

MSU Extension Child & Family Development
The importance of critical thinking for young children.
Kylie Rymanowicz, Michigan State University Extension - May 03, 2016
Critical thinking is essential life skill. Learn why it is so important and how you can help children learn and practice these skills.

We use critical thinking skills every day. They help us to make good decisions, understand the consequences of our actions and solve problems. These incredibly important skills are used in everything from putting together puzzles to mapping out the best route to work. It’s the process of using focus and self-control to solve problems and set and follow through on goals. It utilizes other important life skills like making connections , perspective taking and communicating . Basically, critical thinking helps us make good, sound decisions.
Critical thinking
In her book, “Mind in the Making: The seven essential life skills every child needs,” author Ellen Galinsky explains the importance of teaching children critical thinking skills. A child’s natural curiosity helps lay the foundation for critical thinking. Critical thinking requires us to take in information, analyze it and make judgements about it, and that type of active engagement requires imagination and inquisitiveness. As children take in new information, they fill up a library of sorts within their brain. They have to think about how the new information fits in with what they already know, or if it changes any information we already hold to be true.
Supporting the development of critical thinking
Michigan State University Extension has some tips on helping your child learn and practice critical thinking.
- Encourage pursuits of curiosity . The dreaded “why” phase. Help them form and test theories, experiment and try to understand how the world works. Encourage children to explore, ask questions, test their theories, think critically about results and think about changes they could make or things they could do differently.
- Learn from others. Help children think more deeply about things by instilling a love for learning and a desire to understand how things work. Seek out the answers to all of your children’s “why” questions using books, the internet, friends, family or other experts.
- Help children evaluate information. We are often given lots of information at a time, and it is important we evaluate that information to determine if it is true, important and whether or not we should believe it. Help children learn these skills by teaching them to evaluate new information. Have them think about where or who the information is coming from, how it relates to what they already know and why it is or is not important.
- Promote children’s interests. When children are deeply vested in a topic or pursuit, they are more engaged and willing to experiment. The process of expanding their knowledge brings about a lot of opportunities for critical thinking, so to encourage this action helps your child invest in their interests. Whether it is learning about trucks and vehicles or a keen interest in insects, help your child follow their passion.
- Teach problem-solving skills. When dealing with problems or conflicts, it is necessary to use critical thinking skills to understand the problem and come up with possible solutions, so teach them the steps of problem-solving and they will use critical thinking in the process of finding solutions to problems.
For more articles on child development, academic success, parenting and life skill development, please visit the MSU Extension website.
This article was published by Michigan State University Extension . For more information, visit https://extension.msu.edu . To have a digest of information delivered straight to your email inbox, visit https://extension.msu.edu/newsletters . To contact an expert in your area, visit https://extension.msu.edu/experts , or call 888-MSUE4MI (888-678-3464).
Did you find this article useful?
Early childhood development resources for early childhood professionals.
new - method size: 3 - Random key: 1, method: tagSpecific - key: 1
More About Child & Family Development
Mi parenting resource, bees, building early emotional skills, for early childhood professionals, self-paced positive discipline online course, stories for sprouts and seedlings: the amazing life cycle of plants.
Published on June 17, 2020
More About Family
Ac3 podcast episode 3.
Published on June 30, 2021
ac3-pod-cast-episode-5-families-against-narcotics
Published on December 17, 2021
Facing Challenging Times on the Farm
Published on March 7, 2023
- approaches to learning
- child & family development
- cognition and general knowledge
- early childhood development
- life skills
- msu extension
- rest time refreshers
- approaches to learning,
- child & family development,
- cognition and general knowledge,
- early childhood development,
- life skills,
- msu extension,
- Trying to Conceive
- Signs & Symptoms
- Pregnancy Tests
- Fertility Testing
- Fertility Treatment
- Weeks & Trimesters
- Staying Healthy
- Preparing for Baby
- Complications & Concerns
- Pregnancy Loss
- Breastfeeding
- School-Aged Kids
- Raising Kids
- Personal Stories
- Everyday Wellness
- Safety & First Aid
- Immunizations
- Food & Nutrition
- Active Play
- Pregnancy Products
- Nursery & Sleep Products
- Nursing & Feeding Products
- Clothing & Accessories
- Toys & Gifts
- Ovulation Calculator
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- How to Talk About Postpartum Depression
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
How to Teach Your Child to Be a Critical Thinker
Blue Planet Studio / iStockphoto
What Is Critical Thinking?
- Importance of Critical Thinking
Benefits of Critical Thinking Skills
- Teach Kids to Be Critical Thinkers
Every day kids are bombarded with messages, information, and images. Whether they are at school, online, or talking to their friends, they need to know how to evaluate what they are hearing and seeing in order to form their own opinions and beliefs. Critical thinking skills are the foundation of education as well as an important life skill. Without the ability to think critically, kids will struggle academically, especially as they get older.
In fact, no matter what your child plans to do professionally someday, they will need to know how to think critically, solve problems, and make decisions. As a parent, it's important that you ensure that your kids can think for themselves and have developed a healthy critical mindset before they leave the nest.
Doing so will help them succeed both academically and professionally as well as benefit their future relationships. Here is what you need to know about critical thinking, including how to teach your kids to be critical thinkers.
Critical thinking skills are the ability to imagine, analyze, and evaluate information in order to determine its integrity and validity, such as what is factual and what isn't. These skills help people form opinions and ideas as well as help them know who is being a good friend and who isn't.
"Critical thinking also can involve taking a complex problem and developing clear solutions," says Amy Morin, LCSW, a psychotherapist and author of the best-selling books "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do" and "13 Things Mentally Strong Parents Don't Do."
In fact, critical thinking is an essential part of problem-solving, decision-making, and goal-setting . It also is the basis of education, especially when combined with reading comprehension . These two skills together allow kids to master information.
Why Critical Thinking Skills Are Important
According to the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA), which evaluated 15-year-old children in 44 different countries, more than one in six students in the United States are unable to solve critical thinking problems. What's more, research indicates that kids who lack critical thinking skills face a higher risk of behavioral problems.
If kids are not being critical thinkers, then they are not thinking carefully, says Amanda Pickerill, Ph.D. Pickerill is licensed with the Ohio Department of Education and the Ohio Board of Psychology and is in practice at the Ohio State School for the Blind in Columbus, Ohio.
"Not thinking carefully [and critically] can lead to information being misconstrued; [and] misconstrued information can lead to problems in school, work, and relationships," she says.
Critical thinking also allows kids to gain a deeper understanding of the world including how they see themselves in that world. Additionally, kids who learn to think critically tend to be observant and open-minded.
Amy Morin, LCSW
Critical thinking skills can help someone better understand themselves, other people, and the world around them. [They] can assist in everyday problem-solving, creativity, and productivity.
There are many ways critical thinking skills can benefit your child, Dr. Pickerill says. From being able to solve complex problems in school and determining how they feel about particular issues to building relationships and dealing with peer pressure, critical thinking skills equip your child to deal with life's challenges and obstacles.
"Critical thinking skills [are beneficial] in solving a math problem, in comparing and contrasting [things], and when forming an argument," Dr. Pickerill says. "As a psychologist, I find critical thinking skills also to be helpful in self-reflection. When an individual is struggling to reach a personal goal or to maintain a satisfactory relationship it is very helpful to apply critical thinking."
Critical thinking also fosters independence, enhances creativity, and encourages curiosity. Kids who are taught to use critical thinking skills ask a lot of questions and never just take things at face value—they want to know the "why" behind things.
"Good critical thinking skills also can lead to better relationships, reduced distress, and improved life satisfaction," says Morin. "Someone who can solve everyday problems is likely to feel more confident in their ability to handle whatever challenges life throws their way."
How to Teach Kids to Be Critical Thinkers
Teaching kids to think critically is an important part of parenting. In fact, when we teach kids to be critical thinkers, we are also teaching them to be independent . They learn to form their own opinions and come to their own conclusions without a lot of outside influence. Here are some ways that you can teach your kids to become critical thinkers.
Be a Good Role Model
Sometimes the best way to teach your kids an important life skill is to model it in your own life. After all, kids tend to copy the behaviors they see in their parents. Be sure you are modeling critical thinking in your own life by researching things that sound untrue and challenging statements that seem unethical or unfair.
"Parents, being the critical thinkers that they are, can begin modeling critical thinking from day one by verbalizing their thinking skills," Dr. Pickerill says. "It’s great for children to hear how parents critically think things through. This modeling of critical thinking allows children to observe their parents' thought processes and that modeling lends itself to the child imitating what [they have] observed."
Play With Them
Children are constantly learning by trial and error and play is a great trial and error activity, says Dr, Pickerill. In fact, regularly playing with your child at a very young age is setting the foundation for critical thinking and the depth of their critical thinking skills will advance as they develop, she says.
"You will find your child’s thinking will be more on a concrete level in the earlier years and as they advance in age it will become more abstract," Dr. Pickerill says. "Peer play is also helpful in developing critical thinking skills but parents need to be available to assist when conflicts arise or when bantering takes a turn for the worse."
As your kids get older, you can play board games together or simply spend time talking about something of interest to them. The key is that you are spending quality time together that allows you the opportunity to discuss things on a deeper level and to examine issues critically.
Teach Them to Solve Problems
Morin says one way to teach kids to think critically is to teach them how to solve problems. For instance, ask them to brainstorm at least five different ways to solve a particular problem, she says.
"You might challenge them to move an object from one side of the room to the other without using their hands," she says. "At first, they might think it’s impossible. But with a little support from you, they might see there are dozens of solutions (like using their feet or putting on gloves). Help them brainstorm a variety of solutions to the same problem and then pick one to see if it works."
Over time, you can help your kids see that there are many ways to view and solve the same problem, Morin says.
Encourage Them to Ask Questions
As exhausting as it can be at times to answer a constant barrage of questions, it's important that you encourage your child to question things. Asking questions is the basis of critical thinking and the time you invest in answering your child's questions—or finding the answers together— will pay off in the end.
Your child will learn not only learn how to articulate themselves, but they also will get better and better at identifying untrue or misleading information or statements from others. You also can model this type of questioning behavior by allowing your child to see you question things as well.
Practice Making Choices
Like everything in life, your child will often learn through trial and error. And, part of learning to be a critical thinker involves making decisions. One way that you can get your child thinking about and making choices is to give them a say in how they want to spend their time.
Allow them to say no thank-you to playdates or party invitations if they want. You also can give them an allowance and allow them to make some choices about what to do with the money. Either of these scenarios requires your child to think critically about their choices and the potential consequences before they make a decision.
As they get older, talk to them about how to deal with issues like bullying and peer pressure . And coach them on how to make healthy choices regarding social media use . All of these situations require critical thinking on your child's part.
Encourage Open-Mindedness
Although teaching open-mindedness can be a challenging concept to teach at times, it is an important one. Part of becoming a critical thinker is the ability to be objective and evaluate ideas without bias.
Teach your kids that in order to look at things with an open mind, they need leave their own judgments and assumptions aside. Some concepts you should be talking about that encourage open-mindedness include diversity , inclusiveness , and fairness.
A Word From Verywell
Developing a critical mindset is one of the most important life skills you can impart to your kids. In fact, in today's information-saturated world, they need these skills in order to thrive and survive. These skills will help them make better decisions, form healthy relationships, and determine what they value and believe.
Plus, when you teach your kids to critically examine the world around them, you are giving them an advantage that will serve them for years to come—one that will benefit them academically, professionally, and relationally. In the end, they will not only be able to think for themselves, but they also will become more capable adults someday.
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA): Results from PISA 2012 problem-solving .
Sun RC, Hui EK. Cognitive competence as a positive youth development construct: a conceptual review . ScientificWorldJournal . 2012;2012:210953. doi:10.1100/2012/210953
Ghazivakili Z, Norouzi Nia R, Panahi F, Karimi M, Gholsorkhi H, Ahmadi Z. The role of critical thinking skills and learning styles of university students in their academic performance . J Adv Med Educ Prof . 2014;2(3):95-102. PMID:25512928
Schmaltz RM, Jansen E, Wenckowski N. Redefining critical thinking: teaching students to think like scientists . Front Psychol . 2017;8:459. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00459
By Sherri Gordon Sherri Gordon, CLC is a published author, certified professional life coach, and bullying prevention expert.
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Poetry Worksheet Bundle! Perfect for National Poetry Month.
5 Critical Thinking Skills Every Kid Needs To Learn (And How To Teach Them)
Teach them to thoughtfully question the world around them.

Little kids love to ask questions. “Why is the sky blue?” “Where does the sun go at night?” Their innate curiosity helps them learn more about the world, and it’s key to their development. As they grow older, it’s important to encourage them to keep asking questions and to teach them the right kinds of questions to ask. We call these “critical thinking skills,” and they help kids become thoughtful adults who are able to make informed decisions as they grow older.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking allows us to examine a subject and develop an informed opinion about it. First, we need to be able to simply understand the information, then we build on that by analyzing, comparing, evaluating, reflecting, and more. Critical thinking is about asking questions, then looking closely at the answers to form conclusions that are backed by provable facts, not just “gut feelings” and opinion.
Critical thinkers tend to question everything, and that can drive teachers and parents a little crazy. The temptation to reply, “Because I said so!” is strong, but when you can, try to provide the reasons behind your answers. We want to raise children who take an active role in the world around them and who nurture curiosity throughout their entire lives.
Key Critical Thinking Skills
So, what are critical thinking skills? There’s no official list, but many people use Bloom’s Taxonomy to help lay out the skills kids should develop as they grow up.
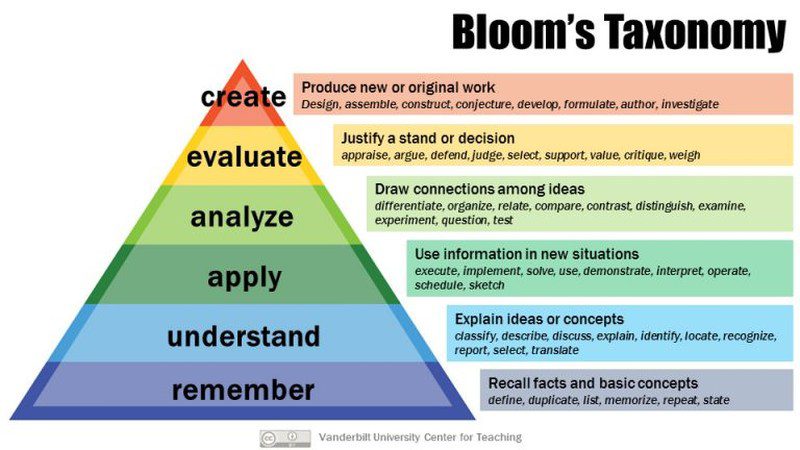
Source: Vanderbilt University
Bloom’s Taxonomy is laid out as a pyramid, with foundational skills at the bottom providing a base for more advanced skills higher up. The lowest phase, “Remember,” doesn’t require much critical thinking. These are the skills kids use when they memorize math facts or world capitals or practice their spelling words. Critical thinking doesn’t begin to creep in until the next steps.
Understanding requires more than memorization. It’s the difference between a child reciting by rote “one times four is four, two times four is eight, three times four is twelve,” versus recognizing that multiplication is the same as adding a number to itself a certain number of times. Schools focus more these days on understanding concepts than they used to; pure memorization has its place, but when a student understands the concept behind something, they can then move on to the next phase.
Application opens up whole worlds to students. Once you realize you can use a concept you’ve already mastered and apply it to other examples, you’ve expanded your learning exponentially. It’s easy to see this in math or science, but it works in all subjects. Kids may memorize sight words to speed up their reading mastery, but it’s learning to apply phonics and other reading skills that allows them to tackle any new word that comes their way.
Analysis is the real leap into advanced critical thinking for most kids. When we analyze something, we don’t take it at face value. Analysis requires us to find facts that stand up to inquiry, even if we don’t like what those facts might mean. We put aside personal feelings or beliefs and explore, examine, research, compare and contrast, draw correlations, organize, experiment, and so much more. We learn to identify primary sources for information, and check into the validity of those sources. Analysis is a skill successful adults must use every day, so it’s something we must help kids learn as early as possible.
Almost at the top of Bloom’s pyramid, evaluation skills let us synthesize all the information we’ve learned, understood, applied, and analyzed, and to use it to support our opinions and decisions. Now we can reflect on the data we’ve gathered and use it to make choices, cast votes, or offer informed opinions. We can evaluate the statements of others too, using these same skills. True evaluation requires us to put aside our own biases and accept that there may be other valid points of view, even if we don’t necessarily agree with them.
In the final phase, we use every one of those previous skills to create something new. This could be a proposal, an essay, a theory, a plan—anything a person assembles that’s unique.
Note: Bloom’s original taxonomy included “synthesis” as opposed to “create,” and it was located between “apply” and “evaluate.” When you synthesize, you put various parts of different ideas together to form a new whole. In 2001, a group of cognitive psychologists removed that term from the taxonomy , replacing it with “create,” but it’s part of the same concept.
How To Teach Critical Thinking
Using critical thinking in your own life is vital, but passing it along to the next generation is just as important. Be sure to focus on analyzing and evaluating, two multifaceted sets of skills that take lots and lots of practice. Start with these 10 Tips for Teaching Kids To Be Awesome Critical Thinkers . Then try these critical thinking activities and games. Finally, try to incorporate some of these 100+ Critical Thinking Questions for Students into your lessons. They’ll help your students develop the skills they need to navigate a world full of conflicting facts and provocative opinions.
One of These Things Is Not Like the Other
This classic Sesame Street activity is terrific for introducing the ideas of classifying, sorting, and finding relationships. All you need are several different objects (or pictures of objects). Lay them out in front of students, and ask them to decide which one doesn’t belong to the group. Let them be creative: The answer they come up with might not be the one you envisioned, and that’s OK!
The Answer Is …
Post an “answer” and ask kids to come up with the question. For instance, if you’re reading the book Charlotte’s Web , the answer might be “Templeton.” Students could say, “Who helped save Wilbur even though he didn’t really like him?” or “What’s the name of the rat that lived in the barn?” Backwards thinking encourages creativity and requires a good understanding of the subject matter.
Forced Analogies
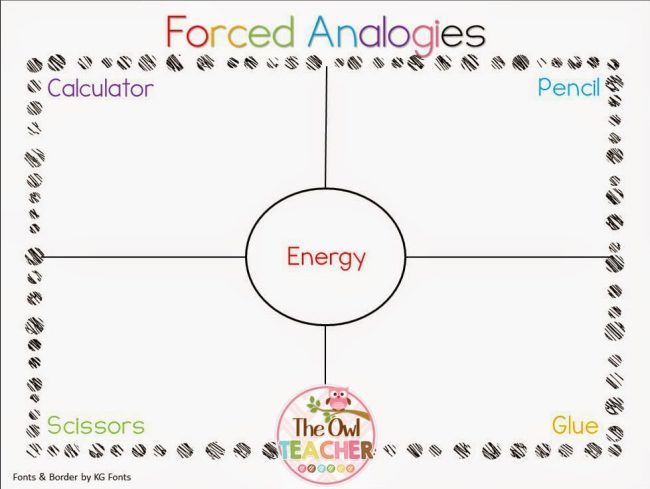
Practice making connections and seeing relationships with this fun game. Kids write four random words in the corners of a Frayer Model and one more in the middle. The challenge? To link the center word to one of the others by making an analogy. The more far out the analogies, the better!
Learn more: Forced Analogies at The Owl Teacher
Primary Sources
Tired of hearing “I found it on Wikipedia!” when you ask kids where they got their answer? It’s time to take a closer look at primary sources. Show students how to follow a fact back to its original source, whether online or in print. We’ve got 10 terrific American history–based primary source activities to try here.
Science Experiments

Hands-on science experiments and STEM challenges are a surefire way to engage students, and they involve all sorts of critical thinking skills. We’ve got hundreds of experiment ideas for all ages on our STEM pages , starting with 50 Stem Activities To Help Kids Think Outside the Box .
Not the Answer
Multiple-choice questions can be a great way to work on critical thinking. Turn the questions into discussions, asking kids to eliminate wrong answers one by one. This gives them practice analyzing and evaluating, allowing them to make considered choices.
Learn more: Teaching in the Fast Lane
Correlation Tic-Tac-Toe

Here’s a fun way to work on correlation, which is a part of analysis. Show kids a 3 x 3 grid with nine pictures, and ask them to find a way to link three in a row together to get tic-tac-toe. For instance, in the pictures above, you might link together the cracked ground, the landslide, and the tsunami as things that might happen after an earthquake. Take things a step further and discuss the fact that there are other ways those things might have happened (a landslide can be caused by heavy rain, for instance), so correlation doesn’t necessarily prove causation.
Learn more: Critical Thinking Tic-Tac-Toe at The Owl Teacher
Inventions That Changed the World
Explore the chain of cause and effect with this fun thought exercise. Start it off by asking one student to name an invention they believe changed the world. Each student then follows by explaining an effect that invention had on the world and their own lives. Challenge each student to come up with something different.
Learn more: Teaching With a Mountain View
Critical Thinking Games

There are so many board games that help kids learn to question, analyze, examine, make judgments, and more. In fact, pretty much any game that doesn’t leave things entirely up to chance (Sorry, Candy Land) requires players to use critical thinking skills. See one teacher’s favorites at the link below.
Learn more: Miss DeCarbo
This is one of those classic critical thinking activities that really prepares kids for the real world. Assign a topic (or let them choose one). Then give kids time to do some research to find good sources that support their point of view. Finally, let the debate begin! Check out 100 Middle School Debate Topics , 100 High School Debate Topics , and 60 Funny Debate Topics for Kids of All Ages .
How do you teach critical thinking skills in your classroom? Come share your ideas and ask for advice in the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, check out 38 simple ways to integrate social-emotional learning throughout the day ..

You Might Also Like

30+ Awesome Career-Readiness Activities That Teach Soft Skills
Students need these skills to succeed in the workplace. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Critical thinking is a 21st-century essential — here’s how to help kids learn it
By Mary Halton on May 9, 2019 in News + Updates
Jordan Awan
If we want children to thrive in our complicated world, we need to teach them how to think, says educator Brian Oshiro. And we can do it with 4 simple questions.
We all want the young people in our lives to thrive, but there’s no clear consensus about what will best put them on the path to future success. Should every child be taught to code? Attain fluency in Mandarin, Spanish, Hindi and English?
Those are great, but they’re not enough, says educator and teacher trainer Brian Oshiro . If we want our children to have flexible minds that can readily absorb new information and respond to complex problems, he says, we need to develop their critical thinking skills.
In adult life, “we all have to deal with questions that are a lot more complicated than those found on a multiple-choice test,” he says in a TEDxXiguan talk. “We need to give students an opportunity to grapple with questions that don’t necessarily have one correct answer. This is more realistic of the types of situations that they’re likely to face when they get outside the classroom.”
How can we encourage kids to think critically from an early age? Through an activity that every child is already an expert at — asking questions.
1. Go beyond “what?” — and ask “how?” and “why?”
Let’s say your child is learning about climate change in school. Their teacher may ask them a question like “What are the main causes of climate change?” Oshiro says there are two problems with this question — it can be answered with a quick web search, and being able to answer it gives people a false sense of security; it makes them feel like they know a topic, but their knowledge is superficial.
At home, prompt your kid to answer questions such as “ How exactly does X cause climate change?” and “ Why should we worry about it?” To answer, they’ll need to go beyond the bare facts and really think about a subject.
Other great questions: “ How will climate change affect where we live?” or “ Why should our town in particular worry about climate change?” Localizing questions gives kids, says Oshiro, “an opportunity to connect whatever knowledge they have to something personal in their lives.”
2. Follow it up with “How do you know this?”
Oshiro says, “They have to provide some sort of evidence and be able to defend their answer against some logical attack.” Answering this question requires kids to reflect on their previous statements and assess where they’re getting their information from.
3. Prompt them to think about how their perspective may differ from other people’s.
Ask a question like “How will climate change affect people living in X country or X city?” or “Why should people living in X country or X city worry about it?” Kids will be pushed to think about the priorities and concerns of others, says Oshiro, and to try to understand their perspectives — essential elements of creative problem-solving.
4. Finally, ask them how to solve this problem.
But be sure to focus the question. For example, rather than ask “How can we solve climate change?” — which is too big for anyone to wrap their mind around — ask “How could we address and solve cause X of climate change?” Answering this question will require kids to synthesize their knowledge. Nudge them to come up with a variety of approaches: What scientific solution could address cause X? What’s a financial solution? Political solution?
You can start this project any time on any topic; you don’t have to be an expert on what your kids are studying. This is about teaching them to think for themselves. Your role is to direct their questions, listen and respond. Meanwhile, your kids “have to think about how they’re going to put this into digestible pieces for you to understand it,” says Oshiro. “It’s a great way to consolidate learning.”
Critical thinking isn’t just for the young, of course. He says, “If you’re a lifelong learner, ask yourself these types of questions in order to test your assumptions about what you think you already know.” As he adds, “We can all improve and support critical thinking by asking a few extra questions each day.”
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Mary Halton is Assistant Ideas Editor at TED, and a science journalist based in the Pacific Northwest.
This post was originally published on TED Ideas . It’s part of the “How to Be a Better Human” series, each of which contains a piece of helpful advice from someone in the TED community; browse through all the posts here.

How Parents Can Teach Kids Critical Thinking
A research-based guide to help highlight the importance of critical thinking..
Posted February 21, 2020
Recent controversy over the role of social media “ swarms ” in the 2020 election have served as a new reminder — as if we needed one — that public discourse is in bad disrepair. In the last few years have seen countless incidents of people — including many who should know better — weighing in on issues prematurely with little nuance and unhelpful vitriol, being duped by badly biased information or outright fake news , and automatically attributing the worst intentions to their opponents.
Liberal democracies have always relied on flawed sources to inform the public, but not until now have we been confronted with an online medium seemingly designed to play on our biases and emotions; encourage knee-jerk reactions, groupthink , and superficiality; and distract us from deeper thinking.
Better critical thinking skills are needed to help us confront these challenges. Nevertheless, we still don’t have a good handle on what it is and, especially, how best to foster it among children of all ages.
The stakes are now higher than ever.
To address this deficit, Reboot Foundation recently put out a Parents’ Guide to critical thinking. I work for Reboot and helped on the guide that attempts to give parents and other adults the tools and understanding they need to help their kids cope with technological upheaval, acquire the skills they need to navigate an ever more complicated and information-rich world, and overcome the pitfalls of biased and emotional reasoning.
1. Starting Young
As researchers have noted for some time now, critical thinking can’t be cleanly separated from cognitive development more generally. So, although many people still think of critical thinking as something that is appropriate to teach only in college or late high school, parents and educators should actually devote attention to developing critical thinking skills at a young age.
Of course, it’s not necessary or even possible to start teaching 4-year-olds high-level logic . But there’s a lot parents can do to open up their children’s minds to the world around them. The most important thing to foster at this young age is what researchers call metacognition : awareness of one’s own thinking and thought processes.
It’s only with metacognition that children will learn to think more strategically, identify errors in their thinking patterns, and recognize their own limitations and the value of others’ perspectives. Here are some good ways to foster these habits of mind.
- Encourage kids’ curiosity by asking them lots of questions about why they think what they think. Parents should also not dismiss children’s speculative questions, but encourage them to think those questions through.
- Encourage active reading by discussing and reflecting on books and asking children to analyze different characters’ thoughts and attitudes. Emphasize and embrace ambiguity.
- Expose them as much as possible to children from different backgrounds — whether cultural, geographical, or socio-economic. These experiences are invaluable.
- Bring children into adult conversations , within appropriate limits of course, and don’t just dismiss their contributions. Even if their contributions are unsophisticated or mistaken, engage with children and help them improve.
2. Putting Emotions in Perspective
Just as children need to learn how to step back from their thought processes, they must also learn how to step back from their emotions. As we’ve seen time and again in our public discourse, emotion is often the enemy of thinking. It can lead us to dismiss legitimate evidence; to shortchange perspectives that would otherwise be valuable; and to say and do things we later regret.
When children are young (ages 5 to 9), fostering emotional management should center around learning to take on new challenges and cope with setbacks. It’s important children be encouraged to try new things and not be protected from failure. These can include both intellectual challenges like learning a new language or musical instrument and physical ones like trying out rock-climbing or running a race.
When children fail — as they will — the adults around them should help them see that failing does not make them failures. Quite the opposite: it’s the only way to become successful.
As they get older, during puberty and adolescence , emotional management skills can help them deal better with confusing physical and social changes and maintain focus on their studies and long-term goals . Critical thinking, in this sense, need not — and should not — be dry or academic. It can have a significant impact on children’s and young adults’ emotional lives and their success beyond the classroom .

3. Learning How to Be Online
Finally, critical thinking development in these challenging times must involve an online component. Good citizenship requires being able to take advantage of the wealth of information the internet offers and knowing how to avoid its many pitfalls.
Parental controls can be useful, especially for younger children, and help them steer clear of inappropriate content. But instilling kids with healthy online habits is ultimately more useful — and durable. Parents should spend time practicing web searches with their kids, teaching them how to evaluate sources and, especially, how to avoid distractions and keep focused on the task at hand.
We’ve all experienced the way the internet can pull us off task and down a rabbit hole of unproductive browsing. These forces can be especially hard for children to resist, and they can have long-term negative effects on their cognitive development.
As they get older, children should learn more robust online research skills , especially in how to identify different types of deceptive information and misinformation . Familiarizing themselves with various fact-checking sites and methods can be especially useful. A recent Reboot study found that schools are still not doing nearly enough to teach media literacy to students.
As kids routinely conduct more and more of their social lives online it’s also vital that they learn to differentiate between the overheated discourse on social media and genuine debate.
The barriers to critical thinking are not insurmountable. But if our public discourse is to come through the current upheaval intact, children, beginning at a young age, must learn the skills to navigate their world thoughtfully and critically.

Ulrich Boser is the founder of The Learning Agency and a senior fellow at the Center for American Progress. He is the author of Learn Better, which Amazon called “the best science book of the year.”
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

10 Engaging Critical Thinking Exercises for Preschool and Elementary School Children
Table of contents.
- Understanding the Importance of Critical Thinking in Early Childhood 1.1 Defining Critical Thinking for Young Learners 1.2 The Role of Critical Thinking in Child Development
- Incorporating Creativity into Critical Thinking Exercises 2.1 The Relationship Between Creativity and Critical Thinking 2.2 Techniques to Foster Creative Thought in Young Minds
- Detailed Guide to Critical Thinking Exercises 3.1 Exercise 1: Storytelling and Problem-Solving 3.1.1 How to Implement This Exercise 3.1.2 Expected Learning Outcomes 3.2 Exercise 2: Spot the Difference Games 3.2.1 How to Implement This Exercise 3.2.2 Expected Learning Outcomes 3.3 Exercise 3: 'What if' Scenarios 3.3.1 How to Implement This Exercise 3.3.2 Expected Learning Outcomes 3.4 Exercise 4: Sorting and Categorizing Activities 3.4.1 How to Implement This Exercise 3.4.2 Expected Learning Outcomes
- Additional Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking at Home
Introduction
Critical thinking is a crucial skill that we must encourage in children from a young age. It's not just about the absorption of knowledge; it's about taking that knowledge, understanding it, analyzing it, and applying it in various real-world scenarios. The development of these mental faculties doesn't just enhance a child's thought process; it can have a significant impact on their academic journey and personal development.
In this article, we explore the importance of critical thinking in early childhood and discuss strategies to promote and nurture this skill at home. From engaging in open-ended conversations to incorporating problem-solving tasks into daily routines, we'll provide practical tips to develop your child's critical thinking abilities.
By fostering critical thinking skills in young learners, we can equip them with essential tools for success - problem-solving abilities, decision-making skills, and the exercise of independent thought. These skills not only contribute to academic achievements but also set the stage for future personal growth and lifelong learning. So let's dive into this exploration of critical thinking in early childhood and discover how we can support our children on their path to becoming critical thinkers.
1. Understanding the Importance of Critical Thinking in Early Childhood
Critical thinking is a crucial skill that we must encourage in children from a young age. It's not just about the absorption of knowledge. It's about taking that knowledge, understanding it, analyzing it, and applying it in various real-world scenarios. The development of these mental faculties doesn't just enhance a child's thought process; it can have a significant impact on their academic journey and personal development.
Critical thinking is a multi-faceted skill that contributes to a child's overall cognitive development.

It encompasses problem-solving abilities, decision-making skills, and the exercise of independent thought. Engaging children in activities that require these mental faculties, such as open-ended play with building blocks or puzzles, can stimulate critical thinking. Such activities encourage kids to apply logic and reason to navigate challenges.
Promoting critical thinking isn't limited to solitary activities. It involves fostering an environment that values active discussion and exposes children to a variety of perspectives, encouraging them to evaluate different viewpoints critically. This approach enhances their ability to analyze, evaluate, and make informed decisions.
Engaging children in activities that involve role-playing or pretend play can also stimulate critical thinking. These activities encourage children to think creatively, allowing them to broaden their imaginative boundaries while exercising their cognitive muscles.
However, the development of critical thinking skills doesn't happen in isolation; it is closely tied to the development of problem-solving abilities. To enhance these abilities, children need opportunities for hands-on learning and exploration. This approach could involve puzzles that require critical thinking or real-life scenarios that demand practical problem-solving. Encouraging a child to think creatively, ask questions, and consider multiple solutions to a problem can foster these abilities.
Moreover, developing critical thinking skills is closely linked to a child's decision-making abilities. By providing them with opportunities to make choices and experience the consequences of their decisions, children can learn important decision-making skills that will benefit them in various aspects of their lives. This process also involves teaching children about the importance of considering others' perspectives and values when making decisions.
Fostering independent thinking is another critical aspect of developing critical thinking skills.

Being able to think independently and make their own decisions can help children become more self-reliant. Providing opportunities for problem-solving and decision-making, letting kids tackle challenges on their own, and guiding them when needed can aid in this process.
Finally, it's important to remember that critical thinking plays a significant role in academic success. It helps children analyze information, think logically, solve problems effectively, and engage in higher-order thinking. Moreover, it fosters creativity, curiosity, and a love for learning, all of which contribute to academic success. Therefore, by promoting and nurturing critical thinking in early childhood, we can set the stage for a successful academic journey.
In conclusion, fostering critical thinking in children has numerous benefits—improved problem-solving, better decision-making, enhanced independent thought, and a higher likelihood of academic success. It's a skill that can help children navigate the complexities of life and make well-informed decisions, making it an indispensable part of early childhood development.
1.1. Defining Critical Thinking for Young Learners
The process of fostering critical thinking in young learners is a multi-faceted endeavor. It involves nurturing their ability to create connections between different concepts, to question what they're learning, and to evaluate the information to which they're exposed. It also relies on their capacity to apply their knowledge in creative ways. This approach promotes curiosity, encourages flexibility, and develops open-mindedness.
The essence of critical thinking exercises for children at this stage isn't about solving complex problems, but rather about cultivating their ability to think independently. This requires opportunities for decision-making and problem-solving, which can be facilitated through activities that engage their imaginative and cognitive abilities. As children make choices and find solutions to challenges, they develop critical thinking skills, building confidence in their abilities.
A supportive and non-judgmental environment is key to fostering independent thinking. When children feel safe to express their opinions and ideas, they are more likely to explore their thoughts. This can be further bolstered by asking open-ended questions and engaging in meaningful discussions, stimulating their creativity and independent thought processes.
Activities like brainstorming sessions, building and designing challenges, storytelling exercises, and collaborative problem-solving games, can be highly effective. These provide children with opportunities to explore different perspectives, coming up with innovative solutions while developing their creativity and problem-solving skills in a fun and engaging way.
To promote curiosity and open-mindedness, it's important to expose children to a diverse range of subjects, topics, and perspectives. This can involve asking open-ended questions that encourage exploration, promoting an attitude of critical thinking, and creating an inclusive learning environment. With this approach, children feel safe to ask questions and express their thoughts, nurturing curiosity and open-mindedness.
Critical thinking is a vital part of early childhood education, helping children develop cognitive skills, problem-solving abilities, and decision-making capabilities. It allows children to evaluate different perspectives, analyze information, and make informed judgments, fostering their love for learning and setting a strong foundation for future academic and personal success.
Flexible thinking can be cultivated by providing diverse experiences and promoting critical thinking and decision-making. Presenting puzzles and challenges that require alternative solutions can also enhance their flexibility in thinking.
To help children make connections and ask thoughtful questions, it's beneficial to incorporate interactive activities and provide opportunities for exploration. Visual aids, real-life examples, and relatable scenarios can help to enhance their understanding and ability to make connections.
In promoting decision-making skills, it's crucial to provide children with activities that engage their critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. As children participate in these activities, they develop their decision-making skills in a practical and experiential manner. Ultimately, understanding the consequences of their actions is a significant part of this learning journey, instilling a sense of responsibility and awareness in young learners.
1.2. The Role of Critical Thinking in Child Development
Critical thinking is a pivotal cornerstone in the developmental journey of a child, paving the way for a broad spectrum of beneficial outcomes. It equips children with the ability to perceive, comprehend, and interpret their surrounding environment, acting as a catalyst for creative and innovative thinking. Additionally, it instills a sense of self-assurance and self-reliance in children. Furthermore, it augments their communication competencies, bolsters their concentration levels, and nurtures an inherent enthusiasm for knowledge acquisition. The cultivation of these critical thinking skills in early childhood can provide a robust foundation for future scholastic achievements and foster a lifelong love for learning.
The role of critical thinking in child development extends to the cultivation of problem-solving abilities, fostering independent thought, and enabling children to make informed decisions. The very essence of critical thinking lies in its encouragement of children to dissect information, appraise evidence, and consider diverse viewpoints before arriving at conclusions. By nurturing these skills, children become adept at navigating the myriad complexities of the world, creatively resolving problems, and evolving into lifelong learners.
Promoting critical thinking skills in children can be achieved through a myriad of approaches. One effective method involves stimulating open-ended discussions and questions, enabling children to evaluate and analyze diverse perspectives. Engaging children in problem-solving activities and puzzles encourages logical reasoning and decision-making. Moreover, offering opportunities for hands-on experiments and investigations can enhance children's observational and analytical skills. Introducing literature and storytelling that provoke critical thinking can also be beneficial. Indeed, creating a learning environment that fosters curiosity, exploration, and independent thought is instrumental in cultivating critical thinking abilities in children.
Critical thinking in early childhood education confers several benefits, from fostering problem-solving skills, logical reasoning, and creative thought, to enhancing the child's ability to analyze and evaluate information crucial for informed decision-making. Furthermore, it encourages independent thought, helping children morph into self-directed learners. By encouraging children to think critically from a young age, educators can lay a resilient foundation for their future academic and personal success.
A variety of activities can be employed to stimulate critical thinking in children, encompassing problem-solving, reasoning, and analysis. Puzzles, brain teasers, logic games, and open-ended questions all constitute excellent examples. Moreover, group discussions and debates can also foster critical thinking skills by challenging children to consider differing perspectives and substantiate their arguments with evidence.
Critical thinking is a vital component of academic success. It empowers students to dissect information, evaluate arguments, and make informed decisions. Students equipped with strong critical thinking skills can effectively resolve problems, think creatively, and communicate their ideas with clarity. Such skills enable them to excel in their academic pursuits and evolve into lifelong learners. Additionally, critical thinking fosters deeper comprehension of complex concepts, encourages independent thought, and nurtures intellectual curiosity.
Encouraging independent thought in children can be accomplished through various strategies. Providing opportunities for decision-making and problem-solving is particularly effective. A supportive, non-judgmental environment where children feel secure expressing their thoughts and ideas can also encourage independent thinking. Engaging in meaningful discussions and providing open-ended questions can further stimulate their creativity and independent thought processes.
Language and communication skills can be enhanced through critical thinking by encouraging students to engage in debates and discussions on a variety of topics. This requires them to critically analyze arguments and present their own viewpoints. Additionally, providing challenging reading materials and prompting students to analyze and evaluate the content can foster critical thinking skills while improving language proficiency. Activities that require problem-solving and critical thinking in language learning tasks can also prove beneficial in developing their communication skills.
Cultivating a love for learning through critical thinking involves creating an environment that encourages curiosity and exploration. Encourage students to ask questions and think critically about the information they encounter. Provide opportunities for hands-on learning and problem-solving activities that require students to analyze, evaluate, and apply their knowledge. By connecting lessons to real-world applications and encouraging students to pursue their own interests and passions, educators can effectively promote a love for learning.
2. Incorporating Creativity into Critical Thinking Exercises
While creativity and critical thinking might seem like distinct concepts, they are closely intertwined facets of a child's cognitive development. Understanding and analyzing information forms the backbone of critical thinking, while creativity is all about utilizing this information to forge new, innovative ideas and solutions. Merging creativity into critical thinking exercises can transform the learning process into a more interactive and enjoyable experience for children, feeding their imaginations and sparking their curiosity.
When we look at the cognitive development of children, creativity aids children in thinking outside the conventional box, thereby giving them the leverage to form unique answers to problems. It promotes curiosity, exploration, and an understanding of different perspectives, thereby enriching their problem-solving skills. On the other hand, critical thinking trains children to scrutinize and evaluate information objectively. This imparts the ability to reason logically, facilitating them to make informed decisions. Merging these two skills allows children to deal with problems systematically and thoughtfully, weighing the advantages and disadvantages of various approaches.
Moreover, blending creativity and critical thinking endorses effective communication and fosters collaboration. When children are prodded to think both creatively and critically, they become more confident in expressing their perspectives. Additionally, they learn to listen to and appreciate the viewpoints of others, encouraging positive teamwork and meaningful discussions.
A handful of creative thinking activities can prove helpful for children aged between 4 to 8. For instance, children can be motivated to develop their stories, complete with unique characters, settings, and plotlines. Art can be another effective tool, where children can channel their creativity through drawing, painting, or sculpting. Problem-solving games like puzzles, riddles, or building blocks can stimulate their critical thinking abilities. Role-playing and brainstorming sessions can also foster their creative thinking skills.
Critical thinking exercises can be made more engaging and fun through hands-on activities like puzzles, interactive projects, or games that require problem-solving skills. Incorporating elements of creativity and imagination, such as storytelling or role-playing, can make these exercises enjoyable. Simultaneously, opportunities for collaborative learning and group discussions can enhance the engagement level, facilitating children to learn from one another and exchange ideas.
Creativity in early childhood education is paramount for a child's development. It aids them in exploring their imagination, thinking critically, and problem-solving. By fostering creativity, educators can help children develop essential skills such as communication, collaboration, and innovation. This also leads to increased self-confidence and love for learning, setting a robust foundation for a child's future academic and personal success.
Various resources, including interactive games, puzzles, hands-on activities, educational toys, and books that foster imagination and problem-solving skills, can help develop creativity and critical thinking in children aged 4 to 8. Providing a stimulating environment that allows children to explore, experiment, and engage in open-ended activities and materials like building blocks, art supplies, and puzzles can foster their creativity and problem-solving abilities.
In conclusion, integrating creativity into critical thinking exercises can significantly boost a child's cognitive abilities, making them more proficient problem solvers. It enables children to explore different possibilities, challenge assumptions, and develop a profound understanding of concepts. Overall, it provides children with essential skills like problem-solving, effective communication, and decision-making, which prove to be valuable in various aspects of their lives.
2.1. The Relationship Between Creativity and Critical Thinking
Creativity and critical thinking, when intertwined, pave the way for innovative thought and effective problem-solving. The amalgamation of these two aspects inspires children to transcend traditional ideas and explore fresh, uncharted territories of thought. But how can we successfully marry these two concepts in the minds of young learners?
We can begin by fostering an environment that welcomes non-linear and imaginative thinking. This can be achieved by introducing activities that require exploration of varied perspectives while offering the freedom to generate multiple solutions. Employing brainstorming, mind mapping, or role-playing as effective tools can significantly aid this process.
Furthermore, introducing visual and artistic elements into critical thinking exercises can spark creativity. For example, children can be encouraged to present their critical thinking prowess through visual representations or multimedia tools, thereby nurturing their innovative thinking while honing their analytical abilities.
Children stand to gain a lot from this blend of creativity and critical thinking. It promotes 'out-of-the-box' thinking, kindles imagination, and reinforces their problem-solving skills. Creativity allows children to express their unique perspective while critical thinking equips them to analyze their surroundings, evaluate evidence, and make informed decisions. As a result, children acquire a well-rounded approach to problem-solving, which significantly contributes to their cognitive development and future success.
Hands-on activities like the "Build a Bridge" challenge or the "Design a Rube Goldberg Machine" activity can prove particularly effective. In the bridge-building challenge, for instance, children can use popsicle sticks, straws, and tape to design and construct a bridge capable of supporting the weight of small objects or toy cars. Similarly, in the Rube Goldberg Machine challenge, children are tasked with creating a complex machine that performs a simple task through a series of cause-and-effect actions. These activities not only engage children in an entertaining manner but also cultivate their creativity, innovation, and problem-solving skills.
Encouraging open-ended play, exposure to varied experiences and perspectives, and creating an inclusive environment that appreciates their thoughts and ideas can help stimulate their imagination and problem-solving skills. In addition, engaging children in activities that promote critical thinking, such as puzzles, riddles, and brain teasers, can help them think beyond conventional boundaries and foster innovative thinking.
Promoting creativity in problem-solving also involves cultivating an atmosphere that encourages innovative thinking and embraces diversity in perspectives. Regular brainstorming sessions, fostering an experimentation-friendly culture, providing diverse resources, promoting collaboration, allowing autonomy, and celebrating creativity are some ways to achieve this.
Nonetheless, enhancing critical thinking through creative activities involves engaging students in tasks that require problem-solving, analysis, and evaluation. Activities such as brainstorming, role-playing, and project-based learning can be effective in promoting critical thinking skills. Encouraging students to think outside the box, explore different perspectives, and make connections between different concepts can also help develop their critical thinking abilities.
Remember, nurturing creativity and critical thinking in children sets the foundation for a lifetime of learning and growth. It enables them to become resilient problem solvers, effective communicators, and lifelong learners, qualities indispensable for success in their academic, personal, and professional life.
2.2. Techniques to Foster Creative Thought in Young Minds
Curiosity and exploration are vital catalysts in a child's development and can be cultivated through a plethora of stimulating activities. These include interactive experiments, nature excursions, museum visits, and reading books that ignite their interest. It's also essential to establish a secure and supportive milieu where children can delve into questions and explore their passions comfortably. This method of fostering curiosity and granting exploration opportunities can instill a lifelong adoration for learning.
Imaginative play, a crucial cornerstone in child development, offers myriad benefits. It spurs creativity and innovation by allowing children to fashion and investigate their unique worlds. Cognitive skills such as problem-solving, decision-making, and critical thinking are elevated through this form of play. It also fosters social and emotional maturity as children learn to interact, collaborate, and negotiate in pretend play scenarios. Moreover, imaginative play accelerates the development of language and communication skills through storytelling and role-playing, thereby playing a pivotal role in holistic child development.
Promoting open-ended questions among children necessitates an environment that nurtures curiosity and critical thinking. Setting up open-ended discussions and dialogues allows this. Inspire children to express their thoughts, ideas, and emotions, and ask supplementary questions that can't be answered with a simple "yes" or "no". Providing open-ended resources and activities, like art materials or building blocks, can also kindle creativity and problem-solving abilities. Modeling open-ended questioning and demonstrating active listening when children answer also aids in fostering an air of exploration and discovery in a child's learning journey.
Creating a safe and supportive framework for children's creativity means offering outlets for self-expression and exploration. Varied resources that stimulate their imagination, such as art supplies, building blocks, and musical instruments, can help. Cultivating a positive, inclusive ambiance where children feel emboldened to take risks and communicate their ideas without fear of judgment or reprisal is equally crucial. Effective behavior guidelines and respectful, constructive conflict resolution can contribute to a safe and supportive atmosphere for fostering creativity.
The development of critical thinking skills in children is integral to their comprehensive growth, enabling them to evaluate information, make reasoned judgments, and resolve problems effectively. By nurturing these skills, children become capable of independent thought and informed decision-making, crucial for academic success and future personal and professional development. Encouraging and fostering critical thinking skills in children can help them become active learners, curious problem solvers, and confident decision-makers.
An effective way to foster creative thinking in children is through varied strategies. Open-ended activities that allow children to explore their imagination and develop unique solutions can be encouraged. This might involve inspiring them to engage in imaginative play, such as storytelling or block building. Asking open-ended questions that stimulate their thinking and encourage multiple ideas can also be a powerful strategy. Creating a supportive and non-judgmental environment where children feel safe expressing their ideas is also key to nurturing their creative thinking skills.
3. Detailed Guide to Critical Thinking Exercises
Let's delve into some captivating activities that can foster critical thinking and imagination in both preschoolers and elementary school children. These activities are tailored to infuse amusement and interaction, thus sparking a more thoughtful and innovative mindset in your young ones.
For preschoolers, creativity is best stirred through open-ended fun. Supply them with a plethora of art materials, like crayons, markers, paper, and playdough, to let their imagination run wild. Simultaneously, enable their kinetic learning by incorporating music and movement in their daily routine. This can be achieved by allowing them to express themselves through dance and pretend-play. Moreover, storytelling is a powerful tool to ignite their creative streak and widen their imaginative horizon.
As for elementary school children, it's crucial to engage them in activities that probe them to analyze and evaluate information rather than merely recollecting facts. Teachers can play a vital role here by integrating open-ended questions and problem-solving tasks into their lessons that stimulate critical thinking. Additionally, enabling collaborative learning and discussion sessions can allow students to consider diverse perspectives and challenge their own assumptions. Moreover, teachers themselves should model critical thinking skills and provide feedback that encourages self-reflection. Through this approach, a supportive and stimulating learning environment is created that aids children in honing their critical thinking abilities.
Furthermore, encouraging young children to ask open-ended questions translates into the development of their problem-solving and reasoning abilities. Encountering real-life problems is an effective way of nurturing their analytical and creative thinking skills. Engaging them in discussions about varied topics helps them learn to express their thoughts effectively, analyze information, and evaluate different viewpoints. An environment that stimulates curiosity and exploration cultivates research skills and independent learning. Lastly, promoting decision-making empowers them to analyze options, evaluate consequences, and make informed decisions.
Remember, these critical thinking skills are the cornerstone of their cognitive development and lay the groundwork for lifelong learning. By incorporating activities that promote critical thinking, children can fine-tune their analytical and reasoning abilities, which are critical for their overall growth and success in future academic and personal endeavors.
3.1 Exercise 1: Storytelling and Problem-Solving
Storytelling can be an impactful instrument for nurturing critical thinking in young learners. This creative exercise fosters a dynamic environment wherein children can forge their own narratives, recognize potential challenges within these tales, and devise inventive resolutions.
Children can be prompted to submerge themselves into different narratives and viewpoints through storytelling. This exposure aids them in processing information, forming connections, and applying critical thinking about their surroundings. Some of the potent strategies that storytelling can harness to develop critical thinking in children include:
- Open-Ended Questions: Prompting children to delve deeper into the narrative by posing open-ended questions encourages them to analyze plotlines, characters, and underlying themes. Questions such as "What might have happened if the narrative was set in a different context?" or "What inspired the protagonist to make that choice?" spark lively discussions and critical thinking.
- Perspective Analysis: Storytelling serves as a gateway to introduce children to a plethora of perspectives and experiences. Encouraging them to contemplate varying viewpoints and scrutinize character motives and decisions fosters empathy, making children realize that situations can be interpreted differently.
- Problem-Solving: Narratives that present characters with challenges or predicaments offer children opportunities for problem-solving. Encouraging children to devise their own innovative solutions fosters their critical thinking about different problem-solving approaches.
- Real-Life Connections: Facilitating children to apply narratives to their own experiences enables them to relate character actions and decisions to real-world situations. Encouraging them to critically analyze how they would react in similar circumstances enhances their critical thinking skills.
Storytelling, with its rich narratives, is a conduit for diverse perspectives, ideas, and experiences. This exposure broadens children's thinking horizons and boosts their analytical and evaluative skills. The problem-solving element in storytelling cultivates creativity, as it encourages children to devise their individual interpretations and solutions. This, in turn, fosters active listening and creativity, as children are propelled to discern the narrative and draw connections between different components of the tale.
On the whole, storytelling can be a dynamic tool for developing children's critical thinking skills by nurturing analytical thinking, problem-solving capabilities, and creativity.
3.1.1 How to Implement This Exercise
Engaging children in interactive storytelling can be a powerful way to nurture their creativity and critical thinking skills. Start by choosing a story that will captivate your child's interest. As you read, involve them actively in the storytelling process. This could include using props, puppets, or visuals to bring the characters and scenarios to life, which can make the story more compelling and relatable for your child.
To encourage participation, ask your child open-ended questions and encourage them to repeat certain phrases or act out parts of the story. You can also integrate songs and movement into the session, singing tunes related to the plot or having your child perform simple actions that align with the narrative.
Engaging your child's senses can make the story a more immersive experience. Introduce scents, textures, or sounds that relate to the story. You might also want to provide hands-on activities post-reading that relate to the story's plot or themes. This can include crafts, games, or experiments that allow your child to explore and further engage with the story.
After the storytelling session, turn your focus to nurturing your child's problem-solving skills. Present characters in the story with challenging situations that require them to think critically. Encourage your child to brainstorm and explore different options to solve the problem. You could also encourage your child to change the story's ending or resolve a dilemma faced by a character in the story. This not only promotes creative thinking but also enhances their ability to analyze a situation from different perspectives.
Moreover, encourage your child to retell the story in their own words or create alternative endings. This allows them to express their creativity and make the discussion more interactive. You can supplement this activity with multimedia resources related to the story, like videos or audio clips, providing a multi-sensory experience. Connecting the story to their real-life experiences can also enhance their engagement and foster deeper understanding.
Remember, the key to these activities is flexibility. Adapt these techniques according to your child's age and interests. The primary objective is to create an engaging environment that promotes creativity and critical thinking. Through interactive storytelling, you can enrich your child's learning experience and nurture their imagination, exploration, and problem-solving skills.
3.1.2 Expected Learning Outcomes
Engaging young minds in stimulating activities not only refines their creativity, but it also hones problem-solving and critical thinking skills, and strengthens their language and communication abilities. Moreover, it lays the foundation for a deep-rooted love for storytelling and reading.
To nurture creativity, the environment in which children are raised plays a crucial role. It should be supportive and stimulating, promoting open-ended play and exploration. Through this, children are encouraged to wield their imagination, leading to the birth of unique ideas. A child's creativity can be enhanced by introducing a range of materials and activities such as art supplies, building blocks, and props for pretend play. These opportunities for free expression, backed by positive reinforcement for their creative pursuits, play a significant role in fostering creativity.
Enhancing problem-solving skills in children calls for an array of activities that promote critical thought. Puzzle-solving, for instance, with jigsaw puzzles, Sudoku, or Rubik's cube, can be an effective strategy as these activities necessitate logical thinking. Building blocks or Lego structures, scavenger hunts, role-playing, and STEM activities are other tools that can be used to encourage problem-solving, as they stimulate spatial reasoning, teamwork, critical thinking, and innovation.
Developing critical thinking skills in children is a significant aspect of their education, and there are several ways to foster these skills. Encouraging children to ask open-ended questions that require critical thought can help develop their analytical and reasoning abilities. Providing opportunities for problem-solving and teaching decision-making skills are other effective methods. Encouraging creativity and innovative thinking, and teaching children to analyze information critically are equally important. Lastly, promoting reflection can help children to develop self-awareness, which is a critical aspect of critical thinking.
Cultivating language and communication skills in children requires a multi-pronged approach. Reading from an early age, engaging children in meaningful conversations, encouraging creative writing, and using educational resources such as language-learning apps can all significantly enhance these skills.
Fostering a love for storytelling and reading in children can be achieved by engaging them in imaginative play and storytelling activities. Regular visits to the library, creating a reading-friendly environment at home, and providing a variety of reading materials can further nurture their love for reading. Set a daily reading routine and celebrate reading milestones to create a positive association with reading.
Lastly, imagination can be encouraged in children through play, which helps them develop problem-solving skills, social skills, and emotional intelligence. Whether it's through pretend play, building with blocks, or engaging in imaginative storytelling, playtime can foster a child's imagination and support their overall growth and development.
Remember, the development of these skills is a gradual process, and continuous support, encouragement, and patience are crucial along the journey.
3.2 Exercise 2: Spot the Difference Games
"Spot the Difference" games serve as a fantastic tool that allows children to hone their observation skills, meticulousness, and foster their critical thinking abilities. These games engage children in an intriguing activity, where they are presented with two nearly identical pictures, and their task is to identify the disparities.
The mechanics of "Spot the Difference" games are relatively simple yet engaging. Children are provided with two similar images and are asked to scrutinize them closely. They are encouraged to notice the minute details - the colors, shapes, objects, and patterns within the pictures. The exercise begins with concentrating on a specific portion of the image, gradually moving their focus across different parts, identifying differences along the way. Children can either physically mark the differences or can make a mental note of them. The primary objective is to figure out all the disparities within a particular time frame or a given number of attempts. The game provides an enjoyable and testing medium to assess and strengthen their observational skills.
The benefits of "Spot the Difference" games are manifold. They serve as an effective method to enhance children's observational skills, meticulousness, and focus. Moreover, these games boost cognitive abilities such as problem-solving and critical thinking. It is a hands-on way to cultivate a child's visual discrimination skills - a key facet in developing visual perception abilities. In essence, these games offer an interactive and entertaining platform for children to train their brains and augment their cognitive prowess.
It's important to note that "Spot the Difference" games aren't just fun; they're also a cognitive workout. These games require and enhance a range of mental skills, such as observation, attention to detail, critical thinking, and visual discrimination. These are key skills for problem-solving and decision-making - cognitive processes that are fundamental to critical thinking. Thus, by playing "Spot the Difference", your child will be having fun and learning at the same time.
3.2.1 How to Implement This Exercise
Playing 'spot the difference' games is a fantastic way to foster critical thinking skills in children. Set your child up with a pair of similar images, and ask them to highlight the disparities between the two. Encourage them to verbalize their observations and the reasoning that led them to identify these differences. As your child becomes more adept at this exercise, consider making it more challenging. You could increase the number of differences in the images or use pictures that are more complex.
Creating spot the difference pictures can be an entertaining and engaging activity. Begin by choosing two similar images that contain small differences. This can be a photograph, a drawing, or another visual representation. Then, use image editing software to make subtle changes to one of the images. This could include adding or removing objects, changing colors, or altering details.
After you've made the edits, compare the images side by side to identify the differences. Keep track of the specific changes you've made. Then, put the two images side by side on the puzzle, ensuring you remove any obvious clues to the differences. This can involve cropping certain parts of the images or covering them with shapes or patterns.
To help guide your child, you can add numbers or subtle hints near each difference. This will make the puzzle more interactive and enjoyable. When you've created your spot the difference picture, test it with others to ensure the differences are challenging but not too difficult to find. Adjust the picture based on feedback.
If you’re looking for a readily available option, you can visit websites like magickids.me. This website offers various interactive activities for children, including spot the difference games that can help them improve their observation and critical thinking skills.
Remember, the aim here is to stimulate your child's observation and reasoning skills. Whether you're designing your own puzzles or using ones from the internet, the key is to ensure that the activity remains challenging and engaging. This not only strengthens your child's critical thinking abilities but also makes learning a fun experience.
3.2.2 Expected Learning Outcomes
The exercise in question is designed to finely tune your child's observational prowess, amplify their attention to detail, and nourish their critical thinking skills. It's also a catalyst for building concentration, instilling patience, and fostering the virtue of perseverance.
Observational skills, often honed through consistent mindfulness practices and activities that demand focused attention, are integral to this exercise. Practices like mindful observation, where your child is encouraged to actively observe their surroundings, discerning minute details, colors, shapes, and sounds, or indulging in visual puzzles could be a boon to their observational skills. Experiences like nature walks, art appreciation, and memory games that necessitate the remembering and recalling of details can also play a significant role in this regard.
The exercise is not merely aimed at improving your child’s observational skills but also at enhancing their attention to detail. This can be achieved through activities like puzzles or brain teasers that need careful observation and analysis, games that involve finding hidden objects or spotting differences between pictures, mindfulness exercises that focus on the present moment and sensory details, or activities that require meticulous organization and planning.
The exercise also focuses on fostering critical thinking abilities, which play a pivotal role in your child’s education. The exercise encourages children to analyze information, actively participate in discussions, debates or problem-solving exercises, reflect on their learnings, and consider different viewpoints on a given topic. Teaching students problem-solving strategies and techniques hep them approach complex problems with a critical mindset and find effective solutions.
In addition to these, the exercise is designed to boost concentration and focus, emphasizing the importance of creating a conducive environment for work or study. Strategies such as eliminating distractions, breaking tasks into smaller chunks, practicing mindfulness or meditation, taking regular breaks, maintaining an organized workspace, and ensuring sufficient sleep and exercise are all part of the process.
Patience is another virtue that this exercise seeks to cultivate, with strategies like practicing mindfulness, setting realistic expectations, taking breaks when needed, practicing deep breathing, developing empathy, and practicing gratitude.
Finally, the exercise is also geared towards fostering perseverance, achieved through setting realistic and achievable goals, providing regular feedback and encouragement, teaching strategies for problem-solving and decision-making, and creating a supportive and positive learning environment.
3.3 Exercise 3: 'What if' Scenarios
Leveraging 'What if' scenarios is a profound approach to spark creative thinking and promote problem-solving abilities in children. With this method, children are invited to contemplate various circumstances and conceive innovative solutions.
Through this exercise, children delve into a realm of brainstorming, facing problem-solving puzzles and engaging in imaginative play. These activities foster a sense of exploration, prompting children to express their ideas uninhibitedly. It leads them to navigate a multitude of perspectives, thereby encouraging a vibrant spirit of creativity.
Engrossing children in interactive games and puzzles is an effective strategy that fosters critical thinking skills and problem-solving capabilities. By engaging children in creative problem-solving exercises like brainstorming and role-playing, they learn to develop solutions or alternatives to real-life scenarios. This practical approach equips children to employ problem-solving skills in a real-world context.
To stimulate a child's imagination, it is essential to create opportunities for creative play and exploration. Storytelling, pretend play, and arts and crafts are brilliant activities that help cultivate their imagination. Exposing children to an array of books, music, and experiences further inspires their creativity and imagination, creating an enriching environment for their growth.
Encouraging creative problem-solving skills in children can be achieved through an array of activities and approaches. Open-ended play, such as building blocks or imaginative play, enables children to explore a myriad of solutions and think critically. Furthermore, incorporating storytelling and role-playing stimulates their imagination, leading them to conceive creative solutions. It is crucial to foster a supportive and non-judgmental environment, allowing children to express their ideas freely and take calculated risks.
Exercise like 'What if' scenarios significantly improve children's problem-solving skills. By presenting hypothetical situations and asking children to consider various outcomes and solutions, they learn to approach problems from multiple perspectives. This exercise of thinking creatively and exploring different possibilities empowers children to become confident problem solvers.
Imaginative scenarios serve as an excellent tool to promote critical thinking in children. Creating situations that require them to think critically and develop creative solutions enhances their problem-solving skills. Activities like storytelling, role-playing, and problem-solving games play a pivotal role in this process. By imagining different scenarios and envisaging possible outcomes, children can significantly enhance their critical thinking skills.
3.3.1 How to Implement This Exercise
Imagine the fun and intrigue of asking your child: "What if you could fly?" or "What if you became invisible for a day?". This is an example of a 'what if' scenario, a simple yet effective strategy to stimulate your child's creative thinking and problem-solving abilities.
'What if' scenarios are open-ended tasks that ignite your child's imagination and foster innovative thinking. These hypothetical situations encourage children to venture beyond the realms of reality and conceive their own unique solutions, ideas, and outcomes. This approach not only nurtures their creativity, but also instills a sense of curiosity, paving the way for lifelong learning.
Discussing your child's responses to these scenarios provides valuable insights into their thought processes. It allows you to understand the reasoning behind their ideas and solutions, further fostering a non-judgmental environment where your child feels comfortable expressing their thoughts and taking risks.
In addition to 'what if' scenarios, you can also promote creative thinking through various activities such as art projects, storytelling, and problem-solving tasks. These activities are designed to have multiple possible solutions, thus nurturing the ability to think outside the box.
Moreover, providing opportunities for unstructured play and reducing screen time can also help stimulate your child's creativity and imagination. For instance, pretend play, arts and crafts, and storytelling are all activities that afford children the chance to explore their ideas and come up with unique solutions.
Remember to provide a variety of materials and toys that can be utilized in imaginative ways. This helps to develop their problem-solving skills as they learn to use different items resourcefully.
Moreover, consider incorporating hands-on activities and puzzles into your child's routine. These not only engage your child physically but also enhance their critical thinking skills as they tackle challenges and devise solutions.
Above all, promoting a growth mindset in your child is crucial. This mindset, which sees mistakes and failures as part of the learning process, motivates children to take risks, be innovative, and learn from their experiences.
In conclusion, fostering creative thinking in children is crucial for their development. It not only enhances their cognitive abilities but also contributes to their emotional and social well-being. By integrating these strategies into your child's daily activities, you are setting the foundation for a future filled with imagination, innovation, and success.
3.3.2 Expected Learning Outcomes
Nurturing creativity and fostering problem-solving prowess in children is a multifaceted endeavor. It involves providing a myriad of opportunities that encourage self-expression, exploration, and critical thinking. This can be achieved through open-ended activities such as art projects, building exercises using blocks, or imaginative play. By granting children the autonomy to make their own choices, we cultivate their problem-solving skills and independence. An array of resources, like art supplies, books, and objects from nature, can serve as sparks to fire up their creativity.
In terms of enhancing problem-solving skills, certain activities can prove especially beneficial. For example, puzzles of varying difficulty levels require children to think critically, analyze the situation, and ultimately find a solution. Brain teasers and riddles stimulate their creativity and demand innovative solutions. Group problem-solving activities help in developing teamwork, collaboration skills, and learn from varied perspectives. Strategy games like chess, checkers, or Sudoku require forward thinking, strategic planning, and logical decisions. Lastly, hands-on STEM projects that require problem-solving skills such as building a structure using blocks, designing and constructing a simple machine, or conducting science experiments keep the learning process fun and interactive.
A child's imagination can be cultivated through a variety of strategies. Open-ended toys and materials that allow for creativity are invaluable. Reading books together and exposing children to different forms of literature can stimulate their imagination. Engaging in imaginative play with your child, such as creating stories or playing make-believe games, can further enhance this ability.
Curiosity, while not directly discussed, is an undercurrent that runs through all these activities. Curious minds are naturally inclined towards exploration, innovation, and learning, making curiosity an integral aspect of child development.
Open-mindedness is another crucial quality to foster in children. Providing them exposure to diverse perspectives and experiences through books, movies, cultural events, and community activities is essential. Encouraging empathy, respect for others' opinions and ideas, and asking questions to challenge their own assumptions will aid in developing open-mindedness.
Thus, through a blend of creativity, problem-solving activities, and fostering imagination, curiosity, and open-mindedness, children can be equipped with the critical thinking skills they need to navigate their world.
3.4 Exercise 4: Sorting and Categorizing Activities
The process of sorting and categorizing is a powerful way to foster critical thinking in early learners. This method promotes the development of essential cognitive abilities such as analysis, comparison, and classification. Rooted in the fundamental principles of logic and organization, sorting and categorizing activities enable children to examine objects or ideas, discern their attributes, and arrange them accordingly.
These activities can take several forms, from arranging objects by size, color, or shape to classifying animals according to their habitats or characteristics. They might involve organizing a collection of toys or items, or sorting different types of foods in a simulated grocery store scenario. Each activity requires the child to engage in problem-solving, thereby not only boosting their critical thinking skills but also paving the way for a deeper understanding of the world around them.
Introducing these activities in the classroom or at home is an effective strategy for promoting critical thinking. Here are some techniques to utilize:
- Begin with tangible materials: Use physical objects that students can handle and sort. This concrete approach provides a more intuitive understanding of the sorting and categorizing process before introducing abstract concepts.
- Offer clear guidelines: Explain the rules or criteria of sorting and categorizing explicitly. Understanding these parameters helps children make decisive classifications.
- Employ visual aids: Graphs, charts, or diagrams can assist in visualizing the sorting process. These tools assist in structuring information and identifying connections between categories.
- Facilitate collaboration: Encourage group work and discussions. The process of sorting and categorizing together nurtures communication and teamwork.
- Harness technology: Implement educational apps or digital resources that offer dynamic sorting and categorizing exercises. This approach enhances student engagement and enjoyment.
- Extend the learning: Apply sorting and categorizing skills to real-life scenarios. Activities such as scavenger hunts or field trips provide opportunities to use these skills practically.
As part of making the learning process an engaging endeavor, consider incorporating interactive games or hands-on activities. Employ materials that are visually stimulating, such as vibrant sorting cards or toys. You can also introduce an element of competition, turning the activity into a challenge or race. Integrating technology, such as online sorting games or educational apps, adds an interactive element that makes learning dynamic.
Developing critical thinking skills in early childhood is integral to cultivating independent thinkers. Through these skills, children learn to analyze information, consider different viewpoints, and make informed decisions. It also lays the foundation for creativity and innovation, as children learn to approach challenges with an open mind, setting them up for academic success.
Research supports the effectiveness of sorting and categorizing activities for cognitive development in children. These tasks enhance cognitive flexibility, attention span, and memory. They also contribute to the development of logical reasoning skills, thereby improving academic performance.
Consider visiting educational websites, forums, and apps, or even reaching out to educators and educational professionals for more resources and materials. Platforms such as Magickids offer a wealth of activities designed to enhance sorting and categorizing skills in children. Their stories section may also involve sorting and categorizing elements within storytelling activities.
In conclusion, sorting and categorizing activities equip children with key cognitive skills, setting a strong foundation for their future academic success and equipping them with the critical thinking skills necessary to navigate a complex world.
3.4.1 How to Implement This Exercise
Teaching children to categorize, classify, and sort objects doesn't have to be a chore. Transform it into an engaging and fun-filled learning experience! For instance, you can organize an activity involving a variety of objects, where children are asked to sort them into categories based on distinct attributes. Whether it's color, shape, size, or function, this exercise not only stimulates their cognitive abilities but also enhances their critical thinking skills.
Let's delve deeper into the specifics. For a color sorting game, you could use colored objects like blocks, buttons, or toys and ask the children to group them according to color. In a shape sorting activity, provide objects of various shapes and lay down the challenge of sorting them into corresponding shape groups. Sorting can also be done by size, where children classify objects from smallest to largest or vice versa. Alternatively, you could focus on texture and have the children sort out objects that are rough, smooth, soft, or hard.
Meanwhile, a more complex task would involve categorization based on function. For instance, children could sort kitchen utensils based on their use or purpose. Or you could mix things up and have them sort objects from different categories like animals, vehicles, and fruits into their respective categories. For older children, consider a number sorting game where they are tasked with arranging numbers in ascending or descending order.
Keep in mind that the goal is to make the process interactive and stimulating. Using colorful materials, incorporating games, and providing positive reinforcement can go a long way in achieving this.
Beyond physical objects, the digital world offers an abundance of resources for teaching sorting and categorization skills. Online interactive games or apps can prove especially useful. Websites like 'magickids.me' propose a wide array of sorting games for preschoolers that can be an exciting addition to your child's learning routine.
Ultimately, through these hands-on activities and games, children can learn to observe and describe the attributes of objects they encounter in their everyday lives. As a result, their understanding of categorization deepens, their observation skills improve, and they develop a solid foundation for logical thinking and decision-making.
So next time you want to engage your little ones in a learning activity, remember that sorting and categorizing can be more than just a task – it can be a fun and rewarding adventure!
3.4.2 Expected Learning Outcomes
Cultivating the critical thinking skills of children forms a bedrock for their cognitive advancement and ability to tackle problems. Several strategies are available to encourage these abilities and are instrumental in forming analytical capabilities essential for success in academics and future pursuits.
A highly effective method involves fostering thought-provoking queries and activities that demand children to critically evaluate situations. This could be as simple as asking the child to explain their reasoning behind a decision or brainstorm alternative solutions to a problem.
Engaging children in hands-on activities requiring decision-making and problem-solving is another effective approach. Activities such as puzzles, building blocks, and science experiments serve as excellent mediums to stimulate critical thinking and problem-solving skills as they demand children to creatively tackle and overcome challenges.
Creating a non-judgmental and supportive environment where children can freely express their thoughts and ideas is vital. This not only fosters independent thinking and analysis but also helps in nurturing their critical thinking skills.
Modeling critical thinking skills is another crucial factor. By parents discussing their reasoning and decision-making process, a child gets an understanding of the importance of critical thinking and a framework for developing their own skills.
Developing observation skills in children can be achieved through activities such as nature walks, scavenger hunts, picture puzzles, memory games, art activities, mystery boxes, and listening activities. Such activities not only make learning fun but also strengthen their ability to observe and engage with their surroundings.
Teaching organizational skills forms an integral part of a child's development. Techniques such as creating schedules, using checklists, setting up designated spaces for activities, and encouraging task prioritization and management are effective ways to instill these skills from an early age.
Attention to detail is another skill that can be honed through activities requiring keen observation and focus, such as puzzles and matching games. Activities that follow step-by-step instructions, such as crafts or cooking, can further enhance a child's attention to detail.
Understanding categories and attributes may pose a challenge for children, but with the use of visual aids, hands-on activities, real-life examples, and mnemonic devices, these concepts can be comprehensively grasped.
In conclusion, a combination of open-ended questioning, hands-on activities, a supportive environment, and modeling critical thinking skills can significantly enhance children's critical thinking skills. Incorporating activities that promote observation skills, organizational abilities, attention to detail, and understanding of categories and attributes can complement this learning process, fostering a holistic cognitive development in children.
4. Additional Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking at Home
Beyond the engaging exercises we've outlined, a wealth of strategies exist that can be seamlessly interwoven into everyday routines to elevate the critical thinking abilities of children. These approaches transform learning into a captivating journey, enriching your child's daily experiences.
Applying open-ended conversations is a prime strategy to boost critical thinking. It's essential to create an environment where children feel comfortable expressing their viewpoints, questioning the world around them, and offering evidence for their reasoning. This dialogue nurtures their ability to consider multiple angles and refines their logical reasoning skills.
Introducing problem-solving tasks into your child's routine presents another golden opportunity. Offering real-world scenarios or puzzles pushes them to dissect information, contemplate various solutions, and decide based on their analysis. This process sharpens their decision-making abilities and cultivates problem-solving skills, both of which are integral to critical thinking.
Furthermore, broadening your child's perspective through exposure to diverse viewpoints can pay dividends. Accomplishing this can be as simple as reading multi-faceted books featuring a range of characters and themes, watching educational documentaries, or fostering debates about current affairs. This variety stimulates critical thinking about differing vantage points.
Finally, promoting independent thinking and challenging assumptions is crucial. Encourage your child to scrutinize information they encounter, seeking data and facts to back up their conclusions. This approach enhances their analytical abilities and fosters critical thought.
Engaging in daily activities that call for decision-making such as puzzles or logic games, debates about current events, or thought-provoking discussions can also help inculcate critical thinking skills. Encouraging your child to ask probing questions, explore diverse perspectives, and back up their views with evidence can create a fertile ground for critical thought.
Also, consider integrating fun, problem-solving activities into your child's routine. Solving puzzles, participating in board games that require strategic thinking, hands-on science experiments, group discussions, and coding are all excellent avenues to ignite critical thinking skills. Remember, these activities should be both age-appropriate and enjoyable to keep your child engaged and motivated.
All these strategies can transform the home into a thriving hub of learning that fosters and nourishes critical thinking skills in children. Remember, the aim is to make the learning process enjoyable and enthralling, keeping your child curious and invested in their intellectual growth.
4.1 Encouraging Open-Ended Questions
Open-ended inquiries are a powerful tool to promote critical thinking in children, allowing them to express their thoughts and ideas more freely. Rather than resorting to simple yes/no questions that offer little room for cognitive exploration, aim for questions that demand greater thought and detailed responses. For instance, instead of asking 'Did you like the story?', pose a more stimulating question such as 'What did you like about the story and why?'
This approach not only nurtures critical thinking but also promotes expressive thought. Children are encouraged to delve deeper into their thoughts and articulate their reasons, which helps to enhance their reasoning skills. Furthermore, engaging them in discussions where they explain their logic further reinforces these abilities. The ultimate goal is to ensure kids develop a habit of critically analyzing information, evaluating different viewpoints, and forming informed judgments.
Realizing the importance of critical thinking in child development, it's crucial to incorporate it into everyday activities. Whether it's through problem-solving tasks like puzzles or brain teasers, or through creative outlets like art, music, or storytelling, these activities stimulate their cognitive abilities while fostering creativity and curiosity. These exercises not only enhance their cognitive abilities but also imbue them with a willingness to explore new ideas, which is fundamental for academic success and future career growth.
In addition to open-ended questions, other strategies can also be employed to foster critical thinking. These include analyzing and evaluating information, promoting creativity and imagination, teaching decision-making skills, and fostering a growth mindset. When children are taught to analyze and evaluate information by examining different perspectives, they enhance their ability to think critically and make informed decisions. Creativity and imagination, on the other hand, can be nurtured through activities like storytelling, art, or role-playing that require innovative thinking.
Remember, we are aiming to create an environment that's supportive and non-judgmental, where children feel comfortable expressing their thoughts and ideas. This can be achieved by engaging in meaningful conversations, validating their opinions, and actively listening to their responses. Lastly, encouraging a growth mindset helps children view challenges and failures as opportunities for learning and growth, a crucial aspect of critical thinking. It's important to adapt these strategies according to the age and developmental stage of the children to achieve optimal results.
4.2 Fostering a Curiosity-Driven Environment
Cultivating a child's innate curiosity is akin to planting a seed for lifelong learning. This process is fostered by creating an environment that promotes exploration, stokes their questions and celebrates their quest for answers. One practical approach involves presenting children with a variety of novel and enriching experiences, like nature walks, museum visits, or hands-on scientific experiments.
The availability of educational resources such as books, facilitates meaningful conversations, ignites their imagination, and fuels their quest for knowledge. It is equally important to nurture a safe and supportive atmosphere where children feel comfortable asking questions and making mistakes, which are crucial for learning.
When it comes to nurturing curiosity, activities that engage their senses and captivate their interest are particularly effective. Storytelling, for instance, can spark their imagination and trigger a barrage of questions. Likewise, hands-on experiments and science projects provide opportunities for children to explore and unravel the mysteries of the world around them. Outdoor activities, such as nature walks or visits to museums, too, can pique their curiosity and inspire a thirst for knowledge.
Imaginative play, facilitated by open-ended play materials, can also trigger curiosity and creativity in children. Such an environment fosters exploration and questioning, letting children follow their interests and engage in hands-on learning. This can involve art supplies, building blocks, nature exploration tools, or even science experiments.
For children, asking questions and seeking answers is a fundamental aspect of their cognitive and intellectual development. As educators and parents, it is our responsibility to foster a sense of curiosity and provide opportunities for exploration and discovery. By creating a supportive environment where children feel comfortable asking questions without the fear of judgment, we can help them thrive.
Modeling curiosity, asking open-ended questions, and providing access to diverse resources, such as books, educational videos, and interactive activities, can stimulate their curiosity and encourage them to seek answers. Moreover, praising and acknowledging children's efforts in asking questions and seeking answers can further enhance their curiosity and motivate their quest for knowledge.
In essence, a curiosity-driven environment not only promotes active learning, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills but also fosters creativity, innovation, and a passion for learning. When children are encouraged to be curious, they are more engaged, motivated, and perform better academically. The benefits of promoting curiosity are extensive and integral to a child's overall development. By fostering curiosity, we are planting the seeds for a lifelong love of learning.
Critical thinking is a crucial skill that we must encourage in children from a young age. It goes beyond the absorption of knowledge; it involves understanding, analyzing, and applying that knowledge in real-world scenarios. By fostering critical thinking skills in young learners, we can equip them with essential tools for success - problem-solving abilities, decision-making skills, and the exercise of independent thought.
Through engaging activities such as open-ended conversations, problem-solving tasks, storytelling, and sorting and categorizing exercises, we can promote and nurture critical thinking in children. These activities stimulate their imagination, creativity, and curiosity while developing their analytical and reasoning abilities. They also provide opportunities for children to explore different perspectives, make connections between concepts, and think critically about the information they encounter.
The development of critical thinking skills not only enhances a child's thought process but also has a significant impact on their academic journey and personal development. It sets the stage for future personal growth and lifelong learning. By fostering independent thought and decision-making abilities, we can help children become self-reliant and confident learners.
In conclusion, fostering critical thinking skills in early childhood has numerous benefits - improved problem-solving abilities, better decision-making skills, enhanced independent thought, and a higher likelihood of academic success. It is a skill that empowers children to navigate the complexities of life and make well-informed decisions. By incorporating strategies to promote critical thinking at home through engaging activities, we can support our children on their path to becoming critical thinkers.
So let's dive into this exploration of critical thinking in early childhood and discover how we can support our children on their path to becoming critical thinkers by integrating these strategies into our daily routines!
For more resources on supporting your child's development or if you're looking for interactive games or apps to enhance critical thinking skills in your child aged 4-8 years old check out magickids.me .
- Collaborate
How to Develop Critical Thinking Skills in Children

I recently chatted with Nikki from the “What I Wish My Mother Taught Me,” podcast. We talked about critical thinking skills, why they are important in early childhood, and how parents can encourage these skills in their young children. I’ve summarized our discussion here so you can learn more about this crucial topic.
First, What Are Critical Thinking Skills?
“Simply put, students who are able to think critically are able to solve problems effectively. Merely having knowledge or information is not enough. To be effective in the workplace (and in their personal lives), students must be able to solve problems to make effective decisions; they must be able to think critically.” Lisa Gueldenzoph Snyder & Mark J. Snyder
My basic definition of critical thinking involves a set of higher-level skills that allow us to take in new information, carefully process and analyze it, and use it to form ideas and opinions. These skills are essential to everyday life. They help us –adults and children alike– make informed decisions, problem-solve, plan and set goals, and even communicate and collaborate with others.
I truly believe early childhood is a great time to start encouraging these important skills in our little ones. We can start to lay the groundwork early; this way they have time to practice and refine these skills as they mature and develop. It’s important to do this because they will continue to use these critical thinking skills in and out of the classroom, in their relationships, and eventually in their careers.
How Can Adults Encourage Critical Thinking Skills in Children?

Here are some of my recommendations for fostering these skills in young children:
1. Prioritize Play
Oftentimes people look at play as if it’s just fun and games , but it is actually fundamental to a child’s overall development. It’s how children learn about the world around them as well as how to interact with the people around them. Through play, children not only develop cognitive, academic, and motor skills but also social-emotional ones. Ideally, children should be given the opportunity to explore myriad materials and scenarios. This means that parents should allow them to play in different settings (indoors/ outdoors,) with a variety of toys and objects, and give them chances to play independently too. Open-ended toys are ideal because the play opportunities are endless and there isn’t one set or right way of playing with them. This allows for greater creativity and more meaningful learning experiences.
2. Create an Open Learning Environment
Parents should create a home that welcomes questions, brainstorming, investigations, and even failure. Adults should provide opportunities to problem-solve and experiment. STEM activities are great practice for this. When kids are involved in explorations, ask them open-ended questions, help them come up with predictions and hypotheses, and don’t intervene immediately. Let them try their own strategies first. Their solutions might not look like yours and that’s okay.
Here are a few of my favorite activities and/or games for preschoolers that encourage critical thinking skills:
- Read a variety of books with diverse themes and characters. While reading books, ask story-related questions, “Who, What, When, Where? Why?” Additionally, ask them to make predictions, at the beginning of the story, about what they think will happen. Then, ask them to make inferences. In other words, see if their predictions have changed after learning new information.
- Play guessing games like “I Spy” or “What’s in the box?” where you provide abstract clues to help them find an answer.
- Set up STEM activities where they have to find the solution to a problem. For example, building bridges, structures, or vehicles with loose parts of recyclable materials.
- Play games to determine the similarities or differences between objects.
3. Model Critical Thinking Skills and Conduct Research
Another aspect of critical thinking is researching information. We live in the time of the internet—where so much information is at our fingertips, but this also leaves us susceptible to misinformation. Critical thinking skills are necessary for determining what’s factual and what’s not. So, if your child asks you a question and you’re unsure of the answer, let them look up the answer with you. Look in reputable sources like encyclopedias, scientific journals/publications, etc. Or ask an expert, like a librarian, to help you locate appropriate sources. Let them know that not everything you see or read online is accurate. So, it may be necessary to look for multiple reputable sources. This will help them down the road when it comes time to do this on their own.
4. Encourage Open-Mindedness And Social-Emotional Learning
Finally, open-mindedness and social-emotional learning are key components to critical thinking. Young children can learn to be open-minded through exposure and by example–meaning the adults in their life should model this behavior themselves. Additionally, adults should expose their children to different cultures, backgrounds, and experiences. This can be with food, books, television, music, visiting museums, etc. All of these strategies help to develop empathy as well. Role-playing activities can help them develop more of an awareness of what others may feel, think, or experience. Finally, these strategies allow children to be creative and independent thinkers, learn to communicate more effectively, understand the opinions and experiences of others, be open to multiple solutions, and not fear failure.
What Parents/Caregivers Should Avoid
There are a few things parents/caregivers do, often unintentionally, that can stifle the development of critical thinking skills.
- This might be a bit controversial for some old-school parents, but expecting blind obedience from your child isn’t always a good thing. In fact, it can leave them more susceptible to predatory behavior and peer pressure. Sure, there are some people out there who may believe that children should be “seen and not heard” and that they should follow the orders of their parents and authority figures without question. However, it can lead to children blindly following the ideas and suggestions of potential negative influences too– without considering the consequences. To combat this, parents should again create a welcoming environment that allows for respectful questioning, discussions, and collaboration.
- The second issue is not providing children with opportunities to try (and fail) things on their own. Parents should avoid constant interference as well as trying to fix all of their child’s problems. Sometimes the best way for a child to learn a new skill is to try, try, and try again.
So much of what we already do as parents and educators can help our children to develop crucial life skills i.e. academic, motor, social-emotional, etc. The same goes for critical thinking skills. By encouraging curiosity and exploration, open-ended discussions, and providing opportunities to problem-solve, our children can pick up important critical thinking skills that can set them up for success in school and in life.
Now talk to me! What do you do at home to encourage critical thinking skills? Leave a comment below.
‘This post was featured by Twinkl in their Exams and Revision Blog ‘
SAVE TO PINTEREST

Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
KidsKonnect
Reading Comprehension Cause and Effect Context Clues Compare and Contrast
Noun Worksheets Writing Prompts Compound Words Figurative Language
The Wizard of Oz Hans Christian Andersen Types of Writing Text Structure
Literary Devices
Alliteration Hyperbole Metaphor Irony
Subject Verb Agreement Poetry Climax Rhyme
View all reading worksheets
Action Verbs Tragedy Transition Words Phonics
View all writing worksheets
Dramatic Irony Cacophony Anaphora Setting
View all literature worksheets
Abbreviations Transition Words Conclusion Situational Irony
View all literary device worksheets
Women’s History
Inspirational Women Women's History Month First Lady of the US Women's Equality Day International Women's Day
View all Women's History worksheets
American Revolution
American Revolution Patriots & Loyalists Patrick Henry Sons of Liberty
View all American Revolution worksheets
US Constitution US Independence Trail of Tears The Pilgrims
View all US History worksheets
Ancient History
Ancient China Ancient Mayan Ancient Rome Ancient Aztec
View all Ancient History worksheets
World History
Roaring Twenties Industrial Revolution Middle Ages The Renaissance
View all World History worksheets
Famous Wars
World War 1 World War 2 Vietnam War American Civil War
View all Famous War worksheets
Anne Frank Sally Ride Neil Armstrong Christopher Columbus
View all famous figure worksheets
Joe Biden Donald Trump Abraham Lincoln George Washington
View all President worksheets
Roald Dahl Dr Seuss JK Rowling Michael Morpurgo
View all author worksheets
Civil Rights
Rosa Parks Sojourner Truth Medger Evers Martin Luther King
Elvis Presley Johann Sebastian Bach Ella Fitzgerald Wolfgang Mozart
View all musician worksheets
Thomas Edison Albert Einstein Henry Ford Wright Brothers
View all inventor worksheets
Muhammad Ali Michael Jordan Jackie Robinson Jesse Owens
View all athlete worksheets
Nat Turner Ruby Bridges Harriet Tubman Booker T Washington Malcolm X
View all civil rights worksheets
Natural Wonders
River Nile Mount Everest Sahara Desert Mount Etna Ancient Pyramids Amazon River
Landmarks/Sights
Mount Rushmore Statue Of Liberty White House Stonehenge Great Wall of China Santa Fe Trail
New York Texas South Carolina Alaska Nevada Ohio
Australia United Kingdom China Canada Argentina Brazil
Mount Fuji Mississippi River Rocky Mountains Volcano Glacier The Great Barrier Reef
View all natural wonders worksheets
Hoover Dam Bermuda Triangle Leaning Tower Of Pisa Arc De Triomphe Golden Gate Bridge Colosseum
View all landmark worksheets
California Colorado Indiana Florida Washington Georgia
View all US state worksheets
Poland Greece Philippines Japan France India
View all country worksheets
April Topics
April Fools’ Day World Autism Awareness Day International Children’s Book Day Passover Eid Al-Fitr Ramadan Patriots’ Day Rama Navami Earth Day World Book Day
View all Seasonal worksheets
Social Emotional Learning
Morals and Values Self Management Ethics Depression Relationship Skills Self-Awareneess Self-Esteem Emotions and Feelings Goal-Setting Interpersonal Skills
View all Social-Emotional Learning worksheets
Celebrations
Easter Saint Patrick’s Day Valentines Day Chinese New Year Rosh Hashanah Thanksgiving Flag Day Cinco de Mayo Beginning Of Lent Yom Kippur View all Celebrations worksheets
Remembrance
Pearl Harbor Day Veterans’ Day Memorial Day Battle Of The Somme D-Day 9/11 Anzac Day Martin Luther King Jr. Day International Women’s Day Victoria Day View all Remembrance worksheets
Camels Fox Bears Penguin Wolf Beavers Mountain Lion Red Panda Snow Leopard White Tigers Silverback Gorilla Okapi
View all mammal worksheets
Marine Life
Crabs Starfish Fish Octopus Great White Shark Dolphin Walrus Narwhal Megalodon Shark Killer Whale Beluga Whale Lionfish
View all marine life worksheets
Insects/Invertebrates/Reptiles
Millipede Praying Mantis Ladybug Ants Spider Iguana Chameleon Komodo Dragon Lizard Bearded Dragon Gila Monster Snakes
View all insect worksheets
Eagle Peregrine Falcon Snowy Owl Emu Woodpecker Albatross Swan Quail Bald Eagle Hummingbird Peacock
View all Bird worksheets
Natural World
Avalanche Flood Tsunami Natural Disasters Fossils Ice Age
View all natural world worksheets
Earth Sciences
Water Cycle Global Warming Deciduous Forests Hurricane Sandy Hurricane Katrina Global Warming
View all earth science worksheets
Food Chain Fossils Photosynthesis Cells Ecosystem Plants
View all biology worksheets
Solar System Black Holes Eclipse Stars and Constellations The Moon Comets
View all space worksheets
Chemistry/Physics
Magnetism Graduated Cylinders Solid, Liquid, Gas Gravity Light Sound
View all science worksheets
Kangaroo Horse Bear Lion Lizard Octopus
View all animal worksheets
Addition Sentences Single Digital Addition Two-Digit Addition Three Digit Addition Repeated Addition
View all Addition Worksheets
Ordinal Numbers Cardinal Numbers Rounding Numbers Odd & Even Numbers Comparing Numbers
View all Numbers Worksheets
Counting Money Subtracting Money Change Money Coin Name & Value Calculate Change (Money)
View all Money Worksheets
Number Line Single Digit Subtraction Place Value Subtraction Sentences Input & Output Tables
View all Math Worksheets
Why Is Developing Critical Thinking Skills Important for Kids?
Search for worksheets.
What does it mean to think critically? In psychology, there’s little agreement over the meaning of critical thinking, even though everyone agrees that critical thinking skills are vital for academic performance and career development. But, should teaching critical thinking for kids be a central learning objective?
Keep reading to find out, as this is the question we’ll focus on today. First, we’ll take a brief overview of critical thinking as a cognitive phenomenon and choose a definition, so we both have a clearer understanding of the process when we discuss it further. Then, we’ll take a deep dive into the scientific evidence that’s been piling up. Finally, based on that evidence, we’ll talk about the benefits of teaching critical thinking skills to kids.
A Brief Overview
Before we can argue that teaching critical thinking to kids is important, we need to make sure we’re on the same page concerning what critical thinking is, what are the underlying processes shaping critical thinking skills, and how critical thinking develops.
What Is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is a cognitive process that we use to analyze information from our environment with reflective skepticism when deciding what to believe. In other words, critical thinking is a mental activity that allows us to examine the things presented to us in a unique way, so we can take the best course of action.
To illustrate this, let’s think of a practical example. In the classroom, kids are required to learn by reading the educational material on a specific topic. Promoting critical thinking would be to examine the material with the goal of deciding whether it’s reliable, informative, biased vs. objective, and figuring out what are the author’s motives. The following questions reflect critical thinking:
- Who is the author and why did they write this piece of information?
For example, they have professionally studied the topic for years.
- What is the message that they want to share?
For example, the author believes XX, has convincing arguments, and wants to share them with the world.
- How does this piece of information fit with everything else I know on this topic?
For example, this explains/contradicts the claims we’ve read last time.
- Do I need additional information on this topic before I can reach a conclusion?
For example, the author didn’t explain how XX develops, and I need to read more about that before accepting/rejecting their arguments.
- Should I trust this information? Why/Why not?
For example, the author didn’t include any references to support the claims (facts) on which they’ve based their arguments. Can I be sure they’re not lying?
- What did I learn from this piece of information?
For example, I’ve learned arguments supporting the topic, but I still need to see other points of view or see what critics say.
- What are my next steps?
For example, read another text on this topic from another point of view.
What Are Critical Thinking Skills?
In the last paragraph, we’ve talked about critical thinking as if it’s one unit or process within our cognition. However, the truth is that complex processes, such as critical thinking, are better viewed as a collection or function of many different more basic mental processes, such as attention, logic, memory, etc.
Unfortunately, when it comes to the mechanism underlying critical thinking, the disagreement among experts is just as strong as with its definition. Different authors identify different skills which they believe are vital for critical thinking. Of course, there’s overlap, and we’ll take a look at the skills and mechanisms which are accepted by most professionals.
According to Kompf & Bond (2001) , critical thinking involves rationality, reasoning, logic, previous knowledge, metacognition, intelligence, decision making, problem-solving, and a moral component (reflective thinking).
Rationality and logic are two mechanisms frequently mentioned in other literature, too. This is because for most authors critical thinking is considered to be logically correct thinking . In other words, this would mean that kids who think critically can distinguish between logically true and logically false claims. In practice, critical thinking can be promoted by developing logical reasoning skills such as deduction, induction, and abduction .
However, some authors, such as Kerry S. Walters, argue that logical reasoning is necessary but not sufficient for rationality. Therefore, imagination, conceptual creativity, and intuition are also included in rationality, which might be important to keep in mind, when we discuss the benefits of teaching critical thinking for kids.
To conclude, the following skills are considered to be part of critical thinking by most experts:
- Comprehension (decode meaning)
- Analysis (identify arguments)
- Inference (draw logically valid conclusions)
- Evaluation (assess the credibility/quality of claims)
- Explanation (present arguments for own conclusions)
- Self-regulation (self-monitor and self-correct)
How to Develop Critical Thinking?
We’ve already touched upon this topic when we mentioned the practical skills involved in critical thinking. There are a lot of elements that children need to master first, such as logical thinking, mental visualization, deduction, and induction. Then, they need to learn how to use these elements to find patterns, make decisions, and think in a unique way.
Safe to say, teaching critical thinking skills is a challenge that requires patience and a lot of practical experience. For these reasons, we don’t believe we can do justice to such a complex question in one paragraph, especially considering how important it’s for teachers and homeschooling parents to know where to start and how to make progress. However, we can discuss the development of critical thinking for kids in a separate article, which is exactly what we did!
If you want to know how to develop critical thinking through practical examples and exercises, check out our article “ 11 Ways to Help Your Child Develop Critical Thinking Skills. ”
And, in the meantime, let’s see why critical thinking is so important for kids!
Why Is Critical Thinking Important for Kids?
We can easily argue that critical thinking is one of the most important elements of literacy! Once children have developed critical thinking they’ll be able to make reasonable judgments, identify problems, come up with solutions, and filter reliable information necessary for independent learning.
Another way to think about critical thinking is through the concept of digital literacy. Kids receive most of the information online where we can’t control who posts and what. This becomes a problem when we take into consideration that not everyone is qualified to speak or write on a specific topic, or they deliberately spread false information. Critical thinking for kids is a defense mechanism that shields them from becoming victims to such dangers.
There are many other theoretical considerations and practical examples that illustrate the importance of critical thinking for kids. Let’s go over the most important ones.
What Can Scientific Findings Tell Us?
If we want to make a serious case about the importance of critical skills, we have to go beyond the theories and some teachers’ experiences and take a look at the science. What can we learn from psychological and pedagogical research findings?
Murawski published a study in the Journal of Learning in Higher Education in 2014 , where she discussed critical thinking in the classroom. According to her, educators who teach students critical thinking skills, give control to students to take over their learning process. In other words, children will then approach the course in a more effective manner, ask more challenging questions, and participate in the learning process more intensely.
However, as Carroll from the University of New Orleans cleverly remarks in his study , even though all teachers agree that basic knowledge and skills are not enough to define student achievement and critical thinking is more than necessary, assessments in almost all of the classrooms included in the study focused on basic knowledge and skills measured through multiple-choice questions. This brings up the issue of how much critical thinking is developed in schools and what are the effects of such variability.
Ernst & Monroe’s study from 2007, published in the Environmental Education Research Journal , might shed some light on these issues. The authors investigated how environment-based curriculums (EBL) influence the development of critical thinking skills and a disposition toward critical thinking. The results show that, indeed, environment-based learning had a positive effect (improved) on students’ critical thinking skills.
On the other hand, some evidence from a study in 2001, published in Instructional Science , shows that peer interaction is not effective for improving critical thinking skills. Unfortunately, this further illustrates the fact that critical thinking skills are incredibly complex and many teaching programs might get unsatisfactory results because they use non-effective methods.
Another interesting take on critical thinking gives Loes et al. in their 2016 study which investigates the relationship between diverse experiences and critical thinking. The authors argue that students will be more likely to engage in effortful and complex modes of thought when they encounter new and unique situations.
We also have evidence that argument maps improve critical thinking, which in turn make better learners out of students. More specifically, Rider and Thomason (2014 ) investigated the claims and gave support to the claims that students learn to better understand and critique arguments, improve in their reading and writing, and become clearer in their thinking through argument mapping (a method improving critical thinking).
Finally, another study by Abduljaleel Alwali closely examined the benefits of critical thinking in high school and concluded that critical thinking positively impacts perception, individuality, general analytical skills, academic performance, metacognition, practical applications of theoretical knowledge, and decision-making.
What do these studies tell us about the importance of critical thinking for kids in general? Keep reading, because everything that we’ve learned from these studies will be summarized and explained in greater detail in our next paragraph.
Benefits of Teaching Critical Thinking for Kids
By now, we’ve seen that there are many findings supporting some, if not all of the benefits associated with critical thinking. While we still need a lot more research to be done before we can completely demystify the neurological basis of critical thinking, it is more than clear that this is an incredibly important cognitive process that could literally change students’ lives. Here’s how!
Critical Thinking Promotes Creative Problem-Solving Skills
In some of the studies, we’ve seen that teachers do not believe that students’ achievements are mirrored only in the knowledge of facts or basic skills. All educators agree there’s more to education, including creativity and learning how to think. Well, teaching critical thinking is one way to go beyond factual knowledge, stimulate creativity, and allow students to look for innovative solutions to common problems.
Critical Thinking Creates Independence
Another science-backed benefit of critical thinking is control and independence. In other words, students who are curious and are not afraid to question the information they get, usually take initiative and go on their own to find answers. This means that they think more deeply about the topic, want to know more details, and hear other opinions before making conclusions. All of this makes them more independent, as they’ll seek information beyond what’s given to them by the teacher, which is the first step toward independent learning.
Critical Thinking Promotes Curiosity
The basis of continuous independent learning is curiosity. For a child to learn on their own, they need to be internally motivated, which is always associated with curiosity, one way or another. Moreover, the nature of critical thinking means to evaluate information by questioning aspects of it and relating it with previous knowledge. This is a very intense mental process that requires intentionality. If kids are not curious or internally motivated, chances are they won’t think too deeply about the issue. Teaching critical thinking is one way to make kids more curious about knowledge in general.
Critical Thinking Stimulates Metacognition
Metacognition is a cognitive process that refers to one’s ability to think about thinking. It sounds a little weird, but it’s very simple. Because we have metacognition we’re aware of our own mental processes. We know whether we understand something and how we perform based on self-monitoring. It’s also the ability to see ourselves as thinkers or learners. How is it associated with critical thinking? Well, questioning and challenging information are only possible under the assumption that we are aware of how these pieces of information relate to our previous knowledge. It also entails questioning ourselves and finding new relations between the things we’ve learned before. This is why thinking critically means to use and practice metacognition.
Critical Thinking Creates Resilience
Finally, one of the most important practical applications of critical thinking skills is improved literacy, which makes kids more resilient to manipulation, brainwashing, false information, and other dangers that lurk on the internet and in-person in the form of peer pressure, bullying, and more. Kids will have the ability to better analyse the situation and ultimately make better decisions.
More generally, if we think of resilience as an ability to solve and overcome problems, then we can also argue that since critical thinking improves problem-solving skills, it acts as a protective factor for students in both educational and social contexts.
Before You Go
Critical thinking for kids is a truly essential topic that deserves more attention. As we’ve seen, critical thinking is associated with many other cognitive skills important for academic success, but also life in general. If educators dedicate more time for developing critical thinking skills, they can help students become more engaged in the learning process, independent, and efficient problem-solvers.
In case you’re wondering how you can achieve that in your classroom, let us remind you to check out our article on developing critical thinking skills among children. There, we’ve shared many different practical examples and exercises you can easily incorporate in the classroom.
Furthermore, visit our main website and browse through our large collection of worksheet packs . Most of our resources are interactive and promote critical thinking skills in children through the exercises included in each topic.
Plus, make sure to follow our blog by subscribing to our newsletter . We regularly share insightful guides that break down complex topics, such as critical thinking for kids, in a clear and easy to read tone. This way, you can stay up to date with all the new trends and teaching practices in education, without losing yourself in the sea of information online.
Sign up to be notified when we release new articles and worksheets!
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Related Articles
Link/cite this page.
If you reference any of the content on this page on your own website, please use the code below to cite this page as the original source.
Link will appear as Why Is Developing Critical Thinking Skills Important for Kids?: https://kidskonnect.com - KidsKonnect, September 3, 2021
KidsKonnect is a growing library of high-quality, printable worksheets for teachers and homeschoolers.
Home Facts Privacy About Blog Contact Terms
Safe & Secure
We pride ourselves on being a safe website for both teachers and students. KidsKonnect uses a secure SSL connection to encrypt your data and we only work with trusted payment processors Stripe and PayPal.
- Parenting Tips
- Products We Love
- Kids Activities
- Celebrating Her

23 Activities to Develop Critical Thinking Skills in Children
Are you looking for ways to help your child become a better problem solver and decision maker?
Do you want to prepare them for success in the 21st century, where critical thinking skills are highly valued?
Look no further, because in this post we will share 23 engaging activities that can help your child develop critical thinking skills. From puzzles and games to real-life scenarios and creative challenges, these activities will not only enhance your child’s thinking abilities but also keep them entertained and curious. As a parent, it is important to give your child the tools they need to succeed, and critical thinking skills are a vital part of that toolkit.
So, let’s dive in and discover some fun and effective ways to help your child develop critical thinking skills!
Table of Contents
What is critical thinking skills?
Critical thinking is a cognitive process that involves analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information to make informed decisions and solve problems effectively. It involves the ability to question assumptions, examine evidence, and consider multiple perspectives to arrive at logical and evidence-based conclusions.
For example, when playing a game of chess, a player must analyze the board, anticipate their opponent’s moves, and make strategic decisions based on the available information. Similarly, when conducting research, an individual must evaluate the credibility and reliability of sources and synthesize information to form a coherent argument.
Importance of developing critical thinking skills in children
Developing critical thinking skills in children is crucial for their overall cognitive and social-emotional development. Research has shown that children who possess strong critical thinking skills are better equipped to make sound decisions, solve complex problems, and communicate effectively with others.
One study conducted by the University of California, Los Angeles found that students who received training in critical thinking showed significant improvements in their reading and writing abilities. These students also demonstrated higher levels of creativity and were better able to understand and analyze complex issues.
In addition, developing critical thinking skills can help children become more independent and confident in their decision-making abilities. They learn to evaluate information and evidence, identify biases, and consider different perspectives before making a decision. This can lead to a greater sense of self-awareness and a better understanding of their own strengths and weaknesses.
Furthermore, critical thinking skills are essential in today’s rapidly changing world. As technology continues to advance and the job market evolves, individuals who possess strong critical thinking skills are more likely to succeed. They are better equipped to adapt to new challenges and to identify new opportunities.
Overall, the development of critical thinking skills is essential for children’s long-term success and well-being. By providing them with opportunities to practice critical thinking skills through various activities and experiences, parents and educators can help children become effective problem solvers, communicators, and decision-makers.
Recommended reading: How To Teach Your Child To Think Out Of The Box
Recommended reading: 9 Fun Activities to Build Listening Skills in Children
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Raising Children 101 (@raising_children_101)
Activities to develop critical thinking skills in children
Critical thinking skills can be developed through various activities that require individuals to analyze and evaluate information, develop hypotheses, and test their ideas using evidence.
- Read Books Together: Reading books with children helps to develop their critical thinking skills. Encourage them to ask questions about the story, analyze the characters’ actions, and make predictions about the outcome.
- Board Games: Board games are a fun way to develop critical thinking skills in children. Games such as chess, checkers, and monopoly require children to think strategically and make decisions based on the outcome of their moves. Playing board games also encourages children to think creatively and come up with unique solutions to problems.
- Encourage Questions: Encourage children to ask questions about the world around them. This can help them to develop their analytical skills and learn how to evaluate information.
- Play “What If” Games: “What If” games encourage children to think creatively and critically. For example, ask them what they would do if they were stranded on a deserted island or if they could travel through time.
- Brainstorm Solutions: Encourage children to brainstorm solutions to problems they encounter. This can help them develop their problem-solving skills and learn how to think critically.
- Mind Mapping: Mind mapping is a great activity to improve critical thinking skills in children. It helps children to organize their ideas and think creatively. Give your child a topic and ask them to create a mind map by writing down all their thoughts and ideas related to the topic. This activity can help your child to improve their brainstorming skills and connect different ideas.
- Play Sudoku: Sudoku is a logic-based game that requires critical thinking skills. It requires children to think logically and use deductive reasoning to solve a problem. Sudoku puzzles can be found in many newspapers and online.
- Conduct Research: Encourage children to conduct research on a topic that interests them. This can help them develop their analytical skills and learn how to evaluate information.
- Watch Documentaries: Documentaries are a great way to develop critical thinking skills in children. Encourage them to ask questions about the information presented and analyze the content.
- Play “What’s Missing”: “What’s Missing” is a memory game that requires children to think critically and remember information. For example, lay out several objects and ask them to identify which one is missing.
- Play “I Spy”: “I Spy” is a game that requires children to think critically and observe their surroundings. It can help develop their analytical and problem-solving skills.
- Play Charades: Charades is a game that requires children to think creatively and critically. It helps develop their problem-solving and analytical skills.
- Play “20 Questions”: “20 Questions” is a game that requires children to ask questions and think critically. It can help them develop their analytical and problem-solving skills.
- Play “Would You Rather”: “Would You Rather” is a game that encourages children to think critically and make informed decisions. It helps them develop their problem-solving skills.
- Play “Spot the Differences”: “Spot the Differences” is a game that requires children to think critically and observe their surroundings. It helps develop their analytical skills.
- Play “Who Am I”: “Who Am I” is a game that requires children to think critically and ask questions. It helps develop their analytical and problem-solving skills.
- Write Stories: Encourage children to write stories that require critical thinking skills. For example, they could be asked to create a story that involves problem-solving, decision-making, or predicting an outcome. This activity encourages children to think creatively and come up with unique solutions to problems, helping them develop their critical thinking skills.
- Science Experiments: Science experiments are a fun way to develop critical thinking skills in children by encouraging them to ask questions, analyze data, and draw conclusions.. Encourage children to think about the scientific method and predict what will happen during an experiment. This encourages children to think about cause and effect and develops their critical thinking skills.
- Mystery Box: A mystery box is a great way to develop critical thinking skills in children. Place a number of items in a box and ask children to guess what the items are based on their shape, texture, and weight. This activity encourages children to think creatively and use deductive reasoning to solve a problem.
- Coding: Coding is a great way to develop critical thinking skills in children. It requires children to think logically and use deductive reasoning to solve problems. There are many online resources available that teach children how to code.
- Debate: Debating is a great way to develop critical thinking skills in children. It requires children to think critically and come up with logical arguments to support their position. Debating also helps children develop their communication skills and learn how to express their thoughts and opinions effectively.
- Brain Teasers: Brain teasers are a fun way to develop critical thinking skills in children. They require children to think creatively and use deductive reasoning to solve problems. Brain teasers can be found in many puzzle books and online.
- Puzzles: Puzzles are an excellent way to enhance critical thinking skills in children. Give your child puzzles that require them to use their logical reasoning, problem-solving, and spatial reasoning skills. Puzzles can be in the form of jigsaw puzzles, crossword puzzles, or any other puzzle that requires critical thinking.
By incorporating these activities into your child’s daily routine, you can help them to develop critical thinking skills that will benefit them throughout their lives. These activities can be a fun and engaging way for children to learn and develop their cognitive skills.
- Development
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Subscribe Today
Trusted parenting advice for all ages The movement for children’s mental health Supportive environment for mothers for a holistic living Celebrating moms
Join the newsletter to experience a sense of tribe and read stories full of inspiration and drive!
When People Make Comments About Your Child’s Appearance
Exposure to traffic air pollution affecting brain: how to protect your child, importance of emotional intelligence in kids.

Latest Posts
Are labels harmful for your child, teach your child how to deal with disappointments, helping your perfectionist child: strategies for parents, related posts, teaching your child about sustainable eating practices, women too have the right to enjoy holidays. period., bad parenting and it’s impact on child’s mental health, is your child assertive enough.

raising_children_101
Raising Children 101 is all about helping parents create beautiful memories for their children by understanding them better.
Popular Posts
How to teach your child to tell time, how can i find out what my child is learning from friends, school, and the media, 12 effective ways to respond when your kids complain, popular categories.
- Parenting 336
- Parenting Tips 295
- Well-being 60
- Self Care 52
- Products We Love 48
- Education 36
- Kids Activities 19
Stay connected
- Write For Us
- Terms and conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Returns and Refunds
©raisingchildren101.com. All rights reserved
Engaging Preschoolers with Critical Literacy Through Counter-Storytelling: A Qualitative Case Study
- Published: 05 August 2020
- Volume 49 , pages 633–646, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
- So Jung Kim 1 &
- Alyse C. Hachey 2
2483 Accesses
9 Citations
Explore all metrics
Despite the importance of traditional children’s literature in children’s literacy learning, little is still known about how fairytales can be effectively used for pedagogical purposes to facilitate young children’s critical participation in early literacy instruction. The main purpose of this article is to explore the intersection of literature-based instruction, multimodality, and early critical literacy pedagogies by examining how young children negotiate, represent, and (re)create their voices through engaging in counter-storytelling. The study was conducted at a kindergarten classroom located in a metropolitan city in South Korea. Using a qualitative case study method, multimodal data were collected for 5 months through classroom observations, one-to-one interviews with the parents and the teacher, observational field notes, and children’s artifacts. Findings suggest that it is important for teachers to value young children’s voices as storytellers and create a fluid and dynamic literacy atmosphere where young children explore their voice in exciting, intriguing, and multimodal ways. It also indicates that teachers need to encourage children to think critically and creatively through developmentally, culturally, and linguistically appropriate curricular activities.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

Similar content being viewed by others

Enriching Critical Literacy Through Children's Literature: A Case Study in South Korea
So Jung Kim & Se Jeong Yang

Opening up spaces for early Critical Literacy: Korean kindergarteners exploring diversity through multicultural picture books
So Jung Kim
Literacy Through Photography: Multimodal and Visual Literacy in a Third Grade Classroom
Angela M. Wiseman, Marita Mäkinen & Reijo Kupiainen
The conversation was spoken in Korean originally but translated into English by a third person. The accuracy of the translation was checked through official Korean Translation Services.
112 is an emergency police phone number in Korea.
Albers, P., & Sanders, J. (Eds.). (2010). Literacies, the arts and multimodality . Urbana, IL: National Council of Teachers of English.
Google Scholar
Beach, R. (1993). A teacher’s introduction to reader-response theories . Urbana, IL: National Council of Teachers of English.
Beach, R., & Freedman, K. (1992). Responding as a cultural act: Adolescents’ responses to magazine ads and short stories. In J. Many & C. Cox (Eds.), Reader stance and literary understanding (pp. 162–190). Norwood, NJ: Alex Publishing Corporation.
Beck, A. S. (2005). A place for critical literacy. Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy, 48 (5), 394–400.
Books, G. (2004). 잭과 콩나무 [Jack and the Beanstalk] . Seoul: Geylim.
Brooks, W., & McNair, J. C. (2009). “But this story of mine is not unique”: A review of research on African American children's literature. Review of Educational Research, 79 (1), 125–162.
Brown, S. (2008). Play is more than fun. TED Talk. Retrieved from: https://www.ted.com/talks/stuart_brown_says_play_is_more_than_fun_it_s_vital#t-566747
Castillo-Montoya, M. (2016). Preparing for interview research: The interview protocol refinement framework. The Qualitative Report, 21 (5), 811–831.
Crawford, P. A., & Hade, D. H. (2000). Inside the picture, outside the page: Semiotics and the reading of wordless picturebooks. Journal of Research in Childhood Education., 15 (1), 66–80.
Corbin, J., & Strauss, A. (2008). Basics of qualitative research: Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Creswell, J. W. (2015). Educational research. Planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research (5th ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson Education.
Delgado, B. D., & Villalpando, O. (2002). An apartheid of knowledge in the academy: The struggle over "legitimate" knowledge for faculty of color. Equity and Excellence in Education, 35 (1), 169–180.
DeWaelsche, S. A. (2015). Critical thinking, questioning and student engagement in Korean university English courses. Linguistics and Education, 32 , 131–147.
Disney Storybook Art. (2014). 신데렐라 [Cinderella] . Seoul: Dreaming Snail.
Docherty, S. (2014). 5 Reasons why fairy tales are good for children . Retrieved from https://www.scottishbooktrust.com/blog/reading/2014/06/5-reasons-why-fairy-tales-are-good-for-children.
Dooley, C. M., & Matthews, M. W. (2009). Emergent comprehension: Understanding comprehension development among young literacy learners. Journal of Early Childhood Literacy, 9 (3), 269–294.
Dozier, C., Johnston, P., & Rogers, R. (2006). Critical literacy/critical teaching: Tools for preparing responsive teachers . New York, NY: Teachers College Press.
Dyson, A. H. (2008). Staying in the (curricular) lines: Practice constraints and possibilities in childhood writing. Written Communication, 25 (1), 119–159.
Dyson, A. H., & Genishi, C. (2005). On the case . New York, NY: Teachers College Press.
Emerson, R. M., Fretz, R. I., & Shaw, L. L. (2011). Writing ethnographic fieldnotes . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Enciso, P. (1997). Negotiating the meaning of difference: Talking back to multicultural literature. In T. Rogers & A. O. Soter (Eds.), Reading across cultures: Teaching literature in a diverse society (pp. 13–41). New York, NY: Teachers College.
Fish, S. E. (1980). Is there a text in this class?: The authority of interpretative communities . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Freire, P. (2000). Pedagogy of the oppressed . New York, NY: Contimuum.
Gee, J. P. (1999). An introduction to discourse analysis theory and method (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Routledge.
Gonzalez, N., Moll, L. C., & Amanti, C. (Eds.). (2005). Funds of Knowledge: Theorizing practice in households, communities and classrooms . Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Goss, M., Galbraith, P., & Renshaw, P. (2002). Socially mediated metacognition: Creating collaborative zones of proximal development in small group problem solving. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 49 , 193–223.
Hamel, J. (1993). Case study methods . Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publications.
Hamilton, M., & Weiss, M. (2005). Children tell stories. Teaching and using storytelling in the classroom . Katonah, NY: Richard C. Owen.
Hour, H. (2000). Dynamic aspect of fairy tales: Social and emotional competence through fairy tales. Scandinavian Journal of Educational Research, 44 (1), 91–105.
Huang, S. (2011). Reading “further and beyond the text': Student perspectives of critical literacy in EFL reading and writing. Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy, 55 (2), 145–154. https://doi.org/10.1002/JAAL.00017 .
Article Google Scholar
Jewitt, C. (2008). Multi-modal discourse across the curriculum. In M. Martin-Jones & A. De Mejia (Eds.), Encyclopedia of language and education, discourse and education (pp. 357–367). New Jersey, NY: Springer.
Jikyungsa. (2006). 빨간 모자 [Little Red Riding Hood] . Seoul: Jikyungsa.
Johnson, D. (2012). The joy of children’s literature . Boston, MA: Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
Kelly, L. B. (2017). Welcoming Counter story in the primary literacy classroom. Journal of Critical Thought and Praxis, 6 (1) Article 4. Retrieved from: https://lib.dr.iastate.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1124&context=jctp
Kelly, L. B., & Moses, L. (2018). Children’s literature that sparks inferential discussion. Reading Teacher, 1 , 221–229.
KICCE (2013). Policy brief . Retrieved from https://kicce.re.kr/eng/newsletter_mail/pdf/201401_brief.pdf.
Kim, S. J. (2012). Critical literacy in East Asian literacy classrooms. Perspectives on Global Development and Technology, 11 (1), 131–144.
Kim, S. J. (2016). Opening up spaces for early critical literacy: Korean kindergarteners exploring diversity through multicultural books. Australian Journal of Language and Literacy, 39 (2), 176–187.
Kim, S. J. (2019). Children as creative authors: The possibilities of counter-storytelling with preschool children. Kappa Delta Pi Record, 55 (2), 72–77.
Kirk, J., & Miller, M. L. (1986). Reliability and validity in qualitative research . Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
Kress, G. (2009). Multimodality: A social semiotic approach to contemporary communication . London, UK: Routledge.
Lee, H. J., & Lee, J. (2012). Who gets the best grades at top universities? An exploratory analysis of institution-wide interviews with the highest achievers at a top Korean University. Asia Pacific Education Review, 13 (4), 665–676.
Leland, C., Harste, J., & Huber, K. (2005). Out of the box: Critical literacy in a first-gradeclassroom. Language Arts, 82 (5), 257–268.
Lenters, K., & Winters, K. (2013). Fracturing writing spaces: Multimodal storytelling ignites process writing. Reading Teacher, 67 (3), 227–237.
Lewison, M., Leland, C., Harste, J., & Christensen, L. (2015). Creating critical classrooms: K-8 reading and writing with an edge . New York, NY: Routledge.
Love, B. J. (2004). Brown plus 50 counter-storytelling: A critical race theory analysis of the “majoritarian achievement gap” story. Equity & Excellence in Education, 37 , 227–246.
Marshall, E. (2016). Counter-storytelling through graphic life writing. Language Arts, 94 (2), 79–93.
McLaren, P. (2007). Life in school . Los Angeles, CA: Pearson.
Moller, K. J. (2004). Creating zones of possibility for struggling readers: A study of one fourth graders’ shifting roles in literature discussions. Journal of Literacy Research, 36 (4), 419–460.
National Education Association. (2012). Preparing 21st century students for a global society: An educator's guide to “the four Cs.” Retrieved from https://www.nea.org/assets/docs/A-Guide-to-Four-Cs.pdf.
Nodelman, P., & Reimer, M. (2003). The pleasures of children’s literature . Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon.
Panca, I., Georgescub, A., & Zahariab, M. (2015). Why children should learn to tell stories in primary school? Social and Behavioral Sciences, 187 , 591–595.
Patton, M. Q. (2015). Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practice (4th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Shaskan, T. S. (2014). 늑대가 들려주는 빨간모자 이야기[The story of Little Red Riding Hood: From the wolf’s perspective] . Seoul: Kids M.
Seidman, I. (2013). Interviewing as qualitative research: A guide for researchers in Education and the Social Sciences (4th ed.). New York, NY: Teachers College Press.
Siegel, M. (2006). Rereading the signs: Multimodal transformations in the field of literacy education. Language Arts, 84 (1), 65–77.
Sipe, L. (2000). The construction of literary understanding by first and second graders in oral response to picture storybook read-alouds. Reading Research Quarterly, 35 (2), 252–275.
Sipe, L. (2008). Storytime . New York, NY: Teachers College Press.
Solórzano, D. G., & Yosso, T. J. (2002). Critical race methodology: Counter-storytelling as an analytical framework for education research. Qualitative Inquiry, 8 (1), 23–44.
Stake, R. (2005). Multiple case study analysis . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Sung, Y. K., & Apple, M. W. (2003). Democracy, technology and curriculum: lessons from the critical practices of Korean teachers. In M. W. Apple (Ed.), The state and the politics of knowledge (pp. 177–192). New York, NY: Routledge.
Vasquez, V. (2014). Negotiating critical literacies with young children . Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Virtue, D. C., & Vogler, K. E. (2009). Pairing folktales with textbooks and nonfiction in teaching about culture. Social Studies and the Young Learner, 21 (3), 21–25.
Wright, S. (2010). Understanding creativity in early childhood: Meaning Making and children’s drawing . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Education, The University of Texas at El Paso, Education Bldg. Rm. 603, 500 W., El Paso, TX, 79968, USA
College of Education, The University of Texas at El Paso, 500 W. University Ave., EDUC 601D, El Paso, TX, 79968, USA
Alyse C. Hachey
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to So Jung Kim .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Kim, S.J., Hachey, A.C. Engaging Preschoolers with Critical Literacy Through Counter-Storytelling: A Qualitative Case Study. Early Childhood Educ J 49 , 633–646 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10643-020-01089-7
Download citation
Published : 05 August 2020
Issue Date : July 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10643-020-01089-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Counter-storytelling
- Early critical literacy
- Multimodality
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
15+ Top Critical Thinking Activities for Preschoolers and Kindergartners
As parents, we must give our children the best possible education and skills to help them succeed in life. We need to understand the importance of critical thinking abilities in children.
Providing them with the proper education, tools, and resources is insufficient. They must also be equipped with the skills to think critically and solve problems.
What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is a skill that helps children develop the ability to make informed decisions, think objectively and creatively, and develop problem-solving skills. By teaching our children to think critically, we give them the resources they need to make intelligent decisions and develop a strong foundation for their future.
Your child will be better equipped to make sound decisions and solve problems by developing critical thinking abilities.
Listed below are significant things that you should know about critical thinking-
- Critical thinking is the process of evaluating information, facts, and arguments to make a reasoned decision or judgment.
- Critical thinking is an essential skill for kids to become successful in their lives. It is the ability to think logically, systematically, and reflectively and to make sound decisions and judgments.
- Kids must develop this skill to create creative solutions to problems, make informed decisions, and think flexibly.
Why is Critical Thinking important?
The importance of critical thinking abilities for kids cannot be overstated.
- It helps kids to analyze, reason, and make decisions based on facts, evidence, and logic.
- It also enables them to develop innovative ideas and solve complex problems.
- With critical thinking skills, kids can develop the capacity to recognize their own biases and assumptions and challenge their own ideas and beliefs.
- By teaching kids the importance of critical thinking and incorporating it into their day-to-day activities, we can help them become better decision-makers and problem-solvers.
- By encouraging kids to engage in more critical thinking activities, they become more self-aware and independent, which helps them to make better decisions.
- They also start to build their problem-solving and communication skills, which can be used in various areas of life.
- Finally, with critical thinking skills, kids can gain self-confidence, understand their reasoning, and develop a deeper understanding of the world around them.
Critical Thinking Activities for Preschoolers and Kindergarteners.
Some of the most common critical thinking activities include:
- Storytime,
- Engaging in conversations,
- Asking creative questions,
- Puzzles and riddles,
- Sorting,
- Matching and pairing,
- Introduction to coding and robotics,
- Exploring different scenarios.
These activities help build essential skills such as problem-solving and strengthen the importance of critical thinking abilities for kids.
How to introduce These activities to your kids?
Introducing such activities at a young age can be critical to introduce into their daily routine as this assists with developing cognitive skills and prepares them for academic success.
It also creates an environment where children can foster and practice self-reflection and understanding and encourage independent thought. These activities can include role-playing, problem-solving, question-and-answer sessions, puzzles, story mapping, group discussions, and board games.
- Role plays will help kids identify their actions’ cause and effect.
- Problem-solving will allow them to think before making decisions.
- At the same time, question and answer sessions will help to assess their understanding of concepts.
- Picture completing and story mapping activities will help to develop their memory and imagination.
- Lastly, group discussions will help to build their communication and collaboration skills.
These activities build critical thinking skills in kids, motor skills, and creativity. So, including these classroom activities is essential to help develop their critical thinking abilities.

8 Activities for critical thinking development
These activities can help them explore the world around them, develop their own opinions and make decisions on their own. Here is a list of activities that can help boost kids’ critical thinking abilities:
1. “What am I?”
With regards to these “What am I?” riddles, kids appear to enjoy them. Why not put this inherent enthusiasm to use in some practice of critical thinking? You only need to think of a person, place, or thing and tell your child about it.
“I live in the sky, and I am hot. Don’t look directly at me. I will disappear at night. What am I?”
This is one that your child can easily deduce.
2. Prediction of the story.
When you are reading a story to your child and notice that you are getting close to the end, stop and ask her how she thinks the story will end.
Pay attention to their response. Have fun with the conversation, and ask them to explain their choice. It can be silly and fun, but it should offer some logic to keep the critical thinking flowing.
3. X and O’s
Play X and O’s with your child, but keep it simple using a whiteboard, colorful pens, or even candy to keep it fun. Set your goal to win. Be unforgiving in your gaming abilities and play as a child versus a parent.
Check to see if your youngster can keep up. If not, well, good luck again, little one. Teach them it’s okay to lose, but remember the intention behind it.
4. Start with the current reality
While showing your kid how to go from cereal spilling to the starting strides is logical, it’s most straightforward for you to begin where you are now.
In other words, suppose you just served your child a dinner of chicken, cheesy broccoli, and mashed potatoes. Still, they won’t eat them because the potatoes weren’t from McDonald’s. “How do you know these aren’t from McDonald’s?” you should inquire of them.
Assist them in making the answer more explicit by listening to their explanation.
They could become so perplexed that they might give in, eat the potatoes, focus on their logic, and explain in perfect English why they are not McDonald’s.
5. True or False
This is as simple as it gets. Give your child two sticky notes to complete the task: one with the words “true” and “false” on it.
Say something like, “A group of monkeys is called a herd.” Your child will carefully consider whether the statement is accurate before writing true or false on the right sticky note.
Your child will now describe the reasoning behind the selected sticky note. Enjoy.
6. Community Engagement Activity
This community engagement activity requires analytical skills to figure out what can be recycled in the classroom and their neighborhood. Students can practice social responsibility and socialize with people around them while making recycling bins from recyclable cardboard boxes. They can do this by creating the bins themselves.
7. What can I do?
Students will learn that despite the fact that conflicts are a normal part of life, it is essential to have problem-solving skills to resolve them through this lesson.
You can make notes or a problem-solving wheel for kids and give them a situation. After that, ask your kid to choose what they’ll do in such a situation. Additionally, this is an excellent opportunity to improve their social awareness and interpersonal skills.
8. 25 uses of Me
Pick a regular item and set a clock for five minutes. Ask students to think of 25 ways to use the object in that time frame. Rarities like “coatrack” and “stool” are encouraged because the apparent answers will quickly run out.
What is the takeaway?
In conclusion, critical thinking activities are vital in helping to build a strong foundation for preschoolers and kindergarteners. By providing a balanced mix of activities, kids can develop the ability to think outside the box and become better problem-solvers.
These activities can help kids develop their critical thinking abilities, which can help them later in life. As kids grow older, their critical thinking abilities can help them make better decisions, understand complex topics, and interact with others more efficiently.
Q: How can parents inspire independence in their preschoolers?
A: By giving their preschoolers age-appropriate responsibilities, allowing them to make decisions, and rewarding their efforts and successes, parents may help their preschoolers to be independent. Allowing their child to dress and wash their teeth can support their development of self-help abilities.
Q: How can parents motivate their toddlers to lead healthy, active lifestyles?
A: By giving their preschoolers chances for physical activity, such as outdoor play, dance, and sports, parents may encourage their preschoolers to be active and healthy.
I’m a former teacher (and mother of Two Childs) with a background in child development. I’m here to help you with play-based learning activities and crafts for kids ages 0 – 8. ( Cledemy.com is my Next startup on Pre to 8th Grade Printable and Worksheet Education Resources)
Join our active Facebook group for creative and fun activities, games, and other child development ideas.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Building Critical Thinking in Kids: 4 Proven Strategies
Critical thinking matters for academics, work and relationships. Here’s how to lay the foundations at home.

Prisma is the world’s most engaging virtual school that combines a fun, real-world curriculum with powerful mentorship from experienced coaches and a supportive peer community
When it comes to problem-solving, creativity and critical thinking go hand in hand .
If we understand creativity as a mindset of “yes and,” we can consider critical thinking as, “yes but” — the ability to step back and take distance from the information presented to us, before interpreting it and drawing conclusions.
The importance of critical thinking can’t be overstated: As kids are bombarded with information from a young age — with new channels, platforms and media springing up regularly — they need to balance an open mind with healthy skepticism.
Yet a critical mindset is not enough.
Imagine you were suddenly dropped into a boardroom where they were presenting data on greenhouse gasses while trying to solve climate change. You couldn’t just use your critical thinking skills to make a decision. You would need to know about the science behind it, as well as the geopolitical dynamics that contribute to the problem.
In other words, you can’t teach critical thinking in a vacuum.
As with creativity, critical thinking requires a wide and deep interdisciplinary knowledge base in the topics that you care about. A child’s critical thinking skills must be honed specifically in areas such as media literacy, data literacy, and textual analysis. Just because you learn critical thinking in English doesn't mean you can apply it in science; while certain features are transferable, a child needs the opportunity to learn the important skills and techniques required by each discipline — and take their theoretical knowledge out for a spin in the real world.
Sign up for more research-backed guides in your inbox
- Prisma is an accredited, project-based, online program for grades 4-12.
- Our personalized curriculum builds love of learning and prepares kids to thrive.
- Our middle school , high school , and parent-coach programs provide 1:1 coaching and supportive peer cohorts .
How to help children develop critical thinking skills at home
1. start from their interests.
To build higher-order thinking skills, start with whatever topic or activity engrosses your kids.
For many kids, this means screen time.
“Screentime” often evokes fear in parents, but if kids get news from social media, media literacy is one of the most important life skills we can teach them. Sit with them as they read, and ask them open-ended questions about the material they’re consuming. At the same time, talk about what you read — show them the sites and/or the physical material — and let them know why you trust it.
Pick a current event, something that excites them — it could be anything from a new release from their favorite artist to a local happening — and ask them to find multiple articles for a simple compare-and-contrast:
-What images are being used to accompany the story and what feelings do they evoke? -What does the headline announce, how is the lede presented, and what evidence does the author give to support it?
-How are they impacted by a video versus a written story?
-How is the story presented in the context of the publication?
-When a story is being shared by an influencer on a social media platform, how does that presentation impact their interest in — and belief of — a story?
Data literacy is another facet of critical thinking to introduce to your kids. Our middle school learners make predictions based on data — an activity that can lend itself to kids who love sports or are curious about the stock market.
But there are countless ways to design creative problem solving activities for any discipline: As part of the project-based approach at Prisma, we hold collaborative workshops where kids get the opportunity to solve discipline-specific problems: In the “World of Wonder” theme, Prisma learners decide how to power a city using their knowledge about Earth Science; in “Unsolved Mysteries,” they cross reference different sources of evidence to get to the bottom of historical puzzles; in “Build a Business,” they pretend they are on Shark Tank and decide which businesses to invest in.
It’s all about teaching specific problem solving skills across different contexts: with their interests as a guide, introduce them to a range of disciplines.
Remember, it’s not the what it’s the how: as they acquire different literacies, the experiences will build on one another. Start in their comfort zone, introduce critical thinking activities into whatever engrosses your kids, and then edge outwards.
2. Put them in the driver’s seat
When kids feel empowered to speak up, share — and defend — their opinion, and engage in a back-and-forth with others, you are helping them foster critical thinking skills.
Get your kids involved in their education, give them choice, and plenty of opportunities to practice. This could mean evaluating what book they want to read next or which online math program works best for them. Listen carefully, and ask them to provide justification for their choice. They’ll be less likely to offer empty complaints when they’ll been a part of the process, and more likely to think through productive solutions.
Our Prisma learners know they’ll be asked to give feedback on the curriculum, offer suggestions for future themes, and propose their own clubs. That real-world payoff incentivizes them to give their best: They know they have to engage critically with their education, if they want their opinions to be taken seriously.
3. Practice metacognition
One of the enemies of critical thinking is impulsivity: an idea comes into our head and we instantly are sure it’s right.
The antidote is metacognition (thinking about our own thinking): as we teach kids in our Prisma high school Life Skills curriculum, you need to be aware of your own thought processes and your own biases to be able to step back and loosen your grip on that initial reaction. As kids start to become aware of their own cognitive biases, they learn to recognize them in other people as well.
Math is a great area to practice critical thinking activities: Teach multiple strategies to solve the same problem, and then ask them to explain how they got to the right answer and why they chose a certain approach. If you’re homeschooling as part of a cohort, take the opportunity to have all the kids share their unique, to help emphasize the diversity of potential tactics.
Metacognition can be incorporated at every phase of the learning process, from when they sketch out their first theories to when they present their final version. Get your kids used to talking about why they gravitate towards certain approaches and which ones they might want to consider modifying or phasing out, if they're working to improve a skill or technique. This kind of reflection should be a part of any assessment process, as it feeds directly into developing a growth mindset .
4. Be a role model
Young children learn by watching and imitating. Every interaction with your child is an opportunity to model critical thinking, from the types of questions you ask to your response to the complex problems you face in everyday life.
Walk them through the decision-making process for your household, like how you comparison shop for appliances or choose a birthday party venue. These everyday problems are a great opportunity for you to model metacognition when the stakes are relatively low for them.
Join our community of families all over the world doing school differently.
Want to learn more about how Prisma can empower your child to thrive?
More from our blog
Recommendations.
Prisma Newsletter
- Our Mission

4 Strategies for Sparking Critical Thinking in Young Students
Fostering investigative conversation in grades K–2 isn’t easy, but it can be a great vehicle to promote critical thinking.
In the middle of class, a kindergartner spotted an ant and asked the teacher, “Why do ants come into the classroom?” Fairly quickly, educational consultant Cecilia Cabrera Martirena writes , students started sharing their theories: Maybe the ants were cold, or looking for food, or lonely.
Their teacher started a KWL chart to organize what students already knew, what they wanted to know, and, later, what they had learned. “As many of the learners didn’t read or write yet, the KWL was created with drawings and one or two words,” Cabrera Martirena writes. “Then, as a group, they decided how they could gather information to answer that first question, and some possible research routes were designed.”
As early elementary teachers know, young learners are able to engage in critical thinking and participate in nuanced conversations, with appropriate supports. What can teachers do to foster these discussions? Elementary teacher Jennifer Orr considered a few ideas in an article for ASCD .
“An interesting question and the discussion that follows can open up paths of critical thinking for students at any age,” Orr says. “With a few thoughtful prompts and a lot of noticing and modeling, we as educators can help young students engage in these types of academic conversations in ways that deepen their learning and develop their critical thinking skills.”
While this may not be an “easy process,” Orr writes—for the kids or the teacher—the payoff is students who from a young age are able to communicate new ideas and questions; listen and truly hear the thoughts of others; respectfully agree, disagree, or build off of their peers’ opinions; and revise their thinking.
4 Strategies for Kick-Starting Powerful Conversations
1. Encourage Friendly Debate: For many elementary-aged children, it doesn’t take much provoking for them to share their opinions, especially if they disagree with each other. Working with open-ended prompts that “engage their interest and pique their curiosity” is one key to sparking organic engagement, Orr writes. Look for prompts that allow them to take a stance, arguing for or against something they feel strongly about.
For example, Orr says, you could try telling first graders that a square is a rectangle to start a debate. Early childhood educator Sarah Griffin proposes some great math talk questions that can yield similar results:
- How many crayons can fit in a box?
- Which takes more snow to build: one igloo or 20 snowballs?
- Estimate how many tissues are in a box.
- How many books can you fit in your backpack?
- Which would take less time: cleaning your room or reading a book?
- Which would you rather use to measure a Christmas tree: a roll of ribbon or a candy cane? Why?
Using pictures can inspire interesting math discussions as well, writes K–6 math coach Kristen Acosta . Explore counting, addition, and subtraction by introducing kids to pictures “that have missing pieces or spaces” or “pictures where the objects are scattered.” For example, try showing students a photo of a carton of eggs with a few eggs missing. Ask questions like, “what do you notice?” and “what do you wonder?” and see how opinions differ.
2. Put Your Students in the Question: Centering students’ viewpoints in a question or discussion prompt can foster deeper thinking, Orr writes. During a unit in which kids learned about ladybugs, she asked her third graders, “What are four living and four nonliving things you would need and want if you were designing your own ecosystem?” This not only required students to analyze the components of an ecosystem but also made the lesson personal by inviting them to dream one up from scratch.
Educator Todd Finley has a list of interesting writing prompts for different grades that can instead be used to kick off classroom discussions. Examples for early elementary students include:
- Which is better, giant muscles or incredible speed? Why?
- What’s the most beautiful person, place, or thing you’ve ever seen? Share what makes that person, place, or thing so special.
- What TV or movie characters do you wish were real? Why?
- Describe a routine that you often or always do (in the morning, when you get home, Friday nights, before a game, etc.).
- What are examples of things you want versus things you need?
3. Open Several Doors: While some students take to classroom discussions like a duck to water, others may prefer to stay on dry land. Offering low-stakes opportunities for students to dip a toe into the conversation can be a great way to ensure that everyone in the room can be heard. Try introducing hand signals that indicate agreement, disagreement, and more. Since everyone can indicate their opinion silently, this supports students who are reluctant to speak, and can help get the conversation started.
Similarly, elementary school teacher Raquel Linares uses participation cards —a set of different colored index cards, each labeled with a phrase like “I agree,” “I disagree,” or “I don’t know how to respond.” “We use them to assess students’ understanding, but we also use them to give students a voice,” Linares says. “We obviously cannot have 24 scholars speaking at the same time, but we want everyone to feel their ideas matter. Even if I am very shy and I don’t feel comfortable, my voice is still heard.” Once the students have held up the appropriate card, the discussion gets going.
4. Provide Discussion Sentence Starters: Young students often want to add their contribution without connecting it to what their peers have said, writes district-level literacy leader Gwen Blumberg . Keeping an ear out for what students are saying to each other is an important starting point when trying to “lift the level of talk” in your classroom. Are kids “putting thoughts into words and able to keep a conversation going?” she asks.
Introducing sentence starters like “I agree…” or “I feel differently…” can help demonstrate for students how they can connect what their classmate is saying to what they would like to say, which grows the conversation, Blumberg says. Phrases like “I’d like to add…” help students “build a bridge from someone else’s idea to their own.”
Additionally, “noticing and naming the positive things students are doing, both in their conversation skills and in the thinking they are demonstrating,” Orr writes, can shine a light for the class on what success looks like. Celebrating when students use these sentence stems correctly, for example, helps reinforce these behaviors.
“Students’ ability to clearly communicate with others in conversation is a critical literacy skill,” Blumberg writes, and teachers in grades K–2 can get students started on the path to developing this skill by harnessing their natural curiosity and modeling conversation moves.

Seven Popular Critical Thinking Activities for Preschoolers
In this post, we will discover seven critical thinking activities for preschoolers that are simple, easy to set up and fun to play.
Critical thinking is one of the most important skills that children need to master in order to become successful in tomorrow’s world.
I remember when I was a student, schools relied heavily on memorization and basically repeating as accurately as possible what the teacher or a book said. Schools praised “recorder students”.
Although things have started to change and in some schools, logical thinking is encouraged and taught, unfortunately, many schools still have this antiquated system in which children simply repeat a list of facts.
Kids need to be able to process information, analyze a situation, make inferences, compare and contrast.
As parents, we need to help our children reach a higher level of logical reasoning as it is a prized skill nowadays.
Although children will develop their thinking skills through day-to-day interactions, we can also help them build a strong foundation by playing logical thinking games with them whenever possible.
To this end, here are seven simple critical thinking activities for preschoolers that are easy to set up. Most only require building blocks, pen and paper, toys that you already have in your house or a printable.
This post ma y contain affiliate links and I may earn a small commission when you click on the links at no additional cost to you. As an Amazon Affiliate, I earn from qualifying purchases. You can read my full disclosure here .
Thinking Games for Preschoolers
The odd one out.

The Odd One Out is a great thinking game to play with kids. It improves their critical thinking by using their knowledge of patterns, vocabulary, differences and similarities.
There are a few ways of playing The Odd One Out:
- online games
- using toys around the house
- as a listening activity by saying words
For those who are new to this game, let me explain it. You present the child with four objects or images. Three of those objects have something in common while the fourth is not connected in any way to the three. The child has to identify the “intruder”. Of course, the game is not limited to four objects, you can choose to have more.
What Comes Next (Patterns)

A good yet simple reasoning game for kids is What Comes Next. Patterns teach children what comes next thus teaching them to make logical connections and use their critical thinking.
Understanding patterns help us make educated guesses, assumptions and provide order in a world that may seem chaotic.
What Comes Next is a simple game that, like The Odd One Out, can be played using worksheets, toys around the house, apps and computer games.
I like playing this game with building blocks as it allows me to practice colours, sizes, numbers and more.
Books offer great opportunities to practice reasoning skills.
When reading to your child, simply stop and ask open-ended questions like “What do you think will happen to X (the character)?” or “What do you think X will do now?”
This will encourage the child to make assumptions and come up with creative answers.
There’s nothing better than a riddle to fire up those brain cells and improve their thinking skills. Riddles are great because they help children focus on one problem until they find the solution, they exercise the brain (like any muscle, it needs to be used in order to stay in shape), they encourage children to think outside the box and come up with creative answers, not to mention that they are fun and don’t need any prep work.
The internet is full of riddles for kids so all you have to do is search for some. Here are some ideas.
Match the shadow

Shadow Matching is a simple activity for young kids that helps them enhance their problem-solving skills. It is a great activity for visual discrimination and memory, observing patterns, similarities and differences.
You can download this cute Farm Animals Shadow Matching Game for free.
Tic Tac Toe

Most of us are familiar with this game as it has been around for a very long time (ancient Egyptians have invented it, would you believe it).
Tic Tac Toe is a simple game, although apparently there are 255.000 different outcomes, that can be played with kids as young as two or three years of age.
The rules are easy to understand: there are two players, one has X as a symbol and the other one a 0. They play on a 3×3 grid and the goal is for the players to put their symbols three times in a row, either vertically, horizontally or diagonally.
You can play Tic Tac Toe either the traditional way, with pen and paper, or get the game with manipulatives which will definitely be more attractive for kids.
This Tic Tac Toe from Melissa&Doug looks fantastic!
Choose something…

This is a simple, yet effective critical thinking activity for preschoolers, although it can very well be played with toddlers as well.
You can play this game using either images or toys around the house. The idea is simple: present the child with six toys (there can be more or less depending on the child’s age). Make sure that some toys have similarities (colour, shape, material etc).
The child has to choose the correct toy/image based on your description. Take the picture above as an example. Some of the sentences that I used with my boy were:
- Choose something that is round but hasn’t got bumps on it.
- Choose something that is a cube and made of wood.
- Choose something that is a cube but hasn’t got numbers on it.
- Choose something that has a square shape but it’s not a cube.

Although it is true that children will develop their critical thinking through everyday interactions, we can always help them boost this very important skill by playing games with them like the ones presented above.
Brain-Boosting Memory Match Games
Fun Activities for Critical Thinking
Shape Matc hing Activity from Recycled Paper
Activities for Thinking Skills Development
I hope you found this post useful and that these critical thinking activities for preschoolers will provide moments of fun and learning for your little one(s).
If you liked this article don’t forget to share it 😉

Mom of two wonderful children, dedicated teacher and book lover.
5 thoughts on “Seven Popular Critical Thinking Activities for Preschoolers”
Great ideas! My daughter is about to start preschool and one of the activities we were encouraged to do over school holidays was asking to guess what will happen next in a book. I think she’d really enjoyable the other suggestions too.
These are all great ideas that are sure to get kids engaged! I know for sure my four year old loves questions, so he’ll respond really well to these. Thank you for the fantastic post 🙂
Great activities. I love engaging kids in critical thinking activities and puzzle, keeps their mind sharp and help develop their problem solving skills.
You have great ideas for preschool critical thinking activities! Lately, my three-year-old daughter has been into doing pattern activities. We have a large bowl of those colored glass flat stones that you find at an arts and craft store. We made really cool patterns with them by color. The other day, she made a super long pattern with them going down the hallway!
Critical thinking is such an important skill to pass to our children. Thanks for the tips!
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- NAEYC Login
- Member Profile
- Hello Community
- Accreditation Portal
- Online Learning
- Online Store
Popular Searches: DAP ; Coping with COVID-19 ; E-books ; Anti-Bias Education ; Online Store
Message in a Backpack™. Asking Questions to Stretch Your Child’s Thinking

You are here
When you ask your children questions—especially big, open-ended ones—you support their language development and critical thinking. Instead of asking questions with a one-word answer (“Who is your friend?”) or only one right answer (“What color is the crayon?”), try to open the door to conversations in a new way. During family routines like mealtimes or bathtime, while reading bedtime stories together or taking walks, or when you ask your child about their day at preschool, use the following strategies to encourage them to talk about themselves, their ideas, and their reflections.
1. Ask open-ended questions to spark conversations. Pose questions that will encourage your child to analyze, evaluate, and create, such as
- What was the best (hardest, funniest, saddest) thing about your day at preschool?
- What book did your teacher read today? Tell me the story.
- If you had written the story, how would you have changed it?
- If you were cooking for our family, what would you make for breakfast (lunch, dinner)? Why?
(See “Sample Open-Ended Questions” below for more examples.)
2. Allow plenty of wait time. Children need time to process what you’re saying, think about it, and then answer. Give them at least a few seconds to respond, and vary the time according to their needs. You know your child best! If the question is one they don’t yet have the vocabulary to answer, modify it. During bathtime, for example, if your child doesn’t answer when you ask where they think it would be most fun to take a bath, ask if they would rather take a bath at home or at Grandma’s house and why. As your child grows and develops, their vocabulary will expand.
3. Listen to your child’s responses. Use active listening strategies: make eye contact, encourage your child to share their ideas, and restate or summarize what they say. For example, “You’ve told me that you love all of the books your teacher reads about animals. Let’s go to the library and see if we can find some other books about animals to read at home. Which animals would you like to start with?”
4. Ask another question or make a comment after your child answers. This further extends your conversation. If you aren’t sure how to respond, you can almost always say, “What else can we add to that?” or “Tell me more about that.” For example, “You told me yesterday that your favorite song in preschool is ‘Wheels on the Bus.’ Let’s make up a song to that tune to sing at breakfast that starts with, “One food on the table is toast, toast, toast . . .”
5. Have fun together! Don’t be afraid to use some big, juicy words to expand your child’s vocabulary. You’ll be amazed how they add these words to their conversations, once introduced. For example, “You have told me so much about the rock collection in preschool. Maybe you will be a geologist when you grow up.” Or “Let’s listen to that song you told me about when an orchestra performs it, rather than just a small band.”

Download the PDF for this Message in a Backpack™ here!
Sample Open-Ended Questions
Questions to ask about your child’s day:
- Did something happen today that made you feel proud? Tell me about it.
- What book did your teacher read today? Tell me the story.
- What foods did you see at preschool today that were new or different? Tell me about them.
Questions to ask during mealtimes:
- What are some words we could use to describe the chicken (rice, vegetables) we’re eating? Let’s think of words that describe how it smells (tastes, sounds like when we chew).
- How could we make a menu to show what we’re going to have for dinner tomorrow?
Questions to ask before a bedtime story:
- What do you think the story will be about? (Look at the front and back covers.)
- Do you think this will be a story that really happened (nonfiction) or a pretend story? Why?
- What does the illustration (picture) on the front (back) cover make you think of? How does it make you feel? Why?
Questions to ask after reading a bedtime story:
- What did you think about the story? Did you like it? Why?
- What was your favorite part? Why?
- Can you think of a different ending? Tell me about it.
- What would you like to tell the author (illustrator) about the book?
To read more, check out Big Questions for Young Minds , by Janis Strasser and Lisa Mufson Bresson, published by NAEYC. Visit NAEYC.org/resources/pubs/books/big-questions-young-minds .
Photograph: © Getty Images Copyright © 2024 by the National Association for the Education of Young Children. See permissions and reprints online at NAEYC.org/resources/permissions .
Janis Strasser is professor emerita from William Paterson University. She has been a kindergarten/preschool teacher, Head Start education coordinator, and consultant, and she has written many articles for Young Children and Teaching Young Children . For the past several years, Dr. Strasser has been working with preschool teachers on the island of Anguilla during the winter months.
Vol. 17, No. 3
Print this article
🎨 Free Coloring Book for Kids Get your copy →
- Why Kokotree?
- Learning App for Toddlers
- Learning App for Preschoolers
- Download Kokotree App
- About Kokotree

EduTech Award Winner
Kokotree Early Education App
- Preschool Games and Activities
Critical Thinking Activities for Preschoolers
Written by: Kokotree
Last updated: October 16, 2022

K ids are sponges. They soak up information and learn new things every day, whether we realize it or not! One of the best things we can do as parents are to help foster our children’s natural ability to think critically by providing engaging critical thinking activities for preschoolers.
What is Critical Thinking for Preschoolers?
Why teach preschoolers critical thinking, how to teach preschoolers critical thinking, here’s a list of critical thinking activities suitable for preschoolers:, the importance of predictions, the observation phase, discussing results, reading to complement experiments, the takeaway for parents, toy scenarios, relational language, drawing maps, real-world applications, parental involvement, starting simple, adding complexity, story-based patterning, encourage observations, parent tips, fold and cut, mirror images, symmetry in nature, question and understand, what parents should know, picture cards, daily routines, storytime sequencing, cooking together, parent’s role, a skill for life, animal sorting, food categories, color coding, advanced classifying, ask questions, skill building, simple pairings, attribute matching, word pairings, “what doesn’t belong”, ask open-ended questions, why analogies matter, mixed criteria, question and discuss, importance for cognitive development, basic counting with objects, count and compare, counting games, skip counting, the “guess the number” game, subtraction and addition, why counting matters, using everyday scenarios, hands-on activities, beyond just numbers, make it a game, questions to prompt thinking, importance in daily life.
Critical thinking for preschoolers refers to their ability to process information independently, make connections, reason, and make well-thought-out decisions. It involves encouraging curiosity, asking questions, and understanding the “why” behind concepts.
Teaching critical thinking to preschoolers is essential as it fosters independence, boosts problem-solving skills, and prepares them for future academic and life challenges. It also enhances their creativity, adaptability, and ability to navigate complex situations.
To teach preschoolers critical thinking, introduce open-ended questions, provide hands-on experiences, encourage curiosity, engage in storytelling, promote problem-solving activities, and create an environment where they feel safe to express ideas and make mistakes.
- Sorting and Categorizing : Provide a mix of objects and have them sort them by various attributes (color, size, shape, texture).
- Story Sequencing : Use picture cards to tell a story and ask them to arrange them in the correct order.
- What’s Missing? Game : Set up a few items, let the child study them, then remove one when they aren’t looking and ask which one is missing.
- Pattern Recognition : Use colored blocks or beads to create a pattern and have them continue it.
- Cause and Effect Experiments : Simple experiments like “What happens when you drop a ball?” or “What happens if you put paper in water?”
- True or False Questions : A type of assessment where learners decide whether a given statement is accurate, often used to test knowledge on specific facts or concepts quickly.
- Memory Games : Classic games like ‘Simon says’ or matching card games.
- Question of the Day: Start the day with an open-ended question like, “Why is the sky blue?” or “How do plants grow?”
- Role Play : Encourage them to act out different scenarios, which helps in understanding different perspectives.
- Building Challenges: Using blocks or LEGO, set a challenge like “Can you build a bridge?” or “Make a house with a garage.”
- Problem Solving Scenarios: Give them hypothetical problems to solve, like “What would you do if your toy broke?” or “How can you share three apples with four friends?”
- Picture Interpretation: Show them a complex picture and ask open-ended questions about what they see, think, and wonder.
- Mystery Bag: Put an object in a bag and have them feel it without looking, then guess what it is.
- Puzzle Time: Regular puzzles are great for problem-solving and spatial recognition.
- Would you Rather Questions : Fun scenarios like “Would you rather be a fish or a bird?” This encourages reasoning and justification.
- Exploring Nature: Nature walks where they can observe, question, and learn about the environment.
- Music Exploration: Play different types of music and discuss how each one makes them feel.
- Story Creation: Give them a start, like “There’s a dragon in the garden…” and let them continue.
- Sensory Bins : Bins filled with sand, water beads, rice, or other materials where they can explore, measure, and experiment.
- Group Discussions: After a story or activity, discuss as a group what happened, why, and what might happen next.
- Prediction Activities: Activities where they predict what might happen next, whether in a story or a simple experiment.
Integrating these activities into a preschooler’s daily routine will help foster an environment of curiosity, exploration, and deepened understanding.
Science Experiments
Science experiments offer a unique avenue for diving into critical thinking activities for kids. Let’s break down how you can turn simple experiments into a world of exploration and reasoning for your little one.
Before starting any experiment, ask your child to make a prediction. Whether it’s guessing what color will result from mixing two paints or what will happen when you add salt to ice, predictions engage your child’s anticipatory skills.
While performing the experiment and science activity , encourage your child to observe keenly. What do they see, smell, or hear? Encourage them to note these observations down or share them with you. This engages their senses and promotes active learning during preschool .
After the experiment, sit down with your child and discuss what happened. Compare their initial predictions with the actual results. Did something unexpected happen? Great! This is a fantastic moment to introduce the concept of ’cause and effect,’ a cornerstone in critical thinking for preschoolers.
Consider pairing these experiments with related books. Reading material can help cement the scientific concepts you’ve explored, making the learning experience well-rounded.
Your role is crucial. The questions you ask and the encouragement you give can transform a simple science experiment into a treasure trove of critical thinking activities. It’s not just about the ‘doing’; it’s also about the ‘thinking’ that goes along with it.
By taking the time to prepare, observe, and discuss, you’re not just teaching science but instilling critical thinking skills that will last a lifetime.
Spatial Relationships
Understanding spatial relationships is a key aspect of critical thinking preschool activities. Not only does this skill lay the groundwork for geometry and other advanced math concepts, but it also helps your child navigate through the world more effectively. So, how can you turn understanding spatial relationships into a critical thinking exercise for your preschooler?
Start by engaging your child with simple toy scenarios. For example, provide your child with a toy car and present a challenge: Can they position the car “under” the table or “next to” a book? This forces them to think critically about space and how different objects relate.
In these spatial activities , the language you use is crucial. Words like “under,” “over,” “next to,” “behind,” and “in front of” enrich their vocabulary and conceptual understanding. Make a game out of it; ask them to place their toy “beside” the couch, then “beneath” a chair, and so on.
Drawing simple maps can also be a fun way to explore spatial relationships. You and your child can draw a map of a room in your house or even a treasure map. This helps your child think critically about space on a two-dimensional scale.
Use real-world situations to apply these concepts. For example, you could ask your child to help you find the shortest path from the car to the entrance of a store. This engages them in problem-solving and turns an everyday task into a critical thinking game for kids.
Your involvement is essential. The prompts you give and the questions you ask can be geared towards understanding the reasoning behind their choices. Why did they think the car should go “under” the table and not “on top of it”? Their answers can offer insightful glimpses into their thought processes.
Integrating these activities into your child’s routine provides essential tools for their cognitive development. It’s not just about understanding spatial relationships; it’s about setting the foundation for logical reasoning and problem-solving—skills that are vital for future learning.
Patterning is an enjoyable and instructive way to introduce activities to develop critical thinking skills in preschoolers. Recognizing and creating patterns help children understand order and make predictions, essential skills for both math and everyday life. So how can you engage your child in patterning activities?
Begin with straightforward activities. Give your child a set of blocks in different colors or shapes and ask them to arrange them in a simple pattern, like “red-blue-red-blue” or “circle-square-circle-square.
You can introduce more complex ones as they get comfortable with simpler patterns. For example, try a pattern that involves more than two colors or shapes, like “red-blue-green-red-blue-green.”
To make it more engaging, try creating a story around the pattern. Maybe the colored blocks are “cars in a parade” or “fruits in a basket.” Stories make the patterns more relatable and help in creating a rich context around what might otherwise be an abstract concept.
After your child has made a pattern, ask them to describe it to you. What do they see? What comes next? Why? This forces them to articulate their thought process, thereby improving both their language and critical thinking skills.
Your involvement in these patterning activities amplifies their effectiveness. Ask open-ended questions like, “Why did you choose to put the red block there?” or “What do you think comes next?” Your questions can guide them through the reasoning process, making these exercises not just patterning activities but also reasoning activities for preschoolers.
By incorporating patterning into playtime, you’re doing more than teaching colors and shapes; you’re instilling the ability to recognize relationships between objects—a skill that forms the basis of logical reasoning and critical thought.
Symmetry is not just an aesthetic concept; it’s a brilliant way to cultivate critical thinking in preschoolers. When children recognize or create symmetrical objects or arrangements, they’re learning about balance, equality, and relational properties—core elements in critical thinking preschool activities . Here’s how you can engage your child with symmetry.
The easiest way to start is by folding a piece of paper in half and cutting shapes along the folded edge. When you unfold the paper, you’ll have a symmetrical shape. Ask your child what they notice about the two halves. Are they the same or different? Why?
Another activity is to place a small divider between two identical sets of blocks. Build a pattern or shape with one set and ask your child to replicate it as a mirror image using the other set of blocks. This not only teaches symmetry but also enhances their observational skills.
Take a nature walk and ask your child to find examples of symmetry, like leaves, flowers, or even animals. Discuss what makes these objects symmetrical. This offers a more dynamic, interactive approach to understanding symmetry and engages them in critical thinking games for kids.
As always, your involvement and the questions you ask can bring depth to the activity. Why is it easier to find symmetry in some objects than in others? Why do they think symmetry exists in nature? These questions prompt deeper thinking and understanding.
Symmetry activities are more than just a game; they provide a foundation for more complex mathematical concepts like geometry. Furthermore, they encourage your child to think about balance and fairness, abstract concepts that have real-world applications.
Symmetry activities offer a multi-faceted approach to critical thinking for preschoolers, combining math, nature, and everyday observations into a rich tapestry of learning experiences.
Subscribe to Kokotree!
Get free parenting tips, news, updates, and content from Kokotree.
Sequencing is an invaluable exercise that aids in developing a wide range of skills, from language and literacy to logic and problem-solving. This makes it one of the must-try critical thinking activities for preschoolers. Below are some ways you can approach sequencing with your child:
Start simple by using a set of picture cards that tell a story. Scatter them and ask your child to place them in a logical order. This helps them understand the concept of beginnings, middles, and ends, crucial for both storytelling and understanding sequences in daily life.
Use everyday routines as an opportunity for sequencing activities. Whether it’s getting dressed, preparing a simple snack, or cleaning up toys, ask your child to describe the sequence of actions needed to complete these tasks. This not only cements their understanding of everyday activities but also naturally integrates critical thinking into their day.
During storytime, pause to ask your child what they think will happen next or what came before a specific event. Encourage them to explain their reasoning. This turns storytime into an exercise in prediction and recall, both important components of sequencing and critical thinking for preschoolers.
Involve your child in simple cooking or baking activities . Ask them to describe the sequence of steps involved in the recipe. This not only helps in understanding sequencing but also incorporates elements of measurement and timing, adding layers to their critical thinking skills.
Your role is to facilitate and challenge. Ask questions like, “What will happen if we change the order of these steps?” or “Why do you think this comes after that?” By doing so, you’re transforming simple sequencing activities into deeper reasoning activities for preschoolers.
Sequencing isn’t just for stories or games; it’s a skill your child will use in academic settings and everyday life. By incorporating sequencing into various activities, you’re providing your child with a toolbox of skills for organizing information, problem-solving, and critically thinking about the world around them.
Classifying
The ability to classify and categorize is fundamental to human cognition and an excellent entry point for critical thinking preschool activities. Classifying allows children to make sense of the world by grouping items based on shared characteristics or qualities. Here are some ways to involve your preschooler in classifying activities:
One of the most engaging ways to introduce classification is through animals. Provide your child with a set of toy animals and ask them to group them by various criteria: type (mammals, birds, reptiles), habitat (water, land, air), or even by the number of legs. This exercise not only enhances their understanding of biology but also hones their observation and reasoning skills.
Another fun activity involves sorting food items. You could give your child a mix of plastic fruits, vegetables, and junk food items and ask them to separate them into corresponding categories. This also serves as a great opportunity to discuss healthy eating habits .
For younger children, color can be the most straightforward attribute to classify. Offer them an assortment of beads, blocks, or other multi-colored items and ask them to sort these based on color. This is a simple yet effective exercise in classification.
As your child becomes more proficient, you can introduce multiple levels of classification. For example, they could first sort animals by type and then sort those types by size or diet. This adds layers to their critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
Remember, your involvement is crucial. Asking questions like, “Why did you decide to group these together?” or “What makes these items similar or different?” can deepen their understanding and turn the activity into a rich discussion. This elevates it from a mere exercise into a critical thinking game for kids.
Classification activities offer much more than just an understanding of categories. They help build logical thinking, improve vocabulary, and can even introduce basic scientific concepts. These are all essential stepping stones in developing robust critical thinking skills for your preschooler.
By regularly incorporating classifying exercises into your child’s playtime, you are actively helping them construct a framework for understanding the world in a more organized and logical manner.
Analogies are one of the more advanced yet highly effective critical thinking activities for kids. They challenge children to identify relationships between disparate things by finding a common thread. While it may seem like a complex skill, it can be broken down into simpler components for preschoolers to understand. Here’s how to make analogies an accessible and engaging activity for your little one.
Begin with objects that are obviously related but different, like an apple and an orange. Ask your child to explain how they are similar or different. The goal is to get them thinking about attributes that aren’t immediately obvious, like the fact that both are fruits despite differing in color, taste, and texture.
Provide your child with a collection of assorted items and ask them to match them based on one common attribute. For example, a spoon and a fork could be matched because they’re both utensils, even though one is used for scooping and the other for piercing food.
As your child becomes more comfortable with the concept, move on to word-based analogies. You could start with opposites like hot/cold or day/night. Ask your child what makes these pairs opposites and to think of other examples.
A fun twist on analogies is the “What doesn’t belong?” game. Present your child with a group of three or four items where one item is notably different. Ask them to identify the odd one out and explain why it doesn’t belong. This game turns analogies into critical thinking games for kids that are both educational and engaging.
As always, your participation enhances the activity. Ask open-ended questions like, “Why do you think these two are alike?” or “Can you think of other things that are similar in this way?” These questions encourage a deeper exploration of the concept, making it an excellent activity to develop critical thinking skills.
Analogies help build a variety of skills including vocabulary, reasoning abilities, and problem-solving skills. They encourage children to make connections between different pieces of information, a critical skill not just in academic settings but in everyday decision-making.
By incorporating analogies into your routine, you help your child develop an essential tool for interpreting the world around them, boosting their critical thinking and cognitive abilities.
Sorting and Categorizing
Sorting and categorizing activities are foundational for preschool-aged children and serve as a cornerstone for developing critical thinking skills. They not only help kids recognize patterns but also teach them how to make educated judgments. Here’s how you can make sorting and categorizing a fun and enlightening experience for your little one.
Sorting by shape is one of the simplest ways to begin. Provide your child with an array of different shapes like circles, squares, and triangles. You can use household items like buttons, blocks, or even cut-out paper shapes. Ask your child to separate these items into different piles based on their shapes.
Colors offer another straightforward criterion for sorting. You can use colored balls, beads, or toys and ask your child to group them based on their color. This is a simple but effective way to get children to focus on characteristics, thereby introducing them to the basics of categorization.
Sorting by size provides a slightly more advanced challenge and introduces the concept of relativity. Give your child a mix of big and small objects, and ask them to sort them into ‘big’ and ‘small’ groups. As they get better at this, you can introduce medium-sized items for a greater challenge.
As your child becomes more proficient, you can make the activity more complex by mixing criteria. For instance, they can sort by both color and size, creating groups of small red items, large red items, small blue items, and so on. This type of multi-criteria sorting is a great way to sharpen their critical thinking abilities.
Make sure to ask questions during these activities. Queries like, “Why did you put this here?” or “What makes these two items the same?” promote reasoning and dialogue. You can thereby elevate sorting and categorizing from a simple task to one of the essential critical thinking activities for preschoolers.
Sorting and categorizing lay the groundwork for mathematical concepts and logical reasoning. These activities train the mind to identify, compare, and analyze objects based on specific characteristics, making them powerful tools in shaping a child’s cognitive abilities.
Sorting and categorizing can be as simple or as complex as you make them, but their benefits for critical thinking and overall cognitive development are immense. By incorporating these activities into your child’s routine, you’re setting the stage for more complex intellectual feats as they grow.
Counting may appear to be a simple skill, but it’s much more than just reciting numbers. It’s a fundamental aspect of early education that sets the stage for more advanced math and critical thinking skills. Here’s how to make counting a multifaceted learning experience for your preschooler.
Start with the basics by using everyday objects like toys, fruits, or even items in a room. Ask your child to count them and tell you how many there are in total. This not only teaches them to associate numbers with quantities but also introduces them to the concept of ‘totality’—an important foundational idea for future math skills.
Once your child can count confidently, introduce them to the concept of comparing quantities. Place two groups of objects in front of them and ask questions like, “Which group has more?” or “How many more cars are there than trucks?” This introduces them to the skill of evaluating quantities, an essential part of critical thinking.
Turn counting into critical thinking games for kids. Whether it’s counting the number of steps in a staircase as they climb or counting the number of red cars they see while on a drive, games make the counting process engaging and fun.
As your child becomes more proficient, you can introduce the concept of skip counting—counting by twos, fives, or tens. This helps them understand multiplication at an early age and strengthens their number sense, paving the way for more complex math skills.
For a fun twist, you can play the “Guess the Number” game where you think of a number within a range they can understand, and they have to guess it. This helps them understand the concepts of ‘greater than’ and ‘less than,’ valuable tools for reasoning activities for preschoolers.
Simple addition and subtraction can also be introduced through counting. For example, you can start with five apples, take two away, and then ask how many are left. Or you could add two more and ask how many there are now. This helps your child understand the principles of arithmetic in a hands-on manner.
Counting isn’t just a math skill; it’s a critical thinking skill. It lays the groundwork for understanding more complex relationships between numbers and fosters logical reasoning skills that will be crucial in later stages of education.
By incorporating these various counting activities into your child’s routine, you’ll be helping them develop not just their ability to count but also their critical thinking abilities, making it a quintessential activity for their cognitive development.
Comparing Quantities
The ability to compare and contrast different quantities is not just a math skill; it’s one of the important activities to develop critical thinking skills. This skill helps children understand relationships between different sets, a critical component for problem-solving and logical reasoning. Here are some ways to explore this concept with your preschooler.
Begin with two sets of clearly different quantities. For instance, you could use four apples and two oranges. Ask your child to point out which set has more and which has fewer items. Reinforce the terms “more,” “less,” and “equal” to build their comparative vocabulary.
Use day-to-day experiences to create comparative situations. For example, you could ask, “Are there more people in the living room or the kitchen?” or “Do we have more forks or more spoons?” These questions not only hone their observational skills but also make them critically evaluate their surroundings.
Use toys or building blocks to physically create sets of different quantities. Ask your child to compare them. This hands-on approach can make abstract concepts more concrete for young minds.
Expand the concept of comparison beyond mere numerical quantities. For instance, ask them to compare the heights of different family members , the size of different rooms, or the loudness of different sounds. This broadens the scope of comparison and enhances their critical thinking skills.
Introduce critical thinking games for kids that focus on comparing quantities. For example, play a game where they have to divide a set of toys among siblings or friends, ensuring everyone gets an “equal” number. This not only reinforces the concept of comparison but also introduces the idea of fairness.
Always remember to ask follow-up questions. Inquire, “How did you know this set has more?” or “What makes you think there are fewer blocks here?” This encourages them to articulate their thought process, deepening their understanding and reasoning abilities.
Understanding the skill of comparing quantities is essential in daily decision-making. It aids in evaluating choices and in forming reasoned judgments. Therefore, it is an indispensable skill, relevant not just as a form of critical thinking for preschoolers but as a life skill.
Teaching your child to compare quantities provides them with the tools to make better decisions, solve problems , and navigate the world more effectively. It’s a cornerstone activity in developing their overall cognitive abilities.
Overall, preschoolers can engage in many different critical thinking activities to help develop their cognitive abilities . By providing your child with opportunities to learn, explore, and think critically, you can help them become more confident and capable learners throughout their lives!
Stay Up to Date with Kokotree!
Be the first to know about new content launches and announcements.
Kokotree News

Basic Sign Language for Toddlers

10 Stories That Inspire Coping Skills in Kids

Preschool Safety: An Essential Guide for Parents

How to Teach Preschoolers First-Principles Thinking

How to Teach Preschoolers Second-Order Thinking

Coloring for Problem-Solving Development in Preschoolers
Featured posts.

Sign Up for Kokotree! Start Now!
Already have an account? Sign in
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Use .
Looking for strategies or have questions about how to support your child’s education? Ask our AI-powered assistant.
Parent Resources for Learning > Critical Thinking > 5 Fun Critical Thinking Games to Play with Your Child
5 Fun Critical Thinking Games to Play with Your Child
by Dr. Jody LeVos | Mar 27, 2024 | Critical Thinking

Playing games is a great way for your child to develop their critical thinking skills—and the metaphor of a game is a great way to think about these important life skills!
Every time your child works through a problem they need to solve, a sequence they need to memorize, or a decision they need to make, they’re making their way toward the goal of improving their critical thinking.
It’s like a game where the reward at the end is better decision-making, stronger reasoning skills, and academic and professional success!
Kids will keep playing this game over the course of their lives, connecting new ideas to old ones and discarding one opinion for another. Each time, they’ll get better.
Ready to start? We’ve got some fun and easy game ideas for you!
The Short Cut
- Critical thinking is one of the 5 C’s that help kids thrive in school and life (an essential part of the Begin Approach to learning)
- The ability to think critically—as opposed to being intelligent—has been linked to wellness and fewer “negative life events”
- Good critical thinking activities often involve following rules, breaking tasks into sequences, asking questions, and understanding multiple perspectives
- Games (like this memory game ) are a fantastic way to develop critical thinking with kids because you can slip in challenges with the fun!
Why Is Critical Thinking Important?
Critical thinking is a necessary skill for understanding the world.
Through weighing options, studying different perspectives, and making good choices, our children can lead their lives in a positive and healthy way.
Critical thinking allows our kids to:
- Analyze information and make decisions
- Recall short sequences of information and simple instructions
- Ignore distractions to focus on a task
- Grasp the differences between sources of information
- Reason using logic
- Make connections between things
It’s one of the most important contributors to their overall well-being!

6 Critical Thinking Exercises for Everyday Life
Games aren’t the only critical thinking exercises that work well for kids. They also encounter many opportunities to build their skills on any given day.
How can you tap into those chances? Try these techniques.
1. Explain Things
No doubt you often find yourself on the receiving end of your child’s questions. Try to answer all of them. Daunting as that might sound (we know!), this helps your child learn how to formulate the questions they need to ask to make good judgments.
2. Back Up Rules with Good Reasons
Help your child understand the reasons behind rules. (A typical Q&A volley: “Please find a quiet activity to do after dinner.” “Why?” “Because your brother is asleep and we don’t want to wake him up.”)
This kind of exchange allows your child to understand why you’re asking them to do something, which fosters critical thinking.
3. Play Real-Life Problem-Solving Games
Playing strategy games—even simple ones designed for kids—develops analytical skills. You can also have fun turning household tasks into problem-solving games, like figuring out which socks go to which person when you’re folding laundry.
4. Cultivate Curiosity
Encourage your child to ask questions and dig deep to find answers. Curiosity leads to challenging assumptions and gaining new information. Ultimately it helps your child develop complex thinking skills.
5. Encourage Open-Mindedness
Help your child learn to be flexible in their thinking by giving them time to gather information before they make decisions. Considering various solutions helps kids learn that more than one way to do things can be correct.
6. Model Analytical Thinking
Our kids are always watching us. One of the best ways to influence your child’s critical thinking skills is by talking through decisions as you make them. (“I want to walk to the store. I can take a shortcut, but it’s on that dirt path and I’m wearing new sneakers. I want to keep them clean, so I’ll walk on the road instead.”)
5 Games to Guide Your Child’s Critical Thinking

There are many educational critical thinking games you can play at home that help kids improve their skills! We’ve gathered a few we love:
This classic guessing game encourages analytical thinking and problem-solving skills (like deduction) as your child searches for specific objects based on clues.
Plus, it‘s highly portable! Play it in the car, on a walk, or even at the grocery store!
What You Need
- Nothing except space!
- Explain you’ll take turns identifying an object in your space.
- Model the game by going first. Choose an object that both of you can see.
- Then share one detail about it. (“I spy something purple.”)
- Ask your child to guess what you’ve chosen.
- If your child is stumped or getting frustrated, add more clues (“The purple thing is a food, and it’s over by the apples.”)
- Trade roles so that your child chooses something for you to guess.
More Ways to Play
- Choose different rules, such as “the object has to start with a specific sound or letter of the alphabet,” or “share three adjectives that describe the object,” or “make up one phrase this object might say”
2. Once Upon a Time
Storytelling is a great way to work on critical thinking skills like understanding cause and effect, choice-making, and sequencing. This game also taps into kids’ creativity (another one of the 5 C’s) through making up stories.
- Nothing but your imagination!
- Explain you’re going to build a story together by taking turns, one sentence at a time. You can give an example by reciting a story that your child already knows.
- Give an exciting first sentence that jumps into action, such as, “Once upon a time, a kid was on a rocket ship headed to Mars, when a meteor hit and fuel began to leak.”
- Ask your child to continue the story. If they get stuck, try asking them questions like “What did the rocket ship do next?” or “What did the kid do first to fix the problem?” or “How did the kid feel?”
- Continue taking turns until you come to a natural ending.
- Write down the story as you tell it, then read it out loud
- Create a book out of the story, using paper, markers, and a stapler or tape (art projects use many critical thinking skills)
- Use a prop to center the story around, like a toy or a stuffed animal
- Go outside and tell a story based on what you imagine you see in the clouds
3. Bet You Can Build It!
Designing a structure takes curiosity, planning, trial and error, and problem-solving. You can turn this activity into a game by laying out rules to follow.
- Marshmallows
- Craft sticks
- Cardboard tubes
- Anything else you’ve got at home!
- Gather your materials.
- Give your child the rules for the building challenge. (“Create the tallest building you can without it tipping over” or “Use all the marshmallows and toothpicks.”)
- Work on the structure together or each do your own.
- Celebrate when you’ve finished!
- Use a timer to add urgency to the game
- Bring the game to the floor and use bigger building materials, like blocks or plastic bricks
- Bring it outside and use objects found in nature
Get your child moving their whole body as they use planning, organization, and problem-solving skills to find their way through a maze.
- A surface to draw on, like a sidewalk, driveway, or playground blacktop
- Objects to use as obstacles
- A finish-line treasure (a favorite toy, a treat, etc.)
- Draw a maze with chalk. Try making a path by drawing borders on each side or a “tightrope” by only drawing one line your child will need to balance on as they walk.
- Add dead ends to make the maze more challenging.
- Use objects to create obstacles for your child to problem-solve a way past.
- Add a treasure at the finish to engage their imagination.
- Have your child start at one end and try to find their way through!
- Hone in on the treasure component of the maze by creating a scavenger hunt .
- Ask your child to draw a map of the maze when they’ve finished.
5. Obstacle Course
An obstacle course builds real-life skills. To get through their days, kids need to be able to remember lots of information (just think about all the rules at school!).
They also encounter problem-solving based on sequencing and memorizing shortcuts, directions, and solutions.
Think about learning how to write. Letters have to be in a specific order to make a word. That’s sequencing.
Or you may allow your child to walk to school or the bus stop on their own. That’s all about memorizing directions.
Obstacle courses can help them practice these skills!
- Masking tape or chalk
- Jump rope or broom
- Big bouncy ball
- Play tunnel, table, or chair
- Board or pool noodle
- Log and plank
- Pillows, bean bag chairs, or large stuffed animal
- Any other objects you want!
- Gather your objects—you can play this game inside or outside.
- Design a path for your child by placing interactive objects along it. For instance, they can jump over the broom, crawl under the table, and balance on the log and plank.
- Show your child the sequence. You can demonstrate it or have them do a trial run.
- Let them start!
- Try asking your child to do the course backwards or blindfolded—with a partner!
- On a hot day (and outdoors!), add water components like carrying a bucket of water or running through a sprinkler
- Draw a map and instead of telling your child how to move through the course, give them the map to follow
- Add a fun time component and challenge your child to finish the course faster each time they do it
Cultivating Critical Thinking Skills with Begin
Because critical thinking is such an essential skill set, at Begin we build it into our age- and stage-matched learning membership . Kids can learn sequencing, make their own games, do science experiments, and more with award-winning activity kits from Little Passports , the codeSpark coding app , and more!
Take our online quiz today to discover which stage of the Begin membership is best for your family!

As our Chief Learning Officer, Jody leads a highly knowledgeable team of early learning experts at Begin. She has a Ph.D. in Developmental Science, focused on children’s mathematical and cognitive development.
View all posts
Dr. Jody LeVos
Related posts.

9 Effective Emotional Regulation Activities for Kids in 2024
Emotional regulation allows your child to adapt their response to a situation or environment. If a friend’s birthday party gets canceled, they might feel disappointed but not distraught. Or if a classmate hits them by accident with a ball in gym class, they might...
Keep Reading →

Bring Calm to Your Child’s Body with These 8 Breathing Exercises
Even one minute of breathing can reduce stress and anxiety for your child. Check out these exercises to see which might help your child learn how to find calm.

6 Key Goals for Enhancing Social Skills in Children at Home
Social skills are the building blocks of healthy relationships. Find out how to set social skills goals for your child and practice achieving them!

5 Activities for Teaching Kindness Lessons to Kids
Showing kindness means focusing your attention on another person, recognizing what they are feeling and what they need, and then offering them something. It’s giving your sister the last cookie in the jar. It’s playing a game because it’s your friend’s favorite....
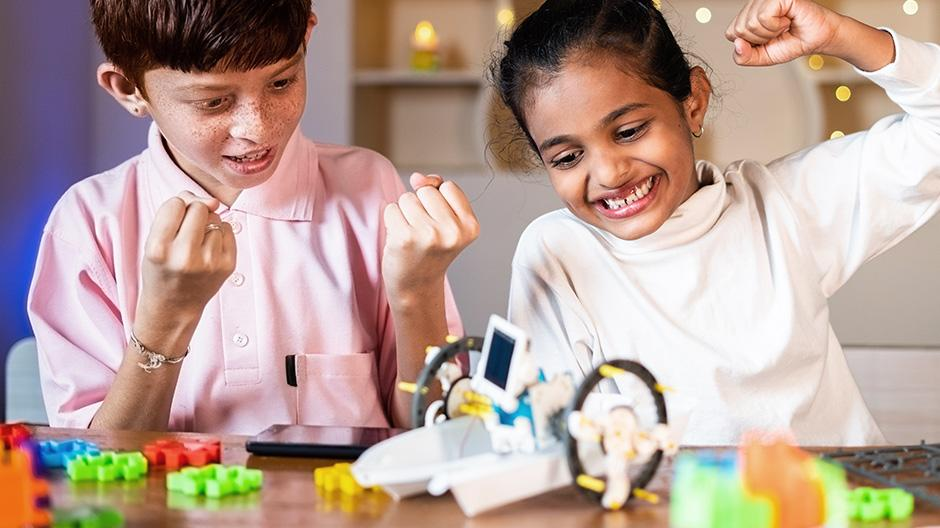

13 Invention Ideas for Kids and Why They Matter
Inventing new things helps kids develop creativity and critical thinking. Try these 13 invention ideas!
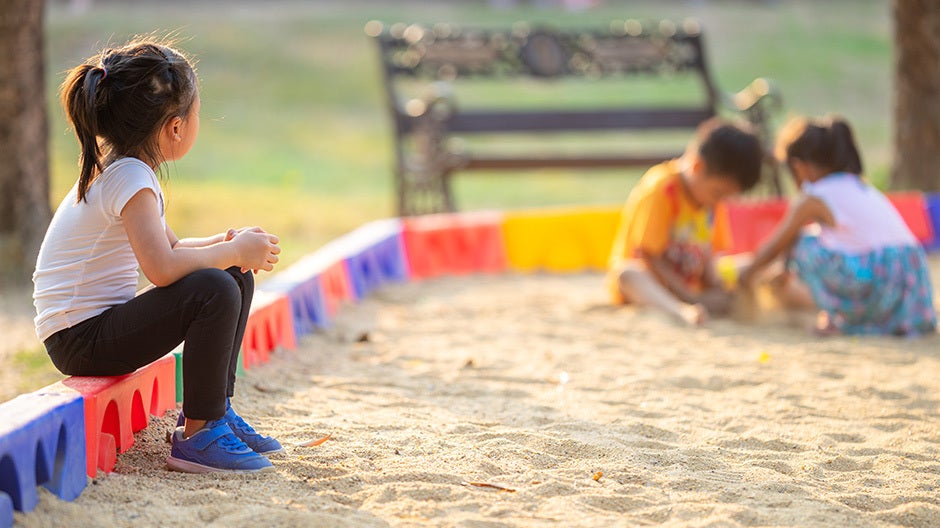

Building Character through Vicarious Learning in Child Behavior
“Kids are sponges.” Parents, teachers, and caregivers say this all the time, and you’ve probably seen it for yourself. A 3-year-old mimics her older brother’s language. A 5-year-old acts out something they see on TV. Behavior and vocabulary spread through an...

6 Free Creativity-Building Preschool Art Activities
Preschoolers are creative superheroes. From age 3 to age 4, a kid’s artistic abilities explode (sometimes literally, if they’re dropping paint or a bucket of crayons!). Their drawings become more recognizable, they may start to play pretend and invent friends...

A Guide to Receptive Language for Parents and Caregivers
Receptive language skills help kids understand and respond to verbal, nonverbal, and written communication. Find out how!
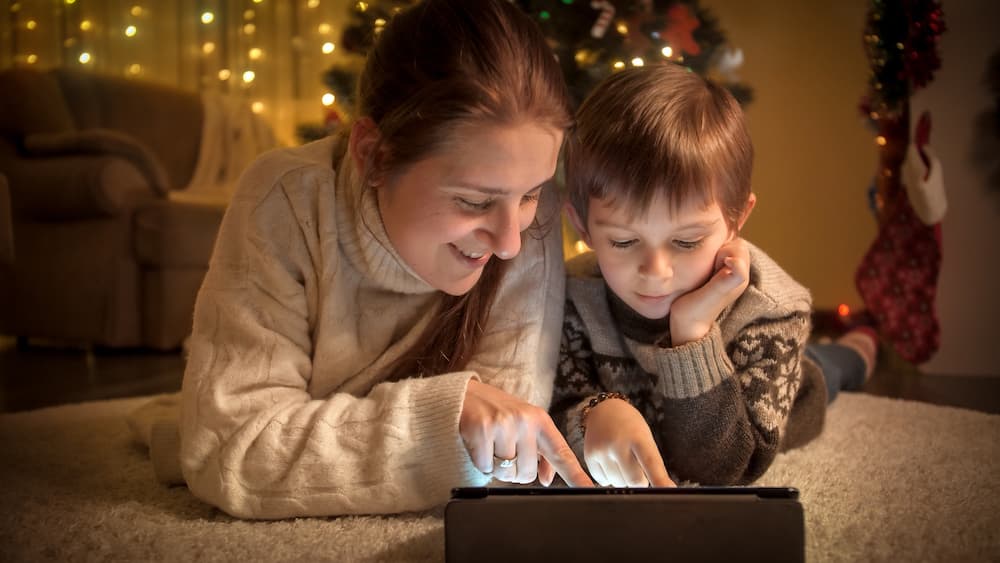

6 Tips on Managing Screen Time for the Holidays
Learn to manage screen time during the holidays in ways you feel good about with Dr. Sarah Bren and Begin.

Make Your Own Flowers to Celebrate World Kindness Day
Build Character with your family on World Kindness Day with DIY yellow flowers to give out!

Outdoor Winter Scavenger Hunt
Build critical thinking skills and get kids outside with this winter scavenger hunt!

Explore Many Ways to Give Thanks with Fun Printables for Kids
Gratitude is an important part of Character, one of the 5 C’s that help kids thrive in school and life. Get two printables to help!
Critical thinking definition

Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement.
Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process, which is why it's often used in education and academics.
Some even may view it as a backbone of modern thought.
However, it's a skill, and skills must be trained and encouraged to be used at its full potential.
People turn up to various approaches in improving their critical thinking, like:
- Developing technical and problem-solving skills
- Engaging in more active listening
- Actively questioning their assumptions and beliefs
- Seeking out more diversity of thought
- Opening up their curiosity in an intellectual way etc.
Is critical thinking useful in writing?
Critical thinking can help in planning your paper and making it more concise, but it's not obvious at first. We carefully pinpointed some the questions you should ask yourself when boosting critical thinking in writing:
- What information should be included?
- Which information resources should the author look to?
- What degree of technical knowledge should the report assume its audience has?
- What is the most effective way to show information?
- How should the report be organized?
- How should it be designed?
- What tone and level of language difficulty should the document have?
Usage of critical thinking comes down not only to the outline of your paper, it also begs the question: How can we use critical thinking solving problems in our writing's topic?
Let's say, you have a Powerpoint on how critical thinking can reduce poverty in the United States. You'll primarily have to define critical thinking for the viewers, as well as use a lot of critical thinking questions and synonyms to get them to be familiar with your methods and start the thinking process behind it.
Are there any services that can help me use more critical thinking?
We understand that it's difficult to learn how to use critical thinking more effectively in just one article, but our service is here to help.
We are a team specializing in writing essays and other assignments for college students and all other types of customers who need a helping hand in its making. We cover a great range of topics, offer perfect quality work, always deliver on time and aim to leave our customers completely satisfied with what they ordered.
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows:
- Select the topic and the deadline of your essay.
- Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the essay writing process you struggle with.
- Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
- Select your prefered payment type, sit back and relax!
With lots of experience on the market, professionally degreed essay writers , online 24/7 customer support and incredibly low prices, you won't find a service offering a better deal than ours.

Fine-Tuned Finances
21 Considerations Before Introducing Religion in Your Child’s Upbringing
Posted: January 28, 2024 | Last updated: January 28, 2024

While parents are allowed to their own opinions on how to raise their children. It is sometimes important to get an unbiased perspective that challenges our own in order to understand a different perspective. Raising children can be a contested subject especially when it involves religion. Here are 21 reasons that parents who raise their children without religion understand.
Developing Critical Thinking
Encouraging children to question, analyze, and make decisions based on logic helps develop their critical thinking skills. Religion often comes with a set of beliefs that followers are expected to accept without question, which can hinder this development. Teaching children to think critically enables them to make informed decisions and understand the world around them more comprehensively.

Promoting Independent Thought
Raising a child without religious influence allows them to form their own opinions and beliefs based on their experiences and knowledge. They learn to weigh different perspectives and make decisions based on their own judgments rather than adhering to prescribed beliefs. This fosters a sense of independence and confidence in their abilities.

Avoiding Fear-Based Motivations
Many religions use the concept of reward and punishment (heaven and hell, for instance) to motivate followers. Teaching children to behave well out of fear of punishment can create anxiety and stress. Encouraging positive behavior for its own sake leads to a healthier mindset and intrinsic motivation.

Building Tolerance and Open-Mindedness
Exposing children to a variety of beliefs and cultures promotes tolerance and open-mindedness. Relying solely on religious teachings can sometimes lead to a narrow worldview, making it harder for children to accept differing beliefs. Teaching inclusivity and acceptance helps in building a more harmonious society.

Encouraging Questioning and Curiosity
Fostering a sense of curiosity and the desire to learn is crucial in child development. Some religious teachings discourage questioning, promoting blind faith instead. Encouraging children to ask questions and seek answers helps in developing their research and problem-solving skills.

Understanding the Value of Evidence
Teaching children to seek evidence and base their beliefs on facts rather than faith helps develop a rational mindset. This approach prepares them for real-world problem-solving, where evidence-based decisions are crucial. It also helps in distinguishing between reliable and unreliable sources of information.

Avoiding Gender Bias and Stereotypes
Many religions have traditional views on gender roles that can perpetuate stereotypes and bias. Raising children without these influences allows them to see all genders as equal and capable of fulfilling any role they choose. This promotes equality and helps in breaking down gender barriers.

Fostering a Sense of Accountability
Teaching children that their actions have consequences in this life rather than in an afterlife fosters a sense of accountability and responsibility. They learn to take responsibility for their actions and understand their impact on others. This leads to a more ethical and responsible behavior.

Promoting a Love for Science and Learning
Religious beliefs sometimes contradict scientific findings, leading to confusion or rejection of scientific knowledge. Encouraging a love for science and learning from a young age fosters curiosity and a desire to understand the world. This can lead to innovation and a better understanding of our universe.

Building Emotional Resilience
Teaching children to find strength within themselves, rather than relying on a higher power, builds emotional resilience. They learn to cope with challenges, find solutions to their problems, and seek support from their community. This inner strength and resilience are crucial for navigating life’s ups and downs.

Encouraging Equality and Social Justice
Many religious texts contain outdated views on social issues, and following these teachings can perpetuate inequality. Teaching children about equality and social justice helps in creating a fairer society and promotes respect for all individuals, regardless of their background.

Avoiding Sectarianism and Religious Conflict
Growing up without religious bias can help in reducing sectarianism and religious conflict. Children learn to see beyond religious labels, promoting unity and reducing discrimination. This is crucial in building a peaceful and inclusive society.

Fostering a Global Mindset
A secular upbringing encourages children to think globally, understanding that humanity is connected regardless of religious beliefs. They learn to appreciate diverse cultures and beliefs, leading to a more integrated and harmonious world.

Building a Moral Foundation Without Fear
You can teach children about ethics and morals without the fear of divine punishment. They learn to do what is right because it is right, not out of fear of retribution. This creates a stronger internal moral compass.

Encouraging a Sense of Wonder About the Universe
Without religious explanations for the universe’s existence, children can explore and wonder about the cosmos. This encourages a sense of awe and curiosity, driving them to learn more about the world around them.

Building a Supportive Community
Secular communities can provide support and a sense of belonging without the need for religious affiliation. Children learn the importance of community and supporting one another, fostering a sense of connection and belonging.
Avoiding Guilt and Shame Associated With Religious Doctrines
Religious doctrines can sometimes instill feelings of guilt and shame in followers. Raising children without these influences allows them to develop a healthier self-esteem and self-worth.

Promoting Physical Health and Well-Being
Some religions impose dietary restrictions or fasting, impacting a child’s physical health. Encouraging balanced nutrition and healthy eating habits contributes to their overall well-being and development.

Encouraging Artistic and Creative Expression
Religions sometimes view certain forms of artistic expression as unacceptable. Encouraging creativity in all its forms allows children to explore their talents and express themselves freely.

Building a Sense of Empathy and Compassion
Teaching children to empathize with others, regardless of their religious beliefs, fosters compassion and kindness. They learn to help others simply because it is the right thing to do, not because of religious mandates.

Fostering a Love for Humanity and Our Planet
Encouraging children to care for the planet and all its inhabitants fosters a love for humanity and a desire to make the world a better place. They learn to take action for the greater good, contributing positively to society.

“No Boomers Allowed”: 15 States Where Retirees Are NOT Welcome
If you’re planning a significant change during retirement, it’s crucial to think about the kind of home you desire and the aspects you should steer clear of. “If you’re thinking about making a big move in retirement, it’s important to consider what characteristics you want in your new home and which ones to avoid at all costs,” suggests experts. To assist you, we’ve compiled a catalog of the 15 least favorable states for retirement.

16 UNACCEPTABLE THINGS BOOMERS GOT AWAY WITH IN THEIR YOUTH THAT WOULD SPARK OUTRAGE TODAY
Looking back on the childhood of the boomer generation, it becomes evident that certain things once considered appropriate would never pass today’s standards. The cultural landscape has evolved significantly, leading us to recognize 16 aspects of their upbringing that would be deemed wholly unacceptable today. From unsupervised outdoor adventures to unfiltered television content, the boomer generation got away with various experiences that would undoubtedly raise eyebrows in today’s world. Let’s delve into these intriguing elements of their upbringing and reflect on how far society has come.

STUCK IN THE 60S: 10 THINGS BABY BOOMERS REFUSE TO LET GO OF
Memories of the “good old days” keep us trapped in the past. Baby boomers love to retell tales of how it was “in my day.” At the same time, millennials will tell them to get with the times. Being stuck in a time warp from which they don’t want to snap out of, here are things that baby boomers still think are fantastic. STUCK IN THE 60S: 10 THINGS BABY BOOMERS REFUSE TO LET GO OF

IT’S TIME TO LET GO: 30 OUTDATED BOOMER HOME TRENDS THAT DESPERATELY NEED TO BE SHOWN THE EXIT!
With the advances of social media, home trends, décor, and fads change faster than ever before. While some trends become instant classics, others can be redundant, unsensible, or just downright hideous. In a popular online forum, users shared the home fads they’re tired of seeing. We’ve compiled a list of these most disliked home décor fads, so grab a cup of coffee, and let’s look into these less-than-inspiring home design options!

BOOMERS FED UP: THE NEVER-ENDING SAGA OF MILLENNIAL BLAME FOR FINANCIAL FAILURES – ENOUGH IS ENOUGH!
Millennials look at their current economic situation with despair. The feeling amongst them is that the boomers are the cause of their woes. Boomers are considered to be a group of individuals who are self-serving, greedy, and short-sighted. But is this the case?
More for You
The 14 Smells That Ants Absolutely Hate
Bungling Russian helicopter pilots reveal site of 'decoy' fighter jets painted on air bases by landing on them
What Is Sea Foam And Should You Use It In Your Vehicle?
The Best Way To Keep Bananas From Turning Brown Too Fast
The Most Iconic Wedding Gowns In History
Nate Berkus And Jeremiah Brent's Simple Tip For Making Any Home Smell Amazing
These Are the 16 Smells Rats Hate the Most
Barbara Baldavin, Actress on ‘Star Trek' and ‘Medical Center,' Dies at 85
Democrats Are Voting for a Republican in a Blue State
Beyoncé’s Country Album Isn’t Meant for Nashville
36-year-old brought in $77,000 in passive income from Etsy in 2023—she spends 5-10 minutes per day on it
12 Concealed Kitchen Storage Hacks You’ll Want to Use Immediately
How to get rid of stink bugs, according to an entomologist
Reed Blankenship doubles his salary after earning performance escalator for 2023 season
My Hero Academia: Biggest Story Inconsistencies
When Will The US Gen 6 Fighter Jets Enter Service?
28 of the Funniest Lies People Told to Children
Student raises concern over school cafeteria practice with photo of meal: 'This has been an ongoing problem'
'Preparing strikes on Israeli embassies': The coming Iranian response to Syria strike
Repel Fleas From Your Home With An Ingredient From Your Kitchen
- Open access
- Published: 26 March 2024
The effect of “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” on the critical thinking of midwifery students: Evidence from China
- Yuji Wang 1 na1 ,
- Yijuan Peng 1 na1 &
- Yan Huang 1
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 340 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
143 Accesses
Metrics details
Assessment ability lies at the core of midwives’ capacity to judge and treat clinical problems effectively. Influenced by the traditional teaching method of “teacher-led and content-based”, that teachers involve imparting a large amount of knowledge to students and students lack active thinking and active practice, the clinical assessment ability of midwifery students in China is mostly at a medium or low level. Improving clinical assessment ability of midwifery students, especially critical thinking, is highly important in practical midwifery education. Therefore, we implemented a new teaching program, “typical case discussion and scenario simulation”, in the Midwifery Health Assessment course. Guided by typical cases, students were organized to actively participate in typical case discussions and to promote active thinking and were encouraged to practice actively through scenario simulation. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the effect of this strategy on the critical thinking ability of midwifery students.
A total of 104 midwifery students in grades 16–19 at the West China School of Nursing, Sichuan University, were included as participants through convenience sampling. All the students completed the Midwifery Health Assessment course in the third year of university. Students in grades 16 and 17 were assigned to the control group, which received routine teaching in the Midwifery Health Assessment, while students in grades 18 and 19 were assigned to the experimental group, for which the “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” teaching mode was employed. The Critical Thinking Disposition Inventory-Chinese Version (CTDI-CV) and Midwifery Health Assessment Course Satisfaction Questionnaire were administered after the intervention.
After the intervention, the critical thinking ability of the experimental group was greater than that of the control group (284.81 ± 27.98 and 300.94 ± 31.67, p = 0.008). Furthermore, the experimental group exhibited higher scores on the four dimensions of Open-Mindedness (40.56 ± 5.60 and 43.59 ± 4.90, p = 0.005), Analyticity (42.83 ± 5.17 and 45.42 ± 5.72, p = 0.020), Systematicity (38.79 ± 4.70 and 41.88 ± 6.11, p = 0.006), and Critical Thinking Self-Confidence (41.35 ± 5.92 and 43.83 ± 5.89, p = 0.039) than did the control group. The course satisfaction exhibited by the experimental group was greater than that exhibited by the control group (84.81 ± 8.49 and 90.19 ± 8.41, p = 0.002).
The “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” class mode can improve the critical thinking ability of midwifery students and enhance their curriculum satisfaction. This approach carries a certain degree of promotional significance in medical education.
Typical case discussion and scenario simulation can improve midwifery students’ critical thinking ability.
Typical case discussion and scenario simulation can enhance students’ learning interest and guide students to learn independently.
Midwifery students were satisfied with the new teaching mode.
Peer Review reports
Maternal and neonatal health are important indicators to measure of the level of development of a country’s economy, culture and health care. The positive impact of quality midwifery education on maternal and newborn health is acknowledged in the publication framework for action strengthening quality midwifery education issued by the World Health Organization (WHO) [ 1 ]. Extensive evidence has shown that skilled midwifery care is crucial for reducing preventable maternal and neonatal mortality [ 2 , 3 , 4 ]. Clinical practice features high requirements for the clinical thinking ability of midwives, which refers to the process by which medical personnel analyze and integrate data with professional medical knowledge in the context of diagnosis and treatment as well as discover and solve problems through logical reasoning [ 5 ]. Critical thinking is a thoughtful process that is purposeful, disciplined, and self-directed and that aims to improve decisions and subsequent actions [ 6 ]. In 1986, the American Association of Colleges of Nursing formulated the “Higher Education Standards for Nursing Specialty”, which emphasize the fact that critical thinking is the primary core competence that nursing graduates should possess [ 7 ]. Many studies have shown that critical thinking can help nurses detect, analyze and solve problems creatively in clinical work and is a key factor in their ability to make correct clinical decisions [ 8 , 9 , 10 ].
However, the traditional teaching method used for midwifery students in China is “teacher-led and content-based”, and it involves efficiently and conveniently imparting a large amount of knowledge to students over a short period. Students have long failed to engage in active thinking and active practice, and the cultivation of critical thinking has long been ignored [ 5 ]. As a result, the critical thinking ability of midwifery students in China is mostly at a medium or low level [ 5 ]. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a new teaching mode to improve the critical thinking ability of midwifery students.
In 2014, Professor Xuexin Zhang of Fudan University, Shanghai, China, proposed a novel teaching method: the divided class mode. The basic idea of this approach is to divide the class time into two parts. The teachers explain the theoretical knowledge in the first lesson, and the students discuss that knowledge in the second lesson. This approach emphasizes the guiding role of teachers and encourages and empowers students to take responsibility for their studies [ 11 ]. Research has shown that the divided class mode can improve students’ enthusiasm and initiative as well as teaching effectiveness [ 12 ].
The problem-originated clinical medical curriculum mode of teaching was first established at McMaster University in Canada in 1965. This model is based on typical clinical cases and a problem-oriented heuristic teaching model [ 13 ]. The process of teaching used in this approach is guided by typical cases with the goal of helping students combine theoretical knowledge and practical skills. This approach can enhance the enthusiasm and initiative of students by establishing an active learning atmosphere. Students are encouraged to discuss and analyze typical cases to promote their ability to digest and absorb theoretical knowledge. Research has shown that the problem-originated clinical medical curriculum teaching mode can enhance students’ confidence and improve their autonomous learning and exploration ability. Scenario simulation teaching can provide students with real scenarios, allowing them to practice and apply their knowledge in a safe environment [ 14 ], which can effectively improve their knowledge and clinical skills and enhance their self-confidence [ 15 , 16 ].
Based on the teaching concept of divided classes, our research team established a new teaching model of “typical case discussion and scenario simulation”. Half of the class time is allocated for students to discuss typical cases and carry out scenario simulations to promote their active thinking and active practice. The Midwifery Health Assessment is the final professional core course that midwifery students must take in our school before clinical practice. All students must complete the course in Grade 3. Teaching this course is important for cultivating the critical thinking and clinical assessment ability of midwifery students. Therefore, our team adopted the new teaching mode of "typical case discussion and scenario simulation" in the teaching of this course. This study explored the teaching mode’s ability to improve the critical thinking ability of midwifery students.
Study design
The study employed a semiexperimental design.
Participants
A convenience sample of 104 third-year midwifery students who were enrolled in the Midwifery Health Assessment course volunteered to participate in this research at a large public university in Sichuan Province from February 2019 to June 2022 (grades 16 to 19). All the students completed the course in the third year of university. Students in grades 16 and 17 were assigned to the control group, which received the traditional teaching mode. Students in grades 18 and 19 were assigned to the experimental group, in which context the “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” class mode was used. The exclusion criteria for midwifery students were as follows: (1) dropped out of school during the study, (2) took continuous leave from school for more than two weeks, or (3) were unable to complete the questionnaire. The elimination criterion for midwifery students was that all the items were answered in the same way. No significant differences in students’ scores in their previous professional courses (Midwifery) were observed between the two groups. Textbooks, teachers, and teaching hours were the same for both groups.
Development of the “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” class mode
This study is based on the implementation of the new century higher education teaching reform project at Sichuan University. With the support of Sichuan University, we first established a “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” class mode team. The author of this paper was the head of the teaching reform project and served as a consultant, and the first author is responsible for supervising the implementation of the project. Second, the teaching team discussed and developed a standard process for the “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” class mode. Third, the entire team received intensive training in the standard process for the “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” class mode.
Implementation of the “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” class mode
Phase i (before class).
Before class, in accordance with the requirements for evaluating different periods of pregnancy, the teacher conceptualized typical cases and then discussed those cases with the teaching team and made any necessary modifications. After the completion of the discussion, the modified cases were released to the students through the class group. To ensure students’ interest, they were guided through the task of discovering and solving relevant problems using an autonomous learning approach.
Phase II (the first week)
Typical case discussion period. The Midwifery Health Assessment course was taught by 5 teachers and covered 5 health assessment periods, namely, the pregnancy preparation, pregnancy, delivery, puerperium and neonatal periods. The health assessment course focused on each period over 2 consecutive teaching weeks, and 2 lessons were taught per week. The first week focused on the discussion of typical cases. In the first lesson, teachers introduced typical cases, taught key knowledge or difficult evaluation content pertaining to the different periods, and explored the relevant knowledge framework. In the second lesson, teachers organized group discussions, case analyses and intergroup communications for the typical cases. They were also responsible for coordinating and encouraging students to participate actively in the discussion. After the discussion, teachers and students reviewed the definitions, treatments and evaluation points associated with the typical cases. The teachers also encouraged students to internalize knowledge by engaging in a process of summary and reflection to achieve the purpose of combining theory with practice.
Phase III (the second week)
Scenario simulation practice period. The second week focused on the scenario simulation practice period. In the first lesson, teachers reviewed the focus of assessment during the different periods and answered students’ questions. In the second lesson, students performed typical case assessment simulations in subgroups. After the simulation, the teachers commented on and summarized the students’ simulation evaluation and reviewed the evaluation points of typical cases to improve the students’ evaluation ability.
The organizational structure and implementation of the “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” class mode showed in Fig. 1 .
“Typical case discussion and scenario simulation” teaching mode diagram
A demographic questionnaire designed for this purpose was used to collect relevant information from participants, including age, gender, single-child status, family location, experience with typical case discussion or scenario simulation and scores in previous professional courses (Midwifery).
The Critical Thinking Disposition Inventory-Chinese Version (CTDI-CV) was developed by Peng et al. to evaluate the critical thinking ability of midwifery students [ 17 ]. The scale contains 70 items across a total of seven dimensions, namely, open-mindedness, truth-seeking, analytical ability, systematic ability, self-confidence in critical thinking, thirst for knowledge, and cognitive maturity. Each dimension is associated with 10 items, and each item is scored on a 6-point Likert scale, with 1 indicating “extremely agree” and 6 representing “extremely disagree”. The scale includes 30 positive items, which receive scores ranging from “extremely agree” to “extremely disagree” on a scale of 6 to 1, and 40 negative items, which receive scores ranging from “extremely agree” to “extremely disagree” on a scale of 1 to 6. A total score less than 210 indicates negative critical thinking ability, scores between 211 and 279 indicate an unclear meaning, scores of 280 or higher indicate positive critical thinking ability, and scores of 350 or higher indicate strong performance. The score range of each trait is 10–60 points; a score of 30 points or fewer indicates negative trait performance, scores between 31 and 39 points indicate that the trait meaning is incorrect, scores of 40 points or higher indicate positive trait performance, and scores of 50 points or higher indicate extremely positive trait performance. The Cronbach’s α coefficient of the scale was 0.90, thus indicating good content validity and structure. The higher an individual’s score on this measure is, the better that individual’s critical thinking ability.
The evaluation of teaching results was based on a questionnaire used to assess undergraduate course satisfaction, and the researchers deleted and modified items in the questionnaire to suit the context of the “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” teaching mode. Two rounds of discussion were held within the study group to form the final version of the Midwifery Health Assessment satisfaction questionnaire. The questionnaire evaluates the effect of teaching in terms of three dimensions, namely, curriculum content, curriculum teaching and curriculum evaluation. The questionnaire contains 21 items, each of which is scored on a 5-point Likert scale, with 1 indicating “extremely disagree” and 5 representing “extremely agree”. The higher the score is, the better the teaching effect.
Data collection and statistical analysis
We input the survey data into the “Wenjuanxing” platform ( https://www.wjx.cn/ ), which specializes in questionnaire services. At the beginning of the study, an electronic questionnaire was distributed to the students in the control group via student WeChat and QQ groups for data collection. After the intervention, an electronic questionnaire was distributed to the students in the experimental group for data collection in the final class of the Midwifery Health Assessment course. All the data were collected by the first author (Yuji Wang). When students had questions about the survey items, the first author (Yuji Wang) immediately explained the items in detail. To ensure the integrity of the questionnaire, the platform required all the items to be answered before submission.
Statistical Package for Social Sciences Version 26.0 (SPSS 26.0) software was used for data analysis. The Shapiro‒Wilk test was used to test the normality of the data. The measurement data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (X ± S), and an independent sample t test was used for comparisons among groups with a normal distribution. The data presented as the number of cases (%), and the chi-square test was performed. A P value < 0.05 indicated that a difference was statistically significant.
Ethical considerations
The study was funded by the New Century Teaching Reform Project of Sichuan University and passed the relevant ethical review. Oral informed consent was obtained from all individual participants in the study.
Characteristics of the participants
A total of 104 third-year midwifery students were enrolled from February 2019 to June 2022, and 98.1% (102/144) of these students completed the survey. Two invalid questionnaires that featured the same answers for each item were eliminated. A total of 100 participants were ultimately included in the analysis. Among the participants, 48 students were assigned to the control group, and 52 students were assigned to the experimental group. The age of the students ranged from 19 to 22 years, and the mean age of the control group was 20.50 years (SD = 0.61). The mean age of the experimental group was 20.63 years (SD = 0.65). Of the 100 students who participated in the study, the majority (96.0%) were women. No significant differences were observed between the intervention and control groups in terms of students’ demographic information (i.e., age, gender, status as an only child, or family location), experience with scenario simulation or typical case discussion and scores in previous Midwifery courses (Table 1 ).
Examining the differences in critical thinking ability between the two groups
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of the new teaching mode of “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” on improving the critical thinking ability of midwifery students. Independent sample t tests were used to examine the differences in critical thinking ability between the two groups (Table 2 ). The results showed that the total critical thinking scores obtained by the experimental group were greater than those obtained by the control group (284.81 ± 27.98 and 300.94 ± 31.67, p = 0.008). The differences in four dimensions (Open-Mindedness (40.56 ± 5.60 and 43.59 ± 4.90, p = 0.005), Analyticity (42.83 ± 5.17 and 45.42 ± 5.72, p = 0.020), Systematicity (38.79 ± 4.70 and 41.88 ± 6.11, p = 0.006), and Critical Thinking Self-Confidence (41.35 ± 5.92 and 43.83 ± 5.89, p = 0.039)) were statistically significant.
Examining the differences in curriculum satisfaction between the two groups
To evaluate the effect of the new teaching mode of “the typical case discussion and scenario simulation” on the course satisfaction of midwifery students. Independent sample t tests were used to examine the differences in course satisfaction between the two groups (Table 3 ). The results showed that the curriculum satisfaction of the experimental group was greater than that of the control group (84.81 ± 8.49 and 90.19 ± 8.41, p = 0.002). Independent sample t tests were used to examine the differences in the three dimensions of curriculum satisfaction between the two groups (Table 3 ). The results showed that the average scores of the intervention group on the three dimensions were significantly greater than those of the control group (curricular content: 20.83 ± 1.96 and 22.17 ± 2.23, p = 0.002; curriculum teaching: 34.16 ± 3.89 and 36.59 ± 3.66, p = 0.002; curriculum evaluation: 29.81 ± 3.27 and 31.42 ± 3.19, p = 0.015).
Midwifery is practical and intensive work. To ensure maternal and child safety, midwives must make decisions and take action quickly. Therefore, midwives should have both critical thinking ability and clinical decision-making ability [ 18 ]. In addition, the Australian Nursing and Midwifery Accreditation Council (ANMAC) regulates the educational requirements for the programs required for registration as a midwife. According to these standards, education providers must incorporate learning activities into curricula to encourage the development and application of critical thinking and reflective practice [ 19 ]. Therefore, the challenge of cultivating the critical thinking ability of midwifery students is an urgent problem that must be solved. However, influenced by the traditional teaching method of “teacher-led and content-based”, the critical thinking ability of midwifery students in China is mostly at a medium or low level. In order to improve the critical thinking ability of midwifery students. Our research team has established a new teaching model, the “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” class model. And applied to the midwifery core curriculum Midwifery Health Assessment. This study aimed to investigate the implementation of a novel systematic and structured teaching model for midwifery students and to provide evidence regarding how to improve the critical thinking ability of midwives.
The results showed that the total CTDI-CV score obtained for the experimental group was greater than that obtained for the control group. These findings indicate that the “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” class mode had a positive effect on the cultivation of students’ critical thinking ability, a conclusion which is similar to the findings of Holdsworth et al. [ 20 ], Lapkin et al. [ 21 ] and Demirören M et al. [ 22 ]. We indicate the following reasons that may explain these results.The core aim of the typical case discussion teaching mode is to raise questions based on typical clinical cases and to provide heuristic teaching to students [ 23 ]. This approach emphasizes asking questions based on specific clinical cases, which enables students to engage in targeted learning. Moreover, scenario simulation allows students to attain certain inner experiences and emotions and actively participate in curriculum practice, which can enhance their ability to remember and understand knowledge [ 24 ]. Through the divided class mode, half of the class time was divided into the students. This method emphasizes the guiding role of teachers and encourages and empowers students to assume learning responsibilities. In addition, students can think, communicate and discuss actively [ 22 , 23 ]. Furthermore, this approach created opportunities for students to analyze and consider problems independently and give students sufficient time to internalize and absorb knowledge and deepen their understanding of relevant knowledge, which can increase their confidence in their ability to address such problems and improve their critical thinking ability [ 12 , 25 , 26 ].
In addition, the results showed that except for Truth-Seeking and Systematicity, the other five dimensions were all positive. These findings are similar to the results reported by Atakro et al.. and Sun et al. [ 27 , 28 ]. Through the intervention, the Systematicity scores became positive, suggesting that the new teaching mode can help students deal with problems in an organized and purposeful way. However, Truth-Seeking still did not become positive; this notion focuses on intellectual honesty, i.e., the disposition to be courageous when asking questions and to be honest and objective in the pursuit of knowledge even when the topics under investigation do not support one’s self-interest [ 29 ]. Studies have shown that this factor is related to the traditional teaching mode used [ 30 ]. The traditional teaching mode focuses on knowledge infusion, helps students remember the greatest possible amount of knowledge in a short time, and does not focus on guiding students to seek knowledge with sincerity and objectivity. Therefore, in future educational practice, we should focus on cultivating students’ ability to seek truth and engage in systematization.
Student evaluative feedback is an important way to test the effectiveness teaching mode. Therefore, understanding students’ evaluations of the effects of classroom teaching is key to promoting teaching reform and improving teaching quality. Therefore, we distributed a satisfaction questionnaire pertaining to the midwifery health assessment curriculum, which was based on the “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” class mode, with the goal of investigating curriculum satisfaction in terms of three dimensions (curriculum content, curriculum teaching and curriculum evaluation). The results showed that the satisfaction scores for each dimension increased significantly. This finding suggests that the new teaching method can enrich the teaching content, diversify the teaching mode and improve students’ curriculum evaluations.
In summary, the “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” class mode focuses on typical cases as its main content. Students’ understanding of this content is deepened through group discussion and scenario simulation. The subjectivity of students in curriculum learning should be accounted for. Students can be encouraged to detect, analyze and solve problems with the goal of improving their critical thinking ability. Moreover, this approach can also enhance curriculum satisfaction. It is recommended that these tools should be used continuously in future curriculum teaching.
This study has several limitations. First, the representativeness of the sample may be limited since the participants were recruited from specific universities in China. Second, we used historical controls, which are less effective than simultaneous controlled trials. Third, online self-report surveys are susceptible to response biases, although we included quality control measurements in the process of data collection. Fourth, we did not use the same critical thinking instrument, CTDI-CV, to investigate the critical thinking of the students in the experimental group or the control group before intervention but used professional course grades from the Midwifery for substitution comparison. This may not be a sufficient substitute. However, these comparisons could be helpful since those grades included some sort of evaluation of critical thinking. In light of these limitations, future multicenter simultaneous controlled studies should be conducted. Nonetheless, this study also has several strengths. First, no adjustment of teachers or change in learning materials occurred since the start of the midwifery health assessment, thus ensuring that the experimental and control groups featured the same teaching materials, teachers and teaching hours. In addition, to ensure the quality of the research, the first author of this paper participated in the entirety of the course teaching.
The “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” class mode can improve the critical thinking of midwifery students, which is helpful for ensuring maternal and child safety. Students are highly satisfied with the new teaching mode, and this approach has a certain degree of promotional significance. However, this approach also entails higher requirements for both teachers and students.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
World Health Organisation, Strengthening quality midwifery education for Universal Health Coverage2030,2019, https://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/topics/quality-of-care/midwifery/strengthening-midwifery-education/en/ (accessed 21.01.20).
Akombi BJ, Renzaho AM. Perinatal mortality in Sub-Saharan Africa: a meta-analysis of demographic and health surveys. Ann Glob Health. 2019;85(1):106.
Article Google Scholar
Campbell OM, Graham WJ. Strategies for reducing maternal mortality: getting on with what works. Lancet. 2006;368(9543):1284–99.
Gage AD, Carnes F, Blossom J, Aluvaala J, Amatya A, Mahat K, Malata A, Roder-DeWan S, Twum-Danso N, Yahya T, et al. In low- and middle-income countries, is delivery in high-quality obstetric facilities geographically feasible? Health Aff (Millwood). 2019;38(9):1576–84.
Xing C, Zhou Y, Li M, Wu Q, Zhou Q, Wang Q, Liu X. The effects of CPBL + SBAR teaching mode among the nursing students. Nurse Educ Today. 2021;100:104828.
Carter AG, Creedy DK, Sidebotham M. Critical thinking evaluation in reflective writing: development and testing of Carter assessment of critical thinking in midwifery (Reflection). Midwifery. 2017;54:73–80.
Yeh SL, Lin CT, Wang LH, Lin CC, Ma CT, Han CY. The Outcomes of an Interprofessional simulation program for new graduate nurses. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(21):13839.
Chang MJ, Chang YJ, Kuo SH, Yang YH, Chou FH. Relationships between critical thinking ability and nursing competence in clinical nurses. J Clin Nurs. 2011;20(21–22):3224–32.
Shoulders B, Follett C, Eason J. Enhancing critical thinking in clinical practice: implications for critical and acute care nurses. Dimens Crit Care Nurs. 2014;33(4):207–14.
Jalalpour H, Jahani S, Asadizaker M, Sharhani A, Heybar H. The impact of critical thinking training using critical thinking cards on clinical decision-making of CCU nurses. J Family Med Prim Care. 2021;10(10):3650–6.
Xuexin Z. PAD class: a new attempt in university teaching reform. Fudan Educ Forum. 2014;12(5):5–10 [in Chinese].
Google Scholar
Zhai J, Dai L, Peng C, Dong B, Jia Y, Yang C. Application of the presentation-assimilation-discussion class in oral pathology teaching. J Dent Educ. 2022;86(1):4–11.
Colliver JA. Effectiveness of problem-based learning curricula: research and theory. Acad Med. 2000;75(3):259–66.
Bryant K, Aebersold ML, Jeffries PR, Kardong-Edgren S. Innovations in simulation: nursing leaders’ exchange of best practices. Clin Simul Nurs. 2020;41:33-40.e31.
Cicero MX, Whitfill T, Walsh B, Diaz MC, Arteaga G, Scherzer DJ, Goldberg S, Madhok M, Bowen A, Paesano G, et al. 60 seconds to survival: a multisite study of a screen-based simulation to improve prehospital providers disaster triage skills. AEM Educ Train. 2018;2(2):100–6.
Lee J, Lee H, Kim S, Choi M, Ko IS, Bae J, Kim SH. Debriefing methods and learning outcomes in simulation nursing education: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nurse Educ Today. 2020;87:104345.
Peng G, Wang J, Chen M, Chen H, Bai S, Li J, Li Y, Cai J, Wang L. Yin Validity and reliability of the Chinese critical thinking disposition inventory Chin. J Nurs. 2004;39(09):7–10 [in Chinese].
Papathanasiou IV, Kleisiaris CF, Fradelos EC, Kakou K, Kourkouta L. Critical thinking: the development of an essential skill for nursing students. Acta Inform Med. 2014;22(4):283–6.
Australian Nursing and Midwifery Accreditation Council Midwife accreditation standards, 2014 ANMAC, Canberra. 2014. https://anmac.org.au/document/midwife-accreditation-standards-2014 .
Holdsworth C, Skinner EH, Delany CM. Using simulation pedagogy to teach clinical education skills: a randomized trial. Physiother Theory Pract. 2016;32(4):284–95.
Lapkin S, Fernandez R, Levett-Jones T, Bellchambers H. The effectiveness of using human patient simulation manikins in the teaching of clinical reasoning skills to undergraduate nursing students: a systematic review. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2010;8(16):661–94.
Demirören M, Turan S, Öztuna D. Medical students’ self-efficacy in problem-based learning and its relationship with self-regulated learning. Med Educ Online. 2016;21:30049.
Spaulding WB, Neufeld VR. Regionalization of medical education at McMaster University. Br Med J. 1973;3(5871):95–8.
Rossler KL, Kimble LP. Capturing readiness to learn and collaboration as explored with an interprofessional simulation scenario: A mixed-methods research study. Nurse Educ Today. 2016;36:348–53.
Yang YL, Luo L, Qian Y, Yang F. Cultivation of undergraduates’ self-regulated learning ability in medical genetics based on PAD class. Yi Chuan. 2020;42(11):1133–9.
Felton A, Wright N. Simulation in mental health nurse education: the development, implementation and evaluation of an educational innovation. Nurse Educ Pract. 2017;26:46–52.
Atakro CA, Armah E, Menlah A, Garti I, Addo SB, Adatara P, Boni GS. Clinical placement experiences by undergraduate nursing students in selected teaching hospitals in Ghana. BMC Nurs. 2019;18:1.
Sun Y, Yin Y, Wang J, Ding Z, Wang D, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Wang Y. Critical thinking abilities among newly graduated nurses: a cross-sectional survey study in China. Nurs Open. 2023;10(3):1383–92.
Wangensteen S, Johansson IS, Björkström ME, Nordström G. Critical thinking dispositions among newly graduated nurses. J Adv Nurs. 2010;66(10):2170–81.
Salsali M, Tajvidi M, Ghiyasvandian S. Critical thinking dispositions of nursing students in Asian and non-Asian countries: a literature review. Glob J Health Sci. 2013;5(6):172–8.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
The study was supported by Sichuan University’s New Century Education and Teaching Reform Project (SCU9316).
Author information
Yuji Wang and Yijuan Peng are co-first authors.
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Nursing, West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University/West China School of Nursing, Sichuan University/Key Laboratory of Birth Defects and Related Diseases of Women and Children (Sichuan University), No. 20 Third Section, Renmin South Road, Chengdu, Sichuan Province, 610041, China
Yuji Wang, Yijuan Peng & Yan Huang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Yuji Wang, Yijuan Peng and Yan Huang. The first draft of the manuscript were written by Yuji Wang and Yijuan Peng, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yan Huang .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study was supported by Sichuan University. And it was approved by the Ethics Review Committee of West China School of Nursing, Sichuan University. As it is a teaching research with no harm to samples, we only obtained oral informed consents from the participants including teachers and midwifery students and it was approved by the Ethics Review Committee of West China School of Nursing, Sichuan University(approval number 2021220). We comfirm that all methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations in Ethics Approval and Consent to participate in Declarations.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Wang, Y., Peng, Y. & Huang, Y. The effect of “typical case discussion and scenario simulation” on the critical thinking of midwifery students: Evidence from China. BMC Med Educ 24 , 340 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05127-5
Download citation
Received : 19 November 2022
Accepted : 02 February 2024
Published : 26 March 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05127-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Medical education
- Critical thinking
- Nurse midwives
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Aurora Beacon-News | Problem-solving, critical thinking on display…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Aurora Beacon-News Sports
- Aurora Beacon-News Opinion
- All Suburbs
Aurora Beacon-News
Aurora beacon-news | problem-solving, critical thinking on display at robotics event at aurora municipal airport.

Robots and the kids that built and operated them took center stage all day Friday at the Aurora Municipal Airport in Sugar Grove as 17 students 9 to 16 years old squared off in a competition during the first-ever Elite Robotics Camp, hosted by the U.S. Engineering League and the Wong Center for Education.
The Friday showcase was the culmination of a week-long camp program that included four days of workshops held at the Hampton Inn in Aurora.
A press release issued by the robotics camp said the 17 students involved spent time with a variety of national champions from multiple countries under Anthony Hsu of OFDL Robotics Lab Taiwan, “one of the world’s most accomplished coaches.”
Susan Mackafey, publicist for the Robotics group, said the event in Aurora came about as a result of the competitions that the Wong group hosts worldwide. William Wong, the founder of the Wong Center for Education, is the national organizer for the World Robot Olympiad, according to a press release.
“There were some students from Ukraine and Kazakhstan wondering if there would be any other kind of competitions as they wanted to hone their skills with one of the experts,” she said. “Will Wong ran with it, and has arranged the camp and the competition going on this Friday.”
Two of the camp members from Ukraine – Margo Proutorbva and Sofia Sova – were sponsored by the Wong Center for Education.
“It’s been an emotional trip for them,” Mackafey said, given the war going on in their homeland. “A lot of the kids are looking to train and do this as their careers and they love to compete. There are various levels of this competition that take place on a global scale.”
Local students were on hand as well, some of whom are being sponsored by the Wong Foundation, sources said.
Wong, of Naperville, was supervising Friday at the airport facility and said he started a robotics program with kids back in 2008.
“STEM has become a lot of the focus,” Wong said. “Even before I started, STEM was a big word. Engineering coding has always been there. It’s just how can we have kids do more of it. What’s happened is there are education companies like LEGO and other companies that have built robots that allow us to teach kids robotics in an easy fashion and we can create real world challenges off those robots so they literally are engineering, building and creating, designing and working with teams to have robots do tasks.”
Other than the collaborative learning, Wong said the biggest takeaways of the program “are problem-solving, figuring out how to make things work, a lot of trial-and-error, analysis and critical thinking.”
“There is teamwork, but the biggest is perseverance and working through the problems,” he said. “If the robot doesn’t work the first time or the second time or the 100th time, they are truly going through the engineering process – building, design and the whole cycle.”

Margo Proutorbva, 14, spoke about robotics and said through an interpreter she got interested in them two years ago.
“I’ve learned to assemble them,” she said. “The most difficult part of this has been when you assemble a robot with someone else – it’s way easier when you do it on your own. My robot can grab different objects, follow lines and turn in different ways.”
David Sharos is a freelance reporter for The Beacon-News.
More in Aurora Beacon-News

Aurora Beacon-News | Fox Valley gardeners itching to get back outside to ‘work the soil’

Aurora Beacon-News | Oswego approves video gambling at two more gas stations

Daily Southtown Sports | Baseball and local scores for the Southland, Aurora, Elgin, Naperville and Lake County

Aurora Beacon-News Sports | After winning nationals, Wisconsin-bound Patrick Hilby wants more for Aurora Central Catholic. ‘A prizefighter, man.’
Trending nationally.
- One week later, clearer picture of Key Bridge victims emerges
- New Central Florida highway will wirelessly charge cars on the go
- AT&T says a data breach leaked millions of customers’ information online. Were you affected?
- Silicon Valley billionaires planning Solano County ‘California Forever’ utopia score big win in $510 million fight against farmers
- California could be first state to give workers right to ignore boss’s after-hours calls, texts, emails

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Basically, critical thinking helps us make good, sound decisions. Critical thinking. In her book, "Mind in the Making: The seven essential life skills every child needs," author Ellen Galinsky explains the importance of teaching children critical thinking skills. A child's natural curiosity helps lay the foundation for critical thinking.
Kokotree is the #1 learning app for kids. Activate your child's learning with fun educational videos and games for toddlers, preschoolers, parents, and families. Explore the importance of critical thinking for preschoolers and learn strategies to help them develop these essential skills in a fun, engaging way.
1. Introduction and background. To think is human, everyone thinks, however, not everyone thinks well and not all educators teach students how to think well (Ennis, 2011; Pithers & Soden, 2000).The importance of developing critical thinking in students has been proposed as the most important skill set the education system can develop in students (Thompson, 2011).
Critical thinking skills are the foundation of education as well as an important life skill. Without the ability to think critically, kids will struggle academically, especially as they get older. In fact, no matter what your child plans to do professionally someday, they will need to know how to think critically, solve problems, and make ...
Critical thinking is one of the most important skills that children should learn from an early age, as it is a cognitive 'tool' that they will need in adulthood. Every day, children are exposed to a huge amount of information, either through images, books, TV or online, or through discussions with parents, peers or teachers.
Using critical thinking in your own life is vital, but passing it along to the next generation is just as important. Be sure to focus on analyzing and evaluating, two multifaceted sets of skills that take lots and lots of practice. Start with these 10 Tips for Teaching Kids To Be Awesome Critical Thinkers. Then try these critical thinking ...
This is about teaching them to think for themselves. Your role is to direct their questions, listen and respond. Meanwhile, your kids "have to think about how they're going to put this into digestible pieces for you to understand it," says Oshiro. "It's a great way to consolidate learning.". Critical thinking isn't just for the ...
The most important thing to foster at this young age is what researchers call metacognition: awareness of one's own thinking and thought processes. It's only with metacognition that children ...
Introduction. The importance of fostering and developing critical thinking (CT) in children from a young age (Lai Citation 2011) has been widely discussed and endorsed in scholarship (Facione Citation 2011; Lipman Citation 1991).Education policy often highlights CT skills as an essential component of twenty-first-century skills - the set of skills needed to solve the challenges of a rapidly ...
This is about teaching them to think for themselves. Your role is to direct their questions, listen and respond. Meanwhile, your kids "have to think about how they're going to put this into digestible pieces for you to understand it," says Oshiro. "It's a great way to consolidate learning.". Critical thinking isn't just for the ...
Table of Contents. Understanding the Importance of Critical Thinking in Early Childhood 1.1 Defining Critical Thinking for Young Learners 1.2 The Role of Critical Thinking in Child Development; Incorporating Creativity into Critical Thinking Exercises 2.1 The Relationship Between Creativity and Critical Thinking 2.2 Techniques to Foster Creative Thought in Young Minds
4. Encourage Open-Mindedness And Social-Emotional Learning. Finally, open-mindedness and social-emotional learning are key components to critical thinking. Young children can learn to be open-minded through exposure and by example-meaning the adults in their life should model this behavior themselves.
Finally, one of the most important practical applications of critical thinking skills is improved literacy, which makes kids more resilient to manipulation, brainwashing, false information, and other dangers that lurk on the internet and in-person in the form of peer pressure, bullying, and more. Kids will have the ability to better analyse the ...
As we consider the importance of critical thinking for kids, we must first denote the foundational skills needed for critical thinking, then consider ways this thinking positively impacts problem-solving and supports academic success. We'll also share some suggestions for fun projects that connect creativity to nurturing young minds that ...
Play Sudoku: Sudoku is a logic-based game that requires critical thinking skills. It requires children to think logically and use deductive reasoning to solve a problem. Sudoku puzzles can be found in many newspapers and online. Conduct Research: Encourage children to conduct research on a topic that interests them.
Teaching critical thinking to children is an especially important issue in South Korea due to the prevalence of teacher-centered lessons and an authority-reverent culture. According to Sung and Apple ( 2003 ), Korean students are not accustomed to expressing a critical perspective to either teachers or texts.
By teaching kids the importance of critical thinking and incorporating it into their day-to-day activities, we can help them become better decision-makers and problem-solvers. By encouraging kids to engage in more critical thinking activities, they become more self-aware and independent, which helps them to make better decisions. ...
Example 1: STEAMing with projects. One method for integrating STEAM in your classroom is through child-centered projects. For example, Ms. White's year-round class of 4- and 5-year-olds was particularly interested in learning about seeds and plant growth. To support the children's interests, Ms. White proposed that the class plan, design ...
The importance of critical thinking can't be overstated: As kids are bombarded with information from a young age — with new channels, platforms and media springing up regularly — they need to balance an open mind with healthy skepticism. ... How to help children develop critical thinking skills at home. 1. Start from their interests. To ...
Teachers can foster critical thinking in the early elementary grades by guiding students to develop their conversation skills. ... While this may not be an "easy process," Orr writes—for the kids or the teacher—the payoff is students who from a young age are able to communicate new ideas and questions; listen and truly hear the thoughts ...
The Odd One Out. The Odd One Out is a great thinking game to play with kids. It improves their critical thinking by using their knowledge of patterns, vocabulary, differences and similarities. There are a few ways of playing The Odd One Out: worksheets. online games. using toys around the house.
Janis Strasser is professor emerita from William Paterson University. She has been a kindergarten/preschool teacher, Head Start education coordinator, and consultant, and she has written many articles for Young Children and Teaching Young Children.For the past several years, Dr. Strasser has been working with preschool teachers on the island of Anguilla during the winter months.
To teach preschoolers critical thinking, introduce open-ended questions, provide hands-on experiences, encourage curiosity, engage in storytelling, promote problem-solving activities, and create an environment where they feel safe to express ideas and make mistakes. Here's a list of critical thinking activities suitable for preschoolers ...
Why Is Critical Thinking Important? Critical thinking is a necessary skill for understanding the world. Through weighing options, studying different perspectives, and making good choices, our children can lead their lives in a positive and healthy way. Critical thinking allows our kids to: Analyze information and make decisions
Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement. Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process ...
Primary school teachers have strongly criticised a Department of Education decision to stop using data on the number of pupils with complex needs as a criteria in deciding the level of additional ...
Encouraging children to question, analyze, and make decisions based on logic helps develop their critical thinking skills. Religion often comes with a set of beliefs that followers are expected to ...
Assessment ability lies at the core of midwives' capacity to judge and treat clinical problems effectively. Influenced by the traditional teaching method of "teacher-led and content-based", that teachers involve imparting a large amount of knowledge to students and students lack active thinking and active practice, the clinical assessment ability of midwifery students in China is mostly ...
Robots and the kids that built and operated them took center stage all day Friday at the Aurora Municipal Airport in Sugar Grove as 17 students 9 to 16 years old squared off in a competition ...