

Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: Class 11
- Post comments: 0 Comments
In Class 11 Final Exams there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Downloads of CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions Animal Kingdom to know their preparation level.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 11 Biology Paper, There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Animal Kingdom Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1: Animals in which the cells are arranged in two embryonic layers, an external ectoderm, and an internal endoderm, are called diploblastic animals, e.g., coelenterates. An undifferentiated layer, mesoglea, is present in between the ectoderm and the endoderm.
Coelom – The presence or absence of a cavity between the body wall and the gut wall is very important in classification. The body cavity, which is lined by mesoderm is called coelom. Animals possessing coelom are called coelomates, e.g., annelids, mollusks, arthropods, echinoderms, hemichordates, and chordates. In some animals, the body cavity is not lined by mesoderm, instead, the mesoderm is present as scattered pouches in between the ectoderm and endoderm. Such a body cavity is called pseudo coelom and the animals possessing them are called pseudocoelomates, e.g., aschelminthes. The animals in which the body cavity is absent are called acoelomates, e.g., Platyhelminthes.
Segmentation – In some animals, the body is externally and internally divided into segments with a serial repetition of at least some organs. For example, in earthworms, the body shows a pattern called metameric segmentation, and the phenomenon is known as metamerism.
Notochord – It is a mesodermally derived rod-like structure formed on the dorsal side during embryonic development in some animals. Animals with notochord are called chordates and those animals which do not form this structure are called non-chordates, e.g., porifera to echinoderms.
1.) Diploblastic animals are characterized by _________________.
- a) External ectoderm cell arrangement
- b) Internal endoderm cell arrangement
- c) Both a and b
- d) None of the above
Ans: c) Both a and b
2.) In coelomates, the body cavity is surfaced by____________
- a) Ectoderm
- b) Mesoderm
- c) scattered pouches
- d) Endoderm
Ans: b) Mesoderm
What distinguishes gymnosperms from other seed-producing plants? A) The ovules are enclosed by an ovary wall B) The ovules and seeds remain exposed C) The roots are always fibrous D) The leaves are never compound
What type of roots is associated with N2-fixing cyanobacteria in gymnosperms? A) Tap roots B) Fibrous roots C) Mycorrhizal roots D) Coralloid roots
In gymnosperms like conifers, what is the function of the needle-like leaves? A) Increase water absorption B) Enhance pollination C) Reduce surface area to minimize water loss D) Attract insects for pollination
Which gymnosperm is known for being one of the tallest tree species? A) Cycas B) Pinus C) Sequoia D) Mycorrhiza
What are the male cones or strobili in gymnosperms called? A) Macrosporangiate B) Megasporophylls C) Microsporangiate D) Megaspores
Which type of sporophylls bears the megasporangia in gymnosperms? A) Microsporophylls B) Macrosporophylls C) Strobili D) Male cones
How many megaspores are formed by the megaspore mother cell in gymnosperms? A) One B) Two C) Three D) Four
In which gymnosperm are male cones and megasporophylls borne on different trees? A) Sequoia B) Pinus C) Cycas D) Mycorrhiza
What kind of spores do gymnosperms produce? A) Heterosporous, producing both microspores and megaspores B) Homosporous, producing only one type of spore C) Only megaspores D) Only microspores
Which part of the gymnosperm is protected by envelopes and referred to as an ovule? A) Pollen grain B) Nucellus C) Microsporangia D) Archegonia
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate

You Might Also Like
Mcq questions class 11 accountancy chapter 11 accounts from incomplete records with answers, class 11 chemistry case study questions chapterwise pdf download, mcq questions class 11 english snapshots chapter 7 birth with answers, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

The Topper Combo Flashcards
- Contains the Latest NCERT in just 350 flashcards.
- Colourful and Interactive
- Summarised Important reactions according to the latest PYQs of NEET(UG) and JEE
No thanks, I’m not interested!
myCBSEguide
- Class 11 Biology Case...
Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you are finding it difficult to solve Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions, you are not alone. Many students face difficulties in solving such questions, as they require in-depth knowledge of the subject. However, with the right resources and guidance, it is possible to overcome these difficulties. One of the best resources for Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions is the myCBSEguide app.
myCBSEguide provides detailed information and Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions that can help you understand the concepts better. Class 11 Biology students can also find several practice questions at the end of each chapter that can help Class 11 Biology students in understanding the concept better.
Biology: The study of living organisms
Biology is the study of life and all living things. It is a natural science that covers a wide range of topics, from the structure and function of the human body to the behavior of plants and animals. Class 11 biology students learn about the various branches of biology, such as anatomy, physiology, ecology, and evolution. In addition, they also study the cell, the building block of all living things. By understanding how cells work, students can better understand how the body works as a whole.
Class 11 students entering the world of Biology
For Class 11 students, biology is the foundation for Class 12 CBSE students. It is a vital topic that helps students grasp the fundamental notions of life and living beings. Cell structure and function, genetics, evolution, ecology, and plant and animal physiology are all themes addressed in biology. Biology is a fascinating topic that teaches students about the natural world around them. Biology is an excellent foundation for Class 11 CBSE students who want to pursue a career in medicine. Biology is critical for understanding the human body and its processes, as well as developing medical remedies.
Significance of Biology for class 11 students
- Biology encourages students to learn the fundamentals of biology.
- It promotes a rational/scientific attitude toward issues such as population, environment, and development by encouraging the acquisition of new information and its application to individuals and society.
- It raises public knowledge of environmental issues, problems, and remedies.
- It raises students’ understanding of the diversity of living species and fosters respect for other living beings.
- It understands that even the most complicated biological phenomena are based on fundamentally simple processes.
Case study questions in Class 11 Biology
Case studies are a part of to Class 11 biology examination paper pattern. These case studies can be used to assess a student’s understanding of a subject as well as their ability to apply that understanding in a real-world context. Incorporating case study questions into Class 11 Biology can provide students with a more hands-on and realistic experience with the subject. Class 11 Biology students can better learn how chemical concepts are utilized in the real world by going through real-life problems. Class 11 Biology Case study questions can also aid in the development of critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
Examples of Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
We must solve a range of Class 11 Biology case study questions in order to achieve high grades in Biology. Class 11 Biology students must be seeking some examples of case study questions in order to improve their grades. myCBSEguide has prepared a variety of Class 11 Biology case study questions that will undoubtedly assist all students studying the subject. We have compiled a selection of Class 11 Biology case study questions for you. Have a look at the following Class 11 Biology case study question examples.
Class 11 Biology case study questions 1
Read the following and answer any four questions: The detailed structure of the membrane was studied only after the advent of the electron microscope in the 1950s. Meanwhile, chemical studies on the cell membrane, especially in human red blood cells (RBCs), enabled the scientists to deduce the possible structure of the plasma membrane. These studies showed that the cell membrane is composed of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates.
- Nucleic acid
- Carbohydrate
- Phosphoglycerides
- Glycoproteins
- Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
- Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
- Assertion is true but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false.
Answer Key:
- (b) The lipids are arranged in a bilayer in the plasma membrane with the polar head towards the outer sides and the hydrophobic tails towards the inner part.
- (a) The lipid component of the membrane mainly consists of phosphoglycerides.
- (c) In human beings, the membrane of the erythrocyte has approximately 52 percent protein and 40 percent lipids.
- (b) Depending on the ease of extraction, membrane proteins can be classified into two types – integral or peripheral.
- (b) The plasma membrane is selectively permeable to some molecules present on either side of it. Neutral solutes may move across the membrane by the process of simple diffusion along the concentration gradient, i.e., from higher concentration to the lower. Hence, both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Class 11 Biology case study questions 2
Read the following and answer any four questions: Plastids are found in all plant cells and in euglenoids. These are easily observed under the microscope as they are large. They bear some specific pigments, thus imparting specific colours to the plants. Plastids consist of numerous membrane layers embedded in a material called the stroma. They have their own genome and ribosomes.
- Leucoplasts
- Chloroplasts
- Chromoplasts
- Carotenoids
- Amyloplasts
- Aleuroplasts
- Elaioplasts
- (a) The leucoplasts are the colourless plastids of varied shapes and sizes with stored nutrients.
- (b) The aleuroplasts store proteins in grains.
- (a) Amyloplasts are leucoplasts store carbohydrates (starch) in potato.
- (c) The space limited by the inner membrane of the chloroplast is called the stroma.
- (c) The chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments which are responsible for trapping light energy essential for photosynthesis. The chromoplasts impart colours to the parts of the plant as yellow, orange or red colour. Hence, Assertion is true but reason is false.
Class 11 Biology case study questions 3
Read the following and answer any four questions: In human beings, the lungs are situated in the thoracic chamber which is formed dorsally by the vertebral column, ventrally by the sternum, laterally by the ribs, and on the lower side by the dome-shaped diaphragm. The anatomical setup of the lungs in the thorax is such that any change in the volume of the thoracic cavity will be reflected in the lung (pulmonary) cavity. Such an arrangement is essential for breathing. Breathing involves two stages – inspiration and expiration. During inspiration, the atmospheric air is drawn in and during expiration, the alveolar air is released out.
- 12 – 16
- 70 – 72
- Ribs lift up
- Diaphragm flattens
- Ribs flatten
- Both ribs lift up and diaphragm flattens
- Tidal volume
- Inspiratory Reserve Volume
- Residual Volume
- Vital Capacity
- 6000 to 8000 mL
- 2500 mL to 3000 mL
- 1000 mL to 1100 mL
- 1100 mL to 1200 mL
- The movement of air into and out of the lungs is carried out by creating a pressure gradient.
- Expiration can occur if the pressure within the lungs (intra-pulmonary pressure) is less than the atmospheric pressure.
- The diaphragm and a specialised set of muscles help in generation of pressure gradients.
- Expiration is initiated by the contraction of diaphragm which increases the volume of thoracic chamber in the antero-posterior axis.
Choose from below the correct alternative.
- a. Only I is true
- b. I and IV are true
- c. III and II are true
- d. I and III are true
- (a) On an average, a healthy human breathes 12-16 times/minute.
- (d) When we breathe in, the ribs are lifted up and the diaphragm flattens which increases the size of the chest cavity. Because of this, the air is sucked into the lungs and fills the expanded alveoli.
- (a) Volume of air inspired or expired during normal respiration is called tidal volume.
- (d) Residual volume of air is the remaining air in the lungs even after a forcible expiration. This averages 1100 mL to 1200 mL.
- (d) The movement of air into and out of the lungs is carried out by creating a pressure gradient between the lungs and the atmosphere. Inspiration can occur if the pressure within the lungs (intra-pulmonary pressure) is less than the atmospheric pressure. The diaphragm and a specialized set of muscles – external and internal intercostals between the ribs, help in the generation of pressure gradients. Inspiration is initiated by the contraction of the diaphragm which increases the volume of thoracic chamber in the antero-posterior axis. Hence, statements I and III are true.
Class 11 Biology case study questions 4
Read the following and answer any four questions: Exchange of gases also occurs between blood and tissues. O 2 and CO 2 are exchanged in these sites by simple diffusion mainly based on pressure/concentration gradient. The solubility of the gases, as well as the thickness of the membranes involved in diffusion, are also some important factors that can affect the rate of diffusion.
- Atmospheric pressure
- Partial pressure
- Differential pressure
- Capillary pressure
- pO 2 – 104 mm Hg, pCO 2 – 40 mm Hg
- pO 2 – 104 mm Hg, pCO 2 – 140 mm Hg
- pO 2 – 95 mm Hg, pCO 2 – 40 mm Hg
- pO 2 – 40 mm Hg, pCO 2 – 45 mm Hg
- The given diagram represents the exchange of gases at the alveolus and the body tissues with blood and the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- The amount of CO 2 that can diffuse through the diffusion membrane per unit difference in partial pressure is much lesser compared to that of O 2 .
- All the factors in our body are favourable for the diffusion of O 2 from tissues to alveoli and that of CO 2 from alveoli to tissues.
- The total thickness of the diffusion membrane is much less than a millimetre.
- Only I is true
- I and IV are true
- III and II are true
- I and III are true
- (b) Pressure contributed by an individual gas in a mixture of gases is called partial pressure.
- (a) Alveoli are the primary sites of exchange of gases.
- (c) The diffusion membrane is made up of three major layers.
- (d) The values of pO 2 and pCO 2 in the body tissues is: pO 2 – 104 mm Hg, pCO 2 – 40 mm Hg.
- (b) The given diagram represents the exchange of gases at the alveolus and the body tissues with blood and the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The amount of CO 2 that can diffuse through the diffusion membrane per unit difference in partial pressure is much higher compared to that of O 2 . All the factors in our body are favourable for the diffusion of O 2 from alveoli to tissues and that of CO 2 from tissues to alveoli. The total thickness of diffusion membrane is much less than a millimetre.
Dealing with Class 11 Biology case study questions
There are a number of different ways to approach Class 11 Biology case study questions, but the most important thing is to make sure that Class 11 Biology students answer all parts of the question and provide as much detail as possible. In some cases, you may need to research the topic further in order to be able to answer the Class 11 Biology case study questions fully.
When dealing with Class 11 Biology case study questions, it is also important to think about the different perspectives that might be involved. For example, if you are asked to evaluate a particular decision made by a scientist, you will need to consider the impact of that decision from both the scientist’s perspective and the perspective of those affected by the decision.
Answering case study questions can be challenging, but it is an important skill to develop if you want to pursue a career in fields such as business or law. With practice, Class 11 Biology students will be able to approach these questions with confidence and provide well-reasoned, detailed answers.
Class 11 Biology curriculum: As fascinating as Biology itself
The current curriculum of Class 11 Biology provides students with up-to-date principles as well as more extensive exposure to current topics in the discipline. Class 11 Biology curriculum also strives to emphasize the basic concepts that are shared by animals, plants, and microbes, as well as the link between Biology and other fields of study. Class 11 Biology structure provides for a straightforward, sequential flow of ideas. It connects the science of biology to actual life through technological advancements. It connects biological discoveries and breakthroughs to everyday issues including the environment, industry, health, and agriculture. The new curriculum of Class 11 Biology also emphasizes scientific ideas and their application, while ensuring that enough chances and opportunities for mastering and recognizing fundamental concepts remain within its framework.
CBSE Class 11 Biology (Code No. 044)
COURSE STRUCTURE
myCBSEguide: An app as intriguing as biology
If you’re looking for an app that’s as intriguing as biology, myCBSEguide is a perfect choice. With millions of downloads, it’s one of the most popular apps on the App Store, and for good reason. myCBSEguide offers extensive coverage of the CBSE curriculum, with detailed explanations of concepts, thousands of practice questions, case study questions and much more. Whether you’re a student, teacher, or parent, myCBSEguide is an essential tool for anyone wanting to learn more about biology.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Computer Science Case Study Questions
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Not Able To Find Desired Paper or Worksheet SEARCH
Find papers & worksheets search, case study questions class 11 biology chapter 4 animal kingdom.
- (0) Comments
- 9 Downloads
Related Papers
Click to view more related papers, display_name = "class 11" && $paper->display_name = "class 12") { // echo $paper->display_name." questions papers and worksheets"; } //else { // echo $paper->display_name." sample papers and previous year papers"; //} //>, cbse class 11 biology chapter wise important questions - free pdf download.
CBSE Important Questions for Class 11 Biology are available in Printable format for Free Download.Here you may find NCERT Important Questions and Extra Questions for Class 11 Biology chapter wise with answers also. These questions will act as chapter wise test papers for Class 11 Biology. These Important Questions for Class 11 Biology are as per latest NCERT and CBSE Pattern syllabus and assure great success in achieving high score in Board Examinations
Total Papers :
Biology Topics to be covered for Class 11 Science
- The Living World
- Biological Classification
- Plant Kingdom
- Animal Kingdom
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Structural Organisation in Animals
- Cell-The Unit of Life
- Biomolecules
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Transport in Plants
- Mineral Nutrition
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Respiration in Plants
- Plant - Growth and Development
- Digestion and Absorption
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Excretory Products and Their Elimination
- Locomotion and Movement
- Neural Control and Coordination
- Chemical Coordination and Integration
Structure of CBSE Biology Sample Paper for Class 12 Science is
For Preparation of exams students can also check out other resource material
CBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Papers
CBSE Class 11 Biology Worksheets
CBSE Class 11 Biology Question Papers
CBSE Class 11 Biology Test Papers
CBSE Class 11 Biology Revision Notes
Question Bank of Other Subjects of Class 11
Importance of Question Bank for Exam Preparation?
There are many ways to ascertain whether a student has understood the important points and topics of a particular chapter and is he or she well prepared for exams and tests of that particular chapter. Apart from reference books and notes, Question Banks are very effective study materials for exam preparation. When a student tries to attempt and solve all the important questions of any particular subject , it becomes very easy to gauge how much well the topics have been understood and what kind of questions are asked in exams related to that chapter.. Some of the other advantaging factors of Question Banks are as follows
- Since Important questions included in question bank are collections of questions that were asked in previous exams and tests thus when a student tries to attempt them they get a complete idea about what type of questions are usually asked and whether they have learned the topics well enough. This gives them an edge to prepare well for the exam.Students get the clear idea whether the questions framed from any particular chapter are mostly either short or long answer type questions or multiple choice based and also marks weightage of any particular chapter in final exams.
- CBSE Question Banks are great tools to help in analysis for Exams. As it has a collection of important questions that were asked previously in exams thereby it covers every question from most of the important topics. Thus solving questions from the question bank helps students in analysing their preparation levels for the exam. However the practice should be done in a way that first the set of questions on any particular chapter are solved and then solutions should be consulted to get an analysis of their strong and weak points. This ensures that they are more clear about what to answer and what can be avoided on the day of the exam.
- Solving a lot of different types of important questions gives students a clear idea of what are the main important topics of any particular chapter that needs to focussed on from examination perspective and should be emphasised on for revision before attempting the final paper. So attempting most frequently asked questions and important questions helps students to prepare well for almost everything in that subject.
- Although students cover up all the chapters included in the course syllabus by the end of the session, sometimes revision becomes a time consuming and difficult process. Thus, practicing important questions from Question Bank allows students to check the preparation status of each and every small topic in a chapter. Doing that ensures quick and easy insight into all the important questions and topics in each and every individual. Solving the important questions also acts as the revision process.
Question Bank of Other Classes
To Prepare better for CBSE paperclass; ?> " title="Download Free CBSE Papers">Ribblu.com brings to you all the previous years papers & worksheets of subject; ?//> for CBSE paperclass; ?>. This CBSE paper and worksheet can be instrumental in students achieving maximum marks in their exams. These Papers and worksheets help students gain confidence and make them ready to face their school examinations. These Papers and worksheets school wise, covers important concepts from an examination perspective. Students and parents can download all the available papers & worksheets directly in the form of PDF. One can use these papers and worksheets to get extensive practice and familiarise themselves with the format of the question paper.
You can help other users
Be the first to write comment .
Upload papers and the more your paper get downloaded the more you earn the points
You may send papers on email [email protected] along with userid
- Downloaded by: Tarun Vijh
- Downloaded by: Rakesh
Rules and regulations for uploads
Write your comment, report this paper, how to earn points.
Upload Papers / Worksheets and Earn 50 Points.
The uploaded material should be original paper or worksheet of any school. Check out some videos on how to upload papers on ribblu
Rate & Review your school and Earn 25 Points.
Review any school that you may be knowing and once your review is approved, you will be credited with 25 points.
Answer on question posted on JustAsk and earn 15 points.
JustAsk is a platform where you can help others to find answers of any question. Share your Knowledge. Answer questions and once approved you will earn 15 points
Complete your profile and earn upto 25 Points.
Edit and complete your user profile and earn points. The more details you submit, the more points you will earn.
Download Ribblu Mobile App and you will (Earn 20 Points) (one time only)
CBSE Schools
- CBSE Schools In Delhi
- CBSE Schools In Noida
- CBSE Schools In Greater Noida
- CBSE Schools In Faridabad
- CBSE Schools In Ghaziabad
- CBSE Schools In Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools In Mumbai
- CBSE Schools In Pune
- CBSE Schools In Bangalore
- CBSE Schools In Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools In Kolkata
- CBSE Schools In Chennai
- CBSE Schools In Patna
- CBSE Schools In Meerut
- CBSE Schools In Kanpur
- CBSE Schools In Indore
- CBSE Schools In Ludhiana
- CBSE Schools In Dehradun
Top Schools
- Schools In Delhi
- Schools In Noida
- Schools In Greater Noida
- Schools In Faridabad
- Schools In Ghaziabad
- Schools In Gurgaon
- Schools In Mumbai
- Schools In Pune
- Schools In Bangalore
- Schools In Hyderabad
- Schools In Kolkata
- Schools In Chennai
- Schools In Patna
- Schools In Meerut
- Schools In Kanpur
- Schools In Indore
- Schools In Ludhiana
- Schools In Dehradun
Other Schools
- Pre Nursery Schools In Noida
- Day Boarding Schools In Noida
- Pre Nursery Schools In Gurgaon
- Pre Nursery Schools In Delhi
- Play Schools In Delhi
- Day Boarding Schools In Delhi
CBSE Papers
- CBSE Class 1 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 2 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 3 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 4 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 5 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 6 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 7 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 8 Sample Papers
Paper Categories
- Question Bank
- Question Papers
- Revision Notes
- Sample Papers
- Test Papers
- CBSE Class 9 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 11 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Sample Papers

- New QB365-SLMS
- NEET Materials
- JEE Materials
- Banking first yr Materials
- TNPSC Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Materials
- 5th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 11th Standard CBSE Biology question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 11th Standard CBSE Biology books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and Scholorships in one place.
Latest 11th Standard CBSE Case study Questions Update
11th biology biological classification chapter case study question with answers cbse, 11th biology the living world chapter case study question with answers cbse, 11th standard cbse study materials.

11th Standard CBSE Subjects


Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

Latest CBSE 11th Standard CBSE Study Material Updates
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- CBSE Important Questions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4- Anatomy of Flowering Plant

Download CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Important Questions Free PDF
This article talks about the CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 4- Animal Kingdom important questions free PDF. The questions are designed by the experts considering the latest NCERT syllabus issued by the CBSE board . These questions are created by Biology experts after detailed research on exam patterns and previous years' question papers .
Solving these important questions will help students to prepare for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 effectively for their exams. The important concepts will be cleared by practising these questions. These questions cover the important topic of the chapters. Students can refer to CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Important Questions for revision as well. It will boost students' confidence and help them in fetching more marks during the exam. There are high chances that some of these questions covered in the pdf may be asked in the examination.
Download CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 4- Animal Kingdom important questions free PDF through the link below.
Download CBSE Class 11 Biology Important Questions 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 11 Biology Important Questions for other chapters:
Topics Covered in Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 - Animal Kingdom
The Tissue System
Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants
Secondary Growth

Study Important Questions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 - Animal Kingdom
Very Short Answer Questions. (1 Mark)
1. What is mesoglea? Where is it found?
Ans: Mesoglea is an undifferentiated layer present in between ectoderm and endoderm. It is found in Coelenterates.
2. When is the development of an organism called indirect?
Ans: The development of an organism is called indirect when a larval stage (birth form) is morphologically distinct from an adult.
3. Why are corals important?
Ans: Corals have a skeleton composed of calcium carbonate which gets deposited and can lead to the formation of landforms. Example: - Lakshadweep (a coral island).
4. What is the difference between class Amphibia and class Reptilia in respect of their skin?
Ans: The difference between amphibia and reptilia are:
5. Which phylum consists of organisms with a cellular level of organisation?
Ans: Phylum Porifera consists of organisms with a cellular level of organisation. Example: - Sponges
6. Name the arthropod which is an (i) Living fossil, (ii) Gregarious pest.
Ans:
(i) Living fossil: - Limulus (King crab),
(ii) Gregarious pest: - Locusta (Locust).
7. Which organ helps in excretion in (i) Arthropods, (ii) Hemichordates?
(i) Organs of excretion in Arthropods: - Malpighian tubules,
(ii) Organs of excretion in Hemichordates: - Proboscis gland.
8. Name an example of egg-laying mammals.
Ans: The duck-billed platypus is an example of an egg-laying mammal.
9. What is polymorphism?
Ans: The phenomenon when an organism has different kinds of zooids for different functions is called polymorphism.
10. Which animal is popularly called ploughman of nature & why?
Ans: Earthworms are popularly referred to as ploughmen of nature (or friends of farmers) because they bring subsoil to the surface and create fine burrows for aeration.
11. What are the organs of excretion in annelids & insects?
(i) Organs of excretion in annelids: - Nephridia
(ii) Organs of excretion in insects: - Malpighian tubules
12. Name a free-living & parasitic Platyhelminthes.
(i) Free-living Platyhelminthes: – Planaria (Freshwater flatworm)
(ii) Parasitic Platyhelminthes: – Taenia (Tapeworms)
13. Name two adaptations for an aerial mode of life.
Ans: Two adaptations for an aerial mode of life are: -
(i) Forelimbs are modified into wings.
(ii) Uricotelic excretion & pneumatic bones.
14. Name the organs of defence in paramecium.
Ans: Trichocysts are organs of defence in paramecium.
15. Name the second largest animal phylum.
Ans: Mollusca is the second-largest animal phylum.
16. What are acoelomate animals?
Ans: The animals which do not have a coelom or body cavity are called acoelomate animals. Examples are Porifera, coelenterates and flatworms.
17. Name the larva found in Mollusca & Annelid.
Ans: The larva found in Mollusca and Annelida is the Trochophore larva.
18. Name two viviparous fishes.
Ans: Pristis (Sawfish) and scoliodon (Dogfish)are two viviparous fishes.
19. What are flame cells?
Ans: Flame cells are excretory organs found in Platyhelminthes and related animals. They have flickering cilia or flagella that move the absorbed excretory products into a system of ducts.
20. Name a vertebrate in which jaws are absent.
Ans: Petromyzon (Sea lamprey) is a vertebrate in which jaws are absent.
21. Assign the phylum to which the following animals belong – pheretima & sponge.
Ans: Pheretima belongs to phylum Annelida & sponge belongs to phylum Sponge (Porifera).
22. What is metamerism?
Ans: In some Bilateria, the body consists of many segments & shows repetitions of parts. This type of segmentation is called metamerism.
Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
1. Distinguish between poikilotherms and homeotherms organisms.
Ans: The difference between poikilotherms and homeotherms organisms are:
2. Define metagenesis with a suitable example.
Ans: Metagenesis is the phenomenon of alternation of generations between sexual and asexual modes of reproduction. Cnidarians have two forms in their life cycle: - the polyp form and the medusa form. Polyps (sporophyte) produces medusa asexually whereas the medusa (gametophyte) produces the polyp sexually. Example: - Obelia.
3. List any four identifying features of Arthropoda & give examples.
Ans: Four identifying features of Arthropoda are: -
(i) Animals with jointed appendages;
(ii) Triploblastic, coelomate, and bilaterally symmetrical animals;
(iii) The body of animals is covered by a chitinous cuticle (hard exoskeleton), and segments are not separated by septa.
(iv) Arthropods are unisexual animals.
(v) Examples include Crab, Apis, Spider and Anopheles.
4. Distinguish between diploblastic & triploblastic animals.
Ans: The difference between diploblastic and triploblastic animals are:
5. What are protochordates? How is it classified?
Ans: Protochordate is an organism that belongs to the lower chordates and is generally found in marine water. Their body is bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, and coelomate. At a certain stage of their lives, their bodies develop a long, rod-like structure called the notochord. There are three subphyla: -
(i) Hemichordata (Half chordate)
Example: - Balanoglossus
(ii) Urochordata (Tail cord)
Example: - Salpa & Herdmania
(iii) Cephalochordata (Head cord)
Example: - Amphioxus
6. Mention the unique features of nematodes.
Ans: The unique features of nematodes are: -
(i) Syncytial (no mesodermal lining).
(ii) Body wall musculature is made of special types of muscles.
(iii) Sexual dimorphism is quite clear.
(iv) Their body is triploblastic and bilaterally symmetrical.
(v) They are generally cylindrical in shape.
(vi) Their body has a false cavity (pseudocoelomate).
(vii) The alimentary canal is distinct, having the mouth and the anus.
7. Point out differences between dogfish & catfish.
Ans: The differences between a dogfish and catfish are:
8. Outline the role of the coelom in animals.
Ans: The coelom is the space between the body wall & the alimentary canal of organisms. It is lined by mesoderm. Visceral organs lie in the coelom. Flatworms do not have a coelom. Hence, they are called acoelomates. Pseudocoelom is found in the roundworm. Annelids are coelomate animals.
9. Mention the unique features of the phylum Mollusca.
Ans: Unique features of phylum Mollusca are: -
(i) Body soft as well as unsegmented.
(ii) The body is covered by a calcareous shell and mantle.
(iii) The body is divided into - head, visceral mass and foot.
(iv) Buccal mass possesses radula.
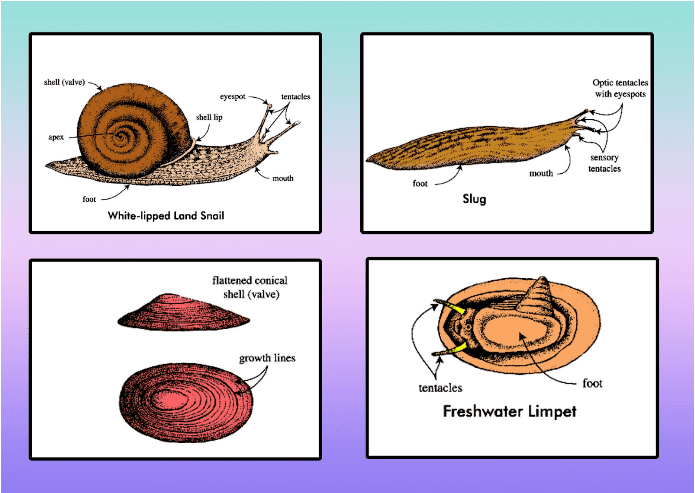
Figure: Unique features of Mollusca
10. Distinguish between insects & Arachnida.
Ans: The difference between insects and arachnids are:
11. Why are echinoderms considered closer to chordates than any other phylum?
Ans: Echinoderms are considered closer to chordates because, like chordates, they are deuterostomes i.e., the anal region develops earlier than the mouth region. Their larvae are also closer to protochordate.
12. Distinguish between bony fish & cartilaginous fish.
Ans: The difference between bony fish and cartilaginous fish are:
13. Give the reason why a snail & an octopus are classified under the same phylum?
Ans: Snails and octopus are classified under the phylum Mollusca due to the following three common characteristics: -
(i) Presence of a mantle cavity for respiration and excretion etc.
(ii) Presence of radula for feeding.
(iii) Presence of foot and shell.
14. List three basic chordate characters.
Ans: The three basic characters of chordates are: -
(i) Notochord: - A dorsal solid notochord is present throughout life or within the larval stage.
(ii) Nerve cord: - A hollow nerve cord is present dorsally.
(iii) Pharyngeal gill slits: - A perforated pharynx is present in young conditions or throughout life.
15. Give any four characteristics of hemichordate.
Ans: The four characteristics of hemichordate are: -
(i) These are worm-like marine animals that have an organ-system level of organization.
(ii) Their body is bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and coelomate (having true coelom).
(iii) The body is cylindrical and is divided into anterior proboscis, collar and a long trunk.
(iv) Respiration occurs through gills.
16. Distinguish between centipede & millipede.
Ans: The difference between centipede and millipede are:
17. Give the reason why Arthropoda constitute the largest group of the animal kingdom.
Ans: Arthropoda constitutes the largest group of the animal kingdom: -
(i) Have an organ level of organization.
(ii) Bilaterally symmetrical, segmented, triploblastic, coelomate animals.
(iii) Body enclosed by the chitinous cuticle.
(iv) They have jointed appendages.
(v) Trachea or book gills for respiration.
18. Differentiate between male & female Ascaris.
Ans: The difference between male and female Ascaris are:
19. List three adaptations that help the birds (Aves) in flying.
Ans: The three adaptations that help the birds (Aves) in flying are: -
(i) Lightweight smooth feathers.
(ii) Flight muscles contain white fibres which are poorer in mitochondria and lack myoglobin.
(iii) The long bones are hollow (Pneumatic bones) and filled with air.
20. List the characteristic features of class Mammalian.
Ans: The characteristic features of class Mammalian are: -
(i) These animals are warm-blooded (homeotherms), hairy, and have mammary glands, which produce milk.
(ii) Oil glands and sweat glands are present in their skin.
(iii) The skull is dicondylic, i.e., it has two occipital condyles.
(iv) The lungs are responsible for respiration.
(v) The heart has four chambers.
Short Answer Question (3 Marks)
1. What are the features of Class Aves that help them for flying?
Ans: The features of class Aves that help them in flying are - lightweight smooth feathers, long bones (pneumatic bones) with internal spaces filled with air, air sacs connected to lungs to supplement respiration and streamlined shape of the body.
2. “All vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates” justify the statement.
Ans: All vertebrates are chordates because they possess three basic chordate features:
(i) All chordates possess a dorsal solid notochord throughout life or in the larval stage.
(ii) All chordates possess a dorsal hollow nerve cord.
(iii) All chordates have pharyngeal gill slits in some stages of the life cycle.
All chordates are not vertebrates. Vertebrates have vertebral columns but protochordate and agnatha have notochord that is not replaced by the vertebral column.
3. “Mammals are the most successful & dominant animals today” Give evidence.
Ans: Mammals are the most successful and dominant animals on the planet today. They thrive in the majority of the world's environments. The unique characteristics of mammals are: -
(i) Body covered with hair.
(ii) Presence of sweat and sebaceous glands in the skin.
(iii) Presence of mammary glands in females that produce milk.
(iv) Presence of a pair of external ears and three ear ossicles i.e., malleus, incus and stapes.
(vi) RBCs are biconcave and lack a nucleus (enucleated).
(vii) The testis is located outside the abdomen in a special pouch called the scrotum.
(viii) Mostly viviparous (produces young ones).
(ix) The embryo is attached to the uterine wall with the help of the placenta.
(x) The skull is dicondylic, i.e., it has two occipital condyles.
4. Enlist the main characteristics & examples of phylum Porifera.
Ans: The main characteristics of phylum Porifera are: -
(i) They are commonly known as sponges.
(ii) They are generally marine.
(iii) Their body is diploblastic and bilaterally symmetrical.
(iv) They possess a water transport mechanism.
(v) They are extremely primitive multicellular animals with a cellular level of organisation.
(vi) Water can enter by pores called Ostia in the body wall directly or through the canal into the spongocoel. It goes out through the osculum. It is known as the canal system.
(vii) The body is supported by a skeleton that consists of spicules
(viii) Sexes are not separate.
(ix) They reproduce asexually by fragmentation.
(x) They also reproduce sexually by the formation of gametes.
(xi) Fertilization is internal.
(xii) Example- Euplectella, Spongilla, Sycon, Euspongia etc.
5. What is the basis of the classification of Animalia?
Ans: The basis of classification of Animalia are: -
(i) Notochord: - It is a rod-like structure found in the chordates. It is not found in non-chordates.
(ii) Symmetry: - It is the plan of arrangement of body parts. They are of three types: - Asymmetrical, radially symmetrical, and bilaterally symmetrical.
(iii) Organisation: - Animals have a cellular grade of organisation. Their bodies are made up of cells, while others have tissues, organs, and organ systems.
Embryonic layers: - Ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm are three embryonic layers that give rise to different organs in the body. These are also called germinal layers. Some animals are diploblastic, for example-sponges, but others are triploblastic having three germinal layers.
6. Give important characters of phylum Nemathelmintnes.
Ans: The important characters of phylum Nemathelmintnes are: -
(i) They are commonly known as nematodes or roundworms.
(ii) Their body is covered by a cuticle.
(iii) Their body is bilaterally symmetrical.
(iv) Animals have elongated cylindrical and spindle-shaped bodies with pointed ends.
(v) The body cavity is pseudocoelomate (false coelom).
(vi) There is no muscle layer in the alimentary canal.
(vii) There is no respiratory organ or blood vascular system.
(viii) Example – Ascaris, Rhabditis and Ancylostoma.
7. Members of which phylum are known as “segmented worm” Write about their body symmetry, mode of excretion & respiration.
Ans: Members of the phylum Annelida are also referred to as segmented worms. Their body is metamerically segmented. Example: - Nereis, Pheretima and Hirudinaria.
(i) Body Symmetry: - Segmented worms have typical metameric segmentation. Their body consists of segments called metamere or somites and ring-like grooves called annuli.
(ii) Excretion: - The excretory unit is coiled tubules called nephridia.
(iii) Respiration: - Respiration occurs by means of gills or skin. The skin is supplied with a large number of blood vessels. It is permeable and plays an important role in the exchange of gases.
8. Differentiate between Annelida & Arthropoda.
Ans: The difference between Annelida and Arthropoda are:
9. What are the basic plans of body design in animals?
Ans: Animals can be classified into three basic plans:
(i) Cell Aggregate Plan: - It is found in simple animals such as sponges, which have clusters of cells with the rudimentary division of labour.
(ii) Blind Sacs Plan: - It is found in coelenterates and flatworms. They have a digestive cavity with only one opening to the outside world. Food is ingested and undigested waste is expelled through this opening in the mouth. The cells are more specialised and have a division of labour.
(iii) Tube- within a tube plan: - It is found in more complex forms. In this plan, the body cavity forms one tube within which another tube, the alimentary canal, is located, opening on one side by the mouth and the other by the anus.
10. Mention the important characters of the phylum Echinodermata and give examples.
Ans: The important characters of phylum Echinodermata are: -
(i) The term Echinodermate means "spiny skin," and it refers to a group of animals represented by common forms such as starfish and sea urchins.
(ii) The skin forms a hard, spiny protective skeletal covering.
(iii) They are sluggish marine forms.
(iv) They usually show pentamerous radial symmetry.
(v) The radial symmetry is superficial and the body in fact can be divided only into two halves.
(vi) They have a coelom as well as a water vascular system.
(vii) Locomotion takes place through the use of numerous hollow tube feet.
(viii) Excretion occurs by means of diffusion through the body.
(ix) Fertilization occurs in the open sea.
(x) The development includes free swimming diploneural larva.
(xi) Example: - Asterias, Sea Urchin and Sea cucumber.
11. Give three important distinguishing characters of arthropods, reptiles and mammals.
Ans: Three important distinguishing characters of arthropods, reptiles and mammals are:
(i) Arthropods: - Arthropods have jointed appendages, segmented bodies divided into the head, thorax, and abdomen, a hard non-living chitinous exoskeleton, and compound eyes. Example: - Insects, centipedes, etc.
(ii) Reptiles: - They are cold-blooded, the body is covered by scales, possess two pairs of limbs and lay eggs. Example: - Lizard, snake etc.
(iii) Mammals: They are warm-blooded, have a hairy body, an external ear, give birth to young, have small pointed teeth, and a long snout. Example: - Dog, monkey, lion etc.
12. Mention the important characteristics of coelenterate and give examples.
Ans: The important characteristics of coelenterates are: -
(i) They are marine animals that may be solitary or colonial.
(ii) The body consists of two germ layers, the ectoderm and endoderm (diploblastic).
(iii) Their body is radially symmetrical.
(iv) They are acoelomate animals i.e., lack true coelom. They exhibit a blind sac body plan.
(v) They have a holozoic form of nutrition.
(vi) The body encloses a large central cavity known as coelenteron, which has a single opening to the outside. Coelenterons is also known as a gastrovascular cavity.
(vii) They have either intracellular or extracellular modes of digestion.
(viii) They commonly show polymorphism. There are two types of individuals: a polyp (asexual form) and a medusa (sexual form).
(ix) They have tentacles, which are usually thread-like outgrowths.
(x) Stinging cells or nematocysts are present.
(xi) Their larvae are ciliated and free-swimming.
(xii) Example: - Obelia, Aurelia, Hydra, Metridium etc.
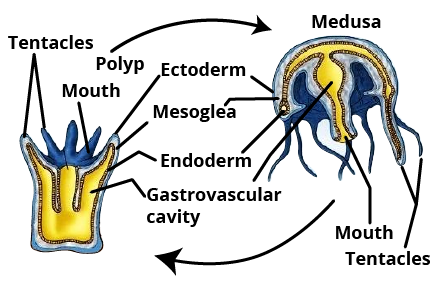
Figure: Alteration of generation in coelenterates
13. Differentiate between flightless and flying birds.
Ans: The difference between flightless and flying birds are:
Long Answer Questions (5 Marks)
1. How are non-chordates different from chordates? Write the major phyla of non-chordate and give examples.
Ans: The non-chordates are different from chordates in the following ways:
The following are the major phyla of non-chordates: -
(i) Phylum Porifera: - They are commonly known as sponges. They are generally marine; the body is diploblastic and bilaterally symmetrical. They possess a water transport mechanism. Example- Euplectella, Spongilla, Sycon and Euspongia etc.
(ii) Phylum Coelenterata: - They are marine animals. Their body is radially symmetrical, diploblastic and acoelomate. They exhibit a blind sac body plan. They commonly show polymorphism. There are two types of individuals: a polyp (asexual form) and a medusa (sexual form). Example: - Obelia, Aurelia, Hydra and Metridium etc.
(iii) Phylum Platyhelminthes: - Their body is dorsoventrally flattened and exhibits bilateral symmetry. They are triploblastic and acoelomate. Their body is soft and unsegmented. They are mostly parasitic in nature. Example: - Taenia (Tapeworms), Fasciola (Liver fluke) and Taenia saginata (Beef tapeworm).
(iv) Phylum Nematoda: - They are generally cylindrical in shape. Body wall musculature is made of special types of muscles. Sexual dimorphism is quite clear. Their body is triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical and has a false cavity (pseudocoelomate). The alimentary canal is distinct, having the mouth and the anus. Example: - Ascaris and Enterobius.
(v) Phylum Annelida: - They are coelomate, triploblastic and exhibit organ system level organization. Their body is elongated and metamerically segmented. They have a well-developed circulatory and digestive system. They respire through their body surface and the excretory organs are Nephridia. Example: - Earthworm, Leeches, Lugworms and Polychaetes.
(vi) Phylum Arthropoda: - They have an organ level of organization. Their body is bilaterally symmetrical, segmented, triploblastic and coelomate. They have jointed appendages and the body is enclosed by the chitinous cuticle. They possess trachea or book gills for respiration. Example: - Lobsters, Crabs and Spiders.
(vii) Phylum Mollusca: - They are bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic. They have an organ-system level of organization. Their body is soft, unsegmented and covered by a mantle and shell. Their body is divided into three main regions – head, a visceral mass, and ventral foot. Example: - Clams, Octopus, Mussels, Pila and Oyster.
(viii) Phylum Echinodermata: - They are sluggish marine forms. Their skin forms a hard, spiny protective skeletal covering. They usually show pentamerous radial symmetry. They have a coelom as well as a water vascular system. Locomotion takes place through the use of numerous hollow tube feet. Example: - Sea Urchins and Seastar.
2. Enlist the main features of Aschelminthes and give examples.
Ans: The main features of Aschelminthes are: -
(i) They are called roundworms as they appear circular in C.S.
(ii) Free-living, aquatic, terrestrial or parasitic.
(iii) The organization of the body is organ level.
(iv) Bilaterally symmetrical animals.
(v) They are triploblastic and pseudocoelomate.
(vi) Alimentation is complete with the muscular or pharynx.
(vii) Sexes are Separate.
(viii) The body is covered by a cuticle.
(ix) Fertilization is internal.
(x) Example: - Filarial worm (Wuchereria), Ascaris, Pinworm (Enterobius) and Hookworm (Ancylostoma).
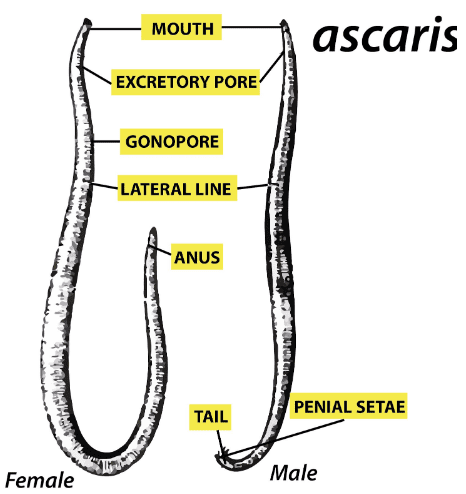
Figure: Male and female Ascaris
3. Enlist the main salient features of phylum Ctenophora.
Ans: The main salient features of phylum Ctenophora are:
(i) Ctenophores are marine animals having transparent and flat or oval body shapes.
(ii) The polyp phase is absent in the life cycle of ctenophores.
(iii) These are bilaterally symmetrical and lack cnidoblast cells.
(iv) When the tentacles are present, they are two in number and contain colloblast cells.
(v) They move by cilia which join together to form comb plates. There are eight median comb plates.
(vi) The gastrovascular cavity is branched and open to the outside by the stomodeum.
(vii) They are diploblastic, but the mesoglea differs from that of cnidaria.
(viii) The presence of special sense organs at the opposite end of the mouth is the main characteristic of this phylum.
(ix) They reproduce only by means of sexual reproduction.
(x) They do not have a larval phase in their life cycle.
(xi) Example: -Ctenophora (Pleurobrachia), ctenophore, ctenoplana, Beroe and Hormiphora.
Figure: Ctenophora
Download Important Questions of Animal Kingdom Class 11 PDF
Topics covered in Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 important questions are:
Animals features and basis of classification
Levels of the organization
The symmetry of animals
Segmentation
The study of different types of the phylum.

Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 - Animal Kingdom Summary
The animal kingdom is one of the five-kingdom proposed by R.H. Whittaker and it comprises multicellular eukaryotic organisms that do not possess a cell wall. As millions of species are described till now of different structures and forms. The classification was very necessary for the systematic positioning of newly described species.
Basis of Classification - Animal kingdom is classified based on the different essential characteristics like level of organization, habitat, and symmetry. There are different levels of organization such as the cellular level of organization, tissue level of the organization, organ level of organization, and the organ system level of organization.
There are different patterns of the organ system like the digestive system, in which some might be complete and others can be an incomplete digestive system. Circulatory system, open type, and closed type. The symmetry of the animal is of three types bilateral symmetry, radial symmetry, and asymmetrical.
Coelom - The body cavity which is lined by the mesoderm is known as a coelom. Some of the classifications are made on the presence and absence of coelom. On the basics of the coelom, animals can be divided into three different types: coelomates, pseudocoelomates, and coelomates.
Mainly animals have three types of the body like cell aggregate body plan, this type of body plan is found in the sponges. Blind sac body plan and is found in the coelenterates, flatworms, and ctenophores. And the third one is a tube within the tube body plan and it is found in the aschelminthes.
Segmentation - Body of some of the animals are divided into segments externally, as well as internal or some of them with a serial repetition of at least some organs. Segmentation can be mainly of two types: metameric segmentation and pseudo metameric segmentation. Metameric segmentation divides the body both externally as well as internally and in pseudo metameric segmentation, the body is divided into parts or segments.
Practice Questions for CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 4: Animal Kingdom
Very short answer type questions.
Define permanent tissues.
Write three different types of meristematic tissue.
Which cell is responsible for curling the leaves in plants during water stress?
Short Answer Type Questions
Why are phloem and xylem considered as complex tissues?
Write the difference between guard cell and epidermal cell.
Define guard cells.
Long Answer Type Questions
Explain the secondary growth in roots with a diagram.
What are monocotyledonous plants?
What is the difference between dicot roots and monocot roots?
Extra Questions for Practice
What are bulliform cells?
What are guard cells and epidermal cells?
Explain Hutchinson’s system of classification?
Define Mesophyll.
Define Pith.
Benefits of Solving CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Important Questions
Following are some of the benefits of solving CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Important Questions
Practising important questions will give students an overall idea about the important topics of the chapter.
Students can enhance their time management skills by solving important questions in a given time period.
Solving various types of questions for this chapter will enhance their problem-solving skills.
Students will be aware of the difficulty level of the questions, and the way questions can be framed in the exam
Practising questions repeatedly will enhance their confidence level.
Students will be able to handle any type of question in the exam, even the complex ones.
CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 important questions are the perfect study material for the students to get a strong hold on the important concepts. Practising the questions repeatedly will surely help students to confidently attempt questions in less time during exams. Apart from Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 important questions , Vedantu also provides Class 11 Chapter wise and Subject wise important questions. Explore the website to get the Class 11 Chapter wise and Subject wise important questions .
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 11

FAQs on CBSE Important Questions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4- Anatomy of Flowering Plant
1. What do we mean by the anatomy of flowering plants?
The study of the interior structure and organization of plants or plant organs is known as plant anatomy (part of plants). Plant anatomy is the study of diverse plant tissues, their kinds, and how they are organized to generate various plant organs.
2. What is a modified shoot and why is it called so?
The flower of a flowering plant is called its modified shoot. The flower is considered a modified stalk since the internodes are greatly condensed and the appendages such as sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels (pistil) are often many.
3. Is the morphology of flowering plants chapter important for NEET?
In Vedantu's NEET chapterwise weightage analysis, the Morphology of Flowering Plants chapter accounts for about 4% of the total number of questions answered in the NEET medical entrance test during the previous eight years. Some of the important subtopics like Root, Stem, Leaf, Inflorescence, Flower, Fruit, and seed are equally important contributing topics.
4. What are the methods of doing the anatomy of plants?
The anatomy of flowering plants can be done by knowing some basic facts that It is made up of simple tissues like parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma. Parenchymatous cells are commonly seen in the cortex, pericycle, pith, and medullary rays, as well as main stems and roots. The mesophyll is the ground tissue of leaves that is made up of thin-walled chloroplast-containing cells.
5. What is the difference between dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants?
According to Vedantu. flowering plants are classified as monocots or dicots. The cotyledon is the leaf of an embryo in a seed-bearing plant, which is followed by germination. it produces the seedling's initial leaves. Monocot and dicot plants are distinguished by four major characteristics: stems, roots, leaves, and flowers. Check out Vedantu for detailed answer.
CBSE Class 11 Biology Important Questions
Cbse study materials.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 11 Biology
Chapter 1: The Living World Chapter 2: Biological Classification Chapter 3: Plant Kingdom Chapter 4: Animal Kingdom Chapter 5: Morphology of Flowering Plants Chapter 6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants Chapter 7: Structural Organisation in Animals Chapter 8: The Unit of Life Chapter 9: Biomolecules Chapter 10: Cell Cycle and Cell Division Chapter 11: Transport in Plants Chapter 12: Mineral Nutrition Chapter 13: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Chapter 14: Respiration in Plants Chapter 15: Plant Growth and Development Chapter 16: Digestion and Absorption Chapter 17: Breathing and Exchange of Gases Chapter 18: Body Fluids and Circulation Chapter 19: Excretory Products and Their Elimination Chapter 20: Locomotion and Movement Chapter 21: Neural Control and Coordination Chapter 22: Chemical Coordination and Integration
Share this:
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
CBSE Expert
Case Study Questions for Class 11 Biology PDF Download
We have provided here Case Study questions for Class 11 Biology for final board exams. You can read these chapter-wise Case Study questions. These questions are prepared by subject experts and experienced teachers. The answer key is also provided so that you can check the correct answer for each question. Practice these questions to score well in your exams.

CBSE 11th Standard CBSE Biology question papers, important notes, study materials, Previous Year Questions, Syllabus, and exam patterns. Free 11th Standard CBSE Biology books and syllabus online. Important keywords, Case Study Questions, and Solutions.
Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
CBSE Class 11 Biology question paper will have case study questions too. These case-based questions will be objective type in nature. So, Class 11 Biology students must prepare themselves for such questions. First of all, you should study NCERT Textbooks line by line, and then you should practice as many questions as possible.
Chapter-wise Solved Case Study Questions for Class 11 Biology
- Chapter 1 : The Living World
- Chapter 2 : Biological Classification
- Chapter 3 : Plant Kingdom
- Chapter 4 : Animal Kingdom
- Chapter 5 : Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Chapter 6 : Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Chapter 7 : Structural Organisation in Animals
- Chapter 8 : Cell : The Unit of Life
- Chapter 9 : Biomolecules
- Chapter 10 : Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Chapter 11 : Transport in Plants
- Chapter 12 : Mineral Nutrition
- Chapter 13 : Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Chapter 14 : Respiration in Plants
- Chapter 15 : Plant Growth and Development
- Chapter 16 : Digestion and Absorption
- Chapter 17 : Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Chapter 18 : Body Fluids and Circulation
- Chapter 19 : Excretory Products and their Elimination
- Chapter 20 : Locomotion and Movement
- Chapter 21 : Neural Control and Coordination
- Chapter 22 : Chemical Coordination and Integration
Class 11 MCQ Questions
Class 11 students should go through important Case Study problems for Biology before the exams. This will help them to understand the type of Case Study questions that can be asked in Grade 11 Biology examinations. Our expert faculty for standard 11 Biology have designed these questions based on the trend of questions that have been asked in last year’s exams. The solutions have been designed in a manner to help the grade 11 students understand the concepts and also easy to learn solutions.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!

DK Goel Solutions
- Exam Questions
- Exam Questions Class 11
Biology Class 11 Exam Questions
Please refer to Biology Class 11 Exam Questions with solutions below. These important exams solved questions have been prepared based on the latest books and syllabus issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Our team of expert teachers of Class 11 Biology has designed these based on the latest examination guidelines and the type of questions expected to come in the examinations.
Exam Questions Class 11 Biology
We have provided exam questions with solutions for all chapters in Standard 11 Biology. You should learn these before the examinations as the answers have been designed to help you get better marks. You can click on the chapter-wise links below to access all problems and solutions for free. These will also help you to clear all concepts and improve your understanding of Biology in Class 11.
Chapterwise Important Questions Class 11 Biology
Unit 1: Diversity in the Living World
Unit 2: Structural Organisation in Plants and Animals
Unit 3: Cell- Structure and Functions
Unit 4: Plant Physiology
Unit 5: Human Physiology
It is important for students to prepare for Class 11 Biology exams properly and practice questions and answers which have been designed based on the latest guidelines on the type of questions to be asked in the upcoming class 11 Biology examination. We have also provided MCQ Questions for Class 11 Biology which will be very useful for students. This year more MCQ-based questions and Case study-based questions are expected in examinations. We have provided all the latest questions which are expected to come in exams on our website. Students in Class 11 should download these questions in Pdf and share with teachers and friends.

Related Posts
Exam question for class 11 business studies chapter 10 internal trade, exam question for class 11 business studies chapter 1 business trade and commerce.

Exam Question for Class 11 Biology Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom PDF Download
The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom contains a vast collection of questions to practise. By practising these questions of Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom, students can strengthen their problem solving skills as well as reasoning skills; these skills can be used in further chapters and real-life problems. These questions of Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom can also help students to build a strong foundation for the chapter.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom PDF
The Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom can be a bit confusing if students are not able to understand the concepts properly. For that purpose students need to start practising Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom questions from the NCERT textbook. After practising those questions, students can prefer referring to the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom PDF which is available in the Selfstudys website.
Exercise Wise NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
In the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom, a plethora of exercises are given so that students can understand the concepts as well as can solve confusions then and there. By practising exercise wise questions, students can learn to approach different questions of Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom in different and creative ways.
Formula wise NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
The questions in the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom are arranged according to each and every formula. By practising the questions of Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom formula wise, students can become more confident while applying the formulas. By applying the right formulas in the right questions of Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom, students can score good marks in those questions.
Where can Students Find the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom?
Students can find the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom, steps to attempt are clearly explained below:
- Visit the Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards NCERT Books & Solutionss which can be seen in the navigation bar.
- A drop down menu will appear, select NCERT Solutionss from the list.
- A new page will appear, select Class 11 from the list of classes.
- Now select the subject Biology from the list.
- Again a new page will appear, select the chapter Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom.
Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
The features of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom is considered to be distinctive trait, some important features are discussed below:
- Based on NCERT Syllabus: The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom revision are based on the NCERT syllabus so that by referring to it students can have an updated knowledge.
- Different Levels of Questions: In the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom theory, different levels of questions are asked; that is easy to difficult.
- Hints and Solutionss are Given: In the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom PDF, hints and Solutionss are given so that students can easily solve all their doubts and confusions.
- All Exercises are Covered: Inside the Class 11 Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom, all the exercises are covered in the NCERT Solutions; accordingly students can learn to approach in different ways.
- Diagrams are Given: Diagrams are generally considered to be visual representation of the Class 11 Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom questions and concepts; the same is followed in NCERT Solutions.
- Available in the PDF: The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom is available in the PDF so that students can access answers whenever they want to.
What Are the Advantages of Using NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom provides plenty of advantages, some of the advantages are discussed below:
- Improves Performance: By solving questions in the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom revision, students can improve their problem solving skills and can increase the chances of getting good marks in the test. The Solutions helps students understand the concepts of Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom as well as questions effectively and efficiently.
- Builds Confidence: By solving questions from NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom revision, students can build their confidence as it provides a variety of questions. Being confident while attempting Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom questions can help one to get right and accurate answers.
- Enhances the Learning Process: By using the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom theory, students can enhance their learning process and can reinforce the learning strategies.
- Saves Time and Effort: Students don’t need to search for answers as it is already available in the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom PDF as it saves both time and effort of students.
- Easy to Understand: As the answers of Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom are very simple this makes students understand all levels of questions easily.
- Helps to Maintain Accuracy: Accuracy is considered to be the freedom from making mistakes; students can maintain the accuracy level by solving Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom questions from NCERT Solutions.
Is NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Right for Students?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom is right for students as it is arranged according to the latest syllabus,some of the key factors are discussed below:
- To Understand Concepts: The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom revision is considered to be the right one as it allows students to understand the concepts easily.
- Comprehensive Coverage: The topics are covered in a comprehensive way in the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom theory so it is right for students to refer.
- Reliable: Students can be dependent on the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom PDF as the questions and answers are accurate and reliable. Accordingly, students don’t need to check for the right answers of Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom questions from other reference materials.
- Improves Problem Solving Skills: It is a skill in which students tend to look up to questions of Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom in a logical way and solve those questions in a logical way. So to improve problem solving skills while attempting questions of Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom, students can refer to the NCERT Solutions of Class 11 Biology.
- Follows the Latest Syllabus: The Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom questions in the NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology follows the latest syllabus so it is right for students to choose it.
- Can Solve Questions with Ease: Students can choose the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology so that they can solve the Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom questions with ease.
When Is the Best Time to Use NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom can be used at any time while preparing; but is it better to follow the given tips:
- After Completing the Chapter: Students can prefer utilising the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom revision after completing the chapter thoroughly.
- To Identify Gaps in Knowledge: It is advisable for students to utilise the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom theory if they want to identify the gaps in their knowledge. After identification of gaps, students can also eliminate those gaps by solving the Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom questions on a regular basis.
- To Verify the Answers: Once students have attempted the questions of Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom then they can prefer utilising the NCERT Solutions so that they can match their own answers.
- To Practise More Questions: If students want to practise more questions on Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom then they can prefer using the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology. By practising more Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom questions, students can easily enhance their problem solving skills.
- To Revise: The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom PDF can be utilised as good study material as through it, students can easily revise the topics and concepts.
- To Build Strong Foundation: If students want to build a strong foundation for the Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom, then they can prefer to utilise the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology. By building a strong foundation, students can score good marks in questions related to Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom.
What are the Challenges Faced While Referring to the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom?
While referring to the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom, students may face challenges, those challenges are discussed below:
- Lack of Understanding: Students may struggle to understand the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom revision if they don’t have a clear understanding of the concepts and topics. In this case, students need to have a clear understanding of the Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom concepts.
- Lengthy Solutionss: Some answers in the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom theory can be lengthy so in this case students may face difficulty in understanding the Solutions. To overcome this, students can break the answers of Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom questions into smaller parts.
- Technical Language: If the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom PDF contains any kind of technical language then some students may face difficulty in understanding those words.
- Lack of Visual Aids: If there are not enough visual diagrams of Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom questions, then they may face difficulty in understanding the NCERT Class 11 Biology Solutionss. To overcome this, students may refer to the Selfstudys website as there are enough visual diagrams related to Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom.
- Limited Scope: The NCERT Solutionss for Class 11 Biology provides a limited number of Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom questions to solve; for this students need to refer to other study materials which can be available on the website.
- Inadequate Explanations: Some answers of Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom may not provide adequate explanations in the NCERT Solutionss; so in this case students may face difficulty understanding the questions.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


Notes of Ch 4 Animal Kingdom| Class 11th Biology
Study material and notes of ch 4 animal kingdom class 11th biology.
- Basis of Classification
- Phylum Porifera
- Phylum Coelenterata
- Phylum Ctenophora
- Phylum Plathyhelminthes
- Phylum Aschelminthes
- Phylum Annelida
- Phylum Arthropoda
- Phulum Mollusca
- Phylum Echinodermata
- Phyum Hemichordata
- Phylum Chordata
- Division of Vertebrata
- Super-class: Pisces
- Super Class: Tetrapoda
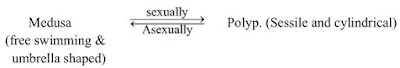
Contact Form
- Biology Important Questions
- Class 11 - Biology
CBSE Important Questions for Class 11 Biology
CBSE Important Questions for Class 11 Biology are prepared by the subject experts and are extensively helpful for students in their board exam preparations. Biology is a core subject which involves a detailed study of life and living organism. Students who are preparing for competitive examination such as NEET require deep knowledge of the Biology subject. This page provides students with additional CBSE Important Questions to practise and test their knowledge. These CBSE Class 11 Biology Important Questions will help in annual exam preparation and competitive exams.
Class 11 Biology Important Questions
Students can find the Biology chapter-wise CBSE Important Questions for Class 11 in the table below. These important questions also include questions which have been frequently asked in past years. Furthermore, solutions are provided for these questions, emphasising ease of study. Click on the links below to start exploring.
To practise more important questions or explore other topics of CBSE Class 11 , students can register at BYJU’S. Furthermore, discover useful resources and study materials on BYJU’S App. Download the App today to secure more marks in Biology.
Also, Access Class 11 Biology Sample Papers .
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
It really helped me a lot in my exams
These questions are very important
I study well in Byju’s
I this is very nice
Really helpful
Tq byjus it really helped me
Help full to me thanks 🙏🙏
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 11 Biology Biomolecules
Case study questions class 11 biology chapter 9 biomolecules.
CBSE Class 11 Case Study Questions Biology Biomolecules. Important Case Study Questions for Class 11 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Biomolecules.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 11 Biology Biomolecules
Enzymes are composed of one or several polypeptide chains. However, there are a number of cases in which non-protein constituents called co-factors are bound to the enzyme to make the enzyme catalytically active. In these instances, the protein portion of the enzymes is called the apoenzyme. Three kinds of cofactors may be identified: prosthetic groups, co-enzymes and metal ions. Prosthetic groups are organic compounds and are distinguished from other cofactors in that they are tightly bound to the apoenzyme. For example, in peroxidase and catalase, which catalyze the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen, haem is the prosthetic group and it is a part of the active site of the enzyme. Co-enzymes are also organic compounds but their association with the apoenzyme is only transient, usually occurring during the course of catalysis. Furthermore, co-enzymes serve as co-factors in a number of different enzyme catalyzed reactions. The essential chemical components of many coenzymes are vitamins, e.g., coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and NADP contain the vitamin niacin. A number of enzymes require metal ions for their activity which form coordination bonds with side chains at the active site and at the same time form one or more cordination bonds with the substrate, e.g., zinc is a cofactor for the proteolytic enzyme carboxypeptidase. Catalytic activity is lost when the co-factor is removed from the enzyme which testifies that they play a crucial role in the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
1.) In complex of protein and co-factors, protein is referred as ___________________.
a) Proenzyme
b) Coenzyme
c) Apoenzyme
d.) Proteinase enzyme.
2.) ________________ Co-factor are found very tightly bound to the apoenzyme.
a.) Co-enzyme
b.) Proenzyme
c,) Proteinase
d.) Prosthetic
3.) Enlist the type of co-factor with examples.
4.) Define co-factors.
5.) What result come off if co-factor is removed from the enzyme?
3.) Three kinds of cofactors
- Prosthetic groups – e.g. Haem
- Co-enzymes – e.g. Niacin
- Metal ions – e.g. zinc
4.) Co-factor are the non-protein constituents are bound to the enzyme to make the enzyme catalytically active. Enzymes are composed of one or several polypeptide chains. However, there are a number of cases in which non-protein constituents are bound to the enzyme to make the enzyme catalytically active.
5.) Catalytic activity is lost when the co-factor is removed from the enzyme which testifies that they play a crucial role in the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
The activity of an enzyme can be affected by a change in the conditions which can alter the tertiary structure of the protein. These include temperature, pH, and change in substrate concentration or binding of specific chemicals that regulate its activity. Temperature and pH Enzymes generally function in a narrow range of temperature and pH. Each enzyme shows its highest activity at a particular temperature and pH called the optimum temperature and optimum pH. Activity declines both below and above the optimum value. Low temperature preserves the enzyme in a temporarily inactive state whereas high temperature destroys enzymatic activity because proteins are denatured by heat.
Concentration of Substrate With the increase in substrate concentration, the velocity of the enzymatic reaction rises at first. The reaction ultimately reaches a maximum velocity (Vmax) which is not exceeded by any further rise in concentration of the substrate. This is because the enzyme molecules are fewer than the substrate molecules and after saturation of these molecules, there are no free enzyme molecules to bind with the additional substrate molecules.
The activity of an enzyme is also sensitive to the presence of specific chemicals that bind to the enzyme. When the binding of the chemical shuts off enzyme activity, the process is called inhibition and the chemical is called an inhibitor.
When the inhibitor closely resembles the substrate in its molecular structure and inhibits the activity of the enzyme, it is known as competitive inhibitor. Due to its close structural similarity with the substrate, the inhibitor competes with the substrate for the substrate binding site of the enzyme. Consequently, the substrate cannot bind and as a result, the enzyme action declines, e.g., inhibition of succinic dehydrogenase by malonate which closely resembles the substrate succinate in structure. Such competitive inhibitors are often used in the control of bacterial pathogens.
1.) _______________ is a chemical compound or molecule which is responsible for decrease or stop the enzyme activity by binding to an enzyme.
a.) Catalyser
b) Inhibitor
c) Regulator
d) Controller
2.) _______________ preserve the enzyme and keep them in temporarily inactive state.
a.) Optimum pH
c) Optimum temperature
d) Low temperature
3.) Give reason – why most of the enzymes destroyed in high temperature condition?
4.) Explain the relation between substrate concentration and enzymatic activity?
5.) Explain competitive inhibition and inhibitor.
3.) Enzymes are composed of one or several polypeptide chains. Almost all enzymes are protein. High temperature condition destroys enzymatic activity because proteins are denatured by heat.
4.) Concentration of Substrate With the increase in substrate concentration, the velocity of the enzymatic reaction rises at first. The reaction ultimately reaches a maximum velocity (Vmax) which is not exceeded by any further rise in concentration of the substrate. This is because the enzyme molecules are fewer than the substrate molecules and after saturation of these molecules, there are no free enzyme molecules to bind with the additional substrate molecules.
5.) When the inhibitor closely resembles the substrate in its molecular structure and inhibits the activity of the enzyme, it is known as competitive inhibitor. Due to its close structural similarity with the substrate, the inhibitor competes with the substrate for the substrate binding site of the enzyme. Consequently, the substrate cannot bind and as a result, the enzyme action declines. This phenomenon is called as competitive inhibition.
Almost all enzymes are proteins. There are some nucleic acids that behave like enzymes. These are called ribozymes. An enzyme like any protein has a primary structure, i.e., amino acid sequence of the protein. An enzyme like any protein has the secondary and the tertiary structure. When you look at a tertiary structure you will notice that the backbone of the protein chain folds upon itself, the chain criss-crosses itself and hence, many crevices or pockets are made. One such pocket is the ‘active site’. An active site of an enzyme is a crevice or pocket into which the substrate fits. Thus enzymes, through their active site, catalyse reactions at a high rate. Enzyme catalysts differ from inorganic catalysts in many ways, but one major difference needs mention. Inorganic catalysts work efficiently at high temperatures and high pressures, while enzymes get damaged at high temperatures (say above 40°C). However, enzymes isolated from organisms who normally live under extremely high temperatures (e.g., hot vents and sulphur springs), are stable and retain their catalytic power even at high temperatures (upto 80°-90°C). Thermal stability is thus an important quality of such enzymes isolated from thermophilic organisms.
1.) _____________ is the pocket like region of an enzyme into which substrate molecules bind.
a) Protein site
b) Co-factors
c) Coenzyme
d) Active site
2.) Identify incorrect statement
Statement 1 – Nucleic acids which behave like enzymes are commonly termed as nucliozymes.
Statement 2 – An enzyme like any protein has a primary, secondary and the tertiary structure.
Statement 3 – Enzyme catalysts differ from inorganic catalysts in many ways.
Statement 4 – All enzymes are proteins.
b) Both 1 & 3
d.) None of the above
3.) How active site of enzymes are formed?
4.) Explain how Enzyme catalysts differ from inorganic catalysts?
5.) What is ribozymes?
3.) Enzyme have primary, secondary and tertiary structure like proteins. In tertiary structure, backbone of the protein chain folds upon itself, the chain criss-crosses itself and leads to the formation of many crevices or pockets are made. These pockets are referred as active site of enzyme. An active site of an enzyme is a crevice or pocket into which the substrate fits.
4.) Enzyme catalysts differ from inorganic catalysts in many ways. Inorganic catalysts work efficiently at high temperatures and high pressures, while enzymes get damaged at high temperatures (above 40°C). There are some exceptions such as enzyme isolated from thermophilic organisms.
5.) There are some nucleic acid behave like an enzymes, these nucleic acid is termed as ribozymes.
Metabolic pathways can lead to a more complex structure from a simpler structure (for example, acetic acid becomes cholesterol) or lead to a simpler structure from a complex structure (for example, glucose becomes lactic acid in our skeletal muscle). The former cases are called biosynthetic pathways or anabolic pathways. The latter constitute degradation and hence are called catabolic pathways. Anabolic pathways, as expected, consume energy. Assembly of a protein from amino acids requires energy input. On the other hand, catabolic pathways lead to the release of energy. For example, when glucose is degraded to lactic acid in our skeletal muscle, energy is liberated. This metabolic pathway from glucose to lactic acid which occurs in 10 metabolic steps is called glycolysis. Living organisms have learnt to trap this energy liberated during degradation and store it in the form of chemical bonds. As and when needed, this bond energy is utilised for biosynthetic, osmotic and mechanical work that we perform. The most important form of energy currency in living systems is the bond energy in a chemical called adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
There are thousands of chemical compounds in a living organism, otherwise called as metabolites or biomolecules, are present at concentrations characteristic of each of them. For example, the blood concentration of glucose in a normal healthy individual is 4.2 mmol/L– 6.1 mmol/L, while that of hormones would be nanograms/mL. The most important fact of biological systems is that all living organisms exist in a steady-state characterised by concentrations of each of these biomolecules. These biomolecules are in a metabolic flux. Any chemical or physical process moves spontaneously to equilibrium. The steady state is a non-equilibrium state. Systems at equilibrium cannot perform work. As living organisms work continuously, they cannot afford to reach equilibrium. Hence the living state is a non-equilibrium steady state to be able to perform work; living process is a constant effort to prevent falling into equilibrium. This is achieved by energy input. Metabolism provides a mechanism for the production of energy. Hence the living state and metabolism are synonymous. Without metabolism there cannot be a living state.
1.) ________________ is the destructive process, which involves complex structure breakdown into simple form.
a) Amphibolic pathway
b) Anabolic pathway
c) Catabolic pathway
d) None of the above
2.) ______________ is the normal glucose concentration in normal healthy individual.
a) 9 mmol/L– 6.8 mmol/L
b) 5 mmol/L– 6.5 mmol/L
c) 0 mmol/L– 7.1 mmol/L
d) 2 mmol/L– 6.1 mmol/L
3.) Give any one example of catabolic reaction that take place in human body.
4.) Give the name of chemical bond in which energy liberated during degradation of metabolites, is stored.
5.) Define anabolic pathways and catabolic pathways.
3.) Glucose becomes lactic acid in our skeletal muscle is the catabolic pathway reaction, which constitute degradation of biomolecule and release energy.
4.) In Living organism energy liberated during degradation of metabolites stored in the form of chemical bonds i.e. ATP. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the most important form of energy currency in living systems.
5) Anabolic pathway – Metabolic pathways which leads to a more complex structure from a simpler structure are termed as anabolic pathways or biosynthetic pathways.
Catabolic pathway – Metabolic pathways which leads to a simpler structure from a complex structure are termed as catabolic pathways.
Proteins are heteropolymers containing strings of amino acids. Structure of molecules means different things in different contexts. In inorganic chemistry, the structure invariably refers to the molecular formulae (e.g., NaCl, MgCl2, etc.). Organic chemists always write a two dimensional view of the molecules while representing the structure of the molecules (e.g., benzene, naphthalene, etc.). Physicists conjure up the three dimensional views of molecular structures while biologists describe the protein structure at four levels. The sequence of amino acids i.e., the positional information in a protein – which is the first amino acid, which is second, and so on – is called the primary structure of a protein. A protein is imagined as a line, the left end represented by the first amino acid and the right end represented by the last amino acid. The first amino acid is also called as N-terminal amino acid. The last amino acid is called the C-terminal amino acid. A protein thread does not exist throughout as an extended rigid rod. The thread is folded in the form of a helix, only some portions of the protein thread are arranged in the form of a helix. In proteins, only right handed helices are observed. Other regions of the protein thread are folded into other forms in what is called the secondary structure. In addition, the long protein chain is also folded upon itself like a hollow woollen ball, giving rise to the tertiary structure. This gives us a 3-dimensional view of a protein. Tertiary structure is absolutely necessary for the many biological activities of proteins.
Some proteins are an assembly of more than one polypeptide or subunits. The manner in which these individual folded polypeptides or subunits are arranged with respect to each other (e.g. linear string of spheres, spheres arranged one upon each other in the form of a cube or plate etc.) is the architecture of a protein otherwise called the quaternary structure of a protein (Fig. 9.4 d). Adult human haemoglobin consists of 4 subunits. Two of these are identical to each other. Hence, two subunits of α type and two subunits of β type together constitute the human haemoglobin (Hb).
In a polypeptide or a protein, amino acids are linked by a peptide bond which is formed when the carboxyl (-COOH) group of one amino acid reacts with the amino (-NH2 ) group of the next amino acid with the elimination of a water moiety (the process is called dehydration). In a polysaccharide the individual monosaccharides are linked by a Glycosidic bond. This bond is also formed by dehydration. This bond is formed between two carbon atoms of two adjacent monosaccharides. In a nucleic acid a phosphate moiety links the 3’-carbon of one sugar of one nucleotide to the 5’-carbon of the sugar of the succeeding nucleotide. The bond between the phosphate and hydroxyl group of sugar is an ester bond. As there is one such ester bond on either side, it is called phosphodiester bond. Nucleic acids exhibit a wide variety of secondary structures. For example, one of the secondary structures exhibited by DNA is the famous Watson – Crick Model. This model says that DNA exists as a double helix. The two strands of polynucleotides are antiparallel i.e., run in the opposite direction. The backbone is formed by the sugar-phosphate-sugar chain. The nitrogen bases are projected more or less perpendicular to this backbone but face inside. A and G of one strand compulsorily base pairs with T and C, respectively, on the other strand.There are two hydrogen bonds between A and T and three hydrogen bonds between G and C. Each strand appears like a helical staircase.
1.) To form polypeptide molecules, number of amino acids joined together by _______________ bond.
a.) Covalent bond
b) Glycosidic bond
c) Peptide bond
d) Phosphodiester bond
2.) Number of monosaccharides are joined together by _____________ to form polysaccharide.
a.) Phosphodiester bond
c) Hydrogen bond
d) Ester bond
3.) Define N-terminal amino acid and c-terminal amino acid.
4.) Explain how amino acid chain formed in the formation of polypeptide molecule.
5.) Name the bond present between nitrogen bases ( A and G / T and C ) of nucleic acid.
3) The first amino acid present in amino acid chain is also called as N-terminal amino acid. The last amino acid is called the C-terminal amino acid.
4) When the carboxyl (-COOH) group of one amino acid reacts with the amino (-NH2) group of the next amino acid, they form peptide bond between them. This way formation of amino acid chain continuous which leads to the polypeptide.
5) The nitrogen bases A and G of one strand compulsorily base pairs with T and C, respectively, there are two hydrogen bonds between A and T and three hydrogen bonds between G and C.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Tripura board class 6 bengali solutions chapter 11 ছেলেবেলা, assam scert class 8 geography and economics chapter 2 solutions, sikkim scert class 5 evs chapter 9 water- a life source solution, sikkim scert class 5 evs chapter 10 experiments with water solution.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

COMMENTS
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Case Study 1: Animals in which the cells are arranged in two embryonic layers, an external ectoderm, and an internal endoderm, are called diploblastic animals, e.g., coelenterates. An undifferentiated ...
Class 11 Biology case study questions 1. Read the following and answer any four questions: The detailed structure of the membrane was studied only after the advent of the electron microscope in the 1950s. Meanwhile, chemical studies on the cell membrane, especially in human red blood cells (RBCs), enabled the scientists to deduce the possible ...
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom. CASE 1. Though all members of Animalia are multicellular, all of them do not exhibit the same pattern of organisation of cells. For example, in sponges, the cells are arranged as loose cell aggregates, i.e., they exhibit cellular level of organisation.
Download PDF of Case Study Questions Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom. Practice CBSE Class 11 Biology Important Questions Chapter Wise, MCQ's, Extra Questions for Exams. ... get the clear idea whether the questions framed from any particular chapter are mostly either short or long answer type questions or multiple choice based and also ...
Practice Questions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom. 1. The clam nervous system is composed of: (a) labial palps. (b) one pair of ganglia. (c) two pairs of ganglia. (d) three pairs of ganglia. 2. ______ are devoid of respiratory, excretory and circulatory organs. (a) Threadworms.
CBSE 11th Standard CBSE Biology question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 11th Standard CBSE Biology books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and Scholorships in one place
Yes, the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 are completely free of cost. At BYJU'S, the subject matter experts design the solutions to help students understand the concepts efficiently. The solutions contain explanations in simple language to boost the board exam preparation of students. Students can refer to the NCERT Solutions ...
Monocot and dicot plants are distinguished by four major characteristics: stems, roots, leaves, and flowers. Check out Vedantu for detailed answer. Get chapter-wise important questions for CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom with answers on Vedantu. Download the PDF for free and revise these important questions for CBSE exam 2024-25.
Case Study Questions for Class 11 Biology. Chapter 1: The Living World. Chapter 2: Biological Classification. Chapter 3: Plant Kingdom. Chapter 4: Animal Kingdom. Chapter 5: Morphology of Flowering Plants. Chapter 6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants. Chapter 7: Structural Organisation in Animals. Chapter 8: The Unit of Life.
Chapter-wise Solved Case Study Questions for Class 11 Biology. Chapter 1 : The Living World. Chapter 2 : Biological Classification. Chapter 3 : Plant Kingdom. Chapter 4 : Animal Kingdom. Chapter 5 : Morphology of Flowering Plants. Chapter 6 : Anatomy of Flowering Plants. Chapter 7 : Structural Organisation in Animals.
CBSE Biology Value Based Questions Class 11th Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom PDF. The purpose of the Biology Value Based Questions is to make students aware of how basic values are needed in the analysis of different situations and how students require to recognize those values in their daily lives. Some questions are subject related.
Chapterwise Important Questions Class 11 Biology. Unit 1: Diversity in the Living World. Chapter 1 The Living World. Chapter 2 Biological Classification. Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom. Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom. Unit 2: Structural Organisation in Plants and Animals. Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants. Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom contains a vast collection of questions to practise. By practising these questions of Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom, students can strengthen their problem solving skills as well as reasoning skills; these skills can be used in further chapters and real-life problems. These questions ...
Study Material and Notes of Ch 4 Animal Kingdom Class 11th Biology. (a) Cellular level : Cells are arranged as loose cell aggregates. Example: sponges. (b) Tissue level : The cells performing the same function are arranged into tissues. Example: Coelenterates.
Answer key. 1) b. 2) b. 3) Synthesis phase (S phase) is the phase in cell cycle marks the period during which DNA replicates. During this time the amount of DNA per cell doubles. 4) Cytokinesis is the process of cell division, which divides the cytoplasm of a parental cell and leads to formation of two daughter cells.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 11 Biology Neural Control and Coordination. CASE 1
Click on the links below to start exploring. Important Questions Chapter 1: The Living World. Important Questions Chapter 2: Biological Classification. Important Questions Chapter 3: Plant Kingdom. Important Questions Chapter 4: Animal Kingdom. Important Questions Chapter 5: Morphology of Flowering Plants.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 11 Biology Morphology of Flowering Plants. CASE 1. In majority of the dicotyledonous plants, the direct elongation of the radicle leads to the formation of primary root which grows inside the soil. It bears lateral roots of several orders that are referred to as secondary, tertiary, etc. roots.
Statement 1 - Theodore Schwann reported the presence of cell membrane. Statement 2 - Rudolph Virchowgive the cell theory a final shape. Statement 3 - New cells arise from pre-existing cells. Statement 4 - Living organisms are composed of cells and products of cells. a.) Statement 1 and 3 are incorrect.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 11 Biology Biomolecules. CASE 1. Enzymes are composed of one or several polypeptide chains.