

What Is Research Methodology?

I f you’re new to formal academic research, it’s quite likely that you’re feeling a little overwhelmed by all the technical lingo that gets thrown around. And who could blame you – “research methodology”, “research methods”, “sampling strategies”… it all seems never-ending!
In this post, we’ll demystify the landscape with plain-language explanations and loads of examples (including easy-to-follow videos), so that you can approach your dissertation, thesis or research project with confidence. Let’s get started.
Research Methodology 101
- What exactly research methodology means
- What qualitative , quantitative and mixed methods are
- What sampling strategy is
- What data collection methods are
- What data analysis methods are
- How to choose your research methodology
- Example of a research methodology

What is research methodology?
Research methodology simply refers to the practical “how” of a research study. More specifically, it’s about how a researcher systematically designs a study to ensure valid and reliable results that address the research aims, objectives and research questions . Specifically, how the researcher went about deciding:
- What type of data to collect (e.g., qualitative or quantitative data )
- Who to collect it from (i.e., the sampling strategy )
- How to collect it (i.e., the data collection method )
- How to analyse it (i.e., the data analysis methods )
Within any formal piece of academic research (be it a dissertation, thesis or journal article), you’ll find a research methodology chapter or section which covers the aspects mentioned above. Importantly, a good methodology chapter explains not just what methodological choices were made, but also explains why they were made. In other words, the methodology chapter should justify the design choices, by showing that the chosen methods and techniques are the best fit for the research aims, objectives and research questions.
So, it’s the same as research design?
Not quite. As we mentioned, research methodology refers to the collection of practical decisions regarding what data you’ll collect, from who, how you’ll collect it and how you’ll analyse it. Research design, on the other hand, is more about the overall strategy you’ll adopt in your study. For example, whether you’ll use an experimental design in which you manipulate one variable while controlling others. You can learn more about research design and the various design types here .
Need a helping hand?
What are qualitative, quantitative and mixed-methods?
Qualitative, quantitative and mixed-methods are different types of methodological approaches, distinguished by their focus on words , numbers or both . This is a bit of an oversimplification, but its a good starting point for understanding.
Let’s take a closer look.
Qualitative research refers to research which focuses on collecting and analysing words (written or spoken) and textual or visual data, whereas quantitative research focuses on measurement and testing using numerical data . Qualitative analysis can also focus on other “softer” data points, such as body language or visual elements.
It’s quite common for a qualitative methodology to be used when the research aims and research questions are exploratory in nature. For example, a qualitative methodology might be used to understand peoples’ perceptions about an event that took place, or a political candidate running for president.
Contrasted to this, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research aims and research questions are confirmatory in nature. For example, a quantitative methodology might be used to measure the relationship between two variables (e.g. personality type and likelihood to commit a crime) or to test a set of hypotheses .
As you’ve probably guessed, the mixed-method methodology attempts to combine the best of both qualitative and quantitative methodologies to integrate perspectives and create a rich picture. If you’d like to learn more about these three methodological approaches, be sure to watch our explainer video below.
What is sampling strategy?
Simply put, sampling is about deciding who (or where) you’re going to collect your data from . Why does this matter? Well, generally it’s not possible to collect data from every single person in your group of interest (this is called the “population”), so you’ll need to engage a smaller portion of that group that’s accessible and manageable (this is called the “sample”).
How you go about selecting the sample (i.e., your sampling strategy) will have a major impact on your study. There are many different sampling methods you can choose from, but the two overarching categories are probability sampling and non-probability sampling .
Probability sampling involves using a completely random sample from the group of people you’re interested in. This is comparable to throwing the names all potential participants into a hat, shaking it up, and picking out the “winners”. By using a completely random sample, you’ll minimise the risk of selection bias and the results of your study will be more generalisable to the entire population.
Non-probability sampling , on the other hand, doesn’t use a random sample . For example, it might involve using a convenience sample, which means you’d only interview or survey people that you have access to (perhaps your friends, family or work colleagues), rather than a truly random sample. With non-probability sampling, the results are typically not generalisable .
To learn more about sampling methods, be sure to check out the video below.
What are data collection methods?
As the name suggests, data collection methods simply refers to the way in which you go about collecting the data for your study. Some of the most common data collection methods include:
- Interviews (which can be unstructured, semi-structured or structured)
- Focus groups and group interviews
- Surveys (online or physical surveys)
- Observations (watching and recording activities)
- Biophysical measurements (e.g., blood pressure, heart rate, etc.)
- Documents and records (e.g., financial reports, court records, etc.)
The choice of which data collection method to use depends on your overall research aims and research questions , as well as practicalities and resource constraints. For example, if your research is exploratory in nature, qualitative methods such as interviews and focus groups would likely be a good fit. Conversely, if your research aims to measure specific variables or test hypotheses, large-scale surveys that produce large volumes of numerical data would likely be a better fit.

What are data analysis methods?
Data analysis methods refer to the methods and techniques that you’ll use to make sense of your data. These can be grouped according to whether the research is qualitative (words-based) or quantitative (numbers-based).
Popular data analysis methods in qualitative research include:
- Qualitative content analysis
- Thematic analysis
- Discourse analysis
- Narrative analysis
- Interpretative phenomenological analysis (IPA)
- Visual analysis (of photographs, videos, art, etc.)
Qualitative data analysis all begins with data coding , after which an analysis method is applied. In some cases, more than one analysis method is used, depending on the research aims and research questions . In the video below, we explore some common qualitative analysis methods, along with practical examples.
- Descriptive statistics (e.g. means, medians, modes )
- Inferential statistics (e.g. correlation, regression, structural equation modelling)
How do I choose a research methodology?
As you’ve probably picked up by now, your research aims and objectives have a major influence on the research methodology . So, the starting point for developing your research methodology is to take a step back and look at the big picture of your research, before you make methodology decisions. The first question you need to ask yourself is whether your research is exploratory or confirmatory in nature.
If your research aims and objectives are primarily exploratory in nature, your research will likely be qualitative and therefore you might consider qualitative data collection methods (e.g. interviews) and analysis methods (e.g. qualitative content analysis).
Conversely, if your research aims and objective are looking to measure or test something (i.e. they’re confirmatory), then your research will quite likely be quantitative in nature, and you might consider quantitative data collection methods (e.g. surveys) and analyses (e.g. statistical analysis).
Designing your research and working out your methodology is a large topic, which we cover extensively on the blog . For now, however, the key takeaway is that you should always start with your research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread). Every methodological choice you make needs align with those three components.
Example of a research methodology chapter
In the video below, we provide a detailed walkthrough of a research methodology from an actual dissertation, as well as an overview of our free methodology template .

Learn More About Methodology

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Triangulation: The Ultimate Credibility Enhancer
Triangulation is one of the best ways to enhance the credibility of your research. Learn about the different options here.

Research Limitations 101: What You Need To Know
Learn everything you need to know about research limitations (AKA limitations of the study). Includes practical examples from real studies.

In Vivo Coding 101: Full Explainer With Examples
Learn about in vivo coding, a popular qualitative coding technique ideal for studies where the nuances of language are central to the aims.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
200 Comments
Thank you for this simple yet comprehensive and easy to digest presentation. God Bless!
You’re most welcome, Leo. Best of luck with your research!
I found it very useful. many thanks
This is really directional. A make-easy research knowledge.
Thank you for this, I think will help my research proposal
Thanks for good interpretation,well understood.
Good morning sorry I want to the search topic
Thank u more
Thank you, your explanation is simple and very helpful.
Very educative a.nd exciting platform. A bigger thank you and I’ll like to always be with you
That’s the best analysis
So simple yet so insightful. Thank you.
This really easy to read as it is self-explanatory. Very much appreciated…
Thanks for this. It’s so helpful and explicit. For those elements highlighted in orange, they were good sources of referrals for concepts I didn’t understand. A million thanks for this.
Good morning, I have been reading your research lessons through out a period of times. They are important, impressive and clear. Want to subscribe and be and be active with you.
Thankyou So much Sir Derek…
Good morning thanks so much for the on line lectures am a student of university of Makeni.select a research topic and deliberate on it so that we’ll continue to understand more.sorry that’s a suggestion.
Beautiful presentation. I love it.
please provide a research mehodology example for zoology
It’s very educative and well explained
Thanks for the concise and informative data.
This is really good for students to be safe and well understand that research is all about
Thank you so much Derek sir🖤🙏🤗
Very simple and reliable
This is really helpful. Thanks alot. God bless you.
very useful, Thank you very much..
thanks a lot its really useful
in a nutshell..thank you!
Thanks for updating my understanding on this aspect of my Thesis writing.
thank you so much my through this video am competently going to do a good job my thesis
Thanks a lot. Very simple to understand. I appreciate 🙏
Very simple but yet insightful Thank you
This has been an eye opening experience. Thank you grad coach team.
Very useful message for research scholars
Really very helpful thank you
yes you are right and i’m left
Research methodology with a simplest way i have never seen before this article.
wow thank u so much
Good morning thanks so much for the on line lectures am a student of university of Makeni.select a research topic and deliberate on is so that we will continue to understand more.sorry that’s a suggestion.
Very precise and informative.
Thanks for simplifying these terms for us, really appreciate it.
Thanks this has really helped me. It is very easy to understand.
I found the notes and the presentation assisting and opening my understanding on research methodology
Good presentation
Im so glad you clarified my misconceptions. Im now ready to fry my onions. Thank you so much. God bless
Thank you a lot.
thanks for the easy way of learning and desirable presentation.
Thanks a lot. I am inspired
Well written
I am writing a APA Format paper . I using questionnaire with 120 STDs teacher for my participant. Can you write me mthology for this research. Send it through email sent. Just need a sample as an example please. My topic is ” impacts of overcrowding on students learning
Thanks for your comment.
We can’t write your methodology for you. If you’re looking for samples, you should be able to find some sample methodologies on Google. Alternatively, you can download some previous dissertations from a dissertation directory and have a look at the methodology chapters therein.
All the best with your research.
Thank you so much for this!! God Bless
Thank you. Explicit explanation
Thank you, Derek and Kerryn, for making this simple to understand. I’m currently at the inception stage of my research.
Thnks a lot , this was very usefull on my assignment
excellent explanation
I’m currently working on my master’s thesis, thanks for this! I’m certain that I will use Qualitative methodology.
Thanks a lot for this concise piece, it was quite relieving and helpful. God bless you BIG…
I am currently doing my dissertation proposal and I am sure that I will do quantitative research. Thank you very much it was extremely helpful.
Very interesting and informative yet I would like to know about examples of Research Questions as well, if possible.
I’m about to submit a research presentation, I have come to understand from your simplification on understanding research methodology. My research will be mixed methodology, qualitative as well as quantitative. So aim and objective of mixed method would be both exploratory and confirmatory. Thanks you very much for your guidance.
OMG thanks for that, you’re a life saver. You covered all the points I needed. Thank you so much ❤️ ❤️ ❤️
Thank you immensely for this simple, easy to comprehend explanation of data collection methods. I have been stuck here for months 😩. Glad I found your piece. Super insightful.
I’m going to write synopsis which will be quantitative research method and I don’t know how to frame my topic, can I kindly get some ideas..
Thanks for this, I was really struggling.
This was really informative I was struggling but this helped me.
Thanks a lot for this information, simple and straightforward. I’m a last year student from the University of South Africa UNISA South Africa.
its very much informative and understandable. I have enlightened.
An interesting nice exploration of a topic.
Thank you. Accurate and simple🥰
This article was really helpful, it helped me understanding the basic concepts of the topic Research Methodology. The examples were very clear, and easy to understand. I would like to visit this website again. Thank you so much for such a great explanation of the subject.
Thanks dude
Thank you Doctor Derek for this wonderful piece, please help to provide your details for reference purpose. God bless.
Many compliments to you
Great work , thank you very much for the simple explanation
Thank you. I had to give a presentation on this topic. I have looked everywhere on the internet but this is the best and simple explanation.
thank you, its very informative.
Well explained. Now I know my research methodology will be qualitative and exploratory. Thank you so much, keep up the good work
Well explained, thank you very much.
This is good explanation, I have understood the different methods of research. Thanks a lot.
Great work…very well explanation
Thanks Derek. Kerryn was just fantastic!
Great to hear that, Hyacinth. Best of luck with your research!
Its a good templates very attractive and important to PhD students and lectuter
Thanks for the feedback, Matobela. Good luck with your research methodology.
Thank you. This is really helpful.
You’re very welcome, Elie. Good luck with your research methodology.
Well explained thanks
This is a very helpful site especially for young researchers at college. It provides sufficient information to guide students and equip them with the necessary foundation to ask any other questions aimed at deepening their understanding.
Thanks for the kind words, Edward. Good luck with your research!
Thank you. I have learned a lot.
Great to hear that, Ngwisa. Good luck with your research methodology!
Thank you for keeping your presentation simples and short and covering key information for research methodology. My key takeaway: Start with defining your research objective the other will depend on the aims of your research question.
My name is Zanele I would like to be assisted with my research , and the topic is shortage of nursing staff globally want are the causes , effects on health, patients and community and also globally
Thanks for making it simple and clear. It greatly helped in understanding research methodology. Regards.
This is well simplified and straight to the point
Thank you Dr
I was given an assignment to research 2 publications and describe their research methodology? I don’t know how to start this task can someone help me?
Sure. You’re welcome to book an initial consultation with one of our Research Coaches to discuss how we can assist – https://gradcoach.com/book/new/ .
Thanks a lot I am relieved of a heavy burden.keep up with the good work
I’m very much grateful Dr Derek. I’m planning to pursue one of the careers that really needs one to be very much eager to know. There’s a lot of research to do and everything, but since I’ve gotten this information I will use it to the best of my potential.
Thank you so much, words are not enough to explain how helpful this session has been for me!
Thanks this has thought me alot.
Very concise and helpful. Thanks a lot
Thank Derek. This is very helpful. Your step by step explanation has made it easier for me to understand different concepts. Now i can get on with my research.
I wish i had come across this sooner. So simple but yet insightful
really nice explanation thank you so much
I’m so grateful finding this site, it’s really helpful…….every term well explained and provide accurate understanding especially to student going into an in-depth research for the very first time, even though my lecturer already explained this topic to the class, I think I got the clear and efficient explanation here, much thanks to the author.
It is very helpful material
I would like to be assisted with my research topic : Literature Review and research methodologies. My topic is : what is the relationship between unemployment and economic growth?
Its really nice and good for us.
THANKS SO MUCH FOR EXPLANATION, ITS VERY CLEAR TO ME WHAT I WILL BE DOING FROM NOW .GREAT READS.
Short but sweet.Thank you
Informative article. Thanks for your detailed information.
I’m currently working on my Ph.D. thesis. Thanks a lot, Derek and Kerryn, Well-organized sequences, facilitate the readers’ following.
great article for someone who does not have any background can even understand
I am a bit confused about research design and methodology. Are they the same? If not, what are the differences and how are they related?
Thanks in advance.
concise and informative.
Thank you very much
How can we site this article is Harvard style?
Very well written piece that afforded better understanding of the concept. Thank you!
Am a new researcher trying to learn how best to write a research proposal. I find your article spot on and want to download the free template but finding difficulties. Can u kindly send it to my email, the free download entitled, “Free Download: Research Proposal Template (with Examples)”.
Thank too much
Thank you very much for your comprehensive explanation about research methodology so I like to thank you again for giving us such great things.
Good very well explained.Thanks for sharing it.
Thank u sir, it is really a good guideline.
so helpful thank you very much.
Thanks for the video it was very explanatory and detailed, easy to comprehend and follow up. please, keep it up the good work
It was very helpful, a well-written document with precise information.
how do i reference this?
MLA Jansen, Derek, and Kerryn Warren. “What (Exactly) Is Research Methodology?” Grad Coach, June 2021, gradcoach.com/what-is-research-methodology/.
APA Jansen, D., & Warren, K. (2021, June). What (Exactly) Is Research Methodology? Grad Coach. https://gradcoach.com/what-is-research-methodology/
Your explanation is easily understood. Thank you
Very help article. Now I can go my methodology chapter in my thesis with ease
I feel guided ,Thank you
This simplification is very helpful. It is simple but very educative, thanks ever so much
The write up is informative and educative. It is an academic intellectual representation that every good researcher can find useful. Thanks
Wow, this is wonderful long live.
Nice initiative
thank you the video was helpful to me.
Thank you very much for your simple and clear explanations I’m really satisfied by the way you did it By now, I think I can realize a very good article by following your fastidious indications May God bless you
Thanks very much, it was very concise and informational for a beginner like me to gain an insight into what i am about to undertake. I really appreciate.
very informative sir, it is amazing to understand the meaning of question hidden behind that, and simple language is used other than legislature to understand easily. stay happy.
This one is really amazing. All content in your youtube channel is a very helpful guide for doing research. Thanks, GradCoach.
research methodologies
Please send me more information concerning dissertation research.
Nice piece of knowledge shared….. #Thump_UP
This is amazing, it has said it all. Thanks to Gradcoach
This is wonderful,very elaborate and clear.I hope to reach out for your assistance in my research very soon.
This is the answer I am searching about…
realy thanks a lot
Thank you very much for this awesome, to the point and inclusive article.
Thank you very much I need validity and reliability explanation I have exams
Thank you for a well explained piece. This will help me going forward.
Very simple and well detailed Many thanks
This is so very simple yet so very effective and comprehensive. An Excellent piece of work.
I wish I saw this earlier on! Great insights for a beginner(researcher) like me. Thanks a mil!
Thank you very much, for such a simplified, clear and practical step by step both for academic students and general research work. Holistic, effective to use and easy to read step by step. One can easily apply the steps in practical terms and produce a quality document/up-to standard
Thanks for simplifying these terms for us, really appreciated.
Thanks for a great work. well understood .
This was very helpful. It was simple but profound and very easy to understand. Thank you so much!
Great and amazing research guidelines. Best site for learning research
hello sir/ma’am, i didn’t find yet that what type of research methodology i am using. because i am writing my report on CSR and collect all my data from websites and articles so which type of methodology i should write in dissertation report. please help me. i am from India.
how does this really work?
perfect content, thanks a lot
As a researcher, I commend you for the detailed and simplified information on the topic in question. I would like to remain in touch for the sharing of research ideas on other topics. Thank you
Impressive. Thank you, Grad Coach 😍
Thank you Grad Coach for this piece of information. I have at least learned about the different types of research methodologies.
Very useful content with easy way
Thank you very much for the presentation. I am an MPH student with the Adventist University of Africa. I have successfully completed my theory and starting on my research this July. My topic is “Factors associated with Dental Caries in (one District) in Botswana. I need help on how to go about this quantitative research
I am so grateful to run across something that was sooo helpful. I have been on my doctorate journey for quite some time. Your breakdown on methodology helped me to refresh my intent. Thank you.
thanks so much for this good lecture. student from university of science and technology, Wudil. Kano Nigeria.
It’s profound easy to understand I appreciate
Thanks a lot for sharing superb information in a detailed but concise manner. It was really helpful and helped a lot in getting into my own research methodology.
Comment * thanks very much
This was sooo helpful for me thank you so much i didn’t even know what i had to write thank you!
You’re most welcome 🙂
Simple and good. Very much helpful. Thank you so much.
This is very good work. I have benefited.
Thank you so much for sharing
This is powerful thank you so much guys
I am nkasa lizwi doing my research proposal on honors with the university of Walter Sisulu Komani I m on part 3 now can you assist me.my topic is: transitional challenges faced by educators in intermediate phase in the Alfred Nzo District.
Appreciate the presentation. Very useful step-by-step guidelines to follow.
I appreciate sir
wow! This is super insightful for me. Thank you!
Indeed this material is very helpful! Kudos writers/authors.
I want to say thank you very much, I got a lot of info and knowledge. Be blessed.
I want present a seminar paper on Optimisation of Deep learning-based models on vulnerability detection in digital transactions.
Need assistance
Dear Sir, I want to be assisted on my research on Sanitation and Water management in emergencies areas.
I am deeply grateful for the knowledge gained. I will be getting in touch shortly as I want to be assisted in my ongoing research.
The information shared is informative, crisp and clear. Kudos Team! And thanks a lot!
hello i want to study
Hello!! Grad coach teams. I am extremely happy in your tutorial or consultation. i am really benefited all material and briefing. Thank you very much for your generous helps. Please keep it up. If you add in your briefing, references for further reading, it will be very nice.
All I have to say is, thank u gyz.
Good, l thanks
thank you, it is very useful
Thank you so much for the insightful tips.
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is A Literature Review (In A Dissertation Or Thesis) - Grad Coach - […] the literature review is to inform the choice of methodology for your own research. As we’ve discussed on the Grad Coach blog,…
- Free Download: Research Proposal Template (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] Research design (methodology) […]
- Dissertation vs Thesis: What's the difference? - Grad Coach - […] and thesis writing on a daily basis – everything from how to find a good research topic to which…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 6. The Methodology
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The methods section describes actions taken to investigate a research problem and the rationale for the application of specific procedures or techniques used to identify, select, process, and analyze information applied to understanding the problem, thereby, allowing the reader to critically evaluate a study’s overall validity and reliability. The methodology section of a research paper answers two main questions: How was the data collected or generated? And, how was it analyzed? The writing should be direct and precise and always written in the past tense.
Kallet, Richard H. "How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper." Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004): 1229-1232.
Importance of a Good Methodology Section
You must explain how you obtained and analyzed your results for the following reasons:
- Readers need to know how the data was obtained because the method you chose affects the results and, by extension, how you interpreted their significance in the discussion section of your paper.
- Methodology is crucial for any branch of scholarship because an unreliable method produces unreliable results and, as a consequence, undermines the value of your analysis of the findings.
- In most cases, there are a variety of different methods you can choose to investigate a research problem. The methodology section of your paper should clearly articulate the reasons why you have chosen a particular procedure or technique.
- The reader wants to know that the data was collected or generated in a way that is consistent with accepted practice in the field of study. For example, if you are using a multiple choice questionnaire, readers need to know that it offered your respondents a reasonable range of answers to choose from.
- The method must be appropriate to fulfilling the overall aims of the study. For example, you need to ensure that you have a large enough sample size to be able to generalize and make recommendations based upon the findings.
- The methodology should discuss the problems that were anticipated and the steps you took to prevent them from occurring. For any problems that do arise, you must describe the ways in which they were minimized or why these problems do not impact in any meaningful way your interpretation of the findings.
- In the social and behavioral sciences, it is important to always provide sufficient information to allow other researchers to adopt or replicate your methodology. This information is particularly important when a new method has been developed or an innovative use of an existing method is utilized.
Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article. Psychology Writing Center. University of Washington; Denscombe, Martyn. The Good Research Guide: For Small-Scale Social Research Projects . 5th edition. Buckingham, UK: Open University Press, 2014; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Groups of Research Methods
There are two main groups of research methods in the social sciences:
- The e mpirical-analytical group approaches the study of social sciences in a similar manner that researchers study the natural sciences . This type of research focuses on objective knowledge, research questions that can be answered yes or no, and operational definitions of variables to be measured. The empirical-analytical group employs deductive reasoning that uses existing theory as a foundation for formulating hypotheses that need to be tested. This approach is focused on explanation.
- The i nterpretative group of methods is focused on understanding phenomenon in a comprehensive, holistic way . Interpretive methods focus on analytically disclosing the meaning-making practices of human subjects [the why, how, or by what means people do what they do], while showing how those practices arrange so that it can be used to generate observable outcomes. Interpretive methods allow you to recognize your connection to the phenomena under investigation. However, the interpretative group requires careful examination of variables because it focuses more on subjective knowledge.
II. Content
The introduction to your methodology section should begin by restating the research problem and underlying assumptions underpinning your study. This is followed by situating the methods you used to gather, analyze, and process information within the overall “tradition” of your field of study and within the particular research design you have chosen to study the problem. If the method you choose lies outside of the tradition of your field [i.e., your review of the literature demonstrates that the method is not commonly used], provide a justification for how your choice of methods specifically addresses the research problem in ways that have not been utilized in prior studies.
The remainder of your methodology section should describe the following:
- Decisions made in selecting the data you have analyzed or, in the case of qualitative research, the subjects and research setting you have examined,
- Tools and methods used to identify and collect information, and how you identified relevant variables,
- The ways in which you processed the data and the procedures you used to analyze that data, and
- The specific research tools or strategies that you utilized to study the underlying hypothesis and research questions.
In addition, an effectively written methodology section should:
- Introduce the overall methodological approach for investigating your research problem . Is your study qualitative or quantitative or a combination of both (mixed method)? Are you going to take a special approach, such as action research, or a more neutral stance?
- Indicate how the approach fits the overall research design . Your methods for gathering data should have a clear connection to your research problem. In other words, make sure that your methods will actually address the problem. One of the most common deficiencies found in research papers is that the proposed methodology is not suitable to achieving the stated objective of your paper.
- Describe the specific methods of data collection you are going to use , such as, surveys, interviews, questionnaires, observation, archival research. If you are analyzing existing data, such as a data set or archival documents, describe how it was originally created or gathered and by whom. Also be sure to explain how older data is still relevant to investigating the current research problem.
- Explain how you intend to analyze your results . Will you use statistical analysis? Will you use specific theoretical perspectives to help you analyze a text or explain observed behaviors? Describe how you plan to obtain an accurate assessment of relationships, patterns, trends, distributions, and possible contradictions found in the data.
- Provide background and a rationale for methodologies that are unfamiliar for your readers . Very often in the social sciences, research problems and the methods for investigating them require more explanation/rationale than widely accepted rules governing the natural and physical sciences. Be clear and concise in your explanation.
- Provide a justification for subject selection and sampling procedure . For instance, if you propose to conduct interviews, how do you intend to select the sample population? If you are analyzing texts, which texts have you chosen, and why? If you are using statistics, why is this set of data being used? If other data sources exist, explain why the data you chose is most appropriate to addressing the research problem.
- Provide a justification for case study selection . A common method of analyzing research problems in the social sciences is to analyze specific cases. These can be a person, place, event, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis that are either examined as a singular topic of in-depth investigation or multiple topics of investigation studied for the purpose of comparing or contrasting findings. In either method, you should explain why a case or cases were chosen and how they specifically relate to the research problem.
- Describe potential limitations . Are there any practical limitations that could affect your data collection? How will you attempt to control for potential confounding variables and errors? If your methodology may lead to problems you can anticipate, state this openly and show why pursuing this methodology outweighs the risk of these problems cropping up.
NOTE: Once you have written all of the elements of the methods section, subsequent revisions should focus on how to present those elements as clearly and as logically as possibly. The description of how you prepared to study the research problem, how you gathered the data, and the protocol for analyzing the data should be organized chronologically. For clarity, when a large amount of detail must be presented, information should be presented in sub-sections according to topic. If necessary, consider using appendices for raw data.
ANOTHER NOTE: If you are conducting a qualitative analysis of a research problem , the methodology section generally requires a more elaborate description of the methods used as well as an explanation of the processes applied to gathering and analyzing of data than is generally required for studies using quantitative methods. Because you are the primary instrument for generating the data [e.g., through interviews or observations], the process for collecting that data has a significantly greater impact on producing the findings. Therefore, qualitative research requires a more detailed description of the methods used.
YET ANOTHER NOTE: If your study involves interviews, observations, or other qualitative techniques involving human subjects , you may be required to obtain approval from the university's Office for the Protection of Research Subjects before beginning your research. This is not a common procedure for most undergraduate level student research assignments. However, i f your professor states you need approval, you must include a statement in your methods section that you received official endorsement and adequate informed consent from the office and that there was a clear assessment and minimization of risks to participants and to the university. This statement informs the reader that your study was conducted in an ethical and responsible manner. In some cases, the approval notice is included as an appendix to your paper.
III. Problems to Avoid
Irrelevant Detail The methodology section of your paper should be thorough but concise. Do not provide any background information that does not directly help the reader understand why a particular method was chosen, how the data was gathered or obtained, and how the data was analyzed in relation to the research problem [note: analyzed, not interpreted! Save how you interpreted the findings for the discussion section]. With this in mind, the page length of your methods section will generally be less than any other section of your paper except the conclusion.
Unnecessary Explanation of Basic Procedures Remember that you are not writing a how-to guide about a particular method. You should make the assumption that readers possess a basic understanding of how to investigate the research problem on their own and, therefore, you do not have to go into great detail about specific methodological procedures. The focus should be on how you applied a method , not on the mechanics of doing a method. An exception to this rule is if you select an unconventional methodological approach; if this is the case, be sure to explain why this approach was chosen and how it enhances the overall process of discovery.
Problem Blindness It is almost a given that you will encounter problems when collecting or generating your data, or, gaps will exist in existing data or archival materials. Do not ignore these problems or pretend they did not occur. Often, documenting how you overcame obstacles can form an interesting part of the methodology. It demonstrates to the reader that you can provide a cogent rationale for the decisions you made to minimize the impact of any problems that arose.
Literature Review Just as the literature review section of your paper provides an overview of sources you have examined while researching a particular topic, the methodology section should cite any sources that informed your choice and application of a particular method [i.e., the choice of a survey should include any citations to the works you used to help construct the survey].
It’s More than Sources of Information! A description of a research study's method should not be confused with a description of the sources of information. Such a list of sources is useful in and of itself, especially if it is accompanied by an explanation about the selection and use of the sources. The description of the project's methodology complements a list of sources in that it sets forth the organization and interpretation of information emanating from those sources.
Azevedo, L.F. et al. "How to Write a Scientific Paper: Writing the Methods Section." Revista Portuguesa de Pneumologia 17 (2011): 232-238; Blair Lorrie. “Choosing a Methodology.” In Writing a Graduate Thesis or Dissertation , Teaching Writing Series. (Rotterdam: Sense Publishers 2016), pp. 49-72; Butin, Dan W. The Education Dissertation A Guide for Practitioner Scholars . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin, 2010; Carter, Susan. Structuring Your Research Thesis . New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2012; Kallet, Richard H. “How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper.” Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004):1229-1232; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008. Methods Section. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Rudestam, Kjell Erik and Rae R. Newton. “The Method Chapter: Describing Your Research Plan.” In Surviving Your Dissertation: A Comprehensive Guide to Content and Process . (Thousand Oaks, Sage Publications, 2015), pp. 87-115; What is Interpretive Research. Institute of Public and International Affairs, University of Utah; Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Methods and Materials. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College.
Writing Tip
Statistical Designs and Tests? Do Not Fear Them!
Don't avoid using a quantitative approach to analyzing your research problem just because you fear the idea of applying statistical designs and tests. A qualitative approach, such as conducting interviews or content analysis of archival texts, can yield exciting new insights about a research problem, but it should not be undertaken simply because you have a disdain for running a simple regression. A well designed quantitative research study can often be accomplished in very clear and direct ways, whereas, a similar study of a qualitative nature usually requires considerable time to analyze large volumes of data and a tremendous burden to create new paths for analysis where previously no path associated with your research problem had existed.
To locate data and statistics, GO HERE .
Another Writing Tip
Knowing the Relationship Between Theories and Methods
There can be multiple meaning associated with the term "theories" and the term "methods" in social sciences research. A helpful way to delineate between them is to understand "theories" as representing different ways of characterizing the social world when you research it and "methods" as representing different ways of generating and analyzing data about that social world. Framed in this way, all empirical social sciences research involves theories and methods, whether they are stated explicitly or not. However, while theories and methods are often related, it is important that, as a researcher, you deliberately separate them in order to avoid your theories playing a disproportionate role in shaping what outcomes your chosen methods produce.
Introspectively engage in an ongoing dialectic between the application of theories and methods to help enable you to use the outcomes from your methods to interrogate and develop new theories, or ways of framing conceptually the research problem. This is how scholarship grows and branches out into new intellectual territory.
Reynolds, R. Larry. Ways of Knowing. Alternative Microeconomics . Part 1, Chapter 3. Boise State University; The Theory-Method Relationship. S-Cool Revision. United Kingdom.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Methods and the Methodology
Do not confuse the terms "methods" and "methodology." As Schneider notes, a method refers to the technical steps taken to do research . Descriptions of methods usually include defining and stating why you have chosen specific techniques to investigate a research problem, followed by an outline of the procedures you used to systematically select, gather, and process the data [remember to always save the interpretation of data for the discussion section of your paper].
The methodology refers to a discussion of the underlying reasoning why particular methods were used . This discussion includes describing the theoretical concepts that inform the choice of methods to be applied, placing the choice of methods within the more general nature of academic work, and reviewing its relevance to examining the research problem. The methodology section also includes a thorough review of the methods other scholars have used to study the topic.
Bryman, Alan. "Of Methods and Methodology." Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management: An International Journal 3 (2008): 159-168; Schneider, Florian. “What's in a Methodology: The Difference between Method, Methodology, and Theory…and How to Get the Balance Right?” PoliticsEastAsia.com. Chinese Department, University of Leiden, Netherlands.
- << Previous: Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Next: Qualitative Methods >>
- Last Updated: Oct 24, 2024 10:02 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
Published on 25 February 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research.
It should include:
- The type of research you conducted
- How you collected and analysed your data
- Any tools or materials you used in the research
- Why you chose these methods
- Your methodology section should generally be written in the past tense .
- Academic style guides in your field may provide detailed guidelines on what to include for different types of studies.
- Your citation style might provide guidelines for your methodology section (e.g., an APA Style methods section ).
Make your writing flawless in 1 upload
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
How to write a research methodology, why is a methods section important, step 1: explain your methodological approach, step 2: describe your data collection methods, step 3: describe your analysis method, step 4: evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made, tips for writing a strong methodology chapter, frequently asked questions about methodology.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Upload my document
Your methods section is your opportunity to share how you conducted your research and why you chose the methods you chose. It’s also the place to show that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated .
It gives your research legitimacy and situates it within your field, and also gives your readers a place to refer to if they have any questions or critiques in other sections.
You can start by introducing your overall approach to your research. You have two options here.
Option 1: Start with your “what”
What research problem or question did you investigate?
- Aim to describe the characteristics of something?
- Explore an under-researched topic?
- Establish a causal relationship?
And what type of data did you need to achieve this aim?
- Quantitative data , qualitative data , or a mix of both?
- Primary data collected yourself, or secondary data collected by someone else?
- Experimental data gathered by controlling and manipulating variables, or descriptive data gathered via observations?
Option 2: Start with your “why”
Depending on your discipline, you can also start with a discussion of the rationale and assumptions underpinning your methodology. In other words, why did you choose these methods for your study?
- Why is this the best way to answer your research question?
- Is this a standard methodology in your field, or does it require justification?
- Were there any ethical considerations involved in your choices?
- What are the criteria for validity and reliability in this type of research ?
Once you have introduced your reader to your methodological approach, you should share full details about your data collection methods .
Quantitative methods
In order to be considered generalisable, you should describe quantitative research methods in enough detail for another researcher to replicate your study.
Here, explain how you operationalised your concepts and measured your variables. Discuss your sampling method or inclusion/exclusion criteria, as well as any tools, procedures, and materials you used to gather your data.
Surveys Describe where, when, and how the survey was conducted.
- How did you design the questionnaire?
- What form did your questions take (e.g., multiple choice, Likert scale )?
- Were your surveys conducted in-person or virtually?
- What sampling method did you use to select participants?
- What was your sample size and response rate?
Experiments Share full details of the tools, techniques, and procedures you used to conduct your experiment.
- How did you design the experiment ?
- How did you recruit participants?
- How did you manipulate and measure the variables ?
- What tools did you use?
Existing data Explain how you gathered and selected the material (such as datasets or archival data) that you used in your analysis.
- Where did you source the material?
- How was the data originally produced?
- What criteria did you use to select material (e.g., date range)?
The survey consisted of 5 multiple-choice questions and 10 questions measured on a 7-point Likert scale.
The goal was to collect survey responses from 350 customers visiting the fitness apparel company’s brick-and-mortar location in Boston on 4–8 July 2022, between 11:00 and 15:00.
Here, a customer was defined as a person who had purchased a product from the company on the day they took the survey. Participants were given 5 minutes to fill in the survey anonymously. In total, 408 customers responded, but not all surveys were fully completed. Due to this, 371 survey results were included in the analysis.
Qualitative methods
In qualitative research , methods are often more flexible and subjective. For this reason, it’s crucial to robustly explain the methodology choices you made.
Be sure to discuss the criteria you used to select your data, the context in which your research was conducted, and the role you played in collecting your data (e.g., were you an active participant, or a passive observer?)
Interviews or focus groups Describe where, when, and how the interviews were conducted.
- How did you find and select participants?
- How many participants took part?
- What form did the interviews take ( structured , semi-structured , or unstructured )?
- How long were the interviews?
- How were they recorded?
Participant observation Describe where, when, and how you conducted the observation or ethnography .
- What group or community did you observe? How long did you spend there?
- How did you gain access to this group? What role did you play in the community?
- How long did you spend conducting the research? Where was it located?
- How did you record your data (e.g., audiovisual recordings, note-taking)?
Existing data Explain how you selected case study materials for your analysis.
- What type of materials did you analyse?
- How did you select them?
In order to gain better insight into possibilities for future improvement of the fitness shop’s product range, semi-structured interviews were conducted with 8 returning customers.
Here, a returning customer was defined as someone who usually bought products at least twice a week from the store.
Surveys were used to select participants. Interviews were conducted in a small office next to the cash register and lasted approximately 20 minutes each. Answers were recorded by note-taking, and seven interviews were also filmed with consent. One interviewee preferred not to be filmed.
Mixed methods
Mixed methods research combines quantitative and qualitative approaches. If a standalone quantitative or qualitative study is insufficient to answer your research question, mixed methods may be a good fit for you.
Mixed methods are less common than standalone analyses, largely because they require a great deal of effort to pull off successfully. If you choose to pursue mixed methods, it’s especially important to robustly justify your methods here.
Next, you should indicate how you processed and analysed your data. Avoid going into too much detail: you should not start introducing or discussing any of your results at this stage.
In quantitative research , your analysis will be based on numbers. In your methods section, you can include:
- How you prepared the data before analysing it (e.g., checking for missing data , removing outliers , transforming variables)
- Which software you used (e.g., SPSS, Stata or R)
- Which statistical tests you used (e.g., two-tailed t test , simple linear regression )
In qualitative research, your analysis will be based on language, images, and observations (often involving some form of textual analysis ).
Specific methods might include:
- Content analysis : Categorising and discussing the meaning of words, phrases and sentences
- Thematic analysis : Coding and closely examining the data to identify broad themes and patterns
- Discourse analysis : Studying communication and meaning in relation to their social context
Mixed methods combine the above two research methods, integrating both qualitative and quantitative approaches into one coherent analytical process.
Above all, your methodology section should clearly make the case for why you chose the methods you did. This is especially true if you did not take the most standard approach to your topic. In this case, discuss why other methods were not suitable for your objectives, and show how this approach contributes new knowledge or understanding.
In any case, it should be overwhelmingly clear to your reader that you set yourself up for success in terms of your methodology’s design. Show how your methods should lead to results that are valid and reliable, while leaving the analysis of the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results for your discussion section .
- Quantitative: Lab-based experiments cannot always accurately simulate real-life situations and behaviours, but they are effective for testing causal relationships between variables .
- Qualitative: Unstructured interviews usually produce results that cannot be generalised beyond the sample group , but they provide a more in-depth understanding of participants’ perceptions, motivations, and emotions.
- Mixed methods: Despite issues systematically comparing differing types of data, a solely quantitative study would not sufficiently incorporate the lived experience of each participant, while a solely qualitative study would be insufficiently generalisable.
Remember that your aim is not just to describe your methods, but to show how and why you applied them. Again, it’s critical to demonstrate that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated.
1. Focus on your objectives and research questions
The methodology section should clearly show why your methods suit your objectives and convince the reader that you chose the best possible approach to answering your problem statement and research questions .
2. Cite relevant sources
Your methodology can be strengthened by referencing existing research in your field. This can help you to:
- Show that you followed established practice for your type of research
- Discuss how you decided on your approach by evaluating existing research
- Present a novel methodological approach to address a gap in the literature
3. Write for your audience
Consider how much information you need to give, and avoid getting too lengthy. If you are using methods that are standard for your discipline, you probably don’t need to give a lot of background or justification.
Regardless, your methodology should be a clear, well-structured text that makes an argument for your approach, not just a list of technical details and procedures.
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research. Developing your methodology involves studying the research methods used in your field and the theories or principles that underpin them, in order to choose the approach that best matches your objectives.
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyse data (e.g. interviews, experiments , surveys , statistical tests ).
In a dissertation or scientific paper, the methodology chapter or methods section comes after the introduction and before the results , discussion and conclusion .
Depending on the length and type of document, you might also include a literature review or theoretical framework before the methodology.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research.
For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
Statistical sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population. There are various sampling methods you can use to ensure that your sample is representative of the population as a whole.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 October 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/methodology/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
- Table of Contents

Dissertation Methodology
In any research, the methodology chapter is one of the key components of your dissertation. It provides a detailed description of the methods you used to conduct your research and helps readers understand how you obtained your data and how you plan to analyze it. This section is crucial for replicating the study and validating its results.
Here are the basic elements that are typically included in a dissertation methodology:
- Introduction : This section should explain the importance and goals of your research .
- Research Design : Outline your research approach and why it’s appropriate for your study. You might be conducting an experimental research, a qualitative research, a quantitative research, or a mixed-methods research.
- Data Collection : This section should detail the methods you used to collect your data. Did you use surveys, interviews, observations, etc.? Why did you choose these methods? You should also include who your participants were, how you recruited them, and any ethical considerations.
- Data Analysis : Explain how you intend to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, thematic analysis, content analysis, etc., depending on the nature of your study.
- Reliability and Validity : Discuss how you’ve ensured the reliability and validity of your study. For instance, you could discuss measures taken to reduce bias, how you ensured that your measures accurately capture what they were intended to, or how you will handle any limitations in your study.
- Ethical Considerations : This is where you state how you have considered ethical issues related to your research, how you have protected the participants’ rights, and how you have complied with the relevant ethical guidelines.
- Limitations : Acknowledge any limitations of your methodology, including any biases and constraints that might have affected your study.
- Summary : Recap the key points of your methodology chapter, highlighting the overall approach and rationalization of your research.
Types of Dissertation Methodology
The type of methodology you choose for your dissertation will depend on the nature of your research question and the field you’re working in. Here are some of the most common types of methodologies used in dissertations:
Experimental Research
This involves creating an experiment that will test your hypothesis. You’ll need to design an experiment, manipulate variables, collect data, and analyze that data to draw conclusions. This is commonly used in fields like psychology, biology, and physics.
Survey Research
This type of research involves gathering data from a large number of participants using tools like questionnaires or surveys. It can be used to collect a large amount of data and is often used in fields like sociology, marketing, and public health.
Qualitative Research
This type of research is used to explore complex phenomena that can’t be easily quantified. Methods include interviews, focus groups, and observations. This methodology is common in fields like anthropology, sociology, and education.
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research uses numerical data to answer research questions. This can include statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. It’s common in fields like economics, psychology, and health sciences.
Case Study Research
This type of research involves in-depth investigation of a particular case, such as an individual, group, or event. This methodology is often used in psychology, social sciences, and business.
Mixed Methods Research
This combines qualitative and quantitative research methods in a single study. It’s used to answer more complex research questions and is becoming more popular in fields like social sciences, health sciences, and education.
Action Research
This type of research involves taking action and then reflecting upon the results. This cycle of action-reflection-action continues throughout the study. It’s often used in fields like education and organizational development.
Longitudinal Research
This type of research involves studying the same group of individuals over an extended period of time. This could involve surveys, observations, or experiments. It’s common in fields like psychology, sociology, and medicine.
Ethnographic Research
This type of research involves the in-depth study of people and cultures. Researchers immerse themselves in the culture they’re studying to collect data. This is often used in fields like anthropology and social sciences.
Structure of Dissertation Methodology
The structure of a dissertation methodology can vary depending on your field of study, the nature of your research, and the guidelines of your institution. However, a standard structure typically includes the following elements:
- Introduction : Briefly introduce your overall approach to the research. Explain what you plan to explore and why it’s important.
- Research Design/Approach : Describe your overall research design. This can be qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods. Explain the rationale behind your chosen design and why it is suitable for your research questions or hypotheses.
- Data Collection Methods : Detail the methods you used to collect your data. You should include what type of data you collected, how you collected it, and why you chose this method. If relevant, you can also include information about your sample population, such as how many people participated, how they were chosen, and any relevant demographic information.
- Data Analysis Methods : Explain how you plan to analyze your collected data. This will depend on the nature of your data. For example, if you collected quantitative data, you might discuss statistical analysis techniques. If you collected qualitative data, you might discuss coding strategies, thematic analysis, or narrative analysis.
- Reliability and Validity : Discuss how you’ve ensured the reliability and validity of your research. This might include steps you took to reduce bias or increase the accuracy of your measurements.
- Ethical Considerations : If relevant, discuss any ethical issues associated with your research. This might include how you obtained informed consent from participants, how you ensured participants’ privacy and confidentiality, or any potential conflicts of interest.
- Limitations : Acknowledge any limitations in your research methodology. This could include potential sources of bias, difficulties with data collection, or limitations in your analysis methods.
- Summary/Conclusion : Briefly summarize the key points of your methodology, emphasizing how it helps answer your research questions or hypotheses.
How to Write Dissertation Methodology
Writing a dissertation methodology requires you to be clear and precise about the way you’ve carried out your research. It’s an opportunity to convince your readers of the appropriateness and reliability of your approach to your research question. Here is a basic guideline on how to write your methodology section:
1. Introduction
Start your methodology section by restating your research question(s) or objective(s). This ensures your methodology directly ties into the aim of your research.
2. Approach
Identify your overall approach: qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods. Explain why you have chosen this approach.
- Qualitative methods are typically used for exploratory research and involve collecting non-numerical data. This might involve interviews, observations, or analysis of texts.
- Quantitative methods are used for research that relies on numerical data. This might involve surveys, experiments, or statistical analysis.
- Mixed methods use a combination of both qualitative and quantitative research methods.
3. Research Design
Describe the overall design of your research. This could involve explaining the type of study (e.g., case study, ethnography, experimental research, etc.), how you’ve defined and measured your variables, and any control measures you’ve implemented.
4. Data Collection
Explain in detail how you collected your data.
- If you’ve used qualitative methods, you might detail how you selected participants for interviews or focus groups, how you conducted observations, or how you analyzed existing texts.
- If you’ve used quantitative methods, you might detail how you designed your survey or experiment, how you collected responses, and how you ensured your data is reliable and valid.
5. Data Analysis
Describe how you analyzed your data.
- If you’re doing qualitative research, this might involve thematic analysis, discourse analysis, or grounded theory.
- If you’re doing quantitative research, you might be conducting statistical tests, regression analysis, or factor analysis.
Discuss any ethical issues related to your research. This might involve explaining how you obtained informed consent, how you’re protecting participants’ privacy, or how you’re managing any potential harms to participants.
7. Reliability and Validity
Discuss the steps you’ve taken to ensure the reliability and validity of your data.
- Reliability refers to the consistency of your measurements, and you might discuss how you’ve piloted your instruments or used standardized measures.
- Validity refers to the accuracy of your measurements, and you might discuss how you’ve ensured your measures reflect the concepts they’re supposed to measure.
8. Limitations
Every study has its limitations. Discuss the potential weaknesses of your chosen methods and explain any obstacles you faced in your research.
9. Conclusion
Summarize the key points of your methodology, emphasizing how it helps to address your research question or objective.
Example of Dissertation Methodology
An Example of Dissertation Methodology is as follows:
Chapter 3: Methodology
- Introduction
This chapter details the methodology adopted in this research. The study aimed to explore the relationship between stress and productivity in the workplace. A mixed-methods research design was used to collect and analyze data.
Research Design
This study adopted a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys with qualitative interviews to provide a comprehensive understanding of the research problem. The rationale for this approach is that while quantitative data can provide a broad overview of the relationships between variables, qualitative data can provide deeper insights into the nuances of these relationships.
Data Collection Methods
Quantitative Data Collection : An online self-report questionnaire was used to collect data from participants. The questionnaire consisted of two standardized scales: the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) to measure stress levels and the Individual Work Productivity Questionnaire (IWPQ) to measure productivity. The sample consisted of 200 office workers randomly selected from various companies in the city.
Qualitative Data Collection : Semi-structured interviews were conducted with 20 participants chosen from the initial sample. The interview guide included questions about participants’ experiences with stress and how they perceived its impact on their productivity.
Data Analysis Methods
Quantitative Data Analysis : Descriptive and inferential statistics were used to analyze the survey data. Pearson’s correlation was used to examine the relationship between stress and productivity.
Qualitative Data Analysis : Interviews were transcribed and subjected to thematic analysis using NVivo software. This process allowed for identifying and analyzing patterns and themes regarding the impact of stress on productivity.
Reliability and Validity
To ensure reliability and validity, standardized measures with good psychometric properties were used. In qualitative data analysis, triangulation was employed by having two researchers independently analyze the data and then compare findings.
Ethical Considerations
All participants provided informed consent prior to their involvement in the study. They were informed about the purpose of the study, their rights as participants, and the confidentiality of their responses.
Limitations
The main limitation of this study is its reliance on self-report measures, which can be subject to biases such as social desirability bias. Moreover, the sample was drawn from a single city, which may limit the generalizability of the findings.
Where to Write Dissertation Methodology
In a dissertation or thesis, the Methodology section usually follows the Literature Review. This placement allows the Methodology to build upon the theoretical framework and existing research outlined in the Literature Review, and precedes the Results or Findings section. Here’s a basic outline of how most dissertations are structured:
- Acknowledgements
- Literature Review (or it may be interspersed throughout the dissertation)
- Methodology
- Results/Findings
- References/Bibliography
In the Methodology chapter, you will discuss the research design, data collection methods, data analysis methods, and any ethical considerations pertaining to your study. This allows your readers to understand how your research was conducted and how you arrived at your results.
Advantages of Dissertation Methodology
The dissertation methodology section plays an important role in a dissertation for several reasons. Here are some of the advantages of having a well-crafted methodology section in your dissertation:
- Clarifies Your Research Approach : The methodology section explains how you plan to tackle your research question, providing a clear plan for data collection and analysis.
- Enables Replication : A detailed methodology allows other researchers to replicate your study. Replication is an important aspect of scientific research because it provides validation of the study’s results.
- Demonstrates Rigor : A well-written methodology shows that you’ve thought critically about your research methods and have chosen the most appropriate ones for your research question. This adds credibility to your study.
- Enhances Transparency : Detailing your methods allows readers to understand the steps you took in your research. This increases the transparency of your study and allows readers to evaluate potential biases or limitations.
- Helps in Addressing Research Limitations : In your methodology section, you can acknowledge and explain the limitations of your research. This is important as it shows you understand that no research method is perfect and there are always potential weaknesses.
- Facilitates Peer Review : A detailed methodology helps peer reviewers assess the soundness of your research design. This is an important part of the publication process if you aim to publish your dissertation in a peer-reviewed journal.
- Establishes the Validity and Reliability : Your methodology section should also include a discussion of the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your measurements, which is crucial for establishing the overall quality of your research.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Methodology – Types, Examples and...

Research Results Section – Writing Guide and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Implications in Research – Types, Examples and...

Thesis Statement – Examples, Writing Guide

Informed Consent in Research – Types, Templates...
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Your Methods

Ensure understanding, reproducibility and replicability
What should you include in your methods section, and how much detail is appropriate?
Why Methods Matter
The methods section was once the most likely part of a paper to be unfairly abbreviated, overly summarized, or even relegated to hard-to-find sections of a publisher’s website. While some journals may responsibly include more detailed elements of methods in supplementary sections, the movement for increased reproducibility and rigor in science has reinstated the importance of the methods section. Methods are now viewed as a key element in establishing the credibility of the research being reported, alongside the open availability of data and results.
A clear methods section impacts editorial evaluation and readers’ understanding, and is also the backbone of transparency and replicability.
For example, the Reproducibility Project: Cancer Biology project set out in 2013 to replicate experiments from 50 high profile cancer papers, but revised their target to 18 papers once they understood how much methodological detail was not contained in the original papers.
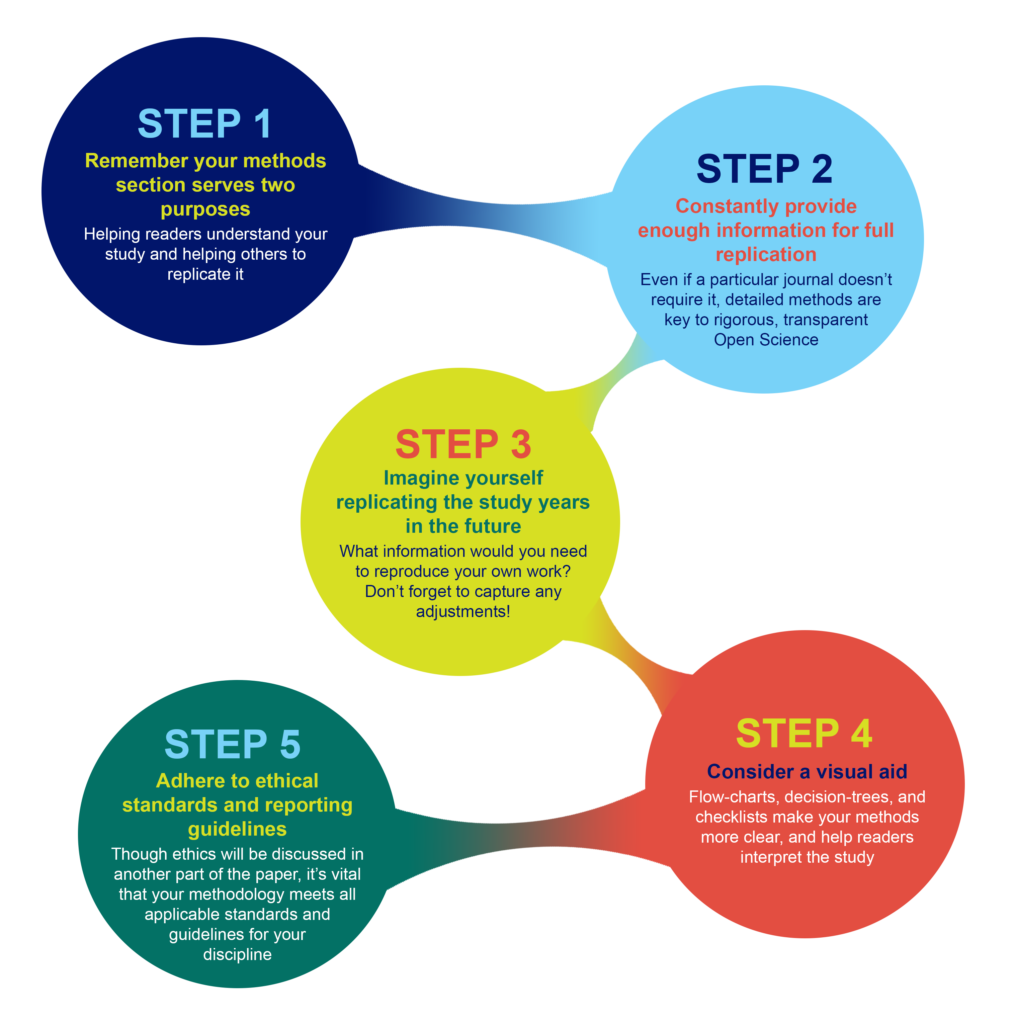
What to include in your methods section
What you include in your methods sections depends on what field you are in and what experiments you are performing. However, the general principle in place at the majority of journals is summarized well by the guidelines at PLOS ONE : “The Materials and Methods section should provide enough detail to allow suitably skilled investigators to fully replicate your study. ” The emphases here are deliberate: the methods should enable readers to understand your paper, and replicate your study. However, there is no need to go into the level of detail that a lay-person would require—the focus is on the reader who is also trained in your field, with the suitable skills and knowledge to attempt a replication.
A constant principle of rigorous science
A methods section that enables other researchers to understand and replicate your results is a constant principle of rigorous, transparent, and Open Science. Aim to be thorough, even if a particular journal doesn’t require the same level of detail . Reproducibility is all of our responsibility. You cannot create any problems by exceeding a minimum standard of information. If a journal still has word-limits—either for the overall article or specific sections—and requires some methodological details to be in a supplemental section, that is OK as long as the extra details are searchable and findable .
Imagine replicating your own work, years in the future
As part of PLOS’ presentation on Reproducibility and Open Publishing (part of UCSF’s Reproducibility Series ) we recommend planning the level of detail in your methods section by imagining you are writing for your future self, replicating your own work. When you consider that you might be at a different institution, with different account logins, applications, resources, and access levels—you can help yourself imagine the level of specificity that you yourself would require to redo the exact experiment. Consider:
- Which details would you need to be reminded of?
- Which cell line, or antibody, or software, or reagent did you use, and does it have a Research Resource ID (RRID) that you can cite?
- Which version of a questionnaire did you use in your survey?
- Exactly which visual stimulus did you show participants, and is it publicly available?
- What participants did you decide to exclude?
- What process did you adjust, during your work?
Tip: Be sure to capture any changes to your protocols
You yourself would want to know about any adjustments, if you ever replicate the work, so you can surmise that anyone else would want to as well. Even if a necessary adjustment you made was not ideal, transparency is the key to ensuring this is not regarded as an issue in the future. It is far better to transparently convey any non-optimal methods, or methodological constraints, than to conceal them, which could result in reproducibility or ethical issues downstream.
Visual aids for methods help when reading the whole paper
Consider whether a visual representation of your methods could be appropriate or aid understanding your process. A visual reference readers can easily return to, like a flow-diagram, decision-tree, or checklist, can help readers to better understand the complete article, not just the methods section.
Ethical Considerations
In addition to describing what you did, it is just as important to assure readers that you also followed all relevant ethical guidelines when conducting your research. While ethical standards and reporting guidelines are often presented in a separate section of a paper, ensure that your methods and protocols actually follow these guidelines. Read more about ethics .
Existing standards, checklists, guidelines, partners
While the level of detail contained in a methods section should be guided by the universal principles of rigorous science outlined above, various disciplines, fields, and projects have worked hard to design and develop consistent standards, guidelines, and tools to help with reporting all types of experiment. Below, you’ll find some of the key initiatives. Ensure you read the submission guidelines for the specific journal you are submitting to, in order to discover any further journal- or field-specific policies to follow, or initiatives/tools to utilize.
Tip: Keep your paper moving forward by providing the proper paperwork up front
Be sure to check the journal guidelines and provide the necessary documents with your manuscript submission. Collecting the necessary documentation can greatly slow the first round of peer review, or cause delays when you submit your revision.
Randomized Controlled Trials – CONSORT The Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) project covers various initiatives intended to prevent the problems of inadequate reporting of randomized controlled trials. The primary initiative is an evidence-based minimum set of recommendations for reporting randomized trials known as the CONSORT Statement .
Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses – PRISMA The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses ( PRISMA ) is an evidence-based minimum set of items focusing on the reporting of reviews evaluating randomized trials and other types of research.
Research using Animals – ARRIVE The Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments ( ARRIVE ) guidelines encourage maximizing the information reported in research using animals thereby minimizing unnecessary studies. (Original study and proposal , and updated guidelines , in PLOS Biology .)
Laboratory Protocols Protocols.io has developed a platform specifically for the sharing and updating of laboratory protocols , which are assigned their own DOI and can be linked from methods sections of papers to enhance reproducibility. Contextualize your protocol and improve discovery with an accompanying Lab Protocol article in PLOS ONE .
Consistent reporting of Materials, Design, and Analysis – the MDAR checklist A cross-publisher group of editors and experts have developed, tested, and rolled out a checklist to help establish and harmonize reporting standards in the Life Sciences . The checklist , which is available for use by authors to compile their methods, and editors/reviewers to check methods, establishes a minimum set of requirements in transparent reporting and is adaptable to any discipline within the Life Sciences, by covering a breadth of potentially relevant methodological items and considerations. If you are in the Life Sciences and writing up your methods section, try working through the MDAR checklist and see whether it helps you include all relevant details into your methods, and whether it reminded you of anything you might have missed otherwise.
Summary Writing tips
The main challenge you may find when writing your methods is keeping it readable AND covering all the details needed for reproducibility and replicability. While this is difficult, do not compromise on rigorous standards for credibility!

- Keep in mind future replicability, alongside understanding and readability.
- Follow checklists, and field- and journal-specific guidelines.
- Consider a commitment to rigorous and transparent science a personal responsibility, and not just adhering to journal guidelines.
- Establish whether there are persistent identifiers for any research resources you use that can be specifically cited in your methods section.
- Deposit your laboratory protocols in Protocols.io, establishing a permanent link to them. You can update your protocols later if you improve on them, as can future scientists who follow your protocols.
- Consider visual aids like flow-diagrams, lists, to help with reading other sections of the paper.
- Be specific about all decisions made during the experiments that someone reproducing your work would need to know.

Don’t
- Summarize or abbreviate methods without giving full details in a discoverable supplemental section.
- Presume you will always be able to remember how you performed the experiments, or have access to private or institutional notebooks and resources.
- Attempt to hide constraints or non-optimal decisions you had to make–transparency is the key to ensuring the credibility of your research.
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…

What is Research Methodology? Definition, Types, and Examples

Research methodology 1,2 is a structured and scientific approach used to collect, analyze, and interpret quantitative or qualitative data to answer research questions or test hypotheses. A research methodology is like a plan for carrying out research and helps keep researchers on track by limiting the scope of the research. Several aspects must be considered before selecting an appropriate research methodology, such as research limitations and ethical concerns that may affect your research.
The research methodology section in a scientific paper describes the different methodological choices made, such as the data collection and analysis methods, and why these choices were selected. The reasons should explain why the methods chosen are the most appropriate to answer the research question. A good research methodology also helps ensure the reliability and validity of the research findings. There are three types of research methodology—quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-method, which can be chosen based on the research objectives.
What is research methodology ?
A research methodology describes the techniques and procedures used to identify and analyze information regarding a specific research topic. It is a process by which researchers design their study so that they can achieve their objectives using the selected research instruments. It includes all the important aspects of research, including research design, data collection methods, data analysis methods, and the overall framework within which the research is conducted. While these points can help you understand what is research methodology, you also need to know why it is important to pick the right methodology.

Having a good research methodology in place has the following advantages: 3
- Helps other researchers who may want to replicate your research; the explanations will be of benefit to them.
- You can easily answer any questions about your research if they arise at a later stage.
- A research methodology provides a framework and guidelines for researchers to clearly define research questions, hypotheses, and objectives.
- It helps researchers identify the most appropriate research design, sampling technique, and data collection and analysis methods.
- A sound research methodology helps researchers ensure that their findings are valid and reliable and free from biases and errors.
- It also helps ensure that ethical guidelines are followed while conducting research.
- A good research methodology helps researchers in planning their research efficiently, by ensuring optimum usage of their time and resources.
Writing the methods section of a research paper? Let Paperpal help you achieve perfection
Types of research methodology.
There are three types of research methodology based on the type of research and the data required. 1
- Quantitative research methodology focuses on measuring and testing numerical data. This approach is good for reaching a large number of people in a short amount of time. This type of research helps in testing the causal relationships between variables, making predictions, and generalizing results to wider populations.
- Qualitative research methodology examines the opinions, behaviors, and experiences of people. It collects and analyzes words and textual data. This research methodology requires fewer participants but is still more time consuming because the time spent per participant is quite large. This method is used in exploratory research where the research problem being investigated is not clearly defined.
- Mixed-method research methodology uses the characteristics of both quantitative and qualitative research methodologies in the same study. This method allows researchers to validate their findings, verify if the results observed using both methods are complementary, and explain any unexpected results obtained from one method by using the other method.
What are the types of sampling designs in research methodology?
Sampling 4 is an important part of a research methodology and involves selecting a representative sample of the population to conduct the study, making statistical inferences about them, and estimating the characteristics of the whole population based on these inferences. There are two types of sampling designs in research methodology—probability and nonprobability.
- Probability sampling
In this type of sampling design, a sample is chosen from a larger population using some form of random selection, that is, every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. The different types of probability sampling are:
- Systematic —sample members are chosen at regular intervals. It requires selecting a starting point for the sample and sample size determination that can be repeated at regular intervals. This type of sampling method has a predefined range; hence, it is the least time consuming.
- Stratified —researchers divide the population into smaller groups that don’t overlap but represent the entire population. While sampling, these groups can be organized, and then a sample can be drawn from each group separately.
- Cluster —the population is divided into clusters based on demographic parameters like age, sex, location, etc.
- Convenience —selects participants who are most easily accessible to researchers due to geographical proximity, availability at a particular time, etc.
- Purposive —participants are selected at the researcher’s discretion. Researchers consider the purpose of the study and the understanding of the target audience.
- Snowball —already selected participants use their social networks to refer the researcher to other potential participants.
- Quota —while designing the study, the researchers decide how many people with which characteristics to include as participants. The characteristics help in choosing people most likely to provide insights into the subject.
What are data collection methods?
During research, data are collected using various methods depending on the research methodology being followed and the research methods being undertaken. Both qualitative and quantitative research have different data collection methods, as listed below.
Qualitative research 5
- One-on-one interviews: Helps the interviewers understand a respondent’s subjective opinion and experience pertaining to a specific topic or event
- Document study/literature review/record keeping: Researchers’ review of already existing written materials such as archives, annual reports, research articles, guidelines, policy documents, etc.
- Focus groups: Constructive discussions that usually include a small sample of about 6-10 people and a moderator, to understand the participants’ opinion on a given topic.
- Qualitative observation : Researchers collect data using their five senses (sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing).
Quantitative research 6
- Sampling: The most common type is probability sampling.
- Interviews: Commonly telephonic or done in-person.
- Observations: Structured observations are most commonly used in quantitative research. In this method, researchers make observations about specific behaviors of individuals in a structured setting.
- Document review: Reviewing existing research or documents to collect evidence for supporting the research.
- Surveys and questionnaires. Surveys can be administered both online and offline depending on the requirement and sample size.
Let Paperpal help you write the perfect research methods section. Start now!
What are data analysis methods.
The data collected using the various methods for qualitative and quantitative research need to be analyzed to generate meaningful conclusions. These data analysis methods 7 also differ between quantitative and qualitative research.
Quantitative research involves a deductive method for data analysis where hypotheses are developed at the beginning of the research and precise measurement is required. The methods include statistical analysis applications to analyze numerical data and are grouped into two categories—descriptive and inferential.
Descriptive analysis is used to describe the basic features of different types of data to present it in a way that ensures the patterns become meaningful. The different types of descriptive analysis methods are:
- Measures of frequency (count, percent, frequency)
- Measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode)
- Measures of dispersion or variation (range, variance, standard deviation)
- Measure of position (percentile ranks, quartile ranks)
Inferential analysis is used to make predictions about a larger population based on the analysis of the data collected from a smaller population. This analysis is used to study the relationships between different variables. Some commonly used inferential data analysis methods are:
- Correlation: To understand the relationship between two or more variables.
- Cross-tabulation: Analyze the relationship between multiple variables.
- Regression analysis: Study the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable.
- Frequency tables: To understand the frequency of data.
- Analysis of variance: To test the degree to which two or more variables differ in an experiment.
Qualitative research involves an inductive method for data analysis where hypotheses are developed after data collection. The methods include:
- Content analysis: For analyzing documented information from text and images by determining the presence of certain words or concepts in texts.
- Narrative analysis: For analyzing content obtained from sources such as interviews, field observations, and surveys. The stories and opinions shared by people are used to answer research questions.
- Discourse analysis: For analyzing interactions with people considering the social context, that is, the lifestyle and environment, under which the interaction occurs.
- Grounded theory: Involves hypothesis creation by data collection and analysis to explain why a phenomenon occurred.
- Thematic analysis: To identify important themes or patterns in data and use these to address an issue.
How to choose a research methodology?
Here are some important factors to consider when choosing a research methodology: 8
- Research objectives, aims, and questions —these would help structure the research design.
- Review existing literature to identify any gaps in knowledge.
- Check the statistical requirements —if data-driven or statistical results are needed then quantitative research is the best. If the research questions can be answered based on people’s opinions and perceptions, then qualitative research is most suitable.
- Sample size —sample size can often determine the feasibility of a research methodology. For a large sample, less effort- and time-intensive methods are appropriate.
- Constraints —constraints of time, geography, and resources can help define the appropriate methodology.
Got writer’s block? Kickstart your research paper writing with Paperpal now!
How to write a research methodology .
A research methodology should include the following components: 3,9
- Research design —should be selected based on the research question and the data required. Common research designs include experimental, quasi-experimental, correlational, descriptive, and exploratory.
- Research method —this can be quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method.
- Reason for selecting a specific methodology —explain why this methodology is the most suitable to answer your research problem.
- Research instruments —explain the research instruments you plan to use, mainly referring to the data collection methods such as interviews, surveys, etc. Here as well, a reason should be mentioned for selecting the particular instrument.
- Sampling —this involves selecting a representative subset of the population being studied.
- Data collection —involves gathering data using several data collection methods, such as surveys, interviews, etc.
- Data analysis —describe the data analysis methods you will use once you’ve collected the data.
- Research limitations —mention any limitations you foresee while conducting your research.
- Validity and reliability —validity helps identify the accuracy and truthfulness of the findings; reliability refers to the consistency and stability of the results over time and across different conditions.
- Ethical considerations —research should be conducted ethically. The considerations include obtaining consent from participants, maintaining confidentiality, and addressing conflicts of interest.
Streamline Your Research Paper Writing Process with Paperpal
The methods section is a critical part of the research papers, allowing researchers to use this to understand your findings and replicate your work when pursuing their own research. However, it is usually also the most difficult section to write. This is where Paperpal can help you overcome the writer’s block and create the first draft in minutes with Paperpal Copilot, its secure generative AI feature suite.
With Paperpal you can get research advice, write and refine your work, rephrase and verify the writing, and ensure submission readiness, all in one place. Here’s how you can use Paperpal to develop the first draft of your methods section.
- Generate an outline: Input some details about your research to instantly generate an outline for your methods section
- Develop the section: Use the outline and suggested sentence templates to expand your ideas and develop the first draft.
- P araph ras e and trim : Get clear, concise academic text with paraphrasing that conveys your work effectively and word reduction to fix redundancies.
- Choose the right words: Enhance text by choosing contextual synonyms based on how the words have been used in previously published work.
- Check and verify text : Make sure the generated text showcases your methods correctly, has all the right citations, and is original and authentic. .
You can repeat this process to develop each section of your research manuscript, including the title, abstract and keywords. Ready to write your research papers faster, better, and without the stress? Sign up for Paperpal and start writing today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the key components of research methodology?
A1. A good research methodology has the following key components:
- Research design
- Data collection procedures
- Data analysis methods
- Ethical considerations
Q2. Why is ethical consideration important in research methodology?
A2. Ethical consideration is important in research methodology to ensure the readers of the reliability and validity of the study. Researchers must clearly mention the ethical norms and standards followed during the conduct of the research and also mention if the research has been cleared by any institutional board. The following 10 points are the important principles related to ethical considerations: 10
- Participants should not be subjected to harm.
- Respect for the dignity of participants should be prioritized.
- Full consent should be obtained from participants before the study.
- Participants’ privacy should be ensured.
- Confidentiality of the research data should be ensured.
- Anonymity of individuals and organizations participating in the research should be maintained.
- The aims and objectives of the research should not be exaggerated.
- Affiliations, sources of funding, and any possible conflicts of interest should be declared.
- Communication in relation to the research should be honest and transparent.
- Misleading information and biased representation of primary data findings should be avoided.

Q3. What is the difference between methodology and method?
A3. Research methodology is different from a research method, although both terms are often confused. Research methods are the tools used to gather data, while the research methodology provides a framework for how research is planned, conducted, and analyzed. The latter guides researchers in making decisions about the most appropriate methods for their research. Research methods refer to the specific techniques, procedures, and tools used by researchers to collect, analyze, and interpret data, for instance surveys, questionnaires, interviews, etc.
Research methodology is, thus, an integral part of a research study. It helps ensure that you stay on track to meet your research objectives and answer your research questions using the most appropriate data collection and analysis tools based on your research design.
Accelerate your research paper writing with Paperpal. Try for free now!
- Research methodologies. Pfeiffer Library website. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://library.tiffin.edu/researchmethodologies/whatareresearchmethodologies
- Types of research methodology. Eduvoice website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://eduvoice.in/types-research-methodology/
- The basics of research methodology: A key to quality research. Voxco. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.voxco.com/blog/what-is-research-methodology/
- Sampling methods: Types with examples. QuestionPro website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.questionpro.com/blog/types-of-sampling-for-social-research/
- What is qualitative research? Methods, types, approaches, examples. Researcher.Life blog. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://researcher.life/blog/article/what-is-qualitative-research-methods-types-examples/
- What is quantitative research? Definition, methods, types, and examples. Researcher.Life blog. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://researcher.life/blog/article/what-is-quantitative-research-types-and-examples/
- Data analysis in research: Types & methods. QuestionPro website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.questionpro.com/blog/data-analysis-in-research/#Data_analysis_in_qualitative_research
- Factors to consider while choosing the right research methodology. PhD Monster website. Accessed August 17, 2023. https://www.phdmonster.com/factors-to-consider-while-choosing-the-right-research-methodology/
- What is research methodology? Research and writing guides. Accessed August 14, 2023. https://paperpile.com/g/what-is-research-methodology/
- Ethical considerations. Business research methodology website. Accessed August 17, 2023. https://research-methodology.net/research-methodology/ethical-considerations/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Dangling Modifiers and How to Avoid Them in Your Writing
- Research Outlines: How to Write An Introduction Section in Minutes with Paperpal Copilot
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
- What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)
Language and Grammar Rules for Academic Writing
Climatic vs. climactic: difference and examples, you may also like, what are the types of literature reviews , abstract vs introduction: what is the difference , mla format: guidelines, template and examples , machine translation vs human translation: which is reliable..., dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write a research proposal: (with examples..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal.
15 Research Methodology Examples

Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch)
Tio Gabunia is an academic writer and architect based in Tbilisi. He has studied architecture, design, and urban planning at the Georgian Technical University and the University of Lisbon. He has worked in these fields in Georgia, Portugal, and France. Most of Tio’s writings concern philosophy. Other writings include architecture, sociology, urban planning, and economics.
Learn about our Editorial Process

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]

Research methodologies can roughly be categorized into three group: quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-methods.
- Qualitative Research : This methodology is based on obtaining deep, contextualized, non-numerical data. It can occur, for example, through open-ended questioning of research particiapnts in order to understand human behavior. It’s all about describing and analyzing subjective phenomena such as emotions or experiences.
- Quantitative Research: This methodology is rationally-based and relies heavily on numerical analysis of empirical data . With quantitative research, you aim for objectivity by creating hypotheses and testing them through experiments or surveys, which allow for statistical analyses.
- Mixed-Methods Research: Mixed-methods research combines both previous types into one project. We have more flexibility when designing our research study with mixed methods since we can use multiple approaches depending on our needs at each time. Using mixed methods can help us validate our results and offer greater predictability than just either type of methodology alone could provide.
Below are research methodologies that fit into each category.

Qualitative Research Methodologies
1. case study.
Conducts an in-depth examination of a specific case, individual, or event to understand a phenomenon.
Instead of examining a whole population for numerical trend data, case study researchers seek in-depth explanations of one event.
The benefit of case study research is its ability to elucidate overlooked details of interesting cases of a phenomenon (Busetto, Wick & Gumbinger, 2020). It offers deep insights for empathetic, reflective, and thoughtful understandings of that phenomenon.
However, case study findings aren’t transferrable to new contexts or for population-wide predictions. Instead, they inform practitioner understandings for nuanced, deep approaches to future instances (Liamputtong, 2020).

2. Grounded Theory
Grounded theory involves generating hypotheses and theories through the collection and interpretation of data (Faggiolani, n.d.). Its distinguishing features is that it doesn’t test a hypothesis generated prior to analysis, but rather generates a hypothesis or ‘theory’ that emerges from the data.
It also involves the application of inductive reasoning and is often contrasted with the hypothetico-deductive model of scientific research. This research methodology was developed by Barney Glaser and Anselm Strauss in the 1960s (Glaser & Strauss, 2009).
The basic difference between traditional scientific approaches to research and grounded theory is that the latter begins with a question, then collects data, and the theoretical framework is said to emerge later from this data.
By contrast, scientists usually begin with an existing theoretical framework , develop hypotheses, and only then start collecting data to verify or falsify the hypotheses.
3. Ethnography
In ethnographic research , the researcher immerses themselves within the group they are studying, often for long periods of time.
This type of research aims to understand the shared beliefs, practices, and values of a particular community by immersing the researcher within the cultural group.
Although ethnographic research cannot predict or identify trends in an entire population, it can create detailed explanations of cultural practices and comparisons between social and cultural groups.
When a person conducts an ethnographic study of themselves or their own culture, it can be considered autoethnography .
Its strength lies in producing comprehensive accounts of groups of people and their interactions.
Common methods researchers use during an ethnographic study include participant observation , thick description, unstructured interviews, and field notes vignettes. These methods can provide detailed and contextualized descriptions of their subjects.
Example Study
Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street by Karen Ho involves an anthropologist who embeds herself with Wall Street firms to study the culture of Wall Street bankers and how this culture affects the broader economy and world.
4. Phenomenology
Phenomenology to understand and describe individuals’ lived experiences concerning a specific phenomenon.
As a research methodology typically used in the social sciences , phenomenology involves the study of social reality as a product of intersubjectivity (the intersection of people’s cognitive perspectives) (Zahavi & Overgaard, n.d.).
This philosophical approach was first developed by Edmund Husserl.
5. Narrative Research
Narrative research explores personal stories and experiences to understand their meanings and interpretations.
It is also known as narrative inquiry and narrative analysis(Riessman, 1993).
This approach to research uses qualitative material like journals, field notes, letters, interviews, texts, photos, etc., as its data.
It is aimed at understanding the way people create meaning through narratives (Clandinin & Connelly, 2004).
6. Discourse Analysis
A discourse analysis examines the structure, patterns, and functions of language in context to understand how the text produces social constructs.
This methodology is common in critical theory , poststructuralism , and postmodernism. Its aim is to understand how language constructs discourses (roughly interpreted as “ways of thinking and constructing knowledge”).
As a qualitative methodology , its focus is on developing themes through close textual analysis rather than using numerical methods. Common methods for extracting data include semiotics and linguistic analysis.
7. Action Research
Action research involves researchers working collaboratively with stakeholders to address problems, develop interventions, and evaluate effectiveness.
Action research is a methodology and philosophy of research that is common in the social sciences.
The term was first coined in 1944 by Kurt Lewin, a German-American psychologist who also introduced applied research and group communication (Altrichter & Gstettner, 1993).
Lewin originally defined action research as involving two primary processes: taking action and doing research (Lewin, 1946).
Action research involves planning, action, and information-seeking about the result of the action.
Since Lewin’s original formulation, many different theoretical approaches to action research have been developed. These include action science, participatory action research, cooperative inquiry, and living educational theory among others.
Using Digital Sandbox Gaming to Improve Creativity Within Boys’ Writing (Ellison & Drew, 2019) is a study conducted by a school teacher who used video games to help teach his students English. It involved action research, where he interviewed his students to see if the use of games as stimuli for storytelling helped draw them into the learning experience, and iterated on his teaching style based on their feedback (disclaimer: I am the second author of this study).
See More: Examples of Qualitative Research
Quantitative Research Methodologies
8. experimental design.
As the name suggests, this type of research is based on testing hypotheses in experimental settings by manipulating variables and observing their effects on other variables.
The main benefit lies in its ability to manipulate specific variables to determine their effect on outcomes which is a great method for those looking for causational links in their research.
This is common, for example, in high-school science labs, where students are asked to introduce a variable into a setting in order to examine its effect.
9. Non-Experimental Design
Non-experimental design observes and measures associations between variables without manipulating them.
It can take, for example, the form of a ‘fly on the wall’ observation of a phenomenon, allowing researchers to examine authentic settings and changes that occur naturally in the environment.
10. Cross-Sectional Design
Cross-sectional design involves analyzing variables pertaining to a specific time period and at that exact moment.
This approach allows for an extensive examination and comparison of distinct and independent subjects, thereby offering advantages over qualitative methodologies such as case studies or surveys.
While cross-sectional design can be extremely useful in taking a ‘snapshot in time’, as a standalone method, it is not useful for examining changes in subjects after an intervention. The next methodology addresses this issue.
The prime example of this type of study is a census. A population census is mailed out to every house in the country, and each household must complete the census on the same evening. This allows the government to gather a snapshot of the nation’s demographics, beliefs, religion, and so on.
11. Longitudinal Design
Longitudinal research gathers data from the same subjects over an extended period to analyze changes and development.
In contrast to cross-sectional tactics, longitudinal designs examine variables more than once, over a pre-determined time span, allowing for multiple data points to be taken at different times.
A cross-sectional design is also useful for examining cohort effects , by comparing differences or changes in multiple different generations’ beliefs over time.
With multiple data points collected over extended periods ,it’s possible to examine continuous changes within things like population dynamics or consumer behavior. This makes detailed analysis of change possible.
12. Quasi-Experimental Design
Quasi-experimental design involves manipulating variables for analysis, but uses pre-existing groups of subjects rather than random groups.
Because the groups of research participants already exist, they cannot be randomly assigned to a cohort as with a true experimental design study. This makes inferring a causal relationship more difficult, but is nonetheless often more feasible in real-life settings.
Quasi-experimental designs are generally considered inferior to true experimental designs.
13. Correlational Research
Correlational research examines the relationships between two or more variables, determining the strength and direction of their association.
Similar to quasi-experimental methods, this type of research focuses on relationship differences between variables.
This approach provides a fast and easy way to make initial hypotheses based on either positive or negative correlation trends that can be observed within dataset.
Methods used for data analysis may include statistic correlations such as Pearson’s or Spearman’s.
Mixed-Methods Research Methodologies
14. sequential explanatory design (quan→qual).
This methodology involves conducting quantitative analysis first, then supplementing it with a qualitative study.
It begins by collecting quantitative data that is then analyzed to determine any significant patterns or trends.
Secondly, qualitative methods are employed. Their intent is to help interpret and expand the quantitative results.
This offers greater depth into understanding both large and smaller aspects of research questions being addressed.
The rationale behind this approach is to ensure that your data collection generates richer context for gaining insight into the particular issue across different levels, integrating in one study, qualitative exploration as well as statistical procedures.
15. Sequential Exploratory Design (QUAL→QUAN)
This methodology goes in the other direction, starting with qualitative analysis and ending with quantitative analysis.
It starts with qualitative research that delves deeps into complex areas and gathers rich information through interviewing or observing participants.
After this stage of exploration comes to an end, quantitative techniques are used to analyze the collected data through inferential statistics.
The idea is that a qualitative study can arm the researchers with a strong hypothesis testing framework, which they can then apply to a larger sample size using qualitative methods.
When I first took research classes, I had a lot of trouble distinguishing between methodologies and methods.
The key is to remember that the methodology sets the direction, while the methods are the specific tools to be used. A good analogy is transport: first you need to choose a mode (public transport, private transport, motorized transit, non-motorized transit), then you can choose a tool (bus, car, bike, on foot).
While research methodologies can be split into three types, each type has many different nuanced methodologies that can be chosen, before you then choose the methods – or tools – to use in the study. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses, so choose wisely!
Altrichter, H., & Gstettner, P. (1993). Action Research: A closed chapter in the history of German social science? Educational Action Research , 1 (3), 329–360. https://doi.org/10.1080/0965079930010302
Audi, R. (1999). The Cambridge dictionary of philosophy . Cambridge ; New York : Cambridge University Press. http://archive.org/details/cambridgediction00audi
Clandinin, D. J., & Connelly, F. M. (2004). Narrative Inquiry: Experience and Story in Qualitative Research . John Wiley & Sons.
Creswell, J. W. (2008). Educational Research: Planning, Conducting, and Evaluating Quantitative and Qualitative Research . Pearson/Merrill Prentice Hall.
Faggiolani, C. (n.d.). Perceived Identity: Applying Grounded Theory in Libraries . https://doi.org/10.4403/jlis.it-4592
Gauch, H. G. (2002). Scientific Method in Practice . Cambridge University Press.
Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (2009). The Discovery of Grounded Theory: Strategies for Qualitative Research . Transaction Publishers.
Kothari, C. R. (2004). Research Methodology: Methods and Techniques . New Age International.
Kuada, J. (2012). Research Methodology: A Project Guide for University Students . Samfundslitteratur.
Lewin, K. (1946). Action research and minority problems. Journal of Social Issues , 2, 4 , 34–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-4560.1946.tb02295.x
Mills, J., Bonner, A., & Francis, K. (2006). The Development of Constructivist Grounded Theory. International Journal of Qualitative Methods , 5 (1), 25–35. https://doi.org/10.1177/160940690600500103
Mingers, J., & Willcocks, L. (2017). An integrative semiotic methodology for IS research. Information and Organization , 27 (1), 17–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infoandorg.2016.12.001
OECD. (2015). Frascati Manual 2015: Guidelines for Collecting and Reporting Data on Research and Experimental Development . Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/science-and-technology/frascati-manual-2015_9789264239012-en
Peirce, C. S. (1992). The Essential Peirce, Volume 1: Selected Philosophical Writings (1867–1893) . Indiana University Press.
Reese, W. L. (1980). Dictionary of Philosophy and Religion: Eastern and Western Thought . Humanities Press.
Riessman, C. K. (1993). Narrative analysis . Sage Publications, Inc.
Saussure, F. de, & Riedlinger, A. (1959). Course in General Linguistics . Philosophical Library.
Thomas, C. G. (2021). Research Methodology and Scientific Writing . Springer Nature.
Zahavi, D., & Overgaard, S. (n.d.). Phenomenological Sociology—The Subjectivity of Everyday Life .

- Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) #molongui-disabled-link 6 Types of Societies (With 21 Examples)
- Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) #molongui-disabled-link 25 Public Health Policy Examples
- Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Cultural Differences Examples
- Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) #molongui-disabled-link Social Interaction Types & Examples (Sociology)

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Forums Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write Research Methodology
Last Updated: May 27, 2024 Approved
This article was co-authored by Alexander Ruiz, M.Ed. and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Alexander Ruiz is an Educational Consultant and the Educational Director of Link Educational Institute, a tutoring business based in Claremont, California that provides customizable educational plans, subject and test prep tutoring, and college application consulting. With over a decade and a half of experience in the education industry, Alexander coaches students to increase their self-awareness and emotional intelligence while achieving skills and the goal of achieving skills and higher education. He holds a BA in Psychology from Florida International University and an MA in Education from Georgia Southern University. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, several readers have written to tell us that this article was helpful to them, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 532,429 times.
The research methodology section of any academic research paper gives you the opportunity to convince your readers that your research is useful and will contribute to your field of study. An effective research methodology is grounded in your overall approach – whether qualitative or quantitative – and adequately describes the methods you used. Justify why you chose those methods over others, then explain how those methods will provide answers to your research questions. [1] X Research source
Describing Your Methods

- In your restatement, include any underlying assumptions that you're making or conditions that you're taking for granted. These assumptions will also inform the research methods you've chosen.
- Generally, state the variables you'll test and the other conditions you're controlling or assuming are equal.

- If you want to research and document measurable social trends, or evaluate the impact of a particular policy on various variables, use a quantitative approach focused on data collection and statistical analysis.
- If you want to evaluate people's views or understanding of a particular issue, choose a more qualitative approach.
- You can also combine the two. For example, you might look primarily at a measurable social trend, but also interview people and get their opinions on how that trend is affecting their lives.

- For example, if you conducted a survey, you would describe the questions included in the survey, where and how the survey was conducted (such as in person, online, over the phone), how many surveys were distributed, and how long your respondents had to complete the survey.
- Include enough detail that your study can be replicated by others in your field, even if they may not get the same results you did. [4] X Research source

- Qualitative research methods typically require more detailed explanation than quantitative methods.
- Basic investigative procedures don't need to be explained in detail. Generally, you can assume that your readers have a general understanding of common research methods that social scientists use, such as surveys or focus groups.

- For example, suppose you conducted a survey and used a couple of other research papers to help construct the questions on your survey. You would mention those as contributing sources.
Justifying Your Choice of Methods

- Describe study participants specifically, and list any inclusion or exclusion criteria you used when forming your group of participants.
- Justify the size of your sample, if applicable, and describe how this affects whether your study can be generalized to larger populations. For example, if you conducted a survey of 30 percent of the student population of a university, you could potentially apply those results to the student body as a whole, but maybe not to students at other universities.

- Reading other research papers is a good way to identify potential problems that commonly arise with various methods. State whether you actually encountered any of these common problems during your research.

- If you encountered any problems as you collected data, explain clearly the steps you took to minimize the effect that problem would have on your results.

- In some cases, this may be as simple as stating that while there were numerous studies using one method, there weren't any using your method, which caused a gap in understanding of the issue.
- For example, there may be multiple papers providing quantitative analysis of a particular social trend. However, none of these papers looked closely at how this trend was affecting the lives of people.
Connecting Your Methods to Your Research Goals

- Depending on your research questions, you may be mixing quantitative and qualitative analysis – just as you could potentially use both approaches. For example, you might do a statistical analysis, and then interpret those statistics through a particular theoretical lens.

- For example, suppose you're researching the effect of college education on family farms in rural America. While you could do interviews of college-educated people who grew up on a family farm, that would not give you a picture of the overall effect. A quantitative approach and statistical analysis would give you a bigger picture.

- If in answering your research questions, your findings have raised other questions that may require further research, state these briefly.
- You can also include here any limitations to your methods, or questions that weren't answered through your research.

- Generalization is more typically used in quantitative research. If you have a well-designed sample, you can statistically apply your results to the larger population your sample belongs to.
Template to Write Research Methodology

Community Q&A
- Organize your methodology section chronologically, starting with how you prepared to conduct your research methods, how you gathered data, and how you analyzed that data. [13] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Write your research methodology section in past tense, unless you're submitting the methodology section before the research described has been carried out. [14] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Discuss your plans in detail with your advisor or supervisor before committing to a particular methodology. They can help identify possible flaws in your study. [15] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://expertjournals.com/how-to-write-a-research-methodology-for-your-academic-article/
- ↑ http://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/methodology
- ↑ https://www.skillsyouneed.com/learn/dissertation-methodology.html
- ↑ https://uir.unisa.ac.za/bitstream/handle/10500/4245/05Chap%204_Research%20methodology%20and%20design.pdf
- ↑ https://elc.polyu.edu.hk/FYP/html/method.htm
About This Article

To write a research methodology, start with a section that outlines the problems or questions you'll be studying, including your hypotheses or whatever it is you're setting out to prove. Then, briefly explain why you chose to use either a qualitative or quantitative approach for your study. Next, go over when and where you conducted your research and what parameters you used to ensure you were objective. Finally, cite any sources you used to decide on the methodology for your research. To learn how to justify your choice of methods in your research methodology, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Prof. Dr. Ahmed Askar
Apr 18, 2020
Did this article help you?

M. Mahmood Shah Khan
Mar 17, 2020
Shimola Makondo
Jul 20, 2019
Zain Sharif Mohammed Alnadhery
Jan 7, 2019
Lundi Dukashe
Feb 17, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper

Writing a research paper is both an art and a skill, and knowing how to write the methods section of a research paper is the first crucial step in mastering scientific writing. If, like the majority of early career researchers, you believe that the methods section is the simplest to write and needs little in the way of careful consideration or thought, this article will help you understand it is not 1 .
We have all probably asked our supervisors, coworkers, or search engines “ how to write a methods section of a research paper ” at some point in our scientific careers, so you are not alone if that’s how you ended up here. Even for seasoned researchers, selecting what to include in the methods section from a wealth of experimental information can occasionally be a source of distress and perplexity.
Additionally, journal specifications, in some cases, may make it more of a requirement rather than a choice to provide a selective yet descriptive account of the experimental procedure. Hence, knowing these nuances of how to write the methods section of a research paper is critical to its success. The methods section of the research paper is not supposed to be a detailed heavy, dull section that some researchers tend to write; rather, it should be the central component of the study that justifies the validity and reliability of the research.
Are you still unsure of how the methods section of a research paper forms the basis of every investigation? Consider the last article you read but ignore the methods section and concentrate on the other parts of the paper . Now think whether you could repeat the study and be sure of the credibility of the findings despite knowing the literature review and even having the data in front of you. You have the answer!

Having established the importance of the methods section , the next question is how to write the methods section of a research paper that unifies the overall study. The purpose of the methods section , which was earlier called as Materials and Methods , is to describe how the authors went about answering the “research question” at hand. Here, the objective is to tell a coherent story that gives a detailed account of how the study was conducted, the rationale behind specific experimental procedures, the experimental setup, objects (variables) involved, the research protocol employed, tools utilized to measure, calculations and measurements, and the analysis of the collected data 2 .
In this article, we will take a deep dive into this topic and provide a detailed overview of how to write the methods section of a research paper . For the sake of clarity, we have separated the subject into various sections with corresponding subheadings.
Table of Contents
What is the methods section of a research paper ?
The methods section is a fundamental section of any paper since it typically discusses the ‘ what ’, ‘ how ’, ‘ which ’, and ‘ why ’ of the study, which is necessary to arrive at the final conclusions. In a research article, the introduction, which serves to set the foundation for comprehending the background and results is usually followed by the methods section, which precedes the result and discussion sections. The methods section must explicitly state what was done, how it was done, which equipment, tools and techniques were utilized, how were the measurements/calculations taken, and why specific research protocols, software, and analytical methods were employed.
Why is the methods section important?
The primary goal of the methods section is to provide pertinent details about the experimental approach so that the reader may put the results in perspective and, if necessary, replicate the findings 3 . This section offers readers the chance to evaluate the reliability and validity of any study. In short, it also serves as the study’s blueprint, assisting researchers who might be unsure about any other portion in establishing the study’s context and validity. The methods plays a rather crucial role in determining the fate of the article; an incomplete and unreliable methods section can frequently result in early rejections and may lead to numerous rounds of modifications during the publication process. This means that the reviewers also often use methods section to assess the reliability and validity of the research protocol and the data analysis employed to address the research topic. In other words, the purpose of the methods section is to demonstrate the research acumen and subject-matter expertise of the author(s) in their field.
Structure of methods section of a research paper
Similar to the research paper, the methods section also follows a defined structure; this may be dictated by the guidelines of a specific journal or can be presented in a chronological or thematic manner based on the study type. When writing the methods section , authors should keep in mind that they are telling a story about how the research was conducted. They should only report relevant information to avoid confusing the reader and include details that would aid in connecting various aspects of the entire research activity together. It is generally advisable to present experiments in the order in which they were conducted. This facilitates the logical flow of the research and allows readers to follow the progression of the study design.

It is also essential to clearly state the rationale behind each experiment and how the findings of earlier experiments informed the design or interpretation of later experiments. This allows the readers to understand the overall purpose of the study design and the significance of each experiment within that context. However, depending on the particular research question and method, it may make sense to present information in a different order; therefore, authors must select the best structure and strategy for their individual studies.
In cases where there is a lot of information, divide the sections into subheadings to cover the pertinent details. If the journal guidelines pose restrictions on the word limit , additional important information can be supplied in the supplementary files. A simple rule of thumb for sectioning the method section is to begin by explaining the methodological approach ( what was done ), describing the data collection methods ( how it was done ), providing the analysis method ( how the data was analyzed ), and explaining the rationale for choosing the methodological strategy. This is described in detail in the upcoming sections.
How to write the methods section of a research paper
Contrary to widespread assumption, the methods section of a research paper should be prepared once the study is complete to prevent missing any key parameter. Hence, please make sure that all relevant experiments are done before you start writing a methods section . The next step for authors is to look up any applicable academic style manuals or journal-specific standards to ensure that the methods section is formatted correctly. The methods section of a research paper typically constitutes materials and methods; while writing this section, authors usually arrange the information under each category.
The materials category describes the samples, materials, treatments, and instruments, while experimental design, sample preparation, data collection, and data analysis are a part of the method category. According to the nature of the study, authors should include additional subsections within the methods section, such as ethical considerations like the declaration of Helsinki (for studies involving human subjects), demographic information of the participants, and any other crucial information that can affect the output of the study. Simply put, the methods section has two major components: content and format. Here is an easy checklist for you to consider if you are struggling with how to write the methods section of a research paper .
- Explain the research design, subjects, and sample details
- Include information on inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Mention ethical or any other permission required for the study
- Include information about materials, experimental setup, tools, and software
- Add details of data collection and analysis methods
- Incorporate how research biases were avoided or confounding variables were controlled
- Evaluate and justify the experimental procedure selected to address the research question
- Provide precise and clear details of each experiment
- Flowcharts, infographics, or tables can be used to present complex information
- Use past tense to show that the experiments have been done
- Follow academic style guides (such as APA or MLA ) to structure the content
- Citations should be included as per standard protocols in the field
Now that you know how to write the methods section of a research paper , let’s address another challenge researchers face while writing the methods section —what to include in the methods section . How much information is too much is not always obvious when it comes to trying to include data in the methods section of a paper. In the next section, we examine this issue and explore potential solutions.

What to include in the methods section of a research paper
The technical nature of the methods section occasionally makes it harder to present the information clearly and concisely while staying within the study context. Many young researchers tend to veer off subject significantly, and they frequently commit the sin of becoming bogged down in itty bitty details, making the text harder to read and impairing its overall flow. However, the best way to write the methods section is to start with crucial components of the experiments. If you have trouble deciding which elements are essential, think about leaving out those that would make it more challenging to comprehend the context or replicate the results. The top-down approach helps to ensure all relevant information is incorporated and vital information is not lost in technicalities. Next, remember to add details that are significant to assess the validity and reliability of the study. Here is a simple checklist for you to follow ( bonus tip: you can also make a checklist for your own study to avoid missing any critical information while writing the methods section ).
- Structuring the methods section : Authors should diligently follow journal guidelines and adhere to the specific author instructions provided when writing the methods section . Journals typically have specific guidelines for formatting the methods section ; for example, Frontiers in Plant Sciences advises arranging the materials and methods section by subheading and citing relevant literature. There are several standardized checklists available for different study types in the biomedical field, including CONSORT (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials) for randomized clinical trials, PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analysis) for systematic reviews and meta-analysis, and STROBE (STrengthening the Reporting of OBservational studies in Epidemiology) for cohort, case-control, cross-sectional studies. Before starting the methods section , check the checklist available in your field that can function as a guide.
- Organizing different sections to tell a story : Once you are sure of the format required for structuring the methods section , the next is to present the sections in a logical manner; as mentioned earlier, the sections can be organized according to the chronology or themes. In the chronological arrangement, you should discuss the methods in accordance with how the experiments were carried out. An example of the method section of a research paper of an animal study should first ideally include information about the species, weight, sex, strain, and age. Next, the number of animals, their initial conditions, and their living and housing conditions should also be mentioned. Second, how the groups are assigned and the intervention (drug treatment, stress, or other) given to each group, and finally, the details of tools and techniques used to measure, collect, and analyze the data. Experiments involving animal or human subjects should additionally state an ethics approval statement. It is best to arrange the section using the thematic approach when discussing distinct experiments not following a sequential order.
- Define and explain the objects and procedure: Experimental procedure should clearly be stated in the methods section . Samples, necessary preparations (samples, treatment, and drug), and methods for manipulation need to be included. All variables (control, dependent, independent, and confounding) must be clearly defined, particularly if the confounding variables can affect the outcome of the study.
- Match the order of the methods section with the order of results: Though not mandatory, organizing the manuscript in a logical and coherent manner can improve the readability and clarity of the paper. This can be done by following a consistent structure throughout the manuscript; readers can easily navigate through the different sections and understand the methods and results in relation to each other. Using experiment names as headings for both the methods and results sections can also make it simpler for readers to locate specific information and corroborate it if needed.
- Relevant information must always be included: The methods section should have information on all experiments conducted and their details clearly mentioned. Ask the journal whether there is a way to offer more information in the supplemental files or external repositories if your target journal has strict word limitations. For example, Nature communications encourages authors to deposit their step-by-step protocols in an open-resource depository, Protocol Exchange which allows the protocols to be linked with the manuscript upon publication. Providing access to detailed protocols also helps to increase the transparency and reproducibility of the research.
- It’s all in the details: The methods section should meticulously list all the materials, tools, instruments, and software used for different experiments. Specify the testing equipment on which data was obtained, together with its manufacturer’s information, location, city, and state or any other stimuli used to manipulate the variables. Provide specifics on the research process you employed; if it was a standard protocol, cite previous studies that also used the protocol. Include any protocol modifications that were made, as well as any other factors that were taken into account when planning the study or gathering data. Any new or modified techniques should be explained by the authors. Typically, readers evaluate the reliability and validity of the procedures using the cited literature, and a widely accepted checklist helps to support the credibility of the methodology. Note: Authors should include a statement on sample size estimation (if applicable), which is often missed. It enables the reader to determine how many subjects will be required to detect the expected change in the outcome variables within a given confidence interval.
- Write for the audience: While explaining the details in the methods section , authors should be mindful of their target audience, as some of the rationale or assumptions on which specific procedures are based might not always be obvious to the audience, particularly for a general audience. Therefore, when in doubt, the objective of a procedure should be specified either in relation to the research question or to the entire protocol.
- Data interpretation and analysis : Information on data processing, statistical testing, levels of significance, and analysis tools and software should be added. Mention if the recommendations and expertise of an experienced statistician were followed. Also, evaluate and justify the preferred statistical method used in the study and its significance.
What NOT to include in the methods section of a research paper
To address “ how to write the methods section of a research paper ”, authors should not only pay careful attention to what to include but also what not to include in the methods section of a research paper . Here is a list of do not’s when writing the methods section :
- Do not elaborate on specifics of standard methods/procedures: You should refrain from adding unnecessary details of experiments and practices that are well established and cited previously. Instead, simply cite relevant literature or mention if the manufacturer’s protocol was followed.
- Do not add unnecessary details : Do not include minute details of the experimental procedure and materials/instruments used that are not significant for the outcome of the experiment. For example, there is no need to mention the brand name of the water bath used for incubation.
- Do not discuss the results: The methods section is not to discuss the results or refer to the tables and figures; save it for the results and discussion section. Also, focus on the methods selected to conduct the study and avoid diverting to other methods or commenting on their pros or cons.
- Do not make the section bulky : For extensive methods and protocols, provide the essential details and share the rest of the information in the supplemental files. The writing should be clear yet concise to maintain the flow of the section.
We hope that by this point, you understand how crucial it is to write a thoughtful and precise methods section and the ins and outs of how to write the methods section of a research paper . To restate, the entire purpose of the methods section is to enable others to reproduce the results or verify the research. We sincerely hope that this post has cleared up any confusion and given you a fresh perspective on the methods section .
As a parting gift, we’re leaving you with a handy checklist that will help you understand how to write the methods section of a research paper . Feel free to download this checklist and use or share this with those who you think may benefit from it.

References
- Bhattacharya, D. How to write the Methods section of a research paper. Editage Insights, 2018. https://www.editage.com/insights/how-to-write-the-methods-section-of-a-research-paper (2018).
- Kallet, R. H. How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper. Respiratory Care 49, 1229–1232 (2004). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15447808/
- Grindstaff, T. L. & Saliba, S. A. AVOIDING MANUSCRIPT MISTAKES. Int J Sports Phys Ther 7, 518–524 (2012). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3474299/
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

Paperpal Review: Key Features, Pricing Plans, and How-to-Use

How to Structure a Dissertation?

Methodology
Ai generator.

Methodology refers to the systematic study of methods used in research. It includes Research Methodology , which is the framework for conducting investigations, and Survey Methodology , which involves techniques for collecting and analyzing survey data. A key part of any methodology is the Research Question, guiding the study’s focus and direction.
What is Methodology?
Methodology refers to the systematic study of methods used in research, encompassing principles and procedures that guide scientific investigations. It includes Research Methodology, which outlines the framework for conducting studies, and Survey Methodology, which involves techniques for collecting and analyzing survey data.
Examples of Methodology
- Surveys : Distributing questionnaires to gather quantitative data from a large sample.
- Interviews : Conducting one-on-one conversations to collect detailed qualitative data.
- Focus Groups : Facilitating group discussions to explore participants’ perceptions and opinions.
- Case Studies : Performing in-depth analysis of a single subject or group to understand complex issues.
- Experiments : Implementing controlled tests to determine causal relationships between variables.
- Participant Observation : Observing and engaging with participants in their natural environment.
- Longitudinal Studies : Tracking the same individuals over an extended period to observe changes.
- Cross-Sectional Studies : Analyzing data from different groups at a single point in time.
- Content Analysis : Systematically analyzing text or media to identify patterns and themes.
- Secondary Data Analysis : Using existing data collected by others to conduct new analyses.
- Meta-Analysis : Combining results from multiple studies to draw a broader conclusion.
- Delphi Technique : Gathering expert opinions through multiple rounds of questionnaires to achieve consensus.
- Ethnography : Immersing in a community to understand its culture and practices.
- Grounded Theory : Developing theories based on data collected during the research.
- Action Research : Collaborating with participants to address a problem and implement solutions.
- Comparative Method : Comparing different groups or cases to identify similarities and differences.
- Historical Analysis : Examining historical records to understand past events and trends.
- Systematic Review : Summarizing and evaluating existing research on a specific topic.
- Descriptive Research : Describing characteristics of a population or phenomenon.
- Narrative Inquiry : Studying personal stories and experiences to gain insights.
- Visual Analysis : Analyzing visual materials such as photographs and videos.
- Experimental Design : Using control and experimental groups to test hypotheses.
- Phenomenology : Exploring individuals’ lived experiences to understand their perceptions.
- Biographical Research : Studying an individual’s life history and experiences.
- Field Experiments : Conducting experiments in natural settings.
- Survey Design : Creating and administering surveys to collect data.
- Program Evaluation : Assessing the effectiveness of a program or intervention.
- Network Analysis : Examining relationships and interactions within a network.
- Discourse Analysis : Studying language use in texts and conversations.
- Quasi-Experimental Design : Implementing studies with non-randomized control and treatment groups.
Examples of Methodology in a Sentences
- The interview methodology involved conducting in-depth, one-on-one interviews with participants.
- A survey methodology was used to gather data from a large population using structured questionnaires.
- The case study methodology focused on an in-depth analysis of a single organization.
- Ethnographic methodology involved immersing researchers in the community to observe daily activities.
- A mixed-methods approach was utilized, combining quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews.
- Experimental methodology included a control group and a treatment group to test the hypothesis.
- Participant observation was employed to understand the behaviors and interactions within the group.
- The longitudinal study methodology tracked participants over several years to observe changes.
- Content analysis was used to analyze the themes and patterns in social media posts.
- The focus group methodology gathered diverse opinions on the new product concept.
- A cross-sectional study was conducted to compare different population groups at a single point in time.
- Action research methodology involved the participants in the research process to improve practices.
- The phenomenological methodology aimed to understand individuals’ lived experiences.
- Grounded theory methodology was used to develop a theory based on data collected from participants.
- The narrative research methodology focused on the stories and personal accounts of the participants.
- Secondary data analysis involved analyzing data previously collected by other researchers.
- Delphi methodology gathered expert opinions through multiple rounds of questionnaires.
- Comparative methodology analyzed differences and similarities between two distinct groups.
- The meta-analysis methodology combined results from multiple studies to draw a comprehensive conclusion.
- Historical research methodology examined past events to understand their impact on the present.
- The survey methodology included both closed-ended and open-ended questions to capture detailed responses.
- Field experiments were conducted to test the intervention in a natural setting.
- Discourse analysis examined the language and communication patterns within the texts.
- The biographical research methodology studied individuals’ life histories and personal experiences.
- Quantitative content analysis was used to count and analyze the frequency of specific words or themes.
- Case-control study methodology compared individuals with a specific condition to those without it.
- Systematic review methodology evaluated and synthesized findings from existing research studies.
- Experimental design methodology manipulated variables to observe their effect on the outcome.
- Visual ethnography involved analyzing visual materials such as photographs and videos.
- Clinical trial methodology tested the efficacy and safety of new medical treatments through controlled experiments.
Methodology Examples in Project Proposal
1. Survey Methodology : We will distribute online surveys to 500 participants to gather quantitative data on customer satisfaction levels.
2. Interview Methodology : Conduct semi-structured interviews with 20 key stakeholders to gain insights into project requirements and expectations.
3. Focus Group Methodology : Facilitate focus groups with selected users to discuss and refine the design of the new software interface.
4 . Case Study Methodology : Analyze three case studies of similar projects to identify best practices and potential pitfalls.
5. Experimental Methodology : Implement a controlled experiment to test the impact of the new training program on employee productivity.
6. Ethnographic Methodology : Engage in participant observation within the target community for three months to understand user behavior and cultural influences.
7. Mixed Methods Approach : Combine quantitative data from surveys with qualitative insights from interviews to provide a comprehensive analysis of project outcomes.
8. Action Research Methodology : Collaborate with project team members to iteratively implement and assess improvements, ensuring continuous feedback and adaptation.
9. Content Analysis : Review and analyze project-related documents and communications to identify common themes and areas for improvement.
10. Delphi Methodology : Use the Delphi technique to gather and refine expert opinions through multiple rounds of questionnaires to achieve a consensus on project goals and strategies.
Methodology Examples in Report
Example 1: survey methodology.
In this study, we employed a survey methodology to collect data from participants. The survey was designed to gather information on consumer preferences and behaviors. The key steps in our survey methodology were as follows:
- Population : All residents of City X aged 18 and above.
- Sample Size : 500 participants selected through random sampling.
- Questionnaire : A structured questionnaire with 25 closed-ended questions.
- Pilot Testing : Conducted with 50 participants to ensure clarity and reliability of the questions.
- Mode : Online survey distributed via email.
- Duration : Data collection spanned over two weeks from January 10 to January 24, 2024.
- Software : SPSS version 26.
- Techniques : Descriptive statistics, cross-tabulations, and chi-square tests.
Example 2: Experimental Methodology
This experiment aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of a new teaching method on students’ performance. The experimental methodology comprised the following steps:
- Selection : 100 high school students from School Y.
- Grouping : Randomly assigned to control (n=50) and experimental (n=50) groups.
- Pre-test : Administered to both groups to assess initial knowledge levels.
- Intervention : The experimental group received the new teaching method, while the control group continued with the traditional method for six weeks.
- Post-test : Conducted to measure knowledge acquisition and retention.
- Teaching Aids : Interactive multimedia tools for the experimental group.
- Traditional Tools : Textbooks and lectures for the control group.
- Software : R programming language.
- Techniques : T-tests to compare pre-test and post-test scores between groups.
Example 3: Qualitative Methodology
For this research, we utilized a qualitative methodology to explore the experiences of healthcare workers during the pandemic. The methodology included:
- Selection : 30 healthcare workers from various hospitals.
- Sampling Technique : Purposive sampling to ensure diverse perspectives.
- Interviews : Semi-structured interviews conducted in-person and via Zoom.
- Duration : Each interview lasted approximately 45-60 minutes.
- Recording : With participants’ consent, interviews were a-recorded and transcribed verbatim.
- Approach : Thematic analysis.
- Software : NVivo for coding and organizing themes.
- Validation : Member checking and peer debriefing to ensure credibility.
Example 4: Case Study Methodology
In this case study, we investigated the implementation of a new software system in Company Z. The methodology involved:
- Criteria : Companies that recently implemented the software within the past year.
- Company Profile : Medium-sized company with 200 employees.
- Interviews : Conducted with key stakeholders including IT staff, managers, and end-users.
- Documents : Analysis of company reports, project plans, and user feedback forms.
- Observations : On-site visits to observe the software in use.
- Techniques : Triangulation to corroborate findings from multiple sources.
- Framework : SWOT analysis to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to the software implementation.
Example 5: Mixed-Methods Methodology
This mixed-methods study examined the impact of remote work on employee productivity and well-being. The methodology comprised both quantitative and qualitative components:
- Survey : Online survey with Likert-scale questions administered to 300 employees.
- Analysis : Regression analysis to identify factors affecting productivity.
- Focus Groups : Three focus groups with 8-10 participants each to discuss remote work experiences.
- Thematic Analysis : Coding and theme development using Atlas.ti.
- Data Triangulation : Combined findings from both quantitative and qualitative data to provide a comprehensive understanding of the impact of remote work.
Quantitative Methodology Examples
- Survey Research : Conducting a large-scale survey to collect numerical data on consumer preferences.
- Experimental Design : Implementing a controlled experiment to test the effects of a new drug on patient recovery rates.
- Cross-Sectional Study : Analyzing data from different population groups at a single point in time to identify correlations.
- Longitudinal Study : Tracking the same group of individuals over several years to observe changes in health outcomes.
- Secondary Data Analysis : Using existing datasets from government databases to analyze employment trends.
- Quasi-Experimental Design : Comparing outcomes between a group receiving an intervention and a non-randomized control group.
- Descriptive Statistics : Summarizing and describing the main features of a dataset using measures such as mean, median, and mode.
- Regression Analysis : Investigating the relationship between independent variables and a dependent variable to predict outcomes.
- Correlation Study : Measuring the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables, such as income and education level.
- Time Series Analysis : Analyzing data points collected or recorded at specific time intervals to identify trends over time.
Types of Methodology
1. qualitative methodology.
This involves collecting non-numerical data to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. Methods include:
- Interviews : Conducting one-on-one conversations to gather detailed insights.
- Focus Groups : Facilitating group discussions to explore a specific topic.
- Observations : Watching and recording behaviors in a natural setting.
2. Quantitative Methodology
This focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis. Methods include:
- Surveys : Using questionnaires to collect data from a large number of respondents.
- Experiments : Conducting controlled tests to determine cause-and-effect relationships.
- Secondary Data Analysis : Analyzing existing data collected by other researchers.
3. Mixed Methods
This combines both qualitative and quantitative approaches. It provides a comprehensive understanding by integrating diverse data sources.
- Sequential Explanatory Design : Collecting and analyzing quantitative data first, followed by qualitative data to explain the quantitative results.
- Concurrent Triangulation : Collecting both types of data simultaneously to cross-verify findings.
4. Case Study Methodology
This involves an in-depth study of a particular case within a real-world context. Methods include:
- Document Analysis : Reviewing existing documents related to the case.
- Interviews : Gathering detailed information from individuals involved in the case.
- Observations : Observing the case in its natural setting to gather contextual data.
5. Ethnographic Methodology
This focuses on studying cultures and communities. Methods include:
- Participant Observation : Engaging with the community while observing their behaviors and interactions.
- Field Notes : Recording detailed notes of observations and experiences in the field.
- Interviews : Conducting interviews with community members to gain deeper insights.
Each of these methodologies provides a different approach to research, helping researchers to choose the most appropriate method for their specific study objectives.
Importance of Methodology in Research
1. ensures research validity and reliability.
- Validity : Methodology ensures that the research measures what it is intended to measure. It guarantees that the results accurately represent the phenomenon being studied.
- Reliability : It ensures consistency in the research results. Reliable methodologies produce stable and consistent results over repeated trials.
2. Provides a Clear Research Framework
- Structured Process : Methodology provides a detailed plan outlining the steps involved in the research process. This structure helps researchers stay organized and focused.
- Replicability : A well-defined methodology allows other researchers to replicate the study, verifying results and contributing to the body of knowledge.
3. Enhances Credibility and Objectivity
- Transparency : Clearly documenting the research methodology enhances the transparency of the study, allowing others to understand how data was collected and analyzed.
- Objectivity : By following a systematic approach, methodology minimizes biases and ensures objective analysis and interpretation of data.
4. Facilitates Data Collection and Analysis
- Appropriate Tools and Techniques : Methodology helps in selecting the most suitable tools and techniques for data collection and analysis, ensuring accurate and relevant data is gathered.
- Efficient Analysis : With a clear methodological framework, data analysis becomes more efficient, leading to valid conclusions and insights.
5. Supports Theory Development and Hypothesis Testing
- Theory Development : Methodologies, particularly in qualitative research, help in developing new theories based on observed patterns and themes.
- Hypothesis Testing : In quantitative research, methodologies are crucial for testing hypotheses, allowing researchers to confirm or refute their assumptions.
Synonyms of Methodology
How to write a methodology, 1. introduction.
Begin with a brief overview of the research problem and objectives. Explain why the chosen methodology is appropriate for addressing the research question.
2. Research Design
Describe the overall approach of your study:
- Qualitative , Quantitative , or Mixed Methods .
- Provide a rationale for your choice.
3. Data Collection Methods
Detail the specific methods you will use to collect data:
- Surveys : Include information about the type of survey, sample size, and how respondents are selected.
- Interviews : Describe the format (structured, semi-structured, or unstructured), and the selection process for participants.
- Observations : Explain what will be observed, the context, and how observations will be recorded.
- Experiments : Outline the experimental design, control variables, and the procedure.
4. Data Analysis Methods
Explain how you will analyze the collected data:
- Quantitative Analysis : Statistical tests, software used, and how you will ensure reliability and validity.
- Qualitative Analysis : Coding processes, thematic analysis, or other methods used to interpret data.
5. Sampling
Describe your sampling strategy:
- Population : Define the population from which your sample will be drawn.
- Sample Size : Justify the size of your sample.
- Sampling Technique : Explain whether you will use random sampling, stratified sampling, convenience sampling, etc.
6. Ethical Considerations
Detail how you will address ethical issues:
- Informed Consent : How you will obtain and document consent from participants.
- Confidentiality : Measures to protect the privacy of participants.
- Approval : Mention any institutional review board (IRB) or ethics committee approvals.
7. Limitations
Acknowledge potential limitations of your methodology:
- Discuss possible weaknesses and how they may impact your results.
- Explain steps you will take to mitigate these limitations.
8. Conclusion
Summarize the key points of your methodology. Reinforce why your chosen methods are the best fit for your research objectives.
FAQ’s
What are qualitative methods.
Qualitative methods involve non-numerical data collection, like interviews and observations, to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences.
What are quantitative methods?
Quantitative methods involve numerical data collection and statistical analysis to identify patterns, relationships, or trends.
What is a mixed-methods approach?
A mixed-methods approach combines qualitative and quantitative methods to provide a comprehensive analysis.
How do you choose a methodology?
Choosing a methodology depends on the research question, objectives, and the type of data needed.
What is a research design?
Research design is the framework that guides the collection and analysis of data, ensuring the research question is effectively addressed.
What is the difference between methodology and methods?
Methodology refers to the overall approach and rationale, while methods are specific techniques used for data collection and analysis.
What is a case study?
A case study is an in-depth examination of a particular instance, event, or individual to explore or illustrate broader principles.
What is an experiment in research?
An experiment involves manipulating variables to determine their effect on other variables, establishing cause-and-effect relationships.
What is a survey?
A survey is a data collection method using questionnaires or interviews to gather information from a large group.
What is sampling in research?
Sampling is selecting a subset of a population to represent the whole, ensuring the study’s findings are generalizable.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Key things to know about U.S. election polling in 2024

Confidence in U.S. public opinion polling was shaken by errors in 2016 and 2020. In both years’ general elections, many polls underestimated the strength of Republican candidates, including Donald Trump. These errors laid bare some real limitations of polling.
In the midterms that followed those elections, polling performed better . But many Americans remain skeptical that it can paint an accurate portrait of the public’s political preferences.
Restoring people’s confidence in polling is an important goal, because robust and independent public polling has a critical role to play in a democratic society. It gathers and publishes information about the well-being of the public and about citizens’ views on major issues. And it provides an important counterweight to people in power, or those seeking power, when they make claims about “what the people want.”
The challenges facing polling are undeniable. In addition to the longstanding issues of rising nonresponse and cost, summer 2024 brought extraordinary events that transformed the presidential race . The good news is that people with deep knowledge of polling are working hard to fix the problems exposed in 2016 and 2020, experimenting with more data sources and interview approaches than ever before. Still, polls are more useful to the public if people have realistic expectations about what surveys can do well – and what they cannot.
With that in mind, here are some key points to know about polling heading into this year’s presidential election.
Probability sampling (or “random sampling”). This refers to a polling method in which survey participants are recruited using random sampling from a database or list that includes nearly everyone in the population. The pollster selects the sample. The survey is not open for anyone who wants to sign up.
Online opt-in polling (or “nonprobability sampling”). These polls are recruited using a variety of methods that are sometimes referred to as “convenience sampling.” Respondents come from a variety of online sources such as ads on social media or search engines, websites offering rewards in exchange for survey participation, or self-enrollment. Unlike surveys with probability samples, people can volunteer to participate in opt-in surveys.
Nonresponse and nonresponse bias. Nonresponse is when someone sampled for a survey does not participate. Nonresponse bias occurs when the pattern of nonresponse leads to error in a poll estimate. For example, college graduates are more likely than those without a degree to participate in surveys, leading to the potential that the share of college graduates in the resulting sample will be too high.
Mode of interview. This refers to the format in which respondents are presented with and respond to survey questions. The most common modes are online, live telephone, text message and paper. Some polls use more than one mode.
Weighting. This is a statistical procedure pollsters perform to make their survey align with the broader population on key characteristics like age, race, etc. For example, if a survey has too many college graduates compared with their share in the population, people without a college degree are “weighted up” to match the proper share.
How are election polls being conducted?
Pollsters are making changes in response to the problems in previous elections. As a result, polling is different today than in 2016. Most U.S. polling organizations that conducted and publicly released national surveys in both 2016 and 2022 (61%) used methods in 2022 that differed from what they used in 2016 . And change has continued since 2022.
One change is that the number of active polling organizations has grown significantly, indicating that there are fewer barriers to entry into the polling field. The number of organizations that conduct national election polls more than doubled between 2000 and 2022.
This growth has been driven largely by pollsters using inexpensive opt-in sampling methods. But previous Pew Research Center analyses have demonstrated how surveys that use nonprobability sampling may have errors twice as large , on average, as those that use probability sampling.
The second change is that many of the more prominent polling organizations that use probability sampling – including Pew Research Center – have shifted from conducting polls primarily by telephone to using online methods, or some combination of online, mail and telephone. The result is that polling methodologies are far more diverse now than in the past.
(For more about how public opinion polling works, including a chapter on election polls, read our short online course on public opinion polling basics .)
All good polling relies on statistical adjustment called “weighting,” which makes sure that the survey sample aligns with the broader population on key characteristics. Historically, public opinion researchers have adjusted their data using a core set of demographic variables to correct imbalances between the survey sample and the population.
But there is a growing realization among survey researchers that weighting a poll on just a few variables like age, race and gender is insufficient for getting accurate results. Some groups of people – such as older adults and college graduates – are more likely to take surveys, which can lead to errors that are too sizable for a simple three- or four-variable adjustment to work well. Adjusting on more variables produces more accurate results, according to Center studies in 2016 and 2018 .
A number of pollsters have taken this lesson to heart. For example, recent high-quality polls by Gallup and The New York Times/Siena College adjusted on eight and 12 variables, respectively. Our own polls typically adjust on 12 variables . In a perfect world, it wouldn’t be necessary to have that much intervention by the pollster. But the real world of survey research is not perfect.
Predicting who will vote is critical – and difficult. Preelection polls face one crucial challenge that routine opinion polls do not: determining who of the people surveyed will actually cast a ballot.
Roughly a third of eligible Americans do not vote in presidential elections , despite the enormous attention paid to these contests. Determining who will abstain is difficult because people can’t perfectly predict their future behavior – and because many people feel social pressure to say they’ll vote even if it’s unlikely.
No one knows the profile of voters ahead of Election Day. We can’t know for sure whether young people will turn out in greater numbers than usual, or whether key racial or ethnic groups will do so. This means pollsters are left to make educated guesses about turnout, often using a mix of historical data and current measures of voting enthusiasm. This is very different from routine opinion polls, which mostly do not ask about people’s future intentions.
When major news breaks, a poll’s timing can matter. Public opinion on most issues is remarkably stable, so you don’t necessarily need a recent poll about an issue to get a sense of what people think about it. But dramatic events can and do change public opinion , especially when people are first learning about a new topic. For example, polls this summer saw notable changes in voter attitudes following Joe Biden’s withdrawal from the presidential race. Polls taken immediately after a major event may pick up a shift in public opinion, but those shifts are sometimes short-lived. Polls fielded weeks or months later are what allow us to see whether an event has had a long-term impact on the public’s psyche.
How accurate are polls?
The answer to this question depends on what you want polls to do. Polls are used for all kinds of purposes in addition to showing who’s ahead and who’s behind in a campaign. Fair or not, however, the accuracy of election polling is usually judged by how closely the polls matched the outcome of the election.
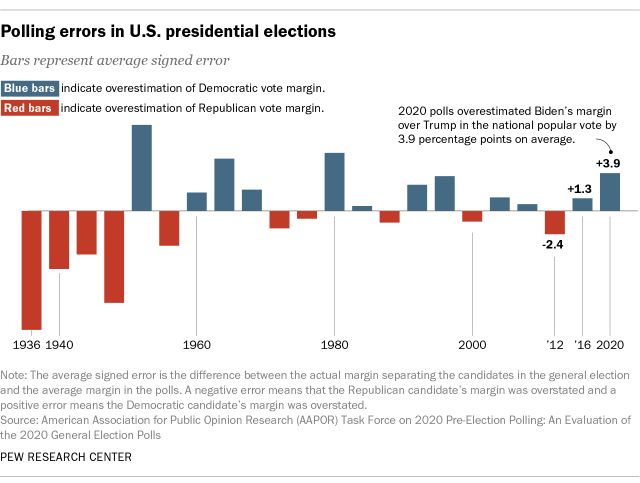
By this standard, polling in 2016 and 2020 performed poorly. In both years, state polling was characterized by serious errors. National polling did reasonably well in 2016 but faltered in 2020.
In 2020, a post-election review of polling by the American Association for Public Opinion Research (AAPOR) found that “the 2020 polls featured polling error of an unusual magnitude: It was the highest in 40 years for the national popular vote and the highest in at least 20 years for state-level estimates of the vote in presidential, senatorial, and gubernatorial contests.”
How big were the errors? Polls conducted in the last two weeks before the election suggested that Biden’s margin over Trump was nearly twice as large as it ended up being in the final national vote tally.
Errors of this size make it difficult to be confident about who is leading if the election is closely contested, as many U.S. elections are .
Pollsters are rightly working to improve the accuracy of their polls. But even an error of 4 or 5 percentage points isn’t too concerning if the purpose of the poll is to describe whether the public has favorable or unfavorable opinions about candidates , or to show which issues matter to which voters. And on questions that gauge where people stand on issues, we usually want to know broadly where the public stands. We don’t necessarily need to know the precise share of Americans who say, for example, that climate change is mostly caused by human activity. Even judged by its performance in recent elections, polling can still provide a faithful picture of public sentiment on the important issues of the day.
The 2022 midterms saw generally accurate polling, despite a wave of partisan polls predicting a broad Republican victory. In fact, FiveThirtyEight found that “polls were more accurate in 2022 than in any cycle since at least 1998, with almost no bias toward either party.” Moreover, a handful of contrarian polls that predicted a 2022 “red wave” largely washed out when the votes were tallied. In sum, if we focus on polling in the most recent national election, there’s plenty of reason to be encouraged.
Compared with other elections in the past 20 years, polls have been less accurate when Donald Trump is on the ballot. Preelection surveys suffered from large errors – especially at the state level – in 2016 and 2020, when Trump was standing for election. But they performed reasonably well in the 2018 and 2022 midterms, when he was not.
During the 2016 campaign, observers speculated about the possibility that Trump supporters might be less willing to express their support to a pollster – a phenomenon sometimes described as the “shy Trump effect.” But a committee of polling experts evaluated five different tests of the “shy Trump” theory and turned up little to no evidence for each one . Later, Pew Research Center and, in a separate test, a researcher from Yale also found little to no evidence in support of the claim.
Instead, two other explanations are more likely. One is about the difficulty of estimating who will turn out to vote. Research has found that Trump is popular among people who tend to sit out midterms but turn out for him in presidential election years. Since pollsters often use past turnout to predict who will vote, it can be difficult to anticipate when irregular voters will actually show up.
The other explanation is that Republicans in the Trump era have become a little less likely than Democrats to participate in polls . Pollsters call this “partisan nonresponse bias.” Surprisingly, polls historically have not shown any particular pattern of favoring one side or the other. The errors that favored Democratic candidates in the past eight years may be a result of the growth of political polarization, along with declining trust among conservatives in news organizations and other institutions that conduct polls.
Whatever the cause, the fact that Trump is again the nominee of the Republican Party means that pollsters must be especially careful to make sure all segments of the population are properly represented in surveys.
The real margin of error is often about double the one reported. A typical election poll sample of about 1,000 people has a margin of sampling error that’s about plus or minus 3 percentage points. That number expresses the uncertainty that results from taking a sample of the population rather than interviewing everyone . Random samples are likely to differ a little from the population just by chance, in the same way that the quality of your hand in a card game varies from one deal to the next.
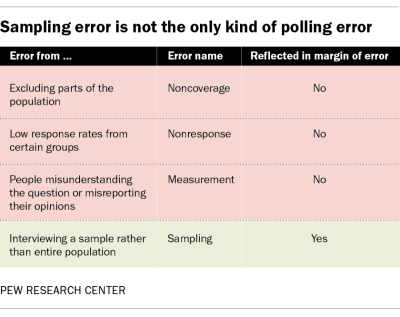
The problem is that sampling error is not the only kind of error that affects a poll. Those other kinds of error, in fact, can be as large or larger than sampling error. Consequently, the reported margin of error can lead people to think that polls are more accurate than they really are.
There are three other, equally important sources of error in polling: noncoverage error , where not all the target population has a chance of being sampled; nonresponse error, where certain groups of people may be less likely to participate; and measurement error, where people may not properly understand the questions or misreport their opinions. Not only does the margin of error fail to account for those other sources of potential error, putting a number only on sampling error implies to the public that other kinds of error do not exist.
Several recent studies show that the average total error in a poll estimate may be closer to twice as large as that implied by a typical margin of sampling error. This hidden error underscores the fact that polls may not be precise enough to call the winner in a close election.
Other important things to remember
Transparency in how a poll was conducted is associated with better accuracy . The polling industry has several platforms and initiatives aimed at promoting transparency in survey methodology. These include AAPOR’s transparency initiative and the Roper Center archive . Polling organizations that participate in these organizations have less error, on average, than those that don’t participate, an analysis by FiveThirtyEight found .
Participation in these transparency efforts does not guarantee that a poll is rigorous, but it is undoubtedly a positive signal. Transparency in polling means disclosing essential information, including the poll’s sponsor, the data collection firm, where and how participants were selected, modes of interview, field dates, sample size, question wording, and weighting procedures.
There is evidence that when the public is told that a candidate is extremely likely to win, some people may be less likely to vote . Following the 2016 election, many people wondered whether the pervasive forecasts that seemed to all but guarantee a Hillary Clinton victory – two modelers put her chances at 99% – led some would-be voters to conclude that the race was effectively over and that their vote would not make a difference. There is scientific research to back up that claim: A team of researchers found experimental evidence that when people have high confidence that one candidate will win, they are less likely to vote. This helps explain why some polling analysts say elections should be covered using traditional polling estimates and margins of error rather than speculative win probabilities (also known as “probabilistic forecasts”).
National polls tell us what the entire public thinks about the presidential candidates, but the outcome of the election is determined state by state in the Electoral College . The 2000 and 2016 presidential elections demonstrated a difficult truth: The candidate with the largest share of support among all voters in the United States sometimes loses the election. In those two elections, the national popular vote winners (Al Gore and Hillary Clinton) lost the election in the Electoral College (to George W. Bush and Donald Trump). In recent years, analysts have shown that Republican candidates do somewhat better in the Electoral College than in the popular vote because every state gets three electoral votes regardless of population – and many less-populated states are rural and more Republican.
For some, this raises the question: What is the use of national polls if they don’t tell us who is likely to win the presidency? In fact, national polls try to gauge the opinions of all Americans, regardless of whether they live in a battleground state like Pennsylvania, a reliably red state like Idaho or a reliably blue state like Rhode Island. In short, national polls tell us what the entire citizenry is thinking. Polls that focus only on the competitive states run the risk of giving too little attention to the needs and views of the vast majority of Americans who live in uncompetitive states – about 80%.
Fortunately, this is not how most pollsters view the world . As the noted political scientist Sidney Verba explained, “Surveys produce just what democracy is supposed to produce – equal representation of all citizens.”
- Survey Methods
- Trust, Facts & Democracy
- Voter Files

Scott Keeter is a senior survey advisor at Pew Research Center .

Courtney Kennedy is Vice President of Methods and Innovation at Pew Research Center .
How do people in the U.S. take Pew Research Center surveys, anyway?
How public polling has changed in the 21st century, what 2020’s election poll errors tell us about the accuracy of issue polling, a field guide to polling: election 2020 edition, methods 101: how is polling done around the world, most popular.
901 E St. NW, Suite 300 Washington, DC 20004 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan, nonadvocacy fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It does not take policy positions. The Center conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, computational social science research and other data-driven research. Pew Research Center is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts , its primary funder.
© 2024 Pew Research Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research Methodology Example. An Example of Research Methodology could be the following: ... Writing a research methodology involves explaining the methods and techniques you used to conduct research, collect data, and analyze results. It's an essential section of any research paper or thesis, as it helps readers understand the validity and ...
How to write up the methodology chapter. First off, it's worth noting that the exact structure and contents of the methodology chapter will vary depending on the field of research (e.g., humanities, chemistry or engineering) as well as the university.So, be sure to always check the guidelines provided by your institution for clarity and, if possible, review past dissertations from your ...
What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips. Published on August 25, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on September 5, 2024. Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing ...
Methodology tips: a video discussion covering various tips to help you write a high-quality methodology chapter Private coaching : Get hands-on help with your research methodology PS - If you're working on a dissertation, be sure to also check out our collection of dissertation and thesis examples here .
Research methodology examples and application. To further understand research methodology, let's explore some examples of research methodology: a. Qualitative research methodology example: A study exploring the impact of author branding on author popularity might utilize in-depth interviews to gather personal experiences and perspectives. b.
Example: Reporting data collection methods and research design All participants were told that the survey concerned students' general knowledge and would take a maximum of thirty minutes. After arriving at the laboratory individually, they were assured confidentiality, and they provided informed consent.
Research methodology is the process or the way you intend to execute your entire research. A research methodology provides a description of the process you will undertake to convert your idea into a study. Read more to find out about types, structure, importance, and tips on research methodology.
What is research methodology? Research methodology simply refers to the practical "how" of a research study. More specifically, it's about how a researcher systematically designs a study to ensure valid and reliable results that address the research aims, objectives and research questions. Specifically, how the researcher went about deciding:
I. Groups of Research Methods. There are two main groups of research methods in the social sciences: The empirical-analytical group approaches the study of social sciences in a similar manner that researchers study the natural sciences.This type of research focuses on objective knowledge, research questions that can be answered yes or no, and operational definitions of variables to be measured.
Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research. It should include:
Where to Write Dissertation Methodology. In a dissertation or thesis, the Methodology section usually follows the Literature Review. This placement allows the Methodology to build upon the theoretical framework and existing research outlined in the Literature Review, and precedes the Results or Findings section.
Your data analysis methods; A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research objectives and that you use the right kind of analysis for your data. You might have to write up a research design as a standalone assignment, or it might be part of a larger research proposal or other project. In either case, you ...
Your Methods Section contextualizes the results of your study, giving editors, reviewers and readers alike the information they need to understand and interpret your work. Your methods are key to establishing the credibility of your study, along with your data and the results themselves. A complete methods section should provide enough detail for a skilled researcher to replicate your process ...
Research methodology 1,2 is a structured and scientific approach used to collect, analyze, and interpret quantitative or qualitative data to answer research questions or test hypotheses. A research methodology is like a plan for carrying out research and helps keep researchers on track by limiting the scope of the research.
Research methodologies can roughly be categorized into three group: quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-methods. Qualitative Research: This methodology is based on obtaining deep, contextualized, non-numerical data. It can occur, for example, through open-ended questioning of research particiapnts in order to understand human behavior.
Learn how to write a strong methodology chapter that allows readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research. A good methodology chapter incl...
Restate your research problem. Begin your research methodology section by listing the problems or questions you intend to study. Include your hypotheses, if applicable, or what you are setting out to prove through your research. In your restatement, include any underlying assumptions that you're making or conditions that you're taking for granted.
Methods section is a crucial part of a manuscript and emphasizes the reliability and validity of a research study. And knowing how to write the methods section of a research paper is the first step in mastering scientific writing. Read this article to understand the importance, purpose, and the best way to write the methods section of a research paper.
You can also take a mixed methods approach, where you use both qualitative and quantitative research methods.. Primary vs. secondary research. Primary research is any original data that you collect yourself for the purposes of answering your research question (e.g. through surveys, observations and experiments). Secondary research is data that has already been collected by other researchers (e ...
The research methodology is essential to a dissertation, thesis, or research paper as it explains the methods applied to collect and analyze data. This chapter from EduBirdie research paper writing services enables readers to estimate the validity and credibility of your research by providing the following information:
Methodology refers to the systematic study of methods used in research. It includes Research Methodology, which is the framework for conducting investigations, and Survey Methodology, which involves techniques for collecting and analyzing survey data. A key part of any methodology is the Research Question, guiding the study's focus and direction.
This refers to a polling method in which survey participants are recruited using random sampling from a database or list that includes nearly everyone in the population. The pollster selects the sample. The survey is not open for anyone who wants to sign up. Online opt-in polling (or "nonprobability sampling").