
Research Question 101 📖
Everything you need to know to write a high-quality research question
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2023
If you’ve landed on this page, you’re probably asking yourself, “ What is a research question? ”. Well, you’ve come to the right place. In this post, we’ll explain what a research question is , how it’s differen t from a research aim, and how to craft a high-quality research question that sets you up for success.
Research Question 101
What is a research question.
- Research questions vs research aims
- The 4 types of research questions
- How to write a research question
- Frequently asked questions
- Examples of research questions
As the name suggests, the research question is the core question (or set of questions) that your study will (attempt to) answer .
In many ways, a research question is akin to a target in archery . Without a clear target, you won’t know where to concentrate your efforts and focus. Essentially, your research question acts as the guiding light throughout your project and informs every choice you make along the way.
Let’s look at some examples:
What impact does social media usage have on the mental health of teenagers in New York?
How does the introduction of a minimum wage affect employment levels in small businesses in outer London?
How does the portrayal of women in 19th-century American literature reflect the societal attitudes of the time?
What are the long-term effects of intermittent fasting on heart health in adults?
As you can see in these examples, research questions are clear, specific questions that can be feasibly answered within a study. These are important attributes and we’ll discuss each of them in more detail a little later . If you’d like to see more examples of research questions, you can find our RQ mega-list here .

Research Questions vs Research Aims
At this point, you might be asking yourself, “ How is a research question different from a research aim? ”. Within any given study, the research aim and research question (or questions) are tightly intertwined , but they are separate things . Let’s unpack that a little.
A research aim is typically broader in nature and outlines what you hope to achieve with your research. It doesn’t ask a specific question but rather gives a summary of what you intend to explore.
The research question, on the other hand, is much more focused . It’s the specific query you’re setting out to answer. It narrows down the research aim into a detailed, researchable question that will guide your study’s methods and analysis.
Let’s look at an example:
Research Aim: To explore the effects of climate change on marine life in Southern Africa.
Research Question: How does ocean acidification caused by climate change affect the reproduction rates of coral reefs?
As you can see, the research aim gives you a general focus , while the research question details exactly what you want to find out.
Need a helping hand?
Types of research questions
Now that we’ve defined what a research question is, let’s look at the different types of research questions that you might come across. Broadly speaking, there are (at least) four different types of research questions – descriptive , comparative , relational , and explanatory .
Descriptive questions ask what is happening. In other words, they seek to describe a phenomena or situation . An example of a descriptive research question could be something like “What types of exercise do high-performing UK executives engage in?”. This would likely be a bit too basic to form an interesting study, but as you can see, the research question is just focused on the what – in other words, it just describes the situation.
Comparative research questions , on the other hand, look to understand the way in which two or more things differ , or how they’re similar. An example of a comparative research question might be something like “How do exercise preferences vary between middle-aged men across three American cities?”. As you can see, this question seeks to compare the differences (or similarities) in behaviour between different groups.
Next up, we’ve got exploratory research questions , which ask why or how is something happening. While the other types of questions we looked at focused on the what, exploratory research questions are interested in the why and how . As an example, an exploratory research question might ask something like “Why have bee populations declined in Germany over the last 5 years?”. As you can, this question is aimed squarely at the why, rather than the what.
Last but not least, we have relational research questions . As the name suggests, these types of research questions seek to explore the relationships between variables . Here, an example could be something like “What is the relationship between X and Y” or “Does A have an impact on B”. As you can see, these types of research questions are interested in understanding how constructs or variables are connected , and perhaps, whether one thing causes another.
Of course, depending on how fine-grained you want to get, you can argue that there are many more types of research questions , but these four categories give you a broad idea of the different flavours that exist out there. It’s also worth pointing out that a research question doesn’t need to fit perfectly into one category – in many cases, a research question might overlap into more than just one category and that’s okay.
The key takeaway here is that research questions can take many different forms , and it’s useful to understand the nature of your research question so that you can align your research methodology accordingly.

How To Write A Research Question
As we alluded earlier, a well-crafted research question needs to possess very specific attributes, including focus , clarity and feasibility . But that’s not all – a rock-solid research question also needs to be rooted and aligned . Let’s look at each of these.
A strong research question typically has a single focus. So, don’t try to cram multiple questions into one research question; rather split them up into separate questions (or even subquestions), each with their own specific focus. As a rule of thumb, narrow beats broad when it comes to research questions.
Clear and specific
A good research question is clear and specific, not vague and broad. State clearly exactly what you want to find out so that any reader can quickly understand what you’re looking to achieve with your study. Along the same vein, try to avoid using bulky language and jargon – aim for clarity.
Unfortunately, even a super tantalising and thought-provoking research question has little value if you cannot feasibly answer it. So, think about the methodological implications of your research question while you’re crafting it. Most importantly, make sure that you know exactly what data you’ll need (primary or secondary) and how you’ll analyse that data.
A good research question (and a research topic, more broadly) should be rooted in a clear research gap and research problem . Without a well-defined research gap, you risk wasting your effort pursuing a question that’s already been adequately answered (and agreed upon) by the research community. A well-argued research gap lays at the heart of a valuable study, so make sure you have your gap clearly articulated and that your research question directly links to it.
As we mentioned earlier, your research aim and research question are (or at least, should be) tightly linked. So, make sure that your research question (or set of questions) aligns with your research aim . If not, you’ll need to revise one of the two to achieve this.
FAQ: Research Questions
Research question faqs, how many research questions should i have, what should i avoid when writing a research question, can a research question be a statement.
Typically, a research question is phrased as a question, not a statement. A question clearly indicates what you’re setting out to discover.
Can a research question be too broad or too narrow?
Yes. A question that’s too broad makes your research unfocused, while a question that’s too narrow limits the scope of your study.
Here’s an example of a research question that’s too broad:
“Why is mental health important?”
Conversely, here’s an example of a research question that’s likely too narrow:
“What is the impact of sleep deprivation on the exam scores of 19-year-old males in London studying maths at The Open University?”
Can I change my research question during the research process?
How do i know if my research question is good.
A good research question is focused, specific, practical, rooted in a research gap, and aligned with the research aim. If your question meets these criteria, it’s likely a strong question.
Is a research question similar to a hypothesis?
Not quite. A hypothesis is a testable statement that predicts an outcome, while a research question is a query that you’re trying to answer through your study. Naturally, there can be linkages between a study’s research questions and hypothesis, but they serve different functions.
How are research questions and research objectives related?
The research question is a focused and specific query that your study aims to answer. It’s the central issue you’re investigating. The research objective, on the other hand, outlines the steps you’ll take to answer your research question. Research objectives are often more action-oriented and can be broken down into smaller tasks that guide your research process. In a sense, they’re something of a roadmap that helps you answer your research question.
Need some inspiration?
If you’d like to see more examples of research questions, check out our research question mega list here . Alternatively, if you’d like 1-on-1 help developing a high-quality research question, consider our private coaching service .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Literature Reviews
- 1. Define your research question
- Getting started
- Types of reviews
Define topic
Brainstorming, limit scope, how ai can help, helpful resources.
- 2. Plan your search
- 3. Search the literature
- 4. Organize your results
- 5. Synthesize your findings
- 6. Write the review
- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools
- Thompson Writing Studio This link opens in a new window
- Need to write a systematic review? This link opens in a new window

Contact a Librarian
Ask a Librarian
Mission animated icons created by Freepik - Flaticon
For example, the following research question is too broad.
Does social media affect mental health in college students?
A more focused research question could be:
Does social media play a role in the number of eating disorder diagnoses in college-aged women?
Need some guidance? Contact your subject librarian for a research consultation or reach out to [email protected] .
Start the brainstorming process:
- Begin by identifying a broad topic of research interest (the more you're personally interested in it, the better!). Write it down to clarify your focus.
- Narrow down your scope by considering specific areas within this topic that you want to explore.
- Identify key themes and elements related to these specific areas. These will be the building blocks of your investigation.
- Finally, integrate these key areas and elements into a well-crafted research question.
One way to brainstorm is to use a flowchart.

The scope of a topic encompasses the boundaries and constraints you set for your research. The more precise your research question, the smoother the research process becomes.
Feeling stuck? Here are some ways you can narrow down your topic:
- geographic location
- time period
- discipline/field of study
- age group, etc.

You: I need to conduct a literature review about social media, mental health, and college students. What are some example research questions within this topic?
ChatGPT:
- How does the frequency and nature of social media use impact the mental health of college students?
- What role do specific social media platforms play in influencing the mental well-being of college students?
- How do online social interactions on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, or Twitter relate to the mental health outcomes of college students?
- Are there differences in the association between social media use and mental health outcomes based on demographic factors such as gender, age, or academic major among college students?
- What strategies do college students employ to cope with negative mental health effects associated with social media use?
- How does the perception of social support through online platforms affect the mental health of college students?
- To what extent does the comparison of oneself to others on social media contribute to mental health challenges among college students?
- What interventions or educational programs are effective in promoting positive mental health behaviors in the context of social media use for college students?
- How do social media literacy and awareness programs impact the mental health attitudes and behaviors of college students?
- What is the relationship between the use of social media for academic and social purposes and the mental health outcomes of college students?
Generative AI tools : ChatGPT , Google Gemini (formerly Bard) , Claude , Microsoft Copilot
For more information on how to incorporate AI tools into your research, check out the section on AI Tools .
- Developing Your Research Question
- Developing a Researchable Question
- Brainstorming tips from UNC Writing Center
- << Previous: Types of reviews
- Next: 2. Plan your search >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 8:42 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.duke.edu/litreviews

Services for...
- Faculty & Instructors
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- International Students
- Patrons with Disabilities
- Harmful Language Statement
- Re-use & Attribution / Privacy
- Support the Libraries

- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Good Research Question (w/ Examples)
What is a Research Question?
A research question is the main question that your study sought or is seeking to answer. A clear research question guides your research paper or thesis and states exactly what you want to find out, giving your work a focus and objective. Learning how to write a hypothesis or research question is the start to composing any thesis, dissertation, or research paper. It is also one of the most important sections of a research proposal .
A good research question not only clarifies the writing in your study; it provides your readers with a clear focus and facilitates their understanding of your research topic, as well as outlining your study’s objectives. Before drafting the paper and receiving research paper editing (and usually before performing your study), you should write a concise statement of what this study intends to accomplish or reveal.
Research Question Writing Tips
Listed below are the important characteristics of a good research question:
A good research question should:
- Be clear and provide specific information so readers can easily understand the purpose.
- Be focused in its scope and narrow enough to be addressed in the space allowed by your paper
- Be relevant and concise and express your main ideas in as few words as possible, like a hypothesis.
- Be precise and complex enough that it does not simply answer a closed “yes or no” question, but requires an analysis of arguments and literature prior to its being considered acceptable.
- Be arguable or testable so that answers to the research question are open to scrutiny and specific questions and counterarguments.
Some of these characteristics might be difficult to understand in the form of a list. Let’s go into more detail about what a research question must do and look at some examples of research questions.
The research question should be specific and focused
Research questions that are too broad are not suitable to be addressed in a single study. One reason for this can be if there are many factors or variables to consider. In addition, a sample data set that is too large or an experimental timeline that is too long may suggest that the research question is not focused enough.
A specific research question means that the collective data and observations come together to either confirm or deny the chosen hypothesis in a clear manner. If a research question is too vague, then the data might end up creating an alternate research problem or hypothesis that you haven’t addressed in your Introduction section .
The research question should be based on the literature
An effective research question should be answerable and verifiable based on prior research because an effective scientific study must be placed in the context of a wider academic consensus. This means that conspiracy or fringe theories are not good research paper topics.
Instead, a good research question must extend, examine, and verify the context of your research field. It should fit naturally within the literature and be searchable by other research authors.
References to the literature can be in different citation styles and must be properly formatted according to the guidelines set forth by the publishing journal, university, or academic institution. This includes in-text citations as well as the Reference section .
The research question should be realistic in time, scope, and budget
There are two main constraints to the research process: timeframe and budget.
A proper research question will include study or experimental procedures that can be executed within a feasible time frame, typically by a graduate doctoral or master’s student or lab technician. Research that requires future technology, expensive resources, or follow-up procedures is problematic.
A researcher’s budget is also a major constraint to performing timely research. Research at many large universities or institutions is publicly funded and is thus accountable to funding restrictions.
The research question should be in-depth
Research papers, dissertations and theses , and academic journal articles are usually dozens if not hundreds of pages in length.
A good research question or thesis statement must be sufficiently complex to warrant such a length, as it must stand up to the scrutiny of peer review and be reproducible by other scientists and researchers.
Research Question Types
Qualitative and quantitative research are the two major types of research, and it is essential to develop research questions for each type of study.
Quantitative Research Questions
Quantitative research questions are specific. A typical research question involves the population to be studied, dependent and independent variables, and the research design.
In addition, quantitative research questions connect the research question and the research design. In addition, it is not possible to answer these questions definitively with a “yes” or “no” response. For example, scientific fields such as biology, physics, and chemistry often deal with “states,” in which different quantities, amounts, or velocities drastically alter the relevance of the research.
As a consequence, quantitative research questions do not contain qualitative, categorical, or ordinal qualifiers such as “is,” “are,” “does,” or “does not.”
Categories of quantitative research questions
Qualitative research questions.
In quantitative research, research questions have the potential to relate to broad research areas as well as more specific areas of study. Qualitative research questions are less directional, more flexible, and adaptable compared with their quantitative counterparts. Thus, studies based on these questions tend to focus on “discovering,” “explaining,” “elucidating,” and “exploring.”
Categories of qualitative research questions
Quantitative and qualitative research question examples.

Good and Bad Research Question Examples
Below are some good (and not-so-good) examples of research questions that researchers can use to guide them in crafting their own research questions.
Research Question Example 1
The first research question is too vague in both its independent and dependent variables. There is no specific information on what “exposure” means. Does this refer to comments, likes, engagement, or just how much time is spent on the social media platform?
Second, there is no useful information on what exactly “affected” means. Does the subject’s behavior change in some measurable way? Or does this term refer to another factor such as the user’s emotions?
Research Question Example 2
In this research question, the first example is too simple and not sufficiently complex, making it difficult to assess whether the study answered the question. The author could really only answer this question with a simple “yes” or “no.” Further, the presence of data would not help answer this question more deeply, which is a sure sign of a poorly constructed research topic.
The second research question is specific, complex, and empirically verifiable. One can measure program effectiveness based on metrics such as attendance or grades. Further, “bullying” is made into an empirical, quantitative measurement in the form of recorded disciplinary actions.
Steps for Writing a Research Question
Good research questions are relevant, focused, and meaningful. It can be difficult to come up with a good research question, but there are a few steps you can follow to make it a bit easier.
1. Start with an interesting and relevant topic
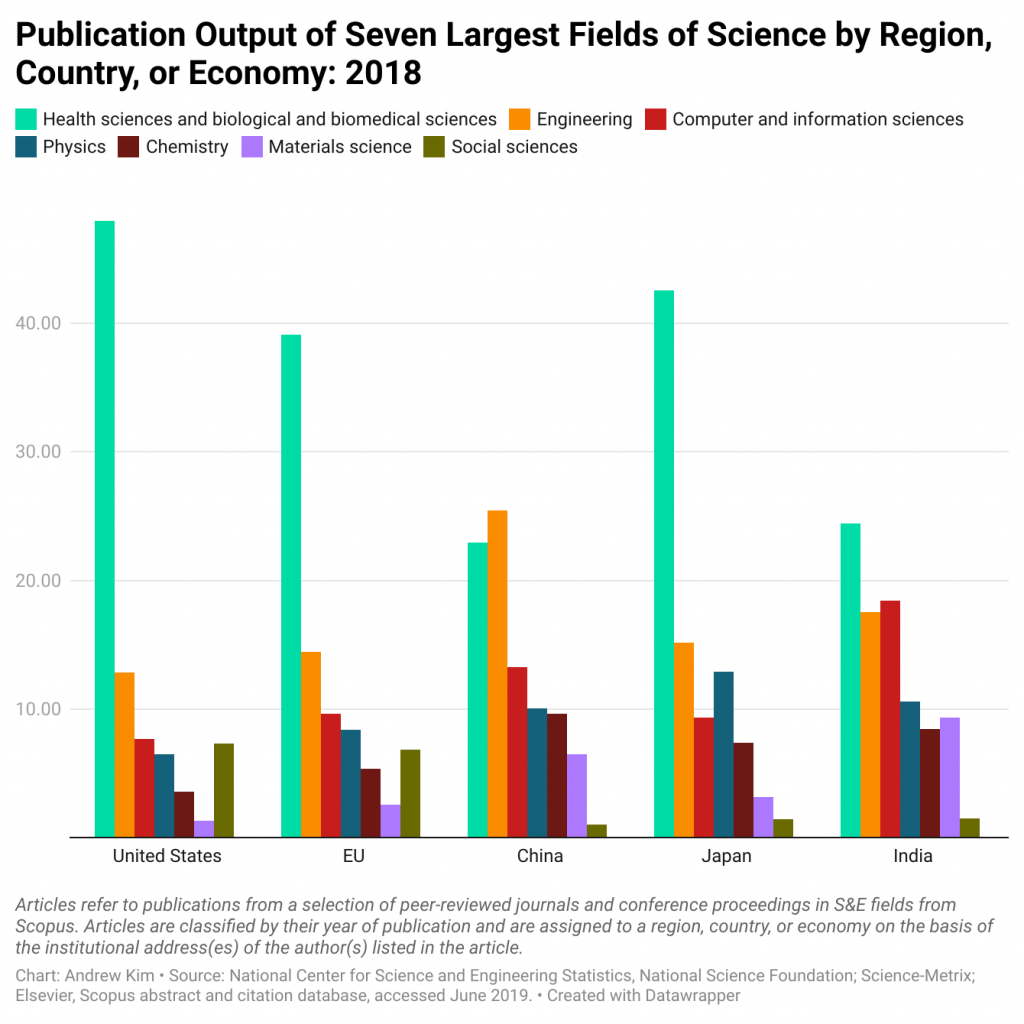
Choose a research topic that is interesting but also relevant and aligned with your own country’s culture or your university’s capabilities. Popular academic topics include healthcare and medical-related research. However, if you are attending an engineering school or humanities program, you should obviously choose a research question that pertains to your specific study and major.
Below is an embedded graph of the most popular research fields of study based on publication output according to region. As you can see, healthcare and the basic sciences receive the most funding and earn the highest number of publications.
2. Do preliminary research
You can begin doing preliminary research once you have chosen a research topic. Two objectives should be accomplished during this first phase of research. First, you should undertake a preliminary review of related literature to discover issues that scholars and peers are currently discussing. With this method, you show that you are informed about the latest developments in the field.
Secondly, identify knowledge gaps or limitations in your topic by conducting a preliminary literature review . It is possible to later use these gaps to focus your research question after a certain amount of fine-tuning.
3. Narrow your research to determine specific research questions
You can focus on a more specific area of study once you have a good handle on the topic you want to explore. Focusing on recent literature or knowledge gaps is one good option.
By identifying study limitations in the literature and overlooked areas of study, an author can carve out a good research question. The same is true for choosing research questions that extend or complement existing literature.
4. Evaluate your research question
Make sure you evaluate the research question by asking the following questions:
Is my research question clear?
The resulting data and observations that your study produces should be clear. For quantitative studies, data must be empirical and measurable. For qualitative, the observations should be clearly delineable across categories.
Is my research question focused and specific?
A strong research question should be specific enough that your methodology or testing procedure produces an objective result, not one left to subjective interpretation. Open-ended research questions or those relating to general topics can create ambiguous connections between the results and the aims of the study.
Is my research question sufficiently complex?
The result of your research should be consequential and substantial (and fall sufficiently within the context of your field) to warrant an academic study. Simply reinforcing or supporting a scientific consensus is superfluous and will likely not be well received by most journal editors.

Editing Your Research Question
Your research question should be fully formulated well before you begin drafting your research paper. However, you can receive English paper editing and proofreading services at any point in the drafting process. Language editors with expertise in your academic field can assist you with the content and language in your Introduction section or other manuscript sections. And if you need further assistance or information regarding paper compositions, in the meantime, check out our academic resources , which provide dozens of articles and videos on a variety of academic writing and publication topics.
Research: From selecting a topic to writing the bibliography
- Selecting a Topic
- Developing a Research Question
- What Type of Source Do I Need?
- Selecting the Best Place to Search
- Search Like a Pro
- Evaluating Information
Research Questions Worth Asking
This video from the UMD, Global Campus gives a good introduction to research questions.
What is a research question?
Once you have selected a topic, you need to develop a research question. You may be used to working with a thesis statement, but a thesis statement is an answer. If you start your research with an answer, you might miss something important or your paper might be too one-sided. Starting with a question allows you to explore your topic while still having it clearly defined.
A good research question is specific and focused.
Topic : Netflix
Research Question : How has the rise of streaming television changed the nature of advertising during television shows?
Topic : the environmental impact of fracking
Research Question : What are some of the most effective ways of protecting local ground water from the waste water produced by fracking?
Tip: Beware of research questions that are too broad or too narrow.
Too Broad: Why is reality television so popular?
Too Narrow: What are the economic and social consequences of the popularity of Jersey Shore on the lives of teenagers living in Omaha, Nebraska?
Tip: be willing to tweak your research question as you go.
Research Question: How has the rise of streaming television changed the nature of advertising during television shows?
Potential Research Finding: Advertising during television hasn't changed much recently.
New Research Question: Why has advertising on television been able to remain the same when how we watch television has changed so much?
Examples of Research Questions
The assignment is a 10-15 page paper relying primarily on scholarly resources.
- How is malaria treated?
- Will tablet computing replace the need for laptops?
- How much has the popularity of Harry Potter improved the reading scores of second graders in Missouri?
- At what point in time will the need for nurses in pedatric wards outpace the graduation rates from nursing schools?
- In what ways have online communities changed the nature of support systems available for people with Attention Deficit Disorder?
- How has mountaintop removal mining in western Kentucky impacted the migratory habits of the local bird population?
- << Previous: Selecting a Topic
- Next: What Type of Source Do I Need? >>
- Last Updated: May 20, 2024 9:38 PM
- URL: https://libguides.gwu.edu/research
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write a Research Question: Types and Examples

The first step in any research project is framing the research question. It can be considered the core of any systematic investigation as the research outcomes are tied to asking the right questions. Thus, this primary interrogation point sets the pace for your research as it helps collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work.
Typically, the research question guides the stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. Depending on the use of quantifiable or quantitative data, research questions are broadly categorized into quantitative or qualitative research questions. Both types of research questions can be used independently or together, considering the overall focus and objectives of your research.
What is a research question?
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, and arguable question on which your research and writing are centered. 1 It states various aspects of the study, including the population and variables to be studied and the problem the study addresses. These questions also set the boundaries of the study, ensuring cohesion.
Designing the research question is a dynamic process where the researcher can change or refine the research question as they review related literature and develop a framework for the study. Depending on the scale of your research, the study can include single or multiple research questions.
A good research question has the following features:
- It is relevant to the chosen field of study.
- The question posed is arguable and open for debate, requiring synthesizing and analysis of ideas.
- It is focused and concisely framed.
- A feasible solution is possible within the given practical constraint and timeframe.
A poorly formulated research question poses several risks. 1
- Researchers can adopt an erroneous design.
- It can create confusion and hinder the thought process, including developing a clear protocol.
- It can jeopardize publication efforts.
- It causes difficulty in determining the relevance of the study findings.
- It causes difficulty in whether the study fulfils the inclusion criteria for systematic review and meta-analysis. This creates challenges in determining whether additional studies or data collection is needed to answer the question.
- Readers may fail to understand the objective of the study. This reduces the likelihood of the study being cited by others.
Now that you know “What is a research question?”, let’s look at the different types of research questions.
Types of research questions
Depending on the type of research to be done, research questions can be classified broadly into quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods studies. Knowing the type of research helps determine the best type of research question that reflects the direction and epistemological underpinnings of your research.
The structure and wording of quantitative 2 and qualitative research 3 questions differ significantly. The quantitative study looks at causal relationships, whereas the qualitative study aims at exploring a phenomenon.
- Quantitative research questions:
- Seeks to investigate social, familial, or educational experiences or processes in a particular context and/or location.
- Answers ‘how,’ ‘what,’ or ‘why’ questions.
- Investigates connections, relations, or comparisons between independent and dependent variables.
Quantitative research questions can be further categorized into descriptive, comparative, and relationship, as explained in the Table below.
- Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional, and more flexible. It concerns broad areas of research or more specific areas of study to discover, explain, or explore a phenomenon. These are further classified as follows:
- Mixed-methods studies
Mixed-methods studies use both quantitative and qualitative research questions to answer your research question. Mixed methods provide a complete picture than standalone quantitative or qualitative research, as it integrates the benefits of both methods. Mixed methods research is often used in multidisciplinary settings and complex situational or societal research, especially in the behavioral, health, and social science fields.
What makes a good research question
A good research question should be clear and focused to guide your research. It should synthesize multiple sources to present your unique argument, and should ideally be something that you are interested in. But avoid questions that can be answered in a few factual statements. The following are the main attributes of a good research question.
- Specific: The research question should not be a fishing expedition performed in the hopes that some new information will be found that will benefit the researcher. The central research question should work with your research problem to keep your work focused. If using multiple questions, they should all tie back to the central aim.
- Measurable: The research question must be answerable using quantitative and/or qualitative data or from scholarly sources to develop your research question. If such data is impossible to access, it is better to rethink your question.
- Attainable: Ensure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific.
- You have the expertise
- You have the equipment and resources
- Realistic: Developing your research question should be based on initial reading about your topic. It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline.
- Based on some sort of rational physics
- Can be done in a reasonable time frame
- Timely: The research question should contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on.
- Novel
- Based on current technologies.
- Important to answer current problems or concerns.
- Lead to new directions.
- Important: Your question should have some aspect of originality. Incremental research is as important as exploring disruptive technologies. For example, you can focus on a specific location or explore a new angle.
- Meaningful whether the answer is “Yes” or “No.” Closed-ended, yes/no questions are too simple to work as good research questions. Such questions do not provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation before providing an answer.
Steps for developing a good research question
The importance of research questions cannot be understated. When drafting a research question, use the following frameworks to guide the components of your question to ease the process. 4
- Determine the requirements: Before constructing a good research question, set your research requirements. What is the purpose? Is it descriptive, comparative, or explorative research? Determining the research aim will help you choose the most appropriate topic and word your question appropriately.
- Select a broad research topic: Identify a broader subject area of interest that requires investigation. Techniques such as brainstorming or concept mapping can help identify relevant connections and themes within a broad research topic. For example, how to learn and help students learn.
- Perform preliminary investigation: Preliminary research is needed to obtain up-to-date and relevant knowledge on your topic. It also helps identify issues currently being discussed from which information gaps can be identified.
- Narrow your focus: Narrow the scope and focus of your research to a specific niche. This involves focusing on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature or extending or complementing the findings of existing literature. Another approach involves constructing strong research questions that challenge your views or knowledge of the area of study (Example: Is learning consistent with the existing learning theory and research).
- Identify the research problem: Once the research question has been framed, one should evaluate it. This is to realize the importance of the research questions and if there is a need for more revising (Example: How do your beliefs on learning theory and research impact your instructional practices).
How to write a research question
Those struggling to understand how to write a research question, these simple steps can help you simplify the process of writing a research question.
Sample Research Questions
The following are some bad and good research question examples
- Example 1
- Example 2
References:
- Thabane, L., Thomas, T., Ye, C., & Paul, J. (2009). Posing the research question: not so simple. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia/Journal canadien d’anesthésie , 56 (1), 71-79.
- Rutberg, S., & Bouikidis, C. D. (2018). Focusing on the fundamentals: A simplistic differentiation between qualitative and quantitative research. Nephrology Nursing Journal , 45 (2), 209-213.
- Kyngäs, H. (2020). Qualitative research and content analysis. The application of content analysis in nursing science research , 3-11.
- Mattick, K., Johnston, J., & de la Croix, A. (2018). How to… write a good research question. The clinical teacher , 15 (2), 104-108.
- Fandino, W. (2019). Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia , 63 (8), 611.
- Richardson, W. S., Wilson, M. C., Nishikawa, J., & Hayward, R. S. (1995). The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP journal club , 123 (3), A12-A13
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- 6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs in the World of Research
Language and grammar rules for academic writing, you may also like, academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , 9 steps to publish a research paper, what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging, 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., presenting research data effectively through tables and figures.
Literature Reviews
- Getting Started
- Choosing a Type of Review
Developing a Research Question
Finding example literature reviews.
- Searching the Literature
- Searching Tips
- ChatGPT [beta]
- Documenting your Search
- Using Citation Managers
- Concept Mapping
- Writing the Review
- Further Resources
Goldilocker Tool

UM Librarians have developed a quick tool called Goldilocker to help beginners who are struggling to refine their Research Question.
DEVELOPING A RESEARCH QUESTION
Before searching for sources, you need to formulate a Research Question — this is what you are trying to answer using the existing academic literature. The Research Question pinpoints the focus of the review .
Your first step involves choosing, exploring, and focusing a topic. At this stage you might discover that you need to tweak your topic or the scope of your research as you learn more about the topic in the literature.
THINGS TO KEEP IN MIND:
- The question must be "researchable" — it can be answered with accessible facts and data
- Questions often start with How, Why, What, Which
- The question opens the door for other areas of inquiry — it identifies a gap in existing research
- Questions should be open-ended and focus on cause and effect
TRY TO AVOID:
- Simple yes/no questions, or questions with an easy answer (what is the radius of the moon?)
- Questions that can only be answered by an opinion (does it smell nice when it rains?)
- Questions that involve secret information (what is the recipe for Coca-Cola?)
- Questions that are too broad or too narrow
REFINING YOUR RESEARCH QUESTION
Two examples of refining research questions that could be considered either too broad or too narrow.
USING DATABASE FILTER TOOLS
It can be helpful to read existing literature reviews on your topic to get an idea of major themes, how authors structure their arguments, or what reviews look like in your discipline.
DOCUMENT TYPE FILTERS
Many library databases have the option to highlight just Review Articles after you perform a search. Filters above show what the Document Type filter looks like, with a "Review" option. These examples are from Scopus and ProQuest. The "Review" filter here refers to free-standing, comprehensive Review Articles on a topic, as opposed to a shorter literature review inside a scholarly article.
LIT REVIEWS INSIDE ARTICLES
It is also worth taking a look at the shorter literature reviews inside scholarly articles. These can sometimes be called "Background" or "Background Literature." Look for a section typically following the Introduction that covers the history or gives context on the paper's topic.

EXAMPLE REVIEW ARTICLES
Here are a few examples of Review Articles in different disciplines. Note sometimes an article can be a Review Article without the word "review" in the title.
HUMANITIES — Art — " Art and Crime: Conceptualising Graffiti in the City " from the journal Geography Compass
SCIENCES — Climate Change — " Mercury Isotopes in Earth and Environmental Sciences " from the journal Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences
SOCIAL SCIENCES — Psychology — " Structural Competency and the Future of Firearm Research " from the journal Social Science & Medicine
- << Previous: Choosing a Type of Review
- Next: Searching the Literature >>
- Last Updated: May 9, 2024 11:44 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.umich.edu/litreview

How to Develop a Good Research Question? — Types & Examples
Cecilia is living through a tough situation in her research life. Figuring out where to begin, how to start her research study, and how to pose the right question for her research quest, is driving her insane. Well, questions, if not asked correctly, have a tendency to spiral us!
Image Source: https://phdcomics.com/
Questions lead everyone to answers. Research is a quest to find answers. Not the vague questions that Cecilia means to answer, but definitely more focused questions that define your research. Therefore, asking appropriate question becomes an important matter of discussion.
A well begun research process requires a strong research question. It directs the research investigation and provides a clear goal to focus on. Understanding the characteristics of comprising a good research question will generate new ideas and help you discover new methods in research.
In this article, we are aiming to help researchers understand what is a research question and how to write one with examples.
Table of Contents
What Is a Research Question?
A good research question defines your study and helps you seek an answer to your research. Moreover, a clear research question guides the research paper or thesis to define exactly what you want to find out, giving your work its objective. Learning to write a research question is the beginning to any thesis, dissertation , or research paper. Furthermore, the question addresses issues or problems which is answered through analysis and interpretation of data.
Why Is a Research Question Important?
A strong research question guides the design of a study. Moreover, it helps determine the type of research and identify specific objectives. Research questions state the specific issue you are addressing and focus on outcomes of the research for individuals to learn. Therefore, it helps break up the study into easy steps to complete the objectives and answer the initial question.
Types of Research Questions
Research questions can be categorized into different types, depending on the type of research you want to undergo. Furthermore, knowing the type of research will help a researcher determine the best type of research question to use.
1. Qualitative Research Question
Qualitative questions concern broad areas or more specific areas of research. However, unlike quantitative questions, qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional and more flexible. Qualitative research question focus on discovering, explaining, elucidating, and exploring.
i. Exploratory Questions
This form of question looks to understand something without influencing the results. The objective of exploratory questions is to learn more about a topic without attributing bias or preconceived notions to it.
Research Question Example: Asking how a chemical is used or perceptions around a certain topic.
ii. Predictive Questions
Predictive research questions are defined as survey questions that automatically predict the best possible response options based on text of the question. Moreover, these questions seek to understand the intent or future outcome surrounding a topic.
Research Question Example: Asking why a consumer behaves in a certain way or chooses a certain option over other.
iii. Interpretive Questions
This type of research question allows the study of people in the natural setting. The questions help understand how a group makes sense of shared experiences with regards to various phenomena. These studies gather feedback on a group’s behavior without affecting the outcome.
Research Question Example: How do you feel about AI assisting publishing process in your research?
2. Quantitative Research Question
Quantitative questions prove or disprove a researcher’s hypothesis through descriptions, comparisons, and relationships. These questions are beneficial when choosing a research topic or when posing follow-up questions that garner more information.
i. Descriptive Questions
It is the most basic type of quantitative research question and it seeks to explain when, where, why, or how something occurred. Moreover, they use data and statistics to describe an event or phenomenon.
Research Question Example: How many generations of genes influence a future generation?
ii. Comparative Questions
Sometimes it’s beneficial to compare one occurrence with another. Therefore, comparative questions are helpful when studying groups with dependent variables.
Example: Do men and women have comparable metabolisms?

iii. Relationship-Based Questions
This type of research question answers influence of one variable on another. Therefore, experimental studies use this type of research questions are majorly.
Example: How is drought condition affect a region’s probability for wildfires.
How to Write a Good Research Question?

1. Select a Topic
The first step towards writing a good research question is to choose a broad topic of research. You could choose a research topic that interests you, because the complete research will progress further from the research question. Therefore, make sure to choose a topic that you are passionate about, to make your research study more enjoyable.
2. Conduct Preliminary Research
After finalizing the topic, read and know about what research studies are conducted in the field so far. Furthermore, this will help you find articles that talk about the topics that are yet to be explored. You could explore the topics that the earlier research has not studied.
3. Consider Your Audience
The most important aspect of writing a good research question is to find out if there is audience interested to know the answer to the question you are proposing. Moreover, determining your audience will assist you in refining your research question, and focus on aspects that relate to defined groups.
4. Generate Potential Questions
The best way to generate potential questions is to ask open ended questions. Questioning broader topics will allow you to narrow down to specific questions. Identifying the gaps in literature could also give you topics to write the research question. Moreover, you could also challenge the existing assumptions or use personal experiences to redefine issues in research.
5. Review Your Questions
Once you have listed few of your questions, evaluate them to find out if they are effective research questions. Moreover while reviewing, go through the finer details of the question and its probable outcome, and find out if the question meets the research question criteria.
6. Construct Your Research Question
There are two frameworks to construct your research question. The first one being PICOT framework , which stands for:
- Population or problem
- Intervention or indicator being studied
- Comparison group
- Outcome of interest
- Time frame of the study.
The second framework is PEO , which stands for:
- Population being studied
- Exposure to preexisting conditions
- Outcome of interest.
Research Question Examples
- How might the discovery of a genetic basis for alcoholism impact triage processes in medical facilities?
- How do ecological systems respond to chronic anthropological disturbance?
- What are demographic consequences of ecological interactions?
- What roles do fungi play in wildfire recovery?
- How do feedbacks reinforce patterns of genetic divergence on the landscape?
- What educational strategies help encourage safe driving in young adults?
- What makes a grocery store easy for shoppers to navigate?
- What genetic factors predict if someone will develop hypothyroidism?
- Does contemporary evolution along the gradients of global change alter ecosystems function?
How did you write your first research question ? What were the steps you followed to create a strong research question? Do write to us or comment below.
Frequently Asked Questions
Research questions guide the focus and direction of a research study. Here are common types of research questions: 1. Qualitative research question: Qualitative questions concern broad areas or more specific areas of research. However, unlike quantitative questions, qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional and more flexible. Different types of qualitative research questions are: i. Exploratory questions ii. Predictive questions iii. Interpretive questions 2. Quantitative Research Question: Quantitative questions prove or disprove a researcher’s hypothesis through descriptions, comparisons, and relationships. These questions are beneficial when choosing a research topic or when posing follow-up questions that garner more information. Different types of quantitative research questions are: i. Descriptive questions ii. Comparative questions iii. Relationship-based questions
Qualitative research questions aim to explore the richness and depth of participants' experiences and perspectives. They should guide your research and allow for in-depth exploration of the phenomenon under investigation. After identifying the research topic and the purpose of your research: • Begin with Broad Inquiry: Start with a general research question that captures the main focus of your study. This question should be open-ended and allow for exploration. • Break Down the Main Question: Identify specific aspects or dimensions related to the main research question that you want to investigate. • Formulate Sub-questions: Create sub-questions that delve deeper into each specific aspect or dimension identified in the previous step. • Ensure Open-endedness: Make sure your research questions are open-ended and allow for varied responses and perspectives. Avoid questions that can be answered with a simple "yes" or "no." Encourage participants to share their experiences, opinions, and perceptions in their own words. • Refine and Review: Review your research questions to ensure they align with your research purpose, topic, and objectives. Seek feedback from your research advisor or peers to refine and improve your research questions.
Developing research questions requires careful consideration of the research topic, objectives, and the type of study you intend to conduct. Here are the steps to help you develop effective research questions: 1. Select a Topic 2. Conduct Preliminary Research 3. Consider Your Audience 4. Generate Potential Questions 5. Review Your Questions 6. Construct Your Research Question Based on PICOT or PEO Framework
There are two frameworks to construct your research question. The first one being PICOT framework, which stands for: • Population or problem • Intervention or indicator being studied • Comparison group • Outcome of interest • Time frame of the study The second framework is PEO, which stands for: • Population being studied • Exposure to preexisting conditions • Outcome of interest
A tad helpful
Had trouble coming up with a good research question for my MSc proposal. This is very much helpful.
This is a well elaborated writing on research questions development. I found it very helpful.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles
![what does a good research question look like What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Industry News
- Trending Now
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Diversity and Inclusion
The Silent Struggle: Confronting gender bias in science funding
In the 1990s, Dr. Katalin Kariko’s pioneering mRNA research seemed destined for obscurity, doomed by…
Setting Rationale in Research: Cracking the code for excelling at research
Research Problem Statement — Find out how to write an impactful one!
Experimental Research Design — 6 mistakes you should never make!

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Questions
Definition:
Research questions are the specific questions that guide a research study or inquiry. These questions help to define the scope of the research and provide a clear focus for the study. Research questions are usually developed at the beginning of a research project and are designed to address a particular research problem or objective.
Types of Research Questions
Types of Research Questions are as follows:
Descriptive Research Questions
These aim to describe a particular phenomenon, group, or situation. For example:
- What are the characteristics of the target population?
- What is the prevalence of a particular disease in a specific region?
Exploratory Research Questions
These aim to explore a new area of research or generate new ideas or hypotheses. For example:
- What are the potential causes of a particular phenomenon?
- What are the possible outcomes of a specific intervention?
Explanatory Research Questions
These aim to understand the relationship between two or more variables or to explain why a particular phenomenon occurs. For example:
- What is the effect of a specific drug on the symptoms of a particular disease?
- What are the factors that contribute to employee turnover in a particular industry?
Predictive Research Questions
These aim to predict a future outcome or trend based on existing data or trends. For example :
- What will be the future demand for a particular product or service?
- What will be the future prevalence of a particular disease?
Evaluative Research Questions
These aim to evaluate the effectiveness of a particular intervention or program. For example:
- What is the impact of a specific educational program on student learning outcomes?
- What is the effectiveness of a particular policy or program in achieving its intended goals?
How to Choose Research Questions
Choosing research questions is an essential part of the research process and involves careful consideration of the research problem, objectives, and design. Here are some steps to consider when choosing research questions:
- Identify the research problem: Start by identifying the problem or issue that you want to study. This could be a gap in the literature, a social or economic issue, or a practical problem that needs to be addressed.
- Conduct a literature review: Conducting a literature review can help you identify existing research in your area of interest and can help you formulate research questions that address gaps or limitations in the existing literature.
- Define the research objectives : Clearly define the objectives of your research. What do you want to achieve with your study? What specific questions do you want to answer?
- Consider the research design : Consider the research design that you plan to use. This will help you determine the appropriate types of research questions to ask. For example, if you plan to use a qualitative approach, you may want to focus on exploratory or descriptive research questions.
- Ensure that the research questions are clear and answerable: Your research questions should be clear and specific, and should be answerable with the data that you plan to collect. Avoid asking questions that are too broad or vague.
- Get feedback : Get feedback from your supervisor, colleagues, or peers to ensure that your research questions are relevant, feasible, and meaningful.
How to Write Research Questions
Guide for Writing Research Questions:
- Start with a clear statement of the research problem: Begin by stating the problem or issue that your research aims to address. This will help you to formulate focused research questions.
- Use clear language : Write your research questions in clear and concise language that is easy to understand. Avoid using jargon or technical terms that may be unfamiliar to your readers.
- Be specific: Your research questions should be specific and focused. Avoid broad questions that are difficult to answer. For example, instead of asking “What is the impact of climate change on the environment?” ask “What are the effects of rising sea levels on coastal ecosystems?”
- Use appropriate question types: Choose the appropriate question types based on the research design and objectives. For example, if you are conducting a qualitative study, you may want to use open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed responses.
- Consider the feasibility of your questions : Ensure that your research questions are feasible and can be answered with the resources available. Consider the data sources and methods of data collection when writing your questions.
- Seek feedback: Get feedback from your supervisor, colleagues, or peers to ensure that your research questions are relevant, appropriate, and meaningful.
Examples of Research Questions
Some Examples of Research Questions with Research Titles:
Research Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
- Research Question : What is the relationship between social media use and mental health, and how does this impact individuals’ well-being?
Research Title: Factors Influencing Academic Success in High School
- Research Question: What are the primary factors that influence academic success in high school, and how do they contribute to student achievement?
Research Title: The Effects of Exercise on Physical and Mental Health
- Research Question: What is the relationship between exercise and physical and mental health, and how can exercise be used as a tool to improve overall well-being?
Research Title: Understanding the Factors that Influence Consumer Purchasing Decisions
- Research Question : What are the key factors that influence consumer purchasing decisions, and how do these factors vary across different demographics and products?
Research Title: The Impact of Technology on Communication
- Research Question : How has technology impacted communication patterns, and what are the effects of these changes on interpersonal relationships and society as a whole?
Research Title: Investigating the Relationship between Parenting Styles and Child Development
- Research Question: What is the relationship between different parenting styles and child development outcomes, and how do these outcomes vary across different ages and developmental stages?
Research Title: The Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy in Treating Anxiety Disorders
- Research Question: How effective is cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating anxiety disorders, and what factors contribute to its success or failure in different patients?
Research Title: The Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity
- Research Question : How is climate change affecting global biodiversity, and what can be done to mitigate the negative effects on natural ecosystems?
Research Title: Exploring the Relationship between Cultural Diversity and Workplace Productivity
- Research Question : How does cultural diversity impact workplace productivity, and what strategies can be employed to maximize the benefits of a diverse workforce?
Research Title: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
- Research Question: How can artificial intelligence be leveraged to improve healthcare outcomes, and what are the potential risks and ethical concerns associated with its use?
Applications of Research Questions
Here are some of the key applications of research questions:
- Defining the scope of the study : Research questions help researchers to narrow down the scope of their study and identify the specific issues they want to investigate.
- Developing hypotheses: Research questions often lead to the development of hypotheses, which are testable predictions about the relationship between variables. Hypotheses provide a clear and focused direction for the study.
- Designing the study : Research questions guide the design of the study, including the selection of participants, the collection of data, and the analysis of results.
- Collecting data : Research questions inform the selection of appropriate methods for collecting data, such as surveys, interviews, or experiments.
- Analyzing data : Research questions guide the analysis of data, including the selection of appropriate statistical tests and the interpretation of results.
- Communicating results : Research questions help researchers to communicate the results of their study in a clear and concise manner. The research questions provide a framework for discussing the findings and drawing conclusions.
Characteristics of Research Questions
Characteristics of Research Questions are as follows:
- Clear and Specific : A good research question should be clear and specific. It should clearly state what the research is trying to investigate and what kind of data is required.
- Relevant : The research question should be relevant to the study and should address a current issue or problem in the field of research.
- Testable : The research question should be testable through empirical evidence. It should be possible to collect data to answer the research question.
- Concise : The research question should be concise and focused. It should not be too broad or too narrow.
- Feasible : The research question should be feasible to answer within the constraints of the research design, time frame, and available resources.
- Original : The research question should be original and should contribute to the existing knowledge in the field of research.
- Significant : The research question should have significance and importance to the field of research. It should have the potential to provide new insights and knowledge to the field.
- Ethical : The research question should be ethical and should not cause harm to any individuals or groups involved in the study.
Purpose of Research Questions
Research questions are the foundation of any research study as they guide the research process and provide a clear direction to the researcher. The purpose of research questions is to identify the scope and boundaries of the study, and to establish the goals and objectives of the research.
The main purpose of research questions is to help the researcher to focus on the specific area or problem that needs to be investigated. They enable the researcher to develop a research design, select the appropriate methods and tools for data collection and analysis, and to organize the results in a meaningful way.
Research questions also help to establish the relevance and significance of the study. They define the research problem, and determine the research methodology that will be used to address the problem. Research questions also help to determine the type of data that will be collected, and how it will be analyzed and interpreted.
Finally, research questions provide a framework for evaluating the results of the research. They help to establish the validity and reliability of the data, and provide a basis for drawing conclusions and making recommendations based on the findings of the study.
Advantages of Research Questions
There are several advantages of research questions in the research process, including:
- Focus : Research questions help to focus the research by providing a clear direction for the study. They define the specific area of investigation and provide a framework for the research design.
- Clarity : Research questions help to clarify the purpose and objectives of the study, which can make it easier for the researcher to communicate the research aims to others.
- Relevance : Research questions help to ensure that the study is relevant and meaningful. By asking relevant and important questions, the researcher can ensure that the study will contribute to the existing body of knowledge and address important issues.
- Consistency : Research questions help to ensure consistency in the research process by providing a framework for the development of the research design, data collection, and analysis.
- Measurability : Research questions help to ensure that the study is measurable by defining the specific variables and outcomes that will be measured.
- Replication : Research questions help to ensure that the study can be replicated by providing a clear and detailed description of the research aims, methods, and outcomes. This makes it easier for other researchers to replicate the study and verify the results.
Limitations of Research Questions
Limitations of Research Questions are as follows:
- Subjectivity : Research questions are often subjective and can be influenced by personal biases and perspectives of the researcher. This can lead to a limited understanding of the research problem and may affect the validity and reliability of the study.
- Inadequate scope : Research questions that are too narrow in scope may limit the breadth of the study, while questions that are too broad may make it difficult to focus on specific research objectives.
- Unanswerable questions : Some research questions may not be answerable due to the lack of available data or limitations in research methods. In such cases, the research question may need to be rephrased or modified to make it more answerable.
- Lack of clarity : Research questions that are poorly worded or ambiguous can lead to confusion and misinterpretation. This can result in incomplete or inaccurate data, which may compromise the validity of the study.
- Difficulty in measuring variables : Some research questions may involve variables that are difficult to measure or quantify, making it challenging to draw meaningful conclusions from the data.
- Lack of generalizability: Research questions that are too specific or limited in scope may not be generalizable to other contexts or populations. This can limit the applicability of the study’s findings and restrict its broader implications.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
- Research Questions: Definitions, Types + [Examples]

Research questions lie at the core of systematic investigation and this is because recording accurate research outcomes is tied to asking the right questions. Asking the right questions when conducting research can help you collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work, positively.
The right research questions are typically easy to understand, straight to the point, and engaging. In this article, we will share tips on how to create the right research questions and also show you how to create and administer an online questionnaire with Formplus .
What is a Research Question?
A research question is a specific inquiry which the research seeks to provide a response to. It resides at the core of systematic investigation and it helps you to clearly define a path for the research process.
A research question is usually the first step in any research project. Basically, it is the primary interrogation point of your research and it sets the pace for your work.
Typically, a research question focuses on the research, determines the methodology and hypothesis, and guides all stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. With the right research questions, you will be able to gather useful information for your investigation.
Types of Research Questions
Research questions are broadly categorized into 2; that is, qualitative research questions and quantitative research questions. Qualitative and quantitative research questions can be used independently and co-dependently in line with the overall focus and objectives of your research.
If your research aims at collecting quantifiable data , you will need to make use of quantitative research questions. On the other hand, qualitative questions help you to gather qualitative data bothering on the perceptions and observations of your research subjects.
Qualitative Research Questions
A qualitative research question is a type of systematic inquiry that aims at collecting qualitative data from research subjects. The aim of qualitative research questions is to gather non-statistical information pertaining to the experiences, observations, and perceptions of the research subjects in line with the objectives of the investigation.
Types of Qualitative Research Questions
- Ethnographic Research Questions
As the name clearly suggests, ethnographic research questions are inquiries presented in ethnographic research. Ethnographic research is a qualitative research approach that involves observing variables in their natural environments or habitats in order to arrive at objective research outcomes.
These research questions help the researcher to gather insights into the habits, dispositions, perceptions, and behaviors of research subjects as they interact in specific environments.
Ethnographic research questions can be used in education, business, medicine, and other fields of study, and they are very useful in contexts aimed at collecting in-depth and specific information that are peculiar to research variables. For instance, asking educational ethnographic research questions can help you understand how pedagogy affects classroom relations and behaviors.
This type of research question can be administered physically through one-on-one interviews, naturalism (live and work), and participant observation methods. Alternatively, the researcher can ask ethnographic research questions via online surveys and questionnaires created with Formplus.
Examples of Ethnographic Research Questions
- Why do you use this product?
- Have you noticed any side effects since you started using this drug?
- Does this product meet your needs?
- Case Studies
A case study is a qualitative research approach that involves carrying out a detailed investigation into a research subject(s) or variable(s). In the course of a case study, the researcher gathers a range of data from multiple sources of information via different data collection methods, and over a period of time.
The aim of a case study is to analyze specific issues within definite contexts and arrive at detailed research subject analyses by asking the right questions. This research method can be explanatory, descriptive , or exploratory depending on the focus of your systematic investigation or research.
An explanatory case study is one that seeks to gather information on the causes of real-life occurrences. This type of case study uses “how” and “why” questions in order to gather valid information about the causative factors of an event.
Descriptive case studies are typically used in business researches, and they aim at analyzing the impact of changing market dynamics on businesses. On the other hand, exploratory case studies aim at providing answers to “who” and “what” questions using data collection tools like interviews and questionnaires.
Some questions you can include in your case studies are:
- Why did you choose our services?
- How has this policy affected your business output?
- What benefits have you recorded since you started using our product?
An interview is a qualitative research method that involves asking respondents a series of questions in order to gather information about a research subject. Interview questions can be close-ended or open-ended , and they prompt participants to provide valid information that is useful to the research.
An interview may also be structured, semi-structured , or unstructured , and this further influences the types of questions they include. Structured interviews are made up of more close-ended questions because they aim at gathering quantitative data while unstructured interviews consist, primarily, of open-ended questions that allow the researcher to collect qualitative information from respondents.
You can conduct interview research by scheduling a physical meeting with respondents, through a telephone conversation, and via digital media and video conferencing platforms like Skype and Zoom. Alternatively, you can use Formplus surveys and questionnaires for your interview.
Examples of interview questions include:
- What challenges did you face while using our product?
- What specific needs did our product meet?
- What would you like us to improve our service delivery?
Quantitative Research Questions
Quantitative research questions are questions that are used to gather quantifiable data from research subjects. These types of research questions are usually more specific and direct because they aim at collecting information that can be measured; that is, statistical information.
Types of Quantitative Research Questions
- Descriptive Research Questions
Descriptive research questions are inquiries that researchers use to gather quantifiable data about the attributes and characteristics of research subjects. These types of questions primarily seek responses that reveal existing patterns in the nature of the research subjects.
It is important to note that descriptive research questions are not concerned with the causative factors of the discovered attributes and characteristics. Rather, they focus on the “what”; that is, describing the subject of the research without paying attention to the reasons for its occurrence.
Descriptive research questions are typically closed-ended because they aim at gathering definite and specific responses from research participants. Also, they can be used in customer experience surveys and market research to collect information about target markets and consumer behaviors.
Descriptive Research Question Examples
- How often do you make use of our fitness application?
- How much would you be willing to pay for this product?
- Comparative Research Questions
A comparative research question is a type of quantitative research question that is used to gather information about the differences between two or more research subjects across different variables. These types of questions help the researcher to identify distinct features that mark one research subject from the other while highlighting existing similarities.
Asking comparative research questions in market research surveys can provide insights on how your product or service matches its competitors. In addition, it can help you to identify the strengths and weaknesses of your product for a better competitive advantage.
The 5 steps involved in the framing of comparative research questions are:
- Choose your starting phrase
- Identify and name the dependent variable
- Identify the groups you are interested in
- Identify the appropriate adjoining text
- Write out the comparative research question
Comparative Research Question Samples
- What are the differences between a landline telephone and a smartphone?
- What are the differences between work-from-home and on-site operations?
- Relationship-based Research Questions
Just like the name suggests, a relationship-based research question is one that inquires into the nature of the association between two research subjects within the same demographic. These types of research questions help you to gather information pertaining to the nature of the association between two research variables.
Relationship-based research questions are also known as correlational research questions because they seek to clearly identify the link between 2 variables.
Read: Correlational Research Designs: Types, Examples & Methods
Examples of relationship-based research questions include:
- What is the relationship between purchasing power and the business site?
- What is the relationship between the work environment and workforce turnover?
Examples of a Good Research Question
Since research questions lie at the core of any systematic investigations, it is important to know how to frame a good research question. The right research questions will help you to gather the most objective responses that are useful to your systematic investigation.
A good research question is one that requires impartial responses and can be answered via existing sources of information. Also, a good research question seeks answers that actively contribute to a body of knowledge; hence, it is a question that is yet to be answered in your specific research context.
- Open-Ended Questions
An open-ended question is a type of research question that does not restrict respondents to a set of premeditated answer options. In other words, it is a question that allows the respondent to freely express his or her perceptions and feelings towards the research subject.
Examples of Open-ended Questions
- How do you deal with stress in the workplace?
- What is a typical day at work like for you?
- Close-ended Questions
A close-ended question is a type of survey question that restricts respondents to a set of predetermined answers such as multiple-choice questions . Close-ended questions typically require yes or no answers and are commonly used in quantitative research to gather numerical data from research participants.
Examples of Close-ended Questions
- Did you enjoy this event?
- How likely are you to recommend our services?
- Very Likely
- Somewhat Likely
- Likert Scale Questions
A Likert scale question is a type of close-ended question that is structured as a 3-point, 5-point, or 7-point psychometric scale . This type of question is used to measure the survey respondent’s disposition towards multiple variables and it can be unipolar or bipolar in nature.
Example of Likert Scale Questions
- How satisfied are you with our service delivery?
- Very dissatisfied
- Not satisfied
- Very satisfied
- Rating Scale Questions
A rating scale question is a type of close-ended question that seeks to associate a specific qualitative measure (rating) with the different variables in research. It is commonly used in customer experience surveys, market research surveys, employee reviews, and product evaluations.
Example of Rating Questions
- How would you rate our service delivery?
Examples of a Bad Research Question
Knowing what bad research questions are would help you avoid them in the course of your systematic investigation. These types of questions are usually unfocused and often result in research biases that can negatively impact the outcomes of your systematic investigation.
- Loaded Questions
A loaded question is a question that subtly presupposes one or more unverified assumptions about the research subject or participant. This type of question typically boxes the respondent in a corner because it suggests implicit and explicit biases that prevent objective responses.
Example of Loaded Questions
- Have you stopped smoking?
- Where did you hide the money?
- Negative Questions
A negative question is a type of question that is structured with an implicit or explicit negator. Negative questions can be misleading because they upturn the typical yes/no response order by requiring a negative answer for affirmation and an affirmative answer for negation.
Examples of Negative Questions
- Would you mind dropping by my office later today?
- Didn’t you visit last week?
- Leading Questions
A l eading question is a type of survey question that nudges the respondent towards an already-determined answer. It is highly suggestive in nature and typically consists of biases and unverified assumptions that point toward its premeditated responses.
Examples of Leading Questions
- If you enjoyed this service, would you be willing to try out our other packages?
- Our product met your needs, didn’t it?
Read More: Leading Questions: Definition, Types, and Examples
How to Use Formplus as Online Research Questionnaire Tool
With Formplus, you can create and administer your online research questionnaire easily. In the form builder, you can add different form fields to your questionnaire and edit these fields to reflect specific research questions for your systematic investigation.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to create an online research questionnaire with Formplus:
- Sign in to your Formplus accoun t, then click on the “create new form” button in your dashboard to access the Form builder.
- In the form builder, add preferred form fields to your online research questionnaire by dragging and dropping them into the form. Add a title to your form in the title block. You can edit form fields by clicking on the “pencil” icon on the right corner of each form field.
- Save the form to access the customization section of the builder. Here, you can tweak the appearance of your online research questionnaire by adding background images, changing the form font, and adding your organization’s logo.
- Finally, copy your form link and share it with respondents. You can also use any of the multiple sharing options available.
Conclusion
The success of your research starts with framing the right questions to help you collect the most valid and objective responses. Be sure to avoid bad research questions like loaded and negative questions that can be misleading and adversely affect your research data and outcomes.
Your research questions should clearly reflect the aims and objectives of your systematic investigation while laying emphasis on specific contexts. To help you seamlessly gather responses for your research questions, you can create an online research questionnaire on Formplus.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- abstract in research papers
- bad research questions
- examples of research questions
- types of research questions
- busayo.longe

You may also like:
Research Summary: What Is It & How To Write One
Introduction A research summary is a requirement during academic research and sometimes you might need to prepare a research summary...

How to Write An Abstract For Research Papers: Tips & Examples
In this article, we will share some tips for writing an effective abstract, plus samples you can learn from.
How to do a Meta Analysis: Methodology, Pros & Cons
In this article, we’ll go through the concept of meta-analysis, what it can be used for, and how you can use it to improve how you...
How to Write a Problem Statement for your Research
Learn how to write problem statements before commencing any research effort. Learn about its structure and explore examples
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.63(8); 2019 Aug
Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls
Wilson fandino.
Guys' and St Thomas' Hospital National Health Service Foundation Trust, London, United Kingdom
The process of formulating a good research question can be challenging and frustrating. While a comprehensive literature review is compulsory, the researcher usually encounters methodological difficulties in the conduct of the study, particularly if the primary study question has not been adequately selected in accordance with the clinical dilemma that needs to be addressed. Therefore, optimising time and resources before embarking in the design of a clinical protocol can make an impact on the final results of the research project. Researchers have developed effective ways to convey the message of how to build a good research question that can be easily recalled under the acronyms of PICOT (population, intervention, comparator, outcome, and time frame) and FINER (feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, and relevant). In line with these concepts, this article highlights the main issues faced by clinicians, when developing a research question.
INTRODUCTION
What is your research question? This is very often one of the first queries made by statisticians, when researchers come up with an interesting idea. In fact, the findings of a study may only acquire relevance if they provide an accurate and unbiased answer to a specific question,[ 1 , 2 ] and it has been suggested that up to one-third of the time spent in the whole process—from the conception of an idea to the publication of the manuscript—could be invested in finding the right primary study question.[ 3 ] Furthermore, selecting a good research question can be a time-consuming and challenging task: in one retrospective study, Mayo et al . reported that 3 out of 10 articles published would have needed a major rewording of the question.[ 1 ] This paper explores some recommendations to consider before starting any research project, and outlines the main difficulties faced by young and experienced clinicians, when it comes time to turn an exciting idea into a valuable and feasible research question.
OPTIMISATION OF TIME AND RESOURCES
Focusing on the primary research question.
The process of developing a new idea usually stems from a dilemma inherent to the clinical practice.[ 2 , 3 , 4 ] However, once the problem has been identified, it is tempting to formulate multiple research questions. Conducting a clinical trial with more than one primary study question would not be feasible. First, because each question may require a different research design, and second, because the necessary statistical power of the study would demand unaffordable sample sizes. It is the duty of editors and reviewers to make sure that authors clearly identify the primary research question, and as a consequence, studies approaching more than one primary research question may not be suitable for publication.
Working in the right environment
Teamwork is essential to find the appropriate research question. Working in the right environment will enable the investigator to interact with colleagues with different backgrounds, and create opportunities to exchange experiences in a collaborative way between clinicians and researchers. Likewise, it is of paramount importance to get involved colleagues with expertise in the field (lead clinicians, education supervisors, research mentors, department chairs, epidemiologists, biostatisticians, and ethical consultants, among others), and ask for their guidance.[ 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 ]
Evaluating the pertinence of the study
The researcher should wonder if, on the basis of the research question formulated, there is a need for a study to address the problem, as clinical research usually entails a large investment of resources and workforce involvement. Thus, if the answer to the posed clinical question seems to be evident before starting the study, investing in research to address the problem would become superfluous. For example, in a clinical trial, Herzog-Niescery et al . compared laryngeal masks with cuffed and uncuffed tracheal tubes, in the context of surgeons' exposure to sevoflurane, in infants undergoing adenoidectomy. However, it appears obvious that cuffed tracheal tubes are preferred to minimise surgeons' exposure to volatile gases, as authors concluded after recruiting 60 patients.[ 9 ]
Conducting a thorough literature review
Any research project requires the identification of at least one of three problems: the evidence is scarce, the existing literature yields conflicting results, or the results could be improved. Hence, a comprehensive review of the topic is imperative, as it allows the researcher to identify this gap in the literature, formulate a hypothesis and develop a research question.[ 2 ] To this end, it is crucial to be attentive to new ideas, keep the imagination roaming with reflective attitude, and remain sceptical to the new-gained information.[ 4 , 7 ]
Narrowing the research question
A broad research question may encompass an unaffordable extensive topic. For instance, do supraglottic devices provide similar conditions for the visualization of the glottis aperture in a German hospital? Such a general research question usually needs to be narrowed, not only by cutting away unnecessary components (a German hospital is irrelevant in this context), but also by defining a target population, a specific intervention, an alternative treatment or procedure to be compared with the intervention, a measurable primary outcome, and a time frame of the study. In contrast, an example of a good research question would be: among children younger than 1 year of age undergoing elective minor procedures, to what extent the insertion times are different, comparing the Supreme™ laryngeal mask airway (LMA) to Proseal™ LMA, when placed after reaching a BIS index <60?[ 10 ] In this example, the core ingredients of the research question can be easily identified as: children <1 year of age undergoing minor elective procedures, Supreme™ LMA, Proseal™ LMA and insertion times at anaesthetic induction when reaching a BIS index <60. These components are usually gathered in the literature under the acronym of PICOT (population, intervention, comparator, outcome and time frame, respectively).[ 1 , 3 , 5 ]
PICOT FRAMEWORK
Table 1 summarises the foremost questions likely to be addressed when working on PICOT frame.[ 1 , 6 , 8 ] These components are also applicable to observational studies, where the exposure takes place of the intervention.[ 1 , 11 ] Remarkably, if after browsing the title and the abstract of a paper, the reader is not able to clearly identify the PICOT parameters, and elucidate the question posed by the authors, there should be reasonable scepticism regarding the scientific rigor of the work.[ 12 , 13 ] All these elements are crucial in the design and methodology of a clinical trial, as they can affect the feasibility and reliability of results. Having formulated the primary study question in the context of the PICOT framework [ Table 1 ],[ 1 , 6 , 8 ] the researcher should be able to elucidate which design is most suitable for their work, determine what type of data needs to be collected, and write a structured introduction tailored to what they want to know, explicitly mentioning the primary study hypothesis, which should lead to formulate the main research question.[ 1 , 2 , 6 , 8 ]
Key questions to be answered when working with the PICOT framework (population, intervention, comparator, outcome, and time frame) in a clinical research design
Occasionally, the intended population of the study needs to be modified, in order to overcome any potential ethical issues, and/or for the sake of convenience and feasibility of the project. Yet, the researcher must be aware that the external validity of the results may be compromised. As an illustration, in a randomised clinical trial, authors compared the ease of tracheal tube insertion between C-MAC video laryngoscope and direct laryngoscopy, in patients presenting to the emergency department with an indication of rapid sequence intubation. However, owing to the existence of ethical concerns, a substantial amount of patients requiring emergency tracheal intubation, including patients with major maxillofacial trauma and ongoing cardiopulmonary resuscitation, had to be excluded from the trial.[ 14 ] In fact, the design of prospective studies to explore this subset of patients can be challenging, not only because of ethical considerations, but because of the low incidence of these cases. In another study, Metterlein et al . compared the glottis visualisation among five different supraglottic airway devices, using fibreroptic-guided tracheal intubation in an adult population. Despite that the study was aimed to explore the ease of intubation in patients with anticipated difficult airway (thus requiring fibreoptic tracheal intubation), authors decided to enrol patients undergoing elective laser treatment for genital condylomas, as a strategy to hasten the recruitment process and optimise resources.[ 15 ]
Intervention
Anaesthetic interventions can be classified into pharmacological (experimental treatment) and nonpharmacological. Among nonpharmacological interventions, the most common include anaesthetic techniques, monitoring instruments and airway devices. For example, it would be appropriate to examine the ease of insertion of Supreme™ LMA, when compared with ProSeal™ LMA. Notwithstanding, a common mistake is the tendency to be focused on the data aimed to be collected (the “stated” objective), rather than the question that needs to be answered (the “latent” objective).[ 1 , 4 ] In one clinical trial, authors stated: “we compared the Supreme™ and ProSeal™ LMAs in infants by measuring their performance characteristics, including insertion features, ventilation parameters, induced changes in haemodynamics, and rates of postoperative complications”.[ 10 ] Here, the research question has been centered on the measurements (insertion characteristics, haemodynamic variables, LMA insertion characteristics, ventilation parameters) rather than the clinical problem that needs to be addressed (is Supreme™ LMA easier to insert than ProSeal™ LMA?).
Comparators in clinical research can also be pharmacological (e.g., gold standard or placebo) or nonpharmacological. Typically, not more than two comparator groups are included in a clinical trial. Multiple comparisons should be generally avoided, unless there is enough statistical power to address the end points of interest, and statistical analyses have been adjusted for multiple testing. For instance, in the aforementioned study of Metterlein et al .,[ 15 ] authors compared five supraglottic airway devices by recruiting only 10--12 participants per group. In spite of the authors' recommendation of using two supraglottic devices based on the results of the study, there was no mention of statistical adjustments for multiple comparisons, and given the small sample size, larger clinical trials will undoubtedly be needed to confirm or refute these findings.[ 15 ]
A clear formulation of the primary outcome results of vital importance in clinical research, as the primary statistical analyses, including the sample size calculation (and therefore, the estimation of the effect size and statistical power), will be derived from the main outcome of interest. While it is clear that using more than one primary outcome would not be appropriate, it would be equally inadequate to include multiple point measurements of the same variable as the primary outcome (e.g., visual analogue scale for pain at 1, 2, 6, and 12 h postoperatively).
Composite outcomes, in which multiple primary endpoints are combined, may make it difficult to draw any conclusions based on the study findings. For example, in a clinical trial, 200 children undergoing ophthalmic surgery were recruited to explore the incidence of respiratory adverse events, when comparing desflurane with sevoflurane, following the removal of flexible LMA during the emergence of the anaesthesia. The primary outcome was the number of respiratory events, including breath holding, coughing, secretions requiring suction, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, and mild desaturation.[ 16 ] Should authors had claimed a significant difference between these anaesthetic volatiles, it would have been important to elucidate whether those differences were due to serious adverse events, like laryngospasm or bronchospasm, or the results were explained by any of the other events (e.g., secretions requiring suction). While it is true that clinical trials evaluating the occurrence of adverse events like laryngospasm/bronchospasm,[ 16 , 17 ] or life-threating complications following a tracheal intubation (e.g., inadvertent oesophageal placement, dental damage or injury of the larynx/pharynx)[ 14 ] are almost invariably underpowered, because the incidence of such events is expected to be low, subjective outcomes like coughing or secretions requiring suction should be avoided, as they are highly dependent on the examiner's criteria.[ 16 ]
Secondary outcomes are useful to document potential side effects (e.g., gastric insufflation after placing a supraglottic device), and evaluate the adherence (say, airway leak pressure) and safety of the intervention (for instance, occurrence, or laryngospasm/bronchospasm).[ 17 ] Nevertheless, the problem of addressing multiple secondary outcomes without the adequate statistical power is habitual in medical literature. A good illustration of this issue can be found in a study evaluating the performance of two supraglottic devices in 50 anaesthetised infants and neonates, whereby authors could not draw any conclusions in regard to potential differences in the occurrence of complications, because the sample size calculated made the study underpowered to explore those differences.[ 17 ]
Among PICOT components, the time frame is the most likely to be omitted or inappropriate.[ 1 , 12 ] There are two key aspects of the time component that need to be clearly specified in the research question: the time of measuring the outcome variables (e.g. visual analogue scale for pain at 1, 2, 6, and 12 h postoperatively), and the duration of each measurement (when indicated). The omission of these details in the study protocol might lead to substantial differences in the methodology used. For instance, if a study is designed to compare the insertion times of three different supraglottic devices, and researchers do not specify the exact moment of LMA insertion in the clinical trial protocol (i.e., at the anaesthetic induction after reaching a BIS index < 60), placing an LMA with insufficient depth of anaesthesia would have compromised the internal validity of the results, because inserting a supraglottic device in those patients would have resulted in failed attempts and longer insertion times.[ 10 ]
FINER CRITERIA
A well-elaborated research question may not necessarily be a good question. The proposed study also requires being achievable from both ethical and realistic perspectives, interesting and useful to the clinical practice, and capable to formulate new hypotheses, that may contribute to the generation of knowledge. Researchers have developed an effective way to convey the message of how to build a good research question, that is usually recalled under the acronym of FINER (feasible, interesting, novel, ethical and relevant).[ 5 , 6 , 7 ] Table 2 highlights the main characteristics of FINER criteria.[ 7 ]
Main features of FINER criteria (Feasibility, interest, novelty, ethics, and relevance) to formulate a good research question. Adapted from Cummings et al .[ 7 ]
Novelty and relevance
Although it is clear that any research project should commence with an accurate literature interpretation, in many instances it represents the start and the end of the research: the reader will soon realise that the answer to several questions can be easily found in the published literature.[ 5 ] When the question overcomes the test of a thorough literature review, the project may become novel (there is a gap in the knowledge, and therefore, there is a need for new evidence on the topic) and relevant (the paper may contribute to change the clinical practice). In this context, it is important to distinguish the difference between statistical significance and clinical relevance: in the aforementioned study of Oba et al .,[ 10 ] despite the means of insertion times were reported as significant for the Supreme™ LMA, as compared with ProSeal™ LMA, the difference found in the insertion times (528 vs. 486 sec, respectively), although reported as significant, had little or no clinical relevance.[ 10 ] Conversely, a statistically significant difference of 12 sec might be of clinical relevance in neonates weighing <5 kg.[ 17 ] Thus, statistical tests must be interpreted in the context of a clinically meaningful effect size, which should be previously defined by the researcher.
Feasibility and ethical aspects
Among FINER criteria, there are two potential barriers that may prevent the successful conduct of the project and publication of the manuscript: feasibility and ethical aspects. These obstacles are usually related to the target population, as discussed above. Feasibility refers not only to the budget but also to the complexity of the design, recruitment strategy, blinding, adequacy of the sample size, measurement of the outcome, time of follow-up of participants, and commitment of clinicians, among others.[ 3 , 7 ] Funding, as a component of feasibility, may also be implicated in the ethical principles of clinical research, because the choice of the primary study question may be markedly influenced by the specific criteria demanded in the interest of potential funders.
Discussing ethical issues with local committees is compulsory, as rules applied might vary among countries.[ 18 ] Potential risks and benefits need to be carefully weighed, based upon the four principles of respect for autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, and justice.[ 19 ] Although many of these issues may be related to the population target (e.g., conducting a clinical trial in patients with ongoing cardiopulmonary resuscitation would be inappropriate, as would be anaesthetising patients undergoing elective LASER treatment for condylomas, to examine the performance of supraglottic airway devices),[ 14 , 15 ] ethical conflicts may also arise from the intervention (particularly those involving the occurrence of side effects or complications, and their potential for reversibility), comparison (e.g., use of placebo or sham procedures),[ 19 ] outcome (surrogate outcomes should be considered in lieu of long term outcomes), or time frame (e.g., unnecessary longer exposition to an intervention). Thus, FINER criteria should not be conceived without a concomitant examination of the PICOT checklist, and consequently, PICOT framework and FINER criteria should not be seen as separated components, but rather complementary ingredients of a good research question.
Undoubtedly, no research project can be conducted if it is deemed unfeasible, and most institutional review boards would not be in a position to approve a work with major ethical problems. Nonetheless, whether or not the findings are interesting, is a subjective matter. Engaging the attention of readers also depends upon a number of factors, including the manner of presenting the problem, the background of the topic, the intended audience, and the reader's expectations. Furthermore, the interest is usually linked to the novelty and relevance of the topic, and it is worth nothing that editors and peer reviewers of high-impact medical journals are usually reluctant to accept any publication, if there is no novelty inherent to the research hypothesis, or there is a lack of relevance in the results.[ 11 ] Nevertheless, a considerable number of papers have been published without any novelty or relevance in the topic addressed. This is probably reflected in a recent survey, according to which only a third of respondents declared to have read thoroughly the most recent papers downloaded, and at least half of those manuscripts remained unread.[ 20 ] The same study reported that up to one-third of papers examined remained uncited after 5 years of publication, and only 20% of papers accounted for 80% of the citations.[ 20 ]
Formulating a good research question can be fascinating, albeit challenging, even for experienced investigators. While it is clear that clinical experience in combination with the accurate interpretation of literature and teamwork are essential to develop new ideas, the formulation of a clinical problem usually requires the compliance with PICOT framework in conjunction with FINER criteria, in order to translate a clinical dilemma into a researchable question. Working in the right environment with the adequate support of experienced researchers, will certainly make a difference in the generation of knowledge. By doing this, a lot of time will be saved in the search of the primary study question, and undoubtedly, there will be more chances to become a successful researcher.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.

New NASA Black Hole Visualization Takes Viewers Beyond the Brink
Ever wonder what happens when you fall into a black hole? Now, thanks to a new, immersive visualization produced on a NASA supercomputer, viewers can plunge into the event horizon, a black hole’s point of no return.
“People often ask about this, and simulating these difficult-to-imagine processes helps me connect the mathematics of relativity to actual consequences in the real universe,” said Jeremy Schnittman, an astrophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, who created the visualizations. “So I simulated two different scenarios, one where a camera — a stand-in for a daring astronaut — just misses the event horizon and slingshots back out, and one where it crosses the boundary, sealing its fate.”
The visualizations are available in multiple forms. Explainer videos act as sightseeing guides, illuminating the bizarre effects of Einstein’s general theory of relativity. Versions rendered as 360-degree videos let viewers look all around during the trip, while others play as flat all-sky maps.
To create the visualizations, Schnittman teamed up with fellow Goddard scientist Brian Powell and used the Discover supercomputer at the NASA Center for Climate Simulation . The project generated about 10 terabytes of data — equivalent to roughly half of the estimated text content in the Library of Congress — and took about 5 days running on just 0.3% of Discover’s 129,000 processors. The same feat would take more than a decade on a typical laptop.
The destination is a supermassive black hole with 4.3 million times the mass of our Sun, equivalent to the monster located at the center of our Milky Way galaxy.
“If you have the choice, you want to fall into a supermassive black hole,” Schnittman explained. “Stellar-mass black holes, which contain up to about 30 solar masses, possess much smaller event horizons and stronger tidal forces, which can rip apart approaching objects before they get to the horizon.”
This occurs because the gravitational pull on the end of an object nearer the black hole is much stronger than that on the other end. Infalling objects stretch out like noodles, a process astrophysicists call spaghettification .
The simulated black hole’s event horizon spans about 16 million miles (25 million kilometers), or about 17% of the distance from Earth to the Sun. A flat, swirling cloud of hot, glowing gas called an accretion disk surrounds it and serves as a visual reference during the fall. So do glowing structures called photon rings, which form closer to the black hole from light that has orbited it one or more times. A backdrop of the starry sky as seen from Earth completes the scene.
As the camera approaches the black hole, reaching speeds ever closer to that of light itself, the glow from the accretion disk and background stars becomes amplified in much the same way as the sound of an oncoming racecar rises in pitch. Their light appears brighter and whiter when looking into the direction of travel.
The movies begin with the camera located nearly 400 million miles (640 million kilometers) away, with the black hole quickly filling the view. Along the way, the black hole’s disk, photon rings, and the night sky become increasingly distorted — and even form multiple images as their light traverses the increasingly warped space-time.
In real time, the camera takes about 3 hours to fall to the event horizon, executing almost two complete 30-minute orbits along the way. But to anyone observing from afar, it would never quite get there. As space-time becomes ever more distorted closer to the horizon, the image of the camera would slow and then seem to freeze just shy of it. This is why astronomers originally referred to black holes as “frozen stars.”
At the event horizon, even space-time itself flows inward at the speed of light, the cosmic speed limit. Once inside it, both the camera and the space-time in which it's moving rush toward the black hole's center — a one-dimensional point called a singularity , where the laws of physics as we know them cease to operate.
“Once the camera crosses the horizon, its destruction by spaghettification is just 12.8 seconds away,” Schnittman said. From there, it’s only 79,500 miles (128,000 kilometers) to the singularity. This final leg of the voyage is over in the blink of an eye.
In the alternative scenario, the camera orbits close to the event horizon but it never crosses over and escapes to safety. If an astronaut flew a spacecraft on this 6-hour round trip while her colleagues on a mothership remained far from the black hole, she’d return 36 minutes younger than her colleagues. That’s because time passes more slowly near a strong gravitational source and when moving near the speed of light.
“This situation can be even more extreme,” Schnittman noted. “If the black hole were rapidly rotating, like the one shown in the 2014 movie ‘Interstellar,’ she would return many years younger than her shipmates.”
By Francis Reddy NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center , Greenbelt, Md. Media Contact: Claire Andreoli 301-286-1940 [email protected] NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Related Terms
- Astrophysics
- Black Holes
- Galaxies, Stars, & Black Holes
- Galaxies, Stars, & Black Holes Research
- Goddard Space Flight Center
- Supermassive Black Holes
- The Universe
Explore More

Kan Yang: Translating Science Ideas into Engineering Concepts
As team lead of the Instrument Design Laboratory, Kan Yang turns science concepts into engineering reality. Name: Kan YangTitle: Team Lead of the Instrument Design LaboratoryFormal Job Classification: Technical ManagerOrganization: Instrument Systems and Technology Division, Engineering and Technology Directorate (Code 550) What do you do and what is most interesting about your role here at […]

Discovery Alert: Mini-Neptune in Double Star System is a Planetary Puzzle

NASA Tool Gets Ready to Image Faraway Planets
A technology demo on the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will help increase the variety of distant planets scientists can directly image. The Roman Coronagraph Instrument on NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will help pave the way in the search for habitable worlds outside our solar system by testing new tools that block starlight, […]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
The examples of research questions provided in this guide have illustrated what good research questions look like. The key points outlined below should help researchers in the pursuit: The development of a research question is an iterative process that involves continuously updating one's knowledge on the topic and refining ideas at all ...
A well-crafted research question (or set of questions) sets the stage for a robust study and meaningful insights. But, if you're new to research, it's not always clear what exactly constitutes a good research question. In this post, we'll provide you with clear examples of quality research questions across various disciplines, so that you can approach your research project with confidence!
In essence, the research question that guides the sciences and social sciences should do the following three things:2. 1) Post a problem. 2) Shape the problem into a testable hypothesis. 3) Report the results of the tested hypothesis. There are two types of data that can help shape research questions in the sciences and social sciences ...
Types of research questions. Now that we've defined what a research question is, let's look at the different types of research questions that you might come across. Broadly speaking, there are (at least) four different types of research questions - descriptive, comparative, relational, and explanatory. Descriptive questions ask what is happening. In other words, they seek to describe a ...
Most professional researchers focus on topics they are genuinely interested in studying. Writers should choose a broad topic about which they genuinely would like to know more. An example of a general topic might be "Slavery in the American South" or "Films of the 1930s.". Do some preliminary research on your general topic.
Assess your chosen research question using the FINER criteria that helps you evaluate whether the research is Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant. 1. Formulate the final research question, while ensuring it is clear, well-written, and addresses all the key elements of a strong research question.
Identifying a well-defined research question is the first step in the literature review process. For undergraduates, professors will often assign a broad topic for a literature review assignment. You will need to more narrowly define your question before you can begin the research process. Do a preliminary search on your topic in either Google ...
A good research question should: Be clear and provide specific information so readers can easily understand the purpose. Be focused in its scope and narrow enough to be addressed in the space allowed by your paper. Be relevant and concise and express your main ideas in as few words as possible, like a hypothesis.
You may be used to working with a thesis statement, but a thesis statement is an answer. If you start your research with an answer, you might miss something important or your paper might be too one-sided. Starting with a question allows you to explore your topic while still having it clearly defined. A good research question is specific and ...
Choose a broad topic, such as "learner support" or "social media influence" for your study. Select topics of interest to make research more enjoyable and stay motivated. Preliminary research. The goal is to refine and focus your research question. The following strategies can help: Skim various scholarly articles.
The Research Question pinpoints the focus of the review. Your first step involves choosing, exploring, and focusing a topic. At this stage you might discover that you need to tweak your topic or the scope of your research as you learn more about the topic in the literature. ... Filters above show what the Document Type filter looks like, with a ...
Moreover, these questions seek to understand the intent or future outcome surrounding a topic. Research Question Example: Asking why a consumer behaves in a certain way or chooses a certain option over other. iii. Interpretive Questions. This type of research question allows the study of people in the natural setting.
Abstract. Good science is driven by rigorous questions. Much like the foundation of a house, a research question must be carefully constructed to prevent downstream problems in project execution. And yet, pharmacy researchers and scholars across all career stages may find themselves struggling when developing research questions.
Definition: Research questions are the specific questions that guide a research study or inquiry. These questions help to define the scope of the research and provide a clear focus for the study. Research questions are usually developed at the beginning of a research project and are designed to address a particular research problem or objective.
A good research question is one that requires impartial responses and can be answered via existing sources of information. Also, a good research question seeks answers that actively contribute to a body of knowledge; hence, it is a question that is yet to be answered in your specific research context. Open-Ended Questions
A good research question should match the purpose for an assignment and provide a thesis statement or argument. These strategies can help you turn a mishmash of general information into a good research question. What does a good research question look like? Research questions ask us to consider all the small
The process of formulating a good research question can be challenging and frustrating. While a comprehensive literature review is compulsory, the researcher usually encounters methodological difficulties in the conduct of the study, particularly if the primary study question has not been adequately selected in accordance with the clinical dilemma that needs to be addressed.
Do you know a good research question when you read one? What makes it good? Could you effortlessly explain its characteristics to someone outside of design?B...
First published online February 26, 2024. What Does Good Qualitative Research Look Like? How to Do It? Bin Xu View all authors and affiliations. Based on: The Science and Art of Interviewing, by Kathleen Gerson and Sarah Damaske. New York: Oxford University Press, 2021. 280 pp. $26.99 paper. ISBN: 9780199324293.
Innovation in qualitative research is a thorny issue. It first requires a shared understanding of what innovation actually means in this context. One definition is 'the intentional introduction and application of ideas, processes, products or procedures, new to the relevant unit of adoption, designed to significantly benefit' (Lê and ...
Now, thanks to a new, immersive visualization produced on a NASA supercomputer, viewers can plunge into the event horizon, a black hole's point of no return. In this visualization of a flight toward a supermassive black hole, labels highlight many of the fascinating features produced by the effects of general relativity along the way.
This interactive map complements the static control-of-terrain maps that ISW daily produces with high-fidelity.