

Products & Services Section in a Business Plan (+ Examples)
- March 21, 2024
- Business Plan , How to Write

In this blog post, we’ll guide you through writing the products and services section of your business plan. We’ll cover how to describe what you’re selling and why it’s important in your business plan.
Whether you’re launching a new startup or creating a business plan for an existing business, this section is crucial for showing the value you bring to customers. Let’s get started!
Why do we include them in a business plan?
The products and services section of a business plan is more than just a list of what a company sells; it’s a vital narrative that tells the story of the business’s core offerings and their significance to the market.
This section is paramount for readers (especially potential investors) to grasp the essence of what the business is about, the unique problems it solves, or the specific needs it addresses.
A meticulously crafted products and services segment does much more than describe offerings. Indeed, it lays the groundwork for comprehensive marketing strategies , informs operational planning, and financial projections.
Moreover, understanding the business’s offerings in depth enables stakeholders to envision the company’s value proposition and competitive edge.
Where should you include them?
In a business plan, the Products and Services section is typically included within the business overview section.
This allows you to first introduce the business model and what it offers to customers. Only after this you can provide more details of the products and services.
The Products and Services section should clearly detail what you are selling, highlight the unique value proposition . It should also ideally explain how it meets the needs of your target market if it isn’t obvious. T
What to include: 2 Examples
Begin with a clear, engaging description of each product or service you offer. For services, describe the process, customer experience, and outcome. For products, discuss the materials, technology, and any unique features.
Services example: a Cryotherapy business plan

Products example: a Brewery business plan

Privacy Overview
How to describe your product and service in a business plan like a pro
It’s deceiving.
You’d think that this part of a business plan does exactly what it says on the tin–describe your product & service offering– right ?
And yes, you are partially right.
But there’s a very specific way in which this description should be written to make sure that your business has the best chance of succeeding – in real life and under the eagle eye of a potential backer (if you’re preparing a business plan for external financing purposes).
Keep reading to find out the secret sauce to writing a winning product and service description:
WHAT is the Product and Service Description in a Business Plan?
This business plan section is also known as:
- Product and/or Service Overview
HOW Do You Write a Product and Service Description in a Business Plan?
So, what should a good product/service overview contain?
Here are some items to consider including into this section:
1. Portfolio:
The range of products and/or services that a business offers to potential and current customers.
2. Features and benefits (value proposition):
Explain what the product/service does and how it works.
3. Problem and solution (value proposition cont.):
The problem(s) the product or service solves. Every business needs to solve a problem that its customers face. Explain what the problem is and how the product or service solves it.
4. Innovation:
If the company is doing something new and different, explain why the world needs the innovation.
5. Proprietary advantages:
Any proprietary features that contribute to a competitive advantage. This could include: intellectual property (e.g., copyright, trademark, patent filings, trade secret), exclusive agreements with suppliers or vendors, exclusive licenses (e.g., for a product, service or technology), company’s own research and development activities.
6. Development stage:
Current stage of development of the product / service (e.g., idea, development, testing, prototype, already on the market).
7. Product life-cycle:
Estimate the life span of the product or service.
Specify whether the product or service under consideration is a short-lived fad or has a long-term potential.
8. Future:
Mention plans for changes and new additions to the current portfolio of products / services.
Describe any plans to move into new markets in the future (e.g., serving different types or sizes of customers, industries, geographic areas).
Make your best guess at when the business will be ready to address these markets and what it needs to do first to be ready.
9. Limitations:
If applicable, explain any risks or limitations associated with the product (e.g., liability issues like guarantees or returns), along with any legal advice received regarding these issues.
10. Visual aids:
Use photos, images, diagrams and other graphics to help the reader visualize and learn about the products / services.
If the business is tackling several distinct problems through different products / services, describe the solutions individually .
However, for a large line of products / services, there is no need to list each one, just identifying the general categories will suffice.
How LONG Is the Product and Service Chapter of a Business Plan?
This part of a business plan can be very short, just a couple of paragraphs, or it can spread over multiple pages, depending on how many products/services you offer and how much explanation they require.
If your products or services are particularly complex , technical , innovative , or proprietary , you will want to provide more information and spend considerable time describing them.
This is especially true if you are seeking funding for a new product or service, particularly one that is not immediately understandable to the business plan readers, and if potential funders are likely to be motivated by the specifics.
In any case, when describing a product or service, provide just enough information to paint a clear picture of what it is and does . A brief explanation of what you will be making, selling or doing is appropriate here.
Excessive detail makes this section cumbersome for a reader to wade through. Reserve detailed descriptions (e.g., production processes) for the Appendix.
In any case, it is a good idea to first summarize the value proposition of each product or service into a one short sentence, and only then continue with a more detailed description of the product or service.
If any images or graphics are available that would contribute to the understanding of the product or service, the writers of a business plan should use them.
Otherwise, include any product or service details , such as technical specifications, drawings, photos, patent documents and other support information, in the Appendix section of the business plan document.
TOP 4 TIPS for Writing a Product and Service Overview
Tip #1: features v. benefits.
Don’t just list the features of the product / service.
Instead, describe the specific benefits it will offer to customers – from their perspective.
Make it clear what your customers will gain through buying your product or service. Include information about the specific benefits of your product or service – from your customers’ perspective.
Features are not the same thing as benefits. And you need to understand both.
Confused? Let’s clarify:
What Is the Difference Between Features and Benefits?
Tip #2: problem v. solution.
If at all possible, present the information in the Problem >> Solution format.
Start by describing the key problem that your customers have, immediately followed by the solution with which you will address this need for your target market.
Tip #3: Competitive Advantage
You should also comment on your ability to meet consumers’ key problems or unmet needs in a way that brings your product or service advantages over the competition.
For example:
- If you have a common business, such as a restaurant:
Explain why your customers need your particular restaurant. Do you offer lower prices? More convenient hours? A better location? A different concept, such as a vegan ice-cream pop up store? A specialty that is not otherwise available in your area, such as a Peruvian ceviche or Hungarian goulash?
- If your company is doing something new and innovative :
What is it about the existing solutions that is subpar? Maybe you are improving on a mediocre product category, such as creating better medical uniforms for healthcare workers (e.g., more flattering cut, trendy designs, sustainable materials). Or perhaps your new blockchain solution has the potential to entirely eliminate the middle-men in an entire industry.
Although the subject of competitive advantage regarding the business as a whole will be fully explored in the Market and Competitor Analysis part of a business plan, it is advisable to touch on it here also – in the context of the company’s products and service.
Tip #4: Validating the Problem and Solution
Speaking of which, when you are doing market research and analysis for your business plan, remember to validate the problem and solution your product or service is addressing.
There is a plethora of minor issues out there that people are perfectly fine with just tolerating. To build a solid business, though, you need a problem that a sufficient number of people are motivated to solve. That is, that they recognize it as a problem that’s worth paying you to solve. Even if they didn’t realize it was solvable until they were presented with your solution.
So, how do you get evidence that prospects are willing to pay for your solution?
Validation of Problem
Describe what you’ve done so far to confirm that the problem you are focused on is a real problem for your customers.
- Existing Business:
For an established business, this is probably just a matter of recapping your success in the marketplace. Your customers have already voted with their wallets.
- New Business:
For a startup, it is important to survey and have conversations with as many potential customers as possible about where they are having problems, how they solve them today, and validate that they are interested enough in addressing those problems to pay for a good solution.
Validation of Solution
Describe how you have tested your ideas with existing or potential customers to confirm that there is a good market for the products or services you plan to offer. Summarize the positive customer feedback or market traction that you have achieved with your solution so far.
For an established business, the answers probably lie in your paying customer base – their existence itself, combined with their repeat business, word-of-mouth referrals, follow-up customer surveys, and other indicators of customer satisfaction.
For a new business, you can start validating your solution immediately by trying it out with potential customers, even informally or at no charge, to get their opinion. If your product or service does not exist yet, talk to prospects about what you plan to offer and measure their feedback.
In summary, this section should answer the million dollar question:
What makes you think that people will buy, be satisfied with, and recommend your products or services?
Related Questions
What are products and services.
Products and services are items that businesses offer for sale to a market. While services are intangible, meaning that they do not exist in a physical form, products are of tangible nature, in other words – you can touch them.
What is a Product Line?
Product line is a group of related products that are all produced or sold by one entity and typically marketed under one brand name.
What is a Service Line?
Service line is a group of related services that are all produced or sold by one entity and typically marketed under one brand name.
Sign up for our Newsletter
Get more articles just like this straight into your mailbox.
Related Posts
Recent Posts

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

How to Write Products and Services Section of Business Plan
Business plan products and services section gives details of your product or service, how it is different and if you have a reliable manufacturing or sourcing system for the product.
How do you write the business plan products and services section?
Key questions to answer in the business plan products and services section.
Show competitive advantages of your product or service. Convince investors or lenders that you can outperform competition; you’ll likely get the funding you need.
Use this article as a guide when writing the product and service section of your business plan.
Hire business plan writer now!

Your goal in writing the business plan products and services section should be to explain your offering in simple, layman’s terms.
Anyone reading about your products or services should be able to understand:
- what you are offering
- what is the unique value you are offering
- how will you do quality assurance
- How will you meet the increased demand?
The product service plan section should include the following.
Explain Your Products or Services
Explain your product or service in detail. Try to include a brief about all the aspects of your product or service that will improve the consumers’ lives or increase business efficiency.
Show why your Product is Unique
Talk about the distinctive features of your product. Show what competitors are offering and explain how your offer is unique and better.
Emphasize the Benefits
Your hopes of capturing a share of the market depend on the benefits your product or service provides. Describe the benefits in terms customers can relate to.
For example, if you are offering the same features as the competitors but at a low price, highlight the low price.
Manufacturing, Sourcing, and Fulfillment
Explain if you will manufacture your products or you’ll source. If you are going to source the product from a manufacturer, how will you select the manufacturer?
Also, briefly explain the product supply chain and fulfillment process. Potential lenders may want to know if your supply chain and fulfillment system can handle high demand.
Be Short and Concise
Keep to the point. The Product service section in a business plan is about introducing your offering with a fair amount of detail. However, don’t make it lengthy.
You will discuss your product or service in every section of the business plan one way or another.
Show your Expertise
A product coming from an acknowledged expert gets more acceptance in the market.
Show your education or experience with the offering. If your business has any patents, trademarks, or special permits, make sure you showcase them. That way, you can establish yourself as an authority.
For a sole proprietor, you can include your experience or education. For example, when an athlete starts a fitness brand, it becomes a quick success. However, other similar businesses face struggles at the start.
Explain in Simple Language
Make a detailed plan of product service but explain everything in simple language.
Every industry has its jargon and buzzwords. People familiar with your product can understand the technical details, but the lenders or investors may not know much about your industry.
Here is a pro tip for this. When you have written the product or service description, ask a trusted friend or family member to read it and explain your product to you. That way, you can know if your product service part of the business plan is generally understandable.
What is your Exclusive Advantage?
Your exclusive advantage is what makes you stand out. You spotted your exclusive advantage when you developed your product or service offering. Explain that exclusive advantage here.
If you think there is no exclusive advantage, see if you can lower your price or provide better after-sale support. Even if your exclusive advantage is indirectly related to your product, it can help you get ahead fast.
Assume you are talking to the customer
When you walk into the customer’s shoes, you can understand their needs better.
Assume you are talking to an actual customer and convincing them to buy from you. They know your competition and they know what they need. You will have to talk in layman’s terms without missing any important details. You will need to focus on your competitive advantage.
You will write an excellent product or service section when you think you are explaining it to a potential customer.
- Do you have a ready product or an under-development product?
- When will you bring new products or services to the market?
- What is the unique advantage of your product or service?
- What are the competitive advantages of your product or service?
- Does your product or service have any competitive disadvantages?
- Are you bound to charge a price in a short range, or can you charge a different price with a better offer?
- Are your business operating costs reasonable?
- Will you manufacture your products or buy from a supplier?
- Do you sub-contract the parts of your product to different manufacturers and assemble the product at your facility?
- Will you be able to keep a steady and reliable supply chain for your product when demand rises?
WiseBusinessPlans is one of the best business plan writing companies !
In the products and services section, describe your offerings in detail, including their features, benefits, and uniqueness. Include information on pricing, any proprietary technology or intellectual property, and how your products or services meet customer needs.
Differentiate your products or services from competitors by highlighting their unique selling points, such as superior quality, innovative features, customizable options, or exceptional customer service. Explain how these differentiators give you a competitive advantage.
Yes, it’s important to outline your pricing strategy in the products and services section. Explain your pricing model, whether it’s based on cost-plus, value-based, or market-based pricing. Justify your pricing strategy by considering factors such as market demand, competitors’ pricing, and perceived value.
Demonstrate the market need for your products or services by providing market research and analysis. Include data on customer demographics, target market size, and any trends or consumer preferences that support the demand for your offerings.
Yes, you can mention future product or service expansion plans in the products and services section. Briefly outline your growth strategy, such as introducing new product lines, expanding into new markets, or offering additional services. However, focus primarily on your current offerings and their value proposition.
Access our free business plan examples now!
Quick links.

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

ZenBusinessPlans
Home » Business Plans
How to Describe your Product in a Business Plan

The product or products your business intends to produce or offer will have to be described in the product description section of your business plan. This section of your business plan is meant to explain how your product will stand out from comparable items in the market.
You have to clearly explain its concept, coupled with all aspects of purchasing, manufacturing, packaging, and distribution. You should also identify your suppliers, costs, and how the product you are offering fits into the current market.
Note that the product description in your business plan is more than a simple listing of product features. In this section, you will need to highlight your product’s most unique characteristics that will ensure it stands out in the marketplace and attract buyers who won’t mind paying your price.
Note that a properly written product description in your business plan can entice investors and help your business grow. Make sure you describe what you are offering in layman’s terms, to guarantee that someone who isn’t conversant with your business will grasp and be excited about it.
It may also be necessary to provide some basic background if this is an area or industry that people are not so familiar with. While you write up the Products and Services description section of your business plan, always keep your reader in mind.
What to Include in the Products and Services Description Section of Your Business Plan
Just as was noted above, the products and services section of your business plan will have to explain in detail your product or service, its demand in your market, and how it intends to compete with other businesses selling the same or similar products or services. Nonetheless, the product and services description section of your business plan is expected to include:
The Product or Service Description
It is important the product description section of your business plan clearly explains the concept of your product, coupled with all aspects of purchasing, manufacturing, packaging, and distribution. What are your product and service, and how does it work? How will this product benefit your customers? How do you plan to make it or how do you intend to get it made?
Product Comparison
This section of your business plan will also have to explain how your product compares with similar products in the market. What makes this product or service unique or better than what’s already obtainable in the market? Why would anyone prefer your product or do business with you?
You will need to describe how and why you are competitive. How do you stand out, and why do your business and everything it offers have such a viable chance at succeeding? In talking about your product or service, always try to answer why a client would want it and how it can make their lives better or more profitable?
Accreditations/Intellectual Property
For businesses that have had their product tested by industry experts, you must include this information when describing your product. Don’t forget to highlight any certifications, trademarks, copyrights, or patents.
Have it in mind that these added advantages or achievements can give you and your product an upper hand. Verified patents and trademarks can also heighten the value of your product especially since it shows that only your company can manufacture the product for the life of the patent.
Have it in mind that a product’s life cycle includes the idea, prototype, and expansion stages. If you are still in the idea stage, you must buttress in your description how you intend to get the product made and why your product matters.
If you maybe already have a prototype, outline your plans for evaluating the prototype and manufacturing your product. If your business has been making the product but is looking to expand to keep up with demand, ensure you explain this when describing your product in your business plan.
You will also want to include the cost of your product and how that cost aligns with other comparable products on the market. In very concise detail, explain how you came to this price, including the cost to manufacture, selling price, and profit margin.
Sales and Distribution Strategy
Also, take your time to explain how and where you will sell your product. Have in mind that your options may include online stores, brick-and-mortar locations, and vendors. If you already have vendors selling your product, ensure to note who they are and their locations in this section of your business plan.
Fulfillment
When describing your product in your business plan, it is also important you describe your plan to ensure your product gets to the intended customers. This should include manufacturing details and delivery specifics. If you plan to outsource the production of your goods, don’t forget to note manufacturer specifics such as location and production time. Also, remember to include the approximate delivery times and methods.
Requirements
Will you require any special equipment or technology to provide your product or service? Also explain if any specialized technology, materials, or equipment will be required to manufacture your product.
You will also have to explain your plans for product development and introduction especially as your business grows.
Photos or Brochures
Also, make sure that your potential investors can get a good insight into your product through photos and brochures. Don’t forget that your business plan is expected to have an appendix for photos and brochures. Also, don’t forget to refer to them in the product description section.
Tips for Writing a Product Description
To ensure you describe your product thoroughly, here are some vital tips to guide you;
- Always remember the reader. The product description section of your business plan must note your product’s most vital information. Always remember to make this section very easy to read and understand. Consider making it better by leveraging numbered lists and bullets.
- Focus on benefits. When describing your product, you must explain how its features can provide value to consumers. Translate your features into benefits, and remember that the aim is to describe how your product or service will be a solution to a problem or improve a client or customer’s life.
- Highlight the features of your product or service. To attain substantial success in any business, your business will need the ability to set itself apart from other businesses that offer or sell the same products and services. Take your time to analyze key features, such as price point or level of service, or anything that makes your product unique in the market.
- Show off a little. Don’t forget that you are selling a product and also selling yourself as the most viable provider of that product. Ensure to include all vital educational or industry-specific experiences and awards in this section. If you have endorsements or testimonials specific to your product, include them as well.
- Show the need for your product. Also make sure you explain how your product will cater to a need or improve life, showing why your product is very necessary to the consumer. This is very pertinent if your product has no current market.
The product and services description section of your business plan is meant to provide the reader with an explicit understanding of why you are in business, what you sell, how you will compete with what’s already available, or how you intend to fill a niche that no one else is currently meeting. Noted above are things you need to consider when creating the product description section of your business plan to ensure that it will indeed grab your readers’ attention.
More on Business Plans
AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
INTEGRATIONS
Quickbooks Sync and compare with your quickbooks data
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
Xero Sync and compare with your Xero data
See how it works →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
BY USE CASE
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
Write Products and Services Section of a Business Plan
Free Product & Service Description Worksheet
Ayush Jalan
- January 3, 2024

The core purpose of any business is to sell its offerings to its target customers.
To do this, you devise a plethora of strategies, tactics, and plans. While that is important, your sales ultimately depend on the value you provide to your customers through your products and services.
FYI, we have used the term “product” in this article to refer to both products and services unless mentioned otherwise.
Table of Contents
What is a Products & Services Section?
- What’s Included in the Products & Services Section
- 6 Tips on Writing a Good Products & Services Section
The products and services section of your business plan is where you mention and elaborate on your product range, product descriptions, pricing strategies, and other relevant details.
If you’re looking for partners or investors, this section plays a crucial role in persuading them. What you include in this section and how you write it can deeply impact whether or not your investors will seal the deal with you.
What’s Included in the Products and Services Section
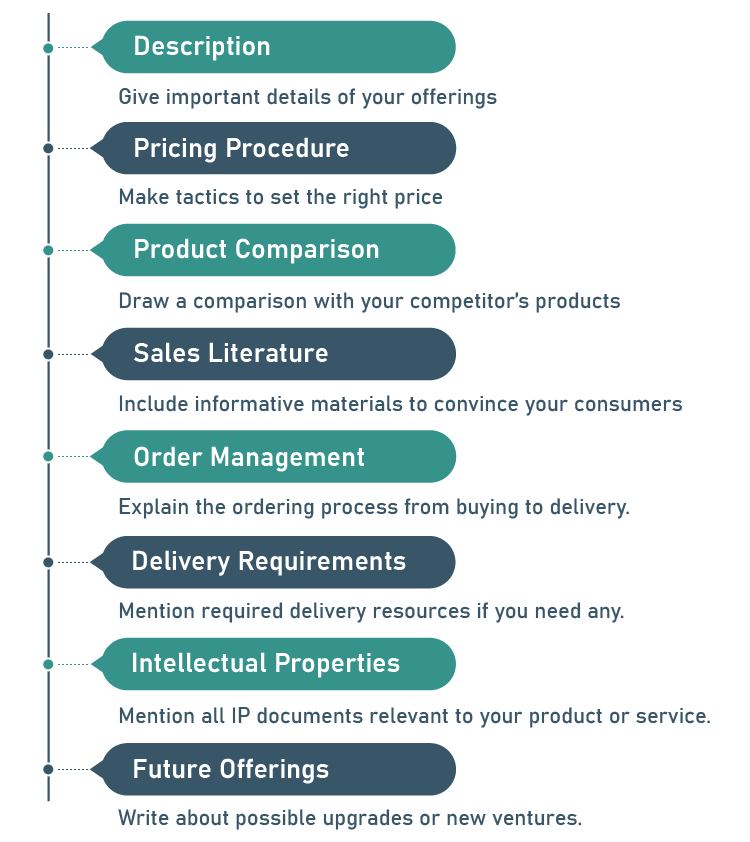
In the products and services section of your business plan, you provide an overview of what you offer. Here are all the key elements your products and services section should cover:
1. Description
In this part, you include all the important details of your offerings. To write an accurate description, you can use the 5W2H method and answer these questions:
- Who can use this product? Mention the details of your ideal customer.
- What are the fundamental aspects of your product? These may include features, materials, ingredients, costs, dimensions, etc.
- When should someone use this product? Mention the occasion, or the season if it’s a seasonal product. You can also mention if it is designed for a specific purpose.
- Where should your customers use the product? Is it used indoors or outdoors? Specify these details.
- Why should your customers use your product? Mention how the product fulfills their needs.
- How should they use your product? Mention if there are any important user instructions.
- How much should they use it? Mention the ideal frequency of usage that’s essential to follow while using the product.
2. Pricing Procedure

A pricing strategy refers to the tactics you use to set a price for your products and services. There are several pricing strategies to choose from; you can pick the one that best fits your business model .
There are several things to consider before setting your price. Conduct a price analysis to get an idea of which pricing strategy works for you. Here are the steps involved in conducting a pricing analysis:
Determine cost of goods sold ( COGS ):
To calculate the total cost of your products and services, add all the expenses that you incurred before the sale. This will include costs such as manufacturing, labor, warehousing, distributing, packaging and labeling, marketing, etc.
Collect data about the price preferences of your customers:
Study your competitors’ prices:, consider all the legal and ethical aspects:.
After conducting a pricing analysis, you can look at these pricing strategies to choose one for your business.
3. Product Comparison
Regardless of what you’re selling, chances are someone in the market is already selling it. Unlike direct competitors, indirect competitors are those who sell similar products with slight variations.
Looking at your competitors can help you draw a comparison. To do that, examine their products and services and list down the similarities and differences.
Categorize this information into qualitative and quantitative aspects and organize it in tables. Finally, summarize it by including your advantages over competitors. Also, include how you will leverage them to balance your drawbacks.
4. Sales Literature
Sales literature refers to the promotional and informative materials you use to inform, clarify, and convince your customers to make buying decisions. These include brochures, catalogs, newsletters, price lists, customer testimonials, and case studies .
List out all the sales literature you use or plan to market your products and services; explain the information it conveys in brief. Another integral part of your sales literature is your website; explain how it contributes to your sales.
Perhaps you run a blog to promote your products and inform your customers about new releases. Maybe you sell your products and services directly from your website; in that case, your sales literature material will go there.
Sales literature is a quick and attractive tool to market your products and services.
5. Order Management
Order processing refers to the stages from the moment a customer places an order to the delivery of the product paired with after-sales services. Here, you explain how customers will order or buy the product and the delivery process.
For instance, if you are an online retail store , your order processing may include these stages:
- Order Placement
- Order processing
- Picking inventory
- Product Delivery
- Customer support
Depending on your offerings, your order processing workflow can have several stages. Describe each step and provide elaborate details about the execution.
6. Delivery Requirements
If the delivery or creation of your products and services needs any resources, you mention them here. These include equipment, vehicles, technology, and software.
For instance, a cafe owner will need kitchen equipment and IT solutions to run and provide its services. These should be mentioned in this part of the products and services section.
To cite another example, a consumer electronics company needs an IT infrastructure and production facility to create its products. For delivery, it needs vehicles and an online portal for customers to place and receive orders. All these are mentioned here.
7. Intellectual Properties
Mention all the IP documents that are related to your products and services. These include trademarks, seller permits, patents, other licenses, etc. Here you can also include any legal issues you are currently facing. Explain how you are dealing with the existing issues.
Further, mention the issues that might occur in the future and the counteractive measures you will take to prevent them. These include adding safety labels, and disclaimers, opting for insurance policies, etc.
8. Future Offerings
This is a chance to impress your investors or partners by briefing them about your future products or services. This shows that you’re already working on new ideas which help convey your potential and dedication.
If your future products are an extension of your current ones, you can rodenticide an outline of the improvements made. Mon whether your future products are under development or ready for launch.
6 Tips on Writing a Good Products and Services Section

1. Opt for a customer-centric approach:
Your goal is to cater to the needs of your customers through your products or services. Hence, write as if you are talking to your customers and directly addressing their issues. Point out how your product will make their lives better and easier.
2. Keep it simple:
Clearly represent the information. You can use bullet points and lists to convey your message. You can also use tables and charts to display product comparisons, strengths, etc.
3. Ditch buzzwords and industrial jargon:
Everyone who reads your business plan may not understand the industrial jargon and buzzwords. Therefore, it is best to skip the complicated lingo and use layman’s terms.
4. Specify market pain points:
Elaborate on the problems your target audience is facing. You can gather this data by conducting a market analysis. Mention the various pain points and the features of your product that address them. Consider citing examples and relevant statistics to display how your product solves a customer problem .
5. Emphasize your USP:
Highlight the benefits and the unique features of your products and services. Mention the things you do differently than your competitors and how you offer more value in comparison.
6. Flaunt your achievements:
Make sure to show off the business milestones you’ve achieved such as awards, news articles, customer reviews, etc. You can also include your past sales numbers, your customer base, and the projects you fulfilled. These instill trust and help investors, clients, and partners to make decisions.
Persuade Interest with a Products and Services Section
Products and services are the lifeblood of your business. An accurate representation of your offerings is crucial to scoring funding and demonstrating your potential to grow in the market.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
About the Author

Ayush is a writer with an academic background in business and marketing. Being a tech-enthusiast, he likes to keep a sharp eye on the latest tech gadgets and innovations. When he's not working, you can find him writing poetry, gaming, playing the ukulele, catching up with friends, and indulging in creative philosophies.
Related Articles

How to Write a Market Analysis for a Business Plan?

How to Write Pricing Strategy for Your Business Plan

How to Write a Customer Analysis Section for Your Business Plan
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee

How To Write the Products and Services of a Business Plan
Crucial to business plans designed to secure funding or partnerships, your products and services section needs to showcase the quality, value, and benefits your business offers.
It’s not just a list of what your business is going to produce or provide. Instead, it outlines what you make or do, why your market needs your products or services, how you will compete with other companies selling the same or similar products or services, and what you will charge.
What To Include In The Products and Services Section
When looking at how to write the Products and Services section of your plan, be sure to include:
- A description of the products or services you offer or plan to offer
- A pricing model for your products or service, including how you set your prices and how you will make a profit. Include a breakdown of your Costs of Goods (COG) and Costs of Services (COS), what your contingency plan is in the event of a shift in market conditions, changes to laws, or availability of supplies, and your markup strategy.
- A comparison of your competitors’ products or services against yours, including a survey of what your competitors charge for similar items, along with a discussion explaining your pricing strategy
- Any sales literature or marketing materials you will use, including your website’s role in your sales efforts.
- An outline of how your orders will be processed or fulfilled.
- Any needs required to create or deliver your products (for example, up-to-date computer equipment)
- Any intellectual property (trademarks) or legal issues needing to be addressed.
- Future product or services
How to Make The Products & Service Section Appealing
Ideally, this section should elicit excitement in your reader and entice them to fund your business or work with you.
Here are few ways to accomplish this when deciding how to write the Products and Services section of your business plan:
- Showcase why there is a need for your product or service. Doing so is especially important if you’re introducing a new concept or invention or introducing your product or service into a place where there is currently no market for it.
- Emphasize the features of your product or service. How does it differ from that of your competitors in terms of make, shape, form, or appearance? Or price point? Or the level of service? What makes it unique?
- Focus on benefits. Once you’ve identified what features make your product unique, it’s vital to show how those features provide value to consumers. Is your product cheaper? Is your service faster? You want to clearly indicate how your product or service will fix a problem or improve a client or customer’s life.
- Be clear and concise and talk in layman’s terms. Avoid getting bogged down in lengthy descriptions or unnecessary details. Use bullet points and numbered lists to highlight important information. Don’t assume that your potential funders, partners, or customers have the same level of knowledge. Instead, consider the reader doesn’t know as much as you do when explaining your offering. Stay away from acronyms, jargon, industry buzzwords, and aim to be customer-oriented. If you have to use acronyms or jargon, always provide a definition.
- “ Why are you the best person to provide your products and services?”
- “What education or experience do you have that makes you qualified to provide them?”
Have Questions? Looking To Get Started?
- Your Name *
- Email Address *
- Phone Number
Don’t forget to include any testimonials, awards, or accolades you’ve received as well as any patents, copyrights, or trademarks you own or have applications for. Have you had the product tested or certified? Gotten approvals from industry experts? Including these details adds credibility to your overall business plan.
- Identify any liability issues: A liability lawsuit can significantly change the landscape of your business. Even if you don’t foresee any liability issues, include a statement to that effect rather than not address it at all. If there is a liability issue, real or apparent, acknowledge it and describe how you’ll deal with it. Let the reader know you will take all necessary steps to protect your business, your products, and yourself from litigation.
- Be precise in your product or service descriptions. For example, you don’t want only to say, “I sell shoes.” You want instead to say, “I sell leather boots targeted at women aged 16 – 25 who buy online”. Wherever possible, also include pictures of your products.
Questions to Answer in Your Products & Services Section
- Are your products or services in development or existing and on the market?
- If they currently aren’t on the market, what is the timeline for bringing them to it? Do you have a prototype?
- What makes your product or service different? What are your competitive advantages? What are your competitive disadvantages, and how will you overcome them?
- Is your pricing an issue? Are your operating costs low enough to allow for a reasonable profit margin?
- Where are you acquiring your products? Do you manufacture them, or do you assemble them using third-party components? Do you purchase from suppliers or wholesalers? If demand increases, do you have a steady supply of products available?
- How are you going to sell your product or service? Will it be available online or in retail stores? Do you have any vendors lined up?
Once you’ve answered these questions, stop and reread the section. Ask yourself if you’ve tried to answer why a client would want your product or service. Consider whether your offering will make your customers’ lives better or more accretive.
Examine the need you are fulfilling or the problem you are solving. More importantly, does the section give the reader a clear understanding of why you’re in business, what you sell, and how you differ from your competitors?
After completing this exercise, if you’re still unsure or would like more support about how to write the Products and Services section of your business plan, we invite you to reach out to our team at Bsbcon.
We are available to help small-medium-sized enterprises worldwide tackle their most critical challenges and capture their most significant opportunities. We make a point to understand new trends, digital options, and partnerships that help our clients today and tomorrow. Call us toll-free at 1(888) 880-1898, write [email protected] , or fill out our contact form here .
Let's Get Started!
How can we help you.
Get in touch with us or visit our office
- United States
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How to Write the Products or Services Section
Learn about this essential part of a business plan
Alyssa Gregory is an entrepreneur, writer, and marketer with 20 years of experience in the business world. She is the founder of the Small Business Bonfire, a community for entrepreneurs, and has authored more than 2,500 articles for The Balance and other popular small business websites.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/alyssa-headshot-2018-5b73ee0046e0fb002531cb50.png)
Describe and Compare
Price points, order fulfillment, tips for writing the products or services section.
The products or services section of your business plan should clearly describe what you are selling with an emphasis on the value you're providing to your customers or clients. Include an in-depth look at all of the elements related to what you are selling.
The section needs to explain exactly what you are selling and how it fits in the marketplace. It's easier to describe the value provided if you are the only business in the area selling the product or service in question, but it is likely competitors are doing something similar.
Provide information about your competitors' offerings, how they are similar to yours, and how they are different. It's possible your business has a slightly different take on the product or service or is targeting a slightly different audience. It's also possible what you are offering is almost identical to what your competitors are offering, but demand in the marketplace is high enough to support multiple businesses doing the same thing. Explain your situation.
In addition to describing the actual products or services, break down how much they will cost. Products may come in different sizes, quantities, or varieties that will impact price, and services might be more or less extensive depending on the price being charged.
Address what competitors are doing in this regard as well. Perhaps you are offering higher or lower quality for a different demographic, but be clear about the cost and who can afford it.
Explain what happens once someone purchases what you are selling. If it is a product, they might buy it from a retail store, have it delivered from your online shop, or perhaps they submit a custom order in advance and pick it up at a later date.
If you are offering a service, it might be something that involves clients coming to you, or you might go to them. Whatever the details, make sure the process is clear.
If special technology is involved, outline what it entails. This could be specific technology you need in order to provide your services, or it might be technology clients or customers need in order to take advantage of what you're selling.
For example, if signing up clients for a training seminar, you might need specific hardware and software for a presentation. Perhaps you are selling software that requires the latest version of a particular operating system. Be sure these details are provided.
Make your description of available products or services an effective part of your business plan by following these tips:
- Focus on the customer: The purpose of the products or services section is to clearly express the benefits you're providing to your customers or clients. Focus on that goal by addressing how what you are selling benefits your customers. Show how it makes their lives better, easier, or more profitable.
- Get to the point: State the value upfront, then elaborate throughout the rest of the section while providing supporting materials. For example, if the primary benefit of what you are offering is that it saves time, state as much right away. Follow this statement with details about how it saves time and data to support the claim.
- Keep It simple: Assume the reader has little to no understanding of your industry and product or service. You're the expert in the industry, but the basics may not be as clear to those reading your business plan.
- Show what makes you unique: While describing similar products and services that are already in existence, take some time in your description to express how your product or service stands out as something different.
- Include the fine print: While the bulk of your products or services section should focus on the end result, you also should include information about your pricing and how you arrived at that price point.
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated May 7, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.

Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
USF Libraries Hours by campus
Libraries locations.
- Libraries Hours
- Outages & Maintenance Alerts
RESEARCH TOOLS
- Subject & Course Guides
- USF Libraries Catalog
- Quicksearch All-in-one-search
- Citing Sources
- Find my Librarian
GUIDES / HOW-TO
- Tutorials & Workshops
- Finding Books and Articles
- Finding Reserves
- Checking Out & Renewing
- Reserve a Study Room
- Additional Help Topics
- star Other Services
- For Faculty
- For Graduate Students
- For Undergrads
- Requesting Books & Articles (ILL)
- Textbook Affordability (TAP)
- Library Instruction
- Laptop Checkout
- Schedule Research Help
- Geographic Information Systems
- Data Management Planning
- Copyright & Intellectual Property
- Scholarly Publishing
- Other Services
COLLECTIONS
- What are Collections?
- Special Collections
- Digital Collections
- Digital Heritage & Humanities
- Digital Commons @ USF
- Oral Histories
- Online Exhibitions
- Printing in the Library
- IT Help Desk
- Digital Media Commons (DMC)
- Writing Studio
- Office of Development
- Office for Undergraduate Research
- Directions to the Library
- Library Info & Floor Maps
- Connect From Off Campus
- Renew Materials Online
- Check UBorrow Status
- Printing Help
- Report a Problem
- About the USF Libraries
Business Plan & Pitch Presentation
- #1. Executive Summary
- #2. Description, Objectives, and Product/Services
- #3. Market Research
- #4. Marketing and Sales Plan
- #5. Financial Analysis and Projections
- #6. Appendix
- How To Pitch Your Business Plan
Business Description
This section will include, but is not limited to:
- The registered business name
- Physical location(s)
- Names of founders and key members, including relevant experience and qualifications
- Information about the legal structure (LLC, sole proprietorship, etc.)
- Business history, including any milestones or notable achievements
Business Objectives
In this section, you'll outline the core purpose and mission of your business. Condense your company's primary objectives and guiding principles into a concise statement (a few sentences). This is where you define your business's nature, fundamental values, corporate culture, and your desired positioning within the marketplace.
Products and Services
Provide details about your business's products or services. The following should be included:
- Product or service description
- Product or service use and appeal (explain why it is used and what constitutes its appeal)
- Stage of development (how the product or service has evolved to present state, and how it is expected to evolve in future)
- Explain how products are created or how services are delivered, including information about suppliers, manufacturing, or service processes
Resources for Developing Your Business Description, Defining Business Objectives, and Detailing Products and Services Components:
- Business Plans Handbook Actual business plans compiled by, and aimed at, entrepreneurs seeking funding for small businesses. Presents sample plans taken from businesses in the manufacturing, retail and service industries which serve as examples of how to approach, structure and compose business plans.
- Business Plans For Dummies Textbook that leads you through the process of creating a comprehensive, accurate, and useful business plan.
- The Ernst and Young Business Plan Guide Textbook that leads you carefully through every aspect involved in researching, writing, and presenting a winning business plan.
- Business Plan Development Guide Textbook and its accompanying spreadsheet templates serve as a guide for developing a business plan.
- ABI/INFORM Global This link opens in a new window Database providing in-depth coverage of business and economic conditions, management techniques, theory, and practice of business, advertising, marketing, economics, human resources, finance, taxation, computers, and more.
- Business Source Premier This link opens in a new window Database providing articles from journals and magazines covering business subjects including accounting, finance, economics, marketing, MIS, and operations management.
- << Previous: #1. Executive Summary
- Next: #3. Market Research >>
- Last Updated: May 3, 2024 11:28 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.usf.edu/business_plan
- AI Content Shield
- AI KW Research
- AI Assistant
- SEO Optimizer
- AI KW Clustering
- Customer reviews
- The NLO Revolution
- Press Center
- Help Center
- Content Resources
- Facebook Group
How to Craft a Detailed Product Description in Business Plan
Table of Contents
A well-written product description in your business plan has the potential to attract investors and aid in the expansion of your company.
In addition to describing your manufactured goods, your product description should emphasize the benefits of the goods. These benefits must align with your business.
This article discusses developing a product description for a business plan and offers writing advice to help you craft your own.
What Is a Product Description in Business Plan?
The product description in the business plan describes all the products the company produces .
A business plan product description describes a product or service, the firm supplying it, the problem it answers, the price, and the target market. Your product description should explain how your products differ from similar ones on the market or why they’re needed if no market exists.
Product descriptions should be factual and not promotional or salesy. As with other business papers, a product description should be in the first person, so it doesn’t appear overly promotional.
A product description in a business plan should be understandable, so the value of your products is clear.
What Does a Product Description Entail?
A product description introduces your product to potential investors and customers. The following items below should be included in the document when presenting your product to potential investors and customers.
1. Features and Benefits of the Product
Describe the features and benefits of your product. If your product addresses a problem for customers, this section should convey that information.
2. Your Product Vs. Competition
Take a look at the competition and see how your product stacks up. Make a case for why your product is better than your competition’s offerings.
3. Price of Product
Include the price of your product and how it compares to other similar products on the market in your pitch. The cost of production, the selling price, and the profit margin all need to be discussed.
4. Trademarks
You should add this information if you’ve had your product tested by professionals in the field. Including any certifications, intellectual property, copyrights, or patents is also a good idea.
These awards and honors bolster your product’s credibility. As a result of being awarded patents and trademarks, your company is the only one that can make this product. This increases the product’s worth.
5. the Life Cycle of the Product
The idea, prototype, and expansion stages are part of a product’s life cycle. If you’re still in the concept stage, use this section to explain how you’ll build the product and why it’s necessary.
If you already have a prototype, discuss how you intend to evaluate it and manufacture your product. Include it here if you have been producing your product but need to grow to meet demand.
6. Distribution and Sales Strategy
Describe your product’s distribution strategy, including how and where it will be sold. Vendors, brick-and-mortar stores, and online retailers are examples of possible sales channels. If you already have a list of suppliers selling your goods, insert their names and addresses here.
7. Product Delivery to Final Consumer
How do you intend to get your product into the hands of your clients? All the manufacturing and shipping details should be included here. Include information on the manufacturer, such as their location and manufacturing time. It is advisable to outsource the production of your goods, including delivery schedules and methods.
8. Resources
Identify any unique equipment, materials, or technology required to produce your product.
9. Future Expansion Projections
As your firm grows, describe your product development and introduction plans.
10. Evidence in the Form of Photos and Brochures
Photos and brochures can help investors visualize your goods. Include pictures and brochures in an appendix to your business plan, but reference them in the product description.
With a business plan product description, you’ll enlighten the reader about the firm, the product, and its market .
A product description tells the reader what the product is. It also explains how it works, how it benefits the company and consumers, and how much it costs.

Abir Ghenaiet
Abir is a data analyst and researcher. Among her interests are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing. As a humanitarian and educator, she actively supports women in tech and promotes diversity.
Explore All Product Description Generator Articles
T-shirt product description: essential tips to increase sales.
Product description is essential for the success of your t-shirt brand. A well-crafted t-shirt product description can be the difference…
- Product Description Generator
How to Create a Template for Product Description
Have you ever experienced customers asking many questions about a product you are selling through your store? Maybe because you…
Top Service Description Examples You Should Explore
The way you write your product or service descriptions has a direct effect on your sales figures. However, many small…
Want To Write SEO Friendly Product Descriptions?
A successful eCommerce business relies heavily on its product descriptions. A strong description gives you the ability to allay any…
Benefits of Effective Amazon Product Descriptions
Amazon is a powerful tool for sellers and entrepreneurs. As the competition on Amazon and the e-commerce world gets more…
Examples of Cool Product Descriptions for Clothes
The clothing business is growing, and demand has never been higher. It’s a lot of work bringing new ideas to…
Sample Business Plan
Learn the Essential Elements of a Full Business Plan
- Famous Inventions
- Famous Inventors
- Patents & Trademarks
- Invention Timelines
- Computers & The Internet
- American History
- African American History
- African History
- Ancient History and Culture
- Asian History
- European History
- Latin American History
- Medieval & Renaissance History
- Military History
- The 20th Century
- Women's History
The following business plan for the fictional firm of "Acme Management Technology" (AMT) is an example of what a completed business plan might look like. This example is provided as part of the instructions and detailed descriptions included in the Components of a Business Plan.
Sample Business Plan for Acme Management Technology
1.0 executive summary.
By focusing on its strengths, its key customers , and the company's underlying core values, Acme Management Technology will increase sales to more than $10 million in three years, while also improving the gross margin on sales and cash management and working capital .
This business plan leads the way by renewing our vision and strategic focus of adding value to our target market segments—the small business and high-end home office users in our local market. It also provides a step-by-step plan for improving our sales, gross margin, and profitability.
This plan includes this summary, and chapters on the company, products & services, market focus, action plans & forecasts, management team, and financial plan.
1.1 Objectives
- Sales increased to more than $10 million by the third year.
- Bring gross margin back up to above 25% and maintain that level.
- Sell $2 million of service, support, and training by 2022.
- Improve inventory turnover to six turns next year, seven in 2021, and eight in 2022.
1.2 Mission
AMT is built on the assumption that the management of information technology for business is like legal advice, accounting, graphic arts, and other bodies of knowledge, in that it is not inherently a do-it-yourself prospect. Smart business people who aren't computer hobbyists need to find quality vendors of reliable hardware, software, service, and support and they need to use these quality vendors as they use their other professional service suppliers—as trusted allies.
AMT is such a vendor. It serves its clients as a trusted ally, providing them with the loyalty of a business partner and the economics of an outside vendor. We make sure that our clients have what they need in order to run their businesses at peak performance levels, with maximum efficiency and reliability.
Many of our information applications are mission-critical, so we assure our clients that we'll be there when they need us.
1.3 Keys to Success
- Differentiate from box-pushing, price-oriented businesses by offering and delivering service and support—and charging for it accordingly.
- Increase gross margin to more than 25%.
- Increase our non-hardware sales to 20% of the total sales by the third year.
2.0 Company Summary
AMT is a 10-year-old computer reseller with sales of $7 million per year, declining margins, and market pressure. It has a good reputation, excellent people, and a steady position in the local market, but has been having difficulty maintaining healthy financials.
2.1 Company Ownership
AMT is a privately-held C corporation owned in majority by its founder and president, Ralph Jones. There are six part owners, including four investors and two past employees. The largest of these (in percent of ownership) are Frank Dudley, our attorney, and Paul Karots, our public relations consultant. Neither owns more than 15%, but both are active participants in management decisions.
2.2 Company History
AMT has been caught in the vise grip of margin squeezes that have affected computer resellers worldwide. Although the chart titled "Past Financial Performance" shows that we've had healthy growth in sales, it also indicates declining gross margin and declining profits .
The more detailed numbers in Table 2.2 include other indicators of some concern: As can be seen in the chart, the gross margin percentage has been declining steadily, and nventory turnover is getting steadily worse as well.
All of these concerns are part of the general trend affecting computer resellers. The margin squeeze is happening throughout the computer industry, worldwide.
Balance Sheet: 2018
Short-Term Assets
- Cash—$55,432
- Accounts receivable—$395,107
- Inventory—$651,012
- Other Short-term Assets—$25,000
- Total Short-term Assets—$1,126,551
Long-Term Assets
- Capital Assets—$350,000
- Accumulated Depreciation—$50,000
- Total Long-term Assets—$300,000
- Total Assets—$1,426,551
Debt and Equity
- Accounts Payable—$223,897
- Short-term Notes—$90,000
- Other ST Liabilities—$15,000
- Subtotal Short-term Liabilities—$328,897
- Long-term Liabilities—$284,862
- Total Liabilities—$613,759
- Paid in Capital—$500,000
- Retained Earnings—$238,140
- Earnings (over three years)—$437,411, $366,761, $74,652
- Total Equity—$812,792
- Total Debt and Equity—$1,426,551
Other Inputs: 2017
- Payment days—30
- Sales on credit—$3,445,688
- Receivables turnover—8.72%
2.4 Company Locations and Facilities
We have one location—a 7,000 square-foot brick & mortar facility located in a suburban shopping center conveniently close to the downtown area. Along with sales, it includes a training area, service department, offices, and showroom area.
3.0 Products and Services
AMT sells personal computer technology for small business including personal computer hardware, peripherals, networks, software, support, service, and training.
Ultimately, we are selling information technology . We sell reliability and confidence. We sell the assurance to small business people that their business will not suffer any information technology disasters or critical downtimes.
AMT serves its clients as a trusted ally, providing them with the loyalty of a business partner and the economics of an outside vendor. We make sure that our clients have what they need to run their businesses at peak performance levels, with maximum efficiency and reliability. Since many of our information applications are mission-critical, we give our clients the confidence that we'll be there when they need us.
3.1 Product and Service Description
In personal computers , we support three main lines:
- The Super Home is our smallest and least expensive, initially positioned by its manufacturer as a home computer. We use it mainly as an inexpensive workstation for small business installations. Its specifications include: (add relevant information)
- The Power User is our main up-scale line and our most important system for high-end home and small business main workstations, because of (add relevant information) Its key strengths are: (add relevant information) Its specifications include: (add relevant information)
- The Business Special is an intermediate system, used to fill the gap in positioning. Its specifications include: (add information)
In peripherals , accessories and other hardware, we carry a complete line of necessary items from cables to forms to mousepads to... (add relevant information)
In service and support , we offer a range of walk-in or depot service, maintenance contracts, and on-site guarantees. We haven't had much success in selling service contracts. Our networking capabilities include... (add relevant information)
In software , we sell a complete line of... (add relevant information)
In training , we offer... (add relevant information)
3.2 Competitive Comparison
The only way we can hope to differentiate effectively is to brand the vision of the company as a trusted information technology ally to our clients. We will not be able to compete in any effective way with the chains using boxes or products as appliances. We need to offer a real alliance that feels personal.
The benefits we sell include many intangibles: confidence, reliability, knowing that somebody will be there to answer questions and help at critical times.
These are complex products that require serious knowledge and experience to use, which we have, while our competitors sell only the products themselves.
Unfortunately, we cannot sell the products at a higher price simply because we offer services; the market has shown that it will not support that concept. We must also sell the service and charge for it separately.
3.3 Sales Literature
Copies of our brochure and advertisements are attached as appendices. Of course, one of our first tasks will be to change the messaging of our literature to make sure we are selling the company, rather than the product.
3.4 Sourcing
Our costs are part of the margin squeeze. As price competition increases, the squeeze between the manufacturer's price into channels and the end-users ultimate buying price continues.
Our margins are declining steadily for our hardware lines. We generally buy at... (add relevant information) Our margins are thus being squeezed from 25% from five years ago to closer to 13 to 15% at present. A similar trend shows for our main-line peripherals, with prices for printers and monitors declining steadily. We are also starting to see that same trend with software...(add relevant information)
To hold costs down as much as possible, we concentrate our purchasing with Hauser, which offers 30-day net terms and overnight shipping from the warehouse in Dayton. We need to continue to make sure our volume gives us negotiating strength.
In accessories and add-ons, we can still get decent margins of 25 to 40%.
For software, margins are: (add relevant information)
3.5 Technology
For years, we have supported both Windows and Macintosh technology for CPUs, although we've switched vendors many times for the Windows (and previously DOS) lines. We are also supporting Novell, Banyon, and Microsoft networking, Xbase database software, and Claris application products.
3.6 Future Products and Services
We must remain on top of emerging technologies because this is our bread and butter. For networking, we need to provide better knowledge of cross-platform technologies. We are also under pressure to improve our understanding of the direct-connect Internet and related communications. Finally, although we have a good command of desktop publishing, we are concerned about improving integrated fax, copier, printer, and voicemail technology into the computer system.
4.0 Market Analysis Summary
AMT focuses on local markets, small business, and home office, with a special focus on the high-end home office and the five-to-20 unit small business office.
4.1 Market Segmentation
The segmentation allows some room for estimates and nonspecific definitions. We focus on a small-medium level of small business, and it's hard to locate data to make an exact classification. Our target companies are large enough to require the kind of high-quality information technology management we offer but too small to have a separate computer management staff (such as an MIS department). We say that our target market has 10 to 50 employees, and requires five to 20 connect workstations in a local area network, however, the definition is flexible.
Defining the high-end home office is even more difficult. We generally know the characteristics of our target market, but we can't find easy classifications that fit into available demographics. The high-end home office business is a business, not a hobby. It generates enough money to merit the owner's paying real attention to the quality of information technology management, meaning that both budget and productivity concerns warrant working with our level of quality service and support. We can assume that we aren't talking about home offices used only part-time by people who work elsewhere during the day and that our target market home office needs powerful technology and sufficient links between computing, telecommunications, and video assets.
4.2 Industry Analysis
We are part of the computer reselling business, which includes several kinds of businesses:
- Computer dealers : storefront computer resellers, usually less than 5,000 square feet, often focused on a few main brands of hardware, usually offering only a minimum of software and variable amounts of service and support. Many are old-fashioned (1980s-style) computer stores that offer relatively few reasons for buyers to shop with them. Their service and support are not usually very good, and their prices are normally higher than those at larger stores.
- Chain stores and computer superstores : these include major chains such as CompUSA, Best Buy, Future Shop, etc. They almost always have a footprint of over 10,000 square feet of space, usually offer decent walk-in service, and are often warehouse-like locations where people go to find products in boxes with very aggressive pricing, but little support.
- Mail order/Online retailers : the market is served increasingly by mail order and online retailers that offer aggressive pricing of a boxed product. For the purely price-driven buyer, who buys boxes and expects no service, these are very good options.
- Others : there are many other channels through which people buy their computers, however, most are variations of the three main types above.
4.2.1 Industry Participants
- The national chains are a growing presence: CompUSA, Best Buy, and others. They benefit from national advertising, economies of scale, volume buying, and a general trend toward name-brand loyalty for buying in the channels as well as for products.
- Local computer stores are threatened. These tend to be small businesses, owned by people who started them because they liked computers. They are under-capitalized and under-managed. Margins are squeezed as they compete against chains, in a competition based on price more than on service and support.
4.2.2 Distribution Patterns
Small business buyers are accustomed to buying from vendors who visit their offices. They expect the copy machine vendors, office products vendors, and office furniture vendors, as well as the local graphic artists, freelance writers, or whomever, to visit their office to make their sales.
There is usually a lot of leakage in ad-hoc purchasing through local chain stores and mail order. Often the administrators try to discourage this but are only partially successful.
Unfortunately, our home office target buyers don't expect to buy from us. Many of them turn immediately to the superstores (office equipment, office supplies, and electronics) and mail order to look for the best price, without realizing that there is a better option for them at only a little bit more.
4.2.3 Competition and Buying Patterns
The small business buyers understand the concept of service and support and are much more likely to pay for it when the offering is clearly stated.
There is no doubt that we face stiffer competition from box pushers than from other service providers. We need to effectively compete against the idea that businesses should buy computers as plug-in appliances that don't need ongoing service, support, and training.
Our focus group sessions indicated that our target home office buyers think about the price but would buy based on quality service if the offering were properly presented. They think about the price because that's all they ever see. We have very good indications that many would rather pay 10 to 20% more for a relationship with a long-term vendor providing back-up and quality service and support, however, they end up in the box-pusher channels because they aren't aware of the alternatives.
Availability is also very important. The home office buyers tend to want immediate, local solutions to problems.
4.2.4 Main Competitors
Chain stores:
- We have Store 1 and Store 2 already within the valley, and Store 3 is expected by the end of next year. If our strategy works, we will have differentiated ourselves sufficiently to avoid competition against these stores.
- Strengths: national image, high volume, aggressive pricing, economies of scale.
- Weaknesses: lack of product, service and support knowledge, lack of personal attention.
Other local computer stores:
- Store 4 and Store 5 are both in the downtown area. They are both competing against the chains in an attempt to match prices. When asked, the owners will complain that margins are squeezed by the chains and customers buy based on price only. They say they tried offering services and that buyers didn't care, instead preferring lower prices. We think the problem is that they didn't really offer good service, and also that they didn't differentiate from the chains.
4.3 Market Analysis
The home offices in Tintown are an important growing market segment. Nationally, there are approximately 30 million home offices, and the number is growing at 10% per year. Our estimate in this plan for the home offices in our market service area is based on an analysis published four months ago in the local newspaper.
There are several types of home offices. For the focus of our plan, the most important are those that are real businesses offices from which people earn their primary income. These are likely to be people in professional services such as graphic artists, writers, and consultants, some accountants—and the occasional lawyer, doctor, or dentist. We will not be focusing on the market segment that includes part-time home offices with people who are employed during the day but work at home at night, people who work at home to provide themselves with a part-time income, or people who maintain home offices relating to their hobbies.
Small business within our market includes virtually any business with a retail, office, professional, or industrial location outside of the home, and fewer than 30 employees. We estimate there are 45,000 such businesses in our market area.
The 30-employee cutoff is arbitrary. We find that the larger companies turn to other vendors, but we can sell to departments of larger companies, and we shouldn't give up such leads when we get them.
Market Analysis . . . (numbers and percentages)
5.0 Strategy and Implementation Summary
- Emphasize service and support.
We must differentiate ourselves from the box pushers. We need to establish our business offering as a clear and viable alternative to the price-only kind of buying for our target market.
- Build a relationship-oriented business.
Build long-term relationships with clients, not single-transaction deals with customers. Become their computer department, not just a vendor. Make them understand the value of the relationship.
- Focus on target markets.
We need to focus our offerings on small business as the key market segment we should own. This means the five to 20 unit system, connected by a local area network, in a company with five to 50 employees. Our values—training, installation, service, support, knowledge—are more clearly differentiated in this segment.
As a corollary, the high end of the home office market is also appropriate. We do not want to compete for buyers who go to chain stores or buy from mail-order outlets, but we definitely want to be able to sell individual systems to the smart home office buyers who want a reliable, full-service vendor.
- Differentiate and fulfill the promise.
We can't just market and sell service and support; we must deliver as well. We need to make sure we have the knowledge-intensive business and service-intensive business we claim to have.
5.1 Marketing Strategy
The marketing strategy is the core of the main strategy:
- Emphasize service and support
- Build a relationship business
- Focus on small business and high-end home office as key target markets
5.1.2 Pricing Strategy
We must charge appropriately for the high-end, high-quality service and support we offer. Our revenue structure has to match our cost structure, so the salaries we pay to assure good service and support must be balanced by the revenue we charge.
We cannot build the service and support revenue into the price of products. The market can't bear the higher prices, and the buyer feels ill-used when they see the same product priced lower at the chains. Despite the logic behind it, the market doesn't support this concept.
Therefore, we must make sure that we deliver and charge for service and support. Training, service, installation, networking support—all of this must be readily available and priced to sell and deliver revenue.
5.1.3 Promotion Strategy
We depend on newspaper advertising as our main outlet to reach new buyers. As we change strategies, however, we need to change the way we promote ourselves:
- Advertising
We'll be developing our core positioning message: "24 Hour On-Site Service—365 Days a Year With No Extra Charges" to differentiate our service from the competition. We will be using local newspaper advertising, radio, and cable TV to launch the initial campaign.
- Sales Brochure
Our collaterals have to sell the store and visiting the store, not the specific book or discount pricing.
- Direct Mail
We must radically improve our direct mail efforts, reaching our established customers with training, support services, upgrades, and seminars.
- Local Media
It's time to work more closely with the local media . We could offer the local radio station a regular talk show on technology for small business, as one example. We could also reach out to local news outlets to let them know we have experts who are able to address issues relating to technology for small business/home offices should the need arise.
5.2 Sales Strategy
- We need to sell the company, not the product. We sell AMT, not Apple, IBM, Hewlett-Packard, or Compaq, or any of our software brand names.
- We have to sell our service and support. The hardware is like the razor, and the support, service, software services, training, and seminars are the razor blades. We need to serve our customers with what they need.
The Yearly Total Sales chart summarizes our ambitious sales forecast. We expect sales to increase from $5.3 million last year to more than $7 million next year and to more than $10 million in the last year of this plan.
5.2.1 Sales Forecast
The important elements of the sales forecast are shown in the Total Sales by Month in Year 1 table. The non-hardware sales increase to about $2 million total in the third year.
Sales Forecast … (numbers and percentages)
5.2.2 Startup Summary
- 93% of startup costs will go to assets.
- The building will be purchased with a down payment of $8,000 on a 20-year mortgage. The espresso machine will cost $4,500 (straight-line depreciation, three years).
- Startup costs will be financed through a combination of owner investment, short-term loans, and long-term borrowing. The startup chart shows the distribution of financing.
Other miscellaneous expenses include:
- Marketing/advertising consultancy fees of $1,000 for our company logo and assistance in designing our grand-opening ads and brochures.
- Legal fees for corporate organization filings: $300.
- Retail merchandising/designing consultancy fees of $3,500 for store layout and fixture purchasing.
- Components of a Business Plan
- The Meaning of "Horticulture"
- Marketing Plan for a Business Venture
- 20 High-Paying Business Careers
- How to Sell Your Trees for Timber
- Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost Practice Question
- What Is Demographics? Definition, Usage, Examples in Advertising
- Gross Domestic Product
- Bungalow Homes by Mail
- What Is Derived Demand? Definition and Examples
- The Pink Tax: Economic Gender Discrimination
- Free MBA Program
- All About the Two-Part Tariff
- Start a Desktop Publishing or Graphic Design Business
- Making a Living from Genealogy
- How to Register as a Government Contractor
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
- Write Your Business Plan | Part 1 Overview Video
- The Basics of Writing a Business Plan
- How to Use Your Business Plan Most Effectively
- 12 Reasons You Need a Business Plan
- The Main Objectives of a Business Plan
- What to Include and Not Include in a Successful Business Plan
- The Top 4 Types of Business Plans
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Presenting Your Business Plan in 10 Slides
- 6 Tips for Making a Winning Business Presentation
- 3 Key Things You Need to Know About Financing Your Business
- 12 Ways to Set Realistic Business Goals and Objectives
- How to Perfectly Pitch Your Business Plan in 10 Minutes
- Write Your Business Plan | Part 2 Overview Video
- How to Fund Your Business Through Friends and Family Loans and Crowdsourcing
- How to Fund Your Business Using Banks and Credit Unions
- How to Fund Your Business With an SBA Loan
- How to Fund Your Business With Bonds and Indirect Funding Sources
- How to Fund Your Business With Venture Capital
- How to Fund Your Business With Angel Investors
- How to Use Your Business Plan to Track Performance
- How to Make Your Business Plan Attractive to Prospective Partners
- Is This Idea Going to Work? How to Assess the Potential of Your Business.
- When to Update Your Business Plan
- Write Your Business Plan | Part 3 Overview Video
- How to Write the Management Team Section to Your Business Plan
- How to Create a Strategic Hiring Plan
- How to Write a Business Plan Executive Summary That Sells Your Idea
- How to Build a Team of Outside Experts for Your Business
- Use This Worksheet to Write a Product Description That Sells
- What Is Your Unique Selling Proposition? Use This Worksheet to Find Your Greatest Strength.
- How to Raise Money With Your Business Plan
- Customers and Investors Don't Want Products. They Want Solutions.
- Write Your Business Plan | Part 4 Overview Video
- 5 Essential Elements of Your Industry Trends Plan
- How to Identify and Research Your Competition
- Who Is Your Ideal Customer? 4 Questions to Ask Yourself.
- How to Identify Market Trends in Your Business Plan
- How to Define Your Product and Set Your Prices
- How to Determine the Barriers to Entry for Your Business
- How to Get Customers in Your Store and Drive Traffic to Your Website
- How to Effectively Promote Your Business to Customers and Investors
- Write Your Business Plan | Part 5 Overview Video
- What Equipment and Facilities to Include in Your Business Plan
- How to Write an Income Statement for Your Business Plan
- How to Make a Balance Sheet
- How to Make a Cash Flow Statement
- How to Use Financial Ratios to Understand the Health of Your Business
- How to Write an Operations Plan for Retail and Sales Businesses
- How to Make Realistic Financial Forecasts
- How to Write an Operations Plan for Manufacturers
- What Technology Needs to Include In Your Business Plan
- How to List Personnel and Materials in Your Business Plan
- The Role of Franchising
- The Best Ways to Follow Up on a Buisiness Plan
- The Best Books, Sites, Trade Associations and Resources to Get Your Business Funded and Running
- How to Hire the Right Business Plan Consultant
- Business Plan Lingo and Resources All Entrepreneurs Should Know
- How to Write a Letter of Introduction
- What To Put on the Cover Page of a Business Plan
- How to Format Your Business Plan
- 6 Steps to Getting Your Business Plan In Front of Investors
Use This Worksheet to Write a Product Description That Sells It is vitally important that your business plan is able to build a convincing case for the product or service that you plan on selling.
By Eric Butow Edited by Dan Bova Oct 27, 2023
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
This is part 6 / 9 of Write Your Business Plan: Section 3: Selling Your Product and Team series.
Every business has something to sell, and the product section is where you tell readers what it is you're selling. (For simplicity's sake, the term "product" is used to refer to both products and services unless otherwise indicated.) This is clearly a very important section of your plan. Even if you have assembled a brilliant managerial team, or have strong financial underpinnings, unless you have something to sell or at least plans to develop something new, you don't really have a business at all. Business is about providing people with something they need. Your business should solve a problem, make life easier, expedite a process, or even simply entertain, but you need to be selling something to have a business.
Although many businesses are founded to develop new, never-before-seen products, they're still built around a product, even though it may not exist at the moment. And even for these development-stage enterprises, it's just as important to describe the planned-for product and make a presentation that illustrates what people can expect.
Related: How to Craft a Business Plan That Will Turn Investors' Heads
What Is Your Product or Service?
It's easy to talk eloquently about a product you believe in. Some highly marketing-oriented businesses, in fact, are built as much on the ability to wax rhapsodic about a product as they are on the ability to buy or source compelling products to begin with. Think of J. Peterman, the catalog operation that became famous—and highly successful—by selling prosaic products with the help of romantic, overblown advertising copy, prior to going bankrupt in 1999.
It's important in your plan to be able to build a convincing case for the product or service upon which your business will be built. The product description section is where you do that.
Related: How to Write a Business Plan
Product Description Worksheet
Features describe the make, shape, form, or appearance of a product, the characteristics that you use to describe products. These features convey benefits to the customer. Benefits (perceived benefits) are the emotional or other end results that your product or service provides that customer, the satisfaction or fulfillment of needs that a customer receives from your products or services. In the famous phrase, "My factories make cosmetics, we sell hope," cosmetics are the products, hope is the benefit.

Here are a few sample product descriptions:
Street Beat is a new type of portable electronic rhythm machine used to create musical backgrounds for street dances, fairs, concerts, picnics, sporting events, and other outdoor productions. The product is less costly than a live rhythm section and offers better sound quality than competing systems. Its combination of features will appeal to sports promoters, fair organizers, and charitable and youth organizations.
Troubleshooting Times is the only monthly magazine for the nation's 6,000 owners of electronics repair shops. It provides timely news of industry trends, service product reviews, and consumer product service tips written in a language service shop owners can understand.
HOBO, the Home Business Organization, provides business consulting services to entrepreneurs who work out of their homes. The group connects home business owners with experts who have extensive experience counseling home business owners in management, finance, marketing, and lifestyle issues. Unlike entrepreneurial peer groups, which charge members for attending sessions whether or not they receive useful advice, HOBO will guarantee its services, asking home business owners to pay only if they derive solid benefit from the service.
Related: How to Define Your Product and Set Your Prices
A business plan product description has to be less image-conscious than an advertising brochure but more appealing than a simple spec sheet. You don't want to give the appearance of trying to dazzle readers with a glitzy product sales pitch filled with a lot of hype. On the other hand, you want to give them a sampling of how you are going to position and promote the product.
And remember, a business plan product description is not only concerned with consumer appeal. Issues of manufacturability are of paramount concern to plan readers, who may have seen any number of plans describing exciting products that, in the end, proved impossible to design and build economically.
If your product or service has special features that will make it easy to build and distribute, say so. For instance, the portable rhythm machine maker should point out in the business plan that the devices will be constructed using new special-purpose integrated circuits derived from military applications, which will vastly increase durability and quality while reducing costs.
Related: The Basics of Writing a Business Plan
Plan Pointer: Get Creative
No ideas to differentiate your product? Steal someone else's. That is, combine your product with another to create something new. Dry cleaners do this when they offer coupons for the neighborhood pizza parlor—which gives out cleaning coupons with each pie. It's called cooperative marketing.
Related: The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Business Plan
More in Write Your Business Plan
Section 1: the foundation of a business plan, section 2: putting your business plan to work, section 3: selling your product and team, section 4: marketing your business plan, section 5: organizing operations and finances, section 6: getting your business plan to investors.
Successfully copied link
- Contact Sales
- Try Azure for free
What is Azure?
The Azure cloud platform is more than 200 products and cloud services designed to help you bring new solutions to life—to solve today’s challenges and create the future. Build, run, and manage applications across multiple clouds, on-premises, and at the edge, with the tools and frameworks of your choice.
Trust your cloud
Get security from the ground up, backed by a team of experts, and proactive compliance trusted by enterprises, governments, and startups.
Operate hybrid seamlessly
On-premises, across multiple clouds, and at the edge—we’ll meet you where you are. Integrate and manage your environments with services designed for hybrid cloud.
Build on your terms
With a commitment to open source, and support for all languages and frameworks, build how you want, and deploy where you want to.
Be future-ready
Continuous innovation from Microsoft supports your development today, and your product visions for tomorrow.
compliance offerings—the largest portfolio in the industry.
of Fortune 500 companies trust their business on Azure.
investment (US dollars) per year in security to protect customers’ data from cyberthreats.
Solutions do the work for you
Find answers to the business challenges you face with an Azure solution that brings together everything you need—related products, services, and third-party applications. From DevOps to business analytics to the Internet of Things , you’ll be up and running quickly with a scalable, cost-effective solution that works with your existing investments.
Develop solutions for proactive, personalized healthcare.
Financial services
Better serve customers, empower employees, and optimize risk management.
Build secure solutions to better serve and protect your citizens.
Deliver personal, seamless, and differentiated experiences.
Manufacturing
Respond quicker to customer feedback and market trends.
Companies doing great things with Azure
"We did look at different platforms, including Azure, Google, Amazon, and VMware. If we wanted to put the whole city in the cloud, we needed Azure."
Chris McMasters, Chief Information Officer, City of Corona, CA

Creating better experiences for 15.4 million customers worldwide
ASOS, a top online fashion retailer, delivered a more personalized, mobile-first experience with Azure.
Onboarding developers in hours instead of weeks
Daimler AG quickly attracts and onboards top talent to innovate faster using the Azure development environment.
Popular questions about Azure
Is azure secure.
Yes, security and privacy are foundational for Azure. Microsoft is committed to the highest levels of trust, transparency, standards conformance, and regulatory compliance—with the most comprehensive set of compliance offerings of any cloud service provider.
How can Azure help if I outsource my IT?
IT partners use Azure to deploy, manage, and support customers’ existing solutions, and to offer ready-made or custom solutions. Ask your IT partner how your organization can take advantage of Azure to meet your business goals. Or, find an Azure partner that fits your needs. Explore a wide network of partners with verified Azure capabilities.
What other customers are using Azure?
Of the Fortune 500 companies, 95 percent rely on Azure for trusted cloud services. Companies of all sizes and maturities use Azure in their digital transformation.
Is it only for Windows apps and services?
No. Azure supports open source technologies, so you can use the tools and technologies you prefer. Run virtually any application using your data source, with your operating system, on your device. With Azure, you have choices.
Will Azure really save me money?
With no upfront cost, you only pay for what you use. Azure provides flexible purchasing and pricing options for all your cloud scenarios, such as the Azure Hybrid Benefit, and offers extensive tools to help manage your cloud spend.
Can I try Azure services?
Yes. Create an Azure free account to experiment and build in the cloud. You’ll get access to free Azure products and services, plus a $200 credit to use in your first 30 days.
Will Azure work for my industry?
Azure provides solutions for all industries, through proven combinations of cloud products and services. Address your industry-specific business challenges today, and prepare for the future by innovating with Azure solutions.
How does Azure compare to other clouds?
Azure is the only consistent hybrid cloud, delivers unparalleled developer productivity, provides comprehensive, multilayered security, including the largest compliance coverage of any cloud provider, and you’ll pay less for Azure as AWS is five times more expensive than Azure for Windows Server and SQL Server.
Get popular products free each month for a year
Take your first steps with Azure videos, demos, and training.
Get answers to your questions from a Microsoft expert.
Browse quickstarts, samples, and tutorials.
Product Quality Manager
Add a favorite.
Don’t have an Apple ID?
- Create one now
- Forgot your Apple ID or password?
Description
Minimum qualifications, key qualifications.
- Expert quality management, planning, and engineering skills
- Domain expert for all things quality including Quality Plans, FMEA’s, auditing, corrective and preventative actions, and sampling methodologies for IQC, assembly, and OQC
- Demonstrated capability with quality statistical techniques including SPC, sampling AQL’s, and measurement system analysis
- Working knowledge of advanced quality techniques such as design of experiments, correlation analysis, and reliability analysis
- Basic understanding of metrology and GDT
- Discriminating eye for demanding cosmetic categorization and supplier inspection
- Keen problem solving analytical skills capable of getting to root cause quickly in challenging environments and with tight deadlines
- Effective interpersonal and communication skills with the ability to manage and drive issues to closure in a global organization
- High-volume manufacturing experience with a detailed understanding of production processes, testing, kitting, and packaging (e.g., consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices, etc.)
- Supplier management experience
- Thorough with excellent written and verbal communication skills; Mandarin is a plus
Preferred Qualifications
Education & experience, additional requirements, pay & benefits.
- At Apple, base pay is one part of our total compensation package and is determined within a range. This provides the opportunity to progress as you grow and develop within a role. The base pay range for this role is between $160,700 and $241,500, and your base pay will depend on your skills, qualifications, experience, and location. Apple employees also have the opportunity to become an Apple shareholder through participation in Apple’s discretionary employee stock programs. Apple employees are eligible for discretionary restricted stock unit awards, and can purchase Apple stock at a discount if voluntarily participating in Apple’s Employee Stock Purchase Plan. You’ll also receive benefits including: Comprehensive medical and dental coverage, retirement benefits, a range of discounted products and free services, and for formal education related to advancing your career at Apple, reimbursement for certain educational expenses — including tuition. Additionally, this role might be eligible for discretionary bonuses or commission payments as well as relocation. Learn more about Apple Benefits. Note: Apple benefit, compensation and employee stock programs are subject to eligibility requirements and other terms of the applicable plan or program.
Apple is an equal opportunity employer that is committed to inclusion and diversity. We take affirmative action to ensure equal opportunity for all applicants without regard to race, color, religion, sex, sexual orientation, gender identity, national origin, disability, Veteran status, or other legally protected characteristics. Learn more about your EEO rights as an applicant.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In a business plan, the Products and Services section is typically included within the business overview section. This allows you to first introduce the business model and what it offers to customers. Only after this you can provide more details of the products and services. The Products and Services section should clearly detail what you are ...
1. Portfolio: The range of products and/or services that a business offers to potential and current customers. 2. Features and benefits (value proposition): Explain what the product/service does and how it works. 3. Problem and solution (value proposition cont.): The problem (s) the product or service solves.
How to Write the Business Plan Products and Services Section. Get tips on writing the products and services part of your business plan. By Randy Duermyer. Updated on October 14, 2022. Reviewed by. Thomas J. Catalano. Fact checked by David Rubin. In This Article. The Products and Services Section.
Updated January 3, 2024. A complete business plan describes what you sell: either products, services, or both. This section needs to be more than a simple list of what you provide. It should detail the problem you're solving, the value you provide, how it compares to the competition, and logistical information like pricing and distribution.
In the Products and Services section of your business plan, you will clearly describe--yep--the products and services your business will provide. Keep in mind that highly detailed or technical ...
The Product service section in a business plan is about introducing your offering with a fair amount of detail. However, don't make it lengthy. ... When you have written the product or service description, ask a trusted friend or family member to read it and explain your product to you. That way, you can know if your product service part of ...
To begin with, you should provide a description of the broader categories your products or services belong to. Once this is addressed, you can go into more detail, explaining each of the key products and services that your business offers. In this section, you should explain: What each of your products or services are. Who are they aimed at.
Nonetheless, the product and services description section of your business plan is expected to include: The Product or Service Description; It is important the product description section of your business plan clearly explains the concept of your product, coupled with all aspects of purchasing, manufacturing, packaging, and distribution.
What's Included in the Products and Services Section. In the products and services section of your business plan, you provide an overview of what you offer. Here are all the key elements your products and services section should cover: 1. Description. In this part, you include all the important details of your offerings.
A description of the products or services you offer or plan to offer A pricing model for your products or service, including how you set your prices and how you will make a profit. Include a breakdown of your Costs of Goods (COG) and Costs of Services (COS), what your contingency plan is in the event of a shift in market conditions, changes to ...
Your business plan should have an appendix for photos and brochures, but be sure to refer to them in the product description section. Related: 10 Important Components of a Successful Business Plan Product description example Family Treasure Knits Products and Services Family Treasure Knits manufactures high-quality, custom-knitted blankets. My ...
Focus on the customer: The purpose of the products or services section is to clearly express the benefits you're providing to your customers or clients. Focus on that goal by addressing how what you are selling benefits your customers. Show how it makes their lives better, easier, or more profitable. Get to the point: State the value upfront ...
Traditional business plans use some combination of these nine sections. Executive summary. Briefly tell your reader what your company is and why it will be successful. Include your mission statement, your product or service, and basic information about your company's leadership team, employees, and location.
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you're going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are. Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future.
A business plan product description isn't only concerned with consumer appeal. Issues of manufacturability are of paramount concern to plan readers, who may have seen any number of plans ...
Provide details about your business's products or services. The following should be included: Product or service description; Product or service use and appeal (explain why it is used and what constitutes its appeal) Stage of development (how the product or service has evolved to present state, and how it is expected to evolve in future)
Here's how to write one that works for your business. 1. Start with your basics. The goal of a business description is to introduce any reader to your company—-and to do that quickly. So when you're getting started writing this description, it's a good idea to list out the basic information that you'll need to include.
The product description in the business plan describes all the products the company produces. A business plan product description describes a product or service, the firm supplying it, the problem it answers, the price, and the target market. Your product description should explain how your products differ from similar ones on the market or why ...
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
Time For Completion: Approximately 5-25 hours In this section you get the chance to clearly explain the products or services your business will offer. The information provided in this section will become the basis of your marketing plan. Product description should be written so the reader can easily understand what the product is and what it does.
1.1 Objectives. Sales increased to more than $10 million by the third year. Bring gross margin back up to above 25% and maintain that level. Sell $2 million of service, support, and training by 2022. Improve inventory turnover to six turns next year, seven in 2021, and eight in 2022.
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
If your product or service has special features that will make it easy to build and distribute, say so. For instance, the portable rhythm machine maker should point out in the business plan that ...
Include the results of any market trials, surveys or focus groups. Describe the product's benefits to the customer. For example, if the product reduces wrinkles on the face, saves money or increases efficiency, explain in detail how it does each of these things. If there is a family of products, discuss the customer benefits of each one.
Edit and Download. Remember to create SMART goals for your marketing plan and strategy. SMART goals are Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant and Time-Bound. In the template above, notice how the target is defined as a percentage. You can also add a deadline to your marketing goal to make it time-bound.
A business might develop a marketing plan for a specific need, campaign, or goal within its larger mission. Here are some examples: Launching a new product or service. Carrying out campaigns through different marketing channels, including social media, email marketing, print media, TV, or offline events Implementing paid advertising
The Azure cloud platform is more than 200 products and cloud services designed to help you bring new solutions to life—to solve today's challenges and create the future. Build, run, and manage applications across multiple clouds, on-premises, and at the edge, with the tools and frameworks of your choice. Start free Your most popular ...
Weekly Hours: 40. Role Number: 200553221. As a member of a multi-functional design team at Apple, you will help to create the next generation of the world's finest mobile devices. You will conceive, design, and bring into production products that will re-define the mobile experience. You will work closely with many different cross functional ...
- Highly visible individual contributor role that collaborates with all management levels from line supervision to executive management to ensure Accessories Quality - Supports the New Products Introduction team by specifying and implementing the Product Quality Plan for new iOS accessory products - Drives closure of technical operational issues related to SMT, Final Assembly, Test, and ...
Access to OpenAI expertise. Dedicated account team and prioritized support. Tailored onboarding & live trainings. Consolidated invoicing. "You essentially have the knowledge of the most knowledgeable person—instantly. We believe that is a transformative capability for our company.". Jeff McMillan, Head of Innovation at Morgan Stanley.