An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.9(7); 2013 Jul


Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
Marco pautasso.
1 Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France
2 Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,

The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
Researching and writing for Economics students
4 literature review and citations/references.

Figure 4.1: Literature reviews and references
Your may have done a literature survey as part of your proposal. This will be incorporated into your dissertation, not left as separate stand-alone. Most economics papers include a literature review section, which may be a separate section, or incorporated into the paper’s introduction. (See organising for a standard format.)
Some disambiguation:
A ‘Literature survey’ paper: Some academic papers are called ‘literature surveys’. These try to summarise and discuss the existing work that has been done on a particular topic, and can be very useful. See, for example, works in The Journal of Economic Perspectives, the Journal of Economic Literature, the “Handbook of [XXX] Economics”
Many student projects and undergraduate dissertations are mainly literature surveys.
4.1 What is the point of a literature survey?
Your literature review should explain:
what has been done already to address your topic and related questions, putting your work in perspective, and
what techniques others have used, what are their strengths and weaknesses, and how might they be relevant tools for your own analysis.

Figure 4.2: Take notes on this as you read, and write them up.
4.2 What previous work is relevant?
Focus on literature that is relevant to your topic only.
But do not focus only on articles about your exact topic ! For example, if your paper is about the relative price of cars in the UK, you might cite papers (i) about the global automobile market, (ii) about the theory and evidence on competition in markets with similar features and (iii) using econometric techniques such as “hedonic regression” to estimate “price premia” in other markets and in other countries.
Consider: If you were Colchester a doctor and wanted to know whether a medicine would be effective for your patients, would you only consider medical studies that ran tests on Colchester residents, or would you consider more general national and international investigations?
4.3 What are “good” economics journal articles?
You should aim to read and cite peer-reviewed articles in reputable economics journals. (Journals in other fields such as Finance, Marketing and Political Science may also be useful.) These papers have a certain credibility as they have been checked by several referees and one or more editors before being published. (In fact, the publication process in Economics is extremely lengthy and difficult.)
Which journals are “reputable”? Economists spend a lot of time thinking about how to rank and compare journals (there are so many papers written about this topic that they someone could start a “Journal of Ranking Economics Journals”. For example, “ REPEC ” has one ranking, and SCIMAGO/SCOPUS has another one. You may want to focus on journals ranked in the top 100 or top 200 of these rankings. If you find it very interesting and relevant paper published somewhere that is ranked below this, is okay to cite it, but you may want to be a bit more skeptical of its findings.
Any journal you find on JSTOR is respectable, and if you look in the back of your textbooks, there will be references to articles in journals, most of which are decent.
You may also find unpublished “working papers”; these may also be useful as references. However, it is more difficult to evaluate the credibility of these, as they have not been through a process of peer review. However, if the author has published well and has a good reputation, it might be more likely that these are worth reading and citing.
Unpublished “working papers”
You may also find unpublished “working papers” or ‘mimeos’; these may also be useful as references. In fact, the publication process in Economics is so slow (six years from first working paper to publication is not uncommon) that not consulting working papers often means not being current.
However, it is more difficult to evaluate the credibility of this ‘grey literature’, as they have not been through a process of peer review. However, if the author has published well and has a good reputation, it might be more likely that these are worth reading and citing. Some working paper series are vetted, such as NBER; in terms of credibility, these might be seen as something in between a working paper and a publication.
Which of the following are “peer-reviewed articles in reputable economics journals”? Which of the following may be appropriate to cite in your literature review and in your final project? 8
Klein, G, J. (2011) “Cartel Destabilization and Leniency Programs – Empirical Evidence.” ZEW - Centre for European Economic Research Discussion Paper No. 10-107
Spencer, B. and Brander, J.A. (1983) “International R&D Rivalry and Industrial Strategy”, Review of Economic Studies Vol. 50, 707-722
Troisi, Jordan D., Andrew N. Christopher, and Pam Marek. “Materialism and money spending disposition as predictors of economic and personality variables.” North American Journal of Psychology 8.3 (2006): 421.
The Economist,. ‘Good, Bad And Ugly’. Web. 11 Apr. 2015. [accessed on…]
Mecaj, Arjola, and María Isabel González Bravo. “CSR Actions and Financial Distress: Do Firms Change Their CSR Behavior When Signals of Financial Distress Are Identified?.” Modern Economy 2014 (2014).
Universities, U. K. “Creating Prosperity: the role of higher education in driving the UK’s creative economy.” London Universities UK (2010).
4.4 How to find and access articles
You should be able to find and access all the relevant articles online. Leafing through bound volumes and photocopying should not be neededs. (Having been a student in the late 90’s and 2000’s, I wish I could get those hours back.)

Figure 4.3: The old way!
Good online tools include Jstor (jstor.org) and Google Scholar (scholar.google.co.uk). Your university should have access to Jstor, and Google is accessible to all (although the linked articles may require special access). You will usually have the ‘most access’ when logged into your university or library computing system.If you cannot access a paper, you may want to consult a reference librarian.
It is also ok, if you cannot access the journal article itself, to use the last working paper version (on Google scholar find this in the tab that says “all X versions”, where X is some number, and look for a PDF). However, authors do not always put up the most polished versions, although they should do to promote open-access. As a very last resort, you can e-mail the author and ask him or her to send you the paper.
When looking for references, try to find ones published in respected refereed economics journals (see above ).
4.5 Good starting points: Survey article, course notes, and textbooks
A “survey article” is a good place to start; this is a paper that is largely a categorization and discussion of previous work on a particular topic. You can often find such papers in journals such as
- the Journal of Economic Perspectives,
- the Journal of Economic Surveys,
- and the Journal of Economic Literature.
These will be useful as a “catalog” of papers to read and considers citing. They are also typically very readable and offer a decent introduction to the issue or the field.
It is also helpful to consult module (course) notes and syllabi from the relevant field. Do not only limit yourself to the ones at your own university; many of universities make their course materials publicly accessible online. These will not only typically contain reading lists with well-respected and useful references, they may also contain slides and other material that will help you better understand your topic and the relevant issues.
However, be careful not to take material from course notes without properly citing it. (Better yet, try to find the original paper that the course notes are referring to.)
Textbooks serve as another extremely useful jumping off point. Look through your own textbooks and other textbooks in the right fields. Textbooks draw from, and cite a range of relevant articles and papers. (You may also want to go back to textbooks when you are finding the articles you are reading too difficult. Textbooks may present a simpler version of the material presented in an article, and explain the concepts better.)
4.6 Backwards and forwards with references
When you find a useful paper, look for its “family.” You may want to go back to earlier, more fundamental references, by looking at the articles that this paper cited. See what is listed as “keywords” (these are usually given at the top of the paper), and “JEL codes”. Check what papers this paper cites, and check what other papers cited this paper. On Google scholar you can follow this with a link “Cited by…” below the listed article. “Related articles” is also a useful link.
4.7 Citations
Keep track of all references and citations
You may find it helpful to use software to help you manage your citations
A storage “database” of citations (e.g., Jabref, Zotero, Endnote, Mendeley); these interface well with Google Scholar and Jstor
An automatic “insert citation” and “insert bibliography” in your word processing software
Use a tool like Endnote to manage and insert the bibliographies, or use a bibliography manager software such as Zotero or Jabref,
Further discussion: Citation management tools
List of works cited
Put your list of references in alphabetical order by author’s last name (surname).
Include all articles and works that you cite in your paper; do not include any that you don’t cite.
Avoiding plagiarism and academic offenses**
Here is a definition of plagiarism
The main point is that you need to cite everything that is not your own work. Furthermore, be clear to distinguish what is your own work and your own language and what is from somewhere/someone else.
Why cite? Not just to give credit to others but to make it clear that the remaining uncited content is your own.
Here are some basic rules:
(Rephrased from University of Essex material, as seen in Department of Economics, EC100 Economics for Business Handbook 2017-18, https://www1.essex.ac.uk/economics/documents/EC100-Booklet_2017.pdf accessed on 20 July 2019, pp. 15-16)
Do not submit anything that is not your own work.
Never copy from friends.
Do not copy your own work or previously submitted work. (Caveat: If you are submitting a draft or a ‘literature review and project plan’ at an earlier stage, this can be incorporated into your final submission.
Don’t copy text directly into your work, unless:
- you put all passages in quotation marks: beginning with ’ and ending with ’, or clearly offset from the main text
- you cite the source of this text.
It is not sufficient merely to add a citation for the source of copied material following the copied material (typically the end of a paragraph). You must include the copied material in quotation marks. … Ignorance … is no defence.’ (ibid, pp. 15 )
(‘Ibid’ means ‘same as the previous citation’.)
Your university may use sophisticated plagiarism-detection software. Markers may also report if the paper looks suspect
Before final submission, they may ask you to go over your draft and sign that you understand the contents and you have demonstrated that the work is your own.
Not being in touch with your supervisor may put you under suspicion.
Your university may give a Viva Voce oral exam if your work is under suspicion. It is a cool-sounding word but probably something you want to avoid.
Your university may store your work in its our database, and can pursue disciplinary action, even after you have graduated.
Penalties may be severe, including failure with no opportunity to retake the module (course). You may even risk your degree!
Comprehension questions; answers in footnotes
True or false: “If you do not directly quote a paper you do not need to cite it” 9
You should read and cite a paper (choose all that are correct)… 10
- If it motivates ‘why your question is interesting’ and how it can be modeled economically
- Only if it asks the same question as your paper
- Only if it is dealing with the same country/industry/etc as you are addressing
- If it has any connection to your topic, question, or related matters
- If it answers a similar question as your paper
- If it uses and discusses techniques that inform those you are using
4.8 How to write about previous authors’ analysis and findings
Use the right terminology.
“Johnson et al. (2000) provide an analytical framework that sheds substantial doubt on that belief. When trying to obtain a correlation between institutional efficiency and wealth per capita, they are left with largely inconclusive results.”
They are not trying to “obtain a correlation”; they are trying to measure the relationship and test hypotheses.
“Findings”: Critically examine sources
Don’t take everything that is in print (or written online) as gospel truth. Be skeptical and carefully evaluate the arguments and evidence presented. Try to really survey what has been written, to consider the range of opinions and the preponderance of the evidence. You also need to be careful to distinguish between “real research” and propaganda or press releases.
The returns to higher education in Atlantis are extremely high. For the majority of Atlanian students a university degree has increased their lifetime income by over 50%, as reported in the “Benefits of Higher Education” report put out by the Association of Atlantian Universities (2016).
But don’t be harsh without explanation:
Smith (2014) found a return to education in Atlantis exceeding 50%. This result is unlikely to be true because the study was not a very good one.
“Findings:” “They Proved”
A theoretical economic model can not really prove anything about the real world; they typically rely on strong simplifying assumptions.
Through their economic model, they prove that as long as elites have incentives to invest in de facto power, through lobbying or corruption for example, they will invest as much as possible in order to gain favourable conditions in the future for their businesses.
In their two period model, which assumes \[details of key assumptions here\] , they find that when an elite Agent has an incentive to invest in de facto power, he invests a strictly positive amount, up to the point where marginal benefit equals marginal cost”
Empirical work does not “prove” anything (nor does it claim to).
It relies on statistical inference under specific assumptions, and an intuitive sense that evidence from one situation is likely to apply to other situations.
“As Smith et al (1999) proved using data from the 1910-1920 Scandanavian stock exchange, equity prices always increase in response to reductions in corporate tax rates.”
“Smith et al (199) estimated a VAR regression for a dynamic CAP model using data from the 1910-1920 Scandanavian stock exchange. They found a strongly statistically significant negative coefficient on corporate tax rates. This suggests that such taxes may have a negative effect on publicly traded securities. However, as their data was from a limited period with several simultaneous changes in policy, and their results are not robust to \[something here\] , further evidence is needed on this question.”
Use the language of classical 11 statistics:
Hypothesis testing, statistical significance, robustness checks, magnitudes of effects, confidence intervals.
Note that generalisation outside the data depends on an intuitive sense that evidence from one situation is likely to apply to other situations.
“Findings”: How do you (or the cited paper) claim to identify a causal relationship?
This policy was explained by Smith and Johnson (2002) in their research on subsidies and redistribution in higher education. Their results showed that people with higher degree have higher salaries and so pay higher taxes. Thus subsidizing higher education leads to a large social gain.
The results the student discusses seem to show an association between higher degrees and higher salaries. The student seems to imply that the education itself led to higher salaries. This has not been shown by the cited paper. Perhaps people who were able to get into higher education would earn higher salaries anyway. There are ways economists used to try to identify a “causal effect” (by the way, this widely used term is redundant as all effects must have a cause), but a mere association between two variables is not enough
As inflation was systematically lower during periods of recession, we see that too low a level of inflation increases unemployment.
Economists have long debated the nature of this “Phillips curve” relationship. There is much work trying to determine whether the association (to the extent it exists) is a causal one. We could not rule out reverse causality, or third factor that might cause changes in both variables.
4.9 …Stating empirical results
Don’t write: “I accept the null hypothesis.”
Do write: “The results fail to reject the null hypothesis, in spite of a large sample size and an estimate with small standard errors” (if this is the case)
Note: The question of what to infer from acceptance/rejection of null hypotheses is a complex difficult one in Classical (as opposed to Bayesian) statistics. This difficulty is in part philosophical: classical hypothesis testing is deductive , while inference is necessarily inductive.
4.10 What to report
You need to read this paper more clearly; it is not clear what they conclude nor what their evidence is.
4.11 Organising your literature review
A common marking comment:
These papers seem to be discussed in random order – you need some structure organising these papers thematically, by finding, by technique, or chronologically perhaps.
How should you organise it? In what order?
Thematically (usually better)
By method, by theoretical framework, by results or assumptions, by field
Chronologically (perhaps within themes)
Exercise: Compare how the literature review section is organized in papers you are reading.

Figure 4.4: Organising a set of references
Q: What sort of structure am I using in the above outline?
It may also be helpful to make a ‘table’ of the relevant literature, as in the figure below. This will help you get a sense of the methods and results, and how the papers relate, and how to assess the evidence. You may end up putting this in the actual paper.

Figure 4.5: Organisational table from Reinstein and Riener, 2012b
4.12 What if you have trouble reading and understanding a paper?
Consult a survey paper, textbook, or lecture notes that discuss this paper and this topic
Try to find an easier related paper
Ask your supervisor for help; if he or she can
Try to understand what you can; do not try to “fake it”
4.13 Some literature survey do’s and don’ts
Do not cite irrelevant literature.
Do not merely list all the papers you could find.
Discuss them, and their relevance to your paper.
What are their strengths and weaknesses? What techniques do they use, and what assumptions do they rely on? How do they relate to each other?
Use correct citation formats.
Try to find original sources (don’t just cite a web link).
Don’t just cut and paste from other sources. And make sure to attribute every source and every quote. Be clear: which part of your paper is your own work and what is cited from others? The penalties for plagiarism can be severe!
- Critically examine the sources, arguments, and methods
4.14 Comprehension questions: literature review
How to discuss empirical results: “Causal” estimation, e.g., with Instrumental Variables
Which is the best way to state it? 12
“As I prove in table 2, more lawyers lead to slower growth (as demonstrated by the regression analysis evidence).”
“Table 2 provides evidence that a high share of lawyers in a city’s population leads to slower growth.”
3.“Table 2 shows that a high share of lawyers in a city’s population is correlated with slower growth.”
Which is better? 13
- “However, when a set of observable determinants of city growth (such as Census Region growth) are accounted for, the estimate of this effect becomes less precise.”
- “In the correct regression I control for all determinants of city growth and find that there is no effect of lawyers on growth”
Stating empirical results: descriptive
“Using the US data from 1850-1950, I find that inflation is lower during periods of recession. This is statistically significant in a t-test [or whatever test] at the 99% level, and the difference is economically meaningful. This is consistent with the theory of …, which predicts that lower inflation increases unemployment. However, other explanations are possible, including reverse causality, and unmeasured covarying lags and trends.”
“I find a significantly lower level of inflation during periods of recession, and the difference is economically meaningful. This relationship is statistically significant and the data is accurately measured. Thus I find that inflation increases unemployment.”
Some tips on writing a good paper– relevant to literature reviews
- Answer the question
- Provide clear structure and signposting
- Demonstrate an ability for critical analysis
- Refer to your sources
- Produce a coherent, clear argument
- Take time to proofread for style and expresssion
- Source “Assignment Writing Skills EBS 3rd year 2012”"
Answer: only b is a ‘peer reviewed article in a reputable economics journal’. All of these might be useful to cite, however. ↩
False. You need to cite any content and ideas that are not your own. ↩
Answers: 1, 5, and 6. Note that 2 and 3 are too narrow criteria, and 4 is too broad. ↩
or Bayesian if you like ↩
The second one; if this is really causal evidence. ↩
The first one. There is no ‘correct regression’. It is also not really correct in classical statistics to ‘find no effect’. ↩
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
- University of Oregon Libraries
- Research Guides
How to Write a Literature Review
- 4. Manage Your References
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it Describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the Question
- 2. Review Discipline Styles
- Searching Article Databases
- Finding Full-Text of an Article
- Citation Chaining
- When to Stop Searching
Manage your references
Why do i have to cite my sources, citation styles, major citation styles - official and credible guidance.
- 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
- 6. Synthesize
- 7. Write a Literature Review
Citation Management Tools
Citation managers help you collect, organize, cite, and share research. Click on the links below for guidance on using these tools.

Learning Opportunities
For help learning these tools, contact an expert listed on the tool's guide or sign up for one of our workshops:
- Sign up for UO Libraries workshops here!

As p art of your lit review, you'll need to provide a list of references -- your professors want to know where you found your information.
Your professor will also require that you use a specific format ("style") for citing your references, such as one of these:
- APA (American Psychological Association)
- Chicago Manual of Style
- MLA (Modern Language Association)
University Library provides an online guide to help you cite your sources correctly in multiple styles.
Citation styles
In academic writing, there are many different formats for citing the sources you use in your research. Here are a few of the most common, and their related disciplines.
Accessibility note: Below is a chart with two columns for format and discipline.
Note: Regardless of which format you use, you must include the same basic bibliographic information when citing a source.
Official Style Manuals
There are many different types of academic and professional writing styles. The four guidebooks below represent some of the major ones. Use these guides to learn how professional researchers and writers prepare their manuscripts for publication or sharing.
Online Style Resources
Although these resources are not official, they are still credible and very useful! If one of these websites doesn't answer your question, check out the official style guide or contact a librarian for help!

UO Research Guides
These helpful guided from UO Libraries provide information on various citation styles.
- Citation and Plagiarism by Genifer Snipes Last Updated May 3, 2024 2295 views this year
- Introductory How-To Tutorials for MLA and APA Styles from UO Libraries by Genifer Snipes Last Updated May 3, 2024 41 views this year
- << Previous: When to Stop Searching
- Next: 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate >>
- Last Updated: May 3, 2024 5:17 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.uoregon.edu/litreview
Contact Us Library Accessibility UO Libraries Privacy Notices and Procedures

1501 Kincaid Street Eugene, OR 97403 P: 541-346-3053 F: 541-346-3485
- Visit us on Facebook
- Visit us on Twitter
- Visit us on Youtube
- Visit us on Instagram
- Report a Concern
- Nondiscrimination and Title IX
- Accessibility
- Privacy Policy
- Find People

3 Literature Review
Charitianne Williams
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to do the following:
- Understand the purpose and function of a literature review.
- Structure a literature review according to basic genre expectations.
- Synthesize ideas from multiple sources using a synthesis matrix.
- Choose between narrative or parenthetical citation and direct quoting, or paraphrase with intent and purpose.
I. Introduction
The purpose of a literature review is just that—it reviews. This means that literature reviews examine a text after it was produced, with all the benefits that hindsight allows a reader. In popular culture, we commonly review movies, restaurants, vacation spots, products, etc. In those reviews, you look back at the single thing you are reviewing and your experience with it. You focus on the strengths and weaknesses of your experience and judge the experience as positive or negative while recommending or not recommending the place or product and explaining why.
An academic literature review does something different, although some of the skills and strategies you use remain the same. The job of a literature review is to examine a collection of research or scholarship (not a single thing or text) on a given topic and show how that scholarship fits together. Literature reviews summarize, describe, evaluate, and synthesize the work of other authors and researchers while looking for common trends/patterns, themes, inconsistencies, and gaps in this previous research. The main strategy writers of a literature review use is synthesis.
SYNTHESIS: the combination of ideas and elements to form a complete system or theory.
A good metaphor for synthesis is cooking! Imagine the ingredients for a loaf of bread laid out on a kitchen cabinet. Each ingredient—eggs, milk, flour, sugar, salt, yeast—have their own purpose and can be combined in different ways to form food other than bread. Knowing all of those individual attributes that make an egg an egg, or the difference between yeast and flour, is what makes you a chef. When you combine all these ingredients according to the recipe, you get something different than all the ingredients on their own: and most of us would rather eat a slice of bread than a spoonful of flour. The product of synthesis is like bread. Synthesis takes a list of ingredients and makes them into something more than the ingredients alone.
Usually, the writers of a literature review will start with a question that they want to answer through informed and research-based evidence gathered while reading others’ work on related topics. The “thesis” or controlling idea of a literature review may be that same question ( “This review seeks to answer…” ) or it may be a statement describing the reviewed research. The thesis reflects the purpose of the literature review as a genre and is different from the thesis you will write for the research paper that argues a claim or asserts a new idea.
Example 3.1: Look at this thesis statement taken from the introduction of a literature review in environmental psychology on the relationship between “nature sounds” and restorative environments:
From this example, we can learn many things about literature reviews:
- They are explicit and focused on their topic. The opening states an observable truth about the current research ( emphasizes nature ), is followed by a general condition ( positive psychological experiences) within that research, and then finally focuses on describing how a particular outcome is achieved (listening to nature sounds is restorative).
- They seek to pre vent or eliminate misunderstanding. Note the use of specialized key terms, exacting transitional phrases, and meaningful verbs in the thesis such as “ restorative environments,” “in particular,” and “ generate .”
- They seek to forward understanding. In other words, literature reviews examine and link together evidence described and validated in the research of others so a reader can learn how a field is developing. ( Research seems to agree that nature sounds can relieve stress and fatigue–this review will examine that conclusion so readers can understand/ build on how and why.)
Moving from the beginning to the very end of the literature review, we can also learn many things about literature reviews from the sources used. Think of each text listed in the References section of a literature review as contributing pieces to a gigantic puzzle.
Example 3.2: Look at the first three articles listed in the References for the article excerpted above:
Abbott, L. C., Taff, D., Newman, P., Benfield, J. A., and Mowen, A. J. (2016). The influence of natural sounds on attention restoration. J. Park Recreation Adm. 34, 5–15. doi: 10.18666/JPRA-2016-V34-I3-6893
Aletta, F., and Kang, J. (2019). Promoting healthy and supportive acoustic environments: going beyond the quietness. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 16:4988. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16244988
Aletta, F., Oberman, T., and Kang, J. (2018). Associations between positive health-related effects and soundscapes perceptual constructs: a systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 15:2392. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15112392
None of these sources are exactly the same. One focuses on sound and attention, the next two on sound and health, and none of them are quite the same as sound and restoration —but they are all pieces of the puzzle that give a full understanding of how sound and restorative environments relate.
As the author of the literature review, it is your job to join the pieces together, giving your reader a complete picture of what researchers know about your topic.
Literature reviews are an indispensable tool for researchers. Instead of having to read dozens of articles on a topic, a researcher could instead read a literature review that synthesizes what is known and puts each piece of scholarship into conversation with the others. This could be not only quicker, but also more valuable.
Have you heard the saying that the whole is more than the sum of its parts? The knowledge constructed by a well-written literature review often outweighs the knowledge constructed by simply reading each article in the References section on its own because the author of a literature review processes and analyzes the information for the reader.
Literature reviews occur in two general forms—as a background section in a scholarly work or as a stand-alone genre in and of itself. In both situations, the basic purpose and structure of the literature review is similar: it is the length and the scope that varies. For example, consider the previous chapter, the Proposal. In most proposals, you will want to convince your audience that you are informed on the background of your topic—a literature review is how you would do that. Since a proposal is commonly a short text, you do not have the space to summarize every piece of research. You must select an important set and synthesize that information into a small section signaling your expertise.
On the other hand, consider a professional journal intended to keep its readers up to date on new technologies and findings in a specific field or career. New ideas and discoveries are emerging every day, and it can be difficult to stay on top of all of these new findings, understand how they fit together, and also keep track of your own career responsibilities! A magazine might hire an author to read all the new research on a specific topic and synthesize it into a single article, a state-of-the-art review, so that practitioners in a field can read a single 25-page article instead of 100 25-page articles.
More Resources 3.1: Literature Reviews
II. Rhetorical Considerations: Voice
Using the scholarship of other writers and researchers is one of the things that differentiates academic writing from other types of writing. Using others’ scholarship in a meaningful way that creates new knowledge without mischaracterizing the original findings takes effort, attention, and usually several rounds of revision and rewriting. One of the issues is voice , which refers to the attitude and tone of a text—think of it as what the text “sounds like” in your head as you read it. Voice is an important element of cohesion , or what some people think of as “flow.” Creating a consistent voice in the mind of your reader helps them fit all the information in a text together in the way the author intends. Check out this advice from APAstyle.org about academic style and voice.
Think back to your annotated bibliography and how you created your summaries. You probably used key terms from the original authors’ texts, but because you had to take whole articles and restate the meaning in a short paragraph, there wasn’t room to just repeat the words of the original author. So you had to write the summaries in your voice . If you used those key terms correctly and in ways similar to original authors, those key terms probably did not interfere with cohesiveness and voice. However, in the literature review, you have many more voices to synthesize than you did to summarize in the annotated bibliography. Maintaining a consistent and cohesive voice will be challenging. An important way to maintain voice is through paraphrasing, discussed later in this chapter.
More Resources 3.2: Transitions
Another important way to maintain cohesion is through the use of metadiscourse (see Chapter 2) and transitional phrases. See this link for the use and meaning of transitional phrases, sometimes called signposts .
III. The Literature Review Across the Disciplines
Example 3.3: Academic and Professional Examples
Structure of Literature Reviews
While the details vary across disciplines, all literature reviews tend to have similar basic structure. The introduction of a literature review informs the reader on the topic by defining key terms, citing key researchers or research periods in the field, and introducing the main focus of the review in a descriptive thesis statement. The introduction also explains the organization of the review. In a literature review, you organize your discussion of the research by topic or theme— not article or author. This is in direct contrast to the annotated bibliography, which is often the first step in the writing process for a literature review.
In the annotated bibliography, you organize your entries in alphabetical order by authors’ last names. Each annotation is directly connected to a single text. A literature review is connected to a collection of texts, and therefore must be organized in a way that reflects this.
Example 3.4: Let’s examine the full paragraph that the thesis statement we analyzed earlier came from:
A systematic review by Aletta et al. (2018) has identified links between positive urban soundscapes (which may also include nature sounds) and health and well-being, including stress recovery. Given the emphasis on nature w ithin restorative environments (see Hartig et al., 2014 ), the present narrative literature review focuses on evidence for positive psychological experiences of nature sounds and soundscapes specifically, and in particular how listening to these can generate perceptions and outcomes of restoration from stress and fatigue. This review has five key objectives, summarized in Figure 1 [in the article] . First, it explores literature regarding the impact of nature sounds on perceptions and experiences of wider natural environments. Second, it examines evidence regarding cognitive and affective appraisals of nature sounds and their contributions to overall perceptions of restorative environments. Third, literature regarding restorative outcomes in response to nature sounds is assessed. Fourth, the relevance of key restoration theories to this top ic is examined and areas where these theories are limited are identified. Fifth, a possible new theoretical area of interest—semantic associations with nature—is discussed and exemplified by recent acoustics research (Ratcliffe, 2021, emphasis added).
Notice how the thesis statement (in bold ) is followed by an explicit description of the five key objectives—which correspond to the titles (usually called headings ) of the five major sections of the body of the literature review. The introduction basically outlines the body of the literature review to make it easier for a researcher to find the specific information they are looking for. What follows each of these headings is an analysis and synthesis of the topic described in the heading—which is what we mean when we say a literature review is organized by topic.
Example 3.5: See how the body sections of a literature review synthesize research and evidence in relation to a focused topic. Read this example taken from a literature review in another discipline, nursing.
The introduction states that the review’s purpose is to understand the issues facing nurses in situations such as the COVID-19 pandemic. The researchers found several themes in the research that all contributed to nurses’ experiences. This paragraph describes one of those themes which the authors label “Professional collegiality”:
3.2.2. Professional collegiality
Professional camaraderie amongst nursing colleagues working during a pandemic was high (Ives et al., 2009, Kim, 2018, Liu a nd Liehr , 2009). Nurses acknowledged the importance of caring for their co-workers and in sharing the load. Some nurses associated the experience with working on a battlefield, whereby they worked together as a team protecting one another (Chung et al., 20 05, Kang et al., 2018, Liu and Liehr , 2009). Appreciation of their nursing colleagues was demonstrated through sharing their experiences, willingness to work together and encouraging a team spirit (Shih et al., 2007, Chung et al., 2005, Chiang et al., 2007 ). (Ratcliffe, 2021, p.4)
In this single paragraph, there are seven different research articles cited, and some of them are cited twice. There is no way to write a coherent paragraph summarizing seven different research articles at once—instead, the authors of this paragraph reviewed what the researchers said about collegiality, found where their findings pointed in the same direction, and put those connections into their own words. This is the importance of the review’s body section: it is here where you really dig into the content, meaning, and implications of the scholarship you are discussing.
The end of a literature review looks different from the one- or two-paragraph conclusion we are used to in other texts. The end is often made up of multiple sections, each with a slightly different purpose, although all are probably recognizable to you. A “Discussion” section is almost always present, where the author summarizes the most important findings of each section. In most cases, the “Discussion” section does not contain new information, but ties the different body sections together in ways that provide a deeper analysis.
The end of a literature review may also contain an “Implications for Future Research” or “Resolution” after the Discussion—sometimes this final section is even called “Conclusion.” What this last section looks like is often dependent upon the type of review you are writing, and whether the review is standing alone as a complete text or part of a larger project.
In any situation, across all disciplines, it is important to understand how your literature review is meant to inform the reader and what kind of review is appropriate for the context, in order to decide how you should structure the beginning and end of your review.
Types of Literature Reviews
There are different types of literature reviews, although in undergraduate study the Traditional or Narrative Review is most common. Narrative reviews are somewhat exploratory in their content—in a narrative review you are synthesizing the results of specific texts selected for their connection to your topic. Narrative reviews almost always end with a section describing areas for future research if they are a stand-alone text, or a section describing why the author’s research is so needed if part of a larger research article. The chart below outlines the key differences between three major literature review types. Notice that each type has a slightly different purpose. You might think about which type best fits your project as you read.
Table 3.1: Types of Literature Reviews
More Resources 3.3: Literature Review Structures
IV. Research Strategies: Developing a Methodology
Systematic and scoping reviews should always contain a Research Methodology that explains to your reader exactly how you found the research you are reviewing. Often Narrative Reviews will also contain a research methodology, although it will be slightly different since they are not comprehensive reviews, meaning, they do not attempt to find all the research on a topic—by design, they cover only a specific portion. Even if you are not required to write up your methodology, you need clear research strategies to find the appropriate scholarship for your literature review.
Example 3.6: Check out this excerpt from the methods sections from a psychology literature review. Note how the authors clearly describe what types of sources they’ll be using as well as their steps throughout the research process.
Drawing on individual case studies, archival reports, correlational studies, and laboratory and field experiments, this monograph scrutinizes a sequence of events during which confessions may be obtained from criminal suspects and used as evidence. First, we examine the pre-interrogation interview, a process by which police …( Kassin and Gudjonsson , 2004, p.33)
Example 3.7: Here is another example from the field of education. In it the authors describe two separate searches they performed to gather the literature—the first search used key terms they decided upon before reading any scholarship, and the second search used the terms that they found were common to that first set of texts (see more about key terms here and in the Annotated Bibliography chapter).
We conducted two rounds of literature searches, utilizing the following databases: World CAT (general search), EB SCO Academic Search Complete, EBSCO Education Source, and Linguistics and Language Behavior Abstracts (ProQuest). In the first round, we searched using every possible combination of the following terms: ‘race,’ ‘language teaching,’ ‘ethnicity,’ ‘language p edagogy,’ ‘Whiteness,’ ‘racialized,’ ‘antiracism,’ and ‘ nativeness .’ For the second round of our literature search, we searched using terms that we saw emerging from the literature such as ‘racial identities of language learners,’ ‘racial identities of lan guage teachers,’ ‘language varieties and language teaching,’ ‘race and language teacher education,’ ‘race and educational policy,’ ‘race and language programs,’ and ‘race and language curriculum’ and also repeated our earlier searches in order to keep the literature updated. (Von Esch et al., 2020, p. 392)
No matter the type of research (see a description of qualitative vs. quantitative research ), the specific genres (see descriptions of academic research genres ), or the time frame (see a discussion on the importance of publication date ) you use for your review, it is important to think through the options, make a decision, and incorporate all your research knowledge—use of key terms, use of subject filters, use of specialized databases, etc.—into a coherent and meaningful process that results in the best scholarship for your inquiry and review.
Here’s a video to help you get started on using databases for research:
Library Referral: Connecting the Conversation with Scholarly Sources and Beyond
(by Annie R. Armstrong)
Research involves drawing from numerous voices from a range of source types. The sources you choose to include in your conversation are context-specific and might vary depending on your topic or the parameters of your assignment. Review your assignment description and talk to your instructor about guidelines. While most research papers emphasize scholarly sources, expertise isn’t always equated with scholarliness and you might want to branch out. For example, a research paper focusing on exploitation of Native American land and communities by the mining industry should make some attempt to include sources generated by the communities under discussion, especially if their point of view is not represented in the peer-reviewed, scholarly sources you’ve found. Think about who the stakeholders are as related to various aspects of your topic and how you can tap into their voices through available resources. You may want to consult a librarian about this.
The chart below summarizes the breadth of source types available through library websites versus the open web:
Table 3.2: Scholarly Sources and Beyond
V. Reading Strategies: Intertextuality and Graphic Organizers
Typically we think of reading as something we do to learn the content of a text—and this is absolutely true! But true understanding means knowing the relationships between and impact of separate but related topics, which might mean understanding how different texts—generally focused on one topic—overlap or differ.
Intertextuality refers to the connections that exist between texts. Intertextuality as a reading strategy means looking for the connections between the text you are reading and others you have already read; anticipating connections with other texts that you have not yet read, but plan to; as well as connections to whole disciplines, fields, and social phenomena. Reading for intertextuality means looking for opportunities to connect texts with each other, and keeping track of those connections in a productive way.
This means note-taking is essential to intertextual reading. Once you have thought carefully about why you are reading a text, what types of information to look for, and what you will do with that information, you can better decide how to keep track of that information. In regards to literature reviews, one type of graphic organizer dominates: the Synthesis Matrix.
The synthesis matrix is a way to keep track of the themes, concepts, and patterns that are emerging from your reading—NOT all the individual content of each article. This is important, yes, and you will need the citations, but literature reviews move one step further into the topic than simply identifying the pieces. You will need to synthesize.
If you have an annotated bibliography of sources already, it is the perfect way to start your synthesis matrix. An annotated bibliography is often the first step in preparing for a literature review, and is quite similar to an ingredient list, if we are using the metaphor from the introduction. (For a detailed description of how to write an annotated bibliography, see Chapter 1 ).
In your annotations, you will have selected the most important information that text supplies in relation to your topic. For an example, let’s take the Conference on College Composition and Communication’s statement “ Students’ Right to Their Own Language ,” which contains two annotated bibliographies. The second uses more recent sources and looks most like the annotated bibliographies you will write as a student, so let’s start there.
Example 3.8: Here are three annotations from that bibliography. As you read, take notice of the different highlighted colors. Phrases italicized and highlighted green identify ideas related to linguistic identity , phrases bolded and highlighted in blue identify concepts related to grammar analysis , and phrases underlined and highlighted orange identify groups and ideas related to educational objectives :
Fought, Carmen. Chicano English in Context. New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2003.
Based primarily on data collected from adolescent and young adult native speakers in Los Angeles , this book is a comprehensive sociolinguistic study of language and language change in Latino/a communities. It provides the basics of Chicano English (CE) structure (phonology, syntax, and semantics) and its connection to the social and cultural identity of its speakers, along with detailed analyses of particular sociolinguistic variables. Emphasis is given to the historical, social, and linguistic contexts of CE. In addition, the differences between native and non-native CE speakers are covered. A final chapter discusses the future of research on CE.
Lippi-Green, Rosina. English with an Accent: Language, Ideology, and Discrimination in the United States . London and New York: Routledge, 1997.
The author examines linguistic facts about the structure and function of language , explores commonly held myths about language, and develops a model of “the language subordination process.” Then, using a case-study approach, she applies the model to specific institutional practices (e.g., in education, news media, business) to show how false assumptions about language lead to language subordination. The author analyzes specific groups and individuals (speakers of African American English, Southern U.S. English, and the foreign-language accent of Latinos and Asian Americans) and discusses why and how some embrace linguistic assimilation while others resist it.
Nero, Shondel J. Englishes in Contact: Anglophone Caribbean Students in an Urban College. Cresskill, NJ: Hampton Press, 2001.
This qualitative study of four anglophone Caribbean students at a New York City college offers an in-depth examination of the students’ written and spoken language and the challenges faced by both students and teachers as such students acquire academic literacy. Case studies of the four participants include excerpts from tape-recorded interviews, which reflect their linguistic self-perception, and sociolinguistic and educational experiences in their home countries and in New York City. Samples of their college writing over four semesters are represented and analyzed on morphosyntactic and discourse levels to determine the patterns that emerge when Creole English speakers attempt to write Standard Written English. Related issues such as language and identity , language attitudes, and educational responses to ethnolinguistic diversity are also discussed.
Once you have identified a concept like “language and identity” for your literature review, you can start getting “intertextual”! Review your other annotated sources and your new sources for their discussion of language and identity, as well as parallel concepts—what else do researchers address when they discuss language and identity? What do they discuss instead? Go back to the methods you used to come up with key terms for your literature search—the same strategies now apply to your reading. Also look for “umbrella” concepts, patterns in methodologies—anything that emerges while you read intertextually, focusing on the text in front of you while also remembering all the others you read before. Look for the themes in your annotated bibliography and keep track of the page numbers where these themes appear—plan to go back to those pages several times as you write your literature review.
This is a different type of reading than you did for the annotated bibliography, and might mean you go back and reread your sources several times in this new way—don’t think of this as just repeating labor you have already performed. This is new work, designed to uncover new things in the research. Re-reading articles multiple times is something all serious writers do, and something you should do, too. It isn’t redundant, it is recur sive .
Table 3.3: Synthesis Matrix for Individuals’ Choices in Linguistic Identity
Put your sources into conversations around your themes, as shown in the table above. Notice that the top row names the themes covered in that column, put into original wording similar, but not identical, to the wording in the annotated bibliographies. Not every source will address every topic—not every article is the same. The last row starts to describe what is happening in each column across the whole collection of texts. In this way, your synthesis matrix takes the ingredient list provided by the annotated bibliography and makes it into a recipe for your final product—the literature review.
More Resources 3.4: Synthesis Matrix
VI. Writing Strategies: Citation, Quotation, and Paraphrase
Citation is when you use the work of other authors in your writing and mark that portion of your writing so your reader understands what idea is being “borrowed.” Citation also tells your reader where they could find that original idea in the original text, and how your text fits together with the web of other texts related to your topic: in other words, citations help create intertextuality. A citation placed in your sentences should refer directly to the full bibliographic information in your Works Cited or References page.
As you read in Chapter 1, there are different styles of citation including AMA, APA, CMS, and MLA. You can refer back to that chapter for a more detailed explanation of each. In this section, we’ll cover the basics that are common to citation practices. Most academic styles use the original author’s last name as the central part of the in-text citation, since References pages usually list cited works alphabetically by last name, but some use footnotes or endnotes instead, listing works in the order they were cited. It is important to know which academic style you are using for your literature review so that you can make the right choice.
In-text citation takes one of two forms: parenthetical or narrative. In a narrative citation the author of the original work is mentioned in the sentence.
Example 3.9: Here’s an example taken from the introduction of the same literature review discussed in the Research Strategies: Developing a Methodology section of this chapter.
Several pieces offered a comprehensive review of the historical literature on the formation of Black English as a construct in the context of slavery and Jim Crow, and the historical teaching of Black English within the U .S. context, including Wheeler ( 2016 ) and Alim and Baugh (2007). Wheeler (2016) equated Standard English with ‘White’ English and challenged its hegemony in dialectically diverse classrooms. She named the “racism inherent in [fostering] bidialectalism [th rough teaching]” (p. 380), arguing that we are acknowledging that the only way for African-Americans to be upwardly mobile was to learn how to speak ‘White’ English. Alim (2010) , explained, “By uncritically presenting language varieties as ‘equal’ but diff ering in levels of ‘appropriateness,’ language and Dialect Awareness programs run the risk of silently legitimizing ‘Standard English’” (p. 215)…. Current work addressing AAVE studies has been shifting focus to translingualism and to promoting such pedag ogies as code-meshing (Young, Barrett, Young Rivera and Lovejoy, 2014) and translanguaging (García & Wei, García and Wei, 2014) , embedded in a critical analysis of the racial logics underpinning the denigration of some languages. This work, combined with e xtensive examinations of the connections between race, language, teaching, and identity ( e.g. Flores & Rosa, 2015; Alim et al., 2016 ), has laid a foundation for a raciolinguistics approach to teaching, which we return to later in this article. (Von Esch et al., 2020, p. 399, emphasis added .)
In the first sentence, we see two narrative citations just before the period. These citations state the authors’ names as a part of the sentence, and put the publication date of the articles in parenthesis. It makes sense to use a narrative citation in the topic sentence, since most of the paragraph is a synthesis of Wheeler and Alim’s research. The second sentence starts with Wheeler’s name in the subject position, and the fourth sentence starts with Alim’s name in the subject position—both are narrative citations, a form chosen by the author to emphasize the importance and similarities in the two articles.
In the last two sentences, we see parenthetical citations. The citation information is in parenthesis within the sentences, which focuses the reader on the ideas, not the research itself. Imagine you were reading this article out loud—you would most certainly say the narrative citations “Wheeler” and “Alim”; you might choose not to say “Young, Barrett, Young-Rivera, & Lovejoy, 2014,” though, and no one listening to you would notice the omission. This is the most important difference between narrative and parenthetical citation—narrative draws attention to the researchers, while parenthetical allows a focus on ideas. In academic writing, you often have reason to use both, but it is important to note that using parenthetical citation is less disruptive to your voice—it keeps a reader focused on the ideas you are explaining.
Usually you are citing a type of quotation in your text (although different disciplines have other situations that they cite). Direct quotation and paraphrase are usually what we talk about when we talk about using resources in your writing, although summary is cited as well.
Direct quotation is when you take the original words of one author and place them in your own text. When you quote in your own writing, you mark the copied text—usually with quotation marks “” around the text and a citation afterwards. Quoting is useful when the original author is an important authority on a topic or if you want to define/describe another’s point of view in a way that leaves no room for misinterpretation.
In a literature review, a direct quote will almost always be accompanied by a narrative citation. But direct quoting can cause some issues in your own text, such as a sudden shift in voice and a loss of cohesion; the potential for misunderstanding and misrepresentation, since the quote has been separated from its original context; and wordiness —quotes can take up too much space both in terms of the quote itself, and of the explanation and context you must provide for the introduced idea. For these reasons, literature reviews do not contain much direct quoting.
Paraphrasing is a way to accomplish similar goals to direct quoting without causing the same problems. Paraphrasing is when you use only the original author’s key terms and ideas, but your own words. Paraphrasing still contains a citation afterwards that directs the reader to the full bibliographic information in your Works Cited, but does not require quotation marks since the language is yours. Paraphrase may be longer or shorter than the original author’s text, and uses both narrative and parenthetical citation. Paraphrase also allows you to cite more than one piece of research containing the same idea in a single sentence, such as the last sentence in the example paragraph above. This kind of citation string is important to literature reviews because it clearly identifies patterns and trends in research findings.
Key Takeaways
- Literature reviews are a synthesis of what other researchers have discovered on your topic. Think of reviews as “the big picture.”
- Taking so much information from other sources can get confusing–use section headings to keep your review organized and clear.
- Diverse citation, quotation, and paraphrasing techniques are necessary to help your reader understand where the ideas are coming from, AND to help make the ideas “stick together.”
- Keeping all the new knowledge you are learning from your sources organized is hard! Take notes using citations and use a graphic organizer to keep yourself on track.
Fernandez, Lord, H., Halcomb, E., Moxham, L., Middleton, R., Alananzeh, I., & Ellwood, L. (2020). Implications for COVID-19: A systematic review of nurses’ experiences of working in acute care hospital settings during a respiratory pandemic. International Journal of Nursing Studies , 111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2020.103637
Kassin, S. M., & Gudjonsson, G. H. (2004). The psychology of confessions. Psychological Science in the Public Interest , 5 (2), 33–67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-1006.2004.00016.x
National Council of Teachers of English. (2018, June 16). Students’ right to their own language (with bibliography) . Conference on College Composition and Communication. Retrieved July 24, 2022, from https://cccc.ncte.org/cccc/resources/positions/srtolsummary
NEIU Libraries. (2020). “How should I search in a database?” YouTube . https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8fgBF0EuH_o
Ratcliffe, E. (2021). Summary Flowchart [Image]. Frontiers in Psychology. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.570563/full#B3
Ratcliffe, E. (2021). Sound and soundscape in restorative natural environments: A narrative literature review. Frontiers in Psychology , 12 . https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.570563
Sasaki. K. (2022). Synthesis and Recipes [Image].
Von Esch, K., Motha, S., & Kubota, R. (2020). Race and language teaching. Language Teaching, 53 (4), 391-421. doi:10.1017/S0261444820000269
Writing for Inquiry and Research Copyright © 2023 by Charitianne Williams is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Boatwright Memorial Library
Citing sources research guide: literature reviews.
- Quick Citing in Databases
- Chicago/Turabian
- ASA & AAA (Soc/Ant)
- ACS (Chemistry)
- AP (Associated Press)
- APSA (Political Science)
- SBL (Society of Biblical Literature)
- Harvard Style
- MS Word Help
- DOIs (Digital Object Identifiers)
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Literature Reviews
- EndNote Web
- Citation exercises This link opens in a new window
Literature Reviews: Overview
This video from NCSU Libraries gives a helpful overview of literature reviews. Even though it says it's "for graduate students," the principles are the same for undergraduate students too!
Reading a Scholarly Article
- Reading a Scholarly Article or Literature Review Highlights sections of a scholarly article to identify structure of a literature review.
- Anatomy of a Scholarly Article (NCSU Libraries) Interactive tutorial that describes parts of a scholarly article typical of a Sciences or Social Sciences research article.
- Evaluating Information | Reading a Scholarly Article (Brown University Library) Provides examples and tips across disciplines for reading academic articles.
- Reading Academic Articles for Research [LIBRE Project] Gabriel Winer & Elizabeth Wadell (ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative (OERI))
Literature Review Examples
What is a Literature Review?
The literature review is a written explanation by you, the author, of the research already done on the topic, question or issue at hand. What do we know (or not know) about this issue/topic/question?
- A literature review provides a thorough background of the topic by giving your reader a guided overview of major findings and current gaps in what is known so far about the topic.
- The literature review is not a list (like an annotated bibliography) -- it is a narrative helping your reader understand the topic and where you will "stand" in the debate between scholars regarding the interpretation of meaning and understanding why things happen. Your literature review helps your reader start to see the "camps" or "sides" within a debate, plus who studies the topic and their arguments.
- A good literature review should help the reader sense how you will answer your research question and should highlight the preceding arguments and evidence you think are most helpful in moving the topic forward.
- The purpose of the literature review is to dive into the existing debates on the topic to learn about the various schools of thought and arguments, using your research question as an anchor. If you find something that doesn't help answer your question, you don't have to read (or include) it. That's the power of the question format: it helps you filter what to read and include in your literature review, and what to ignore.
How Do I Start?
Essentially you will need to:
- Identify and evaluate relevant literature (books, journal articles, etc.) on your topic/question.
- Figure out how to classify what you've gathered. You could do this by schools of thought, different answers to a question, the authors' disciplinary approaches, the research methods used, or many other ways.
- Use those groupings to craft a narrative, or story, about the relevant literature on this topic.
- Remember to cite your sources properly!
- Research: Getting Started Visit this guide to learn more about finding and evaluating resources.
- Literature Review: Synthesizing Multiple Sources (IUPUI Writing Center) An in-depth guide on organizing and synthesizing what you've read into a literature review.
- Guide to Using a Synthesis Matrix (NCSU Writing and Speaking Tutorial Service) Overview of using a tool called a Synthesis Matrix to organize your literature review.
- Synthesis Matrix Template (VCU Libraries) A word document from VCU Libraries that will help you create your own Synthesis Matrix.
Additional Tutorials and Resources
- UR Writer's Web: Using Sources Guidance from the UR Writing Center on how to effectively use sources in your writing (which is what you're doing in your literature review!).
- Write a Literature Review (VCU Libraries) "Lit Reviews 101" with links to helpful tools and resources, including powerpoint slides from a literature review workshop.
- Literature Reviews (UNC Writing Center) Overview of the literature review process, including examples of different ways to organize a lit review.
- “Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review.” Pautasso, Marco. “Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review.” PLOS Computational Biology, vol. 9, no. 7, July 2013, p. e1003149.
- Writing the Literature Review Part I (University of Maryland University College) Video that explains more about what a literature review is and is not. Run time: 5:21.
- Writing the Literature Review Part II (University of Maryland University College) Video about organizing your sources and the writing process. Run time: 7:40.
- Writing a Literature Review (OWL @ Purdue)
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliographies
- Next: Zotero >>
- Last Updated: Mar 20, 2024 9:09 AM
- URL: https://libguides.richmond.edu/citingsources

- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: May 15, 2024 9:53 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as you go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.

Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface with the option to save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.
- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., how to write a successful book chapter for..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, what is academic writing: tips for students.

Citation Styles
- Chicago Style
- Annotated Bibliographies
What is a Lit Review?
How to write a lit review.
- Video Introduction to Lit Reviews
Main Objectives
Examples of lit reviews, additional resources.
- Zotero (Citation Management)
What is a literature review?
- Either a complete piece of writing unto itself or a section of a larger piece of writing like a book or article
- A thorough and critical look at the information and perspectives that other experts and scholars have written about a specific topic
- A way to give historical perspective on an issue and show how other researchers have addressed a problem
- An analysis of sources based on your own perspective on the topic
- Based on the most pertinent and significant research conducted in the field, both new and old

- A descriptive list or collection of summaries of other research without synthesis or analysis
- An annotated bibliography
- A literary review (a brief, critical discussion about the merits and weaknesses of a literary work such as a play, novel or a book of poems)
- Exhaustive; the objective is not to list as many relevant books, articles, reports as possible
- To convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic
- To explain what the strengths and weaknesses of that knowledge and those ideas might be
- To learn how others have defined and measured key concepts
- To keep the writer/reader up to date with current developments and historical trends in a particular field or discipline
- To establish context for the argument explored in the rest of a paper
- To provide evidence that may be used to support your own findings
- To demonstrate your understanding and your ability to critically evaluate research in the field
- To suggest previously unused or underused methodologies, designs, and quantitative and qualitative strategies
- To identify gaps in previous studies and flawed methodologies and/or theoretical approaches in order to avoid replication of mistakes
- To help the researcher avoid repetition of earlier research
- To suggest unexplored populations
- To determine whether past studies agree or disagree and identify strengths and weaknesses on both sides of a controversy in the literature

- Choose a topic that is interesting to you; this makes the research and writing process more enjoyable and rewarding.
- For a literature review, you'll also want to make sure that the topic you choose is one that other researchers have explored before so that you'll be able to find plenty of relevant sources to review.

- Your research doesn't need to be exhaustive. Pay careful attention to bibliographies. Focus on the most frequently cited literature about your topic and literature from the best known scholars in your field. Ask yourself: "Does this source make a significant contribution to the understanding of my topic?"
- Reading other literature reviews from your field may help you get ideas for themes to look for in your research. You can usually find some of these through the library databases by adding literature review as a keyword in your search.
- Start with the most recent publications and work backwards. This way, you ensure you have the most current information, and it becomes easier to identify the most seminal earlier sources by reviewing the material that current researchers are citing.
The organization of your lit review should be determined based on what you'd like to highlight from your research. Here are a few suggestions:
- Chronology : Discuss literature in chronological order of its writing/publication to demonstrate a change in trends over time or to detail a history of controversy in the field or of developments in the understanding of your topic.
- Theme: Group your sources by subject or theme to show the variety of angles from which your topic has been studied. This works well if, for example, your goal is to identify an angle or subtopic that has so far been overlooked by researchers.
- Methodology: Grouping your sources by methodology (for example, dividing the literature into qualitative vs. quantitative studies or grouping sources according to the populations studied) is useful for illustrating an overlooked population, an unused or underused methodology, or a flawed experimental technique.

- Be selective. Highlight only the most important and relevant points from a source in your review.
- Use quotes sparingly. Short quotes can help to emphasize a point, but thorough analysis of language from each source is generally unnecessary in a literature review.
- Synthesize your sources. Your goal is not to make a list of summaries of each source but to show how the sources relate to one another and to your own work.
- Make sure that your own voice and perspective remains front and center. Don't rely too heavily on summary or paraphrasing. For each source, draw a conclusion about how it relates to your own work or to the other literature on your topic.
- Be objective. When you identify a disagreement in the literature, be sure to represent both sides. Don't exclude a source simply on the basis that it does not support your own research hypothesis.
- At the end of your lit review, make suggestions for future research. What subjects, populations, methodologies, or theoretical lenses warrant further exploration? What common flaws or biases did you identify that could be corrected in future studies?

- Double check that you've correctly cited each of the sources you've used in the citation style requested by your professor (APA, MLA, etc.) and that your lit review is formatted according to the guidelines for that style.
Your literature review should:
- Be focused on and organized around your topic.
- Synthesize your research into a summary of what is and is not known about your topic.
- Identify any gaps or areas of controversy in the literature related to your topic.
- Suggest questions that require further research.
- Have your voice and perspective at the forefront rather than merely summarizing others' work.
- Cyberbullying: How Physical Intimidation Influences the Way People are Bullied
- Use of Propofol and Emergence Agitation in Children
- Eternity and Immortality in Spinoza's 'Ethics'
- Literature Review Tutorials and Samples - Wilson Library at University of La Verne
- Literature Reviews: Introduction - University Library at Georgia State
- Literature Reviews - The Writing Center at UNC Chapel Hill
- Writing a Literature Review - Boston College Libraries
- Write a Literature Review - University Library at UC Santa Cruz
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliographies
- Next: Zotero (Citation Management) >>
- Last Updated: Jan 17, 2024 2:47 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.elac.edu/Citation
Libraries | Research Guides
Literature reviews, what is a literature review, learning more about how to do a literature review.
- Planning the Review
- The Research Question
- Choosing Where to Search
- Organizing the Review
- Writing the Review
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the literature you have read.
- Sage Research Methods Core Collection This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. – Publisher
- Next: Planning the Review >>
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 10:39 AM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/literaturereviews
- Undergraduate courses
- Postgraduate courses
- Foundation courses
- Apprenticeships
- Part-time and short courses
- Apply undergraduate
- Apply postgraduate
Search for a course
Search by course name, subject, and more
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- (suspended) - Available in Clearing Not available in Clearing location-sign UCAS
Fees and funding
- Tuition fees
- Scholarships
- Funding your studies
- Student finance
- Cost of living support
Why study at Kent
Student life.
- Careers and employability
- Student support and wellbeing
- Our locations
- Placements and internships
- Year abroad
- Student stories
- Schools and colleges
- International
- International students
- Your country
- Applicant FAQs
- International scholarships
- University of Kent International College
- Campus Tours
- Applicant Events
- Postgraduate events
- Maps and directions
- Research strengths
- Research centres
- Research impact
Research institutes
- Durrell Institute of Conservation and Ecology
- Institute of Cyber Security for Society
- Institute of Cultural and Creative Industries
- Institute of Health, Social Care and Wellbeing
Research students
- Graduate and Researcher College
- Research degrees
- Find a supervisor
- How to apply
Popular searches
- Visits and Open Days
- Jobs and vacancies
- Accommodation
- Student guide
- Library and IT
- Partner with us
- Student Guide
- Student Help
- Health & wellbeing
- Student voice
- Living at Kent
- Careers & volunteering
- Diversity at Kent
- Finance & funding
- Life after graduation
Literature reviews
Writing a literature review.
The following guide has been created for you by the Student Learning Advisory Service . For more detailed guidance and to speak to one of our advisers, please book an appointment or join one of our workshops . Alternatively, have a look at our SkillBuilder skills videos.
Preparing a literature review involves:
- Searching for reliable, accurate and up-to-date material on a topic or subject
- Reading and summarising the key points from this literature
- Synthesising these key ideas, theories and concepts into a summary of what is known
- Discussing and evaluating these ideas, theories and concepts
- Identifying particular areas of debate or controversy
- Preparing the ground for the application of these ideas to new research
Finding and choosing material
Ensure you are clear on what you are looking for. ask yourself:.
- What is the specific question, topic or focus of my assignment?
- What kind of material do I need (e.g. theory, policy, empirical data)?
- What type of literature is available (e.g. journals, books, government documents)?
What kind of literature is particularly authoritative in this academic discipline (e.g. psychology, sociology, pharmacy)?
How much do you need?
This will depend on the length of the dissertation, the nature of the subject, and the level of study (undergraduate, Masters, PhD). As a very rough rule of thumb – you may choose 8-10 significant pieces (books and/or articles) for an 8,000 word dissertation, up to 20 major pieces of work for 12-15,000 words, and so on. Bear in mind that if your dissertation is based mainly around an interaction with existing scholarship you will need a longer literature review than if it is there as a prelude to new empirical research. Use your judgement or ask your supervisor for guidance.
Where to find suitable material
Your literature review should include a balance between substantial academic books, journal articles and other scholarly publications. All these sources should be as up-to-date as possible, with the exception of ‘classic texts’ such as major works written by leading scholars setting out formative ideas and theories central to your subject. There are several ways to locate suitable material:
Module bibliography: for undergraduate dissertations, look first at the bibliography provided with the module documentation. Choose one or two likely looking books or articles and then scan through the bibliographies provided by these authors. Skim read some of this material looking for clues: can you use these leads to identify key theories and authors or track down other appropriate material?
Library catalogue search engine: enter a few key words to capture a range of items, but avoid over-generalisations; if you type in something as broad as ‘social theory’ you are likely to get several thousand results. Be more specific: for example, ‘Heidegger, existentialism’. Ideally, you should narrow the field to obtain just a few dozen results. Skim through these quickly to identity texts which are most likely to contribute to your study.
Library bookshelves: browse the library shelves in the relevant subject area and examine the books that catch your eye. Check the contents and index pages, or skim through the introductions (or abstracts, in the case of journal articles) to see if they contain relevant material, and replace them if not. Don’t be afraid to ask one of the subject librarians for further help. Your supervisor may also be able to point you in the direction of some of the important literature , but remember this is your literature search, not theirs.
Online: for recent journal articles you will almost certainly need to use one of the online search engines. These can be found on the ‘Indexing Services’ button on the Templeman Library website. Kent students based at Medway still need to use the Templeman pages to access online journals, although you can get to these pages through the Drill Hall Library catalogue. Take a look as well at the Subject Guides on both the Templeman and DHL websites.
Check that you have made the right selection by asking:
- Has my search been wide enough to ensure that I have identified all the relevant material, but narrow enough to exclude irrelevant material?
- Is there a good enough sample of literature for the level (PhD, Masters, undergraduate) of my dissertation or thesis?
- Have I considered as many alternative points of view as possible?
- Will the reader find my literature review relevant and useful?
Assessing the literature
Read the material you have chosen carefully, considering the following:
- The key point discussed by the author: is this clearly defined
- What evidence has the author produced to support this central idea?
- How convincing are the reasons given for the author’s point of view?
- Could the evidence be interpreted in other ways?
- What is the author's research method (e.g. qualitative, quantitative, experimental, etc.)?
- What is the author's theoretical framework (e.g. psychological, developmental, feminist)?
- What is the relationship assumed by the author between theory and practice?
- Has the author critically evaluated the other literature in the field?
- Does the author include literature opposing their point of view?
- Is the research data based on a reliable method and accurate information?
- Can you ‘deconstruct’ the argument – identify the gaps or jumps in the logic?
- What are the strengths and limitations of this study?
- What does this book or article contribute to the field or topic?
- What does this book or article contribute to my own topic or thesis?
As you note down the key content of each book or journal article (together with the reference details of each source) record your responses to these questions. You will then be able to summarise each piece of material from two perspectives:
Content: a brief description of the content of the book or article. Remember, an author will often make just one key point; so, what is the point they are making, and how does it relate to your own research project or assignment?
Critical analysis: an assessment of the relative strengths and weaknesses of the evidence used, and the arguments presented. Has anything conveniently been left out or skated over? Is there a counter-argument, and has the author dealt with this adequately? Can the evidence presented be interpreted another way? Does the author demonstrate any obvious bias which could affect their reliability? Overall, based on the above analysis of the author’s work, how do you evaluate its contribution to the scholarly understanding and knowledge surrounding the topic?
Structuring the literature review
In a PhD thesis, the literature review typically comprises one chapter (perhaps 8-10,000 words), for a Masters dissertation it may be around 2-3,000 words, and for an undergraduate dissertation it may be no more than 2,000 words. In each case the word count can vary depending on a range of factors and it is always best, if in doubt, to ask your supervisor.
The overall structure of the section or chapter should be like any other: it should have a beginning, middle and end. You will need to guide the reader through the literature review, outlining the strategy you have adopted for selecting the books or articles, presenting the topic theme for the review, then using most of the word limit to analyse the chosen books or articles thoroughly before pulling everything together briefly in the conclusion.
Some people prefer a less linear approach. Instead of simply working through a list of 8-20 items on your book review list, you might want to try a thematic approach, grouping key ideas, facts, concepts or approaches together and then bouncing the ideas off each other. This is a slightly more creative (and interesting) way of producing the review, but a little more risky as it is harder to establish coherence and logical sequencing.
Whichever approach you adopt, make sure everything flows smoothly – that one idea or book leads neatly to the next. Take your reader effortlessly through a sequence of thought that is clear, accurate, precise and interesting.
Writing up your literature review
As with essays generally, only attempt to write up the literature review when you have completed all the reading and note-taking, and carefully planned its content and structure. Find an appropriate way of introducing the review, then guide the reader through the material clearly and directly, bearing in mind the following:
- Be selective in the number of points you draw out from each piece of literature; remember that one of your objectives is to demonstrate that you can use your judgement to identify what is central and what is secondary.
- Summarise and synthesise – use your own words to sum up what you think is important or controversial about the book or article.
- Never claim more than the evidence will support. Too many dissertations and theses are let down by sweeping generalisations. Be tentative and careful in the way you interpret the evidence.
- Keep your own voice – you are entitled to your own point of view provided it is based on evidence and clear argument.
- At the same time, aim to project an objective and tentative tone by using the 3rd person, (for example, ‘this tends to suggest’, ‘it could be argued’ and so on).
- Even with a literature review you should avoid using too many, or overlong, quotes. Summarise material in your own words as much as possible. Save the quotes for ‘punch-lines’ to drive a particular point home.
- Revise, revise, revise: refine and edit the draft as much as you can. Check for fluency, structure, evidence, criticality and referencing, and don’t forget the basics of good grammar, punctuation and spelling.

Teaching and Research guides
Literature reviews.
- Introduction
- Plan your search
- Where to search
- Refine and update your search
- Finding grey literature
- Writing the review
Referencing overview
Easy cite referencing tool, choosing a reference manager.
- Reviewing research methodologies
- Get material not at RMIT
- Further help
A large part of conducting and writing a literature review is to reference the relevant sources that you have found.
A number of referencing tools are available that can help you manage your references.
RMIT University provides a license to the EndNote software program, although there are alternative reference management software available.
The Library has also developed Easy Cite , providing examples for key referencing styles.
Request referencing support
- Request Research Advice HDR students are welcome to request assistance with EndNote, or referencing in general.
EndNote is a software program that helps you to:
- gather, store and manage references
- automatically create and format bibliographies in your referencing style
- search and retrieve records from catalogues and databases
- insert citations directly into documents in your referencing style
- EndNote: a beginner's guide Library's official guide on learning and using EndNote.
Alternatives to EndNote
- Reference management tools EndNote, Mendeley and Zotero are just some of the tools used for managing references and bibliographies.
- Reference managers This guide provides an introduction to three common Reference Managers - EndNote, Zotero and Mendeley. It also provides a comparison guide and instructions to help get you started.

This module is part of the Research and Writing Skills for Academic and Graduate Researchers . It helps researchers decide which reference manager to use to organise their references in their work. The module explores the features of three popular reference managers – Endnote, Zotero and Mendeley – and helps in the decision of which one is best for research practices.
Learn how to choose a reference manager
Book cover attribution : "Research and Writing Skills for Academic and Graduate Researchers" by RMIT University Library is licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0 . Cover design by Dr. Lisa Cianci. Artwork 'Luwaytini' by Mark Cleaver, Palawa (underlayed), All rights reserved. Cover image: Human Skills by Vicons Design from Noun Project .
- << Previous: Writing the review
- Next: Reviewing research methodologies >>

- Last Updated: May 13, 2024 7:34 AM
- URL: https://rmit.libguides.com/literature-review

Literature Reviews
- 5. Synthesize your findings
- Getting started
- Types of reviews
- 1. Define your research question
- 2. Plan your search
- 3. Search the literature
- 4. Organize your results
How to synthesize
Approaches to synthesis.
- 6. Write the review
- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools
- Thompson Writing Studio This link opens in a new window
- Need to write a systematic review? This link opens in a new window

Contact a Librarian
Ask a Librarian
In the synthesis step of a literature review, researchers analyze and integrate information from selected sources to identify patterns and themes. This involves critically evaluating findings, recognizing commonalities, and constructing a cohesive narrative that contributes to the understanding of the research topic.
Here are some examples of how to approach synthesizing the literature:
💡 By themes or concepts
🕘 Historically or chronologically
📊 By methodology
These organizational approaches can also be used when writing your review. It can be beneficial to begin organizing your references by these approaches in your citation manager by using folders, groups, or collections.
Create a synthesis matrix
A synthesis matrix allows you to visually organize your literature.
Topic: ______________________________________________
Topic: Chemical exposure to workers in nail salons
- << Previous: 4. Organize your results
- Next: 6. Write the review >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 8:42 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.duke.edu/litreviews

Services for...
- Faculty & Instructors
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- International Students
- Patrons with Disabilities
- Harmful Language Statement
- Re-use & Attribution / Privacy
- Support the Libraries

- Open access
- Published: 14 May 2024
Effect of cytoplasmic fragmentation on embryo development, quality, and pregnancy outcome: a systematic review of the literature
- Ariella Yazdani 1 , 3 ,
- Iman Halvaei 2 ,
- Catherine Boniface 1 &
- Navid Esfandiari ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0979-5236 1 , 4
Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology volume 22 , Article number: 55 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
30 Accesses
Metrics details
The role of cytoplasmic fragmentation in human embryo development and reproductive potential is widely recognized, albeit without standard definition nor agreed upon implication. While fragmentation is best understood to be a natural process across species, the origin of fragmentation remains incompletely understood and likely multifactorial. Several factors including embryo culture condition, gamete quality, aneuploidy, and abnormal cytokinesis seem to have important role in the etiology of cytoplasmic fragmentation. Fragmentation reduces the volume of cytoplasm and depletes embryo of essential organelles and regulatory proteins, compromising the developmental potential of the embryo. While it has been shown that degree of fragmentation and embryo implantation potential are inversely proportional, the degree, pattern, and distribution of fragmentation as it relates to pregnancy outcome is debated in the literature. This review highlights some of the challenges in analysis of fragmentation, while revealing trends in our evolving knowledge of how fragmentation may relate to functional development of the human embryos, implantation, and pregnancy outcome.
Introduction
Human preimplantation embryo scoring systems have been widely used to predict blastocyst development and implantation rate after in-vitro fertilization (IVF). The grading of embryos on day-2 and -3 after fertilization is largely subjective and interpretation varies across IVF laboratories, as it is commonly based on morphological appearance. Characteristics in early embryo grading schema include the amount of cytoplasmic fragmentation (CF) during early cleavage, speed of cellular division, number, size, and symmetry of cells (blastomeres). As defined by the Istanbul consensus workshop on embryo assessment, a fragment is “an extracellular membrane-bound cytoplasmic structure that is < 45 µm diameter in a day-2 embryo and < 40 µm diameter in a day-3 embryo” [ 1 ]. There are several different systems to evaluate embryo morphology including Hill’s scoring system [ 2 ] Cummins' grading system [ 3 ] ASEBIR grading system [ 1 ], the UK/ACE grading scheme [ 4 ]; each system has its own classification for degree of fragmentation as well as embryo grade. This heterogeneity further complicates analysis of fragmentation in relation to outcomes.
CF has been shown to occur early in embryonic division and is a common phenomenon seen in embryos cultured in vitro. CF has traditionally been used as a metric of embryo implantation potential [ 3 , 5 , 6 , 7 ]. The amount and pattern of fragments are analyzed in early development, incorporated into the embryo grade depending on grading system, and used to help select the most developmentally competent embryo to be transferred during an IVF cycle. This classification system is important as a proportion of embryos within a single cohort will not successfully develop to the blastocyst stage in vitro. Although there are various contributing factors to an embryo’s developmental capacity and viability, it is largely agreed upon that fragmentation plays an important role. It seems that the etiology of embryo fragmentation is not fully understood but it may be related to several factors like gamete quality, culture condition, and genetic abnormalities in the embryo [ 8 ]. It is difficult to directly compare and quantify relative degrees of fragmentation across studies. However, it has been repeatedly shown that the extent of fragmentation and implantation potential are inversely proportional [ 5 , 7 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 ]. While a low degree of fragmentation does not seem to significantly impact embryo viability, severe fragmentation does [ 7 , 22 , 23 ]. Alongside the cell to cytoplasmic ratio, the pattern and distribution of fragmentation influence the developmental quality of the embryo [ 7 , 24 ]. There are two main patterns of embryo cytoplasmic fragments: scattered and concentrated. The former is characterized by fragment contact within several blastomeres and is related to aneuploidy [ 25 ]. Time-lapse studies have shown that fragmentation is thought to be a dynamic process, where some fragments can be expelled or reintroduced into the cells as the embryo continues to divide [ 25 , 26 ]. Fragments can also easily move or rotate around the associated blastomere and change their position in the embryo [ 27 ].
Current grading systems used to evaluate cleavage-stage embryos are largely based on day-2 or -3 morphology. This can be problematic, as developmental growth of an embryo is variable and the grade of a developing embryo at one point in time is not guaranteed to persist. For example, studies have suggested that embryo selection on day-2 or -3 based on morphological grade can be unreliable and lead to negative pregnancy outcomes [ 28 , 29 , 30 ]. Accordingly, new parameters for predicting implantation success have been proposed including extended embryo culture to the blastocyst stage to day-5, -6 or -7 [ 31 ]. Delaying embryo transfer to the blastocyst stage is advantageous as it can limit the number of unsuccessful embryo transfers and biochemical pregnancies or clinical pregnancy losses in IVF. While there are multiple reports on the impact of cleavage-stage embryo quality on blastocyst formation and blastocyst quality [ 32 , 33 ], few have specifically looked at the degree of fragmentation as a predictive variable.
In this systematic review, we comprehensively reviewed the available literature on the origin and characteristics of CF, factors affecting CF, and the effect of CF and fragment removal on embryo development and pregnancy rate.
Materials and methods
A search was conducted on October 10, 2023, using PubMed and Google Scholar databases in accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis guidelines [ 34 ]. In PubMed, the search terms “embryo*[tw] OR cleavage stage [tw] OR "Embryonic Structures"[Mesh] OR "Embryonic Development"[Mesh] OR "Embryo, Mammalian"[Mesh] OR "Cleavage Stage, Ovum"[Mesh]” AND “cytoplasm*[tw] AND fragment*[tw] AND “(Blastocyst*[tw] OR "Blastocyst"[Mesh]) AND (form* OR develop* OR quality*)” were used. A title search in Google Scholar using search terms as above and “embryo cytoplasm fragmentation”, “blastocyst quality”, “blastocyst development” was performed. Only full-text publications in English were included. Full-text articles which did not have any mention of cytoplasmic or embryo fragmentation were excluded, however articles which mentioned both DNA fragmentation and CF were included. Since most of the studies discussing CF also discussed other morphologic features of the embryo, studies that mention embryo morphology, grade or quality were also included. Articles that looked at non-human embryo fragmentation, case reports, case series, book chapters and review papers were excluded. Titles and abstracts were screened, and study quality and bias were assessed. The primary outcomes of interest were embryo quality, blastocyst formation, and pregnancy outcome.
Figure 1 provides details of study screening and inclusion. There were 206 studies screened between the two search engines PubMed ( n =106) and Google Scholar ( n =100). There were 18 duplicates giving a total of 188 articles. Due to the small number of studies from the search criteria, no filter of time was placed. After removal of non-full text articles, articles that used non-human embryos, and articles not relevant to the topic, 20 articles were eligible for inclusion. Forty relevant references from the articles were also extracted, reviewed, and included in this review. These additional articles were reviewed with the same inclusion and exclusion criteria as mentioned above. A total of 60 articles were included in the qualitative synthesis of this review.
Article Identification and Screening
Origin and etiology of CF
The etiology of CF is not completely understood. There are several proposed theories as to why embryos display variable degrees of fragmentation. Fragmentation has been shown to be a natural, unpredictable process both in vitro and in vivo and is documented in various species [ 35 , 36 ]. This suggests that embryo fragmentation is neither species-specific nor solely a byproduct of in vitro culture. Assisted reproductive technology (ART) and IVF techniques, such as time-lapse microscopy (TLM) and transmission electron microscopic (TEM) analyses, have recently allowed for further understanding of embryo developmental potential and fragmentation (Figs. 2 and 3 ). Seven of the included studies in this review propose potential hypotheses as to the origin of CF (Table 1 ). Three of the articles evaluated gamete quality as related to fragmentation in a developing embryo [ 37 , 38 , 39 ].
Human cleavage stage embryos a) Day-2 embryo at 4-cell stage with no fragmentation, b) fragmented Day-2 embryo, c) Day-3 embryo at 8-cell stage with no fragmentation, d) fragmented Day-3 embryo, e) Day-5 cavitating Morula with no fragmentation, f) fragmented Day-5 cavitating Morula
Ultrastructure and organelle microtopography of an embryo fragment by transmission electron microscopy. Ly: primary lysosome, M: mitochondrion, rM: remnant of regressing mitochondrion, MV: mitochondria-vesicle complex, V: vesicle; scale bar: 1 µM
An early study showed that sperm DNA oxidation has been associated with embryo development and quality, and therefore linked to CF [ 37 ]. Nucleolar asynchrony in the zygote from sperm DNA fragmentation has previously been shown to predict future low-quality blastocyst development. A positive correlation has also been found between the percentage of sperm OxiDNA-stained cells with embryo fragmentation on day-2 and -3 of development. Sperm DNA oxidation may therefore be associated with fragmented, nonviable, poor-quality embryos [ 37 ] . A recent study also showed the negative correlation between sperm DNA fragmentation and blastomere DNA fragmentation and blastulation rate [ 40 ]. Further studies are needed to confirm the impact of sperm DNA oxidation on embryo fragmentation.
An observational study documented the degree of fragmentation of human embryos as they progressed through mitotic cell cycles [ 38 ]. In this study, the authors analyzed nearly 2,000 oocytes and 372 embryos, and found that increased embryo fragmentation (>50%) was associated with a specific pattern of development: delayed first division (oocyte spindle detected at 36.2 hours after hCG injection vs. 35.5 hours in low fragmentation), a significantly earlier start of the second mitosis (8.9 hours vs. 10.8 hours after the first mitosis), and a significant delay of the third mitosis after the second mitosis (2.2. hours vs. 0.6 hours). The authors did not comment on whether fragmentation could be a result of the cell dividing before proper chromosome alignment, or if existing aneuploidy resulted in erroneous cleavage patterns [ 38 ].
Polar body (PB) fragmentation has also been investigated in relation to cytoplasmic fragmentation. Ebner et al., in a prospective study analyzed the relationship between a fragmented first PB and embryo quality in patients undergoing ICSI. Two groups of oocytes were analyzed according to PB fragmentation: intact first PBs and those with fragmented PBs. Forty-two hours after ICSI, embryo morphology (i.e., number of blastomeres and degree of fragmentation) was recorded. Overall, a significantly higher percentage of cytoplasmic fragmentation was seen in day-2 embryos that originated from oocytes with fragmented first PBs than those with intact PBs ( P < 0.05). This study further supports the concept that oocyte quality contributes to overall embryo fragmentation and provides evidence that preselection of oocytes may contribute to the prognosis of embryo quality and blastocyst development [ 39 ]. The role of PB fragmentation on embryo quality was confirmed in other studies [ 41 , 42 ], however, a recent study has not recommended considering PB status as a tool for embryo selection [ 43 ].
Beyond analysis of gamete quality, other studies have shown a biochemical relationship between embryo competence and fragmentation. One study showed that disturbances in E-cadherin, a cell adhesion protein that plays a critical role in morphogenesis, occur in embryos with cleavage abnormalities and extensive cytoplasmic fragmentation, suggesting a possible mechanism to the loss of embryonic viability [ 44 ]. Further, by using mitochondrial fluorescence techniques, Van Blerkom et al., found that mitochondrial distribution at the pronuclear stage may be an epigenetic factor related to the organization of the embryo and further embryonic development [ 45 ]. Blastomeres that were deficient in mitochondria and thus ATP at the first or second cell division remained undivided and often died during subsequent culture. Although this study examined morphologically normal (unfragmented) cleavage-stage embryos, it may support the idea that perinuclear mitochondrial distribution and microtubular organization influence developmental capacity of early cleavage-stage embryos [ 45 ]. Higher numbers of mitochondria reported in fragmented compared to the normal blastomeres show the rapid depletion of ATP in the fragmented embryos [ 21 ]. There have also been reports of increased gene transcription of mitochondrial factors like OXPHOS complexes, ATP synthase, and mtDNA content in highly fragmented embryos compared to controls [ 46 ]. Mitochondrial activity is lower and more centralized in fragmented embryos compared to good quality embryos on day-3 [ 47 ]. Mitochondria are the main source of ATP for embryo mitosis, and their proper function is essential for embryo development. More research is needed to elucidate the morphology and role of mitochondria in embryo development, especially in relation to fragmentation.
A subsequent study by Van Blerkom et al., analyzed the temporal and spatial aspects of fragmentation through TLM and TEM analyses from the pronuclear to the 10-12-cell stage. Through TLM, the authors visualized the non-discrete, dynamic nature of fragments and noted that many were “bleb-elaborations” of the plasma membrane and cytoplasm. They characterized two patterns of fragmentation: definitive and pseudo-fragmentation. Definitive fragmentation was described as fragments detached from a blastomere, and pseudo-fragmentation was assigned when the fragments were no longer detectable during subsequent development. Often one developing embryo would show both fragmentation patterns at different stages of development, suggesting that these patterns may have different etiologies and effects on embryo development competence [ 47 ]. Hardarson et al., similarly used TLM to document that fragments are dynamic and can be internalized throughout cleavage during culture periods. The contents of the fragments were noted to be internalized and released into the cytoplasm of the blastomere and seen on multiple time-lapse photographs as a cytoplasmic turbulence. This is the first reported evidence that cellular fragments can “disappear” during the culture period in human IVF [ 26 ]. It seems that in mild to moderate CF, the timing of embryo evaluation and grading can affect the reported percent of fragmentation.
Lastly, we have included a preliminary study performed by Sermondade et al., that suggests a specific subgroup of patients who have had repeated IVF failures (presumably due to a recurring high rate of fragmented embryos) may benefit from early intrauterine embryo transfer at the zygote stage (2PN) [ 48 ]. Data showed a delivery rate per oocyte retrieval of 18.9%, which was significantly higher than the delivery rate of 7.5% in the matched control group. The results were encouraging and suggestive of a safe, non-invasive rescue strategy for patients who experience recurrent highly fragmented embryos and failed IVF attempts. The data further suggests that fertilized oocytes of this subgroup may have deficiencies in certain maternal factors (i.e., stress-response factors) that do not allow normal embryo development in culture environments [ 48 ]. Another study was also confirmed application of zygote transfer in patients with history of low-quality embryos [ 49 ]. However, further studies are required to verify the impact of this technique for patients with history of fragmented embryos.
Apoptosis is another proposed etiology of fragmentation. Apoptosis may occur in blastomeres with defective cytoplasm or abnormal chromosomes, leading to embryo fragmentation [ 50 ]. There are several studies reporting apoptosis in both fragments and neighboring blastomeres in a fragmented embryo [ 24 , 50 ]. Chi et al., showed that fragments are associated with both apoptosis and necrosis [ 21 ]. One of the factors that appears to induce apoptosis in blastomeres is suboptimal culture conditions such as hypoxia [ 51 ]. In addition, there are controversial reports on the role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in embryo fragmentation [ 52 , 53 ]. It has been shown that ROS are present at high levels in the culture media of fragmented embryos [ 52 , 54 ]. Chen et al., recently showed that embryo culture in 5% oxygen, from days 1 to 3, is associated with higher embryo quality and live birth rate compared to 20% oxygen [ 55 ]. The effects of culture condition modifications, such as hypoxia and ROS, on embryo fragmentation need to be clarified to understand the importance of culture condition in this process.
Membrane compartmentalization of DNA, abnormal cytokinesis, and extra vesicular formation are other proposed theories for embryo fragmentation [ 8 ]. Defects or damages in mitochondria are associated with low ATP and high ROS production leading to a compromised cell division and cytokinesis [ 27 ]. In addition, there is a correlation between embryo fragmentation and ploidy status. Chavez et al., showed that CF was seen in a high proportion of aneuploid embryos, and that meiotic and mitotic errors may cause fragmentation in different cell development stages. Meiotic errors were associated with fragmentation at one-cell stage while mitotic errors were associated with fragmentation at interphase or after first cytokinesis [ 56 ]. Chromosomally abnormal embryos often have severe fragmentation, which may be another cause of CF [ 55 , 57 ].
Overall, the precise cause of CF has yet to be clearly defined. The above investigations have elucidated potential sources and associations of what is likely a complex and multifactorial process and represent our current understanding of CF origin.
What is contained in CF?
Four of the included studies used various technological advances to study the contents of CF in human embryos (Table 2 ). Two studies used TEM methods to evaluate fragment ultrastructure (Fig. 3 ) [ 21 , 58 ]. Fragments were extracted from embryos with 10-50% fragmentation and the ultrastructure evaluated by TEM. Micrographs showed that the fragments had a distinct membrane containing cytoplasmic organelles including mitochondria, mitochondria-vesicle complexes, Golgi apparatus, primary lysosomes, and vacuoles. Mitochondria were the most abundant structure.
In an additional evaluation of CF contents, Johansson et al., analyzed DNA content of fragments to define a cutoff diameter for an anucleate fragment or blastomere. Findings showed that 98% of fragments <45 µm on day-2 and 97% of those <40 µm on day-3 contained no DNA and, if not reabsorbed into a blastomere, showed a loss of cytoplasm. Presence of essential blastomere organelles such as mitochondria, mRNA, and proteins within cytoplasmic fragments were related to embryo development arrest [ 59 ]. Lastly, Chi et al., also used TEM to examine ultrastructure of the human fragmented embryos and found that blastomeres with anucleate fragments contained fewer mitochondria in their cytoplasm compared to normal blastomeres [ 21 ].
Cell death and CF
Eight of the included studies analyzed the relationship between cell death and embryo fragmentation (Table 3 ). Five studies analyzed the status of chromatin in arrested fragmented embryos through a combined technique for simultaneous nuclear and terminal transferase-mediated DNA end labelling (TUNEL) [ 24 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 ]. Two studies used a comet assay to analyze DNA fragmentation [ 21 , 63 ]. Four of the eight studies used Annexin V staining [ 21 , 61 , 62 , 63 ] with three including the presence of propidium iodide (PI) to compare apoptosis to necrosis [ 21 , 61 , 63 ].
Jurisicova et al., used a combined nuclear and fragmented DNA labeling approach which allowed distinction between chromatin status and DNA fragmentation, which serve as markers of apoptosis versus necrosis respectively [ 60 ]. After fertilization, embryos were stained with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). In cases of compromised cell membrane integrity, DAPI stain was observed in the cytoplasm as a sign of necrosis. Concomitant use of TUNEL labeling reflected the integrity of the DNA and allowed distinction between necrotic and apoptotic cells. Through combined techniques of DAPI/TUNEL, TEM, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and stereomicroscopic observations, 153 of 203 (75.4%) fragmented early cleavage-stage embryos displayed signs of apoptosis (i.e., chromatin condensation, cellular shrinkage, DNA fragmentation, presence of cell corpses) with or without normal nuclei [ 60 ].
Similarly, Levy et al., analyzed early arrested or fragmented preimplantation embryos and the pattern of DNA fragmentation using TUNEL assay and the presence of phosphatidylserine through Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labelled Annexin V, a phosphatidylserine binding protein. The authors observed TUNEL staining in one or more nuclei of 15 out of 50 (30%) arrested embryos from the 2-cell stage to uncompacted morulae, all of which had high degrees of CF. Furthermore, embryos with regular-sized blastomeres without fragmentation were all TUNEL negative [ 50 ].
A separate prospective study by Antczak et al., explored the possible association between fragmentation and apoptosis using PI and Annexin V staining of plasma membrane phosphatidylserine and TUNEL analysis of blastomere DNA [ 24 ]. In contradistinction to prior studies, these authors found no direct correlation between fragmentation and apoptosis. Virtually all blastomeres that were PI negative, intact or fragmented, showed no TUNEL or annexin V fluorescence, suggesting no signs of apoptosis [ 24 ].
Liu et al., used a similar methodology of TUNEL labeling and Annexin V staining to detect markers of apoptosis in fragmented human embryos derived from IVF [ 61 ]. Overall, highly fragmented embryos had apoptotic features including bright fluorescence (positive TUNEL labeling signifying DNA fragmentation) on the cell corpses and in intact blastomeres [ 61 ]. By staining cells with both annexin V and PI, this study was able to demonstrate that apoptosis occurs frequently in fragmented human embryos and the coexistence of apoptotic, necrotic and viable sibling blastomeres can occur. Sibling blastomeres within an embryo often showed apoptotic features that led to secondary necrosis while others did not initiate apoptosis. The authors did not find a significant difference in the expression frequency of apoptotic genes between viable and nonviable or arrested embryos [ 61 ].
Chi et al., stained human embryos ( n =10) with annexin V and PI and found that human fragmented embryos exhibited characteristics of both necrosis and apoptosis [ 20 ]. Rather than TUNEL assay, these authors used a modified sperm comet assay to investigate DNA fragmentation of human fragmented embryos. They found that 6/7 human fragmented embryos (85.1%) stained positively for PI with the intensity of staining increasing with the degree of fragmentation. Of note, DNA fragmentation was observed in fragmented human embryos but not in the normal embryo [ 21 ].
Metcalfe et al., analyzed the expression of 11 BCL-2 family genes in normally developing embryos and in severely fragmented embryos [ 64 ]. They found that the expression of BCL-2 family genes was highest in the pronuclear stage and eight-cell stages, and lowest at the two-cell, four-cell, and blastocyst stages in developmentally intact embryos. Furthermore, the expression did not change in fragmented embryos, suggesting that embryo fragmentation does not likely compromise mRNA integrity and gene detection [ 64 ]. However, like Liu et al., [ 61 ] these authors did detect far fewer pro-apoptotic BCL-2 genes in fragmented embryos at the eight-cell stage. The authors noted that these findings do not distinguish between iatrogenic apoptosis from suboptimal in-vitro culture conditions [ 64 ]. A separate study by Jurisicova et al. similarly analyzed gene expression at the 2-, 4- and 8-cell stage of fragmented embryos. Embryos that had 30-50% fragmentation showed a significant increase in Hrk mRNA levels, a BCL-2 protein encoding gene ( P = 0.016). Further, these authors found an increase in Caspase-3 mRNA in fragmented embryos, as well as induction of Caspase-3-like enzyme activity in nucleated fragments, although this finding was not statistically significant [ 65 ].
Van Blerkom et al., also used TUNEL assay in conjunction with the comet assay as a method of identifying the specific pattern of cell death (necrosis, lysis or apoptosis) and the extent of DNA damage in developing embryos [ 47 ]. They analyzed the integrity of the plasma membrane through annexin V staining with PI. They examined both transient and persistent fragment clusters at day-3 and 3.5 embryos for evidence of programed cell death using time-lapse video and TEM. In contrast to previous studies, they found no indication of nuclear DNA damage or loss of membrane integrity. These results, led the authors to hypothesize that the fragmentation observed was not characteristic of programed cell death, but rather resembled features of oncosis. The culture in this study was not severely oxygen-deprived and thus the authors concluded that this oncosis-like process was potentially a result of disproportionate mitochondrial segregation during the first cleavage division. Without sufficient mitochondria, the early blastomeres did not maintain adequate ATP for normal cell function which may have precipitated an ATP-driven oncosis-like process [ 47 ].
Lastly, a study by Bencomo et al., found correlations between the degree of apoptosis in human granulosa-lutein (GL) cells, the outcome of IVF-ET cycle, the percentage of embryo fragmentation, and patient’s age [ 66 ]. Human GL cells were collected from follicular fluid, cultured for 48 hours, and marked with caspACE FITC-VAD-FMK, a fluorescent marker for activated caspases. Results showed that GL cells of older women (>38 years old) were significantly more susceptible to apoptosis at 43.2 ± 18.0% compared to the younger group (<38 years old) with a mean percentage of apoptotic cells 33 ± 17.2%. Women who had a positive pregnancy had a lower level of apoptosis in GL cultures than those who did not get pregnant (30.2 ± 14% vs. 40.4 ± 19.5%). There was a positive correlation between embryo fragmentation and GL cell apoptosis ( r = 0.214). Overall, the level of apoptosis of cultured GL cells was correlated with IVF outcome [ 66 ].
These studies demonstrate the diversity among techniques to evaluate cell death in the developing embryo. TUNEL labeling, sperm comet assay, annexin V staining or some combination of these techniques have been described. Furthermore, there are discrepancies between the stage at which apoptosis might occur, with majority of studies cited here suggesting that cell death occurs in early stages of development before blastocyst formation. While some studies suggest that fragmented embryos display signs of apoptosis, these findings are still disputed and the distinction between apoptosis and necrosis is not clearly defined in the literature.
Patient age and CF
There are inconsistencies within the literature regarding the relationship between maternal age and CF. A total of six studies in this review focused on this relationship (Table 4 ). Three of the studies found a positive correlation between patient age and degree of embryo fragmentation [ 67 , 68 , 69 ]. The other three studies found no age-related correlation between embryo fragmentation or quality [ 7 , 70 , 71 ].
A retrospective study by Ziebe et al., compared the relationship between age of women undergoing IVF and the proportion of anucleate fragmentation in cleavage-stage embryos. Using a logistic regression analysis, the authors compared the percentage of transfers using fragmented embryos with age; the odds of fragmentation increased by 3% per year (OR 1.033 [95% CI 0.996, 1.071]). There was a linear relationship between age and embryo fragmentation rate, with an increase in fragmentation of 0.76% per year (95% CI -0.09%, 1.61%) [ 68 ].
Keltz et al., assessed various predictors of embryo fragmentation in IVF and found that increased maternal age and lower number of oocytes and embryos were associated with increased embryo fragmentation. There was a significant difference between cycles with fragmented embryos ( n =74) at a mean age of 36.9 ± 4.24 years as compared to cycles with no fragmented embryos ( n =234) at a mean age of 35.4 ± 4.74 years. Overall, this retrospective analysis of fresh IVF cycles found that embryo fragmentation is indeed associated with older age and ultimately poor cycle outcome [ 67 ].
Contrary to these findings, an early study by Alikani et al., showed no relationship between maternal age and CF [ 7 ]. In a retrospective analysis of degree and pattern of embryo fragmentation on days 2 and 3, they defined five patterns of fragmentation. Both the degree and pattern of fragmentation impacted pregnancy and implantation rate, but the authors found no correlation between appearance of any CF pattern and maternal age. The average maternal age in their population was 35.7 ± 4.25 years [ 7 ]. Another study by Stensen et al., analyzed the effect of chronological age on oocyte quality (assessed by maturity) and embryo quality (assessed by cleavage-stage, blastomere size and embryo fragmentation). Women were divided into five age groups: ≤25, 26–30, 31–35, 36–40 and ≥41 years. The embryo morphological score was based on fragmentation and blastomere size with score of 0-4 where score of 4 being equally sized blastomeres and no fragmentation and score of 0 being cleavage arrest or morphologically abnormal embryo. The mean oocyte score and embryo morphology score were not found to be significantly different across the age groups [ 70 ]. Wu et al., also showed that age does not influence embryo fragmentation. Patient ages ranged from 20 to 44 years with a mean age of 30.6 ± 4.6 years and were divided into age groups of ≤29, 30–34, 35–37, 38–40, and ≥41 years of age. Analysis of embryos with similar degrees of fragmentation was used to assess whether maternal age was associated with embryo fragmentation and blastocyst development. There was no correlation between age and embryo fragmentation as a continuous variable ( r = 0.02; P = 0.25) nor was there a correlation when age was divided into the groups ( P = 0.2). They also found that neither age ( r = -0.08; P =0.16) nor degree of fragmentation ( r = -0.01; P = 0.81) had a significant impact on blastocyst development [ 71 ].
Recently, a retrospective time-lapse study evaluated the implantation rate of 379 fragmented embryos. The results showed that there was an association between advanced maternal age and fragmentation. Fragmentation rate was higher in patients ˃35 compared to patients ≤35 years old. It seems that the lower quality of oocytes in older patients results in increasing fragmentation [ 69 ]. Overall, the included studies have differing conclusions on the effect of maternal age and CF; varying definitions and analysis of CF remain a limitation.
IVF vs ICSI procedures and CF
Five of the included studies compared embryo quality between conventional IVF and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) procedures (Table 5 ). Two of these studies found that ICSI was associated with impaired embryo morphology compared to IVF [ 72 , 73 ], while the other three showed no difference in embryo quality between the two fertilization modalities [ 74 , 75 , 76 ]. There were no studies within our search that identified embryos created by ICSI having greater morphology grade, or less embryo fragmentation, than IVF.
Frattarelli et al., directly examined the effect of ICSI on embryo fragmentation and implantation rate compared to IVF. There was a significant difference in mean embryo grade between IVF and ICSI. IVF patients had significantly more grade I, or non-fragmented, embryos compared to the ICSI group ( P < 0.01). However, there was no significant difference in mean number of embryos per embryo grade II – IV [ 72 ].
Similarly, Hsu et al., compared embryo quality, morphology, and cleavage after ICSI with standard IVF patients. They defined the grading system from 1 – 5, ranging from no fragments (grade 1) to severe or complete fragmentation (grade 5). They found that for the overall population, when comparing ICSI and IVF patients after matching for age and number of embryos transferred, the number of embryos with good morphology was significantly greater in the IVF group compared to ICSI ( P < 0.006). The average morphology scores, similar to the results of Frattarelli et al., were significantly different between the ICSI group and the IVF group. They also found IVF patients’ embryos to have significantly better cleavage rate than those from ICSI patients ( P < 0.001) [ 73 ].
Garello et al., evaluated if fertilization via ICSI influences pronuclear orientation, PB placement, and embryo quality when compared to IVF. Embryos were assessed using morphology, and grouped as good (grades 1-2), average (grades 3-4), or poor (grades 5-6). Embryos were also assessed for cleavage regularity and proportion of fragmentation (0, <20%, 20–50%, >50%). There was no statistically significant difference in mean morphology (good, average, poor) between the groups, although they did note an apparent increase in grade 4 versus grade 3 embryos after ICSI procedure. The two groups had similar proportions of fragmentation [ 74 ].
Two other studies took a unique approach in comparing embryo quality in ICSI and IVF patients by using randomized sibling oocytes [ 75 , 76 ]. Yoeli et al., studied oocytes retrieved from patients with a less than 40% fertilization rate in a previous standard IVF cycle and divided these oocytes into a conventional insemination group and an ICSI group. Each group had over 1400 oocytes. Overall, there was no significant difference between the IVF and ICSI groups in terms of cleavage rate or rate of high-quality embryos (both Grade A embryos with ≤10% fragmentation and embryos with ≤20% fragmentation) [ 75 ]. Ruiz et al., also analyzed sibling oocytes in patients who had failed intrauterine insemination attempts. The authors similarly found no significant difference in fertilization rates and degree of fragmentation between ICSI and standard IVF groups [ 76 ]. Most studies included in the search criteria showed that ART techniques such as ICSI do not significantly impact fragmentation rate in developing embryos, suggesting that ICSI is not a significant contributor to poorer outcomes by way of embryo fragmentation. Of note, the timing of cumulus cell denudation after conventional IVF is a matter of debate; none of the included studies in this review performed short-time insemination. In a meta-analysis reviewing denudation times, the number of good quality embryos produced after retaining cumulus cells was similar to those produced after early removal of these cells, suggesting that brief insemination has no impact on CF [ 77 ]. Liu et al. also showed that short insemination time is not associated with different outcomes in terms of embryo development [ 78 ].
Effect of CF on embryo development
It is commonly believed that CF has detrimental effects on embryo development. Thirteen of the included studies found a negative effect of CF on embryo development (Table 6 ). Various approaches have been used to propose a hypothesis as to how increased fragmentation impedes embryo development.
Van Blerkom et al., showed through time-lapse video and TEM that fragments physically impede cell-cell interactions, interfering with compaction, cavitation, and blastocyst formation [ 63 ]. In an ultrastructural observational study by Sathananthan et al., 15 embryos were cultured with human ampullary cell lines and TEM used to evaluate embryo development. They noted degeneration of blastomeres, including incomplete incorporation of chromatin into nuclei and formation of micronuclei, which was possibly a consequence of being adjacent to blastomere fragments [ 79 ]. A much larger prospective study by Antczak and Van Blerkom analyzed 2293 fertilized eggs from 257 IVF cycles to examine the effect of fragmentation on the distribution of eight regulatory proteins. Fragmentation reduced the volume of cytoplasm and depleted embryos of essential organelles or regulatory proteins, compromising the embryo developmental potential. They also found that specific fragmentation patterns during various stages of embryo development, i.e., 2- and 4-cell stages, were associated with embryo viability and therefore could have clinical application in the selection of embryos for transfer [ 24 ]. As previously mentioned, fragmentation may affect compacted/morula and blastocyst quality [ 80 ]. Cell exclusion at this stage is due to failure or abnormal expression of proteins involved in compaction [ 44 , 81 ]. Blastomeres may also irregularly divide, resulting in fragmentation and exclusion from compaction [ 82 ], and excluded cells have a high rate of aneuploidy [ 83 ]. Blastocyst quality from fully compacted embryos has been reported to be higher than blastocysts with partial compaction [ 84 ].
The hypothesis that fragmentation reflects inherent embryogenetic abnormalities, such as aneuploidy, increased mosaicism, or polyploidy, is supported by multiple studies in this review [ 55 , 57 , 85 ]. Morphologically poor-quality embryos, defined by amount of fragmentation, were often found to have concomitant chromosomal abnormalities [ 57 , 85 ]. Culture environment has also been implicated in presence and degree of fragmentation. For example, Morgan et al., using video-cinematography found that embryos cultured on a monolayer of feeder cells had fewer fragments than did embryos cultured alone [ 86 ]. In addition to aneuploidy and external environment, degree of fragmentation also appears to be related to embryo quality. Both Alikani et al., and Hardy et al., have shown that a small degree of fragmentation (<15%) on day-2 embryos did not affect blastocyst formation but increased (> 15%) fragmentation was associated with significantly reduced blastocyst development [ 23 , 87 ]. Similarly, a prospective study of over 4000 embryos by Guerif et al., showed that the rate of blastocyst formation increased significantly with decreased fragmentation (<20%) on day-2 embryos [ 32 ].
A separate study by Ivec et al., graded day-4 and -5 morulae based on the degree of fragmentation (<5%, 5%–20%, or >20%) and compared their blastocyst development rate. They found a negative correlation between degree of fragmentation and clinically usable blastocysts, optimal blastocysts, and those with a hatching zona pellucida. Through logistic regression analysis, they found that with each increase in percentage of fragmentation in morulae, there was a 4% decrease in the odds of hatching (OR: 0.96, 95% CI: 0.95–0.98; P < 0.001) and optimal blastocyst formation (OR: 0.96, 95% CI: 0.94–0.97; P < 0.001) [ 88 ]. It is important to point out that the degree of embryo fragmentation, no matter at what stage of development, is measured subjectively without standardized methods. One study from Hnida et al., included here recognized this limitation and used a computer-controlled system for multilevel embryo morphology analysis [ 89 ]. The degree of fragmentation was evaluated based on digital image sequences and correlated to the blastomere size. Fragments were defined to be anucleate with an average diameter of <40 µm. Not surprisingly, the mean blastomere volume decreased significantly with increasing degree of fragmentation ( P < 0.001). In addition, average blastomere size was significantly affected by the degree of fragmentation and multinuclearity which may function as a biomarker for embryo quality [ 89 ]. Furthermore, Sjöblom et al., analyzed the relationship of morphological characteristics to the developmental potential of embryos [ 90 ]. These authors, similar to Hnida et al., found that a large cytoplasmic deficit, i.e., blastomeres not filling the space under the zona, was detrimental to blastocyst development (P < 0.044). However, this is the only study in which the extent of CF observed was not significantly associated with blastocyst development [ 90 ]. Another study using time-lapse imaging showed an association between cytoplasmic fragments at the two-cell stage and perivitelline threads. Perivitelline threads can be observed as the cytoplasmic membrane withdraws from the zona pellucida during embryo cleavage. Ultimately, the presence of these threads, despite the level of fragmentation, did not affect embryo development [ 91 ]. As demonstrated by the studies described here, the degree of CF has a largely negative effect on embryo development.
Effect of CF on embryo implantation and pregnancy
In addition to evaluating the effect of CF on preimplantation embryo development, it is important to assess the effect of CF on implantation and pregnancy outcomes. Five of the included studies have shown a negative effect of CF on implantation or pregnancy outcome (Table 7 ). Assuming that increased fragmentation is detrimental to embryo development, implantation, and pregnancy outcome, it is important to understand the embryo scoring system that determines the best embryo for transfer. Giorgetti et al., used single embryo transfers to devise an embryo scoring pattern to best predict successful implantation. Not surprisingly, higher pregnancy rates were observed with embryos that displayed no fragmentation. The authors found that both pregnancy rate and live birth rate were significantly correlated with a 4-point score based on cleavage rate, fragmentation, irregularities displayed, and presence of a 4-cell embryo on day-2 [ 12 ].
Racowsky et al., assessed if multiple evaluations of an embryo improve selection quality and thus implantation and pregnancy success. They noted that an increased level of fragmentation on both day-2 and -3 was associated with a significant reduction in the number of fetuses that developed to 12 weeks. They also noted that severe fragmentation (>50%) impaired overall embryo viability and may be related to low pregnancy rates and high risk of congenital malformations. The authors ultimately concluded that single day morphological evaluation on day-2 or day-3 has the same predictive value to a multi-day scoring system [ 22 ].
Another retrospective analysis of 460 fresh embryo transfers by Ebner et al., sought to determine the impact of embryo fragmentation on not just pregnancy, but also obstetric and perinatal outcomes. There was a significant relationship between fragmentation and implantation and clinical pregnancy rate, but not with multiple pregnancy rate or ongoing pregnancy rate [ 10 ]. Alikani et al., also studied embryo fragmentation and its implications for implantation and pregnancy rate and included fragmentation pattern into their discussion. They too found a significant decrease in implantation and pregnancy rate as the degree of fragmentation increased. They identified an effect on pregnancy rate when the degree of fragmentation was greater than 35%. The authors went on to discuss that not all fragmentations are detrimental to the embryo development and that the pattern of fragmentation matters. They found that fragmentation pattern type IV, defined as having large fragments distributed randomly and associated with uneven cells, had significantly lower implantation and clinical pregnancy rates when compared to types I-III. They concluded that detaching blastomere cytoplasm as large fragments is most detrimental to embryo development and implantation rate. In contrast, small, scattered fragments (type III) did not seem to appreciably affect the cell number or pose a serious threat to further development [ 7 ].
Lastly, Paternot et al., used sequential imaging techniques and a computer-assisted scoring system to study blastocyst development and the effect of fragmentation on clinical pregnancy. The authors reviewed the volume reduction over time as a measure of embryo fragmentation. They analyzed volumes on day-1 to -3 and found a significant association between total embryo volume and pregnancy rate on both day-2 ( P = 0.003) and day-3 ( P = 0.0003), with the total volume measured on day-3 being the best predictor of pregnancy outcome [ 92 ]. In contrast, Lahav-Baratz recently showed that there was no association between fragmentation rate and abortion or live birth rate. It was concluded that fragmented embryos still have implantation potential and could be considered for transfer when applicable [ 69 ].
Effect of CF removal on embryo development
The effect of fragment removal on IVF outcomes has been controversial. Six of the studies included in this review discussed the impact of removing fragments on embryo development (Table 8 ) [ 7 , 67 , 93 , 94 , 95 , 96 ]. The literature is mixed, with some studies showing improvement in embryo development quality after fragmentation removal [ 7 , 93 ], and others showing no difference at all [ 70 , 94 , 95 ].
Alikani et al., were one of the first investigators to define various patterns of fragmentation and perform microsurgical fragment removal to improve implantation potential [ 7 ]. The authors found that the pattern and degree of fragmentation, and not merely the presence of fragmentation, was significant. When assisted hatching and microsurgical fragment removal was performed, there was an overall 4% increase in implantation rate. They concluded that the removal of the fragments possibly restored the spatial relationship of the cells and limited the interference of cell-cell contact. Further, their preliminary data showed that blastocysts formed after fragment removal were better organized than their unmanipulated counterparts [ 7 ].
Eftekhari-Yazdi et al., similarly studied the effect of fragment removal on blastocyst formation and quality of embryos [ 93 ]. They compared day-2 embryos without removal of fragments to those that fragments were microsurgically removed. There were significantly higher quality embryos in defragmented group compared to the control. Furthermore, fragment removal improved the blastocyst quality compared to the control group. There was also a reduction of apoptotic and necrotic cells in experimental group when compared with the control group [ 93 ].
Two separate studies by Keltz et al., assessed implantation, clinical pregnancy, and birth outcomes after defragmentation [ 67 ], as well as embryo development and fragmentation rate after day-3 embryo defragmentation [ 94 ]. The authors first compared cycle outcomes between low-grade embryos that underwent micromanipulation for fragment removal (>10% fragmentation) and high-grade embryos that did not undergo defragmentation but were hatched on day 3. When compared, the defragmented group showed no difference in rates of implantation, clinical pregnancy, live birth, spontaneous abortion, or fetal defects as compared to the cycles that included all top-grade embryos. Factors associated with poor IVF prognosis and formation of embryo fragments included advanced age, decreased number of oocytes and embryos, and embryo grade [ 67 ].
A separate prospective randomized study by Keltz et al., looked more specifically at day-5 fragmentation, compaction, morulation and blastulation rates after low grade day-3 embryo defragmentation [ 94 ]. Paired embryos from the same patient, not intended to be transferred, were randomly placed in either the experimental group, assisted hatching and embryo defragmentation, or control group (assisted hatching alone). Paired embryos had no difference in mean cell number, percent fragmentation, and grade before randomization. Results showed that on day-5, embryos in the defragmentation group had significantly diminished fragmentation when compared with controls; however, there was no difference in compaction rate, morula formation rate or blastocyst formation rate. Embryo grade generally improved in the treatment group, but this was not statistically significant. Overall, in both groups, improved embryo development was significantly associated with lower levels of fragmentation in the day-3 embryos, supporting the idea that defragmented embryos maintain their reduced fragmented state throughout preimplantation development. Of note, this study had 35 embryos in each group and was limited to lower grade embryos not intended for transfer [ 94 ].
Another, larger prospective randomized study by Halvaei et al., compared the effect of microsurgical removal of fragments on ART outcomes. The authors divided 150 embryos with 10-50% fragmentation into three groups, case ( n =50), sham ( n =50), and control ( n =50). They found no significant difference in rates of clinical pregnancy, miscarriage, live birth, multiple pregnancies, or congenital anomalies between these groups, ultimately showing that cosmetic microsurgery on preimplantation embryos to remove CFs had no beneficial effect [ 95 ].
Lastly, a pilot study by Yumoto et al., aimed to decrease CF in developing embryos by removing the zona pellucida of abnormally fertilized (3PN) donated oocytes [ 96 ]. Although they did not attempt to remove fragments themselves, this study is included as ZP-free oocytes are sometimes encountered in or because of ART procedures, i.e., ICSI. The results suggest that the rate of fragmentation is decreased after mechanical ZP removal. The authors concluded that ZP is not always necessary for normal embryo development since the ZP-free embryos developed normally, maintained their cell adhesions, and had a decreased rate of fragmentation [ 96 ]. It seems that defragmentation of an aneuploid or severely fragmented embryo, only improves the embryo morphology grade but the quality and fate of embryo is not changed [ 97 ].
CF and chromosomal abnormalities in embryo
Although the relationship between DNA fragmentation and chromosomal abnormalities has been more commonly explored in the literature, CF may also be related to intrinsic chromosomal abnormalities in developing embryos. Fourteen studies included in this review explored this relationship (Table 9 ) [ 55 , 56 , 85 , 98 , 99 , 100 , 101 , 102 , 103 , 104 , 105 , 106 , 107 , 108 ].
CF was rarely seen in embryos with normal chromosomal content. Findikli et al., studied DNA fragmentation and aneuploidy in poor quality embryos by TUNEL and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) techniques. Within seven chromosomally abnormal embryos, each had variable degrees of CF [ 98 ]. This study suggests that DNA fragmentation, being a sign of chromosomal abnormalities, may exist together with CF.
An earlier study by Munne et al., examined 524 embryos using FISH analysis for three to five chromosomes. While controlling for age, they divided the embryos into three groups: arrested, slow and/or fragmented, or morphologically and developmentally normal. They found that polyploidy was the most common chromosomal abnormality in the arrested embryo group and decreased with increasing embryonic competence, with 44.5% polyploidy in arrested compared to 2.1% in morphologically normal embryos. Maternal age was not associated with polyploidy rates, but aneuploidy significantly increased with maternal age in morphologically normal human embryos [ 57 ]. Another early study by Almeida and Bolton also examined the relationship between chromosomal abnormalities and embryonic developmental potential. They found that cleavage-stage embryos with poor morphology, defined as irregular shaped blastomeres with severe fragmentation, showed a higher incidence of chromosomal abnormalities than those with good morphology [ 100 ]. Magli et al., found a more direct relationship between chromosomal abnormalities and embryo fragmentation in a larger retrospective study of nearly 1600 embryos. There was a strong association between percentage of fragmentation and chromosomal abnormalities (monosomies and trisomies), where 90% of chromosomal abnormalities were found in embryos with greater than 40% fragmentation [ 101 ].
Another retrospective study comparing maternal age to embryo morphology and chromosomal abnormalities was conducted by Moayeri et al., By examining nine chromosomes in day-3 embryos, they found that morphology predicted chromosomal status in the advanced maternal age group (≥38 years old), but not in younger patients. Fragmentation alone predicted euploidy in both the advanced maternal age and younger groups. This suggests that cellular fragmentation may be a predictor of chromosomal competence and thus embryo developmental potential [ 102 ].
In contrast, Baltaci et al., examined 1,000 embryos and concluded that embryo morphology was not predictive of euploidy and that a considerable number of chromosomally abnormal embryos with good development potential may be selected for embryo transfer. They used FISH for five chromosomes and found that a large proportion of both normal and aneuploid embryos were evaluated as top quality (grade I). For example, 66% of chromosomally abnormal embryos were of good quality (grade I and II). They found no significant difference among aneuploid embryos when distributed by age. However, a higher embryo quality found in normal compared to aneuploid embryos [ 103 ].
In addition, Pellestor et al., compared the relationship between morphology and chromosomal abnormalities in two separate studies. The first study found that aneuploidy was the most frequently observed abnormality after cytogenetic analysis of preimplantation embryos [ 55 ]. They defined the quality of embryos as good (grade I and II) and poor (grades III and IV). There was an increased chromosomal abnormality in poor quality embryos (84.3%) when compared to embryos with good quality (33.9%). Both aneuploidy and fragmentation were shown to be predominant in poor quality embryos, whereas mosaicism and polyploidy were the most frequent abnormalities in good quality embryos [ 55 ]. Pellestor et al., also performed cytogenetic analysis on 411 poor-quality embryos (grade IV) [ 85 ]. Ninety percent of the successfully analyzed cases showed abnormal chromosome complements, with aneuploidy being the most frequently observed. These results further support that a large majority of poor grade embryos are chromosomally abnormal and ultimately offer low chance of reproductive success for either embryo transfer or cryopreservation [ 85 ].
A separate study by Chavez et al., combined time-lapse imaging with karyotypic status of blastomeres in the 4-cell embryo to test whether blastomere behavior may reflect chromosomal abnormalities, using array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH), during early cleavage [ 56 ]. In time-lapse observations, a large proportion of aneuploid and triploid, but not euploid embryos, exhibited cellular fragmentation. They showed that the probability of aneuploidy increased with higher fragmentation and only 65% of the fragmented embryo would be expected to form blastocyst. Furthermore, all the aneuploid embryos with additional unbalanced sub-chromosomal errors exhibited CF. The authors concluded that although fragmentation alone at a single point in time does not predict embryo developmental potential, time-lapse imaging with dynamic fragmentation screening may help detect embryonic aneuploidy [ 56 ].
Two more recent studies also used aCGH to evaluate the association between embryo ploidy and fragmentation. Vera-Rodriguez et al., in a retrospective study, compared the rate of embryo aneuploidy between two groups of high (≥25%) and low (˂25%) fragmentation. They found that the rate of aneuploidy in high and low fragmentation was 62.5 and 46.3%, respectively. However, the difference was not statistically significant concluding that using degree of fragmentation alone is not suggested to predict the embryo ploidy status [ 107 ]. Minasi et al., in a case series evaluated 1730 blastocyst ploidy with aCGH. They showed that there is no significant difference between day-3 embryo morphology and embryo ploidy. However, the quality of blastocyst (inner cell mass grade, trophectoderm grade, degree of expansion) was associated with embryo ploidy [ 106 ].
In a recent meta-analysis, it was shown there is trend between degree of fragmentation and rate of aneuploidy [ 109 ]. A major source of controversy in both early and recent studies on aneuploidy and fragmentation is the variation in the methods and criteria used to evaluate these factors. One of the aspects that differ across studies include the technique for detecting aneuploidy; FISH vs aCGH. Recent studies have used aCGH to detect aneuploidy and found no clear relationship in this regard. Also, the quality of the matching between groups, the design of the study (retrospective vs prospective), the timing of the fragmentation assessment, the use of time-lapse imaging to monitor the fate of fragments are the other reasons for this discrepancy. There is still the lack of a clear cut-off point for the percentage of fragmentation to predict aneuploidy. Further powerful studies using new methods like next gene sequencing and tile-lapse systems are recommended to shed light on the relationship between fragmentation and aneuploidy.
The literature highlights that poor quality embryos have a higher incidence of chromosomal abnormalities. Notably, CF is rarely observed in embryos with normal chromosomal content. Technological advancements, such as TLM, offer promising avenues to enhance our understanding and detection of embryonic aneuploidy. Overall, these studies underscore the complexity of the relationship between fragmentation and chromosomal abnormalities, emphasizing the need for continued research to refine embryo selection strategies and improve reproductive outcomes.
Discussion and conclusion
The role of fragmentation in human embryo development and reproductive potential is widely recognized, albeit without standard definition nor agreed upon implication. While it has been shown that degree of fragmentation and embryo implantation potential are inversely proportional [ 5 , 7 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 ], the degree, pattern, and distribution of fragmentation as it relates to pregnancy outcome is debated in the literature. Our qualitative synthesis of 60 articles related to the study of embryo fragmentation and reproductive outcomes highlighted some of the challenges in analysis of fragmentation, while revealing trends in our evolving knowledge of how fragmentation may relate to functional development of the human embryo.
While fragmentation is best understood to be a natural process across species, the origin of fragmentation remains incompletely understood and likely multifactorial. Degree of fragmentation has been plausibly correlated to sperm DNA oxidation [ 37 ], errors in division [ 37 ], mitochondrial distribution [ 45 ], and overall embryo quality [ 39 ]. However, some causes of fragmentation are based on outdated studies and require validation in future research with higher quality and more advanced techniques. While cause of fragmentation remains a focus of investigation, advances in technology have allowed for more detailed analysis of its effect on embryo development and reproductive outcome. At the cellular level, increased fragmentation has been shown to be associated with higher rates of apoptosis, necrosis, and programmed cell death of cleavage-stage embryos [ 60 , 61 , 62 ]. Given the recognized significance of fragmentation on embryo development, it follows that many studies have been focused on IVF and ART impacts on fragmentation, as well as determining quantitative reproductive outcomes. In terms of other influences on degree of fragmentation, patient age was not universally found to be significantly associated with fragmentation [ 7 , 70 , 71 ] although age is certainly known to influence embryo quality. Most studies included in the search criteria showed that ART such as ICSI do not significantly impact fragmentation rate in developing embryos [ 74 , 75 , 76 ]. Those studies that found significant differences in embryo grading either between conventional fertilization and ICSI either did not find a difference in implantation or pregnancy rate or did not study it, suggesting that ICSI is not a significant contributor to poorer ART outcomes by way of embryo fragmentation.
In synthesizing the available data on ART and pregnancy outcomes with varying degrees of embryo fragmentation, most included studies did find a negative impact of increasing fragmentation on reproductive success while severe fragmentation does appear to be associated with poorer implantation rate and clinical pregnancy rate. This association may be related to the observation that increased fragmentation at the cleavage-stage embryo is related to chromosomal abnormalities incompatible with ongoing development or pregnancy.
The reviewed studies have several limitations. There are different grading systems in use that may impact detecting and reporting the degree of CF. Different criteria and terminology used in different studies may in turn make the comparison of outcome measures difficult. Another factor is the distribution pattern of CF. There are two types of scattered and concentrated fragments with different prognoses that is not considered in grading systems. Therefore, due to the lack of a standard cleavage-stage embryo grading system, comparing different studies should be done with caution. In addition, evaluation of embryo fragmentation is mostly based on individual observation which is subjective and has inter- and intra-observer subjectivity leading to high variable results even if performed by an experienced embryologist [ 110 ]. TLM is considered as a non-invasive tool and evaluates the embryo quality continuously and without the need to remove the embryo from the incubator [ 111 ]. The use of this technology allows for the analysis of embryo morphokinetics and has advanced knowledge of the developing embryo. Recently, artificial intelligence (AI) including machine learning and neural network has gained popularity in various fields of medicine including IVF and embryology. Accuracy of AI in prediction of fragmentation has been studied with encouraging results [ 112 ]. Further advances in technology will promote the use of AI as a tool in defining the effect of fragmentation on human embryo development and reproductive potential.
Although the precise origin and the importance of external or iatrogenic factors on fragmentation of cleavage-stage embryos varies in the literature, there is more consensus regarding severe fragmentation worsening reproductive outcomes. Given this important pattern, and the availability of increasingly sophisticated embryologic technology, further research is warranted to characterize more completely preventative or rescue techniques to improve reproductive outcomes.
Availability of data and materials
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Balaban B, Brison D, Calderon G, Catt J, Conaghan J, Cowan L, et al. The Istanbul consensus workshop on embryo assessment: proceedings of an expert meeting. Hum Reprod. 2011;26:1270–83.
Article Google Scholar
Hill GA, Freeman M, Bastias MC, Jane Rogers B, Herbert CM, Osteen KG, et al. The influence of oocyte maturity and embryo quality on pregnancy rate in a program for in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer. Fertil Steril. 1989;52:801–6.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Cummins JM, Breen TM, Harrison KL, Shaw JM, Wilson LM, Hennessey JF. A formula for scoring human embryo growth rates in in vitro fertilization: Its value in predicting pregnancy and in comparison with visual estimates of embryo quality. J In Vitro Fertil Embryo Transfer. 1986;3:284–95.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Cutting R, Morroll D, Roberts SA, Pickering S, Rutherford A, on behalf of the BFS and ACE. Elective Single Embryo Transfer: Guidelines for Practice British Fertility Society and Association of Clinical Embryologists. Hum Fertil. 2008;11:131–46.
Edwards RG, Fishel SB, Cohen J, Fehilly CB, Purdy JM, Slater JM, et al. Factors influencing the success of in vitro fertilization for alleviating human infertility. J In Vitro Fert Embryo Transf. 1984;1:3–23.
Puissant F, Van Rysselberge M, Barlow P, Deweze J, Leroy F. Embryo scoring as a prognostic tool in IVF treatment. Hum Reprod. 1987;2:705–8.
Alikani M, Cohen J, Tomkin G, Garrisi GJ, Mack C, Scott RT. Human embryo fragmentation in vitro and its implications for pregnancy and implantation. Fertil Steril. 1999;71:836–42.
Cecchele A, Cermisoni GC, Giacomini E, Pinna M, Vigano P. Cellular and Molecular Nature of Fragmentation of Human Embryos. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:1349.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Claman P, Armant DR, Seibel MM, Wang TA, Oskowitz SP, Taymor ML. The impact of embryo quality and quantity on implantation and the establishment of viable pregnancies. J In Vitro Fert Embryo Transf. 1987;4:218–22.
Ebner T, Yaman C, Moser M, Sommergruber M, Pölz W, Tews G. Embryo fragmentation in vitro and its impact on treatment and pregnancy outcome. Fertil Steril. 2001;76:281–5.
Erenus M, Zouves C, Rajamahendran P, Leung S, Fluker M, Gomel V. The effect of embryo quality on subsequent pregnancy rates after in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril. 1991;56:707–10.
Giorgetti C, Terriou P, Auquier P, Hans E, Spach JL, Salzmann J, et al. Embryo score to predict implantation after in-vitro fertilization: based on 957 single embryo transfers. Hum Reprod. 1995;10:2427–31.
Holte J, Berglund L, Milton K, Garello C, Gennarelli G, Revelli A, et al. Construction of an evidence-based integrated morphology cleavage embryo score for implantation potential of embryos scored and transferred on day 2 after oocyte retrieval. Hum Reprod. 2007;22:548–57.
Roseboom TJ, Vermeiden JP, Schoute E, Lens JW, Schats R. The probability of pregnancy after embryo transfer is affected by the age of the patient, cause of infertility, number of embryos transferred and the average morphology score, as revealed by multiple logistic regression analysis. Hum Reprod. 1995;10:3035–41.
Shulman A, Ben-Nun I, Ghetler Y, Kaneti H, Shilon M, Beyth Y. Relationship between embryo morphology and implantation rate after in vitro fertilization treatment in conception cycles. Fertil Steril. 1993;60:123–6.
Staessen C, Janssenswillen C, Van den Abbeel E, Devroey P, Van Steirteghem AC. Avoidance of triplet pregnancies by elective transfer of two good quality embryos. Hum Reprod. 1993;8:1650–3.
Visser DS, Fourie FR. The applicability of the cumulative embryo score system for embryo selection and quality control in an in-vitro fertilization/embryo transfer programme. Hum Reprod. 1993;8:1719–22.
Volpes A, Sammartano F, Coffaro F, Mistretta V, Scaglione P, Allegra A. Number of good quality embryos on day 3 is predictive for both pregnancy and implantation rates in in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection cycles. Fertil Steril. 2004;82:1330–6.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Ziebe S, Petersen K, Lindenberg S, Andersen AG, Gabrielsen A, Andersen AN. Embryo morphology or cleavage stage: how to select the best embryos for transfer after in-vitro fertilization. Hum Reprod. 1997;12:1545–9.
Fujimoto VY, Browne RW, Bloom MS, Sakkas D, Alikani M. Pathogenesis, developmental consequences, and clinical correlations of human embryo fragmentation. Fertil Steril. 2011;95:1197–204.
Chi H-J, Koo J-J, Choi S-Y, Jeong H-J, Roh S-I. Fragmentation of embryos is associated with both necrosis and apoptosis. Fertil Steril. 2011;96:187–92.
Racowsky C, Ohno-Machado L, Kim J, Biggers JD. Is there an advantage in scoring early embryos on more than one day? Hum Reprod. 2009;24:2104–13.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hardy K, Stark J, Winston RML. Maintenance of the inner cell mass in human blastocysts from fragmented embryos. Biol Reprod. 2003;68:1165–9.
Antczak M, Van Blerkom J. Temporal and spatial aspects of fragmentation in early human embryos: possible effects on developmental competence and association with the differential elimination of regulatory proteins from polarized domains. Hum Reprod. 1999;14:429–47.
Mio Y, Maeda K. Time-lapse cinematography of dynamic changes occurring during in vitro development of human embryos. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;199(660):e1-5.
Google Scholar
Hardarson T, Löfman C, Coull G, Sjögren A, Hamberger L, Edwards RG. Internalization of cellular fragments in a human embryo: time-lapse recordings. Reprod Biomed Online. 2002;5:36–8.
Van Blerkom J. The Enigma of Fragmentation in Early Human Embryos: Possible Causes and Clinical Relevance. Essential IVF. Boston: Springer US; 2004. 377–421.
Rijnders PM, Jansen CA. The predictive value of day 3 embryo morphology regarding blastocyst formation, pregnancy and implantation rate after day 5 transfer following in-vitro fertilization or intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Hum Reprod. 1998;13:2869–73.
Graham J, Han T, Porter R, Levy M, Stillman R, Tucker MJ. Day 3 morphology is a poor predictor of blastocyst quality in extended culture. Fertil Steril. 2000;74:495–7.
Milki AA, Hinckley MD, Gebhardt J, Dasig D, Westphal LM, Behr B. Accuracy of day 3 criteria for selecting the best embryos. Fertil Steril. 2002;77:1191–5.
Gardner DK, Vella P, Lane M, Wagley L, Schlenker T, Schoolcraft WB. Culture and transfer of human blastocysts increases implantation rates and reduces the need for multiple embryo transfers. Fertil Steril. 1998;69:84–8.
Guerif F, Le Gouge A, Giraudeau B, Poindron J, Bidault R, Gasnier O, et al. Limited value of morphological assessment at days 1 and 2 to predict blastocyst development potential: a prospective study based on 4042 embryos. Hum Reprod. 2007;22:1973–81.
Rienzi L, Ubaldi F, Iacobelli M, Romano S, Minasi MG, Ferrero S, et al. Significance of morphological attributes of the early embryo. Reprod Biomed Online. 2005;10:669–81.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
Killeen ID, Moore NW. The morphological appearance and development of sheep ova fertilized by surgical insemination. J Reprod Fertil. 1971;24:63–70.
Enders AC, Hendrickx AG, Binkerd PE. Abnormal development of blastocysts and blastomeres in the rhesus monkey. Biol Reprod. 1982;26:353–66.
Meseguer M, Martínez-Conejero JA, O’Connor JE, Pellicer A, Remohí J, Garrido N. The significance of sperm DNA oxidation in embryo development and reproductive outcome in an oocyte donation program: a new model to study a male infertility prognostic factor. Fertil Steril. 2008;89:1191–9.
Stensen MH, Tanbo TG, Storeng R, Åbyholm T, Fedorcsak P. Fragmentation of human cleavage-stage embryos is related to the progression through meiotic and mitotic cell cycles. Fertil Steril. 2015;103:374-81.e4.
Ebner T. First polar body morphology and blastocyst formation rate in ICSI patients. Human Reproduction. 2002;17:2415–8.
Sedó CA, Bilinski M, Lorenzi D, Uriondo H, Noblía F, Longobucco V, et al. Effect of sperm DNA fragmentation on embryo development: clinical and biological aspects. JBRA Assist Reprod. 2017;21:343–50.
PubMed Central Google Scholar
Rose BI, Laky D. Polar body fragmentation in IVM oocytes is associated with impaired fertilization and embryo development. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2013;30:679–82.
Zhou W, Fu L, Sha W, Chu D, Li Y. Relationship of polar bodies morphology to embryo quality and pregnancy outcome. Zygote. 2016;24:401–7.
Yang Y, Tan W, Chen C, Jin L, Huang B. Correlation of the position and status of the polar body from the fertilized oocyte to the euploid status of blastocysts. Front Genet. 2022;13:1006870. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.1006870 .
Alikani M. Epithelial cadherin distribution in abnormal human pre-implantation embryos. Hum Reprod. 2005;20:3369–75.
Van Blerkom J, Davis P, Alexander S. Differential mitochondrial distribution in human pronuclear embryos leads to disproportionate inheritance between blastomeres: relationship to microtubular organization ATP content and competence. Hum Reprod. 2000;15:2621–33.
Otasevic V, Surlan L, Vucetic M, Tulic I, Buzadzic B, Stancic A, et al. Expression patterns of mitochondrial OXPHOS components, mitofusin 1 and dynamin-related protein 1 are associated with human embryo fragmentation. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2016;28:319–27.
Wilding M, Dale B, Marino M, di Matteo L, Alviggi C, Pisaturo ML, et al. Mitochondrial aggregation patterns and activity in human oocytes and preimplantation embryos. Hum Reprod. 2001;16:909–17.
Sermondade N, Delarouzière V, Ravel C, Berthaut I, Verstraete L, Mathieu E, et al. Characterization of a recurrent poor-quality embryo morphology phenotype and zygote transfer as a rescue strategy. Reprod Biomed Online. 2012;24:403–9.
Gat I, Levron J, Yerushalmi G, Dor J, Brengauz M, Orvieto R. Should zygote intrafallopian transfer be offered to all patients with unexplained repeated in-vitro fertilization cycle failures? J Ovarian Res. 2014;7:7.
Yang HW, Hwang KJ, Kwon HC, Kim HS, Choi KW, Oh KS. Detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and apoptosis in human fragmented embryos. Hum Reprod. 1998;13:998–1002.
Chen EY, Fujinaga M, Giaccia AJ. Hypoxic microenvironment within an embryo induces apoptosis and is essential for proper morphological development. Teratology. 1999;60:215–25.
Lee T-H, Lee M-S, Liu C-H, Tsao H-M, Huang C-C, Yang Y-S. The association between microenvironmental reactive oxygen species and embryo development in assisted reproduction technology cycles. Reprod Sci. 2012;19:725–32.
Lan K-C, Lin Y-C, Chang Y-C, Lin H-J, Tsai Y-R, Kang H-Y. Limited relationships between reactive oxygen species levels in culture media and zygote and embryo development. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2019;36:325–34.
Bedaiwy MA, Falcone T, Mohamed MS, Aleem AAN, Sharma RK, Worley SE, et al. Differential growth of human embryos in vitro: Role of reactive oxygen species. Fertil Steril. 2004;82:593–600.
Pellestor F, Girardet A, Andréo B, Arnal F, Humeau C. Relationship between morphology and chromosomal constitution in human preimplantation embryo. Mol Reprod Dev. 1994;39:141–6.
Chavez SL, Loewke KE, Han J, Moussavi F, Colls P, Munne S, et al. Dynamic blastomere behaviour reflects human embryo ploidy by the four-cell stage. Nat Commun. 2012;3:1251.
Munné S, Alikani M, Tomkin G, Grifo J, Cohen J. Embryo morphology, developmental rates, and maternal age are correlated with chromosome abnormalities. Fertil Steril. 1995;64(2):382–91. Corrected and republished in: Fertil Steril. 2019 Oct;112(4 Suppl1):e71–e80.
Halvaei I, Khalili MA, Nottola SA. A novel method for transmission electron microscopy study of cytoplasmic fragments from preimplantation human embryos. Microsc Res Tech. 2016;79:459–62.
Johansson M, Hardarson T, Lundin K. There is a cutoff limit in diameter between a blastomere and a small anucleate fragment. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2003;20:309–13.
Jurisicova A, Varmuza S, Casper RF. Programmed cell death and human embryo fragmentation. Mol Hum Reprod. 1996;2:93–8.
Liu HC, He ZY, Mele CA, Veeck LL, Davis O, Rosenwaks Z. Expression of apoptosis-related genes in human oocytes and embryos. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2000;17:521–33.
Levy R, Benchaib M, Cordonier H, Souchier C, Guerin JF. Annexin V labelling and terminal transferasemediated DNA end labelling (TUNEL) assay in human arrested embryos. Mol Hum Reprod. 1998;4(8):775–83. https://doi.org/10.1093/molehr/4.8.775 .
Van Blerkom J, Davis P, Alexander S. A microscopic and biochemical study of fragmentation phenotypes in stage-appropriate human embryos. Hum Reprod. 2001;16(4):719–29. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/16.4.719 .
Metcalfe AD, Hunter HR, Bloor DJ, Lieberman BA, Picton HM, Leese HJ, Kimber SJ, Brison DR. Expression of 11 members of the BCL-2 family of apoptosis regulatory molecules during human preimplantation embryo development and fragmentation. Mol Reprod Dev. 2004;68(1):35–50. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrd.20055 .
Jurisicova A, Antenos M, Varmuza S, Tilly J, Casper R. Expression of apoptosis-related genes during human preimplantation embryo development: potential roles for the Harakiri gene product and Caspase-3 in blastomere fragmentation. Mol Hum Reprod. 2003;9:133–41.
Bencomo E, Pérez R, Arteaga M-F, Acosta E, Peña O, Lopez L, et al. Apoptosis of cultured granulosa-lutein cells is reduced by insulin-like growth factor I and may correlate with embryo fragmentation and pregnancy rate. Fertil Steril. 2006;85:474–80.
Keltz MD, Skorupski JC, Bradley K, Stein D. Predictors of embryo fragmentation and outcome after fragment removal in in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril. 2006;86:321–4.
Ziebe S, Loft A, Petersen JH, Andersen AG, Lindenberg S, Petersen K, et al. Embryo quality and developmental potential is compromised by age. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2001;80:169–74.
Lahav-Baratz S, Blais I, Koifman M, Dirnfeld M, Oron G. Evaluation of fragmented embryos implantation potential using time-lapse technology. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2023;49:1560–70.
Stensen MH, Tanbo T, Storeng R, Byholm T, Fèdorcsak P. Routine morphological scoring systems in assisted reproduction treatment fail to reflect age-related impairment of oocyte and embryo quality. Reprod Biomed Online. 2010;21:118–25.
Wu DH, Reynolds K, Maxwell R, Lindheim SR, Aubuchon M, Thomas MA. Age does not influence the effect of embryo fragmentation on successful blastocyst development. Fertil Steril. 2011;95:2778–80.
Frattarelli JL, Leondires MP, Miller BT, Segars JH. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection increases embryo fragmentation without affecting clinical outcome. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2000;17:207–12.
Hsu MI, Mayer J, Aronshon M, Lanzendorf S, Muasher S, Kolm P, et al. Embryo implantation in in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection: impact of cleavage status, morphology grade, and number of embryos transferred. Fertil Steril. 1999;72:679–85.
Garello C, Baker H, Rai J, Montgomery S, Wilson P, Kennedy CR, et al. Pronuclear orientation, polar body placement, and embryo quality after intracytoplasmic sperm injection and in-vitro fertilization: further evidence for polarity in human oocytes? Hum Reprod. 1999;14:2588–95.
Yoeli R, Orvieto R, Ashkenazi J, Shelef M, Ben-Rafael Z, Bar-Hava I. Comparison of embryo quality between intracytoplasmic sperm injection and in vitro fertilization in sibling oocytes. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2008;25:23–8.
Ruiz A, Remohí J, Minguez Y, Guanes PP, Simón C, Pellicer A. The role of in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection in couples with unexplained infertility after failed intrauterine insemination. Fertil Steril. 1997;68:171–3.
Zhang XD, Liu JX, Liu WW, Gao Y, Han W, Xiong S, et al. Time of insemination culture and outcomes of in vitro fertilization: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2013;19:685–95.
Liu J, Zhang X, Yang Y, Zhao J, Hao D, Zhang J, et al. Long-time vs. short-time insemination of sibling eggs. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12:3756–60.
Sathananthan H, Bongso A, Ng SC, Ho J, Mok H, Ratnam S. Ultrastructure of preimplantation human embryos co-cultured with human ampullary cells. Hum Reprod. 1990;5:309–18.
Coticchio G, Barrie A, Lagalla C, Borini A, Fishel S, Griffin D, et al. Plasticity of the human preimplantation embryo: developmental dogmas, variations on themes and self-correction. Hum Reprod Update. 2021;27:848–65.
Watson AJ. The cell biology of blastocyst development. Mol Reprod Dev. 1992;33:492–504.
Hur C, Nanavaty V, Yao M, Desai N. The presence of partial compaction patterns is associated with lower rates of blastocyst formation, sub-optimal morphokinetic parameters and poorer morphologic grade. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2023;21:12.
Lagalla C, Tarozzi N, Sciajno R, Wells D, Di Santo M, Nadalini M, et al. Embryos with morphokinetic abnormalities may develop into euploid blastocysts. Reprod Biomed Online. 2017;34:137–46.
Ebner T, Moser M, Shebl O, Sommergruber M, Gaiswinkler U, Tews G. Morphological analysis at compacting stage is a valuable prognostic tool for ICSI patients. Reprod Biomed Online. 2009;18:61–6.
Pellestor F, Dufour MC, Arnal F, Humeau C. Direct assessment of the rate of chromosomal abnormalities in grade IV human embryos produced by in-vitro fertilization procedure. Hum Reprod. 1994;9(2):293–302. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a138497 .
Morgan K, Wiemer K, Steuerwald N, Hoffman D, Maxson W, Godke R. Use of videocinematography to assess morphological qualities of conventionally cultured and cocultured embryos. Hum Reprod. 1995;10:2371–6.
Alikani M, Calderon G, Tomkin G, Garrisi J, Kokot M, Cohen J. Cleavage anomalies in early human embryos and survival after prolonged culture in-vitro. Hum Reprod. 2000;15:2634–43.
Ivec M, Kovacic B, Vlaisavljevic V. Prediction of human blastocyst development from morulas with delayed and/or incomplete compaction. Fertil Steril. 2011;96:1473-1478.e2.
Hnida C, Engenheiro E, Ziebe S. Computer-controlled, multilevel, morphometric analysis of blastomere size as biomarker of fragmentation and multinuclearity in human embryos. Hum Reprod. 2004;19:288–93.
Sjöblom P, Menezes J, Cummins L, Mathiyalagan B, Costello MF. Prediction of embryo developmental potential and pregnancy based on early stage morphological characteristics. Fertil Steril. 2006;86:848–61.
Kellam L, Pastorelli LM, Bastida AM, Senkbeil A, Montgomery S, Fishel S, et al. Perivitelline threads in cleavage-stage human embryos: observations using time-lapse imaging. Reprod Biomed Online. 2017;35:646–56.
Paternot G, Debrock S, De Neubourg D, D’Hooghe TM, Spiessens C. Semi-automated morphometric analysis of human embryos can reveal correlations between total embryo volume and clinical pregnancy. Hum Reprod. 2013;28:627–33.
Eftekhari-Yazdi P, Valojerdi MR, Ashtiani SK, Eslaminejad MB, Karimian L. Effect of fragment removal on blastocyst formation and quality of human embryos. Reprod Biomed Online. 2006;13:823–32.
Keltz M, Fritz R, Gonzales E, Ozensoy S, Skorupski J, Stein D. Defragmentation of low grade day 3 embryos resulted in sustained reduction in fragmentation, but did not improve compaction or blastulation rates. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:2406–8.
Halvaei I, Khalili MA, Esfandiari N, Safari S, Talebi AR, Miglietta S, et al. Ultrastructure of cytoplasmic fragments in human cleavage stage embryos. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2016;33:1677–84.
Yumoto K, Shimura T, Mio Y. Removing the zona pellucida can decrease cytoplasmic fragmentations in human embryos: a pilot study using 3PN embryos and time-lapse cinematography. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2020;37:1349–54.
Sordia-Hernandez LH, Morales-Martinez FA, Frazer-Moreira LM, Villarreal-Pineda L, Sordia-Piñeyro MO, Valdez-Martinez OH. Clinical Pregnancy After Elimination of Embryo Fragments Before Fresh Cleavage-stage Embryo Transfer. J Family Reprod Health. 2020;14(3):198–204. https://doi.org/10.18502/jfrh.v14i3.4674 .
Findikli N, Kahraman S, Kumtepe Y, Donmez E, Benkhalifa M, Biricik A, et al. Assessment of DNA fragmentation and aneuploidy on poor quality human embryos. Reprod Biomed Online. 2004;8:196–206.
Munné S, Alikani M, Tomkin G, Grifo J, Cohen J. Embryo morphology, developmental rates, and maternal age are correlated with chromosome abnormalities. Fertil Steril. 1995;64:382–91.
Almeida PA, Bolton VN. The relationship between chromosomal abnormality in the human preimplantation embryo and development in vitro. Reprod Fertil Dev. 1996;8:235–41.
Magli MC, Gianaroli L, Ferraretti AP. Chromosomal abnormalities in embryos. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001;183(Suppl 1):S29-34.
Moayeri SE, Allen RB, Brewster WR, Kim MH, Porto M, Werlin LB. Day-3 embryo morphology predicts euploidy among older subjects. Fertil Steril. 2008;89:118–23.
Baltaci V, Satiroglu H, Kabukçu C, Ünsal E, Aydinuraz B, Üner Ö, et al. Relationship between embryo quality and aneuploidies. Reprod Biomed Online. 2006;12:77–82.
Ziebe S, Lundin K, Loft A, Bergh C, Nyboe Anderson A, Selleskog U. FISH analysis for chromosomes 13, 16, 18, 21, 22, X and Y in all blastomeres of IVF pre-embryos from 144 randomly selected donated human oocytes and impact on pre-embryo morphology. Hum Reprod. 2003;18:2575–81.
Delimitreva SM, Zhivkova RS, Vatev ITS, Toncheva DI. Chromosomal disorders and nuclear and cell destruction in cleaving human embryos. Int J Dev Biol. 2005;49:409–16.
Minasi MG, Colasante A, Riccio T, Ruberti A, Casciani V, Scarselli F, Spinella F, Fiorentino F, Varricchio MT, Greco E. Correlation between aneuploidy, standard morphology evaluation and morphokinetic development in 1730 biopsied blastocysts: a consecutive case series study. Hum Reprod. 2016;31(10):2245–54. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dew183 . Epub 2016 Sep 2.
Vera-Rodriguez M, Chavez SL, Rubio C, Reijo Pera RA, Simon C. Prediction model for aneuploidy in early human embryo development revealed by single-cell analysis. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7601. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8601 .
Magli MC, Gianaroli L, Ferraretti AP, Lappi M, Ruberti A, Farfalli V. Embryo morphology and development are dependent on the chromosomal complement. Fertil Steril. 2007;87(3):534–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2006.07.1512 . Epub 2006 Nov 21.
Bamford T, Barrie A, Montgomery S, Dhillon-Smith R, Campbell A, Easter C, et al. Morphological and morphokinetic associations with aneuploidy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2022;28:656–86.
Baxter Bendus AE, Mayer JF, Shipley SK, Catherino WH. Interobserver and intraobserver variation in day 3 embryo grading. Fertil Steril. 2006;86:1608–15.
Lundin K, Park H. Time-lapse technology for embryo culture and selection. Ups J Med Sci. 2020;125:77–84.
Leahy BD, Jang WD, Yang HY, Struyven R, Wei D, Sun Z, et al. Automated Measurements of Key Morphological Features of Human Embryos for IVF. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics). 2020.
Download references
We did not receive any funding to prepare this manuscript. We are grateful for receiving an editorial waiver for this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Sciences, University of Vermont Medical Center, The Robert Larner College of Medicine at the University of Vermont, Burlington, VT, 05405, USA
Ariella Yazdani, Catherine Boniface & Navid Esfandiari
Department of Anatomical Sciences, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran
Iman Halvaei
Present address: Obstetrics and Gynecology Institute, Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH, 44195, USA
Ariella Yazdani
Division of Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences, University of Vermont, 111 Colchester Avenue, Burlington, Vermont, 05401, USA
Navid Esfandiari
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors have made substantial contributions to this manuscript. NE designed the work, critically reviewed and edited the manuscript. AY, IH and CB made substantial contribution in writing the manuscript. All authors have approved the paper for submission.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Navid Esfandiari .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This is a review paper and does not involve human participants, human data or human tissue.
Consent for publication
This manuscript does not contain any individual person’s data in any form (including any individual details, images or videos).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Yazdani, A., Halvaei, I., Boniface, C. et al. Effect of cytoplasmic fragmentation on embryo development, quality, and pregnancy outcome: a systematic review of the literature. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 22 , 55 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-024-01217-7
Download citation
Received : 20 November 2023
Accepted : 01 April 2024
Published : 14 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-024-01217-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Fragmentation
- Embryo development
- Implantation
- In vitro fertilization
- Pregnancy outcome
Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology
ISSN: 1477-7827
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 12 May 2024
Association between problematic social networking use and anxiety symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Mingxuan Du 1 ,
- Chengjia Zhao 2 ,
- Haiyan Hu 1 ,
- Ningning Ding 1 ,
- Jiankang He 1 ,
- Wenwen Tian 1 ,
- Wenqian Zhao 1 ,
- Xiujian Lin 1 ,
- Gaoyang Liu 1 ,
- Wendan Chen 1 ,
- ShuangLiu Wang 1 ,
- Pengcheng Wang 3 ,
- Dongwu Xu 1 ,
- Xinhua Shen 4 &
- Guohua Zhang 1
BMC Psychology volume 12 , Article number: 263 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
186 Accesses
Metrics details
A growing number of studies have reported that problematic social networking use (PSNU) is strongly associated with anxiety symptoms. However, due to the presence of multiple anxiety subtypes, existing research findings on the extent of this association vary widely, leading to a lack of consensus. The current meta-analysis aimed to summarize studies exploring the relationship between PSNU levels and anxiety symptoms, including generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, and fear of missing out. 209 studies with a total of 172 articles were included in the meta-analysis, involving 252,337 participants from 28 countries. The results showed a moderately positive association between PSNU and generalized anxiety (GA), social anxiety (SA), attachment anxiety (AA), and fear of missing out (FoMO) respectively (GA: r = 0.388, 95% CI [0.362, 0.413]; SA: r = 0.437, 95% CI [0.395, 0.478]; AA: r = 0.345, 95% CI [0.286, 0.402]; FoMO: r = 0.496, 95% CI [0.461, 0.529]), and there were different regulatory factors between PSNU and different anxiety subtypes. This study provides the first comprehensive estimate of the association of PSNU with multiple anxiety subtypes, which vary by time of measurement, region, gender, and measurement tool.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Social network refers to online platforms that allow users to create, share, and exchange information, encompassing text, images, audio, and video [ 1 ]. The use of social network, a term encompassing various activities on these platforms, has been measured from angles such as frequency, duration, intensity, and addictive behavior, all indicative of the extent of social networking usage [ 2 ]. As of April 2023, there are 4.8 billion social network users globally, representing 59.9% of the world’s population [ 3 ]. The usage of social network is considered a normal behavior and a part of everyday life [ 4 , 5 ]. Although social network offers convenience in daily life, excessive use can lead to PSNU [ 6 , 7 ], posing potential threats to mental health, particularly anxiety symptoms (Rasmussen et al., 2020). Empirical research has shown that anxiety symptoms, including generalized anxiety (GA), social anxiety (SA), attachment anxiety (AA), and fear of missing out (FoMO), are closely related to PSNU [ 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 ]. While some empirical studies have explored the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms, their conclusions are not consistent. Some studies have found a significant positive correlation [ 13 , 14 , 15 ], while others have found no significant correlation [ 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 ]. Furthermore, the degree of correlation varies widely in existing research, with reported r-values ranging from 0.12 to 0.80 [ 20 , 21 ]. Therefore, a systematic meta-analysis is necessary to clarify the impact of PSNU on individual anxiety symptoms.
Previous research lacks a unified concept of PSNU, primarily due to differing theoretical interpretations by various authors, and the use of varied standards and diagnostic tools. Currently, this phenomenon is referred to by several terms, including compulsive social networking use, problematic social networking use, excessive social networking use, social networking dependency, and social networking addiction [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 ]. These conceptual differences hinder the development of a cohesive and systematic research framework, as it remains unclear whether these definitions and tools capture the same underlying construct [ 27 ]. To address this lack of uniformity, this paper will use the term “problematic use” to encompass all the aforementioned nomenclatures (i.e., compulsive, excessive, dependent, and addictive use).
Regarding the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms, two main perspectives exist: the first suggests a positive correlation, while the second proposes a U-shaped relationship. The former perspective, advocating a positive correlation, aligns with the social cognitive theory of mass communication. It posits that PSNU can reinforce certain cognitions, emotions, attitudes, and behaviors [ 28 , 29 ], potentially elevating individuals’ anxiety levels [ 30 ]. Additionally, the cognitive-behavioral model of pathological use, a primary framework for explaining factors related to internet-based addictions, indicates that psychiatric symptoms like depression or anxiety may precede internet addiction, implying that individuals experiencing anxiety may turn to social networking platforms as a coping mechanism [ 31 ]. Empirical research also suggests that highly anxious individuals prefer computer-mediated communication due to the control and social liberation it offers and are more likely to have maladaptive emotional regulation, potentially leading to problematic social network service use [ 32 ]. Turning to the alternate perspective, it proposes a U-shaped relationship as per the digital Goldilocks hypothesis. In this view, moderate social networking usage is considered beneficial for psychosocial adaptation, providing individuals with opportunities for social connection and support. Conversely, both excessive use and abstinence can negatively impact psychosocial adaptation [ 33 ]. In summary, both perspectives offer plausible explanations.
Incorporating findings from previous meta-analyses, we identified seven systematic reviews and two meta-analyses that investigated the association between PSNU and anxiety. The results of these meta-analyses indicated a significant positive correlation between PSNU and anxiety (ranging from 0.33 to 0.38). However, it is evident that these previous meta-analyses had certain limitations. Firstly, they focused only on specific subtypes of anxiety; secondly, they were limited to adolescents and emerging adults in terms of age. In summary, this systematic review aims to ascertain which theoretical perspective more effectively explains the relationship between PSNU and anxiety, addressing the gaps in previous meta-analyses. Additionally, the association between PSNU and anxiety could be moderated by various factors. Drawing from a broad research perspective, any individual study is influenced by researcher-specific designs and associated sample estimates. These may lead to bias compared to the broader population. Considering the selection criteria for moderating variables in empirical studies and meta-analyses [ 34 , 35 ], the heterogeneity of findings on problematic social network usage and anxiety symptoms could be driven by divergence in sample characteristics (e.g., gender, age, region) and research characteristics (measurement instrument of study variables). Since the 2019 coronavirus pandemic, heightened public anxiety may be attributed to the fear of the virus or heightened real life stress. The increased use of electronic devices, particularly smartphones during the pandemic, also instigates the prevalence of problematic social networking. Thus, our analysis focuses on three moderators: sample characteristics (participants’ gender, age, region), measurement tools (for PSNU and anxiety symptoms) and the time of measurement (before COVID-19 vs. during COVID-19).
The present study was conducted in accordance with the 2020 statement on Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [ 36 ]. To facilitate transparency and to avoid unnecessary duplication of research, this study was registered on PROSPERO, and the number is CRD42022350902.
Literature search
Studies on the relationship between the PSNU and anxiety symptoms from 2000 to 2023 were retrieved from seven databases. These databases included China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang Data, Chongqing VIP Information Co. Ltd. (VIP), Web of Science, ScienceDirect, PubMed, and PsycARTICLES. The search strings consisted of (a) anxiety symptoms, (b) social network, and (c) Problematic use. As shown in Table 1 , the keywords for anxiety are as follows: anxiety, generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, fear of missing out, and FoMO. The keywords for social network are as follows: social network, social media, social networking site, Instagram, and Facebook. The keywords for addiction are as follows: addiction, dependence, problem/problematic use, excessive use. The search deadline was March 19, 2023. A total of 2078 studies were initially retrieved and all were identified ultimately.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Retrieved studies were eligible for the present meta-analysis if they met the following inclusion criteria: (a) the study provided Pearson correlation coefficients used to measure the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms; (b) the study reported the sample size and the measurement instruments for the variables; (c) the study was written in English and Chinese; (d) the study provided sufficient statistics to calculate the effect sizes; (e) effect sizes were extracted from independent samples. If multiple independent samples were investigated in the same study, they were coded separately; if the study was a longitudinal study, they were coded by the first measurement. In addition, studies were excluded if they: (a) examined non-problematic social network use; (b) had an abnormal sample population; (c) the results of the same sample were included in another study and (d) were case reports or review articles. Two evaluators with master’s degrees independently assessed the eligibility of the articles. A third evaluator with a PhD examined the results and resolved dissenting views.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Two evaluators independently coded the selected articles according to the following characteristics: literature information, time of measurement (before the COVID-19 vs. during the COVID-19), sample source (developed country vs. developing country), sample size, proportion of males, mean age, type of anxiety, and measurement instruments for PSNU and anxiety symptoms. The following principles needed to be adhered to in the coding process: (a) effect sizes were extracted from independent samples. If multiple independent samples were investigated in the same study, they were coded separately; if the study was a longitudinal study, it was coded by the first measurement; (b) if multiple studies used the same data, the one with the most complete information was selected; (c) If studies reported t or F values rather than r , the following formula \( r=\sqrt{\frac{{t}^{2}}{{t}^{2}+df}}\) ; \( r=\sqrt{\frac{F}{F+d{f}_{e}}}\) was used to convert them into r values [ 37 , 38 ]. Additionally, if some studies only reported the correlation matrix between each dimension of PSNU and anxiety symptoms, the following formula \( {r}_{xy}=\frac{\sum {r}_{xi}{r}_{yj}}{\sqrt{n+n(n-1){r}_{xixj}}\sqrt{m+m(m-1){r}_{yiyj}}}\) was used to synthesize the r values [ 39 ], where n or m is the number of dimensions of variable x or variable y, respectively, and \( {r}_{xixj} \) or \( {r}_{yiyj}\) represents the mean of the correlation coefficients between the dimensions of variable x or variable y, respectively.
Literature quality was determined according to the meta-analysis quality evaluation scale developed [ 40 ]. The quality of the post-screening studies was assessed by five dimensions: sampling method, efficiency of sample collection, level of publication, and reliability of PSNU and anxiety symptom measurement instruments. The total score of the scale ranged from 0 to 10; higher scores indicated better quality of the literature.
Data analysis
All data were performed using Comprehensive Meta Analysis 3.3 (CMA 3.3). Pearson’s product-moment coefficient r was selected as the effect size index in this meta-analysis. Firstly, \( {\text{F}\text{i}\text{s}\text{h}\text{e}\text{r}}^{{\prime }}\text{s} Z=\frac{1}{2}\times \text{ln}\left(\frac{1+r}{1-r}\right)\) was used to convert the correlation coefficient to Fisher Z . Then the formula \( SE=\sqrt{\frac{1}{n-3}}\) was used to calculate the standard error ( SE ). Finally, the summary of r was obtained from the formula \( r=\frac{{e}^{2z}-1}{{e}^{2z}+1}\) for a comprehensive measure of the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms [ 37 , 41 ].
Although the effect sizes estimated by the included studies may be similar, considering the actual differences between studies (e.g., region and gender), the random effects model was a better choice for data analysis for the current meta-analysis. The heterogeneity of the included study effect sizes was measured for significance by Cochran’s Q test and estimated quantitatively by the I 2 statistic [ 42 ]. If the results indicate there is a significant heterogeneity (the Q test: p -value < 0.05, I 2 > 75) and the results of different studies are significantly different from the overall effect size. Conversely, it indicates there are no differences between the studies and the overall effect size. And significant heterogeneity tends to indicate the possible presence of potential moderating variables. Subgroup analysis and meta-regression analysis were used to examine the moderating effect of categorical and continuous variables, respectively.
Funnel plots, fail-safe number (Nfs) and Egger linear regression were utilized to evaluate the publication bias [ 43 , 44 , 45 ]. The likelihood of publication bias was considered low if the intercept obtained from Egger linear regression was not significant. A larger Nfs indicated a lower risk of publication bias, and if Nfs < 5k + 10 (k representing the original number of studies), publication bias should be a concern [ 46 ]. When Egger’s linear regression was significant, the Duval and Tweedie’s trim-and-fill was performed to correct the effect size. If there was no significant change in the effect size, it was assumed that there was no serious publication bias [ 47 ].
A significance level of P < 0.05 was deemed applicable in this study.
Sample characteristics
The PRISMA search process is depicted in Fig. 1 . The database search yielded 2078 records. After removing duplicate records and screening the title and abstract, the full text was subject to further evaluation. Ultimately, 172 records fit the inclusion criteria, including 209 independent effect sizes. The present meta-analysis included 68 studies on generalized anxiety, 44 on social anxiety, 22 on attachment anxiety, and 75 on fear of missing out. The characteristics of the selected studies are summarized in Table 2 . The majority of the sample group were adults. Quality scores for selected studies ranged from 0 to 10, with only 34 effect sizes below the theoretical mean, indicating high quality for the included studies. The literature included utilized BSMAS as the primary tool to measure PSNU, DASS-21-A to measure GA, IAS to measure SA, ECR to measure AA, and FoMOS to measure FoMO.
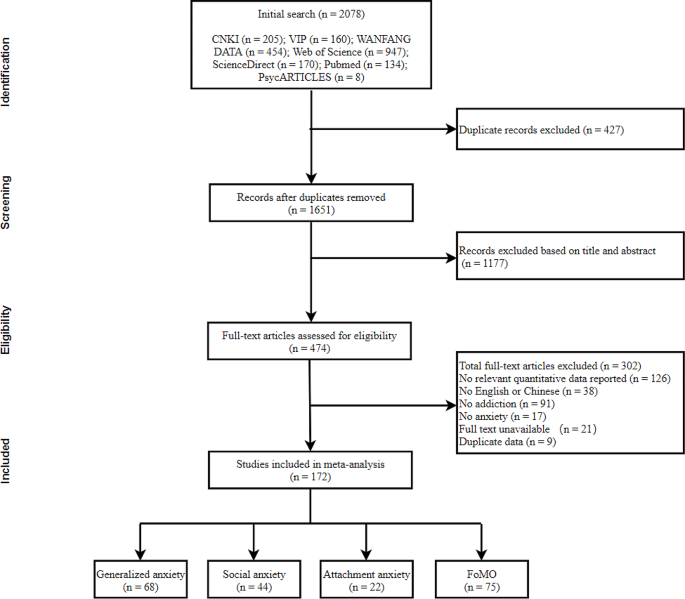
Flow chart of the search and selection strategy
Overall analysis, homogeneity tests and publication bias
As shown in Table 3 , there was significant heterogeneity between PSNU and all four anxiety symptoms (GA: Q = 1623.090, I 2 = 95.872%; SA: Q = 1396.828, I 2 = 96.922%; AA: Q = 264.899, I 2 = 92.072%; FoMO: Q = 1847.110, I 2 = 95.994%), so a random effects model was chosen. The results of the random effects model indicate a moderate positive correlation between PSNU and anxiety symptoms (GA: r = 0.350, 95% CI [0.323, 0.378]; SA: r = 0.390, 95% CI [0.347, 0.431]; AA: r = 0.345, 95% CI [0.286, 0.402]; FoMO: r = 0.496, 95% CI [0.461, 0.529]).
Figure 2 shows the funnel plot of the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms. No significant symmetry was seen in the funnel plot of the relationship between PSNU and GA and between PSNU and SA. And the Egger’s regression results also indicated that there might be publication bias ( t = 3.775, p < 0.001; t = 2.309, p < 0.05). Therefore, it was necessary to use fail-safe number (Nfs) and the trim and fill method for further examination and correction. The Nfs for PSNU and GA as well as PSNU and SA are 4591 and 7568, respectively. Both Nfs were much larger than the standard 5 k + 10. After performing the trim and fill method, 14 effect sizes were added to the right side of the funnel plat (Fig. 2 .a), the correlation coefficient between PSNU and GA changed to ( r = 0.388, 95% CI [0.362, 0.413]); 10 effect sizes were added to the right side of the funnel plat (Fig. 2 .b), the correlation coefficient between PSNU and SA changed to ( r = 0.437, 95% CI [0.395, 0.478]). The correlation coefficients did not change significantly, indicating that there was no significant publication bias associated with the relationship between PSNU and these two anxiety symptoms (GA and SA).
Funnel plot of the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms. Note: Black dots indicated additional studies after using trim and fill method; ( a ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and GA; ( b ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and SA; ( c ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and AA; ( d ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and FoMO
Sensitivity analyses
Initially, the findings obtained through the one-study-removed approach indicated that the heterogeneities in the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms were not attributed to any individual study. Nevertheless, it is important to note that sensitivity analysis should be performed based on literature quality [ 223 ] since low-quality literature could potentially impact result stability. In the relationship between PSNU and GA, the 10 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.402, 95% CI [0.375, 0.428]); In the relationship between PSNU and SA, the 8 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.431, 95% CI [0.387, 0.472]); In the relationship between PSNU and AA, the 5 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.367, 95% CI [0.298, 0.433]); In the relationship between PSNU and FoMO, the 11 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.508, 95% CI [0.470, 0.544]). The revised estimates indicate that meta-analysis results were stable.
Moderator analysis
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between psnu and ga.
The results of subgroup analysis and meta-regression are shown in Table 4 , the time of measurement significantly moderated the correlation between PSNU and GA ( Q between = 19.268, df = 2, p < 0.001). The relation between the two variables was significantly higher during the COVID-19 ( r = 0.392, 95% CI [0.357, 0.425]) than before the COVID-19 ( r = 0.270, 95% CI [0.227, 0.313]) or measurement time uncertain ( r = 0.352, 95% CI [0.285, 0.415]).
The moderating effect of the PSNU measurement was significant ( Q between = 6.852, df = 1, p = 0.009). The relation was significantly higher when PSNU was measured with the BSMAS ( r = 0.373, 95% CI [0.341, 0.404]) compared to others ( r = 0.301, 95% CI [0.256, 0.344]).
The moderating effect of the GA measurement was significant ( Q between = 60.061, df = 5, p < 0.001). Specifically, when GA measured by the GAD ( r = 0.398, 95% CI [0.356, 0.438]) and the DASS-21-A ( r = 0.433, 95% CI [0.389, 0.475]), a moderate positive correlation was observed. However, the correlation was less significant when measured using the STAI ( r = 0.232, 95% CI [0.187, 0.276]).
For the relation between PSNU and GA, the moderating effect of region, gender and age were not significant.
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between PSNU and SA
The effects of the moderating variables in the relation between PSNU and SA were shown in Table 5 . The results revealed a gender-moderated variances between the two variables (b = 0.601, 95% CI [ 0.041, 1.161], Q model (1, k = 41) = 4.705, p = 0.036).
For the relation between PSNU and SA, the moderating effects of time of measurement, region, measurement of PSNU and SA, and age were not significant.
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between PSNU and AA
The effects of the moderating variables in the relation between PSNU and AA were shown in Table 6 , region significantly moderated the correlation between PSNU and AA ( Q between = 6.410, df = 2, p = 0.041). The correlation between the two variables was significantly higher in developing country ( r = 0.378, 95% CI [0.304, 0.448]) than in developed country ( r = 0.242, 95% CI [0.162, 0.319]).
The moderating effect of the PSNU measurement was significant ( Q between = 6.852, df = 1, p = 0.009). Specifically, when AA was measured by the GPIUS-2 ( r = 0.484, 95% CI [0.200, 0.692]) and the PMSMUAQ ( r = 0.443, 95% CI [0.381, 0.501]), a moderate positive correlation was observed. However, the correlation was less significant when measured using the BSMAS ( r = 0.248, 95% CI [0.161, 0.331]) and others ( r = 0.313, 95% CI [0.250, 0.372]).
The moderating effect of the AA measurement was significant ( Q between = 17.283, df = 2, p < 0.001). The correlation was significantly higher when measured using the ECR ( r = 0.386, 95% CI [0.338, 0.432]) compared to the RQ ( r = 0.200, 95% CI [0.123, 0.275]).
For the relation between PSNU and AA, the moderating effects of time of measurement, region, gender, and age were not significant.
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between PSNU and FoMO
The effects of the moderating variables in the relation between PSNU and FoMO were shown in Table 7 , the moderating effect of the PSNU measurement was significant ( Q between = 8.170, df = 2, p = 0.017). Among the sub-dimensions, the others was excluded because there was only one sample. Specifically, when measured using the FoMOS-MSME ( r = 0.630, 95% CI [0.513, 0.725]), a moderate positive correlation was observed. However, the correlation was less significant when measured using the FoMOS ( r = 0.472, 95% CI [0.432, 0.509]) and the T-S FoMOS ( r = 0.557, 95% CI [0.463, 0.639]).
For the relationship between PSNU and FoMO, the moderating effects of time of measurement, region, measurement of PSNU, gender and age were not significant.
Through systematic review and meta-analysis, this study established a positive correlation between PSNU and anxiety symptoms (i.e., generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, and fear of missing out), confirming a linear relationship and partially supporting the Social Cognitive Theory of Mass Communication [ 28 ] and the Cognitive Behavioral Model of Pathological Use [ 31 ]. Specifically, a significant positive correlation between PSNU and GA was observed, implying that GA sufferers might resort to social network for validation or as an escape from reality, potentially alleviating their anxiety. Similarly, the meta-analysis demonstrated a strong positive correlation between PSNU and SA, suggesting a preference for computer-mediated communication among those with high social anxiety due to perceived control and liberation offered by social network. This preference is often accompanied by maladaptive emotional regulation, predisposing them to problematic use. In AA, a robust positive correlation was found with PSNU, indicating a higher propensity for such use among individuals with attachment anxiety. Notably, the study identified the strongest correlation in the context of FoMO. FoMO’s significant association with PSNU is multifaceted, stemming from the real-time nature of social networks that engenders a continuous concern about missing crucial updates or events. This drives frequent engagement with social network, thereby establishing a direct link to problematic usage patterns. Additionally, social network’s feedback loops amplify this effect, intensifying FoMO. The culture of social comparison on these platforms further exacerbates FoMO, as users frequently compare their lives with others’ selectively curated portrayals, enhancing both their social networking usage frequency and the pursuit for social validation. Furthermore, the integral role of social network in modern life broadens FoMO’s scope, encompassing anxieties about staying informed and connected.
The notable correlation between FoMO and PSNU can be comprehensively understood through various perspectives. FoMO is inherently linked to the real-time nature of social networks, which cultivates an ongoing concern about missing significant updates or events in one’s social circle [ 221 ]. This anxiety prompts frequent engagement with social network, leading to patterns of problematic use. Moreover, the feedback loops in social network algorithms, designed to enhance user engagement, further intensify this fear [ 224 ]. Additionally, social comparison, a common phenomenon on these platforms, exacerbates FoMO as users continuously compare their lives with the idealized representations of others, amplifying feelings of missing out on key social experiences [ 225 ]. This behavior not only increases social networking usage but also is closely linked to the quest for social validation and identity construction on these platforms. The extensive role of social network in modern life further amplifies FoMO, as these platforms are crucial for information exchange and maintaining social ties. FoMO thus encompasses more than social concerns, extending to anxieties about staying informed with trends and dynamics within social networks [ 226 ]. The multifaceted nature of FoMO in relation to social network underscores its pronounced correlation with problematic social networking usage. In essence, the combination of social network’s intrinsic characteristics, psychological drivers of user behavior, the culture of social comparison, and the pervasiveness of social network in everyday life collectively make FoMO the most pronouncedly correlated anxiety type with PSNU.
Additionally, we conducted subgroup analyses on the timing of measurement (before COVID-19 vs. during COVID-19), measurement tools (for PSNU and anxiety symptoms), sample characteristics (participants’ region), and performed a meta-regression analysis on gender and age in the context of PSNU and anxiety symptoms. It was found that the timing of measurement, tools used for assessing PSNU and anxiety, region, and gender had a moderating effect, whereas age did not show a significant moderating impact.
Firstly, the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms was significantly higher during the COVID-19 period than before, especially between PSNU and GA. However, the moderating effect of measurement timing was not significant in the relationship between PSNU and other types of anxiety. This could be attributed to the increased uncertainty and stress during the pandemic, leading to heightened levels of general anxiety [ 227 ]. The overuse of social network for information seeking and anxiety alleviation might have paradoxically exacerbated anxiety symptoms, particularly among individuals with broad future-related worries [ 228 ]. While the COVID-19 pandemic altered the relationship between PSNU and GA, its impact on other types of anxiety (such as SA and AA) may not have been significant, likely due to these anxiety types being more influenced by other factors like social skills and attachment styles, which were minimally impacted by the epidemic.
Secondly, the observed variance in the relationship between PSNU and AA across different economic contexts, notably between developing and developed countries, underscores the multifaceted influence of socio-economic, cultural, and technological factors on this dynamic. The amplified connection in developing countries may be attributed to greater socio-economic challenges, distinct cultural norms regarding social support and interaction, rising social network penetration, especially among younger demographics, and technological disparities influencing accessibility and user experience [ 229 , 230 ]. Moreover, the role of social network as a coping mechanism for emotional distress, potentially fostering insecure attachment patterns, is more pronounced in these settings [ 231 ]. These findings highlight the necessity of considering contextual variations in assessing the psychological impacts of social network, advocating for a nuanced understanding of how socio-economic and cultural backgrounds mediate the relationship between PSNU and mental health outcomes [ 232 ]. Additionally, the relationship between PSNU and other types of anxiety (such as GA and SA) presents uniform characteristics across different economic contexts.
Thirdly, the significant moderating effects of measurement tools in the context of PSNU and its correlation with various forms of anxiety, including GA, and AA, are crucial in interpreting the research findings. Specifically, the study reveals that the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale (BSMAS) demonstrates a stronger correlation between PSNU and GA, compared to other tools. Similarly, for AA, the Griffiths’ Problematic Internet Use Scale 2 (GPIUS2) and the Problematic Media Social Media Use Assessment Questionnaire (PMSMUAQ) show a more pronounced correlation with AA than the BSMAS or other instruments, but for SA and FoMO, the PSNU instrument doesn’t significantly moderate the correlation. The PSNU measurement tool typically contains an emotional change dimension. SA and FoMO, due to their specific conditional stimuli triggers and correlation with social networks [ 233 , 234 ], are likely to yield more consistent scores in this dimension, while GA and AA may be less reliable due to their lesser sensitivity to specific conditional stimuli. Consequently, the adjustment effects of PSNU measurements vary across anxiety symptoms. Regarding the measurement tools for anxiety, different scales exhibit varying degrees of sensitivity in detecting the relationship with PSNU. The Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale (GAD) and the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales 21 (DASS-21) are more effective in illustrating a strong relationship between GA and PSNU than the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI). In the case of AA, the Experiences in Close Relationships-21 (ECR-21) provides a more substantial correlation than the Relationship Questionnaire (RQ). Furthermore, for FoMO, the Fear of Missing Out Scale - Multi-Social Media Environment (FoMOS-MSME) is more indicative of a strong relationship with PSNU compared to the standard FoMOS or the T-S FoMOS. These findings underscore the importance of the selection of appropriate measurement tools in research. Different tools, due to their unique design, focus, and sensitivity, can reveal varying degrees of correlation between PSNU and anxiety disorders. This highlights the need for careful consideration of tool characteristics and their potential impact on research outcomes. It also cautions against drawing direct comparisons between studies without acknowledging the possible variances introduced by the use of different measurement instruments.
Fourthly, the significant moderating role of gender in the relationship between PSNU and SA, particularly pronounced in samples with a higher proportion of females. Women tend to engage more actively and emotionally with social network, potentially leading to an increased dependency on these platforms when confronting social anxiety [ 235 ]. This intensified use might amplify the association between PSNU and SA. Societal and cultural pressures, especially those related to appearance and social status, are known to disproportionately affect women, possibly exacerbating their experience of social anxiety and prompting a greater reliance on social network for validation and support [ 236 ]. Furthermore, women’s propensity to seek emotional support and express themselves on social network platforms [ 237 ] could strengthen this link, particularly in the context of managing social anxiety. Consequently, the observed gender differences in the relationship between PSNU and SA underscore the importance of considering gender-specific dynamics and cultural influences in psychological research related to social network use. In addition, gender consistency was observed in the association between PSNU and other types of anxiety, indicating no significant gender disparities.
Fifthly, the absence of a significant moderating effect of age on the relationship between PSNU and various forms of anxiety suggests a pervasive influence of social network across different age groups. This finding indicates that the impact of PSNU on anxiety is relatively consistent, irrespective of age, highlighting the universal nature of social network’s psychological implications [ 238 ]. Furthermore, this uniformity suggests that other factors, such as individual psychological traits or socio-cultural influences, might play a more crucial role in the development of anxiety related to social networking usage than age [ 239 ]. The non-significant role of age also points towards a potential generational overlap in social networking usage patterns and their psychological effects, challenging the notion that younger individuals are uniquely susceptible to the adverse effects of social network on mental health [ 240 ]. Therefore, this insight necessitates a broader perspective in understanding the dynamics of social network and mental health, one that transcends age-based assumptions.
Limitations
There are some limitations in this research. First, most of the studies were cross-sectional surveys, resulting in difficulties in inferring causality of variables, longitudinal study data will be needed to evaluate causal interactions in the future. Second, considerable heterogeneity was found in the estimated results, although heterogeneity can be partially explained by differences in study design (e.g., Time of measurement, region, gender, and measurement tools), but this can introduce some uncertainty in the aggregation and generalization of the estimated results. Third, most studies were based on Asian samples, which limits the generality of the results. Fourth, to minimize potential sources of heterogeneity, some less frequently used measurement tools were not included in the classification of measurement tools, which may have some impact on the results of heterogeneity interpretation. Finally, since most of the included studies used self-reported scales, it is possible to get results that deviate from the actual situation to some extent.
This meta-analysis aims to quantifies the correlations between PSNU and four specific types of anxiety symptoms (i.e., generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, and fear of missing out). The results revealed a significant moderate positive association between PSNU and each of these anxiety symptoms. Furthermore, Subgroup analysis and meta-regression analysis indicated that gender, region, time of measurement, and instrument of measurement significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and specific anxiety symptoms. Specifically, the measurement time and GA measurement tools significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and GA. Gender significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and SA. Region, PSNU measurement tools, and AA measurement tools all significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and AA. The FoMO measurement tool significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and FoMO. Regarding these findings, prevention interventions for PSNU and anxiety symptoms are important.
Data availability
The datasets are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Problematic social networking use
- Generalized anxiety
- Social anxiety
- Attachment anxiety
Fear of miss out
Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale
Facebook Addiction Scale
Facebook Intrusion Questionnaire
Generalized Problematic Internet Use Scale 2
Problematic Mobile Social Media Usage Assessment Questionnaire
Social Network Addiction Tendency Scale
Brief Symptom Inventory
The anxiety subscale of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
The anxiety subscale of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale
State-Trait Anxiety Inventory
Interaction Anxiousness Scale
Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale
Social Anxiety Scale for Social Media Users
Social Anxiety for Adolescents
Social Anxiety Subscale of the Self-Consciousness Scale
Social Interaction Anxiety Scale
Experiences in Close Relationship Scale
Relationship questionnaire
Fear of Missing Out Scale
FoMO Measurement Scale in the Mobile Social Media Environment
Trait-State Fear of missing Out Scale
Rozgonjuk D, Sindermann C, Elhai JD, Montag C. Fear of missing out (FoMO) and social media’s impact on daily-life and productivity at work: do WhatsApp, Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat Use disorders mediate that association? Addict Behav. 2020;110:106487.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Mieczkowski H, Lee AY, Hancock JT. Priming effects of social media use scales on well-being outcomes: the influence of intensity and addiction scales on self-reported depression. Social Media + Soc. 2020;6(4):2056305120961784.
Article Google Scholar
Global digital population as of April. 2023 [ https://www.statista.com/statistics/617136/digital-population-worldwide/ ].
Marengo D, Settanni M, Fabris MA, Longobardi C. Alone, together: fear of missing out mediates the link between peer exclusion in WhatsApp classmate groups and psychological adjustment in early-adolescent teens. J Social Personal Relationships. 2021;38(4):1371–9.
Marengo D, Fabris MA, Longobardi C, Settanni M. Smartphone and social media use contributed to individual tendencies towards social media addiction in Italian adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic. Addict Behav. 2022;126:107204.
Müller SM, Wegmann E, Stolze D, Brand M. Maximizing social outcomes? Social zapping and fear of missing out mediate the effects of maximization and procrastination on problematic social networks use. Comput Hum Behav. 2020;107:106296.
Sun Y, Zhang Y. A review of theories and models applied in studies of social media addiction and implications for future research. Addict Behav. 2021;114:106699.
Boustead R, Flack M. Moderated-mediation analysis of problematic social networking use: the role of anxious attachment orientation, fear of missing out and satisfaction with life. Addict Behav 2021, 119.
Hussain Z, Griffiths MD. The associations between problematic social networking Site Use and Sleep Quality, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, Depression, anxiety and stress. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2021;19(3):686–700.
Gori A, Topino E, Griffiths MD. The associations between attachment, self-esteem, fear of missing out, daily time expenditure, and problematic social media use: a path analysis model. Addict Behav. 2023;141:107633.
Marino C, Manari T, Vieno A, Imperato C, Spada MM, Franceschini C, Musetti A. Problematic social networking sites use and online social anxiety: the role of attachment, emotion dysregulation and motives. Addict Behav. 2023;138:107572.
Tobin SJ, Graham S. Feedback sensitivity as a mediator of the relationship between attachment anxiety and problematic Facebook Use. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2020;23(8):562–6.
Brailovskaia J, Rohmann E, Bierhoff H-W, Margraf J. The anxious addictive narcissist: the relationship between grandiose and vulnerable narcissism, anxiety symptoms and Facebook Addiction. PLoS ONE 2020, 15(11).
Kim S-S, Bae S-M. Social Anxiety and Social Networking Service Addiction Proneness in University students: the Mediating effects of Experiential Avoidance and interpersonal problems. Psychiatry Invest. 2022;19(8):702–702.
Zhao J, Ye B, Yu L, Xia F. Effects of Stressors of COVID-19 on Chinese College Students’ Problematic Social Media Use: A Mediated Moderation Model. Front Psychiatry 2022, 13.
Astolfi Cury GS, Takannune DM, Prates Herrerias GS, Rivera-Sequeiros A, de Barros JR, Baima JP, Saad-Hossne R, Sassaki LY. Clinical and Psychological Factors Associated with Addiction and Compensatory Use of Facebook among patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a cross-sectional study. Int J Gen Med. 2022;15:1447–57.
Balta S, Emirtekin E, Kircaburun K, Griffiths MD. Neuroticism, trait fear of missing out, and Phubbing: the mediating role of state fear of missing out and problematic Instagram Use. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2020;18(3):628–39.
Boursier V, Gioia F, Griffiths MD. Do selfie-expectancies and social appearance anxiety predict adolescents’ problematic social media use? Comput Hum Behav. 2020;110:106395.
Worsley JD, McIntyre JC, Bentall RP, Corcoran R. Childhood maltreatment and problematic social media use: the role of attachment and depression. Psychiatry Res. 2018;267:88–93.
de Bérail P, Guillon M, Bungener C. The relations between YouTube addiction, social anxiety and parasocial relationships with YouTubers: a moderated-mediation model based on a cognitive-behavioral framework. Comput Hum Behav. 2019;99:190–204.
Naidu S, Chand A, Pandaram A, Patel A. Problematic internet and social network site use in young adults: the role of emotional intelligence and fear of negative evaluation. Pers Indiv Differ. 2023;200:111915.
Apaolaza V, Hartmann P, D’Souza C, Gilsanz A. Mindfulness, compulsive Mobile Social Media Use, and derived stress: the mediating roles of self-esteem and social anxiety. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2019;22(6):388–96.
Demircioglu ZI, Goncu-Kose A. Antecedents of problematic social media use and cyberbullying among adolescents: attachment, the dark triad and rejection sensitivity. Curr Psychol (New Brunsw NJ) 2022:1–19.
Gao Q, Li Y, Zhu Z, Fu E, Bu X, Peng S, Xiang Y. What links to psychological needs satisfaction and excessive WeChat use? The mediating role of anxiety, depression and WeChat use intensity. BMC Psychol. 2021;9(1):105–105.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Malak MZ, Shuhaiber AH, Al-amer RM, Abuadas MH, Aburoomi RJ. Correlation between psychological factors, academic performance and social media addiction: model-based testing. Behav Inform Technol. 2022;41(8):1583–95.
Song C. The effect of the need to belong on mobile phone social media dependence of middle school students: Chain mediating roles of fear of missing out and maladaptive cognition. Sichuan Normal University; 2022.
Tokunaga RS, Rains SA. A review and meta-analysis examining conceptual and operational definitions of problematic internet use. Hum Commun Res. 2016;42(2):165–99.
Bandura A. Social cognitive theory of mass communication. Media effects. edn.: Routledge; 2009. pp. 110–40.
Valkenburg PM, Peter J, Walther JB. Media effects: theory and research. Ann Rev Psychol. 2016;67:315–38.
Slater MD. Reinforcing spirals: the mutual influence of media selectivity and media effects and their impact on individual behavior and social identity. Communication Theory. 2007;17(3):281–303.
Ahmed E, Vaghefi I. Social media addiction: A systematic review through cognitive-behavior model of pathological use. 2021.
She R, han Mo PK, Li J, Liu X, Jiang H, Chen Y, Ma L, fai Lau JT. The double-edged sword effect of social networking use intensity on problematic social networking use among college students: the role of social skills and social anxiety. Comput Hum Behav. 2023;140:107555.
Przybylski AK, Weinstein N. A large-scale test of the goldilocks hypothesis: quantifying the relations between digital-screen use and the mental well-being of adolescents. Psychol Sci. 2017;28(2):204–15.
Ran G, Li J, Zhang Q, Niu X. The association between social anxiety and mobile phone addiction: a three-level meta-analysis. Comput Hum Behav. 2022;130:107198.
Fioravanti G, Casale S, Benucci SB, Prostamo A, Falone A, Ricca V, Rotella F. Fear of missing out and social networking sites use and abuse: a meta-analysis. Comput Hum Behav. 2021;122:106839.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group* P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):264–9.
Card NA. Applied meta-analysis for social science research. Guilford; 2015.
Peterson RA, Brown SP. On the use of beta coefficients in meta-analysis. J Appl Psychol. 2005;90(1):175.
Hunter JE, Schmidt FL. Methods of meta-analysis: correcting error and bias in research findings. Sage; 2004.
Zhang Y, Li S, Yu G. The relationship between self-esteem and social anxiety: a meta-analysis with Chinese students. Adv Psychol Sci. 2019;27(6):1005–18.
Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JP, Rothstein HR. Introduction to meta-analysis. Wiley; 2021.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539–58.
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315(7109):629–34.
Light RJ, Pillemer DB. Summing up: the science of reviewing research. Harvard University Press; 1984.
Rosenthal R. Meta-Analytic Procedures for Social Science Research Sage Publications: Beverly Hills, 1984, 148 pp. Educational Researcher 1986;15(8):18–20.
Rothstein HR, Sutton AJ, Borenstein M. Publication bias in meta-analysis. Publication bias meta‐analysis: Prev Assess Adjustments 2005:1–7.
Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot–based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta‐analysis. Biometrics. 2000;56(2):455–63.
Al-Mamun F, Hosen I, Griffiths MD, Mamun MA. Facebook use and its predictive factors among students: evidence from a lower- and middle-income country, Bangladesh. Front Psychiatry 2022, 13.
Schou Andreassen C, Billieux J, Griffiths MD, Kuss DJ, Demetrovics Z, Mazzoni E, Pallesen S. The relationship between addictive use of social media and video games and symptoms of psychiatric disorders: a large-scale cross-sectional study. Psychol Addict Behaviors: J Soc Psychologists Addict Behav. 2016;30(2):252–62.
Arikan G, Acar IH, Ustundag-Budak AM. A two-generation study: The transmission of attachment and young adults’ depression, anxiety, and social media addiction. Addict Behav 2022, 124.
Arpaci I, Karatas K, Kiran F, Kusci I, Topcu A. Mediating role of positivity in the relationship between state anxiety and problematic social media use during the COVID-19 pandemic. Death Stud. 2022;46(10):2287–97.
Brailovskaia J, Margraf J. Facebook Addiction Disorder (FAD) among German students-A longitudinal approach. PLoS ONE 2017, 12(12).
Brailovskaia J, Margraf J. The relationship between burden caused by coronavirus (Covid-19), addictive social media use, sense of control and anxiety. Comput Hum Behav. 2021;119:106720–106720.
Brailovskaia J, Margraf J. Addictive social media use during Covid-19 outbreak: validation of the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale (BSMAS) and investigation of protective factors in nine countries. Curr Psychol (New Brunsw NJ) 2022:1–19.
Brailovskaia J, Krasavtseva Y, Kochetkov Y, Tour P, Margraf J. Social media use, mental health, and suicide-related outcomes in Russian women: a cross-sectional comparison between two age groups. Women’s Health (London England). 2022;18:17455057221141292–17455057221141292.
PubMed Google Scholar
Chang C-W, Huang R-Y, Strong C, Lin Y-C, Tsai M-C, Chen IH, Lin C-Y, Pakpour AHH, Griffiths MDD. Reciprocal relationships between Problematic Social Media Use, problematic gaming, and psychological distress among University students: a 9-Month Longitudinal Study. Front Public Health 2022, 10.
Charzynska E, Sussman S, Atroszko PA. Profiles of potential behavioral addictions’ severity and their associations with gender, personality, and well-being: A person-centered approach. Addict Behav 2021, 119.
Chen C-Y, Chen IH, Pakpour AH, Lin C-Y, Griffiths MD. Internet-related behaviors and psychological distress among Schoolchildren during the COVID-19 School Hiatus. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2021;24(10):654–63.
Da Veiga GF, Sotero L, Pontes HM, Cunha D, Portugal A, Relvas AP. Emerging adults and Facebook Use: the validation of the Bergen Facebook Addiction Scale (BFAS). Int J Mental Health Addict. 2019;17(2):279–94.
Dadiotis A, Bacopoulou F, Kokka I, Vlachakis D, Chrousos GP, Darviri C, Roussos P. Validation of the Greek version of the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale in Undergraduate Students. EMBnetjournal 2021, 26.
Fekih-Romdhane F, Jahrami H, Away R, Trabelsi K, Pandi-Perumal SR, Seeman MV, Hallit S, Cheour M. The relationship between technology addictions and schizotypal traits: mediating roles of depression, anxiety, and stress. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23(1).
Flynn S, Noone C, Sarma KM. An exploration of the link between adult attachment and problematic Facebook use. BMC Psychol. 2018;6(1):34–34.
Fung XCC, Siu AMH, Potenza MN, O’Brien KS, Latner JD, Chen C-Y, Chen IH, Lin C-Y. Problematic use of internet-related activities and Perceived Weight Stigma in Schoolchildren: a longitudinal study across different epidemic periods of COVID-19 in China. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Gonzalez-Nuevo C, Cuesta M, Muniz J, Postigo A, Menendez-Aller A, Kuss DJ. Problematic Use of Social Networks during the First Lockdown: User Profiles and the Protective Effect of Resilience and Optimism. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2022, 11(24).
Hou X-L, Wang H-Z, Hu T-Q, Gentile DA, Gaskin J, Wang J-L. The relationship between perceived stress and problematic social networking site use among Chinese college students. J Behav Addictions. 2019;8(2):306–17.
Hussain Z, Wegmann E. Problematic social networking site use and associations with anxiety, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and resilience. Computers Hum Behav Rep. 2021;4:100125.
Imani V, Ahorsu DK, Taghizadeh N, Parsapour Z, Nejati B, Chen H-P, Pakpour AH. The mediating roles of anxiety, Depression, Sleepiness, Insomnia, and Sleep Quality in the Association between Problematic Social Media Use and Quality of Life among patients with Cancer. Healthcare 2022, 10(9).
Islam MS, Sujan MSH, Tasnim R, Mohona RA, Ferdous MZ, Kamruzzaman S, Toma TY, Sakib MN, Pinky KN, Islam MR et al. Problematic smartphone and Social Media Use among Bangladeshi College and University students amid COVID-19: the role of Psychological Well-Being and Pandemic related factors. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Islam MS, Jahan I, Dewan MAA, Pontes HM, Koly KN, Sikder MT, Rahman M. Psychometric properties of three online-related addictive behavior instruments among Bangladeshi school-going adolescents. PLoS ONE 2022, 17(12).
Jahan I, Hosen I, Al Mamun F, Kaggwa MM, Griffiths MD, Mamun MA. How has the COVID-19 pandemic impacted Internet Use behaviors and facilitated problematic internet use? A Bangladeshi study. Psychol Res Behav Manage. 2021;14:1127–38.
Jiang Y. Problematic social media usage and anxiety among University Students during the COVID-19 pandemic: the mediating role of Psychological Capital and the moderating role of academic burnout. Front Psychol. 2021;12:612007–612007.
Kim M-R, Oh J-W, Huh B-Y. Analysis of factors related to Social Network Service Addiction among Korean High School Students. J Addictions Nurs. 2020;31(3):203–12.
Koc M, Gulyagci S. Facebook addiction among Turkish college students: the role of psychological health, demographic, and usage characteristics. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2013;16(4):279–84.
Lin C-Y, Namdar P, Griffiths MD, Pakpour AH. Mediated roles of generalized trust and perceived social support in the effects of problematic social media use on mental health: a cross-sectional study. Health Expect. 2021;24(1):165–73.
Lin C-Y, Imani V, Griffiths MD, Brostrom A, Nygardh A, Demetrovics Z, Pakpour AH. Temporal associations between morningness/eveningness, problematic social media use, psychological distress and daytime sleepiness: mediated roles of sleep quality and insomnia among young adults. J Sleep Res 2021, 30(1).
Lozano Blasco R, Latorre Cosculluela C, Quilez Robres A. Social Network Addiction and its impact on anxiety level among University students. Sustainability 2020, 12(13).
Marino C, Musetti A, Vieno A, Manari T, Franceschini C. Is psychological distress the key factor in the association between problematic social networking sites and poor sleep quality? Addict Behav 2022, 133.
Meshi D, Ellithorpe ME. Problematic social media use and social support received in real-life versus on social media: associations with depression, anxiety and social isolation. Addict Behav 2021, 119.
Mitropoulou EM, Karagianni M, Thomadakis C. Social Media Addiction, Self-Compassion, and Psychological Well-Being: a structural equation Model. Alpha Psychiatry. 2022;23(6):298–304.
Ozimek P, Brailovskaia J, Bierhoff H-W. Active and passive behavior in social media: validating the Social Media Activity Questionnaire (SMAQ). Telematics Inf Rep. 2023;10:100048.
Phillips WJ, Wisniewski AT. Self-compassion moderates the predictive effects of social media use profiles on depression and anxiety. Computers Hum Behav Rep. 2021;4:100128.
Reer F, Festl R, Quandt T. Investigating problematic social media and game use in a nationally representative sample of adolescents and younger adults. Behav Inform Technol. 2021;40(8):776–89.
Satici B, Kayis AR, Griffiths MD. Exploring the Association between Social Media Addiction and relationship satisfaction: psychological distress as a Mediator. Int J Mental Health Addict 2021.
Sediri S, Zgueb Y, Ouanes S, Ouali U, Bourgou S, Jomli R, Nacef F. Women’s mental health: acute impact of COVID-19 pandemic on domestic violence. Archives Womens Mental Health. 2020;23(6):749–56.
Shabahang R, Shim H, Aruguete MS, Zsila A. Oversharing on Social Media: anxiety, Attention-Seeking, and Social Media Addiction Predict the breadth and depth of sharing. Psychol Rep 2022:332941221122861–332941221122861.
Sotero L, Ferreira Da Veiga G, Carreira D, Portugal A, Relvas AP. Facebook Addiction and emerging adults: the influence of sociodemographic variables, family communication, and differentiation of self. Escritos De Psicología - Psychol Writings. 2019;12(2):81–92.
Stockdale LA, Coyne SM. Bored and online: reasons for using social media, problematic social networking site use, and behavioral outcomes across the transition from adolescence to emerging adulthood. J Adolesc. 2020;79:173–83.
Wang Z, Yang H, Elhai JD. Are there gender differences in comorbidity symptoms networks of problematic social media use, anxiety and depression symptoms? Evidence from network analysis. Pers Indiv Differ. 2022;195:111705.
White-Gosselin C-E, Poulin F. Associations Between Young Adults’ Social Media Addiction, Relationship Quality With Parents, and Internalizing Problems: A Path Analysis Model. 2022.
Wong HY, Mo HY, Potenza MN, Chan MNM, Lau WM, Chui TK, Pakpour AH, Lin C-Y. Relationships between Severity of Internet Gaming Disorder, Severity of Problematic Social Media Use, Sleep Quality and Psychological Distress. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17(6).
Yam C-W, Pakpour AH, Griffiths MD, Yau W-Y, Lo C-LM, Ng JMT, Lin C-Y, Leung H. Psychometric testing of three Chinese online-related addictive Behavior instruments among Hong Kong University students. Psychiatr Q. 2019;90(1):117–28.
Yuan Y, Zhong Y. A survey on the use of social networks and mental health of college students during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Campus Life Mental Health\. 2021;19(3):209–12.
Google Scholar
Yurdagul C, Kircaburun K, Emirtekin E, Wang P, Griffiths MD. Psychopathological consequences related to problematic Instagram Use among adolescents: the mediating role of body image dissatisfaction and moderating role of gender. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2021;19(5):1385–97.
Zhang W, Pu J, He R, Yu M, Xu L, He X, Chen Z, Gan Z, Liu K, Tan Y, et al. Demographic characteristics, family environment and psychosocial factors affecting internet addiction in Chinese adolescents. J Affect Disord. 2022;315:130–8.
Zhang L, Wu Y, Jin T, Jia Y. Revision and validation of the Chinese short version of social media disorder. Mod Prev Med. 2021;48(8):1350–3.
Zhang X, Fan L. The influence of anxiety on colleges’ life satisfaction. Chin J Health Educ. 2021;37(5):469–72.
Zhao M, Wang H, Dong Y, Niu Y, Fang Y. The relationship between self-esteem and wechat addiction among undergraduate students: the multiple mediating roles of state anxiety and online interpersonal trust. J Psychol Sci. 2021;44(1):104–10.
Zhao J, Zhou Z, Sun B, Zhang X, Zhang L, Fu S. Attentional Bias is Associated with negative emotions in problematic users of Social Media as measured by a dot-probe Task. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19(24).
Atroszko PA, Balcerowska JM, Bereznowski P, Biernatowska A, Pallesen S, Schou Andreassen C. Facebook addiction among Polish undergraduate students: validity of measurement and relationship with personality and well-being. Comput Hum Behav. 2018;85:329–38.
Chen Y, Li R, Zhang P, Liu X. The moderating role of state attachment anxiety and avoidance between social anxiety and social networking sites Addiction. Psychol Rep. 2020;123(3):633–47.
Chen B, Zheng X, Sun X. The relationship between problematic social media use and online social anxiety: the roles of social media cognitive overload and dispositional mindfulness. Psychol Dev Educ. 2023;39(5):743–51.
Chentsova VO, Bravo AJ, Mezquita L, Pilatti A, Hogarth L, Cross-Cultural AS. Internalizing symptoms, rumination, and problematic social networking site use: a cross national examination among young adults in seven countries. Addict Behav 2023, 136.
Chu X, Ji S, Wang X, Yu J, Chen Y, Lei L. Peer phubbing and social networking site addiction: the mediating role of social anxiety and the moderating role of Family Financial Difficulty. Front Psychol. 2021;12:670065–670065.
Dempsey AE, O’Brien KD, Tiamiyu MF, Elhai JD. Fear of missing out (FoMO) and rumination mediate relations between social anxiety and problematic Facebook use. Addict Behav Rep. 2019;9:100150–100150.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yildiz Durak H, Seferoglu SS. Modeling of variables related to problematic social media usage: Social desirability tendency example. Scand J Psychol. 2019;60(3):277–88.
Ekinci N, Akat M. The relationship between anxious-ambivalent attachment and social appearance anxiety in adolescents: the serial mediation of positive Youth Development and Instagram Addiction. Psychol Rep 2023:332941231159600–332941231159600.
Foroughi B, Griffiths MD, Iranmanesh M, Salamzadeh Y. Associations between Instagram Addiction, academic performance, social anxiety, Depression, and life satisfaction among University students. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2022;20(4):2221–42.
He L. Influence mechanism and intervention suggestions on addiction of social network addiction. Gannan Normal University; 2021.
Hu Y. The influencing mechanism of type D personality on problematic social networking sites use among adolescents and intervention research. Central China Normal University; 2020.
Jia L. A study of the relationship between neuroticism, perceived social support, social anxiety and problematic social network use in high school students. Harbin Normal University; 2022.
Lee-Won RJ, Herzog L, Park SG. Hooked on Facebook: the role of social anxiety and need for Social Assurance in Problematic Use of Facebook. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2015;18(10):567–74.
Li H. Social anxiety and internet interpersonal addiction in adolescents and countermeasures. Central China Normal University; 2022.
Lin W-S, Chen H-R, Lee TS-H, Feng JY. Role of social anxiety on high engagement and addictive behavior in the context of social networking sites. Data Technol Appl. 2019;53(2):156–70.
Liu Y. The influence of family function on social media addiction in adolescents: the chain mediation effect of social anxiety and resilience. Hunan Normal University; 2021.
Lyvers M, Salviani A, Costan S, Thorberg FA. Alexithymia, narcissism and social anxiety in relation to social media and internet addiction symptoms. Int J Psychology: J Int De Psychologie. 2022;57(5):606–12.
Majid A, Yasir M, Javed A, Ali P. From envy to social anxiety and rumination: how social media site addiction triggers task distraction amongst nurses. J Nurs Adm Manag. 2020;28(3):504–13.
Mou Q, Zhuang J, Gao Y, Zhong Y, Lu Q, Gao F, Zhao M. The relationship between social anxiety and academic engagement among Chinese college students: a serial mediation model. J Affect Disord. 2022;311:247–53.
Ruggieri S, Santoro G, Pace U, Passanisi A, Schimmenti A. Problematic Facebook use and anxiety concerning use of social media in mothers and their offspring: an actor-partner interdependence model. Addict Behav Rep. 2020;11:100256–100256.
Ruiz MJ, Saez G, Villanueva-Moya L, Exposito F. Adolescent sexting: the role of body shame, Social Physique anxiety, and social networking site addiction. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2021;24(12):799–805.
She R, Kit Han Mo P, Li J, Liu X, Jiang H, Chen Y, Ma L, Tak Fai Lau J. The double-edged sword effect of social networking use intensity on problematic social networking use among college students: the role of social skills and social anxiety. Comput Hum Behav. 2023;140:107555.
Stănculescu E. The Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale Validity in a Romanian sample using item response theory and network analysis. Int J Mental Health Addict 2022.
Teng X, Lei H, Li J, Wen Z. The influence of social anxiety on social network site addiction of college students: the moderator of intentional self-regulation. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2021;29(3):514–7.
Tong W. Influence of boredom on the problematic mobile social networks usage in adolescents: multiple chain mediator. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2019;27(5):932–6.
Tu W, Jiang H, Liu Q. Peer victimization and adolescent Mobile Social Addiction: mediation of social anxiety and gender differences. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19(17).
Wang S. The influence of college students self-esteem, social anxiety and fear of missing out on the problematic mobile social networks usage. Huaibei Normal University; 2021.
Wang X. The impact of peer relationship and social anxiety on secondary vocational school students’ problematic social network use and intervention study. Huaibei Normal University; 2022.
Wegmann E, Stodt B, Brand M. Addictive use of social networking sites can be explained by the interaction of internet use expectancies, internet literacy, and psychopathological symptoms. J Behav Addictions. 2015;4(3):155–62.
Yang W. The relationship between the type of internet addiction and the personality traits in college students. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2004.
Yang Z. The relationship between social variables and social networking usage among shanghai working population. East China Normal University; 2013.
Zhang C. The relationship between perceived social support and problematic social network use among junior high school students: a chain mediation model and an intervention study. Hebei University; 2022.
Zhang J, Chang F, Huang D, Wen X. The relationship between neuroticism and the problematic mobile social networks use in adolescents: the mediating role of anxiety and positive self-presentation. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2021;29(3):598–602.
Zhang Z. College students’ loneliness and problematic social networking use: Chain mediation of social self-efficacy and social anxiety. Shanghai Normal University; 2019.
Zhu B. Discussion on mechanism of social networking addiction——Social anxiety, craving and excitability. Liaoning Normal University; 2017.
Blackwell D, Leaman C, Tramposch R, Osborne C, Liss M. Extraversion, neuroticism, attachment style and fear of missing out as predictors of social media use and addiction. Pers Indiv Differ. 2017;116:69–72.
Chen A. From attachment to addiction: the mediating role of need satisfaction on social networking sites. Comput Hum Behav. 2019;98:80–92.
Chen Y, Zhong S, Dai L, Deng Y, Liu X. Attachment anxiety and social networking sites addiction in college students: a moderated mediating model. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2019;27(3):497–500.
Li J. The relations among problematic social networks usage behavior, Childhood Trauma and adult attachment in University students. Hunan Agricultural University; 2020.
Liu C, Ma J-L. Adult attachment orientations and social networking site addiction: the Mediating effects of Online Social Support and the fear of missing out. Front Psychol. 2019;10:2629–2629.
Mo S, Huang W, Xu Y, Tang Z, Nie G. The impact of medical students’ attachment anxiety on the use of problematic social networking sites during the epidemic. Psychol Monthly. 2022;17(9):1–4.
Teng X. The effect of attachment anxiety on problematic mobile social network use: the role of loneliness and self-control. Harbin Normal University; 2021.
Worsley JD, Mansfield R, Corcoran R. Attachment anxiety and problematic social media use: the Mediating Role of Well-Being. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2018;21(9):563–8.
Wu Z. The effect of adult attachment on problematic social network use: the chain mediating effect of loneliness and fear of missing out. Jilin University; 2022.
Xia N. The impact of attachment anxiety on adolescent problem social networking site use: a moderated mediation model. Shihezi University; 2022.
Young L, Kolubinski DC, Frings D. Attachment style moderates the relationship between social media use and user mental health and wellbeing. Heliyon 2020, 6(6).
Bakioglu F, Deniz M, Griffiths MD, Pakpour AH. Adaptation and validation of the online-fear of missing out inventory into Turkish and the association with social media addiction, smartphone addiction, and life satisfaction. BMC Psychol. 2022;10(1):154–154.
Bendayan R, Blanca MJ. Spanish version of the Facebook Intrusion Questionnaire (FIQ-S). Psicothema. 2019;31(2):204–9.
Blachnio A, Przepiorka A. Facebook intrusion, fear of missing out, narcissism, and life satisfaction: a cross-sectional study. Psychiatry Res. 2018;259:514–9.
Casale S, Rugai L, Fioravanti G. Exploring the role of positive metacognitions in explaining the association between the fear of missing out and social media addiction. Addict Behav. 2018;85:83–7.
Chen Y, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Wang K. Effect of fear of’ missing out on college students negative social adaptation: Chain¬ - mediating effect of rumination and problematic social media use. China J Health Psychol. 2022;30(4):581–6.
Cheng S, Zhang X, Han Y. Relationship between fear of missing out and phubbing on college students: the chain intermediary effect of intolerance of uncertainty and problematic social media use. China J Health Psychol. 2022;30(9):1296–300.
Cui Q, Wang J, Zhang J, Li W, Li Q. The relationship between loneliness and negative emotion in college students: the chain-mediating role of fear of missing out and social network sites addiction. J Jining Med Univ. 2022;45(4):248–51.
Ding Q, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Zhou Z. The more gossip, the more addicted: the relationship between interpersonal curiosity and social networking sites addiction tendencies in college students. Psychol Dev Educ. 2022;38(1):118–25.
Fabris MA, Marengo D, Longobardi C, Settanni M. Investigating the links between fear of missing out, social media addiction, and emotional symptoms in adolescence: the role of stress associated with neglect and negative reactions on social media. Addict Behav. 2020;106:106364.
Fang J, Wang X, Wen Z, Zhou J. Fear of missing out and problematic social media use as mediators between emotional support from social media and phubbing behavior. Addict Behav. 2020;107:106430.
Gao Z. The study on the relationship and intervention among fear of missing out self-differentiation and problematic social media use of college students. Yunnan Normal University; 2021.
Gioia F, Fioravanti G, Casale S, Boursier V. The Effects of the Fear of Missing Out on People’s Social Networking Sites Use During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Mediating Role of Online Relational Closeness and Individuals’ Online Communication Attitude. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Gu X. Study on the Inhibitory Effect of Mindfulness Training on Social Media Addiction of College Students. Wuhan University; 2020.
Gugushvili N, Taht K, Schruff-Lim EM, Ruiter RA, Verduyn P. The Association between Neuroticism and problematic social networking sites Use: the role of fear of missing out and Self-Control. Psychol Rep 2022:332941221142003–332941221142003.
Hou J. The study on FoMO and content social media addiction among young people. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2021.
Hu R, Zhang B, Yang Y, Mao H, Peng Y, Xiong S. Relationship between college students’ fear of missing and wechat addiction: a cross-lagged analysis. J Bio-education. 2022;10(5):369–73.
Hu G. The relationship between basic psychological needs satisfaction and the use of problematic social networks by college students: a moderated mediation model and online intervention studies. Jiangxi Normal University; 2020.
Jiang Y, Jin T. The relationship between adolescents’ narcissistic personality and their use of problematic mobile social networks: the effects of fear of missing out and positive self-presentation. Chin J Special Educ 2018(11):64–70.
Li J. The effect of positive self-presentation on social networking sites on problematic use of social networking sites: a moderated mediation model. Henan University; 2020.
Li J, Zhang Y, Zhang X. The impact of Freshmen Social Exclusion on problematic Social Network Use: a Moderated Mediation Model. J Heilongjiang Vocat Inst Ecol Eng. 2023;36(1):118–22.
Li M. The relationship between fear of missing out and social media addiction among middle school students——The moderating role of self-control. Kashi University; 2022.
Li R, Dong X, Wang M, Wang R. A study on the relationship between fear of missing out and social network addiction. New Educ Era 2021(52):122–3.
Li Y. Fear of missing out or social avoidance? The influence of peer exclusion on problematic social media use among adolescents in Guangdong Province and Macao. Guangzhou University; 2020.
Ma J, Liu C. The effect of fear of missing out on social networking sites addiction among college students: the mediating roles of social networking site integration use and social support. Psychol Dev Educ. 2019;35(5):605–14.
Mao H. A follow-up study on the mechanism of the influence of university students’ Qi deficiency quality on WeChat addiction. Hunan University of Chinese Medicine; 2021.
Mao Y. The effect of dual filial piety to the college students ’internet social dependence: the mediation of maladaptive cognition and fear of missing out. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2021.
Moore K, Craciun G. Fear of missing out and personality as predictors of Social networking sites usage: the Instagram Case. Psychol Rep. 2021;124(4):1761–87.
Niu J. The relationship of college students’ basic psychological needs and social media dependence: the mediating role of fear of missing out. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2021.
Pi L, Li X. Research on the relationship between loneliness and problematic mobile social media usage: evidence from variable-oriented and person-oriented analyses. China J Health Psychol. 2023;31(6):936–42.
Pontes HM, Taylor M, Stavropoulos V. Beyond Facebook Addiction: the role of cognitive-related factors and Psychiatric Distress in Social networking site addiction. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2018;21(4):240–7.
Quaglieri A, Biondi S, Roma P, Varchetta M, Fraschetti A, Burrai J, Lausi G, Marti-Vilar M, Gonzalez-Sala F, Di Domenico A et al. From Emotional (Dys) Regulation to Internet Addiction: A Mediation Model of Problematic Social Media Use among Italian Young Adults. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2022, 11(1).
Servidio R, Koronczai B, Griffiths MD, Demetrovics Z. Problematic smartphone Use and Problematic Social Media Use: the predictive role of Self-Construal and the Mediating Effect of Fear Missing Out. Front Public Health 2022, 10.
Sheldon P, Antony MG, Sykes B. Predictors of problematic social media use: personality and life-position indicators. Psychol Rep. 2021;124(3):1110–33.
Sun C, Li Y, Kwok SYCL, Mu W. The relationship between intolerance of uncertainty and problematic Social Media Use during the COVID-19 pandemic: a serial mediation model. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19(22).
Tang Z. The relationship between loneliness and problematic social networks use among college students: the mediation of fear of missing out and the moderation of social support. Jilin University; 2022.
Tomczyk Ł, Selmanagic-Lizde E. Fear of missing out (FOMO) among youth in Bosnia and Herzegovina — Scale and selected mechanisms. Child Youth Serv Rev. 2018;88:541–9.
Unal-Aydin P, Ozkan Y, Ozturk M, Aydin O, Spada MM. The role of metacognitions in cyberbullying and cybervictimization among adolescents diagnosed with major depressive disorder and anxiety disorders: a case-control study. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy; 2023.
Uram P, Skalski S. Still logged in? The Link between Facebook Addiction, FoMO, Self-Esteem, Life satisfaction and loneliness in social media users. Psychol Rep. 2022;125(1):218–31.
Varchetta M, Fraschetti A, Mari E, Giannini AM. Social Media Addiction, fear of missing out (FoMO) and online vulnerability in university students. Revista Digit De Investigación en Docencia Universitaria. 2020;14(1):e1187.
Wang H. Study on the relationship and intervention between fear of missing and social network addiction in college students. Yunnan Normal University; 2021.
Wang M, Yin Z, Xu Q, Niu G. The relationship between shyness and adolescents’ social network sites addiction: Moderated mediation model. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2020;28(5):906–9.
Wegmann E, Oberst U, Stodt B, Brand M. Online-specific fear of missing out and internet-use expectancies contribute to symptoms of internet-communication disorder. Addict Behav Rep. 2017;5:33–42.
Wegmann E, Brandtner A, Brand M. Perceived strain due to COVID-19-Related restrictions mediates the Effect of Social needs and fear of missing out on the risk of a problematic use of Social Networks. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Wei Q. Negative emotions and problematic social network sites usage: the mediating role of fear of missing out and the moderating role of gender. Central China Normal University; 2018.
Xiong L. Effect of social network site use on college students’ social network site addiction: A moderated mediation model and attention bias training intervention study. Jiangxi Normal University; 2022.
Yan H. The influence of college students’ basic psychological needs on social network addiction: The intermediary role of fear of missing out. Wuhan University; 2020.
Yan H. The status and factors associated with social media addiction among young people——Evidence from WeChat. Chongqing University; 2021.
Yang L. Research on the relationship of fear of missing out, excessive use of Wechat and life satisfaction. Beijing Forestry University; 2020.
Yin Y, Cai X, Ouyang M, Li S, Li X, Wang P. FoMO and the brain: loneliness and problematic social networking site use mediate the association between the topology of the resting-state EEG brain network and fear of missing out. Comput Hum Behav. 2023;141:107624.
Zhang C. The parental rejection and problematic social network sites with adolescents: the chain mediating effect of basic psychological needs and fear of missing out. Central China Normal University; 2022.
Zhang J. The influence of basic psychological needs on problematic mobile social networks usage of adolescent: a moderated mediation model. Liaocheng University; 2020.
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Jin J, Yu G. The relationship between fear of missing out and social media addiction: a cross-lagged analysis. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2021;29(5):1082–5.
Zhang Y, Jiang W, Ding Q, Hong M. Social comparison orientation and social network sites addiction in college students: the mediating role of fear of missing out. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2019;27(5):928–31.
Zhou J, Fang J. Social network sites support and addiction among college students: a moderated mediation model. Psychology: Techniques Appl. 2021;9(5):293–9.
Andreassen CS, Torsheim T, Brunborg GS, Pallesen S. Development of a Facebook addiction scale. Psychol Rep. 2012;110(2):501–17.
Andreassen CS, Billieux J, Griffiths MD, Kuss DJ, Demetrovics Z, Mazzoni E, Pallesen S. The relationship between addictive use of social media and video games and symptoms of psychiatric disorders: a large-scale cross-sectional study. Psychol Addict Behav. 2016;30(2):252.
Elphinston RA, Noller P. Time to face it! Facebook intrusion and the implications for romantic jealousy and relationship satisfaction. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2011;14(11):631–5.
Caplan SE. Theory and measurement of generalized problematic internet use: a two-step approach. Comput Hum Behav. 2010;26(5):1089–97.
Jiang Y. Development of problematic mobile social media usage assessment questionnaire for adolescents. Psychology: Techniques Appl. 2018;6(10):613–21.
Wang X. College students’ social network addiction tendency: Questionnaire construction and correlation research. Master’s thesis Southwest University; 2016.
Derogatis LR. Brief symptom inventory 18. Johns Hopkins University Baltimore; 2001.
Lovibond PF, Lovibond SH. The structure of negative emotional states: comparison of the Depression anxiety stress scales (DASS) with the Beck Depression and anxiety inventories. Behav Res Ther. 1995;33(3):335–43.
Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB, Löwe B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(10):1092–7.
Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 1983;67(6):361–70.
Spielberger CD, Gonzalez-Reigosa F, Martinez-Urrutia A, Natalicio LF, Natalicio DS. The state-trait anxiety inventory. Revista Interamericana de Psicologia/Interamerican Journal of Psychology 1971, 5(3&4).
Marteau TM, Bekker H. The development of a six-item short‐form of the state scale of the Spielberger State—trait anxiety inventory (STAI). Br J Clin Psychol. 1992;31(3):301–6.
Leary MR. Social anxiousness: the construct and its measurement. J Pers Assess. 1983;47(1):66–75.
Liebowitz MR. Social phobia. Modern problems of pharmacopsychiatry 1987.
Alkis Y, Kadirhan Z, Sat M. Development and validation of social anxiety scale for social media users. Comput Hum Behav. 2017;72:296–303.
La Greca AM, Stone WL. Social anxiety scale for children-revised: factor structure and concurrent validity. J Clin Child Psychol. 1993;22(1):17–27.
Fenigstein A, Scheier MF, Buss AH. Public and private self-consciousness: Assessment and theory. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1975;43(4):522.
Mattick RP, Clarke JC. Development and validation of measures of social phobia scrutiny fear and social interaction anxiety. Behav Res Ther. 1998;36(4):455–70.
Peters L, Sunderland M, Andrews G, Rapee RM, Mattick RP. Development of a short form Social Interaction anxiety (SIAS) and Social Phobia Scale (SPS) using nonparametric item response theory: the SIAS-6 and the SPS-6. Psychol Assess. 2012;24(1):66.
Brennan KA, Clark CL, Shaver PR. Self-report measurement of adult attachment: an integrative overview. Attachment Theory Close Relationships. 1998;46:76.
Wei M, Russell DW, Mallinckrodt B, Vogel DL. The experiences in Close Relationship Scale (ECR)-short form: reliability, validity, and factor structure. J Pers Assess. 2007;88(2):187–204.
Bartholomew K, Horowitz LM. Attachment styles among young adults: a test of a four-category model. J Personal Soc Psychol. 1991;61(2):226.
Przybylski AK, Murayama K, DeHaan CR, Gladwell V. Motivational, emotional, and behavioral correlates of fear of missing out. Comput Hum Behav. 2013;29(4):1841–8.
Xiaokang S, Yuxiang Z, Xuanhui Z. Developing a fear of missing out (FoMO) measurement scale in the mobile social media environment. Libr Inform Service. 2017;61(11):96.
Bown M, Sutton A. Quality control in systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2010;40(5):669–77.
Turel O, Qahri-Saremi H. Problematic use of social networking sites: antecedents and consequence from a dual-system theory perspective. J Manage Inform Syst. 2016;33(4):1087–116.
Chou H-TG, Edge N. They are happier and having better lives than I am: the impact of using Facebook on perceptions of others’ lives. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2012;15(2):117–21.
Beyens I, Frison E, Eggermont S. I don’t want to miss a thing: adolescents’ fear of missing out and its relationship to adolescents’ social needs, Facebook use, and Facebook related stress. Comput Hum Behav. 2016;64:1–8.
Di Blasi M, Gullo S, Mancinelli E, Freda MF, Esposito G, Gelo OCG, Lagetto G, Giordano C, Mazzeschi C, Pazzagli C. Psychological distress associated with the COVID-19 lockdown: a two-wave network analysis. J Affect Disord. 2021;284:18–26.
Yang X, Hu H, Zhao C, Xu H, Tu X, Zhang G. A longitudinal study of changes in smart phone addiction and depressive symptoms and potential risk factors among Chinese college students. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):252.
Kuss DJ, Griffiths MD. Social networking sites and addiction: ten lessons learned. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017;14(3):311.
Ryan T, Chester A, Reece J, Xenos S. The uses and abuses of Facebook: a review of Facebook addiction. J Behav Addictions. 2014;3(3):133–48.
Elhai JD, Levine JC, Dvorak RD, Hall BJ. Non-social features of smartphone use are most related to depression, anxiety and problematic smartphone use. Comput Hum Behav. 2017;69:75–82.
Jackson LA, Wang J-L. Cultural differences in social networking site use: a comparative study of China and the United States. Comput Hum Behav. 2013;29(3):910–21.
Ahrens LM, Mühlberger A, Pauli P, Wieser MJ. Impaired visuocortical discrimination learning of socially conditioned stimuli in social anxiety. Soc Cognit Affect Neurosci. 2014;10(7):929–37.
Elhai JD, Yang H, Montag C. Fear of missing out (FOMO): overview, theoretical underpinnings, and literature review on relations with severity of negative affectivity and problematic technology use. Brazilian J Psychiatry. 2020;43:203–9.
Barker V. Older adolescents’ motivations for social network site use: the influence of gender, group identity, and collective self-esteem. Cyberpsychology Behav. 2009;12(2):209–13.
Krasnova H, Veltri NF, Eling N, Buxmann P. Why men and women continue to use social networking sites: the role of gender differences. J Strateg Inf Syst. 2017;26(4):261–84.
Palmer J. The role of gender on social network websites. Stylus Knights Write Showc 2012:35–46.
Vannucci A, Flannery KM, Ohannessian CM. Social media use and anxiety in emerging adults. J Affect Disord. 2017;207:163–6.
Primack BA, Shensa A, Sidani JE, Whaite EO, yi Lin L, Rosen D, Colditz JB, Radovic A, Miller E. Social media use and perceived social isolation among young adults in the US. Am J Prev Med. 2017;53(1):1–8.
Twenge JM, Campbell WK. Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: evidence from a population-based study. Prev Med Rep. 2018;12:271–83.
Download references
This research was supported by the Social Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 23BSH135).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Mental Health, Wenzhou Medical University, 325035, Wenzhou, China
Mingxuan Du, Haiyan Hu, Ningning Ding, Jiankang He, Wenwen Tian, Wenqian Zhao, Xiujian Lin, Gaoyang Liu, Wendan Chen, ShuangLiu Wang, Dongwu Xu & Guohua Zhang
School of Education, Renmin University of China, 100872, Beijing, China
Chengjia Zhao
School of Media and Communication, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Dongchuan Road 800, 200240, Shanghai, China
Pengcheng Wang
Department of Neurosis and Psychosomatic Diseases, Huzhou Third Municipal Hospital, 313002, Huzhou, China
Xinhua Shen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
GZ, XS, XL and MD prepared the study design, writing - review and editing. MD and CZ wrote the main manuscript text. MD and HH analyzed data and edited the draft. ND, JH, WT, WZ, GL, WC, SW, PW and DX conducted resources and data curation. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Xinhua Shen or Guohua Zhang .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Du, M., Zhao, C., Hu, H. et al. Association between problematic social networking use and anxiety symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychol 12 , 263 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01705-w
Download citation
Received : 25 January 2024
Accepted : 03 April 2024
Published : 12 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01705-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Fear of missing out
- Meta-analysis
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Figure 4.1: Literature reviews and references. Your may have done a literature survey as part of your proposal. This will be incorporated into your dissertation, not left as separate stand-alone. Most economics papers include a literature review section, which may be a separate section, or incorporated into the paper's introduction.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review. As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications.
As p art of your lit review, you'll need to provide a list of references -- your professors want to know where you found your information. Your professor will also require that you use a specific format ("style") for citing your references, such as one of these: APA (American Psychological Association) Chicago Manual of Style
Think of each text listed in the References section of a literature review as contributing pieces to a gigantic puzzle. Example 3.2: Look at the first three articles listed in the References for the article excerpted above: Abbott, L. C., Taff, D., Newman, P., Benfield, J. A., and Mowen, A. J. (2016). The influence of natural sounds on ...
The purpose of the literature review is to dive into the existing debates on the topic to learn about the various schools of thought and arguments, using your research question as an anchor. If you find something that doesn't help answer your question, you don't have to read (or include) it. That's the power of the question format: it helps you ...
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
Reference list Number of Authors Three or more One or more Timeline Months to years, Average eighteen months Weeks to months Requirement Thorough knowledge of topic ... Literature Review A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources that provides an overview of a particular topic. Literature reviews are a collection of
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
Include References/Works Cited List. As you are writing the literature review you will mention the author names and the publication years in your text, but you will still need to compile comprehensive citations for each entry at the end of your review. Follow APA, MLA, or Chicago style guidelines, as your course requires.
Peer Review ; Zotero Reference Manager; Literature Review. ... Also known as 'narrative literature review'. " Key takeaways from the Psi Chi webinar So You Need to Write a Literature Review via APA Style.org. Examples of Literature Reviews. Financial socialization: A decade in review (2021)
Literature reviews establish the foundation of academic inquires. However, in the planning field, we lack rigorous systematic reviews. In this article, through a systematic search on the methodology of literature review, we categorize a typology of literature reviews, discuss steps in conducting a systematic literature review, and provide suggestions on how to enhance rigor in literature ...
Step 4: Write. Be selective. Highlight only the most important and relevant points from a source in your review. Use quotes sparingly. Short quotes can help to emphasize a point, but thorough analysis of language from each source is generally unnecessary in a literature review. Synthesize your sources.
In the literature review, the "elements" are the findings of the literature you gather and read; the "new whole" is the conclusion you draw from those findings. Your goal is to compare and contrast, critically evaluate, interpret, so that you can draw conclusion. Each work should be critically summarized and evaluated for its premise ...
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. ... Call Number: Main Library Core Reference - 2 North Q180.55.M4 F56 2020 ...
Even with a literature review you should avoid using too many, or overlong, quotes. Summarise material in your own words as much as possible. Save the quotes for 'punch-lines' to drive a particular point home. Revise, revise, revise: refine and edit the draft as much as you can. Check for fluency, structure, evidence, criticality and ...
The contribution of the specific literature review can take a number of forms, and it should be judged in relationship to the field to which it wants to contribute. Depending on a number of factors, such as the maturity of the field or state of knowledge, different contributions could be valuable. ... Reference price research: Review and ...
A large part of conducting and writing a literature review is to reference the relevant sources that you have found. A number of referencing tools are available that can help you manage your references. RMIT University provides a license to the EndNote software program, although there are alternative reference management software available.
It could be only one. Conceivably, it could be none. For a master's thesis in literature, the minimum might be one secondary source for each thousand word. In imagine, in that case, that it might be double than many for a doctoral disseration. In that case, the number secondary sources for doctoral thesis would have to be around 150.
How to synthesize. In the synthesis step of a literature review, researchers analyze and integrate information from selected sources to identify patterns and themes. This involves critically evaluating findings, recognizing commonalities, and constructing a cohesive narrative that contributes to the understanding of the research topic. Synthesis.
Also, if the whole dissertation is 12,000 I'd expect to see at least 30 references (I'm an academic editor) 🙂. See more. Hi, we were just told to write the literature review but that it should be no more than around 4,000 words. Nothing was mentioned about how many references should be in the literature review though.
A literature review was chosen as it offers a flexible way of working that suits this study's broad research questions. We were however inspired by the procedure of scoping review and the methods employed followed the guidance by Armstrong et al. (2011) : preparation, searches, assessment of relevance, mapping, and compilation.
Six of the studies included in this review discussed the impact of removing fragments on embryo development (Table 8) [7, 67, 93,94,95,96]. The literature is mixed, with some studies showing improvement in embryo development quality after fragmentation removal [7, 93], and others showing no difference at all [70, 94, 95].
Introduction Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the dominant primary renal malignant neoplasm, encompassing a significant portion of renal tumors. The presence of synchronous yet histologically distinct ipsilateral RCCs, however, is an exceptionally uncommon phenomenon that is rather under-described in the literature regarding etiology, diagnosis, management, and later outcomes during follow-up ...
@article{Girgis2024WideCT, title={Wide Complex Tachycardia as a Rare Pointer of Intra-aortic Balloon Pump Migration Into the Left Ventricle: A Case Report and Literature Review}, author={Kyrillos Girgis and Desmond Aroke and Danielle Retcho and Grettel Gonzalez Garcia and Sammir S Dekowski and Rafail Beshai and Jessica Celenza-Salvatore and ...
A growing number of studies have reported that problematic social networking use (PSNU) is strongly associated with anxiety symptoms. However, due to the presence of multiple anxiety subtypes, existing research findings on the extent of this association vary widely, leading to a lack of consensus. The current meta-analysis aimed to summarize studies exploring the relationship between PSNU ...
The present literature study delves into the development of language teaching methodologies, with particular emphasis on three well-known techniques: Grammar Translation, Direct Method, and Audiolingual Method. The background underscores how pedagogical ideas have changed throughout time and stresses the historical context of language learning. The evaluation analyzes important academic ...