick all the boxes, like being concise, straightforward, relevant, and accurate. Your final hypothesis has to be well-structured as well.
Research projects are an exciting and crucial part of being a scholar. And once you have your research question, you need a great hypothesis to begin conducting research. Thus, knowing how to write a hypothesis is very important.
Now that you have a firmer grasp on what a good hypothesis constitutes, the different kinds there are, and what process to follow, you will find it much easier to write your hypothesis, which ultimately helps your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace Discover . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
It includes everything you need, including a repository of over 270 million research papers across disciplines, SEO-optimized summaries and public profiles to show your expertise and experience.
If you found these tips on writing a research hypothesis useful, head over to our blog on Statistical Hypothesis Testing to learn about the top researchers, papers, and institutions in this domain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what is the definition of hypothesis.
According to the Oxford dictionary, a hypothesis is defined as “An idea or explanation of something that is based on a few known facts, but that has not yet been proved to be true or correct”.
2. What is an example of hypothesis?
The hypothesis is a statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables. An example: "If we increase the number of new users who join our platform by 25%, then we will see an increase in revenue."
3. What is an example of null hypothesis?
A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between two variables. The null hypothesis is written as H0. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect. For example, if you're studying whether or not a particular type of exercise increases strength, your null hypothesis will be "there is no difference in strength between people who exercise and people who don't."
4. What are the types of research?
• Fundamental research
• Applied research
• Qualitative research
• Quantitative research
• Mixed research
• Exploratory research
• Longitudinal research
• Cross-sectional research
• Field research
• Laboratory research
• Fixed research
• Flexible research
• Action research
• Policy research
• Classification research
• Comparative research
• Causal research
• Inductive research
• Deductive research
5. How to write a hypothesis?
• Your hypothesis should be able to predict the relationship and outcome.
• Avoid wordiness by keeping it simple and brief.
• Your hypothesis should contain observable and testable outcomes.
• Your hypothesis should be relevant to the research question.
6. What are the 2 types of hypothesis?
• Null hypotheses are used to test the claim that "there is no difference between two groups of data".
• Alternative hypotheses test the claim that "there is a difference between two data groups".
7. Difference between research question and research hypothesis?
A research question is a broad, open-ended question you will try to answer through your research. A hypothesis is a statement based on prior research or theory that you expect to be true due to your study. Example - Research question: What are the factors that influence the adoption of the new technology? Research hypothesis: There is a positive relationship between age, education and income level with the adoption of the new technology.
8. What is plural for hypothesis?
The plural of hypothesis is hypotheses. Here's an example of how it would be used in a statement, "Numerous well-considered hypotheses are presented in this part, and they are supported by tables and figures that are well-illustrated."
9. What is the red queen hypothesis?
The red queen hypothesis in evolutionary biology states that species must constantly evolve to avoid extinction because if they don't, they will be outcompeted by other species that are evolving. Leigh Van Valen first proposed it in 1973; since then, it has been tested and substantiated many times.
10. Who is known as the father of null hypothesis?
The father of the null hypothesis is Sir Ronald Fisher. He published a paper in 1925 that introduced the concept of null hypothesis testing, and he was also the first to use the term itself.
11. When to reject null hypothesis?
You need to find a significant difference between your two populations to reject the null hypothesis. You can determine that by running statistical tests such as an independent sample t-test or a dependent sample t-test. You should reject the null hypothesis if the p-value is less than 0.05.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)

- Manuscript Preparation
What is and How to Write a Good Hypothesis in Research?
- 4 minute read
- 306.3K views
Table of Contents
One of the most important aspects of conducting research is constructing a strong hypothesis. But what makes a hypothesis in research effective? In this article, we’ll look at the difference between a hypothesis and a research question, as well as the elements of a good hypothesis in research. We’ll also include some examples of effective hypotheses, and what pitfalls to avoid.
What is a Hypothesis in Research?
Simply put, a hypothesis is a research question that also includes the predicted or expected result of the research. Without a hypothesis, there can be no basis for a scientific or research experiment. As such, it is critical that you carefully construct your hypothesis by being deliberate and thorough, even before you set pen to paper. Unless your hypothesis is clearly and carefully constructed, any flaw can have an adverse, and even grave, effect on the quality of your experiment and its subsequent results.
Research Question vs Hypothesis
It’s easy to confuse research questions with hypotheses, and vice versa. While they’re both critical to the Scientific Method, they have very specific differences. Primarily, a research question, just like a hypothesis, is focused and concise. But a hypothesis includes a prediction based on the proposed research, and is designed to forecast the relationship of and between two (or more) variables. Research questions are open-ended, and invite debate and discussion, while hypotheses are closed, e.g. “The relationship between A and B will be C.”
A hypothesis is generally used if your research topic is fairly well established, and you are relatively certain about the relationship between the variables that will be presented in your research. Since a hypothesis is ideally suited for experimental studies, it will, by its very existence, affect the design of your experiment. The research question is typically used for new topics that have not yet been researched extensively. Here, the relationship between different variables is less known. There is no prediction made, but there may be variables explored. The research question can be casual in nature, simply trying to understand if a relationship even exists, descriptive or comparative.
How to Write Hypothesis in Research
Writing an effective hypothesis starts before you even begin to type. Like any task, preparation is key, so you start first by conducting research yourself, and reading all you can about the topic that you plan to research. From there, you’ll gain the knowledge you need to understand where your focus within the topic will lie.
Remember that a hypothesis is a prediction of the relationship that exists between two or more variables. Your job is to write a hypothesis, and design the research, to “prove” whether or not your prediction is correct. A common pitfall is to use judgments that are subjective and inappropriate for the construction of a hypothesis. It’s important to keep the focus and language of your hypothesis objective.
An effective hypothesis in research is clearly and concisely written, and any terms or definitions clarified and defined. Specific language must also be used to avoid any generalities or assumptions.
Use the following points as a checklist to evaluate the effectiveness of your research hypothesis:
- Predicts the relationship and outcome
- Simple and concise – avoid wordiness
- Clear with no ambiguity or assumptions about the readers’ knowledge
- Observable and testable results
- Relevant and specific to the research question or problem
Research Hypothesis Example
Perhaps the best way to evaluate whether or not your hypothesis is effective is to compare it to those of your colleagues in the field. There is no need to reinvent the wheel when it comes to writing a powerful research hypothesis. As you’re reading and preparing your hypothesis, you’ll also read other hypotheses. These can help guide you on what works, and what doesn’t, when it comes to writing a strong research hypothesis.
Here are a few generic examples to get you started.
Eating an apple each day, after the age of 60, will result in a reduction of frequency of physician visits.
Budget airlines are more likely to receive more customer complaints. A budget airline is defined as an airline that offers lower fares and fewer amenities than a traditional full-service airline. (Note that the term “budget airline” is included in the hypothesis.
Workplaces that offer flexible working hours report higher levels of employee job satisfaction than workplaces with fixed hours.
Each of the above examples are specific, observable and measurable, and the statement of prediction can be verified or shown to be false by utilizing standard experimental practices. It should be noted, however, that often your hypothesis will change as your research progresses.
Language Editing Plus
Elsevier’s Language Editing Plus service can help ensure that your research hypothesis is well-designed, and articulates your research and conclusions. Our most comprehensive editing package, you can count on a thorough language review by native-English speakers who are PhDs or PhD candidates. We’ll check for effective logic and flow of your manuscript, as well as document formatting for your chosen journal, reference checks, and much more.

- Research Process
Systematic Literature Review or Literature Review?

What is a Problem Statement? [with examples]
You may also like.

Make Hook, Line, and Sinker: The Art of Crafting Engaging Introductions

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider

The Clear Path to An Impactful Paper: ②

The Essentials of Writing to Communicate Research in Medicine

Changing Lines: Sentence Patterns in Academic Writing
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
Research Hypothesis In Psychology: Types, & Examples
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A research hypothesis, in its plural form “hypotheses,” is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method .
Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding
Some key points about hypotheses:
- A hypothesis expresses an expected pattern or relationship. It connects the variables under investigation.
- It is stated in clear, precise terms before any data collection or analysis occurs. This makes the hypothesis testable.
- A hypothesis must be falsifiable. It should be possible, even if unlikely in practice, to collect data that disconfirms rather than supports the hypothesis.
- Hypotheses guide research. Scientists design studies to explicitly evaluate hypotheses about how nature works.
- For a hypothesis to be valid, it must be testable against empirical evidence. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
- Hypotheses are informed by background knowledge and observation, but go beyond what is already known to propose an explanation of how or why something occurs.
Predictions typically arise from a thorough knowledge of the research literature, curiosity about real-world problems or implications, and integrating this to advance theory. They build on existing literature while providing new insight.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Alternative hypothesis.
The research hypothesis is often called the alternative or experimental hypothesis in experimental research.
It typically suggests a potential relationship between two key variables: the independent variable, which the researcher manipulates, and the dependent variable, which is measured based on those changes.
The alternative hypothesis states a relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable affects the other).
A hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a key component of the scientific method. Some key points about hypotheses:
- Important hypotheses lead to predictions that can be tested empirically. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
In summary, a hypothesis is a precise, testable statement of what researchers expect to happen in a study and why. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
An experimental hypothesis predicts what change(s) will occur in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated.
It states that the results are not due to chance and are significant in supporting the theory being investigated.
The alternative hypothesis can be directional, indicating a specific direction of the effect, or non-directional, suggesting a difference without specifying its nature. It’s what researchers aim to support or demonstrate through their study.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable does not affect the other). There will be no changes in the dependent variable due to manipulating the independent variable.
It states results are due to chance and are not significant in supporting the idea being investigated.
The null hypothesis, positing no effect or relationship, is a foundational contrast to the research hypothesis in scientific inquiry. It establishes a baseline for statistical testing, promoting objectivity by initiating research from a neutral stance.
Many statistical methods are tailored to test the null hypothesis, determining the likelihood of observed results if no true effect exists.
This dual-hypothesis approach provides clarity, ensuring that research intentions are explicit, and fosters consistency across scientific studies, enhancing the standardization and interpretability of research outcomes.

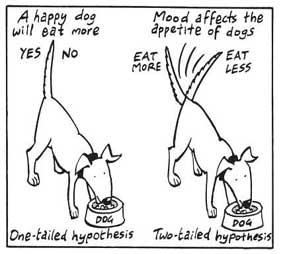
Nondirectional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis, also known as a two-tailed hypothesis, predicts that there is a difference or relationship between two variables but does not specify the direction of this relationship.
It merely indicates that a change or effect will occur without predicting which group will have higher or lower values.
For example, “There is a difference in performance between Group A and Group B” is a non-directional hypothesis.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional (one-tailed) hypothesis predicts the nature of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. It predicts in which direction the change will take place. (i.e., greater, smaller, less, more)
It specifies whether one variable is greater, lesser, or different from another, rather than just indicating that there’s a difference without specifying its nature.
For example, “Exercise increases weight loss” is a directional hypothesis.
Falsifiability
The Falsification Principle, proposed by Karl Popper , is a way of demarcating science from non-science. It suggests that for a theory or hypothesis to be considered scientific, it must be testable and irrefutable.
Falsifiability emphasizes that scientific claims shouldn’t just be confirmable but should also have the potential to be proven wrong.
It means that there should exist some potential evidence or experiment that could prove the proposition false.
However many confirming instances exist for a theory, it only takes one counter observation to falsify it. For example, the hypothesis that “all swans are white,” can be falsified by observing a black swan.
For Popper, science should attempt to disprove a theory rather than attempt to continually provide evidence to support a research hypothesis.
Can a Hypothesis be Proven?
Hypotheses make probabilistic predictions. They state the expected outcome if a particular relationship exists. However, a study result supporting a hypothesis does not definitively prove it is true.
All studies have limitations. There may be unknown confounding factors or issues that limit the certainty of conclusions. Additional studies may yield different results.
In science, hypotheses can realistically only be supported with some degree of confidence, not proven. The process of science is to incrementally accumulate evidence for and against hypothesized relationships in an ongoing pursuit of better models and explanations that best fit the empirical data. But hypotheses remain open to revision and rejection if that is where the evidence leads.
- Disproving a hypothesis is definitive. Solid disconfirmatory evidence will falsify a hypothesis and require altering or discarding it based on the evidence.
- However, confirming evidence is always open to revision. Other explanations may account for the same results, and additional or contradictory evidence may emerge over time.
We can never 100% prove the alternative hypothesis. Instead, we see if we can disprove, or reject the null hypothesis.
If we reject the null hypothesis, this doesn’t mean that our alternative hypothesis is correct but does support the alternative/experimental hypothesis.
Upon analysis of the results, an alternative hypothesis can be rejected or supported, but it can never be proven to be correct. We must avoid any reference to results proving a theory as this implies 100% certainty, and there is always a chance that evidence may exist which could refute a theory.
How to Write a Hypothesis
- Identify variables . The researcher manipulates the independent variable and the dependent variable is the measured outcome.
- Operationalized the variables being investigated . Operationalization of a hypothesis refers to the process of making the variables physically measurable or testable, e.g. if you are about to study aggression, you might count the number of punches given by participants.
- Decide on a direction for your prediction . If there is evidence in the literature to support a specific effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a directional (one-tailed) hypothesis. If there are limited or ambiguous findings in the literature regarding the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a non-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis.
- Make it Testable : Ensure your hypothesis can be tested through experimentation or observation. It should be possible to prove it false (principle of falsifiability).
- Clear & concise language . A strong hypothesis is concise (typically one to two sentences long), and formulated using clear and straightforward language, ensuring it’s easily understood and testable.
Consider a hypothesis many teachers might subscribe to: students work better on Monday morning than on Friday afternoon (IV=Day, DV= Standard of work).
Now, if we decide to study this by giving the same group of students a lesson on a Monday morning and a Friday afternoon and then measuring their immediate recall of the material covered in each session, we would end up with the following:
- The alternative hypothesis states that students will recall significantly more information on a Monday morning than on a Friday afternoon.
- The null hypothesis states that there will be no significant difference in the amount recalled on a Monday morning compared to a Friday afternoon. Any difference will be due to chance or confounding factors.
More Examples
- Memory : Participants exposed to classical music during study sessions will recall more items from a list than those who studied in silence.
- Social Psychology : Individuals who frequently engage in social media use will report higher levels of perceived social isolation compared to those who use it infrequently.
- Developmental Psychology : Children who engage in regular imaginative play have better problem-solving skills than those who don’t.
- Clinical Psychology : Cognitive-behavioral therapy will be more effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety over a 6-month period compared to traditional talk therapy.
- Cognitive Psychology : Individuals who multitask between various electronic devices will have shorter attention spans on focused tasks than those who single-task.
- Health Psychology : Patients who practice mindfulness meditation will experience lower levels of chronic pain compared to those who don’t meditate.
- Organizational Psychology : Employees in open-plan offices will report higher levels of stress than those in private offices.
- Behavioral Psychology : Rats rewarded with food after pressing a lever will press it more frequently than rats who receive no reward.
- Privacy Policy

Home » What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation.
Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments and the collection and analysis of data. It is an essential element of the scientific method, as it allows researchers to make predictions about the outcome of their experiments and to test those predictions to determine their accuracy.
Types of Hypothesis
Types of Hypothesis are as follows:
Research Hypothesis
A research hypothesis is a statement that predicts a relationship between variables. It is usually formulated as a specific statement that can be tested through research, and it is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is no significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as a starting point for testing the research hypothesis, and if the results of the study reject the null hypothesis, it suggests that there is a significant difference or relationship between variables.
Alternative Hypothesis
An alternative hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is a significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as an alternative to the null hypothesis and is tested against the null hypothesis to determine which statement is more accurate.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the direction of the relationship between variables. For example, a researcher might predict that increasing the amount of exercise will result in a decrease in body weight.
Non-directional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between variables but does not specify the direction. For example, a researcher might predict that there is a relationship between the amount of exercise and body weight, but they do not specify whether increasing or decreasing exercise will affect body weight.
Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a statement that assumes a particular statistical model or distribution for the data. It is often used in statistical analysis to test the significance of a particular result.
Composite Hypothesis
A composite hypothesis is a statement that assumes more than one condition or outcome. It can be divided into several sub-hypotheses, each of which represents a different possible outcome.
Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is a statement that is based on observed phenomena or data. It is often used in scientific research to develop theories or models that explain the observed phenomena.
Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement that assumes only one outcome or condition. It is often used in scientific research to test a single variable or factor.
Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is a statement that assumes multiple outcomes or conditions. It is often used in scientific research to test the effects of multiple variables or factors on a particular outcome.
Applications of Hypothesis
Hypotheses are used in various fields to guide research and make predictions about the outcomes of experiments or observations. Here are some examples of how hypotheses are applied in different fields:
- Science : In scientific research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain natural phenomena. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular variable on a natural system, such as the effects of climate change on an ecosystem.
- Medicine : In medical research, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of treatments and therapies for specific conditions. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new drug on a particular disease.
- Psychology : In psychology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of human behavior and cognition. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular stimulus on the brain or behavior.
- Sociology : In sociology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of social phenomena, such as the effects of social structures or institutions on human behavior. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of income inequality on crime rates.
- Business : In business research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain business phenomena, such as consumer behavior or market trends. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new marketing campaign on consumer buying behavior.
- Engineering : In engineering, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of new technologies or designs. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the efficiency of a new solar panel design.
How to write a Hypothesis
Here are the steps to follow when writing a hypothesis:
Identify the Research Question
The first step is to identify the research question that you want to answer through your study. This question should be clear, specific, and focused. It should be something that can be investigated empirically and that has some relevance or significance in the field.
Conduct a Literature Review
Before writing your hypothesis, it’s essential to conduct a thorough literature review to understand what is already known about the topic. This will help you to identify the research gap and formulate a hypothesis that builds on existing knowledge.
Determine the Variables
The next step is to identify the variables involved in the research question. A variable is any characteristic or factor that can vary or change. There are two types of variables: independent and dependent. The independent variable is the one that is manipulated or changed by the researcher, while the dependent variable is the one that is measured or observed as a result of the independent variable.
Formulate the Hypothesis
Based on the research question and the variables involved, you can now formulate your hypothesis. A hypothesis should be a clear and concise statement that predicts the relationship between the variables. It should be testable through empirical research and based on existing theory or evidence.
Write the Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is the opposite of the alternative hypothesis, which is the hypothesis that you are testing. The null hypothesis states that there is no significant difference or relationship between the variables. It is important to write the null hypothesis because it allows you to compare your results with what would be expected by chance.
Refine the Hypothesis
After formulating the hypothesis, it’s important to refine it and make it more precise. This may involve clarifying the variables, specifying the direction of the relationship, or making the hypothesis more testable.
Examples of Hypothesis
Here are a few examples of hypotheses in different fields:
- Psychology : “Increased exposure to violent video games leads to increased aggressive behavior in adolescents.”
- Biology : “Higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will lead to increased plant growth.”
- Sociology : “Individuals who grow up in households with higher socioeconomic status will have higher levels of education and income as adults.”
- Education : “Implementing a new teaching method will result in higher student achievement scores.”
- Marketing : “Customers who receive a personalized email will be more likely to make a purchase than those who receive a generic email.”
- Physics : “An increase in temperature will cause an increase in the volume of a gas, assuming all other variables remain constant.”
- Medicine : “Consuming a diet high in saturated fats will increase the risk of developing heart disease.”
Purpose of Hypothesis
The purpose of a hypothesis is to provide a testable explanation for an observed phenomenon or a prediction of a future outcome based on existing knowledge or theories. A hypothesis is an essential part of the scientific method and helps to guide the research process by providing a clear focus for investigation. It enables scientists to design experiments or studies to gather evidence and data that can support or refute the proposed explanation or prediction.
The formulation of a hypothesis is based on existing knowledge, observations, and theories, and it should be specific, testable, and falsifiable. A specific hypothesis helps to define the research question, which is important in the research process as it guides the selection of an appropriate research design and methodology. Testability of the hypothesis means that it can be proven or disproven through empirical data collection and analysis. Falsifiability means that the hypothesis should be formulated in such a way that it can be proven wrong if it is incorrect.
In addition to guiding the research process, the testing of hypotheses can lead to new discoveries and advancements in scientific knowledge. When a hypothesis is supported by the data, it can be used to develop new theories or models to explain the observed phenomenon. When a hypothesis is not supported by the data, it can help to refine existing theories or prompt the development of new hypotheses to explain the phenomenon.
When to use Hypothesis
Here are some common situations in which hypotheses are used:
- In scientific research , hypotheses are used to guide the design of experiments and to help researchers make predictions about the outcomes of those experiments.
- In social science research , hypotheses are used to test theories about human behavior, social relationships, and other phenomena.
- I n business , hypotheses can be used to guide decisions about marketing, product development, and other areas. For example, a hypothesis might be that a new product will sell well in a particular market, and this hypothesis can be tested through market research.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Here are some common characteristics of a hypothesis:
- Testable : A hypothesis must be able to be tested through observation or experimentation. This means that it must be possible to collect data that will either support or refute the hypothesis.
- Falsifiable : A hypothesis must be able to be proven false if it is not supported by the data. If a hypothesis cannot be falsified, then it is not a scientific hypothesis.
- Clear and concise : A hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner so that it can be easily understood and tested.
- Based on existing knowledge : A hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and research in the field. It should not be based on personal beliefs or opinions.
- Specific : A hypothesis should be specific in terms of the variables being tested and the predicted outcome. This will help to ensure that the research is focused and well-designed.
- Tentative: A hypothesis is a tentative statement or assumption that requires further testing and evidence to be confirmed or refuted. It is not a final conclusion or assertion.
- Relevant : A hypothesis should be relevant to the research question or problem being studied. It should address a gap in knowledge or provide a new perspective on the issue.
Advantages of Hypothesis
Hypotheses have several advantages in scientific research and experimentation:
- Guides research: A hypothesis provides a clear and specific direction for research. It helps to focus the research question, select appropriate methods and variables, and interpret the results.
- Predictive powe r: A hypothesis makes predictions about the outcome of research, which can be tested through experimentation. This allows researchers to evaluate the validity of the hypothesis and make new discoveries.
- Facilitates communication: A hypothesis provides a common language and framework for scientists to communicate with one another about their research. This helps to facilitate the exchange of ideas and promotes collaboration.
- Efficient use of resources: A hypothesis helps researchers to use their time, resources, and funding efficiently by directing them towards specific research questions and methods that are most likely to yield results.
- Provides a basis for further research: A hypothesis that is supported by data provides a basis for further research and exploration. It can lead to new hypotheses, theories, and discoveries.
- Increases objectivity: A hypothesis can help to increase objectivity in research by providing a clear and specific framework for testing and interpreting results. This can reduce bias and increase the reliability of research findings.
Limitations of Hypothesis
Some Limitations of the Hypothesis are as follows:
- Limited to observable phenomena: Hypotheses are limited to observable phenomena and cannot account for unobservable or intangible factors. This means that some research questions may not be amenable to hypothesis testing.
- May be inaccurate or incomplete: Hypotheses are based on existing knowledge and research, which may be incomplete or inaccurate. This can lead to flawed hypotheses and erroneous conclusions.
- May be biased: Hypotheses may be biased by the researcher’s own beliefs, values, or assumptions. This can lead to selective interpretation of data and a lack of objectivity in research.
- Cannot prove causation: A hypothesis can only show a correlation between variables, but it cannot prove causation. This requires further experimentation and analysis.
- Limited to specific contexts: Hypotheses are limited to specific contexts and may not be generalizable to other situations or populations. This means that results may not be applicable in other contexts or may require further testing.
- May be affected by chance : Hypotheses may be affected by chance or random variation, which can obscure or distort the true relationship between variables.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
What Is A Research (Scientific) Hypothesis? A plain-language explainer + examples
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
If you’re new to the world of research, or it’s your first time writing a dissertation or thesis, you’re probably noticing that the words “research hypothesis” and “scientific hypothesis” are used quite a bit, and you’re wondering what they mean in a research context .
“Hypothesis” is one of those words that people use loosely, thinking they understand what it means. However, it has a very specific meaning within academic research. So, it’s important to understand the exact meaning before you start hypothesizing.
Research Hypothesis 101
- What is a hypothesis ?
- What is a research hypothesis (scientific hypothesis)?
- Requirements for a research hypothesis
- Definition of a research hypothesis
- The null hypothesis
What is a hypothesis?
Let’s start with the general definition of a hypothesis (not a research hypothesis or scientific hypothesis), according to the Cambridge Dictionary:
Hypothesis: an idea or explanation for something that is based on known facts but has not yet been proved.
In other words, it’s a statement that provides an explanation for why or how something works, based on facts (or some reasonable assumptions), but that has not yet been specifically tested . For example, a hypothesis might look something like this:
Hypothesis: sleep impacts academic performance.
This statement predicts that academic performance will be influenced by the amount and/or quality of sleep a student engages in – sounds reasonable, right? It’s based on reasonable assumptions , underpinned by what we currently know about sleep and health (from the existing literature). So, loosely speaking, we could call it a hypothesis, at least by the dictionary definition.
But that’s not good enough…
Unfortunately, that’s not quite sophisticated enough to describe a research hypothesis (also sometimes called a scientific hypothesis), and it wouldn’t be acceptable in a dissertation, thesis or research paper . In the world of academic research, a statement needs a few more criteria to constitute a true research hypothesis .
What is a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes – specificity , clarity and testability .
Let’s take a look at these more closely.
Need a helping hand?
Hypothesis Essential #1: Specificity & Clarity
A good research hypothesis needs to be extremely clear and articulate about both what’ s being assessed (who or what variables are involved ) and the expected outcome (for example, a difference between groups, a relationship between variables, etc.).
Let’s stick with our sleepy students example and look at how this statement could be more specific and clear.
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
As you can see, the statement is very specific as it identifies the variables involved (sleep hours and test grades), the parties involved (two groups of students), as well as the predicted relationship type (a positive relationship). There’s no ambiguity or uncertainty about who or what is involved in the statement, and the expected outcome is clear.
Contrast that to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – and you can see the difference. “Sleep” and “academic performance” are both comparatively vague , and there’s no indication of what the expected relationship direction is (more sleep or less sleep). As you can see, specificity and clarity are key.

Hypothesis Essential #2: Testability (Provability)
A statement must be testable to qualify as a research hypothesis. In other words, there needs to be a way to prove (or disprove) the statement. If it’s not testable, it’s not a hypothesis – simple as that.
For example, consider the hypothesis we mentioned earlier:
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
We could test this statement by undertaking a quantitative study involving two groups of students, one that gets 8 or more hours of sleep per night for a fixed period, and one that gets less. We could then compare the standardised test results for both groups to see if there’s a statistically significant difference.
Again, if you compare this to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – you can see that it would be quite difficult to test that statement, primarily because it isn’t specific enough. How much sleep? By who? What type of academic performance?
So, remember the mantra – if you can’t test it, it’s not a hypothesis 🙂

Defining A Research Hypothesis
You’re still with us? Great! Let’s recap and pin down a clear definition of a hypothesis.
A research hypothesis (or scientific hypothesis) is a statement about an expected relationship between variables, or explanation of an occurrence, that is clear, specific and testable.
So, when you write up hypotheses for your dissertation or thesis, make sure that they meet all these criteria. If you do, you’ll not only have rock-solid hypotheses but you’ll also ensure a clear focus for your entire research project.
What about the null hypothesis?
You may have also heard the terms null hypothesis , alternative hypothesis, or H-zero thrown around. At a simple level, the null hypothesis is the counter-proposal to the original hypothesis.
For example, if the hypothesis predicts that there is a relationship between two variables (for example, sleep and academic performance), the null hypothesis would predict that there is no relationship between those variables.
At a more technical level, the null hypothesis proposes that no statistical significance exists in a set of given observations and that any differences are due to chance alone.
And there you have it – hypotheses in a nutshell.
If you have any questions, be sure to leave a comment below and we’ll do our best to help you. If you need hands-on help developing and testing your hypotheses, consider our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research journey.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

16 Comments
Very useful information. I benefit more from getting more information in this regard.
Very great insight,educative and informative. Please give meet deep critics on many research data of public international Law like human rights, environment, natural resources, law of the sea etc
In a book I read a distinction is made between null, research, and alternative hypothesis. As far as I understand, alternative and research hypotheses are the same. Can you please elaborate? Best Afshin
This is a self explanatory, easy going site. I will recommend this to my friends and colleagues.
Very good definition. How can I cite your definition in my thesis? Thank you. Is nul hypothesis compulsory in a research?
It’s a counter-proposal to be proven as a rejection
Please what is the difference between alternate hypothesis and research hypothesis?
It is a very good explanation. However, it limits hypotheses to statistically tasteable ideas. What about for qualitative researches or other researches that involve quantitative data that don’t need statistical tests?
In qualitative research, one typically uses propositions, not hypotheses.
could you please elaborate it more
I’ve benefited greatly from these notes, thank you.
This is very helpful
well articulated ideas are presented here, thank you for being reliable sources of information
Excellent. Thanks for being clear and sound about the research methodology and hypothesis (quantitative research)
I have only a simple question regarding the null hypothesis. – Is the null hypothesis (Ho) known as the reversible hypothesis of the alternative hypothesis (H1? – How to test it in academic research?
this is very important note help me much more
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is Research Methodology? Simple Definition (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] Contrasted to this, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research aims and objectives are confirmatory in nature. For example,…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
User Preferences
Content preview.
Arcu felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis:
- Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate
- Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident
Keyboard Shortcuts
5.2 - writing hypotheses.
The first step in conducting a hypothesis test is to write the hypothesis statements that are going to be tested. For each test you will have a null hypothesis (\(H_0\)) and an alternative hypothesis (\(H_a\)).
When writing hypotheses there are three things that we need to know: (1) the parameter that we are testing (2) the direction of the test (non-directional, right-tailed or left-tailed), and (3) the value of the hypothesized parameter.
- At this point we can write hypotheses for a single mean (\(\mu\)), paired means(\(\mu_d\)), a single proportion (\(p\)), the difference between two independent means (\(\mu_1-\mu_2\)), the difference between two proportions (\(p_1-p_2\)), a simple linear regression slope (\(\beta\)), and a correlation (\(\rho\)).
- The research question will give us the information necessary to determine if the test is two-tailed (e.g., "different from," "not equal to"), right-tailed (e.g., "greater than," "more than"), or left-tailed (e.g., "less than," "fewer than").
- The research question will also give us the hypothesized parameter value. This is the number that goes in the hypothesis statements (i.e., \(\mu_0\) and \(p_0\)). For the difference between two groups, regression, and correlation, this value is typically 0.
Hypotheses are always written in terms of population parameters (e.g., \(p\) and \(\mu\)). The tables below display all of the possible hypotheses for the parameters that we have learned thus far. Note that the null hypothesis always includes the equality (i.e., =).
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of hypothesis
Did you know.
The Difference Between Hypothesis and Theory
A hypothesis is an assumption, an idea that is proposed for the sake of argument so that it can be tested to see if it might be true.
In the scientific method, the hypothesis is constructed before any applicable research has been done, apart from a basic background review. You ask a question, read up on what has been studied before, and then form a hypothesis.
A hypothesis is usually tentative; it's an assumption or suggestion made strictly for the objective of being tested.
A theory , in contrast, is a principle that has been formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data. It is used in the names of a number of principles accepted in the scientific community, such as the Big Bang Theory . Because of the rigors of experimentation and control, it is understood to be more likely to be true than a hypothesis is.
In non-scientific use, however, hypothesis and theory are often used interchangeably to mean simply an idea, speculation, or hunch, with theory being the more common choice.
Since this casual use does away with the distinctions upheld by the scientific community, hypothesis and theory are prone to being wrongly interpreted even when they are encountered in scientific contexts—or at least, contexts that allude to scientific study without making the critical distinction that scientists employ when weighing hypotheses and theories.
The most common occurrence is when theory is interpreted—and sometimes even gleefully seized upon—to mean something having less truth value than other scientific principles. (The word law applies to principles so firmly established that they are almost never questioned, such as the law of gravity.)
This mistake is one of projection: since we use theory in general to mean something lightly speculated, then it's implied that scientists must be talking about the same level of uncertainty when they use theory to refer to their well-tested and reasoned principles.
The distinction has come to the forefront particularly on occasions when the content of science curricula in schools has been challenged—notably, when a school board in Georgia put stickers on textbooks stating that evolution was "a theory, not a fact, regarding the origin of living things." As Kenneth R. Miller, a cell biologist at Brown University, has said , a theory "doesn’t mean a hunch or a guess. A theory is a system of explanations that ties together a whole bunch of facts. It not only explains those facts, but predicts what you ought to find from other observations and experiments.”
While theories are never completely infallible, they form the basis of scientific reasoning because, as Miller said "to the best of our ability, we’ve tested them, and they’ve held up."
- proposition
- supposition
hypothesis , theory , law mean a formula derived by inference from scientific data that explains a principle operating in nature.
hypothesis implies insufficient evidence to provide more than a tentative explanation.
theory implies a greater range of evidence and greater likelihood of truth.
law implies a statement of order and relation in nature that has been found to be invariable under the same conditions.
Examples of hypothesis in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'hypothesis.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
Greek, from hypotithenai to put under, suppose, from hypo- + tithenai to put — more at do
1641, in the meaning defined at sense 1a
Phrases Containing hypothesis
- counter - hypothesis
- nebular hypothesis
- null hypothesis
- planetesimal hypothesis
- Whorfian hypothesis
Articles Related to hypothesis

This is the Difference Between a...
This is the Difference Between a Hypothesis and a Theory
In scientific reasoning, they're two completely different things
Dictionary Entries Near hypothesis
hypothermia
hypothesize
Cite this Entry
“Hypothesis.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/hypothesis. Accessed 4 May. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of hypothesis, medical definition, medical definition of hypothesis, more from merriam-webster on hypothesis.
Nglish: Translation of hypothesis for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of hypothesis for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about hypothesis
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, how to use accents and diacritical marks, popular in wordplay, 12 star wars words, the words of the week - may 3, 9 superb owl words, 10 words for lesser-known games and sports, your favorite band is in the dictionary, games & quizzes.

Hypothesis Words
Words related to hypothesis.
Below is a massive list of hypothesis words - that is, words related to hypothesis. The top 4 are: theory , supposition , conjecture and speculation . You can get the definition(s) of a word in the list below by tapping the question-mark icon next to it. The words at the top of the list are the ones most associated with hypothesis, and as you go down the relatedness becomes more slight. By default, the words are sorted by relevance/relatedness, but you can also get the most common hypothesis terms by using the menu below, and there's also the option to sort the words alphabetically so you can get hypothesis words starting with a particular letter. You can also filter the word list so it only shows words that are also related to another word of your choosing. So for example, you could enter "theory" and click "filter", and it'd give you words that are related to hypothesis and theory.
You can highlight the terms by the frequency with which they occur in the written English language using the menu below. The frequency data is extracted from the English Wikipedia corpus, and updated regularly. If you just care about the words' direct semantic similarity to hypothesis, then there's probably no need for this.
There are already a bunch of websites on the net that help you find synonyms for various words, but only a handful that help you find related , or even loosely associated words. So although you might see some synonyms of hypothesis in the list below, many of the words below will have other relationships with hypothesis - you could see a word with the exact opposite meaning in the word list, for example. So it's the sort of list that would be useful for helping you build a hypothesis vocabulary list, or just a general hypothesis word list for whatever purpose, but it's not necessarily going to be useful if you're looking for words that mean the same thing as hypothesis (though it still might be handy for that).
If you're looking for names related to hypothesis (e.g. business names, or pet names), this page might help you come up with ideas. The results below obviously aren't all going to be applicable for the actual name of your pet/blog/startup/etc., but hopefully they get your mind working and help you see the links between various concepts. If your pet/blog/etc. has something to do with hypothesis, then it's obviously a good idea to use concepts or words to do with hypothesis.
If you don't find what you're looking for in the list below, or if there's some sort of bug and it's not displaying hypothesis related words, please send me feedback using this page. Thanks for using the site - I hope it is useful to you! 🐗
- supposition
- speculation
- explanation
- scientific method
- proposition
- theoretical
- hypothetical
- possibility
- experiments
- scientifically
- correlation
- evolutionary
- observation
- historicism
- scientific theory
- formal logic
- hypothesize
- empirical evidence
- extrapolation
- mechanistic
- galileo galilei
- evolutionary theory
- laboratory experiments
- plausible explanation
- epidemiological studies
- observational studies
- conclusively
- null hypothesis
- conspiracy theory
- darwin theory
- meta analysis
- genetic predisposition
- falsifiability
- definitively
- interpretation
- conclusions
- mathematical models
- causal relationship
- working hypothesis
- assumptions
- incontrovertible
- immunological
- suppositions
- authors conclude
- epidemiological
- counter intuitive
- probabilities
- circumstantial
- computer simulations
- randomized trials
- phenomenology
- hypothesized
- empirically
- formulation
- correlations
- experimentally
- justification
- experimentation
- methodology
- conjectural
- probability
- generalization
- implication
- characterization
- presumption
- abnormality
- predisposition
- probabilistic
- phenomenological
- mathematical
- distinguishes
- morphological
- computability
- ratiocination
- variability
- conjectured
- qualitative
- approximation
- generalized
- calculation
- structuralism
- theoretical account
- generalisation
- transcendentalism
- presumptive
- counterfactual
- dialectical
- contentions
- philosophic
- rationality
- metaphysics
- rationalism
- philosophize
- stoichiology
- mitochondrial
- climatology
- philosophical
- deliberation
- pathogenesis
- philosopher
- ratiocinate
- epistemology
- counterfactual conditional
- interpolation
- authenticate
- deconstruction
- consideration
- formal system
- postulation
- psychological
- theoretician
- disconfirmation
- deliberative
- logical consequence
- neuroscience
- pseudoscience
- conceptualization
- anthropology
- philip wadler
- systematics
- presupposition
- behaviorism
- prokaryotes
- verifiability
- deflationary
- preconception
- conceptional
- theatre of ancient greece
- ancient greek
- technoscience
- antiscience
- multiscience
- scienceless
- subvocalization
- bionanoscience
- second guess
- phylogenies
- macroevolution
- abiogenesis
- atherogenesis
- hermaphroditism
- multicellularity
- coevolution
- parapsychological
- microevolution
- sociobiology
- endosymbiosis
- anthropoids
- dedifferentiation
- paleoecology
- catastrophism
- introgression
- determinist
- superorganism
- thermoregulation
- autoregulation
- counterargument
- self evident
- mathematical logic
- robert bellarmine
- falsificationism
- mathematical model
- verificationism
- conceptual framework
- existential quantification
- mathematical statement
- universal quantification
- philosophy of science
- philosophical doctrine
- hard science
- natural history
- verifiability principle
- non sequitur
- social science
- have reason
- determine truth
- exact science
- logical argument
- formal science
- philosophy of mind
- critical think
- cognitive science
- school subject
- theoretical physic
- beg question
- impact statement
- scientific discipline
- topic category
- deductive reasoning
- cross examine
- punctuated equilibrium
- assortative mating
- suppressor gene
- gaia hypothesis
- electron microscopic
- quantum theory
- general relativity
- quantum chromodynamics
- karl popper
- circumstantial evidence
- confirmation holism
- conventional wisdom
- thought experiment
- crucial experiment
- imre lakatos
- exploratory research
- paul feyerabend
- statistical test
- sample size
- deductive-nomological model
- carl gustav hempel
- alternative hypothesis
That's about all the hypothesis related words we've got! I hope this list of hypothesis terms was useful to you in some way or another. The words down here at the bottom of the list will be in some way associated with hypothesis, but perhaps tenuously (if you've currenly got it sorted by relevance, that is). If you have any feedback for the site, please share it here , but please note this is only a hobby project, so I may not be able to make regular updates to the site. Have a nice day! 🕸
- Search Menu
- Advance articles
- EJIL: Talk!
- The Podcast!
- EJIL: Live!
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- Why Publish?
- About European Journal of International Law
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Article Contents
1 introduction, 2 an overview of the book, 3 eppur si muove, shai dothan, review of product kanstantsin dzehtsiarou. can the european court of human rights shape european public order.
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Shai Dothan, Shai Dothan, Review of product Kanstantsin Dzehtsiarou. Can the European Court of Human Rights Shape European Public Order? , European Journal of International Law , 2024;, chae020, https://doi.org/10.1093/ejil/chae020
- Permissions Icon Permissions
An old parable shows the importance of focusing on understanding actions and their motivations instead of focusing on words. The British king goes hunting with his entourage. Suddenly, one of the king’s servants runs out of a bush, and when he sees the king aiming his gun at him, he screams: ‘Don’t shoot me. I am not a deer.’ The king takes careful aim and shoots the servant dead. While everyone is rushing to the servant’s dead body, a baron asks the king: ‘Why did you shoot him? He said he is not a deer.’ ‘Really?’ the king said. ‘I thought he screamed: Shoot me, I am a deer.’ The king clearly has a hearing problem, but the reason he shot the servant has nothing to do with his hearing. It has everything to do with his decision to listen to what he thought the servant said instead of building a reasonable theory of the identity of the English-speaking creature in his sights.
This review of Kanstantsin Dzehtsiarou’s carefully researched and clearly written book argues that the book also perhaps gives too much emphasis to what the European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR) is saying and not enough emphasis given to what the court is doing. The book focuses on the language that judges use in their judgments and interviews – in particular, their use of the term ‘European public order’. Even when an impressive array of evidence is gathered by Dzehtsiarou to show that this phrase means close to nothing, the book continues to focus on what the phrase could mean. The book not only tries to define European public order, but it also tries to examine a variety of potential interpretations of this term and to check them against the Court’s doctrines and legal techniques. But the most interesting enigma that emerges from the many details in the book is that the phrase ‘European public order’ is repeated so consistently by the Court despite its ambiguous nature. This review argues that such repetition may involve a long-term strategy on the part of the Court.
Although the book tries to prove that the ECtHR cannot act strategically as a unified actor because of the diverse motives of the actors, this argument is unconvincing. To adopt a strategy as the most reasonable explanation for a court’s behaviour, it is not necessary to ascertain exactly the motives of every individual judge involved. Instead, it is possible to infer judicial strategy when it provides the best possible explanation for the Court’s actions. The very fact that a meaningless phrase like ‘European public order’ is repeated so consistently by the Court and its judges hints that perhaps certain behaviours of the Court are designed to serve long-term goals, such as preserving its legitimacy with certain audiences by using commonly accepted forms of reasoning.
This review explores the difference between building a theory about the ‘true’ meaning of abstract legal terms and building a theory about the strategy motivating institutions. It argues that the study of international courts generally could benefit from a focus on the latter kind of investigation.
In Can the European Court of Human Rights Shape European Public Order? , Dzehtsiarou shows that the ECtHR refers to the term ‘European public order’ on numerous occasions. The Court repeatedly declares that the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR) is a constitutional instrument of European public order. However, despite the apparent fundamental importance of the term, the book demonstrates that the term ‘European public order’ is incredibly vague and that its meaning is unclear. The book proves this consistently in a series of detailed steps. In Chapter 2, the book recounts Dzehtsiarou’s search for all judgments that refer to European public order. The judgments are categorized by topic, and every example of a judgment that refers to European public order is analysed with the legal context of that particular case. The different topics that Dzehtsiarou finds that refer to European public order are: (i) the Court’s territorial jurisdiction; (ii) the interaction of the Court with other international organizations; (iii) the binding force of the ECtHR’s interim measures; (iv) the criteria for admissibility of applications at the Court; (v) democracy as an aspect of the European public order; and (vi) the scope of the substantive provisions of the ECHR. The book’s analysis of judgments is rich and, beyond supporting its argument, provides a useful overview of many of the ECtHR’s doctrines of interest to anyone keen on understanding the Court’s methods of reasoning.
Based on this analysis of judgments, Dzehtsiarou considers that there are several potential roles for the term ‘European public order’: (i) the term can be used to imply that the ECHR applies all over the territory of Europe; (ii) the term can be used to shape the interpretation of substantive rights in the ECHR; (iii) the term can be used to justify procedural innovation that would allow the ECtHR to expand its authority; and/or (iv) the term can be used to signal the relative importance of a right compared to others. All these possible roles of the term ‘European public order’ are shown by Dzehtsiarou to be unhelpful when they are applied in the ECtHR judgments.
As Dzehtsiarou shows in this chapter, the way in which the term is used is too abstract to assist in judicial interpretation because it can easily lead to contradictory results. For example, in situations that involve a balancing between certain rights, the only way to determine which right should receive priority is by stipulating which right is more essential for European public order. Because the Court does not specify which rights are crucial for European public order, it does not provide any guidance on the proper result of balancing conflicting rights.
Chapter 3 looks at the term ‘public order’ in a variety of other contexts: the ECHR and its protocols, private international law and national law. The chapter shows that the term either has a different meaning in these settings than it has in the ECtHR’s judgments or it is amorphous and imprecise in other contexts as well. For example, the ECHR refers to public order to indicate only the idea of preventing disorder to protect the societies of member states, but this is not the same way the term is used in the Court’s judgments, which refer to European public order rather than to the public order that is internal to states. Further, at a national level, the concept of public order is amorphous and changes constantly. The chapter also argues that to be considered a useful concept, public order should comply with the following benchmarks: it should protect a common set of values, it should attempt to protect against some external intervention, it should set a hierarchy of human rights and it should have a viable enforcement mechanism to support its application. The ECtHR does not fully comply with any of these conditions regarding the use of the concept ‘European public order’.
Dzehtsiarou then turns to the question of the legitimacy of the Court in Chapter 4, arguing that this will be undermined should the ECtHR attempt to shape the European public order; it is not a proper function for a court to undertake this task precisely because of the term’s vagueness. Dzehtsiarou argues that courts fulfil a technical function of resolving cases and a meta-function of implementing more abstract goals, such as developing the law within their jurisdiction. Were the ECtHR to view the promotion of a vague notion of a European public order as one such meta-function, this attempt could only fail and, as a result, damage the Court’s legitimacy. Dzehtsiarou identifies two reasons for this failure: (i) the term ‘European public order’ is too vague to create a clear programme for the Court; and (ii) there is no agreement by either scholars or judges that promoting European public order ought to be the purpose of the Court at all, and, therefore, attempting to promote this goal may be considered illegitimate by the member states.
Developing this idea further, Chapter 5 surveys the legal techniques, such as pilot judgments, that allow the ECtHR to set broad standards of behaviour across Europe. As Dzehtsiarou’s argument goes, even if the term ‘European public order’ is too vague to be useful, the goal of shaping public order could be understood as attempting to reach the more clearly defined goal of promoting rules of general application in Europe. This more specific goal could be supported by integrating new legal techniques in the Court’s judgments. In his examination of the Court’s jurisprudence, Dzehtsiarou shows that doctrinal innovations such as the procedure of pilot judgments and the increasing use of interim measures help the Court promote general rules across Europe. This chapter also shows some of the ECHR’s reform efforts that have been initiated by the contracting parties and examines what they are directed at doing. Dzehtsiarou explains that some of these reforms do not seem dedicated to allowing the ECtHR to develop rules that can be generally applied in Europe. For example, Protocol no. 15 to the Convention puts greater emphasis on subsidiarity and the margin of appreciation. 1 These are doctrines that promote judicial restraint, limiting the ability of the ECtHR to mould a European public order by developing general legal rules. Other reforms, in contrast, have given the Court new tools that could potentially help it to develop European public order such as extending the use of advisory opinions in Protocol no. 16 and creating an infringement procedure at the ECtHR in Protocol no. 14. 2 The effectiveness of these tools in shaping European public order, however, is still questionable.
The next chapter moves from examining what judges say in the judgments they author to what they say in interviews that Dzehtsiarou conducted with them, providing a different perspective on the intentions of judges. Chapter 6 describes numerous interviews that Dzehtsiarou conducted with judges that reveal they are far from uniform in their views about the Court’s role vis-à-vis the promotion of European public order. The chapter explains that unclear terms like European public order are repeated without any guiding strategy and spread through the Court’s jurisprudence in what Dzehtsiarou calls the ‘Brownian motion’ of legal terms.
Dzehtsiarou’s book argues that the ECtHR cannot shape the European public order both because this term is too vague to be useful and because the Court cannot behave strategically in the manner required to shape European public order. Both claims combine to show that, despite the frequent reference to European public order, the term does not serve a major role in shaping the ECtHR’s case law. However, while the first claim is convincingly argued for, there are weaknesses in the argument for the second claim. In addition to the vagueness of the term European public order, Dzehtsiarou’s book provides a series of reasons why setting out to achieve a coherent European public order is a bad goal for the ECtHR. Among these reasons is the claim that the Court should defer to the states to protect its legitimacy, given that the Court does not have an effective enforcement mechanism and consequently must rely on legitimacy to secure compliance. Furthermore, the Court is not designed to be a constitutional court that sets general standards for the conduct of European states. These reasons seem sensible and can certainly be supported by some of the Court’s jurisprudence, as the book demonstrates well.
However, Dzehtsiarou’s book also claims that the ECtHR cannot behave strategically, in general. This explicit claim rests on other arguments that are not as convincing. The book explains that the Court has 47 judges (although, at the time of writing, it is 46 after the Russian judge’s position was eliminated), each of whom is equal and independent from the others. In addition, the Court’s presidents, who could potentially lead a more unified strategy, have limited powers, and they change frequently. To this must be added Dzehtsiarou’s observation that the judges disagree with each other about the goals of the Court, preventing the possibility of forming a united strategic body.
Yet this only suggests that it is difficult to locate a particular person who exercises strategy in the ECtHR or a particular position from which such a strategy can be applied. This does not mean that the Court does not behave as if it is motivated by some underlying strategy. The economist Milton Friedmann explained that, when a scholar describes a complicated phenomenon, such as the existence of strategic behaviour, they should do so not by explaining accurately all the mechanisms that lead to this behaviour. Instead, the scholar should adopt assumptions about reality that lead to hypotheses that accurately predict the phenomenon. 3 The ECtHR is not a rational individual; it is a court that is led by many people with their own interests and wishes. But if assuming the Court behaves rationally can help to describe its behaviour based on the hypothesis that the Court is motivated by a certain strategy, then the best possible description of the Court is that it follows that strategy. Identifying a strategic trend in the Court’s judgments does not indicate that all or any of the people involved in shaping the Court’s judgments are fully aware of the trajectory of the Court, associate it with some strategic goal and consciously navigate the Court towards this goal. However, trends that seem to serve a certain logic indicate that the Court as an institution can be explained as if it is rationally and strategically pursuing a certain goal.
If there is no possible mechanism for collective behaviour that could support strategic behaviour by the ECtHR, this implies that scholars need to reject any description of the Court as behaving strategically. However, Dzehtsiarou’s book does not prove that mechanisms that allow for strategic behaviour by the Court are impossible, only that these mechanisms are unknown. Dzehtsiarou also argues that a few potential forms of strategy, such as the collective action of the judges to consciously promote a common vision of European public order, are unlikely. Nevertheless, the book provides proof that judges can and do follow each other without the guiding hand of any individual. If that is true, this means that strategies can evolve spontaneously and be practised by judges who follow other judges who either devised a strategy or just luckily stumbled upon a form of behaviour that is useful for the Court or for themselves. The proof that judges do follow each other and, hence, can follow behavioural trends without a clear common intention comes from what the book calls the ‘Brownian motion’ of the concept of European public order. The ‘Brownian motion’ is the phenomenon of repeatedly referring to the concept of European public order in a variety of new circumstances without proper attention to the context in which the concept was born. Many different judges use the same terminology again and again without sharing any conscious goal for their practice. This type of behaviour proves that judges mimic each other, at least some of the time.
But if judges mimic each other when they refer to a common argument without any grand plan that they are aware of, as Dzehtsiarou’s book suggests, why would they not follow each other without being aware of the general strategy in other cases? Specifically, if there are actions that could help the reputation and legitimacy of the Court, perhaps judges can engage in these actions repeatedly, even if not all judges are fully aware of the consequences of these actions? For example, scholars have observed that, when courts are criticized by powerful political adversaries, judges tend to write fewer dissenting opinions. 4 There is no memo sent to the judges telling them to dissent less and agree more. But maybe some judges realize that dissents are counterproductive when they inflame the criticism of the Court, lead to unwanted attention 5 or increase the chances of overruling. 6 Their colleagues copy them and do the same. The Court as a whole would behave in a strategic manner that would help it to avoid backlash, with few judges or, possibly, even no judges at all articulating this goal and the means to achieve it.
To demonstrate a strategy in the behaviour of the ECtHR, it is not necessary to expose all the mechanisms of influence between the judges and other staff. It is only necessary to make the assumption that the Court is behaving as a strategic actor and to devise hypotheses about the way in which the Court would be expected to behave. If these hypotheses are confirmed by observation of the Court’s behaviour, the assumption that the Court behaves strategically should be adopted. As mentioned, describing the Court as if it followed a strategy does not require identifying the individuals that lead the Court and engage in strategic behaviour. This is not to say that there is no evidence supporting the view that there are individuals in the Court with strategic ideas or the ability to fulfil them. Some presidents have been dominant in terms of their intellectual observation or agenda about the Court’s future. Good examples are President Luzius Wildhaber and President Robert Spano who charted a vision for the Court even in their academic writing. 7 Furthermore, the fact that the Court’s registrar directly controls the entire legal staff gives the registrar plenty of power to strategize by centrally shaping the opinions signed by many judges at the same time. The legal staff, and the registrar who controls them, have substantial power to influence judgments because the staff is absolutely essential for the work of many judges. Many judges need the help of their staff even to fully comprehend texts in English and French, the Court’s two official languages. 8
But the point of this review is not that there are influential individuals with a coherent strategy for leading the ECtHR. The point is that it does not matter what judges say or think if the aim is to build a theory of the Court’s behaviour. If the goal is to establish a theory of the ECtHR’s behaviour, then the relevant question is whether there is evidence that shows strategic behaviour that explains the Court’s actions because it concurs with the available observations of these actions. Dzehtsiarou’s book does not provide any reason to think that the Court does not act as if it is strategic. On the contrary, by proving that a peculiar phrase – European public order – is used repeatedly without anyone knowing why, the book proves that at least some strategy that is fully acknowledged by no one may certainly be considered the best explanation for the behaviour of the Court.
In conclusion, based on the rich and detailed information about the practice of the ECtHR provided by Dzehtsiarou, one cannot rule out the possibility that the ECtHR behaves strategically. A strategic explanation may describe a variety of the ECtHR’s practices, including the strange practice of repeating certain forms of reasoning that mean very little. This review does not attempt to provide a full explanation for why the particular phrase ‘European public order’ is used. A potential guess is that, to sustain the feeling of a mutual endeavour, the judges need to share some form of terminology that they do not understand. Analysing the meaning of this terminology itself will not serve to decipher the strategy of the Court. But exposing the fact that this terminology persists despite being incredibly vague, as Dzehtsiarou’s book does with great care, provides the first step towards a theory that would view the ECtHR as a unified actor acting strategically to maintain its legitimacy by repeatedly using a certain set of terms.
I thank Patrick Barry for useful discussions of this review. This research is funded by the Danish National Research Foundation Grant no. DNRF105 and conducted under the auspices of iCourts, the Danish National Research Foundation’s Centre of Excellence for International Courts.
Protocol no. 15 to the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms 2013, ETS 213.
Protocol no. 14 to the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms 2004, ETS 194; Protocol no. 16 to the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms 2013, ETS 214.
See Friedman, ‘The Methodology of Positive Economics’, in D.M. Hausman (ed.), The Philosophy of Economics: An Anthology (3rd edn, 2007) 145 , at 153–154 (arguing that assumptions need to be checked not by their truth value but, rather, by their ability to lead to a good hypothesis).
See Post, ‘The Supreme Court Opinion as Institutional Practice: Dissent, Legal Scholarship, and Decisionmaking in the Taft Court’, 85 Minnesota Law Review (2001) 1267, at 1314–1319 (arguing that, in the first half of the 1920s, the US Supreme Court suppressed dissents because of heavy criticism against it. When the criticism of the Court decreased, dissents appeared again. In addition to the strategic reason that could explain the tendency of the Court as a whole, the article suggests a variety of personal reasons such as the leadership of Chief Justice Taft and the composition of the Court, at 1319–1328).
See R.A. Posner, How Judges Think (2008), at 32.
See Fuld, ‘The Voices of Dissent’, 62 Columbia Law Review (1962) 923, at 927.
See, e.g., Wildhaber, ‘The European Court of Human Rights: The Past, The Present, The Future’, 22 American University International Law Review (2007) 521; Spano, ‘The Rule of Law as the Lodestar of the European Convention on Human Rights: The Strasburg Court and the Independence of the Judiciary’, 27 European Law Journal (2021) 211 .
See McKaskle, ‘The European Court of Human Rights: What It Is, How It Works, and Its Future’, 40 University of San Francisco Law Review (2005) 1, at 26–31.
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1464-3596
- Print ISSN 0938-5428
- Copyright © 2024 EJIL
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Android Police
How to write word macros.
Record macros for your repetitive tasks and draft your Word documents in no time
Word macros are one-click marvels that automate repetitive tasks in Microsoft Word. If you are tired of going through the same routine while drafting documents, create macros and finish your tasks quickly. Word macros save mouse clicks and keyboard strokes in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications). It may sound complex at a glance, but it isn't. Microsoft made it easy to write macros without any programming knowledge.
You can record Word macros using the desktop apps only. The feature isn't available in Word for iPhone and Android users. Here's how to write Word macros and streamline tedious and time-consuming tasks.
How to create, record, and run Excel macros
Tips to plan for effective macros.
Before you record a macro in Word, plan it in advance. You need a clear idea of which actions you want to record in a macro.
A macro recorder captures everything. A single mishap can ruin your outcome. Instead of deleting and starting a macro again, practice it several times. For instance, if you insert the wrong picture, remove it and add the correct one again. Word records it and performs the same when you run a macro. Here are the things to consider before writing a macro.
- Plan your action and memorize steps before recording a macro.
- Memorize keyboard shortcuts for popular text editing features. Word doesn't record your mouse for navigation in a document area. It should create a smooth macro.
- Trim the number of steps in a macro to keep it efficient.
- Test your macro a couple of times to get your output as expected.
Common examples of Word macros
Are you still confused about using macros in Microsoft Word? Check out some of the usual use cases for Word macros.
- Enter common text: Insert usual text like a company address, terms and conditions, disclaimers, and more with a macro.
- Check grammar and spell check: Run a grammar check with a single click.
- Remove the clutter from the document: Fix formatting issues, spaces, line breaks, and more.
- Insert tables with a specific format: Insert tables with specific headers in one go.
- Generate Table of Contents: Create and update a table of contents.
These are some of the examples of using a macro. Your preferences may vary.
Record Word macros
In the example below, we create a Word macro to insert a table and write a legal disclaimer in a document.
- Launch Microsoft Word and create a new document.
- Go to the View tab and select Macros .
- Microsoft Word stores your macro. It's ready to use from the same menu.
You can use the assigned button or keyboard shortcut or open View > Macros > View macros , select a macro, and click Run . Then, run it to confirm your desired output with a newly created macro.
If you are a developer and familiar with VBA, press Alt + F11 to open Visual Basic. Then, write a new macro from the Insert > Module menu.
Advantages of writing Word macros
Here are the top benefits of using a Word macro.
- Reduces errors in a document.
- Speed up repetitive tasks.
- Creates consistency in documents.
- Endless possibilities.
- Saves time and improves productivity for complex tasks in a document.
Macros require a learning curve. We recommend spending time with them to create useful macros for your routine tasks.
Manage Word macros
When you click Stop recording under the Macros menu, Word saves the recording automatically. You can't test and save it manually. If you want to edit or delete an existing macro, use the steps below.
Enjoy a productivity boost with Word macros
If recording macros is complicated, import one from the web. When you download a document containing macros from the web and open it on your computer, Word blocks macros due to security concerns. If you trust the document source, head to Word settings and enable macros .
trending now in World News

Israeli hostage, 18, says Hamas captor wanted to marry, have...

Hamas leader says proposed cease-fire deal closest to meeting...

Over 6,000 Russian troops killed in six-day period bringing death...

Creepy love den of Hitler's propaganda chief Joseph Goebbels...

Elderly American couple stranded in Spain after Norwegian Cruise...

Shocking video shows the moment beauty queen is gunned down after...

These three words may reveal when Kate Middleton will return to...

North Korea propaganda song praising Kim Jong Un going viral on...
Over 6,000 russian troops killed in six-day period bringing death toll to nearly 500k since war began.
- View Author Archive
- Get author RSS feed
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
An estimated 1,260 Russian troops were killed on the battlefield Saturday – the sixth straight day Russia lost over 1,000 men to fighting, according to new estimates.
The slaughter brings the total Russian deaths to nearly 500,000 troops since Vladimir Putin launched his full-scale invasion on Ukraine more than two years ago.
The figures from the general staff of Ukraine’s Armed Forces were validated by the United Kingdom’s Ministry of Defense in a statement Saturday.
With a depleted fighting force, Russia has started actively recruiting women for the war, The New York Times reported, even extending the efforts into prisons.

Recruitment is also an issue for Ukraine’s military, which has started tracking down draft evaders, The Guardian reported.
In addition to the heavy loss of personnel, Russia has also lost 7,366 tanks, 348 airplanes, 325 helicopters, 9,611 drones, 26 ships and boats, and one submarine since the start of the war.
These latest estimates come as Ukraine claimed to have downed 13 drones launched overnight from the Russian region of Belgorod on the northeastern border of Ukraine. Kyiv also claimed it shot down another Russian Su-25 fighter jet over the eastern region of Donetsk on Saturday, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky said, the Kyiv Independent reported .

Falling drone debris injured six people – including two women and a child – on the ground, and started fires at residential and office buildings in Kharkiv, according to reports .
The Independent further reported that Russia also fired four surface-to-air guided missiles toward Ukraine, but it was unclear if they reached any of their intended targets.
Meanwhile, new drone footage showed the devastation wrought on Ocheretyn, a small village in eastern Ukraine that has been overtaken by Russian troops.

The footage shows no signs of life on the ground and virtually every building in the village has been destroyed as Russia continues its brutal campaign.
In other developments:
- Zelensky said he’s willing to consider an all-for-all prisoner of war exchange with Russia, and is expected to discuss the proposal at the upcoming Peace Summit in Switzerland in June. “All reasonable countries support this route,” Zelensky said Friday, adding P.O.W. swaps have been occurring, “but they are slower than we would like.”
- The United States and the G-7 are reportedly mulling a $50 million aid package for Ukraine , utilizing the windfall profits from frozen, interest-accruing Russian assets. G-7 leaders will met next month in Italy.
- Ukraine’s warfare wish list is long, but at the top is the MQ-9 Reaper reconnaissance drone. The U.S.-made drones would help Ukraine better identify targets and conduct surveillance operations, Politico reported . However, U.S. officials fear Russia could shoot the $30 million drones down and gain valuable intelligence.
- Russian officials claim NATO is planning for war with the nation, and pointed to military drills, being carried out for months near the Russian border as proof.
- A Ukrainian security official said sea baby drones – unmanned aquatic vessels designed to explode upon impact – are key to the nation’s ongoing defense strategy. The drones have been used to target the 12-mile long, $3 billion-to-construct Crimean Bridge, which the official said is “ doomed .”
With Post wires
Share this article:

Advertisement
Vietnamese backpacker Joy finds community in the outback town of Birdsville
Joy Nguyệt says arriving in outback Queensland from Vietnam to swarms of flies in an isolated and dusty town was initially terrifying.
"I was a bit worried at that time and I sent a picture to my parents, and they said I cannot stay here," she said.
"They said, 'Where are the people?' There's nothing."
The 29-year-old landed in Birdsville, 1,500 kilometres west of Brisbane, expecting a bustling airport but instead walked straight off the runway and across the road to the local hotel.
But it's been seven months and Joy, or Ánh as she's known back home, has chosen to extend her stay in the small outback town.
Birdsville, with its population of 110, is situated on the edge of the Munga-Thirri Simpson desert and is known for its rolling red sand dunes and events like the Big Red Bash.
But it's the locals and day to day life working at the roadhouse that have Joy hooked.
"I like the life, I like the people," she said.
"You get to know them better than living in a city."
Learning in more ways than one
Joy was working remotely as a recruiter when she felt it was time for a new adventure, and decided to travel to Australia on a working holiday visa.
She saw a post on a community Facebook page from a previous Vietnamese employer at the town's roadhouse, a one-stop shop for fuel, groceries, and a friendly conversation.
"Every people [sic] in town come to the roadhouse to buy things and I get to know people that way," she said.
True to her name, the locals love her, and some are even teaching her how to drive.
Resident Greg Watkins spends his Sunday afternoons jumping in the car with Joy.
Like many people in town, Mr Watkins wears many hats and refers to himself as an "odd jobs man".
"I thought, 'Well there's no driving instructors out here' and rather than her jumping in a car and driving around vacant country roads, she needs to learn how to drive correctly," he said.
Driving around the streets of Birdsville – or street rather – is quite different to driving in the city.
"We've only got two give way signs in town and no roundabouts.
"I try and create traffic for her while she's driving, and I'll say there's a car on your right."
Mr Watkins says Joy is a quick learner.
"I call her a bit of a sponge, ever since she's got here she's wanted to learn things and takes a lot of things in," he said.
"She's come from a community where there's lots and lots of people, to a town where there's very few.
"She worked right through the summer in 40 degrees, day after day, and didn't complain."
Word of mouth keeps outback businesses staffed
Backpackers like Joy keep the outback turning, particularly in the busy season.
A couple of hundred kilometres away, Windorah has a population of about 100 people and, like Birdsville, can see tens of thousands travel through during the tourist season between April and October.
Marilyn Simpson, the owner of the only pub in town, said they "need the backpackers to be able to function".
"There were some scary times post-COVID when so many people hit the outback and we couldn't do it, we didn't have the staff," she said.
While numbers are "back to normal" now, things are set to change yet again.
From July 1, British backpackers — who make up the largest population of working holiday makers – will no longer have to complete 88 days of regional work, prompting fears of an outback worker shortage.
But Ms Simpson isn't too concerned.
"This year I've got predominantly Italian and Argentinian and that is because of … word of mouth."
Reputation travels fast in the world of backpacking – one worker from last season recommends a friend for the next, until the pub is filled with Argentinian backpackers.
Ms Simpson said she prefers this method rather than hiring through agencies, which she calls a "costly exercise".
"I like meeting them and sharing our culture and sharing their experience," she said.
ABC Western Qld — local news in your inbox
- X (formerly Twitter)
Related Stories
Fears visa change for british backpackers spells trouble for outback businesses.
Green carpet rolled out for tourists heading to the outback as desert disappears
A $300,000 redundancy gamble switched Greg's 'vanilla life' into rockstar mode
- Multiculturalism

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Developing a hypothesis (with example) Step 1. Ask a question. Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project. Example: Research question.
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
Another example for a directional one-tailed alternative hypothesis would be that. H1: Attending private classes before important exams has a positive effect on performance. Your null hypothesis would then be that. H0: Attending private classes before important exams has no/a negative effect on performance.
Associative Hypothesis Examples. There is an association between the number of hours spent on social media and the level of anxiety in teenagers. Daily consumption of green tea is associated with weight loss in adults. The frequency of public transport use correlates with the level of urban air pollution.
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process. Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test ...
A hypothesis is a tentative, testable answer to a scientific question. Once a scientist has a scientific question she is interested in, the scientist reads up to find out what is already known on the topic. Then she uses that information to form a tentative answer to her scientific question. Sometimes people refer to the tentative answer as "an ...
3. Simple hypothesis. A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, "Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking. 4.
An effective hypothesis in research is clearly and concisely written, and any terms or definitions clarified and defined. Specific language must also be used to avoid any generalities or assumptions. Use the following points as a checklist to evaluate the effectiveness of your research hypothesis: Predicts the relationship and outcome.
Examples. A research hypothesis, in its plural form "hypotheses," is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
Learning how to write a hypothesis comes down to knowledge and strategy. So where do you start? Learn how to make your hypothesis strong step-by-step here.
Definition: Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation. Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments ...
Here are some good research hypothesis examples: "The use of a specific type of therapy will lead to a reduction in symptoms of depression in individuals with a history of major depressive disorder.". "Providing educational interventions on healthy eating habits will result in weight loss in overweight individuals.".
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes - specificity, clarity and testability. Let's take a look at these more closely.
Hypothesis-testing (Quantitative hypothesis-testing research) - Quantitative research uses deductive reasoning. - This involves the formation of a hypothesis, collection of data in the investigation of the problem, analysis and use of the data from the investigation, and drawing of conclusions to validate or nullify the hypotheses.
Synonyms for HYPOTHESIS: theory, thesis, proposition, premise, assumption, suggestion, guess, supposition; Antonyms of HYPOTHESIS: fact, knowledge, assurance, certainty
The Royal Society - On the scope of scientific hypotheses (Apr. 24, 2024) scientific hypothesis, an idea that proposes a tentative explanation about a phenomenon or a narrow set of phenomena observed in the natural world. The two primary features of a scientific hypothesis are falsifiability and testability, which are reflected in an "If ...
There are 5 main steps in hypothesis testing: State your research hypothesis as a null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis (H o) and (H a or H 1 ). Collect data in a way designed to test the hypothesis. Perform an appropriate statistical test. Decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis. Present the findings in your results ...
5.2 - Writing Hypotheses. The first step in conducting a hypothesis test is to write the hypothesis statements that are going to be tested. For each test you will have a null hypothesis ( H 0) and an alternative hypothesis ( H a ). When writing hypotheses there are three things that we need to know: (1) the parameter that we are testing (2) the ...
hypothesis: [noun] an assumption or concession made for the sake of argument. an interpretation of a practical situation or condition taken as the ground for action.
Theory vs. Hypothesis: Basics of the Scientific Method. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Jun 7, 2021 • 2 min read. Though you may hear the terms "theory" and "hypothesis" used interchangeably, these two scientific terms have drastically different meanings in the world of science.
Below is a massive list of hypothesis words - that is, words related to hypothesis. The top 4 are: theory, supposition, conjecture and speculation. You can get the definition(s) of a word in the list below by tapping the question-mark icon next to it. The words at the top of the list are the ones most associated with hypothesis, and as you go ...
The book focuses on the language that judges use in their judgments and interviews - in particular, their use of the term 'European public order'. ... But if assuming the Court behaves rationally can help to describe its behaviour based on the hypothesis that the Court is motivated by a certain strategy, then the best possible description ...
Check out some of the usual use cases for Word macros. Enter common text: Insert usual text like a company address, terms and conditions, disclaimers, and more with a macro.
Now when you ask Copilot a question in Word chat, an answer will be generated using the rich, people-centric data and insights in the Microsoft cloud and Microsoft Graph. That way, you can stay in the app and maintain focus on creating your document. A blank Word document with Copilot open on the side.
Russia's also lost an estimated 7,366 tanks, 348 airplanes, 325 helicopters, 9,611 drones, 26 ships and boats, and one submarine since the start of the war.
Word of mouth keeps outback businesses staffed. Backpackers like Joy keep the outback turning, particularly in the busy season. A couple of hundred kilometres away, Windorah has a population of ...