Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples

How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Shona McCombes .
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more variables . An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls. A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Step 1: ask a question.
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2: Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalise more complex constructs.
Step 3: Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
Step 4: Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
Step 6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
A hypothesis is not just a guess. It should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, May 06). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 3 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/hypothesis-writing/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, operationalisation | a guide with examples, pros & cons, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Research Hypothesis: Good & Bad Examples
What is a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis is an attempt at explaining a phenomenon or the relationships between phenomena/variables in the real world. Hypotheses are sometimes called “educated guesses”, but they are in fact (or let’s say they should be) based on previous observations, existing theories, scientific evidence, and logic. A research hypothesis is also not a prediction—rather, predictions are ( should be) based on clearly formulated hypotheses. For example, “We tested the hypothesis that KLF2 knockout mice would show deficiencies in heart development” is an assumption or prediction, not a hypothesis.
The research hypothesis at the basis of this prediction is “the product of the KLF2 gene is involved in the development of the cardiovascular system in mice”—and this hypothesis is probably (hopefully) based on a clear observation, such as that mice with low levels of Kruppel-like factor 2 (which KLF2 codes for) seem to have heart problems. From this hypothesis, you can derive the idea that a mouse in which this particular gene does not function cannot develop a normal cardiovascular system, and then make the prediction that we started with.
What is the difference between a hypothesis and a prediction?
You might think that these are very subtle differences, and you will certainly come across many publications that do not contain an actual hypothesis or do not make these distinctions correctly. But considering that the formulation and testing of hypotheses is an integral part of the scientific method, it is good to be aware of the concepts underlying this approach. The two hallmarks of a scientific hypothesis are falsifiability (an evaluation standard that was introduced by the philosopher of science Karl Popper in 1934) and testability —if you cannot use experiments or data to decide whether an idea is true or false, then it is not a hypothesis (or at least a very bad one).
So, in a nutshell, you (1) look at existing evidence/theories, (2) come up with a hypothesis, (3) make a prediction that allows you to (4) design an experiment or data analysis to test it, and (5) come to a conclusion. Of course, not all studies have hypotheses (there is also exploratory or hypothesis-generating research), and you do not necessarily have to state your hypothesis as such in your paper.
But for the sake of understanding the principles of the scientific method, let’s first take a closer look at the different types of hypotheses that research articles refer to and then give you a step-by-step guide for how to formulate a strong hypothesis for your own paper.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Hypotheses can be simple , which means they describe the relationship between one single independent variable (the one you observe variations in or plan to manipulate) and one single dependent variable (the one you expect to be affected by the variations/manipulation). If there are more variables on either side, you are dealing with a complex hypothesis. You can also distinguish hypotheses according to the kind of relationship between the variables you are interested in (e.g., causal or associative ). But apart from these variations, we are usually interested in what is called the “alternative hypothesis” and, in contrast to that, the “null hypothesis”. If you think these two should be listed the other way round, then you are right, logically speaking—the alternative should surely come second. However, since this is the hypothesis we (as researchers) are usually interested in, let’s start from there.
Alternative Hypothesis
If you predict a relationship between two variables in your study, then the research hypothesis that you formulate to describe that relationship is your alternative hypothesis (usually H1 in statistical terms). The goal of your hypothesis testing is thus to demonstrate that there is sufficient evidence that supports the alternative hypothesis, rather than evidence for the possibility that there is no such relationship. The alternative hypothesis is usually the research hypothesis of a study and is based on the literature, previous observations, and widely known theories.
Null Hypothesis
The hypothesis that describes the other possible outcome, that is, that your variables are not related, is the null hypothesis ( H0 ). Based on your findings, you choose between the two hypotheses—usually that means that if your prediction was correct, you reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative. Make sure, however, that you are not getting lost at this step of the thinking process: If your prediction is that there will be no difference or change, then you are trying to find support for the null hypothesis and reject H1.
Directional Hypothesis
While the null hypothesis is obviously “static”, the alternative hypothesis can specify a direction for the observed relationship between variables—for example, that mice with higher expression levels of a certain protein are more active than those with lower levels. This is then called a one-tailed hypothesis.
Another example for a directional one-tailed alternative hypothesis would be that
H1: Attending private classes before important exams has a positive effect on performance.
Your null hypothesis would then be that
H0: Attending private classes before important exams has no/a negative effect on performance.
Nondirectional Hypothesis
A nondirectional hypothesis does not specify the direction of the potentially observed effect, only that there is a relationship between the studied variables—this is called a two-tailed hypothesis. For instance, if you are studying a new drug that has shown some effects on pathways involved in a certain condition (e.g., anxiety) in vitro in the lab, but you can’t say for sure whether it will have the same effects in an animal model or maybe induce other/side effects that you can’t predict and potentially increase anxiety levels instead, you could state the two hypotheses like this:
H1: The only lab-tested drug (somehow) affects anxiety levels in an anxiety mouse model.
You then test this nondirectional alternative hypothesis against the null hypothesis:
H0: The only lab-tested drug has no effect on anxiety levels in an anxiety mouse model.
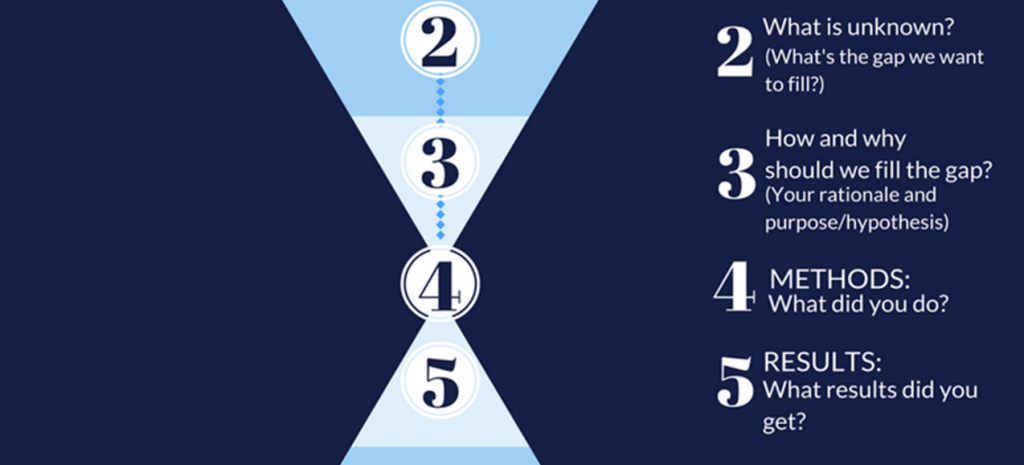
How to Write a Hypothesis for a Research Paper
Now that we understand the important distinctions between different kinds of research hypotheses, let’s look at a simple process of how to write a hypothesis.
Writing a Hypothesis Step:1
Ask a question, based on earlier research. Research always starts with a question, but one that takes into account what is already known about a topic or phenomenon. For example, if you are interested in whether people who have pets are happier than those who don’t, do a literature search and find out what has already been demonstrated. You will probably realize that yes, there is quite a bit of research that shows a relationship between happiness and owning a pet—and even studies that show that owning a dog is more beneficial than owning a cat ! Let’s say you are so intrigued by this finding that you wonder:
What is it that makes dog owners even happier than cat owners?
Let’s move on to Step 2 and find an answer to that question.
Writing a Hypothesis Step 2:
Formulate a strong hypothesis by answering your own question. Again, you don’t want to make things up, take unicorns into account, or repeat/ignore what has already been done. Looking at the dog-vs-cat papers your literature search returned, you see that most studies are based on self-report questionnaires on personality traits, mental health, and life satisfaction. What you don’t find is any data on actual (mental or physical) health measures, and no experiments. You therefore decide to make a bold claim come up with the carefully thought-through hypothesis that it’s maybe the lifestyle of the dog owners, which includes walking their dog several times per day, engaging in fun and healthy activities such as agility competitions, and taking them on trips, that gives them that extra boost in happiness. You could therefore answer your question in the following way:
Dog owners are happier than cat owners because of the dog-related activities they engage in.
Now you have to verify that your hypothesis fulfills the two requirements we introduced at the beginning of this resource article: falsifiability and testability . If it can’t be wrong and can’t be tested, it’s not a hypothesis. We are lucky, however, because yes, we can test whether owning a dog but not engaging in any of those activities leads to lower levels of happiness or well-being than owning a dog and playing and running around with them or taking them on trips.
Writing a Hypothesis Step 3:
Make your predictions and define your variables. We have verified that we can test our hypothesis, but now we have to define all the relevant variables, design our experiment or data analysis, and make precise predictions. You could, for example, decide to study dog owners (not surprising at this point), let them fill in questionnaires about their lifestyle as well as their life satisfaction (as other studies did), and then compare two groups of active and inactive dog owners. Alternatively, if you want to go beyond the data that earlier studies produced and analyzed and directly manipulate the activity level of your dog owners to study the effect of that manipulation, you could invite them to your lab, select groups of participants with similar lifestyles, make them change their lifestyle (e.g., couch potato dog owners start agility classes, very active ones have to refrain from any fun activities for a certain period of time) and assess their happiness levels before and after the intervention. In both cases, your independent variable would be “ level of engagement in fun activities with dog” and your dependent variable would be happiness or well-being .
Examples of a Good and Bad Hypothesis
Let’s look at a few examples of good and bad hypotheses to get you started.
Good Hypothesis Examples
Bad hypothesis examples, tips for writing a research hypothesis.
If you understood the distinction between a hypothesis and a prediction we made at the beginning of this article, then you will have no problem formulating your hypotheses and predictions correctly. To refresh your memory: We have to (1) look at existing evidence, (2) come up with a hypothesis, (3) make a prediction, and (4) design an experiment. For example, you could summarize your dog/happiness study like this:
(1) While research suggests that dog owners are happier than cat owners, there are no reports on what factors drive this difference. (2) We hypothesized that it is the fun activities that many dog owners (but very few cat owners) engage in with their pets that increases their happiness levels. (3) We thus predicted that preventing very active dog owners from engaging in such activities for some time and making very inactive dog owners take up such activities would lead to an increase and decrease in their overall self-ratings of happiness, respectively. (4) To test this, we invited dog owners into our lab, assessed their mental and emotional well-being through questionnaires, and then assigned them to an “active” and an “inactive” group, depending on…
Note that you use “we hypothesize” only for your hypothesis, not for your experimental prediction, and “would” or “if – then” only for your prediction, not your hypothesis. A hypothesis that states that something “would” affect something else sounds as if you don’t have enough confidence to make a clear statement—in which case you can’t expect your readers to believe in your research either. Write in the present tense, don’t use modal verbs that express varying degrees of certainty (such as may, might, or could ), and remember that you are not drawing a conclusion while trying not to exaggerate but making a clear statement that you then, in a way, try to disprove . And if that happens, that is not something to fear but an important part of the scientific process.
Similarly, don’t use “we hypothesize” when you explain the implications of your research or make predictions in the conclusion section of your manuscript, since these are clearly not hypotheses in the true sense of the word. As we said earlier, you will find that many authors of academic articles do not seem to care too much about these rather subtle distinctions, but thinking very clearly about your own research will not only help you write better but also ensure that even that infamous Reviewer 2 will find fewer reasons to nitpick about your manuscript.
Perfect Your Manuscript With Professional Editing
Now that you know how to write a strong research hypothesis for your research paper, you might be interested in our free AI proofreader , Wordvice AI, which finds and fixes errors in grammar, punctuation, and word choice in academic texts. Or if you are interested in human proofreading , check out our English editing services , including research paper editing and manuscript editing .
On the Wordvice academic resources website , you can also find many more articles and other resources that can help you with writing the other parts of your research paper , with making a research paper outline before you put everything together, or with writing an effective cover letter once you are ready to submit.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Definition, Format, Examples, and Tips
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amy Morin, LCSW, is a psychotherapist and international bestselling author. Her books, including "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do," have been translated into more than 40 languages. Her TEDx talk, "The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong," is one of the most viewed talks of all time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/VW-MIND-Amy-2b338105f1ee493f94d7e333e410fa76.jpg)
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis.
- Operationalization
Hypothesis Types
Hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process.
Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance. The hypothesis might be: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
At a Glance
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.
The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. At this point, researchers then begin to develop a testable hypothesis.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore numerous factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk adage that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
How to Formulate a Good Hypothesis
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
The Importance of Operational Definitions
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
Operational definitions are specific definitions for all relevant factors in a study. This process helps make vague or ambiguous concepts detailed and measurable.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in various ways. Clearly defining these variables and how they are measured helps ensure that other researchers can replicate your results.
Replicability
One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable.
Replication means repeating an experiment in the same way to produce the same results. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. For example, how would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
To measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming others. The researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness in this situation.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative population sample and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have higher reading scores than students who do not receive the intervention."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "There is no difference in anxiety levels between people who take St. John's wort supplements and those who do not."
- "There is no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
- "There is no difference in aggression levels between children who play first-person shooter games and those who do not."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "People who take St. John's wort supplements will have less anxiety than those who do not."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
- "Children who play first-person shooter games will show higher levels of aggression than children who do not."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when conducting an experiment is difficult or impossible. These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can examine how the variables are related. This research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
Experimental Research Methods
Experimental methods are used to demonstrate causal relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher systematically manipulates a variable of interest (known as the independent variable) and measures the effect on another variable (known as the dependent variable).
Unlike correlational studies, which can only be used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, experimental methods can be used to determine the actual nature of the relationship—whether changes in one variable actually cause another to change.
The hypothesis is a critical part of any scientific exploration. It represents what researchers expect to find in a study or experiment. In situations where the hypothesis is unsupported by the research, the research still has value. Such research helps us better understand how different aspects of the natural world relate to one another. It also helps us develop new hypotheses that can then be tested in the future.
Thompson WH, Skau S. On the scope of scientific hypotheses . R Soc Open Sci . 2023;10(8):230607. doi:10.1098/rsos.230607
Taran S, Adhikari NKJ, Fan E. Falsifiability in medicine: what clinicians can learn from Karl Popper [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jun 17;:]. Intensive Care Med . 2021;47(9):1054-1056. doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06432-z
Eyler AA. Research Methods for Public Health . 1st ed. Springer Publishing Company; 2020. doi:10.1891/9780826182067.0004
Nosek BA, Errington TM. What is replication ? PLoS Biol . 2020;18(3):e3000691. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000691
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Nevid J. Psychology: Concepts and Applications. Wadworth, 2013.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Research Hypothesis In Psychology: Types, & Examples
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A research hypothesis, in its plural form “hypotheses,” is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method .
Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding
Some key points about hypotheses:
- A hypothesis expresses an expected pattern or relationship. It connects the variables under investigation.
- It is stated in clear, precise terms before any data collection or analysis occurs. This makes the hypothesis testable.
- A hypothesis must be falsifiable. It should be possible, even if unlikely in practice, to collect data that disconfirms rather than supports the hypothesis.
- Hypotheses guide research. Scientists design studies to explicitly evaluate hypotheses about how nature works.
- For a hypothesis to be valid, it must be testable against empirical evidence. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
- Hypotheses are informed by background knowledge and observation, but go beyond what is already known to propose an explanation of how or why something occurs.
Predictions typically arise from a thorough knowledge of the research literature, curiosity about real-world problems or implications, and integrating this to advance theory. They build on existing literature while providing new insight.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Alternative hypothesis.
The research hypothesis is often called the alternative or experimental hypothesis in experimental research.
It typically suggests a potential relationship between two key variables: the independent variable, which the researcher manipulates, and the dependent variable, which is measured based on those changes.
The alternative hypothesis states a relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable affects the other).
A hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a key component of the scientific method. Some key points about hypotheses:
- Important hypotheses lead to predictions that can be tested empirically. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
In summary, a hypothesis is a precise, testable statement of what researchers expect to happen in a study and why. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
An experimental hypothesis predicts what change(s) will occur in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated.
It states that the results are not due to chance and are significant in supporting the theory being investigated.
The alternative hypothesis can be directional, indicating a specific direction of the effect, or non-directional, suggesting a difference without specifying its nature. It’s what researchers aim to support or demonstrate through their study.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable does not affect the other). There will be no changes in the dependent variable due to manipulating the independent variable.
It states results are due to chance and are not significant in supporting the idea being investigated.
The null hypothesis, positing no effect or relationship, is a foundational contrast to the research hypothesis in scientific inquiry. It establishes a baseline for statistical testing, promoting objectivity by initiating research from a neutral stance.
Many statistical methods are tailored to test the null hypothesis, determining the likelihood of observed results if no true effect exists.
This dual-hypothesis approach provides clarity, ensuring that research intentions are explicit, and fosters consistency across scientific studies, enhancing the standardization and interpretability of research outcomes.
Nondirectional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis, also known as a two-tailed hypothesis, predicts that there is a difference or relationship between two variables but does not specify the direction of this relationship.
It merely indicates that a change or effect will occur without predicting which group will have higher or lower values.
For example, “There is a difference in performance between Group A and Group B” is a non-directional hypothesis.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional (one-tailed) hypothesis predicts the nature of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. It predicts in which direction the change will take place. (i.e., greater, smaller, less, more)
It specifies whether one variable is greater, lesser, or different from another, rather than just indicating that there’s a difference without specifying its nature.
For example, “Exercise increases weight loss” is a directional hypothesis.
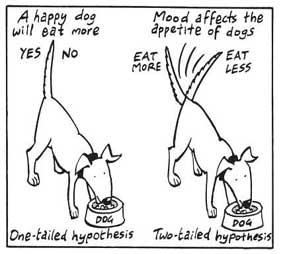
Falsifiability
The Falsification Principle, proposed by Karl Popper , is a way of demarcating science from non-science. It suggests that for a theory or hypothesis to be considered scientific, it must be testable and irrefutable.
Falsifiability emphasizes that scientific claims shouldn’t just be confirmable but should also have the potential to be proven wrong.
It means that there should exist some potential evidence or experiment that could prove the proposition false.
However many confirming instances exist for a theory, it only takes one counter observation to falsify it. For example, the hypothesis that “all swans are white,” can be falsified by observing a black swan.
For Popper, science should attempt to disprove a theory rather than attempt to continually provide evidence to support a research hypothesis.
Can a Hypothesis be Proven?
Hypotheses make probabilistic predictions. They state the expected outcome if a particular relationship exists. However, a study result supporting a hypothesis does not definitively prove it is true.
All studies have limitations. There may be unknown confounding factors or issues that limit the certainty of conclusions. Additional studies may yield different results.
In science, hypotheses can realistically only be supported with some degree of confidence, not proven. The process of science is to incrementally accumulate evidence for and against hypothesized relationships in an ongoing pursuit of better models and explanations that best fit the empirical data. But hypotheses remain open to revision and rejection if that is where the evidence leads.
- Disproving a hypothesis is definitive. Solid disconfirmatory evidence will falsify a hypothesis and require altering or discarding it based on the evidence.
- However, confirming evidence is always open to revision. Other explanations may account for the same results, and additional or contradictory evidence may emerge over time.
We can never 100% prove the alternative hypothesis. Instead, we see if we can disprove, or reject the null hypothesis.
If we reject the null hypothesis, this doesn’t mean that our alternative hypothesis is correct but does support the alternative/experimental hypothesis.
Upon analysis of the results, an alternative hypothesis can be rejected or supported, but it can never be proven to be correct. We must avoid any reference to results proving a theory as this implies 100% certainty, and there is always a chance that evidence may exist which could refute a theory.
How to Write a Hypothesis
- Identify variables . The researcher manipulates the independent variable and the dependent variable is the measured outcome.
- Operationalized the variables being investigated . Operationalization of a hypothesis refers to the process of making the variables physically measurable or testable, e.g. if you are about to study aggression, you might count the number of punches given by participants.
- Decide on a direction for your prediction . If there is evidence in the literature to support a specific effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a directional (one-tailed) hypothesis. If there are limited or ambiguous findings in the literature regarding the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a non-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis.
- Make it Testable : Ensure your hypothesis can be tested through experimentation or observation. It should be possible to prove it false (principle of falsifiability).
- Clear & concise language . A strong hypothesis is concise (typically one to two sentences long), and formulated using clear and straightforward language, ensuring it’s easily understood and testable.
Consider a hypothesis many teachers might subscribe to: students work better on Monday morning than on Friday afternoon (IV=Day, DV= Standard of work).
Now, if we decide to study this by giving the same group of students a lesson on a Monday morning and a Friday afternoon and then measuring their immediate recall of the material covered in each session, we would end up with the following:
- The alternative hypothesis states that students will recall significantly more information on a Monday morning than on a Friday afternoon.
- The null hypothesis states that there will be no significant difference in the amount recalled on a Monday morning compared to a Friday afternoon. Any difference will be due to chance or confounding factors.
More Examples
- Memory : Participants exposed to classical music during study sessions will recall more items from a list than those who studied in silence.
- Social Psychology : Individuals who frequently engage in social media use will report higher levels of perceived social isolation compared to those who use it infrequently.
- Developmental Psychology : Children who engage in regular imaginative play have better problem-solving skills than those who don’t.
- Clinical Psychology : Cognitive-behavioral therapy will be more effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety over a 6-month period compared to traditional talk therapy.
- Cognitive Psychology : Individuals who multitask between various electronic devices will have shorter attention spans on focused tasks than those who single-task.
- Health Psychology : Patients who practice mindfulness meditation will experience lower levels of chronic pain compared to those who don’t meditate.
- Organizational Psychology : Employees in open-plan offices will report higher levels of stress than those in private offices.
- Behavioral Psychology : Rats rewarded with food after pressing a lever will press it more frequently than rats who receive no reward.
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples
Learn How To Write A Hypothesis For Your Next Research Project!

Undoubtedly, research plays a crucial role in substantiating or refuting our assumptions. These assumptions act as potential answers to our questions. Such assumptions, also known as hypotheses, are considered key aspects of research. In this blog, we delve into the significance of hypotheses. And provide insights on how to write them effectively. So, let’s dive in and explore the art of writing hypotheses together.
Table of Contents
What is a Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is a crucial starting point in scientific research. It is an educated guess about the relationship between two or more variables. In other words, a hypothesis acts as a foundation for a researcher to build their study.
Here are some examples of well-crafted hypotheses:
- Increased exposure to natural sunlight improves sleep quality in adults.
A positive relationship between natural sunlight exposure and sleep quality in adult individuals.
- Playing puzzle games on a regular basis enhances problem-solving abilities in children.
Engaging in frequent puzzle gameplay leads to improved problem-solving skills in children.
- Students and improved learning hecks.
S tudents using online paper writing service platforms (as a learning tool for receiving personalized feedback and guidance) will demonstrate improved writing skills. (compared to those who do not utilize such platforms).
- The use of APA format in research papers.
Using the APA format helps students stay organized when writing research papers. Organized students can focus better on their topics and, as a result, produce better quality work.
The Building Blocks of a Hypothesis
To better understand the concept of a hypothesis, let’s break it down into its basic components:
- Variables . A hypothesis involves at least two variables. An independent variable and a dependent variable. The independent variable is the one being changed or manipulated, while the dependent variable is the one being measured or observed.
- Relationship : A hypothesis proposes a relationship or connection between the variables. This could be a cause-and-effect relationship or a correlation between them.
- Testability : A hypothesis should be testable and falsifiable, meaning it can be proven right or wrong through experimentation or observation.
Types of Hypotheses
When learning how to write a hypothesis, it’s essential to understand its main types. These include; alternative hypotheses and null hypotheses. In the following section, we explore both types of hypotheses with examples.
Alternative Hypothesis (H1)
This kind of hypothesis suggests a relationship or effect between the variables. It is the main focus of the study. The researcher wants to either prove or disprove it. Many research divides this hypothesis into two subsections:
- Directional
This type of H1 predicts a specific outcome. Many researchers use this hypothesis to explore the relationship between variables rather than the groups.
- Non-directional
You can take a guess from the name. This type of H1 does not provide a specific prediction for the research outcome.
Here are some examples for your better understanding of how to write a hypothesis.
- Consuming caffeine improves cognitive performance. (This hypothesis predicts that there is a positive relationship between caffeine consumption and cognitive performance.)
- Aerobic exercise leads to reduced blood pressure. (This hypothesis suggests that engaging in aerobic exercise results in lower blood pressure readings.)
- Exposure to nature reduces stress levels among employees. (Here, the hypothesis proposes that employees exposed to natural environments will experience decreased stress levels.)
- Listening to classical music while studying increases memory retention. (This hypothesis speculates that studying with classical music playing in the background boosts students’ ability to retain information.)
- Early literacy intervention improves reading skills in children. (This hypothesis claims that providing early literacy assistance to children results in enhanced reading abilities.)
- Time management in nursing students. ( Students who use a nursing research paper writing service have more time to focus on their studies and can achieve better grades in other subjects. )
Null Hypothesis (H0)
A null hypothesis assumes no relationship or effect between the variables. If the alternative hypothesis is proven to be false, the null hypothesis is considered to be true. Usually a null hypothesis shows no direct correlation between the defined variables.
Here are some of the examples
- The consumption of herbal tea has no effect on sleep quality. (This hypothesis assumes that herbal tea consumption does not impact the quality of sleep.)
- The number of hours spent playing video games is unrelated to academic performance. (Here, the null hypothesis suggests that no relationship exists between video gameplay duration and academic achievement.)
- Implementing flexible work schedules has no influence on employee job satisfaction. (This hypothesis contends that providing flexible schedules does not affect how satisfied employees are with their jobs.)
- Writing ability of a 7th grader is not affected by reading editorial example. ( There is no relationship between reading an editorial example and improving a 7th grader’s writing abilities.)
- The type of lighting in a room does not affect people’s mood. (In this null hypothesis, there is no connection between the kind of lighting in a room and the mood of those present.)
- The use of social media during break time does not impact productivity at work. (This hypothesis proposes that social media usage during breaks has no effect on work productivity.)
As you learn how to write a hypothesis, remember that aiming for clarity, testability, and relevance to your research question is vital. By mastering this skill, you’re well on your way to conducting impactful scientific research. Good luck!
Importance of a Hypothesis in Research
A well-structured hypothesis is a vital part of any research project for several reasons:
- It provides clear direction for the study by setting its focus and purpose.
- It outlines expectations of the research, making it easier to measure results.
- It helps identify any potential limitations in the study, allowing researchers to refine their approach.
In conclusion, a hypothesis plays a fundamental role in the research process. By understanding its concept and constructing a well-thought-out hypothesis, researchers lay the groundwork for a successful, scientifically sound investigation.
How to Write a Hypothesis?
Here are five steps that you can follow to write an effective hypothesis.
Step 1: Identify Your Research Question
The first step in learning how to compose a hypothesis is to clearly define your research question. This question is the central focus of your study and will help you determine the direction of your hypothesis.
Step 2: Determine the Variables
When exploring how to write a hypothesis, it’s crucial to identify the variables involved in your study. You’ll need at least two variables:
- Independent variable : The factor you manipulate or change in your experiment.
- Dependent variable : The outcome or result you observe or measure, which is influenced by the independent variable.
Step 3: Build the Hypothetical Relationship
In understanding how to compose a hypothesis, constructing the relationship between the variables is key. Based on your research question and variables, predict the expected outcome or connection. This prediction should be specific, testable, and, if possible, expressed in the “If…then” format.
Step 4: Write the Null Hypothesis
When mastering how to write a hypothesis, it’s important to create a null hypothesis as well. The null hypothesis assumes no relationship or effect between the variables, acting as a counterpoint to your primary hypothesis.
Step 5: Review Your Hypothesis
Finally, when learning how to compose a hypothesis, it’s essential to review your hypothesis for clarity, testability, and relevance to your research question. Make any necessary adjustments to ensure it provides a solid basis for your study.
In conclusion, understanding how to write a hypothesis is crucial for conducting successful scientific research. By focusing on your research question and carefully building relationships between variables, you will lay a strong foundation for advancing research and knowledge in your field.
Hypothesis vs. Prediction: What’s the Difference?
Understanding the differences between a hypothesis and a prediction is crucial in scientific research. Often, these terms are used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings and functions. This segment aims to clarify these differences and explain how to compose a hypothesis correctly, helping you improve the quality of your research projects.
Hypothesis: The Foundation of Your Research
A hypothesis is an educated guess about the relationship between two or more variables. It provides the basis for your research question and is a starting point for an experiment or observational study.
The critical elements for a hypothesis include:
- Specificity: A clear and concise statement that describes the relationship between variables.
- Testability: The ability to test the hypothesis through experimentation or observation.
To learn how to write a hypothesis, it’s essential to identify your research question first and then predict the relationship between the variables.
Prediction: The Expected Outcome
A prediction is a statement about a specific outcome you expect to see in your experiment or observational study. It’s derived from the hypothesis and provides a measurable way to test the relationship between variables.
Here’s an example of how to write a hypothesis and a related prediction:
- Hypothesis: Consuming a high-sugar diet leads to weight gain.
- Prediction: People who consume a high-sugar diet for six weeks will gain more weight than those who maintain a low-sugar diet during the same period.
Key Differences Between a Hypothesis and a Prediction
While a hypothesis and prediction are both essential components of scientific research, there are some key differences to keep in mind:
- A hypothesis is an educated guess that suggests a relationship between variables, while a prediction is a specific and measurable outcome based on that hypothesis.
- A hypothesis can give rise to multiple experiment or observational study predictions.
To conclude, understanding the differences between a hypothesis and a prediction, and learning how to write a hypothesis, are essential steps to form a robust foundation for your research. By creating clear, testable hypotheses along with specific, measurable predictions, you lay the groundwork for scientifically sound investigations.
Here’s a wrap-up for this guide on how to write a hypothesis. We’re confident this article was helpful for many of you. We understand that many students struggle with writing their school research . However, we hope to continue assisting you through our blog tutorial on writing different aspects of academic assignments.
For further information, you can check out our reverent blog or contact our professionals to avail amazing writing services. Paper perk experts tailor assignments to reflect your unique voice and perspectives. Our professionals make sure to stick around till your satisfaction. So what are you waiting for? Pick your required service and order away!
How to write a good hypothesis?
How to write a hypothesis in science, how to write a research hypothesis, how to write a null hypothesis, what is the format for a scientific hypothesis, how do you structure a proper hypothesis, can you provide an example of a hypothesis, what is the ideal hypothesis structure.
The ideal hypothesis structure includes the following;
- A clear statement of the relationship between variables.
- testable prediction.
- falsifiability.
If your hypothesis has all of these, it is both scientifically sound and effective.
How to write a hypothesis for product management?
Writing a hypothesis for product management involves a simple process:
- First, identify the problem or question you want to address.
- State your assumption or belief about the solution to that problem. .
- Make a hypothesis by predicting a specific outcome based on your assumption.
- Make sure your hypothesis is specific, measurable, and testable.
- Use experiments, data analysis, or user feedback to validate your hypothesis.
- Make informed decisions for product improvement.
Following these steps will help you in effectively formulating hypotheses for product management.
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score
- Privacy Policy

Home » What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation.
Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments and the collection and analysis of data. It is an essential element of the scientific method, as it allows researchers to make predictions about the outcome of their experiments and to test those predictions to determine their accuracy.
Types of Hypothesis
Types of Hypothesis are as follows:
Research Hypothesis
A research hypothesis is a statement that predicts a relationship between variables. It is usually formulated as a specific statement that can be tested through research, and it is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is no significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as a starting point for testing the research hypothesis, and if the results of the study reject the null hypothesis, it suggests that there is a significant difference or relationship between variables.
Alternative Hypothesis
An alternative hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is a significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as an alternative to the null hypothesis and is tested against the null hypothesis to determine which statement is more accurate.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the direction of the relationship between variables. For example, a researcher might predict that increasing the amount of exercise will result in a decrease in body weight.
Non-directional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between variables but does not specify the direction. For example, a researcher might predict that there is a relationship between the amount of exercise and body weight, but they do not specify whether increasing or decreasing exercise will affect body weight.
Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a statement that assumes a particular statistical model or distribution for the data. It is often used in statistical analysis to test the significance of a particular result.
Composite Hypothesis
A composite hypothesis is a statement that assumes more than one condition or outcome. It can be divided into several sub-hypotheses, each of which represents a different possible outcome.
Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is a statement that is based on observed phenomena or data. It is often used in scientific research to develop theories or models that explain the observed phenomena.
Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement that assumes only one outcome or condition. It is often used in scientific research to test a single variable or factor.
Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is a statement that assumes multiple outcomes or conditions. It is often used in scientific research to test the effects of multiple variables or factors on a particular outcome.
Applications of Hypothesis
Hypotheses are used in various fields to guide research and make predictions about the outcomes of experiments or observations. Here are some examples of how hypotheses are applied in different fields:
- Science : In scientific research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain natural phenomena. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular variable on a natural system, such as the effects of climate change on an ecosystem.
- Medicine : In medical research, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of treatments and therapies for specific conditions. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new drug on a particular disease.
- Psychology : In psychology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of human behavior and cognition. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular stimulus on the brain or behavior.
- Sociology : In sociology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of social phenomena, such as the effects of social structures or institutions on human behavior. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of income inequality on crime rates.
- Business : In business research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain business phenomena, such as consumer behavior or market trends. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new marketing campaign on consumer buying behavior.
- Engineering : In engineering, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of new technologies or designs. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the efficiency of a new solar panel design.
How to write a Hypothesis
Here are the steps to follow when writing a hypothesis:
Identify the Research Question
The first step is to identify the research question that you want to answer through your study. This question should be clear, specific, and focused. It should be something that can be investigated empirically and that has some relevance or significance in the field.
Conduct a Literature Review
Before writing your hypothesis, it’s essential to conduct a thorough literature review to understand what is already known about the topic. This will help you to identify the research gap and formulate a hypothesis that builds on existing knowledge.
Determine the Variables
The next step is to identify the variables involved in the research question. A variable is any characteristic or factor that can vary or change. There are two types of variables: independent and dependent. The independent variable is the one that is manipulated or changed by the researcher, while the dependent variable is the one that is measured or observed as a result of the independent variable.
Formulate the Hypothesis
Based on the research question and the variables involved, you can now formulate your hypothesis. A hypothesis should be a clear and concise statement that predicts the relationship between the variables. It should be testable through empirical research and based on existing theory or evidence.
Write the Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is the opposite of the alternative hypothesis, which is the hypothesis that you are testing. The null hypothesis states that there is no significant difference or relationship between the variables. It is important to write the null hypothesis because it allows you to compare your results with what would be expected by chance.
Refine the Hypothesis
After formulating the hypothesis, it’s important to refine it and make it more precise. This may involve clarifying the variables, specifying the direction of the relationship, or making the hypothesis more testable.
Examples of Hypothesis
Here are a few examples of hypotheses in different fields:
- Psychology : “Increased exposure to violent video games leads to increased aggressive behavior in adolescents.”
- Biology : “Higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will lead to increased plant growth.”
- Sociology : “Individuals who grow up in households with higher socioeconomic status will have higher levels of education and income as adults.”
- Education : “Implementing a new teaching method will result in higher student achievement scores.”
- Marketing : “Customers who receive a personalized email will be more likely to make a purchase than those who receive a generic email.”
- Physics : “An increase in temperature will cause an increase in the volume of a gas, assuming all other variables remain constant.”
- Medicine : “Consuming a diet high in saturated fats will increase the risk of developing heart disease.”
Purpose of Hypothesis
The purpose of a hypothesis is to provide a testable explanation for an observed phenomenon or a prediction of a future outcome based on existing knowledge or theories. A hypothesis is an essential part of the scientific method and helps to guide the research process by providing a clear focus for investigation. It enables scientists to design experiments or studies to gather evidence and data that can support or refute the proposed explanation or prediction.
The formulation of a hypothesis is based on existing knowledge, observations, and theories, and it should be specific, testable, and falsifiable. A specific hypothesis helps to define the research question, which is important in the research process as it guides the selection of an appropriate research design and methodology. Testability of the hypothesis means that it can be proven or disproven through empirical data collection and analysis. Falsifiability means that the hypothesis should be formulated in such a way that it can be proven wrong if it is incorrect.
In addition to guiding the research process, the testing of hypotheses can lead to new discoveries and advancements in scientific knowledge. When a hypothesis is supported by the data, it can be used to develop new theories or models to explain the observed phenomenon. When a hypothesis is not supported by the data, it can help to refine existing theories or prompt the development of new hypotheses to explain the phenomenon.
When to use Hypothesis
Here are some common situations in which hypotheses are used:
- In scientific research , hypotheses are used to guide the design of experiments and to help researchers make predictions about the outcomes of those experiments.
- In social science research , hypotheses are used to test theories about human behavior, social relationships, and other phenomena.
- I n business , hypotheses can be used to guide decisions about marketing, product development, and other areas. For example, a hypothesis might be that a new product will sell well in a particular market, and this hypothesis can be tested through market research.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Here are some common characteristics of a hypothesis:
- Testable : A hypothesis must be able to be tested through observation or experimentation. This means that it must be possible to collect data that will either support or refute the hypothesis.
- Falsifiable : A hypothesis must be able to be proven false if it is not supported by the data. If a hypothesis cannot be falsified, then it is not a scientific hypothesis.
- Clear and concise : A hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner so that it can be easily understood and tested.
- Based on existing knowledge : A hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and research in the field. It should not be based on personal beliefs or opinions.
- Specific : A hypothesis should be specific in terms of the variables being tested and the predicted outcome. This will help to ensure that the research is focused and well-designed.
- Tentative: A hypothesis is a tentative statement or assumption that requires further testing and evidence to be confirmed or refuted. It is not a final conclusion or assertion.
- Relevant : A hypothesis should be relevant to the research question or problem being studied. It should address a gap in knowledge or provide a new perspective on the issue.
Advantages of Hypothesis
Hypotheses have several advantages in scientific research and experimentation:
- Guides research: A hypothesis provides a clear and specific direction for research. It helps to focus the research question, select appropriate methods and variables, and interpret the results.
- Predictive powe r: A hypothesis makes predictions about the outcome of research, which can be tested through experimentation. This allows researchers to evaluate the validity of the hypothesis and make new discoveries.
- Facilitates communication: A hypothesis provides a common language and framework for scientists to communicate with one another about their research. This helps to facilitate the exchange of ideas and promotes collaboration.
- Efficient use of resources: A hypothesis helps researchers to use their time, resources, and funding efficiently by directing them towards specific research questions and methods that are most likely to yield results.
- Provides a basis for further research: A hypothesis that is supported by data provides a basis for further research and exploration. It can lead to new hypotheses, theories, and discoveries.
- Increases objectivity: A hypothesis can help to increase objectivity in research by providing a clear and specific framework for testing and interpreting results. This can reduce bias and increase the reliability of research findings.
Limitations of Hypothesis
Some Limitations of the Hypothesis are as follows:
- Limited to observable phenomena: Hypotheses are limited to observable phenomena and cannot account for unobservable or intangible factors. This means that some research questions may not be amenable to hypothesis testing.
- May be inaccurate or incomplete: Hypotheses are based on existing knowledge and research, which may be incomplete or inaccurate. This can lead to flawed hypotheses and erroneous conclusions.
- May be biased: Hypotheses may be biased by the researcher’s own beliefs, values, or assumptions. This can lead to selective interpretation of data and a lack of objectivity in research.
- Cannot prove causation: A hypothesis can only show a correlation between variables, but it cannot prove causation. This requires further experimentation and analysis.
- Limited to specific contexts: Hypotheses are limited to specific contexts and may not be generalizable to other situations or populations. This means that results may not be applicable in other contexts or may require further testing.
- May be affected by chance : Hypotheses may be affected by chance or random variation, which can obscure or distort the true relationship between variables.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and...

Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and...

Context of the Study – Writing Guide and Examples

Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example...

How to Write a Hypothesis [31 Tips + Examples]
Writing hypotheses can seem tricky, but it’s essential for a solid scientific inquiry.
Here is a quick summary of how to write a hypothesis:
Write a hypothesis by clearly defining your research question, identifying independent and dependent variables, formulating a measurable prediction, and ensuring it can be tested through experimentation. Include an “if…then” statement for clarity.
I’ve crafted dozens in my research, from basic biology experiments to business marketing strategies.
Let me walk you through how to write a solid hypothesis, step by step.
Writing a Hypothesis: The Basics

Table of Contents
A hypothesis is a statement predicting the relationship between variables based on observations and existing knowledge. To craft a good hypothesis:
- Identify variables – Determine the independent and dependent variables involved.
- Predict relationships – Predict the interaction between these variables.
- Test the statement – Ensure the hypothesis is testable and falsifiable.
A solid hypothesis guides your research and sets the foundation for your experiment.
31 Tips for Writing a Hypothesis
There are at least 31 tips to write a good hypothesis.
Keep reading to learn every tip plus three examples to make sure that you can instantly apply it to your writing.
Tip 1: Start with a Clear Research Question
A clear research question ensures your hypothesis is targeted.
- Identify the broad topic you’re curious about, then refine it to a specific question.
- Use guiding questions like “What impact does variable X have on variable Y?”
- How does fertilizer affect plant growth?
- Does social media influence mental health in teens?
- Can personalized ads increase customer engagement?
Tip 2: Do Background Research
Research helps you understand current knowledge and any existing gaps.
- Review scholarly articles, reputable websites, and textbooks.
- Focus on understanding the relationships between variables in existing research.
- Academic journals like ScienceDirect or JSTOR.
- Google Scholar.
- Reputable news articles.
Tip 3: Identify Independent and Dependent Variables
The independent variable is what you change or control. The dependent variable is what you measure.
- Clearly define these variables to make your hypothesis precise.
- Think of different factors that could be influencing your dependent variable.
- Type of fertilizer (independent) and plant growth (dependent).
- Amount of screen time (independent) and anxiety levels (dependent).
- Marketing strategies (independent) and customer engagement (dependent).
Tip 4: Make Your Hypothesis Testable
A hypothesis must be measurable and falsifiable.
- Ensure your hypothesis can be supported or refuted through data collection.
- Include numerical variables or qualitative changes to ensure measurability.
- “Increasing screen time will increase anxiety levels in teenagers.”
- “Using fertilizer X will yield higher crop productivity.”
- “A/B testing marketing strategies will show higher engagement with personalized ads.”
Tip 5: Be Specific and Concise
Keep your hypothesis straightforward and to the point.
- Avoid vague terms that could mislead or cause confusion.
- Clearly outline what you’re measuring and how the variables interact.
- “Replacing chemical fertilizers with organic ones will result in slower plant growth.”
- “A social media break will decrease anxiety in high school students.”
- “Ads targeting user preferences will boost click-through rates by 10%.”
Tip 6: Choose Simple Language
Use simple, understandable language to ensure clarity.
- Avoid jargon and overly complex terms that could confuse readers.
- Make the hypothesis comprehensible to non-experts in the field.
- “Organic fertilizer will reduce plant growth.”
- “High schoolers will feel less anxious after a social media detox.”
- “Targeted ads will increase customer engagement.”
Tip 7: Formulate a Null Hypothesis
A null hypothesis assumes no relationship between variables.
- Create a counterpoint to your main hypothesis, asserting that there is no effect.
- This allows you to compare results directly and identify statistical significance.
- “Fertilizer type will not affect plant growth.”
- “Social media use will not influence anxiety.”
- “Targeted ads will not affect customer engagement.”
Tip 8: State Alternative Hypotheses
Provide alternative hypotheses to explore other plausible relationships.
- They offer a contingency plan if your primary hypothesis is not supported.
- These should still align with your research question and measurable variables.
- “Fertilizer X will only affect plant growth if used in specific soil types.”
- “Social media might impact anxiety only in certain age groups.”
- “Customer engagement might only improve with highly personalized ads.”
Tip 9: Use “If…Then” Statements
“If…then” statements simplify the cause-and-effect structure.
- The “if” clause identifies the independent variable, while “then” identifies the dependent.
- It makes your hypothesis easier to understand and directly testable.
- “If plants receive organic fertilizer, then their growth rate will slow.”
- “If teens stop using social media, then their anxiety will decrease.”
- “If ads are personalized, then click-through rates will increase.”
Tip 10: Avoid Assumptions
Don’t assume the audience understands your variables or relationships.
- Clearly define terms and relationships to avoid misinterpretation.
- Provide background context where necessary for clarity.
- Define “anxiety” as a feeling of worry or unease.
- Specify “plant growth” as the height and health of plants.
- Describe “personalized ads” as ads matching user preferences.
Tip 11: Review Existing Literature
Previous research offers insights into forming a hypothesis.
- Conduct a thorough literature review to identify trends and gaps.
- Use these studies to refine and build upon your hypothesis.
- Studies showing a link between screen time and anxiety.
- Research on organic versus chemical fertilizers.
- Customer behavior analysis in different marketing channels.
Tip 12: Consider Multiple Variables
Hypotheses with multiple variables can offer deeper insights.
- Explore combinations of independent and dependent variables to see their relationships.
- Plan experiments accordingly to distinguish separate effects.
- Studying fertilizer type and soil composition effects on plant growth.
- Testing social media use frequency and content type on anxiety.
- Analyzing marketing strategies combined with product preferences.
Tip 13: Review Ethical Considerations
Ethics are essential for trustworthy research.
- Avoid hypotheses that could cause harm to participants or the environment.
- Seek approval from relevant ethical boards or committees.
- Avoiding experiments causing undue stress to teenagers.
- Preventing chemical contamination when testing fertilizers.
- Respecting privacy with personalized ads.
Tip 14: Test with Pilot Studies
Small-scale pilot studies test feasibility and refine hypotheses.
- Use them to identify potential issues and adjust before full-scale research.
- Ensure pilot tests align with ethical standards.
- Testing different fertilizer types on small plant samples.
- Trying brief social media breaks with a small group of teens.
- Conducting A/B tests on ad personalization with a subset of customers.
Tip 15: Build Hypotheses on Existing Theories
Existing theories provide strong foundations.
- Use established frameworks to develop or refine your hypothesis.
- Testing theoretical predictions can yield meaningful data.
- Applying agricultural theories on soil and crop management.
- Using psychology theories on screen addiction and mental health.
- Referencing marketing theories like consumer behavior analysis.
Tip 16: Address Real-World Problems
Solve real-world problems through practical hypotheses.
- Make sure your research question has relevant, impactful applications.
- Focus on everyday challenges where actionable insights can help.
- Testing new eco-friendly farming methods.
- Reducing anxiety by improving digital wellbeing.
- Improving marketing ROI with personalized strategies.
Tip 17: Aim for Clear, Measurable Outcomes
The results should be easy to measure and interpret.
- Quantify your dependent variable or use defined qualitative measures.
- Avoid overly broad or ambiguous outcomes.
- Measuring plant growth as a percentage change in height.
- Quantifying anxiety levels through standard surveys.
- Tracking click-through rates as a percentage of total views.

Tip 18: Stay Open to Unexpected Results
Not all hypotheses yield expected results.
- Be open to learning new insights, even if they contradict your prediction.
- Unexpected findings often reveal unique, significant knowledge.
- Unexpected fertilizer types boosting growth differently than anticipated.
- Screen time affecting anxiety differently across various age groups.
- Targeted ads backfiring with specific customer segments.
Tip 19: Keep Hypotheses Relevant
Ensure your hypothesis aligns with the purpose of your research.
- Avoid straying from the original question or focusing on tangential issues.
- Stick to the research scope to ensure accurate and meaningful data.
- Focus on a specific type of fertilizer for plant growth.
- Restrict studies to relevant age groups for anxiety research.
- Keep marketing hypotheses within the same target customer segment.
Tip 20: Collaborate with Peers
Collaboration strengthens hypothesis development.
- Work with colleagues or mentors for valuable feedback.
- Peer review helps identify flaws or assumptions in your hypothesis.
- Reviewing hypothesis clarity with a lab partner.
- Sharing research plans with a mentor to refine focus.
- Engaging in academic peer-review groups.
Tip 21: Re-evaluate Hypotheses Periodically
Revising hypotheses ensures relevance.
- Update based on new literature, data, or technological advances.
- A dynamic approach keeps your research current.
- Refining fertilizer studies with recent organic farming research.
- Adjusting social media hypotheses for new platforms like TikTok.
- Modifying marketing hypotheses based on changing customer preferences.
Tip 22: Develop Compelling Visuals
Illustrating hypotheses can help communicate relationships effectively.
- Use diagrams or flowcharts to show how variables interact visually.
- Infographics make it easier for others to grasp your research concept.
- A flowchart showing fertilizer effects on different plant growth stages.
- Diagrams illustrating social media use and its psychological impact.
- Infographics depicting how various marketing strategies boost engagement.
Tip 23: Refine Your Data Collection Plan
A solid data collection plan is vital for a testable hypothesis.
- Determine the best ways to measure your dependent variable.
- Ensure your data collection tools are reliable and accurate.
- Using a ruler and image analysis software to measure plant height.
- Designing standardized surveys to assess anxiety levels consistently.
- Setting up click-through tracking with analytics software.
Tip 24: Focus on Logical Progression
Ensure your hypothesis logically follows your research question.
- The relationship between variables should naturally flow from your observations.
- Avoid logical leaps that might confuse your reasoning.
- Predicting plant growth after observing effects of different fertilizers.
- Linking anxiety to social media use based on screen time studies.
- Connecting ad personalization with customer behavior data.
Tip 25: Test Against Diverse Samples
Testing across diverse samples ensures broader applicability.
- Avoid drawing conclusions from overly narrow sample groups.
- Try to include different demographics or subgroups in your testing.
- Testing fertilizer effects on multiple plant species.
- Including different age groups in anxiety research.
- Experimenting with personalized ads across varied customer segments.
Tip 26: Use Control Groups
Control groups provide a baseline for comparison.
- Compare your test group with a control group under unchanged conditions.
- This allows you to isolate the effect of your independent variable.
- Comparing plant growth with organic versus no fertilizer.
- Testing anxiety levels with and without social media breaks.
- Comparing personalized ads with general marketing content.
Tip 27: Consider Practical Constraints
Work within realistic constraints for your resources and timeline.
- Assess the feasibility of testing your hypothesis.
- Modify the hypothesis if the required testing is unmanageable.
- Reducing fertilizer types to a manageable number for testing.
- Shortening social media detox periods to realistic durations.
- Targeting only specific marketing strategies to optimize testing.
Tip 28: Recognize Bias Risks
Biases can skew hypothesis formation.
- Acknowledge your assumptions and how they may affect your research.
- Minimize biases by clearly defining and measuring variables.
- Avoiding assumptions that organic fertilizer is inherently better.
- Ensuring survey questions don’t lead to specific anxiety outcomes.
- Testing marketing strategies objectively without favoring any method.
Tip 29: Prepare for Peer Review
Peer review ensures your hypothesis holds up to scrutiny.
- Provide a clear rationale for why your hypothesis is sound.
- Address potential criticisms to strengthen your research.
- Showing your plant growth study builds on existing fertilizer research.
- Demonstrating social media anxiety links through data and literature.
- Supporting your marketing hypotheses with solid behavioral data.
Tip 30: Create a Research Proposal
A proposal outlines your hypothesis, methodology, and significance.
- It ensures your hypothesis is clear and your methods are well-thought-out.
- Proposals also help secure funding or institutional approval.
- A proposal for fertilizer studies linking plant growth and soil health.
- Research plans connecting social media habits to anxiety measures.
- Marketing proposals tying customer behavior to personalized advertising.
Tip 31: Document Your Findings
Recording findings helps validate or challenge your hypothesis.
- Document the methodology, data, and conclusions clearly.
- This allows others to verify, replicate, or expand on your work.
- Recording fertilizer effects on plant height in different soil types.
- Survey results linking social media use with anxiety levels.
- Click-through data proving personalized ads’ impact on engagement.
Check out this really good video about how to write a hypothesis:
Hypothesis Examples for Different Situations
Let’s look at some examples of how to write a hypothesis in different circumstances.
- Marketing Analysis : “If personalized ads are shown to our target demographic, then click-through rates will increase by at least 10%.”
- Process Improvement : “If automated workflows replace manual data entry, then task completion times will decrease by 20%.”
- Product Development : “If adding a chatbot feature to our app increases customer support efficiency, then user satisfaction will improve by 15%.”
- Biology Experiment : “If students grow plants with different fertilizers, then the organic fertilizer will result in slower growth compared to the chemical fertilizer.”
- Psychology Research : “If high school students take a break from social media, then their levels of anxiety will decrease.”
- Environmental Study : “If a controlled forest area is exposed to a certain pollutant, then the local plant species will show signs of damage within two weeks.”
Professional Contacts
- Medical Research : “If a novel treatment method is applied to patients with chronic illness, then their recovery rate will increase significantly compared to standard treatment.”
- Technology Research : “If machine learning algorithms analyze big data sets, then the accuracy of predictive models will surpass traditional data analysis.”
- Engineering Project : “If new composite materials replace standard components in bridge construction, then the resulting structure will be more durable.”
Super Personal
- Gardening Experiment : “If different types of compost are used in home gardens, then plants receiving homemade compost will yield the most produce.”
- Fitness Routine : “If consistent strength training is combined with a high-protein diet, then muscle mass will increase more than with diet alone.”
- Cooking Techniques : “If searing is added before baking, then the resulting roast will retain more moisture.”
Final Thoughts: How to Write a Hypothesis
Crafting hypotheses is both a science and an art. It’s about channeling curiosity into testable questions that propel meaningful discovery.
Each well-thought-out hypothesis is a stepping stone that could lead to the breakthrough you’ve been seeking.
Stay curious and let your research journey unfold.
Read This Next:
- How to Write a Topic Sentence (30+ Tips & Examples)
- How to Describe a Graph in Writing [+ 22 Examples]
- How to Write an Address (21+ Examples)
- How to Write an Email (Ultimate Guide + 60 Examples)
- How to Write a Recommendation Letter (Examples & Templates)

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write a Hypothesis? Types and Examples

All research studies involve the use of the scientific method, which is a mathematical and experimental technique used to conduct experiments by developing and testing a hypothesis or a prediction about an outcome. Simply put, a hypothesis is a suggested solution to a problem. It includes elements that are expressed in terms of relationships with each other to explain a condition or an assumption that hasn’t been verified using facts. 1 The typical steps in a scientific method include developing such a hypothesis, testing it through various methods, and then modifying it based on the outcomes of the experiments.
A research hypothesis can be defined as a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study. 2 Hypotheses help guide the research process and supplement the aim of the study. After several rounds of testing, hypotheses can help develop scientific theories. 3 Hypotheses are often written as if-then statements.
Here are two hypothesis examples:
Dandelions growing in nitrogen-rich soils for two weeks develop larger leaves than those in nitrogen-poor soils because nitrogen stimulates vegetative growth. 4
If a company offers flexible work hours, then their employees will be happier at work. 5
Table of Contents
- What is a hypothesis?
- Types of hypotheses
- Characteristics of a hypothesis
- Functions of a hypothesis
- How to write a hypothesis
- Hypothesis examples
- Frequently asked questions
What is a hypothesis?

A hypothesis expresses an expected relationship between variables in a study and is developed before conducting any research. Hypotheses are not opinions but rather are expected relationships based on facts and observations. They help support scientific research and expand existing knowledge. An incorrectly formulated hypothesis can affect the entire experiment leading to errors in the results so it’s important to know how to formulate a hypothesis and develop it carefully.
A few sources of a hypothesis include observations from prior studies, current research and experiences, competitors, scientific theories, and general conditions that can influence people. Figure 1 depicts the different steps in a research design and shows where exactly in the process a hypothesis is developed. 4
There are seven different types of hypotheses—simple, complex, directional, nondirectional, associative and causal, null, and alternative.
Types of hypotheses
The seven types of hypotheses are listed below: 5 , 6,7
- Simple : Predicts the relationship between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable.
Example: Exercising in the morning every day will increase your productivity.
- Complex : Predicts the relationship between two or more variables.
Example: Spending three hours or more on social media daily will negatively affect children’s mental health and productivity, more than that of adults.
- Directional : Specifies the expected direction to be followed and uses terms like increase, decrease, positive, negative, more, or less.
Example: The inclusion of intervention X decreases infant mortality compared to the original treatment.
- Non-directional : Does not predict the exact direction, nature, or magnitude of the relationship between two variables but rather states the existence of a relationship. This hypothesis may be used when there is no underlying theory or if findings contradict prior research.
Example: Cats and dogs differ in the amount of affection they express.
- Associative and causal : An associative hypothesis suggests an interdependency between variables, that is, how a change in one variable changes the other.
Example: There is a positive association between physical activity levels and overall health.
A causal hypothesis, on the other hand, expresses a cause-and-effect association between variables.
Example: Long-term alcohol use causes liver damage.
- Null : Claims that the original hypothesis is false by showing that there is no relationship between the variables.
Example: Sleep duration does not have any effect on productivity.
- Alternative : States the opposite of the null hypothesis, that is, a relationship exists between two variables.
Example: Sleep duration affects productivity.

Characteristics of a hypothesis
So, what makes a good hypothesis? Here are some important characteristics of a hypothesis. 8,9
- Testable : You must be able to test the hypothesis using scientific methods to either accept or reject the prediction.
- Falsifiable : It should be possible to collect data that reject rather than support the hypothesis.
- Logical : Hypotheses shouldn’t be a random guess but rather should be based on previous theories, observations, prior research, and logical reasoning.
- Positive : The hypothesis statement about the existence of an association should be positive, that is, it should not suggest that an association does not exist. Therefore, the language used and knowing how to phrase a hypothesis is very important.
- Clear and accurate : The language used should be easily comprehensible and use correct terminology.
- Relevant : The hypothesis should be relevant and specific to the research question.
- Structure : Should include all the elements that make a good hypothesis: variables, relationship, and outcome.
Functions of a hypothesis
The following list mentions some important functions of a hypothesis: 1
- Maintains the direction and progress of the research.
- Expresses the important assumptions underlying the proposition in a single statement.
- Establishes a suitable context for researchers to begin their investigation and for readers who are referring to the final report.
- Provides an explanation for the occurrence of a specific phenomenon.
- Ensures selection of appropriate and accurate facts necessary and relevant to the research subject.
To summarize, a hypothesis provides the conceptual elements that complete the known data, conceptual relationships that systematize unordered elements, and conceptual meanings and interpretations that explain the unknown phenomena. 1

How to write a hypothesis
Listed below are the main steps explaining how to write a hypothesis. 2,4,5
- Make an observation and identify variables : Observe the subject in question and try to recognize a pattern or a relationship between the variables involved. This step provides essential background information to begin your research.
For example, if you notice that an office’s vending machine frequently runs out of a specific snack, you may predict that more people in the office choose that snack over another.
- Identify the main research question : After identifying a subject and recognizing a pattern, the next step is to ask a question that your hypothesis will answer.
For example, after observing employees’ break times at work, you could ask “why do more employees take breaks in the morning rather than in the afternoon?”
- Conduct some preliminary research to ensure originality and novelty : Your initial answer, which is your hypothesis, to the question is based on some pre-existing information about the subject. However, to ensure that your hypothesis has not been asked before or that it has been asked but rejected by other researchers you would need to gather additional information.
For example, based on your observations you might state a hypothesis that employees work more efficiently when the air conditioning in the office is set at a lower temperature. However, during your preliminary research you find that this hypothesis was proven incorrect by a prior study.
- Develop a general statement : After your preliminary research has confirmed the originality of your proposed answer, draft a general statement that includes all variables, subjects, and predicted outcome. The statement could be if/then or declarative.
- Finalize the hypothesis statement : Use the PICOT model, which clarifies how to word a hypothesis effectively, when finalizing the statement. This model lists the important components required to write a hypothesis.
P opulation: The specific group or individual who is the main subject of the research
I nterest: The main concern of the study/research question
C omparison: The main alternative group
O utcome: The expected results
T ime: Duration of the experiment
Once you’ve finalized your hypothesis statement you would need to conduct experiments to test whether the hypothesis is true or false.
Hypothesis examples
The following table provides examples of different types of hypotheses. 10 ,11

Key takeaways
Here’s a summary of all the key points discussed in this article about how to write a hypothesis.
- A hypothesis is an assumption about an association between variables made based on limited evidence, which should be tested.
- A hypothesis has four parts—the research question, independent variable, dependent variable, and the proposed relationship between the variables.
- The statement should be clear, concise, testable, logical, and falsifiable.
- There are seven types of hypotheses—simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative and causal, null, and alternative.
- A hypothesis provides a focus and direction for the research to progress.
- A hypothesis plays an important role in the scientific method by helping to create an appropriate experimental design.
Frequently asked questions
Hypotheses and research questions have different objectives and structure. The following table lists some major differences between the two. 9
Here are a few examples to differentiate between a research question and hypothesis.
Yes, here’s a simple checklist to help you gauge the effectiveness of your hypothesis. 9 1. When writing a hypothesis statement, check if it: 2. Predicts the relationship between the stated variables and the expected outcome. 3. Uses simple and concise language and is not wordy. 4. Does not assume readers’ knowledge about the subject. 5. Has observable, falsifiable, and testable results.
As mentioned earlier in this article, a hypothesis is an assumption or prediction about an association between variables based on observations and simple evidence. These statements are usually generic. Research objectives, on the other hand, are more specific and dictated by hypotheses. The same hypothesis can be tested using different methods and the research objectives could be different in each case. For example, Louis Pasteur observed that food lasts longer at higher altitudes, reasoned that it could be because the air at higher altitudes is cleaner (with fewer or no germs), and tested the hypothesis by exposing food to air cleaned in the laboratory. 12 Thus, a hypothesis is predictive—if the reasoning is correct, X will lead to Y—and research objectives are developed to test these predictions.
Null hypothesis testing is a method to decide between two assumptions or predictions between variables (null and alternative hypotheses) in a statistical relationship in a sample. The null hypothesis, denoted as H 0 , claims that no relationship exists between variables in a population and any relationship in the sample reflects a sampling error or occurrence by chance. The alternative hypothesis, denoted as H 1 , claims that there is a relationship in the population. In every study, researchers need to decide whether the relationship in a sample occurred by chance or reflects a relationship in the population. This is done by hypothesis testing using the following steps: 13 1. Assume that the null hypothesis is true. 2. Determine how likely the sample relationship would be if the null hypothesis were true. This probability is called the p value. 3. If the sample relationship would be extremely unlikely, reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis. If the relationship would not be unlikely, accept the null hypothesis.

To summarize, researchers should know how to write a good hypothesis to ensure that their research progresses in the required direction. A hypothesis is a testable prediction about any behavior or relationship between variables, usually based on facts and observation, and states an expected outcome.
We hope this article has provided you with essential insight into the different types of hypotheses and their functions so that you can use them appropriately in your next research project.
References
- Dalen, DVV. The function of hypotheses in research. Proquest website. Accessed April 8, 2024. https://www.proquest.com/docview/1437933010?pq-origsite=gscholar&fromopenview=true&sourcetype=Scholarly%20Journals&imgSeq=1
- McLeod S. Research hypothesis in psychology: Types & examples. SimplyPsychology website. Updated December 13, 2023. Accessed April 9, 2024. https://www.simplypsychology.org/what-is-a-hypotheses.html
- Scientific method. Britannica website. Updated March 14, 2024. Accessed April 9, 2024. https://www.britannica.com/science/scientific-method
- The hypothesis in science writing. Accessed April 10, 2024. https://berks.psu.edu/sites/berks/files/campus/HypothesisHandout_Final.pdf
- How to develop a hypothesis (with elements, types, and examples). Indeed.com website. Updated February 3, 2023. Accessed April 10, 2024. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/how-to-write-a-hypothesis
- Types of research hypotheses. Excelsior online writing lab. Accessed April 11, 2024. https://owl.excelsior.edu/research/research-hypotheses/types-of-research-hypotheses/
- What is a research hypothesis: how to write it, types, and examples. Researcher.life website. Published February 8, 2023. Accessed April 11, 2024. https://researcher.life/blog/article/how-to-write-a-research-hypothesis-definition-types-examples/
- Developing a hypothesis. Pressbooks website. Accessed April 12, 2024. https://opentext.wsu.edu/carriecuttler/chapter/developing-a-hypothesis/
- What is and how to write a good hypothesis in research. Elsevier author services website. Accessed April 12, 2024. https://scientific-publishing.webshop.elsevier.com/manuscript-preparation/what-how-write-good-hypothesis-research/
- How to write a great hypothesis. Verywellmind website. Updated March 12, 2023. Accessed April 13, 2024. https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-a-hypothesis-2795239
- 15 Hypothesis examples. Helpfulprofessor.com Published September 8, 2023. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://helpfulprofessor.com/hypothesis-examples/
- Editage insights. What is the interconnectivity between research objectives and hypothesis? Published February 24, 2021. Accessed April 13, 2024. https://www.editage.com/insights/what-is-the-interconnectivity-between-research-objectives-and-hypothesis
- Understanding null hypothesis testing. BCCampus open publishing. Accessed April 16, 2024. https://opentextbc.ca/researchmethods/chapter/understanding-null-hypothesis-testing/#:~:text=In%20null%20hypothesis%20testing%2C%20this,said%20to%20be%20statistically%20significant
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)
- What are Journal Guidelines on Using Generative AI Tools
Measuring Academic Success: Definition & Strategies for Excellence
What are scholarly sources and where can you find them , you may also like, how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, how to ace grant writing for research funding..., powerful academic phrases to improve your essay writing , how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., how to write a successful book chapter for..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai.

- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems
- Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books
Hypothesis Examples

A hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a test. It forms the basis for designing an experiment in the scientific method . A good hypothesis is testable, meaning it makes a prediction you can check with observation or experimentation. Here are different hypothesis examples.
Null Hypothesis Examples
The null hypothesis (H 0 ) is also known as the zero-difference or no-difference hypothesis. It predicts that changing one variable ( independent variable ) will have no effect on the variable being measured ( dependent variable ). Here are null hypothesis examples:
- Plant growth is unaffected by temperature.
- If you increase temperature, then solubility of salt will increase.
- Incidence of skin cancer is unrelated to ultraviolet light exposure.
- All brands of light bulb last equally long.
- Cats have no preference for the color of cat food.
- All daisies have the same number of petals.
Sometimes the null hypothesis shows there is a suspected correlation between two variables. For example, if you think plant growth is affected by temperature, you state the null hypothesis: “Plant growth is not affected by temperature.” Why do you do this, rather than say “If you change temperature, plant growth will be affected”? The answer is because it’s easier applying a statistical test that shows, with a high level of confidence, a null hypothesis is correct or incorrect.
Research Hypothesis Examples
A research hypothesis (H 1 ) is a type of hypothesis used to design an experiment. This type of hypothesis is often written as an if-then statement because it’s easy identifying the independent and dependent variables and seeing how one affects the other. If-then statements explore cause and effect. In other cases, the hypothesis shows a correlation between two variables. Here are some research hypothesis examples:
- If you leave the lights on, then it takes longer for people to fall asleep.
- If you refrigerate apples, they last longer before going bad.
- If you keep the curtains closed, then you need less electricity to heat or cool the house (the electric bill is lower).
- If you leave a bucket of water uncovered, then it evaporates more quickly.
- Goldfish lose their color if they are not exposed to light.
- Workers who take vacations are more productive than those who never take time off.
Is It Okay to Disprove a Hypothesis?
Yes! You may even choose to write your hypothesis in such a way that it can be disproved because it’s easier to prove a statement is wrong than to prove it is right. In other cases, if your prediction is incorrect, that doesn’t mean the science is bad. Revising a hypothesis is common. It demonstrates you learned something you did not know before you conducted the experiment.
Test yourself with a Scientific Method Quiz .
- Mellenbergh, G.J. (2008). Chapter 8: Research designs: Testing of research hypotheses. In H.J. Adèr & G.J. Mellenbergh (eds.), Advising on Research Methods: A Consultant’s Companion . Huizen, The Netherlands: Johannes van Kessel Publishing.
- Popper, Karl R. (1959). The Logic of Scientific Discovery . Hutchinson & Co. ISBN 3-1614-8410-X.
- Schick, Theodore; Vaughn, Lewis (2002). How to think about weird things: critical thinking for a New Age . Boston: McGraw-Hill Higher Education. ISBN 0-7674-2048-9.
- Tobi, Hilde; Kampen, Jarl K. (2018). “Research design: the methodology for interdisciplinary research framework”. Quality & Quantity . 52 (3): 1209–1225. doi: 10.1007/s11135-017-0513-8
Related Posts
User Preferences
Content preview.
Arcu felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis:
- Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate
- Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident
Keyboard Shortcuts
5.2 - writing hypotheses.
The first step in conducting a hypothesis test is to write the hypothesis statements that are going to be tested. For each test you will have a null hypothesis (\(H_0\)) and an alternative hypothesis (\(H_a\)).
When writing hypotheses there are three things that we need to know: (1) the parameter that we are testing (2) the direction of the test (non-directional, right-tailed or left-tailed), and (3) the value of the hypothesized parameter.
- At this point we can write hypotheses for a single mean (\(\mu\)), paired means(\(\mu_d\)), a single proportion (\(p\)), the difference between two independent means (\(\mu_1-\mu_2\)), the difference between two proportions (\(p_1-p_2\)), a simple linear regression slope (\(\beta\)), and a correlation (\(\rho\)).
- The research question will give us the information necessary to determine if the test is two-tailed (e.g., "different from," "not equal to"), right-tailed (e.g., "greater than," "more than"), or left-tailed (e.g., "less than," "fewer than").
- The research question will also give us the hypothesized parameter value. This is the number that goes in the hypothesis statements (i.e., \(\mu_0\) and \(p_0\)). For the difference between two groups, regression, and correlation, this value is typically 0.
Hypotheses are always written in terms of population parameters (e.g., \(p\) and \(\mu\)). The tables below display all of the possible hypotheses for the parameters that we have learned thus far. Note that the null hypothesis always includes the equality (i.e., =).

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, what is a hypothesis and how do i write one.
General Education

Think about something strange and unexplainable in your life. Maybe you get a headache right before it rains, or maybe you think your favorite sports team wins when you wear a certain color. If you wanted to see whether these are just coincidences or scientific fact, you would form a hypothesis, then create an experiment to see whether that hypothesis is true or not.
But what is a hypothesis, anyway? If you’re not sure about what a hypothesis is--or how to test for one!--you’re in the right place. This article will teach you everything you need to know about hypotheses, including:
- Defining the term “hypothesis”
- Providing hypothesis examples
- Giving you tips for how to write your own hypothesis
So let’s get started!

What Is a Hypothesis?
Merriam Webster defines a hypothesis as “an assumption or concession made for the sake of argument.” In other words, a hypothesis is an educated guess . Scientists make a reasonable assumption--or a hypothesis--then design an experiment to test whether it’s true or not. Keep in mind that in science, a hypothesis should be testable. You have to be able to design an experiment that tests your hypothesis in order for it to be valid.
As you could assume from that statement, it’s easy to make a bad hypothesis. But when you’re holding an experiment, it’s even more important that your guesses be good...after all, you’re spending time (and maybe money!) to figure out more about your observation. That’s why we refer to a hypothesis as an educated guess--good hypotheses are based on existing data and research to make them as sound as possible.
Hypotheses are one part of what’s called the scientific method . Every (good) experiment or study is based in the scientific method. The scientific method gives order and structure to experiments and ensures that interference from scientists or outside influences does not skew the results. It’s important that you understand the concepts of the scientific method before holding your own experiment. Though it may vary among scientists, the scientific method is generally made up of six steps (in order):
- Observation
- Asking questions
- Forming a hypothesis
- Analyze the data
- Communicate your results
You’ll notice that the hypothesis comes pretty early on when conducting an experiment. That’s because experiments work best when they’re trying to answer one specific question. And you can’t conduct an experiment until you know what you’re trying to prove!
Independent and Dependent Variables
After doing your research, you’re ready for another important step in forming your hypothesis: identifying variables. Variables are basically any factor that could influence the outcome of your experiment . Variables have to be measurable and related to the topic being studied.
There are two types of variables: independent variables and dependent variables. I ndependent variables remain constant . For example, age is an independent variable; it will stay the same, and researchers can look at different ages to see if it has an effect on the dependent variable.
Speaking of dependent variables... dependent variables are subject to the influence of the independent variable , meaning that they are not constant. Let’s say you want to test whether a person’s age affects how much sleep they need. In that case, the independent variable is age (like we mentioned above), and the dependent variable is how much sleep a person gets.
Variables will be crucial in writing your hypothesis. You need to be able to identify which variable is which, as both the independent and dependent variables will be written into your hypothesis. For instance, in a study about exercise, the independent variable might be the speed at which the respondents walk for thirty minutes, and the dependent variable would be their heart rate. In your study and in your hypothesis, you’re trying to understand the relationship between the two variables.
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
The best hypotheses start by asking the right questions . For instance, if you’ve observed that the grass is greener when it rains twice a week, you could ask what kind of grass it is, what elevation it’s at, and if the grass across the street responds to rain in the same way. Any of these questions could become the backbone of experiments to test why the grass gets greener when it rains fairly frequently.
As you’re asking more questions about your first observation, make sure you’re also making more observations . If it doesn’t rain for two weeks and the grass still looks green, that’s an important observation that could influence your hypothesis. You'll continue observing all throughout your experiment, but until the hypothesis is finalized, every observation should be noted.
Finally, you should consult secondary research before writing your hypothesis . Secondary research is comprised of results found and published by other people. You can usually find this information online or at your library. Additionally, m ake sure the research you find is credible and related to your topic. If you’re studying the correlation between rain and grass growth, it would help you to research rain patterns over the past twenty years for your county, published by a local agricultural association. You should also research the types of grass common in your area, the type of grass in your lawn, and whether anyone else has conducted experiments about your hypothesis. Also be sure you’re checking the quality of your research . Research done by a middle school student about what minerals can be found in rainwater would be less useful than an article published by a local university.

Writing Your Hypothesis
Once you’ve considered all of the factors above, you’re ready to start writing your hypothesis. Hypotheses usually take a certain form when they’re written out in a research report.
When you boil down your hypothesis statement, you are writing down your best guess and not the question at hand . This means that your statement should be written as if it is fact already, even though you are simply testing it.
The reason for this is that, after you have completed your study, you'll either accept or reject your if-then or your null hypothesis. All hypothesis testing examples should be measurable and able to be confirmed or denied. You cannot confirm a question, only a statement!
In fact, you come up with hypothesis examples all the time! For instance, when you guess on the outcome of a basketball game, you don’t say, “Will the Miami Heat beat the Boston Celtics?” but instead, “I think the Miami Heat will beat the Boston Celtics.” You state it as if it is already true, even if it turns out you’re wrong. You do the same thing when writing your hypothesis.
Additionally, keep in mind that hypotheses can range from very specific to very broad. These hypotheses can be specific, but if your hypothesis testing examples involve a broad range of causes and effects, your hypothesis can also be broad.

The Two Types of Hypotheses
Now that you understand what goes into a hypothesis, it’s time to look more closely at the two most common types of hypothesis: the if-then hypothesis and the null hypothesis.
#1: If-Then Hypotheses
First of all, if-then hypotheses typically follow this formula:
If ____ happens, then ____ will happen.
The goal of this type of hypothesis is to test the causal relationship between the independent and dependent variable. It’s fairly simple, and each hypothesis can vary in how detailed it can be. We create if-then hypotheses all the time with our daily predictions. Here are some examples of hypotheses that use an if-then structure from daily life:
- If I get enough sleep, I’ll be able to get more work done tomorrow.
- If the bus is on time, I can make it to my friend’s birthday party.
- If I study every night this week, I’ll get a better grade on my exam.
In each of these situations, you’re making a guess on how an independent variable (sleep, time, or studying) will affect a dependent variable (the amount of work you can do, making it to a party on time, or getting better grades).
You may still be asking, “What is an example of a hypothesis used in scientific research?” Take one of the hypothesis examples from a real-world study on whether using technology before bed affects children’s sleep patterns. The hypothesis read s:
“We hypothesized that increased hours of tablet- and phone-based screen time at bedtime would be inversely correlated with sleep quality and child attention.”
It might not look like it, but this is an if-then statement. The researchers basically said, “If children have more screen usage at bedtime, then their quality of sleep and attention will be worse.” The sleep quality and attention are the dependent variables and the screen usage is the independent variable. (Usually, the independent variable comes after the “if” and the dependent variable comes after the “then,” as it is the independent variable that affects the dependent variable.) This is an excellent example of how flexible hypothesis statements can be, as long as the general idea of “if-then” and the independent and dependent variables are present.
#2: Null Hypotheses
Your if-then hypothesis is not the only one needed to complete a successful experiment, however. You also need a null hypothesis to test it against. In its most basic form, the null hypothesis is the opposite of your if-then hypothesis . When you write your null hypothesis, you are writing a hypothesis that suggests that your guess is not true, and that the independent and dependent variables have no relationship .
One null hypothesis for the cell phone and sleep study from the last section might say:
“If children have more screen usage at bedtime, their quality of sleep and attention will not be worse.”
In this case, this is a null hypothesis because it’s asking the opposite of the original thesis!
Conversely, if your if-then hypothesis suggests that your two variables have no relationship, then your null hypothesis would suggest that there is one. So, pretend that there is a study that is asking the question, “Does the amount of followers on Instagram influence how long people spend on the app?” The independent variable is the amount of followers, and the dependent variable is the time spent. But if you, as the researcher, don’t think there is a relationship between the number of followers and time spent, you might write an if-then hypothesis that reads:
“If people have many followers on Instagram, they will not spend more time on the app than people who have less.”
In this case, the if-then suggests there isn’t a relationship between the variables. In that case, one of the null hypothesis examples might say:
“If people have many followers on Instagram, they will spend more time on the app than people who have less.”
You then test both the if-then and the null hypothesis to gauge if there is a relationship between the variables, and if so, how much of a relationship.

4 Tips to Write the Best Hypothesis
If you’re going to take the time to hold an experiment, whether in school or by yourself, you’re also going to want to take the time to make sure your hypothesis is a good one. The best hypotheses have four major elements in common: plausibility, defined concepts, observability, and general explanation.
#1: Plausibility
At first glance, this quality of a hypothesis might seem obvious. When your hypothesis is plausible, that means it’s possible given what we know about science and general common sense. However, improbable hypotheses are more common than you might think.
Imagine you’re studying weight gain and television watching habits. If you hypothesize that people who watch more than twenty hours of television a week will gain two hundred pounds or more over the course of a year, this might be improbable (though it’s potentially possible). Consequently, c ommon sense can tell us the results of the study before the study even begins.
Improbable hypotheses generally go against science, as well. Take this hypothesis example:
“If a person smokes one cigarette a day, then they will have lungs just as healthy as the average person’s.”
This hypothesis is obviously untrue, as studies have shown again and again that cigarettes negatively affect lung health. You must be careful that your hypotheses do not reflect your own personal opinion more than they do scientifically-supported findings. This plausibility points to the necessity of research before the hypothesis is written to make sure that your hypothesis has not already been disproven.
#2: Defined Concepts
The more advanced you are in your studies, the more likely that the terms you’re using in your hypothesis are specific to a limited set of knowledge. One of the hypothesis testing examples might include the readability of printed text in newspapers, where you might use words like “kerning” and “x-height.” Unless your readers have a background in graphic design, it’s likely that they won’t know what you mean by these terms. Thus, it’s important to either write what they mean in the hypothesis itself or in the report before the hypothesis.
Here’s what we mean. Which of the following sentences makes more sense to the common person?
If the kerning is greater than average, more words will be read per minute.
If the space between letters is greater than average, more words will be read per minute.
For people reading your report that are not experts in typography, simply adding a few more words will be helpful in clarifying exactly what the experiment is all about. It’s always a good idea to make your research and findings as accessible as possible.

Good hypotheses ensure that you can observe the results.
#3: Observability
In order to measure the truth or falsity of your hypothesis, you must be able to see your variables and the way they interact. For instance, if your hypothesis is that the flight patterns of satellites affect the strength of certain television signals, yet you don’t have a telescope to view the satellites or a television to monitor the signal strength, you cannot properly observe your hypothesis and thus cannot continue your study.
Some variables may seem easy to observe, but if you do not have a system of measurement in place, you cannot observe your hypothesis properly. Here’s an example: if you’re experimenting on the effect of healthy food on overall happiness, but you don’t have a way to monitor and measure what “overall happiness” means, your results will not reflect the truth. Monitoring how often someone smiles for a whole day is not reasonably observable, but having the participants state how happy they feel on a scale of one to ten is more observable.
In writing your hypothesis, always keep in mind how you'll execute the experiment.
#4: Generalizability
Perhaps you’d like to study what color your best friend wears the most often by observing and documenting the colors she wears each day of the week. This might be fun information for her and you to know, but beyond you two, there aren’t many people who could benefit from this experiment. When you start an experiment, you should note how generalizable your findings may be if they are confirmed. Generalizability is basically how common a particular phenomenon is to other people’s everyday life.
Let’s say you’re asking a question about the health benefits of eating an apple for one day only, you need to realize that the experiment may be too specific to be helpful. It does not help to explain a phenomenon that many people experience. If you find yourself with too specific of a hypothesis, go back to asking the big question: what is it that you want to know, and what do you think will happen between your two variables?

Hypothesis Testing Examples
We know it can be hard to write a good hypothesis unless you’ve seen some good hypothesis examples. We’ve included four hypothesis examples based on some made-up experiments. Use these as templates or launch pads for coming up with your own hypotheses.
Experiment #1: Students Studying Outside (Writing a Hypothesis)
You are a student at PrepScholar University. When you walk around campus, you notice that, when the temperature is above 60 degrees, more students study in the quad. You want to know when your fellow students are more likely to study outside. With this information, how do you make the best hypothesis possible?
You must remember to make additional observations and do secondary research before writing your hypothesis. In doing so, you notice that no one studies outside when it’s 75 degrees and raining, so this should be included in your experiment. Also, studies done on the topic beforehand suggested that students are more likely to study in temperatures less than 85 degrees. With this in mind, you feel confident that you can identify your variables and write your hypotheses:
If-then: “If the temperature in Fahrenheit is less than 60 degrees, significantly fewer students will study outside.”
Null: “If the temperature in Fahrenheit is less than 60 degrees, the same number of students will study outside as when it is more than 60 degrees.”
These hypotheses are plausible, as the temperatures are reasonably within the bounds of what is possible. The number of people in the quad is also easily observable. It is also not a phenomenon specific to only one person or at one time, but instead can explain a phenomenon for a broader group of people.
To complete this experiment, you pick the month of October to observe the quad. Every day (except on the days where it’s raining)from 3 to 4 PM, when most classes have released for the day, you observe how many people are on the quad. You measure how many people come and how many leave. You also write down the temperature on the hour.
After writing down all of your observations and putting them on a graph, you find that the most students study on the quad when it is 70 degrees outside, and that the number of students drops a lot once the temperature reaches 60 degrees or below. In this case, your research report would state that you accept or “failed to reject” your first hypothesis with your findings.
Experiment #2: The Cupcake Store (Forming a Simple Experiment)
Let’s say that you work at a bakery. You specialize in cupcakes, and you make only two colors of frosting: yellow and purple. You want to know what kind of customers are more likely to buy what kind of cupcake, so you set up an experiment. Your independent variable is the customer’s gender, and the dependent variable is the color of the frosting. What is an example of a hypothesis that might answer the question of this study?
Here’s what your hypotheses might look like:
If-then: “If customers’ gender is female, then they will buy more yellow cupcakes than purple cupcakes.”
Null: “If customers’ gender is female, then they will be just as likely to buy purple cupcakes as yellow cupcakes.”
This is a pretty simple experiment! It passes the test of plausibility (there could easily be a difference), defined concepts (there’s nothing complicated about cupcakes!), observability (both color and gender can be easily observed), and general explanation ( this would potentially help you make better business decisions ).

Experiment #3: Backyard Bird Feeders (Integrating Multiple Variables and Rejecting the If-Then Hypothesis)
While watching your backyard bird feeder, you realized that different birds come on the days when you change the types of seeds. You decide that you want to see more cardinals in your backyard, so you decide to see what type of food they like the best and set up an experiment.
However, one morning, you notice that, while some cardinals are present, blue jays are eating out of your backyard feeder filled with millet. You decide that, of all of the other birds, you would like to see the blue jays the least. This means you'll have more than one variable in your hypothesis. Your new hypotheses might look like this:
If-then: “If sunflower seeds are placed in the bird feeders, then more cardinals will come than blue jays. If millet is placed in the bird feeders, then more blue jays will come than cardinals.”
Null: “If either sunflower seeds or millet are placed in the bird, equal numbers of cardinals and blue jays will come.”
Through simple observation, you actually find that cardinals come as often as blue jays when sunflower seeds or millet is in the bird feeder. In this case, you would reject your “if-then” hypothesis and “fail to reject” your null hypothesis . You cannot accept your first hypothesis, because it’s clearly not true. Instead you found that there was actually no relation between your different variables. Consequently, you would need to run more experiments with different variables to see if the new variables impact the results.
Experiment #4: In-Class Survey (Including an Alternative Hypothesis)
You’re about to give a speech in one of your classes about the importance of paying attention. You want to take this opportunity to test a hypothesis you’ve had for a while:
If-then: If students sit in the first two rows of the classroom, then they will listen better than students who do not.
Null: If students sit in the first two rows of the classroom, then they will not listen better or worse than students who do not.
You give your speech and then ask your teacher if you can hand out a short survey to the class. On the survey, you’ve included questions about some of the topics you talked about. When you get back the results, you’re surprised to see that not only do the students in the first two rows not pay better attention, but they also scored worse than students in other parts of the classroom! Here, both your if-then and your null hypotheses are not representative of your findings. What do you do?
This is when you reject both your if-then and null hypotheses and instead create an alternative hypothesis . This type of hypothesis is used in the rare circumstance that neither of your hypotheses is able to capture your findings . Now you can use what you’ve learned to draft new hypotheses and test again!
Key Takeaways: Hypothesis Writing
The more comfortable you become with writing hypotheses, the better they will become. The structure of hypotheses is flexible and may need to be changed depending on what topic you are studying. The most important thing to remember is the purpose of your hypothesis and the difference between the if-then and the null . From there, in forming your hypothesis, you should constantly be asking questions, making observations, doing secondary research, and considering your variables. After you have written your hypothesis, be sure to edit it so that it is plausible, clearly defined, observable, and helpful in explaining a general phenomenon.
Writing a hypothesis is something that everyone, from elementary school children competing in a science fair to professional scientists in a lab, needs to know how to do. Hypotheses are vital in experiments and in properly executing the scientific method . When done correctly, hypotheses will set up your studies for success and help you to understand the world a little better, one experiment at a time.

What’s Next?
If you’re studying for the science portion of the ACT, there’s definitely a lot you need to know. We’ve got the tools to help, though! Start by checking out our ultimate study guide for the ACT Science subject test. Once you read through that, be sure to download our recommended ACT Science practice tests , since they’re one of the most foolproof ways to improve your score. (And don’t forget to check out our expert guide book , too.)
If you love science and want to major in a scientific field, you should start preparing in high school . Here are the science classes you should take to set yourself up for success.
If you’re trying to think of science experiments you can do for class (or for a science fair!), here’s a list of 37 awesome science experiments you can do at home

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Research Paper Guides
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
How to Write a Hypothesis: Step-by-Step Guide and Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
Each academic research revolves around specific statement or problem — a research hypothesis.
A hypothesis is a suggested prediction for a phenomenon or observed event, based on prior knowledge or research. It is a tentative statement that can be tested through further investigation and analysis. A hypothesis usually takes the form of a statement that suggests a relationship between two or more variables.
Every research project, be it a a term paper, research paper or a dissertation, should begin with defining a hypothesis. While this may seem simple, in reality beginners face a lot of problems. This includes difficulty with formulating a hypothesis accurately and capturing the main idea. In this blog post, we will tell you how to write a hypothesis so it is accurate and correct.
What Is a Research Hypothesis: Expanded Definition
A research hypothesis is a statement or assumption that answers a question you asked earlier but haven't tested yet. In fact, this is basis of your work which you use to prove or reject your assumption. Major research projects most often deal with several hypotheses. These relate to various aspects of an issue under study. Thus, you will divide assumptions by research sectors and study them in a segmented manner. When making an assignment, one must work based on an existing theory and gained knowledge. One must also take into account that it must be testable. That is, it can be rejected or confirmed with methods of scientific research. Hypothesis example may look like this:

In your work, you must prove or reject this hypothesis by providing survey results. Show some statistical analysis , study of reports and other processed data.
Remeber that you can hire a paper writer who will integrate survey outcomes and conduct statistical analysis in your research paper hypothesis.
Variables in Hypotheses
To make a qualitative guess, you should consider variables in your hypothesis. They can be divided into independent and dependent ones. In fact, you must establish causal relationship between two or more variables. Independent ( confounding variable ) is what researcher can control or change, i.e. initial condition. Dependent ( extraneous variable ) is what researcher studies. It is observed in created conditions. Before you start learning how to write an assignment with independent and dependent variables, you should define the main idea of your work. For example, you take an assumption that eating hedgehog meat reduces risk of cardiovascular disease. Independent variable is hedgehog meat consumption, which is cause. Improvement in cardiovascular health is a dependent variable – an intended effect.
How to Write a Hypothesis: 5 Simple Writing Steps
Novice researchers most frequently ask how to write a hypothesis statement. This is a complex process that includes compilation of laconic predictions. These are based on conducted experiments. We can support you in this task. We have developed 5 steps for researchers so they can write a high-quality and comprehensive assignment.
Step 1. Generate a Question Before Writing Your Hypothesis
At the first stage of writing a hypothesis for a research paper you must define a research question that you need to answer. It should be focused on particular problem. Try to make it specific and yet suitable for research within framework of your project. To write quality assignment, you must use 6 classic statements. Thus, you must clarify: who, what, where, when, why and how. You must make question understandable in terms of positioning problem. Example of correct hypothesis:

Step 2. Gather Preliminary Research for Your Hypothesis
Before writing a research hypothesis, conduct some preliminary research to find out if your assumption is working and can be proved. You will get the key insights through observations or experiments. You can also use results of your colleagues who have already studied this issue. Thus, you will build a concept with formulated variables. You will study them and identify relationships between them.
Step 3. Write a Strong Hypothesis
With results of preliminary preparation and research questions, you can study how to write a strong hypothesis . First of all, highlight the main testing problem. You must formulate it as briefly as possible. Try to avoid stretching statements in an attempt to make paper longer. Be as clear as possible, avoid vague judgments. For example:

This is not good option. It is better to apply hypothesis in the form of:

This is a clear sentence that is devoid of unnecessary details. It allows you to immediately see an expected effect. Get practical help in writing research paper if you wish for more quality.
Step 4. Refine Your Research Hypothesis
Make sure a hypothesis for a research proposal formulated correctly. You must check if it has following elements:
- Dependent and independent variables.
- An object or phenomenon for testing.
- Expected outcome of study that you plan to work through. This must be part of an experiment or an observation.
This way, you will specify question under study. You also will be able to verify it if needed. That is, you will move from general to particular.
Step 5. Write a Null Hypothesis
You may need to write a null hypothesis. Why and when, you may ask? When you use this method for processing specific statistics. You should specify if you plan to prove your point on its basis. In fact, it is clear position that doesn’t establish links between variables. For example, this statement is null hypothesis:

It is basis for presenting one's own opinion. It allows to build an evidence base stemming from researcher's evidence.
What Is the Difference Between a Null Hypothesis and an Alternative Hypothesis
To better understand how to write null and alternative hypothesis that will form backbone of study, examine testable statements. Based on results, null hypothesis is prepared. It is a statement with no connection between variables. At the same time, scientists usually work with an alternative hypothesis. Here, they have already found a connection between phenomena. Ever considered custom research paper writing service ? So, the above statement about frequency of doctor visits can be modified to research of:

Hypothesis Examples
Quite often, researchers find it difficult to formulate basis for writing a research paper . Therefore, some examples of hypothesis will be useful for them. This will correspond to if-then connections. With their help you will also briefly outline the main part of current research. We will help you in formulating an assignment and offer several working options:

Tips on Writing a Hypothesis
It’s difficult to start writing a hypothesis for a research proposal. Especially for aspiring academics! After all, it is important that an assignment is clear and specific. It must also be viable for further development. Here are some tips to help you formulate your statement:
- Analyze interesting aspects. Review current studies and problems on the selected topic. Highlight what you wanted to explore, perhaps it will be a concept close to your previous works.
- Clarify the details. Spend time on preliminary analysis. You must also highlight controversial aspects and contemporary issues. Sometimes, even well-researched phenomena can be promising.
- Focus on your own work. It’s always easier to continue than to start anew. At the same time, you might not have considered all the theses in the previous study.
- Make the variables clear. Avoid ambiguous statements.
Sounds a bit difficult? College paper help is there for you.
How to Write a Scientific Hypothesis: Final Thoughts
So, if you've come this far, you should already know how to how to write a hypothesis step by step. Before starting writing, analyze the problem and the topic. You should highlight the thesis that can be developed further. We recommend going through the following steps:
- Define the question you expect to receive an answer to.
- Do some preliminary research.
- Write it strongly.
- Refine it with variables, subject and phenomenon, and expected result.
- Make a null hypothesis and consider a different option.
Let our assistants write your hypothesis for you! Choose a paper writer to your liking, send them your requirements and get a great paper in no-time!
Frequently Asked Questions About Writing a Good Hypothesis
1. how can i improve my hypothesis.
To make the hypothesis working and of high quality, be sure you select both independent and dependent variables and add them to the statement. Examine the relationships of these elements. Think if you can prove them and explain them in further research.
2. Is there a maximum number of hypotheses that is allowed in one research paper?
You can write as many hypotheses as you want for your paper, because it all depends on your view on the topic and the desire to develop it in several directions. The main thing is that your project shouldn't be overloaded with too many hypotheses and that you pay enough attention to each of them.
3. How do I test my hypothesis?
It’s easy to test the statement before you write a hypothesis for a research proposal. Do an experiment: ask your question and try answering it. If you succeed, this assignment can be used for more detailed study.
4. How long is a hypothesis?
While writing the hypothesis, you must make it as direct as possible and, at the same time, clear it of extraneous judgments. Typically, it's 20 words long. We don’t recommend exceeding this volume, so as not to face difficulties in interpretation.

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
You may also like


Statistics Made Easy
How to Write Hypothesis Test Conclusions (With Examples)
A hypothesis test is used to test whether or not some hypothesis about a population parameter is true.
To perform a hypothesis test in the real world, researchers obtain a random sample from the population and perform a hypothesis test on the sample data, using a null and alternative hypothesis:
- Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): The sample data occurs purely from chance.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H A ): The sample data is influenced by some non-random cause.
If the p-value of the hypothesis test is less than some significance level (e.g. α = .05), then we reject the null hypothesis .
Otherwise, if the p-value is not less than some significance level then we fail to reject the null hypothesis .
When writing the conclusion of a hypothesis test, we typically include:
- Whether we reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
- The significance level.
- A short explanation in the context of the hypothesis test.
For example, we would write:
We reject the null hypothesis at the 5% significance level. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that…
Or, we would write:
We fail to reject the null hypothesis at the 5% significance level. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that…
The following examples show how to write a hypothesis test conclusion in both scenarios.
Example 1: Reject the Null Hypothesis Conclusion
Suppose a biologist believes that a certain fertilizer will cause plants to grow more during a one-month period than they normally do, which is currently 20 inches. To test this, she applies the fertilizer to each of the plants in her laboratory for one month.
She then performs a hypothesis test at a 5% significance level using the following hypotheses:
- H 0 : μ = 20 inches (the fertilizer will have no effect on the mean plant growth)
- H A : μ > 20 inches (the fertilizer will cause mean plant growth to increase)
Suppose the p-value of the test turns out to be 0.002.
Here is how she would report the results of the hypothesis test:
We reject the null hypothesis at the 5% significance level. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that this particular fertilizer causes plants to grow more during a one-month period than they normally do.
Example 2: Fail to Reject the Null Hypothesis Conclusion
Suppose the manager of a manufacturing plant wants to test whether or not some new method changes the number of defective widgets produced per month, which is currently 250. To test this, he measures the mean number of defective widgets produced before and after using the new method for one month.
He performs a hypothesis test at a 10% significance level using the following hypotheses:
- H 0 : μ after = μ before (the mean number of defective widgets is the same before and after using the new method)
- H A : μ after ≠ μ before (the mean number of defective widgets produced is different before and after using the new method)
Suppose the p-value of the test turns out to be 0.27.
Here is how he would report the results of the hypothesis test:
We fail to reject the null hypothesis at the 10% significance level. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that the new method leads to a change in the number of defective widgets produced per month.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials provide additional information about hypothesis testing:
Introduction to Hypothesis Testing 4 Examples of Hypothesis Testing in Real Life How to Write a Null Hypothesis
Featured Posts
Hey there. My name is Zach Bobbitt. I have a Masters of Science degree in Applied Statistics and I’ve worked on machine learning algorithms for professional businesses in both healthcare and retail. I’m passionate about statistics, machine learning, and data visualization and I created Statology to be a resource for both students and teachers alike. My goal with this site is to help you learn statistics through using simple terms, plenty of real-world examples, and helpful illustrations.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Join the Statology Community
Sign up to receive Statology's exclusive study resource: 100 practice problems with step-by-step solutions. Plus, get our latest insights, tutorials, and data analysis tips straight to your inbox!
By subscribing you accept Statology's Privacy Policy.
What Are Examples of a Hypothesis?
- Scientific Method
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
A hypothesis is an explanation for a set of observations. Here are examples of a scientific hypothesis.
Although you could state a scientific hypothesis in various ways, most hypotheses are either "If, then" statements or forms of the null hypothesis . The null hypothesis is sometimes called the "no difference" hypothesis. The null hypothesis is good for experimentation because it's simple to disprove. If you disprove a null hypothesis, that is evidence for a relationship between the variables you are examining.
Examples of Null Hypotheses
- Hyperactivity is unrelated to eating sugar.
- All daisies have the same number of petals.
- The number of pets in a household is unrelated to the number of people living in it.
- A person's preference for a shirt is unrelated to its color.
Examples of If, Then Hypotheses
- If you get at least 6 hours of sleep, you will do better on tests than if you get less sleep.
- If you drop a ball, it will fall toward the ground.
- If you drink coffee before going to bed, then it will take longer to fall asleep.
- If you cover a wound with a bandage, then it will heal with less scarring.
Improving a Hypothesis to Make It Testable
You may wish to revise your first hypothesis in order to make it easier to design an experiment to test. For example, let's say you have a bad breakout the morning after eating a lot of greasy food. You may wonder if there is a correlation between eating greasy food and getting pimples. You propose the hypothesis:
Eating greasy food causes pimples.
Next, you need to design an experiment to test this hypothesis. Let's say you decide to eat greasy food every day for a week and record the effect on your face. Then, as a control, you'll avoid greasy food for the next week and see what happens. Now, this is not a good experiment because it does not take into account other factors such as hormone levels, stress, sun exposure, exercise, or any number of other variables that might conceivably affect your skin.
The problem is that you cannot assign cause to your effect . If you eat french fries for a week and suffer a breakout, can you definitely say it was the grease in the food that caused it? Maybe it was the salt. Maybe it was the potato. Maybe it was unrelated to diet. You can't prove your hypothesis. It's much easier to disprove a hypothesis.
So, let's restate the hypothesis to make it easier to evaluate the data:
Getting pimples is unaffected by eating greasy food.
So, if you eat fatty food every day for a week and suffer breakouts and then don't break out the week that you avoid greasy food, you can be pretty sure something is up. Can you disprove the hypothesis? Probably not, since it is so hard to assign cause and effect. However, you can make a strong case that there is some relationship between diet and acne.
If your skin stays clear for the entire test, you may decide to accept your hypothesis . Again, you didn't prove or disprove anything, which is fine
- Null Hypothesis Examples
- Difference Between Independent and Dependent Variables
- Examples of Independent and Dependent Variables
- What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
- Null Hypothesis Definition and Examples
- The 10 Most Important Lab Safety Rules
- What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
- Understanding Simple vs Controlled Experiments
- What Is a Testable Hypothesis?
- What 'Fail to Reject' Means in a Hypothesis Test
- Scientific Method Vocabulary Terms
- Scientific Hypothesis Examples
- How To Design a Science Fair Experiment
- Six Steps of the Scientific Method
- An Example of a Hypothesis Test
.webp)
A Business Hypothesis: How to Improve Your Outcomes When Deciding
.webp)
“So, Tom. Can you explain what your business hypothesis was?”
“No,” came the curt reply.
“Okay, so let me understand this. You’ve got an increase in conversion rates — which, don’t get me wrong, is good — but you're not sure why. Is that right?”
“I made several changes last week, so it must have been one of them...”
“Yes, but which one?” I questioned.
Tom looked flustered as he searched for a plausible story. “The truth is Tom, you don’t know and that isn’t helping us increase conversion.”
I’ve lost count of the times I’ve had conversations like this.

Tom was like so many other entrepreneurs who like to tinker.
Often driven by limited evidence, people like Tom make changes based on supposition . Their starting point comes from what they read online. If survivorship bias had a smell, entrepreneurial homes would reek like a field being fertilized with manure.
What they lack is a theory—a rational argument for why they are making a change. A business hypothesis explains that if you make a change, then this should be the outcome.
Unlike Tom, when you work from a hypothesis, you have a proposed explanation of what you expect to happen. You use good experiments to test your theory, giving you a conclusion that could stand up in court (if needed).
In this article, I will explain how I helped Tom incorporate a hypothesis-led approach into his way of working. You will have the foundations to begin using hypotheses as a framework in your work.
Let’s dig in.
What is a Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is a statement of your expectation of making a change. It's taking what you think will happen and framing it as an experiment to record the result.
As the Economist, Milton Friedman said:
The only relevant test of the validity of a hypothesis is comparison of prediction with experience.
Now a business hypothesis goes a stage further.
Through good experiments, It captures the expected value that the change will create. It enshrines the return on investment that demonstrates the opportunity on offer.
The ROI also creates an objective measure, giving a baseline to measure the outcome.
So, in summary, a hypothesis is:
- A hypothesis is a testable statement that reflects your predictions.
- It offers a theory of what might happen based on our experiences and knowledge.
- It is testable so that you can measure the outcome against your prediction.
Not Hypothesising: A Wasted Opportunity
Tom was trying to experiment, but not in a data-driven way.
When I began consulting with Tom, he gave me a long list of different things he had tried. He wanted to increase conversion so he changed the button users click on. Tom had tried different button sizes, various shapes, colours, and the copy — the list was lengthy.
But he had no idea whether they worked or not.
He had this pretty line graph with peaks and troughs. He tried to argue these were due to the changes he had made. But without a starting hypothesis, I shot down his argument.
“You’re not making fact-based decisions ”, I told Tom. “ Even worse, you’re declaring success subjectively when you lack supporting evidence to back you up. You are wasting the opportunities you have infront of you.”
In truth, Tom was aflected by survivirship bias, confirmation bias , and outcome bias . Although he wasn’t taking a wild guess, Tom was taking insights from some ‘expert’ and using that to guide what he should change and when.
It’s a common sight among those who fail to be data-driven.
Without a hypothesis, Tom was defeating any hope of progress other than success via a fluke.
I remembered what Gavin, an old accountant friend of mine once said:
Businesses are often successful in spite of themselves and rather than because of themselves.
By not defining the outcome Tom wanted or expected, he was no different to the businesses Gavin talked about.
Tom wasn't making the most of the opportunities he had. He was wasting them.
A Business Hypothesis Approach
Before we could get to the process of creating and testing hypotheses, we needed to improve the presentation of data.
To do this, I set up some XmR charts to track the metrics Tom wanted to focus on.

We looked at higher-level metrics:
- Website Visitors
- Email subscribers
- Conversion rate
- Page views per visitor
- Bounce rate
These charts revealed what I suspected. None of the improvements Tom had made caused the numbers to move outside of routine variation (If you don’t know about routine variation, you need to digest this: Becoming Data Driven, From First Principles ).
We needed to move away from looking for potential explanations.
Conversely, our goal was to create a parameter meaning we had a provable explanation.
To do this, I told Tom we should change how he worked.
From now on, he had to write down every change before he made it. He would announce the anticipated results, providing us with enough evidence to determine the accuracy of the hypothesis.
Within each hypothesis, a clear value proposition would be evident giving Tom further justification to experiment. This framework would allow him to become a data-driven decision-maker.
It would bring an end to wasted opportunities.
The Building Blocks Behind The Theory
As I mentioned, for Tom to make this business hypothesis-led approach work, he needed a system to guide him through the different phases.
So I set this up as a simple database in Notion.
.webp)
Let me explain how it works:
The Null Hypothesis
You begin with a null hypothesis. It’s a statement of your baseline performance which we are saying can’t be changed.
The Alternative Hypothesis
The alternative hypothesis is a statement showing how we might disprove the null hypothesis in specific detail.
Over a pre-determined period, the conditions of the alternative hypothesis are put to the test. Providing there is sufficient evidence, then the null hypothesis is proven to be wrong. Importantly, if the alternative hypothesis isn’t proven then the null hypothesis stands until you create a second hypothesis to test.
“This is Epic!”
First, it was a beep.
A subtle notification telling me I had a message. Before I had a chance to read it, the phone started ringing. It was Tom.
“Oh my god!”
“It worked.” “What worked”, I replied.
“The hypothesis thingy you got me to write. It worked.” “This is epic!” Tom declared with delight.
Before he got too carried away, I took a breath and asked Tom to explain in more detail why he was so excited.
Tom explained breathlessly that his alternative hypothesis had been proven. Changing the primary heading and sub-title had increased conversion. Excitedly, he talked me through the null hypothesis.
It said: Readers subscribe to the newsletter via forms on the website at an average rate of 0.58%, with a routine variation between 0.4% and 1.2%.
The alternative hypothesis was as follows: If we change the text on the button from ‘subscribe’ to ‘try free’ then the conversion rate will increase to an average rate of 1%, thus changing the routine variation figures.
The results sustained over 4 weeks revealed an average rate of 1.2%.
Tom’s delight was clear. “Now I can tell what I changed and I have the proof to say with utter conviction, it worked!”
Concluding Thoughts
As Tom quickly discovered, there is no hiding with a hypothesis.
Thoughtless, unvalidated changes can create a lot of wasted opportunities. Before I introduced the Process Behaviour Chart, Tom wasted hours making changes he couldn’t substantiate.
Now, he could prove his theories with this experimentalist approach. A business hypothesis framework that quantified his ideas and objectively qualified his successes or failures. Subjectivity was from a distant past.
That’s why this approach works so well in a business.
Businesses are full of data. So entrepreneurs like Tom can become data-driven. They can make changes because they have hard facts to give them a precision level of appreciation for what is happening.
And if all this sounds a bit too structured and rigid, you might be right.
But does it work?
To find an answer I’ll direct you to a piece I wrote about the way Elon Musk makes decisions. In this article about feedback loops , you’ll find a hypothesis at the heart of the action . Here, the step towards progress is a test which creates a feedback loop.
Without the business hypothesis-led approach, Elon would not be where he is today.
An important hypothesis can develop longer-term thinking and create interest in planning a more thoughtful approach to the next steps.
That’s the real value for me.
Becoming data-driven — through a business hypothesis — leads you to meaningful change that will positively help your business.
How do you formulate a strong business hypothesis?
- Start by identifying a specific business problem or opportunity.
- Clearly define your independent and dependent variables. What factors are you testing?
- Craft your hypothesis as an if-then statement. For instance, “If we reduce response time in customer service, then customer satisfaction will improve.”
Why is hypothesis testing crucial for business decisions?
- Hypothesis testing allows businesses to validate assumptions before implementing strategies.
- By testing hypotheses, organizations can avoid costly mistakes and allocate resources effectively.
- For instance, before launching a new product, a company can test its assumptions about market demand through hypothesis testing.
What are null and alternative hypotheses in business research?
- The null hypothesis (H₀) represents the status quo or no effect. It assumes that any observed differences are due to random chance.
- The alternative hypothesis (Hₐ) proposes a specific effect or relationship. It challenges the null hypothesis.
- In business, these hypotheses guide statistical tests to determine whether evidence supports a change or effect.
What is a good example of a business hypothesis in action?
At the core of Elon Musk's decision-making process is a hypothesis. Every decision he makes, he seeks to test a theory which allows him to make progress. It is a fine example of a effective decision-making .
.webp)
Related Articles

Reasoning from First Principles: How to Master Solving Hard Problems

How to Avoid Damage from Your Biases - Write Your Decisions Down

Reflective Decision-Making: Thinking Your Way to a Better Decision
Become a wiser decision-maker in just 5 minutes per week..

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

10: Hypothesis Testing with One Sample
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 155543

\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
One job of a statistician is to make statistical inferences about populations based on samples taken from the population. Confidence intervals are one way to estimate a population parameter. Another way to make a statistical inference is to make a decision about a parameter. For instance, a car dealer advertises that its new small truck gets 35 miles per gallon, on average. A tutoring service claims that its method of tutoring helps 90% of its students get an A or a B. A company says that women managers in their company earn an average of $60,000 per year.
- 10.1: Prelude to Hypothesis Testing A statistician will make a decision about claims via a process called "hypothesis testing." A hypothesis test involves collecting data from a sample and evaluating the data. Then, the statistician makes a decision as to whether or not there is sufficient evidence, based upon analysis of the data, to reject the null hypothesis.
- 10.2: Null and Alternative Hypotheses The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses. They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis. These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. Since the null and alternative hypotheses are contradictory, you must examine evidence to decide if you have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not.
- 10.3: Outcomes and the Type I and Type II Errors In every hypothesis test, the outcomes are dependent on a correct interpretation of the data. Incorrect calculations or misunderstood summary statistics can yield errors that affect the results. A Type I error occurs when a true null hypothesis is rejected. A Type II error occurs when a false null hypothesis is not rejected.
- 10.4: Distribution Needed for Hypothesis Testing When testing for a single population mean: A Student's t-test should be used if the data come from a simple, random sample and the population is approximately normally distributed, or the sample size is large, with an unknown standard deviation. The normal test will work if the data come from a simple, random sample and the population is approximately normally distributed, or the sample size is large, with a known standard deviation.
- 10.5: Rare Events, the Sample, Decision and Conclusion When the probability of an event occurring is low, and it happens, it is called a rare event. Rare events are important to consider in hypothesis testing because they can inform your willingness not to reject or to reject a null hypothesis. To test a null hypothesis, find the p-value for the sample data and graph the results.
- 10.6: Additional Information and Full Hypothesis Test Examples The hypothesis test itself has an established process. This can be summarized as follows: Determine H0 and Ha. Remember, they are contradictory. Determine the random variable. Determine the distribution for the test. Draw a graph, calculate the test statistic, and use the test statistic to calculate the p-value. (A z-score and a t-score are examples of test statistics.) Compare the preconceived α with the p-value, make a decision (reject or do not reject H0), and write a clear conclusion.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.2.4: Practice Regression of Health and Happiness
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 22163

- Michelle Oja
- Taft College
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Our first practice will include the whole process to calculate all of the equations and the ANOVA Summary Table.
In this scenario, researchers are interested in explaining differences in how happy people are based on how healthy people are. They gather quantitative data on each of these variables from 18 people and fit a linear regression model (another way to say that they constructed a regression line equation) to explain the variability of one variable (say, happiness) based on the variability of the other variable (health). We will follow the four-step hypothesis testing procedure to see if there is a relation between these variables that is statistically significant.
S tep 1: State the Hypotheses
What do you think? Do you think that happiness and health vary in the same direction, in opposite directions, or do not vary together? This sounds like the set up for a research hypothesis for a correlation, and it is! The small change here is that we're focusing on the slope (\(b\) or beta) of the line, rather merely testing if there is a linear relationship.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
What could be a research hypothesis for this scenario? State the research hypothesis in words and symbols.
The research hypothesis should probably be something like, "There will be a positive slope in the regression line for happiness and health."
Symbols: \( \beta > 0 \)
For right now, we haven't made it clear which might be our predictor variable and which might be our criterion variable, the outcome. If we decide that health is the predictor and happiness is the outcome, we could add that we think that changes in health predict changes in happiness. It seems reasonable in this situation to reverse the IV and DV here, and say that change in happiness could also predict changes in health. There's data to support both of these ideas!
The null hypothesis in regression states that there is no relation between our variables so you can't use one variable to predict or explain the other variable.
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
What is the null hypothesis for this scenario? State the null hypothesis in words and symbols.
The null hypothesis is that there is no relationship between health and happiness, so "The slope in the regression line for happiness and health will be zero." Neither variable can predict or explain the other variable.
Symbols: \( \beta = 0 \)
These hypothesis are not as clear-cut as we've previously had because regression analyses can show a lot. If it's easier, you can fall back on the general hypothesis for correlations rather than focus on slopes. However, that misses the addition information that regressions also show: How much variability in one variable is due to the other variable.
Step 2: Find the Critical Value
Because regression and ANOVA are the same analysis, our critical value for regression will come from the same place: the Table of Critical Values of F (found in the first chapter discussing ANOVAs ( BG ANOVAs ), or found through the Common Critical Values page at the end of the book).
The ANOVA Summary Table used for regression uses two types of degrees of freedom. We previously saw that the Degrees of Freedom for our numerator, the Model line, is always 1 in a linear regression, and that the denominator degrees of freedom, from the Error line, is \(N – 2\).
In this instance, we have 18 people so our degrees of freedom for the denominator is 16. Going to our \(F\) table, we find that the appropriate critical value for 1 and 16 degrees of freedom is F Critical = 4.49. Isn't it nice to do the simple things that we learned about seemingly eons ago?
Step 3: Calculate the Test Statistic
The process of calculating the test statistic for regression first involves computing the parameter estimates for the line of best fit. To do this, we first calculate the means, standard deviations, and sum of products for our variables, as shown in Table \(\PageIndex{1}\).
This table should look pretty familiar, as it's the same as the one we used to calculate a correlation when we didn't have have the standard deviation provided.
First things first, let's find the means so that we can start filling in this table.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
What is the average score for the Health variable? What is the average score for the Happiness variable?
\[ \bar{X}_{Hth} = \dfrac{\sum X}{N} = \dfrac{356.02}{18} = 19.78 \nonumber \]
\[ \bar{X}_{Hpp} = \dfrac{\sum X}{N} = \dfrac{314.19}{18} = 17.46 \nonumber \]
Now that we have the means, we can fill in the complete Sum of Products table.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Fill in Table \(\PageIndex{1}\) by finding the differences of each score from that variable's mean, squaring the differences, multiplying them, then finding the sums of each of these.
In Table \(\PageIndex{2}\), the difference scores for each variable (each score minus the mean for that variable) sum to nearly zero, so all is well there. Let's use the sum of those squares to calculate the standard deviation for each variable.
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Calculate the standard deviation of the Health variable.
Using the standard deviation formula: \[s=\sqrt{\dfrac{\sum(X-\overline {X})^{2}}{N-1}} \nonumber \] We can fill in the numbers from the table and N to get: \[s_{Hth}=\sqrt{\dfrac{76.07}{18-1}} = \sqrt{\dfrac{76.07}{17 }}\nonumber \] Some division, then square rooting to get: \[s_{Hth}= \sqrt{4.47 }\nonumber \] \[s_{Hth}= 2.11 \nonumber \]
If you used spreadsheet, you might get 2.12. That's fine, but we'll use 2.11 for future calculations.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Calculate the standard deviation of the Happiness variable.
\[s=\sqrt{\dfrac{\sum(X-\overline {X})^{2}}{N-1}} \nonumber \] \[s_{Hpp}=\sqrt{\dfrac{173.99}{18-1}} = \sqrt{\dfrac{173.99}{17 }}\nonumber \] \[s_{Hpp}= \sqrt{10.23 }\nonumber \] \[s_{Hpp}= 3.20 \nonumber \]
Next up, we must calculate the slope of the line. There are easier ways to show this if we start substituting names for symbols, but let's stick with the names of our variables in this formula:
\[\mathrm{b}=\dfrac{(Diff_{Hth} \times Diff_{Hpp})}{Diff_{Hth}^2} =\dfrac{58.22}{76.07 }=0.77 \nonumber \]
What this equation is telling us to do is pretty simple once we have the Sum of Products table filled out. We just take the sum of the multiplication of each of the differences (that's the most bottom most right cell in the table), and divide that by the sum of the difference scores squared for the Health variable. The result means that as Health (\(X\)) changes by 1 unit, Happiness (\(Y\)) will change by 0.77. This is a positive relation.
Next, we use the slope, along with the means of each variable, to compute the intercept: \(a =\overline{X_y}-b\overline{X_x} \)
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Using the means and the slope (b) that we just calculated, calculate the intercept (a).
\[a =\overline{X_y}-b\overline{X_x} \nonumber \] \[a =\overline{X}_{Hpp}-(b \times \overline{X}_{Hth}) \nonumber \] \[a =17.46-(0.77 * 19.78) \nonumber \] \[a =17.46-(15.23 ) \nonumber \] \[a =2.23 \nonumber \]
This number varies widely based on how many decimal points you save while calculating. The numbers shown are when only two decimal points are used, which is the minimum that you should be writing down and saving.
For this particular problem (and most regressions), the intercept is not an important or interpretable value, so we will not read into it further.
Now that we have all of our parameters estimated, we can give the full equation for our line of best fit: \(\widehat{y} =\mathrm{a}+(\mathrm{b} \times {X}) \)
Example \(\PageIndex{5}\)
Construct the regression line equation for the predicted Happiness score (\(\widehat{y}).
\[\widehat{y} = 2.23 + 0.77\text{x} \nonumber \]
It doesn't quite make sense yet, but you actually just answered many potential research questions! We can also plot this relation in a scatterplot and overlay our line onto it, as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\).
We can use the regression line equation to find predicted values for each observation and use them to calculate our sums of squares for the Model and the Error, but this is tedious to do by hand, so we will let the computer software do the heavy lifting in that column of our ANOVA Summary Table in Table \(\PageIndex{3}\).
Happily, the Total row is still the sum of the other two rows, so that was added, too. Now that we have these, we can fill in the rest of the ANOVA table.
Example \(\PageIndex{6}\)
Fill in the rest of the ANOVA Summary Table from Table \(\PageIndex{3}\).
Happily again, we can do a computation check to make sure that our Degrees of Freedom are correct since the sum of the Model's df and the Error's df should equal the Total df. And since \(1 + 16 = 17\), we're doing well!
This gives us an obtained \(F\) statistic of 5.52, which we will now use to test our hypothesis.
Step 4: Make the Decision
We now have everything we need to make our final decision. Our calculated test statistic was \(F_{Calc} = 5.52\) and our critical value was \(F_{Crit} = 4.49\). Since our calculated test statistic is greater than our critical value, we can reject the null hypothesis because this is still true:
Critical \(<\) Calculated \(=\) Reject null \(=\) There is a linear relationship. \(= p<.05 \)
Critical \(>\) Calculated \(=\) Retain null \(=\) There is not a linear relationship. \(= p>.05\)
Write-Up: Reporting the Results
We got here a sorta roundabout way, so it's hard to figure out what our conclusion should look like. Let's start by including the four components needed for reporting results .
Example \(\PageIndex{7}\)
Use the four components for reporting results to start your concluding paragraph:
- The statistical test is preceded by the descriptive statistics (means).
- The description tells you what the research hypothesis being tested is.
- A "statistical sentence" showing the results is included.
- The results are interpreted in relation to the research hypothesis.
- The average health score was 19.78. The average happiness score was 17.46.
- The research hypothesis was that here will be a positive slope in the regression line for happiness and health.
- The ANOVA results were F(1,16)=5.52, p< .05.
- The results are statistically significant, and the positive Sum or Products shows a positive slope so the research hypothesis is supported.
Let's add one more sentence for a nice little conclusion to our regression analysis: We can predict levels of happiness based on how healthy someone is. So, our final write-up could be something like:
We can predict levels of happiness (M=17.46) based on how healthy someone is (M=19.78) (F(1,16)=5.52, p< .05). The average health score was 19.78. The average happiness score was 17.46. The research hypothesis was supported; there is a positive slope in the regression line for happiness and health.
Yep, that's pretty clunky. As you learn more about regression (in future classes), the research hypotheses will make more sense.
Accuracy in Prediction
We found a large, statistically significant relation between our variables, which is what we hoped for. However, if we want to use our estimated line of best fit for future prediction, we will also want to know how precise or accurate our predicted values are. What we want to know is the average distance from our predictions to our actual observed values, or the average size of the residual (\(Y − \widehat {Y}\)). The average size of the residual is known by a specific name: the standard error of the estimate (\(S_{(Y-\widehat{Y})}\)), which is given by the formula
\[S_{(Y-\widehat{Y})}=\sqrt{\dfrac{\sum(Y-\widehat{Y})^{2}}{N-2}} \nonumber \]
This formula is almost identical to our standard deviation formula, and it follows the same logic. We square our residuals, add them up, then divide by the degrees of freedom. Although this sounds like a long process, we already have the sum of the squared residuals in our ANOVA table! In fact, the value under the square root sign is just the \(SS_E\) divided by the \(df_E\), which we know is called the mean squared error, or \(MS_E\):
\[s_{(Y-\widehat{Y})}=\sqrt{\dfrac{\sum(Y-\widehat{Y})^{2}}{N-2}}=\sqrt{MS_E} \nonumber \]
For our example:
\[s_{(Y-\widehat{Y})}=\sqrt{\dfrac{129.37}{16}}=\sqrt{8.09}=2.84 \nonumber \nonumber \]
So on average, our predictions are just under 3 points away from our actual values.
There are no specific cutoffs or guidelines for how big our standard error of the estimate can or should be; it is highly dependent on both our sample size and the scale of our original \(Y\) variable, so expert judgment should be used. In this case, the estimate is not that far off and can be considered reasonably precise.
Clear as mud? Let's try another practice problem!

COMMENTS
Developing a hypothesis (with example) Step 1. Ask a question. Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project. Example: Research question.
3 Define your variables. Once you have an idea of what your hypothesis will be, select which variables are independent and which are dependent. Remember that independent variables can only be factors that you have absolute control over, so consider the limits of your experiment before finalizing your hypothesis.
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
Simple Hypothesis Examples. Increasing the amount of natural light in a classroom will improve students' test scores. Drinking at least eight glasses of water a day reduces the frequency of headaches in adults. Plant growth is faster when the plant is exposed to music for at least one hour per day.
It seeks to explore and understand a particular aspect of the research subject. In contrast, a research hypothesis is a specific statement or prediction that suggests an expected relationship between variables. It is formulated based on existing knowledge or theories and guides the research design and data analysis. 7.
Another example for a directional one-tailed alternative hypothesis would be that. H1: Attending private classes before important exams has a positive effect on performance. Your null hypothesis would then be that. H0: Attending private classes before important exams has no/a negative effect on performance.
3. Simple hypothesis. A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, "Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking. 4.
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process. Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test ...
Examples. A research hypothesis, in its plural form "hypotheses," is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
Learning how to write a hypothesis comes down to knowledge and strategy. So where do you start? Learn how to make your hypothesis strong step-by-step here. ... proposal or prediction. For example, a research hypothesis is formatted in an if/then statement: If a person gets less than eight hours of sleep, then they will be less motivated at work ...
Step 3: Build the Hypothetical Relationship. In understanding how to compose a hypothesis, constructing the relationship between the variables is key. Based on your research question and variables, predict the expected outcome or connection.
For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new marketing campaign on consumer buying behavior. Engineering: In engineering, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of new technologies or designs. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the efficiency of a new solar panel design. How to write a ...
Ensure that your hypothesis is realistic and can be tested within the constraints of your available resources, time, and ethical considerations. Avoid value judgments: Be neutral and objective. Avoid including personal beliefs, value judgments, or subjective opinions. Stick to empirical statements based on evidence.
Tip 11: Review Existing Literature. Previous research offers insights into forming a hypothesis. Conduct a thorough literature review to identify trends and gaps. Use these studies to refine and build upon your hypothesis. Examples: Studies showing a link between screen time and anxiety.
Here are two hypothesis examples: Dandelions growing in nitrogen-rich soils for two weeks develop larger leaves than those in nitrogen-poor soils because nitrogen stimulates vegetative growth.4. If a company offers flexible work hours, then their employees will be happier at work.5.
Here are some research hypothesis examples: If you leave the lights on, then it takes longer for people to fall asleep. If you refrigerate apples, they last longer before going bad. If you keep the curtains closed, then you need less electricity to heat or cool the house (the electric bill is lower). If you leave a bucket of water uncovered ...
5.2 - Writing Hypotheses. The first step in conducting a hypothesis test is to write the hypothesis statements that are going to be tested. For each test you will have a null hypothesis ( H 0) and an alternative hypothesis ( H a ). Null Hypothesis. The statement that there is not a difference in the population (s), denoted as H 0.
Hypothesis Testing Examples. We know it can be hard to write a good hypothesis unless you've seen some good hypothesis examples. We've included four hypothesis examples based on some made-up experiments. Use these as templates or launch pads for coming up with your own hypotheses. Experiment #1: Students Studying Outside (Writing a Hypothesis)
To write quality assignment, you must use 6 classic statements. Thus, you must clarify: who, what, where, when, why and how. You must make question understandable in terms of positioning problem. Example of correct hypothesis: Step 2. Gather Preliminary Research for Your Hypothesis.
A hypothesis test is used to test whether or not some hypothesis about a population parameter is true.. To perform a hypothesis test in the real world, researchers obtain a random sample from the population and perform a hypothesis test on the sample data, using a null and alternative hypothesis:. Null Hypothesis (H 0): The sample data occurs purely from chance.
Examples of If, Then Hypotheses. If you get at least 6 hours of sleep, you will do better on tests than if you get less sleep. If you drop a ball, it will fall toward the ground. If you drink coffee before going to bed, then it will take longer to fall asleep. If you cover a wound with a bandage, then it will heal with less scarring.
A Business Hypothesis Approach. Before we could get to the process of creating and testing hypotheses, we needed to improve the presentation of data. To do this, I set up some XmR charts to track the metrics Tom wanted to focus on. An Example of a XmR or Process Behaviour Chart. We looked at higher-level metrics:
10.1: Prelude to Hypothesis Testing. A statistician will make a decision about claims via a process called "hypothesis testing." A hypothesis test involves collecting data from a sample and evaluating the data. Then, the statistician makes a decision as to whether or not there is sufficient evidence, based upon analysis of the data, to reject ...
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\) What is the null hypothesis for this scenario? State the null hypothesis in words and symbols. Solution. The null hypothesis is that there is no relationship between health and happiness, so "The slope in the regression line for happiness and health will be zero." Neither variable can predict or explain the other variable.
Hypothesis @example Decorator. When writing production-grade applications, the ability of a Hypothesis to generate a wide range of input test data plays a crucial role in ensuring robustness. However, there are certain inputs/scenarios the testing team might deem mandatory to be tested as part of every test run.