- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Five tips to set yourself apart.
Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or elevate your stature within your organization. But while there are plenty of good speakers in the world, you can set yourself apart out by being the person who can deliver something great over and over. Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired together are more memorable); don’t underestimate the power of your voice (raise and lower it for emphasis); give your audience something extra (unexpected moments will grab their attention); rehearse (the best speakers are the best because they practice — a lot).
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center

9 Differences between Presentation and Public Speaking?
By: Author Shrot Katewa

People often confuse presentation with public speaking. After all, both require you to speak in front of an audience. But, there are subtle and important differences between a presentation and public speaking. It is better to understand this difference so that we can prepare accordingly and get the best results!
So, in this article, I will be sharing with you a few key differences between a presentation and public speaking. So, let’s get started!
1. Communication Format
Traditionally, Public Speaking is giving a speech face to face to a live audience. It comprises various forms of spoken communication skills ranging from imparting a speech or debate to motivational speaking to storytelling to Ted talks to entertaining such as a standup comedian.
However, with technological advancements, such as video conferencing, the concept evolved. In modern times, public speaking can be defined as any form of speaking between the speaker and the audience.
On the other hand, a presentation comprises spoken and visual communication. It may be a slide show or an audiovisual presentation. The topic is presented not only verbally but also by displaying content in writing supported with charts, tables, images, or text.
2. Skills Required

Public speaking is the act of presenting a topic verbally. It is often used as a medium to transfer information, but most importantly, to motivate and encourage the audience.
That said, the only input that goes into public speaking is the speaker, his or her verbal talent and style of communication, all elements displayed collectively as a package.
Whereas presentation requires the presenter to combine verbal and written content and to work with visual presentation programs such as Microsoft power point or Google slides.
3. Time for Preparation
Public speaking is more of an art than just a skill. While you are expected to do a good job when you have time at hand, but a good orator is the one who has the skills to resonate with the audience even when he or she is put on the spot!
At times public speaking may be spontaneous such as extempore. Extempore is a speech that is delivered without preparation. The speaker is given a topic on the spot and is given a minute or two to prepare on the same.
Compared with this presentation is a prepared act. Before the presentation, the presenter is ready with all the required information and facts intertwined in a pre-defined sequence. More often than not, a presentation is on a specific topic and the presenter is given ample amount of time for preparation.
4. Creativity Index
Public speaking is an art that is creative. It may be formal or informal in nature. The style of delivery of every individual is different from others. Every speaker possesses few unique qualities and has complete freedom to design his or her communication style.
Presentation is usually a formal offering. It is a form or act that has to be delivered according to certain pre-set instructions and guidelines. The presenter has limited scope and freedom to divert and add creativity to the presentation. For instance, the most common scope of limitation is the amount of time available to deliver a presentation.
5. Purpose of the Speaker

One of the forms of public speaking is debate. In a debate, every participant speaks either in favor or against the topic. The participant has to convince the audience to agree with his stance – whether right or wrong!
Most forms of public speaking work in a similar fashion. The purpose of the speaker is to convince the audience to agree with the stance of the speaker.
However, in a presentation, a topic is presented comprehensively. The topic is explained in detail highlighting various related points such as advantages, disadvantages, improvement areas, resolution plan, targets, or rewards. The primary aim of the presenter is to educate the audience on the topic, and perhaps drive a call to action.
6. Elements for Effectiveness
Effective public speaking requires the speaker to deliver so efficiently that at the end the audience stands out thrilled, amazed, and persuaded.
An impressive delivery secures more marks than intelligent content. A number of elements such as spontaneity, presence of mind, voice modulations, facial expressions, eye contact, or body language go into the making of an effective speaker. For example, in a singing reality show a participant is judged not only on the basis of his voice quality but also on the way he presents himself while singing, popularly known as the X factor.
Unlike public speaking, a presentation focuses more on content rather than on communication style. The key responsibility of the presenter is to provide the audience with detailed information on the topic covering all its aspects.
An example that may be quoted is that of an author narrating a story through a kid’s YouTube video. In the video, the author narrates the story using various voice modulations to make it entertaining for the kids and to make them feel every emotion of the characters. This case portrays the modern form of public speaking where face-to-face interaction has been eliminated.
At the same time the author presents the story using text, pictures, animations or effects in the video to make the kids visualize the characters and understand the flow of the story.
7. Size of the Audience
In public speaking, a speaker can address an audience ranging from a group of few people to a large gathering with thousands or millions of people. An interview wherein two people are in conversation with each other or a motivational speaker addressing a huge crowd may both be considered examples of public speaking.
On the other hand, a presentation is made to a defined set of people organized together in a small or mid-sized group with a limited number of members. To cite an example, students presenting a case study to the classmates or an advertising agency presenting to its prospective client.
Most large forms of presentations won’t usually exceed an audience that can fill an auditorium often limited to a few hundreds. Whereas, for public speaking, the audience can be a large gathering of thousands of people in a ground!
8. Type of Audience

Generally speaking, the type of audience present during a public speaking event is usually a group or a mass of unknown people. The speaker is neither acquainted with the audience nor related to it in any way. For instance, when a spiritual speaker addresses a group of people he is not familiar with the members of the audience.
As against it, in case of presentation the audience comprises a set of people who are familiar with the speaker. Citing the example of a business presentation, say a supervisor presenting to his team the road map to be followed to meet the annual targets, the presenter and every individual in the audience are connected to each other in professional capacity.
9. Motive of the Audience
In public speaking, the people listening to the speaker do not have a common vested interest and every individual in the audience has his own personal motive to fulfill. To elaborate, using the prior example of a spiritual speaker, it is possible that one individual may have resorted to spirituality to overcome his condition of depression and another individual may be listening to the speaker to learn how to control his anger.
Contrary to the above, in the case of a presentation, all the members participating in the presentation and the speaker have a common vested interest towards which they all intend to work collectively. Drawing from the prior example of a business presentation, the supervisor and all the team members have a common goal of achieving the annual targets.
More Related Topics
- How Much Do Public Speaking Classes Cost? A Quick Guide!
- What is the Difference Between TED and TEDx?
- Why Can’t People Give Presentations? [And How to Get Over it!]
- Toastmasters – Is it Worth it? A Comprehensive Guide!
- Does Taking Xanax Help Before a Presentation? The SURPRISING Truth!

- PRESENTATION SKILLS
What is a Presentation?
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Presentation Skills:
- A - Z List of Presentation Skills
- Top Tips for Effective Presentations
- General Presentation Skills
- Preparing for a Presentation
- Organising the Material
- Writing Your Presentation
- Deciding the Presentation Method
- Managing your Presentation Notes
- Working with Visual Aids
- Presenting Data
- Managing the Event
- Coping with Presentation Nerves
- Dealing with Questions
- How to Build Presentations Like a Consultant
- 7 Qualities of Good Speakers That Can Help You Be More Successful
- Self-Presentation in Presentations
- Specific Presentation Events
- Remote Meetings and Presentations
- Giving a Speech
- Presentations in Interviews
- Presenting to Large Groups and Conferences
- Giving Lectures and Seminars
- Managing a Press Conference
- Attending Public Consultation Meetings
- Managing a Public Consultation Meeting
- Crisis Communications
- Elsewhere on Skills You Need:
- Communication Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Teams, Groups and Meetings
- Effective Speaking
- Question Types
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
The formal presentation of information is divided into two broad categories: Presentation Skills and Personal Presentation .
These two aspects are interwoven and can be described as the preparation, presentation and practice of verbal and non-verbal communication.
This article describes what a presentation is and defines some of the key terms associated with presentation skills.
Many people feel terrified when asked to make their first public talk. Some of these initial fears can be reduced by good preparation that also lays the groundwork for making an effective presentation.
A Presentation Is...
A presentation is a means of communication that can be adapted to various speaking situations, such as talking to a group, addressing a meeting or briefing a team.
A presentation can also be used as a broad term that encompasses other ‘speaking engagements’ such as making a speech at a wedding, or getting a point across in a video conference.
To be effective, step-by-step preparation and the method and means of presenting the information should be carefully considered.
A presentation requires you to get a message across to the listeners and will often contain a ' persuasive ' element. It may, for example, be a talk about the positive work of your organisation, what you could offer an employer, or why you should receive additional funding for a project.
The Key Elements of a Presentation
Making a presentation is a way of communicating your thoughts and ideas to an audience and many of our articles on communication are also relevant here, see: What is Communication? for more.
Consider the following key components of a presentation:
Ask yourself the following questions to develop a full understanding of the context of the presentation.
When and where will you deliver your presentation?
There is a world of difference between a small room with natural light and an informal setting, and a huge lecture room, lit with stage lights. The two require quite different presentations, and different techniques.
Will it be in a setting you are familiar with, or somewhere new?
If somewhere new, it would be worth trying to visit it in advance, or at least arriving early, to familiarise yourself with the room.
Will the presentation be within a formal or less formal setting?
A work setting will, more or less by definition, be more formal, but there are also various degrees of formality within that.
Will the presentation be to a small group or a large crowd?
Are you already familiar with the audience?
With a new audience, you will have to build rapport quickly and effectively, to get them on your side.
What equipment and technology will be available to you, and what will you be expected to use?
In particular, you will need to ask about microphones and whether you will be expected to stand in one place, or move around.
What is the audience expecting to learn from you and your presentation?
Check how you will be ‘billed’ to give you clues as to what information needs to be included in your presentation.
All these aspects will change the presentation. For more on this, see our page on Deciding the Presentation Method .
The role of the presenter is to communicate with the audience and control the presentation.
Remember, though, that this may also include handing over the control to your audience, especially if you want some kind of interaction.
You may wish to have a look at our page on Facilitation Skills for more.
The audience receives the presenter’s message(s).
However, this reception will be filtered through and affected by such things as the listener’s own experience, knowledge and personal sense of values.
See our page: Barriers to Effective Communication to learn why communication can fail.
The message or messages are delivered by the presenter to the audience.
The message is delivered not just by the spoken word ( verbal communication ) but can be augmented by techniques such as voice projection, body language, gestures, eye contact ( non-verbal communication ), and visual aids.
The message will also be affected by the audience’s expectations. For example, if you have been billed as speaking on one particular topic, and you choose to speak on another, the audience is unlikely to take your message on board even if you present very well . They will judge your presentation a failure, because you have not met their expectations.
The audience’s reaction and therefore the success of the presentation will largely depend upon whether you, as presenter, effectively communicated your message, and whether it met their expectations.
As a presenter, you don’t control the audience’s expectations. What you can do is find out what they have been told about you by the conference organisers, and what they are expecting to hear. Only if you know that can you be confident of delivering something that will meet expectations.
See our page: Effective Speaking for more information.
How will the presentation be delivered?
Presentations are usually delivered direct to an audience. However, there may be occasions where they are delivered from a distance over the Internet using video conferencing systems, such as Skype.
It is also important to remember that if your talk is recorded and posted on the internet, then people may be able to access it for several years. This will mean that your contemporaneous references should be kept to a minimum.
Impediments
Many factors can influence the effectiveness of how your message is communicated to the audience.
For example background noise or other distractions, an overly warm or cool room, or the time of day and state of audience alertness can all influence your audience’s level of concentration.
As presenter, you have to be prepared to cope with any such problems and try to keep your audience focussed on your message.
Our page: Barriers to Communication explains these factors in more depth.
Continue to read through our Presentation Skills articles for an overview of how to prepare and structure a presentation, and how to manage notes and/or illustrations at any speaking event.
Continue to: Preparing for a Presentation Deciding the Presentation Method
See also: Writing Your Presentation | Working with Visual Aids Coping with Presentation Nerves | Dealing with Questions Learn Better Presentation Skills with TED Talks
Module 7: Public Speaking
What is public speaking, learning outcomes.
- Discuss key characteristics of public speaking
Public speaking is, simply, an oral presentation or speech delivered to a live audience. It is generally a formal or staged event— although impromptu speeches are a common occurrence—and can be a defining career moment. For example, you may think you’re attending a client meeting only to find yourself called on to explain a procedural or technical point being discussed. Or you may be sitting in a management meeting thinking you are just there to observe when you are asked to elaborate on an aspect of the supporting research and analysis or defend your recommendations.
Impromptu Speaking
Although impromptu speaking isn’t the focus of this module, it is worth noting that this type of speaking is something Toastmaster members train for on an ongoing basis using a technique called “Table Topics.” For more on this technique, read A Table Topics Workout: The Power Packed Exercise for Stretching Your Brain .
Executive presentation coach Peter Khoury has reverse-engineered the characteristics of great speakers for over fifteen years. Combining his findings with scientific research on leadership, he’s distilled this research into the following 9 characteristics of effective public speakers: [1]
Confidence Passion Practice, don’t memorize Speak in a natural voice Authenticity Keep it Short and Sweet Connect with your Audience Paint a Picture through Storytelling Repetition
Like computer failure and natural disasters, finding yourself in a situation requiring public speaking skills is not a matter of whether it will happen but when it will happen. Given the potential career impact, you need to prepare accordingly.
Practice Question
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/9-characteristics-highly-effective-public-speakers-peter-khoury/ ↵
- What is Public Speaking?. Authored by : Nina Burokas. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution


Ace the Presentation

The Ultimate Guide to Public Speaking
Knowing how to communicate effectively is fundamental for both our personal and professional lives.
Speaking in Public is challenging for many people, as some are timid and insecure, or simply require more experience in speaking in front of others .
In this article, you will learn about the basics of public speaking , common speaking challenges that people have, how to address those challenges, and key tips on how to structure your delivery to make your speeches more successful.
Let us start our Guide to Public Speaking with a bit of history. Further along, we will address the importance of communication elements, and we will also bring relevant information on how to use language and structure a public presentation.
The Art of Public Speaking – Origin and Meaning
Oratory or public speaking originated with the need people had to defend themselves from the attacks of the tyrants of Syracuse, thereby meaning a way of setting social justice and a ticket to freedom of speech.
According to Lopes (2000), the art of public speaking comes from Greek origins; the city of Athens was the most crucial center of oratory studies both in rhetoric and eloquence.
In the 5th century BC, with concern for the mastery of the verbal expression arose the oratory in Greece. At that time, ordinary citizens would be usurped of their property and other rights. Only the clergy and high society people would be allowed to reverse social and political situations.
However, with Aristotle, public speaking found fertile ground for its development in his most ancient work on oratory entitled “The Art of Rhetoric .”
Aristotle book refers, respectively:
- The line of argument to be followed by the speaker;
- To teach how the listener learns the ideas;
- The exposition of the structure of the discourse and its parts.
What is Public Speaking?
Public Speaking is an exposition of ideas prepared in an organized way, and that should always be composed of some essential characteristics concerning the organization of thought and reasoning.
Bloch et al. (2002) point out that public speaking expresses what we feel, communicates what we think, and exposes the facts as effectively as possible.
Your audience can be from the child to the most evolved scientist who can absorb what you say.
7 Elements of Speech Communication
1. emitter/ speaker.
The emitter is the person who wants to deliver a message to a particular group of people or individuals; in public speaking, the issuer is known as the speaker.
Factors to be considered:
- Motivation – The presentation can be made to provide/obtain information, to convince the group about a new idea, to “sell” a service, to present results, or to persuade about an argument;
- Credibility – The degree of acceptance of the message shall be directly proportional to the knowledge of the speaker on the subject;
- Performance – Correct use of verbal expression and non-verbal communication with others.
2. Receiver/ Audience
The person or group of persons situated at the other end of the communication chain receives the message and interprets it internally, manifesting this interpretation externally.
The receiver goes the other way, that is, part of the signifiers until reaching the intention of signification.
Therefore, the mapping of characteristics of the target public shall include all attempts to obtain as much information as possible about it: number of persons present, sex, age, race, profession or function in the undertaking, training, level of education, knowledge of the subject to be dealt with, relevant background and expectations or needs.
3. Target/ Content
The content or target is the link between speaker and audience; the object of communication; translation of ideas, objectives, and intentions; the message shall be organized in terms of:
- Content – refers to what will be said regarding a specific subject, and the first step is to define the purpose of the presentation;
- After that, having in mind the main characteristics of the audience and the time available , one should select the most important ideas that will be presented, that is, prioritize the relevant arguments.
4. Structure
The structure concerns the organization of the message. A well-organized message presents everyone its elements connected logically with each other;
When organizing the content, it is essential to divide the presentation into three parts: i) introduction (attractive and inviting), ii) a body (concise, clear and coherent), and a conclusion (emphatic and brief);
The codes are a set of rules combined to generate understanding; the audience will identify this sign system, performing the decoding operation, only if its repertoire is typical of the issuer.
Language is the code most used to establish communication since it is the social agreement of language made by a particular society.
The code is also a set of signs and signals used to transmit the message: verbal language, non-verbal language, sign language, colors.
If the speaker fails one of these elements, the message may not be delivered properly, and there is no communication.
Therefore, it is vital that you thoroughly analyze your target audience to make sure that they understand the set of codes you choose.
6. Channel
The channel functions as a “vein of circulation” of the message, which means the pathway chosen by the sender/speaker to which the message is handed.
When making a presentation, the message can be transmitted in different ways: visual gestures, body movements, facial expressions, posture, tone of voice, variation of height and vocal intensity, and manipulation of objects.
Whenever possible, it is crucial to know the location of the presentation in advance; in this way, some amendments it deems necessary can be removed.
By getting to know the environment you will be delivering your speech, you can plan each movement in the room, reduce the anxiety, the correct position of the equipment, the use of the microphone, etc.
“When troops move, it is essential to know the conditions of the land first; when you know distances, you can draw up direct or indirect attack plans. The understanding of where the battle will be braked shall indicate where they should concentrate or subdivide the forces. ” Sun Tau
The 7 Basic Elements of Public Speaking

An Easy Guide to All 15 Types of Speech

10 Public Speaking Tips for First-Timers

5 Things to Consider when Structuring and Delivering a Public Speaking
1. who is the speaker.
The speaker must know his natural communication behavior, if he speaks little, likes to communicate, has the habit of reading, is reserved or outgoing, so the speaker will know when his linguist skills are or will need to be further explored.
For speech skills to be improved, it is necessary to stimulate the habit of reading, producing texts and performing interpretations of written materials.
Reading aloud and recording the production of speech may also help to know about one’s evolution, deficiencies, and potentialities.
2. Who is the audience?
The speaker refers to the listeners/audience of the message, so the success of the speech is determined by the listener’s understanding or by the action that the experience will generate.
To guarantee that the message is accurately delivered to the audience, it is necessary to adjust the speech to the level of instruction and the current situation of the listener.
And that is determined by how you present the content starting from the structure to the tools you use to deliver it; also, the audience can become more attentive to receive the message have some prior knowledge of the subject.
3. What is the message being delivered?
Refers to the content and type of speech; however, the content is always involved in the service of a determined intention. For a purpose, the communication becomes meaningless if it fails to convey the subject.
4. Why is this message important?
What drives you and makes this message crucial to this crowd you wish to face and deliver it?
The Cruciality of a message has to do with the impression made to the listener after the message is transmitted. This effect to be produced when a speech is concluded must directly connect with the action intended to generate as a response.
Refers to the channel through which the message will be transmitted, being auditory, visual, or both, if it will be necessary to use more audiovisual resources, including microphone, multimedia, and others.
To know which resources will be most effective in the relevance of the message transmission takes into account, among other things, the distance between speaker and listener.
Inappropriate channel selection can lead to ineffective communication. The speaker should ask himself if the message he wishes to spread would be better understood if it was written or spoken, don’t forget about visual impacts.
Did you know that pauses during a speech create a feeling of suspense? A more attentive environment is built from a short crease, and the audience gets ready to receive what you will be saying, so using it share a key message from the content you have prepared.
- Being able to emphasize what one wants to say, providing explanative intonation can also manifest surprise, admiration, or irony;
- The fluency and speed of speech present logical thinking and chained ideas, the use of more than one question mark in an interrogative phrase characterizes a question difficult to answer.
Thus, the use of these resources with balance and variety can confer the speaker’s naturalness, expressiveness, and attitude with the text emitted of greater understanding of the subject by the listener.
Imagine a doctor (speaker) who uses technical language to explain how a symptom a patient (listener) has may turn into a dangerous disease if not taken care of and because he doesn’t master the language (content), he leaves there confused and not understanding how important it is that action is taken.
In such a case, the speaker:
1) Did not assess who the receiver of the message was;
2) Did not adapt the content to its listener;
3) Did not evaluate the intention of the message.
- Its essential point is to assess whether the receiver understands the message;
- Check, whenever possible, by asking questions about what you exposed until that moment or asking him to recall the point’s central issue.

Public Speaking – Fears, blockages, and barriers
Blockages, barriers, tension, and nervousness will always exist, either for beginners or those who already have experience in public speaking.
There’s no getting better if we are not aware of these public speaking barriers .
5 Reasons why you Fear Public Speaking
Unsuccessful experiences .
You may have an experience of public speaking and for some reason didn’t go as expected, which creates in you the false idea that will always give wrong.
The past is the past and does it right; you have to know the wrong steps; remember that people you may know as great speakers did poorly before that would be the example of Mahatma Gandhi.
In 1889, while working as a young lawyer, Mahatma Gandhi froze before a judge and ran out of court, feeling humiliated . “My head was spinning, and it felt like the whole court was doing the same,” Gandhi wrote in a letter.
He called this feeling “the terrible strain of public speaking .” And that’s kept him from even talking at dinners between friends.
When Gandhi decided to dedicate himself to a cause and wanted to convey a message he considered essential profoundly, Gandhi found the motivation he needed to overcome fear.
Lack of Experience
When you do not practice something or do it a few times, you don’t create space for your brain to build learnings, preventing the development of skill, in this case, public speaking.
Cognitive psychologists say that the learning process is a systematic and active process that associates new information to the knowledge we already have on a subject, exploratory and creative.
The billionaire Warren Buffett was terrified of speaking in public early in his career. He attempted to take an oratory course, but he gave up out of fear; however, he was very aware that it would be essential to succeed.
Then, in his second trial, Buffett won a diploma that he boasts with great pride; in his documentary “Becoming Warren Buffet,” Buffet stated:
“In my office, you will not see the degree I got at the University of Nebraska, and you will not see the master’s degree I took at Columbia University. But you’ll see the certificate I received from the Dale Carnegie Course.” Warren Buffett
Perfectionism
Many psychologists describe perfectionism as the need to set high and rigid standards for oneself; a perfectionist follows a series of conduct requirements, created especially for himself, and makes constant self-evaluations.
Excess self-criticism when delivering public speaking may prevent you from seeing any action you do with empathy and can also degrade your self-esteem, which is crucial to standing in front of a podium.
Social anxiety corresponds to the difficulty the person presents in interacting socially, for example, speaking in public. It comes from the fear of being judged, feeling humiliated, or that other person may notice their weaknesses.
Symptoms of anxiety and nervousness are typical when they arise before or during a job interview or in a presentation.
However, when symptoms arise in various situations, especially when you are around other people, it can be a sign of social anxiety disorder, and the person should seek psychological treatment.
Negative self-image
Your self-image is basically how you see yourself, and it’s your internal photography that shows itself to others. And how do you measure the impact of your image on those who hear you?
If you see yourself as someone who can’t do an outstanding performance in public, you probably can’t do it.
If perhaps you said something wrong at the time of school and your classmates laughed at you, you may today be afraid that others will laugh again at what you have to say.
Note that these problems directly influence your ability to speak in public. And that if you change the way you look at yourself, you will significantly improve your potential to express yourself in large groups.
3 Key benefits of Assertive Communication: Easy Tips to Develop it!

11 Best Body Language Tips For Engaging Presentations (#11 is Underrated)

Growing up, we were always taught how we should have manners while talking to others and that there were some things we could not do in front of people like sprawling or even putting our elbows on the table while eating because it was rude. In the examples above, the rudeness comes from gestures, not…
How to Become a Confident Public Speaker – 6 Tips

Ever wondered what it feels like to command a room filled with people just with the way you speak? How to Become a Confident Public Speaker ? No, it’s not a gift (in case you are wondering); rather, it takes practice and time for you to master the art of public speaking. This simply means…
3 Strategies to reduce fear before and during a Speech
Focus on breathing.
A simple exercise to improve breathing is standing with your legs ajar in a posture that bodyweight is proportionally distributed in your two legs.
Place your hands on the waist and fill the lungs with air slowly, then release the air slowly with your mouth half-open.
Repeat the exercise several times until you feel relaxed; this is a good exercise before starting a presentation.
Practice in a safe place (home or with friends)
One of the most effective ways to deal with the fear of public speaking is to practice a presentation in advance. Set the central points of your speech and set up a schematic to remember them all. After that, practice your exposure alone as often as necessary.
Prefer low lights
To reduce anxiety or any fear during public speaking, you can choose to dark the place a little bit to mitigate your excitement and keep your mind clear, and the audience focused and comfortable.
There is one more benefit to having dim lighting; the public laughs more.
Comedians prefer a “poorly lit space,” Peter Mcgraw and Joel Warner described in their book The Humor Code, which seems to “help people feel more protected and thus less inhibited in laughing.”
5 Tips to Win a Crowd Over when Speaking in Public
One of the concerns of a speaker must be to please the audience. If you’ve done a previous study of the type of audience you’ll talk to, and you’ll undoubtedly know how to behave. Meet some challenges to get the viewer’s attention:
1. Be Truthful and Care about the Audience Experience
Do everything so that your professional qualifications and experiences do not demonstrate exhibitionism. Greet everyone with courtesy and issue honesty and professionalism.
Another way of putting this would be – try your best to be charismatic.
2. Use a simple language
Your first strategy is to employ simple language so that your text becomes clear. The choice of words can create intimacy with the receiver and make your speech more pleasurable.
Beforehand knowing the audience to whom you will perform, it will be possible to plan how you will speak and what words to use.
It is essential to mark the vocabulary to be used considering the minor present education level.
3. Instill curiosity in the audience
Cite a fact or ask a question that makes them curious; when it’s time to deliver a speech, always give them new data to support the fresh perspective you want them to get to know.
4. Turn your text into a story
Generally, we will deal with matters related to reality, to a fact-specific, experienced, or relevant to society. In such a case, turn your theme into a story of your or other people and structure it with the same narrative techniques.
See the problem in the subject, what will give life, and arguments to your text. Count as the facts occur, its most critical points, and then conclude.
People usually enjoy storytelling, especially if they are personal experiences related to a subject that is concerning to them it turns the presentation more engaging to them.
5. Know when to change strategies
Notice the extent to which you are pleasing or not if you observe any tiredness movement (people getting up, yawning, talking).
Change your strategy, be more succinct, and instill the participation of all.
Changes in intonation in the course of speech and the use of audiovisual or dynamic resources, too, are usually good strategies to maintain the audience attentive to your presentation.
Public speaking can be difficult if you get familiarized with pitching ideas and sharing your notes and research with unknown people.
However, once you get in it and allow yourself to fail, keep learning and be open to practice and share the knowledge, you learn it quickly.
References and Further Reading
10 Tips for Improving Your Public Speaking Skills.
AcethePresentation. 13 ways to overcome public speaking anxiety.
AcethePresentation. AmadeBai, Emidio. What Makes A Bad Public Speaker? Top 10 Worst Traits To Avoid
High Spark. The Ultimate Public Speaking Guide To Impress Any Audience.
Similar Posts

A 9-Step Practical Guide On How To Analyze A Speech – Speech Analysis of I have A Dream Speech as an Example
A speech, as we all know, is a vocal opinion of a speaker’s stand. Speeches are usually used as an effective tool for rallying support, conveying opinion, as well as influencing the thoughts of others (usually the audience) to accept or agree with the thoughts of the Speaker. For a speech to achieve its goal,…

The 4 Methods or Types of Speech Delivery
On a daily basis, people use several types of speech delivery to connect with others, influence decisions, and motivate change without realizing which occasions a specific method of speech delivery should be used. Today we will talk about 4 types of speech delivery that are commonly used and sometimes happen almost unnoticed. Manuscript Speech Memorized…

Top 41 Famous Speeches IN HISTORY
Speeches have been empowering people for a very long time. They have uplifted the spirits of people and educated them on various topics. There are some famous speeches in history that are considered as one of the best. Why speeches have such a profound effect on people and become timeless? There are many speeches that do…

How to Write a Memorable Speech – 8 Tips
Do you want to learn how to write a memorable speech which will stay in the heart of your audience for quite a long time? Do you intend to address a large number of people, and leave a lasting and memorable impression? Not sure if the words will capture the undivided attention of your audience?…

19+ Public Speaking Techniques and Skills (#18 is Gold)
The art of public speaking has become one of the most sought-after skills in the 21st century. There was indeed a time when oratory skills were exclusive only to political pundits and social critics, but for the better 21st century, this skill will be a requisite tool for the big business. What are public speaking…

15 Ideas To Make A Speech Unique, Memorable & Inspiring
Are you often called to speak in front of others? If yes, then the art of making your speech unique, memorable, and inspiring is something you should be able to do with little or no effort. This is important because listening to a yawn-inducing and lifeless speech is one of the worst things your audience…

The skill you need now: presentation literacy
Share this idea.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)

TED curator Chris Anderson discusses the transformative power of speaking to an audience from the heart.
You’re nervous, right?
Stepping out onto a public stage and having hundreds of pairs of eyes turned your way is terrifying. You dread having to stand up in a company meeting and present your project. What if you get nervous and stumble over your words? What if you completely forget what you were going to say? Maybe you’ll be humiliated! Maybe your career will crater! Maybe the idea you believe in will stay buried forever!
But guess what? Almost everyone has experienced the fear of public speaking. Indeed, surveys that ask people to list their top fears often report public speaking as the most widely selected, ahead of snakes, heights — and even death.
How can this be? There is no tarantula hidden behind the microphone. You have zero risk of plunging off the stage to your death. The audience will not attack you with pitchforks. Then why the anxiety?
It’s because there’s a lot at stake — not just the experience in the moment, but in our longer-term reputation. How others think of us matters hugely. We are profoundly social animals. We crave each other’s affection, respect and support. Our future happiness depends on these realities to a shocking degree. And we sense that what happens on a public stage is going to affect these social currencies, for better or worse. But with the right mindset, you can use your fear as an incredible asset. It can be the driver that will persuade you to prepare for a talk properly.
That’s what happened when Monica Lewinsky (TED Talk: The price of shame ) came to the TED stage. For her, the stakes couldn’t have been higher. Seventeen years earlier, she had been through the most humiliating public exposure imaginable, an experience so intense it almost broke her. Now she was attempting a return to a more visible public life, to reclaim her narrative. But she was not an experienced public speaker, and she knew that it would be disastrous if she messed up. She told me:
“Nervous is too mild a word to describe how I felt. More like . . . Gutted with trepidation. Bolts of fear. Electric anxiety. If we could have harnessed the power of my nerves that morning, I think the energy crisis would have been solved. Not only was I stepping out onto a stage in front of an esteemed and brilliant crowd, but it was also videotaped, with the high likelihood of being made public on a widely viewed platform. I was visited by the echoes of lingering trauma from years of having been publicly ridiculed. Plagued by a deep insecurity I didn’t belong on the TED stage. That was the inner experience against which I battled.”
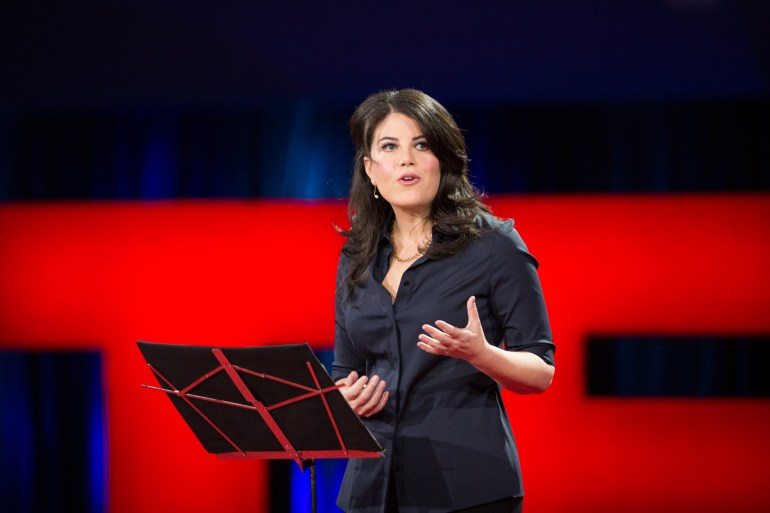

And yet Monica found a way to turn that fear around. Her talk won a standing ovation at the event, rocketed to a million views within a few days and earned rave reviews online. It even prompted a public apology to her from a longtime critic, feminist author Erica Jong.
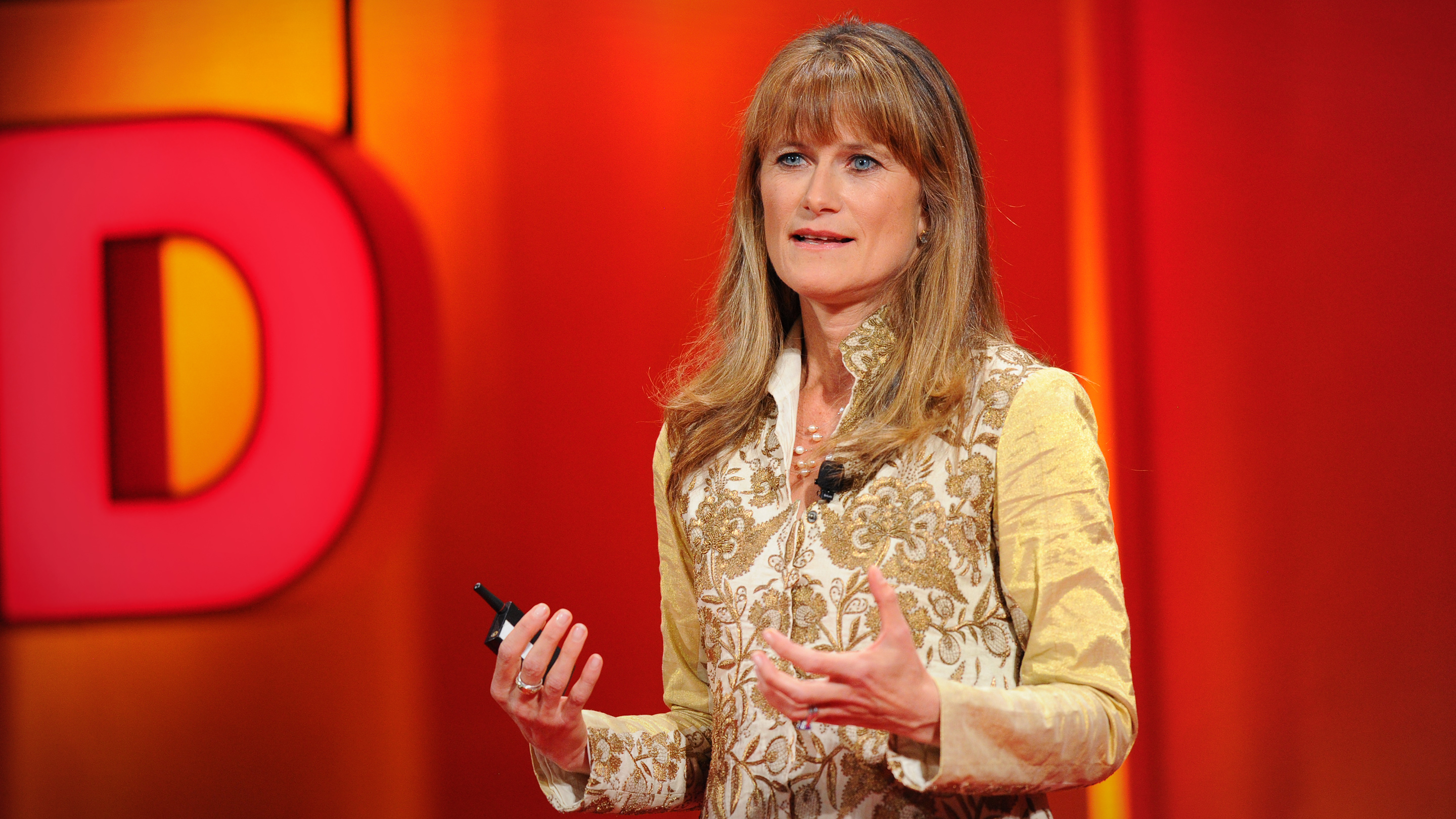
The brilliant woman I am married to, Jacqueline Novogratz (TED Talk: Inspiring a life of immersion ), was also haunted by fear of public speaking. In school, at college and into her twenties, the prospect of a microphone and watching eyes was so scary it was debilitating. But she knew that to advance her work fighting poverty, she’d have to persuade others, and so she just began forcing herself to do it. Today she gives scores of speeches every year, often earning standing ovations.

Indeed, everywhere you look, there are stories of people who were terrified of public speaking but found a way to become really good at it, from Eleanor Roosevelt to Warren Buffett to Princess Diana, who was known to all as “shy Di,” but found a way to speak informally in her own voice, and the world fell in love with her.
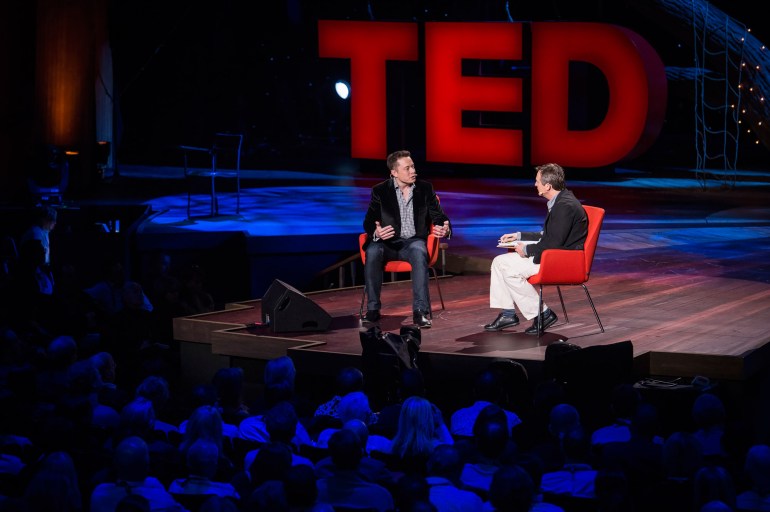

If you can get a talk right, the upside can be amazing. Take the talk that entrepreneur Elon Musk (TED Talk: The mind behind Tesla, SpaceX, SolarCity … ) gave to SpaceX employees on August 2, 2008. Musk was not known as a great public speaker. But that day, his words marked an important turning point for his company. SpaceX had already suffered two failed launches. This was the day of the third launch, and everyone knew failure could force the company’s closure. The Falcon rocket soared off the launch pad, but right after the first stage fell away, disaster struck. The spacecraft exploded. The video feed went dead. Some 350 employees had gathered and, as described by Dolly Singh, the company’s head of talent acquisition, the mood was thick with despair. Musk emerged to speak to them. He told them they’d always known it would be hard, but that despite what had happened, they had already accomplished something that day that few nations, let alone companies, had achieved. They had successfully completed the first stage of a launch and taken a spacecraft to outer space. They simply had to pick themselves up and get back to work. Here’s how Singh described the talk’s climax:
Then Elon said, with as much fortitude and ferocity as he could muster after having been awake for like 20+ hours by this point, “For my part, I will never give up and I mean never.” I think most of us would have followed him into the gates of hell carrying suntan oil after that. It was the most impressive display of leadership that I have ever witnessed. Within moments the energy of the building went from despair and defeat to a massive buzz of determination as people began to focus on moving forward instead of looking back.
That’s the power of a single talk. You might not be leading an organization, but a talk can still open new doors or transform a career.
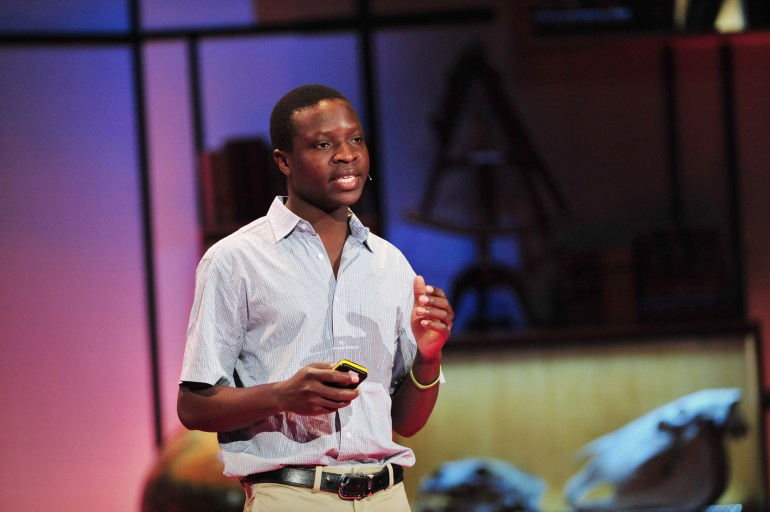
TED speakers have told us delightful stories of the impact of their talks. Yes, there are sometimes book and movie offers, higher speaking fees and unexpected offers of financial support. But the most appealing stories are of ideas advanced, and lives changed. Young Malawian inventor William Kamkwamba’s inspiring talk about building a windmill in his village as a 14-year-old (TED Talk: How I harnessed the wind ) sparked a series of events that led to him being accepted into an engineering program at Dartmouth College.

Here’s a story from my own life: When I first took over leadership of TED in late 2001, I was reeling from the near collapse of the company I had spent 15 years building, and I was terrified of another huge public failure. I had been struggling to persuade the TED community to back my vision for TED, and I feared that it might just fizzle out. Back then, TED was an annual conference in California, owned and hosted by a charismatic architect named Richard Saul Wurman, whose larger-than-life presence infused every aspect of the conference. About 800 people attended every year, and most of them seemed resigned to the fact that TED probably couldn’t survive once Wurman departed. The TED conference of February 2002 was the last to be held under his leadership, and I had one chance and one chance only to persuade TED attendees that the conference would continue just fine. I had never run a conference before, however, and despite my best efforts at marketing the following year’s event, only 70 people had signed up for it.
Early on the last morning of that conference, I had 15 minutes to make my case. And here’s what you need to know about me: I am not naturally a great speaker. I say “um” and “you know” far too often. I will stop halfway through a sentence, trying to find the right word to continue. I can sound overly earnest, soft spoken, conceptual. My quirky British sense of humor is not always shared by others.
I was so nervous about this moment, and so worried that I would look awkward on the stage, that I couldn’t even bring myself to stand. Instead I rolled forward a chair from the back of the stage, sat on it and began.
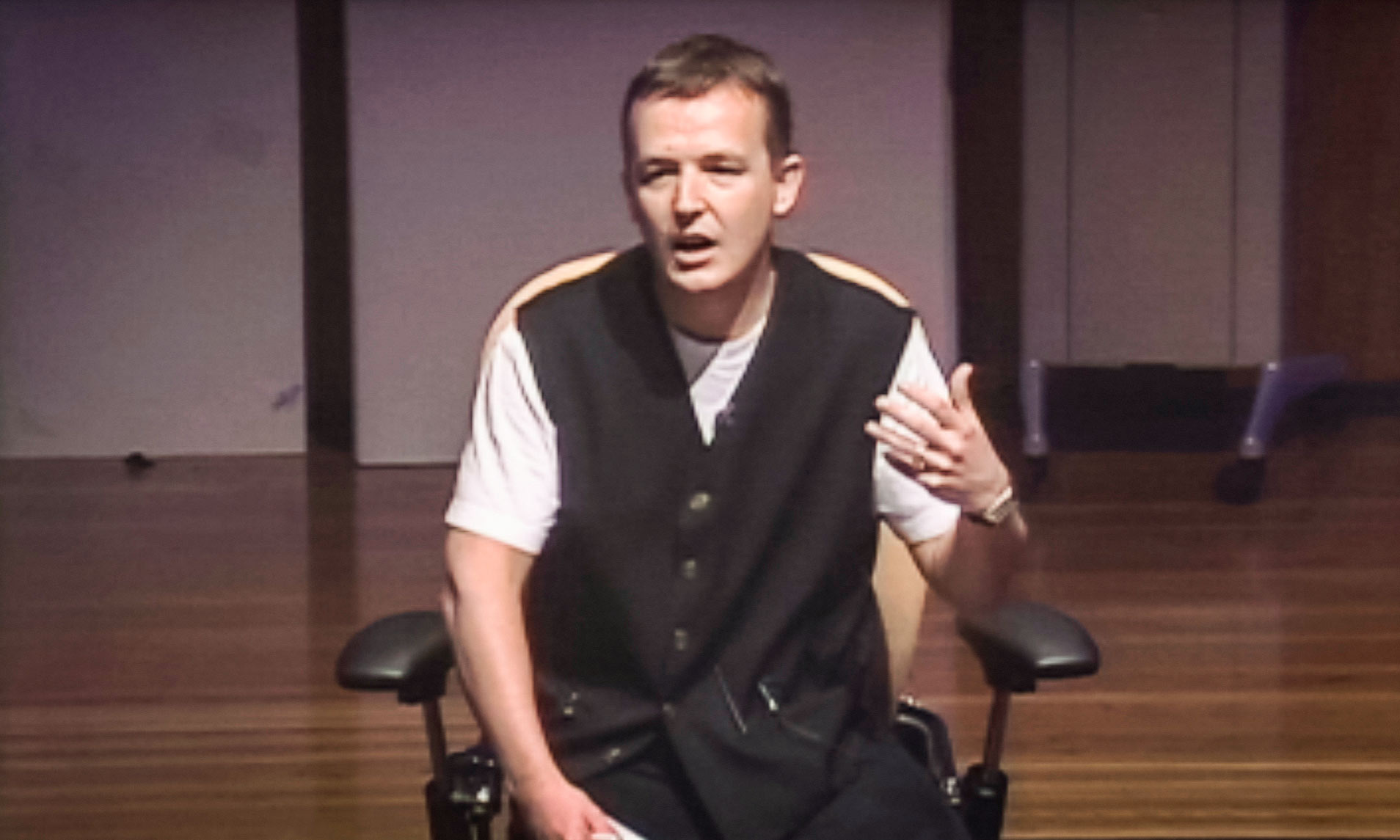

I look back at that talk now and cringe — a lot. If I were critiquing it today, there are a hundred things I would change, starting with the wrinkly white T-shirt I was wearing. And yet … I had prepared carefully what I wanted to say, and I knew there were at least some in the audience desperate for TED to survive. If I could just give those supporters a reason to get excited, perhaps they would turn things around. Because of the recent dotcom bust, many in the audience had suffered business losses as bad as my own. Maybe I could connect with them that way?
I spoke from the heart, with as much openness and conviction as I could summon. I told people I had just gone through a massive business failure. That I’d come to think of myself as a complete loser. That the only way I’d survived mentally was by immersing myself in the world of ideas. That TED had come to mean the world to me — that it was a unique place where ideas from every discipline could be shared. That I would do all in my power to preserve its best values. That, in any case, the conference had brought such intense inspiration and learning to us that we couldn’t possibly let it die … could we?
Oh, and I broke the tension with an apocryphal anecdote about France’s Madame de Gaulle and how she shocked guests at a diplomatic dinner by expressing her desire for “a penis.” In England, I said, we also had that desire, although there we pronounced it happiness and TED had brought genuine happiness my way.
To my utter amazement, at the end of the talk, Jeff Bezos, the head of Amazon, who was seated in the center of the audience, rose to his feet and began clapping. And the whole room stood with him. It was as if the TED community had collectively decided, in just a few seconds, that it would support this new chapter of TED after all. And in the 60-minute break that followed, some 200 people committed to buying passes for the following year’s conference, guaranteeing its success.
If that 15-minute talk had fizzled, TED would have died, four years before ever putting a talk on the Internet.
No matter how little confidence you might have today in your ability to speak in public, there are things you can do to turn that around. Facility with public speaking is not a gift granted at birth to a lucky few. It’s a broad-ranging set of skills. There are hundreds of ways to give a talk, and everyone can find an approach that’s right for them and learn the skills necessary to do it well.
Several years ago, TED’s content director, Kelly Stoetzel, and I went on a global tour in search of speaking talent. In Nairobi, Kenya, we met Richard Turere, a 12-year-old Maasai boy who had come up with a surprising invention. His family raised cattle, and one of the biggest challenges was protecting them at night from lion attacks. Richard had noticed that a stationary campfire didn’t deter the lions, but walking around waving a torch did seem to work. The lions were apparently afraid of moving lights! Richard had somehow taught himself electronics by messing around with parts taken from his parents’ radio. He used that knowledge to devise a system of lights that would turn on and off in sequence, creating a sense of movement. It was built from scrapyard parts — solar panels, a car battery and a motorcycle indicator box. He installed the lights and — presto! — the lion attacks stopped. News of his invention spread and other villages wanted in. Instead of seeking to kill the lions as they had done before, they installed Richard’s “lion lights.” Both villagers and pro-lion environmentalists were happy.
It was an impressive achievement but, at first glance, Richard certainly seemed an unlikely TED speaker. He stood hunched over in a corner of the room, painfully shy. His English was halting, and he struggled to describe his invention coherently. It was hard to imagine him on a stage in California in front of 1,400 people, slotted alongside Sergey Brin and Bill Gates.
But Richard’s story was so compelling that we went ahead anyway and invited him to come speak at TED (TED Talk: My invention that made peace with lions ). In the months before the conference, we worked with him to frame his story — to find the right place to begin, and to develop a natural narrative sequence. Because of his invention, Richard had won a scholarship to one of Kenya’s best schools, where he had the chance to practice his TED Talk several times in front of a live audience. This helped build his confidence to the point where his personality could shine through.
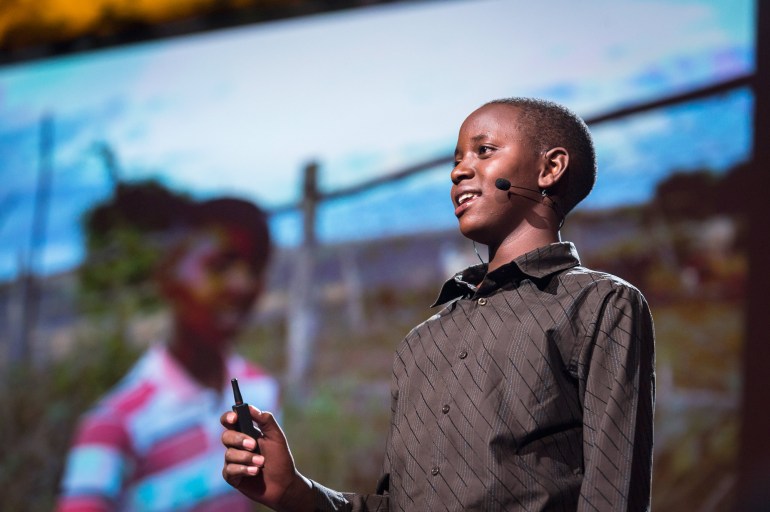

He got on an airplane for the first time in his life and flew to Long Beach, California. As he walked onto the TED stage, you could tell he was nervous, but that only made him more engaging. As Richard spoke, people were hanging on his every word, and every time he smiled, the audience melted. When he finished, people just stood and cheered.
Richard’s tale can encourage us all to believe we might be able to give a decent talk. Your goal is not to be Winston Churchill or Nelson Mandela. It’s to be you. If you’re a scientist, be a scientist; don’t try to be an activist. If you’re an artist, be an artist; don’t try to be an academic. If you’re just an ordinary person, don’t try to fake some big intellectual style; just be you. You don’t have to raise a crowd to its feet with a thunderous oration. Conversational sharing can work just as well. In fact, for most audiences, it’s a lot better. If you know how to talk to a group of friends over dinner, then you know enough to speak publicly.
And technology is opening up new options. We live in an age where you don’t have to be able to speak to thousands of people at a time to have an outsized impact. It could just be you talking intimately to a video camera, and letting the Internet do the rest.
Presentation literacy isn’t an optional extra for the few. It’s a core skill for the twenty-first century. It’s the most impactful way to share who you are and what you care about. If you can learn to do it, your self-confidence will flourish, and you may be amazed at the beneficial impact it can have on your success in life, however you might choose to define that.
If you commit to being the authentic you, I am certain that you will be capable of tapping into the ancient art that is wired inside us. You simply have to pluck up the courage to try.
Excerpted from the book TED Talks: The Official TED Guide to Public Speaking by Chris Anderson. © 2016 by Chris Anderson. Reproduced by permission of Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. All rights reserved.

About the author
Chris Anderson is the curator of TED.
- book excerpt
- Chris Anderson
- Jacqueline Novogratz
- Monica Lewinsky
- presentation literacy
- public speaking
- Richard Turere
- William Kamkwamba
TED Talk of the Day

How to make radical climate action the new normal

6 ways to give that aren't about money

A smart way to handle anxiety -- courtesy of soccer great Lionel Messi

How do top athletes get into the zone? By getting uncomfortable

6 things people do around the world to slow down

Creating a contract -- yes, a contract! -- could help you get what you want from your relationship

Could your life story use an update? Here’s how to do it

6 tips to help you be a better human now

How to have better conversations on social media (really!)

Let’s stop calling them “soft skills” -- and call them “real skills” instead

3 strategies for effective leadership, from a former astronaut

There’s a know-it-all at every job — here’s how to deal

Storytelling is a powerful communication tool — here’s how to use it, from TED

What’s the difference between shyness and introversion? And how can companies help introverts thrive? A Q&A with Susan Cain

Before your next presentation or speech, here's the first thing you must think about

Gallery: When reading is an act of daring
- Public Speaking
- Skills & Tools
Public speaking skills refer to the talent of effectively addressing an audience. Whether it is in front of a group of people you already know or a crowd of complete strangers, your ability to communicate to them with clarity and confidence is known as your public speaking skills.
There may or may not be an opportunity for interaction between the speaker and audience. The basic difference, however, between a casual talk and public speaking is that the latter is more purposeful and meant for celebratory, entertainment, influencing, or informative purposes.
Why is public speaking important
Good public speaking skills can have a huge impact on your career for the following reasons:
- Demonstrates your knowledge . You are always at your best when you can articulate your thoughts clearly and effectively. Public speaking skills help you do exactly that. After all, the true worth of the knowledge you possess can only be realized when you can show and apply it.
- Demonstrates your confidence . Not only does public speaking increase your knowledge during the process of preparation but it also develops and demonstrates your confidence. Whether you are interviewing for a job or hoping for a promotion, your confidence is what will make you stand out among other candidates.
- Helps you lead better . The higher you climb up the career ladder, the greater will be the number of people you shall have to lead. As a result, the need for public speaking skills and the confidence pertinent to it also increases, making it one of the determining characteristic when considering someone for promotion.
How to improve public speaking skills
Following are some helpful tips for improving your public speaking skills:
- Prepare with practice . Once you have prepared a presentation or speech by giving it a logical flow and making it more vibrant with the addition of examples, stories, and visually appealing props, only then your true preparation begins. If you are wondering what that means, remember that practice is the key to preparation. Practice your speech/presentation alone or seek to speak in front of other people until you can speak fluidly with confidence and comfort. This may sometimes require you to tweak your words during practice but it’s preferable to do so in practice instead of doing so at the occasion where you intend to take the mike.
- Accentuate your strengths . Analyze yourself as a public speaker and identify your true strengths and weaknesses. Most of us tend to imitate other public speakers who are popular amongst the crowd. However, the best way is to be yourself and focus on your own strengths. For instance, you might have a good sense of humor that helps in grabbing attention of the crowd, you may be an interesting story teller, or you may be good at clearly explaining complex ideas. Whichever is your strength, utilize it wisely to keep your audience paying attention.
- Keep your ears and eyes open to feedback . Although, all sorts of public speaking do not involve direct interaction between the speaker and his audience, there are various ways in which audience is able to provide feedback. If the audience cannot speak their opinion out loud, as a speaker you should be able to look for nonverbal cues such as the body language or facial expressions of the audience. The feedback, thus, provided by the audience can prove to be a helpful guide in improving one’s public speaking skills.
Job profiles that require this skill

Not yet a member? Sign Up
join cleverism
Find your dream job. Get on promotion fasstrack and increase tour lifetime salary.
Post your jobs & get access to millions of ambitious, well-educated talents that are going the extra mile.
First name*
Company name*
Company Website*
E-mail (work)*
Login or Register
Password reset instructions will be sent to your E-mail.

Introduction to Public Speaking
Criteria for success.
- You keep your audience engaged by speaking clearly and strategically altering your delivery.
- You enhance your message through deliberate movements while minimizing nervous tics and distracting gestures.
- You become more comfortable and confident in your delivery by practicing specific aspects you want to improve in multiple shorter sessions.
Public speaking, or the act of performing a speech in front of a live audience, is an integral part of scientific communication. Your reason for giving a talk may vary—whether you want to share your latest results with a broader audience, impress potential employers, or educate children about science. However, in all of these cases, it’s necessary to engage your audience and communicate your message clearly.
Public speaking has two main components: content (what you say) and delivery (how you say it). The content of your talk determines how impactful your talk can be, and your delivery determines how impactful your talk actually is . Without a strong, engaging delivery, you will lose your audience’s attention and fail to communicate your content. In order to become an engaging speaker, it is necessary to practice what you want to say and how you are going to say it.
These articles on public speaking will focus on the delivery aspect of your talk. From maintaining eye contact and speaking loudly and clearly, to incorporating movements that enhance your message and keep your audience engaged, there are many elements that go into being a great public speaker. Fortunately, these skills can be learned and honed and with enough practice will become second nature. In turn, improving your presentation skills will help you feel more confident standing in front of an audience and help you present your ideas and results to your audience more clearly.
Analyze your audience
As in any other form of scientific communication, your audience during a presentation can vary widely. Are you presenting a poster in a more intimate, one-on-one or small group setting? Are you presenting a talk to a room full of scientists from various fields? Or are you talking to the general public? Understanding who your audience will be ahead of time will help you pick the right tone you want to use while delivering your presentation.
During your talk, you will receive subtle feedback from your audience that you can use to alter how you proceed—is your audience engaged, dozing off, looking elsewhere, or focused more on your slides than on you? Staying present and actively adjusting your volume, tone of voice, and body language can alter how your message is conveyed, how you are perceived, and whether you can keep your audience’s attention.
We have broken down public speaking skills into verbal and nonverbal communication, and tips on how to practice more efficiently.
- Verbal – Speaking clearly, loudly, and in an engaging fashion can make or break a presentation. This article goes into more detail on how to use your voice effectively.
- Nonverbal – Standing in front of an audience can be nervewracking! This article addresses how you can use nonverbal cues like eye contact and body language to convey confidence and a strong stage presence.
- How to practice effectively – Practicing is an essential part of preparing for a presentation that often gets overlooked because we run out of time. This article will help you identify areas you want to improve and guide you through the process of practicing.
- The day of your presentation – You have enough to remember before your presentation! To help take off some of the stress, we’ve put together a short list of tips to help you be at your best.
For help with presentation content and design, visit our articles on Slideshows and Posters .

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals
6 presentation skills and how to improve them

Jump to section
What are presentation skills?
The importance of presentation skills, 6 presentation skills examples, how to improve presentation skills.
Tips for dealing with presentation anxiety
Learn how to captivate an audience with ease
Capturing an audience’s attention takes practice.
Over time, great presenters learn how to organize their speeches and captivate an audience from start to finish. They spark curiosity, know how to read a room , and understand what their audience needs to walk away feeling like they learned something valuable.
Regardless of your profession, you most likely use presentation skills on a monthly or even weekly basis. Maybe you lead brainstorming sessions or host client calls.
Developing effective presentation skills makes it easier to contribute ideas with confidence and show others you’re someone to trust. Although speaking in front of a crowd sometimes brings nerves and anxiety , it also sparks new opportunities.
Presentation skills are the qualities and abilities you need to communicate ideas effectively and deliver a compelling speech. They influence how you structure a presentation and how an audience receives it. Understanding body language , creating impactful visual aids, and projecting your voice all fall under this umbrella.
A great presentation depends on more than what you say. It’s about how you say it. Storytelling , stage presence, and voice projection all shape how well you express your ideas and connect with the audience. These skills do take practice, but they’re worth developing — especially if public speaking makes you nervous.
Engaging a crowd isn’t easy. You may feel anxious to step in front of an audience and have all eyes and ears on you.
But feeling that anxiety doesn’t mean your ideas aren’t worth sharing. Whether you’re giving an inspiring speech or delivering a monthly recap at work, your audience is there to listen to you. Harness that nervous energy and turn it into progress.
Strong presentation skills make it easier to convey your thoughts to audiences of all sizes. They can help you tell a compelling story, convince people of a pitch , or teach a group something entirely new to them. And when it comes to the workplace, the strength of your presentation skills could play a part in getting a promotion or contributing to a new initiative.
To fully understand the impact these skills have on creating a successful presentation, it’s helpful to look at each one individually. Here are six valuable skills you can develop:
1. Active listening
Active listening is an excellent communication skill for any professional to hone. When you have strong active listening skills, you can listen to others effectively and observe their nonverbal cues . This helps you assess whether or not your audience members are engaged in and understand what you’re sharing.
Great public speakers use active listening to assess the audience’s reactions and adjust their speech if they find it lacks impact. Signs like slouching, negative facial expressions, and roaming eye contact are all signs to watch out for when giving a presentation.
2. Body language
If you’re researching presentation skills, chances are you’ve already watched a few notable speeches like TED Talks or industry seminars. And one thing you probably noticed is that speakers can capture attention with their body language.
A mixture of eye contact, hand gestures , and purposeful pacing makes a presentation more interesting and engaging. If you stand in one spot and don’t move your body, the audience might zone out.

3. Stage presence
A great stage presence looks different for everyone. A comedian might aim for more movement and excitement, and a conference speaker might focus their energy on the content of their speech. Although neither is better than the other, both understand their strengths and their audience’s needs.
Developing a stage presence involves finding your own unique communication style . Lean into your strengths, whether that’s adding an injection of humor or asking questions to make it interactive . To give a great presentation, you might even incorporate relevant props or presentation slides.
4. Storytelling
According to Forbes, audiences typically pay attention for about 10 minutes before tuning out . But you can lengthen their attention span by offering a presentation that interests them for longer. Include a narrative they’ll want to listen to, and tell a story as you go along.
Shaping your content to follow a clear narrative can spark your audience’s curiosity and entice them to pay careful attention. You can use anecdotes from your personal or professional life that take your audience along through relevant moments. If you’re pitching a product, you can start with a problem and lead your audience through the stages of how your product provides a solution.
5. Voice projection
Although this skill may be obvious, you need your audience to hear what you’re saying. This can be challenging if you’re naturally soft-spoken and struggle to project your voice.
Remember to straighten your posture and take deep breaths before speaking, which will help you speak louder and fill the room. If you’re talking into a microphone or participating in a virtual meeting, you can use your regular conversational voice, but you still want to sound confident and self-assured with a strong tone.
If you’re unsure whether everyone can hear you, you can always ask the audience at the beginning of your speech and wait for confirmation. That way, they won’t have to potentially interrupt you later.
Ensuring everyone can hear you also includes your speed and annunciation. It’s easy to speak quickly when nervous, but try to slow down and pronounce every word. Mumbling can make your presentation difficult to understand and pay attention to.

6. Verbal communication
Although verbal communication involves your projection and tone, it also covers the language and pacing you use to get your point across. This includes where you choose to place pauses in your speech or the tone you use to emphasize important ideas.
If you’re giving a presentation on collaboration in the workplace , you might start your speech by saying, “There’s something every workplace needs to succeed: teamwork.” By placing emphasis on the word “ teamwork ,” you give your audience a hint on what ideas will follow.
To further connect with your audience through diction, pay careful attention to who you’re speaking to. The way you talk to your colleagues might be different from how you speak to a group of superiors, even if you’re discussing the same subject. You might use more humor and a conversational tone for the former and more serious, formal diction for the latter.
Everyone has strengths and weaknesses when it comes to presenting. Maybe you’re confident in your use of body language, but your voice projection needs work. Maybe you’re a great storyteller in small group settings, but need to work on your stage presence in front of larger crowds.
The first step to improving presentation skills is pinpointing your gaps and determining which qualities to build upon first. Here are four tips for enhancing your presentation skills:
1. Build self-confidence
Confident people know how to speak with authority and share their ideas. Although feeling good about your presentation skills is easier said than done, building confidence is key to helping your audience believe in what you’re saying. Try practicing positive self-talk and continuously researching your topic's ins and outs.
If you don’t feel confident on the inside, fake it until you make it. Stand up straight, project your voice, and try your best to appear engaged and excited. Chances are, the audience doesn’t know you’re unsure of your skills — and they don’t need to.
Another tip is to lean into your slideshow, if you’re using one. Create something colorful and interesting so the audience’s eyes fall there instead of on you. And when you feel proud of your slideshow, you’ll be more eager to share it with others, bringing more energy to your presentation.
2. Watch other presentations
Developing the soft skills necessary for a good presentation can be challenging without seeing them in action. Watch as many as possible to become more familiar with public speaking skills and what makes a great presentation. You could attend events with keynote speakers or view past speeches on similar topics online.
Take a close look at how those presenters use verbal communication and body language to engage their audiences. Grab a notebook and jot down what you enjoyed and your main takeaways. Try to recall the techniques they used to emphasize their main points, whether they used pauses effectively, had interesting visual aids, or told a fascinating story.

3. Get in front of a crowd
You don’t need a large auditorium to practice public speaking. There are dozens of other ways to feel confident and develop good presentation skills.
If you’re a natural comedian, consider joining a small stand-up comedy club. If you’re an avid writer, participate in a public poetry reading. Even music and acting can help you feel more comfortable in front of a crowd.
If you’d rather keep it professional, you can still work on your presentation skills in the office. Challenge yourself to participate at least once in every team meeting, or plan and present a project to become more comfortable vocalizing your ideas. You could also speak to your manager about opportunities that flex your public speaking abilities.
4. Overcome fear
Many people experience feelings of fear before presenting in front of an audience, whether those feelings appear as a few butterflies or more severe anxiety. Try grounding yourself to shift your focus to the present moment. If you’re stuck dwelling on previous experiences that didn’t go well, use those mistakes as learning experiences and focus on what you can improve to do better in the future.
Tips for dealing with presentation anxiety
It’s normal to feel nervous when sharing your ideas. In fact, according to a report from the Journal of Graduate Medical Education, public speaking anxiety is prevalent in 15–30% of the general population .
Even though having a fear of public speaking is common, it doesn’t make it easier. You might feel overwhelmed, become stiff, and forget what you were going to say. But although the moment might scare you, there are ways to overcome the fear and put mind over matter.
Use these tactics to reduce your stress when you have to make a presentation:
1. Practice breathing techniques
If you experience anxiety often, you’re probably familiar with breathing techniques for stress relief . Incorporating these exercises into your daily routine can help you stop worrying and regulate anxious feelings.
Before a big presentation, take a moment alone to practice breathing techniques, ground yourself, and reduce tension. It’s also a good idea to take breaths throughout the presentation to speak slower and calm yourself down .

2. Get organized
The more organized you are, the more prepared you’ll feel. Carefully outline all of the critical information you want to use in your presentation, including your main talking points and visual aids, so you don’t forget anything. Use bullet points and visuals on each slide to remind you of what you want to talk about, and create handheld notes to help you stay on track.
3. Embrace moments of silence
It’s okay to lose your train of thought. It happens to even the most experienced public speakers once in a while. If your mind goes blank, don’t panic. Take a moment to breathe, gather your thoughts, and refer to your notes to see where you left off. You can drink some water or make a quick joke to ease the silence or regain your footing. And it’s okay to say, “Give me a moment while I find my notes.” Chances are, people understand the position you’re in.

4. Practice makes progress
Before presenting, rehearse in front of friends and family members you trust. This gives you the chance to work out any weak spots in your speech and become comfortable communicating out loud. If you want to go the extra mile, ask your makeshift audience to ask a surprise question. This tests your on-the-spot thinking and will prove that you can keep cool when things come up.
Whether you’re new to public speaking or are a seasoned presenter, you’re bound to make a few slip-ups. It happens to everyone. The most important thing is that you try your best, brush things off, and work on improving your skills to do better in your next presentation.
Although your job may require a different level of public speaking than your favorite TED Talk , developing presentation skills is handy in any profession. You can use presentation skills in a wide range of tasks in the workplace, whether you’re sharing your ideas with colleagues, expressing concerns to higher-ups, or pitching strategies to potential clients.
Remember to use active listening to read the room and engage your audience with an interesting narrative. Don’t forget to step outside your comfort zone once in a while and put your skills to practice in front of a crowd. After facing your fears, you’ll feel confident enough to put presentation skills on your resume.
If you’re trying to build your skills and become a better employee overall, try a communications coach with BetterUp.
Elevate your communication skills
Unlock the power of clear and persuasive communication. Our coaches can guide you to build strong relationships and succeed in both personal and professional life.
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
The 11 tips that will improve your public speaking skills
The importance of good speech: 5 tips to be more articulate, learn types of gestures and their meanings to improve your communication, why it's good to have a bff at work and how to find one, why we need to reframe potential into readiness, love them or hate them, meetings promote social learning and growth, what’s my earning potential determining the right salary, show gratitude with “thank you for your leadership and vision” message examples, discover how to get noticed by upper management at work, similar articles, how to write a speech that your audience remembers, impression management: developing your self-presentation skills, 30 presentation feedback examples, your guide to what storytelling is and how to be a good storyteller, how to give a good presentation that captivates any audience, 8 clever hooks for presentations (with tips), communication coach: what they are and how to find one, how to make a presentation interactive and exciting, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care™
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
public speaking
Definition of public speaking
Examples of public speaking in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'public speaking.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
1759, in the meaning defined at sense 1
Dictionary Entries Near public speaking
public speaker
public-spirited
Cite this Entry
“Public speaking.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/public%20speaking. Accessed 20 May. 2024.
More from Merriam-Webster on public speaking
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about public speaking
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, the words of the week - may 17, birds say the darndest things, a great big list of bread words, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), games & quizzes.


- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
What are Public Speaking Skills?
What is Public Speaking Skill? Public speaking skills are the art of effectively conveying ideas and messages to an audience. This blog explores the importance of these skills, providing insights into communication, confidence, and techniques for becoming a proficient speaker. Unlock the secrets to engage, persuade, and inspire through the power of public speaking.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Effective Communication Skills
- English Speaking Course
- Assertiveness Skills Training
- Executive Communication Training
- Interpersonal Skills Training Course

Table of Contents
1) Public Speaking Skills: Definition and importance
2) Key elements of effective Public Speaking Skills
a) Confidence and presence
b) Clear structure and organisation
c) Engaging opening and closing
d) Effective use of voice and body language
e) Powerful visual aids
f) Audience connection
g) Clarity and conciseness
h) Adaptability and flexibility
i) Storytelling and emotional appeal
j) Preparation and practice
3) Benefits of developing Public Speaking Skills
4) Conclusion
Public Speaking Skills: Definition and importance
Many people often ask questions like “What are Public Speaking Skills?” and “Is Public Speaking a skill?”. As it turns out, yes, it is indeed a skill – and an invaluable one at that.
Public Speaking Skills encompass various abilities that allow individuals to present information, persuade others, and engage listeners. It involves organising thoughts, structuring content, and delivering speeches with confidence and clarity. Effective Public Speaking helps people captivate their audience, convey their message persuasively, and leave a lasting impact.
Now, why is Public Speaking Important? It is highly valued in many aspects of life. Whether it's in educational settings, professional environments, or social interactions, being an effective public speaker can open doors to opportunities. These skills are crucial for:
a) Academic success: Public Speaking Skills play a vital role in academic success by allowing students to express their ideas clearly, actively participate in class discussions, and deliver effective presentations. They help students engage with their peers and professors, leading to enhanced learning outcomes.
b) Career advancement: Good Public Speaking Skills are highly valued in the professional world. They enable individuals to confidently deliver presentations, articulate their ideas, and persuade others. Effective Public Speaking helps people stand out in job interviews, team meetings, and client interactions, thus enhancing their chances of career advancement and growth.
c) Leadership development: Public Speaking Skills are closely intertwined with leadership development. Leaders need to effectively communicate their vision, motivate their teams, and influence stakeholders. Proficient public speakers can inspire others, convey their ideas persuasively, and lead with confidence, making them effective leaders in their respective fields.
d) Personal growth: Developing basic Public Speaking Skills has a positive impact on personal growth. It boosts self-confidence, self-esteem, and self-expression. Individuals with strong Public Speaking Skills feel more empowered to share their thoughts and ideas, engage in meaningful conversations, and build stronger relationships in both personal and professional settings.
e) Effective communication: Public Speaking Skills enhance overall communication abilities. They involve not only delivering speeches but also active listening, non-verbal communication, and adapting to different audiences. Effective Public Speaking can help convey messages clearly, connect with listeners, and engage them effectively, leading to better understanding and collaboration.
f) Influence and persuasion: Public Speaking Skills are essential for influencing and persuading others. Whether it's in professional settings, public forums, or personal interactions, the ability to present compelling arguments, influence opinions, and motivate action is crucial. Proficient public speakers understand how to structure their messages, use persuasive language, and appeal to emotions to achieve desired outcomes.
g) Networking and relationship building: Public Speaking Skills greatly contribute to networking and relationship building. They enable individuals to confidently introduce themselves, engage in conversations, and leave a lasting impression. Effective Public Speaking can help connect with diverse audiences, build professional networks, and establish meaningful relationships, opening doors to new opportunities and collaborations.
Unlock your full potential as a confident and impactful speaker - sign up for our Public Speaking Training Course today!
Key elements of effective Public Speaking Skills
Effective Public Speaking skill encompasses several key elements that contribute to delivering impactful and persuasive presentations. By mastering these elements, individuals can engage their audience, convey their message with clarity, and leave a lasting impression. Let us explore the key elements of effective Public Speaking listed as follows:
a) Confidence and presence: Confidence is a fundamental element of effective Public Speaking. Projecting confidence through body language, vocal tone, and eye contact captivates the audience and instills trust.
b) Clear structure and organisation: A well-structured presentation is essential for audience comprehension. Effective public speakers carefully plan and organise their content, ensuring a logical flow of ideas.
c) Engaging opening and closing: The opening and closing of a speech are crucial for making a lasting impact. Skilled speakers use attention-grabbing openings to captivate the audience's interest from the start.
d) Effective use of voice and body language: Vocal variety and expressive body language enhance the delivery of a speech. Effective public speakers use modulation, tone, and pacing to convey meaning and engage their audience.
e) Powerful visual aids: Visual aids such as slides, videos, or props can enhance audience understanding and engagement. Effective Public Speaking requires the strategic use of visual aids to support key messages, simplify complex information, and create visual impact.
f) Audience connection: Effective public speakers understand the importance of connecting with their audience. They tailor their message to the specific needs, interests, and knowledge level of their listeners.
g) Clarity and conciseness: Clear and concise language is vital for effective communication. Effective Public Speaking requires people to choose their words carefully, using simple and accessible language to ensure audience understanding.
h) Adaptability and flexibility: Adaptability is crucial in Public Speaking, as different audiences and contexts require different approaches. Effective speakers are able to gauge audience reactions and adapt their delivery style accordingly.
i) Storytelling and emotional appeal: Stories have a powerful impact on listeners. Effective Public Speaking involves incorporating storytelling techniques to convey their message in a compelling and relatable way.
j) Preparation and practice: The key to effective Public Speaking lies in preparation and practice. Skilled speakers invest time in researching their topic, gathering relevant information, and structuring their speech.
Unlock the power of effective communication and elevate your skills with our comprehensive Effective Communication Skills Training Course – sign up now!
Benefits of developing Public Speaking Skills
Developing skills for Public Speaking offers numerous benefits, including:
a) Enhanced communication abilities: Improved clarity and coherence in expressing ideas.
b) Boosted self-confidence: Overcoming fears and gaining confidence in Public Speaking.
c) Expanded career opportunities: Advancement in professions requiring strong communication skills.
d) Improved leadership abilities: Ability to inspire, motivate, and influence others.
e) Greater influence and persuasion: Convincing and engaging audiences effectively.
f) Expanded networking opportunities: Connecting with like-minded individuals and professionals.
g) Improved critical thinking and problem-solving: Structuring and presenting ideas logically.
h) Personal development and growth: Overcoming challenges and continuous self-improvement.
i) Increased influence in relationships: Better communication and connection with others.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the priceless art of effective Public Speaking is invaluable in personal, academic, and professional spheres. They enable individuals to communicate effectively, build connections, and influence others. By developing these skills through practice, preparation, and a growth mindset, anyone can become a confident and persuasive public speaker. Hope this blog has told you all you needed to know about the Public Speaking Skills!
Want to elevate your communication skills to new heights? Explore our comprehensive Communication Skills Training Courses now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming business skills resources batches & dates.
Fri 28th Jun 2024
Fri 9th Aug 2024
Fri 25th Oct 2024
Fri 27th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
About Stanford GSB
- The Leadership
- Dean’s Updates
- School News & History
- Commencement
- Business, Government & Society
- Centers & Institutes
- Center for Entrepreneurial Studies
- Center for Social Innovation
- Stanford Seed
About the Experience
- Learning at Stanford GSB
- Experiential Learning
- Guest Speakers
- Entrepreneurship
- Social Innovation
- Communication
- Life at Stanford GSB
- Collaborative Environment
- Activities & Organizations
- Student Services
- Housing Options
- International Students
Full-Time Degree Programs
- Why Stanford MBA
- Academic Experience
- Financial Aid
- Why Stanford MSx
- Research Fellows Program
- See All Programs
Non-Degree & Certificate Programs
- Executive Education
- Stanford Executive Program
- Programs for Organizations
- The Difference
- Online Programs
- Stanford LEAD
- Seed Transformation Program
- Aspire Program
- Seed Spark Program
- Faculty Profiles
- Academic Areas
- Awards & Honors
- Conferences
Faculty Research
- Publications
- Working Papers
- Case Studies
Research Hub
- Research Labs & Initiatives
- Business Library
- Data, Analytics & Research Computing
- Behavioral Lab
Research Labs
- Cities, Housing & Society Lab
- Golub Capital Social Impact Lab
Research Initiatives
- Corporate Governance Research Initiative
- Corporations and Society Initiative
- Policy and Innovation Initiative
- Rapid Decarbonization Initiative
- Stanford Latino Entrepreneurship Initiative
- Value Chain Innovation Initiative
- Venture Capital Initiative
- Career & Success
- Climate & Sustainability
- Corporate Governance
- Culture & Society
- Finance & Investing
- Government & Politics
- Leadership & Management
- Markets & Trade
- Operations & Logistics
- Opportunity & Access
- Organizational Behavior
- Political Economy
- Social Impact
- Technology & AI
- Opinion & Analysis
- Email Newsletter
Welcome, Alumni
- Communities
- Digital Communities & Tools
- Regional Chapters
- Women’s Programs
- Identity Chapters
- Find Your Reunion
- Career Resources
- Job Search Resources
- Career & Life Transitions
- Programs & Services
- Career Video Library
- Alumni Education
- Research Resources
- Volunteering
- Alumni News
- Class Notes
- Alumni Voices
- Contact Alumni Relations
- Upcoming Events
Admission Events & Information Sessions
- MBA Program
- MSx Program
- PhD Program
- Alumni Events
- All Other Events
Presence, Structure, Performance: 5 Tips to Improve Your Public Speaking
Our experts’ tips on small changes that can make or break your next presentation.
August 19, 2019

The ability to present your ideas in a clear, confident, and authentic manner can make a huge difference in your business (and personal) success. | iStock/Django
Public speaking ranks high on the list of people’s greatest fears. But the ability to present ideas in a clear, confident, and authentic manner affects your professional and personal success.
Here are a few tips from Stanford GSB communication experts on how paying close attention to word choice, using outlines instead of memorized scripts, and managing your anxiety can improve your next presentation.
1. Give Yourself Structure
Great talks have defined paths. Start by asking yourself, “What does my audience need from me?” Keeping your listeners’ needs at the forefront of your mind connects you to them. Focus on what they are there to learn, instead of making sure each of your talking points is said. You can structure presentations by using frameworks such as Cause and Effect or Past-Present-Future.
2. Own the Room
Making an impression isn’t a choice, it’s an inevitability. And it’s rarely just about what you say, but how you make people feel as you’re speaking. Lecturer Allison Kluger shares how you can exude an executive presence, communicate verbally and with your physicality, and own the room.
3. Nail the Q&A
Panel discussions present a unique set of challenges for a speaker: You must navigate a conversation while still getting your message across. You’re more apt for success if you’re well prepared and structure your answers to link back to other panelists.
4. What the Pros Know
How do you start and end your talk? How do you make complex ideas more approachable? In this video, Lecturer Matt Abrahams shares what he knows about crafting meaningful presentations that make lasting impressions.
5. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Sort of, kind of, I think … this hedging language weakens your idea and litters your communication, says Stanford GSB Lecturer Matt Abrahams. Avoid it at all costs. Other habits to toss out include the urge to memorize or rely on predictable openers like “Hi, my name is … ”.
For media inquiries, visit the Newsroom .
Explore More
Power, culture, persuasion, and the self: communication insights from stanford gsb faculty, lose yourself: the secret to finding flow and being fully present, speak your truth: why authenticity leads to better communication, editor’s picks.

December 03, 2018 Seven Most-Read Stories of 2018 From tips for career satisfaction to an economist’s stint as an Uber driver, here are the stories that caught our readers’ attention.
- Priorities for the GSB's Future
- See the Current DEI Report
- Supporting Data
- Research & Insights
- Share Your Thoughts
- Search Fund Primer
- Teaching & Curriculum
- Affiliated Faculty
- Faculty Advisors
- Louis W. Foster Resource Center
- Defining Social Innovation
- Impact Compass
- Global Health Innovation Insights
- Faculty Affiliates
- Student Awards & Certificates
- Changemakers
- Dean Jonathan Levin
- Dean Garth Saloner
- Dean Robert Joss
- Dean Michael Spence
- Dean Robert Jaedicke
- Dean Rene McPherson
- Dean Arjay Miller
- Dean Ernest Arbuckle
- Dean Jacob Hugh Jackson
- Dean Willard Hotchkiss
- Faculty in Memoriam
- Stanford GSB Firsts
- Certificate & Award Recipients
- Teaching Approach
- Analysis and Measurement of Impact
- The Corporate Entrepreneur: Startup in a Grown-Up Enterprise
- Data-Driven Impact
- Designing Experiments for Impact
- Digital Business Transformation
- The Founder’s Right Hand
- Marketing for Measurable Change
- Product Management
- Public Policy Lab: Financial Challenges Facing US Cities
- Public Policy Lab: Homelessness in California
- Lab Features
- Curricular Integration
- View From The Top
- Formation of New Ventures
- Managing Growing Enterprises
- Startup Garage
- Explore Beyond the Classroom
- Stanford Venture Studio
- Summer Program
- Workshops & Events
- The Five Lenses of Entrepreneurship
- Leadership Labs
- Executive Challenge
- Arbuckle Leadership Fellows Program
- Selection Process
- Training Schedule
- Time Commitment
- Learning Expectations
- Post-Training Opportunities
- Who Should Apply
- Introductory T-Groups
- Leadership for Society Program
- Certificate
- 2023 Awardees
- 2022 Awardees
- 2021 Awardees
- 2020 Awardees
- 2019 Awardees
- 2018 Awardees
- Social Management Immersion Fund
- Stanford Impact Founder Fellowships and Prizes
- Stanford Impact Leader Prizes
- Social Entrepreneurship
- Stanford GSB Impact Fund
- Economic Development
- Energy & Environment
- Stanford GSB Residences
- Environmental Leadership
- Stanford GSB Artwork
- A Closer Look
- California & the Bay Area
- Voices of Stanford GSB
- Business & Beneficial Technology
- Business & Sustainability
- Business & Free Markets
- Business, Government, and Society Forum
- Get Involved
- Second Year
- Global Experiences
- JD/MBA Joint Degree
- MA Education/MBA Joint Degree
- MD/MBA Dual Degree
- MPP/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Computer Science/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Electrical Engineering/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Environment and Resources (E-IPER)/MBA Joint Degree
- Academic Calendar
- Clubs & Activities
- LGBTQ+ Students
- Military Veterans
- Minorities & People of Color
- Partners & Families
- Students with Disabilities
- Student Support
- Residential Life
- Student Voices
- MBA Alumni Voices
- A Week in the Life
- Career Support
- Employment Outcomes
- Cost of Attendance
- Knight-Hennessy Scholars Program
- Yellow Ribbon Program
- BOLD Fellows Fund
- Application Process
- Loan Forgiveness
- Contact the Financial Aid Office
- Evaluation Criteria
- GMAT & GRE
- English Language Proficiency
- Personal Information, Activities & Awards
- Professional Experience
- Letters of Recommendation
- Optional Short Answer Questions
- Application Fee
- Reapplication
- Deferred Enrollment
- Joint & Dual Degrees
- Entering Class Profile
- Event Schedule
- Ambassadors
- New & Noteworthy
- Ask a Question
- See Why Stanford MSx
- Is MSx Right for You?
- MSx Stories
- Leadership Development
- Career Advancement
- Career Change
- How You Will Learn
- Admission Events
- Personal Information
- Information for Recommenders
- GMAT, GRE & EA
- English Proficiency Tests
- After You’re Admitted
- Daycare, Schools & Camps
- U.S. Citizens and Permanent Residents
- Requirements
- Requirements: Behavioral
- Requirements: Quantitative
- Requirements: Macro
- Requirements: Micro
- Annual Evaluations
- Field Examination
- Research Activities
- Research Papers
- Dissertation
- Oral Examination
- Current Students
- Education & CV
- International Applicants
- Statement of Purpose
- Reapplicants
- Application Fee Waiver
- Deadline & Decisions
- Job Market Candidates
- Academic Placements
- Stay in Touch
- Faculty Mentors
- Current Fellows
- Standard Track
- Fellowship & Benefits
- Group Enrollment
- Program Formats
- Developing a Program
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Strategic Transformation
- Program Experience
- Contact Client Services
- Campus Experience
- Live Online Experience
- Silicon Valley & Bay Area
- Digital Credentials
- Faculty Spotlights
- Participant Spotlights
- Eligibility
- International Participants
- Stanford Ignite
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Operations, Information & Technology
- Classical Liberalism
- The Eddie Lunch
- Accounting Summer Camp
- Videos, Code & Data
- California Econometrics Conference
- California Quantitative Marketing PhD Conference
- California School Conference
- China India Insights Conference
- Homo economicus, Evolving
- Political Economics (2023–24)
- Scaling Geologic Storage of CO2 (2023–24)
- A Resilient Pacific: Building Connections, Envisioning Solutions
- Adaptation and Innovation
- Changing Climate
- Civil Society
- Climate Impact Summit
- Climate Science
- Corporate Carbon Disclosures
- Earth’s Seafloor
- Environmental Justice
- Operations and Information Technology
- Organizations
- Sustainability Reporting and Control
- Taking the Pulse of the Planet
- Urban Infrastructure
- Watershed Restoration
- Junior Faculty Workshop on Financial Regulation and Banking
- Ken Singleton Celebration
- Marketing Camp
- Quantitative Marketing PhD Alumni Conference
- Presentations
- Theory and Inference in Accounting Research
- Stanford Closer Look Series
- Quick Guides
- Core Concepts
- Journal Articles
- Glossary of Terms
- Faculty & Staff
- Researchers & Students
- Research Approach
- Charitable Giving
- Financial Health
- Government Services
- Workers & Careers
- Short Course
- Adaptive & Iterative Experimentation
- Incentive Design
- Social Sciences & Behavioral Nudges
- Bandit Experiment Application
- Conferences & Events
- Reading Materials
- Energy Entrepreneurship
- Faculty & Affiliates
- SOLE Report
- Responsible Supply Chains
- Current Study Usage
- Pre-Registration Information
- Participate in a Study
- Founding Donors
- Location Information
- Participant Profile
- Network Membership
- Program Impact
- Collaborators
- Entrepreneur Profiles
- Company Spotlights
- Seed Transformation Network
- Responsibilities
- Current Coaches
- How to Apply
- Meet the Consultants
- Meet the Interns
- Intern Profiles
- Collaborate
- Research Library
- News & Insights
- Program Contacts
- Databases & Datasets
- Research Guides
- Consultations
- Research Workshops
- Career Research
- Research Data Services
- Course Reserves
- Course Research Guides
- Material Loan Periods
- Fines & Other Charges
- Document Delivery
- Interlibrary Loan
- Equipment Checkout
- Print & Scan
- MBA & MSx Students
- PhD Students
- Other Stanford Students
- Faculty Assistants
- Research Assistants
- Stanford GSB Alumni
- Telling Our Story
- Staff Directory
- Site Registration
- Alumni Directory
- Alumni Email
- Privacy Settings & My Profile
- Success Stories
- The Story of Circles
- Support Women’s Circles
- Stanford Women on Boards Initiative
- Alumnae Spotlights
- Insights & Research
- Industry & Professional
- Entrepreneurial Commitment Group
- Recent Alumni
- Half-Century Club
- Fall Reunions
- Spring Reunions
- MBA 25th Reunion
- Half-Century Club Reunion
- Faculty Lectures
- Ernest C. Arbuckle Award
- Alison Elliott Exceptional Achievement Award
- ENCORE Award
- Excellence in Leadership Award
- John W. Gardner Volunteer Leadership Award
- Robert K. Jaedicke Faculty Award
- Jack McDonald Military Service Appreciation Award
- Jerry I. Porras Latino Leadership Award
- Tapestry Award
- Student & Alumni Events
- Executive Recruiters
- Interviewing
- Land the Perfect Job with LinkedIn
- Negotiating
- Elevator Pitch
- Email Best Practices
- Resumes & Cover Letters
- Self-Assessment
- Whitney Birdwell Ball
- Margaret Brooks
- Bryn Panee Burkhart
- Margaret Chan
- Ricki Frankel
- Peter Gandolfo
- Cindy W. Greig
- Natalie Guillen
- Carly Janson
- Sloan Klein
- Sherri Appel Lassila
- Stuart Meyer
- Tanisha Parrish
- Virginia Roberson
- Philippe Taieb
- Michael Takagawa
- Terra Winston
- Johanna Wise
- Debbie Wolter
- Rebecca Zucker
- Complimentary Coaching
- Changing Careers
- Work-Life Integration
- Career Breaks
- Flexible Work
- Encore Careers
- Join a Board
- D&B Hoovers
- Data Axle (ReferenceUSA)
- EBSCO Business Source
- Global Newsstream
- Market Share Reporter
- ProQuest One Business
- Student Clubs
- Entrepreneurial Students
- Stanford GSB Trust
- Alumni Community
- How to Volunteer
- Springboard Sessions
- Consulting Projects
- 2020 – 2029
- 2010 – 2019
- 2000 – 2009
- 1990 – 1999
- 1980 – 1989
- 1970 – 1979
- 1960 – 1969
- 1950 – 1959
- 1940 – 1949
- Service Areas
- ACT History
- ACT Awards Celebration
- ACT Governance Structure
- Building Leadership for ACT
- Individual Leadership Positions
- Leadership Role Overview
- Purpose of the ACT Management Board
- Contact ACT
- Business & Nonprofit Communities
- Reunion Volunteers
- Ways to Give
- Fiscal Year Report
- Business School Fund Leadership Council
- Planned Giving Options
- Planned Giving Benefits
- Planned Gifts and Reunions
- Legacy Partners
- Giving News & Stories
- Giving Deadlines
- Development Staff
- Submit Class Notes
- Class Secretaries
- Board of Directors
- Health Care
- Sustainability
- Class Takeaways
- All Else Equal: Making Better Decisions
- If/Then: Business, Leadership, Society
- Grit & Growth
- Think Fast, Talk Smart
- Spring 2022
- Spring 2021
- Autumn 2020
- Summer 2020
- Winter 2020
- In the Media
- For Journalists
- DCI Fellows
- Other Auditors
- Academic Calendar & Deadlines
- Course Materials
- Entrepreneurial Resources
- Campus Drive Grove
- Campus Drive Lawn
- CEMEX Auditorium
- King Community Court
- Seawell Family Boardroom
- Stanford GSB Bowl
- Stanford Investors Common
- Town Square
- Vidalakis Courtyard
- Vidalakis Dining Hall
- Catering Services
- Policies & Guidelines
- Reservations
- Contact Faculty Recruiting
- Lecturer Positions
- Postdoctoral Positions
- Accommodations
- CMC-Managed Interviews
- Recruiter-Managed Interviews
- Virtual Interviews
- Campus & Virtual
- Search for Candidates
- Think Globally
- Recruiting Calendar
- Recruiting Policies
- Full-Time Employment
- Summer Employment
- Entrepreneurial Summer Program
- Global Management Immersion Experience
- Social-Purpose Summer Internships
- Process Overview
- Project Types
- Client Eligibility Criteria
- Client Screening
- ACT Leadership
- Social Innovation & Nonprofit Management Resources
- Develop Your Organization’s Talent
- Centers & Initiatives
- Student Fellowships
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Public Speaking and Presentations

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Public Speaking and Presentations: Tips for Success
This resource includes tips and suggestions for improving your public speaking skills.
Even if you’ve never spoken in front of a large group before, chances are you will encounter public speaking sometime during your life. Whether you’re giving a presentation for your classmates or addressing local politicians at a city council meeting, public speaking allows you to convey your thoughts and feelings in clear ways. Having the right tools can prepare you for successful public speaking and equip you with high-quality communication skills.
Know Your Audience
Different audiences require different modes of public speaking. How you address a room full of preschoolers will vary from how you address a group of professors at an academic conference. Not only will your vocabulary change, but you might alter your pacing and tone as well.
Knowing your audience also helps you decide the content of your speech. For example, if you’re presenting research to a group of scientists, you might not need to define all your scientific language. However, if you present that same research to a group of individuals who are unfamiliar with your scientific field, you may need to define your terms or use simpler language.
Recognizing the extent to which your audience is familiar with your topic helps you center your presentation around the most important elements and avoid wasting time on information your audience either 1) already knows or 2) does not need to know for the purpose of your speech.
Knowing your audience also means tailoring your information to them. Try to keep things straight and to the point; leave out extraneous anecdotes and irrelevant statistics.
Establish Your Ethos and Feel Confident in Your Subject
It’s important to let your audience know what authority you have over your subject matter. If it’s clear you are familiar with your subject and have expertise, your audience is more likely to trust what you say.
Feeling confident in your subject matter will help establish your ethos. Rather than simply memorizing the content on your PowerPoint slides or your note cards, consider yourself a “mini expert” on your topic. Read up on information related to your topic and anticipate questions from the audience. You might want to prepare a few additional examples to use if people ask follow-up questions. Being able to elaborate on your talking points will help you stay calm during a Q & A section of your presentation.
Stick to a Few Main Points
Organizing your information in a logical way not only helps you keep track of what you’re saying, but it helps your audience follow along as well. Try to emphasize a few main points in your presentation and return to them before you conclude. Summarizing your information at the end of your presentation allows your audience to walk away with a clear sense of the most important facts.
For example, if you gave a presentation on the pros and cons of wind energy in Indiana, you would first want to define wind energy to make sure you and your audience are on the same page. You might also want to give a brief history of wind energy to give context before you go into the pros and cons. From there, you could list a few pros and a few cons. Finally, you could speculate on the future of wind energy and whether Indiana could provide adequate land and infrastructure to sustain wind turbines. To conclude, restate a few of the main points (most likely the pros and cons) and end with the most important takeaway you want the audience to remember about wind energy in Indiana.
Don't be Afraid to Show Your Personality
Delivering information without any sort of flourish or style can be boring. Allowing your personality to show through your speaking keeps you feeling relaxed and natural. Even if you’re speaking about something very scientific or serious, look for ways to let your personality come through your speech.
For example, when Jeopardy! host Alex Trebek announced in March of 2019 that he had stage 4 pancreatic cancer, he still let his trademark dignity and professionalism set the tone for his address. He began his announcement by saying “it’s in keeping with my long-time policy of being open and transparent with our Jeopardy! fan base.” Later, he joked that he would need to overcome his illness in order to fulfill his contract, whose terms required him to host the show for three more years. Though the nature of Trebek's announcement could easily have justified a grim, serious tone, the host instead opted to display the charm that has made him a household name for almost thirty-five years. In doing so, he reminded his audience precisely why he is so well-loved.
Use Humor (When Appropriate)
Using humor at appropriate moments can keep your audience engaged and entertained. While not all occasions are appropriate for humor, look for moments where you can lighten the mood and add some humor.
For example, just two months after the assassination attempt on Ronald Reagan, Reagan was in the middle of giving a speech when a balloon loudly popped while he was speaking. Reagan paused his speech to say “missed me,” then immediately continued speaking. This off-the-cuff humor worked because it was appropriate, spontaneous, and did not really distract from his message.
Similarly, at the end of his final White House Correspondents Dinner, Barack Obama concluded his speech by saying “Obama out” and dropping the mic. Once again, the humor did not distract from his message, but it did provide a light-hearted shift in his tone.
Don't Let Visual Aids Distract From Your Presentation
Visual aids, such as PowerPoints or handouts, often go alongside presentations. When designing visual aids, be sure they do not distract from the content of your speech. Having too many pictures or animations can cause audience members to pay more attention to the visuals rather than what you’re saying.
However, if you present research that relies on tables or figures, having many images may help your audience better visualize the research you discuss. Be aware of the ways different types of presentations demand different types of visual aids.
Be Aware of Your Body Language
When it comes to giving a presentation, nonverbal communication is equally as important as what you’re saying. Having the appropriate posture, gestures, and movement complement the spoken element of your presentation. Below are a few simple strategies to make you appear more confident and professional.
Having confident posture can make or break a presentation. Stand up straight with your shoulders back and your arms at your sides. Slouching or crossing your arms over your chest makes you appear smaller and more insecure. However, be sure you’re not too rigid. Just because you’re standing up tall does not mean you cannot move around.
Eye contact
Making eye contact with your audience not only makes them feel connected to you but it also lets you gauge their response to you. Try to look around the room and connect with different audience members so you’re not staring at the same people the whole time. If you notice your audience starting to nod off, it might be a good time to change your tone or up your energy.
Avoid distracting or compulsive gestures
While hand gestures can help point out information in a slide or on a poster, large or quick gestures can be distracting. When using gestures, try to make them feel like a normal part of your presentation.
It’s also easy to slip into nervous gestures while presenting. Things like twirling your hair or wringing your hands can be distracting to your audience. If you know you do something like this, try to think hard about not doing it while you’re presenting.
Travel (if possible)
If you are presenting on a stage, walking back and forth can help you stay relaxed and look natural. However, be sure you’re walking slowly and confidently and you’re using an appropriate posture (described above). Try to avoid pacing, which can make you appear nervous or compulsive.
Rehearse (if Possible)
The difference between knowing your subject and rehearsing comes down to how you ultimately present your information. The more you rehearse, the more likely you are to eliminate filler words such as like and um . If possible, try practicing with a friend and have them use count the filler words you use. You can also record yourself and play back the video. The more you rehearse, the more confident you will feel when it comes time to actually speak in front of an audience.
Finally, Relax!
Although public speaking takes time and preparation, perhaps one of the most important points is to relax while you’re speaking. Delivering your information in a stiff way prevents you from appearing natural and letting your personality come through. The more relaxed you feel, the more confident your information will come across.

14 Practical Tips to Improve Your Presentation Skills
- The Speaker Lab
- May 11, 2024
Table of Contents
Ever felt complete dread and fear at the thought of stepping up to deliver a presentation? If so, you’re not alone. The fear of public speaking is more common than you might think, but with the right presentation skills , it’s a hurdle that can be overcome.
In this article, we’ll help you master basic confidence-building techniques and conquer advanced communication strategies for engaging presentations. We’ll explore how body language and eye contact can make or break your connection with your audience; delve into preparation techniques like dealing with filler words and nervous habits; discuss tailoring content for different audiences; and much more.
Whether you’re prepping for job interviews or gearing up for big presentations, being prepared is key. With adequate practice and the proper attitude, you can crush your speech or presentation!
Mastering the Basics of Presentation Skills
Presentation skills are not just about speaking in front of a crowd. It’s also about effective communication, audience engagement, and clarity. Mastering these skills can be transformative for everyone, from students to corporate trainers.
Building Confidence in Presentations
Becoming confident when presenting is no small feat. But fear not. Even those who feel jittery at the mere thought of public speaking can become masters with practice and patience. Just remember: stage fright is common and overcoming it is part of the process towards becoming an effective presenter.
Taking deep breaths before you start helps calm nerves while visualizing success aids in building confidence. Also, know that nobody minds if you take a moment to gather your thoughts during your presentation—everybody minds more if they cannot understand what you’re saying because you’re rushing.
The Role of Practice in Enhancing Presentation Skills
In line with old wisdom, practice indeed makes perfect, especially when improving presentation skills. Consistent rehearsals allow us to fine-tune our delivery methods like maintaining eye contact or controlling body language effectively.
You’ll learn better control over filler words through repeated drills. Plus, the extra practice can help you troubleshoot any technical glitches beforehand, saving you the sudden panic during your actual presentations.
Remember that great presenters were once beginners too. Continuous effort will get you there sooner rather than later.
Find Out Exactly How Much You Could Make As a Paid Speaker
Use The Official Speaker Fee Calculator to tell you what you should charge for your first (or next) speaking gig — virtual or in-person!
Body Language and Eye Contact in Presentations
The effectiveness of your presentation can hinge on more than just the words you say. Just as important is your body language .
Impact of Posture on Presentations
Your posture speaks volumes before you utter a word. Standing tall exudes confidence while slouching could signal nervousness or lack of preparation.
If there’s one lesson to take away from our YouTube channel , it’s this: good presenters know their message but great ones feel it through every fiber (or muscle) of their being. The audience can sense that energy when they see open body language rather than crossed arms.
Maintaining Eye Contact During Your Presentation
Eyes are often called windows to the soul for a reason. They’re communication powerhouses. Making eye contact helps build trust with your audience members and keeps them engaged throughout your speech.
Avoid staring at note cards or visual aids too much as this might give an impression that you’re unprepared or uncertain about your chosen topic. Instead, aim to maintain eye contact between 50% of the time during presentations. This commonly accepted “50/70 rule” will help you exhibit adequate confidence to your audience.
If stage fright has gotten a hold on you, take deep breaths before you start speaking in order to stay calm. Make sure that fear doesn’t disrupt your ability to maintain eye-contact during presentations.
If body language and eye contact still feel like a lot to manage during your big presentation, remember our golden rule: nobody minds small mistakes. It’s how you handle questions or mishaps that truly makes a difference—so stay positive and enthusiastic.
Preparation Techniques for Successful Presentations
Presentation skills are like a craft that requires meticulous preparation and practice. Aspects like visual aids and time management contribute to the overall effectiveness of your delivery.
The first step towards delivering an impactful presentation is research and organization. The content should be well-researched, structured logically, and presented in simple language. This will make sure you deliver clear messages without any room for misinterpretation.
Dealing with Filler Words and Nervous Habits
Nervous habits such as excessive use of filler words can distract from your message. Luckily, there are plenty of strategies that can address these issues. For instance, try taking deep breaths before speaking or using note cards until fluency is achieved. In addition, practice regularly to work on eliminating these verbal stumbling blocks.
Avoiding Distractions During Presentations
In a digital age where distractions abound, maintaining focus during presentations has become an even more crucial part of the preparation process. This video by motivational speaker Brain Tracy provides insights on how one could achieve this level of focus required for effective presentations.
Maintaining Confidence Throughout Your Presentation
Confidence comes from thorough understanding of the chosen topic combined with regular practice sessions before the big day arrives. Make use of note cards or cue cards as needed but avoid reading from them verbatim.
Taking control over stage fright starts by arriving early at the venue so that you familiarize yourself with the surroundings, which generally calms nerves down considerably. So next time you feel nervous before a big presentation, remember—thorough preparation can make all the difference.
Engaging Your Audience During Presentations
Connecting with your audience during presentations is an art, and mastering it can take your presentation skills to the next level. Making the message conveyed reach an emotional level is essential, not just conveying facts.
Understanding Your Target Audience
The first step towards engaging your audience is understanding them. Tailor the content of your presentation to their needs and interests. Speak in their language—whether that be professional jargon or everyday slang—to establish rapport and ensure comprehension.
An effective presenter understands who they’re speaking to, what those individuals care about, and how best to communicate complex ideas understandably.
Making Complex Information Understandable
Dense data or complicated concepts can lose even the most interested listener if presented ineffectively. Breaking your key points down into manageable chunks helps maintain attention while promoting retention. Analogies are especially useful for this purpose as they make unfamiliar topics more relatable.
Audience Participation & Questions: A Two-Way Street
Incorporating opportunities for audience participation encourages engagement at another level. It allows listeners to become active participants rather than passive receivers of knowledge.
Consider techniques like live polls or interactive Q&A sessions where you invite questions from attendees mid-presentation instead of saving all queries until the end.
This gives you a chance not only engage but also address any misunderstandings right on spot.
- Treat each question asked as an opportunity—it’s evidence someone has been paying attention. Even challenging questions should be welcomed as they demonstrate an engaged, thoughtful audience.
- Encourage participation. It can be as simple as a show of hands or the use of interactive technologies for live polling during your presentation. This keeps your audience active and invested in the content.
Remember, your presentation isn’t just about putting on a show—it’s about meaningful interaction.
Free Download: 6 Proven Steps to Book More Paid Speaking Gigs in 2024
Download our 18-page guide and start booking more paid speaking gigs today!
Presentation Skills in Specific Contexts
Whether you’re nailing your next job interview, presenting an exciting marketing campaign, or delivering insightful educational content, the context matters. Let’s take a look.
The Art of Job Interviews
A successful job interview often hinges on effective communication and confidence. Here, the target audience is usually small but holds significant influence over your future prospects. Body language plays a crucial role; maintain eye contact to show sincerity and interest while open body language communicates approachability.
Bullet points summarizing key experiences are also helpful for quick recall under pressure. This allows you to present your chosen topic with clarity and positive enthusiasm without relying heavily on note or cue cards.
Pitching in Public Relations & Marketing
In public relations (PR) and marketing contexts, presentations need to capture attention quickly yet hold it long enough to deliver key messages effectively. Visual aids are valuable tools here—they help emphasize points while keeping the audience engaged.
Your aim should be highlighting presentation benefits that resonate with potential clients or partners, making them feel as though ignoring such opportunities would mean missing out big time.
Educational Presentations
An educational setting demands its own unique set of presentation skills where deep understanding trumps flashy visuals. You must make complex information understandable without oversimplifying essential details—the use of analogies can be beneficial here.
Keeping the audience’s attention is critical. Encourage questions and participation to foster a more interactive environment, enhancing learning outcomes for all audience members.
Tips for Becoming a Great Presenter
No single method is suitable for everyone when it comes to speaking in public. However, incorporating continuous improvement and practice into your routine can make you an exceptional presenter.
Tailor Your Presentation to Your Audience
Becoming an excellent speaker isn’t just about delivering information; it’s also about making a connection with the audience. So make sure that you’re taking setting, audience, and topic into consideration when crafting your presentation. What works for one audience may not work for another, so be sure to adapt your presentation styles according to the occasion in order to be truly effective.
The Power of Practice
The art of mastering public speaking skills requires practice —and lots of it . To become a great presenter, focus on improving communication skills through practice and feedback from peers or mentors. Try to seek feedback on every speech delivered and incorporate those pointers in your future presentations. Over time, this cycle of delivery-feedback-improvement significantly enhances your ability to connect with audiences and convey ideas effectively.
If you’re looking for examples of good speakers, our speech breakdowns on YouTube provide excellent examples of experienced presenters who masterfully utilize speaking techniques. Analyzing their strategies could give you great ideas for enhancing your own style.
Finding Your Style
A crucial part of captivating any audience lies in how you deliver the message rather than the message itself. Developing a unique presentation style lets you stand out as an engaging speaker who commands attention throughout their talk. Through — you guessed it — practice, you can develop a personal presentation style that resonates with listeners while showcasing your expertise on the chosen topic.
Your body language plays a pivotal role here: open gestures communicate confidence and enthusiasm towards your subject matter, two qualities essential for keeping audiences hooked. Similarly, using vocal variety adds dynamism to speeches by emphasizing points when needed or creating suspense during storytelling parts of your talk.
Cultivating Passion & Enthusiasm
Showcasing genuine passion for the subject helps keep listeners engaged throughout even lengthy presentations. Sharing stories related to the topic or expressing excitement about sharing knowledge tends to draw people in more than mere data recitation ever could.
Recognize that everybody is distinctive; don’t expect identical results from every speaker. The path to becoming a great presenter involves recognizing your strengths and working tirelessly on areas that need improvement.
FAQs on Presentation Skills
What are good presentation skills.
Good presentation skills include a clear message, confident delivery, engaging body language, audience understanding, and interaction. They also involve effective preparation and practice.
What are the 5 steps of presentation skills?
The five steps of presenting include: planning your content, preparing visual aids if needed, practicing the delivery aloud, performing it with confidence, and finally post-presentation reflection for improvements.
What are the 5 P’s of presentation skills?
The five P’s stand for Preparation (researching your topic), Practice (rehearsing your talk), Performance (delivering with confidence), Posture (standing tall), and Projection (using a strong voice).
What are your presentation skills?
Your personal set of abilities to deliver information effectively is what we call your presentation skill. It can encompass public speaking ability, clarity in speech or writing as well as visual communication talent.
Mastering presentation skills isn’t an overnight process, but practice and perseverance will put you well on your way to becoming an effective speaker.
You’ve learned that confidence plays a crucial role in effective presentations, so take deep breaths, make eye contact, and keep your body language open. As always, preparation is key. Tackle filler words head-on and get comfortable with visual aids for impactful storytelling.
Remember the importance of audience engagement — it’s all about understanding their needs and tailoring your content accordingly. This way, complex information turns into digestible insights.
Above all else: practice! After all, nothing beats experience when it comes to improving public speaking abilities.
- Last Updated: May 9, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.

When, Why and How To Use Signposts in Public Speaking
by Janice Tomich
- Presentation Planning & Public Speaking Skills
Signposts in public speaking are often missed or misunderstood.
You might know signposts by other names such as benchmarks or keypoints. No matter what you call them they are an integral piece to the framework of your speeches or presentations. If they’re not built in, you run the risk of losing your audience soon after you’ve spoken your first few words. As an executive communication coach , I know the value of signposts done well. Here’s what I teach my communication clients about using signposts effectively.
Table of Contents
What Is A Signpost In A Speech?
A signpost is a verbal or visual marker indicating the direction you are taking your speech/presentation or where you are presently at in order to help your audience move through different concepts, connect the dots, and help them stay engaged. Planning when you’ll use signposting is an essential element to planning a well structured, well organized presentation .

Why Are Signposts Important In Your Speech?
Even if you’ve invested multiple hours preparing your presentation your attendees won’t hang in there if you don’t guide them through the different stages you’re speaking about. What you’ll notice instead is eyes looking away and fingers tapping on phones because you’ve lost them.
To compel your audience to keep listening there are many types of signposts to be aware of that you can embed in your next presentation.
Types of Speech or Presentation Signposts
How to build signposts into your presentation opening .
You’ve likely heard many speeches or presentations begin with these typical statements:
- Today, I’m going to talk about…
- I’m going to cover…
- You will learn the following…
These types of statements can help your audience envision what you’ll be speaking about, however a word of caution here.
Don’t start your presentation with signposts. You run the risk of losing your audience because your setup is frankly quite boring. It’s how ‘everyone’ opens their presentations. The folks at Ideo, who are masters of corporate storytelling , call starting a speech this way throat clearing (which no one wants to hear).
You need to entice and hook your audience in with your first words. Starting with signposts won’t accomplish that
Pro Tip: Begin your presentation with a hook. Engage your audience – pull them in. Then (and only then) speak to your signposts (using a light hand) to show your audience where you’ll be taking them.
How To Use Signposts Throughout The Body Of Your Speech
You are the subject matter expert. It’s why you’ve been asked to speak. What you know is not what your audience knows. This is called ‘the curse of knowledge’ and with this often comes an outpouring of information with no structure.
Structure is needed to help your audience stay engaged (and connect the dots to what you’re telling them) by using signposts.
Use examples similar to these when you want your audience to be alerted to important concepts:
- It is important you remember (or make note of)…
- If you take away one gold nugget today this is it…
- Turn to your partner and share what you know about…
When you want your audience to know you’re providing more depth of concept use a signpost similar to this:
- Let’s take a deeper dive into this important idea…
To create a signpost to indicate you’re moving on to a new idea:
- Now that you have a good understanding of x let’s move on to…
- I’m going to do a complete about face now and talk about..
Pro Tip: Take your audience along your information path by dropping crumbs for them to follow so they can walk beside you.

Sucheta Misra Associate VP Inclusion & Diversity and Social Impact Leader
How To Create Signposts In The Conclusion Of Your Presentation
How many times have you been to a presentation where you weren’t quite sure that it was over because the speaker rambled on and then fizzled out? I’ve experienced this so many times I’ve lost count.

To demonstrate your communication expertise it’s important to finish powerfully and confidently so your audience is clear you’ve concluded your presentation:
- These are the most important concepts to take away from today…
- We’ve gone from x to y today. I’ve spoken about…
- We’ve covered lots of information today. Please connect with me…
Pro Tip: A word of caution with your conclusion – do not finish your presentation with a Q & A because you’ll give the floor (and your power) to someone else, risking having delivered a presentation that’s irrelevant. Instead speak to your signposts.
Spoken Signposts vs Visual Signposts
As effective as spoken signposts can be, equally effective are visual signposts. Skilled presenters have moved beyond using reams of bullet points in their presentations and using images in their slidedecks instead.
A carefully chosen image is a great signifier of the concept that will be spoken to next. The example below works well to signify loss of control or old school technology.

If you’re lost and unsure about how to make your presentation compelling, I can help.
What Is The Difference Between A Signpost And A Transition?
A signpost is a marker indicating where you are in your speech/presentation or the direction that you are going. Think of road signs you pass on the highway. For example, a sign that lets you know you are now entering Vancouver. The sign also indicates that Whistler (where you are heading) is 120 km from Vancouver. This is a marker that indicates the direction you will be travelling.
A transition may seem similar, however it is different. It is the actual act of moving your audience from one concept to the next. For example Vancouver is a beautiful city with skiing close by on Grouse and Seymour Mountains, however Whistler is known as a ski town that provides a full skiing experience. This example provides insight into skiing and then carries you along to possibilities.
Can You Have Too Many Signposts?
Yes. Audiences are sophisticated and need a few elements of surprise. When your presentation is too structured you’ll bore them.
The tired and misused recommendation ‘tell them, tell them again, and then one more time for good measure’ is outdated. No one wants to be talked down to or at every turn know what’s coming next.

Gently guide but don’t coddle. It’s okay to highlight statements such as, ‘this is important to note/remember’, however if you say it more than a few times all of those ‘important’ concepts will blur together.
By using signposts your audience will be able to stay with you and your carefully chosen thoughts and ideas. Help them stay on track by providing markers to guide them through your concepts so they will have tangible takeaways.
I help professionals master public speaking and communication skills. Reach out to set up a quick call to discuss how coaching can help you succeed as a speaker and position you as a leader.
Share this post:
Related Posts
How Much Should I Charge to Give a Keynote Speech?
Someone has just asked you how much you charge to give a keynote speech. What should you answer? It depends. I’m a public speaking coach. That gives me an insider’s view of keynote speaking costs
7 Public Speaking Books Actually Worth Your Time
Most people dislike public speaking. In fact, the stats say 73% of people fear delivering presentations or talks. If you are one of the 73%, you don’t have to be. There is an abundance of standout books
Yes, Anyone Can Become a Charismatic Speaker. Here’s how.
Is it possible to become a charismatic speaker if you weren’t born with the talent? Someone asked me that question at one of the first workshops I delivered as a public speaking coach. And it
Janice Tomich Site Map
Testimonials
Social Media
© 2023 Janice Tomich. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy | Terms of Use

Give the keynote. Without the nerves.

COMMENTS
A public speaking presentation is different from an online presentation because an online presentation is available any time. A public speech is typically limited to a specific time or place. Online presentations often use slideshows. Or they use pre-recorded videos of a speaker. (This includes recordings of a live public speaking presentation).
Public speaking skills are the pillars that hold up an excellent presentation and include argument construction, audience engagement, stage presence management, timely delivery, and appropriate pacing. You can also improve your public speaking by using humor, rhetorical questions, and analogies.
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
Presentation skills are the abilities and qualities necessary for creating and delivering a compelling presentation that effectively communicates information and ideas. They encompass what you say, how you structure it, and the materials you include to support what you say, such as slides, videos, or images. You'll make presentations at various ...
Before the presentation, the presenter is ready with all the required information and facts intertwined in a pre-defined sequence. More often than not, a presentation is on a specific topic and the presenter is given ample amount of time for preparation. 4. Creativity Index. Public speaking is an art that is creative.
Public Speaking is an art of effectively and efficiently delivering speeches or presentations to inform, persuade, or entertain an audience. It is an exceptional skill to possess because it has the power to inspire and influence others. A skilled public speaker has the ability to leave a lasting impact on the audience by delivering their ...
A Presentation Is... A presentation is a means of communication that can be adapted to various speaking situations, such as talking to a group, addressing a meeting or briefing a team. A presentation can also be used as a broad term that encompasses other 'speaking engagements' such as making a speech at a wedding, or getting a point across ...
Public speaking is, simply, an oral presentation or speech delivered to a live audience. It is generally a formal or staged event— although impromptu speeches are a common occurrence—and can be a defining career moment. For example, you may think you're attending a client meeting only to find yourself called on to explain a procedural or ...
7 Elements of Speech Communication. 1. Emitter/ Speaker. The emitter is the person who wants to deliver a message to a particular group of people or individuals; in public speaking, the issuer is known as the speaker. Factors to be considered: Motivation - The presentation can be made to provide/obtain information, to convince the group about ...
Facility with public speaking is not a gift granted at birth to a lucky few. It's a broad-ranging set of skills. There are hundreds of ways to give a talk, and everyone can find an approach that's right for them and learn the skills necessary to do it well. ... Presentation literacy isn't an optional extra for the few. It's a core skill ...
Public speaking skills refer to the talent of effectively addressing an audience. Whether it is in front of a group of people you already know or a crowd of complete strangers, your ability to communicate to them with clarity and confidence is known as your public speaking skills. There may or may not be an opportunity for interaction between the speaker and audience. The basic difference ...
Adjust accordingly so you can connect with them throughout your presentation. 2. Practice, practice, practice. Even the most seasoned public speaker needs practice to be effective. Give a mock presentation of your speech in advance, so you can determine if you've organized the information cohesively and clearly.
Public speaking, also called oratory, is the act or skill of delivering speeches on a subject before a live audience.. Public speaking has played an important cultural role in human history. Confucius, an ancient Chinese philosopher and prominent public-speaking scholar, believed that a good speech should impact individual lives, regardless of whether they were in the audience.
Public speaking, or the act of performing a speech in front of a live audience, is an integral part of scientific communication. Your reason for giving a talk may vary—whether you want to share your latest results with a broader audience, impress potential employers, or educate children about science. However, in all of these cases, it's ...
To fully understand the impact these skills have on creating a successful presentation, it's helpful to look at each one individually. Here are six valuable skills you can develop: 1. Active listening. Active listening is an excellent communication skill for any professional to hone.
How to use public speaking in a sentence. the act or process of making speeches in public; the art of effective oral communication with an audience… See the full definition
a) Confidence and presence: Confidence is a fundamental element of effective Public Speaking. Projecting confidence through body language, vocal tone, and eye contact captivates the audience and instills trust. b) Clear structure and organisation: A well-structured presentation is essential for audience comprehension.
Public speaking ranks high on the list of people's greatest fears. But the ability to present ideas in a clear, confident, and authentic manner affects your professional and personal success. ... You can structure presentations by using frameworks such as Cause and Effect or Past-Present-Future. 2. Own the Room. Making an impression isn't a ...
Before your next presentation or speech, here's the first thing you must think about. The next time you're preparing to speak to a group, remember to keep your audience at the center of your communication, says Briar Goldberg, the director of speaking coaching at TED. One way to do this is to ask yourself: "What gift are you giving to your ...
We focus on the "public" at the expense of the "speaking.". To become effective at public speaking, you must do just the opposite: focus on the speaking and let go of the "public.". Think of it as a conversation between you and the audience. If you can carry on a relaxed conversation with one or two people, you can give a great speech.
Public Speaking and Presentations: Tips for Success. This resource includes tips and suggestions for improving your public speaking skills. Even if you've never spoken in front of a large group before, chances are you will encounter public speaking sometime during your life. Whether you're giving a presentation for your classmates or ...
The fear of public speaking is more common than you might think, but with the right presentation skills, it's a hurdle that can be overcome. In this article, we'll help you master basic confidence-building techniques and conquer advanced communication strategies for engaging presentations.
A public speaking skill is any quality that helps candidates maintain a positive presence, engage with their audience and communicate clearly to convey their ideas. These skills allow public speakers to transform a standard presentation into an engaging and exciting event for their guests. These skills are essential in the workplace, as ...
You need to entice and hook your audience in with your first words. Starting with signposts won't accomplish that. Pro Tip: Begin your presentation with a hook. Engage your audience - pull them in. Then (and only then) speak to your signposts (using a light hand) to show your audience where you'll be taking them.
Around 30% of Americans fear public speaking. Terri Sjodin has researched thousands of sales presentations to identify the most common public speaking mistakes.