

17 Stock Market Worksheets PDFs (Plus Stock Market Lessons)
By: Author Amanda L. Grossman
Posted on Last updated: January 9, 2024
Use these 17 stock market worksheet PDFs (and stock market lesson PDFs) to engage your students, kids, and teens.
Teaching students about investing, and looking for some killer stock market worksheet PDFs (that also happen to be free)?

I’ve got you covered.
You don’t have to be a stock market wizard to teach your students, thanks to some great stock market lesson pdfs, lesson plans, and worksheets.
Psst: one of the best ways to teach students about investing and the stock market is to actually have them play it. But don’t worry – they needn’t lose any money. Here are 6 free stock market game for students , and 9 investing board games for kids .
Stock Market Worksheet PDFs
Teaching kids about stocks and how to invest is such a worthy cause – it’s one of the best ways to ensure they’ll have a solid financial future.
I can clearly remember learning (or, at least trying to learn) how to read stock tables in my seminar class back in middle school. We each chose a stock, and then read the stock tables on it from week-to-week over a series of a few months.
At first, reading a stock table is like trying to read hieroglyphics at a museum – it just isn’t intuitive.
But then as we worked through it together, it became less intimidating. Do the same with your own students! They’ll thank you when they’re older.
And you don’t have to do it alone (especially if you’re not confident with investing, yourself).
Whether you’re looking for worksheets to follow specific stocks on the stock market, or company valuation worksheets, or price to earning ratio worksheets – you’ll find them below.
1. One-Page Stock-Monitoring Worksheet
Suggested Age: 4-8 grade
Sometimes, simple is best, right?
Here’s a one-page stock purchase worksheet you can download for free (after you sign up for a free Teachers Pay Teachers account).
It’s a way for your students to choose a stock to buy with $XXX amount of cash, and then to monitor that stock over several weeks.
Other one-page stock market worksheets include:
- Stock Market Research : Suggested Age Range: 7-12 grade
- Stock Market Tracker : Suggested Age Range: 7-12 grade
To go along with this, you’ll likely want to give your students a worksheet on how to read a stock table. I’ve got that coming up, next!
2. Playing an Investment Game
Suggested Age Range: 9-12 grade
The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau came up with this new stock market worksheet where kids work through why they think a company's stocks rose or fell.
This is great, critical thinking they can definitely use when they invest in real life!
Psst: want your child to start buying real stocks? Here are 7 stock apps for kids . And here's a Global Stock Pitch Competition .
3. Stocks, Stocks, Stocks
Suggested Age Range: Not given.
What I love about this teacher guide + accompanying student worksheets is they teach everyone how to read stock market tables.
Because let’s be honest – those can look so intimidating!
4. Stock Investing 101 Worksheet
Suggested Age Range: 7-12 grade
This is a free Microsoft Word document that walks your students through three familiar companies on the stock market: Amazon, Home Depot, and General Motors.
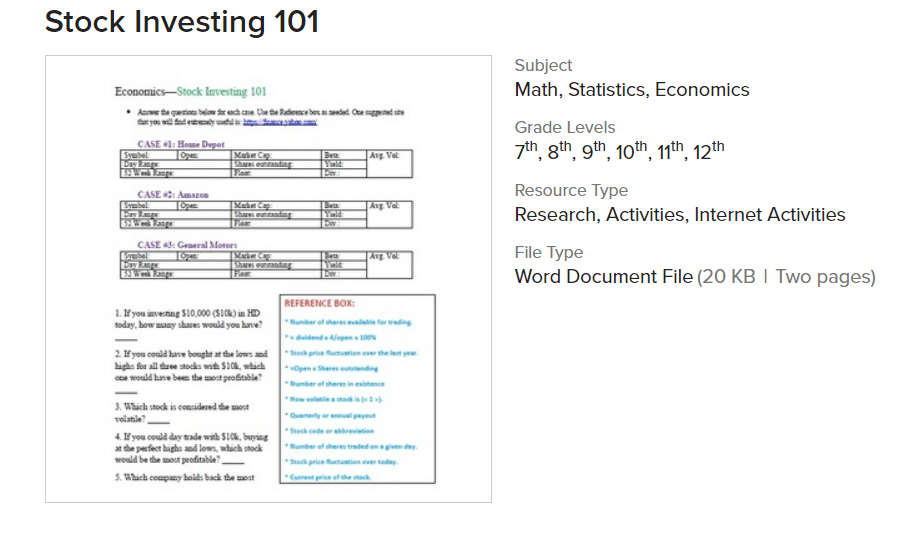
They’re asked to fill in a bunch of info for each one, then more thinking-questions like which stock is the most volatile, and which stock is the most profitable.
5. Stock Market Definitions and Terms
Looking for NYSE terms + an answer key? Great!
This stock market vocabulary worksheet is very simple and straightforward, and will help you to reinforce a lesson on understanding how to maneuver the stock exchange (links to the worksheets are all the way at the bottom).
Psst: don’t forget to download the answer key – that has all the definitions on it.
6. Price to Earnings Ratio Worksheet
A great lesson to teach your students is how to value a stock. You can do this by helping them to figure out the price to earnings using this worksheet.
7. Buy, Sell or Hold?: An Overview of Investing
Practical Money Skills offers both a teacher’s guide and student worksheets talking about what the stock market is, plus has them work through the price to earnings ratio for real-life stocks. This is Lesson #21, FYI.
8. What’s Up with the Stock Market?
BizKids has a great video plus accompanying stock market worksheet pdfs that teach your child to think about investment strategies. Students will also learn how to read a stock ticker.
9. Dividend-Paying Stocks
Suggested Age Range: Teens
Here’s a great, free teaching guide + worksheets on dividend-paying stocks.
Psst: you'll want to check out these fun compound interest activities for kids , too.
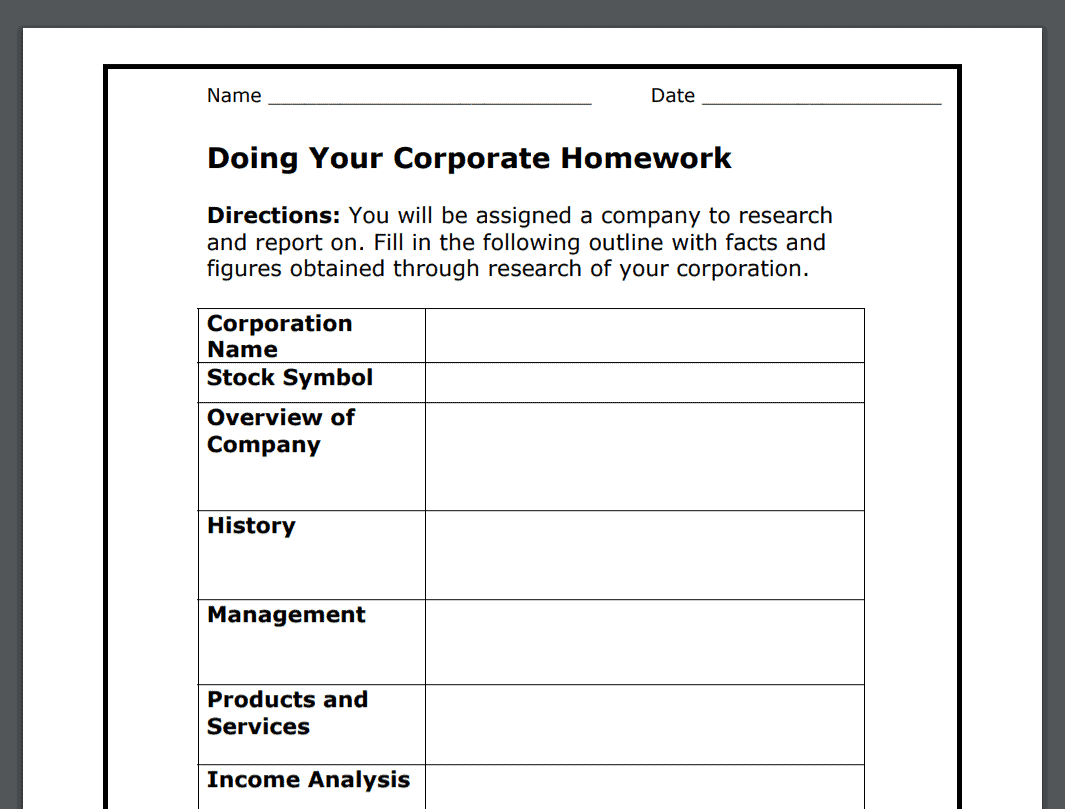
10. Doing Your Corporate Homework
Suggested Age Range: not given.
Either assign a corporation to each student, or let them choose one. Then, have them do research on the company by using this worksheet.
Afterwards, ask them if they should buy that company’s stock or no.
11. Are Stocks a Risky Long-Term Investment?
Suggested Age Range: 7-12 grades
Your students will analyze stock markets returns from 1871 to 2014, and then answer questions to determine whether or not it’s a good idea to invest in stocks over the long term.
Psst: you’ll want to check out my article on 7 best investment books for kids and teens .
Stock Market Lessons PDFs
Looking for more than just a one-page stock market worksheet?
I’ve got exciting stock market lesson PDFs, PowerPoint presentations, and anything else you need to teach your students all about the stock market.
12. Building Your Future: Accumulating Wealth
Suggested Age Range: High school
Are you ready for a really comprehensive set of stock market worksheets and lessons for students?
This is it!
You’ll definitely want to download and read the 22-page Teacher’s Guide that goes along with it.
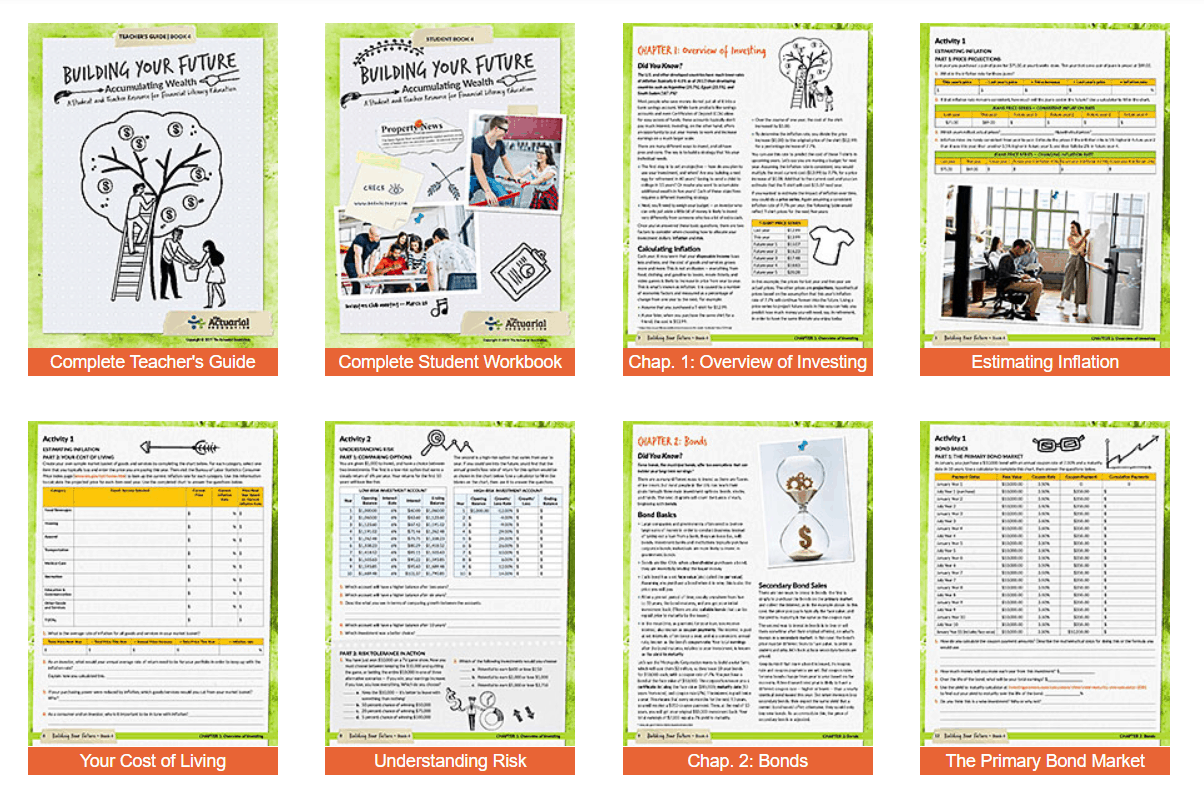
Investing subjects covered (with 39 pages of stock market worksheets) include:
- Overview of investing
- Asset allocation
- Evaluating stocks
- Building a bond portfolio
- Mutual funds
13. EconEdLink’s Buy and Hold: A Stock Market Simulation
Suggested Age: 9-12 grades
Sign up for a free account with EconEdLink, and get access to this great lesson on the stock market.
You and your students will go through a brief simulation on an IPO (Initial Public Offering).
You’ll get access to:
- PowerPoint presentation (with Notes section talking points for teachers)
- Printable Stock, Bonds, and Money cards
- Stock market quiz worksheet + answer key
- Guiding questions
You can use these tools to teach your students things like why diversifying when purchasing stocks is a good idea, and why corporations sell stocks.
14. EconEdLink’s Where Did all the Money Go?
Suggested Age Range: 9-12 grades
I like how this lesson on the Great Depression gives students clues and has them solve the mystery of what caused the Great Depression.
Great lesson on how interdependent everything is – including the stock market, jobs, banks, farmers, etc.
15. Teaching Financial Crisis
Looking to tie in your stock market teaching with actual history about financial crisis (where the stock market has played a major role)?
Personally, I think it’s great to teach kids that recessions and bear stock markets are a natural occurrence, and that they have always bounced back.
This resource has 8 lesson plans to teach financial crisis, specifically by comparing the financial crisis of 1907 to the financial crisis of 2007.
FYI: The worksheets are more like PDFs for kids to reach, but they’re still very informational.
16. Money Working for You Stock Market Lesson Plan
Register with High School Financial Planning, and check out Module 4 on investing, which is an entire lesson plan around investing.
You’ll get the following, all free:
- Instructor lesson packs
- Student lesson packs
- Lesson slide decks
There you have it – some awesome, and free stock market worksheet PDFs for students (both kids and teens) that will help them understand the stock market. Much better than I did at their age, anyway!
- Latest Posts
Amanda L. Grossman
Latest posts by amanda l. grossman ( see all ).
- 50 Banking Activities for Kids (Student Financial Literacy) - February 14, 2024
- 14 Christmas Activities for High School Students (they’ll Actually Find Cool) - December 1, 2023
- 3 Fun Selfie Scavenger Hunts for Teens (Christmas, Fin Lit, etc.) - November 27, 2023
Stash Learn
Menu Toggle
Back to Stash
Home / Investing / 72 Stock Market Terms Every Beginner Trader Should Know
Dec 8, 2023
72 Stock Market Terms Every Beginner Trader Should Know
New to investing? Dive into this breakdown of stock market terms every beginner should know.

Learning to navigate the stock market as a new investor can be intimidating, but getting familiar with basic stock market terms can get you up and running sooner than you’d think.
Understanding stock market fundamentals is key to making smart investing decisions, keeping a pulse on the market, and eventually taking on more complex trading strategies. Use the terms below to get a jump start on learning basic stock market vocabulary and create a strong foundation for your long-term wealth goals . In this article, we’ll cover:
- Asset allocation
- Asset classes
- Averaging down
- Bear market
- Bid-ask spread
- Blue-chip stocks
- Bull market
- Capitalization
- Capital gains
- Common stock
- Current ratio
- Day trading
- Debt-to-equity ratio
- Diversification
- Dividend yield
- Dollar-cost averaging
- Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA )
- Earnings per share (EPS)
- Economic bubble
- Equal weight rating
- Equity income
- Exchange-traded funds (ETFs)
- Expense ratio
- Going short
- Growth and income funds
- Growth stocks
- Head and shoulders pattern
- Index funds
- Initial public offering (IPO)
- Limit order
- Liquidity
- Market index
- Market volatility
- Moving average
- Mutual funds
- Non-fungible token (NFT)
- Order imbalance
- Outstanding shares
- Preferred stock
- Price quote
- Profit margin
- Risk tolerance
- Stock market holidays
- Stock option
- Stock portfolio
- Stock split
- Time horizon
- Value stocks
- Volume-weighted average price (VWAP)
- 52-week range
What is the stock market?
The stock market is a collection of markets where people buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. When someone invests in a stock, their investment is represented by a share, or partial ownership, of that company.
The stock market operates by potential buyers naming the highest price they’ll pay for an asset (the “bid”) and potential sellers naming the lowest price they’re willing to sell for (the “ask”). Trades are typically executed by stockbrokers on behalf of individual investors.
72 stock market terms for new investors
The stock market terms below are a great starting point if you’re new to trading stocks. Study these terms to familiarize yourself with common stock lingo that any new investor should understand.
1. Arbitrage
Arbitrage refers to purchasing an asset from one market and selling it to another market where the selling price is higher than what you paid for it, resulting in profit.

An ask is the selling price that a trader offers for their shares.
3. Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is an investment strategy that aims to balance risk and reward by dividing a certain percentage of investments—like stocks, bonds, real estate, cash, etc.—across different assets in an investment portfolio.
4. Asset Classes
Asset classes are categories of assets, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, or cash.
5. Averaging Down
Averaging down is an investing strategy that involves buying additional shares of an asset or stock after its price has fallen, resulting in a lower average purchase price.
6. Bear Market

A bear market is a market condition in which prices are expected to fall. Typically, this entails major indexes or stocks decreasing by 20% or more compared to previous highs.

Beta is the measure of an asset’s risk in relation to the market. A stock with a beta of 1.5 means that the stock typically moves 50% more than the market in the same direction. Generally, a higher beta indicates a riskier investment—if the market rises 10%, the stock will rise by 15%, but if the market falls by 10%, the stock will fall by 15%.

The price a trader is willing to pay for shares of a stock or other asset.
9. Bid-Ask Spread

Bid-ask spread is the difference between what buyers are willing to pay and the price sellers are asking for a stock.
10. Blockchain
A blockchain is a record-keeping database in which transactions made in Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies are recorded across multiple computers and distributed across the entire network of those computers.
11. Blue-Chip Stocks

Blue-chip stocks are common stocks of well-known companies known for their quality and history of growth.
A bond is a type of security loaned by an investor to a borrower like a company or government used to fund its operations.
13. Bull Market

A bull market is a market condition in which prices are expected to rise.
14. Buyback
A buyback is when a company repurchases outstanding shares to reduce the number of shares on the market and return profits to their investors, resulting in an increased value of the remaining shares.
15. Capitalization

Also known as market cap , capitalization is the total market value of all a company’s outstanding shares. It’s calculated by multiplying the total number of shares by the current share price.
16. Capital Gains
Capital gains refers to the profit earned after selling an asset or investment for a higher price than you paid for it.
17. Common Stock
This is one of the most basic stock market terms to know. Common stock is a type of security that represents ownership in a company. Holders of common stock are able to vote on matters like corporate policies and elect directors within that company.
18. Current Ratio
The current ratio is a measure of a company’s ability to pay short-term debt. It’s determined by dividing current assets by current liabilities.
19. Day Trading
Day trading is the practice of buying and selling shares of stock within a single day.
20. Debt-to-Equity Ratio
Debt-to-equity ratio represents a function of a company’s debt relative to its equity, or the value of its assets minus its liabilities. The ratio is found by dividing total liabilities by total shareholder equity.
21. Diversification
Diversification is an investment strategy that divides investment funds across a variety of assets in order to minimize overall risk.
22. Dividend

“ Dividend ” is one of the most basic terms for the stock market. It’s simply a portion of a company’s earnings paid out to its shareholders.
23. Dividend Yield
A dividend yield is a dividend expressed as a percentage of its stock price .
24. Dollar-Cost Averaging
Dollar-cost averaging is an investment strategy in which you invest a fixed amount on a regular basis regardless of the price of the asset.
25. Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA)
Also known as Dow 30, the Dow Jones Industrial Average is a stock market index consisting of the 30 most-traded blue-chip stocks on the New York Stock Exchange. It’s used to measure the performance of shares among the largest U.S. companies and gauge the overall direction of stock prices.
26. Earnings per Share (EPS)
Earnings per share is a company’s profit divided by its number of outstanding shares, and is used to measure corporate profitability.
27. Economic Bubble
An economic bubble is a situation where asset prices surge to significantly higher levels than the fundamental value of that asset.
28. Equal Weight Rating
An equal weight rating is a measure used by equity analysts to signify how well a stock is performing relative to other stocks. An equal weight rating suggests that a stock will perform similarly with the average of all the stocks being used for comparison.
29. Equity Income
Equity income is used to describe any income received from stock dividends.
30. Exchange
An exchange, or stock exchange, is a marketplace where investors and traders buy and sell stocks. You’ve probably heard of the most well-known exchanges in the U.S.: the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and Nasdaq.
31. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Commonly known as ETFs , exchange-traded funds are a collection of stocks or bonds combined in a single fund that can be purchased and traded on major stock exchanges. Similar to mutual funds, they’re a pooled investment fund, meaning a “pool” of money is aggregated from multiple investors.
32. Expense Ratio
An expense ratio measures the cost of owning a mutual fund, including expenses like the management of the fund, overhead fees, and any other costs associated with running the fund. It’s essentially an administrative fee paid to the company in return for owning the fund. The ratio is measured as a percentage of your total investment—for example, if you invest $10,000 in a fund with an expense ratio of .20%, you’ll pay $20 on top of your investment.
33. Futures
A future is a contract that requires a buyer to purchase a specific asset, and the seller to sell that asset at a certain future date at an agreed-upon price. Futures are a way for investors to hedge current investments—a risk management strategy intended to offset potential losses in other investments.
34. Going Long

Going long refers to the act of buying stock shares with the expectation that the asset’s price will rise, resulting in a profit.
35. Going Short
Going short —the opposite of going long—refers to the act of selling stock shares with the expectation that the asset’s price will fall. When an investor goes short on an asset, they borrow that asset, sell it, and hopefully purchase it later at a lower price if the price does decline, resulting in profit.
36. Growth and Income Funds
This is a type of mutual fund or ETF that has both a history of capital gains (growth) and income generated from dividends (income). Growth and income funds have a two-sided strategy of both long-term growth and short-term income.
37. Growth Stocks
A growth stock is a common stock of a company whose revenues are expected to grow at a significantly higher rate than what’s average for that industry.
38. Head and Shoulders Pattern
The head and shoulders pattern refers to a specific chart formation seen on a technical analysis chart. It appears when a stock price reaches three peaks: when the price peaks then declines; rises above that peak and declines again; and rises a third time (but not as high as the second peak) and then declines again. The second peak represents the formation’s “head,” and the first and third peaks represent the “shoulders.” It’s generally considered to be an indicator of an impending bear market.
39. Index Funds
Index funds are investment funds that follow the performance of a specific benchmark or stock market index, like the S&P 500. When you invest in an index fund , your money is used to invest in every company in that index. This results in a more diverse portfolio than if you were hand-selecting individual stocks, for example.
40. Inflation
Inflation is the rate of increase in prices for goods and services in the economy.
41. Initial Public Offering (IPO)
An IPO refers to a previously private company that becomes public by selling stock
shares on the stock market.
42. Limit Order
A limit order is an order to buy or sell a stock at or below a specific price. Limit orders give traders control over how much they pay.
43. Liquidity
Liquidity measures how quickly and easily a stock can be bought or sold without impacting its price. Cash, for example, is the most liquid asset—no exchange is necessary to gain value from it, and it’s already in its most liquid form. On the other hand, a car is less liquid—regardless of its value, you might have to wait to sell it at its best price.
Sometimes referred to as “buying on margin,” margin is when investors borrow money from a broker to purchase a stock, similar to a loan.
45. Market Index
A market index tracks the performance of a certain collection of stocks, often grouped to represent a certain industry. They’re a tool for investors to gauge the health of the stock market by comparing current and past stock prices.
46. Market Volatility
Market volatility is a measure of how much and how often the value of the stock market fluctuates.
47. Moving Average
A moving average is the average price of stocks or other assets over a specific period of time. Generally used in technical analysis charts, it’s calculated by averaging data from the previous time periods to help investors identify the current direction of price trends.
48. Mutual Funds
Mutual funds are pools of investments from shareholders used to “mutually” buy securities like stocks, bonds, and other assets.
Nasdaq, or National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations, is an electronic exchange where investors can buy and sell stocks through an automated network of computers. It’s the second-largest stock exchange in the world, following the NYSE.
More broadly, Nasdaq can also refer to the Nasdaq Composite Index, a stock market index of over 3,300 companies listed on the Nasdaq exchange. In this context, it can be thought of similarly to other indexes like the DJIA or the S&P 500.
50. Non-Fungible Token (NFT)
A non-fungible token, more commonly known as an NFT, is a blockchain-based financial security. Each NFT represents a unique digital asset. “Non-fungible” indicates that it can’t be replicated or replaced with something else.
51. Order Imbalance
An order imbalance occurs when orders of one type of stock aren’t offset by opposite orders, resulting in an excess of orders for that specific stock and sometimes volatile price changes.
52. OTC Stocks
OTC stocks , or over-the-counter stocks, are securities that are traded on a broker-dealer network instead of on a major U.S. stock exchange. They’re often used by smaller companies who don’t meet the requirements to be listed on a formal stock exchange.
53. Outstanding Shares
Outstanding shares refers to the total number of a company’s shares that have been issued to shareholders, including restricted shares.
54. P/E Ratio
Used to value a company, the P/E ratio , or price-earnings ratio, is the ratio of a company’s share price to the company’s earnings per share.
55. Preferred Stock
Preferred stock is a type of stock that combines characteristics of both common stock and bonds. Owners of preferred stock receive different rights than common stockholders , like receiving dividends before common stockholders, but they generally don’t come with corporate voting rights like common stocks do.
56. Price Quote
A price quote is the price of a stock or other security as quoted on an exchange. Price quotes usually come with important supplemental information to help traders make more informed investment decisions.
57. Profit Margin
Profit margins are used to gauge the profitability of a company. It’s expressed as a percentage and is calculated by dividing the company’s net profit (total revenue minus total expenses) by total revenue.
58. Recession
A recession is defined as a period of decline in economic performance throughout the economy, generally lasting for at least several months.
59. Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance is a measure of the level of risk you’re willing to accept on your investments. Someone with a lower risk tolerance typically sees lower returns on their investments in exchange for lower overall risk in periods of market decline.
60. Roth IRA
A Roth IRA is an individual retirement account that allows you to contribute after-tax dollars, allowing your earnings to grow and be withdrawn tax-free.
The stock market includes shares from thousands of different companies, which are broken into 11 different sectors . A sector is a group of companies with similar business products, services, or characteristics.
Shares are units of ownership in part of a company’s total stock .
63. Stock Market Holidays
While this isn’t necessarily a term or definition, it’s important to know what days you can and can’t buy or sell on the U.S. stock exchange. The U.S. stock market observes 10 holidays a year, closing on those days. In 2023, the observed holidays are New Years Day, Martin Luther King Jr. Day, President’s Day, Good Friday, Memorial Day, Juneteenth National Independence Day, Independence Day, Labor Day, Thanksgiving, and Christmas.
64. Stock Option
A stock option is a contract that gives an investor the right to purchase or sell a specific number of stock shares at a predetermined price within a specified time period.
65. Stock Portfolio
A stock portfolio is an individual’s collection of investments, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other financial assets. While a portfolio refers to all of your investments, they might not be contained in one single account.
66. Stock Split
A stock split occurs when a corporation increases the number of its outstanding shares by distributing more shares to current stockholders. By splitting existing shares into multiple new shares, the stock becomes more affordable.
67. Time Horizon
Time horizon refers to the period of time an investor expects to hold an investment, which will vary based on personal investment goals and strategies. For example, investing in a retirement account like a 401(k) has a longer time horizon, since the funds won’t be withdrawn until you reach retirement age. Generally speaking, longer time horizons correlate to more risk potential in a portfolio, and shorter time horizons correlate to a more conservative (less risky) portfolio.
68. Value Stocks
Value stocks are shares of companies selling at bargain prices that investors expect to rise because the company’s financial fundamentals suggest the shares are actually worth more than the current value.
Volume is a measure of how much a certain stock or other investment has been traded over a certain period of time. Volume is a critical component of strategically analyzing stock market trends, and is often used to determine market strength.
70. Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP)
Volume-weighted average price (VWAP) is a measure of the average trading price of a stock or other asset, adjusted for volume. It’s calculated by dividing the total dollar value of trading in that asset by the volume of trades.
Yield refers to the income earned on an investment over a set period of time, expressed as a percentage of your original investment.
72. 52-week Range
The 52-week range is a technical indicator that measures the lowest and highest price of a stock traded during a 52-week period. Traders use this measure to analyze current stock prices and predict its future movements.
Learning to navigate the stock market and stock trade terms for the first time might feel daunting, but consider this your official first step on the path to developing your investing muscles. When you come across a term you’re unfamiliar with in your own research, refer back to this post until you’ve mastered them. You’ll find that learning these stock terms for beginners is more doable than you think.
The more time you invest in learning stock market terms and fundamentals, the more confident you’ll become as an investor. And if you’re looking for a little more support, consider turning to a platform like Stash . We make it easy to invest what you can afford on a set schedule, all the while providing unlimited financial education and personalized advice based on your risk level—so you can start building long-term wealth , even if you’ve never invested before.

Investing made easy.
Start today with any dollar amount.

FAQs About Stock Market Terms
Have more questions about stock market terms? We have answers.
Why Should You Know Stock Market Terms?
Establishing a working knowledge of stock market terms forms the foundation for the rest of your investment journey. It’s the gateway to crafting a strategic market approach, understanding different trading strategies, and making sense of market fluctuations that will inform your future trading decisions.
How Do You Buy Stocks?
Before investing a dollar, get clear on your investment goals—this informs everything from your investment timeline to the specific investments you’ll choose. From there, the process of buying your first shares of stock is surprisingly easy:
- Open a brokerage account
- Research what stocks you want to buy
- Determine how much you can afford to invest
- Purchase your first share
- Maximize returns with a buy and hold strategy
What Are the Most Used Stock Market Terms?
The most used stock market terms include bear market, bull market, dividend, ask, bid, and blue-chip stocks.
All episodes are available now. You can listen to Teach Me How to Money right here on our site, and via the podcast apps below.

Related Articles

Stocks That Pay Dividends: A Guide to Investing in Dividend Stocks

How To Find Undervalued Stocks: An 8-Step Guide

What Is Passive Investing?

How To Read a Stock Chart: A Beginner’s Guide + Stock Chart Glossary

What Are the Different Types of Investments?

How To Diversify Investments: A Beginner’s Guide for 2024
Invest in yourself.
By using this website you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy . To begin investing on Stash, you must be approved from an account verification perspective and open a brokerage account.
Welcome to Stash101, our free financial education platform. Stash101 is not an investment adviser and is distinct from Stash RIA. Nothing here is considered investment advice.

Stock Market
Stock Market teaches students all about the stock exchange, the bull and bear markets, and what shares are. Students will discover how the stock market started in May of 1792. They will learn about the Buttonwood Agreement and about commissions. The Buttonwood Agreement led to what is now called the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
By the end of this lesson, students will be able to identify and define many of the terms associated with stocks. They will a basic understanding of how the market works and how to make money with investing. There are several suggestions in the “Options for Lesson” section that may aid in your instruction. For instance, you may invite a stock broker to speak with the class and provide additional information.
Description
Additional information, what our stock market lesson plan includes.
Lesson Objectives and Overview: Stock Market is a great lesson for 5th and 6th grade students. Your students will learn all about the stock exchange and related terms. They have likely heard of the stock market, but they may not fully understand it. Students will learn about buying, investing, selling, and trading. And they will even have the chance to simulate the stock exchange and purchase and trade stock.
Classroom Procedure
Every lesson plan provides you with a classroom procedure page that outlines a step-by-step guide to follow. You do not have to follow the guide exactly. The guide helps you organize the lesson and details when to hand out worksheets. It also lists information in the yellow box that you might find useful. You will find the lesson objectives, state standards, and number of class sessions the lesson should take to complete in this area. In addition, it describes the supplies you will need as well as what and how you need to prepare beforehand.
Options for Lesson
You can check out the “Options for Lesson” section of the classroom procedure page for additional suggestions for ideas and activities to incorporate into the lesson. Students may work alone or in groups for the activity. You could also increase or decrease the length of time for the activity. Have students create an imaginary company and give other students a set amount of money to invest in the imaginary companies. Then discuss how students decided on the investments. Invite a stock broker or another financial expert to speak with the class about the stock market, investing, etc. Assign each student a company of which they can research the stock value from the company’s founding up to the present day.
Teacher Notes
The teacher notes page provides an extra paragraph of information to help guide the lesson and remind you what to focus on. While students may have heard about the stock market, they may not really understand what it involves. This lesson is meant to provide a foundational understanding. You might also benefit from teaching this lesson in conjunction with others about money or the economy. The blank lines on this page are available for you to write out thoughts and ideas you have as you prepare the lesson.
STOCK MARKET LESSON PLAN CONTENT PAGES
Introduction to the stock market.
The Stock Market lesson plan contains four pages of content. The word stock simply refers to the supply of a product or maybe a service. And the market is usually a public place where people can buy, sell, or trade those products or services. However, in a financial market, the stock refers to the supply of money that a company has raised. The money comes from people who gave the company money in the hopes that the company will make a profit. In return, the people who gave the money will earn more money.
Stock market , then, is the business of buying and selling stock. It is not a place like a grocery store or a food market. Wall Street is the name of a street in New York City’s financial district, and sometimes we say “Wall Street” to refer to the United States stock market. The financial district is the place where many people (or computers) buy and sell stock for themselves and other people.
The first stock market began on May 17, 1792, when 24 stockbrokers (people who buy and sell stock) and merchants signed the Buttonwood Agreement. This agreement had two provisions. First, the brokers were only to deal with each when buying or selling stock. And second, commissions (the money brokers made on each sale) were to be 0.25%. The agreement was signed underneath a buttonwood tree.
Later, the agreement led to the formation of the New York Stock and Exchange Board. This is now the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), which is a company on Wall Street. It is also the world’s largest stock exchange. It provides a means for buyers and sellers to trade shares of stock in companies registered for public trading. There are other stock exchanges throughout the world as well, such as the London Stock Exchange (LSE) and another American exchange called the NASDAQ (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations) Stock Market.
Using the stock exchanges brokers, people and businesses can invest their money in public companies throughout the world. The public companies often want to grow their business, build more factories, or develop new products. So they turn to the selling of stocks to raise money for the company.
How Stocks Work
The next page outlines how the stock market functions. A company could borrow money from a bank to grow their business, but they would have to pay the money back to the bank. However, instead of borrowing money, a company can issue stock and raise money without going into debt. The people who buy the stock give money to the company to help the business grow.
In some way, you can think of it as opening a lemonade stand. After you open, you realize you don’t have enough money for all the supplies. You ask your parents for some money to help pay for lemons, cups, signage and other supplies. They give you the money, and you start selling. Once you begin making a profit, you pay them back and give them some of your profits. However, if you lose money, your parents will lose their money too. It is a risk they took to help you build your lemonade business.
Only business corporations can issue stock. A business owned by one person (sole-proprietorship) or a few people (partnership) cannot. A corporation has a special legal status and does not depend on the people who run it. And it has legal rights and responsibilities to the people who buy the company’s stock.
Shareholders and Stockholders
People who buy stock in a company own part of the company. Each part they own is called a share. For example, let’s go back to the lemonade stand. If you sold 100 shares of stock in your company at $1.00 per share, a person who purchased one share would own 1% of the company. A person who had 25 shares would own 25% of the company. The people who own the stock are called stockholders or shareholders.
The shareholders usually have voting rights in a company too. They could vote in people for the board of directors, for instance. The board will run the company and make major decisions for the company’s success. Stockholders usually have one vote for each share of stock they own. That means that the more stock a person owns, the greater influence they may have on the company. Quarterly or yearly reports are also sent to stockholders to inform them how the company is doing.
Every stockholder wants the company to grow and earn a profit. If the company earns money, the stockholders share the profits after the expenses are paid. Usually, when people invest money in companies by purchasing stock, they will earn more than they would if they left the money in the bank or made other investments.
For example, if the lemonade stand made a profit of $100, the people who purchased shares of the stock would double their money and earn a 100% profit. Banks and other investments usually yield much less. Of course, not all stocks earn such a high rate of return. But over time, investing in and buying shares of stock in a company usually leads to a greater profit.
On the other hand, if a company does poorly, goes out of business, and loses money, a stockholder can lose the money they invested in the company. The prices of stock for a company, though, will usually rise and fall over time. For example, a share of stock in a company today might cost $23, but tomorrow it could be worth $25 and the next day drop to $22. The rise and fall of stock prices drive people to “play” the stock market for a living.
Playing the Stock Market
There are people who play the stock market by buying and selling stock at the right time to earn money. For example, if the price of a stock goes down, a broker may purchase the stock at the lower price. They hold it for a while until the value of the stock rises or goes up and then sell it. If they can do this, they earn a profit simply by buying and selling stock at the right time.
For example, your lemonade stand stock may be worth $1 a share in the beginning but go up to $1.25 per share. The people who originally invested can now sell their shares for 25 cents profit per share to someone who is willing to buy the stock. The value of the stock could go down, however, and shareholders could lose money.
Students will learn that stock prices fluctuate daily and weekly. People will often hold onto a stock for a much longer period of time. The price of the share will change often, but over a long period of time, the value of stocks often rises. In summary, if a company does well, the value of shares rises. If a company struggles, the value of shares will go down.
Investors and brokers are often the people who follow the stock market very closely and invest another person’s or company’s money. They follow the overall rise and fall of the stock market and watch closely for companies that may increase in value and those that may decrease in value. At the end of each day, the market determines the overall value of stock shares that companies, brokers, and investors bought or sold, or traded. The stock market value is then reported as going “up” or “down.”
There are stock markets throughout the world, and investors will carefully watch what happens to the value of stocks in other countries too. Sometimes this helps them make choices as to whether they should buy or sell shares of stock throughout the day.
Bears and Bulls
There are two groups of investors—bears and bulls. A bear is an investor who believes the stock market will go down and will be cautious when buying stock. A bull is an investor who believes the stock market will go up and put more money into buying shares of stock. Investors can also be bearish or bullish about a single kind of stock. The term bear market describes a time when stock prices are falling. Naturally, then, a bull market is a period of rising stock prices. Bear markets are usually bad; bull markets are good.
Without stocks (the shares of value in a company), many businesses would not have the money to grow and develop their products or services. The idea of a stock market has been around for a long time. In fact, people purchased stocks to finance the Pilgrim’s voyage to America. They hoped the travelers would find something valuable in the New World, ensuring the investors made a profit.
For example, imagine that friends you know want to search for gold reportedly buried in the side of a mountain. Your friends might need money to purchase equipment and tools. You give them the money hoping the gold will be found. If it is, they have agreed to give you a certain percentage of the profit.
STOCK MARKET LESSON PLAN WORKSHEETS
The Stock Market lesson plan includes three worksheets: an activity worksheet, a practice worksheet, and a homework assignment. Each one will reinforce students’ comprehension of lesson material in different ways and help them demonstrate when they learned. Use the guidelines on the classroom procedure page to determine when to distribute each worksheet to the class.
PURCHASE SHARES ACTIVITY WORKSHEET
After dividing into pairs, students will purchase shares of five different stocks. They will have an imaginary $5000 to allocate among the stocks. They will track the rising and falling prices of the stocks over a period of time. The lesson states two weeks. However, you could provide real companies for the students to monitor and adjust the amount of time they will track the prices.
At the beginning of the activity, students will answer a set of questions. After the two weeks pass, they will answer another set of questions based on their experience.
DEFINITION MATCH PRACTICE WORKSHEET
The practice worksheet lists 15 statements. Students will match the definition to the correct term. Afterward, they will answer five other questions, most of which are based on the lesson material.

STOCK MARKET HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT
For the homework assignment, students must first fill in the blanks to 10 questions using the words in the word bank. Afterward, there is another set of statements. Students will determine whether the statement is true or false and mark it appropriately.
Worksheet Answer Keys
There are answer keys for both the practice and homework worksheets at the end of the lesson plan document. Correct answers are in red to make it easy for you to compare them to students’ work. If you choose to administer the lesson pages to your students via PDF, you will need to save a new file that omits these pages. Otherwise, you can simply print out the applicable pages and keep these as reference for yourself when grading assignments.
Related products

Careers: Web Developer

Careers: Astronomer

Careers: Robotics Engineer
Make your life easier with our lesson plans, stay up-to-date with new lessons.

- Lesson Plans
- For Teachers
© 2024 Learn Bright. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions. Privacy Policy.
- Sign Up for Free
- Contests With Prizes
- Mutual Funds
- Making Your First Investments
- Beginner Charts and Analysis
- Technical Analysis
- Advanced Trading Strategies
- Charts and Patterns
- Broker Center
- Investing Course
- Personal Finance Calculators
- Newsletters
- The 10 Terms You Need To Know
- A – G
- H – M
- N – T
- U – Z and #
- Teacher’s Guide
- Lesson Plans
- HowTheMarketWorks In The Classroom
Core Stock Market Project
This project is the “Core”, which most teachers use as the basis for their HTMW class stock game. The other recommendations in this library usually follow this format (with some variation). This makes it very flexible to work with your classes.

This project usually runs between 4 and 16 weeks. Longer contests tend to work better. This is because students are exposed to more “market news” for a longer time, and is a better introduction to “real” investing outside of the classroom.
Project Overview
The goal of this project is to introduce students to basic investing concepts, and get exposure to the real-world financial markets. Each student will build their own portfolio of stocks and mutual funds, with a set of initial investing goals, and regular investing journal entries. At the end of the session, students will create and present a 5-10 minute presentation to the class. The presentation should discuss the goals they set, and how they worked with the changing markets over the course of the contest. Students will also need to submit a report detailing their trading activities.
Project Set-Up
Contest rules.
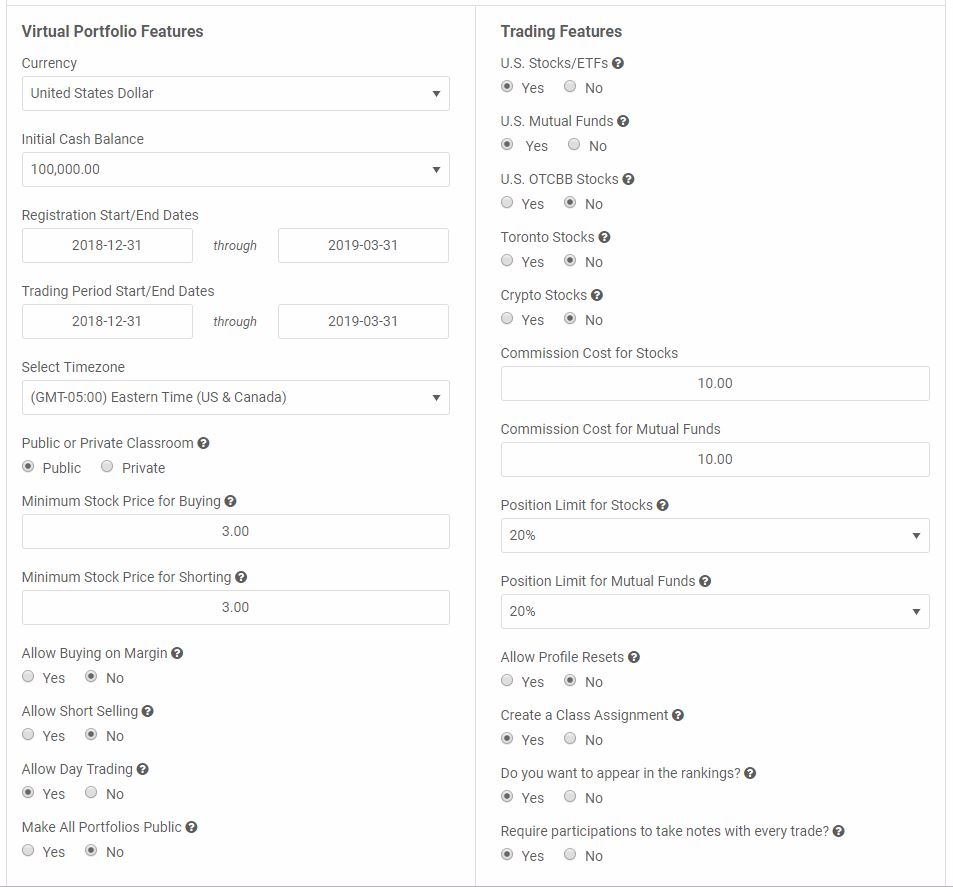
Use these settings to set up your class contest:
- Initial Cash: $100,000
- Registration/Trading Dates: as long as your class allows (we recommend starting this project early – likely before your discuss investing in detail in the class itself)
- Minimum Prices: $3
- Short Selling: OFF
- Day Trading: ON
- Margin Trading: OFF
- Public Portfolios: OFF
- Allow US Stocks and Mutual Funds
- Commission: $10/trade
- Position Limits: 20% (students can’t invest more than 20% of their portfolio in any single stock)
- Create an assignment
- Keep the teacher in the rankings
- Require Trading Notes
You will get a unique registration link to share with your students – this will let them create their login and join you into your class.
You should also add an “Assignment” to your class. Your first “Assignment” should last the first week of the trading period, and include the 10 items in the “Stock Market Basics” section. These are designed to provide students with a basic introduction to what a portfolio is and how to make trades, with short articles, videos, and tutorials.
Assignments keep the experience educational – it provides a clear structure for what your students are expected to learn, while introducing them to the game and how it works!
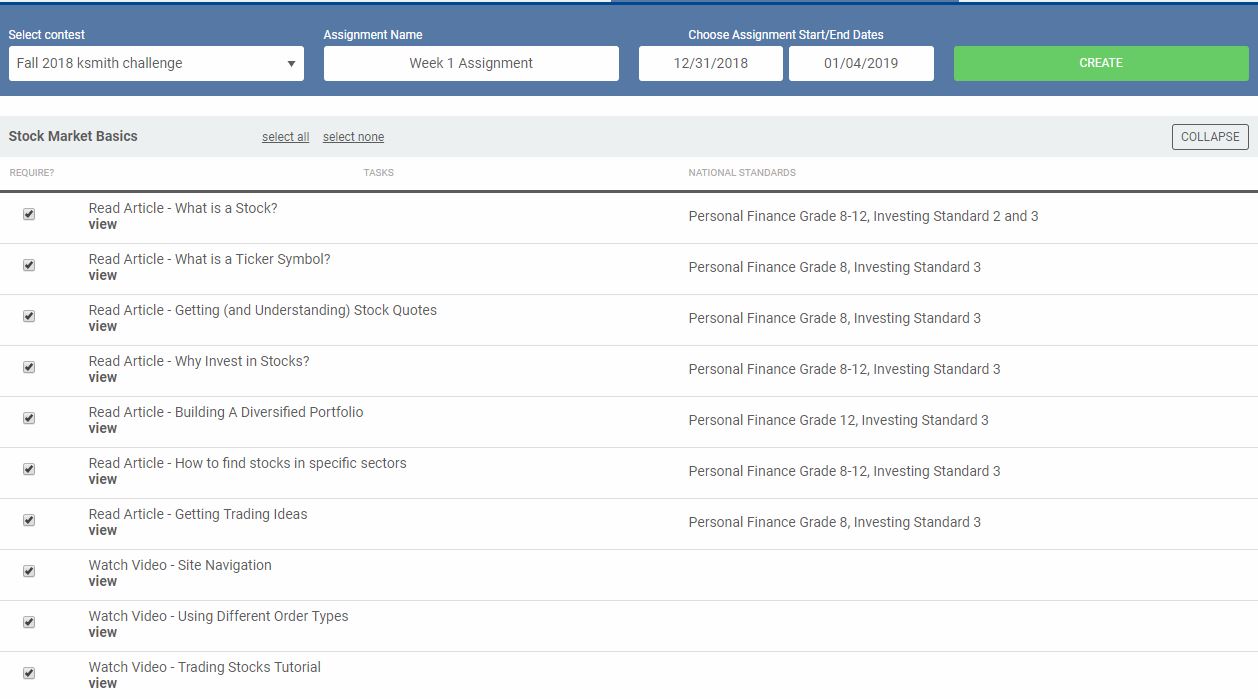
You can create more assignments for each week, including other tasks that align with what you are discussing in class. Most classes assign the next 10 items, under “Intermediate Investing Tips”, as the second week’s assignment.
Project Kick-Off
Kick off the project using our Cornerstone Lesson Plan – this is a short introduction to glossary terms and the concepts of stocks of investing. At the end of the lesson, have students create their logins for your HTMW class contest, and work through the first 10 “Stock Market Basics” lesson. This should usually take about 1 hour.

Next, introduce your students to a few “Scenarios”. These will determine the kinds of portfolios they will build. They can choose between:
- A retirement portfolio – the goal will be constant, slow growth, with an emphasis on avoiding losses (a portfolio for someone who wants to retire in 15 years)
- A growth portfolio – the goal will be high growth with some risk (a portfolio of someone in their 20’s or 30’s looking for high returns)
Now put students into groups of 3-5, based on which scenario they chose. Have each group prepare a list of 10 ticker symbols (ideally from at least 3 different sectors) of companies that they are familiar with, and that they think will perform well for their scenario. Students can find the ticker symbols, sectors, and performance charts for all US and Canadian stocks in the “Quotes” tool on HTMW. This should take between 30 and 45 minutes.
Then break up the groups, and have each student individually should pick 5 of these companies, and add them to their HTMW portfolio. Each student should also write a 1 page summary about why they chose the companies they did, and why they DIDN’T choose the other 5 companies the group identified (this can be homework). This ensures each student will have a unique portfolio, but based on some group thinking.
Weekly Check-In
Ensure all students are checking their HTMW portfolio at least once a week (with the class rankings, most students will be checking a lot more often!). You can post the class rankings at the front of class to make sure students are staying engaged.
Keep using Assignments! You can easily track which students are participating, and remind students who start falling behind. Plus, the lessons are a great supplement to what you are already covering in class!
You will also want to encourage students to continue trading for the duration of the contest. Require students to make at least 3 trades in their portfolio each week (you can require this with an Assignment), and they should both be keeping Trade Notes with each trade, and a 1 paragraph Trade Summary that gives a short summary of what happened in their portfolio each week. This summary should include things like what stocks did well, which did poorly, how did market news impact their holdings, and how it relates back to other class topics under discussion.
Final Report
At the end of the trading period, student’s portfolios will automatically freeze, so they can continue to log in and see how they did at the end of the last day, but not place any new trades.
This gives the opportunity for students to prepare a final “Investment Report”. The Investment Report should be between 3-5 pages, divided into sections.
- A summary of their investing scenario, and how well they achieved their investing objectives
- A graph showing their portfolio performance for the duration of the contest
- A list of significant events during the contest that had a big impact on their portfolio (news reports impacting stock prices, ect)
- A pie chart showing their final holdings
- A profit/loss summary, showing where exactly they made and lost money
- An appendix with all of their weekly investing journals
Happy trading and let us know if you have any questions! If you have your own awesome class stock project that your students really loved, please share so other teachers can give it a try!
Read These Next

Comments are closed.
- Search Search
Browse More Articles
- Choosing Investments
- Beginner Strategies
- Beginner Charts
- Advanced Strategies
- Advanced Charts
- Motley Fool Stock Advisor Review
- Rule Breakers Review
- Best Investment Newsletters
- Best Stocks to Buy Now
- Top 10 Terms
- Teacher's Guide
- In The Classroom

- Find a Branch
- Schwab Brokerage 800-435-4000
- Schwab Password Reset 800-780-2755
- Schwab Bank 888-403-9000
- Schwab Intelligent Portfolios® 855-694-5208
- Schwab Trading Services 888-245-6864
- Workplace Retirement Plans 800-724-7526
... More ways to contact Schwab
Chat
- Schwab International
- Schwab Advisor Services™
- Schwab Intelligent Portfolios®
- Schwab Alliance
- Schwab Charitable™
- Retirement Plan Center
- Equity Awards Center®
- Learning Quest® 529
- Mortgage & HELOC
- Charles Schwab Investment Management (CSIM)
- Portfolio Management Services
- Open an Account
Options Exercise, Assignment, and More: A Beginner's Guide

So your trading account has gotten options approval, and you recently made that first trade—say, a long call in XYZ with a strike price of $105. Then expiration day approaches and, at the time, XYZ is trading at $105.30.
Wait. The stock's above the strike. Is that in the money 1 (ITM) or out of the money 2 (OTM)? Do I need to do something? Do I have enough money in my account? Help!
Don't be that trader. The time to learn the mechanics of options expiration is before you make your first trade.
Here's a guide to help you navigate options exercise 3 and assignment 4 —along with a few other basics.
In the money or out of the money?
The buyer ("owner") of an option has the right, but not the obligation, to exercise the option on or before expiration. A call option 5 gives the owner the right to buy the underlying security; a put option 6 gives the owner the right to sell the underlying security.
Conversely, when you sell an option, you may be assigned—at any time regardless of the ITM amount—if the option owner chooses to exercise. The option seller has no control over assignment and no certainty as to when it could happen. Once the assignment notice is delivered, it's too late to close the position and the option seller must fulfill the terms of the options contract:
- A long call exercise results in buying the underlying stock at the strike price.
- A short call assignment results in selling the underlying stock at the strike price.
- A long put exercise results in selling the underlying stock at the strike price.
- A short put assignment results in buying the underlying stock at the strike price.
An option will likely be exercised if it's in the option owner's best interest to do so, meaning it's optimal to take or to close a position in the underlying security at the strike price rather than at the current market price. After the market close on expiration day, ITM options may be automatically exercised, whereas OTM options are not and typically expire worthless (often referred to as being "abandoned"). The table below spells it out.
- If the underlying stock price is...
- ...higher than the strike price
- ...lower than the strike price
- If the underlying stock price is... A long call is... -->
- ...higher than the strike price ...ITM and typically exercised -->
- ...lower than the strike price ...OTM and typically abandoned -->
- If the underlying stock price is... A short call is... -->
- ...higher than the strike price ...ITM and typically assigned -->
- If the underlying stock price is... A long put is... -->
- ...higher than the strike price ...OTM and typically abandoned -->
- ...lower than the strike price ...ITM and typically exercised -->
- If the underlying stock price is... A short put is... -->
- ...lower than the strike price ...ITM and typically assigned -->
The guidelines in the table assume a position is held all the way through expiration. Of course, you typically don't need to do that. And in many cases, the usual strategy is to close out a position ahead of the expiration date. We'll revisit the close-or-hold decision in the next section and look at ways to do that. But assuming you do carry the options position until the end, there are a few things you need to consider:
- Know your specs . Each standard equity options contract controls 100 shares of the underlying stock. That's pretty straightforward. Non-standard options may have different deliverables. Non-standard options can represent a different number of shares, shares of more than one company stock, or underlying shares and cash. Other products—such as index options or options on futures—have different contract specs.
- Stock and options positions will match and close . Suppose you're long 300 shares of XYZ and short one ITM call that's assigned. Because the call is deliverable into 100 shares, you'll be left with 200 shares of XYZ if the option is assigned, plus the cash from selling 100 shares at the strike price.
- It's automatic, for the most part . If an option is ITM by as little as $0.01 at expiration, it will automatically be exercised for the buyer and assigned to a seller. However, there's something called a do not exercise (DNE) request that a long option holder can submit if they want to abandon an option. In such a case, it's possible that a short ITM position might not be assigned. For more, see the note below on pin risk 7 ?
- You'd better have enough cash . If an option on XYZ is exercised or assigned and you are "uncovered" (you don't have an existing long or short position in the underlying security), a long or short position in the underlying stock will replace the options. A long call or short put will result in a long position in XYZ; a short call or long put will result in a short position in XYZ. For long stock positions, you need to have enough cash to cover the purchase or else you'll be issued a margin 8 call, which you must meet by adding funds to your account. But that timeline may be short, and the broker, at its discretion, has the right to liquidate positions in your account to meet a margin call 9 . If exercise or assignment involves taking a short stock position, you need a margin account and sufficient funds in the account to cover the margin requirement.
- Short equity positions are risky business . An uncovered short call or long put, if assigned or exercised, will result in a short stock position. If you're short a stock, you have potentially unlimited risk because there's theoretically no limit to the potential price increase of the underlying stock. There's also no guarantee the brokerage firm can continue to maintain that short position for an unlimited time period. So, if you're a newbie, it's generally inadvisable to carry an options position into expiration if there's a chance you might end up with a short stock position.
A note on pin risk : It's not common, but occasionally a stock settles right on a strike price at expiration. So, if you were short the 105-strike calls and XYZ settled at exactly $105, there would be no automatic assignment, but depending on the actions taken by the option holder, you may or may not be assigned—and you may not be able to trade out of any unwanted positions until the next business day.
But it goes beyond the exact price issue. What if an option is ITM as of the market close, but news comes out after the close (but before the exercise decision deadline) that sends the stock price up or down through the strike price? Remember: The owner of the option could submit a DNE request.
The uncertainty and potential exposure when a stock price and the strike price are the same at expiration is called pin risk. The best way to avoid it is to close the position before expiration.
The decision tree: How to approach expiration
As expiration approaches, you have three choices. Depending on the circumstances—and your objectives and risk tolerance—any of these might be the best decision for you.
1. Let the chips fall where they may. Some positions may not require as much maintenance. An options position that's deeply OTM will likely go away on its own, but occasionally an option that's been left for dead springs back to life. If it's a long option, the unexpected turn of events might feel like a windfall; if it's a short option that could've been closed out for a penny or two, you might be kicking yourself for not doing so.
Conversely, you might have a covered call (a short call against long stock), and the strike price was your exit target. For example, if you bought XYZ at $100 and sold the 110-strike call against it, and XYZ rallies to $113, you might be content selling the stock at the $110 strike price to monetize the $10 profit (plus the premium you took in when you sold the call but minus any transaction fees). In that case, you can let assignment happen. But remember, assignment is likely in this scenario, but it is not guaranteed.
2. Close it out . If you've met your objectives for a trade, then it might be time to close it out. Otherwise, you might be exposed to risks that aren't commensurate with any added return potential (like the short option that could've been closed out for next to nothing, then suddenly came back into play). Keep in mind, there is no guarantee that there will be an active market for an options contract, so it is possible to end up stuck and unable to close an options position.
The close-it-out category also includes ITM options that could result in an unwanted long or short stock position or the calling away of a stock you didn't want to part with. And remember to watch the dividend calendar. If you're short a call option near the ex-dividend date of a stock, the position might be a candidate for early exercise. If so, you may want to consider getting out of the option position well in advance—perhaps a week or more.
3. Roll it to something else . Rolling, which is essentially two trades executed as a spread, is the third choice. One leg closes out the existing option; the other leg initiates a new position. For example, suppose you're short a covered call on XYZ at the July 105 strike, the stock is at $103, and the call's about to expire. You could attempt to roll it to the August 105 strike. Or, if your strategy is to sell a call that's $5 OTM, you might roll to the August 108 call. Keep in mind that rolling strategies include multiple contract fees, which may impact any potential return.
The bottom line on options expiration
You don't enter an intersection and then check to see if it's clear. You don't jump out of an airplane and then test the rip cord. So do yourself a favor. Get comfortable with the mechanics of options expiration before making your first trade.
1 Describes an option with intrinsic value (not just time value). A call option is in the money (ITM) if the stock price is above the strike price. A put option is ITM if the stock price is below the strike price. For calls, it's any strike lower than the price of the underlying equity. For puts, it's any strike that's higher.
2 Describes an option with no intrinsic value. A call option is out of the money (OTM) if its strike price is above the price of the underlying stock. A put option is OTM if its strike price is below the price of the underlying stock.
3 An options contract gives the owner the right but not the obligation to buy (in the case of a call) or sell (in the case of a put) the underlying security at the strike price, on or before the option's expiration date. When the owner claims the right (i.e. takes a long or short position in the underlying security) that's known as exercising the option.
4 Assignment happens when someone who is short a call or put is forced to sell (in the case of the call) or buy (in the case of a put) the underlying stock. For every option trade there is a buyer and a seller; in other words, for anyone short an option, there is someone out there on the long side who could exercise.
5 A call option gives the owner the right, but not the obligation, to buy shares of stock or other underlying asset at the options contract's strike price within a specific time period. The seller of the call is obligated to deliver, or sell, the underlying stock at the strike price if the owner of the call exercises the option.
6 Gives the owner the right, but not the obligation, to sell shares of stock or other underlying assets at the options contract's strike price within a specific time period. The put seller is obligated to purchase the underlying security at the strike price if the owner of the put exercises the option.
7 When the stock settles right at the strike price at expiration.
8 Margin is borrowed money that's used to buy stocks or other securities. In margin trading, a brokerage firm lends an account owner a portion of the purchase price (typically 30% to 50% of the total price). The loan in the margin account is collateralized by the stock, and if the value of the stock drops below a certain level, the owner will be asked to deposit marginable securities and/or cash into the account or to sell/close out security positions in the account.
9 A margin call is issued when your account value drops below the maintenance requirements on a security or securities due to a drop in the market value of a security or when a customer exceeds their buying power. Margin calls may be met by depositing funds, selling stock, or depositing securities. Charles Schwab may forcibly liquidate all or part of your account without prior notice, regardless of your intent to satisfy a margin call, in the interests of both parties.
Just getting started with options?
More from charles schwab.

Today's Options Market Update

Weekly Trader's Outlook

Options Expiration: Definitions, a Checklist, & More
Related topics.
Options carry a high level of risk and are not suitable for all investors. Certain requirements must be met to trade options through Schwab. Please read the Options Disclosure Document titled " Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options " before considering any options transaction. Supporting documentation for any claims or statistical information is available upon request.
With long options, investors may lose 100% of funds invested. Covered calls provide downside protection only to the extent of the premium received and limit upside potential to the strike price plus premium received.
Short options can be assigned at any time up to expiration regardless of the in-the-money amount.
Investing involves risks, including loss of principal. Hedging and protective strategies generally involve additional costs and do not assure a profit or guarantee against loss.
Commissions, taxes, and transaction costs are not included in this discussion but can affect final outcomes and should be considered. Please contact a tax advisor for the tax implications involved in these strategies.
The information provided here is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered an individualized recommendation or personalized investment advice. The investment strategies mentioned here may not be suitable for everyone. Each investor needs to review an investment strategy for his or her own particular situation before making any investment decision.
All expressions of opinion are subject to change without notice in reaction to shifting market conditions. Data contained herein from third-party providers is obtained from what are considered reliable sources. However, its accuracy, completeness, or reliability cannot be guaranteed.
Examples provided are for illustrative purposes only and not intended to be reflective of results you can expect to achieve.
Short selling is an advanced trading strategy involving potentially unlimited risks and must be done in a margin account. Margin trading increases your level of market risk. For more information, please refer to your account agreement and the Margin Risk Disclosure Statement.
From Interactive Brokers
- More Campus
Finance Courses and Lessons
Featured Lessons
- TWS for Beginners
IBKR Desktop
Financial News and Market Commentary
Featured Articles

Whenever You Call Me, I’ll Be There: May 2, 2024

Stocks Cry Wolf Ahead of Powell: May. 1, 2024
Quantitative Code and News
Quant Articles

- Data Science
Insights on Backtesting

Data Science - Python Development - R Development
Quant Developer: Roadmap, Career, and Skills to Become a Quantitative Developer – Part II
Webinars from Financial Professionals
Webinar Topics
Latest Webinars

May / 08 / 2024 - 12:00 pm - EDT
What Investors Need to Know: Changing Demographics in Canada

May / 09 / 2024 - 6:00 pm - SGT
The 2024 Trader Playbook – The Big Themes for the Year

Financial Market Commentary Podcasts
Listen to IBKR Podcasts on
Featured Podcasts

- Cents of Security
Active vs Passive Investments

- IBKR Podcasts
The Dirt on Crop Progress: A Farmer’s Perspective
API Tools from Interactive Brokers
FIX Protocol
Third-Party Integrations
Featured API Articles

Python Development - REST Development
Handling Options Chains
- Python Development
Intro to the TWS API
Python Development - TWS Excel API
Connecting Python to Excel
Finance Training in the Classroom
Sample Curricula
The IBKR Advantage
Real-world experience for your classroom
IBKR Glossary of Financial Terms
Find by letter or search
Learn more about IBKR accounts
Low Commissions 1 , Global Access, Premiere Technology
Useful Tools and Information
Newsletter Signup
- All Finance Courses
- Beginner Courses
- Intermediate Courses
- Advanced Courses
- Other Trading Products
- IBKR Student Trading Lab
- Fundamentals
- Intro to IBKR Tools
- Advanced IBKR Tools
- Institutions
- Traders’ Insight Home
- IBKR Economic Landscape
- IBKR Commentary
- Fixed Income
- Commodities
- Securities Lending
- Technical Analysis
- IBKR Quant Home
- Quant Development
- Conferences
- C# Development
- C++ Development
- Java Development
- Julia Development
- R Development
- REST Development
- TWS Excel API
- Upcoming Webinars
- Webinars Aired
- Webinar Contributors
- AI & Machine Learning
- Alternative Investments
- Cryptocurrency
- Energy Sector
- Financial Spotlight
- International
- Women in Finance
- Podcasts Home
- Podcasts En Español
- Contributor Podcasts
- Leave a Review
- IBKR-API Home
- Documentation Changelog
- Getting Started
- Market Data Subscriptions
- Order Types
- Web API Documentation
- Web API Reference
- CPAPI v1.0 Documentation
- TWS API Documentation
- TWS API Reference
- Excel ActiveX
- Available/Existing Integrations
- Prospective Integrations
- For Teachers
- For Students
- Educator Trading Lab
- Simulated Competition
- Stock Trading Sample Assignments
- Option Trading Sample Assignments
- Futures Trading Sample Assignments
- Forex Trading Sample Assignments
- Computer Science Sample Assignments
- Economics Sample Assignments
- ESG Sample Assignment
- All Glossary Terms
- IBKR Quant Terms
More Campus Resources
- About The IBKR Campus
- IBKR Campus Contributors
- IBKR Guides
- IBKR Campus Newsletter
- Traders’ Insight Newsletter
- IBKR Webinars Newsletter
- IBKR Quant Newsletter
- IBKR API Newsletter
Stock Trading Sample Assignments and Resources
Ib trading platform basics.
Instruct your students to familiarize themselves with one or more of our three trading platforms – desktop, browser-based and mobile - using a variety of IB educational resources. Specific assignments can test your students' general knowledge of our trading platforms and can be organized based on the contents of QuickStart Guides, Users' Guides or Webinars.
Trader Workstation
Learn the basics of our market maker-designed TWS desktop trading platform.
Documentation
- TWS Users' Guide
Traders' Academy
Ibkr mobile.
Learn the basics of our mobile platform on a cell phone or tablet.
- IBKR Mobile for iOS for iPhone
- IBKR Mobile for iOS for iPad
- IBKR Mobile for Android for Phone
- IBKR Mobile for Android for Table
- IBKR Mobile - iPhone®
- IBKR Mobile - Android©
Stock Orders
Instruct your students to learn the basics of trading by placing basic and advanced orders.
Basic Orders
Place at least three different basic stock order types. For example, market, limit and stop orders.
Order Types page
- Order Types Sort by "stocks" to view all stock order types.
- Market Order
- Limit Order
- TWS Order Types
Reference Material
- IBKR Traders' Insight
Advanced Stock Orders
Instruct your students to place at least three different advanced stock order types. For example, All or None (AON), Bracket and Conditional orders.
- All or None Order
- Bracket Order
- Conditional Order
Short Selling
Instruct your students to place an order to sell short.
Market Data Fields
Add short selling market data fields to Classic TWS.
- Short Selling Market Data Fields
Additional Reference
- Traders' Academy - Securities Lending and Borrowing
- IBKR Traders' Insight - Securities Lending
Statements and Trade Confirmations
Instruct your students to check their daily activity statements and trade confirmation reports. Assignments can include running and analyzing a default statement; creating, running and analyzing a customized statement, and running and analyzing a trade confirmation report.
Statements and Trade Confirmation Reports are available from within Account Management.
Run default statements and create customized statements to view detailed information about the account activity, including positions, cash balances, transactions, and more.
Reporting Users' Guide
- Viewing Activity Statements
- Creating Customized Statements
- Sample Statements
- Trade Confirmation Reports
Run trade confirmation reports to view trade confirmations separately by asset class.
- Sample Trade Confirmation Reports
US Stock Commissions
Instruct your students to familiarize themselves with our commissions.
IB's Stock Commissions
Review IB's stock commissions and other pertinent pricing information.
- Commissions web page
IBKR Campus Newsletters
Get updates on podcasts, webinars, courses, and more from our IBKR pillars.
View the latest financial news articles from the top voices in the industry.
For those wanting to trade markets using computer-power by coders and developers.
Hear about the latest tools and techniques from our own IBKR API staff.
This website uses cookies to collect usage information in order to offer a better browsing experience. By browsing this site or by clicking on the "ACCEPT COOKIES" button you accept our Cookie Policy.
Traders' Insight RSS
To add ibkr traders’ insight to your rss feed, please paste the following link into your reader:, ibkr quant rss, to add ibkr quant to your rss feed, please paste the following link into your reader:, this page contains information regarding options trading.
To view this page, you must acknowledge that you have received the Characteristics & Risks of Standardized Options, also known as the options disclosure document (ODD). Options involve risk and are not suitable for all investors. For more information, click here to read the " Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options " or visit: ibkr.com/occ
By acknowledging this disclosure you are also allowing this website to use "functional" cookies on your browser. To find out more about cookies, see our privacy settings.
Privacy Preference Center
Your privacy.
When you visit any website it may use cookies and web beacons to store or retrieve information on your browser. This information might be about you, your preferences or your device and is typically used to make the website work as expected. The information does not usually directly identify you, but can provide a personalized browsing experience. Because we respect your right to privacy, you can choose not to allow some types of cookies and web beacons. Please click on the different category headings to find out more and change our default settings. However, blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our website and limit the services we can offer.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
Strictly necessary cookies are necessary for the website to function and cannot be switched off in our systems. They are typically set in response to actions made by you which amount to a request for services, such as setting your privacy preferences, logging in or filling in forms. While you can set your browser to block or alert you about these cookies, some parts of the website will not work. These cookies do not store any personally identifiable information.
ALWAYS ACTIVE
Performance Cookies
Performance cookies and web beacons allow us to count visits and traffic sources so we can measure and improve website performance. They help us to know which pages are the most and least popular and see how visitors navigate around our website. All information these cookies and web beacons collect is aggregated and anonymous. If you do not allow these cookies and web beacons we will not know when you have visited our website and will not be able to monitor its performance.
Allow Performance Cookies:
Functional Cookies
Functional cookies enable our website to provide enhanced functionality and personalization. They may be set by us or by third party providers whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies then some or all of these services may not function properly.
Allow Functional Cookies:
Marketing Cookies and Web Beacons
Marketing Cookies and web beacons may be set through our website by our advertising partners. They may be used by those companies to build a profile of your interests and show you relevant adverts on other websites. They do not directly store personal information, but uniquely identify your browser and internet device. If you do not allow these cookies and web beacons, you will experience less targeted advertising. Our website does not track users when they cross to third party websites, does not provide targeted advertising to them and therefore does not respond to "Do Not Track" signals.
Allow Marketing Cookies:
Interactive Brokers Group Cookie Policy
What are Cookies and Web Beacons?
Cookies are pieces of data that a website transfers to a user's hard drive for record-keeping purposes. Web beacons are transparent pixel images that are used in collecting information about website usage, e-mail response and tracking. Generally, cookies may contain information about your Internet Protocol ("IP") addresses, the region or general location where your computer or device is accessing the internet, browser type, operating system and other usage information about the website or your usage of our services, including a history of the pages you view.
How We Use Cookies and Web Beacons
Interactive Brokers Group collects information from cookies and web beacons and stores it in an internal database. This information is retained in accordance with our Privacy Policy. This website uses the following cookies and web beacons:
These cookies are necessary for the website to function and cannot be switched off in our systems. They are usually only set in response to actions made by you which amount to a request for services, such as setting your privacy preferences, logging in or filling in forms. You can configure your browser to block or alert you about these cookies, but certain areas of the site will not function properly. These cookies do not store any personal data.
Performance Cookies and Web Beacons
These cookies and web beacons allow us to count visits and traffic sources so we can measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to know which pages are the most and least popular and see how visitors move around the site. All information that these cookies and web beacons collect is aggregated and, therefore, anonymous. If you do not allow these cookies and web beacons our aggregated statistics will not have a record of your visit. The website uses Google Analytics, a web analytics service provided by Google, Inc. ("Google"). Google Analytics uses cookies to help analyse how you use this website. The information generated by the cookie about your use of this website (including your IP address) will be transmitted to and stored by Google on servers in the United States. Google will use this information for the purposes of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity for website operators and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage. Google may also transfer this information to third parties where required to do so by law, or where such third parties process the information on Google's behalf. Google will not associate your IP address with any other data held by Google.
These cookies enable the website to provide enhanced functionality and personalization. They may be set by us or by third party providers whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies, some or all of these services may not function properly.
These cookies and web beacons may be set throughout our site by our advertising partners. They may be used by those companies to build a profile of your interests and show you relevant advertisements on other sites. They do not store personal information that could identify you directly, but are based on uniquely identifying your browser and internet device. If you do not allow these cookies and web beacons, you will experience less targeted advertising. The website does not track users when they cross to third party websites, does not provide targeted advertising to them and therefore does not respond to Do Not Track ("DNT") signals.
Managing Your Cookie Preferences
You have many choices with regards to the management of cookies on your computer. All major browsers allow you to block or delete cookies from your system. However, if you do decide to disable cookies you may not be able to access some areas of our website or the website may function incorrectly. To learn more about your ability to manage cookies and web beacons and how to disable them, please consult the privacy features in your browser or visit www.allaboutcookies.org. This website may link through to third party websites which may also use cookies and web beacons over which we have no control. We recommend that you check the relevant third parties privacy policy for information about any cookies and web beacons that may be used.
IBKR LLC (U.S.)
We are redirecting you to the Interactive Brokers LLC (U.S.) Website. Should you decide to open an account, you will be redirected to the account application for your region. You can also find the website of the IBKR entity for your region at the bottom of this page.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Options and Derivatives
- Strategy & Education
Assignment: Definition in Finance, How It Works, and Examples
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
What Is an Assignment?
Assignment most often refers to one of two definitions in the financial world:
- The transfer of an individual's rights or property to another person or business. This concept exists in a variety of business transactions and is often spelled out contractually.
- In trading, assignment occurs when an option contract is exercised. The owner of the contract exercises the contract and assigns the option writer to an obligation to complete the requirements of the contract.
Key Takeaways
- Assignment is a transfer of rights or property from one party to another.
- Options assignments occur when option buyers exercise their rights to a position in a security.
- Other examples of assignments can be found in wages, mortgages, and leases.
Uses For Assignments
Assignment refers to the transfer of some or all property rights and obligations associated with an asset, property, contract, or other asset of value. to another entity through a written agreement.
Assignment rights happen every day in many different situations. A payee, like a utility or a merchant, assigns the right to collect payment from a written check to a bank. A merchant can assign the funds from a line of credit to a manufacturing third party that makes a product that the merchant will eventually sell. A trademark owner can transfer, sell, or give another person interest in the trademark or logo. A homeowner who sells their house assigns the deed to the new buyer.
To be effective, an assignment must involve parties with legal capacity, consideration, consent, and legality of the object.
A wage assignment is a forced payment of an obligation by automatic withholding from an employee’s pay. Courts issue wage assignments for people late with child or spousal support, taxes, loans, or other obligations. Money is automatically subtracted from a worker's paycheck without consent if they have a history of nonpayment. For example, a person delinquent on $100 monthly loan payments has a wage assignment deducting the money from their paycheck and sent to the lender. Wage assignments are helpful in paying back long-term debts.
Another instance can be found in a mortgage assignment. This is where a mortgage deed gives a lender interest in a mortgaged property in return for payments received. Lenders often sell mortgages to third parties, such as other lenders. A mortgage assignment document clarifies the assignment of contract and instructs the borrower in making future mortgage payments, and potentially modifies the mortgage terms.
A final example involves a lease assignment. This benefits a relocating tenant wanting to end a lease early or a landlord looking for rent payments to pay creditors. Once the new tenant signs the lease, taking over responsibility for rent payments and other obligations, the previous tenant is released from those responsibilities. In a separate lease assignment, a landlord agrees to pay a creditor through an assignment of rent due under rental property leases. The agreement is used to pay a mortgage lender if the landlord defaults on the loan or files for bankruptcy . Any rental income would then be paid directly to the lender.
Options Assignment
Options can be assigned when a buyer decides to exercise their right to buy (or sell) stock at a particular strike price . The corresponding seller of the option is not determined when a buyer opens an option trade, but only at the time that an option holder decides to exercise their right to buy stock. So an option seller with open positions is matched with the exercising buyer via automated lottery. The randomly selected seller is then assigned to fulfill the buyer's rights. This is known as an option assignment.
Once assigned, the writer (seller) of the option will have the obligation to sell (if a call option ) or buy (if a put option ) the designated number of shares of stock at the agreed-upon price (the strike price). For instance, if the writer sold calls they would be obligated to sell the stock, and the process is often referred to as having the stock called away . For puts, the buyer of the option sells stock (puts stock shares) to the writer in the form of a short-sold position.
Suppose a trader owns 100 call options on company ABC's stock with a strike price of $10 per share. The stock is now trading at $30 and ABC is due to pay a dividend shortly. As a result, the trader exercises the options early and receives 10,000 shares of ABC paid at $10. At the same time, the other side of the long call (the short call) is assigned the contract and must deliver the shares to the long.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/novation.asp-final-f5904e1fe68047ba9d8b6feaf53c1736.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Concept of Stock Market
The concept of Stock Market
The stock market refers to public markets that exist for issuing, buying and selling stocks that trade on a stock exchange or over-the-counter. It is a place where you can buy and sell shares of companies listed there for trading. Stock exchanges list shares of common equity as well as other security types, e.g. corporate bonds and convertible bonds.
The stock market serves two very important purposes. The first is to provide capital to companies that they can use to fund and expand their businesses. The secondary purpose the stock market serves is to give investors – those who purchase stocks – the opportunity to share in the profits of publicly-traded companies.
Investing in the stock market is among the most common ways investors attempt to grow their money, but it’s also among the riskier investment options available. The securities once issued in the primary market become the part of the secondary market. It provides a place or mechanism for active trading of securities among investors themselves. The stock market is a secondary market, which aids to the liquidity of securities traded there on. When investors have to buy securities in the secondary market, they have to contact the securities brokers for opening the account for the purchase of securities. After the account has been opened, the securities broker conveys the order of investor to the securities dealers who handle the inventory of securities. There are two basic types of stock markets- organized stock exchange and over-the-counter market.
An organized stock exchange is the physical locations where securities are traded under some established rules and regulation through the licensed members of the exchange. It is one of the important secondary markets where the investors buy and sell the securities between themselves. Organized stock exchanges facilitate the trading of securities, which are listed in it. This means the securities, which are not listed, are not traded in organized stock exchange. It provides companies with access to capital in exchange for giving investors a slice of ownership.
This trade is either through formal exchanges or over-the-counter (OTC) marketplaces. Over-the-counter (OTC) market was traditionally concerned with the trading of securities which were not listed in an organized stock exchange. However, today the securities listed in organized stock exchange are also traded in OTC market. OTC market is an informal type of market for securities where no compulsory listing of securities is required. Any security can be traded on OTC market as long as a registered dealer is willing to make a market in the security (willing to buy and sell the security). It is not a central physical place like an organized stock exchange, rather it is the network of brokers and dealers scattered across the country. Buy and sell in an OTC market are conducted through negotiated bidding through a network of the communication line and computer system, which links brokers and dealers in an o\OTC market to their clients. The brokers and dealers in the OTC market can compete with both investment bankers and the organized exchanges because they can operate in both primary as well as secondary market.
Information Source:
- accountlearning.blogspot.com
Back Freight
Protective put, bond credit rating, which factors affecting the size of investment in inventories, oxidoreductase – an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, sample settlement release letter format, the little man and his little gun, need for land drainage, assignment on xampp installation process, natural disasters, latest post, needle valve, hydroforming, solving the puzzle of early medieval money, human activities have a significant impact on the deep underground fluid flow, a microbial plastic factory for high-quality green plastic, power optimizer – a dc to dc converter technology.
- Stock Market Simulation
- Budgeting Game
- Financial Literacy Curriculum
- University Trading Room Software
- Custom Virtual Trading Platform
- Custom Financial Literacy Program
- Finance Faculty
- Personal Finance Faculty
- CFA-Focused Universities
- CFP-Focused Universities
- University Site Licenses
- Professor FAQs, videos, sample syllabi, academic research
- High Schools
- Elementary/Middle Schools
- White Label Trading Platforms
- White Label Financial Literacy Platform
- Employee Financial Wellness Programs
- Sponsor a School or University
- Individual Investors
- Investing 101 Course
- WallStreetSurvivor.com
- About Certifications
- Chartered Financial Analyst – CFA
- Certified Financial Planner – CFP
- Certified Public Accountant – CPA
- Securities Industry Essentials – SIE
- Career Center
- Job Search Help
- Market Summary
- Market Movers
- Top Performing ETFs
- Futures Summary
- Economic Rates
- Interactive Charts
- Option Chain
- Company News
- Share Performance
- Financial Statements
- SEC Filings
- Corporate Actions
- Price History
- Analyst Ratings
- Company Profile
Creating and Managing Assignments
What are Assignments?
An Assignment is a list of tasks you can give your students to complete using their virtual portfolio.
Each Assignment has its own start dates and due dates – you can have one long assignment lasting the entire trading session, or give students smaller assignments week by week.
Types of Tasks
There are three types of tasks you can assign:
- Watching tutorial videos demonstrating how to use the StockTrak.com website and research tools.
- Reading educational articles about investing, personal finance, and career development.
- Making certain types of trades.
Tutorial Videos

There are over a dozen tutorial videos available on the StockTrak Video Center . These include:
- Site Navigation : walkthrough of the website, and the portfolio pages and how they work.
- Security Type Tutorials : walkthrough for each security type, showing how they are traded and what makes them unique compared to each other.
- Order Type Tutorials: walkthroughs for limit, stop, and trailing stop orders, along with how to best utilize different order terms.
- Research Tutorial : walkthrough of using the integrated StockTrak research tools.
Including a Tutorial Video in your assignment will require your student to watch that video to get credit. Including an assignment with tutorial videos can greatly speed up how quickly students get familiarized with their portfolios.
Reading Articles
The StockTrak Learning Library has hundreds of articles about investing, personal finance, and career development. You can assign these articles as Required Reading for your class as part of an assignment.
If you assign an article, students will need to read the article and answer a short quiz at the end to get credit.

You can choose whether students can retake the pop quizzes to get a better score. You’ll be able to track the number of attempts and how long students spend on each lesson.
Making Trades
Finally, you can also require your students to make certain types of trades in their StockTrak portfolio. This can be something basic, like placing 10 total trades, or more specific, like using 3 Trailing Stop orders or trading 3 stocks from the Toronto Stock Exchange.
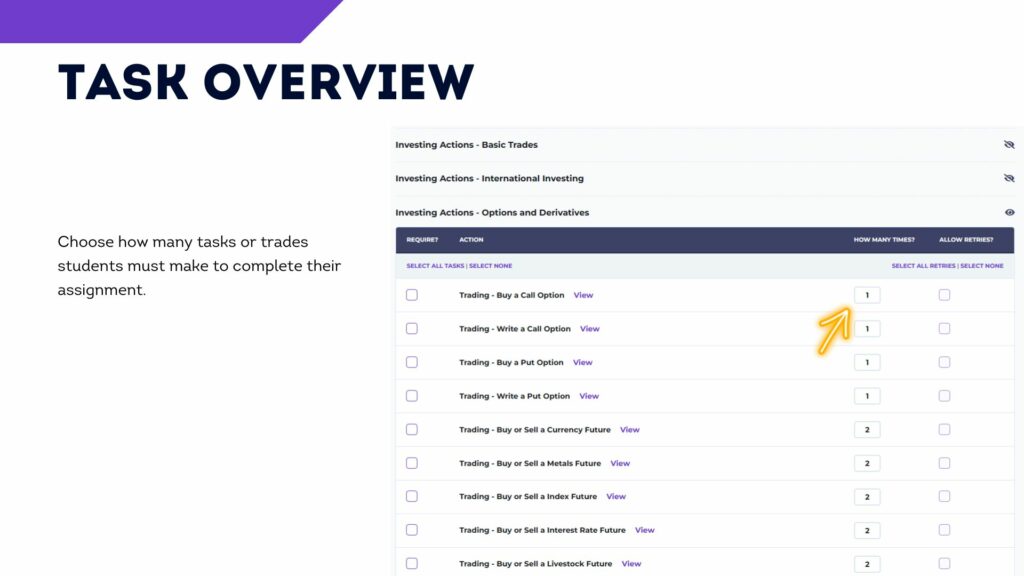
Getting Started With Assignments
Once your class is set-up, you can manage your assignments from the Admin menu. Create a new assignment, or you can view/edit your existing ones from here.
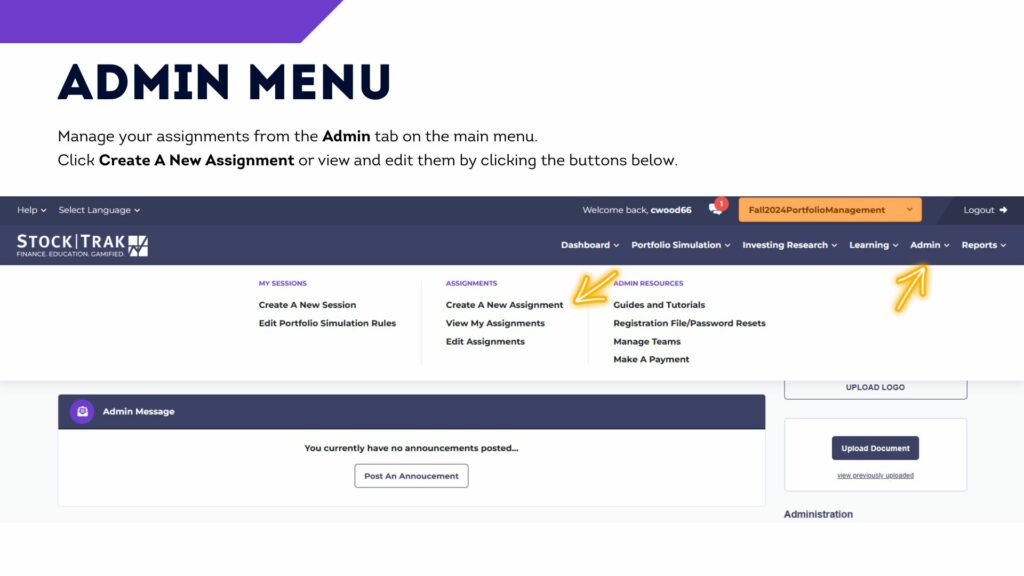
Click Create a New Assignment to go to the Create Assignment page.

Copy an Older Assignment
If you’ve used StockTrak before, you can reuse older assignments by clicking the button Copy Older Assignment . You will still need to set the dates and assignment name after copying over your previous selection of lessons and tasks.
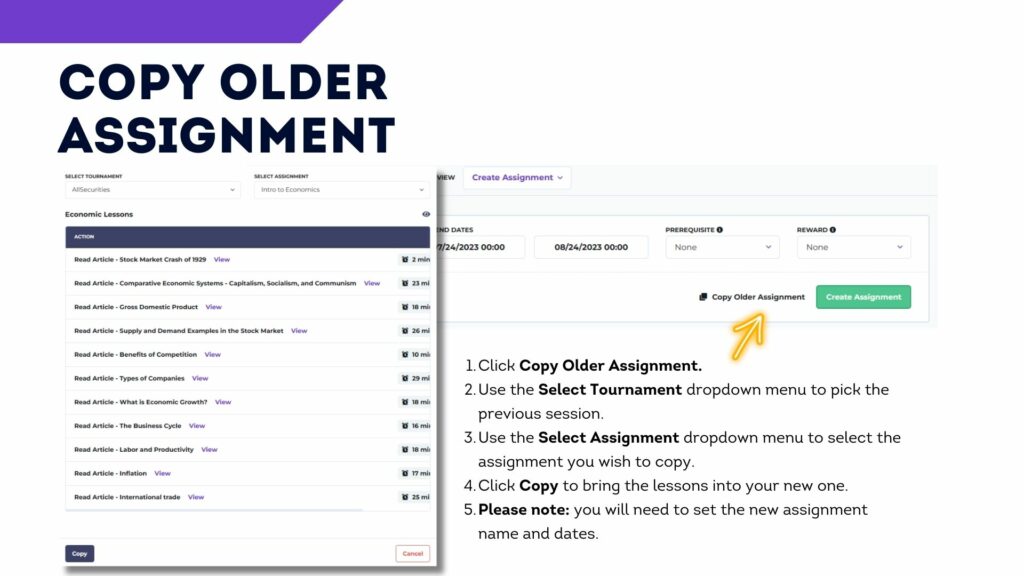
Task Selection
You can either select individual tasks by checking the box in front of the lesson/task name, or a whole section by clicking Select All Tasks. Similarly, allow your students to redo the pop quiz to get a better grade by checking the boxes under Select All Retries .
Click the View button to see what’s included in the lesson. The time estimations will give you a rough idea of how long it will take your students to complete each one.
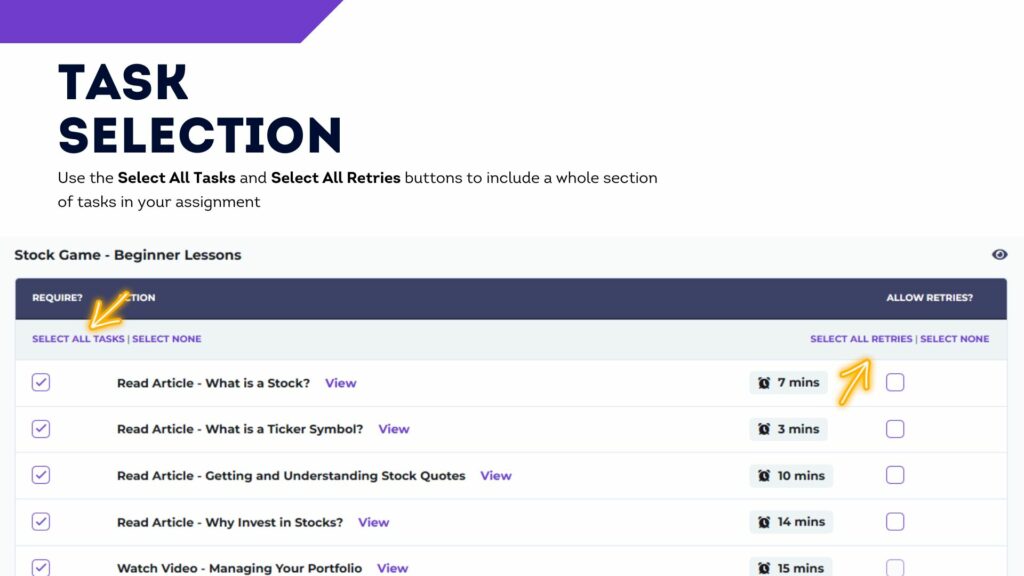
Where to Start
We recommend that every class include the Stock Game – Beginner Lessons as the first assignment. This is a selection of lessons covering basic glossary terms your students will need to know, along with tutorial videos walking them through the different resources available, and how to place their first trade.
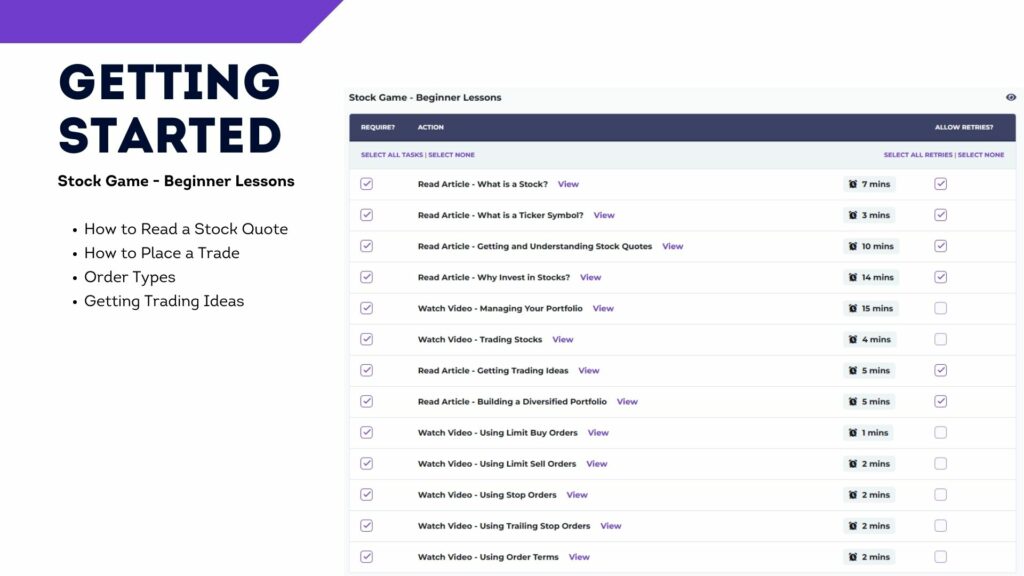
If you’re using StockTrak as part of a Personal Finance class, there are 60 articles and activities covering Personal Finance topics like budgeting, insurance, credit, and debt.
If you are using StockTrak as part of an Investments, Portfolio Management, or Derivatives class, you will have additional articles, videos, and trading tasks focusing on options and derivatives trading.
There is also our 10-chapter Investing 101 Beginner’s Investing Course. This is a self-contained investing e-book of 100 investing topics designed for novice students taking part in department-wide or campus-wide investing challenges. Each chapter ends with a vocabulary quiz and chapter exam that can be assigned individually or altogether.
Create Assignment
Once you’ve selected all the items you want to include in this assignment, click Create Assignment towards the top of the page. You can edit your lesson at any time from the Edit Assignment page.
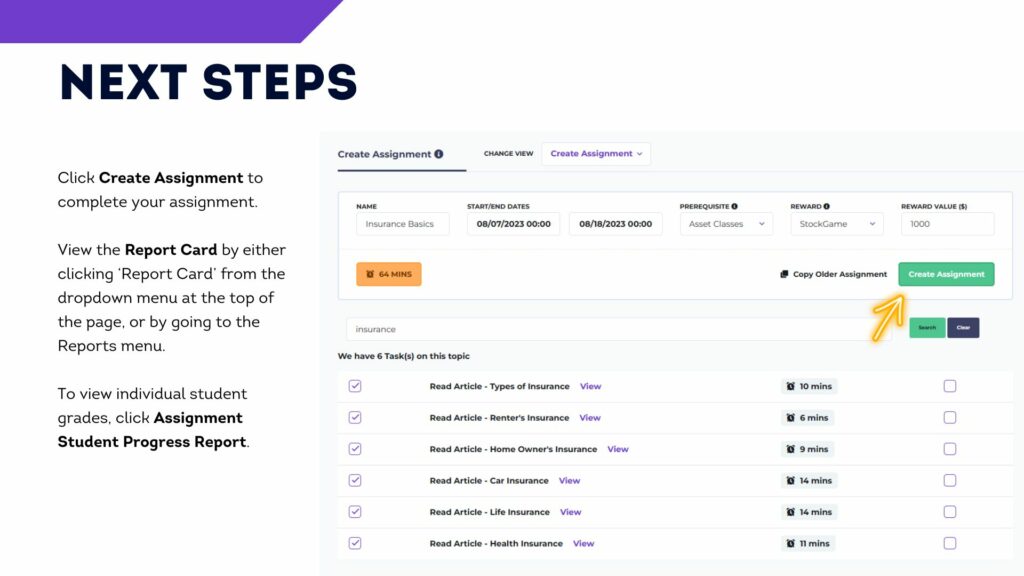
Assignment Report Card
View student progress and grades by either switching to the Report Card option from the drowdown menu at the top of the page. Or you can use the Reports menu and click Assignment Student Progress Report .
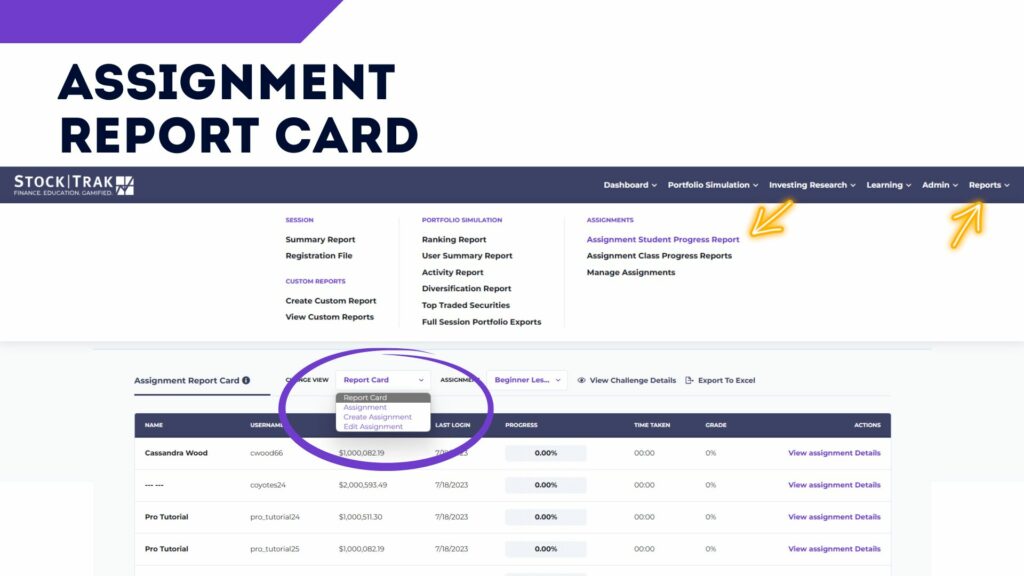
The report card will list all the students in your class, along with their current progress in each assignment. Click View assignment Details to see more information about how long they’ve taken to complete the lesson, their quiz attempts and grades.
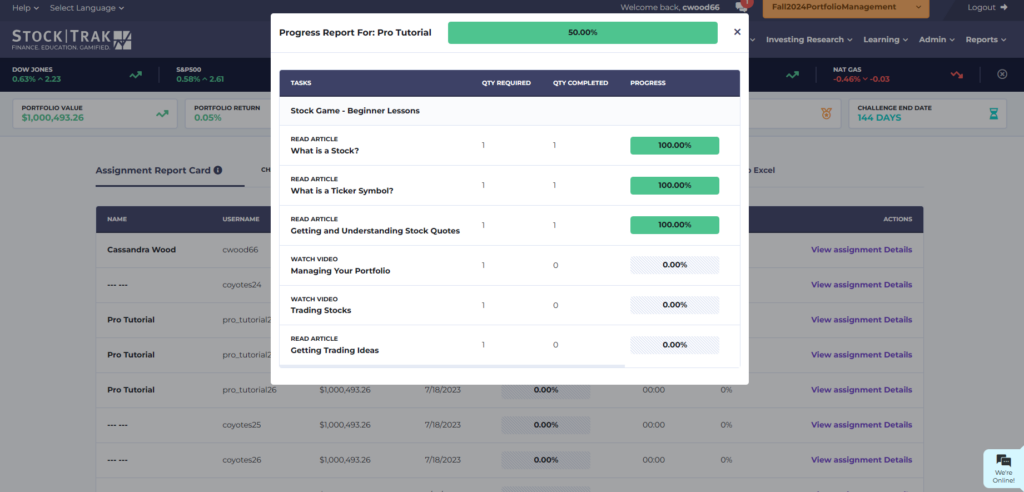
Student Dashboard
When students log into their account, the top widget on their dashboard will list all of their assignments. By clicking Show Tasks they’ll be able to see the individual lessons in your assignment.
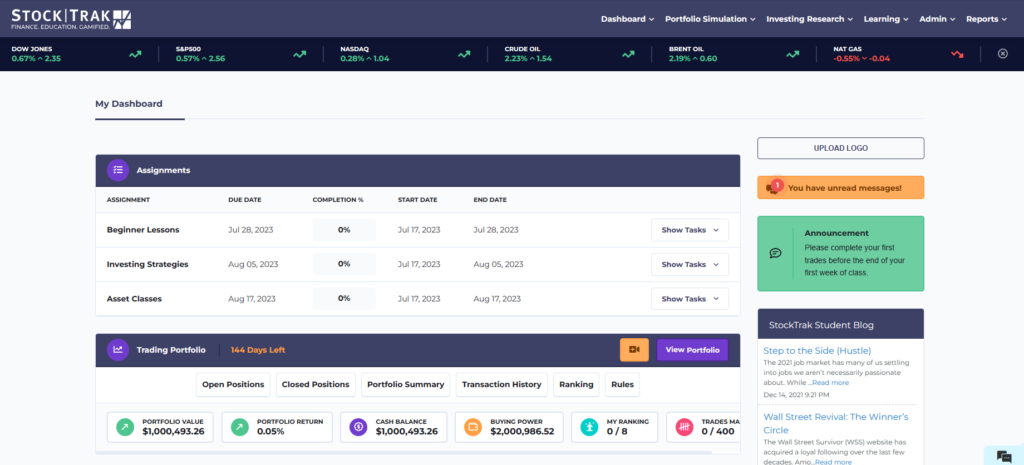
To view the Student Dashboard, click Switch to User Dashboard from the top of the Admin Dashboard.
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My Portfolio
- Latest News
- Stock Market
- Premium News
- Biden Economy
- EV Deep Dive
- Stocks: Most Actives
- Stocks: Gainers
- Stocks: Losers
- Trending Tickers
- World Indices
- US Treasury Bonds
- Top Mutual Funds
- Highest Open Interest
- Highest Implied Volatility
- Stock Comparison
- Advanced Charts
- Currency Converter
- Basic Materials
- Communication Services
- Consumer Cyclical
- Consumer Defensive
- Financial Services
- Industrials
- Real Estate
- Mutual Funds
- Credit cards
- Balance Transfer Cards
- Cash-back Cards
- Rewards Cards
- Travel Cards
- Personal Loans
- Student Loans
- Car Insurance
- Morning Brief
- Market Domination
- Market Domination Overtime
- Opening Bid
- Stocks in Translation
- Lead This Way
- Good Buy or Goodbye?
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Yahoo Finance
Asgn incorporated (asgn).
- Previous Close 95.56
- Day's Range 95.10 - 96.66
- 52 Week Range 63.27 - 106.42
- Volume 293,474
- Avg. Volume 270,443
- Market Cap (intraday) 4.409B
- Beta (5Y Monthly) 1.51
- PE Ratio (TTM) 22.24
- EPS (TTM) 4.32
- Earnings Date Jul 24, 2024 - Jul 29, 2024
- Forward Dividend & Yield --
- Ex-Dividend Date --
- 1y Target Est 94.00
ASGN Incorporated Overview Information Technology Services / Technology
ASGN Incorporated engages in the provision of information technology (IT) services and solutions in the technology, digital, and creative fields for commercial and government sectors in the United States, Canada, and Europe. It operates through two segments: Commercial and Federal Government. The Commercial Segment provides consulting, creative digital marketing, and permanent placement services primarily to enterprise clients. This segment also offers workforce mobilization, modern enterprise, and digital innovation IT consulting services; and cloud, data and analytics, and digital transformation solutions. The Federal Government Segment provides mission-critical solutions to the department of defense, intelligence communities, and federal civilian agencies. This segment offers cloud, cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, machine learning, application and IT modernization, and science and engineering solutions. The company was formerly known as On Assignment, Inc. and changed its name to ASGN Incorporated in April 2018. ASGN Incorporated was founded in 1985 and is based in Glen Allen, Virginia.
Full Time Employees
December 31
Fiscal Year Ends
Information Technology Services
Recent News: ASGN

Apex Systems Earns VETS Indexes Recognized Employer Designation

ASGN First Quarter 2024 Earnings: GAAP EPS Misses Expectations

ASGN Inc (ASGN) Q1 2024 Earnings: Aligns with EPS Projections Amidst Revenue Decline

ASGN Incorporated Reports First Quarter 2024 Results

Apex Systems Enhances Accounts Payable (AP) Automation with ISPnext

Should You Investigate ASGN Incorporated (NYSE:ASGN) At US$94.82?

ASGN Becomes Corporate Champion for Children’s Hospital of Richmond at VCU

ASGN Schedules First Quarter 2024 Earnings Release and Conference Call

Apex Systems Recognized as Best Place to Work for Women in Mexico

ASGN's (NYSE:ASGN) five-year earnings growth trails the 9.5% YoY shareholder returns

ECS Subsidiary Awarded $120M Cybersecurity Contract With Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services

Investors Met With Slowing Returns on Capital At ASGN (NYSE:ASGN)
Performance overview: asgn.
Trailing total returns as of 5/2/2024, which may include dividends or other distributions. Benchmark is S&P 500 .
1-Year Return
3-year return, 5-year return, compare to: asgn.
Select to analyze similar companies using key performance metrics; select up to 4 stocks.
Statistics: ASGN
Valuation measures.
Enterprise Value
Trailing P/E
Forward P/E
PEG Ratio (5yr expected)
Price/Sales (ttm)
Price/Book (mrq)
Enterprise Value/Revenue
Enterprise Value/EBITDA
Financial Highlights
Profitability and income statement.
Profit Margin
Return on Assets (ttm)
Return on Equity (ttm)
Revenue (ttm)
Net Income Avi to Common (ttm)
Diluted EPS (ttm)
Balance Sheet and Cash Flow
Total Cash (mrq)
Total Debt/Equity (mrq)
Levered Free Cash Flow (ttm)
Research Analysis: ASGN
Analyst price targets, analyst recommendations.
- Underperform
People Also Watch
We couldn’t find any results matching your search.
Please try using other words for your search or explore other sections of the website for relevant information.
We’re sorry, we are currently experiencing some issues, please try again later.
Our team is working diligently to resolve the issue. Thank you for your patience and understanding.
News & Insights

How Option Assignment Works: Understanding Options Assignment
May 26, 2023 — 08:00 am EDT
Written by [email protected] for Schaeffer ->
Options assignment is a process in options trading that involves fulfilling the obligations of an options contract.
It occurs when the buyer of an options contract exercises their right to buy or sell the underlying asset. The seller (writer) of the options contract must deliver or receive the underlying asset at the agreed-upon price (strike price).
What is Options Assignment?
Options assignment can happen when the owner of an option exercises their right to buy or sell shares of stock or when options expire in the money (ITM). This process can be complex and involves various factors such as the type of option, expiration date, and market conditions.
There are two main styles of options contracts: American-style and European-style. American-style options allow the buyer of a contract to exercise at any time during the life of the contract. In contrast, European-style options can only be exercised on the expiration date.
Traders selling American-style options are at risk of assignment anytime on or before the expiration date. While they can technically be assigned anytime, the option must be ITM for the owner of the contract to benefit from exercising their right.
On the other hand, many options traders prefer to sell European-style options as it is impossible to be assigned before the expiration date, giving them more flexibility to hold their contract without worrying about being assigned early.
Who is at Risk of Assignment in Options Trading?
Traders with short options positions are at risk of assignment because they have sold the option and are obligated to deliver or receive the underlying asset. If the owner of the options contract decides to exercise their rights, the seller of the options contract must fulfill their obligations.
Traders with long options positions are not at risk of assignment as they are in control of exercising their options. A long option holder has the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying asset at the strike price. If the long option holder decides not to exercise their options, they can let the options contract expire worthless.
What is the Risk of Assignment?
The risks associated with options assignment are primarily centered around the obligations of the seller of the options contract. If the holder of the options contract decides to exercise their right to buy or sell the underlying asset, the seller must fulfill their obligations.
For example, if a trader sold a put option with a $100 strike price, and the stock dropped to $90, they would still have to buy the stock at $100 per share. When an option is ITM, it generally indicates that the seller of the option is in an unfavorable spot.
Of course, if you sold a $100 strike put option when the stock was trading at $120, and now it is trading at $90, the seller is likely regretting their original trade. However, it is impossible always to time the market perfectly, and assignment risk is the risk option sellers must assume.
Traders must be aware of market conditions that could increase the risk of assignment, such as large price movements in the underlying asset. Option selling strategies benefit from a stable market environment, so you must ensure the stock you are trading will remain stable until the expiration date. Events that may cause significant market volatility, such as earnings, are crucial to be aware of when selling options.
How to Avoid Option Assignment
While it may not be possible to avoid options assignment completely, there are several strategies that options traders can use to reduce the likelihood of being assigned.
One strategy is to manage short options positions by closing the position if your strike gets tested. For example, if you sold a $100 strike put when a stock is trading at $120 per share, you can avoid assignment by closing the position before the stock drops under your strike price of $100.
Another strategy is to roll over your option, which means you close it out and simultaneously sell a new contract with a different strike price and/or date. Traders can roll their contracts to the same strike price at a further date or even roll it down or up to ensure their contract stays out of the money (OTM).
These strategies may not always be effective in avoiding assignment. Traders should always be prepared to fulfill their obligations if they are assigned and have a plan to manage their positions accordingly. If a stock moves hard overnight, there is no guarantee you will successfully avoid assignment.
Do You Keep the Premium if You Get Assigned?
Yes, if you get assigned on a short options position, you still keep the premium you received initially. However, it is important to note that if you are assigned, you will also be obligated to fulfill the contract terms by buying or selling the underlying asset at the strike price. This means you may incur additional costs associated with fulfilling your obligation, such as purchasing the underlying asset at an unfavorable price.
What Happens When Your Covered Call Gets Assigned?
If a covered call gets assigned, the seller of the call option must sell the underlying stock at the strike price to the buyer of the call option. The seller will still be able to keep the premium received from the sale of the call option.
For example, if you own a stock at $100 per share and sell a $130 strike call option, you will be forced to sell if the stock is above $130 on the expiration date. Additionally, you can be assigned before the expiration date if the stock is trading above your strike price.
While the covered call seller will still generate a profit from this trade, the downside is you are likely missing out on more upside potential had you not sold the covered call. The seller of the covered call doesn’t have to do anything, as the broker will take care of the assignment for you.
Are Options Automatically Assigned?
If you are an option seller, your option will either be exercised by the buyer or automatically assigned if it is ITM on the expiration date.
If you are an option buyer, your option will not be automatically assigned before expiration. However, most brokers will automatically assign ITM options on the expiration date.
The views and opinions expressed herein are the views and opinions of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of Nasdaq, Inc.

More Related Articles
This data feed is not available at this time.
Sign up for the TradeTalks newsletter to receive your weekly dose of trading news, trends and education. Delivered Wednesdays.
To add symbols:
- Type a symbol or company name. When the symbol you want to add appears, add it to My Quotes by selecting it and pressing Enter/Return.
- Copy and paste multiple symbols separated by spaces.
These symbols will be available throughout the site during your session.
Your symbols have been updated
Edit watchlist.
- Type a symbol or company name. When the symbol you want to add appears, add it to Watchlist by selecting it and pressing Enter/Return.
Opt in to Smart Portfolio
Smart Portfolio is supported by our partner TipRanks. By connecting my portfolio to TipRanks Smart Portfolio I agree to their Terms of Use .

English (USA)
English (UK)
English (Canada)
English (India)
Deutsch (Deutschland)
Deutsch (Österreich)
Deutsch (Schweiz)
Français (France)
Français (Suisse)
Nederlands (Nederland)
Nederlands (België)
- Top Capitalization
- United States
- North America
- Middle East
- Sector Research
- Earnings Calendar
- Equities Analysis
- Most popular
- TESLA, INC.
- HSBC HOLDINGS PLC
- VOLKSWAGEN AG
- NIPPON ACTIVE VALUE FUND PLC
- MERCEDES-BENZ GROUP AG
- Index Analysis
- Indexes News
- EURO STOXX 50
- Currency Cross Rate
- Currency Converter
- Forex Analysis
- Currencies News
- Precious metals
- Agriculture
- Industrial Metals
- Livestock and Cattle
- CRUDE OIL (WTI)
- CRUDE OIL (BRENT)
- Developed Nations
- Emerging Countries
- South America
- Analyst Reco.
- Capital Markets Transactions
- New Contracts
- Profit Warnings
- Appointments
- Press Releases
- Security Transactions
- Earnings reports
- New markets
- New products
- Corporate strategies
- Legal risks
- Share buybacks
- Mergers and acquisitions
- Call Transcripts
- Currency / Forex
- Commodities
- Cryptocurrencies
- Interest Rates
- Asset Management
- Climate and ESG
- Cybersecurity
- Geopolitics
- Central Banks
- Private Equity
- Business Leaders
- All our articles
- Most Read News
- All Analysis
- Satirical Cartoon
- Today's Editorial
- Crypto Recap
- Behind the numbers
- All our investments
- Asia, Pacific
- Virtual Portfolios
- USA Portfolio
- European Portfolio
- Asian Portfolio
- My previous session
- My most visited
- Undervalued stocks
- Dividend Aristocrats
- Trend-Following Stocks
- Yield stocks
- Dividend Kings
- Europe's family businesses
- Millennials
- Biotechnology
- The Internet of Things
- Gold and Silver
- Unusual volumes
- New Historical Highs
- New Historical Lows
- Top Fundamentals
- Sales growth
- Earnings Growth
- Profitability
- Rankings Valuation
- Enterprise value
- Top Consensus
- Analyst Opinion
- Target price
- Estimates Revisions
- Top ranking ESG
- Environment
- Visibility Ranking
- Stock Screener Home
- Strategic Metals
- Pricing Power
- The future of mobility
- Powerful brands
- Oversold stocks
- Overbought stocks
- Close to resistance
- Close to support
- Accumulation Phases
- Most volatile stocks
- Top Investor Rating
- Top Trading Rating
- Top Dividends
- Low valuations
- All my stocks
- Stock Screener
- Stock Screener PRO
- Portfolio Creator
- Event Screener
- Dynamic Chart
- Economic Calendar
- ProRealTime Trading
- Our subscriptions
- Our Stock Picks
- Thematic Investment Lists
On Assignment Stock Nyse
It services & consulting, financials (usd), chart on assignment, latest news about on assignment, latest transcript on on assignment.

Analyst Recommendations on On Assignment
Press releases on assignment, news in other languages on on assignment, managers and directors - on assignment, company profile, sector other it services & consulting.
- Stock Market

COMMENTS
This stock market vocabulary worksheet is very simple and straightforward, and will help you to reinforce a lesson on understanding how to maneuver the stock exchange (links to the worksheets are all the way at the bottom). Psst: don't forget to download the answer key - that has all the definitions on it. 6.
1. The Stock Market Game Kick Off! (3 mins) 2. Intro to Investing (4 mins) 3. Intro to Companies (3 mins) 4. Intro to Stocks (4 mins) 5. Building Your Portfolio (5 mins) 6. The Stock Market Game Trading Portfolio (6 mins) 7. The Stock Market Game Rules (6 mins) 8. Conducting Research (5 mins) 9. Entering Stock Trades (4 mins) 10. Assessing Risk ...
17. Common Stock. This is one of the most basic stock market terms to know. Common stock is a type of security that represents ownership in a company. Holders of common stock are able to vote on matters like corporate policies and elect directors within that company. 18.
STOCK MARKET HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT. For the homework assignment, students must first fill in the blanks to 10 questions using the words in the word bank. Afterward, there is another set of statements. Students will determine whether the statement is true or false and mark it appropriately.
Core Stock Market Project. This project is the "Core", which most teachers use as the basis for their HTMW class stock game. The other recommendations in this library usually follow this format (with some variation). This makes it very flexible to work with your classes. This project usually runs between 4 and 16 weeks.
Stock Market: The stock market refers to the collection of markets and exchanges where the issuing and trading of equities ( stocks of publicly held companies) , bonds and other sorts of ...
A short put assignment results in buying the underlying stock at the strike price. An option will likely be exercised if it's in the option owner's best interest to do so, meaning it's optimal to take or to close a position in the underlying security at the strike price rather than at the current market price.
Instruct your students to familiarize themselves with one or more of our three trading platforms - desktop, browser-based and mobile - using a variety of IB educational resources. Specific assignments can test your students' general knowledge of our trading platforms and can be organized based on the contents of QuickStart Guides, Users ...
Stock Market. Stock market is a place where shares of pubic listed companies are traded. There are two types of stock market : primary & secondary. The primary market is where companies float shares to the general public in an initial public offering (IPO) to raise capital. It is one of the most vital components of a free-market economy, as it ...
The final portion of the stock grade comes from your portfolio's return. If you have $103,000 at the end of the project, your return is ($103k - 100k)/$100k * 100 = 3%. This means if you turn in both reports and the PFIN assignment in a satisfactory manner, you would earn 93% on the project.
The options market can seem to have a language of its own. To the average investor, there are likely a number of unfamiliar terms, but for an individual with a short options position—someone who has sold call or put options—there is perhaps no term more important than "assignment"—the fulfilling of the requirements of an options contract. ...
In this module, you will be working with stock price data for Amazon. This stock is listed on the NASDAQ Stock Market (the second largest U. stock market, after the New York Stock Exchange). You will analyze the change in the stock prices over time as well as the value of investments over time. The Excel workbook for this module consists of 2 tabs.
At Yahoo Finance, you get free stock quotes, up-to-date news, portfolio management resources, international market data, social interaction and mortgage rates that help you manage your financial life.
Assignment: An assignment is the transfer of an individual's rights or property to another person or business. For example, when an option contract is assigned, an option writer has an obligation ...
THE STUDY OF STOCK MARKET. Feb 1, 2015 •. 94 likes • 77,779 views. Shweta Acharya. This my black book which i presented to Mumbai University for the bachelor in management studies (B.M.S) exteral viva held by the latter. Data & Analytics. 1 of 132. THE STUDY OF STOCK MARKET - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Option assignment occurs when the owner of an option exercises their right to buy or sell the underlying asset at a specific price on or before expiration. When a call option is assigned, the owner buys shares at the strike price. For example, if XYZ stock is trading for $45 and you sold one XYZ 50 Put, the put buyer has the right to sell 100 ...
The concept of Stock Market. The stock market refers to public markets that exist for issuing, buying and selling stocks that trade on a stock exchange or over-the-counter. It is a place where you can buy and sell shares of companies listed there for trading. Stock exchanges list shares of common equity as well as other security types, e.g. corporate bonds and convertible bonds.
An Assignment is a list of tasks you can give your students to complete using their virtual portfolio. ... StockTrak.com is a property of Stock-Trak®, the leading provider of web-based stock market simulations for universities, high schools, and the financial services industry. All information is provided on an "as-is" basis for informational ...
Welcome to Step 2: Practice Assignment Technical Analysis for Stock Trading, a place where you can practice the skills you have learned! If you have some knowledge of trading in the market but: struggle with the application in real-time trading scenarios. lack confidence in your trading abilities. are afraid of taking trades.
TBI TrueBlue, Inc. 10.70. +2.72%. Find the latest ASGN Incorporated (ASGN) stock quote, history, news and other vital information to help you with your stock trading and investing.
For example, if you sold a $100 strike put when a stock is trading at $120 per share, you can avoid assignment by closing the position before the stock drops under your strike price of $100.
The stock market in the United States is NYSE while in Canada; it is the Toronto Stock Exchange. Major European examples of stock exchanges include the London Stock Exchange, Paris Bourse, and the Deutsche Bourse. The stock market I had to use for this assignment was the FTSE 100. What is the overall performance of your stock investment?
On Assignment (ZB_11367529.NYSE): Stock quote, stock chart, quotes, analysis, advice, financials and news for Stock On Assignment | Nyse: | Nyse