
- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7

12 Best Artificial Intelligence Topics for Research in 2024
Explore the "12 Best Artificial Intelligence Topics for Research in 2024." Dive into the top AI research areas, including Natural Language Processing, Computer Vision, Reinforcement Learning, Explainable AI (XAI), AI in Healthcare, Autonomous Vehicles, and AI Ethics and Bias. Stay ahead of the curve and make informed choices for your AI research endeavours.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- AI Tools in Performance Marketing Training
- Deep Learning Course
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) Fundamentals with Python
- Machine Learning Course
- Duet AI for Workspace Training

Table of Contents
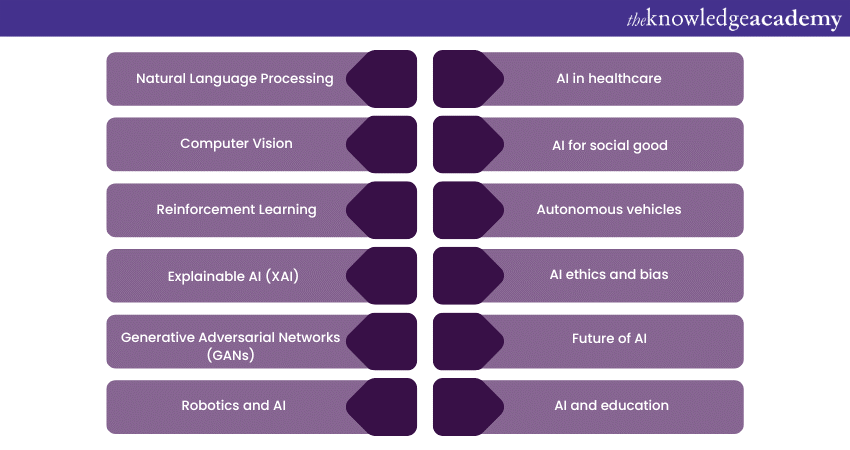
1) Top Artificial Intelligence Topics for Research
a) Natural Language Processing
b) Computer vision
c) Reinforcement Learning
d) Explainable AI (XAI)
e) Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
f) Robotics and AI
g) AI in healthcare
h) AI for social good
i) Autonomous vehicles
j) AI ethics and bias
2) Conclusion
Top Artificial Intelligence Topics for Research
This section of the blog will expand on some of the best Artificial Intelligence Topics for research.
Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is centred around empowering machines to comprehend, interpret, and even generate human language. Within this domain, three distinctive research avenues beckon:
1) Sentiment analysis: This entails the study of methodologies to decipher and discern emotions encapsulated within textual content. Understanding sentiments is pivotal in applications ranging from brand perception analysis to social media insights.
2) Language generation: Generating coherent and contextually apt text is an ongoing pursuit. Investigating mechanisms that allow machines to produce human-like narratives and responses holds immense potential across sectors.
3) Question answering systems: Constructing systems that can grasp the nuances of natural language questions and provide accurate, coherent responses is a cornerstone of NLP research. This facet has implications for knowledge dissemination, customer support, and more.
Computer Vision
Computer Vision, a discipline that bestows machines with the ability to interpret visual data, is replete with intriguing avenues for research:
1) Object detection and tracking: The development of algorithms capable of identifying and tracking objects within images and videos finds relevance in surveillance, automotive safety, and beyond.
2) Image captioning: Bridging the gap between visual and textual comprehension, this research area focuses on generating descriptive captions for images, catering to visually impaired individuals and enhancing multimedia indexing.
3) Facial recognition: Advancements in facial recognition technology hold implications for security, personalisation, and accessibility, necessitating ongoing research into accuracy and ethical considerations.
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement Learning revolves around training agents to make sequential decisions in order to maximise rewards. Within this realm, three prominent Artificial Intelligence Topics emerge:
1) Autonomous agents: Crafting AI agents that exhibit decision-making prowess in dynamic environments paves the way for applications like autonomous robotics and adaptive systems.
2) Deep Q-Networks (DQN): Deep Q-Networks, a class of reinforcement learning algorithms, remain under active research for refining value-based decision-making in complex scenarios.
3) Policy gradient methods: These methods, aiming to optimise policies directly, play a crucial role in fine-tuning decision-making processes across domains like gaming, finance, and robotics.

Explainable AI (XAI)
The pursuit of Explainable AI seeks to demystify the decision-making processes of AI systems. This area comprises Artificial Intelligence Topics such as:
1) Model interpretability: Unravelling the inner workings of complex models to elucidate the factors influencing their outputs, thus fostering transparency and accountability.
2) Visualising neural networks: Transforming abstract neural network structures into visual representations aids in comprehending their functionality and behaviour.
3) Rule-based systems: Augmenting AI decision-making with interpretable, rule-based systems holds promise in domains requiring logical explanations for actions taken.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
The captivating world of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) unfolds through the interplay of generator and discriminator networks, birthing remarkable research avenues:
1) Image generation: Crafting realistic images from random noise showcases the creative potential of GANs, with applications spanning art, design, and data augmentation.
2) Style transfer: Enabling the transfer of artistic styles between images, merging creativity and technology to yield visually captivating results.
3) Anomaly detection: GANs find utility in identifying anomalies within datasets, bolstering fraud detection, quality control, and anomaly-sensitive industries.
Robotics and AI
The synergy between Robotics and AI is a fertile ground for exploration, with Artificial Intelligence Topics such as:
1) Human-robot collaboration: Research in this arena strives to establish harmonious collaboration between humans and robots, augmenting industry productivity and efficiency.
2) Robot learning: By enabling robots to learn and adapt from their experiences, Researchers foster robots' autonomy and the ability to handle diverse tasks.
3) Ethical considerations: Delving into the ethical implications surrounding AI-powered robots helps establish responsible guidelines for their deployment.
AI in healthcare
AI presents a transformative potential within healthcare, spurring research into:
1) Medical diagnosis: AI aids in accurately diagnosing medical conditions, revolutionising early detection and patient care.
2) Drug discovery: Leveraging AI for drug discovery expedites the identification of potential candidates, accelerating the development of new treatments.
3) Personalised treatment: Tailoring medical interventions to individual patient profiles enhances treatment outcomes and patient well-being.
AI for social good
Harnessing the prowess of AI for Social Good entails addressing pressing global challenges:
1) Environmental monitoring: AI-powered solutions facilitate real-time monitoring of ecological changes, supporting conservation and sustainable practices.
2) Disaster response: Research in this area bolsters disaster response efforts by employing AI to analyse data and optimise resource allocation.
3) Poverty alleviation: Researchers contribute to humanitarian efforts and socioeconomic equality by devising AI solutions to tackle poverty.
Unlock the potential of Artificial Intelligence for effective Project Management with our Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Project Managers Course . Sign up now!
Autonomous vehicles
Autonomous Vehicles represent a realm brimming with potential and complexities, necessitating research in Artificial Intelligence Topics such as:
1) Sensor fusion: Integrating data from diverse sensors enhances perception accuracy, which is essential for safe autonomous navigation.
2) Path planning: Developing advanced algorithms for path planning ensures optimal routes while adhering to safety protocols.
3) Safety and ethics: Ethical considerations, such as programming vehicles to make difficult decisions in potential accident scenarios, require meticulous research and deliberation.
AI ethics and bias
Ethical underpinnings in AI drive research efforts in these directions:
1) Fairness in AI: Ensuring AI systems remain impartial and unbiased across diverse demographic groups.
2) Bias detection and mitigation: Identifying and rectifying biases present within AI models guarantees equitable outcomes.
3) Ethical decision-making: Developing frameworks that imbue AI with ethical decision-making capabilities aligns technology with societal values.
Future of AI
The vanguard of AI beckons Researchers to explore these horizons:
1) Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): Speculating on the potential emergence of AI systems capable of emulating human-like intelligence opens dialogues on the implications and challenges.
2) AI and creativity: Probing the interface between AI and creative domains, such as art and music, unveils the coalescence of human ingenuity and technological prowess.
3) Ethical and regulatory challenges: Researching the ethical dilemmas and regulatory frameworks underpinning AI's evolution fortifies responsible innovation.
AI and education
The intersection of AI and Education opens doors to innovative learning paradigms:
1) Personalised learning: Developing AI systems that adapt educational content to individual learning styles and paces.
2) Intelligent tutoring systems: Creating AI-driven tutoring systems that provide targeted support to students.
3) Educational data mining: Applying AI to analyse educational data for insights into learning patterns and trends.
Unleash the full potential of AI with our comprehensive Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Training . Join now!
Conclusion
The domain of AI is ever-expanding, rich with intriguing topics about Artificial Intelligence that beckon Researchers to explore, question, and innovate. Through the pursuit of these twelve diverse Artificial Intelligence Topics, we pave the way for not only technological advancement but also a deeper understanding of the societal impact of AI. By delving into these realms, Researchers stand poised to shape the trajectory of AI, ensuring it remains a force for progress, empowerment, and positive transformation in our world.
Unlock your full potential with our extensive Personal Development Training Courses. Join today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming data, analytics & ai resources batches & dates.
Fri 2nd Aug 2024
Fri 15th Nov 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

181+ Great PhD Research Topics In Artificial Intelligence [2024 Updated]
Are you curious about how smart machines learn and solve problems like humans? That’s what “PhD Research Topics in Artificial Intelligence” explore! Suppose teaching computers to think, learn, and make decisions just like us. These research topics are like treasure maps for scientists who want to discover new ways for machines to understand language, predict diseases, drive cars, and so much more!
In simple words, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is about making computers super smart. These PhD topics cover various fields like healthcare, finance, education, and even space! Scientists are like detectives, trying to find ways for AI to help people live better lives and solve big problems like predicting the weather or creating new medicines.
For example, robots help doctors, predict when accidents might happen on the road, or even explore space without humans! These PhD research topics are like a magical door to a world where machines can do incredible things to make our world safer, healthier, and more amazing. So, let’s take a peek into these topics and see the exciting possibilities AI offers to our future!
Also Like To Know: Top 10 Research Topics for Senior High School Students in 2024
Table of Contents
What Is PhD Research Topics In Artificial Intelligence?
PhD research topics in Artificial Intelligence (AI) refer to specific areas of study and investigation that scholars explore to advance the understanding and development of smart machines. These topics delve into various aspects of AI, aiming to solve complex problems and create innovative solutions using computer systems. Researchers in AI Ph.D. programs investigate diverse fields such as healthcare, finance, robotics, and more, seeking to improve how machines learn, reason, and make decisions.
These topics serve as pathways for scholars to conduct in-depth studies, discover new AI techniques, and apply them to real-world challenges. In essence, Ph.D. research topics in Artificial Intelligence represent the quests scientists undertake to expand AI capabilities, making machines smarter and more proficient in mimicking human intelligence to benefit society in diverse ways.
How Can I Choose Good PhD Research Topics In Artificial Intelligence?
Choosing a good PhD research topic in Artificial Intelligence (AI) involves careful consideration and planning. Here are five steps to help you navigate this process effectively:
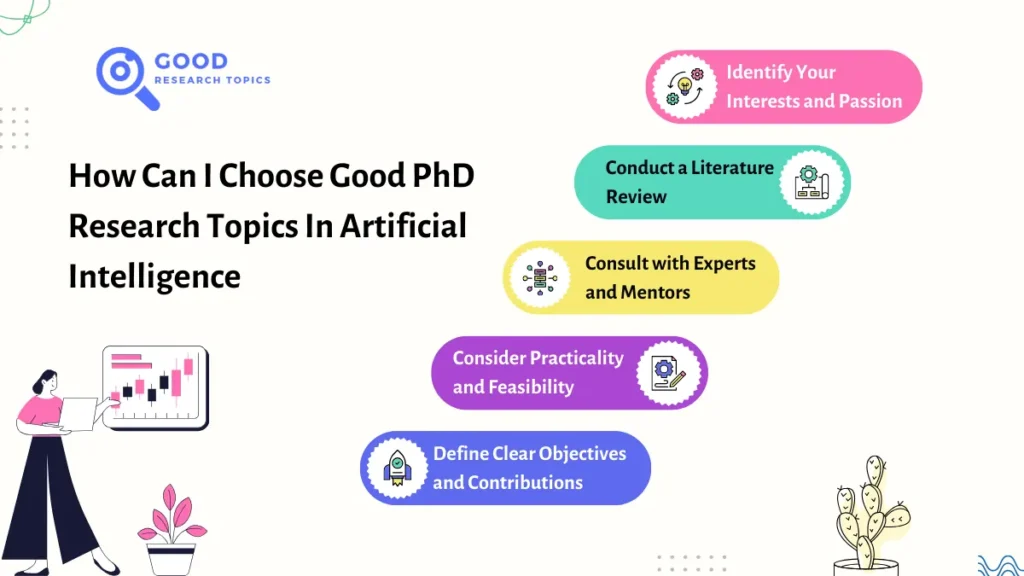
1. Identify Your Interests and Passion
Start by exploring your own interests within the broad field of AI. Reflect on the areas of AI that fascinate you the most—whether it’s machine learning, natural language processing, robotics, healthcare applications, ethics in AI, or any other niche. Choose a topic that aligns with your passion and strengths, as you’ll be dedicating several years to this research.
2. Conduct a Literature Review
Familiarize yourself with the existing research landscape in AI. Look into recent publications, conferences, and journals in the field. This step will help you understand the current trends, gaps, and potential research areas where you can make a meaningful contribution. Consider areas with emerging technologies or unresolved challenges that pique your interest.
3. Consult with Experts and Mentors
Engage with professors, AI professionals, or mentors in the field. Discuss your research interests and seek their guidance. They can provide valuable insights, suggest potential research directions, and help you refine your ideas. Their expertise can assist you in identifying relevant and impactful research topics.
4. Consider Practicality and Feasibility
Evaluate the feasibility of your research topics. Consider the availability of resources, data, and tools required for your proposed research. Ensure that your chosen topic is realistic within the timeframe and constraints of a PhD program. Assess whether you have access to necessary datasets, computing resources, and mentorship.
5. Define Clear Objectives and Contributions
Narrow down your topic and define clear research objectives. Your research should aim to contribute something novel to the field. Consider how your work could fill a gap in current knowledge, propose a solution to an existing problem, or introduce a new perspective. Ensure that your research questions are well-defined and achievable within the scope of a Ph.D.
List of 181+ Great PhD Research Topics In Artificial Intelligence
Here are the most interesting and great PhD Research Topics In Artificial Intelligenc.
Healthcare AI Research Topics
- Personalized Healthcare Plans Using AI-Based Predictive Models
- Ethical Considerations in AI-Based Medical Diagnosis and Treatment
- Robust and Interpretable AI Models for Medical Image Analysis
- Drug Repurposing and Discovery through AI-Driven Approaches
- AI-Powered Remote Patient Monitoring Systems
- Explainable AI for Clinical Decision Support Systems
- AI for Mental Health Diagnosis and Monitoring
- AI-Enhanced Prosthetics and Rehabilitation Systems
- Predictive Models for Epidemic Outbreaks using AI and Machine Learning
- AI in Genomic Medicine: Enhancing Precision Medicine Approaches
Finance Related PhD Research Topics In Artificial Intelligence
- Time Series Forecasting in Financial Markets using AI
- AI-Driven Algorithmic Trading Strategies
- Fraud Detection and Prevention using Machine Learning
- Explainable AI Models for Credit Scoring and Risk Assessment
- AI-Powered Regulatory Compliance in Financial Institutions
- Predictive Analytics for Asset Management and Portfolio Optimization
- AI-Based Robo-Advisors for Personal Finance Management
- Cryptocurrency Price Prediction using Machine Learning
- Reinforcement Learning Models for Financial Decision-Making
- Ethical Implications of AI in Finance: Bias and Fairness Issues
Education AI Research Topics
- Personalized Learning Paths through AI-Based Adaptive Educational Systems
- Automated Essay Scoring using Machine Learning Techniques
- Intelligent Tutoring Systems: AI-Driven Educational Assistance
- AI-Powered Content Creation for Educational Purposes
- AI-Enhanced Tools for Teachers to Improve Classroom Engagement
- Evaluating AI’s Impact on Learning Outcomes and Student Performance
- Gamification in Education: AI Techniques for Enhanced Learning
- Automated Plagiarism Detection and Prevention using AI
- AI-Enabled Accessibility Tools for Inclusive Education
- Ethical Considerations in AI-Driven Education: Data Privacy and Security
Environment and Sustainability PhD Research Topics In Artificial Intelligence
- Climate Change Prediction Models using AI and Big Data Analytics
- AI-Optimized Renewable Energy Systems
- AI-Driven Solutions for Wildlife Conservation and Monitoring
- Smart Grids and Energy Distribution Management using AI
- Environmental Impact Assessment with AI-Based Tools
- AI Applications for Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security
- AI-Based Natural Disaster Prediction and Response Systems
- Green Computing: AI for Energy-Efficient Systems
- Urban Planning and Management through AI and IoT Integration
- Ethical Use of AI in Environmental Conservation and Sustainability
Transportation PhD Research Topics In Artificial Intelligence
- Autonomous Vehicle Navigation and Decision-Making using AI
- Traffic Congestion Management through AI-Optimized Routing Systems
- AI-Based Predictive Maintenance for Transportation Infrastructure
- AI Solutions for Public Transportation Efficiency and Optimization
- Ethics of AI in Transportation: Safety and Liability Concerns
- Smart Traffic Lights and Intersection Management using AI
- Drone Technology and AI for Last-Mile Delivery Systems
- Human-Centric AI Systems for Transportation Accessibility
- AI in Aviation: Optimizing Air Traffic Control and Safety
- AI-Driven Solutions for Sustainable Transportation Planning
Robotics AI Research Topics
- Human-Robot Interaction: Developing Socially Intelligent Robots
- Autonomous Robot Swarms for Collaborative Tasks using AI
- AI-Powered Surgical Robotics: Precision and Safety in Operations
- AI-Enabled Industrial Robotics for Automation and Efficiency
- Explainable AI for Robotics: Transparency in Decision-Making
- Ethical Considerations in Autonomous Robotics: Morality and Responsibility
- AI-Driven Rehabilitation Robotics for Physical Therapy
- AI Applications in Soft Robotics and Biomechanics
- AI and Wearable Robotics: Enhancing Human Capabilities
- AI in Space Exploration: Robotics for Extraterrestrial Missions
Social Sciences PhD Research Topics In Artificial Intelligence
- Sentiment Analysis and Opinion Mining in Social Media using AI
- Predictive Models for Crime Prevention and Law Enforcement
- AI-Based Solutions for Mental Health Support and Counseling
- Cultural Heritage Preservation through AI and Digital Archives
- Ethical Implications of AI in Social Sciences: Bias and Discrimination
- AI-Powered Solutions for Disaster Relief and Humanitarian Aid
- AI and Behavioral Economics: Understanding Human Decision-Making
- AI for Social Network Analysis and Community Detection
- Personalized Social Services using AI: Challenges and Opportunities
- AI-Driven Solutions for Societal Equity and Inclusivity
Manufacturing and Industry AI Research Topics
- Predictive Maintenance and Quality Control in Manufacturing using AI
- AI-Enhanced Supply Chain Optimization and Inventory Management
- Robotics and AI Integration in Smart Factories (Industry 4.0)
- AI for Predictive Analytics in Equipment Failure Prevention
- Ethical Use of AI in Industrial Settings: Worker Safety and Rights
- AI-Powered Optimization of Production Processes
- Cybersecurity in AI-Driven Manufacturing Systems
- Human-Machine Collaboration in Manufacturing: Challenges and Benefits
- AI Applications for Waste Reduction and Sustainable Production
- AI and Additive Manufacturing: Innovations in 3D Printing
Entertainment and Media PhD Research Topics In Artificial Intelligence
- AI-Generated Content Creation in Entertainment Industry
- Recommendation Systems and Personalization in Media Streaming Platforms
- AI-Based Music Composition and Generation
- AI-Powered Gaming: Enhancing User Experience and Realism
- Sentiment Analysis in Movie Reviews and Entertainment Industry
- Ethical Concerns in AI-Generated Media: Authenticity and Ownership
- AI-Driven Storytelling and Narrative Generation
- Virtual Reality and AI: Immersive Media Experiences
- AI in Journalism: Automated News Writing and Fact-Checking
- AI-Enabled Creativity Tools for Content Producers
Law and Governance AI Research Topics
- Legal Document Analysis and Case Law Prediction using AI
- AI-Driven Contract Analysis and Management
- Predictive Models for Legal Decision-Making and Case Outcomes
- Ethics and Bias in AI-Based Judicial Systems
- AI Applications in Legislative Drafting and Policy Formulation
- AI-Enhanced Regulatory Compliance and Governance
- AI for Public Administration and Service Delivery
- Privacy and Security Concerns in AI-Driven Legal Systems
- AI and Human Rights: Ensuring Fairness and Justice
- AI and Electoral Systems: Transparency and Accountability
Agriculture Related PhD Research Topics In Artificial Intelligence
- Precision Agriculture using AI for Crop Monitoring and Yield Prediction
- AI-Based Pest and Disease Detection in Agriculture
- Autonomous Farming: AI-Driven Farm Equipment and Robotics
- Soil Quality Assessment and Management with AI
- AI for Sustainable Water Management in Agriculture
- Ethical Considerations in AI Applications in Agriculture
- AI-Optimized Greenhouse Farming and Controlled Environment Agriculture
- Climate Change Adaptation in Agriculture using AI
- AI-Driven Livestock Monitoring and Health Management
- Smart Farming: IoT and AI Integration in Agricultural Systems
Space and Astronomy AI Research Topics
- AI Applications in Space Exploration and Satellite Systems
- Autonomous Space Probes and Rovers: AI-Driven Missions
- AI for Astronomical Data Analysis and Discovery
- Space Debris Monitoring and Management with AI
- Ethics in AI-Assisted Space Exploration: Environmental Impact
- AI-Enhanced Space Communication and Navigation
- Predictive Models for Space Weather using AI
- AI-Driven Exoplanet Discovery and Characterization
- Autonomous Space Traffic Management with AI
- Robotic Assembly and Maintenance in Space using AI
Psychology and Cognitive Sciences Related PhD Research Topics In Artificial Intelligence
- AI-Driven Cognitive Models and Mental Health Diagnostics
- Ethical Implications of AI in Psychological Studies
- AI-Powered Therapeutic Interventions and Virtual Counseling
- Computational Models of Human Decision-Making with AI
- AI-Based Assistive Technologies for Cognitive Disabilities
- Neuroinformatics and AI: Analyzing Brain Imaging Data
- AI in Behavioral Psychology: Simulating Human Behavior
- Ethical Considerations in AI-Driven Behavioral Studies
- AI and Emotional Intelligence: Developing Emotionally Intelligent Systems
- Personalized Mental Health Care using AI-Driven Approaches
Linguistics and Language AI Research Topics
- Natural Language Understanding and Generation with AI
- AI-Driven Machine Translation and Multilingual Communication
- Sentiment Analysis in Multilingual Texts using AI
- Ethics of AI-Powered Language Models: Bias and Misinformation
- AI-Enhanced Language Learning and Teaching Systems
- AI-Based Phonetics and Speech Recognition Systems
- Cross-Linguistic Analysis and Typology with AI
- Language Evolution Simulation using AI Models
- AI-Enabled Computational Linguistics: Syntax and Semantics
- Multimodal Communication with AI: Text, Speech, and Images
Good PhD Research Topics In Artificial Intelligence In Quantum Computing
- Quantum Machine Learning Algorithms and Applications
- Hybrid Quantum-Classical Models in AI
- Quantum Computing for Optimization Problems in AI
- Quantum Neural Networks and Quantum Data Encoding
- Ethical Considerations in Quantum AI: Privacy and Security
- AI-Driven Quantum Error Correction and Noise Mitigation
- Quantum AI in Cryptography and Secure Communication
- Quantum Computing Simulations for AI Model Training
- Quantum-Inspired Algorithms for AI Applications
- Quantum-Safe AI Systems: Resistant to Future Attacks
Ethics and Philosophy AI Research Topics
- Ethical Frameworks and Guidelines for AI Development
- Explainable AI for Transparent and Interpretable Decision-Making
- Bias and Fairness in AI Algorithms and Decision Systems
- AI and Moral Reasoning: Developing Ethical Machines
- Accountability and Responsibility in AI: Legal and Ethical Perspectives
- AI and Human Rights: Ensuring Dignity and Equality
- Ethical Considerations in AI Research and Experimentation
- AI and Consciousness: Ethical Implications of Sentience
- Trustworthiness and Reliability of AI Systems
- Robustness and Safety in AI: Minimizing Risks and Harm
Cool Cybersecurity PhD Research Topics In Artificial Intelligence
- AI-Enhanced Threat Detection and Intrusion Prevention
- Ethical Hacking and Vulnerability Assessment using AI
- AI-Driven Cyberattack Prediction and Prevention
- Explainable AI for Security Analytics and Incident Response
- AI for Anomaly Detection in Network Traffic
- Secure AI Model Training and Data Privacy Preservation
- AI-Powered Authentication and Access Control Systems
- Adversarial Attacks and Defenses in AI Systems
- AI-Based Security Operations Center (SOC) Automation
- Quantum Computing Threats to AI Security: Mitigation Strategies
Human-Computer Interaction AI Research Topics
- AI-Enabled Personalization and User Modeling
- AI-Based Adaptive User Interfaces and Experiences
- Ethical Design of AI-Driven Human-Computer Interfaces
- AI in Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
- Natural Language Interaction with AI Systems
- AI-Driven Emotion Recognition for User Engagement
- Accessibility and Inclusivity in AI-Enhanced Interfaces
- AI-Powered Recommender Systems for User Preferences
- Ethical Considerations in Persuasive AI Design
- Multimodal Interfaces: Integrating Speech, Vision, and Gesture with AI
General PhD Research Topics In Artificial Intelligence
- Continual Learning and Lifelong Adaptation in AI Systems
- Cognitive Architectures and Human-Like AI Models
- Multi-Agent Systems: Collaboration and Coordination among Intelligent Agents
- Federated Learning: Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning
- AI in Decision Support Systems and Autonomous Agents
- AI for Social Good: Addressing Societal Challenges
- AI-Driven Innovation and Creativity: Art, Music, and Literature Generation
- Quantum Machine Learning: AI Algorithms for Quantum Computing
- AI Governance and Regulation: Policy Frameworks and Standards
- Ethical AI Leadership and Responsible Innovation
Consequently, the world of Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers a vast array of exciting opportunities for PhD research. These PhD Research Topics In Artificial Intelligence serve as gateways to unlocking the potential of intelligent machines, spanning fields such as healthcare, finance, robotics, education, and more. As aspiring researchers delve into these areas, they embark on a journey to expand the boundaries of AI, seeking solutions to complex problems and envisioning innovative applications that can transform our lives.
Choosing a PhD research topic in AI involves a thoughtful process of discovery, where interests, expertise, feasibility, and impact converge. Researchers must strive to select topics that resonate with their passions, align with current trends and challenges, and have the potential to make meaningful contributions to the field.
By immersing themselves in the rich tapestry of AI research, scholars pave the way for advancements that can revolutionize industries, drive societal progress, and shape the future of technology. As they embark on this academic voyage, researchers in AI PhD programs become pioneers, pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation to create a world where intelligent machines work hand in hand with humanity, making remarkable strides toward a brighter, smarter, and more inclusive future.
Which Topic Is Best For Artificial Intelligence?
The best topic for Artificial Intelligence depends on your specific interests, expertise, and the potential for meaningful contributions in that particular area.
How Is AI Used In PhD Research?
AI is utilized in PhD research to enhance data analysis, model complex systems, automate tasks, and develop innovative solutions across various fields.
What Can You Do With A PhD In Artificial Intelligence?
With a PhD in artificial intelligence, you can lead groundbreaking AI research, develop innovative technologies, teach at universities, lead AI teams in industry, or contribute to policy-making and ethical guidelines in AI.
Related Posts

Top 300+ Qualitative Research Topics For High School Students

100+ Most Interesting Google Scholar Research Topics For Students [Updated 2024]
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Research Topics & Ideas
Artifical Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)

If you’re just starting out exploring AI-related research topics for your dissertation, thesis or research project, you’ve come to the right place. In this post, we’ll help kickstart your research topic ideation process by providing a hearty list of research topics and ideas , including examples from past studies.
PS – This is just the start…
We know it’s exciting to run through a list of research topics, but please keep in mind that this list is just a starting point . To develop a suitable research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , and a viable plan to fill that gap.
If this sounds foreign to you, check out our free research topic webinar that explores how to find and refine a high-quality research topic, from scratch. Alternatively, if you’d like hands-on help, consider our 1-on-1 coaching service .

AI-Related Research Topics & Ideas
Below you’ll find a list of AI and machine learning-related research topics ideas. These are intentionally broad and generic , so keep in mind that you will need to refine them a little. Nevertheless, they should inspire some ideas for your project.
- Developing AI algorithms for early detection of chronic diseases using patient data.
- The use of deep learning in enhancing the accuracy of weather prediction models.
- Machine learning techniques for real-time language translation in social media platforms.
- AI-driven approaches to improve cybersecurity in financial transactions.
- The role of AI in optimizing supply chain logistics for e-commerce.
- Investigating the impact of machine learning in personalized education systems.
- The use of AI in predictive maintenance for industrial machinery.
- Developing ethical frameworks for AI decision-making in healthcare.
- The application of ML algorithms in autonomous vehicle navigation systems.
- AI in agricultural technology: Optimizing crop yield predictions.
- Machine learning techniques for enhancing image recognition in security systems.
- AI-powered chatbots: Improving customer service efficiency in retail.
- The impact of AI on enhancing energy efficiency in smart buildings.
- Deep learning in drug discovery and pharmaceutical research.
- The use of AI in detecting and combating online misinformation.
- Machine learning models for real-time traffic prediction and management.
- AI applications in facial recognition: Privacy and ethical considerations.
- The effectiveness of ML in financial market prediction and analysis.
- Developing AI tools for real-time monitoring of environmental pollution.
- Machine learning for automated content moderation on social platforms.
- The role of AI in enhancing the accuracy of medical diagnostics.
- AI in space exploration: Automated data analysis and interpretation.
- Machine learning techniques in identifying genetic markers for diseases.
- AI-driven personal finance management tools.
- The use of AI in developing adaptive learning technologies for disabled students.

AI & ML Research Topic Ideas (Continued)
- Machine learning in cybersecurity threat detection and response.
- AI applications in virtual reality and augmented reality experiences.
- Developing ethical AI systems for recruitment and hiring processes.
- Machine learning for sentiment analysis in customer feedback.
- AI in sports analytics for performance enhancement and injury prevention.
- The role of AI in improving urban planning and smart city initiatives.
- Machine learning models for predicting consumer behaviour trends.
- AI and ML in artistic creation: Music, visual arts, and literature.
- The use of AI in automated drone navigation for delivery services.
- Developing AI algorithms for effective waste management and recycling.
- Machine learning in seismology for earthquake prediction.
- AI-powered tools for enhancing online privacy and data protection.
- The application of ML in enhancing speech recognition technologies.
- Investigating the role of AI in mental health assessment and therapy.
- Machine learning for optimization of renewable energy systems.
- AI in fashion: Predicting trends and personalizing customer experiences.
- The impact of AI on legal research and case analysis.
- Developing AI systems for real-time language interpretation for the deaf and hard of hearing.
- Machine learning in genomic data analysis for personalized medicine.
- AI-driven algorithms for credit scoring in microfinance.
- The use of AI in enhancing public safety and emergency response systems.
- Machine learning for improving water quality monitoring and management.
- AI applications in wildlife conservation and habitat monitoring.
- The role of AI in streamlining manufacturing processes.
- Investigating the use of AI in enhancing the accessibility of digital content for visually impaired users.
Recent AI & ML-Related Studies
While the ideas we’ve presented above are a decent starting point for finding a research topic in AI, they are fairly generic and non-specific. So, it helps to look at actual studies in the AI and machine learning space to see how this all comes together in practice.
Below, we’ve included a selection of AI-related studies to help refine your thinking. These are actual studies, so they can provide some useful insight as to what a research topic looks like in practice.
- An overview of artificial intelligence in diabetic retinopathy and other ocular diseases (Sheng et al., 2022)
- HOW DOES ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE HELP ASTRONOMY? A REVIEW (Patel, 2022)
- Editorial: Artificial Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Drug Repurposing: Methods and Applications (Zheng et al., 2022)
- Review of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Technologies: Classification, Restrictions, Opportunities, and Challenges (Mukhamediev et al., 2022)
- Will digitization, big data, and artificial intelligence – and deep learning–based algorithm govern the practice of medicine? (Goh, 2022)
- Flower Classifier Web App Using Ml & Flask Web Framework (Singh et al., 2022)
- Object-based Classification of Natural Scenes Using Machine Learning Methods (Jasim & Younis, 2023)
- Automated Training Data Construction using Measurements for High-Level Learning-Based FPGA Power Modeling (Richa et al., 2022)
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Assisted Biomedical Systems for Intelligent Healthcare (Manickam et al., 2022)
- Critical Review of Air Quality Prediction using Machine Learning Techniques (Sharma et al., 2022)
- Artificial Intelligence: New Frontiers in Real–Time Inverse Scattering and Electromagnetic Imaging (Salucci et al., 2022)
- Machine learning alternative to systems biology should not solely depend on data (Yeo & Selvarajoo, 2022)
- Measurement-While-Drilling Based Estimation of Dynamic Penetrometer Values Using Decision Trees and Random Forests (García et al., 2022).
- Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis of Oral Diseases: Applications and Pitfalls (Patil et al., 2022).
- Automated Machine Learning on High Dimensional Big Data for Prediction Tasks (Jayanthi & Devi, 2022)
- Breakdown of Machine Learning Algorithms (Meena & Sehrawat, 2022)
- Technology-Enabled, Evidence-Driven, and Patient-Centered: The Way Forward for Regulating Software as a Medical Device (Carolan et al., 2021)
- Machine Learning in Tourism (Rugge, 2022)
- Towards a training data model for artificial intelligence in earth observation (Yue et al., 2022)
- Classification of Music Generality using ANN, CNN and RNN-LSTM (Tripathy & Patel, 2022)
As you can see, these research topics are a lot more focused than the generic topic ideas we presented earlier. So, in order for you to develop a high-quality research topic, you’ll need to get specific and laser-focused on a specific context with specific variables of interest. In the video below, we explore some other important things you’ll need to consider when crafting your research topic.
Get 1-On-1 Help
If you’re still unsure about how to find a quality research topic, check out our Research Topic Kickstarter service, which is the perfect starting point for developing a unique, well-justified research topic.

You Might Also Like:

can one come up with their own tppic and get a search
can one come up with their own title and get a search
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Machine Learning - CMU
Phd program in machine learning.
Carnegie Mellon University's doctoral program in Machine Learning is designed to train students to become tomorrow's leaders through a combination of interdisciplinary coursework, hands-on applications, and cutting-edge research. Graduates of the Ph.D. program in Machine Learning will be uniquely positioned to pioneer new developments in the field, and to be leaders in both industry and academia.
Understanding the most effective ways of using the vast amounts of data that are now being stored is a significant challenge to society, and therefore to science and technology, as it seeks to obtain a return on the huge investment that is being made in computerization and data collection. Advances in the development of automated techniques for data analysis and decision making requires interdisciplinary work in areas such as machine learning algorithms and foundations, statistics, complexity theory, optimization, data mining, etc.
The Ph.D. Program in Machine Learning is for students who are interested in research in Machine Learning. For questions and concerns, please contact us .
The PhD program is a full-time in-person committment and is not offered on-line or part-time.
PhD Requirements
Requirements for the phd in machine learning.
- Completion of required courses , (6 Core Courses + 1 Elective)
- Mastery of proficiencies in Teaching and Presentation skills.
- Successful defense of a Ph.D. thesis.
Teaching Ph.D. students are required to serve as Teaching Assistants for two semesters in Machine Learning courses (10-xxx), beginning in their second year. This fulfills their Teaching Skills requirement.
Conference Presentation Skills During their second or third year, Ph.D. students must give a talk at least 30 minutes long, and invite members of the Speaking Skills committee to attend and evaluate it.
Research It is expected that all Ph.D. students engage in active research from their first semester. Moreover, advisor selection occurs in the first month of entering the Ph.D. program, with the option to change at a later time. Roughly half of a student's time should be allocated to research and lab work, and half to courses until these are completed.
Master of Science in Machine Learning Research - along the way to your PhD Degree.
Other Requirements In addition, students must follow all university policies and procedures .
Rules for the MLD PhD Thesis Committee (applicable to all ML PhDs): The committee should be assembled by the student and their advisor, and approved by the PhD Program Director(s). It must include:
- At least one MLD Core Faculty member
- At least one additional MLD Core or Affiliated Faculty member
- At least one External Member, usually meaning external to CMU
- A total of at least four members, including the advisor who is the committee chair
Financial Support
Application Information
For applicants applying in Fall 2023 for a start date of August 2024 in the Machine Learning PhD program, GRE Scores are REQUIRED. The committee uses GRE scores to gauge quantitative skills, and to a lesser extent, also verbal skills.
Proof of English Language Proficiency If you will be studying on an F-1 or J-1 visa, and English is not a native language for you (native language…meaning spoken at home and from birth), we are required to formally evaluate your English proficiency. We require applicants who will be studying on an F-1 or J-1 visa, and for whom English is not a native language, to demonstrate English proficiency via one of these standardized tests: TOEFL (preferred), IELTS, or Duolingo. We discourage the use of the "TOEFL ITP Plus for China," since speaking is not scored. We do not issue waivers for non-native speakers of English. In particular, we do not issue waivers based on previous study at a U.S. high school, college, or university. We also do not issue waivers based on previous study at an English-language high school, college, or university outside of the United States. No amount of educational experience in English, regardless of which country it occurred in, will result in a test waiver.
Submit valid, recent scores: If as described above you are required to submit proof of English proficiency, your TOEFL, IELTS or Duolingo test scores will be considered valid as follows: If you have not received a bachelor’s degree in the U.S., you will need to submit an English proficiency score no older than two years. (scores from exams taken before Sept. 1, 2021, will not be accepted.) If you are currently working on or have received a bachelor's and/or a master's degree in the U.S., you may submit an expired test score up to five years old. (scores from exams taken before Sept. 1, 2018, will not be accepted.)
Graduate Online Application
- Early Application Deadline – November 29, 2023 (3:00 p.m. EST)
- Final Application Deadline - December 13, 2023 (3:00 p.m. EST)

PhD Assistance
Artificial intelligence research topics for phd manuscripts 2021, introduction.
Imagine a world where knowledge isn’t limited to humans!!! A world in which computers will think and collaborate with humans to create a more exciting universe. Although this future is still a long way off, Artificial Intelligence has made significant progress in recent years. In almost every area of AI, such as quantum computing, healthcare, autonomous vehicles, the internet of things, robotics, and so on, there is a lot of research going on. So much so that the number of annual Published Research Papers on Artificial Intelligence has increased by 90% since 1996.

Keeping this in mind, there are several sub-topics on which you can concentrate if you want to study and write a thesis on Artificial Intelligence. This article covers a few of these subjects and provides a short overview. Here some of the recent Research Topics ,
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine learning – Recent Trands
- How AI and ML can aid healthcare systems in their response to COVID-19
- Machine learning and artificial intelligence in haematology
- Tackling the risk of stranded electricity assets with machine learning and artificial intelligence
Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a type of machine learning that learns by simulating the internal workings of the human brain in order to process data and make decisions.Deep Learning is a form of machine learning that employs artificial neural networks. These neural networks are linked in a web-like structure, similar to the human brain’s networks (basically a condensed version of our brain!).
Artificial neural networks have a web-like structure that allows them to process data in a nonlinear manner, which is a major advantage over conventional algorithms that can only process data in a linear manner. Rank Brain, one of the variables in the Google Search algorithm, is an example of a deep neural network.
Recent research topics
- Artificial intelligence & deep learning : PET and SPECT imaging
- Hierarchical Deep Learning Neural Network (HiDeNN): A computational science and engineering in AI architecture.
- AI for surgical safety: automatic assessment of the critical view of safety in laparoscopic cholecystectomy using Deep Learning
- Deep learning-enabled medical computer vision

Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcing Learning is an aspect of Artificial Intelligence in which a computer learns something in the same way as humans do. Assume the computer is a student, for example. Over time, the hypothetical student learns from its errors. As a outcome of trial and error, Reinforcement Machine Learning Algorithms learn optimal behaviour.
This means that the algorithm determines the next way to proceed by learning behaviours based on its current state that will increase the reward in the future. This also works for robots, just as it does for humans!
Google’s AlphaGo Computer Programme , for example, used Reinforcement Learning to defeat the world champion in the game of Go (a human!) in 2017.
- Experimental quantum speed-up in reinforcement learning agents
- Potential-based multiobjective reinforcement learning approaches to low-impact agents for AI safety
Robotics is an area concerned with the creation of humanoid robots that can assist humans and perform several acts. In certain cases, robots can behave like humans, but can they think like humans as well?
Kismet, a social interaction robot developed at M.I.T.’s Artificial Intelligence Lab, is an example of this. It understands human body language as well as our voice and responds to them appropriately. Another example is NASA’s Robonaut, which was designed to assist astronauts in space.
- Regulating artificial intelligence and robotics: ethics by design in a digital society
- Regional anaesthesia :usages of artificial intelligence and robotics in
- Third Millennium Life Saving Smart Cyberspace Driven by AI and Robotics
Natural Language Processing
Humans can obviously communicate with each other by speech, but now machines can as well! This is known as Natural Language Processing, and it involves machines analysing and understanding language and expression as it is spoken (which means that if you speak to a computer, it might only respond!). Speech recognition, natural language production, natural language translation, and other aspects of NLP are all concerned with language. NLP is recently very important in customer service applications, particularly chatbots. These chatbots use machine learning and natural language processing to communicate with users in textual form and respond to their questions. As a result, you get a personal touch in your customer service experiences without actually speaking with a human.
Here are several research papers in the field of Natural Language Processing that have been published. You can look at them to get more ideas for research and thesis topics on this subject.
- Natural Language Processing–Based Virtual Cofacilitator for Online Cancer Support Groups: Protocol for an Algorithm Development and Validation Study
- Sympathetic the temporal evolution of COVID-19 Research Through machine learning and natural language processing
Computer Vision
The internet is full of images! This is the selfie age, and taking and posting a photo has never been easier. Each day, millions of images are uploaded to the internet and viewed. It’s important for computers to be able to see and understand images in order to make the most of the vast amount of images available online. And, while humans can do this without thinking about it, computers find it more difficult! This is where Computer Vision enters the image.
To extract information from images, Computer Vision utilizes Artificial Intelligence. This knowledge may include object detection in the image, image content recognition to group images together, and so on. Navigation for autonomous vehicles using images of the surroundings is one use of computer vision, such as AutoNav, which was used in the Spirit and Opportunity rovers that landed on Mars.
- Artificial intelligence for surgical safety: automatic assessment of the critical view of safety in laparoscopic cholecystectomy using deep learning
- An Open‐Source Computer Vision Tool for Automated Vocal Fold Tracking From Video endoscopy
Recommender Systems
Do you get movie and series recommendations from Netflix based on your previous choices or favourite genres? This is achieved by Recommender Systems, which offer you advice about what to do next from the vast array of options available online. Content-based Recommendation or even Collaborative Filtering may be used in a Recommender System.
The content of all the products is analysed in Content-Based Recommendation. For example, based on Natural Language Processing performed on the books, you might be recommended books that you may enjoy. Collaborative Filtering, on the other hand, analyses your past reading behaviour and then recommends books based on it.
- Artificial intelligence in recommender systems
- Deep Transfer Tensor Decomposition with Orthogonal Constraint for Recommender Systems.
- Recommender systems for configuration knowledge engineering
Internet Of Things
Artificial intelligence is concerned with the creation of systems that can learn to perform human-like tasks based on prior experience and without the need for human interaction. The Internet of Things, on the other hand, is a network of different devices linked to the internet and capable of collecting and exchanging data.
All of these IoT devices now generate a large amount of data, which must be collected and mined in order to produce actionable results. Artificial Intelligence enters the picture at this stage. The Internet of Things is used to collect and manage the massive amounts of data that Artificial Intelligence algorithms need. As a consequence, these algorithms transform the data into useful actionable results that IoT devices can use.
- Enhanced Medical Systems by using Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things
- Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things in Instrumentation and Control in Waste Biodegradation Plants: Recent Developments
- AIoT-Artificial Intelligence of Things
In this blog discussed the recent enhancement for artificial intelligences and their sub field. This will help to the PhD scholar who are interested to research in artificial intelligences domain.
- Shouval, R., Fein, J. A., Savani, B., Mohty, M., & Nagler, A. (2021). Machine learning and artificial intelligence in haematology. British journal of haematology, 192(2), 239-250.
- van der Schaar, M., Alaa, A. M., Floto, A., Gimson, A., Scholtes, S., Wood, A., … & Ercole, A. (2021). How artificial intelligence and machine learning can help healthcare systems respond to COVID-19. Machine Learning, 110(1), 1-14.
- Nyangon, J. (2021). Tackling the risk of stranded electricity assets with machine learning and artificial intelligence. In Sustainable Energy Investment-Technical, Market and Policy Innovations to Address Risk. IntechOpen.
- Saha, S., Gan, Z., Cheng, L., Gao, J., Kafka, O. L., Xie, X., … & Liu, W. K. (2021). Hierarchical Deep Learning Neural Network (HiDeNN): An artificial intelligence (AI) framework for computational science and engineering. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 373, 113452.
- Mascagni, P., Vardazaryan, A., Alapatt, D., Urade, T., Emre, T., Fiorillo, C., … & Padoy, N. (2021). Artificial intelligence for surgical safety: automatic assessment of the critical view of safety in laparoscopic cholecystectomy using deep learning. Annals of Surgery.
- Esteva, A., Chou, K., Yeung, S., Naik, N., Madani, A., Mottaghi, A., … & Socher, R. (2021). Deep learning-enabled medical computer vision. npj Digital Medicine, 4(1), 1-9.
- artificial intelligence phd topics
- artificial intelligence topics for research paper
- computer science research topics for phd
- PhD research topics in artificial intelligence
- recent phd research topics in artificial intelligence
- research topic for artificial intelligence
- research topics in computer science for phd
- research topics in computer vision

Quick Contact

- Adversial Attacks
- Artificial Intelligence
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and ML ( Machine Learning )
- Big Data Analysis
- Business and Management
- Categories of Research methodology – PhDAssistance
- Category of Research Proposal Services
- coding & algorithm
- Computer Data Science
- Category of Machine Learning – PhDassistance
- Computer Science/Research writing/Manuscript
- Course Work Service
- Data Analytics
- Data Processing
- Deep Networks
- Dissertation Statistics
- economics dissertation
- Editing Services
- Electrical Engineering Category
- Engineering & Technology
- finance dissertation writing
- Gap Identification
- Healthcare Dissertation Writing
- Intrusion-detection-system
- journals publishing
- Life Science Dissertation writing services
- literature review service
- Machine Learning
- medical thesis writing
- Peer review
- PhD Computer Programming
- PhD Dissertation
- Phd Journal Manuscript
- Annotated Bibliography
- PhD Publication Support
- Phd thesis writing services
- Phd Topic Selection
- Categories of PhdAssistance Dissertation
- Power Safety
- problem identification
- Quantitative Analysis
- quantitative research
- Recent Trends
- Referencing and Formatting
- Research Gap
- research journals
- Research Methodology
- research paper
- Research Proposal Service
- secondary Data collection
- Statistical Consulting Services
- Uncategorized
- Data Science
- Data Analysis
- Data Visualization
- Machine Learning
- Deep Learning
- Computer Vision
- Artificial Intelligence
- AI ML DS Interview Series
- AI ML DS Projects series
- Data Engineering
- Web Scrapping
8 Best Topics for Research and Thesis in Artificial Intelligence
- Top 5 Artificial Intelligence(AI) Predictions in 2020
- Top 7 Artificial Intelligence Frameworks to Learn in 2022
- What Are The Ethical Problems in Artificial Intelligence?
- Top 7 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Trends For 2022
- The State of Artificial Intelligence in India and How Far is Too Far?
- 5 Dangers of Artificial Intelligence in the Future
- Top Challenges for Artificial Intelligence in 2020
- Difference Between Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
- What is Artificial Intelligence as a Service (AIaaS) in the Tech Industry?
- 10 Best Artificial Intelligence Project Ideas To Kick-Start Your Career
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Researcher Jobs in China
- Applied Artificial Intelligence in Estonia : A global springboard for startups
- Types of Reasoning in Artificial Intelligence
- Mapping Techniques in Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
- Top 15 Artificial Intelligence(AI) Tools List
- Artificial Intelligence in Robotics
- Top Data Science with Artificial Intelligence Colleges in India
- Difference Between Data Science and Artificial Intelligence
- Difference Between Artificial Intelligence and Human Intelligence
Imagine a future in which intelligence is not restricted to humans!!! A future where machines can think as well as humans and work with them to create an even more exciting universe. While this future is still far away, Artificial Intelligence has still made a lot of advancement in these times. There is a lot of research being conducted in almost all fields of AI like Quantum Computing, Healthcare, Autonomous Vehicles, Internet of Things , Robotics , etc. So much so that there is an increase of 90% in the number of annually published research papers on Artificial Intelligence since 1996. Keeping this in mind, if you want to research and write a thesis based on Artificial Intelligence, there are many sub-topics that you can focus on. Some of these topics along with a brief introduction are provided in this article. We have also mentioned some published research papers related to each of these topics so that you can better understand the research process.

So without further ado, let’s see the different Topics for Research and Thesis in Artificial Intelligence!
1. Machine Learning
Machine Learning involves the use of Artificial Intelligence to enable machines to learn a task from experience without programming them specifically about that task. (In short, Machines learn automatically without human hand holding!!!) This process starts with feeding them good quality data and then training the machines by building various machine learning models using the data and different algorithms. The choice of algorithms depends on what type of data do we have and what kind of task we are trying to automate. However, generally speaking, Machine Learning Algorithms are divided into 3 types i.e. Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms, Unsupervised Machine Learning Algorithms , and Reinforcement Machine Learning Algorithms.
2. Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning that learns by imitating the inner working of the human brain in order to process data and implement decisions based on that data. Basically, Deep Learning uses artificial neural networks to implement machine learning. These neural networks are connected in a web-like structure like the networks in the human brain (Basically a simplified version of our brain!). This web-like structure of artificial neural networks means that they are able to process data in a nonlinear approach which is a significant advantage over traditional algorithms that can only process data in a linear approach. An example of a deep neural network is RankBrain which is one of the factors in the Google Search algorithm.
3. Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement Learning is a part of Artificial Intelligence in which the machine learns something in a way that is similar to how humans learn. As an example, assume that the machine is a student. Here the hypothetical student learns from its own mistakes over time (like we had to!!). So the Reinforcement Machine Learning Algorithms learn optimal actions through trial and error. This means that the algorithm decides the next action by learning behaviors that are based on its current state and that will maximize the reward in the future. And like humans, this works for machines as well! For example, Google’s AlphaGo computer program was able to beat the world champion in the game of Go (that’s a human!) in 2017 using Reinforcement Learning.
4. Robotics
Robotics is a field that deals with creating humanoid machines that can behave like humans and perform some actions like human beings. Now, robots can act like humans in certain situations but can they think like humans as well? This is where artificial intelligence comes in! AI allows robots to act intelligently in certain situations. These robots may be able to solve problems in a limited sphere or even learn in controlled environments. An example of this is Kismet , which is a social interaction robot developed at M.I.T’s Artificial Intelligence Lab. It recognizes the human body language and also our voice and interacts with humans accordingly. Another example is Robonaut , which was developed by NASA to work alongside the astronauts in space.
5. Natural Language Processing
It’s obvious that humans can converse with each other using speech but now machines can too! This is known as Natural Language Processing where machines analyze and understand language and speech as it is spoken (Now if you talk to a machine it may just talk back!). There are many subparts of NLP that deal with language such as speech recognition, natural language generation, natural language translation , etc. NLP is currently extremely popular for customer support applications, particularly the chatbot . These chatbots use ML and NLP to interact with the users in textual form and solve their queries. So you get the human touch in your customer support interactions without ever directly interacting with a human.
Some Research Papers published in the field of Natural Language Processing are provided here. You can study them to get more ideas about research and thesis on this topic.
6. Computer Vision
The internet is full of images! This is the selfie age, where taking an image and sharing it has never been easier. In fact, millions of images are uploaded and viewed every day on the internet. To make the most use of this huge amount of images online, it’s important that computers can see and understand images. And while humans can do this easily without a thought, it’s not so easy for computers! This is where Computer Vision comes in. Computer Vision uses Artificial Intelligence to extract information from images. This information can be object detection in the image, identification of image content to group various images together, etc. An application of computer vision is navigation for autonomous vehicles by analyzing images of surroundings such as AutoNav used in the Spirit and Opportunity rovers which landed on Mars.
7. Recommender Systems
When you are using Netflix, do you get a recommendation of movies and series based on your past choices or genres you like? This is done by Recommender Systems that provide you some guidance on what to choose next among the vast choices available online. A Recommender System can be based on Content-based Recommendation or even Collaborative Filtering. Content-Based Recommendation is done by analyzing the content of all the items. For example, you can be recommended books you might like based on Natural Language Processing done on the books. On the other hand, Collaborative Filtering is done by analyzing your past reading behavior and then recommending books based on that.
8. Internet of Things
Artificial Intelligence deals with the creation of systems that can learn to emulate human tasks using their prior experience and without any manual intervention. Internet of Things , on the other hand, is a network of various devices that are connected over the internet and they can collect and exchange data with each other. Now, all these IoT devices generate a lot of data that needs to be collected and mined for actionable results. This is where Artificial Intelligence comes into the picture. Internet of Things is used to collect and handle the huge amount of data that is required by the Artificial Intelligence algorithms. In turn, these algorithms convert the data into useful actionable results that can be implemented by the IoT devices.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.

- AI-ML-DS Blogs
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
PLOS Computational Biology
PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
Artificial intelligence
Discover multidisciplinary research that explores the opportunities, applications, and risks of machine learning and artificial intelligence across a broad spectrum of disciplines.
Discover artificial intelligence research from PLOS
From exploring applications in healthcare and biomedicine to unraveling patterns and optimizing decision-making within complex systems, PLOS’ interdisciplinary artificial intelligence research aims to capture cutting-edge methodologies, advancements, and breakthroughs in machine learning, showcasing diverse perspectives, interdisciplinary approaches, and societal and ethical implications.
Given their increasing influence in our everyday lives, it is vital to ensure that artificial intelligence tools are both inclusive and reliable. Robust and trusted artificial intelligence research hinges on the foundation of Open Science practices and the meticulous curation of data which PLOS takes pride in highlighting and endorsing thanks to our rigorous standards and commitment to Openness.
Stay up-to-date on artificial intelligence research from PLOS
Research spotlights
As a leading publisher in the field, these articles showcase research that has influenced academia, industry and/or policy.

A performance comparison of supervised machine learning models for Covid-19 tweets sentiment analysis

CellProfiler 3.0: Next- generation image processing for biology

Predicting survival from colorectal cancer histology slides using deep learning: A retrospective multicenter study
Artificial intelligence research topics.
PLOS publishes research across a broad range of topics. Take a look at the latest work in your field.
AI and climate change
Deep learning
AI for healthcare
Artificial neural networks
Natural language processing (NLP)
Graph neural networks (GNNs)
AI ethics and fairness
Machine learning
AI and complex systems
Read the latest research developments in your field
Our commitment to Open Science means others can build on PLOS artificial intelligence research to advance the field. Discover selected popular artificial intelligence research below:
Artificial intelligence based writer identification generates new evidence for the unknown scribes of the Dead Sea Scrolls exemplified by the Great Isaiah Scroll (1QIsaa)
Artificial intelligence with temporal features outperforms machine learning in predicting diabetes
Bat detective—Deep learning tools for bat acoustic signal detection
Bias in artificial intelligence algorithms and recommendations for mitigation
Can machine-learning improve cardiovascular risk prediction using routine clinical data?
Convergence of mechanistic modeling and artificial intelligence in hydrologic science and engineering
Cyberbullying severity detection: A machine learning approach
Diverse patients’ attitudes towards Artificial Intelligence (AI) in diagnosis
Expansion of RiPP biosynthetic space through integration of pan-genomics and machine learning uncovers a novel class of lanthipeptides
Generalizable brain network markers of major depressive disorder across multiple imaging sites
Machine learning algorithm validation with a limited sample size
Neural spiking for causal inference and learning
Review of machine learning methods in soft robotics
Ten quick tips for harnessing the power of ChatGPT in computational biology
Ten simple rules for engaging with artificial intelligence in biomedicine
Browse the full PLOS portfolio of Open Access artificial intelligence articles
25,938 authors from 133 countries chose PLOS to publish their artificial intelligence research*
Reaching a global audience, this research has received over 5,502 news and blog mentions ^ , research in this field has been cited 117,554 times after authors published in a plos journal*, related plos research collections.
Covering a connected body of work and evaluated by leading experts in their respective fields, our Collections make it easier to delve deeper into specific research topics from across the breadth of the PLOS portfolio.
Check out our highlighted PLOS research Collections:

Machine Learning in Health and Biomedicine

Cities as Complex Systems

Open Quantum Computation and Simulation
Stay up-to-date on the latest artificial intelligence research from PLOS
Related journals in artificial intelligence
We provide a platform for artificial intelligence research across various PLOS journals, allowing interdisciplinary researchers to explore artificial intelligence research at all preclinical, translational and clinical research stages.
*Data source: Web of Science . © Copyright Clarivate 2024 | January 2004 – January 2024 ^Data source: Altmetric.com | January 2004 – January 2024
Breaking boundaries. Empowering researchers. Opening science.
PLOS is a nonprofit, Open Access publisher empowering researchers to accelerate progress in science and medicine by leading a transformation in research communication.
Open Access
All PLOS journals are fully Open Access, which means the latest published research is immediately available for all to learn from, share, and reuse with attribution. No subscription fees, no delays, no barriers.
Leading responsibly
PLOS is working to eliminate financial barriers to Open Access publishing, facilitate diversity and broad participation of voices in knowledge-sharing, and ensure inclusive policies shape our journals. We’re committed to openness and transparency, whether it’s peer review, our data policy, or sharing our annual financial statement with the community.
Breaking boundaries in Open Science
We push the boundaries of “Open” to create a more equitable system of scientific knowledge and understanding. All PLOS articles are backed by our Data Availability policy, and encourage the sharing of preprints, code, protocols, and peer review reports so that readers get more context.
Interdisciplinary
PLOS journals publish research from every discipline across science and medicine and related social sciences. Many of our journals are interdisciplinary in nature to facilitate an exchange of knowledge across disciplines, encourage global collaboration, and influence policy and decision-making at all levels
Community expertise
Our Editorial Boards represent the full diversity of the research and researchers in the field. They work in partnership with expert peer reviewers to evaluate each manuscript against the highest methodological and ethical standards in the field.
Rigorous peer review
Our rigorous editorial screening and assessment process is made up of several stages. All PLOS journals use anonymous peer review by default, but we also offer authors and reviewers options to make the peer review process more transparent.
- Who’s Teaching What
- Subject Updates
- MEng program
- Opportunities
- Minor in Computer Science
- Resources for Current Students
- Program objectives and accreditation
- Graduate program requirements
- Admission process
- Degree programs
- Graduate research
- EECS Graduate Funding
- Resources for current students
- Student profiles
- Instructors
- DEI data and documents
- Recruitment and outreach
- Community and resources
- Get involved / self-education
- Rising Stars in EECS
- Graduate Application Assistance Program (GAAP)
- MIT Summer Research Program (MSRP)
- Sloan-MIT University Center for Exemplary Mentoring (UCEM)
- Electrical Engineering
- Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence + Decision-making
- AI and Society
- AI for Healthcare and Life Sciences
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- Biological and Medical Devices and Systems
- Communications Systems
- Computational Biology
- Computational Fabrication and Manufacturing
- Computer Architecture
- Educational Technology
- Electronic, Magnetic, Optical and Quantum Materials and Devices
- Graphics and Vision
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Information Science and Systems
- Integrated Circuits and Systems
- Nanoscale Materials, Devices, and Systems
- Natural Language and Speech Processing
- Optics + Photonics
- Optimization and Game Theory
- Programming Languages and Software Engineering
- Quantum Computing, Communication, and Sensing
- Security and Cryptography
- Signal Processing
- Systems and Networking
- Systems Theory, Control, and Autonomy
- Theory of Computation
- Departmental History
- Departmental Organization
- Visiting Committee
- Explore all research areas
Our research covers a wide range of topics of this fast-evolving field, advancing how machines learn, predict, and control, while also making them secure, robust and trustworthy. Research covers both the theory and applications of ML. This broad area studies ML theory (algorithms, optimization, etc.); statistical learning (inference, graphical models, causal analysis, etc.); deep learning; reinforcement learning; symbolic reasoning ML systems; as well as diverse hardware implementations of ML.

Latest news in artificial intelligence and machine learning
Creating bespoke programming languages for efficient visual ai systems.
Associate Professor Jonathan Ragan-Kelley optimizes how computer graphics and images are processed for the hardware of today and tomorrow.
QS World University Rankings rates MIT No. 1 in 11 subjects for 2024
The Institute also ranks second in five subject areas.
Three from MIT awarded 2024 Guggenheim Fellowships
MIT professors Roger Levy, Tracy Slatyer, and Martin Wainwright appointed to the 2024 class of “trail-blazing fellows.”
To build a better AI helper, start by modeling the irrational behavior of humans
A new technique can be used to predict the actions of human or AI agents who behave suboptimally while working toward unknown goals.
Priya Donti named AI2050 Early Career Fellow
Assistant Professor Priya Donti has been named an AI2050 Early Career Fellow by Schmidt Sciences, a philanthropic initiative from Eric and Wendy Schmidt aimed at helping to solve hard problems in AI.
Upcoming events
Doctoral thesis: guiding deep probabilistic models.
You're viewing this site as a domestic an international student
You're a domestic student if you are:
- a citizen of Australia or New Zealand,
- an Australian permanent resident, or
- a holder of an Australian permanent humanitarian visa.
You're an international student if you are:
- intending to study on a student visa,
- not a citizen of Australia or New Zealand,
- not an Australian permanent resident, or
- a temporary resident (visa status) of Australia.

What's it like to do a PhD in artificial intelligence?
UQ people Published 5 Jan, 2023 · 4-minute read
Studying a PhD in artificial intelligence (AI) places you at the forefront of cutting-edge technology.
Artificial intelligence research continues to expand and evolve every day as we appreciate what our future could look like. This type of technology can help solve all kinds of problems, from small-scale, everyday complications to larger-than-life challenges.
An artificial intelligence PhD can kickstart your research career in this fascinating field and open many other doors as you explore new ways to problem-solve using technology.
We talked to UQ Postdoctoral Research Fellow Sam Hislop-Lynch about his experience studying a Doctor of Philosophy and what he hopes his research using artificial intelligence, and more specifically computer vision (CV), will achieve.
Learn more about studying a PhD at UQ .
PhD topics in artificial intelligence
PhD research topics in artificial intelligence can vary dramatically depending on your interests. Whether you choose your own PhD topic or join an existing PhD project , you could find yourself pursuing research in the areas of:
- data management and data science
- computer vision and multimedia computation
- machine learning and data mining
- optimisation and statistics
- human-centred AI.

Sam landed on a computer vision PhD topic after working with the technology during his undergrad and postgrad studies. His research focuses on optimising traffic flow.
“Motorways often suffer from flow breakdown around ramps and weaving segments, and with our current technology, it's difficult to investigate this and propose solutions,” he says.
“I developed a suite of algorithms and software to allow researchers and practitioners to fly many drones above a motorway, stitch the imagery together and then extract vehicle trajectories from the footage.”
There are just some things that machines can achieve more efficiently and reliably than humans, and Sam’s research is testament to that.
“Ultimately, the research will reveal strategies that can be used to alleviate or prevent traffic flow breakdowns,” he says.
“This might take the form of better road design guidelines or even real-time strategies for mitigating congestion.”
It’s all about being able to see what’s working and what’s not, and it’s computer vision that allows us to do this.
These findings have a knock-on effect on the environment too. Less traffic congestion and stalling means a reduction in vehicle emissions.
At the end of the day, AI is helping us to better understand how we can use machines efficiently and responsibly, and the research undertaken during a PhD can help us to makes strides in this area.
Is a PhD in artificial intelligence worth it?
So, what are the perks of completing a PhD in AI? According to Sam, it teaches you invaluable skills in problem-solving, which can help open many other doors down the line and expand your professional network.

I began working with AI/CV technology because it allowed me to investigate problems that would otherwise be impossible to solve with human pattern recognition alone.
“AI/CV technology allows me to process large amounts of video data with only very little human input.”
Sam recognised that this type of technology was very valuable to several industries outside of transport engineering. The skills he has developed in artificial intelligence and computer vision can be applied in a range of settings and projects, to great effect.
“I’ve leveraged the knowledge that I obtained during my PhD to begin developing software for the mining industry.”
“I intend to pursue this further and expand the scope and number of products I offer,” he says.
Since the completion of his PhD, Sam has branched out into consultancy work while continuing his research. His experience is living proof that a PhD in AI is worth it, if you make the most of the professional opportunities available and think big when it comes to using the skills you’ve learned.
So, what should you consider when deciding whether a PhD in artificial intelligence is the right path for you? Sam encourages you to ask yourself the following:
- Are you interested in the topic?
- Does it align with your long-term goals?
- Where else can this knowledge be applied?
- Can the skills you will learn be used to solve other problems and leverage a better job?

Why study a PhD in artificial intelligence at UQ?
It isn’t just because we have a beautiful campus, state-of-the-art facilities, strong connections with industry leaders and a focus on professional development opportunities. Though all those things certainly help.
Read more about the benefits of studying your PhD at UQ .
Sam explains the specific benefits of studying an artificial intelligence PhD at UQ.
“Apart from the high academic standards and many knowledgeable staff to draw upon, UQ hosts the Wiener supercomputer,” he says.
“This is a purpose-built, bare-metal cluster full of graphical processing units (GPUs) which is well suited to computer vision and AI based research.”
Furthermore, UQ researchers are making strides in several disciplines with the use of AI , including health and medicine, business, society and government, mining, agriculture, defence and energy. Our people are using AI research to protect children , detect cancer and mitigate cyber-attacks .
You too could study a PhD in artificial intelligence at UQ to create positive and lasting change with your research.
Ready to follow your passion for research with a PhD in AI?
Learn more about studying a PhD at UQ
Share this Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Email
Related stories

How to get a PhD
4-minute read

Why do a PhD at UQ?
7-minute read

What makes a good PhD supervisor?
9-minute read

A PhD in renewable energy engineering
3-minute read

- Doing a PhD in Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence and intelligent systems are thought to be the key to the next ‘industrial revolution’. In a data-rich world, developing an artificial intelligence which can learn from its experience and call on human behaviour to make decisions could change the way we live and offer endless economic, social and scientific applications. Nationwide, there is an increasing demand for AI workers, as the world is becoming more reliant on developing technology and automated systems. Consequently, more and more people are pursuing postgraduate research in AI.
What Does a PhD in Artificial Intelligence Focus On?
A PhD in artificial intelligence will give you a deep understanding of AI, allow you to contribute to the development of emerging technology, and equip you with highly applicable technical skills. For example, engineering applications of artificial intelligence include automation of tasks and parametric modelling. Medical applications include using data-science approaches to identify patterns of illness in clinical data. Financial applications include using machine learning platforms to crunch huge amounts of data and help credit lenders in analysing risk and assess potential borrowers.
Artificial Intelligence PhD programme can focus on:
- Machine learning
- Deep learning
- Natural language processing
- Deep neural network architecture
- Human-machine interaction
- Augmented reality
- And countless other areas
Browse PhDs in Artificial Intelligence
Application of artificial intelligence to multiphysics problems in materials design, from text to tech: shaping the future of physics-based simulations with ai-driven generative models, study of the human-vehicle interactions by a high-end dynamic driving simulator, coventry university postgraduate research studentships, discovery of solid state electrolytes using deep learning, entry requirements for a phd in artificial intelligence.
The entry requirements for a PhD in AI are typically an upper second-class honours degree (or international equivalent) in a relevant subject from an accredited university. Subjects considered relevant to artificial intelligence include computer science, engineering, mathematics, statistics, electronics/electrical engineering or science.
Some research courses also require applicants to possess experience in programming, the desired programming language will be specific to the research project. Academic or work experience in machine learning or data science are typically favourable for applications.
International students will also need to meet several minimum English language requirements set by the university, usually as part of a TOEFL or IELTS exam.
Duration and Programme Types
Like most PhDs, a doctoral programme in Artificial Intelligence typically takes 3-4 years full-time, or 6 years part-time .
Aside from the traditional PhD, there is also the CDT PhD. Many Universities have Centres for Doctoral Training (CDTs) which are often funded by the UKRI centre . These CDTs can offer the CDT PhD which is a specialised PhD programme in artificial intelligence. The main difference between a standard PhD in artificial intelligence and a CDT PhD in artificial intelligence is that the latter includes additional modules which give candidates training in neuroscience, entrepreneurship, high performance computing, AI ethics and science communication.
Due to the different research areas you can pursue within the artificial intelligence field, the nature of programmes can vary. Some PhD research programmes are computational based and heavily reliant on coding, mathematics and lab work. Other research programmes can be people facing, involving questionnaires, for example to determine public perception on proposed legislation.
Costs and Funding
Annual tuition fees for PhDs in Artificial Intelligence are typically around £4,000 to £5,000 for UK/EU students. Tuition fees for international students are usually much higher, typically around £25,000 per academic year.
A variety of scholarships and funding support options are available for postgraduate study. For Artificial Intelligence in particular, the UKRI and ESPRC offer a number of studentships and CDT opportunities across varies universities. Many universities have research centres which are partnered with UK research councils and offer fully funded programmes. Funding is generally available for UK/EU students. International students are also eligible for some funding opportunities, but these tend to be less widely available.
Available Career Paths in AI
One of the key advantages of Artificial Intelligence is that it has a wide range of applications, and hence there are many career paths available. As computer systems and data have become more integrated in everyday life, the demand for experts in AI has grown rapidly. This high demand has resulted in many high job security and lucrative salaries.
Examples destinations for an AI PhD student include:
Data Analyst – If you are very analytical research student, you may use your artificial intelligence PhD to pursue a career in data science or analysis. Data analysts can be found in engineering, finance, healthcare, and everywhere in between. They are responsible for data crunching and using their skills to present complex information in a clear manner – visually and orally. Typical duties include record management, maintaining automated processes, monitoring analytics and KPIs, improving algorithms, and creating dashboards for clients. The average salary for data analysts in the UK is around £30,000 – £45,000, though this number can increase drastically depending on the sector.

Cyber Security – As cyber-attacks are becoming more commonplace, industries are looking to develop their cyber security, and salaries are seeing a sharp increase accordingly. AI doctorates are well placed for a career in cyber security, and typical career destinations include security analysts, penetration testers, systems engineers, web developers and cybersecurity consultants. In these roles, you will be responsible for protecting IT infrastructure and help develop security systems.
Machine learning – Often those with a PhD in AI become machine learning engineers, responsible for the development of intelligent systems. Machine learning is a subset of AI which focuses on the idea that machines can be programmed to learn from data and experience to improve decision making without human input. Machine learning is perhaps at the forefront of AI research, and there are numerous programmes look to improve its capabilities. This is well suited for those who enjoy the mathematical and programming side of computer science. Typical duties include managing data pipelines, developing algorithms, liaising with stakeholders, analysing datasets, and leading software design. Entry level salaries are around £35,000 and can exceed £150,000 with experience. Deep learning is similar to machine learning, the main difference is that deep learning aims to create artificial ‘neural networks’.
Postgraduate research often leads to an academic career. As an academic you can propose your own research projects based on your interest and supervise students. As a professor you can shape the next generation of AI experts and as a researcher you can make use of a university’s department resources, facilities and industrial ties to work with cutting edge technology and push the boundaries of our knowledge.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
Our cookies
We use cookies for three reasons: to give you the best experience on PGS, to make sure the PGS ads you see on other sites are relevant , and to measure website usage. Some of these cookies are necessary to help the site work properly and can’t be switched off. Cookies also support us to provide our services for free, and by click on “Accept” below, you are agreeing to our use of cookies .You can manage your preferences now or at any time.
Privacy overview
We use cookies, which are small text files placed on your computer, to allow the site to work for you, improve your user experience, to provide us with information about how our site is used, and to deliver personalised ads which help fund our work and deliver our service to you for free.
The information does not usually directly identify you, but it can give you a more personalised web experience.
You can accept all, or else manage cookies individually. However, blocking some types of cookies may affect your experience of the site and the services we are able to offer.
You can change your cookies preference at any time by visiting our Cookies Notice page. Please remember to clear your browsing data and cookies when you change your cookies preferences. This will remove all cookies previously placed on your browser.
For more detailed information about the cookies we use, or how to clear your browser cookies data see our Cookies Notice
Manage consent preferences
Strictly necessary cookies
These cookies are necessary for the website to function and cannot be switched off in our systems.
They are essential for you to browse the website and use its features.
You can set your browser to block or alert you about these cookies, but some parts of the site will not then work. We can’t identify you from these cookies.
Functional cookies
These help us personalise our sites for you by remembering your preferences and settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers, whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies, then these services may not function properly.
Performance cookies
These cookies allow us to count visits and see where our traffic comes from, so we can measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to know which pages are popular and see how visitors move around the site. The cookies cannot directly identify any individual users.
If you do not allow these cookies we will not know when you have visited our site and will not be able to improve its performance for you.
Marketing cookies
These cookies may be set through our site by social media services or our advertising partners. Social media cookies enable you to share our content with your friends and networks. They can track your browser across other sites and build up a profile of your interests. If you do not allow these cookies you may not be able to see or use the content sharing tools.
Advertising cookies may be used to build a profile of your interests and show you relevant adverts on other sites. They do not store directly personal information, but work by uniquely identifying your browser and internet device. If you do not allow these cookies, you will still see ads, but they won’t be tailored to your interests.
Course type
Qualification, university name, phd degrees in artificial intelligence (ai).
16 degrees at 13 universities in the UK.
Customise your search
Select the start date, qualification, and how you want to study
About Postgraduate Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence (AI) is one of the hottest conversation topics in recent years and one of the most disruptive emerging areas of academic study and research. AI delves into the dynamic field of creating intelligent machines that mimic human cognition, covering topics like machine learning, neural networks, natural language processing and ethical considerations in the field’s development.
AI is a highly technical subject, well suited to those with a background in computer science, engineering, or a related field. Most PhD programmes require a solid master’s degree as well as significant proficiency in programming languages like Python or Java. At PhD level, you’ll also need to develop a proposal for a piece of original research, which will form the foundation of your academic work, or join an existing research project. There are currently eight PhD courses in artificial intelligence in the UK, although this number is almost certainly due to increase in the coming years.
What to Expect
Expect a fascinating dive into the futuristic world of intelligent machines. The field is in its early stages of discovery and your research work will probably fall into one of the following areas; data management and data science, computer vision and multimedia computation, machine learning and data mining, optimisation and statistics, or human-centred AI.
A PhD represents the cutting edge of the field. Much of the most innovative research in AI is conducted in universities, with the products of this work finding application in a myriad of industries and organisations.

Related subjects:
- PhD Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- PhD Animation Software
- PhD Bioinformatics
- PhD Business Information Systems
- PhD Computer Animation
- PhD Computer Architectures
- PhD Computer Communications and Networking
- PhD Computer Cybernetics
- PhD Computer Games Design
- PhD Computer Graphics
- PhD Computer Network Components
- PhD Computer Science and Information Technology
- PhD Computer Security Systems
- PhD Computer Systems
- PhD Computing Methodologies
- PhD Data Science
- PhD Expert Systems
- PhD Geographical Information Systems Software
- PhD Graphics And Multimedia Software
- PhD Health Informatics
- PhD Human Computer Interface Development
- PhD Image Processing
- PhD Informatics
- PhD Information Management
- PhD Information Security
- PhD Information Systems
- PhD Information Technology
- PhD Information Work and Information Use
- PhD Internet Security Systems
- PhD Internet Systems
- PhD Knowledge Management Systems
- PhD Librarianship and Library Management
- PhD Libraries and Librarianship
- PhD Mobile Computing
- PhD Modelling and Simulation Systems
- PhD Multimedia
- PhD Network Systems Management
- PhD Network Systems Management Software
- PhD Pattern Recognition
- PhD Software Development
- PhD Software Engineering
- PhD Software Testing
- PhD Software for Specific Subjects and Industries
- PhD Systems Analysis and Design
- PhD Using Software

- Course title (A-Z)
- Course title (Z-A)
- Price: high - low
- Price: low - high
Artificial Intelligence Enabled Healthcare MRes and MPhil/PhD
Ucl (university college london).
The CDT programme consists of a 1 year MRes followed by a 3 year PhD. Throughout this period the CDT will continue to closely monitor the Read more...
- 1 year Full time degree: £6,035 per year (UK)
- 2 years Part time degree: £2,930 per year (UK)
Artificial Intelligence and Intelligent Agents PhD
Bangor university.
Research topics include knowledge-based systems, logic, multi-agent systems, distributed systems, machine learning, data mining, Read more...
- 3 years Full time degree: £4,712 per year (UK)
Computer Science PhD, MPhil - Knowledge Discovery and Machine Learning
University of leicester.
Computing at Leicester offers supervision for the degrees of Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) - full-time and part-time Master of Philosophy Read more...
- 3 years Full time degree: £4,786 per year (UK)
- 6 years Part time degree: £2,393 per year (UK)
PhD Robotics and Systems Engineering
University of salford.
INTRODUCTION Automation for the Food Industry Research The food industry is very labour intensive and as a result is under threat from Read more...
- 3 years Full time degree: £4,780 per year (UK)
- 5 years Part time degree: £2,390 per year (UK)
Robotics and Autonomous Systems PhD
University of surrey.
Why choose this programme On our Robotics and Autonomous Systems PhD, you’ll study, design and build novel solutions and behaviours for Read more...
- 4 years Full time degree: £4,712 per year (UK)
- 8 years Part time degree: £2,356 per year (UK)
PhD Artificial Intelligence and Music
Queen mary university of london.
The UKRI Centre for Doctoral Training in Artificial Intelligence and Music (AIM) is a leading PhD research programme aimed at the Read more...
PhD with Integrated Study Machine Intelligence for Nano-electronic Devices (MINDS)
University of southampton.
This four-year iPhD is designed to develop and nurture the next generation of technology pioneers who will have the skills, assets and Read more...
- 4 years Full time degree
PhD Robotics
Sheffield hallam university.
Course summary Undertake extensive, supervised studies in the Centre for Automation and Robotics Research Specialise in pertinent Read more...
- 7 years Part time degree: £2,356 per year (UK)
Artificial Intelligence Machine Learning and Advanced Computing PhD
Three fully-funded 4-year PhD scholarships are available to start in October 2021 in the area of Artificial Intelligence machine learning Read more...
DPhil in Autonomous Intelligent Machines and Systems (EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training)
University of oxford.
The Autonomous Intelligent Machines and Systems (AIMS) Centre for Doctoral Training (CDT) provides graduates with the opportunity to Read more...
- 4 years Full time degree: £9,500 per year (UK)
- 8 years Part time degree: £4,750 per year (UK)
Text and Data Mining (PhD/MPhil)
Cardiff university.
Focus your studies on text and data mining through our Computer Science and Informatics research programmes (MPhil, PhD). Studying for a Read more...
- 3 years Full time degree
- 5 years Part time degree
Practice-Oriented Artificial Intelligence PhD
University of bristol.
Practice-oriented artificial intelligence is about bridging the gap between complex problem domains such as those found in science and Read more...
- 4 years Full time degree: £4,758 per year (UK)
Informatics: ANC: Machine Learning, Computational Neuroscience, Computational Biology PhD
The university of edinburgh.
The Institute for Adaptive and Neural Computation (IANC) is a world-leading institute dedicated to the theoretical and empirical study of Read more...
- 6 years Part time degree
PhD Intelligent Systems
Ulster university.
The vision is to develop a bio-inspired computational basis for Artificial Intelligence to power future cognitive technologies. Our mission Read more...
- 6 years Part time degree: £2,390 per year (UK)
Statistics and Machine Learning (DPhil)
The Modern Statistics and Statistical Machine Learning CDT is a four-year DPhil research programme (or eight years if studying Read more...
Informatics: AIAI: Foundations and Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Automated Reasoning, Agents, Data Intensive Research PhD
At the Artificial Intelligence and its Applications Institute, we enable computer systems to reproduce and complement human abilities, work Read more...
Course type:
- Full time PhD
- Part time PhD
Qualification:
Related subjects:.
- How it works

Useful Links
How much will your dissertation cost?
Have an expert academic write your dissertation paper!
Dissertation Services

Get unlimited topic ideas and a dissertation plan for just £45.00
Order topics and plan

Get 1 free topic in your area of study with aim and justification
Yes I want the free topic

Artificial Intelligence Topics for Dissertations
Published by Carmen Troy at January 6th, 2023 , Revised On August 16, 2023

Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the process of building machines, robots, and software that are intelligent enough to act like humans. With artificial intelligence, the world will move into a future where machines will be as knowledgeable as humans, and they will be able to work and act as humans.
When completely developed, AI-powered machines will replace a lot of humans in a lot of fields. But would that take away power from the humans? Would it cause humans to suffer as these machines will be intelligent enough to carry out daily tasks and perform routine work? Will AI wreak havoc in the coming days? Well, these are questions that can only be answered after thorough research.
To understand how powerful AI machines will be in the future and what sort of a world we will witness, here are the best AI topics you can choose for your dissertation.
You may also want to start your dissertation by requesting a brief research proposal from our writers on any of these topics, which includes an introduction to the topic, research question , aim and objectives , literature review along with the proposed methodology of research to be conducted. Let us know if you need any help in getting started.
Check our dissertation examples to get an idea of how to structure your dissertation .
Review the full list of dissertation topics for 2022 here.
You may also be interested in technology dissertation topics , computer engineering dissertation topics , networking dissertation topics , and data security dissertation topics .
2022 Artificial Intelligence Topics for Dissertations
Topic 1: artificial intelligence (ai) and supply chain management- an assessment of the present and future role played by ai in supply chain process: a case of ibm corporation in the us.
Research Aim: This research aims to find the present, and future role AI plays in supply chain management. It will analyze how AI affects various components of the supply chain process, such as procurement, distribution, etc. It will use the case study of IBM Corporation, which uses AI in the US to make the supply chain process more efficient and reduce losses. Moreover, through various technological and business frameworks, it will recommend changes in the current AI-based supply chain models to improve their efficiency.
Topic 2: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Blockchain Technology a Transition Towards Decentralized and Automated Finance- A Study to Find the Role of AI and Blockchains in Making Various Segments of Financial Sector Automated and Decentralized
Research Aim: This study will analyze the role of AI and blockchains in making various segments of financial markets (banking, insurance, investment, stock market, etc.) automated and decentralized. It will find how AI and blockchains can eliminate the part of intimidators and commission charging players such as large banks and corporations to make the economy and financial system more efficient and cheaper. Therefore, it will study applications of various AI and blockchain models to show how they can affect economic governance.
Topic 3: AI and Healthcare- A Comparative Analysis of the Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning Models for Cancer Diagnosis
Research Aim: This study aims to identify the role of AI in modern healthcare. It will analyze the efficacy of the contemporary ML and DL models for cancer diagnosis. It will find how these models diagnose cancer, which technology ML or DL does it better, and how much better efficient. Moreover, it will also discuss criticism of these models and ways to improve them for better results.
Topic 4: Are AI and Big Data Analytics New Tools for Digital Innovation? An Assessment of Available Blockchain and Data Analytics Tools for Startups Development
Research Aim: This study aims to assess the role of present AI and data analytics tools for startups development. It will identify how modern startups use these technologies in their development stages to innovate and increase their effectiveness. Moreover, it will analyze its macroeconomic effects by examining its role in speeding up the startup culture, creating more employment, and rising incomes.
Topic 5: The Role of AI and Robotics in Economic Growth and Development- A Case of Emerging Economies
Research Aim: This study aims to find the impact of AI and Robotics on economic growth and development in emerging economies. It will identify how AI and Robotics speed up production and other business-related processes in emerging economies, create more employment, and raise aggregate income levels. Moreover, it will see how it leads to innovation and increasing attention towards learning modern skills such as web development, data analytics, data science, etc. Lastly, it will use two or three emerging countries as a case study to show the analysis.
Artificial Intelligence Topics
Topic 1: machine learning and artificial intelligence in the next generation wearable devices.
Research Aim: This study will aim to understand the role of machine learning and big data in the future of wearables. The research will focus on how an individual’s health and wellbeing can be improved with devices that are powered by AI. The study will first focus on the concept of ML and its implications in various fields. Then, it will be narrowed down to the role of machine learning in the future of wearable devices and how it can help individuals improve their daily routine and lifestyle and move towards a better and healthier life. The research will then conclude how ML will play its role in the future of wearables and help people improve their well-being.
Topic 2: Automation, machine learning and artificial intelligence in the field of medicine
Research Aim: Machine learning and artificial intelligence play a huge role in the field of medicine. From diagnosis to treatment, artificial intelligence is playing a crucial role in the healthcare industry today. This study will highlight how machine learning and automation can help doctors provide the right treatment to patients at the right time. With AI-powered machines, advanced diagnostic tests are being introduced to track diseases much before their occurrence. Moreover, AI is also helping in developing drugs at a faster pace and personalised treatment. All these aspects will be discussed in this study with relevant case studies.
Topic 3: Robotics and artificial intelligence – Assessing the Impact on business and economics
Research Aim: Businesses are changing the way they work due to technological advancements. Robotics and artificial intelligence have paved the way for new technologies and new methods of working. Many people argue that the introduction of robotics and AI will adversely impact humans as most of them might be replaced by AI-powered machines. While this cannot be denied, this artificial intelligence research topic will aim to understand how much the business will be impacted by these new technologies and assess the future of robotics and artificial intelligence in different businesses.
Topic 4: Artificial intelligence governance: Ethical, legal and social challenges
Research Aim: With artificial intelligence taking over the world, many people have reservations over the technology tracking people and their activities 24/7. They have called for strict governance for these intelligent systems and demanded that this technology be fair and transparent. This research will address these issues and present the ethical, legal, and social challenges governing AI-powered systems. The study will be qualitative in nature and will talk about the various ways through which artificial intelligence systems can be governed. It will also address the challenges that will hinder fair and transparent governance.
Topic 5: Will quantum computing improve artificial intelligence? An analysis
Research Aim: Quantum computing (QC) is set to revolutionize the field of artificial intelligence. According to experts, quantum computing combined with artificial intelligence will change medicine, business, and the economy. This research will first introduce the concept of quantum computing and will explain how powerful it is. The study will then talk about how quantum computing will change and help increase the efficiency of artificially intelligent systems. Examples of algorithms that quantum computing utilises will also be presented to help explain how this field of computer science will help improve artificial intelligence.
Topic 6: The role of deep learning in building intelligent systems
Research Aim: Deep learning, an essential branch of artificial intelligence, utilizes neural networks to assess the various factors similar to a human neural system. This research will introduce the concept of deep learning and discuss how it works in artificial intelligence. Deep learning algorithms will also be explored in this study to have a deeper understanding of this artificial intelligence topic. Using case examples and evidence, the research will explore how deep learning assists in creating machines that are intelligent and how they can process information like a human being. The various applications of deep learning will also be discussed in this study.
Topic 7: Evaluating the role of natural language processing in artificial intelligence
Research Aim: Natural language processing (NLP) is an essential element of artificial intelligence. It provides systems and machines with the ability to read, understand and interpret the human language. With the help of natural language processing, systems can even measure sentiments and predict which parts of human language are important. This research will aim to evaluate the role of this language in the field of artificial intelligence. It will further assist in understanding how natural language processing helps build intelligent systems that various organizations can use. Furthermore, the various applications of NLP will also be discussed.
Topic 8: Application of computer vision in building intelligent systems
Research Aim: Computer vision in the field of artificial intelligence makes systems so smart that they can analyze and understand images and pictures. These machines then derive some intelligence from the image that has been fed to the system. This research will first aim to understand computer vision and its role in artificial intelligence. A framework will be presented that will explain the working of computer vision in artificial intelligence. This study will present the applications of computer vision to clarify further how artificial intelligence uses computer vision to build smart systems.
Topic 9: Analysing the use of the IoT in artificial intelligence
Research Aim: The Internet of things and artificial intelligence are two separate, powerful tools. IoT can connect devices wirelessly, which can perform a set of actions without human intervention. When this powerful tool is combined with artificial intelligence, systems become extremely powerful to simulate human behaviour and make decisions without human interference. This artificial intelligence topic will aim to analyze the use of the internet of things in artificial intelligence. Machines that use IoT and AI will be analyzed, and the study will present how human behaviour is simulated so accurately.
Topic 10: Recommender systems – exploring its power in e-commerce
Research Aim: Recommender systems use algorithms to offer relevant suggestions to users. Be it a product, a service, a search result, or a movie/TV show/series. Users receive tons of recommendations after searching for a particular product or browsing their favourite TV shows list. With the help of AI, recommender systems can offer relevant and accurate suggestions to users. The main aim of this research will be to explore the use of recommender systems in e-commerce. Industry giants use this tool to help customers find the product or service they are looking for and make the right decision. This research will discuss where recommender systems are used, how they are implemented, and their results for e-commerce businesses.
Free Dissertation Topic
Phone Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Graduate PHD
Academic Subject
Area of Research
Frequently Asked Questions
How to find artificial intelligence dissertation topics.
To find artificial intelligence dissertation topics:
- Study recent AI advancements.
- Explore ethical concerns.
- Investigate AI in specific industries.
- Analyze AI’s societal impact.
- Consider human-AI interaction.
- Select a topic aligning with your expertise and passion.
You May Also Like
Portfolio management examines the projects and programs of an organization. There are three aspects involved here: selection, prioritization, and control. This is done by taking into account the strategic goals of the organization.
Consumer psychology has always been a well-known yet understudied field in psychology. The psychology of consumption describes how people adopt, use, and eventually dispose of goods, services, or concepts.
Go through some of the dissertation topics related to Forensic science given below, with their research aim, and get an idea to begin your dissertation.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Explore your training options in 10 minutes Get Started
- Graduate Stories
- Partner Spotlights
- Bootcamp Prep
- Bootcamp Admissions
- University Bootcamps
- Coding Tools
- Software Engineering
- Web Development
- Data Science
- Tech Guides
- Tech Resources
- Career Advice
- Online Learning
- Internships
- Apprenticeships
- Tech Salaries
- Associate Degree
- Bachelor's Degree
- Master's Degree
- University Admissions
- Best Schools
- Certifications
- Bootcamp Financing
- Higher Ed Financing
- Scholarships
- Financial Aid
- Best Coding Bootcamps
- Best Online Bootcamps
- Best Web Design Bootcamps
- Best Data Science Bootcamps
- Best Technology Sales Bootcamps
- Best Data Analytics Bootcamps
- Best Cybersecurity Bootcamps
- Best Digital Marketing Bootcamps
- Los Angeles
- San Francisco
- Browse All Locations
- Digital Marketing
- Machine Learning
- See All Subjects
- Bootcamps 101
- Full-Stack Development
- Career Changes
- View all Career Discussions
- Mobile App Development
- Cybersecurity
- Product Management
- UX/UI Design
- What is a Coding Bootcamp?
- Are Coding Bootcamps Worth It?
- How to Choose a Coding Bootcamp
- Best Online Coding Bootcamps and Courses
- Best Free Bootcamps and Coding Training
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Community College
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Self-Learning
- Bootcamps vs. Certifications: Compared
- What Is a Coding Bootcamp Job Guarantee?
- How to Pay for Coding Bootcamp
- Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans
- Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants
- Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps
- Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your Employer
- GI Bill and Coding Bootcamps
- Tech Intevriews
- Our Enterprise Solution
- Connect With Us
- Publication
- Reskill America
- Partner With Us
- Resource Center
- Bachelor’s Degree
- Master’s Degree
Best Doctorates in Artificial Intelligence: Top PhD Programs, Career Paths, and Salaries
The growing application of advanced technology in our daily lives has led to a high demand for professionals with qualifications in the field of artificial intelligence. The best PhDs in Artificial Intelligence offer tech professionals an opportunity to help meet this increased demand and land the highest-paying artificial intelligence jobs.
A careful look at some important factors for a PhD in Artificial Intelligence, such as program cost, length, and location, will help in determining the right artificial intelligence PhD program for you. This article also discusses some of the best artificial intelligence jobs and what you can expect to earn as a PhD in Artificial Intelligence salary.
Find your bootcamp match
What is a phd in artificial intelligence.
A PhD in Artificial Intelligence is a doctorate program with an artificial intelligence research focus. Students are required to complete original research in various areas of applied artificial intelligence. These areas may include machine learning, artificial neural networks, speech recognition, and processing. PhD students will be assigned an academic advisor who will guide the student throughout their research.
How to Get Into an Artificial Intelligence PhD Program: Admission Requirements
The requirements to get into an artificial intelligence PhD program are a minimum of a Bachelor’s Degree in Computer Science or a related field, such as computer engineering, data science, or statistics. Students will also need a strong background in programming and system analysis, and fluency in several computer languages. There may also be course prerequisites in areas such as English, writing, deep learning, and neural cognitive modeling.
Further requirements may include transcripts of your undergraduate or graduate coursework and standardized tests scores such as the GRE. You may also be required to submit a statement of purpose that includes a description, proposal, or preliminary idea of your research areas of interest for your doctoral thesis.
PhD in Artificial Intelligence Admission Requirements
- Bachelor’s or master’s degree
- Transcripts
- Letters of recommendation
- Statement of purpose
- Standardized test scores
- Strong background in programming languages such as Python and Java
- Knowledge of artificial intelligence subjects such as deep learning, neural and cognitive modeling, or computing
Artificial Intelligence PhD Acceptance Rates: How Hard Is It to Get Into a PhD Program in Artificial Intelligence?
It can be hard to get into a PhD program in Artificial Intelligence. Some programs are highly selective, and acceptance is not always based on merit alone. However, acceptance into some PhD programs is relatively easy if you meet all of the admissions requirements.
How to Get Into the Best Universities
[query_class_embed] how-to-get-into-*school
Best PhDs in Artificial Intelligence: In Brief
Best universities for artificial intelligence phds: where to get a phd in artificial intelligence.
The best universities for artificial intelligence PhDs are Arizona State University, Syracuse University, and Drexel University. They have some of the best artificial intelligence laboratories, high acceptance rates, and the right networks of people. Below is a detailed list of the best schools to get a PhD in Artificial Intelligence.
Arizona State University was founded on March 12, 1885. It is a public research institution that offers various programs at the graduate level including business administration, economics, and computer science. The graduate programs of Arizona State University are well known for their first-class facilities as well as renowned researchers.
PhD in Computer Science
This PhD program at Arizona State University requires 84 credit hours, a written comprehensive exam, an oral comprehensive exam, a prospectus, and a dissertation. The university has an artificial intelligence laboratory where students can conduct research. Some of the topic areas include artificial intelligence, big data, statistical modeling, cloud computing, social computing, data mining, and machine learning.
PhD in Computer Science Overview
- Program Length: Approx. 5 years
- Acceptance Rate: N/A
- Tuition: $11,720/year (in state); $23,544/year (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Awards and fellowships, graduate appointments, distinguished wards
PhD in Computer Science Admission Requirements
- Minimum GPA of 3.5 in last 60 hours of bachelor’s degree or in master’s degree overall
- 3 letters of recommendation
- Curriculum vitae or resume
- Proof of English proficiency
Capitol Technology University is a private research institution founded on June 1, 1927. It is best known for its proven academic excellence, as well as expert guidance in doctoral research. Capitol Technology University offers graduate programs in areas such as aeronautical science, cyber security, business analytics, data science, and computer science.
PhD in Artificial Intelligence
About 60 credits of coursework are required for the PhD in Artificial Intelligence at Capitol Technology University. The program emphasizes the principles of autonomous systems and expounds on how computers operate to match the human-like operation of computers for decision-making and problem-solving processes. The program is available both online and in person.
PhD in Artificial Intelligence Overview
- Program Length: Approx. 3 years
- Tuition: $933/credit
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Hometown Heroes discounts, EdAssist partner discounts, loans
PhD in Artificial Intelligence Admission Requirements
- Master’s degree in a relevant field
- 5 years of work experience
- Application letter
- Application fee: $100
- Official transcripts
- 2 letters of recommendation
Cornell University's main campus in Ithaca was founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White. It is divided into seven undergraduate campuses and seven graduate divisions. Its computer science PhD program is ranked in the top six of such programs in the nation by US News & World Report, and it performs studious and academically-tasking research.
This program is designed for students with a particular interest in the general components of computing processes. Some study areas students can choose to specialize in include artificial intelligence, machine learning, data structures, robotics, natural language processing, quantitative analysis, programming languages and methodology, robotics, and theory of computation.
- Program Length: 4 - 6 years
- Tuition and Fees: $29,500/year
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Teaching assistantships, research assistantships, fellowships, loans
- Application fee of $105
- Undergraduate degree
- Official transcripts
- English language proficiency (for international applicants)
Drexel University offers research and professional degree programs in the arts and sciences, biomedical engineering, education, science and health systems, business, computing, and informatics. Drexel University graduate programs are well known for their flexibility.
Students in this program carry out in-depth and creative research. They may choose from areas such as artificial intelligence, computer vision, human-computer interaction, information assurance, and security research areas. Whatever the path they choose to specialize in, they must meet specified course requirements including 18 credits in computer science courses.
- Program Length: Within 7 years
- Tuition: $1,342/credit
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Private scholarships, student loans, Drexel Dean’s Fellowship, and research, teaching, and graduate assistantships
PhD in Computer and Information Science Admission Requirements
- Official final transcripts from all colleges/universities attended
- Official GRE scores
- Essay/statement of purpose
- Current resume
- Official TOEFL scores (international applicants)
Founded in 1868, Oregon State University is the largest public research university in the state with students from over 100 countries. It offers more than 80 graduate programs in fields such as AI, bioengineering, mechanical engineering, and biological and ecological engineering. It is well known for its abundant learning resources that aid students' research.
PhD in Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
This artificial intelligence and robotics PhD program teaches the theories, algorithms, and systems for making intelligent decisions in complex and uncertain environments. Students can explore research areas like perception and interpretation of sensor data, automated planning and reasoning, and human-machine interaction.
PhD in Artificial Intelligence and Robotics Overview
- Tuition: $557/credit (in state); $1,105/credit (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Graduate, teaching, and research assistantships, graduate diversity recruitment bonus program
PhD in Artificial Intelligence and Robotics Admission Requirements
- Application fee
- Statement of objectives
- Graduate/undergraduate transcripts
- GPA of 3.00
Pace University was founded in 1906 as a business school by St. Clair Pace and Charles A. Pace. It has a main campus in New York City and secondary campuses in Westchester County, New York. It offers PhD programs in clinical psychology, computer science, mental health counseling, nursing, and school psychology.
Only students with demonstrated field experience are accepted into this extremely selective program. Students are closely involved in vital, strategic advanced research projects and make authentic advances in the field in areas such as pattern recognition in medical image segmentation, artificial intelligence, and intelligent systems. Each student is expected to pass three qualification exams.
- Program Length: 3 years
- Tuition: $1,420/credit
- PhD Funding Opportunities : Graduate assistantships, federal work-study, student loans
- Master’s Degree in Computer Science or a related field
- Research presentation
- $70 application fee
- Personal statement
- All official post-secondary transcripts
Syracuse University was founded on March 24, 1870. It offers over 200 graduate programs in fields such as data and research, computer science, and engineering, among others. It is well known for its professional programs, investment in research and innovation, and solid reputation.
PhD in Computer and Information Science and Engineering
The PhD in Computer and Information Science and Engineering program offered at Syracuse University is a well-structured program. Graduate students must complete a minimum of 48 credits in technical graduate courses, as well as other research courses.
In addition, each student must complete at least four credits of professional development courses. A proposal and a dissertation must also be completed and defended by the students.
PhD in Computer and Information Science and Engineering Overview
- Program Length: Within 5 years
- Acceptance Rate: 14.3%
- Tuition: $1,802/credit
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Teaching, research, and graduate assistantships, scholarships, university fellowships, research excellence doctoral funding programs
PhD in Computer and Information Science and Engineering Admission Requirements
- Bachelor’s or Master’s Degree in Computer Engineering, Computer and Information Science, or a related field
- TOEFL score (international applicants)
The University of Colorado is a public research institution located in Boulder, Colorado. It offers over 124 graduate and professional degrees in the arts and sciences, business, education, engineering, law, and music. The university allows students to collaborate with esteemed faculty and researchers and gain world-class expertise in their chosen fields.
This PhD in Computer Science at the University of Colorado requires 30 hours of graduate-level coursework, as well as 30 hours of thesis work. It also requires the completion of a preliminary exam, comprehensive exam, and dissertation defense, typically within six years of beginning your coursework.
- Program Length: Within 6 years
- Tuition: $780/credit (in state); $847/credit (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Assistantships, fellowships, faculty research grants
- At least 3 courses in computer science beyond the introductory level
- Research experience
- Resume with research and publication details
- Copy of transcripts for the required undergraduate degree or master's degree
- Proof of financial support and a funding plan
Founded on August 26, 1817, the University of Michigan is known as one of the first public universities in the nation. It is ranked as the ninth best school for artificial intelligence by US News & World Report. The school offers master’s and PhD programs in areas like aerospace engineering, architecture, urban planning, and dentistry.

"Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!"
Venus, Software Engineer at Rockbot
PhD in Computer Science and Engineering
Intended for students who wish to pursue research or careers as postsecondary teachers, this PhD program is highly recognized for its offerings in relatively broad fields of knowledge. It is known for imparting a demonstrated ability in its graduates to carry out independent research, yielding significant original results.
PhD in Computer Science and Engineering Overview
- Program Length: 4 - 5 years
- Acceptance Rate: 1%
- Tuition and Fees: $14,558/full term (resident); $27,023/full term (nonresident)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Graduate research assistantships on research grants and contracts, teaching assistantships
PhD in Computer Sciences and Engineering Admission Requirements
- Master's or bachelor's degree in any related field
- GPA of at least 3.5
- 3 strong letters of recommendation
- Proof of English proficiency (international students)
With over 11,000 graduate students enrolled, the University of Texas ranks among the 10 best public universities in the country, by US News & World Report. It offers graduate programs in various fields such as accounting, business, engineering, education and development, and computer science.
This program provides cutting-edge research experience as well as expertise in advanced computer science subjects. Through this program, students can specialize in the artificial intelligence track and conduct their research work on topics like information security, computer architecture, assistive technology, computer networks, and deep learning.
- Program Length: Within 8 years
- Tuition and Fees: $347.53/credit (in state); $1,344.63/credit (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Grants and loans; department, institutional, and external fellowships and scholarships; research, teaching, and graduate assistantships
PhD in Computer Science Admission Requirements
- Transcripts of an ABA, BS, or MS degree in Computer Science/related area
- Completed graduate school application
- Resume/curriculum vitae
Can You Get a PhD in Artificial Intelligence Online?
Yes, you can get a PhD in Artificial Intelligence online. Some universities in the United States offer online artificial intelligence doctorate programs, like Capitol Technology University. The amount of time required to complete the online artificial intelligence program is about the same as the in-person program, depending on the institution.
Best Online PhD Programs in Artificial Intelligence
How long does it take to get a phd in artificial intelligence.
It takes about three to five years to get a PhD in Artificial Intelligence. That duration may be longer for people with particularly lengthy or complex research work or for those working part-time toward their PhD.
The reason for the longer duration could be a result of the institution’s requirements, the amount of research required before a thesis can be submitted, a student’s cooperation with their academic supervisor, or the program’s format, that is, whether it is full-time or part-time.
Is a PhD in Artificial Intelligence Hard?
No, a PhD in Artificial Intelligence is not that hard. Getting a PhD in computer-related programs can indeed be difficult, but when compared with other fields of theoretical study in computer science, a PhD in Artificial Intelligence is relatively easier.
PhD programs are very research-focused. What makes the PhD in Artificial Intelligence easier is that more emphasis is placed on empirical evaluation than on performance. That is, you have to prove that your method makes sense intuitively, not that it actually works. For your AI PhD, you can even show how an already established method works in a new area.
How Much Does It Cost to Get a PhD in Artificial Intelligence?
It costs about $19,792 per year to get a PhD in Artificial Intelligence , according to the National Center for Education Statistics. This average varies depending on the type of university involved. For public institutions, annual tuition averages about $12,410, while private universities charge about $26,597 per year. These rates are for in-state students only.
It is important to note that additional fees and costs also apply, such as application fees and department fees. However, most PhD programs have guaranteed financial support, although it doesn’t usually cover the entire cost of the degree.
How to Pay for a PhD in Artificial Intelligence: PhD Funding Options
Some of the PhD funding options available for students include research assistantships, where PhD students assist a member of faculty with their research. Students can also participate in a teaching assistantships, where they assist a professor in various academic-related areas. Instead of being paid for their work, students receive partial or full tuition or a stipend.
Another option for PhD funding is tuition waivers, which are awarded based on things like merit, race, or occupation. There also may be financial scholarships or loans available to help with costs.
Best Online Master’s Degrees
[query_class_embed] online-*subject-masters-degrees
What Is the Difference between an Artificial Intelligence Master’s Degree and PhD?
One difference between an artificial intelligence master’s degree and a PhD is that a master’s degree program consists mostly of classwork and projects, with little intensive research work, while a PhD in Artificial Intelligence predominantly involves intensive research work aimed at finding answers and solutions to existing questions and problems.
It is harder to get a PhD than a master’s degree . In the field of artificial intelligence, master’s students will focus on multiple areas of learning, such as building multi-agent systems, economic systems, or artificial agents. PhD students will be more focused on solving a specific issue, requiring intense focus and strong critical-thinking and problem-solving skills, and making advancements in the field.
Master’s vs PhD in Artificial Intelligence Job Outlook
There is a difference in the job outlook for AI master’s degree holders and AI PhD holders. Those with a PhD in Artificial Intelligence have more job opportunities overall and can expect a higher salary than those with a Master’s Degree in Artificial Intelligence.
Some examples of jobs in artificial intelligence that require a PhD are big data engineer and architect, research scientist, natural language processing engineer, software architect, senior software engineer, and machine learning engineer. Those requiring a master’s degree include computer and information research scientist, data analyst, and artificial intelligence developer.
Difference in Salary for Artificial Intelligence Master’s vs PhD
A PhD in Artificial Intelligence is a terminal degree that brings with it higher salaries than a Master’s in Artificial Intelligence does. Someone with a PhD in the field of artificial intelligence earns about $115,000 per year, according to PayScale.
On the other hand, an artificial intelligence master’s degree holder earns $102,000 per year on average. This means that those with an AI PhD can expect to make about $13,000 more every year than those with an AI master’s degree.
Related Artificial Intelligence Degrees
[query_class_embed] https://careerkarma.com/blog/business-intelligence-degree-online-a-guide/ https://careerkarma.com/blog/best-artificial-intelligence-bachelors-degrees/ https://careerkarma.com/blog/best-online-artificial-intelligence-and-machine-learning-bachelors-degrees/
Why You Should Get a PhD in Artificial Intelligence
You should get a PhD in Artificial Intelligence because it opens the door to more employment opportunities and higher salaries. If you’re already employed, you may be able to keep your job for part or even all of your PhD program. Artificial intelligence is a growing and in-demand field, so obtaining the highest level of education will set you up for continuous opportunities.
Reasons for Getting a PhD in Artificial Intelligence
- More employment opportunities. With a PhD in Artificial Intelligence, landing a good job shouldn’t be a problem. The degree opens the door to more and better career opportunities.
- High-paying jobs. A Doctorate in Artificial Intelligence brings with it not only more career opportunities but also better salaries. PayScale shows that the average salary of a PhD degree holder in the field of artificial intelligence is about $115,000. However, the earning potential with this degree is considerably higher, as much as $200,000 per year for positions like principal scientist.
- Expertise in a versatile field. A doctorate degree in artificial intelligence will provide you with a deep understanding of AI theories and strong technical skills, which you can use to help solve future problems in a wide variety of fields.
- Plentiful research opportunities. With a PhD in Artificial Intelligence, you have the opportunity to engage in numerous research projects, which will increase your overall knowledge in the AI field and imbue you with the ability to find solutions to a wide variety of problems.
Getting a PhD in Artificial Intelligence: Artificial Intelligence PhD Coursework

Getting a PhD in Artificial Intelligence requires significant coursework in addition to the research element of the degree. Some common course topics include advanced data structures and algorithms, natural language learning, intermediate statistics, machine learning in practice, and regression analysis.
Foundations of Machine Learning
This course aims to teach students the founding principles of machine learning, its theory, and the techniques involved. The course includes different categories of machine learning including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
Through this course, students learn the branches of data science and how data is managed and organized to make it easily accessible. The knowledge gained from this course will equip the student with the skills needed for developing effective and useful software designs and algorithms.
Matrix Algebra
This course teaches students how to use matrix algebra in experimental design. Students learn how to analyze complex data and use linear algebra to explore theories that involve two or more matrices. This skill is very useful when conducting research.
Probability and Random Variables
The course on probability and random variables in the field of artificial intelligence aims to teach PhD students how to reduce uncertainty when there is a margin of error as a result of the inadequacy of perfect information.
Machine Learning in Practice
In this course, students will put all that they have learned in the machine learning field into practice. They will apply their skills and knowledge in the areas of mathematics, computing, engineering, and data analysis to real-world datasets and examples.
Best Master’s Degrees
[query_class_embed] *subject-masters-degrees
How to Get a PhD in Artificial Intelligence: Doctoral Program Requirements
To get a PhD in Artificial Intelligence, students must meet specific criteria that vary with each school and program. Some of the more common ones include a competency requirement, a project requirement, a breadth requirement, a teaching requirement, and approval of the thesis. Students also need to pass the necessary examinations before a PhD in Artificial Intelligence can be awarded.
Students are expected to demonstrate competency in various branches of artificial intelligence and all the theories taught in the program. They are also required to perform well on their examinations, usually with a grade of B+ or higher.
PhD students are required to take a specific number of upper-level courses for their degree. These courses need to encompass the different areas of artificial intelligence as well as the research problems and techniques associated with them.
As a way of showcasing the skills they have gained in their years of doctorate studies, PhD students must create and complete a project that’s in harmony with the project requirements of their particular program. This project will be based in a specialized field of artificial intelligence and must be approved by the project supervisors before this requirement can be met.
It is a requirement for PhD students to serve in the position of teaching assistant for at least two semesters or teach a course in their field for at least a semester. These roles allow PhD students to interact with students, sharpening their communication skills and preparing them for a possible career in academics.
Before a PhD in the field of artificial intelligence can be awarded, thesis research will be required of the PhD student. The thesis usually focuses on answering industry-wide problems. Once the thesis has been approved by the school supervising committee, then a doctoral degree in artificial intelligence can be given.
Potential Careers with an Artificial Intelligence Degree
[query_class_embed] how-to-become-a-*profession
PhD in Artificial Intelligence Salary and Job Outlook
The job outlook for artificial intelligence PhD holders is very good, as we are living in a time of rapid technological advancements. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) predicts a growth of 22 percent in jobs like computer and research scientist through 2030. With an average salary of $115,000 for AI PhD holders, as stated above, you can expect to earn a great salary with your degree.
What Can You Do With a PhD in Artificial Intelligence?
With a PhD in Artificial Intelligence, you can get employed by top tech companies and work on a broad array of AI applications, programs, and systems. These include facial-recognition software, self-driving cars and drones, digital personal assistants, and more. AI students gain employment as computer scientists, AI experts, machine learning engineers, computational linguists, and robotics engineers after graduation. Here are some of the best jobs for artificial intelligence PhD holders.
Best Jobs with a PhD in Artificial Intelligence
- Big Data Engineer/Architect
- Software Architect
- Machine Learning Engineer
- Software Engineer
- Data Scientist
What Is the Average Salary for a PhD in Artificial Intelligence?
The average salary for a graduate with a PhD in Artificial Intelligence is $115,000 , according to PayScale. The exact salary you can expect will depend on a wide range of factors, which include your job title and responsibilities, the industry in which you are employed, your specific experience and knowledge, and the company’s geographic region.
Highest-Paying Artificial Intelligence Jobs for PhD Grads
Best artificial intelligence jobs with a doctorate.
The best artificial intelligence jobs with a doctorate degree are software architect, big data engineer/architect, machine learning engineer, data scientist, and software engineer. According to BLS, AI is taking a bigger role in our security , which will lead to even more job prospects in the field.
An artificial intelligence researcher conducts research to create and design new and better ways of solving problems. The models they create are used by data scientists to solve the real-world problems they were designed to solve.
- Salary with an Artificial Intelligence PhD: $131,490
- Job Outlook: 22% job growth from 2020 to 2030
- Number of Jobs: 33,000
- Highest-Paying States: Oregon, Arizona, Texas
Using their experience and research in artificial intelligence and software development, software engineers are capable of leading major software development projects. They can work for big IT companies such as IBM, Intel, Microsoft, and Alphabet.
- Salary with an Artificial Intelligence PhD: $126,668
- Number of Jobs: 1,847,900
- Highest-Paying States: Washington, California, New York
Engineers who work in machine learning are at the crossroads of software design and data science. They use big data technologies and programming structures to build production-ready, flexible, scalable models that can manage terabytes of actual data.
- Salary with an Artificial Intelligence PhD: $112,567
A robotics engineer is in charge of designing robots and robotic systems. With the implementation of AI, they will focus on designing complex robotic communication systems software and hardware components.
- Salary with an Artificial Intelligence PhD: $95,300
- Job Outlook: 7% job growth from 2020 to 2030
- Number of Jobs: 299,200
- Highest-Paying States: New Mexico, Louisiana, District of Columbia
Computational linguists’ job is to make communication possible between humans and machines by teaching computers how to understand us. They have a complex understanding of various programming languages and perform product-specific research in computational linguistics.
- Salary with an Artificial Intelligence PhD: $83,335
Is a PhD in Artificial Intelligence Worth It?
Yes, a PhD in Artificial Intelligence is worth it. Artificial intelligence and cognitive technology are expected to be the catalyst for the next scientific revolution. In a data-rich world, creating AI technology that can learn via developing and drawing conclusions based on human behavior could change the future and offer limitless industrial, social, and scientific possibilities.
As the world becomes more dependent on advancing technologies and intelligent machines, there is an ever-growing market for PhD holders in the field of artificial intelligence. A PhD in Artificial Intelligence will provide you with expertise in the field and qualify you for high demand careers in the field.
Additional Reading About Artificial Intelligence
[query_class_embed] https://careerkarma.com/blog/artificial-intelligence/ https://careerkarma.com/blog/best-ai-blogs/ https://careerkarma.com/blog/online-artificial-intelligence-courses/
PhD in Artificial Intelligence FAQ
A PhD in Artificial Intelligence offers numerous lucrative career opportunities such as robotics engineer, senior software engineer, and machine learning expert. You will also be qualified to teach in a postsecondary institution.
The best places to pursue a PhD in Artificial Intelligence are accredited universities and colleges. Some of the top such institutions in the US include Arizona State University, Drexel University, and Syracuse University.
For students interested in a career in artificial intelligence, a computer science doctoral degree is a popular option. Many colleges and universities offer computer science doctorate programs with a focus on artificial intelligence or machine learning.
Because artificial intelligence is still a relatively new field, it’s difficult to know exactly how profitable the AI sector is. The value of artificial intelligence to the global economy will be $13 trillion by 2030, according to a report by the European Parliament. The world’s growing dependency on technological innovations and intelligent machines indicates that more growth is coming in this field.
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication .
What's Next?
Get matched with top bootcamps
Ask a question to our community, take our careers quiz.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- Visits and Open Days
- Jobs and vacancies
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Accommodation
- Student Guide
- Student email
- Library and IT services
- Staff Guide
- Staff email
- Timetabling
Artificial Intelligence and Data Science Group
Featured story.

Suggested PhD Projects
Here are some suggested topics for PhD projects from our group members. These projects are merely suggestions and illustrate the broad interests of the research group. Potential research students are encouraged and welcome to produce their own suggestions in these research areas or other research areas in the field. All applicants are invited to contact the academic associated with the project when making an application.
Machine Learning for the Pharmacology of Ageing
Contact: alex freitas.
Recently, there has been a growing interest in ageing research, since the proportion of elderly people in the world’s population is expected to increase substantially in the next few decades. As people live longer, it becomes increasingly more common for a person to suffer from multiple age-related diseases. Since old age is the ultimate cause or the greatest risk factor for most of these diseases, progress in ageing research has the potential to lead to a more cost-effective treatment of many age-related diseases in a holistic fashion. In this context, researchers have collected a significant amount of data about ageing-related genes and medical drugs affecting an organism’s longevity – mainly about simpler model organisms, rather than humans. This data is often freely available on the web, which has facilitated the application of machine learning methods to the pharmacology or biomedicine of ageing, to try to discover some knowledge or patterns in such datasets. This project will focus on developing machine learning algorithms for analysing data about the pharmacology of ageing, i.e., data about medical drugs or chemical compounds that can be used as an intervention against ageing, mainly in model organisms. The broad type of machine learning method to be developed will be supervised machine learning (mainly classification), but the specific type of algorithm to be developed will be decided later, depending on the student’s interest and suitability to the target datasets. Note that, although this is an interdisciplinary project, this is a project for a PhD in Computer Science, so the student will be expected to develop a novel machine learning method. As examples of interdisciplinary papers on machine learning for ageing research, see e.g. (the first paper is particularly relevant for this project, whilst the second includes a broader discussion about machine learning for ageing research):
Relevant References:
D.G. Barardo, D. Newby, D. Thornton, T. Ghafourian, J.P. de Magalhaes and A.A. Freitas. Machine learning for predicting lifespan-extending chemical compounds. Aging (Albany NY), 9(7), 1721-1737, 2017.
Fabris, J.P. de Magalhaes, A.A. Freitas. A review of supervised machine learning applied to ageing research. Biogerontology, 18(2), 171-188, April 2017.
Machine Learning with Fairness-Aware Classification Algorithms
This project involves the classification task of machine learning, where an algorithm has to predict the class of an object (e.g. a customer or a patient) based on properties of that object (e.g. characteristics of a customer or patient). There are now many types of classification algorithms, and in general these algorithms were designed with the only (or main) goal of maximizing predictive performance. As a result, the application of such algorithms to real-world data about people often leads to predictions which have a good predictive accuracy but are unfair, in the sense of discriminating (being biased) against certain groups or types of people – characterized e.g. by values of attributes like gender or ethnicity. In the last few years, however, there has been a considerable amount of research on fairness-aware classification algorithms, which take into account the trade-off between achieving a high predictive accuracy and a high degree of fairness. The project will develop new classification algorithms to cope with this trade-off, focusing on classification algorithms that produce interpretable predictive models, rather than black box models.
[1] Friedler, A.A., Scheidegger, C., Venkatasubramanian, S., Choudhary, S., Hamilton, E.P. and Roth, D. A comparative study of fairness-enhancing interventions in machine learning. Proc. 2nd ACM Conf. on Fairness, Accountability and Transparency (FAT’19), 329-338. ACM Press, 2019.
[2] Mehrabi, N., Morstatter, F., Saxena, N., Lerman, K., & Galstyan, A. A survey on bias and fairness in machine learning. arXiv preprint: arXiv:1908.09635. 2019.
Cognition-enabled lifelong robot learning of behavioural and linguistic experience
Contact: ioanna giorgi.
Present-day cognitive robotics models draw on a hypothesised developmental paradigm of human cognitive functions to devise low-order skills in robots, such as perception, manipulation, navigation and motor coordination. These methods exploit embodied and situated cognition theories that are rooted in motor behaviour and the environment. In other words, the body of a physical artefact (e.g., a robot) and its interactions with the environment and other organisms in it contribute to the robot’s cognition. However, it is not clear how these models can explain or scale up to the high-level cognitive competence observed in human behaviour (e.g., reasoning, categorisation, abstraction and voluntary control). One approach to model robot learning of behavioural and cognitive skills is in incremental and developmental stages that resemble child development. According to child psychology and behaviour, conceptual development starts from perceptual clustering (e.g., prelinguistic infants grouping objects by colour) and progresses to nontrivial abstract thinking, which requires a fair amount of language . Thus, to solve the problem of modelling high-level cognitive skills in robots, language, in interaction with the robot’s body, becomes inseparable from cognition. This project is aimed at following a cognitive and developmental approach to robot learning that will allow robots to acquire behavioural and linguistic skills at a high level of cognitive competence and adaptation as humans. This learning should be lifelong : humans apply earlier-learned skills to make sense of continuous novel stimuli, which allows them to develop, grow and adjust to more complex practices. One such cognitive robot can be used across various themes: human-robot interaction using theory of mind (ToM) skills for robots, social robots and joint human-robot collaboration.
Note: The Cognitive Robotics and Autonomous Systems (CoRAS) laboratory at the School of Computing has access to several humanoids (NAO) and socially interactive robot platforms (Buddy Pro, Q.BO One, Amy A1), mobile robots (Turtlebot Waffle Pi, Burger), pet-like companion robots and gadgets like AR Epson glasses and Microsoft HoloLens.
Attention model for agent social learning during human-robot interaction.
Successful human-robot interaction requires that robots learn by observing and imitating human behaviour. The theory of learning behaviour through observation is referred to as social learning . Behavioural learning can also be enhanced by the environment itself and through reinforcement (i.e., establishing and encouraging a pattern of behaviour). One important component of such learning is cognitive attention , which deals with the degree to which we notice a behaviour. Cognitive attention renders some inputs more relevant while diminishing others, with the motivation that more focus is needed for the important stimuli in the context of social learning. Attention brings forth positive reinforcement (reward) or negative reinforcement (punishment). If the reward is greater than the punishment, behaviour is more likely to be imitated and reciprocated. In human-robot interaction, attention is crucial for two reasons: 1) to respond or reciprocate the behaviour appropriately during the interaction, and 2) to learn or imitate that behaviour for contingencies. This project is aimed at devising a cognitive attention model of a robot for social learning. The model will include memory, reasoning, language and multi-sensory data processing, i.e., “natural” stimuli during the interaction such as from vision, speech and sensorimotor experience. It can be based on a cognitive architecture approach or alternative computational approaches. The solution should ideally be encompassing multiple aspects of interaction (verbal and non-verbal), but it can also focus on such specific aspects (e.g., visual attention or intention reading).
How can a robot learn skills from a human tutor
Contact: giovanni masala.
The aim of this project is to enhance robot learning from a human tutor, similar to a child who learns from a human teacher. The agent will develop the ability to communicate through natural language from scratch, by interacting with a tutor, recognising their verbal and non-verbal inputs as well as emotions, and, finally, grounding the word meaning in the external environment. The project will start from an existing neuro-cognitive architecture under development [1], based on a Human-like approach to learning, progressively incrementing knowledge and language capabilities through experience and ample exposure, using a corpus based on early language lexicons (preschool literature). The robot will integrate with visuospatial information-processing mechanisms for embodied language acquisition, exploiting affective mechanisms of emotion detection for learning and cognition. The agent will be embodied into a humanoid robot as opposed to a computer or a virtual assistant, to enable real-world interactions with the humans and the external environment, to learn and refine its natural language understanding abilities guided or depending on the teacher’s emotions and visual input (object associations with the words, facial expression, and gestures). Emotions will influence the cognitive attention of the robotic agent, modulating the selectivity of attention on specific tasks, words, and objects, and motivating actions and behaviour.
[1] Golosio B, Cangelosi A, Gamotina O, MASALA GL, A Cognitive Neural Architecture Able to Learn and Communicate through Natural Language. PLoS ONE 10(11): e0140866, 2015.
Note: The Cognitive Robotics and Autonomous Systems (CoRAS) laboratory at the School of Computing has access to several humanoids (NAO) and socially interactive robot platforms (Buddy Pro, Q.BO One, Amy A1), mobile robots (Turtlebot Waffle Pi, Burger), pet-like companion robots and devices like AR Epson glasses and Microsoft HoloLens.
Explainability and Interpretability of Machine/Deep learning techniques in medical imaging
In medicine is very important the acceptance of Machine Learning systems not only in terms of performance but also considering the degree to which a human can understand the cause of a decision. Nowadays, the application of Computer Aided Detection Systems in radiology is often based on Deep Learning Systems thanks to their high performance. In general, more accurate models are less explainable and there is a scientific interest in the field of Explainable Artificial Intelligence, to develop new methods that explain and interpret ML models. There is not a concrete mathematical definition for interpretability or explainability, nor have they been measured by some metric; however, a number of attempts have been made in order to clarify not only these two terms but also related concepts such as comprehensibility. A possible target (but other medical diseases are allowed) of this research is a model to discover the severity of Breast Arterial Calcifications. Breast arterial calcification (BAC) is calcium deposition in peripheral arterioles. There is increasing evidence that BAC is a good indicator of the risk of cardiovascular disease. The accurate and automated detection of BACs in mammograms remains an unsolved task and the technology is far from clinical deployment. The challenging task is to develop an explainable model applicable to BAC detection, able to discriminate between severe and weak BACs in patients’ images.
Autonomous car makes me sick
Contact: palaniappan ramaswamy.
With the rapid advancements in autonomous car technology, we will soon see cars driving on their own on the roads. While some may dread this lack of control in fear of safety, generally it is much safe and the real issue lies elsewhere. Do you know that many of us will feel sick – motion sickness will become a huge problem and there is not much ongoing work to mitigate this situation. In this project, we will explore using transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (taVNS) as an intervention technology. VNS is a medically approved technology for conditions such as epilepsy. But here we will study the non-invasive version of VNS in mitigating the effects of motion sickness. Functional near infra-red spectroscopy (fNIRS) will be utilised to assess the effect of the taVNS on motion sickness. Some prior signal processing knowledge will be required but knowledge on VNS and fNIRS can be gained from the project.
Stress management
The fundamental aspect of human experience is awareness. Combined with the ability to think, imagine and understand it results into the beautiful cosmic play we experience. However, with it comes along a multitude of problems, often illusory in nature – such as stress, anxiety, anger, negativity, etc. It isn’t hard to guess that in such states our behaviour is significantly altered, usually in harmful ways for both – us and the environment. There are techniques such as meditation, music, humour which can help us come back to our “real” senses and feel happier/peaceful again. So the fundamental enquiry would be about what sort of things do help us achieve a happier state, and moreover what’s their impact on both short term and long term brain functioning. This project will study this aim using EEG.
Information Visualisation Directed by Graph Data Mining
Contact: peter rodgers.
Data visualisation techniques are failing in the face of large data sets. This project attempts to increase the scale of graph data that can be visualised by developing data mining techniques to guide interactive visualisation. This sophisticated combining of information visualisation and data mining promises to greatly improve the size of data understandable by analysts, and will advance the state of the art in both disciplines. On successful completion, publications in high quality venues are envisaged. This project is algorithmically demanding, requiring good coding skills. The implementation language is negotiable, but Java, JavaScript or C++ are all reasonable target languages. Data will be derived from publicly available network intrusion or social network data sets. Tasks in this research project include: (1) implementing graph display software and interface. (2) developing project specific visualisation algorithms. (3) integrating graph pattern matching and other graph data mining systems into the visualisation algorithms.
Visual Analytics for Set Data
Visual Analytics is the process of gaining insights into data through combining AI and information visualization. At present, visual analytics for set based data is largely absent. There are a large number of sources for set based data, including social networks as well as medical and biological information. This project will look at producing set mining algorithms which can then be used to support set visualization methods such as Euler/Venn diagrams or Linear diagrams. Firstly, the use of existing data mining methods will produce useful information about sets and the data instances in them. After this effort, more complex algorithms for subset and set isomorphism will be developed to allow for pattern matching within set data. These set mining methods will be integrated into Euler diagram based exploratory set visualization techniques.
Using Soft Nanomembrane Electronics for Home-based Anxiety Monitoring
Contact: jim ang.
Sensor-enhanced virtual reality systems for mental health care and rehabilitation. New immersive technologies, such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are playing an increasingly important role in the digital health revolution. Significant research has been carried out at University of Kent, in collaboration with medical scientists/practitioners, psychiatrists/psychologists, digital artists and material scientists (for novel sensor design and integration with VR). Such projects include designing VR for dementia care, eating disorder therapy, eye disorder therapy and VR-enabled brain-machine interactions. This PhD research can take on the following directions: (1) Co-design of VR for a specific healthcare domains, involving key stakeholders (e.g. patient representatives, clinicians, etc) to understand the design and deployment opportunities and challenges in realistic health contexts. (2) Deploy and evaluate VR prototypes to study the impact of the technologies in the target groups. (3) Design and evaluate machine learning algorithms to analyse behavioural and physiological signals for clinical meaningful information, e.g. classification of emotion, detection of eye movement, etc.
Relevant publications:
[1] M Mahmood, S Kwon, H Kim, Y Kim, P Siriaraya, J Choi, B Otkhmezuri, K Kang, KJ Yu, YC Jang, CS Ang, W Yeo (2021) Wireless Soft Scalp Electronics and Virtual Reality System for Motor Imagery ‐ Based Brain–Machine Interfaces. Advanced Science. 8(19).
[2] S Mishra, K Yu, Y Kim, Y Lee, M Mahmood, R Herbert, CS Ang, W Yeo, J Intarasirisawat, Y Kown, H Lim (2020). Soft, wireless periocular wearable electronics for real-time detection of eye vergence in a virtual reality toward mobile eye therapies. Science Advances. 6 (11), eaay1729.
[3] L Tabbaa, CS Ang, V Rose, P Siriaraya, I Stewart, KG Jenkins, M Matsangidou (2019) Bring the Outside In: Providing Accessible Experiences Through VR for People with Dementia in Locked Psychiatric Hospitals, Proceedings of the CHI 2019 Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems.
[4] M Matsangidou, B Otkhmezuri, CS Ang, M Avraamides, G Riva, A Gaggioli, D Iosif, M Karekla (2020). “Now I can see me” designing a multi-user virtual reality remote psychotherapy for body weight and shape concerns. Human–Computer Interaction. 1-27.
Optimisation of Queries over Virtual Knowledge Graphs
Contact: elena botoeva.
Virtual Knowledge Graphs (also known as Ontology-Based Data Access) provide user-friendly access to Big Data stored in (possibly multiple) data sources, which can be traditional relational ones or more novel ones such as document and triple stores. In this framework an ontology is used as a conceptual representation of the data, and is connected to the data sources by the means of a mapping. User formulates queries over the ontology using a high-level query language like SPARQL; user queries are then automatically translated into queries over the underlying data sources, and the latter are executed by the database engines. Efficiency of the whole approach is highly dependent on optimality of the data source queries. While the technology is quite developed when the underlying data sources are relational, there are still many open problems when it comes to novel data sources, such as MongoDB, graph databases etc. The objective of this PhD project is to design novel techniques for optimising data source queries arising in the context of Virtual Knowledge Graphs.
Heuristics for Scalable Verification of Neural Networks
Due to the success of Deep Learning neural networks are now being employed in a variety of safety-critical applications such as autonomous driving cars and aircraft landing. Despite showing impressive results at various tasks, neural networks are known to be vulnerable (hence, not robust) to adversarial attacks: imperceptible to human eye perturbations to an input can lead to incorrect classification. Robustness verification of neural networks is currently a very hot topic both in academia and industry as neural networks. One of the main challenges in this field is deriving efficient techniques that can verify networks with hundred thousands / millions of neurons in reasonable time, which is not trivial given that exact verification is not tractable (NP- or coNP-complete for ReLU-based neural networks depending on the exact verification problem). Incomplete approaches generally offer better scalability but at the cost of completeness. The aim of the proposed PhD project will be to learn heuristics for efficient verification of neural networks.
Understanding Spiking Neural Networks
Contact: dominique chu.
Spiking Neural Networks (SNN) are brain-like neural networks. Unlike standard rate coding neural networks, signals are encoded in time. This makes them ideal for processing data that has a temporal component, such as time-series data, video or music. Another advantage of SNNs is that there exists neuromorphic hardware that can efficiently simulate SNNs. SNNs are generally thought to be “more powerful” than standard rate coding networks. However, it is not clear precisely in what sense they are more powerful, or what precisely it is that makes them more powerful. The idea of this project is to investigate this claim using a combination of mathematical and computational methods. As such the project will require an interdisciplinary research methodology at the interface between mathematics, computer science and neuroscience. The project would be suitable for a student who wishes to become and expert in an up-and-coming method in artificial intelligence. It has the scope for both theoretical investigations, but will also require implementing neural networks.
Training algorithms for spiking neural networks
Spiking neural networks encode information through the temporal order of the signals. They are more realistic models of the brain than standard artificial neural networks and they are also more efficient in encoding information. Spiking neural networks are therefore very popular in brain simulations. A disadvantage of spiking neural networks is that there are not many efficient training algorithms available. This project will be about finding novel training algorithms for spiking neural networks and to compare the trained networks with standard artificial neural networks on a number of benchmark AI tasks. An important part of this project will be not only to evaluate how well these spiking neural networks perform in relation to standard networks, but also to understand whether or not they are, as is often claimed, more efficient in the sense that they need smaller networks or fewer computing resources. The main approach of the model will be to gain inspiration from existing theories about how the how the human brain develops and learns. These existing theories will then be adapted so as to develop efficient training algorithms. This project will be primarily within AI, but it will also provide the opportunity to learn and apply techniques and ideas from computational neuroscience.
Machine learning systems to improve medical diagnosis
Contact: daniel soria.
Research shows that machine learning methods are extremely useful to discover or identify patterns that can help clinicians to tailor treatments. However, the implementation of those data mining procedures may be challenging because of high dimensional data sets, and the choice of proper machine learning methods may be tricky.
The aim of the research project will be to design and develop new intelligent machine learning systems with high degree of flexibility suitable for disease prediction/diagnosis, that are also easily understandable and explicable to non-experts in the field. Data will be sought from the UK Biobank, to examine whether the selected features are correlated with the occurrence of specific diseases (e.g., breast cancer), whether these relationships persist in the presence of covariates, and the potential role of comorbidities (e.g., obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases) in the assessment of the developed models
How creative are crime-related texts and what does this tell us about cyber crime?
Contact: shujun li , anna jordanous.
The main aim of the PhD project is to investigate if crime-related texts can be evaluated in terms of creativity using automatic metrics. Such a study will help understand how crime-related texts are crafted (by criminals and by automated tools, possibly via a hybrid human-machine teaming approach), how they have evolved over time, how they are perceived by human receivers, and how new methods can be developed to educate people about tactics of cyber criminals. The four tasks of the PhD project will include the following: (1) collecting a large datasets of crime-related texts; (2) developing some objective (automatable) creativity metrics using supervised machine learning, targeted towards evaluating the creativity of crime-related texts (e.g., phishing emails, online hate speech, grooming, cyber bullying, etc.); (3) applying the creativity metrics to the collected data to see how malevolent creativity has evolved over years and for different crimes; (4) exploring the use of generative AI algorithms to create more creative therefore more deceptive crime-related texts.
Computational creativity and automated evaluation
Contact: anna jordanous.
In exploring how computers can perform creative tasks, computational creativity research has produced many systems that can generate creative products or creative activity. Evaluation, a critical part of the creative process, has not been employed to such a great extent within creative systems. Recent work has concentrated on evaluating the creativity of such computational systems, but there are two issues. Firstly, recent work in evaluation of computational creativity has consisted of the system(s) being evaluated by external evaluators, rather than by the creative system evaluating itself, or evaluation by other creative software agents that may interact with that system. Incorporation of self-evaluation into computational creativity systems *as part of guiding the creative process* is also under explored. In this project the candidate will experiment with incorporating evaluation methods into a creative system and analyse the results to explore how computational creativity systems can incorporate self-evaluation. The creative systems studied could be in the area of musical or linguistic creativity, or in a creative area of the student’s choosing. It is up to the student to decide whether to focus on evaluation methods for evaluating the quality of output from a creative system or the creativity of the system itself (or both). The PhD candidate would be required to propose how they would will explore the above scenarios, for a more specific project. Anna is happy to guide students in this and help them develop their research proposal.
Expressive musical performance software
Traditionally, when computational software performs music the performances can be criticised for being too unnatural, lacking interpretation and, in short, being too mechanical. However much progress has been made within the field of expressive musical performance and musical interpretation expression. Alongside these advances have been interesting findings in musical expectation (i.e. what people expect to hear when listening to a piece of music), as well as work on emotions that are present within music and on how information and meaning are conveyed in music. Each of these advances raises questions of how the relevant aspects could be interpreted by a musical performer. Potential application areas for computer systems that can perform music in an appropriately expressive manner include, for example, improving playback in music notation editors (like Sibelius), or the automated performance of music generated on-the-fly for ‘hold’ music (played when waiting on hold during phone calls). Practical work exploring this could involve writing software that performs existing pieces, or could be to write software that can improvise, interpreting incoming sound/music and generating an appropriate sonic/musical response to it in real time.
Brain-like Computer
Contact: frank wang.
The human brain consists of about one billion neurons. Each neuron forms about 1,000 connections to other neurons, amounting to more than a trillion connections. If each neuron could only help store a single memory, running out of space would be a problem. You might have only a few gigabytes of storage space, similar to the space in an iPod or a USB flash drive. Yet neurons combine so that each one helps with many memories at a time, exponentially increasing the brain’s memory storage capacity to something closer to around 2.5 petabytes (or a million gigabytes). The way our brain organizes data may help us manage continuously increasing data, especially in Cloud computing and Big Data. In this project, you are expected to simulate a brain-like computer. Such a computer should be categorised into the unconventional computer group, which is different from traditional Turing machine (with stored programmes) or Von Neumann computer (with an operating system).
My relevant papers: Adaptive Neuromorphic Architecture , Memristor Neural Networks , Grid-Oriented Storage (IEEE Transactions on Computers) .
My relevant keynote talk at Cambridge: Brain and Brain-Inspired Artificial Intelligence )
New Quantum Computer
Contact: frank wang.
Most recently, Frank Wang published an article on Quantum Information Processing (Springer Nature) to report a new quantum computer that can break Landauer’s Bound. Among a number of physical limits to computation, Landauer’s bound limits the minimum amount of energy for a computer to process a bit of information. In light of this study, we may have to presume the demise of this bound despite the many mysteries uncovered with it over the past 60 years.
My relevant papers: Breaking Landauer’s bound in a spin-encoded quantum computer (Springer Nature) , Can We Break the Landauer Bound in Spin-Based Electronics (IEEE Access) .
My relevant keynote talk at Cambridge: A New Quantum Computer Not Bound By Landauer’s Bound )

- Aviation and Astronautical Sciences
- Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence and Data Science
- Construction and Facilities
- Critical Infrastructure
- Cyber & Information Security
- Cyberpsychology
- Engineering
- Engineering Technologies
- Intelligence and Global Security Studies
- Management of Technology
- Occupational Safety and Health
- Uncrewed Systems
- Doctoral Degrees
- Master's Degrees
- Bachelor's Degrees
- Online Programs
- Associate Degrees
- Certificates
- Minor Degrees
- STEM Events
- Webinars and Podcasts
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- Transfer Students
- Military and Veterans
- International Students
- Admissions Counselor
- Capitol Connections
- Accepted Students
- Project Lead the Way
- Builder Culture
- Campus Life
- Clubs and Organizations
- Centers and Labs
- Online Classes
- The Capitol Commitment
- Top Employers
- Co-ops and Internships
- Professional Education
- Find a Mentor
- Career Services
- Capitol Online Job Board
- Recruiters and Employers
- Why Capitol Tech
- At a Glance
- Mission, Vision and Goals
- Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
- Washington, D.C.
- Capitol History
- Capitol Partners
- News and Events
- Visitors/Campus
- Accreditation
- Recognitions & Awards
- Current Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Alumni & Giving
- News & Events
- Capitology Blog
- Maps / Directions

- Degrees and Programs
Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Artificial Intelligence
- Request Information
Earn a doctorate degree in Artificial Intelligence, help lead innovation in a growing industry
The PhD in Artificial Intelligence is centered upon how computers operate to match the human decision making process in the brain. Your research will be led by AI experts with both research and industrial expertise. This emerging subject is starting to attract attention on the wider issues as the IOT and other advanced computer systems work in our lives.
This is a research based doctorate PhD degree where you will be assigned an academic supervisor almost immediately to guide you through your program and is based on mostly independent study through the entire program. It typically takes a minimum of two years but typically three years to complete if a student works closely with their assigned academic advisor. Under the guidance of your academic supervisor, you will conduct unique research in your chosen field before submitting a Thesis or being published in three academic journals agreed to by the academic supervisor. If by publication route it will require original contribution to knowledge or understanding in the field you are investigating.
As your PhD progresses, you move through a series of progression points and review stages by your academic supervisor. This ensures that you are engaged in a process of research that will lead to the production of a high-quality Thesis and/or publications and that you are on track to complete this in the time available. Following submission of your PhD Thesis or accepted three academic journal articles, you have an oral presentation assessed by an external expert in your field.
Why Capitol?
Learn around your busy schedule
Program is 100% online, with no on-campus classes or residencies required, allowing you the flexibility needed to balance your studies and career.
Proven academic excellence
Study at a university that specializes in industry-focused education in technology fields, with a faculty that includes many industrial and academic experts.
Expert guidance in doctoral research
Capitol’s doctoral programs are supervised by faculty with extensive experience in chairing doctoral dissertations and mentoring students as they launch their academic careers. You’ll receive the guidance you need to successfully complete your doctoral research project and build credentials in the field.
Key Faculty

Dissertation Chair
Degree Details
This program may be completed with a minimum of 60 credit hours, but may require additional credit hours, depending on the time required to complete the dissertation/publication research. Students who are not prepared to defend after completion of the 60 credits will be required to enroll in RSC-899, a one-credit, eight-week continuation course. Students are required to be continuously enrolled/registered in the RSC-899 course until they successfully complete their dissertation defense/exegesis.
The PhD program offers 2 degree completion requirement options.
- Dissertation Option: the student will produce, present, and defend a doctoral dissertation after receiving the required approvals from the student’s Committee and the PhD Review Boards.
- Publication Option: the student will produce, present, and defend doctoral research that is published as articles (3 required) in peer reviewed journals identified by the university and the student’s Committee. Students must receive the required approvals from the student’s Committee and the PhD Review Board prior to publication.
Prior Achieved Credits May Be Accepted
Doctor of Philosophy - 60 credits
Program Objectives:
- Students will integrate and synthesize alternate, divergent, or contradictory perspectives or ideas fully within the field of Artificial Intelligence.
- Students will demonstrate advance knowledge and competencies in Artificial Intelligence.
- Students will analyze existing theories to draw data-supported consultations in Artificial Intelligence.
- Students will analyze theories, tools, and frameworks used in Artificial Intelligence.
- Students will execute a plan to complete a significant piece of scholarly work in Artificial Intelligence.
- Students will evaluate the legal, social, economic, environmental, and ethical impact of actions within Artificial Intelligence and demonstrate advance skill in integrating the results in to the leadership decision-making process.
Learning Outcomes:
Upon graduation, graduates will:
- integrate the theoretical basis and practical applications on Artificial Intelligence in to their professional work;
- demonstrate the highest mastery of Artificial Intelligence;
- evaluate complex problems, synthesize divergent/alternative/contradictory perspectives and ideas fully, and develop advanced solutions to Artificial Intelligence challenges; and
- contribute to the body of knowledge in the study of Artificial Intelligence.
Tuition & Fees
Tuition rates are subject to change.
The following rates are in effect for the 2024-2025 academic year, beginning in Fall 2024 and continuing through Summer 2025:
- The application fee is $100
- The per-credit charge for doctorate courses is $950. This is the same for in-state and out-of-state students.
- Retired military receive a $50 per credit hour tuition discount
- Active duty military receive a $100 per credit hour tuition discount for doctorate level coursework.
- Information technology fee $40 per credit hour.
- High School and Community College full-time faculty and full-time staff receive a 20% discount on tuition for doctoral programs.
Find additional information for 2024-2025 doctorate tuition and fees.
When I was comparing multiple universities, Capitol Tech's admissions staff was responsive, helpful, and caring. This was valuable my deciding factor in choosing Capitol Tech.
-Dr. Jason Collins-Baker PhD in Artificial Intelligence
I chose Capitol for its great reputation in the field I am interested in, as well as its flexibility offering a fully Online program that works very well with my work and family commitments. Another reason was its European PhD program, with which I am familiar since I grew up and studied in Europe (Spain), although I currently live in the United States (California).
-Hector Garcia Villa PhD in Artificial Intelligence
Need more info, or ready to apply?
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Scientists use generative AI to answer complex questions in physics
Press contact :, media download.
*Terms of Use:
Images for download on the MIT News office website are made available to non-commercial entities, press and the general public under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license . You may not alter the images provided, other than to crop them to size. A credit line must be used when reproducing images; if one is not provided below, credit the images to "MIT."
Previous image Next image
When water freezes, it transitions from a liquid phase to a solid phase, resulting in a drastic change in properties like density and volume. Phase transitions in water are so common most of us probably don’t even think about them, but phase transitions in novel materials or complex physical systems are an important area of study.
To fully understand these systems, scientists must be able to recognize phases and detect the transitions between. But how to quantify phase changes in an unknown system is often unclear, especially when data are scarce.
Researchers from MIT and the University of Basel in Switzerland applied generative artificial intelligence models to this problem, developing a new machine-learning framework that can automatically map out phase diagrams for novel physical systems.
Their physics-informed machine-learning approach is more efficient than laborious, manual techniques which rely on theoretical expertise. Importantly, because their approach leverages generative models, it does not require huge, labeled training datasets used in other machine-learning techniques.
Such a framework could help scientists investigate the thermodynamic properties of novel materials or detect entanglement in quantum systems, for instance. Ultimately, this technique could make it possible for scientists to discover unknown phases of matter autonomously.
“If you have a new system with fully unknown properties, how would you choose which observable quantity to study? The hope, at least with data-driven tools, is that you could scan large new systems in an automated way, and it will point you to important changes in the system. This might be a tool in the pipeline of automated scientific discovery of new, exotic properties of phases,” says Frank Schäfer, a postdoc in the Julia Lab in the Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) and co-author of a paper on this approach.
Joining Schäfer on the paper are first author Julian Arnold, a graduate student at the University of Basel; Alan Edelman, applied mathematics professor in the Department of Mathematics and leader of the Julia Lab; and senior author Christoph Bruder, professor in the Department of Physics at the University of Basel. The research is published today in Physical Review Letters.
Detecting phase transitions using AI
While water transitioning to ice might be among the most obvious examples of a phase change, more exotic phase changes, like when a material transitions from being a normal conductor to a superconductor, are of keen interest to scientists.
These transitions can be detected by identifying an “order parameter,” a quantity that is important and expected to change. For instance, water freezes and transitions to a solid phase (ice) when its temperature drops below 0 degrees Celsius. In this case, an appropriate order parameter could be defined in terms of the proportion of water molecules that are part of the crystalline lattice versus those that remain in a disordered state.
In the past, researchers have relied on physics expertise to build phase diagrams manually, drawing on theoretical understanding to know which order parameters are important. Not only is this tedious for complex systems, and perhaps impossible for unknown systems with new behaviors, but it also introduces human bias into the solution.
More recently, researchers have begun using machine learning to build discriminative classifiers that can solve this task by learning to classify a measurement statistic as coming from a particular phase of the physical system, the same way such models classify an image as a cat or dog.
The MIT researchers demonstrated how generative models can be used to solve this classification task much more efficiently, and in a physics-informed manner.
The Julia Programming Language , a popular language for scientific computing that is also used in MIT’s introductory linear algebra classes, offers many tools that make it invaluable for constructing such generative models, Schäfer adds.
Generative models, like those that underlie ChatGPT and Dall-E, typically work by estimating the probability distribution of some data, which they use to generate new data points that fit the distribution (such as new cat images that are similar to existing cat images).
However, when simulations of a physical system using tried-and-true scientific techniques are available, researchers get a model of its probability distribution for free. This distribution describes the measurement statistics of the physical system.
A more knowledgeable model
The MIT team’s insight is that this probability distribution also defines a generative model upon which a classifier can be constructed. They plug the generative model into standard statistical formulas to directly construct a classifier instead of learning it from samples, as was done with discriminative approaches.
“This is a really nice way of incorporating something you know about your physical system deep inside your machine-learning scheme. It goes far beyond just performing feature engineering on your data samples or simple inductive biases,” Schäfer says.
This generative classifier can determine what phase the system is in given some parameter, like temperature or pressure. And because the researchers directly approximate the probability distributions underlying measurements from the physical system, the classifier has system knowledge.
This enables their method to perform better than other machine-learning techniques. And because it can work automatically without the need for extensive training, their approach significantly enhances the computational efficiency of identifying phase transitions.
At the end of the day, similar to how one might ask ChatGPT to solve a math problem, the researchers can ask the generative classifier questions like “does this sample belong to phase I or phase II?” or “was this sample generated at high temperature or low temperature?”
Scientists could also use this approach to solve different binary classification tasks in physical systems, possibly to detect entanglement in quantum systems (Is the state entangled or not?) or determine whether theory A or B is best suited to solve a particular problem. They could also use this approach to better understand and improve large language models like ChatGPT by identifying how certain parameters should be tuned so the chatbot gives the best outputs.
In the future, the researchers also want to study theoretical guarantees regarding how many measurements they would need to effectively detect phase transitions and estimate the amount of computation that would require.
This work was funded, in part, by the Swiss National Science Foundation, the MIT-Switzerland Lockheed Martin Seed Fund, and MIT International Science and Technology Initiatives.
Share this news article on:
Press mentions.
Researchers at MIT and elsewhere have developed a new machine-learning model capable of “predicting a physical system’s phase or state,” report Kyle Wiggers and Devin Coldewey for TechCrunch .
Previous item Next item
Related Links
- Frank Schäfer
- Alan Edelman
- Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
- Department of Mathematics
- Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
Related Topics
- Mathematics
- Computer science and technology
- Artificial intelligence
- Computer modeling
- Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL)
- Electrical Engineering & Computer Science (eecs)
Related Articles

Technique could efficiently solve partial differential equations for numerous applications
Computational model captures the elusive transition states of chemical reactions

Explained: Generative AI

From physics to generative AI: An AI model for advanced pattern generation
More mit news.

An expansive approach to making new compounds
Read full story →

Q&A: A graduating student looks back on his MIT experience

Eleven from MIT awarded 2024 Fulbright fellowships

Robotic palm mimics human touch

Trying to make the grade
Janabel Xia: Algorithms, dance rhythms, and the drive to succeed
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
CS50's Introduction to Artificial Intelligence with Python
Learn to use machine learning in Python in this introductory course on artificial intelligence.
Associated Schools

Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences
What you'll learn.
Graph search algorithms
Reinforcement learning
Machine learning
Artificial intelligence principles
How to design intelligent systems
How to use AI in Python programs
Course description
AI is transforming how we live, work, and play. By enabling new technologies like self-driving cars and recommendation systems or improving old ones like medical diagnostics and search engines, the demand for expertise in AI and machine learning is growing rapidly. This course will enable you to take the first step toward solving important real-world problems and future-proofing your career.
CS50’s Introduction to Artificial Intelligence with Python explores the concepts and algorithms at the foundation of modern artificial intelligence, diving into the ideas that give rise to technologies like game-playing engines, handwriting recognition, and machine translation. Through hands-on projects, students gain exposure to the theory behind graph search algorithms, classification, optimization, reinforcement learning, and other topics in artificial intelligence and machine learning as they incorporate them into their own Python programs. By course’s end, students emerge with experience in libraries for machine learning as well as knowledge of artificial intelligence principles that enable them to design intelligent systems of their own.
Enroll now to gain expertise in one of the fastest-growing domains of computer science from the creators of one of the most popular computer science courses ever, CS50. You’ll learn the theoretical frameworks that enable these new technologies while gaining practical experience in how to apply these powerful techniques in your work.
Instructors

David J. Malan

You may also like
Using Python for Research
Take your introductory knowledge of Python programming to the next level and learn how to use Python 3 for your research.
CS50: Introduction to Computer Science
An introduction to the intellectual enterprises of computer science and the art of programming.

CS50's Understanding Technology
This is CS50’s introduction to technology for students who don’t (yet!) consider themselves computer persons.
These computer science terms are often used interchangeably, but what differences make each a unique technology?
Technology is becoming more embedded in our daily lives by the minute. To keep up with the pace of consumer expectations, companies are relying more heavily on machine learning algorithms to make things easier. You can see its application in social media (through object recognition in photos) or in talking directly to devices (like Alexa or Siri).
While artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), deep learning and neural networks are related technologies, the terms are often used interchangeably, which frequently leads to confusion about their differences. This blog post clarifies some of the ambiguity.
The easiest way to think about AI, machine learning, deep learning and neural networks is to think of them as a series of AI systems from largest to smallest, each encompassing the next.
AI is the overarching system. Machine learning is a subset of AI. Deep learning is a subfield of machine learning, and neural networks make up the backbone of deep learning algorithms. It’s the number of node layers, or depth, of neural networks that distinguishes a single neural network from a deep learning algorithm, which must have more than three.
Artificial intelligence or AI, the broadest term of the three, is used to classify machines that mimic human intelligence and human cognitive functions like problem-solving and learning. AI uses predictions and automation to optimize and solve complex tasks that humans have historically done, such as facial and speech recognition, decision-making and translation.
Categories of AI
The three main categories of AI are:
- Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
- Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI)
ANI is considered “weak” AI, whereas the other two types are classified as “strong” AI. We define weak AI by its ability to complete a specific task, like winning a chess game or identifying a particular individual in a series of photos. Natural language processing and computer vision, which let companies automate tasks and underpin chatbots and virtual assistants such as Siri and Alexa, are examples of ANI. Computer vision is a factor in the development of self-driving cars.
Stronger forms of AI, like AGI and ASI, incorporate human behaviors more prominently, such as the ability to interpret tone and emotion. Strong AI is defined by its ability compared to humans. AGI would perform on par with another human, while ASI—also known as superintelligence—would surpass a human’s intelligence and ability. Neither form of Strong AI exists yet, but research in this field is ongoing.
Using AI for business
An increasing number of businesses, about 35% globally, are using AI, and another 42% are exploring the technology. The development of generative AI , which uses powerful foundation models that train on large amounts of unlabeled data, can be adapted to new use cases and bring flexibility and scalability that is likely to accelerate the adoption of AI significantly. In early tests, IBM has seen generative AI bring time to value up to 70% faster than traditional AI.
Whether you use AI applications based on ML or foundation models, AI can give your business a competitive advantage. Integrating customized AI models into your workflows and systems, and automating functions such as customer service, supply chain management and cybersecurity, can help a business meet customers’ expectations, both today and as they increase in the future.
The key is identifying the right data sets from the start to help ensure that you use quality data to achieve the most substantial competitive advantage. You’ll also need to create a hybrid, AI-ready architecture that can successfully use data wherever it lives—on mainframes, data centers, in private and public clouds and at the edge.
Your AI must be trustworthy because anything less means risking damage to a company’s reputation and bringing regulatory fines. Misleading models and those containing bias or that hallucinate (link resides outside ibm.com) can come at a high cost to customers’ privacy, data rights and trust. Your AI must be explainable, fair and transparent.
Machine learning is a subset of AI that allows for optimization. When set up correctly, it helps you make predictions that minimize the errors that arise from merely guessing. For example, companies like Amazon use machine learning to recommend products to a specific customer based on what they’ve looked at and bought before.
Classic or “nondeep” machine learning depends on human intervention to allow a computer system to identify patterns, learn, perform specific tasks and provide accurate results. Human experts determine the hierarchy of features to understand the differences between data inputs, usually requiring more structured data to learn.
For example, let’s say I showed you a series of images of different types of fast food—“pizza,” “burger” and “taco.” A human expert working on those images would determine the characteristics distinguishing each picture as a specific fast food type. The bread in each food type might be a distinguishing feature. Alternatively, they might use labels, such as “pizza,” “burger” or “taco” to streamline the learning process through supervised learning.
While the subset of AI called deep machine learning can leverage labeled data sets to inform its algorithm in supervised learning, it doesn’t necessarily require a labeled data set. It can ingest unstructured data in its raw form (for example, text, images), and it can automatically determine the set of features that distinguish “pizza,” “burger” and “taco” from one another. As we generate more big data, data scientists use more machine learning. For a deeper dive into the differences between these approaches, check out Supervised versus Unsupervised Learning: What’s the Difference?
A third category of machine learning is reinforcement learning, where a computer learns by interacting with its surroundings and getting feedback (rewards or penalties) for its actions. And online learning is a type of ML where a data scientist updates the ML model as new data becomes available.
To learn more about machine learning, check out the following video:
As our article on deep learning explains, deep learning is a subset of machine learning. The primary difference between machine learning and deep learning is how each algorithm learns and how much data each type of algorithm uses.
Deep learning automates much of the feature extraction piece of the process, eliminating some of the manual human intervention required. It also enables the use of large data sets, earning the title of scalable machine learning . That capability is exciting as we explore the use of unstructured data further, particularly since over 80% of an organization’s data is estimated to be unstructured (link resides outside ibm.com).
Observing patterns in the data allows a deep-learning model to cluster inputs appropriately. Taking the same example from earlier, we might group pictures of pizzas, burgers and tacos into their respective categories based on the similarities or differences identified in the images. A deep-learning model requires more data points to improve accuracy, whereas a machine-learning model relies on less data given its underlying data structure. Enterprises generally use deep learning for more complex tasks, like virtual assistants or fraud detection.
Neural networks, also called artificial neural networks or simulated neural networks, are a subset of machine learning and are the backbone of deep learning algorithms. They are called “neural” because they mimic how neurons in the brain signal one another.
Neural networks are made up of node layers—an input layer, one or more hidden layers and an output layer. Each node is an artificial neuron that connects to the next, and each has a weight and threshold value. When one node’s output is above the threshold value, that node is activated and sends its data to the network’s next layer. If it’s below the threshold, no data passes along.
Training data teach neural networks and help improve their accuracy over time. Once the learning algorithms are fined-tuned, they become powerful computer science and AI tools because they allow us to quickly classify and cluster data. Using neural networks, speech and image recognition tasks can happen in minutes instead of the hours they take when done manually. Google’s search algorithm is a well-known example of a neural network.
As mentioned in the explanation of neural networks above, but worth noting more explicitly, the “deep” in deep learning refers to the depth of layers in a neural network. A neural network of more than three layers, including the inputs and the output, can be considered a deep-learning algorithm. That can be represented by the following diagram:
Most deep neural networks are feed-forward, meaning they only flow in one direction from input to output. However, you can also train your model through back-propagation, meaning moving in the opposite direction, from output to input. Back-propagation allows us to calculate and attribute the error that is associated with each neuron, allowing us to adjust and fit the algorithm appropriately.
While all these areas of AI can help streamline areas of your business and improve your customer experience, achieving AI goals can be challenging because you’ll first need to ensure that you have the right systems to construct learning algorithms to manage your data. Data management is more than merely building the models that you use for your business. You need a place to store your data and mechanisms for cleaning it and controlling for bias before you can start building anything.
At IBM we are combining the power of machine learning and artificial intelligence in our new studio for foundation models, generative AI and machine learning, watsonx.ai™.
Get the latest tech insights and expert thought leadership in your inbox.
Learn more about watsonx.ai
Get our newsletters and topic updates that deliver the latest thought leadership and insights on emerging trends.

The Colorado Sun
Telling stories that matter in a dynamic, evolving state.
Colorado becomes first state with law regulating potential consumer harms of artificial intelligence

Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Original Reporting
The Trust Project

A contentious bill adding guardrails for companies that use artificial intelligence to make big consumer decisions was signed into law Friday by Gov. Jared Polis.
But Polis also took the extra step of writing a letter to lawmakers about his reservations.
“This bill is among the first in the country to attempt to regulate the burgeoning artificial industry on such a scale,” the Democrat wrote. “I appreciate the sponsors’ interest in preventing discrimination and prioritizing consumer protection as Colorado leads in this space.”
But, he added, “I am concerned about the impact this law may have on an industry that is fueling critical technological advancements across our state for consumers and enterprises alike. Government regulation that is applied at the state level in a patchwork across the country can have the effect to tamper innovation and defer competition in an open market.”
There was speculation at the Capitol that Polis may veto the bill, but he said earlier this month that he felt comfortable with the measure because it won’t go into effect for a few years, leaving time for tweaks.
“I’m confident that will leave ample time for any improvements that need to be made prior to it becoming effective,” he told reporters.

Senate Bill 205 aims to reduce discrimination consumers could face when applying for a job, a loan, housing or other services when a machine-based AI system is used to make a “consequential decision.” While other laws exist to protect people of any race, color, gender or other characteristic from intentional discrimination, this law regulates AI systems regardless of intent. A concern is that generative AI systems popularized today by companies like OpenAI don’t always provide accurate answers.
The new law doesn’t go into effect until Feb. 1, 2026.
House Bill 1468 , which was also passed by the General Assembly this year, requires the legislature’s Joint Technology Committee to grow its Artificial Intelligence Impact task force to 17 members from 15 and expand its mission to study issues around AI and technology bias. The panel now must include someone who is an expert in generative AI and a person who is an advocate for individuals who have historically experienced discrimination by artificial intelligence and facial recognition technologies
Many in the Colorado technology community spoke out against Senate Bill 205, including the Colorado Technology Association, which represents more than 300 technology companies in the state.
☀️ READ MORE
As new laws are proposed, colorado companies share how they use ai to make business better, colorado bill to regulate generative artificial intelligence clears its first hurdle at the capitol, in “not quite dead geniuses” diverse life forms create an unusual alliance.
CTA shared a letter with The Sun that it sent to Polis on Thursday that called the lawmaking “rushed” with “very little opportunity for the industry to pressure test and provide input.”
CTA remained concerned by the broad definition of AI, which could describe all software, and an amendment allowing appeals by consumers who received an adverse decision. Since consumers won’t know if a decision was the result of algorithmic discrimination, they could appeal any that they don’t like “simply because it was adverse.” That would be a burden on companies and a disincentive for developers to do business in Colorado.
“Many of these requirements are vague and very broad, and no one seems to have a good understanding of what their application will look like in practice,” the letter said.
The 1,450-member Rocky Mountain AI Interest Group , which was started after OpenAI’s Chat-GPT4 launched an AI chatbot that responded to questions much like a human, also spoke out against the bill as it made its way through the legislature.

“RMAIIG members are still against the law and we’re disappointed it was passed and signed,” Dan Murray, the organization’s founder, said in an email. “We are hopeful, however, that legislators will robustly engage with Colorado’s vibrant AI/tech/startup community over the next 1-2 years to ensure the bill won’t dampen the important tech economy in our state.”
Consumer advocates wanted even greater consumer protections because AI-based discrimination was already occurring — including background checks and resume screening and adjusting auto insurance premiums .
“There are definitely still parts that I don’t like, including what I consider very weak enforcement provisions, a small business exemption that I think is way too broad, and a trade secret exemption that still leaves quite a bit of room for companies to make mischief,” said Matt Scherer, senior policy counsel for the Center for Democracy & Technology , a nonprofit that fights to advance civil rights and liberties in the digital age. “That said, I understand why the bill landed where it did on each of those things, and I think that this bill is as good as I could hope for given that it basically has its origins in model legislation written by an HR tech company .”
Officials with the HR technology company, Workday, said they had engaged with lawmakers in Connecticut and other states but not Colorado. Colorado’s bill was influenced by Connecticut’s, according to one of the bill’s main sponsors, Senate Majority Leader Robert Rodriguez, D-Denver.
But the bill in Connecticut failed, reportedly after a veto threat from the state’s Democratic governor.
In an email, Chandler Morse, Workday’s head of public policy, congratulated Polis on the bill’s passage as “a first-in-the-country approach to regulating AI that balances both trust and innovation and aligns with Workday’s vision for a regulatory framework supporting responsible AI.”.
“While we agree with the Governor about there being room for improvement before the law is implemented,” he said, “Senate Bill 205 represents a critical first step with which we hope other states will align for a much-needed common approach to AI regulation.”
When Colorado’s new law banning cellphone use while driving goes into effect — and when it can lead to a traffic stop
At least 14 people died on colorado slopes this ski season, concentration of real estate agents in colorado springs is 3 times higher than the national rate, type of story: news.
Based on facts, either observed and verified directly by the reporter, or reported and verified from knowledgeable sources.
Tamara Chuang Business & Technology Reporter
Tamara Chuang writes about Colorado business and the local economy for The Colorado Sun, which she cofounded in 2018 with a mission to make sure quality local journalism is a sustainable business. Her focus on the economy during the pandemic... More by Tamara Chuang

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1) Top Artificial Intelligence Topics for Research. a) Natural Language Processing. b) Computer vision. c) Reinforcement Learning. d) Explainable AI (XAI) e) Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) f) Robotics and AI. g) AI in healthcare. h) AI for social good.
PhD research topics in Artificial Intelligence (AI) refer to specific areas of study and investigation that scholars explore to advance the understanding and development of smart machines. These topics delve into various aspects of AI, aiming to solve complex problems and create innovative solutions using computer systems.
Get 1-On-1 Help. If you're still unsure about how to find a quality research topic, check out our Research Topic Kickstarter service, which is the perfect starting point for developing a unique, well-justified research topic. A comprehensive list of research topics ideas in the AI and machine learning area. Includes access to a free webinar ...
The 2023 PhD topics in Artificial Intelligence highlight the dynamic field's growth and promise for revolutionizing industries and improving quality of life. The research emphasizes ethical AI, addressing bias, fairness, and transparency. Advancements in natural language processing make AI more accessible and intuitive.
The Machine Learning (ML) Ph.D. program is a fully-funded doctoral program in machine learning (ML), designed to train students to become tomorrow's leaders through a combination of interdisciplinary coursework, and cutting-edge research. Graduates of the Ph.D. program in machine learning are uniquely positioned to pioneer new developments in ...
Here some of the recent Research Topics, Artificial Intelligence and Machine learning - Recent Trands. How AI and ML can aid healthcare systems in their response to COVID-19. Machine learning and artificial intelligence in haematology. Tackling the risk of stranded electricity assets with machine learning and artificial intelligence.
The online Doctor of Engineering in Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning is a research-based doctoral program. The program is designed to provide graduates with a solid understanding of the latest AI&ML techniques, as well as hands-on experience in applying these techniques to real-world problems. ... Topics include intelligent model ...
An example of a deep neural network is RankBrain which is one of the factors in the Google Search algorithm. 3. Reinforcement Learning. Reinforcement Learning is a part of Artificial Intelligence in which the machine learns something in a way that is similar to how humans learn. As an example, assume that the machine is a student.
Robust and trusted artificial intelligence research hinges on the foundation of Open Science practices and the meticulous curation of data which PLOS takes pride in highlighting and endorsing thanks to our rigorous standards and commitment to Openness. As a leading publisher in the field, these articles showcase research that has influenced ...
A Ph.D. in AI is the highest awarded degree in the field of artificial intelligence. It involves several years of study and research, culminating in a project, thesis, or dissertation of original academic research that expands our knowledge of AI. The main focus of a Ph.D. in AI is research. Students spend about six years researching one topic.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. Our research covers a wide range of topics of this fast-evolving field, advancing how machines learn, predict, and control, while also making them secure, robust and trustworthy. Research covers both the theory and applications of ML. This broad area studies ML theory (algorithms, optimization, etc ...
Some of the topics covered by Artificial Intelligence studies are: computer vision, natural language processing, speech recognition, software engineering principles, autonomous systems, machine learning, image analysis, signal and sound processing, ethics and social implications of AI, etc.
PhD research topics in artificial intelligence can vary dramatically depending on your interests. Whether you choose your own PhD topic or join an existing PhD project, you could find yourself pursuing research in the areas of: data management and data science. computer vision and multimedia computation. machine learning and data mining.
Exploring the Power of AI and ML in Smart Grids: Advancements, Applications, and Challenges. A nexus for research in core and applied AI areas, this journal focuses on the enormous expansion of AI into aspects of modern life such as finance, law, medicine, agriculture, and human learning.
Costs and Funding. Annual tuition fees for PhDs in Artificial Intelligence are typically around £4,000 to £5,000 for UK/EU students. Tuition fees for international students are usually much higher, typically around £25,000 per academic year. A variety of scholarships and funding support options are available for postgraduate study.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is one of the hottest conversation topics in recent years and one of the most disruptive emerging areas of academic study and research. ... or join an existing research project. There are currently eight PhD courses in artificial intelligence in the UK, although this number is almost certainly due to increase in the ...
Topic 1: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Supply Chain Management- An Assessment of the Present and Future Role Played by AI in Supply chain Process: A Case of IBM Corporation in the US. Research Aim: This research aims to find the present, and future role AI plays in supply chain management. It will analyze how AI affects various components of ...
The Artificial Intelligence in Medicine (AIM) PhD track, newly developed by the Department of Biomedical Informatics (DBMI) at Harvard Medical School, will enable future academic, clinical, industry, and government leaders to rapidly transform patient care, improve health equity and outcomes, and accelerate precision medicine by creating new AI technologies that reason across massive-scale ...
1 of 4. Top. Find the best PhD programmes in the field of Artificial Intelligence from top universities worldwide. Check all 80 programmes.
The best universities for artificial intelligence PhDs are Arizona State University, Syracuse University, and Drexel University. They have some of the best artificial intelligence laboratories, high acceptance rates, and the right networks of people. Below is a detailed list of the best schools to get a PhD in Artificial Intelligence.
The Department of Biomedical Informatics offers a PhD in Biomedical Informatics in the areas of Artificial Intelligence in Medicine (AIM) and Bioinformatics and Integrative Genomics (BIG).. The AIM PhD track prepares the next generation of leaders at the intersection of artificial intelligence and medicine. The program's mission is to train exceptional computational students, harnessing ...
Here are some suggested topics for PhD projects from our group members. These projects are merely suggestions and illustrate the broad interests of the research group. ... The project would be suitable for a student who wishes to become and expert in an up-and-coming method in artificial intelligence. It has the scope for both theoretical ...
The PhD in Artificial Intelligence is centered upon how computers operate to match the human decision making process in the brain. Your research will be led by AI experts with both research and industrial expertise. This emerging subject is starting to attract attention on the wider issues as the IOT and other advanced computer systems work in ...
Talk by David W. Bates, Professor in the Department of Rhetoric at UC Berkeley and Author of An Artificial History of Natural Intelligence: Thinking with Machines from Descartes to the Digital Age, with commentary by Merve Tekgurler, PhD student in History at Stanford.
1. Artificial Narrow AI. Artificial Narrow Intelligence, also known as Weak AI (what we refer to as Narrow AI), is the only type of AI that exists today. Any other form of AI is theoretical. It can be trained to perform a single or narrow task, often far faster and better than a human mind can. However, it can't perform outside of its defined ...
Topics View All →. Explore: Machine learning ... a postdoc in the Julia Lab in the Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) and co-author of a paper on this approach. Joining Schäfer on the paper are first author Julian Arnold, a graduate student at the University of Basel; Alan Edelman, applied mathematics professor ...
The American Association of Artificial Intelligence was formed in the 1980s to fill that gap. The organization focused on establishing a journal in the field, holding workshops, and planning an annual conference. The society has evolved into the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) and is "dedicated to advancing ...
This course will enable you to take the first step toward solving important real-world problems and future-proofing your career. CS50's Introduction to Artificial Intelligence with Python explores the concepts and algorithms at the foundation of modern artificial intelligence, diving into the ideas that give rise to technologies like game ...
Artificial intelligence or AI, the broadest term of the three, is used to classify machines that mimic human intelligence and human cognitive functions like problem-solving and learning. AI uses predictions and automation to optimize and solve complex tasks that humans have historically done, such as facial and speech recognition, decision-making and translation.
Colorado becomes first state with law regulating potential consumer harms of artificial intelligence. Many in the technology industry said Senate Bill 205 is too broad. A task force is underway to guide the rollout of the law, which would go into effect February 2026. Tamara Chuang 12:48 PM MDT on May 18, 2024 Updated 12:30 PM MDT on May 20, 2024.