- Kindergarten
- Greater Than Less Than
- Measurement
- Multiplication
- Place Value
- Subtraction
- Punctuation
- 1st Grade Reading
- 2nd Grade Reading
- 3rd Grade Reading
- Cursive Writing
- Alphabet Coloring
- Animals Coloring
- Birthday Coloring
- Boys Coloring
- Buildings Coloring
- Cartoons Coloring
- Christmas Coloring
- Country Flag Coloring
- Country Map Coloring
- Disney Coloring
- Fantasy Coloring
- Food Coloring
- Girls Coloring
- Holidays Coloring
- Music Coloring
- Nature Coloring
- New Year Coloring
- People Coloring
- Religious Coloring
- Sports Coloring
- Toys Coloring
- Transportation Coloring
- US Sports Team Coloring
- Valentine Day Coloring

Unit 12 Probability Homework 4
Displaying top 8 worksheets found for - Unit 12 Probability Homework 4 .
Some of the worksheets for this concept are Probability unit work, Counting outcomes and theoretical probability notes answers, Revision of grade 12 probability part 1, Student resource book unit 4, Unit 3 probability homework booklet ks3 levels 3 8, Algebra 2 unit 12 lesson 1, Algebra 2 unit 12 lesson 1, Algebra 2 unit 12 lesson 1.
Found worksheet you are looking for? To download/print, click on pop-out icon or print icon to worksheet to print or download. Worksheet will open in a new window. You can & download or print using the browser document reader options.
1. Probability unit worksheets
2. 12.4 counting outcomes and theoretical probability notes answers, 3. revision of grade 12 probability part 1, 4. student resource book unit 4, 5. unit 3 probability homework booklet ks3 levels 3-8, 6. algebra 2 unit 12 lesson 1, 7. algebra 2 unit 12 lesson 1, 8. algebra 2 unit 12 lesson 1.

- Share on Facebook
- Tweet This Resource
- Pin This Resource

Geometry Unit 12: Probability
The "Geometry Unit 12: Probability" series contains three video lessons designed for the flipped classroom. Learners watch as videos demonstrate several types of problems highlighting probability concepts, and then work through a series of problems to practice these new skills in preparation for a unit exam. Also included in the module are corrective assignments for those who need extra practice.
Common Core

Introduction to Probability

Introduction to Probability (.html)
Practice packet (.pdf), practice solutions (.pdf), corrective assignment (.pdf).

More Probability
More probability (.html).

Unit 12 Review: Probability
Unit 12 review: probability (.html), unit 12 review: probability (.pdf).
Find what you need to study

Unit 4 Overview: Probability, Random Variables, and Probability Distributions
6 min read • december 30, 2022
Jed Quiaoit

Image from Funny Junk
" Probabilistic reasoning allows statisticians to quantify the likelihood of random events over the long run and to make statistical inferences. Simulations and concrete examples can help students to understand the abstract definitions and calculations of probability. This unit builds on understandings of simulated or empirical data distributions and fundamental principles of probability to represent, interpret, and calculate parameters for theoretical probability distributions for discrete random variables . Interpretations of probabilities and parameters associated with a probability distribution should use appropriate units and relate to the context of the situation." -- College Board
As highlighted by the College Board's blurb of Unit 4, probabilistic reasoning is an important aspect of statistical analysis, as it allows statisticians to make predictions about the likelihood of certain events occurring based on data and probability theory. Simulations and concrete examples can be useful for helping students to understand and apply the abstract concepts of probability and probability distributions. 🧠
In this unit, students learn about theoretical probability distributions , which are used to describe the possible values and likelihoods of a random variable. These distributions can be either discrete or continuous, and they are characterized by specific parameters that describe the shape and behavior of the distribution.
It's important for you and me to understand the context and units of the probabilities and parameters associated with a probability distribution, as this can help them to interpret and apply their analyses to real-world situations!
Probability: What are the Odds?
Have you ever wondered how meteorologists determine the 🌧️ or ❄️ forecasts? What about the likelihood of a sports team winning a game? Analysts like meteorologists or sports analysts use probability models based on similar conditions in the past to predict the likelihood of these things happening in the present! In this unit, you will learn some basics of probability and get a taste of what these statisticians use everyday to keep us safe and sound. 🤗
Probability is the study of possible outcomes and determining the chance of something happening. It is an essential part of statistics since we use probability as one of the main factors in making predictions or testing claims, which is what statistics is all about.
Categorical Variables
The most common type of probability you will encounter in this unit will deal with categorical variables . Recall from Unit 1 and Unit 2 that categorical variables are often represented with frequency tables or two-way tables (example pictured below) . There are some important rules for determining probabilities from these types of displays that are essential to know in order to be successful on the AP exam. 🪑
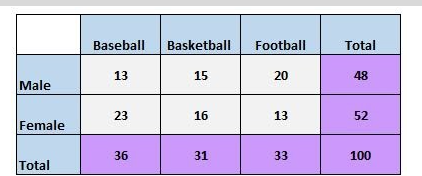
Image from Statology
Quantitative Variables
The other type of variable that you will encounter is quantitative variables . Quantitative variables will generally be dealt with using density curves (example pictured below) , most notably the normal distribution . The normal distribution is the most useful tool in statistics and hinges on a good understanding of probability. 🔔
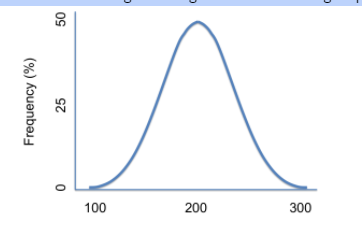
Image from Statistics How To
Probability Rules
There are many important rules and conditions that come into play when determining the probability of certain events happening. In order to be successful on the AP Exam, it is important to familiarize yourself with these rules and conditions.
Independence
The most important probability condition that you need to be aware of is the concept of independence . This will also be essential as we progress to inferential statistics in Units 6-9.
In order to determine whether two events are independent, it's important to consider whether the outcome of one event could potentially affect the outcome of the other . If the outcome of one event has no effect on the outcome of the other, then the events are independent . On the other hand, if the outcome of one event could potentially affect the outcome of the other, then the events are dependent .
For example, in the case of flipping two coins, the outcome of one coin flip has no effect on the outcome of the other, so these events are independent. However, if we consider the probability of it raining on a given day, this probability may be affected by the temperature and other weather conditions. In this case, the events of it raining and the temperature are dependent (or not independent), as the temperature can affect the likelihood of it raining. 🌧️
Mutually Exclusive
Another key concept in probability is when two events are mutually exclusive. Mutually exclusive events are events that cannot occur simultaneously . In other words, if one event occurs, it is not possible for the other event to occur at the same time.
An example of mutually exclusive events is the outcome of rolling a single die. If the die is rolled, the outcome can only be one of the six possible numbers, so the events of rolling a 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 are all mutually exclusive. If the die is rolled and the outcome is a 4, it is not possible for the outcome to be any of the other numbers at the same time. 🎲
Another example: the likelihood of having a hot day and snowing is impossible. Therefore, those two events are mutually exclusive!
Probability Distributions
There are three types of probability distributions we will mainly focus on in this unit: normal distributions, binomial distributions and geometric distributions. All of these have handy calculator functions that will make our work SO much easier! 😊
Normal Distribution
The most popular type of distribution in all data situations is the normal distribution . Whether it be ACT scores, heights of people or blood pressure levels, these all follow normal distributions and make it much easier to calculate where one data point compares to the rest of our data.
Binomial Distribution
It's time to meet a new character in the ever-growing tale of statistics! The binomial distribution is a probability distribution that is used to model the outcome of a series of independent, binary (two-outcome) events. It is characterized by four conditions: 2️⃣
Two possible outcomes (binary): The events being modeled must have only two possible outcomes, such as "success" and "failure" or "heads" and "tails."
Independent trials: The outcome of each event must not be affected by the outcome of any other event in the series.
Fixed number of trials: The total number of events in the series must be fixed and known in advance.
All trials are equally likely of occurring: The probability of each event occurring must be the same for all events in the series.
The binomial distribution is used to determine the probability of a certain number of successes occurring within a fixed number of trials. For example, if you wanted to know the probability of flipping a coin 12 times and getting 10 heads, you could use a binomial distribution to model this.
Binomial distributions are events that involve four conditions:
Two possible outcomes (binary)
Independent trials
Fixed number of trials
All trials are equally likely of occurring
Binomial distributions come in handy when you want to determine the likelihood of a certain number of successes within our fixed number of trials.
For instance, if you wanted to determine the likelihood of flipping a coin 12 times and receiving 10 heads, a binomial distribution would be appropriate.
Geometric Distribution
A geometric distribution is very similar to a binomial distribution , with the only difference being that we do not have a fixed number of trials. A geometric distribution typically involves repeating an action until you get a success. In other words, a geometric distribution models an indefinite number of trials until a success is achieved. 💎
An example of a situation that could be modeled by a geometric distribution is flipping a coin until you get a heads . The geometric distribution would be used to model the number of coin flips needed to achieve a heads.
🎥 Watch: AP Stats Unit 4
Key Terms to Review ( 11 )
Density Curves
Discrete Random Variables
Mutually Exclusive Events
Probabilistic Reasoning
Probability Condition
Theoretical Probability Distributions

Stay Connected
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Assessment. Unit 12 Mid-Unit Quiz (Through Lesson 4) - Form C. ASSESSMENT. ANSWER KEY. EDITABLE ASSESSMENT. EDITABLE KEY.
Verified answer. 4.5 /5. Verified answer. 4.1 /5. Unit 12 probability homework 4 compound probability Get the answers you need, now!
Download Unit 12 Homework answers here. 12.1 Notes Probability and Measurement: 12.2 Notes Permutations and Combinations: ... 12.4 Notes Independent and Dependent Events and Probabilities: 12.5 Notes Mutually Exclusive Events and Probability: 12.6 Notes Two-Way Frequency Tables:
41 Dependent Events Homework 6 43-50 Probability Unit Study Guide StudyGuide 51-52 Probability UnitTest Test PROBABILITY UNIT Table of Contents ©Maneuvering the Middle LLC, 2016. ... (4 or 6) 11. P'(7) 12. P(1) RED BLUE YELLOW YELLOW PURPLE GREEN BLUE Answer the question below. Drink Quantity Water 14 Cola 28 Lemonade 7
12.4 Probability of Compound Events 725 Probability of a Compound Event A card is randomly selected from a standard deck of 52 cards. What is the probability that the card ... HOMEWORK HELP Example 1: Exs. 16-24, 29-34, 42, 43 Example 2: Exs. 16-24, 29-34, 44, 45 Example 3: Exs. 16-24, 29-34, 46, 47 Example 4: Exs. 25-28,
The probability of two or more independent events is the product of the probabilities of the events. P (A and B) = P (A)*P (B) P (A and B and C) = P (A) P (B) P (C) Probability of Dependent Events. The probability of two or more dependent events A and B is the probability of A times the probability of B after A occurs.
Displaying top 8 worksheets found for - Unit 12 Probability Homework 4. Some of the worksheets for this concept are Probability unit work, Counting outcomes and theoretical probability notes answers, Revision of grade 12 probability part 1, Student resource book unit 4, Unit 3 probability homework booklet ks3 levels 3 8, Algebra 2 unit 12 ...
Common Core Algebra 2, Unit 12. The four lessons in Common Core Algebra 2, Unit 12, introduce high schoolers to probability. Topics covered include compound probability and independence, as well as normal distributions. Each topic is introduced with a video, and then viewers practice concepts by completing problem worksheets.
UNIT 12Introduction to Probability . 12. 1 Introduction to Probability. 12.2 Compound Probability and Independence. 12.3 Normal Distributions.
Unit 12: Probability . 6.16 The student will: a) compare and contrast dependent events; and ... Summative Assessments Homework . Day 67 4/29-B Simple Probability . KC 67A : 67B . Day 68 5/3-B Compound Probability . KC 68A : 68B . Day 69 5/5-B Compound Probability KC 69A . 69B . Day 70 5/9-B SOL Practice Day Study for QUIZ . Day 71 5/11-B Review ...
Description. Probability is developed in this 6 lesson unit by using sets, their intersections, and their unions. Two way frequency charts are extensively used to introduce the concept of conditional probabilities. The multiplication of probabilities is used to find the probability of complex events and the product test for independence is ...
Geometry (Second Semester) Notes, Homework, Quizzes, TestsThis bundle contains the following units:• Right Triangles & Trigonometry• Polygons & Quadrilaterals• Transformations• Circles• Volume & Surface Area• ProbabilityThese units contain notes, homework assignments, quizzes, stu. 6. Products. $79.00 $105.80 Save $26.80.
Unit 12 - Probability. Lesson 1 Measuring Chance with Ratios. LESSON/HOMEWORK. LECCIÓN/TAREA. LESSON VIDEO. ANSWER KEY. EDITABLE LESSON. EDITABLE KEY. SMART NOTEBOOK. Lesson 2 Predicting Outcomes. LESSON/HOMEWORK. LECCIÓN/TAREA.
Need a tutor? Click this link and get your first session free! https://gradegetter.com/sign-up?referrer_code=1002For notes, practice problems, and more les...
Terms in this set (14) P (B | A)= P (A and B)/P (A) Probability of one event (A) occuring. If the simple and conditional probabilities are the same, then the events are independent. If the simple and conditional probabilites are not equal, then the events are associated. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Sample ...
View 12.4_SP_Compound_Probability.pdf from GEOMETRY 101 at Lake Highlands H S. Pre-AP Geometry: Unit 12 - Compound Probability 12.4 Homework - Compound Probability Name_ Date_ Period _ 12.4 Determine
Description. Probability Homework Bundle: This resource is a bundled set of homework practice sets and daily content quizzes for Unit 12: Probability designed for Algebra 2 Honors students. The file includes 13 pages of homework assignments plus two forms of a daily content quiz that you can use as a homework check, group work, or exit tickets.
The "Geometry Unit 12: Probability" series contains three video lessons designed for the flipped classroom. Learners watch as videos demonstrate several types of problems highlighting probability concepts, and then work through a series of problems to practice these new skills in preparation for a unit exam.
Any one of the possible results of an action. Simple event. has one outcome or a collection of outcomes. Probability. the chance of an event happening. Random. when each outcome occurs by chance. Complementary Events. The events of one outcome happening and the outcome not happening.
E Homework: Unit 4 (Chapter 12): Section 12.1 Homework Letter The table shows the probability of the letters in the alphabet. The information is based on randomly selecting a letter from a randomly selected passage of text. ... Use the information given in the table and answer the following questions A E 1 O U Probability with respect to the 26 ...
For example, if you wanted to know the probability of flipping a coin 12 times and getting 10 heads, you could use a binomial distribution to model this. Binomial distributions are events that involve four conditions: Two possible outcomes (binary) ... Unit 4 - Probability, Random Variables, & Probability Distributions. Unit 4 Overview ...
Standards Alignment - Powered by EdGate. Table of Contents and Standards Alignment for Common Core Algebra II. Unit 1 - Algebraic Essentials Review. Unit 2 - Functions as the Cornerstones of Algebra II. Unit 3 - Linear Functions, Equations, and Their Algebra. Unit 4 - Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Unit 5 - Sequences and Series.
12/12/2018 Basic Probability Rules HW #2: 5.2 WS HW #2 KEY. 12/14/2018 Conditional Probability ... Unit 04 TEST/QUIZ (whichever is better for your grade) 01/17/2018 FRAPPY Final Exam ...