- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Enter Today's Teacher Appreciation Giveaway!

Who Invented Math? The History of Mathematics
Did math start with the Greeks, or has it always existed?

Who invented math? It’s a deceptively complex question—a lot harder than 2+2. Math has been around forever, but we are always learning more about it.
Short answer: Many different people invented math, including ancient societies and many famous mathematicians who came along later.
The long answer: It depends on what kind of math you’re asking about. Below is a look at the history of mathematics and the people who contributed to developing math as we know it today.
What is math?
- Was math invented or discovered?
So, who invented math?
- Videos about the invention of math
According to Britannica Kids , math is the study of numbers. It’s a kind of language that we use every day to calculate distances, tell time, build things, and so on.
Mathematicians think about math in two areas: pure and applied. Pure math is studying math for its own sake. Figuring out how to solve a particular algorithm or tackling a theory, for example. Applied math is using math to solve real-life problems, like building a house or predicting an earthquake.
There are lots of different types of math: arithmetic, algebra, geometry, trigonometry, statistics, and more.
So, since math is already a part of the world, the first question is, can math be invented at all?
Was math discovered or invented?
Some mathematicians think that math is invented, as people name aspects of math or create new ways of solving problems . Other people think that math is always there— the concepts and ideas exist in nature, just waiting for us to discover them .
Here’s a look at the history of math and many of the societies and people who contributed to its development.
Early Societies

Math has evolved over thousands of years , with input from thousands of mathematicians. We don’t know exactly how prehistoric humans dealt with math problems (like counting how many berries they picked, or figuring out the distance between two places), but researchers believe that people were using addition, multiplication, and other math concepts in early China, India, and Mesopotamia.
In fact, the oldest clay tablets we have with math inscribed on them are more than 4,000 years old. They’re from Mesopotamia. We also have Egyptian papyrus sheets with math written on them. So, there’s evidence of math from the two oldest societies in the world.
Around 1800 B.C.E., the ancient Babylonians developed a number system based on the number 60 (it’s still used today to think about angle measurement). They were the first people we know of to use actual numbers to represent amounts.
It’s clear that, considering the pyramids and their society, the Egyptians used math . They definitely understood geometry and even had a formula for calculating the volume of a truncated pyramid.
The Ancient Greeks
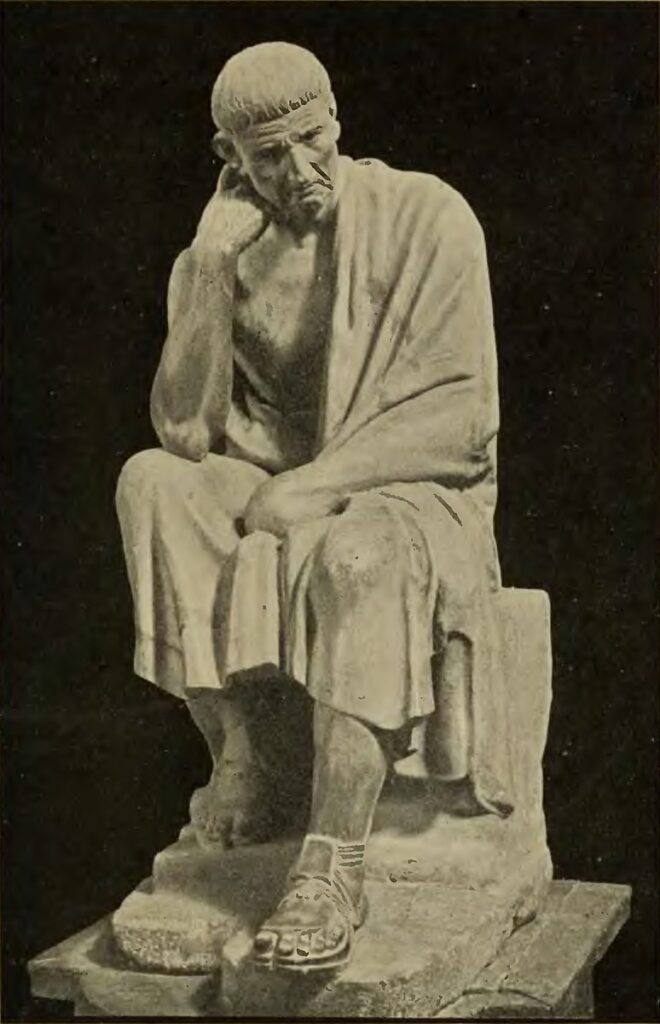

There’s more information about who invented (or discovered) math concepts as human society evolved. The Greeks , more than 2,500 years ago, started doing more advanced math. Plato, Euclid, and Archimedes are still remembered for their mathematical achievements. For example, Pythagoras studied triangles and he invented what we learn about triangles, called the Pythagorean theorem.
We also know that in ancient Greece, math became something to study, and mathematicians started thinking about specific theories and building on one another’s work.
After Ancient Greece
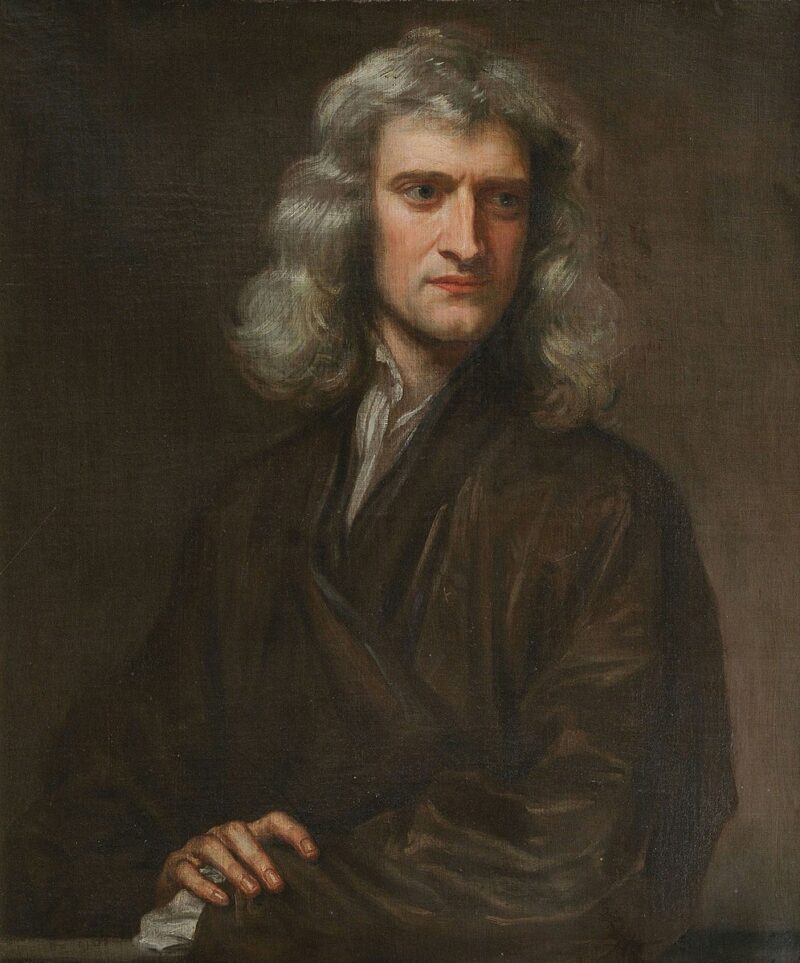

After ancient Greece, mathematicians continued making new discoveries and new theories and solving new problems. In 17th-century England, Sir Isaac Newton developed the field of calculus on his own. At the same time, in Germany, Gottfried Leibniz was also involved in developing calculus. Some mathematicians have created problems and hypotheses that have never been solved, like Bernhard Riemann , who created the Riemann hypothesis , which has been attempted but never proven.
And throughout history, women have also studied math and invented math concepts. For example, Emmy Noether gained recognition for her innovations in advanced algebra, and Katherine Johnson calculated and analyzed flight paths for spacecraft that sent astronauts to the moon. Mathematicians of color who have made significant contributions to mathematics include Fern Hunt , who created math models to describe different kinds of movement, and Mark Dean , a mathematician and computer scientist who holds patents on the computer that all PCs are based upon.
As math has evolved, people are building on what we know to create new types of math and new ways to use math, like applying math to build computers and create game theory , a branch of applied mathematics. So, maybe the question isn’t who invented math, but what will math invent next?
Videos About the Invention of Math
Use these videos to explore how different math concepts came about.
The Origin of Numbers
How Old Is Zero?
Where Do Math Symbols Come From?
Who Invented Algebra?
Who Invented Geometry?
Who Invented Trigonometry?
More Teaching Resources
- Famous Mathematicians
- MacTutor Math Archives
- Chronological List of Mathematicians
- PBS NOVA: How Ancient Cultures Shaped Mathematics
Also check out Magical Math Puzzles and Number Tricks to Wow Students .
Plus, get all the latest teaching tips and tricks when you sign up for our newsletters .
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Origin and Death of Homework Inventor: Roberto Nevilis

Roberto Nevilis is known for creating homework to help students learn on their own. He was a teacher who introduced the idea of giving assignments to be done outside of class. Even though there’s some debate about his exact role, Nevilis has left a lasting impact on education, shaping the way students around the world approach their studies.
Homework is a staple of the modern education system, but few people know the story of its origin.
The inventor of homework is widely considered to be Roberto Nevilis, an Italian educator who lived in the early 20th century.
We will briefly explore Nevilis’ life, how he came up with the concept of homework, and the circumstances surrounding his death.
Roberto Nevilis: The Man Behind Homework Roberto Nevilis was born in Venice, Italy, in 1879. He was the son of a wealthy merchant and received a private education.
He later studied at the University of Venice, where he received a degree in education. After graduation, Nevilis worked as a teacher in various schools in Venice.
Table of Contents
How Homework Was Born
The Birth of Homework According to historical records, Nevilis was frustrated with the lack of discipline in his classroom. He found that students were often too focused on playing and not enough on learning.
To solve this problem , he came up with the concept of homework. Nevilis assigned his students homework to reinforce the lessons they learned in class and encourage them to take their education more seriously.
How did homework become popular?
The Spread of Homework , The idea of homework quickly caught on, and soon other teachers in Italy followed Nevilis’ lead. From Italy, the practice of assigning homework spread to other European countries and, eventually, the rest of the world.
Today, homework is a standard part of the education system in almost every country, and millions of students worldwide spend countless hours each week working on homework assignments.
How did Roberto Nevilis Die?
Death of Roberto Nevilis The exact circumstances surrounding Nevilis’ death are unknown. Some reports suggest that he died in an accident, while others claim he was murdered.
However, the lack of concrete evidence has led to numerous theories and speculation about what happened to the inventor of homework.
Despite the mystery surrounding his death, Nevilis’ legacy lives on through his impact on education.

Facts about Roberto Nevilis
- He is credited with inventing homework to punish his students who misbehaved in class.
- Some accounts suggest he was a strict teacher who believed in disciplining his students with homework.
- There is little concrete evidence to support the claim that Nevilis was the true inventor of homework.
- Some historians believe that the concept of homework has been around for much longer than in the 1900s.
- Despite the lack of evidence, Roberto Nevilis remains a popular figure in the history of education and is often cited as the inventor of homework.
The Legacy of Homework
The legacy of homework is deeply embedded in the educational landscape, reflecting a historical evolution that spans centuries. From its ambiguous origins to the diverse purposes it serves today, homework has played a pivotal role in shaping learning experiences.
While its effectiveness and necessity have been subjects of ongoing debate, homework endures as a tool for reinforcing concepts, fostering independent study habits, and preparing students for future academic and professional challenges.
In the contemporary educational context, the legacy of homework is a complex interplay of tradition, pedagogy, and evolving perspectives on the balance between academic demands and student well-being.
The Complex History of Homework
Throughout history, the evolution of homework can be traced through a series of significant developments. In ancient civilizations, such as Greece and Rome, scholars and philosophers encouraged independent study outside formal learning settings.
The Renaissance era witnessed a surge in written assignments, marking an early precursor to modern homework. The Industrial Revolution further transformed educational practices, as the need for a skilled workforce emphasized the importance of individual learning and practice.

The purposes and perceptions of homework have undergone substantial transformations over time. In the 19th century, homework was often viewed as a means of reinforcing discipline and moral values, with assignments focused on character development.
As educational philosophies evolved, particularly in the 20th century, homework assumed various roles—from a tool for drill and practice to a method for fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Perceptions of homework have fluctuated, with debates arising around issues of workload, equity, and its impact on student well-being. The complex history of homework reveals a dynamic interplay between societal expectations, educational philosophies, and changing perspectives on the purposes of academic assignments.

Conclusion – Who invented homework, and how did he die
Roberto Nevilis was a visionary educator who profoundly impacted the education system. His invention of homework has changed how students learn and has helped countless students worldwide improve their education.
Although the circumstances surrounding his death are unclear, Nevilis’ legacy as the inventor of homework will never be forgotten.
What is Roberto Nevilis’ legacy?
Roberto Nevilis’ legacy is his invention of homework, which has changed how students learn and has helped countless students worldwide improve their education.
Despite the mystery surrounding his death, Nevilis’ legacy as the inventor of homework will never be forgotten.
What was Roberto Nevilis’ background?
Roberto Nevilis was the son of a wealthy merchant and received a private education. He later studied at the University of Venice, where he received a degree in education.
After graduation, Nevilis worked as a teacher in various schools in Venice.
What was Roberto Nevilis’ impact on education?
Roberto Nevilis’ invention of homework has had a profound impact on education. By assigning homework, he helped students reinforce the lessons they learned in class and encouraged them to take their education more seriously.
This concept has spread worldwide and is now a staple of the modern education system.
Is there any evidence to support the theories about Roberto Nevilis’ death?
There is no concrete evidence to support the theories about Roberto Nevilis’ death, and the exact circumstances surrounding his death remain a mystery.
What was Roberto nevilis age?
It is believed that he died of old age. Not much information is available on his exact age at the time of death. Born: 1879 Died: 1954 (aged 75 years)
Where is Roberto Nevilis’s grave
While many have tried to find out about his Grave, little is known about where he is buried. Many people are querying the internet about his Grave. But frankly, I find it weird why people want to know this.
Share this:

History Cooperative
Who Invented Math? The History of Mathematics
Mathematics, the universal language of abstraction and precision, permeates every facet of our lives. But have you ever wondered who first invented this remarkable discipline?
While we may never identify a single inventor, the invention of math is a collective endeavor woven into the tapestry of human history.
Table of Contents
Who Invented Math?
There isn’t a single person who invented math. Mathematics, as we know it today, is often perceived as a universal language that transcends cultures and borders. Yet, it’s essential to recognize that math, like any human endeavor, had its beginnings in the minds of ingenious thinkers from different corners of the world.
The concept of math as a human invention underscores its adaptable and evolving nature. Unlike the laws of nature, which exist independently of human cognition, mathematical systems were developed and refined by humans over generations. We didn’t just start with the Pythagorean Theorem or quadratic equations. Math started off much, much smaller.
The early origins of mathematical knowledge can be traced back to ancient civilizations that thrived thousands of years ago. Mesopotamia, often referred to as the “ Cradle of Civilization ,” saw the emergence of some of the earliest mathematical concepts. In this fertile region, ancient mathematicians devised methods for counting and recording numerical information, essential for administrative and economic purposes. Here, Babylonian mathematics was the backbone of ancient Mesopotamian mathematical education.
Similarly, the ancient Egyptians made significant contributions to early mathematics, particularly in the realm of geometry . Their mastery of geometry allowed them to survey land, build monumental structures, and calculate areas and volumes with remarkable precision. The ancient Egyptians not only built stunning structures, they were more than capable of comprehending geometric concepts that the rest of the world just wasn’t familiar with yet.
READ MORE: Ancient Egypt Timeline: Predynastic Period Until the Persian Conquest
The Indus Valley Civilization, one of the world’s oldest urban cultures, also made strides in mathematics. Archaeological discoveries suggest the existence of a standardized system of weights and measures, indicating a sophisticated understanding of mathematical principles.
So mathematics was not the product of a single individual or culture but a collective endeavor spanning centuries. Early mathematical knowledge was built upon the contributions of countless thinkers and problem solvers, each adding a piece to the puzzle.
Who is the Father of Mathematics?
The “Father of Mathematics” is none other than the ancient Greek mathematician, Archimedes. Born and raised in the Sicilian city of Syracuse, Archimedes is known for his contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and physics. His developments in math include the Archimedean property, the Archimedes principle, and early precursors to modern calculus . It is not to mention that Archimedes wrote a ton regarding mathematics, though many of these are among personal correspondences with Dositheus of Pelusium, the director of mathematics at Alexandria.
READ MORE: Ancient Greece Timeline: Pre-Mycenaean to the Roman Conquest and The Lighthouse of Alexandria: One of the Seven Wonders
Why Was Math Invented?
The invention of mathematics was a response to practical, real-world needs that early societies faced. Understanding why math was invented involves exploring the tangible and essential reasons that drove the development of mathematical concepts.
A Problem-Solving Tool
One of the primary reasons for the invention of math was its utility as a problem-solving tool. Early human societies encountered a myriad of challenges, from tracking the movement of celestial bodies to managing resources and conducting trade. Math provided a structured way to address these challenges, enabling civilizations to make predictions, plan, and optimize various aspects of their existence.
As you can see, math overlapped with a lot of early scientific ideas. No wonder it’s such a significant part of STEM.
Measurement and Quantification
Math was crucial for measurement and quantification, particularly in agriculture and trade. Ancient farmers needed to calculate the area of their fields, determine optimal planting densities, and manage harvests. Similarly, traders and merchants required math to assess the value of goods, establish fair exchange rates, and record transactions accurately.
Math is still central to life in today’s day and age. We’re still out here learning systems of measurement and quantification. Our math teachers were right: math shows up in just about everything. Although it may look different, today’s math of today is the product of thousands of years of human collaboration.
Architectural Advancements
Architecture and construction were areas where math played a pivotal role. Cultures such as the Egyptians and Greeks used mathematical principles to design and build structures that still awe us today. It may not look like much at a passing glance, but ancient construction required rigorous mathematics. From the precision of the Great Pyramid’s dimensions to the symmetry of Greek temples, math was at the core of architectural innovation.
Astronomical Understanding
Observing the heavens and understanding celestial phenomena was crucial for early societies. Math enabled astronomers to predict celestial events like eclipses, track the movements of planets, and create calendars for agricultural and religious purposes. The mathematical achievements in astronomy laid the foundation for modern astronomy and space exploration.
Navigational Excellence
In the Age of Exploration, math became an essential tool for navigation. Sailors used trigonometry to calculate their positions at sea, plot accurate maps, and explore uncharted territories. Without mathematical advancements, the great voyages of discovery would have been significantly more challenging.
Empirical Knowledge
Math allowed for the systematic recording and organization of empirical knowledge. From recording the growth of crops to tracking the positions of stars, math provided a framework to make sense of the world. It transformed empirical observations into structured data that could be analyzed and used for future planning. The complex analysis demanded by mathematics eventually gave way to the Scientific Revolution, which encouraged the emergence of modern sciences.
In essence, math was invented because it offered practical solutions to complex problems encountered by ancient civilizations. Its development was closely intertwined with the progress of human societies, enabling them to thrive, expand, and evolve. The utilitarian nature of math, rooted in the real needs of the time , played a pivotal role in its invention and subsequent advancement. In short, math made things make sense and made ancient life easy-peasy lemon-squeezy (sort of).
When Was Math Invented?
The invention of mathematics is a journey that spans millennia, with its origins lost in the depths of prehistory . Pinpointing an exact moment or a single civilization where math was first conceived is challenging, but through the study of historical artifacts and texts, we can trace an approximate timeline of math’s development.
Prehistoric Beginnings (~ >40,000 Years Ago)
Math, in its most rudimentary form, began with early humans . Archaeological findings reveal evidence of basic counting systems dating back tens of thousands of years. These early numeration systems were essential for tasks such as counting possessions, making sense of natural phenomena, and tracking the passage of time. Most folks started counting on their fingers and then went from there.
READ MORE: How Long Have Humans Existed?
Ancient Mesopotamia (c. 3400 BCE)
The historical record offers some of the earliest written evidence of mathematical thought in ancient Mesopotamia. The Sumerians, who inhabited this region, developed cuneiform symbols to represent numbers and used math for administrative and economic purposes. Clay tablets from this era contain mathematical tables and problems that reflect some of the earliest mathematical texts.
READ MORE: Who Invented Numbers? Unraveling the Origins of Numerical System
Most impressively, the notational system in Babylon, with its famous Babylonian mathematics, had the ability to represent fractions with ease. They had extensive experience with quadratic and cubic equations, calculus, and algebra . Modern mathematics still relies on these early mathematical advancements today.
Ancient Egypt (c. 3000 BCE)
Egyptian civilization also contributed significantly to the early development of math. Hieroglyphic inscriptions show that they had a sophisticated understanding of geometry, which they used for land surveying, construction, and taxation. The Rhind Mathematical Papyrus, dating to around 1650 BCE, is a notable example of Egyptian mathematics. Much like the Mesopotamians, the ancient Egyptians have among the oldest surviving mathematical documents in all of math history.
Ancient India (c. 2000 BCE)
Indian mathematicians made substantial contributions to mathematical thought, particularly in the realms of number theory and algebra. The ancient text known as the “Bakhshali Manuscript,” dated between the 2nd and 3rd centuries CE but containing older material, provides insights into early Indian mathematical ideas. Hallmarks of Indian mathematics include the concept of zero as a number, algebra, and arithmetic. Moreover, they had their own geometric concepts, which were unique compared to that of which is seen in Greek mathematics and later analytical geometry.
Ancient Greece (c. 600 BCE)
The Greeks, with their philosophical and deductive approach, laid the foundations of formal mathematics. Examples of pre-Greek mathematics reveal the use of inductive reasoning rather than the deductive reasoning used by the Greeks in math history.
Figures like Pythagoras and Euclid made profound contributions to geometry and number theory. Euclid’s “Elements,” written around 300 BCE, is a landmark work that influenced mathematical thought for centuries. Meanwhile, Pythagoras is the namesake of many contemporary mathematical terms, such as the Pythagorean Theorem and Pythagorean triples.
Euclid himself became known in history as the “Father of Geometry” for his contributions to the Theory of Proportions and Euclidean geometry. Generally, Euclidean geometry is known as the study of geometric shapes “and figures based on different axioms and theorems.” Later scholars, such as Omar Khayyam of the Islamic Golden Age, would study Euclid’s works and find perceived errors in its contents, such as the controversial parallel postulate.
Islamic Golden Age (8th to 13th centuries CE)
During the Islamic Golden Age, scholars in the Islamic world preserved and expanded upon the mathematical knowledge of earlier civilizations. Notable figures like Al-Khwarizmi, the “Father of Algebra,” and Omar Khayyam, known for his contributions to algebra and geometry, played pivotal roles in advancing mathematics. They expanded upon geometric concepts and various algorithms of the aforementioned civilizations.
The development of mathematics was a gradual process that unfolded over thousands of years, with different cultures contributing to its growth. While specific dates and milestones mark key moments in mathematical history, it’s important to recognize that math evolved organically and was a collective effort shaped by countless individuals and cultures. The invention of mathematics is a testament to humanity’s insatiable curiosity and capacity for intellectual exploration.
Where Was Math Invented?
There is no single location responsible for the invention of math. The invention and evolution of mathematics were not confined to a single region but unfolded in diverse geographical locations across the globe. Each of these regions contributed unique insights and perspectives to the development of mathematical knowledge. In short, math wasn’t isolated to a single country or region: it was, and always has been a global sensation.
Mesopotamia : Located in the fertile crescent between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, Mesopotamia is often regarded as one of the cradles of civilization. It was here that early mathematical concepts like numerical notation and basic arithmetic operations emerged. The Sumerians, Akkadians, and Babylonians in this region made significant contributions to early mathematics.
Egypt : Along the banks of the Nile River, ancient Egypt nurtured its mathematical traditions. The need for precise measurements and calculations to build grand structures like the pyramids fueled the development of geometry in this region. Egyptian mathematics also played a crucial role in agriculture and land management.
India : The Indian subcontinent is home to a rich mathematical heritage dating back thousands of years. Ancient Indian mathematicians made pioneering contributions to number theory, algebra, and geometry. Their texts, including the “ Bakhshali Manuscript ” and the works of scholars like Brahmagupta, who wrote the Brāhmasphuṭasiddhānta , continue to influence mathematical thought.
Greece : The birthplace of classical mathematics, ancient Greece was a hub of intellectual activity. Greek mathematicians like Pythagoras, Euclid, and Archimedes laid the foundations for geometry, number theory, and mathematical proofs. Their rigorous approach to mathematics had a profound and lasting impact on the field.
China : Ancient China boasts a long history of mathematical discoveries, with its earliest known mathematical texts dating back to around 300 BCE. Chinese mathematicians excelled in areas such as algebra, geometry, and number theory. Chinese mathematics included a complex decimal system, in addition to the concept of negative numbers by 200 BCE. Their contributions influenced both Asian and Western mathematical traditions.
The Islamic World : During the Islamic Golden Age, the Middle East and North Africa became centers of mathematical scholarship. Scholars like Al-Khwarizmi, Al-Kindi, and Omar Khayyam made significant advancements in algebra, trigonometry, and geometry. Islamic mathematicians preserved and expanded upon the mathematical knowledge of earlier civilizations, like the ancient Greeks and Indians.
Mesoamerica : In the pre-Columbian Americas, civilizations like the Maya and Aztecs developed complex mathematical systems. The Maya, for instance, created a sophisticated calendar system that involved advanced mathematical calculations . These mathematical traditions were intertwined with astronomy and timekeeping. Meanwhile, the Aztecs developed a base-20 system , along with their own unique symbols used to track these numbers.
Each of these geographical regions fostered unique mathematical developments, often driven by the specific needs and challenges faced by their respective cultures. Honestly, the global diversity of mathematical inventions underscores the universal nature of human curiosity. Humans have the capacity to create and refine mathematical concepts, regardless of geographical boundaries, and that’s pretty astounding if you ask us.
How Was Math Invented?
The invention of math took years in the making! It was not solely about discovering numerical relationships; it also entailed the development of systematic methods, notations, and philosophical underpinnings. Understanding how math was invented involves delving into the processes and intellectual endeavors of early mathematicians.
Early Mathematical Processes
Early mathematicians employed empirical observation and trial-and-error methods to make mathematical discoveries. They engaged in practical problem-solving, seeking solutions to real-world challenges such as trade, agriculture, and construction. Over time, these practical observations led to the formulation of general mathematical principles.
Notation and Symbolism
The development of mathematical notation was a crucial step in the evolution of math. Numerical symbols and written representations of mathematical concepts allowed for the communication and preservation of mathematical knowledge. Different cultures devised various systems of notation. Eventually, symbols and notations became standardized.
Geometry, Arithmetic, and Measurement
Geometry played a central role in the early development of math. Ancient cultures like the Egyptians and Greeks applied geometric principles to land surveying, architecture, and astronomy. Geometry provided a visual and practical foundation for mathematical understanding.
Number Systems
The invention of number systems was fundamental to mathematical progress. Various cultures developed their respective numbering systems, including base-10, base-60, and base-20 systems. These numerical systems facilitated counting, calculations, and record-keeping. These many number systems continue to influence our modern mathematics.
Philosophical Foundations
The philosophical underpinnings of mathematics also played a significant role in its invention. Greek mathematicians, for example, sought to establish rigorous proofs and logical reasoning in mathematics. The idea of axioms and deductive reasoning laid the groundwork for modern mathematical rigor.
READ MORE: History’s Most Famous Philosophers: Socrates, Plato, Aristotle, and More!
A Transcultural Exchange
As cultures interacted through trade and conquest, mathematical ideas and knowledge were exchanged and merged. Societies are going to socialize, after all. The Silk Road , for instance, facilitated the exchange of mathematical concepts between the East and West. This cross-cultural fertilization enriched mathematical thought and led to new discoveries.
Record-Keeping and Texts
The documentation and preservation of mathematical knowledge in written texts were crucial for its dissemination. Ancient texts, inscriptions, and manuscripts played a pivotal role in transmitting mathematical ideas from one generation to the next. As with most ancient history, the presence of a written text is vital to its survival.
The invention of mathematics was a dynamic process that integrated practical needs with intellectual curiosity and cultural exchange. It involved the gradual refinement of methods, notation, and philosophical frameworks. Thus, mathematics transcends mere counting and measurement to become a universal language of abstraction and problem-solving. The collaboration of early mathematicians, driven by the challenges of their times, continues to shape the mathematical landscape we know today.
Mathematical Discovery in the Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution of the 16th and 17th centuries had a massive impact on the mathematical and scientific ideas of the Early Modern Period. During this time, the Greek approach to science and math, as established centuries ago by Greek mathematicians, was replaced. New polymaths flocked to the limelight provided by the scientific upheaval, garnering respect in their field for countless discoveries and contributions. Key figures of the Scientific Revolution include Sir Isaac Newton, Galileo Galilei, René Descartes (who contributed greatly to analytic geometry), and Johannes Kepler.
Math As We Know It: Modern Mathematics
The invention of mathematics is a testament to the ingenuity of human civilizations across the ages. It emerged organically as a response to practical needs, evolving through diverse cultures and regions. While we may never pinpoint a singular inventor, mathematics stands as a collective achievement, enriched by countless contributions.
Mathematics’ enduring importance in fields ranging from science to economics underscores its vital role in shaping our modern world. The collaborative and cumulative nature of mathematical development reminds us that the quest for knowledge transcends boundaries and remains an enduring hallmark of human progress.
How to Cite this Article
There are three different ways you can cite this article.
1. To cite this article in an academic-style article or paper , use:
<a href=" https://historycooperative.org/who-invented-math/ ">Who Invented Math? The History of Mathematics</a>
Leave a Comment Cancel reply

Who Invented Homework? A Big Question Answered with Facts

Crystal Bourque

Delving into the intriguing history of education, one of the most pondered questions arises: Who invented homework?
Love it or hate it, homework is part of student life.
But what’s the purpose of completing these tasks and assignments? And who would create an education system that makes students complete work outside the classroom?
This post contains everything you’ve ever wanted to know about homework. So keep reading! You’ll discover the answer to the big question: who invented homework?
Who Invented Homework?
The myth of roberto nevilis: who is he, the origins of homework, a history of homework in the united states, 5 facts about homework, types of homework.
- What’s the Purpose of Homework?
- Homework Pros
- Homework Cons
When, How, and Why was Homework Invented?

Daniel Jedzura/Shutterstock.com
To ensure we cover the basics (and more), let’s explore when, how, and why was homework invented.
As a bonus, we’ll also cover who invented homework. So get ready because the answer might surprise you!
It’s challenging to pinpoint the exact person responsible for the invention of homework.
For example, Medieval Monks would work on memorization and practice singing. Ancient philosophers would read and develop their teachings outside the classroom. While this might not sound like homework in the traditional form we know today, one could argue that these methods helped to form the basic structure and format.
So let’s turn to recorded history to try and identify who invented homework and when homework was invented.
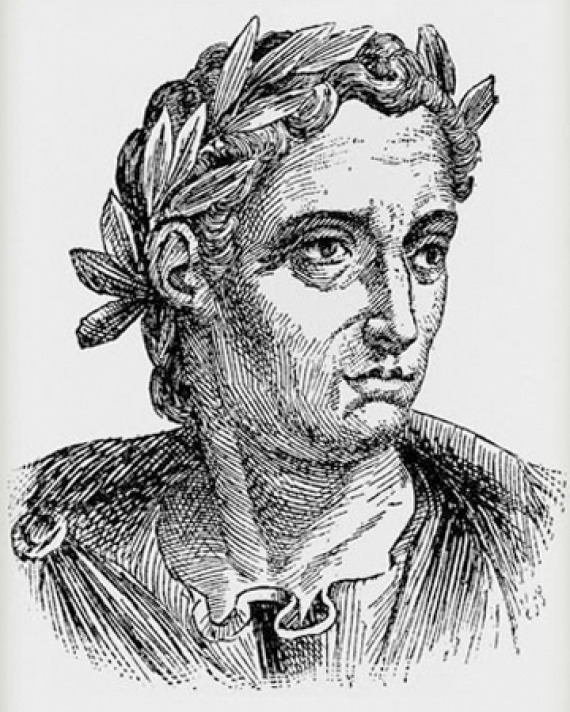
Pliny the Younger

Credit: laphamsquarterly.org
Mention of homework appears in the writings of Pliny the Younger, meaning we can trace the term ‘homework’ back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger (61—112 CE) was an oratory teacher, and often told his students to practice their public speaking outside class.
Pliny believed that the repetition and practice of speech would help students gain confidence in their speaking abilities.
Johann Gottlieb Fichte

Credit: inlibris.com
Before the idea of homework came to the United States, Germany’s newly formed nation-state had been giving students homework for years.
The roots of homework extend to ancient times, but it wasn’t until German Philosopher Johann Gottlieb Fichte (1762—1814) helped to develop the Volksschulen (People’s Schools) that homework became mandatory.
Fichte believed that the state needed to hold power over individuals to create a unified Germany. A way to assert control over people meant that students attending the Volksshulen were required to complete assignments at home on their own time.
As a result, some people credit Fichte for being the inventor of homework.
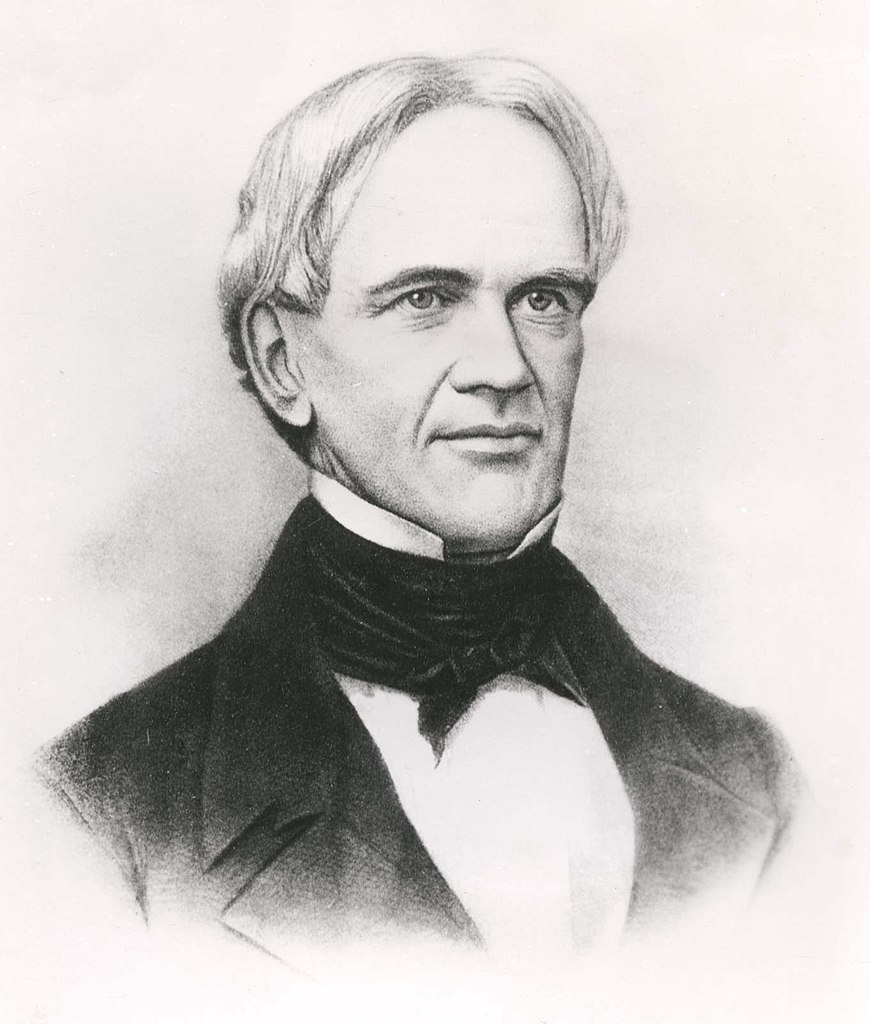
Horace Mann

Credit: commons.wikimedia.org
The idea of homework spread across Europe throughout the 19th century.
So who created homework in the United States?
The history of education and homework now moves to Horace Mann (1796—1859), an American educational reformer, spent some time in Prussia. There, he learned more about Germany’s Volksshulen, forms of education , and homework practices.
Mann liked what he saw and brought this system back to America. As a result, homework rapidly became a common factor in students’ lives across the country.

Credit: medium.com
If you’ve ever felt curious about who invented homework, a quick online search might direct you to a man named Roberto Nevilis, a teacher in Venice, Italy.
As the story goes, Nevilis invented homework in 1905 (or 1095) to punish students who didn’t demonstrate a good understanding of the lessons taught during class.
This teaching technique supposedly spread to the rest of Europe before reaching North America.
Unfortunately, there’s little truth to this story. If you dig a little deeper, you’ll find that these online sources lack credible sources to back up this myth as fact.
In 1905, the Roman Empire turned its attention to the First Crusade. No one had time to spare on formalizing education, and classrooms didn’t even exist. So how could Nevilis spread the idea of homework when education remained so informal?
And when you jump to 1901, you’ll discover that the government of California passed a law banning homework for children under fifteen. Nevilis couldn’t have invented homework in 1905 if this law had already reached the United States in 1901.

Inside Creative House/Shutterstock.com
When it comes to the origins of homework, looking at the past shows us that there isn’t one person who created homework. Instead, examining the facts shows us that several people helped to bring the idea of homework into Europe and then the United States.
In addition, the idea of homework extends beyond what historians have discovered. After all, the concept of learning the necessary skills human beings need to survive has existed since the dawn of man.
More than 100 years have come and gone since Horace Mann introduced homework to the school system in the United States.
Therefore, it’s not strange to think that the concept of homework has changed, along with our people and culture.
In short, homework hasn’t always been considered acceptable. Let’s dive into the history or background of homework to learn why.
Homework is Banned! (The 1900s)
Important publications of the time, including the Ladies’ Home Journal and The New York Times, published articles on the negative impacts homework had on American children’s health and well-being.
As a result, California banned homework for children under fifteen in 1901. This law, however, changed again about a decade later (1917).
Children Needed at Home (The 1930s)
Formed in 1923, The American Child Health Association (ACHA) aimed to decrease the infant mortality rate and better support the health and development of the American child.
By the 1930s, ACHA deemed homework a form of child labor. Since the government recently passed laws against child labor , it became difficult to justify homework assignments. College students, however, could still receive homework tasks as part of their formal schooling.

Studio Romantic/Shutterstock.com
A Shift in Ideas (The 1940s—1950s)
During the early to mid-1900s, the United States entered the Progressive Era. As a result, the country reformed its public education system to help improve students’ learning.
Homework became a part of everyday life again. However, this time, the reformed curriculum required teachers to make the assignments more personal.
As a result, American students would write essays on summer vacations and winter breaks, participate in ‘show and tell,’ and more.
These types of assignments still exist today!

Homework Today (The 2000s)
The focus of American education shifted again when the US Department of Education was founded in 1979, aiming to uplevel education in the country by, among other things, prohibiting discrimination ensuring equal access, and highlighting important educational issues.
In 2022, the controversial nature of homework in public schools and formal education is once again a hot topic of discussion in many classrooms.
According to one study , more than 60% of college and high school students deal with mental health issues like depression and anxiety due to homework. In addition, the large number of assignments given to students takes away the time students spend on other interests and hobbies. Homework also negatively impacts sleep.
As a result, some schools have implemented a ban or limit on the amount of homework assigned to students.
Test your knowledge and check out these other facts about homework:
- Horace Mann is also known as the ‘father’ of the modern school system and the educational process that we know today (read more about Who Invented School ).
- With a bit of practice, homework can improve oratory and writing skills. Both are important in a student’s life at all stages.
- Homework can replace studying. Completing regular assignments reduces the time needed to prepare for tests.
- Homework is here to stay. It doesn’t look like teachers will stop assigning homework any time soon. However, the type and quantity of homework given seem to be shifting to accommodate the modern student’s needs.
- The optimal length of time students should spend on homework is one to two hours. Students who spent one to two hours on homework per day scored higher test results.
- So, while completing assignments outside of school hours may be beneficial, spending, for example, a day on homework is not ideal.
Explore how the Findmykids app can complement your child’s school routine. With features designed to ensure their safety and provide peace of mind, it’s a valuable tool for parents looking to stay connected with their children throughout the day. Download now and stay informed about your child’s whereabouts during their academic journey.

Ground Picture/Shutterstock.com
The U.S. Department of Education provides teachers with plenty of information and resources to help students with homework.
In general, teachers give students homework that requires them to employ four strategies. The four types of homework types include:
- Practice: To help students master a specific skill, teachers will assign homework that requires them to repeat the particular skill. For example, students must solve a series of math problems.
- Preparation: This type of homework introduces students to the material they will learn in the future. An example of preparatory homework is assigning students a chapter to read before discussing the contents in class the next day.
- Extension: When a teacher wants to get students to apply what they’ve learned but create a challenge, this type of homework is assigned. It helps to boost problem-solving skills. For example, using a textbook to find the answer to a question gets students to problem-solve differently.
- Integration: To solidify the student learning experience , teachers will create a task that requires the use of many different skills. An example of integration is a book report. Completing integration homework assignments helps students learn how to be organized, plan, strategize, and solve problems on their own. Encouraging effective study habits is a key idea behind homework, too.
Ultimately, the type of homework students receive should have a purpose, be focused and clear, and challenge students to problem solve while integrating lessons learned.
What’s the Purpose of Homework?
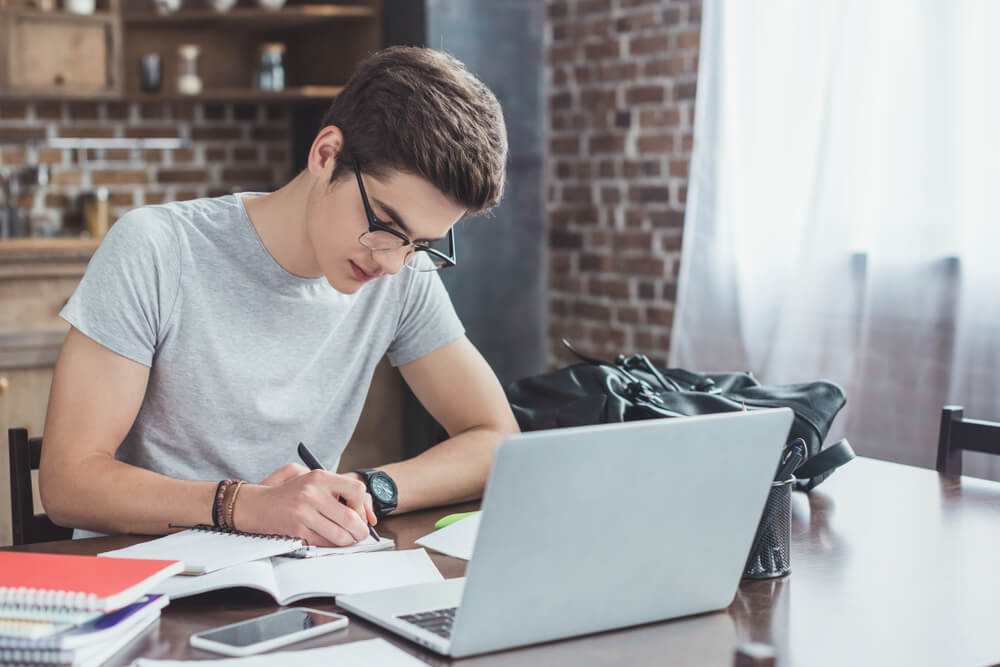

LightField Studios/Shutterstock.com
Homework aims to ensure individual students understand the information they learn in class. It also helps teachers to assess a student’s progress and identify strengths and weaknesses.
For example, school teachers use different types of homework like book reports, essays, math problems, and more to help students demonstrate their understanding of the lessons learned.
Does Homework Improve the Quality of Education?
Homework is a controversial topic today. Educators, parents, and even students often question whether homework is beneficial in improving the quality of education.
Let’s explore the pros and cons of homework to try and determine whether homework improves the quality of education in schools.
Homework Pros:
- Time Management Skills : Assigning homework with a due date helps students to develop a schedule to ensure they complete tasks on time. Personal responsibility amongst students is thereby promoted.
- More Time to Learn : Students encounter plenty of distractions at school. It’s also challenging for students to grasp the material in an hour or less. Assigning homework provides the student with the opportunity to understand the material.
- Improves Research Skills : Some homework assignments require students to seek out information. Through homework, students learn where to seek out good, reliable sources.
Homework Cons:
- Reduced Physical Activity : Homework requires students to sit at a desk for long periods. Lack of movement decreases the amount of physical activity, often because teachers assign students so much homework that they don’t have time for anything else. Time for students can get almost totally taken up with out-of-school assignments.
- Stuck on an Assignment: A student often gets stuck on an assignment. Whether they can’t find information or the correct solution, students often don’t have help from parents and require further support from a teacher. For underperforming students, especially, this can have a negative impact on their confidence and overall educational experience.
- Increases Stress : One of the results of getting stuck on an assignment is that it increases stress and anxiety. Too much homework hurts a child’s mental health, preventing them from learning and understanding the material.
Some research shows that homework doesn’t provide educational benefits or improve performance, and can lead to a decline in physical activities. These studies counter that the potential effectiveness of homework is undermined by its negative impact on students.
However, research also shows that homework benefits students—provided teachers don’t give them too much. Here’s a video from Duke Today that highlights a study on the very topic.
Homework Today
The question of “Who Invented Homework?” delves into the historical evolution of academic practices, shedding light on its significance in fostering responsibility among students and contributing to academic progress. While supported by education experts, homework’s role as a pivotal aspect of academic life remains a subject of debate, often criticized as a significant source of stress. Nonetheless, when balanced with extracurricular activities and integrated seamlessly into the learning process, homework continues to shape and refine students’ educational journeys.
Maybe one day, students won’t need to submit assignments or complete tasks at home. But until then, many students understand the benefits of completing homework as it helps them further their education and achieve future career goals.
Before you go, here’s one more question: how do you feel about homework? Do you think teachers assign too little or too much? Get involved and start a discussion in the comments!

Elena Kharichkina/Shutterstock.com
Who invented homework and why?
The creation of homework can be traced back to the Ancient Roman Pliny the Younger, a teacher of oratory—he is generally credited as being the father of homework! Pliny the Younger asked his students to practice outside of class to help them build confidence in their speaking skills.
Who invented homework as a punishment?
There’s a myth that the Italian educator Roberto Nevilis first used homework as a means of punishing his students in the early 20th century—although this has now been widely discredited, and the story of the Italian teacher is regarded as a myth.
Why did homework stop being a punishment?
There are several reasons that homework ceased being a form of punishment. For example, the introduction of child labor laws in the early twentieth century meant that the California education department banned giving homework to children under the age of fifteen for a time. Further, throughout the 1940s and 1950s, there was a growing emphasis on enhancing students’ learning, making homework assignments more personal, and nurturing growth, rather than being used as a form of punishment.
The picture on the front page: Evgeny Atamanenko/Shutterstock.com

Lockdown left our children with no other option other than remote education. Now that schools…

The school year is now starting again and with that, the Internet is blowing up…

For many, the start of fall marks a period of significant change—the transition to a…
Subscribe now!
Glad you've joined us🎉🎉.

The History of Homework: Why Was it Invented and Who Was Behind It?
- By Emily Summers
- February 14, 2020
Homework is long-standing education staple, one that many students hate with a fiery passion. We can’t really blame them, especially if it’s a primary source of stress that can result in headaches, exhaustion, and lack of sleep.
It’s not uncommon for students, parents, and even some teachers to complain about bringing assignments home. Yet, for millions of children around the world, homework is still a huge part of their daily lives as students — even if it continues to be one of their biggest causes of stress and unrest.
It makes one wonder, who in their right mind would invent such a thing as homework?
Who Invented Homework?
Pliny the younger: when in ancient rome, horace mann: the father of modern homework, the history of homework in america, 1900s: anti-homework sentiment & homework bans, 1930: homework as child labor, early-to-mid 20th century: homework and the progressive era, the cold war: homework starts heating up, 1980s: homework in a nation at risk, early 21 st century, state of homework today: why is it being questioned, should students get homework pros of cons of bringing school work home.

Online, there are many articles that point to Roberto Nevilis as the first educator to give his students homework. He created it as a way to punish his lazy students and ensure that they fully learned their lessons. However, these pieces of information mostly come from obscure educational blogs or forum websites with questionable claims. No credible news source or website has ever mentioned the name Roberto Nevilis as the person who invented homework . In fact, it’s possible that Nevilis never even existed.
As we’re not entirely sure who to credit for creating the bane of students’ existence and the reasons why homework was invented, we can use a few historical trivia to help narrow down our search.
Mentions of the term “homework” date back to as early as ancient Rome. In I century AD, Pliny the Younger , an oratory teacher, supposedly invented homework by asking his followers to practice public speaking at home. It was to help them become more confident and fluent in their speeches. But some would argue that the assignment wasn’t exactly the type of written work that students have to do at home nowadays. Only introverted individuals with a fear of public speaking would find it difficult and stressful.
It’s also safe to argue that since homework is an integral part of education, it’s probable that it has existed since the dawn of learning, like a beacon of light to all those helpless and lost (or to cast darkness on those who despise it). This means that Romans, Enlightenment philosophers, and Middle Age monks all read, memorized, and sang pieces well before homework was given any definition. It’s harder to play the blame game this way unless you want to point your finger at Horace Mann.
In the 19 th century, Horace Mann , a politician and educational reformer had a strong interest in the compulsory public education system of Germany as a newly unified nation-state. Pupils attending the Volksschulen or “People’s Schools” were given mandatory assignments that they needed to complete at home during their own time. This requirement emphasized the state’s power over individuals at a time when nationalists such as Johann Gottlieb Fichte were rallying support for a unified German state. Basically, the state used homework as an element of power play.
Despite its political origins, the system of bringing school assignments home spread across Europe and eventually found their way to Horace Mann, who was in Prussia at that time. He brought the system home with him to America where homework became a daily activity in the lives of students.
Despite homework being a near-universal part of the American educational experience today, it hasn’t always been universally accepted. Take a look at its turbulent history in America.
In 1901, just a few decades after Horace Mann introduced the concept to Americans, homework was banned in the Pacific state of California . The ban affected students younger than 15 years old and stayed in effect until 1917.
Around the same time, prominent publications such as The New York Times and Ladies’ Home Journal published statements from medical professionals and parents who stated that homework was detrimental to children’s health.
In 1930, the American Child Health Association declared homework as a type of child labor . Since laws against child labor had been passed recently during that time, the proclamation painted homework as unacceptable educational practice, making everyone wonder why homework was invented in the first place.
However, it’s keen to note that one of the reasons why homework was so frowned upon was because children were needed to help out with household chores (a.k.a. a less intensive and more socially acceptable form of child labor).
During the progressive education reforms of the late 19 th and early 20 th centuries, educators started looking for ways to make homework assignments more personal and relevant to the interests of individual students. Maybe this was how immortal essay topics such as “What I Want to Be When I Grow Up” and “What I Did During My Summer Vacation” were born.
After World War II, the Cold War heated up rivalries between the U.S. and Russia. Sputnik 1’s launch in 1957 intensified the competition between Americans and Russians – including their youth.
Education authorities in the U.S. decided that implementing rigorous homework to American students of all ages was the best way to ensure that they were always one step ahead of their Russian counterparts, especially in the competitive fields of Math and Science.
In 1986, the U.S. Department of Education’s pamphlet, “What Works,” included homework as one of the effective strategies to boost the quality of education. This came three years after the National Commission on Excellence in Education published “ Nation at Risk: The Imperative for Educational Reform .” The landmark report lambasted the state of America’s schools, calling for reforms to right the alarming direction that public education was headed.
Today, many educators, students, parents, and other concerned citizens have once again started questioning why homework was invented and if it’s still valuable.
Homework now is facing major backlash around the world. With more than 60% of high school and college students seeking counselling for conditions such as clinical depression and anxiety, all of which are brought about by school, it’s safe to say that American students are more stressed out than they should be.
After sitting through hours at school, they leave only to start on a mountain pile of homework. Not only does it take up a large chunk of time that they can otherwise spend on their hobbies and interests, it also stops them from getting enough sleep. This can lead to students experiencing physical health problems, a lack of balance in their lives, and alienation from their peers and society in general.
Is homework important and necessary ? Or is it doing more harm than good? Here some key advantages and disadvantages to consider.
- It encourages the discipline of practice
Using the same formula or memorizing the same information over and over can be difficult and boring, but it reinforces the practice of discipline. To master a skill, repetition is often needed. By completing homework every night, specifically with difficult subjects, the concepts become easier to understand, helping students polish their skills and achieve their life goals.
- It teaches students to manage their time
Homework goes beyond just completing tasks. It encourages children to develop their skills in time management as schedules need to be organized to ensure that all tasks can be completed within the day.
- It provides more time for students to complete their learning process
The time allotted for each subject in school is often limited to 1 hour or less per day. That’s not enough time for students to grasp the material and core concepts of each subject. By creating specific homework assignments, it becomes possible for students to make up for the deficiencies in time.
- It discourages creative endeavors
If a student spends 3-5 hours a day on homework, those are 3-5 hours that they can’t use to pursue creative passions. Students might like to read leisurely or take up new hobbies but homework takes away their time from painting, learning an instrument, or developing new skills.
- Homework is typically geared toward benchmarks
Teachers often assign homework to improve students’ test scores. Although this can result in positive outcomes such as better study habits, the fact is that when students feel tired, they won’t likely absorb as much information. Their stress levels will go up and they’ll feel the curriculum burnout.
- No evidence that homework creates improvements
Research shows that homework doesn’t improve academic performance ; it can even make it worse. Homework creates a negative attitude towards schooling and education, making students dread going to their classes. If they don’t like attending their lessons, they will be unmotivated to listen to the discussions.
With all of the struggles that students face each day due to homework, it’s puzzling to understand why it was even invented. However, whether you think it’s helpful or not, just because the concept has survived for centuries doesn’t mean that it has to stay within the educational system.
Not all students care about the history of homework, but they all do care about the future of their educational pursuits. Maybe one day, homework will be fully removed from the curriculum of schools all over the world but until that day comes, students will have to burn the midnight oil to pass their requirements on time and hopefully achieve their own versions of success.
About the Author
Emily summers.

What Is Fundraising and How Does It Work

Why Choosing Electrician Training Could Be Your Best Move

Tips for balancing technology and your child’s growth

Male and Female Cannabis Flowers Identifying the Differences

Debunking the Myth of Roberto Nevilis: Who Really Invented Homework?

Is the D Important in Pharmacy? Why Pharm.D or RPh Degrees Shouldn’t Matter

How to Email a Professor: Guide on How to Start and End an Email Conversation

Everything You Need to Know About Getting a Post-Secondary Education

Grammar Corner: What’s The Difference Between Analysis vs Analyses?


Who Invented Homework and Why

Who Invented Homework
Italian pedagog, Roberto Nevilis, was believed to have invented homework back in 1905 to help his students foster productive studying habits outside of school. However, we'll sound find out that the concept of homework has been around for much longer.
Homework, which most likely didn't have a specific term back then, already existed even in ancient civilizations. Think Greece, Rome, and even ancient Egypt. Over time, homework became standardized in our educational systems. This happened naturally over time, as the development of the formal education system continued.
In this article, we're going to attempt to find out who invented homework, and when was homework invented, and we're going to uncover if the creator of homework is a single person or a group of them. Read this article through to the end to find out.
Who Created Homework and When?
The concept of homework predates modern educational systems, with roots in ancient Rome. However, Roberto Nevilis is often, yet inaccurately, credited with inventing homework in 1905.Depending on various sources, this invention is dated either in the year 1095 or 1905.
The invention of homework is commonly attributed to Roberto Nevilis, an Italian pedagog who is said to have introduced it as a form of punishment for his students in 1905. However, the concept of homework predates Nevilis and has roots that go back much further in history.
The practice of assigning students work to be done outside of class time can be traced back to ancient civilizations, such as Rome, where Pliny the Younger (AD 61–113) encouraged his students to practice public speaking at home to improve their oratory skills.
It's important to note that the idea of formalized homework has evolved significantly over centuries, influenced by educational theories and pedagogical developments. The purpose and nature of homework have been subjects of debate among educators, with opinions varying on its effectiveness and impact on student learning and well-being.
It might be impossible to answer when was homework invented. A simpler question to ask is ‘what exactly is homework?’.
If you define it as work assigned to do outside of a formal educational setup, then homework might be as old as humanity itself. When most of what people studied were crafts and skills, practicing them outside of dedicated learning times may as well have been considered homework.
Let’s look at a few people who have been credited with formalizing homework over the past few thousand years.
Roberto Nevilis
Stories and speculations on the internet claim Roberto Nevilis is the one who invented school homework, or at least was the first person to assign homework back in 1905.
Who was he? He was an Italian educator who lived in Venice. He wanted to discipline and motivate his class of lackluster students. Unfortunately, claims online lack factual basis and strong proof that Roberto did invent homework.
Homework, as a concept, predates Roberto, and can't truly be assigned to a sole inventor. Moreover, it's hard to quantify where an idea truly emerges, because many ideas emerge from different parts of the world simultaneously or at similar times, therefore it's hard to truly pinpoint who invented this idea.
Pliny the Younger
Another culprit according to the internet lived a thousand years before Roberto Nevilis. Pliny the Younger was an oratory teacher in the first century AD in the Roman Empire.
He apparently asked his students to practice their oratory skills at home, which some people consider one of the first official versions of homework.
It is difficult to say with any certainty if this is the first time homework was assigned though because the idea of asking students to practice something outside classes probably existed in every human civilization for millennia.
Horace Mann
To answer the question of who invented homework and why, at least in the modern sense, we have to talk about Horace Mann. Horace Mann was an American educator and politician in the 19th century who was heavily influenced by movements in the newly-formed German state.
He is credited for bringing massive educational reform to America, and can definitely be considered the father of modern homework in the United States. However, his ideas were heavily influenced by the founding father of German nationalism Johann Gottlieb Fichte.
After the defeat of Napoleon and the liberation of Prussia in 1814, citizens went back to their own lives, there was no sense of national pride or German identity. Johann Gottlieb Fichte came up with the idea of Volkschule, a mandatory 9-year educational system provided by the government to combat this.
Homework already existed in Germany at this point in time but it became a requirement in Volkschule. Fichte wasn't motivated purely by educational reform, he wanted to demonstrate the positive impact and power of a centralized government, and assigning homework was a way of showing the state's power to influence personal and public life.
This effort to make citizens more patriotic worked and the system of education and homework slowly spread through Europe.
Horace Mann saw the system at work during a trip to Prussia in the 1840s and brought many of the concepts to America, including homework.
Who Invented Homework and Why?
Homework's history and objectives have evolved significantly over time, reflecting changing educational goals. Now, that we've gone through its history a bit, let's try to understand the "why". The people or people who made homework understood the advantages of it. Let's consider the following:
- Repetition, a key factor in long-term memory retention, is a primary goal of homework. It helps students solidify class-learned information. This is especially true in complex subjects like physics, where physics homework help can prove invaluable to learning effectively.
- Homework bridges classroom learning with real-world applications, enhancing memory and understanding.
- It identifies individual student weaknesses, allowing focused efforts to address them.
- Working independently at their own pace, students can overcome the distractions and constraints of a classroom setting through homework.
- By creating a continuous learning flow, homework shifts the perspective from viewing each school day as isolated to seeing education as an ongoing process.
- Homework is crucial for subjects like mathematics and sciences, where repetition is necessary to internalize complex processes.
- It's a tool for teachers to maximize classroom time, focusing on expanding understanding rather than just drilling fundamentals.
- Responsibility is a key lesson from homework. Students learn to manage time and prioritize tasks to meet deadlines.
- Research skills get honed through homework as students gather information from various sources.
- Students' creative potential is unleashed in homework, free from classroom constraints.
Struggling with your Homework?
Get your assignments done by real pros. Save your precious time and boost your marks with ease.
Who Invented Homework: Development in the 1900s
Thanks to Horace Mann, homework had become widespread in the American schooling system by 1900, but it wasn't universally popular amongst either students or parents.
The early 1900s homework bans
In 1901, California became the first state to ban homework. Since homework had made its way into the American educational system there had always been people who were against it for some surprising reasons.
Back then, children were expected to help on farms and family businesses, so homework was unpopular amongst parents who expected their children to help out at home. Many students also dropped out of school early because they found homework tedious and difficult.
Publications like Ladies' Home Journal and The New York Times printed statements and articles about the detrimental effects of homework on children's health.
The 1930 child labor laws
Homework became more common in the U.S. around the early 1900s. As to who made homework mandatory, the question remains open, but its emergence in the mainstream sure proved beneficial. Why is this?
Well, in 1930, child labor laws were created. It aimed to protect children from being exploited for labor and it made sure to enable children to have access to education and schooling. The timing was just right.
Speaking of homework, if you’re reading this article and have homework you need to attend to, send a “ do my homework ” request on Studyfy and instantly get the help of a professional right now.
Progressive reforms of the 1940s and 50s
With more research into education, psychology and memory, the importance of education became clear. Homework was understood as an important part of education and it evolved to become more useful and interesting to students.
Homework during the Cold War
Competition with the Soviet Union fueled many aspects of American life and politics. In a post-nuclear world, the importance of Science and Technology was evident.
The government believed that students had to be well-educated to compete with Soviet education systems. This is the time when homework became formalized, accepted, and a fundamental part of the American educational system.
1980s Nation at Risk
In 1983 the National Commission on Excellence in Education published Nation at Risk:
The Imperative for Educational Reform, a report about the poor condition of education in America. Still in the Cold War, this motivated the government in 1986 to talk about the benefits of homework in a pamphlet called “What Works” which highlighted the importance of homework.
Did you like our Homework Post?
For more help, tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert essay editing services!
Who Invented Homework: The Modern Homework Debate
Like it or not, homework has stuck through the times, remaining a central aspect in education since the end of the Cold War in 1991. So, who invented homework 😡 and when was homework invented?
We’ve tried to pinpoint different sources, and we’ve understood that many historical figures have contributed to its conception.
Horace Mann, in particular, was the man who apparently introduced homework in the U.S. But let’s reframe our perspective a bit. Instead of focusing on who invented homework, let’s ask ourselves why homework is beneficial in the first place. Let’s consider the pros and cons:
- Homework potentially enhances memory.
- Homework helps cultivate time management, self-learning, discipline, and cognitive skills.
- An excessive amount of work can cause mental health issues and burnout.
- Rigid homework tasks can take away time for productive and leisurely activities like arts and sports.
Meaningful homework tasks can challenge us and enrich our knowledge on certain topics, but too much homework can actually be detrimental. This is where Studyfy can be invaluable. Studyfy offers homework help.
All you need to do is click the “ do my assignment ” button and send us a request. Need instant professional help? You know where to go now.
Frequently asked questions
Who made homework.
As stated throughout the article, there was no sole "inventor of homework." We've established that homework has already existed in ancient civilizations, where people were assigned educational tasks to be done at home.
Let's look at ancient Greece; for example, students at the Academy of Athens were expected to recite and remember epic poems outside of their institutions. Similar practices were going on in ancient Egypt, China and Rome.
This is why we can't ascertain the sole inventor of homework. While history can give us hints that homework was practiced in different civilizations, it's not far-fetched to believe that there have been many undocumented events all across the globe that happened simultaneously where homework emerged.
Why was homework invented?
We've answered the question of "who invented homework 😡" and we've recognized that we cannot pinpoint it to one sole inventor. So, let's get back to the question of why homework was invented.
Homework arose from educational institutions, remained, and probably was invented because teachers and educators wanted to help students reinforce what they learned during class. They also believed that homework could improve memory and cognitive skills over time, as well as instill a sense of discipline.
In other words, homework's origins can be linked to academic performance and regular students practice. Academic life has replaced the anti-homework sentiment as homework bans proved to cause partial learning and a struggle to achieve conceptual clarity.
Speaking of, don't forget that Studyfy can help you with your homework, whether it's Python homework help or another topic. Don't wait too long to take advantage of expert help when you can do it now.
Is homework important for my learning journey?
Now that we've answered questions on who created homework and why it was invented, we can ask ourselves if homework is crucial in our learning journey.
At the end of the day, homework can be a crucial step to becoming more knowledgeable and disciplined over time.
Exercising our memory skills, learning independently without a teacher obliging us, and processing new information are all beneficial to our growth and evolution. However, whether a homework task is enriching or simply a filler depends on the quality of education you're getting.
We sent you SMS, for complete subscription please reply.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.

Wonder of the Day #1245
Who Invented Math?

MATH — Numbers
Have You Ever Wondered...
Who invented math?
- What is the definition of mathematics?
- When did mathematics get its start?
- discovery ,
- mathematics ,
- measurement ,
- Mesopotamia ,
- operation ,
- prehistoric ,
- Pythagoras ,
- Pythagorean Theorem ,
- trigonometry
Today’s Wonder of the Day was inspired by Dayana from Chicago , IL. Dayana Wonders , “ Who invented math ” Thanks for WONDERing with us, Dayana !
We're sure that more than one student has wished that he could travel back in time and prevent someone from inventing math. Of course, that same wish probably has been made with regard to all subjects that result in homework and difficult tests from time to time .
But would that really be possible…even if time travel existed? Probably not! Why? Unlike a light bulb or a computer, mathematics isn't really an invention . It's really more of a discovery .
Mathematics encompasses many different types of studies, so its discovery can't even be attributed to one person. Instead, mathematics developed slowly over thousands of years with the help of thousands of people!
How did it get started? No one can know for sure, but we can use our imaginations to think about how mathematics might have gotten its start. For example, if we go all the way back to prehistoric humans gathering berries to eat, we can imagine how this basic task probably gave rise for a need for math. If you and your prehistoric buddy gathered a basket full of berries, you'd probably agree to split them evenly. First, you'd need to know how many berries you gathered. That means you'd need to count them. You might first need to come up with names for the basic units of measurement . Is this how counting and the first numbers came about? No one knows, but you can see how this might be how it happened.
Similarly, division might have been born from the need to split that pile of berries evenly. How advanced did prehistoric humans get with mathematics ? Probably not far at all, but a need for certain mathematic principles likely arose from daily life and, as such, were discovered or created out of need rather than invented. Early learning eventually led to more advanced fields of mathematics , such as algebra , geometry , calculus , and trigonometry !
Because many mathematical discoveries were made as a result of necessity, it comes as no surprise that scientists believe that many basic mathematical functions, such as addition, multiplication, and the like, appeared thousands of years ago in various areas at the same time , including China, India, Mesopotamia , and Egypt.
The oldest clay tablets with mathematics date back over 4,000 years ago in Mesopotamia. The oldest written texts on mathematics are Egyptian papyruses. Since these are some of the oldest societies on Earth, it makes sense that they would have been the first to discover the basics of mathematics .
More advanced mathematics can be traced to ancient Greece over 2,500 years ago. Ancient mathematician Pythagoras had questions about the sides of a right triangle. His questioning, research, and testing led to a basic understanding of triangles we still study today, known as the Pythagorean Theorem .
Most experts agree that it was around this time (2,500 years ago) in ancient Greece that mathematics first became an organized science. Since that time , mathematical discoveries have spurred other mathematicians and scientists to build upon the work of others, constantly expanding our understanding of mathematics and its relation to the world around us.
Wonder What's Next?
Be sure to visit Wonderopolis tomorrow as we head to the Sun to check out some killer rays!
If you want to keep the learning from today's Wonder of the Day adding up, grab a few friends or family members and explore the mathematical activities below:
- Put yourself in a caveman's shoes for just a little bit. But cavemen didn't wear shoes! OK, smarty pants, you know what we mean. Take some time to pretend that you're a prehistoric human being. Your days are filled with mere survival. You must find food, water, and shelter. You must protect yourself from the many dangers in the world around you. What uses might you have for math? How might have you developed some basic mathematical skills? Have fun imagining how the very first beginnings of mathematics might have come about.
- For a fun change of pace, interview your math teacher. What does he or she find interesting about the origins of mathematics? Share what you learned in today's Wonder of the Day and ask for input. You never know when your math teacher might be able to provide some unique insight into the history of the subject they teach. Do they remember any special stories from when they first learned about the history of certain mathematical discoveries? Share what you learn with your friends and family members.
- Up for a challenge? Test how much you know about math and its history. Just jump online and navigate to Who invented math? Take the quiz! NOTE: Today's Wonder of the Day probably only addressed a few of the questions you'll see on this quiz, so don't worry if you don't know all the answers. Just look at this quiz as a way to challenge yourself and learn some new math facts!
Did you get it?
Wonder contributors.
We’d like to thank:
katelyn , Kevin and Elisha from AL for contributing questions about today’s Wonder topic!
Keep WONDERing with us!
Wonder Words
- mathematics
- prehistoric
Thanks for your input, Milind. We'll review the content and determine whether an update is necessary.
Addison Batsell
Hi, Addison! We recommend reading Wonder 1268: Why Was School Created? Happy WONDERing!
Math is a very fascinating subject, even if it is sometimes difficult to understand. We hope that you keep Wondering about math with us, Yara!
Yes!!! We're glad you liked this Wonder, too, luke!!
Both science and math are WONDERful subjects, Oliver! Have you checked out our science Wonders?
Hi, Denise! We LOVE Math!! What is your favorite math topic so far??
why is there no south africa or west africa or africa at all! and most importantly there are no specific countries for africa and you werent trying to tell us mesoptamia is a part africa where you cuz it is.
Hi, caleb! We did mention that math appeared thousands of years ago in Egypt, which is in northern Africa! We weren't leaving Africa off our list of places where math first appeared. For more information on Mesopotamia, check out Wonder 861: Where Is the Fertile Crescent? We hope this helps, and thanks for WONDERing with us!!
Hi, hannah! Since we do not the publish date for our Wonders of the Day, you may put the date you accessed this page for information. The following is how you would cite this page:
"Who Invented Math?" Wonderopolis. https://www.wonderopolis.org/wonder/who-invented-math . Accessed 24 Sept. 2017.
Thanks wonderopolis! I was trying to find a way to cite this page for an essay, this really helps.
Great, Van! Make sure you use the date YOU accessed this Wonder :-)
? Thanks, brandon! We're glad that you're WONDERing with us!!
Aryan Sanskrit
Hi, Aryan! That's AWESOME you know so much about this topic! Thanks for sharing the interesting info! :)
I think its great u respond to your people on most sites they dont thats why this is so helpful.
We LOVE responding to our Wonder Friends, Eli!! We're so glad that you're WONDERing with us!!
That's probably a question we can only Wonder about. Pretty amazing to think of how far we have come!
RITA TIWARI
You did, Rita? That's amazing!
Fraction DUde
We can't help you with that one, Fraction Dude but since you ARE the Fraction Dude, we have great confidence that you will figure that one out! ?
Wow, 8411c - that's some heavy stuff! While we may not have given you the answer you were hoping for, we did enjoy starting the conversation of WONDERing about math. Thanks for your comment!
That's great to hear, Gabby! You set a great example of keeping an open mind! It can be popular to hate math but if more people hung in there like you do, they would see how truly useful it can be. Thanks for sharing, Gabby!
Hey, Alina. How did you like this Wonder?
Thanks for sharing your love of math with us, Parth! You might enjoy exploring some of these Wonders about math . Thanks for WONDERing with us!
Thnks Wonderopolis for helping Me So much...???????
Glad to help, Parth! Keep WONDERing with us!
Thanks for visiting Wonderopolis, Nate, and we're sorry you were confused by this Wonder. By doing research, we found that there wasn't just one person who created math. Rather, several cultures around the world developed a variety of mathematical functions.
Thank you for helping me understand?
You're welcome, Nate. Thank YOU for visiting Wonderopolis and learning with us!
We hope this Wonder helped, destiny! :)
It's great that you stopped by Wonderopolis and learned some new things with us, JohnRuel! :)
PAREEZA HUSSAIN
Thanks for stopping by Wonderopolis, Pareeza! We hope you learned more about math! :)
Thank you for joining the discussion, Nasia! We are glad you are WONDERing!
Hi, Landon! We're glad you learned more about the history of math! They probably used math in some way! :)
for me i think Pythagoras is a great inventor too
Hi, thon! Thanks for your comment! He is also a famous math inventor! We encourage you to keep learning about Pythagoras at your library and online! :)
Book worm23
Nobody actually invented math it just evolved over time. They discovered it not invented it.
We're glad you joined the conversation, Book worm23!
The Ancient Egyptians invented math. They used mathematics in order to build Houses, Temples and Pyramids.
Actually no one really invented it. It just evolved over the years.
Thank you for commenting, BlibbyB!
Welcome, KC! We're glad you learned something new! Thanks for sharing those cool facts! :)
well they didn't realy explein the creators of maths, they explained origine of calculation and this is not what we call mathematics is from grec mathema like explained in the article coming from the Pythagoreans, but the modern math origine is from muslim scientists who created the arabien numbers, algebra, algorythm....you can just google History of mathematics. I don't know why they don't teach this things in school even me i did my own search in books to find that...sorry for the english, i'm french
Thank you for joining the discussion, Aksel. This Wonder of the Day just started to scratch the surface on the long history of the development of mathematics. We encourage our Wonder Friends to continue learning by researching online or at their local libraries, like you suggested.
Hi, Parsa and Doni! We encourage you to embark on your own Wonder Journey! You can find lots of information at the library and online! :)
We're THRILLED you liked this Wonder, Dahlia! Keep up the GREAT enthusiasm for WONDERing and learning! :)
Hi, Don! We hope this Wonder helped you learn more about the history of math! We also encourage you to explore the topic at your library and online! :)
I love math and I am doing a research project so I wanted to know who invented math
Hi, Nyla! We hope this Wonder was helpful for your research project! Thanks for stopping by Wonderopolis! :)
We think so, too, zane! We're glad to hear you enjoy math! It's a very important subject and fun to learn about, too! :)
Great WONDERing, Angie! We hope reading the Wonder helped you answer some of your question. You can always keep learning and researching about math at the library and online. Always keep the GREAT enthusiasm for WONDERing and learning! :)
That's awesome, Cristine! Thank you for sharing. We're glad you're WONDERing with us! :)
Hi, Isabela! That may be the case. As the Wonder tells us, no one knows for sure. Thanks for sharing your thoughts about this Wonder question. Keep up the GREAT work! :)
Are you sure? Where did you get that information from then?
Thanks for joining the discussion, Isabela! We appreciate you WONDERing with us. We encourage you to keep researching the history of math at your library and online! :)
Hi, WONDER Friend! We appreciate you sharing your opinion about this Wonder. We understand that sometimes people have different beliefs. We are simply telling the most common information about the invention of math. We hope you understand and will WONDER with us again soon! :)
Hi, WONDER Friend! Thanks for WONDERing with us! We're glad you're extending the Wonder by taking the quiz. Click on "Test Your Knowledge" on the right side. It will link you to the quiz. Have fun and good luck! :)
MURALI KRISHNA
Hi, Murali! Sir. C. V. Raman was a famous physicists, who won a Nobel Peace Prize. We encourage you to keep researching more about him at your library and online. Maybe after researching you could write a biography about him. Check out Wonder #44: What Is a Biography? . Keep up the GREAT thinking! :)
Wonderopolis
Hello, 2q3r! Thanks for commenting! We're glad you WONDERing with us! :)
That's what I'm wondering
Thanks for WONDERing with us, Angie! We hope this Wonder is helpful! We appreciate you stopping by Wonderopolis! :)
Hi, Ethan! Because math concepts were often invented out of necessity, it is difficult to name only one person for inventing math. Instead, people worked together to create solutions and developed math concepts. If you're interested, we encourage you to continue researching the history of math at your library and online. Always keep WONDERing! :)
Kritisundar Barman
Hello, Kritisundar Barman! You're right, that you can count with letters, which are known as roman numerals. Check out Wonder #853: Can You Count with Letters? . Thanks for commenting! :)
We are glad you liked it, Olivia! We encourage you to try giving math a second chance. Math is very helpful for many things. Check out Wonder #9: How Can Math Help You Cook? . Have fun WONDERing! :)
Great connection, Myra! There are many other WONDERS about discoveries and inventions on WONDERopolis. Thanks for WONDERing with us! :)
Love_peace42
Great WONDER, Love_peace42! Math keeps evolving and changing over time. Maybe you can keep researching the topic at your library. We are happy to see you WONDERing! :)
Really!!!!!!!!!!?????????
We're glad you're having fun WONDERing, Clarina! It's GREAT when we're WONDERing, learning, and having fun! :)
We're really glad you learned more about the origins of math, Clarina! We think you may enjoy these two Wonders about ancient history, math and invention! Can You Count with Letters? (https://www.wonderopolis.org/wonder/can-you-count-with-letters/) Do You Know the Greek Alphabet? (https://www.wonderopolis.org/wonder/do-you-know-the-greek-alphabet/)
We're sorry to hear that you were confused with our Wonder about math, Wonder Friend Matt. Thanks for stopping by Wonderopolis today! :)
Thanks for spending time WONDERing about math with us today, Maya! We think it must have been confusing back in ancient times, too. What do you like about math? We hope you have a WONDERful weekend! :)
Andrew Guerrero
We agree that everyday life can lead to many discoveries, Wonder Friend Andrew. Just think of all the possible things that you may be able to discover just by exploring and observing your environment! ;) Thank you for visiting Wonderopolis today! :)
We agree that numbers are important to math. Thank you for joining us to WONDER today! :)
Colby Dawson
We're sorry to hear you didn't like today's Wonder, Colby. We appreciate you letting us know your opinion. You'll have to stop back by and let us know what you think of tomorrow's Wonder. In the mean time, many of our Wonder Friends have really enjoyed Wonder #766: When Will Pigs Fly? We think you may want to check it out! :)
kepodgorski
We sure like hearing what you learned from today's Wonder and video, kepodgorski! Thank you for leaving us this AWESOME comment and continuing to WONDER! :)
Thanks for sharing what you learned about the discovery of math by exploring this Wonder today, James Alex. We hope you stop by and WONDER with us again soon! :)
Hey, Latisha! Thanks so much for your comment about Math. We hope you have a GREAT day too! :)
Welcome back to Wonderopolis, ssobus! We're SO happy you joined us to WONDER about math today! Thank you for sharing your learning with us and for being a GREAT Wonder Friend! :D
ajrodriguez26
Hi there, ajrodriquez! Thanks for sharing your thinking with us today. We hope you join us again soon to do some more WONDERing! :D
We think it is WONDERful that you learned so much from today's Wonder about math, Isai! You ROCK! :D Thanks for WONDERing with us today! :)
We're SO glad that you learned that math and Pi were not invented to torture students. We LOVE discovering new math concepts in Wonderopolis and hope you do too! :) Happy WONDERing! :D
We're glad you learned some new things about the discovery of math today, Wonder Friend Nathan. Thanks so much for visiting Wonderopolis! :D
Thanks for letting us know you thought today's Wonder about Math was COOL! We appreciate your excitement and enthusiasm, Wonder Friend TJ! :D It sounds like you have a very fun day ahead of you! :) We can't wait for you to check back in tomorrow and let us know about your day at Cedar Point. We'd love to hear about any WONDERing you do today! :)
I love this it is great and is very helpful
WONDERful, Michaela! Thanks for stopping by Wonderopolis! We hope you learned something new about math! :)
We are undergoing some spring clearing site maintenance and need to temporarily disable the commenting feature. Thanks for your patience.
Related Wonders for You to Explore
What Is a Multiple?

What Is Probability?

Does Music Help You With Math?

Who Was the First Female and American Indian Engineer?

Who Was Alan Turing?
Drag a word to its definition
Select a Wonder Word:
Match its definition:
Congratulations!
You’ve matched all of the definitions correctly.
Share results
Question 1 of 3
<p class=\"FreeForm\"><span style=\"font-size: 10.0pt; font-family: \'Century Gothic\';\">Mathematics wasn’t really invented, but was more of a what?</span></p>
- a discovery Correct!
- b accident Not Quite!
- c theory Not Quite!
- d creation Not Quite!
Question 2 of 3
<p class=\"FreeForm\"><span style=\"font-size: 10.0pt; font-family: \'Century Gothic\';\">Which ancient Greek mathematician made important initial discoveries about the properties of triangles?</span></p>
- a Plato Not Quite!
- b Nero Not Quite!
- c Pythagorus Correct!
- d Einstein Not Quite!
Question 3 of 3
<p class=\"FreeForm\"><span style=\"font-size: 10.0pt; font-family: \'Century Gothic\';\">Mathematics wasn’t really an organized scientific field of study until about how many years ago?</span></p>
- a 10,000 Not Quite!
- b 50 Not Quite!
- c 50,000 Not Quite!
- d 2,500 Correct!
Quiz Results
Share Results
Spread the joy of wonder, get your wonder daily.
Subscribe to Wonderopolis and receive the Wonder of the Day® via email or SMS
Join the Buzz
Don’t miss our special deals, gifts and promotions. Be the first to know!
Share with the World
Tell everybody about Wonderopolis and its wonders.
Share Wonderopolis
Wonderopolis widget.
Interested in sharing Wonderopolis® every day? Want to add a little wonder to your website? Help spread the wonder of families learning together.
You Got It!

http://www.wonderopolis.org/wonder/who-invented-math
© National Center for Families Learning (NCFL)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Roberto Nevelis, a Venetian educator from the 16th century, is frequently credited with the invention of homework. The story goes that Nevelis assigned tasks to his students outside regular classroom hours to reinforce their learning—a practice that aligns with the essence of homework.
Roberto Nevelis of Venice, Italy, is often credited with having invented homework in 1095—or 1905, depending on your sources. Upon further inspection, however, he seems to be more of an...
In 1880, Francis Amasa Walker convinced the school board in Boston to prohibit teachers from assigning math homework under normal circumstances. In 1900, journalist Edward Bok railed against schools assigning homework to students until age 15. [12]
Who invented math? It’s a deceptively complex question—a lot harder than 2+2. Math has been around forever, but we are always learning more about it. Short answer: Many different people invented math, including ancient societies and many famous mathematicians who came along later.
The inventor of homework is widely considered to be Roberto Nevilis, an Italian educator who lived in the early 20th century. We will briefly explore Nevilis’ life, how he came up with the concept of homework, and the circumstances surrounding his death. Roberto Nevilis: The Man Behind Homework Roberto Nevilis was born in Venice, Italy, in 1879.
Mesopotamia, often referred to as the “ Cradle of Civilization ,” saw the emergence of some of the earliest mathematical concepts. In this fertile region, ancient mathematicians devised methods for counting and recording numerical information, essential for administrative and economic purposes.
Who invented homework and why? The creation of homework can be traced back to the Ancient Roman Pliny the Younger, a teacher of oratory—he is generally credited as being the father of homework! Pliny the Younger asked his students to practice outside of class to help them build confidence in their speaking skills.
No credible news source or website has ever mentioned the name Roberto Nevilis as the person who invented homework. In fact, it’s possible that Nevilis never even existed.
The invention of homework is commonly attributed to Roberto Nevilis, an Italian pedagog who is said to have introduced it as a form of punishment for his students in 1905. However, the concept of homework predates Nevilis and has roots that go back much further in history. .
The oldest clay tablets with mathematics date back over 4,000 years ago in Mesopotamia. The oldest written texts on mathematics are Egyptian papyruses. Since these are some of the oldest societies on Earth, it makes sense that they would have been the first to discover the basics of mathematics.