Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates

How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.9(7); 2013 Jul

Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
Marco pautasso.
1 Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France
2 Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,

The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
Research Methods
- Getting Started
- Literature Review Research
- Research Design
- Research Design By Discipline
- SAGE Research Methods
- Teaching with SAGE Research Methods
Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- What is NOT a Literature Review?
- Purposes of a Literature Review
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Literature Reviews vs. Systematic Reviews
- Systematic vs. Meta-Analysis
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.
Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
- Summarizes and analyzes previous research relevant to a topic
- Includes scholarly books and articles published in academic journals
- Can be an specific scholarly paper or a section in a research paper
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic
- Help gather ideas or information
- Keep up to date in current trends and findings
- Help develop new questions
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Helps focus your own research questions or problems
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Suggests unexplored ideas or populations
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
- Identifies critical gaps, points of disagreement, or potentially flawed methodology or theoretical approaches.
- Indicates potential directions for future research.
All content in this section is from Literature Review Research from Old Dominion University
Keep in mind the following, a literature review is NOT:
Not an essay
Not an annotated bibliography in which you summarize each article that you have reviewed. A literature review goes beyond basic summarizing to focus on the critical analysis of the reviewed works and their relationship to your research question.
Not a research paper where you select resources to support one side of an issue versus another. A lit review should explain and consider all sides of an argument in order to avoid bias, and areas of agreement and disagreement should be highlighted.
A literature review serves several purposes. For example, it
- provides thorough knowledge of previous studies; introduces seminal works.
- helps focus one’s own research topic.
- identifies a conceptual framework for one’s own research questions or problems; indicates potential directions for future research.
- suggests previously unused or underused methodologies, designs, quantitative and qualitative strategies.
- identifies gaps in previous studies; identifies flawed methodologies and/or theoretical approaches; avoids replication of mistakes.
- helps the researcher avoid repetition of earlier research.
- suggests unexplored populations.
- determines whether past studies agree or disagree; identifies controversy in the literature.
- tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
As Kennedy (2007) notes*, it is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the original studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally that become part of the lore of field. In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews.
Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are several approaches to how they can be done, depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study. Listed below are definitions of types of literature reviews:
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply imbedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews.
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical reviews are focused on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [content], but how they said it [method of analysis]. This approach provides a framework of understanding at different levels (i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches and data collection and analysis techniques), enables researchers to draw on a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection and data analysis, and helps highlight many ethical issues which we should be aware of and consider as we go through our study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyse data from the studies that are included in the review. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?"
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to concretely examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review help establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
* Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147.
All content in this section is from The Literature Review created by Dr. Robert Larabee USC
Robinson, P. and Lowe, J. (2015), Literature reviews vs systematic reviews. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health, 39: 103-103. doi: 10.1111/1753-6405.12393

What's in the name? The difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review, and why it matters . By Lynn Kysh from University of Southern California

Systematic review or meta-analysis?
A systematic review answers a defined research question by collecting and summarizing all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria.
A meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of these studies.
Systematic reviews, just like other research articles, can be of varying quality. They are a significant piece of work (the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination at York estimates that a team will take 9-24 months), and to be useful to other researchers and practitioners they should have:
- clearly stated objectives with pre-defined eligibility criteria for studies
- explicit, reproducible methodology
- a systematic search that attempts to identify all studies
- assessment of the validity of the findings of the included studies (e.g. risk of bias)
- systematic presentation, and synthesis, of the characteristics and findings of the included studies
Not all systematic reviews contain meta-analysis.
Meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects of health care than those derived from the individual studies included within a review. More information on meta-analyses can be found in Cochrane Handbook, Chapter 9 .
A meta-analysis goes beyond critique and integration and conducts secondary statistical analysis on the outcomes of similar studies. It is a systematic review that uses quantitative methods to synthesize and summarize the results.
An advantage of a meta-analysis is the ability to be completely objective in evaluating research findings. Not all topics, however, have sufficient research evidence to allow a meta-analysis to be conducted. In that case, an integrative review is an appropriate strategy.
Some of the content in this section is from Systematic reviews and meta-analyses: step by step guide created by Kate McAllister.
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Research Design >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 4:07 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/researchmethods
How to undertake a literature search: a step-by-step guide
Affiliation.
- 1 Literature Search Specialist, Library and Archive Service, Royal College of Nursing, London.
- PMID: 32279549
- DOI: 10.12968/bjon.2020.29.7.431
Undertaking a literature search can be a daunting prospect. Breaking the exercise down into smaller steps will make the process more manageable. This article suggests 10 steps that will help readers complete this task, from identifying key concepts to choosing databases for the search and saving the results and search strategy. It discusses each of the steps in a little more detail, with examples and suggestions on where to get help. This structured approach will help readers obtain a more focused set of results and, ultimately, save time and effort.
Keywords: Databases; Literature review; Literature search; Reference management software; Research questions; Search strategy.
- Databases, Bibliographic*
- Information Storage and Retrieval / methods*
- Nursing Research
- Review Literature as Topic*
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 1:19 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Subject guides
- Researching for your literature review
- Literature reviews
Researching for your literature review: Literature reviews
- Literature sources
- Before you start
- Develop a search strategy
- Keyword search activity
- Subject search activity
- Combined keyword and subject searching
- Online tutorials
- Apply search limits
- Run a search in different databases
- Supplementary searching
- Save your searches
- Manage results
All research, whatever the discipline, needs to be situated in relation to what has already been done in the field.
Reviewing the literature helps you:
- find out what is already known about a topic in order to locate gaps and justify the research being undertaken
- locate the work of important theorists whose ideas will inform the research
- identify useful methodologies, methods and documentary sources
Literature search process
For comprehensive literature searching it is important to be systematic in your approach. This includes developing a plan for your search (including the search terms you will use and the resources you will search), and keeping records of the searches you carry out. The process is listed in steps below, but much of it is iterative rather than linear.

Literature Review versus Systematic Review
You might have heard the term 'Systematic Review'. A systematic review goes further than a literature review in that it aims to locate and evaluate all studies, published and unpublished, relevant to a specific research question.
Systematic reviews use explicit, systematic methods to minimise bias and enable verification and replication. Those produced by the Cochrane Library are often considered to be the 'gold standard'. For more information on systematic reviews please see the Library's Systematic Review guide.
A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies
Meeting the review family: exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Literature sources >>

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
- Open access
- Published: 05 December 2023
A scoping review to identify and organize literature trends of bias research within medical student and resident education
- Brianne E. Lewis 1 &
- Akshata R. Naik 2
BMC Medical Education volume 23 , Article number: 919 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
824 Accesses
1 Citations
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
Physician bias refers to the unconscious negative perceptions that physicians have of patients or their conditions. Medical schools and residency programs often incorporate training to reduce biases among their trainees. In order to assess trends and organize available literature, we conducted a scoping review with a goal to categorize different biases that are studied within medical student (MS), resident (Res) and mixed populations (MS and Res). We also characterized these studies based on their research goal as either documenting evidence of bias (EOB), bias intervention (BI) or both. These findings will provide data which can be used to identify gaps and inform future work across these criteria.
Online databases (PubMed, PsycINFO, WebofScience) were searched for articles published between 1980 and 2021. All references were imported into Covidence for independent screening against inclusion criteria. Conflicts were resolved by deliberation. Studies were sorted by goal: ‘evidence of bias’ and/or ‘bias intervention’, and by population (MS or Res or mixed) andinto descriptive categories of bias.
Of the initial 806 unique papers identified, a total of 139 articles fit the inclusion criteria for data extraction. The included studies were sorted into 11 categories of bias and showed that bias against race/ethnicity, specific diseases/conditions, and weight were the most researched topics. Of the studies included, there was a higher ratio of EOB:BI studies at the MS level. While at the Res level, a lower ratio of EOB:BI was found.
Conclusions
This study will be of interest to institutions, program directors and medical educators who wish to specifically address a category of bias and identify where there is a dearth of research. This study also underscores the need to introduce bias interventions at the MS level.
Peer Review reports
Physician bias ultimately impacts patient care by eroding the physician–patient relationship [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]. To overcome this issue, certain states require physicians to report a varying number of hours of implicit bias training as part of their recurring licensing requirement [ 5 , 6 ]. Research efforts on the influence of implicit bias on clinical decision-making gained traction after the “Unequal Treatment: Confronting Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health Care” report published in 2003 [ 7 ]. This report sparked a conversation about the impact of bias against women, people of color, and other marginalized groups within healthcare. Bias from a healthcare provider has been shown to affect provider-patient communication and may also influence treatment decisions [ 8 , 9 ]. Nevertheless, opportunities within medical education curriculum are created to evaluate biases at an earlier stage of physician-training and provide instruction to intervene them [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. We aimed to identify trends and organize literature on bias training provided during medical school and residency programs since the meaning of ‘bias’ is broad and encompasses several types of attitudes and predispositions [ 13 ].
Several reviews, narrative or systematic in nature, have been published in the field of bias research in medicine and healthcare [ 14 , 15 , 16 ]. Many of these reviews have a broad focus on implicit bias and they often fail to define the patient’s specific attributes- such as age, weight, disease, or condition against which physicians hold their biases. However, two recently published reviews categorized implicit biases into various descriptive characteristics albeit with research goals different than this study [ 17 , 18 ]. The study by Fitzgerald et al. reviewed literature focused on bias among physicians and nurses to highlight its role in healthcare disparities [ 17 ]. While the study by Gonzalez et al. focused on bias curricular interventions across professions related to social determinants of health such as education, law, medicine and social work [ 18 ]. Our research goal was to identify the various bias characteristics that are studied within medical student and/or resident populations and categorize them. Further, we were interested in whether biases were merely identified or if they were intervened. To address these deficits in the field and provide clarity, we utilized a scoping review approach to categorize the literature based on a) the bias addressed and b) the study goal within medical students (MS), residents (Res) and a mixed population (MS and Res).
To date no literature review has organized bias research by specific categories held solely by medical trainees (medical students and/or residents) and quantified intervention studies. We did not perform a quality assessment or outcome evaluation of the bias intervention strategies, as it was not the goal of this work and is standard with a scoping review methodology [ 19 , 20 ]. By generating a comprehensive list of bias categories researched among medical trainee population, we highlight areas of opportunity for future implicit bias research specifically within the undergraduate and graduate medical education curriculum. We anticipate that the results from this scoping review will be useful for educators, administrators, and stakeholders seeking to implement active programs or workshops that intervene specific biases in pre-clinical medical education and prepare physicians-in-training for patient encounters. Additionally, behavioral scientists who seek to support clinicians, and develop debiasing theories [ 21 ] and models may also find our results informative.
We conducted an exhaustive and focused scoping review and followed the methodological framework for scoping reviews as previously described in the literature [ 20 , 22 ]. This study aligned with the four goals of a scoping review [ 20 ]. We followed the first five out of the six steps outlined by Arksey and O’Malley’s to ensure our review’s validity 1) identifying the research question 2) identifying relevant studies 3) selecting the studies 4) charting the data and 5) collating, summarizing and reporting the results [ 22 ]. We did not follow the optional sixth step of undertaking consultation with key stakeholders as it was not needed to address our research question it [ 23 ]. Furthermore, we used Covidence systematic review software (Veritas Health Innovation, Melbourne, Australia) that aided in managing steps 2–5 presented above.
Research question, search strategy and inclusion criteria
The purpose of this study was to identify trends in bias research at the medical school and residency level. Prior to conducting our literature search we developed our research question and detailed the inclusion criteria, and generated the search syntax with the assistance from a medical librarian. Search syntax was adjusted to the requirements of the database. We searched PubMed, Web of Science, and PsycINFO using MeSH terms shown below.
Bias* [ti] OR prejudice*[ti] OR racism[ti] OR homophobia[ti] OR mistreatment[ti] OR sexism[ti] OR ageism[ti]) AND (prejudice [mh] OR "Bias"[Mesh:NoExp]) AND (Education, Medical [mh] OR Schools, Medical [mh] OR students, medical [mh] OR Internship and Residency [mh] OR “undergraduate medical education” OR “graduate medical education” OR “medical resident” OR “medical residents” OR “medical residency” OR “medical residencies” OR “medical schools” OR “medical school” OR “medical students” OR “medical student”) AND (curriculum [mh] OR program evaluation [mh] OR program development [mh] OR language* OR teaching OR material* OR instruction* OR train* OR program* OR curricul* OR workshop*
Our inclusion criteria incorporated studies which were either original research articles, or review articles that synthesized new data. We excluded publications that were not peer-reviewed or supported with data such as narrative reviews, opinion pieces, editorials, perspectives and commentaries. We included studies outside of the U.S. since the purpose of this work was to generate a comprehensive list of biases. Physicians, regardless of their country of origin, can hold biases against specific patient attributes [ 17 ]. Furthermore, physicians may practice in a different country than where they trained [ 24 ]. Manuscripts were included if they were published in the English language for which full-texts were available. Since the goal of this scoping review was to assess trends, we accepted studies published from 1980–2021.
Our inclusion criteria also considered the goal and the population of the study. We defined the study goal as either that documented evidence of bias or a program directed bias intervention. Evidence of bias (EOB) had to originate from the medical trainee regarding a patient attribute. Bias intervention (BI) studies involved strategies to counter biases such as activities, workshops, seminars or curricular innovations. The population studied had to include medical students (MS) or residents (Res) or mixed. We defined the study population as ‘mixed’ when it consisted of both MS and Res. Studies conducted on other healthcare professionals were included if MS or Res were also studied. Our search criteria excluded studies that documented bias against medical professionals (students, residents and clinicians) either by patients, medical schools, healthcare administrators or others, and was focused on studies where the biases were solely held by medical trainees (MS and Res).
Data extraction and analysis
Following the initial database search, references were downloaded and bulk uploaded into Covidence and duplicates were removed. After the initial screening of title and abstracts, full-texts were reviewed. Authors independently completed title and abstract screening, and full text reviews. Any conflicts at the stage of abstract screening were moved to full-text screening. Conflicts during full-text screening were resolved by deliberation and referring to the inclusion and exclusion criteria detailed in the research protocol. The level of agreement between the two authors for full text reviews as measured by inter-rater reliability was 0.72 (Cohen’s Kappa).
A data extraction template was created in Covidence to extract data from included full texts. Data extraction template included the following variables; country in which the study was conducted, year of publication, goal of the study (EOB, BI or both), population of the study (MS, Res or mixed) and the type of bias studied. Final data was exported to Microsoft Excel for quantification. For charting our data and categorizing the included studies, we followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews(PRISMA-ScR) guidelines [ 25 ]. Results from this scoping review study are meant to provide a visual synthesis of existing bias research and identify gaps in knowledge.
Study selection
Our search strategy yielded a total of 892 unique abstracts which were imported into ‘Covidence’ for screening. A total of 86 duplicate references were removed. Then, 806 titles and abstracts were screened for relevance independently by the authors and 519 studies were excluded at this stage. Any conflicts among the reviewers at this stage were resolved by discussion and referring to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Then a full text review of the remaining 287 papers was completed by the authors against the inclusion criteria for eligibility. Full text review was also conducted independently by the authors and any conflicts were resolved upon discussion. Finally, we included 139 studies which were used for data extraction (Fig. 1 ).
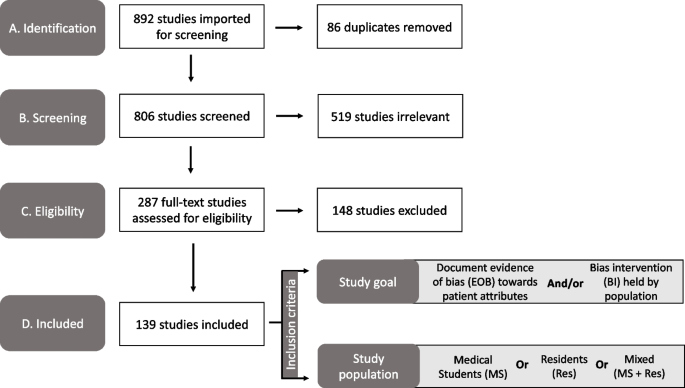
PRISMA diagram of the study selection process used in our scoping review to identify the bias categories that have been reported within medical education literature. Study took place from 2021–2022. Abbreviation: PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Publication trends in bias research
First, we charted the studies to demonstrate the timeline of research focused on bias within the study population of our interest (MS or Res or mixed). Our analysis revealed an increase in publications with respect to time (Fig. 2 ). Of the 139 included studies, fewer studies were published prior to 2001, with a total of only eight papers being published from the years 1985–2000. A substantial increase in publications occurred after 2004, with 2019 being the peak year where most of the studies pertaining to bias were published (Fig. 2 ).
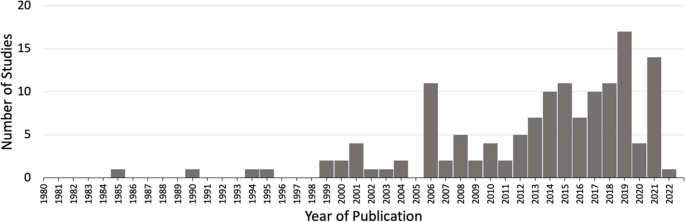
Studies matching inclusion criteria mapped by year of publication. Search criteria included studies addressing bias from 1980–2021 within medical students (MS) or residents (Res) or mixed (MS + Res) populations. * Publication in 2022 was published online ahead of print
Overview of included studies
We present a descriptive analysis of the 139 included studies in Table 1 based on the following parameters: study location, goal of the study, population of the study and the category of bias studied. All of the above parameters except the category of bias included a denominator of 139 studies. Several studies addressed more than one bias characteristic; therefore, we documented 163 biases sorted in 11 categories over the 139 papers. The bias categories that we generated and their respective occurrences are listed in Table 1 . Of the 139 studies that were included, most studies originated in the United States ( n = 89/139, 64%) and Europe ( n = 20/139, 20%).
Sorting of included research by bias category
We grouped the 139 included studies depending on the patient attribute or the descriptive characteristic against which the bias was studied (Table 1 ). By sorting the studies into different bias categories, we aimed to not only quantitate the amount of research addressing a particular topic of bias, but also reveal the biases that are understudied.
Through our analysis, we generated 11 descriptive categories against which bias was studied: Age, physical disability, education level, biological sex, disease or condition, LGBTQ + , non-specified, race/ethnicity, rural/urban, socio-economic status, and weight (Table 1 ). “Age” and “weight” categories included papers that studied bias against older population and higher weight individuals, respectively. The categories “education level” and “socio-economic status” included papers that studied bias against individuals with low education level and individuals belonging to low socioeconomic status, respectively. Within the bias category named ‘biological sex’, we included papers that studied bias against individuals perceived as women/females. Papers that studied bias against gender-identity or sexual orientation were included in its own category named, ‘LGBTQ + ’. The bias category, ‘disease or condition’ was broad and included research on bias against any patient with a specific disease, condition or lifestyle. Studies included in this category researched bias against any physical illnesses, mental illnesses, or sexually transmitted infections. It also included studies that addressed bias against a treatment such as transplant or pain management. It was not significant to report these as individual categories but rather as a whole with a common underlying theme. Rural/urban bias referred to bias that was held against a person based on their place of residence. Studies grouped together in the ‘non-specified bias’ category explored bias without specifying any descriptive characteristic in their methods. These studies did not address any specific bias characteristic in particular but consisted of a study population of our interest (MS or Res or mixed). Based on our analysis, the top five most studied bias categories in our included population within medical education literature were: racial or ethnic bias ( n = 39/163, 24%), disease or condition bias ( n = 29/163, 18%), weight bias ( n = 22/163, 13%), LGBTQ + bias ( n = 21/163, 13%), and age bias ( n = 16/163, 10%) which are presented in Table 1 .
Sorting of included research by population
In order to understand the distribution of bias research based on their populations examined, we sorted the included studies in one of the following: medical students (MS), residents (Res) or mixed (Table 1 ). The following distributions were observed: medical students only ( n = 105/139, 76%), residents only ( n = 19/139, 14%) or mixed which consisted of both medical students and residents ( n = 15/139, 11%). In combination, these results demonstrate that medical educators have focused bias research efforts primarily on medical student populations.
Sorting of included research by goal
A critical component of this scoping review was to quantify the research goal of the included studies within each of the bias categories. We defined the research goal as either to document evidence of bias (EOB) or to evaluate a bias intervention (BI) (see Fig. 1 for inclusion criteria). Some of the included studies focused on both, documenting evidence in addition to intervening biases and those studies were grouped separately. The analysis revealed that 69/139 (50%) of the included studies focused exclusively on documenting evidence of bias (EOB). There were fewer studies ( n = 51/139, 37%) which solely focused on bias interventions such as programs, seminars or curricular innovations. A small minority of the included studies were more comprehensive in that they documented EOB followed by an intervention strategy ( n = 19/139, 11%). These results demonstrate that most bias research is dedicated to documenting evidence of bias among these groups rather than evaluating a bias intervention strategy.
Research goal distribution
Our next objective was to calculate the distribution of studies with respect to the study goal (EOB, BI or both), within the 163 biases studied across the 139 papers as calculated in Table 1 . In general, the goal of the studies favors documenting evidence of bias with the exception of race/ethnic bias which is more focused on bias intervention (Fig. 3 ). Fewer studies were aimed at both, documenting evidence then providing an intervention, across all bias categories.
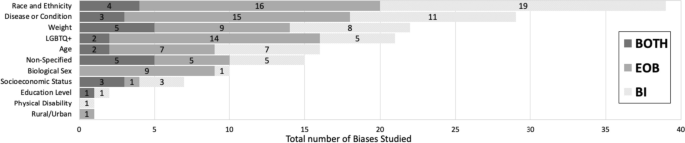
Sorting of total biases ( n = 163) within medical students or residents or a mixed population based on the bias category . Dark grey indicates studies with a dual goal, to document evidence of bias and to intervene bias. Medium grey bars indicate studies which focused on documenting evidence of bias. Light grey bars indicate studies focused on bias intervention within these populations. Numbers inside the bars indicate the total number of biases for the respective study goal. * Non-specified bias includes studies which focused on implicit bias but did not mention the type of bias investigated
Furthermore, we also calculated the ratio of EOB, BI and both (EOB + BI) within each of our population of interest (MS; n = 122, Res; n = 26 and mixed; n = 15) for the 163 biases observed in our included studies. Over half ( n = 64/122, 52%) of the total bias occurrences in MS were focused on documenting EOB (Fig. 4 ). Contrastingly, a shift was observed within resident populations where most biases addressed were aimed at intervention ( n = 12/26, 41%) rather than EOB ( n = 4/26, 14%) (Fig. 4 ). Studies which included both MS and Res (mixed) were primarily focused on documenting EOB ( n = 9/15, 60%), with 33% ( n = 5/15) aimed at bias intervention and 7% ( n = 1/15) which did both (Fig. 4 ). Although far fewer studies were documented in the Res population it is important to highlight that most of these studies were focused on bias intervention when compared to MS population where we documented a majority of studies focused on evidence of bias.
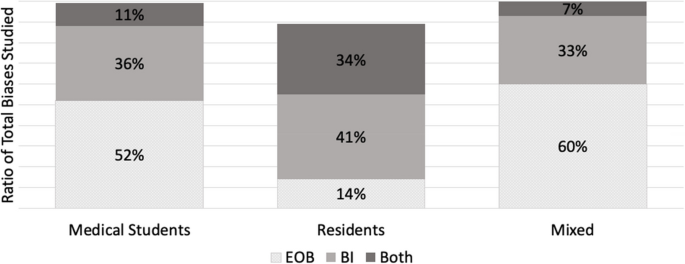
A ratio of the study goal for the total biases ( n = 163) mapped within each of the study population (MS, Res and Mixed). A study goal with a) documenting evidence of bias (EOB) is depicted in dotted grey, b) bias intervention (BI) in medium grey, and c) a dual focus (EOB + BI) is depicted in dark grey. * N = 122 for medical student studies. b N = 26 for residents. c N = 15 for mixed
Addressing biases at an earlier stage of medical career is critical for future physicians engaging with diverse patients, since it is established that bias negatively influences provider-patient interactions [ 171 ], clinical decision-making [ 172 ] and reduces favorable treatment outcomes [ 2 ]. We set out with an intention to explore how bias is addressed within the medical curriculum. Our research question was: how has the trend in bias research changed over time, more specifically a) what is the timeline of papers published? b) what bias characteristics have been studied in the physician-trainee population and c) how are these biases addressed? With the introduction of ‘standards of diversity’ by the Liaison Committee on Medical Education, along with the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) and the American Medical Association (AMA) [ 173 , 174 ], we certainly expected and observed a sustained uptick in research pertaining to bias. As shown here, research addressing bias in the target population (MS and Res) is on the rise, however only 139 papers fit our inclusion criteria. Of these studies, nearly 90% have been published since 2005 after the “Unequal Treatment: Confronting Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health Care” report was published in 2003 [ 7 ]. However, given the well documented effects of physician held bias, we anticipated significantly more number of studies focused on bias at the medical student or resident level.
A key component from this study was that we generated descriptive categories of biases. Sorting the biases into descriptive categories helps to identify a more targeted approach for a specific bias intervention, rather than to broadly intervene bias as a whole. In fact, our analysis found a number of publications (labeled “non-specified bias” in Table 1 ) which studied implicit bias without specifying the patient attribute or the characteristic that the bias was against. In total, we generated 11 descriptive categories of bias from our scoping review which are shown in Table 1 and Fig. 3 . Furthermore, our bias descriptors grouped similar kinds of biases within a single category. For example, the category, “disease or condition” included papers that studied bias against any type of disease (Mental illness, HIV stigma, diabetes), condition (Pain management), or lifestyle. We neither performed a qualitative assessment of the studies nor did we test the efficacy of the bias intervention studies and consider it a future direction of this work.
Evidence suggests that medical educators and healthcare professionals are struggling to find the appropriate approach to intervene biases [ 175 , 176 , 177 ] So far, bias reduction, bias reflection and bias management approaches have been proposed [ 26 , 27 , 178 ]. Previous implicit bias intervention strategies have been shown to be ineffective when biased attitudes of participants were assessed after a lag [ 179 ]. Understanding the descriptive categories of bias and previous existing research efforts, as we present here is only a fraction of the challenge. The theory of “cognitive bias” [ 180 ] and related branches of research [ 13 , 181 , 182 , 183 , 184 ] have been studied in the field of psychology for over three decades. It is only recently that cognitive bias theory has been applied to the field of medical education medicine, to explain its negative influence on clinical decision-making pertaining only to racial minorities [ 1 , 2 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 185 ]. In order to elicit meaningful changes with respect to targeted bias intervention, it is necessary to understand the psychological underpinnings (attitudes) leading to a certain descriptive category of bias (behaviors). The questions which medical educators need to ask are: a) Can these descriptive biases be identified under certain type/s of cognitive errors that elicits the bias and vice versa b) Are we working towards an attitude change which can elicit a sustained positive behavior change among healthcare professionals? And most importantly, c) are we creating a culture where participants voluntarily enroll themselves in bias interventions as opposed to being mandated to participate? Cognitive psychologists and behavioral scientists are well-positioned to help us find answers to these questions as they understand human behavior. Therefore, an interdisciplinary approach, a marriage between cognitive psychologists and medical educators, is key in targeting biases held by medical students, residents, and ultimately future physicians. This review may also be of interest to behavioral psychologists, keen on providing targeted intervening strategies to clinicians depending on the characteristics (age, weight, sex or race) the portrayed bias is against. Further, instead of an individualized approach, we need to strive for systemic changes and evidence-based strategies to intervene biases.
The next element in change is directing intervention strategies at the right stage in clinical education. Our study demonstrated that most of the research collected at the medical student level was focused on documenting evidence of bias. Although the overall number of studies at the resident level were fewer than at the medical student level, the ratio of research in favor of bias intervention was higher at the resident level (see Fig. 3 ). However, it could be helpful to focus on bias intervention earlier in learning, rather than at a later stage [ 186 ]. Additionally, educational resources such as textbooks, preparatory materials, and educators themselves are potential sources of propagating biases and therefore need constant evaluation against best practices [ 187 , 188 ].
This study has limitations. First, the list of the descriptive bias categories that we generated was not grounded in any particular theory so assigning a category was subjective. Additionally, there were studies that were categorized as “nonspecified” bias as the studies themselves did not mention the specific type of bias that they were addressing. Moreover, we had to exclude numerous publications solely because they were not evidence-based and were either perspectives, commentaries or opinion pieces. Finally, there were overall fewer studies focused on the resident population, so the calculated ratio of MS:Res studies did not compare similar sample sizes.
Future directions of our study include working with behavioral scientists to categorize these bias characteristics (Table 1 ) into cognitive error types [ 189 ]. Additionally, we aim to assess the effectiveness of the intervention strategies and categorize the approach of the intervention strategies.
The primary goal of our review was to organize, compare and quantify literature pertaining to bias within medical school curricula and residency programs. We neither performed a qualitative assessment of the studies nor did we test the efficacy of studies that were sorted into “bias intervention” as is typical of scoping reviews [ 22 ]. In summary, our research identified 11 descriptive categories of biases studied within medical students and resident populations with “race and ethnicity”, “disease or condition”, “weight”, “LGBTQ + ” and “age” being the top five most studied biases. Additionally, we found a greater number of studies conducted in medical students (105/139) when compared to residents (19/139). However, most of the studies in the resident population focused on bias intervention. The results from our review highlight the following gaps: a) bias categories where more research is needed, b) biases that are studied within medical school versus in residency programs and c) study focus in terms of demonstrating the presence of bias or working towards bias intervention.
This review provides a visual analysis of the known categories of bias addressed within the medical school curriculum and in residency programs in addition to providing a comparison of studies with respect to the study goal within medical education literature. The results from our review should be of interest to community organizations, institutions, program directors and medical educators interested in knowing and understanding the types of bias existing within healthcare populations. It might be of special interest to researchers who wish to explore other types of biases that have been understudied within medical school and resident populations, thus filling the gaps existing in bias research.
Despite the number of studies designed to provide bias intervention for MS and Res populations, and an overall cultural shift to be aware of one’s own biases, biases held by both medical students and residents still persist. Further, psychologists have recently demonstrated the ineffectiveness of some bias intervention efforts [ 179 , 190 ]. Therefore, it is perhaps unrealistic to expect these biases to be eliminated altogether. However, effective intervention strategies grounded in cognitive psychology should be implemented earlier on in medical training. Our focus should be on providing evidence-based approaches and safe spaces for an attitude and culture change, so as to induce actionable behavioral changes.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Medical student
Evidence of bias
- Bias intervention
Hagiwara N, Mezuk B, Elston Lafata J, Vrana SR, Fetters MD. Study protocol for investigating physician communication behaviours that link physician implicit racial bias and patient outcomes in Black patients with type 2 diabetes using an exploratory sequential mixed methods design. BMJ Open. 2018;8(10):e022623.
Article Google Scholar
Haider AH, Schneider EB, Sriram N, Dossick DS, Scott VK, Swoboda SM, Losonczy L, Haut ER, Efron DT, Pronovost PJ, et al. Unconscious race and social class bias among acute care surgical clinicians and clinical treatment decisions. JAMA Surg. 2015;150(5):457–64.
Penner LA, Dovidio JF, Gonzalez R, Albrecht TL, Chapman R, Foster T, Harper FW, Hagiwara N, Hamel LM, Shields AF, et al. The effects of oncologist implicit racial bias in racially discordant oncology interactions. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(24):2874–80.
Phelan SM, Burgess DJ, Yeazel MW, Hellerstedt WL, Griffin JM, van Ryn M. Impact of weight bias and stigma on quality of care and outcomes for patients with obesity. Obes Rev. 2015;16(4):319–26.
Garrett SB, Jones L, Montague A, Fa-Yusuf H, Harris-Taylor J, Powell B, Chan E, Zamarripa S, Hooper S, Chambers Butcher BD. Challenges and opportunities for clinician implicit bias training: insights from perinatal care stakeholders. Health Equity. 2023;7(1):506–19.
Shah HS, Bohlen J. Implicit bias. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Copyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC.
Google Scholar
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Understanding and Eliminating Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health Care. Unequal Treatment: Confronting Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health Care. In: Smedley BD, Stith AY, Nelson AR, editors. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2003. PMID: 25032386.
Dehon E, Weiss N, Jones J, Faulconer W, Hinton E, Sterling S. A systematic review of the impact of physician implicit racial bias on clinical decision making. Acad Emerg Med. 2017;24(8):895–904.
Oliver MN, Wells KM, Joy-Gaba JA, Hawkins CB, Nosek BA. Do physicians’ implicit views of African Americans affect clinical decision making? J Am Board Fam Med. 2014;27(2):177–88.
Rincon-Subtirelu M. Education as a tool to modify anti-obesity bias among pediatric residents. Int J Med Educ. 2017;8:77–8.
Gustafsson Sendén M, Renström EA. Gender bias in assessment of future work ability among pain patients - an experimental vignette study of medical students’ assessment. Scand J Pain. 2019;19(2):407–14.
Hardeman RR, Burgess D, Phelan S, Yeazel M, Nelson D, van Ryn M. Medical student socio-demographic characteristics and attitudes toward patient centered care: do race, socioeconomic status and gender matter? A report from the medical student CHANGES study. Patient Educ Couns. 2015;98(3):350–5.
Greenwald AG, Banaji MR. Implicit social cognition: attitudes, self-esteem, and stereotypes. Psychol Rev. 1995;102(1):4–27.
Kruse JA, Collins JL, Vugrin M. Educational strategies used to improve the knowledge, skills, and attitudes of health care students and providers regarding implicit bias: an integrative review of the literature. Int J Nurs Stud Adv. 2022;4:100073.
Zestcott CA, Blair IV, Stone J. Examining the presence, consequences, and reduction of implicit bias in health care: a narrative review. Group Process Intergroup Relat. 2016;19(4):528–42.
Hall WJ, Chapman MV, Lee KM, Merino YM, Thomas TW, Payne BK, Eng E, Day SH, Coyne-Beasley T. Implicit racial/ethnic bias among health care professionals and its influence on health care outcomes: a systematic review. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(12):E60–76.
FitzGerald C, Hurst S. Implicit bias in healthcare professionals: a systematic review. BMC Med Ethics. 2017;18(1):19.
Gonzalez CM, Onumah CM, Walker SA, Karp E, Schwartz R, Lypson ML. Implicit bias instruction across disciplines related to the social determinants of health: a scoping review. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2023;28(2):541–87.
Pham MT, Rajić A, Greig JD, Sargeant JM, Papadopoulos A, McEwen SA. A scoping review of scoping reviews: advancing the approach and enhancing the consistency. Res Synth Methods. 2014;5(4):371–85.
Levac D, Colquhoun H, O’Brien KK. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implement Sci. 2010;5:69.
Pat C, Geeta S, Sílvia M. Cognitive debiasing 1: origins of bias and theory of debiasing. BMJ Qual Saf. 2013;22(Suppl 2):ii58.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Thomas A, Lubarsky S, Durning SJ, Young ME. Knowledge syntheses in medical education: demystifying scoping reviews. Acad Med. 2017;92(2):161–6.
Hagopian A, Thompson MJ, Fordyce M, Johnson KE, Hart LG. The migration of physicians from sub-Saharan Africa to the United States of America: measures of the African brain drain. Hum Resour Health. 2004;2(1):17.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, Moher D, Peters MDJ, Horsley T, Weeks L, et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Teal CR, Shada RE, Gill AC, Thompson BM, Frugé E, Villarreal GB, Haidet P. When best intentions aren’t enough: Helping medical students develop strategies for managing bias about patients. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(Suppl 2):S115–8.
Gonzalez CM, Walker SA, Rodriguez N, Noah YS, Marantz PR. Implicit bias recognition and management in interpersonal encounters and the learning environment: a skills-based curriculum for medical students. MedEdPORTAL. 2021;17:11168.
Hoffman KM, Trawalter S, Axt JR, Oliver MN. Racial bias in pain assessment and treatment recommendations, and false beliefs about biological differences between blacks and whites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(16):4296–301.
Mayfield JJ, Ball EM, Tillery KA, Crandall C, Dexter J, Winer JM, Bosshardt ZM, Welch JH, Dolan E, Fancovic ER, et al. Beyond men, women, or both: a comprehensive, LGBTQ-inclusive, implicit-bias-aware, standardized-patient-based sexual history taking curriculum. MedEdPORTAL. 2017;13:10634.
Morris M, Cooper RL, Ramesh A, Tabatabai M, Arcury TA, Shinn M, Im W, Juarez P, Matthews-Juarez P. Training to reduce LGBTQ-related bias among medical, nursing, and dental students and providers: a systematic review. BMC Med Educ. 2019;19(1):325.
Perdomo J, Tolliver D, Hsu H, He Y, Nash KA, Donatelli S, Mateo C, Akagbosu C, Alizadeh F, Power-Hays A, et al. Health equity rounds: an interdisciplinary case conference to address implicit bias and structural racism for faculty and trainees. MedEdPORTAL. 2019;15:10858.
Sherman MD, Ricco J, Nelson SC, Nezhad SJ, Prasad S. Implicit bias training in a residency program: aiming for enduring effects. Fam Med. 2019;51(8):677–81.
van Ryn M, Hardeman R, Phelan SM, Burgess DJ, Dovidio JF, Herrin J, Burke SE, Nelson DB, Perry S, Yeazel M, et al. Medical school experiences associated with change in implicit racial bias among 3547 students: a medical student CHANGES study report. J Gen Intern Med. 2015;30(12):1748–56.
Chary AN, Molina MF, Dadabhoy FZ, Manchanda EC. Addressing racism in medicine through a resident-led health equity retreat. West J Emerg Med. 2020;22(1):41–4.
DallaPiazza M, Padilla-Register M, Dwarakanath M, Obamedo E, Hill J, Soto-Greene ML. Exploring racism and health: an intensive interactive session for medical students. MedEdPORTAL. 2018;14:10783.
Dennis SN, Gold RS, Wen FK. Learner reactions to activities exploring racism as a social determinant of health. Fam Med. 2019;51(1):41–7.
Gonzalez CM, Walker SA, Rodriguez N, Karp E, Marantz PR. It can be done! a skills-based elective in implicit bias recognition and management for preclinical medical students. Acad Med. 2020;95(12S Addressing Harmful Bias and Eliminating Discrimination in Health Professions Learning Environments):S150–5.
Motzkus C, Wells RJ, Wang X, Chimienti S, Plummer D, Sabin J, Allison J, Cashman S. Pre-clinical medical student reflections on implicit bias: Implications for learning and teaching. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(11):e0225058.
Phelan SM, Burke SE, Cunningham BA, Perry SP, Hardeman RR, Dovidio JF, Herrin J, Dyrbye LN, White RO, Yeazel MW, et al. The effects of racism in medical education on students’ decisions to practice in underserved or minority communities. Acad Med. 2019;94(8):1178–89.
Zeidan A, Tiballi A, Woodward M, Di Bartolo IM. Targeting implicit bias in medicine: lessons from art and archaeology. West J Emerg Med. 2019;21(1):1–3.
Baker TK, Smith GS, Jacobs NN, Houmanfar R, Tolles R, Kuhls D, Piasecki M. A deeper look at implicit weight bias in medical students. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2017;22(4):889–900.
Eymard AS, Douglas DH. Ageism among health care providers and interventions to improve their attitudes toward older adults: an integrative review. J Gerontol Nurs. 2012;38(5):26–35.
Garrison CB, McKinney-Whitson V, Johnston B, Munroe A. Race matters: addressing racism as a health issue. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2018;53(5–6):436–44.
Geller G, Watkins PA. Addressing medical students’ negative bias toward patients with obesity through ethics education. AMA J Ethics. 2018;20(10):E948-959.
Onyeador IN, Wittlin NM, Burke SE, Dovidio JF, Perry SP, Hardeman RR, Dyrbye LN, Herrin J, Phelan SM, van Ryn M. The value of interracial contact for reducing anti-black bias among non-black physicians: a Cognitive Habits and Growth Evaluation (CHANGE) study report. Psychol Sci. 2020;31(1):18–30.
Poustchi Y, Saks NS, Piasecki AK, Hahn KA, Ferrante JM. Brief intervention effective in reducing weight bias in medical students. Fam Med. 2013;45(5):345–8.
Ruiz JG, Andrade AD, Anam R, Taldone S, Karanam C, Hogue C, Mintzer MJ. Group-based differences in anti-aging bias among medical students. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2015;36(1):58–78.
Simpson T, Evans J, Goepfert A, Elopre L. Implementing a graduate medical education anti-racism workshop at an academic university in the Southern USA. Med Educ Online. 2022;27(1):1981803.
Wittlin NM, Dovidio JF, Burke SE, Przedworski JM, Herrin J, Dyrbye L, Onyeador IN, Phelan SM, van Ryn M. Contact and role modeling predict bias against lesbian and gay individuals among early-career physicians: a longitudinal study. Soc Sci Med. 2019;238:112422.
Miller DP Jr, Spangler JG, Vitolins MZ, Davis SW, Ip EH, Marion GS, Crandall SJ. Are medical students aware of their anti-obesity bias? Acad Med. 2013;88(7):978–82.
Gonzalez CM, Deno ML, Kintzer E, Marantz PR, Lypson ML, McKee MD. A qualitative study of New York medical student views on implicit bias instruction: implications for curriculum development. J Gen Intern Med. 2019;34(5):692–8.
Gonzalez CM, Kim MY, Marantz PR. Implicit bias and its relation to health disparities: a teaching program and survey of medical students. Teach Learn Med. 2014;26(1):64–71.
Gonzalez CM, Nava S, List J, Liguori A, Marantz PR. How assumptions and preferences can affect patient care: an introduction to implicit bias for first-year medical students. MedEdPORTAL. 2021;17:11162.
Hernandez RA, Haidet P, Gill AC, Teal CR. Fostering students’ reflection about bias in healthcare: cognitive dissonance and the role of personal and normative standards. Med Teach. 2013;35(4):e1082-1089.
Kushner RF, Zeiss DM, Feinglass JM, Yelen M. An obesity educational intervention for medical students addressing weight bias and communication skills using standardized patients. BMC Med Educ. 2014;14:53.
Nazione S, Silk KJ. Patient race and perceived illness responsibility: effects on provider helping and bias. Med Educ. 2013;47(8):780–9.
Ogunyemi D. Defeating unconscious bias: the role of a structured, reflective, and interactive workshop. J Grad Med Educ. 2021;13(2):189–94.
Phelan SM, Burke SE, Hardeman RR, White RO, Przedworski J, Dovidio JF, Perry SP, Plankey M, A Cunningham B, Finstad D, et al. Medical school factors associated with changes in implicit and explicit bias against gay and lesbian people among 3492 graduating medical students. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32(11):1193–201.
Phelan SM, Puhl RM, Burke SE, Hardeman R, Dovidio JF, Nelson DB, Przedworski J, Burgess DJ, Perry S, Yeazel MW, et al. The mixed impact of medical school on medical students’ implicit and explicit weight bias. Med Educ. 2015;49(10):983–92.
Barber Doucet H, Ward VL, Johnson TJ, Lee LK. Implicit bias and caring for diverse populations: pediatric trainee attitudes and gaps in training. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2021;60(9–10):408–17.
Burke SE, Dovidio JF, Przedworski JM, Hardeman RR, Perry SP, Phelan SM, Nelson DB, Burgess DJ, Yeazel MW, van Ryn M. Do contact and empathy mitigate bias against gay and lesbian people among heterosexual first-year medical students? A report from the medical student CHANGE study. Acad Med. 2015;90(5):645–51.
Johnston B, McKinney-Whitson V, Garrison V. Race matters: addressing racism as a health issue. WMJ. 2021;120(S1):S74–7.
Kost A, Akande T, Jones R, Gabert R, Isaac M, Dettmar NS. Use of patient identifiers at the University of Washington School of Medicine: building institutional consensus to reduce bias and stigma. Fam Med. 2021;53(5):366–71.
Madan AK, Aliabadi-Wahle S, Beech DJ. Ageism in medical students’ treatment recommendations: the example of breast-conserving procedures. Acad Med. 2001;76(3):282–4.
Marbin J, Lewis L, Kuo AK, Schudel C, Gutierrez JR. The power of place: travel to explore structural racism and health disparities. Acad Med. 2021;96(11):1569–73.
Phelan SM, Dovidio JF, Puhl RM, Burgess DJ, Nelson DB, Yeazel MW, Hardeman R, Perry S, van Ryn M. Implicit and explicit weight bias in a national sample of 4,732 medical students: the medical student CHANGES study. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014;22(4):1201–8.
Van J, Aloman C, Reau N. Potential bias and misconceptions in liver transplantation for alcohol- and obesity-related liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(10):2089–97.
White-Means S, Zhiyong D, Hufstader M, Brown LT. Cultural competency, race, and skin tone bias among pharmacy, nursing, and medical students: implications for addressing health disparities. Med Care Res Rev. 2009;66(4):436–55.
Williams RL, Vasquez CE, Getrich CM, Kano M, Boursaw B, Krabbenhoft C, Sussman AL. Racial/gender biases in student clinical decision-making: a mixed-method study of medical school attributes associated with lower incidence of biases. J Gen Intern Med. 2018;33(12):2056–64.
Cohen RW, Persky S. Influence of weight etiology information and trainee characteristics on physician-trainees’ clinical and interpersonal communication. Patient Educ Couns. 2019;102(9):1644–9.
Haider AH, Sexton J, Sriram N, Cooper LA, Efron DT, Swoboda S, Villegas CV, Haut ER, Bonds M, Pronovost PJ, et al. Association of unconscious race and social class bias with vignette-based clinical assessments by medical students. JAMA. 2011;306(9):942–51.
Lewis R, Lamdan RM, Wald D, Curtis M. Gender bias in the diagnosis of a geriatric standardized patient: a potential confounding variable. Acad Psychiatry. 2006;30(5):392–6.
Matharu K, Shapiro JF, Hammer RR, Kravitz RL, Wilson MD, Fitzgerald FT. Reducing obesity prejudice in medical education. Educ Health. 2014;27(3):231–7.
McLean ME, McLean LE, McLean-Holden AC, Campbell LF, Horner AM, Kulkarni ML, Melville LD, Fernandez EA. Interphysician weight bias: a cross-sectional observational survey study to guide implicit bias training in the medical workplace. Acad Emerg Med. 2021;28(9):1024–34.
Meadows A, Higgs S, Burke SE, Dovidio JF, van Ryn M, Phelan SM. Social dominance orientation, dispositional empathy, and need for cognitive closure moderate the impact of empathy-skills training, but not patient contact, on medical students’ negative attitudes toward higher-weight patients. Front Psychol. 2017;8:15.
Stone J, Moskowitz GB, Zestcott CA, Wolsiefer KJ. Testing active learning workshops for reducing implicit stereotyping of Hispanics by majority and minority group medical students. Stigma Health. 2020;5(1):94–103.
Symons AB, Morley CP, McGuigan D, Akl EA. A curriculum on care for people with disabilities: effects on medical student self-reported attitudes and comfort level. Disabil Health J. 2014;7(1):88–95.
Ufomata E, Eckstrand KL, Hasley P, Jeong K, Rubio D, Spagnoletti C. Comprehensive internal medicine residency curriculum on primary care of patients who identify as LGBT. LGBT Health. 2018;5(6):375–80.
Aultman JM, Borges NJ. A clinical and ethical investigation of pre-medical and medical students’ attitudes, knowledge, and understanding of HIV. Med Educ Online. 2006;11:1–12.
Bates T, Cohan M, Bragg DS, Bedinghaus J. The Medical College of Wisconsin senior mentor program: experience of a lifetime. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2006;27(2):93–103.
Chiaramonte GR, Friend R. Medical students’ and residents’ gender bias in the diagnosis, treatment, and interpretation of coronary heart disease symptoms. Health Psychol. 2006;25(3):255–66.
Friedberg F, Sohl SJ, Halperin PJ. Teaching medical students about medically unexplained illnesses: a preliminary study. Med Teach. 2008;30(6):618–21.
Gonzales E, Morrow-Howell N, Gilbert P. Changing medical students’ attitudes toward older adults. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2010;31(3):220–34.
Hinners CK, Potter JF. A partnership between the University of Nebraska College of Medicine and the community: fostering positive attitudes towards the aged. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2006;27(2):83–91.
Lee M, Coulehan JL. Medical students’ perceptions of racial diversity and gender equality. Med Educ. 2006;40(7):691–6.
Schmetzer AD, Lafuze JE. Overcoming stigma: involving families in medical student and psychiatric residency education. Acad Psychiatry. 2008;32(2):127–31.
Willen SS, Bullon A, Good MJD. Opening up a huge can of worms: reflections on a “cultural sensitivity” course for psychiatry residents. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2010;18(4):247–53.
Dogra N, Karnik N. First-year medical students’ attitudes toward diversity and its teaching: an investigation at one U.S. medical school. Acad Med. 2003;78(11):1191–200.
Fitzpatrick C, Musser A, Mosqueda L, Boker J, Prislin M. Student senior partnership program: University of California Irvine School of Medicine. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2006;27(2):25–35.
Hoffman KG, Gray P, Hosokawa MC, Zweig SC. Evaluating the effectiveness of a senior mentor program: the University of Missouri-Columbia School of Medicine. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2006;27(2):37–47.
Kantor BS, Myers MR. From aging…to saging-the Ohio State Senior Partners Program: longitudinal and experiential geriatrics education. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2006;27(2):69–74.
Klamen DL, Grossman LS, Kopacz DR. Medical student homophobia. J Homosex. 1999;37(1):53–63.
Kopacz DR, Grossman LS, Klamen DL. Medical students and AIDS: knowledge, attitudes and implications for education. Health Educ Res. 1999;14(1):1–6.
Leiblum SR. An established medical school human sexuality curriculum: description and evaluation. Sex Relatsh Ther. 2001;16(1):59–70.
Rastegar DA, Fingerhood MI, Jasinski DR. A resident clerkship that combines inpatient and outpatient training in substance abuse and HIV care. Subst Abuse. 2004;25(4):11–5.
Roberts E, Richeson NA, Thornhill JTIV, Corwin SJ, Eleazer GP. The senior mentor program at the University of South Carolina School of Medicine: an innovative geriatric longitudinal curriculum. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2006;27(2):11–23.
Burgess DJ, Burke SE, Cunningham BA, Dovidio JF, Hardeman RR, Hou YF, Nelson DB, Perry SP, Phelan SM, Yeazel MW, et al. Medical students’ learning orientation regarding interracial interactions affects preparedness to care for minority patients: a report from medical student CHANGES. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:254.
Burgess DJ, Hardeman RR, Burke SE, Cunningham BA, Dovidio JF, Nelson DB, Perry SP, Phelan SM, Yeazel MW, Herrin J, et al. Incoming medical students’ political orientation affects outcomes related to care of marginalized groups: results from the medical student CHANGES study. J Health Pol Policy Law. 2019;44(1):113–46.
Kurtz ME, Johnson SM, Tomlinson T, Fiel NJ. Teaching medical students the effects of values and stereotyping on the doctor/patient relationship. Soc Sci Med. 1985;21(9):1043–7.
Matharu K, Kravitz RL, McMahon GT, Wilson MD, Fitzgerald FT. Medical students’ attitudes toward gay men. BMC Med Educ. 2012;12:71.
Pearl RL, Argueso D, Wadden TA. Effects of medical trainees’ weight-loss history on perceptions of patients with obesity. Med Educ. 2017;51(8):802–11.
Perry SP, Dovidio JF, Murphy MC, van Ryn M. The joint effect of bias awareness and self-reported prejudice on intergroup anxiety and intentions for intergroup contact. Cultur Divers Ethnic Minor Psychol. 2015;21(1):89–96.
Phelan SM, Burgess DJ, Burke SE, Przedworski JM, Dovidio JF, Hardeman R, Morris M, van Ryn M. Beliefs about the causes of obesity in a national sample of 4th year medical students. Patient Educ Couns. 2015;98(11):1446–9.
Phelan SM, Puhl RM, Burgess DJ, Natt N, Mundi M, Miller NE, Saha S, Fischer K, van Ryn M. The role of weight bias and role-modeling in medical students’ patient-centered communication with higher weight standardized patients. Patient Educ Couns. 2021;104(8):1962–9.
Polan HJ, Auerbach MI, Viederman M. AIDS as a paradigm of human behavior in disease: impact and implications of a course. Acad Psychiatry. 1990;14(4):197–203.
Reuben DB, Fullerton JT, Tschann JM, Croughan-Minihane M. Attitudes of beginning medical students toward older persons: a five-campus study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1995;43(12):1430–6.
Tsai J. Building structural empathy to marshal critical education into compassionate practice: evaluation of a medical school critical race theory course. J Law Med Ethics. 2021;49(2):211–21.
Weyant RJ, Bennett ME, Simon M, Palaisa J. Desire to treat HIV-infected patients: similarities and differences across health-care professions. AIDS. 1994;8(1):117–21.
Ross PT, Lypson ML. Using artistic-narrative to stimulate reflection on physician bias. Teach Learn Med. 2014;26(4):344–9.
Calabrese SK, Earnshaw VA, Krakower DS, Underhill K, Vincent W, Magnus M, Hansen NB, Kershaw TS, Mayer KH, Betancourt JR, et al. A closer look at racism and heterosexism in medical students’ clinical decision-making related to HIV Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP): implications for PrEP education. AIDS Behav. 2018;22(4):1122–38.
Fitterman-Harris HF, Vander Wal JS. Weight bias reduction among first-year medical students: a quasi-randomized, controlled trial. Clin Obes. 2021;11(6):e12479.
Madan AK, Cooper L, Gratzer A, Beech DJ. Ageism in breast cancer surgical options by medical students. Tenn Med. 2006;99(5):37–8, 41.
Bikmukhametov DA, Anokhin VA, Vinogradova AN, Triner WR, McNutt LA. Bias in medicine: a survey of medical student attitudes towards HIV-positive and marginalized patients in Russia, 2010. J Int AIDS Soc. 2012;15(2):17372.
Dijkstra AF, Verdonk P, Lagro-Janssen AL. Gender bias in medical textbooks: examples from coronary heart disease, depression, alcohol abuse and pharmacology. Med Educ. 2008;42(10):1021–8.
Dobrowolska B, Jędrzejkiewicz B, Pilewska-Kozak A, Zarzycka D, Ślusarska B, Deluga A, Kościołek A, Palese A. Age discrimination in healthcare institutions perceived by seniors and students. Nurs Ethics. 2019;26(2):443–59.
Hamberg K, Risberg G, Johansson EE, Westman G. Gender bias in physicians’ management of neck pain: a study of the answers in a Swedish national examination. J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 2002;11(7):653–66.
Magliano L, Read J, Sagliocchi A, Oliviero N, D’Ambrosio A, Campitiello F, Zaccaro A, Guizzaro L, Patalano M. “Social dangerousness and incurability in schizophrenia”: results of an educational intervention for medical and psychology students. Psychiatry Res. 2014;219(3):457–63.
Reis SP, Wald HS. Contemplating medicine during the Third Reich: scaffolding professional identity formation for medical students. Acad Med. 2015;90(6):770–3.
Schroyen S, Adam S, Marquet M, Jerusalem G, Thiel S, Giraudet AL, Missotten P. Communication of healthcare professionals: Is there ageism? Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2018;27(1):e12780.
Swift JA, Hanlon S, El-Redy L, Puhl RM, Glazebrook C. Weight bias among UK trainee dietitians, doctors, nurses and nutritionists. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2013;26(4):395–402.
Swift JA, Tischler V, Markham S, Gunning I, Glazebrook C, Beer C, Puhl R. Are anti-stigma films a useful strategy for reducing weight bias among trainee healthcare professionals? Results of a pilot randomized control trial. Obes Facts. 2013;6(1):91–102.
Yertutanol FDK, Candansayar S, Seydaoğlu G. Homophobia in health professionals in Ankara, Turkey: developing a scale. Transcult Psychiatry. 2019;56(6):1191–217.
Arnold O, Voracek M, Musalek M, Springer-Kremser M. Austrian medical students’ attitudes towards male and female homosexuality: a comparative survey. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2004;116(21–22):730–6.
Arvaniti A, Samakouri M, Kalamara E, Bochtsou V, Bikos C, Livaditis M. Health service staff’s attitudes towards patients with mental illness. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2009;44(8):658–65.
Lopes L, Gato J, Esteves M. Portuguese medical students’ knowledge and attitudes towards homosexuality. Acta Med Port. 2016;29(11):684–93.
Papadaki V, Plotnikof K, Gioumidou M, Zisimou V, Papadaki E. A comparison of attitudes toward lesbians and gay men among students of helping professions in Crete, Greece: the cases of social work, psychology, medicine, and nursing. J Homosex. 2015;62(6):735–62.
Papaharitou S, Nakopoulou E, Moraitou M, Tsimtsiou Z, Konstantinidou E, Hatzichristou D. Exploring sexual attitudes of students in health professions. J Sex Med. 2008;5(6):1308–16.
Roberts JH, Sanders T, Mann K, Wass V. Institutional marginalisation and student resistance: barriers to learning about culture, race and ethnicity. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2010;15(4):559–71.
Wilhelmi L, Ingendae F, Steinhaeuser J. What leads to the subjective perception of a ‘rural area’? A qualitative study with undergraduate students and postgraduate trainees in Germany to tailor strategies against physician’s shortage. Rural Remote Health. 2018;18(4):4694.
Herrmann-Werner A, Loda T, Wiesner LM, Erschens RS, Junne F, Zipfel S. Is an obesity simulation suit in an undergraduate medical communication class a valuable teaching tool? A cross-sectional proof of concept study. BMJ Open. 2019;9(8):e029738.
Ahadinezhad B, Khosravizadeh O, Maleki A, Hashtroodi A. Implicit racial bias among medical graduates and students by an IAT measure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ir J Med Sci. 2022;191(4):1941–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-021-02756-3 .
Hsieh JG, Hsu M, Wang YW. An anthropological approach to teach and evaluate cultural competence in medical students - the application of mini-ethnography in medical history taking. Med Educ Online. 2016;21:32561.
Poreddi V, Thimmaiah R, Math SB. Attitudes toward people with mental illness among medical students. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2015;6(3):349–54.
Mino Y, Yasuda N, Tsuda T, Shimodera S. Effects of a one-hour educational program on medical students’ attitudes to mental illness. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2001;55(5):501–7.
Omori A, Tateno A, Ideno T, Takahashi H, Kawashima Y, Takemura K, Okubo Y. Influence of contact with schizophrenia on implicit attitudes towards schizophrenia patients held by clinical residents. BMC Psychiatry. 2012;12:8.
Banwari G, Mistry K, Soni A, Parikh N, Gandhi H. Medical students and interns’ knowledge about and attitude towards homosexuality. J Postgrad Med. 2015;61(2):95–100.
Lee SY. Obesity education in medical school curricula in Korea. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2018;27(1):35–8.
Aruna G, Mittal S, Yadiyal MB, Acharya C, Acharya S, Uppulari C. Perception, knowledge, and attitude toward mental disorders and psychiatry among medical undergraduates in Karnataka: a cross-sectional study. Indian J Psychiatry. 2016;58(1):70–6.
Wong YL. Review paper: gender competencies in the medical curriculum: addressing gender bias in medicine. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2009;21(4):359–76.
Earnshaw VA, Jin H, Wickersham JA, Kamarulzaman A, John J, Lim SH, Altice FL. Stigma toward men who have sex with men among future healthcare providers in Malaysia: would more interpersonal contact reduce prejudice? AIDS Behav. 2016;20(1):98–106.
Larson B, Herx L, Williamson T, Crowshoe L. Beyond the barriers: family medicine residents’ attitudes towards providing Aboriginal health care. Med Educ. 2011;45(4):400–6.
Wagner AC, Girard T, McShane KE, Margolese S, Hart TA. HIV-related stigma and overlapping stigmas towards people living with HIV among health care trainees in Canada. AIDS Educ Prev. 2017;29(4):364–76.
Tellier P-P, Bélanger E, Rodríguez C, Ware MA, Posel N. Improving undergraduate medical education about pain assessment and management: a qualitative descriptive study of stakeholders’ perceptions. Pain Res Manage. 2013;18(5):259–65.
Loignon C, Boudreault-Fournier A, Truchon K, Labrousse Y, Fortin B. Medical residents reflect on their prejudices toward poverty: a photovoice training project. BMC Med Educ. 2014;14:1050.
Phillips SP, Clarke M. More than an education: the hidden curriculum, professional attitudes and career choice. Med Educ. 2012;46(9):887–93.
Jaworsky D, Gardner S, Thorne JG, Sharma M, McNaughton N, Paddock S, Chew D, Lees R, Makuwaza T, Wagner A, et al. The role of people living with HIV as patient instructors—Reducing stigma and improving interest around HIV care among medical students. AIDS Care. 2017;29(4):524–31.
Sukhera J, Wodzinski M, Teunissen PW, Lingard L, Watling C. Striving while accepting: exploring the relationship between identity and implicit bias recognition and management. Acad Med. 2018;93(11S Association of American Medical Colleges Learn Serve Lead: Proceedings of the 57th Annual Research in Medical Education Sessions):S82-s88.
Harris R, Cormack D, Curtis E, Jones R, Stanley J, Lacey C. Development and testing of study tools and methods to examine ethnic bias and clinical decision-making among medical students in New Zealand: the Bias and Decision-Making in Medicine (BDMM) study. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:173.
Cormack D, Harris R, Stanley J, Lacey C, Jones R, Curtis E. Ethnic bias amongst medical students in Aotearoa/New Zealand: findings from the Bias and Decision Making in Medicine (BDMM) study. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(8):e0201168.
Harris R, Cormack D, Stanley J, Curtis E, Jones R, Lacey C. Ethnic bias and clinical decision-making among New Zealand medical students: an observational study. BMC Med Educ. 2018;18(1):18.
Robinson EL, Ball LE, Leveritt MD. Obesity bias among health and non-health students attending an Australian university and their perceived obesity education. J Nutr Educ Behav. 2014;46(5):390–5.
Sopoaga F, Zaharic T, Kokaua J, Covello S. Training a medical workforce to meet the needs of diverse minority communities. BMC Med Educ. 2017;17:19.
Parker R, Larkin T, Cockburn J. A visual analysis of gender bias in contemporary anatomy textbooks. Soc Sci Med. 2017;180:106–13.
Gomes MdM. Doctors’ perspectives and practices regarding epilepsy. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2000;58(2):221–6.
Caixeta J, Fernandes PT, Bell GS, Sander JW, Li LM. Epilepsy perception amongst university students - A survey. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2007;65:43–8.
Tedrus GMAS, Fonseca LC, da Câmara Vieira AL. Knowledge and attitudes toward epilepsy amongst students in the health area: intervention aimed at enlightenment. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2007;65(4-B):1181–5.
Gomez-Moreno C, Verduzco-Aguirre H, Contreras-Garduño S, Perez-de-Acha A, Alcalde-Castro J, Chavarri-Guerra Y, García-Lara JMA, Navarrete-Reyes AP, Avila-Funes JA, Soto-Perez-de-Celis E. Perceptions of aging and ageism among Mexican physicians-in-training. Clin Transl Oncol. 2019;21(12):1730–5.
Campbell MH, Gromer J, Emmanuel MK, Harvey A. Attitudes Toward Transgender People Among Future Caribbean Doctors. Arch Sex Behav. 2022;51(4):1903-11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-021-02205-3 .
Hatala R, Case SM. Examining the influence of gender on medical students’ decision making. J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 2000;9(6):617–23.
Deb T, Lempp H, Bakolis I, et al. Responding to experienced and anticipated discrimination (READ): anti -stigma training for medical students towards patients with mental illness – study protocol for an international multisite non-randomised controlled study. BMC Med Educ. 2019;19:41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-019-1472-7 .
Morgan S, Plaisant O, Lignier B, Moxham BJ. Sexism and anatomy, as discerned in textbooks and as perceived by medical students at Cardiff University and University of Paris Descartes. J Anat. 2014;224(3):352–65.
Alford CL, Miles T, Palmer R, Espino D. An introduction to geriatrics for first-year medical students. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2001;49(6):782–7.
Stone J, Moskowitz GB. Non-conscious bias in medical decision making: what can be done to reduce it? Med Educ. 2011;45(8):768–76.
Nazione S. Slimming down medical provider weight bias in an obese nation. Med Educ. 2015;49(10):954–5.
Dogra N, Connin S, Gill P, Spencer J, Turner M. Teaching of cultural diversity in medical schools in the United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland: cross sectional questionnaire survey. BMJ. 2005;330(7488):403–4.
Aultman JM, Borges NJ. A clinical and ethical investigation of pre-medical and medical students’ attitudes, knowledge, and understanding of HIV. Med Educ Online. 2006;11(1):4596.
Deb T, Lempp H, Bakolis I, Vince T, Waugh W, Henderson C, Thornicroft G, Ando S, Yamaguchi S, Matsunaga A, et al. Responding to experienced and anticipated discrimination (READ): anti -stigma training for medical students towards patients with mental illness – study protocol for an international multisite non-randomised controlled study. BMC Med Educ. 2019;19(1):41.
Gonzalez CM, Grochowalski JH, Garba RJ, Bonner S, Marantz PR. Validity evidence for a novel instrument assessing medical student attitudes toward instruction in implicit bias recognition and management. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):205.
Ogunyemi D. A practical approach to implicit bias training. J Grad Med Educ. 2021;13(4):583–4.
Dennis GC. Racism in medicine: planning for the future. J Natl Med Assoc. 2001;93(3 Suppl):1S-5S.
Maina IW, Belton TD, Ginzberg S, Singh A, Johnson TJ. A decade of studying implicit racial/ethnic bias in healthcare providers using the implicit association test. Soc Sci Med. 2018;199:219–29.
Blair IV, Steiner JF, Hanratty R, Price DW, Fairclough DL, Daugherty SL, Bronsert M, Magid DJ, Havranek EP. An investigation of associations between clinicians’ ethnic or racial bias and hypertension treatment, medication adherence and blood pressure control. J Gen Intern Med. 2014;29(7):987–95.
Stanford FC. The importance of diversity and inclusion in the healthcare workforce. J Natl Med Assoc. 2020;112(3):247–9.
Education LCoM. Standards on diversity. 2009. https://health.usf.edu/~/media/Files/Medicine/MD%20Program/Diversity/LCMEStandardsonDiversity1.ashx?la=en .
Onyeador IN, Hudson STJ, Lewis NA. Moving beyond implicit bias training: policy insights for increasing organizational diversity. Policy Insights Behav Brain Sci. 2021;8(1):19–26.
Forscher PS, Mitamura C, Dix EL, Cox WTL, Devine PG. Breaking the prejudice habit: mechanisms, timecourse, and longevity. J Exp Soc Psychol. 2017;72:133–46.
Lai CK, Skinner AL, Cooley E, Murrar S, Brauer M, Devos T, Calanchini J, Xiao YJ, Pedram C, Marshburn CK, et al. Reducing implicit racial preferences: II. Intervention effectiveness across time. J Exp Psychol Gen. 2016;145(8):1001–16.
Sukhera J, Watling CJ, Gonzalez CM. Implicit bias in health professions: from recognition to transformation. Acad Med. 2020;95(5):717–23.
Vuletich HA, Payne BK. Stability and change in implicit bias. Psychol Sci. 2019;30(6):854–62.
Tversky A, Kahneman D. Judgment under uncertainty: Heuristics and biases. Science. 1974;185(4157):1124–31.
Miller DT, Ross M. Self-serving biases in the attribution of causality: fact or fiction? Psychol Bull. 1975;82(2):213–25.
Nickerson RS. Confirmation bias: a ubiquitous phenomenon in many guises. Rev Gen Psychol. 1998;2(2):175–220.
Suveren Y. Unconscious bias: definition and significance. Psikiyatride Guncel Yaklasimlar. 2022;14(3):414–26.
Dietrich D, Olson M. A demonstration of hindsight bias using the Thomas confirmation vote. Psychol Rep. 1993;72(2):377–8.
Green AR, Carney DR, Pallin DJ, Ngo LH, Raymond KL, Iezzoni LI, Banaji MR. Implicit bias among physicians and its prediction of thrombolysis decisions for black and white patients. J Gen Intern Med. 2007;22(9):1231–8.
Rushmer R, Davies HT. Unlearning in health care. Qual Saf Health Care. 2004;13 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):ii10-15.
Vu MT, Pham TTT. Gender, critical pedagogy, and textbooks: Understanding teachers’ (lack of) mediation of the hidden curriculum in the EFL classroom. Lang Teach Res. 2022;0(0). https://doi.org/10.1177/13621688221136937 .
Kalantari A, Alvarez A, Battaglioli N, Chung A, Cooney R, Boehmer SJ, Nwabueze A, Gottlieb M. Sex and race visual representation in emergency medicine textbooks and the hidden curriculum. AEM Educ Train. 2022;6(3):e10743.
Satya-Murti S, Lockhart J. Recognizing and reducing cognitive bias in clinical and forensic neurology. Neurol Clin Pract. 2015;5(5):389–96.
Chang EH, Milkman KL, Gromet DM, Rebele RW, Massey C, Duckworth AL, Grant AM. The mixed effects of online diversity training. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(16):7778–83.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Misa Mi, Professor and Medical Librarian at the Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine (OWUB) for her assistance with selection of databases and construction of literature search strategies for the scoping review. The authors also wish to thank Dr. Changiz Mohiyeddini, Professor in Behavioral Medicine and Psychopathology at Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine (OUWB) for his expertise and constructive feedback on our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Foundational Sciences, Central Michigan University College of Medicine, Mt. Pleasant, MI, 48859, USA
Brianne E. Lewis
Department of Foundational Medical Studies, Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine, 586 Pioneer Dr, Rochester, MI, 48309, USA
Akshata R. Naik
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
A.R.N and B.E.L were equally involved in study conception, design, collecting data and analyzing the data. B.E.L and A.R.N both contributed towards writing the manuscript. A.R.N and B.E.L are both senior authors on this paper. All authors reviewed the manuscript.

Corresponding author
Correspondence to Akshata R. Naik .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Lewis, B.E., Naik, A.R. A scoping review to identify and organize literature trends of bias research within medical student and resident education. BMC Med Educ 23 , 919 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-023-04829-6
Download citation
Received : 14 March 2023
Accepted : 01 November 2023
Published : 05 December 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-023-04829-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Preclinical curriculum
- Evidence of bis
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Retirement planning – a systematic review of literature and future research directions
- Published: 28 October 2023
Cite this article
- Kavita Karan Ingale ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3570-4211 1 &
- Ratna Achuta Paluri 2
508 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Rising life expectancy and an aging population across nations are leading to an increased need for long-term financial savings and a focus on the financial well-being of retired individuals amidst changing policy framework. This study is a systematic review based on a scientific way of producing high-quality evidence based on 191 articles from the Scopus and Web of Science databases. It adopts the Theory, Context, Characteristics, and Method (TCCM) framework to analyze literature. This study provides collective insights into financial decision-making for retirement savings and identifies constructs for operationalizing and measuring financial behavior for retirement planning. Further, it indicates the need for an interdisciplinary approach. Though cognitive areas were studied extensively, the non-cognitive areas received little attention. Qualitative research design is gaining prominence in research over other methods, with the sparse application of mixed methods design. The study’s TCCM framework explicates several areas for further research. Furthermore, it guides the practice and policy by integrating empirical evidence and concomitant findings. Coherent synthesis of the extant literature reconciles the highly fragmented field of retirement planning. No research reports prospective areas for further analysis based on the TCCM framework on retirement planning, which highlights the uniqueness of the study.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

A Research Proposal to Examine Psychological Factors Influence on Financial Planning for Retirement in China
Domains and determinants of retirement timing: A systematic review of longitudinal studies
Micky Scharn, Ranu Sewdas, … Allard J. van der Beek

Reinventing Retirement
Deanna L. Sharpe
Data Availability
The research data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgment.
Elderly population is defined as a population aged 65 years and over.
Defined benefit plan guarantees benefits to the employee, while defined contribution plan requires employees to decide on their own investment and bear the financial risks identified with it.
“The old-age dependency ratio is defined as the number of individuals aged 65 and over per 100 people of working age defined as those at ages 20 to 64”(OECD 2023 ).
Adams GA, Rau BL (2011) Putting off tomorrow to do what you want today: planning for Retirement. Am Psychol 66(3):180–192. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0022131
Article Google Scholar
Aegon Cfor, Longevity, Retirement ICR (2016) The Aegon Retirement Readiness Survey 2016. In The Aegon Retirement Readiness Survey 2016 . https://www.aegon.com/contentassets/c6a4b1cdded34f1b85a4f21d4c66e5d3/2016-aegon-retirement-readiness-report-india.pdf
Agarwalla SK, Barua SK, Jacob J, Varma JR (2015) Financial Literacy among Working Young in Urban India. World Development , 67 (2013), 101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2014.10.004
Ajzen I (1991) The theory of Planned Behavior. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process 50:179–211. https://doi.org/10.47985/dcidj.475
Anderson A, Baker F, Robinson DT (2017) Precautionary savings, retirement planning, and misperceptions of financial literacy. J Financ Econ 126(2):383–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfineco.2017.07.008
Atkinson A, Messy FA (2011) Assessing financial literacy in 12 countries: an OECD/INFE international pilot exercise. J Pension Econ Finance 10(4):657–665. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1474747211000539`
Aydin AE, Akben Selcuk E (2019) An investigation of financial literacy, money ethics, and time preferences among college students: a structural equation model. Int J Bank Mark 37(3):880–900. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-05-2018-0120
Bapat D (2020) Antecedents to responsible financial management behavior among young adults: the moderating role of financial risk tolerance. Int J Bank Mark 38(5):1177–1194. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-10-2019-0356
Beckett A, Hewer P, Howcroft B (2000) An exposition of consumer behaviour in the financial services industry. Int J Bank Mark 18(1):15–26. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652320010315325
Białowolski P (2019) Economic sentiment as a driver for household financial behavior. J Behav Experimental Econ 80(August 2017):59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socec.2019.03.006
Binswanger J, Carman KG (2012) How real people make long-term decisions: the case of retirement preparation. J Economic Behav Organ 81(1):39–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2011.08.010
Brounen D, Koedijk KG, Pownall RAJ (2016) Household financial planning and savings behavior. J Int Money Finance 69:95–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jimonfin.2016.06.011
Brown R, Jones M (2015) Mapping and exploring the topography of contemporary financial accounting research. Br Acc Rev 47(3):237–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bar.2014.08.006
Brown S, Gray D (2016) Household finances and well-being in Australia: an empirical analysis of comparison effects. J Econ Psychol 53:17–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2015.12.006
Brown S, Taylor K (2014) Household finances and the big five personality traits. J Econ Psychol 45:197–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2014.10.006
Brown S, Taylor K (2016) Early influences on saving behaviour: analysis of British panel data. J Bank Finance 62:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbankfin.2015.09.011
Brüggen EC, Post T, Schmitz K (2019) Interactivity in online pension planners enhances engagement with retirement planning – but not for everyone. J Serv Mark 33(4):488–501. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSM-02-2018-0082
Bruggen E, Post T, Katharina S (2019) Interactivity in online pension planners enhances engagement with retirement planning but not for everyone. J Serv Mark 33(4):488–501
Calcagno R, Monticone C (2015) Financial literacy and the demand for financial advice. J Bank Finance 50:363–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbankfin.2014.03.013
Campbell JY (2006) Household finance. J Finance 61(4):1553–1604. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6261.2006.00883.x
Choudhury K (2015) Service quality and customers’ behavioural intentions: class and mass banking and implications for the consumer and society. Asia Pac J Mark Logistics 27(5):735–757
Chowdhry N, Jung J, Dholakia U (2018) Association for consumer research. Adv Consum Res 42:42–46
Google Scholar
Clark GL, Knox-Hayes J, Strauss K (2009) Financial sophistication, salience, and the scale of deliberation in UK retirement planning. Environ Plann A 41(10):2496–2515. https://doi.org/10.1068/a41265
Clark R, Lusardi A, Mitchell OS (2017) Employee Financial Literacy and Retirement Plan Behavior: a case study. Econ Inq 55(1):248–259. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecin.12389
Collins JM, Urban C (2016) The role of information on Retirement Planning: evidence from a field study. Econ Inq 54(4):1860–1872. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecin.12349
Creswell J (2009) Research Design Qualitative Quantitative and Mixed Methods Approaches. In Sage Publishing: Vol. Third edit . https://doi.org/10.1002/tl.20234
Csorba L (2020) The determining factors of financial culture, financial literacy, and financial behavior. Public Finance Q 65:67–83. https://doi.org/10.35551/PFQ_2020_1_6
Davidoff T, Gerhard P, Post T (2017) Reverse mortgages: what homeowners (don’t) know and how it matters. J Economic Behav Organ 133:151–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2016.11.007
Davis FD (1989) Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly: Management Information Systems 13(3):319–339. https://doi.org/10.2307/249008
Devlin J (2001) Consumer evaluation and competitive advantage in retail financial services - a research agenda. Eur J Mark 35(5/6):639–660
Dholakia U, Tam L, Yoon S, Wong N (2016) The ant and the grasshopper: understanding personal saving orientation of consumers. J Consum Res 43(1):134–155. https://doi.org/10.1093/jcr/ucw004
Dolls M, Doerrenberg P, Peichl A, Stichnoth H (2018) Do retirement savings increase in response to information about retirement and expected pensions? J Public Econ 158(July 2017):168–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpubeco.2017.12.014
Dragos SL, Dragos CM, Muresan GM (2020) From intention to the decision in purchasing life insurance and private pensions: different effects of knowledge and behavioural factors. J Behav Experimental Econ 87(March):101555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socec.2020.101555
Drever AI, Odders-white E, Kalish CW, Hoagland EM, Nelms EN, Drever AI, Odders-white E, Charles W, Else-quest NM, Hoagland EM, Nelms EN (2015) Foundations of Financial Weil-Being: Insights into the Role of Executive Function, Financial Socialization, and Experience-Based Learning in Childhood and Youth Source : The Journal of Consumer Affairs, Vol. 49, No. 1, Special Issue on Starting Ea. The Journal of Consumer Affairs , 49 (1)
Duflo E, Saez E (2002) Participation and investment decisions in a retirement plan: the influence of colleagues’ choices. J Public Econ 85(1):121–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0047-2727(01)00098-6
Duxbury D, Summers B, Hudson R, Keasey K (2013) How people evaluate defined contribution, annuity-based pension arrangements: a behavioral exploration. J Econ Psychol 34:256–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2012.10.008
Earl J, Bednall T, Muratore A (2015) A matter of time: why some people plan for retirement and others do not. Work Aging and Retirement 1(2):181–189. https://doi.org/10.1093/workar/wau005
Employees Benefits Research Institute (2020) EBRI Retirement Confidence Survey Report (Issue 202)
Engel JF, Kollat DT, Blackwell RD (1968) A model of consumer motivation and behavior. In: Research in consumer behavior. Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Inc., New York, pp 3–20
Erasmus A, Boshoff E, Rousseau G (2001) Consumer decision-making models within the discipline of consumer science: a critical approach. J Family Ecol Consumer Sci /Tydskrif Vir Gesinsekologie En Verbruikerswetenskappe 29(1):82–90. https://doi.org/10.4314/jfecs.v29i1.52799
Farrell L, Fry TRL, Risse L (2016) The significance of financial self-efficacy in explaining women’s personal finance behaviour. J Econ Psychol 54:85–99
Fernandes D, Lynch JG, Netemeyer RG (2014) Financial literacy, financial education, and downstream financial behaviors. Manage Sci 60(8):1861–1883. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.2013.1849
Filbec G, Ricciardi V, Evensky H, Fan S, Holzhauer H, Spieler A (2017) Behavioral finance: a panel discussion. J Behav Experimental Finance 15:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbef.2015.07.003
Fishbein M (1979) A theory of reasoned action: some applications and implications. Nebraska Symposium on Motivation 27:65–116
Fisher PJ, Montalto CP (2010) Effect of saving motives and horizon on saving behaviors. J Econ Psychol 31(1):92–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2009.11.002
Flores SAM, Vieira KM (2014) Propensity toward indebtedness: an analysis using behavioral factors. J Behav Exp Finance 3:1–10
Foxall GR, Pallister JG (1998) Measuring purchase decision involvement for financial services: comparison of the Zaichkowsky and Mittal scales. Int J Bank Mark 16(5):180–194. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652329810228181
Friedman M (1957) Introduction to “A theory of the consumption function”. In: A theory of the consumption function. Princeton University Press, pp 1–6
Frydman C, Camerer CF (2016) The psychology and neuroscience of financial decision making. Trends Cogn Sci 20(9):661–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2016.07.003
Gardarsdóttir RB, Dittmar H (2012) The relationship of materialism to debt and financial well-being: the case of Iceland’s perceived prosperity. J Econ Psychol 33(3):471–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2011.12.008
Gathergood J (2012) Self-control, financial literacy and consumer over-indebtedness. J Econ Psychol 33(3):590–602
Gerhard P, Gladstone JJ, Hoffmann AOI (2018) Psychological characteristics and household savings behavior: the importance of accounting for latent heterogeneity. J Economic Behav Organ 148:66–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2018.02.013
Gibbs PT (2009) Time, temporality, and
Goedde-Menke M, Lehmensiek-Starke M, Nolte S (2014) An empirical test of competing hypotheses for the annuity puzzle. J Econ Psychol 43:75–91
Gough O, Nurullah M (2009) Understanding what drives the purchase decision in pension and investment products. J Financial Serv Mark 14(2):152–172. https://doi.org/10.1057/fsm.2009.14
Griffin B, Loe D, Hesketh B (2012) Using Proactivity, Time Discounting, and the theory of Planned Behavior to identify predictors of Retirement Planning. Educ Gerontol 38(12):877–889. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601277.2012.660857
Gritten A (2011) New insights into consumer confidence in financial services. Int J Bank Mark 29(2):90–106. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652321111107602
Grohmann A (2018) Financial literacy and financial behavior: Evidence from the emerging Asian middle class. Pacific Basin Finance Journal , 48 (November 2017), 129–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pacfin.2018.01.007
Grohmann A, Kouwenberg R, Menkhoff L (2015) Childhood roots of financial literacy. J Econ Psychol 51:114–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2015.09.002
Hair JF, Sarstedt M, Ringle CM, Mena JA (2012) An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research . 414–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-011-0261-6
Hanna SD, Kim KT, Chen SCC (2016) Retirement savings. In: Handbook of consumer finance research, pp 33–43
Harrison T, Waite K, White P (2006) Analysis by paralysis: the pension purchase decision process. Int J Bank Mark 24(1):5–23. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652320610642317
Hastings J, Mitchell O (2011) How financial literact and impatience shape retirement wealth and investment behaviors. Pengaruh Harga Diskon Dan Persepsi Produk Terhadap Nilai Belanja Serta Perilaku Pembelian Konsumen, NBER Working paper, 1–28
Hauff J, Carlander A, Amelie G, Tommy G, Holmen M (2016) Breaking the ice of low financial involvement: does narrative information format from a trusted sender increase savings in mutual funds? Int J Bank Mark 34(2):151–170
Hentzen JK, Hoffmann A, Dolan R, Pala E (2021) Artificial intelligence in customer-facing financial services: a systematic literature review and agenda for future research. Int J Bank Mark. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-09-2021-0417
Hershey DA, Mowen JC (2000) Psychological determinants of financial preparedness for retirement. Gerontologist 40(6):687–697. https://doi.org/10.1093/geront/40.6.687
Hershey DA, Henkens K, Van Dalen HP (2007) Mapping the minds of retirement planners: a cross-cultural perspective. J Cross-Cult Psychol 38(3):361–382. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022022107300280
Hershey DA, Jacobs-Lawson JM, McArdle JJ, Hamagami F (2007b) Psychological foundations of financial planning for retirement. J Adult Dev 14(1–2):26–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10804-007-9028-1
Hershey DA, Jacobs-Lawson JM, McArdle JJ, Hamagami F (2008) Psychological foundations of financial planning for retirement. J Adult Dev 14(1–2):26–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10804-007-9028-1
Hershfield H, Goldstein D, Sharpe W, Fox J, Yeykelis L, Carstensen L, Bailenson J (2011) Increasing saving behavior through age-progressed renderings of the future self. J Mark Res 48:23–37
Hoffmann AOI, Broekhuizen TLJ (2009) Susceptibility to and impact of interpersonal influence in an investment context. J Acad Mark Sci 37:488–503
Hoffmann AOI, Broekhuizen TLJ (2010) Understanding investors’ decisions to purchase innovative products: drivers of adoption timing and range. Int J Res Mark 27(4):342–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijresmar.2010.08.002
Hoffmann AOI, Plotkina D (2020a) Positive framing when assessing the personal resources to manage one’s finances increases consumers’ retirement self-efficacy and improves retirement goal clarity. Psychol Mark 38(12):2286–2304. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.21563
Hoffmann AOI, Plotkina D (2020b) Why and when does financial information affect retirement planning intentions and which consumers are more likely to act on them? Journal of Business Research , 117 (September 2019), 411–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.06.023
Hoffmann AOI, Plotkina D (2021) Let your past define your future. How recalling successful financial experiences can increase beliefs of self-efficacy in financial planning. J Consum Aff 55(3):847–871. https://doi.org/10.1111/joca.12378
Hoffmann AOI, Risse L (2020) Do good things come in pairs? How personality traits help explain individuals’ simultaneous pursuit of a healthy lifestyle and financially responsible behavior. J Consum Aff 54(3):1082–1120. https://doi.org/10.1111/joca.12317
Hsiao YJ, Tsai WC (2018) Financial literacy and participation in the derivatives markets. J Bank Finance 88:15–29
Huhmann BA, McQuitty S (2009) A model of consumer financial numeracy. Int J Bank Mark 27(4):270–293. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652320910968359
Huston SJ (2010) Measuring financial literacy. J Consum Aff 44(2):296–316. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6606.2010.01170.x
Ijevleva K, Arefjevs I (2014) Analysis of the Aggregate Financial Behaviour of customers using the Transtheoretical Model of Change. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 156(April):435–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.11.217
Ingale KK, Paluri RA (2020) Financial literacy and financial behavior: a bibliometric analysis. Rev Behav Finance. https://doi.org/10.1108/RBF-06-2020-0141
Jacobs-Lawson J, Hershey D (2005) Influence of future time perspective, financial knowledge, and financial risk tolerance on retirement savings behavior. Financial Serv Rev 14:331–344. https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8113/44/8/085201
Jappelli T, Padula M (2013) Investment in financial literacy and saving decisions. J Bank Finance 37(8):2779–2792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbankfin.2013.03.019
Kadoya Y, Rahim Khan MS (2020) Financial literacy in Japan: new evidence using financial knowledge, behavior, and attitude. Sustain (Switzerland) 12(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12093683
Kamil NSSN, Musa R, Sahak SZ (2014) Examining the Role of Financial Intelligence Quotient (FiQ) in explaining credit card usage behavior: a conceptual Framework. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 130:568–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.04.066
Kerry MJ (2018) Psychological antecedents of retirement planning: a systematic review. Front Psychol 9(OCT). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01870
Kerry MJ, Embretson SE (2018) An experimental evaluation of competing age predictions of future time perspective between workplace and retirement domains. Front Psychol 8(JAN):1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.02316
Kiliyanni AL, Sivaraman S (2016) The perception-reality gap in financial literacy: evidence from the most literate state in India. Int Rev Econ Educ 23:47–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iree.2016.07.001
Kimiyaghalam F, Mansori S, Safari M, Yap S (2017) Parents’ influence on retirement planning in Malaysia. Family Consumer Sci Res J 45(3):315–325
Klapper L, Lusardi A, Panos GA (2013) Financial literacy and its consequences: evidence from Russia during the financial crisis. J Bank Finance 37(10):3904–3923
Koehler DJ, Langstaff J, Liu WQ (2015) A simulated financial savings task for studying consumption and retirement decision-making. J Econ Psychol 46:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2014.12.004
Kramer MM (2016) Financial literacy, confidence, and financial advice seeking. Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization , 131 (June 2015), 198–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2016.08.016
Kumar S, Tomar S, Verma D (2019) Women’s financial planning for retirement: systematic literature review and future research agenda. Int J Bank Mark 37(1):120–141. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-08-2017-0165
Kwon KN, Lee J (2009) The effects of reference point, knowledge, and risk propensity on the evaluation of financial products. J Bus Res 62(7):719–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2008.07.002
Landerretche OM, Martínez C (2013) Voluntary savings, financial behavior, and pension finance literacy: evidence from Chile. J Pension Econ Finance 12(3):251–297. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1474747212000340
Lee T (2017) (David). Clear, conspicuous, and improving: US corporate websites for critical financial literacy in retirement. International Journal of Bank Marketing , 35 (5), 761–780. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-01-2016-0010
Liang C-J, Wang Wen‐Hung, Farquhar JD (2009) (2009). The influence of customer perceptions on financial performance in financial services. International Journal of Bank Marketing , 27 (2), 129–149
Liberman N, Trope Y (2003) Construal level theory of intertemporal judgment and decision. In: Loewenstein G, Read D, Baumeister R (eds) Time and decision: economic and psychological perspectives on intertemporal choice, pp 245–276
Lim KL, Soutar GN, Lee JA (2013) Factors affecting investment intentions: a consumer behaviour perspective. J Financ Serv Mark 18:301–315
Lin C, Hsiao YJ, Yeh CY (2017) Financial literacy, financial advisors, and information sources on demand for life insurance. Pac Basin Finance J 43(March):218–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pacfin.2017.04.002
Lown JM (2011) Development and validation of a Financial Self-Efficacy Scale. J Financial Couns Plann 22(2):54–63
Lusardi A, Mitchell OS (2007) Baby Boomer retirement security: the roles of planning, financial literacy, and housing wealth. J Monet Econ 54(1):205–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmoneco.2006.12.001
Maloney M, McCarthy A (2017) Understanding pension communications at the organizational level: insights from bounded rationality theory & implications for HRM. Hum Resource Manage Rev 27(2):338–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2016.08.001
Marjanovic Z, Fiksenbaum L, Greenglass E (2018) Financial threat correlates with acute economic hardship and behavioral intentions that can improve one’s personal finances and health. J Behav Experimental Econ 77(April):151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socec.2018.09.012
Marques S, Mariano J, Lima ML, Abrams D (2018) Are you talking to the future me? The moderator role of future self-relevance on the effects of aging salience in retirement savings. J Appl Soc Psychol 48(7):360–368. https://doi.org/10.1111/jasp.12516
McKechnie S (1992) Consumer buying behaviour in financial services: an overview. Int J Bank Mark 10(5):5–39. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652329210016803
Milner T, Rosenstreich D (2013a) A review of consumer decision-making models and development of a new model for financial services. J Financial Serv Mark 18(2):106–120. https://doi.org/10.1057/fsm.2013.7
Milner T, Rosenstreich D (2013b) Insights into mature consumers of financial services. J Consumer Mark 30(3):248–257. https://doi.org/10.1108/07363761311328919
Mitchell OS, Mukherjee A (2017) Assessing the demand for micro pensions among India’s poor. J Econ Ageing 9:30–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeoa.2016.05.004
Mitchell O, Utkus S (2003) Lessons from Behavioral Finance for Retirement Plan Design (PRC WP 2003-6). http://prc.wharton.upenn.edu/prc/prc.html
Modigliani F, Brumberg RH (1954) Utility analysis and the consumption function: an interpretation of cross-section data. In: Kurihara KK (ed) Post-Keynesian economics. Rutgers University Press, New Brunswick, pp 388–436
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Altman D, Antes G, Atkins D, Barbour V, Barrowman N, Berlin JA, Clark J, Clarke M, Cook D, D’Amico R, Deeks JJ, Devereaux PJ, Dickersin K, Egger M, Ernst E, …, Tugwell P (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Monti M, Pelligra V, Martignon L, Berg N (2014) Retail investors and financial advisors: new evidence on trust and advice taking heuristics. J Bus Res 67(8):1749–1757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2014.02.022
Mouna A, Anis J (2017) Financial literacy in Tunisia: its determinants and its implications on investment behavior. Res Int Bus Finance 39:568–577
Mullainathan S, Thaler R (2000) Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Economics Working Paper Series . September
Nga KH, Yeoh KK (2018) An exploratory model on retirement savings behaviour: a Malaysian study. Int J Bus Soc 19(3):637–659
OECD (2023) Old-age dependency ratio (indicator). https://doi.org/10.1787/e0255c98-en . Accessed 13 Oct 2023
Onwuegbuzie AJ, Collins KM (2007) A typology of mixed methods sampling designs in social science research. Qualitative Rep 12(2):474–498
Pallister JG, Wang HC, Foxall GR (2007) An application of the style/involvement model to financial services. Technovation 27(1–2):78–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2005.10.001
Pan L, Pezzuti T, Lu W, Pechmann C (2019) Hyperopia and frugality: different motivational drivers and yet similar effects on consumer spending. J Bus Res 95(August 2018):347–356
Parise G, Peijnenburg K (2017) Understanding the Determinants of Financial Outcomes and Choices: The Role of Noncognitive Abilities. BIS Working Papers
Paul J, Rosado-Serrano A (2019) Gradual internationalization vs Born-Global/International new venture models: a review and research agenda. Int Mark Rev 36(6):830–858. https://doi.org/10.1108/IMR-10-2018-0280
Paul J, Criado AR (2020) The art of writing literature review: what do we know and what do we need to know? Int Bus Rev 29(4):101717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibusrev.2020.101717
Paul J, Khatri P, Kaur Duggal H (2023) Frameworks for developing impactful systematic literature reviews and theory building: what, why and how? J Decis Syst 00(00):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/12460125.2023.2197700
Petkoska J, Earl JK (2009) Understanding the influence of demographic and psychological variables on Retirement Planning. Psychol Aging 24(1):245–251. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0014096
Piotrowska M (2019) The importance of personality characteristics and behavioral constraints for retirement saving. Econ Anal Policy 64:194–220
Plath DA, Stevenson TH (2005) Financial services consumption behavior across Hispanic American consumers. J Bus Res 58(8):1089–1099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2004.03.003
Poterba JM (2015) Saver heterogeneity and the challenge of assessing retirement saving adequacy. Natl Tax J 68(2):377–388. https://doi.org/10.17310/ntj.2015.2.06
Potrich ACG, Vieira KM, Kirch G (2018) How well do women do when it comes to financial literacy? Proposition of an indicator and analysis of gender differences. J Behav Experimental Finance 17:28–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbef.2017.12.005
Rai D, Lin CW (2019) (Wilson). The influence of implicit self-theories on consumer financial decision making. Journal of Business Research , 95 (August 2018), 316–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2018.08.016
Ramalho TB, Forte D (2019) Financial literacy in Brazil – do knowledge and self-confidence relate with behavior? RAUSP Manage J 54(1):77–95. https://doi.org/10.1108/RAUSP-04-2018-0008
Rana J, Paul J (2017) Consumer behavior and purchase intention for organic food: a review and research agenda. J Retailing Consumer Serv 38(June):157–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2017.06.004
Ranyard R, McNair S, Nicolini G, Duxbury D (2020) An item response theory approach to constructing and evaluating brief and in-depth financial literacy scales. J Consum Aff 54(3):1121–1156. https://doi.org/10.1111/joca.12322
RBI Household Finance Committee (2017) Indian household finance. Reserve Bank of India, Mumbai
Ruefenacht M, Schlager T, Maas P, Puustinen P (2015) Drivers of long-term savings behavior from consumer’s perspective. Electron Libr 34(1):1–5
Scholz JK, Seshadri A, Khitatrakun S (2006) Are Americans saving “optimally” for retirement? J Polit Econ 114(4):607–643
Schuabb T, França LH, Amorim SM (2019) Retirement savings model tested with Brazilian private health care workers. Front Psychol 10(JULY):1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01701
Schuhen M, Schurkmann S (2014) International Review of Economics Education. Int Rev Econ Educ 16:1–11
Segel-Karpas D, Werner P (2014) Perceived financial retirement preparedness and its correlates: a national study in Israel. Int J Aging Hum Dev 79(4):279–301. https://doi.org/10.1177/0091415015574177
Seth H, Talwar S, Bhatia A, Saxena A, Dhir A (2020) Consumer resistance and inertia of retail investors: Development of the resistance adoption inertia continuance (RAIC) framework. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services , 55 (August 2019), 102071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2020.102071
Sewell M (2008) Behavioural finance. Economist 389(8604):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1057/9780230280786_5
Shefrin HM, Thaler RH (1988) The behavioral life‐cycle hypothesis. Econ Inq 26(4):609–643
Shim S, Serido J, Tang C (2012) The ant and the grasshopper revisited: the present psychological benefits of saving and future oriented financial behavior. J Econ Psychol 33(1):155–165
Simon HA (1978) Information-processing theory of human problem solving. In: Handbook of learning and cognitive processes, vol 5, pp 271–295
Sivaramakrishnan S, Srivastava M, Rastogi A (2017) Attitudinal factors, financial literacy, and stock market participation. Int J Bank Mark 34(1):1–5
Snyder H (2019) Literature review as a research methodology: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res 104(August):333–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.07.039
Stawski RS, Hershey DA, Jacobs-Lawson JM (2007) Goal clarity and financial planning activities as determinants of retirement savings contributions. Int J Aging Hum Dev 64(1):13–32. https://doi.org/10.2190/13GK-5H72-H324-16P2
Steinert JI, Zenker J, Filipiak U, Movsisyan A, Cluver LD, Shenderovich Y (2018) Do saving promotion interventions increase household savings, consumption, and investments in Sub-saharan Africa? A systematic review and meta-analysis. World Dev 104:238–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2017.11.018
Steinhart Y, Mazursky D (2010) Purchase availability and involvement antecedents among financial products. Int J Bank Mark 28(2):113–135. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652321011018314
Strömbäck C, Lind T, Skagerlund K, Västfjäll D, Tinghög G (2017) Does self-control predict financial behavior and financial well-being? J Behav Experimental Finance 14:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbef.2017.04.002
Strömbäck C, Skagerlund K, Västfjäll D, Tinghög G (2020) Subjective self-control but not objective measures of executive functions predict financial behavior and well-being. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance , 27 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbef.2020.100339
Tam L, Dholakia U (2014) Saving in cycles: how to get people to save more money. Psychol Sci 25(2):531–537. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797613512129
Tang N, Baker A (2016) Self-esteem, financial knowledge and financial behavior. J Econ Psychol 54:164–176
Tate M, Evermann J, Gable G (2015) An integrated framework for theories of individual attitudes toward technology. Inform Manage 52(6):710–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2015.06.005
Taylor MP, Jenkins SP, Sacker A (2011) Financial capability and psychological health. J Econ Psychol 32(5):710–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2011.05.006
Tennyson S, Yang HK (2014) The role of life experience in long-term care insurance decisions. Journal of Economic Psychology , 42 (2014), 175–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2014.04.002
Thaler BRH (1994) Psychology and savings policies. Am Econ Rev 84(2):175–179. http://www.jstor.org/stable/3132220
Thaler R (1980) Toward a positive theory of consumer choice. J Econ Behav Organ 1:39–60
Thaler RH (2005) Advances in behavioral finance. Adv Behav Finance 2:1–694. https://doi.org/10.2307/2329257
Thaler R, Shefrin H (1981) An economic theory of self-control. J Polit Econ 89(2):392–406
Tomar S, Kent Baker H, Kumar S, Hoffmann AOI (2021) Psychological determinants of retirement financial planning behavior. Journal of Business Research , 133 (November 2020), 432–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.05.007
Topa G, Moriano JA, Depolo M, Alcover CM, Morales JF (2009) Antecedents and consequences of retirement planning and decision-making: a meta-analysis and model. J Vocat Behav 75(1):38–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvb.2009.03.002
Topa G, Moriano JA, Depolo M, Alcover CM, Moreno A (2011) Retirement and wealth relationships: Meta-analysis and SEM. Res Aging 33(5):501–528. https://doi.org/10.1177/0164027511410549
Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P (2003) Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J Manag 14(3):207–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8551.00375
Ülkümen G, Cheema A (2011) Framing goals to influence personal savings: the role of specificity and construal level. J Mark Res 48(6):958–969. https://doi.org/10.1509/jmr.09.0516
United Nations, Department of Economic and Social, Affairs PD (2020) (2019). World Population Ageing 2019. In United Nations . http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/ 978-94-007-5204-7_6
Utkarsh, Pandey A, Ashta A, Spiegelman E, Sutan A (2020) Catch them young: impact of financial Socialization, financial literacy and attitude towards money on the financial well-being of young adults. Int J Consumer Stud 44(6):531–541. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcs.12583
Valente TW, Paredes P, Poppe P (1998) Matching the message to the process: the relative ordering of knowledge, attitudes, and practices in behavior change research. Hum Commun Res 24(3):366–385
Van Rooij M, Teppa F (2014) Personal traits and individual choices: taking action in economic and non-economic decisions. J Econ Behav Organ 100:33–43
van Rooij M, Lusardi A, Alessie R (2011) Financial literacy and stock market participation. J Financ Econ 101(2):449–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfineco.2011.03.006
Van Rooij MCJ, Lusardi A, Alessie RJM (2011a) Financial literacy and retirement planning in the Netherlands. J Econ Psychol 32(4):593–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2011.02.004
van Schie RJG, Dellaert BGC, Donkers B (2015) Promoting later planned retirement: construal level intervention impact reverses with age. J Econ Psychol 50:124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2015.06.010
Venkatesh V, Morris M, Davis G, Davis F (2003) Factors influencing the Use of M-Banking by academics: Case Study sms-based M-Banking. MIS Q 27(3):425–478
Vitt LA (2004) Consumers’ financial decisions and the psychology of values. J Financial Service Professionals 58(November):68–77. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true &db=bth&AN=14888952&site=ehost-live
Wang L, Lu W, Malhotra NK (2011) Demographics, attitude, personality, and credit card features correlate with credit card debt: a view from China. J Econ Psychol 32(1):179–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2010.11.006
World Economic Forum (2019) Investing in (and for) our future. Issue June. www.weforum.org
Xia T, Wang Z, Li K (2014) Financial literacy overconfidence and stock market participation. Soc Indic Res 119(3):1233–1245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-013-0555-9
Xiao JJ, Chen C, Chen F (2014) Consumer financial capability and financial satisfaction. Soc Indic Res 118(1):415–432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-013-0414-8
Yeung DY, Zhou X (2017) Planning for retirement: longitudinal effect on retirement resources and post-retirement well-being. Front Psychol 8:1300
Zhou R, Pham MT (2004) Promotion and prevention across mental accounts: when financial products dictate consumers’ investment goals. J Consum Res 31(1):125–135. https://doi.org/10.1086/383429
Download references
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to acknowledge the academicians and researchers who guided the search of the article and would like to thank the experts for the valuable inputs to refine the work.
There is no funding received for this research.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Symbiosis International (Deemed University), Pune, India
Kavita Karan Ingale
Symbiosis Institute of Operations Management, Symbiosis International (Deemed) University, Pune, India
Ratna Achuta Paluri
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Both authors contributed to the conceptualization, research design, methodology, analysis of the data,writing of the manuscript and its revision.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kavita Karan Ingale .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Ingale, K.K., Paluri, R.A. Retirement planning – a systematic review of literature and future research directions. Manag Rev Q (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-023-00377-x
Download citation
Received : 14 December 2022
Accepted : 04 October 2023
Published : 28 October 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-023-00377-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Retirement planning
- Systematic literature review
- Financial behavior
- Household finance
- Long-term savings
- Pension plan
- Financial literacy
- TCCM framework
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Open access
- Published: 04 April 2024
Bibliometric analysis of ChatGPT in medicine
- Sharanya Gande 1 ,
- Murdoc Gould 2 &
- Latha Ganti 3 , 4
International Journal of Emergency Medicine volume 17 , Article number: 50 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
123 Accesses
Metrics details
Introduction
The emergence of artificial intelligence (AI) chat programs has opened two distinct paths, one enhancing interaction and another potentially replacing personal understanding. Ethical and legal concerns arise due to the rapid development of these programs. This paper investigates academic discussions on AI in medicine, analyzing the context, frequency, and reasons behind these conversations.
The study collected data from the Web of Science database on articles containing the keyword “ChatGPT” published from January to September 2023, resulting in 786 medically related journal articles. The inclusion criteria were peer-reviewed articles in English related to medicine.
The United States led in publications (38.1%), followed by India (15.5%) and China (7.0%). Keywords such as “patient” (16.7%), “research” (12%), and “performance” (10.6%) were prevalent. The Cureus Journal of Medical Science (11.8%) had the most publications, followed by the Annals of Biomedical Engineering (8.3%). August 2023 had the highest number of publications (29.3%), with significant growth between February to March and April to May. Medical General Internal (21.0%) was the most common category, followed by Surgery (15.4%) and Radiology (7.9%).
The prominence of India in ChatGPT research, despite lower research funding, indicates the platform’s popularity and highlights the importance of monitoring its use for potential medical misinformation. China’s interest in ChatGPT research suggests a focus on Natural Language Processing (NLP) AI applications, despite public bans on the platform. Cureus’ success in publishing ChatGPT articles can be attributed to its open-access, rapid publication model. The study identifies research trends in plastic surgery, radiology, and obstetric gynecology, emphasizing the need for ethical considerations and reliability assessments in the application of ChatGPT in medical practice.
ChatGPT’s presence in medical literature is growing rapidly across various specialties, but concerns related to safety, privacy, and accuracy persist. More research is needed to assess its suitability for patient care and implications for non-medical use. Skepticism and thorough review of research are essential, as current studies may face retraction as more information emerges.
The emergence of AI chat programs presents two paths: one in which it is used to enhance and optimize the way we interact with queries and problems, becoming a spark that ushers in a new era of rapid academic and technological development, and another in which it is used to replace the need for one’s personal understanding. Additionally, it poses a multitude of ethical considerations and has even created certain legal gray areas, indicative of its development surpassing the speed of societies. This paper will serve as a means to better understand the context of how academic circles, countries, and institutions are discussing AI within the realm of medicine, how much they are discussing it, and conjecturing into why these conversations are occurring using supporting research.
ChatGPT is a Natural Language Processing (NLP) AI software that generates responses to any query a user may input [ 1 ]. It provides quick and clear responses and, as a result, is used widely in the same capacity as a search engine but with a more dynamic ability to interpret complicated questions, compile relevant information, and respond. Holders of professional titles such as PhDs are predicted to be affected by this; they may be at risk of decreasing importance due to AI’s ability to generate the same accurate and precise reports, curtailing the novelty of such research [ 2 ].
Although only existed for less than a year among the public, ChatGPT has made a significant impact on higher education and a variety of academic disciplines, including medicine. ChatGPT’s potential use in medicine arises from its success in aiding with diagnosis and decision-making due to its efficiency, timeliness, and access to a vast wealth of research and information. This allows it to compare medical knowledge between institutions globally, enhance communication among patients and hospital workers, and even assist in answering questions, whether they be medical queries, dosing information, or even medical exams [ 2 , 3 ]. . Another recent use of the platform, which has been considered to simplify the process of medical writing, is its ability to extract medical information and perform searches to create research drafts [ 1 ].
The data set collected was obtained using an advanced search on the Web of Science database for the keyword “ChatGPT,” not case sensitive, resulting in 1440 articles published from January 1st, 2023 to September 30th, 2023. Web of Science was used because of its unique positioning as an interdisciplinary hub for global research boasting its representation of over 256 disciplines and 15 million researchers, and its ability to portray a general climate of research. The Web of Science database also allows filtering by index and category, which was performed to only allow articles from the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED) and Emerging Sources Citation (ESCI) due to their medical focus. The categories were also limited to those pertaining to the medical field; all others were excluded. Analysis was performed on the remaining 786 medically related journal articles containing the keyword “ChatGPT”.
The criterion for inclusion was that the articles be peer-reviewed, pertaining to the medical field, within the data range analyzed, and in the English language. The title, abstract, and keywords of the included studies all included “ChatGPT”.
The Web of Science also allows for data collection of bibliometric information, which can later be imputed into specialized software for interpretation. This interpretation was performed using VOSviewer 1.6.19, a software specialized in analyzing articles bibliometrically producing visual and analytic findings for speculation. The metadata acquired was then examined using 4 different categorical distinctions -- country of origin, journal, month of publication, and keywords -- and mapped using the same software.
There were 786 documents retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection, after filtering for medical-related research that used the term ChatGPT in 2023. The country leading in total number of publications was the US at 38.1% [Fig. 1 ]. Following the US was India and the People’s Republic of China at 15.5% and 7.0% respectively. England and Australia were the fourth and fifth top contributors with 7.5% and 6.5% of total publications [Fig. 2 ].
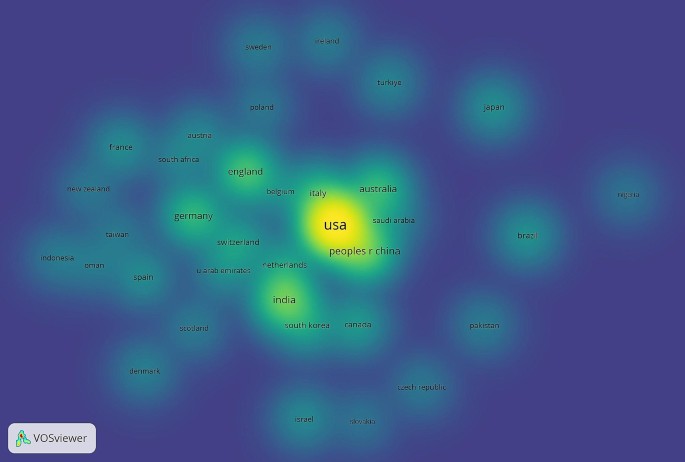
Geographical collaboration network heat map of publications Jan - Sep 2023

Treemap chart of geographic contributions to publications Jan - Sep 2023. The three most prevalent keywords that appear are patient(16.7%), research(12%), and performance(10.6%). Other topically relevant keywords were medical education(4.5%), ethic(1.8%), and plagiarism(1.3%)
The majority of articles analyzed were published in the Cureus Journal of Medical Science(11.8%) [Fig. 3 ]. Annals of Biomedical Engineering followed with the second most publications(8.3%). The third most published journal, Aesthetic Surgery Journal, is significantly less prolific contributing to 2.3% of all the documents analyzed, 72.3% fewer articles than the Annals of Biomedical Engineering. Both the Aesthetic Plastic Journal and the Radiology Journal have published 1.4% percent of all the articles retrieved, tying them as the fourth most substantial journal on ChatGPT. All remaining journals contained eight or fewer(≤ 1.0%) articles on the topic of ChatGPT.
Publication bibliographic coupling by journals Jan - Sep 2023
When indexing the articles by month, January 2023 had the least publications(≤ 0.005%) while August 2023, the latest month included in data collection, had the most(29.3%) [Fig. 4 ]. Of growth, from February to March and from April to May experienced the largest in terms of percentage with 1700% and 134%. The month of August exhibited the highest increase of papers published with 104 more papers than in July, increasing the rate of publication to 83%. June was the only month that did not experience research growth, declining 10% from the previous month.
The Web of Science categories are determined by up to 6 tags associated with any given journal. Web of Science designates its tags using subjects of the journal, author and editorial affiliations, funding, citations, and other elements such as a journal’s bibliographic categorization in other databases and a journal’s sponsors. The category of Medicine General Internal includes the most articles included in the analysis(21.0%), followed by Surgery(15.4%), Radiology(7.9%), and Health Care Science Services (7.8%). All remaining categories contained less than 5% of the journals included in this study.
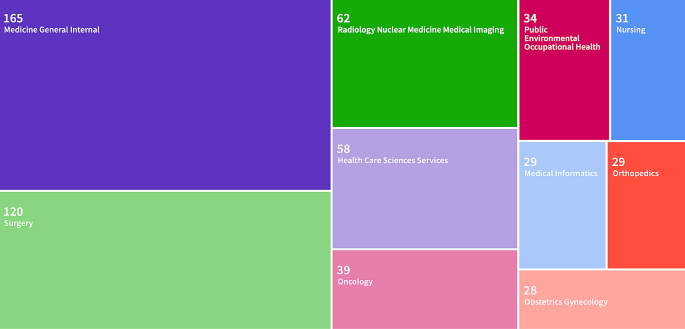
Web of Science Categories Treemap chart of publications Jan - Sep 2023
The 5 most cited articles were also collected for their merit in understanding academic discussions surrounding ChatGPT. The most cited article (121 citations) was “ChatGPT utility in healthcare education, research, and practice: Systematic review on the promising perspectives and valid concerns,” published in March 2023 [ 4 ]. “ChatGPT and other large language models are double-edged swords” and “ChatGPT: the future of discharge summaries” were the second most referenced articles, with 90 citations each [ 5 , 6 ]. “ChatGPT and the future of medical writing” had 84 citations, and “Nonhuman “authors” and implications for the integrity of scientific publications and medical knowledge” had 77 citations [ 7 , 8 ](Biswas, 2023; Flanagin et al., 2023).
Analyzing the three leading countries in publications regarding ChatGPT yields results that deviate from the norm of global research efforts. The leading country in publications, the United States (US), is often considered the highest researching entity due to spending more on research than any other country and offers the least notable finding [ 9 ]. India historically has low research funding, though it is improving, which draws particular attention to their dominance in ChatGPT research [ 10 , 11 ]. Elucidating this finding is India’s status as the second most avid country using ChatGPT, accounting for 8.5% of the total traffic [ 11 ]. Many concerns with ChatGPT’s use and accuracy in medicine go beyond clinical settings and focus on how public use of the platform could lead to medical misinformation. For this reason, the popularity of the platform publicly and privately throughout the country, being mirrored by the country’s research institutions and funding efforts, is crucial in managing potential medical misuse of ChatGPT without explicit medical supervision.
The People’s Republic of China, which is the third most publishing country on ChatGPT with 9.8%, does not allow public access to the platform [ 12 ]. With major universities in the country also passing explicit bans on the platform, findings suggest that ChatGPT is researched abstractly on ethical grounds or with special permissions. Furthermore, these findings suggest that the interest lies not with ChatGPT as a program, but with NLP AI and its applications more generally. Additionally, funding for research in China is set to eclipse the US and tension can be seen with competition for NLP AI research superiority [ 9 , 13 , 14 ]. Further research on the nature of ChatGPT research in China specifically is needed, but findings thus far appear to demonstrate that national bans on the platform do not affect publication outputs.
Cureus is an open-access, peer-reviewed, general medical journal and currently is the most prolific in its publication of articles surrounding ChatGPT. Cureus was one of the first journals to issue a call for papers specifically using ChatGPT, which likely has contributed to its numbers. While Cureus is not technologically specified - as compared to the second most published journal in ChatGPT, Annals of Biomedical Engineering - its dominance in the space can be attributed to its new age structure and business model. Of note, Cureus was one of the first journals to issue a call for papers specifically using ChatGPT, which likely has contributed to its numbers. Cureus’ success in publishing articles on ChatGPT may also hinge on its ability to peer-review articles and publish submitted work quickly [ 15 ]. As such, it participates in “rapid research,” or the practice of publishing articles to appropriately respond to the void of information on what was previously an under-researched topic. What was observed in “rapid research” during the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic is that while the speed of publication of articles was 11.5 times faster than publications on influenza, the rate of retractions and withdrawals was also significantly higher [ 16 , 17 , 18 ].
Medical disciplines
The Aesthetic Surgery Journal and Aesthetic Plastic Journal were two of the most prolific in publishing articles on ChatGPT and surgery was the second largest category, raising questions about ChatGPT’s usage in healthcare fields such as plastic surgery. A bibliometric study that addresses a plastic surgeon’s use of ChatGPT specifically yields four key findings: use in research and creation of original work, clinical applications, surgical education, and ethics/commentary on previous studies [ 19 ]. These findings are reinforced by our study, particularly in regard to the prevalence of the keywords medical education, research, and ethics. The mirroring of these interests fortifies the claim that ChatGPT has significant merit in medical education, with evidence to support that it is being examined for use in surgery but that ethical considerations remain a concern.
Literature surrounding radiology also demonstrates its use in innovative procedures and potential use for mitigating physician workloads [ 20 ]. Our study shows that it was the third most published category, suggesting it is particularly applicable to innovations in radiology, and similar studies support this claim [ 21 ]. ChatGPT is able to learn as it is fed more data and additionally excels at image analysis and pattern recognition. With physician burnout plaguing the healthcare industry, ChatGPTs use in automating such tasks serves as a potential solution [ 22 ]. AI is still subject to error however, and requires careful review if it is to be used in such a way, as to ensure patient safety, demonstrating a need for large in-depth studies into the platform’s reliability as a means of physician automation [ 20 ].
On May 24th, 2023 a bibliometric analysis of ChatGPT in Obstetrics and Gynecology (OBGYN) during a 69-day period found 0 relevant articles on its application [ 23 ]. Our study’s findings show a significant increase with 28 articles categorized under obstetric gynecology reflecting ChatGPTs adoption by more disciplines. Additionally, the disciplines of oncology, nursing, and medical informatics are all represented significantly in the top 10 categories of ChatGPT medical research. ChatGPT and NLP AI’s uses are extraordinarily dynamic; as more research is being done on its accuracy generally in medicine, more disciplines have begun incorporating it practically.
A similar study to this was conducted by Barrington et al. in Sep of 2023. The findings are mirrored by our results even with the addition of a wider date range of data collection. This demonstrates a trend in the direction of ChatGPT’s medical research and also solidifies the need for unresolved gaps in research to be addressed, namely into the limitations of ChatGPT ethically and in regards to accuracy and safety [ 24 ].
Limitations
Among the limitations of this study is its reliance on the Web of Science as the sole source of data. While Web of Science is expansive, there are discrepancies between it and a database such as PubMed, particularly in newer articles [ 25 ]. Additionally, this study only examined the keyword ChatGPT and did not explicitly include other forms of NLP AI limiting its ability to create a general image of this technology in medicine.
As with all medical research, academic interests and concerns are bound to change with the addition of new articles. Especially in the case of ChatGPT given the rapid research that surrounds it and its position as an avant-garde tool, even weeks after the publication of this article can see a reshuffling in research priorities. Despite this fact, the study provided does encompass the largest bibliometric date range on ChatGPT as of this time.
The literature on ChatGPT in medicine is extensive considering how new the platform is. Many medical specialties are exploring applications of the platform, and this study has shown that month over month an increasing number of disciplines are getting involved. Much of this research shares the same limitations, the safety, privacy, and accuracy of using ChatGPT for patient care. This gap in the literature needs further research if proposed applications are to be put into practice. Our analysis also emphasizes much-needed skepticism in reviewing said research, as much of the current studies could be at risk for retraction as more information is found. Concerns around the use of ChatGPT’s use medically in nonclinical settings are also found, a topic that is sorely underrepresented in current findings. The conclusion of this paper necessitates that more research be done into ChatGPT’s reliability for providing appropriate patient care in order to allow for applications in clinical settings, and the implications of ChatGPT’s use in non-medically trained hands.
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Chatgpt and the Future of Medical Writing. | Radiology, doi.org/10.1148/radiol.223312 . Accessed 1 Jan 2024.
Karthikeyan C. Literature Review on pros and cons of ChatGPT implications in Education. Int J Sci Res. 2023. https://doi.org/10.21275/SR23219122412 .
Article Google Scholar
American Medical Association. (Accessed 1. Jan 2024). ChatGPT passed the USMLE. What does it mean for med ed? American Medical Association. https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/digital/chatgpt-passed-usmle-what-does-it-mean-med-ed .
Sallam M. ChatGPT utility in healthcare education, research, and practice: systematic review on the promising perspectives and valid concerns. Healthc (Basel Switzerland). 2023;11(6):887. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11060887 .
Patel SB, Lam K. ChatGPT: the future of discharge summaries? The Lancet. Digit Health. 2023;5(3):e107–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(23)00021-3 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Shen Y, Heacock L, Elias J, Hentel KD, Reig B, Shih G, Moy L. ChatGPT and other large language models are double-edged swords. Radiology. 2023;307(2):e230163. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.230163 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Biswas S. ChatGPT and the future of medical writing. Radiology. 2023;307(2):e223312. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.223312 .
Flanagin A, Bibbins-Domingo K, Berkwits M, Christiansen SL. Nonhuman authors and implications for the integrity of scientific publication and medical knowledge. JAMA: J Am Med Association. 2023;329(8):637. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2023.1344 .
Amy Burke, , Okrent, A., & Hale, K. (n.d.). The state of U.s. science and engineering 2022. Nsf.gov. Retrieved December 17, 2023, from https://ncses.nsf.gov/pubs/nsb20221/u-s-and-global-research-and-development.
Van Noorden R. India by the numbers. Nature. 2015;521(7551):142–3. https://doi.org/10.1038/521142a .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Dandona L, Dandona R, Kumar GA, Cowling K, Titus P, Katoch VM, Swaminathan S. Mapping of health research funding in India. Natl Med J India. 2017;30(6):309–16. https://doi.org/10.4103/0970-258X.239069 .
Hung J, Chen J. The benefits, risks and regulation of using ChatGPT in Chinese academia: a content analysis. Social Sci (Basel Switzerland). 2023;12(7):380. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci12070380 .
Puderbaugh AP, Ellis AP, Payne JW, Scutti S, Conway C. (Jan/Feb 2020). China overtaking US as global research leader. Global Health Matters, 19(1).
Reshetnikova MS. Will China win the AI race? Lecture notes in networks and systems. Springer International Publishing; 2021. pp. 2064–74.
Adler J. A new age of peer reviewed scientific journals. Surg Neurol Int. 2012;3(1):145. https://doi.org/10.4103/2152-7806.103889 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Schonhaut L, Costa-Roldan I, Oppenheimer I, Pizarro V, Han D, Díaz F. Scientific publication speed and retractions of COVID-19 pandemic original articles. Revista Panam De Salud Publica [Pan Am J Public Health]. 2022;461. https://doi.org/10.26633/rpsp.2022.25 .
Khan H, Gupta P, Zimba O, Gupta L. Bibliometric and altmetric analysis of retracted articles on COVID-19. J Korean Med Sci. 2022;37(6). https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e44 .
Standish K. Retracted article: COVID-19, suicide, and femicide: Rapid Research using Google search phrases. J Gen Psychol. 2021;148(3):305–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221309.2021.1874863 .
Liu HY, Alessandri-Bonetti M, Arellano JA, Egro FM. Can ChatGPT be the plastic surgeon’s new digital assistant? A bibliometric analysis and scoping review of ChatGPT in plastic surgery literature. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03709-0 .
Srivastav S, Chandrakar R, Gupta S, Babhulkar V, Agrawal S, Jaiswal A, Prasad R, Wanjari MB. ChatGPT in radiology: the advantages and limitations of artificial intelligence for medical imaging diagnosis. Cureus. 2023;15(7). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.41435 .
Bera K, O’Connor G, Jiang S, Tirumani SH, Ramaiya N. Analysis of ChatGPT publications in radiology: literature so far. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1067/j.cpradiol.2023.10.013 .
Yates SW. Physician stress and burnout. Am J Med. 2020;133(2):160–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.08.034 .
Levin G, Brezinov Y, Meyer R. Exploring the use of ChatGPT in OBGYN: a bibliometric analysis of the first ChatGPT-related publications. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2023;308(6):1785–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-023-07081-x .
Barrington NM, Gupta N, Musmar B, Doyle D, Panico N, Godbole N, Reardon T, D’Amico RS. A bibliometric analysis of the rise of ChatGPT in medical research. Med Sci (Basel Switzerland). 2023;11(3):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci11030061 .
Falagas ME, Pitsouni EI, Malietzis GA, Pappas G. Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, web of Science, and Google Scholar: strengths and weaknesses. FASEB Journal: Official Publication Federation Am Soc Experimental Biology. 2008;22(2):338–42. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.07-9492lsf .
Download references
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Academy of the Lakes, Land O’ Lakes, FL, USA
Sharanya Gande
Rollins College, Winter Park, FL, USA
Murdoc Gould
University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL, USA
Latha Ganti
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, RI Providence, USA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
SG and MG wrote the main manuscript text and prepared figures. LG supervised the project and data analysis. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Latha Ganti .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval.
The study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The University of Central Florida Institutional Board Review determined this study to be exempt.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
Dr. Latha Ganti has an editorial role at Springer Nature.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Gande, S., Gould, M. & Ganti, L. Bibliometric analysis of ChatGPT in medicine. Int J Emerg Med 17 , 50 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12245-024-00624-2
Download citation
Received : 11 January 2024
Accepted : 19 March 2024
Published : 04 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12245-024-00624-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
International Journal of Emergency Medicine
ISSN: 1865-1380
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 02 April 2022
A qualitative study of rural healthcare providers’ views of social, cultural, and programmatic barriers to healthcare access
- Nicholas C. Coombs 1 ,
- Duncan G. Campbell 2 &
- James Caringi 1
BMC Health Services Research volume 22 , Article number: 438 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
23k Accesses
19 Citations
10 Altmetric
Metrics details
Ensuring access to healthcare is a complex, multi-dimensional health challenge. Since the inception of the coronavirus pandemic, this challenge is more pressing. Some dimensions of access are difficult to quantify, namely characteristics that influence healthcare services to be both acceptable and appropriate. These link to a patient’s acceptance of services that they are to receive and ensuring appropriate fit between services and a patient’s specific healthcare needs. These dimensions of access are particularly evident in rural health systems where additional structural barriers make accessing healthcare more difficult. Thus, it is important to examine healthcare access barriers in rural-specific areas to understand their origin and implications for resolution.
We used qualitative methods and a convenience sample of healthcare providers who currently practice in the rural US state of Montana. Our sample included 12 healthcare providers from diverse training backgrounds and specialties. All were decision-makers in the development or revision of patients’ treatment plans. Semi-structured interviews and content analysis were used to explore barriers–appropriateness and acceptability–to healthcare access in their patient populations. Our analysis was both deductive and inductive and focused on three analytic domains: cultural considerations, patient-provider communication, and provider-provider communication. Member checks ensured credibility and trustworthiness of our findings.
Five key themes emerged from analysis: 1) a friction exists between aspects of patients’ rural identities and healthcare systems; 2) facilitating access to healthcare requires application of and respect for cultural differences; 3) communication between healthcare providers is systematically fragmented; 4) time and resource constraints disproportionately harm rural health systems; and 5) profits are prioritized over addressing barriers to healthcare access in the US.
Conclusions
Inadequate access to healthcare is an issue in the US, particularly in rural areas. Rural healthcare consumers compose a hard-to-reach patient population. Too few providers exist to meet population health needs, and fragmented communication impairs rural health systems’ ability to function. These issues exacerbate the difficulty of ensuring acceptable and appropriate delivery of healthcare services, which compound all other barriers to healthcare access for rural residents. Each dimension of access must be monitored to improve patient experiences and outcomes for rural Americans.
Peer Review reports
Unequal access to healthcare services is an important element of health disparities in the United States [ 1 ], and there remains much about access that is not fully understood. The lack of understanding is attributable, in part, to the lack of uniformity in how access is defined and evaluated, and the extent to which access is often oversimplified in research [ 2 ]. Subsequently, attempts to address population-level barriers to healthcare access are insufficient, and access remains an unresolved, complex health challenge [ 3 , 4 , 5 ]. This paper presents a study that aims to explore some of the less well studied barriers to healthcare access, particularly those that influence healthcare acceptability and appropriateness.
In truth, healthcare access entails a complicated calculus that combines characteristics of individuals, their households, and their social and physical environments with characteristics of healthcare delivery systems, organizations, and healthcare providers. For one to fully ‘access’ healthcare, they must have the means to identify their healthcare needs and have available to them care providers and the facilities where they work. Further, patients must then reach, obtain, and use the healthcare services in order to have their healthcare needs fulfilled. Levesque and colleagues critically examined access conceptualizations in 2013 and synthesized all ways in which access to healthcare was previously characterized; Levesque et al. proposed five dimensions of access: approachability, acceptability, availability, affordability and appropriateness [ 2 ]. These refer to the ability to perceive, seek, reach, pay for, and engage in services, respectively.
According to Levesque et al.’s framework, the five dimensions combine to facilitate access to care or serve as barriers. Approachability indicates that people facing health needs understand that healthcare services exist and might be helpful. Acceptability represents whether patients see healthcare services as consistent or inconsistent with their own social and cultural values and worldviews. Availability indicates that healthcare services are reached both physically and in a timely manner. Affordability simplifies one’s capacity to pay for healthcare services without compromising basic necessities, and finally, appropriateness represents the fit between healthcare services and a patient’s specific healthcare needs [ 2 ]. This study focused on the acceptability and appropriateness dimensions of access.
Before the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2; COVID-19) pandemic, approximately 13.3% of adults in the US did not have a usual source of healthcare [ 6 ]. Millions more did not utilize services regularly, and close to two-thirds reported that they would be debilitated by an unexpected medical bill [ 7 , 8 , 9 ]. Findings like these emphasized a fragility in the financial security of the American population [ 10 ]. These concerns were exacerbated by the pandemic when a sudden surge in unemployment increased un- and under-insurance rates [ 11 ]. Indeed, employer-sponsored insurance covers close to half of Americans’ total cost of illness [ 12 ]. Unemployment linked to COVID-19 cut off the lone outlet to healthcare access for many. Health-related financial concerns expanded beyond individuals, as healthcare organizations were unequipped to manage a simultaneous increase in demand for specialized healthcare services and a steep drop off for routine revenue-generating healthcare services [ 13 ]. These consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic all put additional, unexpected pressure on an already fragmented US healthcare system.
Other structural barriers to healthcare access exist in relation to the rural–urban divide. Less than 10% of US healthcare resources are located in rural areas where approximately 20% of the American population resides [ 14 ]. In a country with substantially fewer providers per capita compared to many other developed countries, persons in rural areas experience uniquely pressing healthcare provider shortages [ 15 , 16 ]. Rural inhabitants also tend to have lower household income, higher rates of un- or under-insurance, and more difficulty with travel to healthcare clinics than urban dwellers [ 17 ]. Subsequently, persons in rural communities use healthcare services at lower rates, and potentially preventable hospitalizations are more prevalent [ 18 ]. This disparity often leads rural residents to use services primarily for more urgent needs and less so for routine care [ 19 , 20 , 21 ].
The differences in how rural and urban healthcare systems function warranted a federal initiative to focus exclusively on rural health priorities and serve as counterpart to Healthy People objectives [ 22 ]. The rural determinants of health, a more specific expression of general social determinants, add issues of geography and topography to the well-documented social, economic and political factors that influence all Americans’ access to healthcare [ 23 ]. As a result, access is consistently regarded as a top priority in rural areas, and many research efforts have explored the intersection between access and rurality, namely within its less understood dimensions (acceptability and appropriateness) [ 22 ].
Acceptability-related barriers to care
Acceptability represents the dimension of healthcare access that affects a patient’s ability to seek healthcare, particularly linked to one’s professional values, norms and culture [ 2 ]. Access to health information is an influential factor for acceptable healthcare and is essential to promote and maintain a healthy population [ 24 ]. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, health literacy or a high ‘health IQ’ is the degree to which individuals have the ability to find, understand, and use information and services to inform health-related decisions and actions for themselves and others, which impacts healthcare use and system navigation [ 25 ]. The literature indicates that lower levels of health literacy contribute to health disparities among rural populations [ 26 , 27 , 28 ]. Evidence points to a need for effective health communication between healthcare organizations and patients to improve health literacy [ 24 ]. However, little research has been done in this area, particularly as it relates to technologically-based interventions to disseminate health information [ 29 ].
Stigma, an undesirable position of perceived diminished status in an individual’s social position, is another challenge that influences healthcare acceptability [ 30 ]. Those who may experience stigma fear negative social consequences in relation to care seeking. They are more likely to delay seeking care, especially among ethnic minority populations [ 31 , 32 ]. Social media presents opportunities for the dissemination of misleading medical information; this runs further risk for stigma [ 33 ]. Stigma is difficult to undo, but research has shown that developing a positive relationship with a healthcare provider or organization can work to reduce stigma among patients, thus promoting healthcare acceptability [ 34 ].
A provider’s attempts to engage patients and empower them to be active decision-makers regarding their treatment has also been shown to improve healthcare acceptability. One study found that patients with heart disease who completed a daily diary of weight and self-assessment of symptoms, per correspondence with their provider, had better care outcomes than those who did not [ 35 ]. Engaging with household family members and involved community healers also mitigates barriers to care, emphasizing the importance of a team-based approach that extends beyond those who typically provide healthcare services [ 36 , 37 ]. One study, for instance, explored how individuals closest to a pregnant woman affect the woman’s decision to seek maternity care; partners, female relatives, and community health-workers were among the most influential in promoting negative views, all of which reduced a woman’s likelihood to access care [ 38 ].
Appropriateness-related barriers to care
Appropriateness marks the dimension of healthcare access that affects a patient’s ability to engage, and according to Levesque et al., is of relevance once all other dimensions (the ability to perceive, seek, reach and pay for) are achieved [ 2 ]. The ability to engage in healthcare is influenced by a patient’s level of empowerment, adherence to information, and support received by their healthcare provider. Thus, barriers to healthcare access that relate to appropriateness are often those that indicate a breakdown in communication between a patient with their healthcare provider. Such breakdown can involve a patient experiencing miscommunication, confrontation, and/or a discrepancy between their provider’s goals and their own goals for healthcare. Appropriateness represents a dimension of healthcare access that is widely acknowledged as an area in need of improvement, which indicates a need to rethink how healthcare providers and organizations can adapt to serve the healthcare needs of their communities [ 39 ]. This is especially true for rural, ethnic minority populations, which disproportionately experience an abundance of other barriers to healthcare access. Culturally appropriate care is especially important for members of minority populations [ 40 , 41 , 42 ]. Ultimately, patients value a patient-provider relationship characterized by a welcoming, non-judgmental atmosphere [ 43 , 44 ]. In rural settings especially, level of trust and familiarity are common factors that affect service utilization [ 45 ]. Evidence suggests that kind treatment by a healthcare provider who promotes patient-centered care can have a greater overall effect on a patient’s experience than a provider’s degree of medical knowledge or use of modern equipment [ 46 ]. Of course, investing the time needed to nurture close and caring interpersonal connections is particularly difficult in under-resourced, time-pressured rural health systems [ 47 , 48 ].
The most effective way to evaluate access to healthcare largely depends on which dimensions are explored. For instance, a population-based survey can be used to measure the barrier of healthcare affordability. Survey questions can inquire directly about health insurance coverage, care-related financial burden, concern about healthcare costs, and the feared financial impacts of illness and/or disability. Many national organizations have employed such surveys to measure affordability-related barriers to healthcare. For example, a question may ask explicitly about financial concerns: ‘If you get sick or have an accident, how worried are you that you will not be able to pay your medical bills?’ [ 49 ]. Approachability and availability dimensions of access are also studied using quantitative analysis of survey questions, such as ‘Is there a place that you usually go to when you are sick or need advice about your health?’ or ‘Have you ever delayed getting medical care because you couldn’t get through on the telephone?’ In contrast, the remaining two dimensions–acceptability and appropriateness–require a qualitative approach, as the social and cultural factors that determine a patient’s likelihood of accepting aspects of the services that are to be received (acceptability) and the fit between those services and the patient’s specific healthcare needs (appropriateness) can be more abstract [ 50 , 51 ]. In social science, qualitative methods are appropriate to generate knowledge of what social events mean to individuals and how those individuals interact within them; these methods allow for an exploration of depth rather than breadth [ 52 , 53 ]. Qualitative methods, therefore, are appropriate tools for understanding the depth of healthcare providers’ experiences in the inherently social context of seeking and engaging in healthcare.
In sum, acceptability- and appropriateness-related barriers to healthcare access are multi-layered, complex and abundant. Ensuring access becomes even more challenging if structural barriers to access are factored in. In this study, we aimed to explore barriers to healthcare access among persons in Montana, a historically underserved, under-resourced, rural region of the US. Montana is the fourth largest and third least densely populated state in the country; more than 80% of Montana counties are classified as non-core (the lowest level of urban/rural classification), and over 90% are designated as health professional shortage areas [ 54 , 55 ]. Qualitative methods supported our inquiry to explore barriers to healthcare access related to acceptability and appropriateness.
Participants
Qualitative methods were utilized for this interpretive, exploratory study because knowledge regarding barriers to healthcare access within Montana’s rural health systems is limited. We chose Montana healthcare providers, rather than patients, as the population of interest so we may explore barriers to healthcare access from the perspective of those who serve many persons in rural settings. Inclusion criteria required study participants to provide direct healthcare to patients at least one-half of their time. We defined ‘provider’ as a healthcare organization employee with clinical decision-making power and the qualifications to develop or revise patients’ treatment plans. In an attempt to capture a group of providers with diverse experience, we included providers across several types and specialties. These included advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs), physicians (MDs and DOs), and physician assistants (PAs) who worked in critical care medicine, emergency medicine, family medicine, hospital medicine, internal medicine, pain medicine, palliative medicine, pediatrics, psychiatry, and urgent care medicine. We also included licensed clinical social workers (LCSWs) and clinical psychologists who specialize in behavioral healthcare provision.
Recruitment and Data Collection
We recruited participants via email using a snowball sampling approach [ 56 ]. We opted for this approach because of its effectiveness in time-pressured contexts, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, which has made healthcare provider populations hard to reach [ 57 ]. Considering additional constraints with the pandemic and the rural nature of Montana, interviews were administered virtually via Zoom video or telephone conferencing with Zoom’s audio recording function enabled. All interviews were conducted by the first author between January and September 2021. The average length of interviews was 50 min, ranging from 35 to 70 min. There were occasional challenges experienced during interviews (poor cell phone reception from participants, dropped calls), in which case the interviewer remained on the line until adequate communication was resumed. All interviews were included for analysis and transcribed verbatim into NVivo Version 12 software. All qualitative data were saved and stored on a password-protected University of Montana server. Hard-copy field notes were securely stored in a locked office on the university’s main campus.
Data analysis included a deductive followed by an inductive approach. This dual analysis adheres to Levesque’s framework for qualitative methods, which is discussed in the Definition of Analytic Domains sub-section below. Original synthesis of the literature informed the development of our initial deductive codebook. The deductive approach was derived from a theory-driven hypothesis, which consisted of synthesizing previous research findings regarding acceptability- and appropriateness-related barriers to care. Although the locations, patient populations and specific type of healthcare services varied by study in the existing literature, several recurring barriers to healthcare access were identified. We then operationalized three analytic domains based on these findings: cultural considerations, patient-provider communication, and provider-provider communication. These domains were chosen for two reasons: 1) the terms ‘culture’ and ‘communication’ were the most frequently documented characteristics across the studies examined, and 2) they each align closely with the acceptability and appropriateness dimensions of access to healthcare, respectively. In addition, ‘culture’ is included in the definition of acceptability and ‘communication’ is a quintessential aspect of appropriateness. These domains guided the deductive portion of our analysis, which facilitated the development of an interview guide used for this study.
Interviews were semi-structured to allow broad interpretations from participants and expand the open-ended characterization of study findings. Data were analyzed through a flexible coding approach proposed by Deterding and Waters [ 58 ]. Qualitative content analysis was used, a method particularly beneficial for analyzing large amounts of qualitative data collected through interviews that offers possibility of quantifying categories to identify emerging themes [ 52 , 59 ]. After fifty percent of data were analyzed, we used an inductive approach as a formative check and repeated until data saturation, or the point at which no new information was gathered in interviews [ 60 ]. At each point of inductive analysis, interview questions were added, removed, or revised in consideration of findings gathered [ 61 ]. The Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) was used for reporting all qualitative data for this study [ 62 ]. The first and third authors served as primary and secondary analysts of the qualitative data and collaborated to triangulate these findings. An audit approach was employed, which consisted of coding completed by the first author and then reviewed by the third author. After analyses were complete, member checks ensured credibility and trustworthiness of findings [ 63 ]. Member checks consisted of contacting each study participant to explain the study’s findings; one-third of participants responded and confirmed all findings. All study procedures were reviewed and approved by the Human Subjects Committee of the authors’ institution’s Institutional Review Board.
Definitions of Analytic Domains
Cultural considerations.
Western health systems often fail to consider aspects of patients’ cultural perspectives and histories. This can manifest in the form of a providers’ lack of cultural humility. Cultural humility is a process of preventing imposition of one’s worldview and cultural beliefs on others and recognizing that everyone’s conception of the world is valid. Humility cultivates sensitive approaches in treating patients [ 64 ]. A lack of cultural humility impedes the delivery of acceptable and appropriate healthcare [ 65 ], which can involve low empathy or respect for patients, or dismissal of culture and traditions as superstitions that interfere with standard treatments [ 66 , 67 ]. Ensuring cultural humility among all healthcare employees is a step toward optimal healthcare delivery. Cultural humility is often accomplished through training that can be tailored to particular cultural- or gender-specific populations [ 68 , 69 ]. Since cultural identities and humility have been marked as factors that can heavily influence patients’ access to care, cultural considerations composed our first analytic domain. To assess this domain, we asked participants how they address the unique needs of their patients, how they react when they observe a cultural behavior or attitude from a patient that may not directly align with their treatment plan, and if they have received any multicultural training or training on cultural considerations in their current role.
Patient-provider communication
Other barriers to healthcare access can be linked to ineffective patient-provider communication. Patients who do not feel involved in healthcare decisions are less likely to adhere to treatment recommendations [ 70 ]. Patients who experience communication difficulties with providers may feel coerced, which generates disempowerment and leads patients to employ more covert ways of engagement [ 71 , 72 ]. Language barriers can further compromise communication and hinder outcomes or patient progress [ 73 , 74 ]. Any miscommunication between a patient and provider can affect one’s access to healthcare, namely affecting appropriateness-related barriers. For these reasons, patient-provider communication composed our second analytic domain. We asked participants to highlight the challenges they experience when communicating with their patients, how those complications are addressed, and how communication strategies inform confidentiality in their practice. Confidentiality is a core ethical principle in healthcare, especially in rural areas that have smaller, interconnected patient populations [ 75 ].
Provider-Provider Communication
A patient’s journey through the healthcare system necessitates sufficient correspondence between patients, primary, and secondary providers after discharge and care encounters [ 76 ]. Inter-provider and patient-provider communication are areas of healthcare that are acknowledged to have some gaps. Inconsistent mechanisms for follow up communication with patients in primary care have been documented and emphasized as a concern among those with chronic illness who require close monitoring [ 68 , 77 ]. Similar inconsistencies exist between providers, which can lead to unclear care goals, extended hospital stays, and increased medical costs [ 78 ]. For these reasons, provider-provider communication composed our third analytic domain. We asked participants to describe the approaches they take to streamline communication after a patient’s hospital visit, the methods they use to ensure collaborative communication between primary or secondary providers, and where communication challenges exist.
Healthcare provider characteristics
Our sample included 12 providers: four in family medicine (1 MD, 1 DO, 1 PA & 1 APRN), three in pediatrics (2 MD with specialty in hospital medicine & 1 DO), three in palliative medicine (2 MDs & 1 APRN with specialty in wound care), one in critical care medicine (DO with specialty in pediatric pulmonology) and one in behavioral health (1 LCSW with specialty in trauma). Our participants averaged 9 years (range 2–15) as a healthcare provider; most reported more than 5 years in their current professional role. The diversity of participants extended to their patient populations as well, with each participant reporting a unique distribution of age, race and level of medical complexity among their patients. Most participants reported that a portion of their patients travel up to five hours, sometimes across county- or state-lines, to receive care.
Theme 1: A friction exists between aspects of patients’ rural identities and healthcare systems
Our participants comprised a collection of medical professions and reported variability among health-related reasons their patients seek care. However, most participants acknowledged similar characteristics that influence their patients’ challenges to healthcare access. These identified factors formed categories from which the first theme emerged. There exists a great deal of ‘rugged individualism’ among Montanans, which reflects a self-sufficient and self-reliant way of life. Stoicism marked a primary factor to characterize this quality. One participant explained:
True Montanans are difficult to treat medically because they tend to be a tough group. They don’t see doctors. They don’t want to go, and they don’t want to be sick. That’s an aspect of Montana that makes health culture a little bit difficult.
Another participant echoed this finding by stating:
The backwoods Montana range guy who has an identity of being strong and independent probably doesn’t seek out a lot of medical care or take a lot of medications. Their sense of vitality, independence and identity really come from being able to take care and rely on themselves. When that is threatened, that’s going to create a unique experience of illness.
Similar responses were shared by all twelve participants; stoicism seemed to be heavily embedded in many patient populations in Montana and serves as a key determinant of healthcare acceptability. There are additional factors, however, that may interact with stoicism but are multiply determined. Stigma is an example of this, presented in this context as one’s concern about judgement by the healthcare system. Respondents were openly critical of this perception of the healthcare system as it was widely discussed in interviews. One participant stated:
There is a real perception of a punitive nature in the medical community, particularly if I observe a health issue other than the primary reason for one’s hospital visit, whether that may be predicated on medical neglect, delay of care, or something that may warrant a report to social services. For many of the patients and families I see, it’s not a positive experience and one that is sometimes an uphill barrier that I work hard to circumnavigate.
Analysis of these factors suggest that low use of healthcare services may link to several characteristics, including access problems. Separately, a patient’s perceived stigma from healthcare providers may also impact a patient’s willingness to receive services. One participant put it best by stating
Sometimes, families assume that I didn’t want to see them because they will come in for follow up to meet with me but end up meeting with another provider, which is frustrating because I want to maintain patients on my panel but available time and resource occasionally limits me from doing so. It could be really hard adapting to those needs on the fly, but it’s an honest miss.
When a patient arrives for a healthcare visit and experiences this frustration, it may elicit a patient’s perceptions of neglect or disorganization. This ‘honest miss’ may, in turn, exacerbate other acceptable-related barriers to care.
Theme 2: Facilitating access to healthcare requires application of and respect for cultural differences
The biomedical model is the standard of care utilized in Western medicine [ 79 , 80 ]. However, the US comprises people with diverse social and cultural identities that may not directly align with Western conceptions of health and wellness. Approximately 11.5% of the Montana population falls within an ethnic minority group. 6.4% are of American Indian or Alaska Native origin, 0.5% are of Black or African American origin, 0.8% are of Asian origin and 3.8% are of multiple or other origins. [ 81 ]. Cultural insensitivity is acknowledged in health services research as an active deterrent for appropriate healthcare delivery [ 65 ]. Participants for this study were asked how they react when a patient brings up a cultural attitude or behavior that may impact the proposed treatment plan. Eight participants noted a necessity for humility when this occurs. One participant conceptualized this by stating:
When this happens, I learn about individuals and a way of life that is different to the way I grew up. There is a lot of beauty and health in a non-patriarchal, non-dominating, non-sexist framework, and when we can engage in such, it is really expansive for my own learning process.
The participants who expressed humility emphasized that it is best to work in tandem with their patient, congruently. Especially for those with contrasting worldviews, a provider and a patient working as a team poses an opportunity to develop trust. Without it, a patient can easily fall out of the system, further hindering their ability to access healthcare services in the future. One participant stated:
The approach that ends up being successful for a lot of patients is when we understand their modalities, and they have a sense we understand those things. We have to show understanding and they have to trust. From there, we can make recommendations to help get them there, not decisions for them to obey, rather views based on our experiences and understanding of medicine.
Curiosity was another reaction noted by a handful of participants. One participant said:
I believe patients and their caregivers can be engaged and loving in different ways that don’t always follow the prescribed approach in the ways I’ve been trained, but that doesn’t necessarily mean that they are detrimental. I love what I do, and I love learning new things or new approaches, but I also love being surprised. My style of medicine is not to predict peoples’ lives, rather to empower and support what makes life meaningful for them.
Participants mentioned several other characteristics that they use in practice to prevent cultural insensitivity and support a collaborative approach to healthcare. Table 1 lists these facilitating characteristics and quotes to explain the substance of their benefit.
Consensus among participants indicated that the use of these protective factors to promote cultural sensitivity and apply them in practice is not standardized. When asked, all but two participants said they had not received any culturally-based training since beginning their practice. Instead, they referred to developing skills through “on the job training” or “off the cuff learning.” The general way of medicine, one participant remarked, was to “throw you to the fire.” This suggested that use of standardized cultural humility training modules for healthcare providers was not common practice. Many attributed this to time constraints.
Individual efforts to gain culturally appropriate skills or enhance cultural humility were mentioned, however. For example, three participants reported that they attended medical conferences to discuss cultural challenges within medicine, one participant sought out cultural education within their organization, and another was invited by Native American community members to engage in traditional peace ceremonies. Participants described these additional efforts as uncommon and outside the parameters of a provider’s job responsibilities, as they require time commitments without compensation.
Additionally, eight participants said they share their personal contact information with patients so they may call them directly for medical needs. The conditions and frequency with which this is done was variable and more common among providers in specialized areas of medicine or those who described having a manageable patient panel. All who reported that they shared their personal contact information described it as an aspect of rural health service delivery that is atypical in other, non-rural healthcare systems.
Theme 3: Communication between healthcare providers is systematically fragmented
Healthcare is complex and multi-disciplinary, and patients’ treatment is rarely overseen by a single provider [ 82 ]. The array of provider types and specialties is vast, as is the range of responsibilities ascribed to providers. Thus, open communication among providers both within and between healthcare systems is vital for the success of collaborative healthcare [ 83 ]. Without effective communication achieved between healthcare providers, the appropriate delivery of healthcare services may be become compromised. Our participants noted that they face multiple challenges that complicate communication with other providers. Miscommunication between departments, often implicating the Emergency Department (ED), was a recurring point noted among participants. One participant who is a primary care physician said:
If one of my patients goes to the ER, I don’t always get the notes. They’re supposed to send them to the patient’s primary care doc. The same thing happens with general admissions, but again, I often find out from somebody else that my patient was admitted to the hospital.
This failure to communicate can negatively impact the patient, particularly if time sensitivity or medical complexity is essential to treatment. A patient’s primary care physician is the most accurate source of their medical history; without an effective way to obtain and synthesize a patient’s health information, there may be increased risk of medical error. One participant in a specialty field stated:
One of the biggest barriers I see is obtaining a concise description of a patient’s history and needs. You can imagine if you’re a mom and you’ve got a complicated kid. You head to the ER. The ER doc looks at you with really wide eyes, not knowing how to get information about your child that’s really important.
This concern was highlighted with a specific example from a different participant:
I have been unable to troubleshoot instances when I send people to the ER with a pretty clear indication for admission, and then they’re sent home. For instance, I had an older fellow with pretty severe chronic kidney disease. He presented to another practitioner in my office with shortness of breath and swelling and appeared to have newly onset decompensated heart failure. When I figured this out, I sent him to the ER, called and gave my report. The patient later came back for follow up to find out not only that they had not been admitted but they lost no weight with outpatient dialysis . I feel like a real opportunity was missed to try to optimize the care of the patient simply because there was poor communication between myself and the ER. This poor guy… He ended up going to the ER four times before he got admitted for COVID-19.
In some cases, communication breakdown was reported as the sole cause of a poor outcome. When communication is effective, each essential member of the healthcare team is engaged and collaborating with the same information. Some participants called this process ‘rounds’ when a regularly scheduled meeting is staged between a group of providers to ensure access to accurate patient information. Accurate communication may also help build trust and improve a patient’s experience. In contrast, ineffective communication can result in poor clarity regarding providers’ responsibilities or lost information. Appropriate delivery of healthcare considers the fit between providers and a patient’s specific healthcare needs; the factors noted here suggest that provider-provider miscommunication can adversely affect this dimension of healthcare access.
Another important mechanism of communication is the sharing of electronic medical records (EMRs), a process that continues to shift with technological advances. Innovation is still recent enough, however, for several of our study participants to be able to recall a time when paper charts were standard. Widespread adoption and embrace of the improvements inherent in electronic medical records expanded in the late 2000’s [ 84 ]. EMRs vastly improved the ability to retain, organize, safeguard, and transfer health information. Every participant highlighted EMRs at one point or another and often did so with an underlying sense of anger or frustration. Systematic issues and problems with EMRs were discussed. One participant provided historical context to such records:
Years back, the government aimed to buy an electronic medical record system, whichever was the best, and a number of companies created their own. Each were a reasonable system, so they all got their checks and now we have four completely separate operating systems that do not talk to each other. The idea was to make a router or some type of relay that can share information back and forth. There was no money in that though, so of course, no one did anything about it. Depending on what hospital, clinic or agency you work for, you will most likely work within one of these systems. It was a great idea; it just didn’t get finished.
Seven participants confirmed these points and their impacts on making coordination more difficult, relying on outdated communication strategies more often than not. Many noted this even occurs between facilities within the same city and in separate small metropolitan areas across the state. One participant said:
If my hospital decides to contract with one EMR and the hospital across town contracts with another, correspondence between these hospitals goes back to traditional faxing. As a provider, you’re just taking a ‘fingered crossed’ approach hoping that the fax worked, is picked up, was put in the appropriate inbox and was actually looked at. Information acquisition and making sure it’s timely are unforeseen between EMRs.
Participants reported an “astronomic” number of daily faxes and telephone calls to complete the communication EMRs were initially designed to handle. These challenges are even more burdensome if a patient moves from out of town or out of state; obtaining their medical records was repeatedly referred to as a “chore” so onerous that it often remains undone. Another recurring concern brought up by participants regarded accuracy within EMRs to lend a false sense of security. They are not frequently updated, not designed to be family-centered and not set up to do anything automatically. One participant highlighted these limitations by stating:
I was very proud of a change I made in our EMR system [EPIC], even though it was one I never should have had to make. I was getting very upset because I would find out from my nursing assistant who read the obituary that one of my patients had died. There was a real problem with the way the EMR was notifying PCP’s, so I got an EPIC-level automated notification built into our EMR so that any time a patient died, their status would be changed to deceased and a notification would be sent to their PCP. It’s just really awful to find out a week later that your patient died, especially when you know these people and their families really well. It’s not good care to have blind follow up.
Whether it be a physical or electronic miscommunication between healthcare providers, the appropriate delivery of healthcare can be called to question
Theme 4: Time and resource constraints disproportionately harm rural health systems
Several measures of system capacity suggest the healthcare system in the US is under-resourced. There are fewer physicians and hospital beds per capita compared to most comparable countries, and the growth of healthcare provider populations has stagnated over time [ 15 ]. Rural areas, in particular, are subject to resource limitations [ 16 ]. All participants discussed provider shortages in detail. They described how shortages impact time allocation in their day-to-day operations. Tasks like patient intakes, critical assessments, and recovering information from EMRs take time, of which most participants claimed to not have enough of. There was also a consensus in having inadequate time to spend on medically complex cases. Time pressures were reported to subsequently influence quality of care. One participant stated:
With the constant pace of medicine, time is not on your side. A provider cannot always participate in an enriching dialogue with their patients, so rather than listen and learn, we are often coerced into the mindset of ‘getting through’ this patient so we can move on. This echoes for patient education during discharge, making the whole process more arduous than it otherwise could be if time and resources were not as sparse.
Depending on provider type, specialty, and the size of patient panels, four participants said they have the luxury of extending patient visits to 40 + minutes. Any flexibility with patient visits was regarded as just that: a luxury. Very few providers described the ability to coordinate their schedules as such. This led some study participants to limit the number of patients they serve. One participant said:
We simply don’t have enough clinicians, which is a shame because these people are really skilled, exceptional, brilliant providers but are performing way below their capacity. Because of this, I have a smaller case load so I can engage in a level of care that I feel is in the best interest of my patients. Everything is a tradeoff. Time has to be sacrificed at one point or another. This compromise sets our system up to do ‘ok’ work, not great work.
Of course, managing an overly large number of patients with high complexity is challenging. Especially while enduring the burden of a persisting global pandemic, participants reflected that the general outlook of administering healthcare in the US is to “do more with less.” This often forces providers to delegate responsibilities, which participants noted has potential downsides. One participant described how delegating patient care can cause problems.
Very often will a patient schedule a follow up that needs to happen within a certain time frame, but I am unable to see them myself. So, they are then placed with one of my mid-level providers. However, if additional health issues are introduced, which often happens, there is a high-risk of bounce-back or need to return once again to the hospital. It’s an inefficient vetting process that falls to people who may not have specific training in the labs and imaging that are often included in follow up visits. Unfortunately, it’s a forlorn hope to have a primary care physician be able to attend all levels of a patient’s care.
Several participants described how time constraints stretch all healthcare staff thin and complicate patient care. This was particularly important among participants who reported having a patient panel exceeding 1000. There were some participants, however, who praised the relationships they have with their nurse practitioners and physician’s assistants and mark transparency as the most effective way to coordinate care. Collectively, these clinical relationships were built over long standing periods of time, a disadvantage to providers at the start of their medical career. All but one participant with over a decade of clinical experience mentioned the usefulness of these relationships. The factors discussed in Theme 4 are directly linked to the Availability dimension of access to healthcare. A patient’s ability to reach care is subject to the capacity of their healthcare provider(s). Additionally, further analysis suggests these factors also link to the Appropriateness dimension because the quality of patient-provider relationships may be negatively impacted if a provider’s time is compromised.
Theme 5: Profits are prioritized over addressing barriers to healthcare access in the US.
The US healthcare system functions partially for-profit in the public and private sectors. The federal government provides funding for national programs such as Medicare, but a majority of Americans access healthcare through private employer plans [ 85 ]. As a result, uninsurance rates influence healthcare access. Though the rate of the uninsured has dropped over the last decade through expansion of the Affordable Care Act, it remains above 8 percent [ 86 ]. Historically, there has been ethical criticism in the literature of a for-profit system as it is said to exacerbate healthcare disparities and constitute unfair competition against nonprofit institutions. Specifically, the US healthcare system treats healthcare as a commodity instead of a right, enables organizational controls that adversely affect patient-provider relationships, undermines medical education, and constitutes a medical-industrial complex that threatens influence on healthcare-related public policy [ 87 ]. Though unprompted by the interviewer, participants raised many of these concerns. One participant shared their views on how priorities stand in their practice:
A lot of the higher-ups in the healthcare system where I work see each patient visit as a number. It’s not that they don’t have the capacity to think beyond that, but that’s what their role is, making sure we’re profitable. That’s part of why our healthcare system in the US is as broken as it is. It’s accentuated focus on financially and capitalistically driven factors versus understanding all these other barriers to care.
Eight participants echoed a similar concept, that addressing barriers to healthcare access in their organizations is largely complicated because so much attention is directed on matters that have nothing to do with patients. A few other participants supported this by alluding to a “cherry-picking” process by which those at the top of the hierarchy devote their attention to the easiest tasks. One participant shared an experience where contrasting work demands between administrators and front-line clinical providers produces adverse effects:
We had a new administrator in our hospital. I had been really frustrated with the lack of cultural awareness and curiosity from our other leaders in the past, so I offered to meet and take them on a tour of the reservation. This was meant to introduce them to kids, families and Tribal leaders who live in the area and their interface with healthcare. They declined, which I thought was disappointing and eye-opening.
Analysis of these factors suggest that those who work directly with patients understand patient needs better than those who serve in management roles. This same participant went on to suggest an ulterior motive for a push towards telemedicine, as administrators primarily highlight the benefit of billing for virtual visits instead of the nature of the visits themselves.
This study explored barriers and facilitators to healthcare access from the perspective of rural healthcare providers in Montana. Our qualitative analysis uncovered five key themes: 1) a friction exists between aspects of patients’ rural identities and healthcare systems; 2) facilitating access to healthcare requires application of and respect for cultural differences; 3) communication between healthcare providers is systematically fragmented; 4) time and resource constraints disproportionately harm rural health systems; and 5) profits are prioritized over addressing barriers to healthcare access in the US. Themes 2 and 3 were directly supported by earlier qualitative studies that applied Levesque’s framework, specifically regarding healthcare providers’ poor interpersonal quality and lack of collaboration with other providers that are suspected to result from a lack of provider training [ 67 , 70 ]. This ties back to the importance of cultural humility, which many previous culture-based trainings have referred to as cultural competence. Cultural competence is achieved through a plethora of trainings designed to expose providers to different cultures’ beliefs and values but induces risk of stereotyping and stigmatizing a patient’s views. Therefore, cultural humility is the preferred idea, by which providers reflect and gain open-ended appreciation for a patient’s culture [ 88 ].
Implications for Practice
Perhaps the most substantial takeaway is how embedded rugged individualism is within rural patient populations and how difficult that makes the delivery of care in rural health systems. We heard from participants that stoicism and perceptions of stigma within the system contribute to this, but other resulting factors may be influential at the provider- and organizational-levels. Stoicism and perceived stigma both appear to arise, in part, from an understandable knowledge gap regarding the care system. For instance, healthcare providers understand the relations between primary and secondary care, but many patients may perceive both concepts as elements of a single healthcare system [ 89 ]. Any issue experienced by a patient when tasked to see both a primary and secondary provider may result in a patient becoming confused [ 90 ]. This may also overlap with our third theme, as a disjointed means of communication between healthcare providers can exacerbate patients’ negative experiences. One consideration to improve this is to incorporate telehealth programs into an existing referral framework to reduce unnecessary interfacility transfers; telehealth programs have proven effective in rural and remote settings [ 91 ].
In fact, telehealth has been rolled out in a variety of virtual platforms throughout its evolution, its innovation matched with continued technological advancement. Simply put, telehealth allows health service delivery from a distance; it allows knowledge and practice of clinical care to be in a different space than a patient. Because of this, a primary benefit of telehealth is its impact on improving patient-centered outcomes among those living in rural areas. For instance, text messaging technology improves early infant diagnosis, adherence to recommended diagnostic testing, and participant engagement in lifestyle change interventions [ 92 , 93 , 94 ]. More sophisticated interventions have found their way into smartphone-based technology, some of which are accessible even without an internet connection [ 95 , 96 ]. Internet accessibility is important because a number of study participants noted internet connectivity as a barrier for patients who live in low resource communities. Videoconferencing is another function of telehealth that has delivered a variety of health services, including those which are mental health-specific [ 97 ], and mobile health clinics have been used in rural, hard-to-reach settings to show the delivery of quality healthcare is both feasible and acceptable [ 98 , 99 , 100 ]. While telehealth has potential to reduce a number of healthcare access barriers, it may not always address the most pressing healthcare needs [ 101 ]. However, telehealth does serve as a viable, cost-effective alternative for rural populations with limited physical access to specialized services [ 102 ]. With time and resource limitations acknowledged as a key theme in our study, an emphasis on expanding telehealth services is encouraged as it will likely have significant involvement on advancing healthcare in the future, especially as the COVID-19 pandemic persists [ 103 ].
Implications for Policy
One could argue that most of the areas of fragmentation in the US healthcare system can be linked to the very philosophy on which it is based: an emphasis on profits as highest priority. Americans are, therefore, forced to navigate a health service system that does not work solely in their best interests. It is not surprising to observe lower rates of healthcare usage in rural areas, which may be a result from rural persons’ negative views of the US healthcare system or a perception that the system does not exist to support wellness. These perceptions may interact with ‘rugged individualism’ to squelch rural residents’ engagement in healthcare. Many of the providers we interviewed for this study appeared to understand this and strived to improve their patients’ experiences and outcomes. Though these efforts are admirable, they may not characterize all providers who serve in rural areas of the US. From a policy standpoint, it is important to recognize these expansive efforts from providers. If incentives were offered to encourage maximum efforts be made, it may lessen burden due to physician burnout and fatigue. Of course, there is no easy fix to the persisting limit of time and resources for providers, problems that require workforce expansion. Ultimately, though, the current structure of the US healthcare system is failing rural America and doing little to help the practice of rural healthcare providers.
Implications for Future Research
It is important for future health systems research efforts to consider issues that arise from both individual- and system-level access barriers and where the two intersect. Oftentimes, challenges that appear linked to a patient or provider may actually stem from an overarching system failure. If failures are critically and properly addressed, we may refine our understanding of what we can do in our professional spaces to improve care as practitioners, workforce developers, researchers and advocates. This qualitative study was exploratory in nature. It represents a step forward in knowledge generation regarding challenges in access to healthcare for rural Americans. Although mental health did not come up by design in this study, future efforts exploring barriers to healthcare access in rural systems should focus on access to mental healthcare. In many rural areas, Montana included, rates of suicide, substance use and other mental health disorders are highly prevalent. These characteristics should be part of the overall discussion of access to healthcare in rural areas. Optimally, barriers to healthcare access should continue to be explored through qualitative and mixed study designs to honor its multi-dimensional stature.
Strengths and Limitations
It is important to note first that this study interviewed healthcare providers instead of patients, which served as both a strength and limitation. Healthcare providers were able to draw on numerous patient-provider experiences, enabling an account of the aggregate which would have been impossible for a patient population. However, accounts of healthcare providers’ perceptions of barriers to healthcare access for their patients may differ from patients’ specific views. Future research should examine acceptability- and appropriateness-related barriers to healthcare access in patient populations. Second, study participants were recruited through convenience sampling methods, so results may be biased towards healthcare providers who are more invested in addressing barriers to healthcare access. Particularly, the providers interviewed for this study represented a subset who go beyond expectations of their job descriptions by engaging with their communities and spending additional uncompensated time with their patients. It is likely that a provider who exhibits these behavioral traits is more likely to participate in research aimed at addressing barriers to healthcare access. Third, the inability to conduct face-to-face interviews for our qualitative study may have posed an additional limitation. It is possible, for example, that in-person interviews might have resulted in increased rapport with study participants. Notwithstanding this possibility, the remote interview format was necessary to accommodate health risks to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. Ultimately, given our qualitative approach, results from our study cannot be generalizable to all rural providers’ views or other rural health systems. In addition, no causality can be inferred regarding the influence of aspects of rurality on access. The purpose of this exploratory qualitative study was to probe research questions for future efforts. We also acknowledge the authors’ roles in the research, also known as reflexivity. The first author was the only author who administered interviews and had no prior relationships with all but one study participant. Assumptions and pre-dispositions to interview content by the first author were regularly addressed throughout data analysis to maintain study integrity. This was achieved by conducting analysis by unique interview question, rather than by unique participant, and recoding the numerical order of participants for each question. Our commitment to rigorous qualitative methods was a strength for the study for multiple reasons. Conducting member checks with participants ensured trustworthiness of findings. Continuing data collection to data saturation ensured dependability of findings, which was achieved after 10 interviews and confirmed after 2 additional interviews. We further recognize the heterogeneity in our sample of participants, which helped generate variability in responses. To remain consistent with appropriate means of presenting results in qualitative research however, we shared minimal demographic information about our study participants to ensure confidentiality.
The divide between urban and rural health stretches beyond a disproportionate allocation of resources. Rural health systems serve a more complicated and hard-to-reach patient population. They lack sufficient numbers of providers to meet population health needs. These disparities impact collaboration between patients and providers as well as the delivery of acceptable and appropriate healthcare. The marker of rurality complicates the already cumbersome challenge of administering acceptable and appropriate healthcare and impediments stemming from rurality require continued monitoring to improve patient experiences and outcomes. Our qualitative study explored rural healthcare providers’ views on some of the social, cultural, and programmatic factors that influence access to healthcare among their patient populations. We identified five key themes: 1) a friction exists between aspects of patients’ rural identities and healthcare systems; 2) facilitating access to healthcare requires application of and respect for cultural differences; 3) communication between healthcare providers is systematically fragmented; 4) time and resource constraints disproportionately harm rural health systems; and 5) profits are prioritized over addressing barriers to healthcare access in the US. This study provides implications that may shift the landscape of a healthcare provider’s approach to delivering healthcare. Further exploration is required to understand the effects these characteristics have on measurable patient-centered outcomes in rural areas.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to individual privacy could be compromised but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
All study procedures and methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations from the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. Ethics approval was given by exempt review from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at the University of Montana (IRB Protocol No.: 186–20). Participants received oral and written information about the study prior to interview, which allowed them to provide informed consent for the interviews to be recorded and used for qualitative research purposes. No ethical concerns were experienced in this study pertaining to human subjects.
Consent for publication.
The participants consented to the publication of de-identified material from the interviews.
Riley WJ. Health Disparities: Gaps in Access, Quality and Affordability of Medical Care. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2012;123:167–74.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Levesque J, Harris MF, Russell G. Patient-centred access to health care: conceptualising access at the interface of health systems and populations. Int J Equity Health. 2013;12:18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-9276-12-18 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Serban N. A Multidimensional Framework for Measuring Access. In: Serban N. Healthcare System Access: Measurement, Inference, and Intervention. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons; 2019. p. 13–59.
Google Scholar
Roncarolo F, Boivin A, Denis JL, et al. What do we know about the needs and challenges of health systems? A scoping review of the international literature. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17:636. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-017-2585-5 .
Cabrera-Barona P, Blaschke T. Kienberger S. Explaining Accessibility and Satisfaction Related to Healthcare: A Mixed-Methods Approach. Soc Indic Res. 2017;133,719–739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-016-1371-9 .
Coombs NC, Meriwether WE, Caringi J, Newcomer SR. Barriers to healthcare access among U.S. adults with mental health challenges: A population-based study. SSM Popul Health. 2021;15:100847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssmph.2021.100847 .
Farietta TP, Lu B, Tumin R. Ohio’s Medicaid Expansion and Unmet Health Needs Among Low-Income Women of Reproductive Age. Matern Child Health. 2018;22(12):1771–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-018-2575-1 .
Article Google Scholar
Sommers BD, Blendon RJ, Orav EJ, Epstein AM. Changes in Utilization and Health Among Low-Income Adults After Medicaid Expansion or Expanded Private Insurance. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;1;176(10):1501–1509. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.4419 .
National Alliance on Mental Illness: The Doctor is Out. Continuing Disparities in Access to Mental and Physical Health Care. 2017. https://www.nami.org/Support-Education/Publications-Reports/Public-Policy-Reports/The-Doctor-is-Out . Accessed 29 Aug 2021.
Pollitz K, Lopes L, Kearney A, Rae M, Cox C, Fehr F, Rousseau D, Kaiser Family Foundation. US Statistics on Surprise Medical Billing. JAMA. 2020;323(6):498. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.0065 .
Kahraman C, Orobello C, Cirella GT. hanging Dynamics with COVID-19: Future Outlook. In: XX Cirella GT, editor. Human Settlements: Urbanization, Smart Sector Development, and Future Outlook. Singapore: Springer; 2022. p. 235–52.
Book Google Scholar
Blumenthal D, Fowler EJ, Abrams M, Collins SR. Covid-19 — Implications for the Health Care System. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(15):1483–8. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMsb2021088 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Defêche J, Azarzar S, Mesdagh A, Dellot P, Tytgat A, Bureau F, Gillet L, Belhadj Y, Bontems S, Hayette M-P, Schils R, Rahmouni S, Ernst M, Moutschen M, Darcis G. In-Depth Longitudinal Comparison of Clinical Specimens to Detect SARS-CoV-2. Pathogens. 2021;10(11):1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111362 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Rosenblatt RA, Hart LG. Physicians and rural America. West J Med. 2000;173(5):348–51. https://doi.org/10.1136/ewjm.173.5.348 .
Kaiser Family Foundation Analysis of OECD Data. 2020. https://www.healthsystemtracker.org/chart-collection/u-s-health-care-resources-compare-countries/#item-physicians-density-per-1000-population-2000-2018 . Accessed 31 Oct 2021.
Government Accounting Office. Physician Workforce: Locations and Types of Graduate Training Were Largely Unchanged, and Federal Efforts May Not Be Sufficient to Meet Needs. 2017. https://www.gao.gov/assets/gao-17-411.pdf . Accessed 31 Oct 2021.
The Kaiser Family Foundation: The Uninsured in Rural America. 2003. https://www.kff.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/01/the-uninsured-in-rural-america-update-pdf.pdf . Accessed 15 Sept 2021.
Wright B, Potter AJ, Trivedi AN, Mueller KJ. The Relationship Between Rural Health Clinic Use and Potentially Preventable Hospitalizations and Emergency Department Visits Among Medicare Beneficiaries. J Rural Health. 2018;34(4):423–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/jrh.12253 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Weichelt B, Bendixsen C, Patrick T. A Model for Assessing Necessary Conditions for Rural Health Care’s Mobile Health Readiness: Qualitative Assessment of Clinician-Perceived Barriers. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019;7(11): e11915. https://doi.org/10.2196/11915 .
Mangundu M, Roets L, Janse van Rensberg E. Accessibility of healthcare in rural Zimbabwe: The perspective of nurses and healthcare users. Afr J Prim Health Care Fam Med. 2020;12(1):e1-e7. https://doi.org/10.4102/phcfm.v12i1.2245 .
Rahayu YYS, Araki T, Rosleine D. Factors affecting the use of herbal medicines in the universal health coverage system in Indonesia. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;260: 112974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2020.112974 .
Bolin JN, Bellamy GR, Ferdinand AO, et al. Rural Healthy People 2020: New Decade, Same Challenges. Journal of Rural Health. 2015;31(3):326–33.
Reid S. The rural determinants of health: using critical realism as a theoretical framework. Rural Remote Health. 2019;19(3):5184. https://doi.org/10.22605/RRH5184 .
Wynia MK, Osborn CY. Health literacy and communication quality in health care organizations. J Health Commun. 2010;15 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):102–115. https://doi.org/10.1080/10810730.2010.499981 .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. What is Health Literacy? 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/healthliteracy/learn/index.html . Accessed 25 Feb 2022.
Davis TC, Arnold CL, Rademaker A, et al. Differences in barriers to mammography between rural and urban women. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2012;21(7):748–55. https://doi.org/10.1089/jwh.2011.3397 .
Halverson J, Martinez-Donate A, Trentham-Dietz A, et al. Health literacy and urbanicity among cancer patients. J Rural Health. 2013;29(4):392–402. https://doi.org/10.1111/jrh.12018 .
Zahnd WE, Scaife SL, Francis ML. Health literacy skills in rural and urban populations. Am J Health Behav. 2009;33(5):550–7. https://doi.org/10.5993/ajhb.33.5.8 .
Dogba MJ, Dossa AR, Breton E, Gandonou-Migan R. Using information and communication technologies to involve patients and the public in health education in rural and remote areas: a scoping review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):128. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-019-3906-7 .
Committee on the Science of Changing Behavioral Health Social Norms, Board on Behavioral, Cognitive, and Sensory Sciences, Division of Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education; National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. In: Ending Discrimination Against People with Mental and Substance Use Disorders: The Evidence for Stigma Change. Washington: National Academics Press; 2016. p. 33–52.
Wu Y, Zhou H, Wang Q, Cao M, Medina A, Rozelle S. Use of maternal health services among women in the ethnic rural areas of western China. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):179. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-019-3996-2 .
Meyer E, Hennink M, Rochat R, et al. Working Towards Safe Motherhood: Delays and Barriers to Prenatal Care for Women in Rural and Peri-Urban Areas of Georgia. Matern Child Health J. 2016;20(7):1358–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-016-1997-x .
Heinrich S. Medical science faces the post-truth era: a plea for the grassroot values of science. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2020;33(2):198–202. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACO.0000000000000833 .
Esquivel MM, Chen JC, Woo RK, et al. Why do patients receive care from a short-term medical mission? Survey study from rural Guatemala. J Surg Res. 2017;215:160–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2017.03.056 .
Park LG, Dracup K, Whooley MA, et al. Symptom Diary Use and Improved Survival for Patients With Heart Failure [published correction appears in Circ Heart Fail. 2017 Dec;10(12):]. Circ Heart Fail. 2017;10(11):e003874. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.117.003874 .
Taleb F, Perkins J, Ali NA, et al. Transforming maternal and newborn health social norms and practices to increase utilization of health services in rural Bangladesh: a qualitative review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2015;15:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-015-0501-8 .
Billah SM, Hoque DE, Rahman M, et al. Feasibility of engaging “Village Doctors” in the Community-based Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (C-IMCI): experience from rural Bangladesh. J Glob Health. 2018;8(2): 020413. https://doi.org/10.7189/jogh.08.020413 .
Kaiser JL, Fong RM, Hamer DH, et al. How a woman’s interpersonal relationships can delay care-seeking and access during the maternity period in rural Zambia: An intersection of the Social Ecological Model with the Three Delays Framework. Soc Sci Med. 2019;220:312–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2018.11.011 .
Rao KD, Sheffel A. Quality of clinical care and bypassing of primary health centers in India. Soc Sci Med. 2018;207:80–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2018.04.040 .
Lee YT, Lee YH, Kaplan WA. Is Taiwan’s National Health Insurance a perfect system? Problems related to health care utilization of the aboriginal population in rural townships. Int J Health Plann Manage. 2019;34(1):e6–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/hpm.2653 .
Lyford M, Haigh MM, Baxi S, Cheetham S, Shahid S, Thompson SC. An Exploration of Underrepresentation of Aboriginal Cancer Patients Attending a Regional Radiotherapy Service in Western Australia. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15(2):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15020337 .
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Rohr JM, Spears KL, Geske J, Khandalavala B, Lacey MJ. Utilization of Health Care Resources by the Amish of a Rural County in Nebraska. J Community Health. 2019;44(6):1090–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10900-019-00696-9 .
Johnston K, Harvey C, Matich P, et al. Increasing access to sexual health care for rural and regional young people: Similarities and differences in the views of young people and service providers. Aust J Rural Health. 2015;23(5):257–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajr.12186 .
Legido-Quigley H, Naheed A, de Silva HA, et al. Patients’ experiences on accessing health care services for management of hypertension in rural Bangladesh, Pakistan and Sri Lanka: A qualitative study. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(1): e0211100. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0211100 .
Shaw B, Amouzou A, Miller NP, Bryce J, Surkan PJ. A qualitative exploration of care-seeking pathways for sick children in the rural Oromia region of Ethiopia. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):184. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-017-2123-5 .
Larson E, Vail D, Mbaruku GM, Kimweri A, Freedman LP, Kruk ME. Moving Toward Patient-Centered Care in Africa: A Discrete Choice Experiment of Preferences for Delivery Care among 3,003 Tanzanian Women. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(8): e0135621. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0135621 .
Spleen AM, Lengerich EJ, Camacho FT, Vanderpool RC. Health care avoidance among rural populations: results from a nationally representative survey. J Rural Health. 2014;30(1):79–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/jrh.12032 .
Weisgrau S. Issues in rural health: access, hospitals, and reform. Health Care Financ Rev. 1995;17(1):1–14.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
National Center for Health Statistics. 2018. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/surveys.htm . Accessed 29 Aug 2021.
Sekhon M, Cartwright M, Francis JJ. Acceptability of healthcare interventions: an overview of reviews and development of a theoretical framework. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):88. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-017-2031-8 .
Dyer TA, Owens J, Robinson PG. The acceptability of healthcare: from satisfaction to trust. Community Dent Health. 2016;33(4):242–51. https://doi.org/10.1922/CDH_3902Dyer10 .
Padgett DK. Qualitative and Mixed Methods in Public Health. Thousand Oaks, California: SAGE Publications Inc.; 2012.
Tolley EE, Ulin PR, Mack N, Robinson ET, Succop SM. Qualitative Methods in Public Health: A Field Guide for Applied Research. 2nd ed. San Francisco, California: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2016.
Ingram DD, Franco SJ. 2013 NCHS urban-rural classification scheme for counties. In: National Center for Health Statistics: Vital Health Statistics. 2014. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/series/sr_02/sr02_166.pdf . Accessed 31 Oct 2021.
Health Resources & Services Administration. Health Professional Shortage Area Find. 2021. https://data.hrsa.gov/tools/shortage-area/hpsa-find . Accessed 31 Oct 2021.
Shaghaghi A, Bhopal RS, Sheikh A. Approaches to Recruiting “Hard-To-Reach” Populations into Re-search: A Review of the Literature. Health Promot Perspect. 2011;1(2):86–94. https://doi.org/10.5681/hpp.2011.009 .
Sadler GR, Lee HC, Lim RS, Fullerton J. Recruitment of hard-to-reach population subgroups via adaptations of the snowball sampling strategy. Nurs Health Sci. 2010;12(3):369–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2018.2010.00541.x .
Deterding NM, Waters MC. Flexible Coding of In-depth Interviews: A Twenty-first-century Approach. Sociological Methods & Research. 2021;50(2):708–39. https://doi.org/10.1177/0049124118799377 .
Schreier M, Stamann C, Janssen M, Dahl T, Whittal A. Qualitative Content Analysis: Conceptualizations and Challenges in Research Practice-Introduction to the FQS Special Issue" Qualitative Content Analysis I". InForum Qualitative Sozialforschung/Forum: Qualitative Social Research. 2019;20:26 DEU.
Guest G, Namey E, Chen M. A simple method to assess and report thematic saturation in qualitative research. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(5): e0232076. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0232076 .
Mayring P. Qualitative Content Analysis. Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung/Forum: Qualitative Social Research. 2000;1(2). https://doi.org/10.17169/fqs-1.2.1089 .
O'Brien BC, Harris IB, Beckman TJ, Reed DA, Cook DA. Standards for reporting qualitative research: a synthesis of recommendations. Academic Medicine, Vol. 89, No. 9 / Sept 2014. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACM.0000000000000388 .
Carter N, Bryant-Lukosius D, DiCenso A, Blythe J, Neville AJ. The use of triangulation in qualitative research. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2014;41(5):545–7. https://doi.org/10.1188/14.ONF.545-547 .
Miller S. Cultural humility is the first step to becoming global care providers. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2009;38(1):92–3. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1552-6909.2008.00311.x .
Prasad SJ, Nair P, Gadhvi K, Barai I, Danish HS, Philip AB. Cultural humility: treating the patient, not the illness. Med Educ Online. 2016;21:30908. https://doi.org/10.3402/meo.v21.30908 .
George MS, Davey R, Mohanty I, Upton P. “Everything is provided free, but they are still hesitant to access healthcare services”: why does the indigenous community in Attapadi, Kerala continue to experience poor access to healthcare? Int J Equity Health. 2020;19(1):105. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-020-01216-1 .
Romanelli M, Hudson KD. Individual and systemic barriers to health care: Perspectives of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender adults. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 2017;87(6):714–28. https://doi.org/10.1037/ort0000306 .
Bailie J, Schierhout G, Laycock A, et al. Determinants of access to chronic illness care: a mixed-methods evaluation of a national multifaceted chronic disease package for Indigenous Australians. BMJ Open. 2015;5(11): e008103. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2015-008103 .
Reeve C, Humphreys J, Wakerman J, Carter M, Carroll V, Reeve D. Strengthening primary health care: achieving health gains in a remote region of Australia. Med J Aust. 2015;202(9):483–7. https://doi.org/10.5694/mja14.00894 .
Swan LET, Auerbach SL, Ely GE, Agbemenu K, Mencia J, Araf NR. Family Planning Practices in Appalachia: Focus Group Perspectives on Service Needs in the Context of Regional Substance Abuse. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(4):1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041198 .
Kabia E, Mbau R, Oyando R, et al. “We are called the et cetera”: experiences of the poor with health financing reforms that target them in Kenya. Int J Equity Health. 2019;18(1):98. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-019-1006-2 .
Ho JW, Kuluski K, Im J. “It’s a fight to get anything you need” - Accessing care in the community from the perspectives of people with multimorbidity. Health Expect. 2017;20(6):1311–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/hex.12571 .
Latif A, Mandane B, Ali A, Ghumra S, Gulzar N. A Qualitative Exploration to Understand Access to Pharmacy Medication Reviews: Views from Marginalized Patient Groups. Pharmacy (Basel). 2020;8(2):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy8020073 .
Tschirhart N, Diaz E, Ottersen T. Accessing public healthcare in Oslo, Norway: the experiences of Thai immigrant masseuses. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):722. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-019-4560-9 .
Ireland S, Belton S, Doran F. “I didn’t feel judged”: exploring women’s access to telemedicine abortion in rural Australia. J Prim Health Care. 2020;12(1):49–56. https://doi.org/10.1071/HC19050 .
Stokes T, Tumilty E, Latu ATF, et al. Improving access to health care for people with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in Southern New Zealand: qualitative study of the views of health professional stakeholders and patients. BMJ Open. 2019;9(11): e033524. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2019-033524 .
Jafar TH, Ramakrishnan C, John O, et al. Access to CKD Care in Rural Communities of India: a qualitative study exploring the barriers and potential facilitators. BMC Nephrol. 2020;21(1):26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-020-1702-6 .
Doetsch J, Pilot E, Santana P, Krafft T. Potential barriers in healthcare access of the elderly population influenced by the economic crisis and the troika agreement: a qualitative case study in Lisbon, Portugal. Int J Equity Health. 2017;16(1):184. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-017-0679-7 .
Engel GL. The need for a new medical model: a challenge for biomedicine. Science. 1977;196(4286):129–36. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.847460 .
Risberg G, Hamberg K, Johansson E.E. Gender perspective in medicine: a vital part of medical scientific rationality. A useful model for comprehending structures and hierarchies within medical science. BMC Med. 2006;4(1):1.
Montana Census & Economic Information Center. 2021. https://ceic.mt.gov/ . Accessed 18 Sept 2021.
Smith M, Saunders R, Stuckhardt L, McGinnis JM, Committee on the Learning Health Care System in America, Institute of Medicine. Best Care at Lower Cost: The Path to Continuously Learning Health Care in America. Washington: National Academies Press; 2013.
O’Daniel M, Rosenstein AH, Professional Communication and Team Collaboration. In: Hughes RG, editor. Chapter 33: Patient Safety and Quality: An Evidence-Based Handbook for Nurses. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville; 2008.
Evans RS. Electronic Health Records: Then, Now, and in the Future. Yearb Med Inform. 2016;Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S48-S61. https://doi.org/10.15265/IYS-2016-s006 .
Tikkanen R, Osborn R, Mossialos E, Djordjevic A, Wharton GA. International Health Care System Profiles: United States. The Commonwealth Fund. 2020. https://www.commonwealthfund.org/international-health-policy-center/countries/united-states . Accessed 19 Sept 2021.
Berchick ER, Barnett JC, Upton RD. Health Insurance Coverage in the United States. Washington: United States Census Bureau; 2018.
Brock DW, Buchanan A. Ethical Issues in For-Profit Health Care. In: Gray BH, editor. For-Profit Enterprise in Health Care. Washington: National Academics Press; 1986.
Lekas HM, Pahl K, Fuller Lewis C. Rethinking Cultural Competence: Shifting to Cultural Humility. Health Serv Insights. 2020;13:1178632920970580. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178632920970580 .
Beaulieu MD. Primary and secondary care: Breaking down barriers for our patients with chronic diseases. Can Fam Physician. 2013;59(2):221.
Crafford L, Jenkins LS. Why seek a second consultation at an emergency centre? A qualitative study. Afr J Prim Health Care Fam Med. 2017;9(1):e1–8. https://doi.org/10.4102/phcfm.v9i1.1397 .
Sorensen MJ, von Recklinghausen FM, Fulton G, et al. Secondary overtriage: The burden of unnecessary interfacility transfers in a rural trauma system. JAMA Surg. 2013;148:763–8.
Sutcliffe CG, Thuma PE, van Dijk JH, et al. Use of mobile phones and text messaging to decrease the turnaround time for early infant HIV diagnosis and notification in rural Zambia: an observational study. BMC Pediatr. 2017;17(1):66. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-017-0822-z .
Baldwin LM, Morrison C, Griffin J, et al. Bidirectional Text Messaging to Improve Adherence to Recommended Lipid Testing. J Am Board Fam Med. 2017;30(5):608–14. https://doi.org/10.3122/jabfm.2017.05.170088 .
Albright K, Krantz MJ, Backlund Jarquín P, DeAlleaume L, Coronel-Mockler S, Estacio RO. Health Promotion Text Messaging Preferences and Acceptability Among the Medically Underserved. Health Promot Pract. 2015;16(4):523–32. https://doi.org/10.1177/1524839914566850 .
Cramer ME, Mollard EK, Ford AL, Kupzyk KA, Wilson FA. The feasibility and promise of mobile technology with community health worker reinforcement to reduce rural preterm birth. Public Health Nurs. 2018;35(6):508–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/phn.12543 .
Gbadamosi SO, Eze C, Olawepo JO, et al. A Patient-Held Smartcard With a Unique Identifier and an mHealth Platform to Improve the Availability of Prenatal Test Results in Rural Nigeria: Demonstration Study. J Med Internet Res. 2018;20(1): e18. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.8716 .
Trondsen MV, Tjora A, Broom A, Scambler G. The symbolic affordances of a video-mediated gaze in emergency psychiatry. Soc Sci Med. 2018;197:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2017.11.056 .
Schwitters A, Lederer P, Zilversmit L, et al. Barriers to health care in rural Mozambique: a rapid ethnographic assessment of planned mobile health clinics for ART. Glob Health Sci Pract. 2015;3(1):109–16. https://doi.org/10.9745/GHSP-D-14-00145 .
Kojima N, Krupp K, Ravi K, et al. Implementing and sustaining a mobile medical clinic for prenatal care and sexually transmitted infection prevention in rural Mysore, India. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17(1):189. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2282-3 .
Gorman SE, Martinez JM, Olson J. An assessment of HIV treatment outcomes among utilizers of semi-mobile clinics in rural Kenya. AIDS Care. 2015;27(5):665–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540121.2014.986053 .
Lee S, Black D, Held ML. Factors Associated with Telehealth Service Utilization among Rural Populations. J Health Care Poor Underserved. 2019;30(4):1259–72. https://doi.org/10.1353/hpu.2019.0104 .
Agha Z, Schapira RM, Maker AH. Cost effectiveness of telemedicine for the delivery of outpatient pulmonary care to a rural population. Telemed J E Health. 2002;8(3):281–91. https://doi.org/10.1089/15305620260353171 .
Doraiswamy S, Abraham A, Mamtani R, Cheema S. Use of Telehealth During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Scoping Review. J Med Internet Res. 2020;22(12): e24087. https://doi.org/10.2196/24087 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Center for Biomedical Research Excellence award (P20GM130418) from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institute of Health. The first author was also supported by the University of Montana Burnham Population Health Fellowship. We would like to thank Dr. Christopher Dietrich, Dr. Jennifer Robohm and Dr. Eric Arzubi for their contributions on determining inclusion criteria for the healthcare provider population used for this study.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, and not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Public & Community Health Sciences, University of Montana, 32 Campus Dr, Missoula, MT, 59812, USA
Nicholas C. Coombs & James Caringi
Department of Psychology, University of Montana, 32 Campus Dr, Missoula, MT, 59812, USA
Duncan G. Campbell
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows: study conception and design: NC and JC; data collection: NC; analysis and interpretation of results: NC and JC; draft manuscript preparation: NC, DC and JC; and manuscript editing: NC, DC and JC. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Nicholas C. Coombs .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Coombs, N.C., Campbell, D.G. & Caringi, J. A qualitative study of rural healthcare providers’ views of social, cultural, and programmatic barriers to healthcare access. BMC Health Serv Res 22 , 438 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-022-07829-2
Download citation
Received : 11 January 2022
Accepted : 21 March 2022
Published : 02 April 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-022-07829-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Access to healthcare
- Rural health
- Qualitative methods
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Culture and Creativity
Here are the winners of the 2024 european union prize for literature.
The jury of the European Union Prize of Literature has announced the laureates of the 2024 edition of the prize at the Brussels Book Fair.

For the 2024 edition, emerging authors from 13 countries had been nominated by their country. An international jury composed of seven literary personalities have announced the winner of the Grand Prix and the five special mentions on 4 April 2024, at the Brussels Book Fair.
The 2024 winners
Theis Ørntoft , from Denmark is the winner of the 2024 edition of the EU Prize for Literature. The five authors who have received a mention are
- Todor Todorov from Bulgaria
- Deniz Utlu from Germany
- María Elísabet Bragadóttir from Iceland
- Sholeh Rezazadeh from the Netherlands
- Tina Vrščaj from Slovenia
All works nominated this year showcase the richness and diversity of European literature. At the European Commission, we take pride in supporting a prize that helps talented writers from across Europe connect with readers worldwide through translations and promotion. Let's keep celebrating our diverse European literature!
- said Iliana Ivanova, European Commissioner for Innovation, Research, Culture, Education and Youth.
About the prize
The European Union Prize for Literature recognises emerging fiction writers from the European Union and beyond since its creation in 2009. The Prize celebrates outstanding new literary talents from all 40 countries participating in the Creative Europe programme.
Highlighting the creativity and the immense and diverse wealth of Europe’s contemporary literature in the field of fiction, EUPL promotes the circulation of literature within Europe and encourage greater interest in non-national literary works.
The EUPL is organised by a consortium of associations comprising the Federation of European Publishers (FEP) and the European and International Booksellers Federation (EIBF), with the support of the European Commission.
Related links
Thanks for your feedback.
We are happy to see that your experience was positive. Don't forget to share the pages you like with your friends and colleagues.
If you need to ask a question, please contact Europe direct .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
BACKGROUND. Well-defined, systematic, and transparent methods to identify health research gaps, needs, and priorities are vital to ensuring that available funds target areas with the greatest potential for impact. 1, 2 As defined in the literature, 3, 4 research gaps are defined as areas or topics in which the ability to draw a conclusion for a given question is prevented by insufficient evidence.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
This is generally referred to as the "literature review," "theoretical framework," or "research background." However, for a literature review to become a proper research methodology, as with any other research, follow proper steps need to be followed and action taken to ensure the review is accurate, precise, and trustworthy.
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
Literature review is an essential feature of academic research. Fundamentally, knowledge advancement must be built on prior existing work. To push the knowledge frontier, we must know where the frontier is. By reviewing relevant literature, we understand the breadth and depth of the existing body of work and identify gaps to explore.
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.. Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
A literature review is defined as "a critical analysis of a segment of a published body of knowledge through summary, classification, and comparison of prior research studies, reviews of literature, and theoretical articles." (The Writing Center University of Winconsin-Madison 2022) A literature review is an integrated analysis, not just a summary of scholarly work on a specific topic.
Well-defined, systematic, and transparent methods to identify health research gaps, needs, and priorities are vital to ensuring that available funds target areas with the greatest potential for impact. 1,2 As defined in the literature, 3,4 research gaps are defined as areas or topics in which the ability to draw a conclusion for a given question is prevented by insufficient evidence.
The Literature Research Workflow Web of Science The world's largest and highest quality publisher-neutral citation index. Essential Science Indicators Reveals emerging science trends as well as influential individuals, institutions, papers, journals, and countries across 22 categories of research. Journal Citation Reports
Undertaking a literature search can be a daunting prospect. Breaking the exercise down into smaller steps will make the process more manageable. This article suggests 10 steps that will help readers complete this task, from identifying key concepts to choosing databases for the search and saving the …
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
Purpose. All research, whatever the discipline, needs to be situated in relation to what has already been done in the field. Reviewing the literature helps you: find out what is already known about a topic in order to locate gaps and justify the research being undertaken. locate the work of important theorists whose ideas will inform the research.
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
Research needs are knowledge gaps that significantly inhibit the decisionmaking ability of key stakeholders, who are end users of research, such as patients, clinicians, and ... literature reviews (8 percent); source material reviews (6 percent); reviews of in-progress data
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research ...
We conducted an exhaustive and focused scoping review and followed the methodological framework for scoping reviews as previously described in the literature [20, 22].This study aligned with the four goals of a scoping review [].We followed the first five out of the six steps outlined by Arksey and O'Malley's to ensure our review's validity 1) identifying the research question 2 ...
The literature fails to address the wider needs of people with chronic conditions and is still focused on medical interventions. Given the disease burden and the impact of needs outside of the formal health system, needs assessments should be able to capture the full range and scope of the needs of an individual. ... His research interests ...
Rising life expectancy and an aging population across nations are leading to an increased need for long-term financial savings and a focus on the financial well-being of retired individuals amidst changing policy framework. This study is a systematic review based on a scientific way of producing high-quality evidence based on 191 articles from the Scopus and Web of Science databases. It adopts ...
ProQuest One Education is designed to be a hub for research, teaching and learning - a single destination that users can rely on as their "go-to" resource. It includes the most essential content in the field: Full-text scholarly journals for access to both foundational and evolving research. Thousands of videos of teaching demonstrations ...
This gap in the literature needs further research if proposed applications are to be put into practice. Our analysis also emphasizes much-needed skepticism in reviewing said research, as much of the current studies could be at risk for retraction as more information is found. Concerns around the use of ChatGPT's use medically in nonclinical ...
Too few providers exist to meet population health needs, and fragmented communication impairs rural health systems' ability to function. ... The literature indicates that lower levels of health literacy contribute to health disparities among rural populations ... This research was supported by the Center for Biomedical Research Excellence ...
The need to diagnose heart disease quickly and accurately. This project was driven, like much of Vunjak-Novakovic's research, by a clinical need to diagnose heart diseases more quickly and accurately. This was a project that was several years in the making in which the team added different features piece by piece.
The 2024 winners. Theis Ørntoft, from Denmark is the winner of the 2024 edition of the EU Prize for Literature. The five authors who have received a mention are. Todor Todorov from Bulgaria. Deniz Utlu from Germany. María Elísabet Bragadóttir from Iceland. Sholeh Rezazadeh from the Netherlands. Tina Vrščaj from Slovenia.
Researchers looking for clues to why some types of cancer are on the rise in younger adults say they've found an interesting lead — a connection to accelerated biological aging.
This is why preventing the damage in the first place is so important. A NASA map shows the path and time of the solar eclipse on April 8. No sunglasses, and beware of fake eclipse glasses. The first thing to know is sunglasses will NOT protect your eyes from looking at the eclipse. "Some people mistakenly think putting on very dark sunglasses ...