
- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less

Business Communication - How to Write a Powerful Business Report
Business communication -, how to write a powerful business report, business communication how to write a powerful business report.

Business Communication: How to Write a Powerful Business Report
Lesson 8: how to write a powerful business report.
/en/business-communication/how-to-write-a-formal-business-letter/content/
How to write a powerful business report

When a company needs to make an informed decision, it can create a business report to guide its leaders. Business reports use facts and research to study data, analyze performance, and provide recommendations on a company's future.
Watch the video below to learn how to write and format a business report.
The basics of a business report
Business reports are always formal , objective , and heavily researched . Every fact must be clear and verifiable, regardless of whether the report focuses on a single situation or examines the overall performance of an entire company.
Because objectivity is crucial in a business report, avoid subjective descriptions that tell the reader how to feel. For instance, if sales were down last quarter, don’t say “Sales were terrible last quarter,” but rather let the sales data speak for itself. There should also be no personal pronouns, such as “I think we should invest more capital.” A business report should remain impersonal and framed from the company’s perspective.
The structure of a business report
Although the size of a report can range from one page to 100, structure is always important because it allows readers to navigate the document easily. While this structure can vary due to report length or company standards, we’ve listed a common, reliable structure below:
- Front matter : List your name, job title, contact information, and the date of submission. You can also create a title for the report.
- Background : State the background of the topic you’ll be addressing, along with the purpose of the report itself.
- Key findings : Provide facts , data , and key findings that are relevant to the purpose stated in the background. Be clear and specific, especially because the entire report depends on the information in this section.
- Conclusion : Summarize and interpret the key findings, identify issues found within the data, and answer questions raised by the purpose.
- Recommendations : Recommend solutions to any problems mentioned in the conclusion, and summarize how these solutions would work. Although you’re providing your own opinion in this section, avoid using personal pronouns and keep everything framed through the company’s perspective.
- References : List the sources for all the data you've cited throughout the report. This allows people to see where you got your information and investigate these same sources.
Some companies may also require an executive summary after the front matter section, which is a complete summary that includes the report’s background, key findings, and recommendations. This section lets people learn the highlights quickly without having to read the entire document. The size of an executive summary can range from a paragraph to multiple pages, depending on the length of the report.
As mentioned in Business Writing Essentials , revision is key to producing an effective document. Review your writing to keep it focused and free of proofreading errors, and ensure your factual information is correct and presented objectively. We also recommend you get feedback from a colleague before submitting your work because they can spot errors you missed or find new opportunities for analysis or discussion.
Once you’ve revised your content, think about the report’s appearance . Consider turning your front matter section into a cover page to add some visual polish. You can also create a table of contents if the report is lengthy. If you’re printing it out, use quality paper and a folder or binder to hold the report together. To diversify the presentation of your data, try using bulleted lists, graphics, and charts.
Example of a business report
To demonstrate the principles of this lesson, we’ve created a brief business report for you to review.
Let's start by looking at the first page of this two-page report.

The layout of the front matter is simple and effective, while the background sets the stage in a quick, specific manner. The key findings provide the main takeaways that warrant further investigation, along with a chart to add emphasis and visual variety.
Now let's look at the following page.

The conclusion features a little of the writer's opinion on the key findings, although the writing is still centered around the company's perspective. The recommendations are clear and supported by the data, while the references are thorough.
While business reports may seem intimidating, you have the ability to create a thorough, informative document through practice and careful research. Collect the facts and present them in an organized, objective manner, and you’ll help your business make informed decisions.
/en/business-communication/how-to-write-an-effective-business-email/content/
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Structure a Business Report

- 5-minute read
- 14th March 2019
The content of a business report will depend on what you are writing about. Even the writing style may depend on who you are writing for (although clear, concise and formal is usually best). However, there is a general structure that most business reports follow. In this post, then, we’ll look at how to structure a business report for maximum clarity and professionalism.
1. Title Page
Every business report should feature a title page . The title itself should clearly set out what the report is about. Typically, you should also include your name and the date of the report.
Most business reports begin with a summary of its key points. Try to include:
- A brief description of what the report is about
- How the report was completed (e.g., data collection methods)
- The main findings from the research
- Key conclusions and recommendations
A paragraph or two should suffice for this in shorter business reports. However, for longer or more complex reports, you may want to include a full executive summary .
3. Table of Contents
Short business reports may not need a table of contents, especially if they include a summary. But longer reports should set out the title of each section and the structure of the report. Make sure the headings here match those used in the main text. You may also want to number the sections.
4. Introduction
The introduction is the first part of the report proper. Use it to set out the brief you received when you were asked to compile the report. This will frame the rest of the report by providing:
- Background information (e.g., business history or market information)
- The purpose of the report (i.e., what you set out to achieve)
- Its scope (i.e., what the report will cover and what it will ignore)
These are known as the “terms of reference” for the business report.
5. Methods and Findings
If you are conducting original research, include a section about your methods. This may be as simple as setting out the sources you are using and why you chose them. But it could also include how you have collected and analyzed the data used to draw your conclusions.
After this, you will need to explain your findings. This section will present the results of your research clearly and concisely, making sure to cover all the main points set out in the brief.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
One tip here is to break the findings down into subsections, using headings to guide the reader through your data. Using charts and illustrations , meanwhile, can help get information across visually, but make sure to label them clearly so the reader knows how they relate to the text.
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
The last main section of your report will cover conclusions and recommendations. The conclusion section should summarize what you have learned from the report. If you have been asked to do so, you should also recommend potential courses of action based on your conclusions.
If you are not sure what to suggest here, think back to the objectives set out in your brief.
7. References
If you have used any third-party sources while writing your report, list them in a bibliography after the main report. This could include other business documents, academic articles, or even news reports. The key is to show what you have based your findings and conclusions upon.
8. Appendices (If Applicable)
Finally, you may have gathered extra documentation during your research, such as interview transcripts, marketing material, or financial data. Including this in the main report would make it too long and unfocused, but you can add it to an appendix (or multiple appendices) at the end of the document. It will then be available should your reader need it.
Summary: How to Structure a Business Report
If you are writing a business report, aim to structure it as follows:
- Title Page – Include a clear, informative title, your name, and the date.
- Summary – A brief summary of what the report is about, the data collection methods used, the findings of the report, and any recommendations you want to make.
- Table of Contents – For longer reports, include a table of contents.
- Introduction –Set out the brief you were given for the report.
- Methods and Findings – A description of any methods of data collection and analysis used while composing the report, as well as your findings.
- Conclusions and Recommendations – Any conclusions reached while writing the report, plus recommendations for what to do next (if required).
- References – Sources used in your report listed in a bibliography.
- Appendices – If you have supporting material (e.g., interview transcripts, raw data), add it to an appendix at the end of the document.
Don’t forget, too, that a business report should be clear, concise, and formal. And if you would like help making sure that your business writing is easy to read and error free, just let us know .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- RMIT Australia
- RMIT Europe
- RMIT Vietnam
- RMIT Global
- RMIT Online
- Alumni & Giving

- What will I do?
- What will I need?
- Who will help me?
- About the institution
- New to university?
- Studying efficiently
- Time management
- Mind mapping
- Note-taking
- Reading skills
- Argument analysis
- Preparing for assessment
- Critical thinking and argument analysis
- Online learning skills
- Starting my first assignment
- Researching your assignment
- What is referencing?
- Understanding citations
- When referencing isn't needed
- Paraphrasing
- Summarising
- Synthesising
- Integrating ideas with reporting words
- Referencing with Easy Cite
- Getting help with referencing
- Acting with academic integrity
- Artificial intelligence tools
- Understanding your audience
- Writing for coursework
- Literature review
- Academic style
- Writing for the workplace
- Spelling tips
- Writing paragraphs
- Writing sentences
- Academic word lists
- Annotated bibliographies
- Artist statement
- Case studies
- Creating effective poster presentations
- Essays, Reports, Reflective Writing
- Law assessments
- Oral presentations
- Reflective writing
- Art and design
- Critical thinking
- Maths and statistics
- Sustainability
- Educators' guide
- Learning Lab content in context
- Latest updates
- Students Alumni & Giving Staff Library
Learning Lab
Getting started at uni, study skills, referencing.
- When referencing isn't needed
- Integrating ideas
Writing and assessments
- Critical reading
- Poster presentations
- Postgraduate report writing
Subject areas
For educators.
- Educators' guide
- Writing a business research report
This video explains how to write a business report for postgraduate level students. It covers the introduction, report structure and organisation, writing the report, and business writing.
Introduction
[slide 1: Topic slide]
[slide 2: Outline]
Description:
Sitting at the centre of the screen is: “What am I going to be learning today?” The following four words animate in:
- Introduction
- Report structure and organization
- Writing the report
- Business writing
This resource covers three important features of the writing required for a successful business research report. Following this brief introduction, the second section covers report structure with a focus on suitable ways
to organize content. The third section outlines the features of persuasive writing. And the final section provides tips for strong effective business writing.
[slide 3: What is a business research report?]
A checklist of items that make up a research report:
- Formulates a research
- Reports on research findings
- Recommends actions to achieve desirable outcomes
And is written in a
- Business report format
- Professional business writing style
This assignment provides you with the opportunity to research and write a real workplace report. It will inform the client of important aspects of their research brief. It will also provide recommendations to achieve desirable outcomes. The report will be presented as a written business proposal and as a presentation. This assignment requires a transition from academic writing to professional business writing. A business research report is written in a professional business style that differs from academic writing.
Report structure and organization
[slide 4: Topic slide]
[slide 5: Linear text structure]
[Graphic] Three babushka dolls representing each of the following:
- Whole text
- Paragraph
Overall, reports have a highly structured linear form with a beginning, middle and an end. This is repeated at the section level and the paragraph level.
[slide 6: Part: 1 - Organising content]
A report structure should be broken down into sections, having a beginning, middle and end. An example of this is:
- Executive summary
- Research question
- Problem, context and literature
- Methodology, approach and limitations
- Discussion and data analysis
- Implications (benefits and limitations)
- Recommendation and conclusion
- Considerations of policy adjustments and recommendations for further research
- References
A numbering system is used for the table of contents, and within them a broad example of a research page appears. Here it emphasizes the use of TEEL, and how each paragraph should be linked with one another.
Reports are structured using sections that are clearly organized and use a numbering system. Paragraphs within the sections should be well structured
and ideas should be linked between paragraphs.
[slide 7: Part: 2 - Organising content]
An example of going from general to specific.
- Current trend for businesses to outsource non-core activities
- Increase in demand for Facilities Management (FM) services
- More integrated and strategic approach to providing FM services
- Business now delivers a range of services through a single contract. These include…
General to specific is a useful strategy for organising content in business writing. This is particularly helpful for giving background or an overview.
[slide 8: Report sections]
[Text] We will now go through each of the report sections in detail:
Example. Report structure and headings.
- Report title and authors names
- Recommendations and conclusions
- Consideration of policy adjustments and recommendation for further research
No narration.
[slide 9: Executive summary]
- Briefly summarise the whole report in a logical order
- Outlines context, rationale, objectives, findings, conclusions, recommendations
- Written last, mainly in past tense
A strong executive summary is vital to a successful report as it determines the relevance of the report for the reader. It is the section the reader reads first and provides an overall summary of the whole report. Each major section of the report should be summarised in 1 or 2 sentences.
[Slide 10: Introduction]
- Identifies the main context and issues
- Narrows to project aim/purpose
[Text and graphic example]
Graphic of a triangle point downwards, writing from a general to specific.
Accompanying this the following text:
General (top of the triangle): ‘PICA is a property and financial services company currently offering…’
Specific (bottom of the triangle): ‘PICA requires a business plan for….’
Notice how the introduction narrows the topic from its broader context to the specific purpose of this report. The introduction is written from general to specific, which is a common form found in business writing.
[slide 11: Research question]
Frames the whole report
[Text example]
This report aims to answer the question ‘Is now a good time for PICA to diversify into Facilities Management (FM)’?
- Sub-questions
This research question frames the whole report and focuses the research to a specific area. It is common to have one research question followed by sub questions and these emerge from the larger question being answered.
[slide 12: Problem, context and literature]
Outlines the general situation in the specific business area
- Definitions
- Competitors
- Financial background
The accompanying graphic is of the triangle representation pointing downwards from general to specific.
Problem, context and literature section of the report requires a general
Introduction to the business which then narrows to cover details of competitors and their financial background. Again you are writing from general to specific.
[slide 13: Methodology, approach and limitations]
The research uses an applied strategy with a change focus (Saunders, Lewis & Thornhill 2012).
The main approach is data collection will be This methodology is appropriate because….
The research is based on secondary data, both qualitative and quantitative
Limitations in the research include…
The methodology covers how the research was done, why these methods were chosen, the details of the methods used and the limits of stating explicitly what is covered and what is not.
[slide 14: Discussion and data analysis]
Refer to your research
- Limitations in the research include…
Compare to theory / other research
- Industry bodies and secondary research…
- Eg. This strategy encompasses all aspects of financial reporting (Faulding & Lau 2011)…
Sum up at the end of each section
- In summary, Sydney is well positioned for further growth in residential buildings that require FM services…
It is important to refer to your research to show links between the primary research. In this case industry bodies, secondary research such as academic papers, theory and research and your findings.
[slide: 15: Implications: benefits and limitations]
What do your findings mean for the client?
- The findings outlines above suggests that PICA’s desire to enter the FM industry is expected to be beneficial given that…
- NSW trends demonstrate…
- Evidence suggests that PICA will be required to …
- There are risks associated with entering the FM services market.
It is important to refer to your research to show links between the primary research. In this case industry bodies, secondary research such as academic papers, theory and research and your findings. You need to explain what your research findings mean for your client. These implications will lead into your recommendations in the next section.
[slide 16: Recommendations and conclusions]
[Text and Graphic]
- Restates purpose
- Provides ‘the answer’
- Provides a concluding statement
The accompanying graphic of a triangle representation, this time with it points upward -going from specific to general.
Recommendations
- Suggests steps for further action
Eg. It is recommended that:
o PICA should enter the FM market
o Pica should acquire new…
The conclusion should provide a clear answer to the research question.
The conclusion is the reverse of the introduction it moves from answering the specific research question to showing how it fits into the broader context. In the recommendation section we return to the steps that this specific business should be taking as a result of the report.
[slide 17: Recommendation for further research]
Outline other research
- Based on the research findings, it is recommended that further in-depth analysis be conducted of the competitive landscape.
- PICA should seek legal and tax advice in order to…
Broadening the scope of the research
Examining certain issues in detail
In the final section of your report, outline what other research you think the client should undertake. This could include broadening the scope of the current research or examining certain issues in more detail.
Writing the report
[slide 18: Topic slide]
[slide 19: Paragraphs: TEEL]
[Graphic and Text]
Buns top and bottom: Topic and linking sentence
Condiments and meat: Explanation, evidence and examples
TEEL can be described using a burger metaphor. The topic and linking sentences make up the bun and base of the burger, and the evidence and explanations make the filling.
A paragraph contains one main idea, which is found in the topic sentence.
It is best to put the topic sentence first in the paragraph as this makes reading easier. The rest of the paragraph is made up of explanation and evidence to support the topic sentence.
[slide 20: Paragraph structure: TEEL]
A sample of a paragraph structure is given using the TEEL structure; each of these parts is highlighted.
[Topic] Leighton Contractors is a large-scale FM operation with considerable FM expertise within its own group of companies [end-topic]. [Example] A brief analysis of Leighton’s focus is helpful to PICA as it considers entry to the FM industry as PICA is considering a similar strategy [end-example]. [Evidence] The specific observation of this report is that Leighton focuses its FM operations into specific areas in which its group of companies has expertise, in particular in construction, telecommunications and mining (Leighton Constractors Pty Ltd 2009) [end-evidence]. [Link] This is a key observation as it affirms PICA’s expressed desire to enter FM by leveraging its expertise in Strata Management [end-link].
[slide 21: Persuading the reader]
Grid of icons accompanying the following text:
- Strong topic sentence
- Introduction and summaries for each section
- Effective evaluation and analysis
- Integration of sources to support your view
In a business research report your goal is to persuade the reader to follow your advice. Therefore, it is essential that they believe your understanding of the market is thorough and well researched. The following strategies are useful for writing persuasively.
[slide 22: Strong topic sentence]
[Text examples]
- [underlined] Evolution consulting [end-underlined] recommends that PICA consider acquiring the Port Stevens Group.
- [underlined] The hypothesis [end-underlined] is that now is a good time for PICA to diversify into FM.
Strong topic sentences reinforce your argument and help persuade the reader. Both topic sentences below have a clear direct message.
Notice how the topic sentence comes at the beginning of the sentence.
[slide 23: Introductions and conclusions for sections]
Introduction to a section
It is the belief of the research team that the successful entry into the FM sector will require PICA to target a specific building sub-market.
Conclusion to a section
In a conclusion, from the analysis of overall market trends, PICA would benefit from targeting the residential building sub-market.
Use section introduction and summaries to clearly state and restate your view. This acts as a reminder to the reader and emphasises the consistency
of your argument.
[slide 24: Effective evaluation and analysis]
- Paragraph strategy
- Sentence strategy
It is essential to write convincing evaluations of the strengths, weaknesses and risks. It is this understanding that makes it possible for the company to make decisions about future strategy.
[slide 25: Paragraph strategy]
A graphic illustrating the narration:
At the beginning of a paragraph, the topic sentence (evaluation of risk) should be first written. Followed by an explanation and analysis. Lastly, providing a solution. The language used in the process, should be formal impersonal language.
Here are two useful writing strategies, which make your evaluation
and analysis more effective. They are firstly clear paragraph organization
and secondly use of a formal impersonal style.
[slide 26: Sentence strategy]
Use tentative language
This demonstrates you have a thorough understanding of the level of risk.
- It is advised
- Is minimized
- Will be made
Use passive form
Write in an impersonal style. Suggest your view is based on research rather than opinion.
- Could, would, may, might
- There is a view that,
- There is a perception that
Use active verbs
In business writing it is generally better to write in a
clear and direct style. This includes using active verb forms.
However, when evaluating risks it is useful to write in a more
tentative and indirect style. Using tentative language shows you have a complex understanding of the situation and are aware of the degrees of risk.
It is also useful to write in an impersonal style as this gives your writing authority. It suggest that you are stating the views of the industry or other experts, and not just your own opinion. Passive verb forms generally weaken business writing as they are indirect. However, they are useful in evaluation as their use emphasises the advice itself rather than the voice of the writer.
[slide 27: Integration of sources]
- Supports your view with evidence
- Demonstrates the strength of your research and sources
[slide 28: Referencing in sentences]
Description: Sentence 1:
[Source] ACIF (2013) [end-source] projects that recovery will continue to strengthen for NSW in 2014.
Sentence 2:
Recover of the construction sector will continue to strengthen for NSW in 2014 [source] (ACIF) [end-source]
There are two ways to include references in a sentence at the beginning or at the end. The difference between these two constructions is subtle but it changes the focus of the sentence.
[slide 29: Effects and emphasis]
Source prominent
- Source (ACIF) emphasized as topic
- Common in academic writing where the research itself can be the topic
Information prominent
- Recovery emphasized as topic
- Common in business writing
This sentence emphasizes the source of the information and is common in academic writing. This does not emphasize the view of the student or writer. This sentence puts the information at the beginning of the sentence and emphasizes the writers view. This is useful if the writer wants to persuade the reader to follow his or her advice.
Business writing
[slide 30: Topic slide]
[slide 31: Academic writing and business writing]
Description: Academic
Knowledge and research
- Expected structure
- Academic style
- Uses a range of sources
Business decision-making and action
Workplace / Industry
- Business style
- Uses sources with practical application
There are differences between academic writing and business writing. In academic writing the overall focus is on knowledge and research. In business writing decision making and action are the goal. These differences are important and affect the writing style.
[slide 32: Tips for business writing]
Iconography for the following three points:
- Be direct: Darts board, aimed at the centre
- Be concise: Cutting out words (paper)
- Use strong active verbs: A man lifting up weights
[slide 33: Be direct]
Put the most important information first. So people can easily find it.
Put the topic sentence at the beginning
attitude towards FM services [end-emphasis] have changed to now viewing these costs as life cycle costs (International Facilities Management Association 2011).
[Emphasis] Attitudes towards FM services [end-emphasis] have changed from that of an overhead cost to a life cycle cost (International Facilities Management Association 2011).
Make it easy to read
Clear logical structure, headings, sub-headings and bullet points.
People are busy and will read only minimally. Therefore, one very useful strategy in business writing is to put the most important information first,
so you know the audience will find it. Notice how the first sentence is more difficult to read. In the second sentence the topic is at the beginning of the sentence as this makes the point immediately clear to the reader.
[slide 34: Be concise]
Description: Cut out unnecessary words
Use concise language by replacing wordy phrases with single words.
[slide 35: Use strong active verbs]
Description: Use strong active verbs
[Example 1]
ACIF believes [end-emphasis] that construction projects will experience [end-emphasis] considerable growth in 2014.
[Example 2]
ACIF forecasts [end-emphasis] considerable growth in residential construction investment in 2014.
Strong active verbs convey a clear and remove the need for repetition.
[slide 36: Identify the weaknesses ]
Description: [Poor example]
In terms of non-residential construction projects ACIF (2013) expects that construction investments in NSW will be subject to a considerable growth rate, whereas investments in non-residential construction projects are expected to remain constant for all other region.
How this can be improved
Legend: [strikethrough] = Be concise. [Highlight] = be direct. [Emphasis] = Use strong active words.
[Strikethrough] in terms of [end-strikethrough] [highlight] non-residential [end-highlight] construction projects ACIF (2013) expects [end-emphasis] that [highlight] construction investments in NSW [end-highlight] will be [strikethrough] subject to a considerable growth rate [end-strikethrough] , whereas investments in non-residential construction projects are expected to [end-emphasis] remain constant for all other regions.
[Improved example]
In NSW, construction investment for non-residential projects will grow compared with other regions of Australia (ACIF 2013).
- Overall structure of a report
- Methodology section in a report
- Example of a report
- Report checklist
Still can't find what you need?
The RMIT University Library provides study support , one-on-one consultations and peer mentoring to RMIT students.
- Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Twitter (opens in a new window)
- Instagram (opens in a new window)
- Linkedin (opens in a new window)
- YouTube (opens in a new window)
- Weibo (opens in a new window)
- Copyright © 2024 RMIT University |
- Accessibility |
- Learning Lab feedback |
- Complaints |
- ABN 49 781 030 034 |
- CRICOS provider number: 00122A |
- RTO Code: 3046 |
- Open Universities Australia
Writing up a Research Report
- First Online: 04 January 2024
Cite this chapter

- Stefan Hunziker 3 &
- Michael Blankenagel 3
417 Accesses
A research report is one big argument about how and why you came up with your conclusions. To make it a convincing argument, a typical guiding structure has developed. In the different chapters, there are distinct issues that need to be addressed to explain to the reader why your conclusions are valid. The governing principle for writing the report is full disclosure: to explain everything and ensure replicability by another researcher.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Barros, L. O. (2016). The only academic phrasebook you’ll ever need . Createspace Independent Publishing Platform.
Google Scholar
Field, A. (2016). An adventure in statistics. The reality enigma . SAGE.
Field, A. (2020). Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS statistics (5th ed.). SAGE.
Früh, M., Keimer, I., & Blankenagel, M. (2019). The impact of Balanced Scorecard excellence on shareholder returns. IFZ Working Paper No. 0003/2019. https://zenodo.org/record/2571603#.YMDUafkzZaQ . Accessed: 9 June 2021.
Pearl, J., & Mackenzie, D. (2018). The book of why: The new science of cause and effect. Basic Books.
Yin, R. K. (2013). Case study research: Design and methods (5th ed.). SAGE.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Wirtschaft/IFZ, Campus Zug-Rotkreuz, Hochschule Luzern, Zug-Rotkreuz, Zug, Switzerland
Stefan Hunziker & Michael Blankenagel
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Stefan Hunziker .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Hunziker, S., Blankenagel, M. (2024). Writing up a Research Report. In: Research Design in Business and Management. Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-42739-9_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-42739-9_4
Published : 04 January 2024
Publisher Name : Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN : 978-3-658-42738-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-658-42739-9
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Research Reports: Definition and How to Write Them

Reports are usually spread across a vast horizon of topics but are focused on communicating information about a particular topic and a niche target market. The primary motive of research reports is to convey integral details about a study for marketers to consider while designing new strategies.
Certain events, facts, and other information based on incidents need to be relayed to the people in charge, and creating research reports is the most effective communication tool. Ideal research reports are extremely accurate in the offered information with a clear objective and conclusion. These reports should have a clean and structured format to relay information effectively.
What are Research Reports?
Research reports are recorded data prepared by researchers or statisticians after analyzing the information gathered by conducting organized research, typically in the form of surveys or qualitative methods .
A research report is a reliable source to recount details about a conducted research. It is most often considered to be a true testimony of all the work done to garner specificities of research.
The various sections of a research report are:
- Background/Introduction
- Implemented Methods
- Results based on Analysis
- Deliberation
Learn more: Quantitative Research
Components of Research Reports
Research is imperative for launching a new product/service or a new feature. The markets today are extremely volatile and competitive due to new entrants every day who may or may not provide effective products. An organization needs to make the right decisions at the right time to be relevant in such a market with updated products that suffice customer demands.
The details of a research report may change with the purpose of research but the main components of a report will remain constant. The research approach of the market researcher also influences the style of writing reports. Here are seven main components of a productive research report:
- Research Report Summary: The entire objective along with the overview of research are to be included in a summary which is a couple of paragraphs in length. All the multiple components of the research are explained in brief under the report summary. It should be interesting enough to capture all the key elements of the report.
- Research Introduction: There always is a primary goal that the researcher is trying to achieve through a report. In the introduction section, he/she can cover answers related to this goal and establish a thesis which will be included to strive and answer it in detail. This section should answer an integral question: “What is the current situation of the goal?”. After the research design was conducted, did the organization conclude the goal successfully or they are still a work in progress – provide such details in the introduction part of the research report.
- Research Methodology: This is the most important section of the report where all the important information lies. The readers can gain data for the topic along with analyzing the quality of provided content and the research can also be approved by other market researchers . Thus, this section needs to be highly informative with each aspect of research discussed in detail. Information needs to be expressed in chronological order according to its priority and importance. Researchers should include references in case they gained information from existing techniques.
- Research Results: A short description of the results along with calculations conducted to achieve the goal will form this section of results. Usually, the exposition after data analysis is carried out in the discussion part of the report.
Learn more: Quantitative Data
- Research Discussion: The results are discussed in extreme detail in this section along with a comparative analysis of reports that could probably exist in the same domain. Any abnormality uncovered during research will be deliberated in the discussion section. While writing research reports, the researcher will have to connect the dots on how the results will be applicable in the real world.
- Research References and Conclusion: Conclude all the research findings along with mentioning each and every author, article or any content piece from where references were taken.
Learn more: Qualitative Observation
15 Tips for Writing Research Reports
Writing research reports in the manner can lead to all the efforts going down the drain. Here are 15 tips for writing impactful research reports:
- Prepare the context before starting to write and start from the basics: This was always taught to us in school – be well-prepared before taking a plunge into new topics. The order of survey questions might not be the ideal or most effective order for writing research reports. The idea is to start with a broader topic and work towards a more specific one and focus on a conclusion or support, which a research should support with the facts. The most difficult thing to do in reporting, without a doubt is to start. Start with the title, the introduction, then document the first discoveries and continue from that. Once the marketers have the information well documented, they can write a general conclusion.
- Keep the target audience in mind while selecting a format that is clear, logical and obvious to them: Will the research reports be presented to decision makers or other researchers? What are the general perceptions around that topic? This requires more care and diligence. A researcher will need a significant amount of information to start writing the research report. Be consistent with the wording, the numbering of the annexes and so on. Follow the approved format of the company for the delivery of research reports and demonstrate the integrity of the project with the objectives of the company.
- Have a clear research objective: A researcher should read the entire proposal again, and make sure that the data they provide contributes to the objectives that were raised from the beginning. Remember that speculations are for conversations, not for research reports, if a researcher speculates, they directly question their own research.
- Establish a working model: Each study must have an internal logic, which will have to be established in the report and in the evidence. The researchers’ worst nightmare is to be required to write research reports and realize that key questions were not included.
Learn more: Quantitative Observation
- Gather all the information about the research topic. Who are the competitors of our customers? Talk to other researchers who have studied the subject of research, know the language of the industry. Misuse of the terms can discourage the readers of research reports from reading further.
- Read aloud while writing. While reading the report, if the researcher hears something inappropriate, for example, if they stumble over the words when reading them, surely the reader will too. If the researcher can’t put an idea in a single sentence, then it is very long and they must change it so that the idea is clear to everyone.
- Check grammar and spelling. Without a doubt, good practices help to understand the report. Use verbs in the present tense. Consider using the present tense, which makes the results sound more immediate. Find new words and other ways of saying things. Have fun with the language whenever possible.
- Discuss only the discoveries that are significant. If some data are not really significant, do not mention them. Remember that not everything is truly important or essential within research reports.
Learn more: Qualitative Data
- Try and stick to the survey questions. For example, do not say that the people surveyed “were worried” about an research issue , when there are different degrees of concern.
- The graphs must be clear enough so that they understand themselves. Do not let graphs lead the reader to make mistakes: give them a title, include the indications, the size of the sample, and the correct wording of the question.
- Be clear with messages. A researcher should always write every section of the report with an accuracy of details and language.
- Be creative with titles – Particularly in segmentation studies choose names “that give life to research”. Such names can survive for a long time after the initial investigation.
- Create an effective conclusion: The conclusion in the research reports is the most difficult to write, but it is an incredible opportunity to excel. Make a precise summary. Sometimes it helps to start the conclusion with something specific, then it describes the most important part of the study, and finally, it provides the implications of the conclusions.
- Get a couple more pair of eyes to read the report. Writers have trouble detecting their own mistakes. But they are responsible for what is presented. Ensure it has been approved by colleagues or friends before sending the find draft out.
Learn more: Market Research and Analysis
MORE LIKE THIS

I Am Disconnected – Tuesday CX Thoughts
May 21, 2024

20 Best Customer Success Tools of 2024
May 20, 2024

AI-Based Services Buying Guide for Market Research (based on ESOMAR’s 20 Questions)
Data Information vs Insight: Essential differences
May 14, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
What is a Marketing Research Report and How to Write It?

Table of contents

Enjoy reading this blog post written by our experts or partners.
If you want to see what Databox can do for you, click here .
There is nothing more embarrassing for a marketer than to hear a client say “…this doesn’t quite address the business questions that we need to answer.” And unfortunately, this is a rather common occurrence in market research reporting that most marketers would care to admit.
So, why do most market research reports fail to meet client expectations? Well, in most cases, because there is more emphasis on methodology and analytic techniques used to craft the report rather than relying on data visualization, creative story-telling, and outlining actionable direction/steps.
Now, our next big question is, how do you avoid your client’s dreaded deer-in-the-headlights reaction when presenting such a report? This blog post will answer this and much more, as we go through the following:
What Is a Market Research Report?
Why is market research important, differences between primary and secondary market research, types of market research, market research reports advantages and disadvantages, how to do market research, how to prepare a market research report: 5 steps, marketing research report templates, marketing research reports best practices, bring your market research reports a step further with databox.
The purpose of creating a market research report is to make calculated decisions about business ideas. Market research is done to evaluate the feasibility of a new product or service, through research conducted with potential consumers. The information obtained from conducting market research is then documented in a formal report that should contain the following details:
- The characteristics of your ideal customers
- You customers buying habits
- The value your product or service can bring to those customers
- A list of your top competitors
Every business aims to provide the best possible product or service at the lowest cost possible. Simply said, market research is important because it helps you understand your customers and determine whether the product or service that you are about to launch is worth the effort.
Here is an example of a customer complaint that may result in more detailed market research:
Suppose you sell widgets, and you want your widget business to succeed over the long term. Over the years, you have developed many different ways of making widgets. But a couple of years ago, a customer complained that your widgets were made of a cheap kind of foam that fell apart after six months. You didn’t think at the time that this was a major problem, but now you know it.
The customer is someone you really want to keep. So, you decide to research this complaint. You set up a focus group of people who use widgets and ask them what they think about the specific problem. After the conducted survey you’ll get a better picture of customer opinions, so you can either decide to make the changes regarding widget design or just let it go.
PRO TIP: How Well Are Your Marketing KPIs Performing?
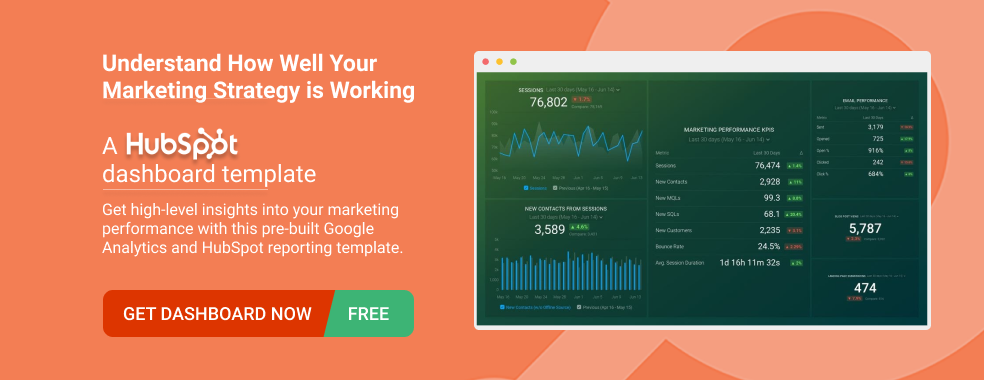
Like most marketers and marketing managers, you want to know how well your efforts are translating into results each month. How much traffic and new contact conversions do you get? How many new contacts do you get from organic sessions? How are your email campaigns performing? How well are your landing pages converting? You might have to scramble to put all of this together in a single report, but now you can have it all at your fingertips in a single Databox dashboard.
Our Marketing Overview Dashboard includes data from Google Analytics 4 and HubSpot Marketing with key performance metrics like:
- Sessions . The number of sessions can tell you how many times people are returning to your website. Obviously, the higher the better.
- New Contacts from Sessions . How well is your campaign driving new contacts and customers?
- Marketing Performance KPIs . Tracking the number of MQLs, SQLs, New Contacts and similar will help you identify how your marketing efforts contribute to sales.
- Email Performance . Measure the success of your email campaigns from HubSpot. Keep an eye on your most important email marketing metrics such as number of sent emails, number of opened emails, open rate, email click-through rate, and more.
- Blog Posts and Landing Pages . How many people have viewed your blog recently? How well are your landing pages performing?
Now you can benefit from the experience of our Google Analytics and HubSpot Marketing experts, who have put together a plug-and-play Databox template that contains all the essential metrics for monitoring your leads. It’s simple to implement and start using as a standalone dashboard or in marketing reports, and best of all, it’s free!
You can easily set it up in just a few clicks – no coding required.
To set up the dashboard, follow these 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the template
Step 2: Connect your HubSpot and Google Analytics 4 accounts with Databox.
Step 3: Watch your dashboard populate in seconds.
Marketing research requires both primary and secondary market research. But what does that mean and what are the main differences?
Primary market research takes in information directly from customers, usually as participants in surveys. Usually, it is consisted of:
- Exploratory Primary Research – This type of research helps to identify possible problem areas, and it’s not focused on discovering specific information about customers. As with any research, exploratory primary research should be conducted carefully. Researchers need to craft an interviewing or surveying plan, and gather enough respondents to ensure reasonable levels of statistical reliability.
- Specific Primary Research – This type of research is one of the best ways to approach a problem because it relies on existing customer data. Specific research provides a deeper, more thorough understanding of the problem and its potential solutions. The greatest advantage of specific research is that it lets you explore a very specific question, and focus on a specific problem or an opportunity.
Secondary market research collects information from other sources such as databases, trend reports, market or government statistics, industry content, etc. We can divide secondary market research into 3 categories:
- Public market data – Public sources range from academic journals and government reports to tax returns and court documents. These sources aren’t always easy to find. Many are available only in print in libraries and archives. You have to look beyond search engines like Google to find public source documents.
- Commercial data – Those are typically created by specialized agencies like Pew, Gartner or Forrester. the research agencies are quite expensive, but they provide a lot of useful information.
- Internal data – Your organization’s databases are gold mines for market research. In the best cases, your salespeople can tell you what they think about customers. Your salespeople are your direct sources of information about the market. Don’t underestimate your internal data.
In general, primary research is more reliable than secondary research, because researchers have to interview people directly. But primary research is expensive and time-consuming. Secondary research can be quicker and less expensive.
There are plenty of ways to conduct marketing research reports. Mostly, the type of research done will depend on your goals. Here are some types of market research often conducted by marketers.
Focus Groups
Product/service use research, observation-based research, buyer persona research, market segmentation research, pricing research, competitive analysis research, customer satisfaction and loyalty research, brand awareness research, campaign research.
An interview is an interactive process of asking and answering questions and observing your respondent’s responses. Interviews are one of the most commonly used tools in market research . An interview allows an organization to observe, in detail, how its consumers interact with its products and services. It also allows an organization to address specific questions.
A focus group is a group of people who get together to discuss a particular topic. A moderator leads the discussion and takes notes. The main benefit of focus groups is that they are quick and easy to conduct. You can gather a group of carefully-selected people, give them a product to try out, and get their feedback within a few hours/days.
Product or service use research helps you obtain useful information about your product or service such as:
- What your current customers do with the product/service
- Which features of the product/service are particularly important to your customers
- What they dislike about the product/service
- What they would change about the product/service
Observation-based research helps you to observe your target audience interacting with your product or service. You will see the interactions and which aspects work well and which could be improved. The main point is to directly experience the feedback from your target audience’s point of view.
Personas are an essential sales tool. By knowing your buyers’ pain points and the challenges they face, you can create better content, target messaging, and campaigns for them. Buyer persona research is based on market research, and it’s built around data that describes your customers’ demographics, behaviors, motivations, and concerns. Sales reporting software can significantly help you develop buyer personas when you gain insights after you collected all information.
Market segmentation research is carried out to better understand existing and potential market segments. The objective is to determine how to target different market segments and how they differ from each other. The three most important steps in writing a market segmentation research report are:
- Defining the problem
- Determining the solution [and]
- Defining the market
Related : 9 Customer Segmentation Tips to Personalize Ecommerce Marketing and Drive More Sales
A price that is too high, or too low, can kill a business. And without good market research, you don’t really know what is a good price for your product. Pricing research helps you define your pricing strategy.
In a competitive analysis, you define your “competition” as any other entity that competes with you in your market, whether you’re selling a widget or a piece of real estate. With competitive analysis research, you can find out things like:
- Who your competitors are
- What they’ve done in the past
- What’s working well for them
- Their weaknesses
- How they’re positioned in the market
- How they market themselves
- What they’re doing that you’re not
Related : How to Do an SEO Competitive Analysis: A Step-by-Step Guide
In today’s marketplace, companies are increasingly focused on customer loyalty. What your customers want is your product, but, more importantly, they want it delivered with a service that exceeds their expectations. Successful companies listen to their customers and respond accordingly. That’s why customer satisfaction and loyalty research is a critical component of that basic equation.
Related : 11 Tactics for Effectively Measuring Your Customer Service ROI
Who you are, what you stand for, what you offer, what you believe in, and what your audience thinks of you is all wrapped up in brand. Brand awareness research tells what your target audience knows about your brand and what’s their experience like.
A campaign research report is a detailed account of how your marketing campaign performed. It includes all the elements that went into creating the campaign: planning, implementation, and measurement.
Here are some of the top advantages and disadvantages of doing market research and crafting market research reports.
- Identify business opportunities – A market research report can be used to analyze potential markets and new products. It can give information about customer needs, preferences, and attitudes. Also, it compare products and services.
- A clear understanding of your customers – A market report gives company’s marketing department an in-depth picture about customers’ needs and wants. This knowledge can be used to improve products, prices, and advertising.
- Mitigates risks – 30% of small businesses fail within the first two years. Why is this so? The answer is that entrepreneurs are risk takers. However, there are risks that could be avoided. A good marketing research will help you identify those risks and allow you to mitigate them.
- Clear data-driven insights – Market research encompasses a wide range of activities, from determining market size and segment to forecasting demand, and from identifying competitors to monitoring pricing. All of these are quantified and measurable which means that gives you a clear path for building unique decisions based on numbers.
Disadvantages
- It’s not cheap – Although market research can be done for as little as $500, large markets like the United States can run into millions of dollars. If a research is done for a specific product, the budget may be even much higher. The budget also depends on the quality of the research. The more expensive it is, the more time the research will take.
- Some insights could be false – For example, if you are conducting a survey, data may be inadequate or inaccurate because respondents can, well, simply be dishonest and lie.
Here are the essential steps you need to take when doing market research:
Define your buyer persona
Identify a persona group to engage, prepare research questions for your market research participants, list your primary competitors, summarize your findings.
The job of a marketing persona is to describe your ideal customer and to tell you what they want, what motivates them, what frustrates them, and what limits them. Finding out these things means you have a better chance of designing your products, services, marketing messages, and brand around real customers. There is no one right way to create a buyer persona, though.
For example, if you’re in an industry focused on education, you could include things like:
- Educational level
- Education background
It’s recommended that you create 3-5 buyer personas for your products, based on your ideal customer.
This should be a representative sample of your target customers so you can better understand their behavior. You want to find people who fit both your target personas and who represent the broader demographic of your market. People who recently made a purchase or purposefully decided not to make one are a good sample to start with.
The questions you use determine the quality of your results. Of course, the quality of your results also depends on the quality of your participants.
Don’t ask questions that imply a yes or no answer. Instead, use open questions. For example, if you are researching customers about yogurt products, you could ask them: „ What have you heard about yogurt ?” or “ What do you think of yogurt ?“.
Avoid questions that use numbers, such as “ How many times a week do you eat yogurt ?”
Avoid questions that suggest a set of mutually exclusive answers, such as “ Do you like yogurt for breakfast, lunch, or dinner ?”
Avoid questions that imply a scale, such as “ Do you like chocolate-flavored yogurt ?”
Market researchers sometimes call one company the top competitor, another middle competitor, and the third one small competitor. However you classify them, you want to identify at least three companies in each category. Now, for each business on your list, list its key characteristics. For example, if your business sells running shoes, a key characteristic might be the product’s quality.
Next, make a list of your small business’s competitive advantages. These include the unique qualities or features of your business that make it the best choice of customers for the products or services it offers. Make a list of these competitive advantages and list them next to the key characteristics you listed for your business.
You have just finished writing your marketing research report. Everything is out there quantified or qualified. You just have to sum it up and focus on the most important details that are going to make a big impact on your decisions. Clear summary leads to a winning strategy!
Related : How to Prepare a Complete Marketing Report: The KPIs, Analysis, & Action Plan You Need
Here’s how to prepare a market research report in 5 simple steps:
Step 1: Cluster the data
Step 2: prepare an outline, step 3: mention the research methods, step 4: include visuals with narrative explanations, step 5: conclude the report with recommendations.
Your first step is to cluster all the available information into a manageable set. Clustering is the process of grouping information together in a way that emphasizes commonalities and minimizes differences. So, in market research, this will help to organize all the information you have about a product, service, or target market and identify your focus areas.
A marketing research report should be written so that other people can understand it:
- Include background information at the beginning to explain who your audience is and what problem you are trying to solve for them.
- In the body of the report, include a description of the methodology – Explain to the reader how your research was done, what was involved, and why you selected the methodology you used.
- Also in the body of the report, include the results of your market research. These may be quantitative or qualitative, but either way they should answer the questions you posed at the beginning.
- Include the executive summary – A summary of the entire report.
The market research methodology section includes details on the type of research, sample size, any limitations of the studies, research design, sample selection, data collection procedures, and statistical analyses used.
Visuals are an essential part of the presentation. Even the best-written text can be difficult to understand. Charts and graphs are easier to understand than text alone, and they help the reader see how the numbers fit the bigger picture.
But visuals are not the whole story. They are only one part of the presentation. Visuals are a cue for the reader. The narrative gives the story, not just the numbers.
Recommendations tend to follow logically from conclusions and are a response to a certain problem. The recommendation should always be relevant to the research rationale, that is, the recommendation should be based on the results of the research reported in the body of the report.
Now, let’s take a look at some dashboard reporting templates you could use to enhance your market research:
- Semrush (Position Tracking) Report
Brand Awareness Report
Sales pipeline performance report, customer success overview report, stripe (mrr & churn) report, semrush (position tracking) report template.
This free SEMRush dashboard template will help you monitor how your website’s search visibility on search engines evolves on a monthly basis. This dashboard contains all of the information you need to make changes and improve the ranking results of your business in Google Search.
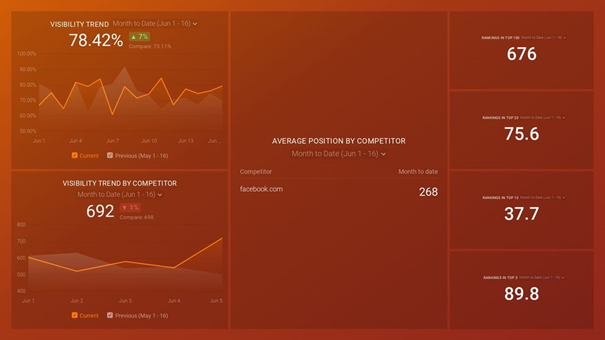
This Brand Awareness Report will help you to get a sense of your brand awareness performance in Google Analytics, Google Organic Search, and Facebook. Use this dashboard to track brand awareness the same way you track other marketing campaigns.
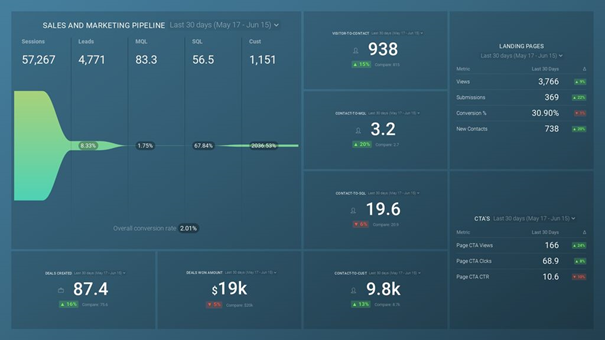
Are your sales and marketing funnel healthy and growing? How is your sales and marketing funnel performing? What are the key conversion rates between your lifecycle stages? With a pipeline performance dashboard , you’ll get all of the answers quickly.
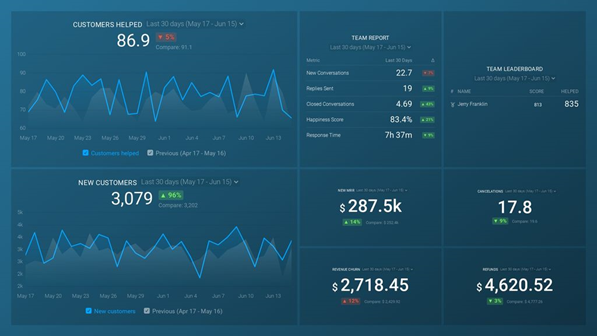
This Customer Success Overview Dashboard allows you to analyze how your customer service team’s responsiveness impacts your business. Use this dashboard to assess the correlation between your customer service performance and churn rate.
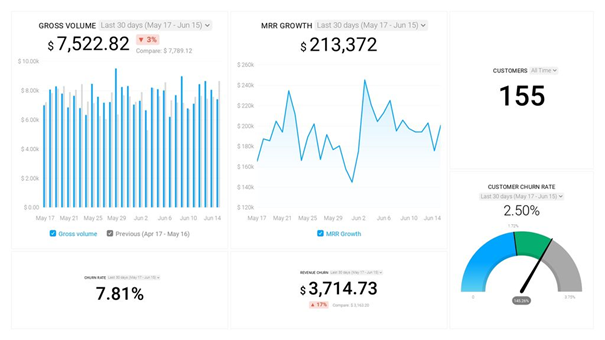
This Stripe dashboard tracks your churn rate and MRR growth in real-time and shows you which customers (and how many of them) you have at any given point in time. All you have to do to get started is to connect your Stripe account.
As we said earlier, there are no strict rules when it comes to writing marketing research reports. On the other hand, you must find your focus if you want to write a report that will make a difference. Here are some best practices you should keep in mind when writing a research report.
- Objectives – The objective of a market research report is to define the problems, identify key issues, and suggest recommendations for further research. If you answer them successfully, you’re on the right way.
- Don’t worry about the format – Be creative. The report could be in a form of a PowerPoint presentation, Excel sheet, interactive dashboard or even a video. Use the format that best fits your audience, but make sure to make it easy to read.
- Include an executive summary, scorecard , or a dashboard – This is really important because time is money, and most people don’t have time to waste. So, how to put everything important in a short role? Address all of the objectives and put them in a graphic dashboard or scorecard. Also, you can write an executive summary template (heart of the report) that can be easily updated and read by managers or CEOs.
- Use storytelling – A good story always makes a great point because it’s so memorable. Your research report results can double the effect with a catchy story.
- Keep it short – It’s not a secret that we are reading so little in the digital era. Use a lot of white space and bullet points. Too much text on a page means less focus for the reader.
- Be organized – Maintain the order of information. It’s important for the reader to navigate through the report easily. If they want to find some details or specific information it would be great to divide all sections with appropriate references.
- Methodological information – Methodological details could be boring. Include only the most important details that the reader needs to know to understand the big picture.
- Use images (or other visualizations) whenever you can – A good picture speaks for 1.000 words! If you can communicate the point visually, don’t hesitate to do it. It would be a lot easier for those who don’t like a lot of text to understand your results. But don’t push them where you can’t.
- Create readable graphs – The crown of marketing research reports is a comprehensive graph. Make sure to design precise and attractive graphs that will power up and round your story.
- Use the Appendix – You can include all secondary information such as methodological details and other miscellaneous data in the Appendix at the end of the report.
Market research reports are all about presenting your data in an easy-to-understand way and making calculated decisions about business ideas. But this is something easier said than done.
When busy stakeholders and executives grab a report, they need something that will give them an idea of the results – the big picture that addresses company wide-business goals.
Can a PowerPoint presentation or a PDF report meet those expectations? Most likely not. But a dashboard can.
Keep in mind that even with the best market analysis in the world, your market research report won’t be actionable if you don’t present the data efficiently and in a way that everyone understands what the next steps are. Databox is your key ally in the matter.
Databox dashboards are designed to help you present your market research data with clarity – from identifying what is influencing your business, and understanding where your brand is situated in the market, to gauging the temperature of your niche or industry before a new product/service launch.
Present your research results with efficient, interactive dashboards now by signing up for a free trial .
Do you want an All-in-One Analytics Platform?
Hey, we’re Databox. Our mission is to help businesses save time and grow faster. Click here to see our platform in action.
- Databox Benchmarks
- Future Value Calculator
- ROI Calculator
- Return On Ads Calculator
- Percentage Growth Rate Calculator
- Report Automation
- Client Reporting
- What is a KPI?
- Google Sheets KPIs
- Sales Analysis Report
- Shopify Reports
- Data Analysis Report
- Google Sheets Dashboard
- Best Dashboard Examples
- Analysing Data
- Marketing Agency KPIs
- Automate Agency Google Ads Report
- Marketing Research Report
- Social Media Dashboard Examples
- Ecom Dashboard Examples

Does Your Performance Stack Up?
Are you maximizing your business potential? Stop guessing and start comparing with companies like yours.

A Message From Our CEO
At Databox, we’re obsessed with helping companies more easily monitor, analyze, and report their results. Whether it’s the resources we put into building and maintaining integrations with 100+ popular marketing tools, enabling customizability of charts, dashboards, and reports, or building functionality to make analysis, benchmarking, and forecasting easier, we’re constantly trying to find ways to help our customers save time and deliver better results.
Grew up as a Copywriter. Evolved into the Content creator. Somewhere in between, I fell in love with numbers that can portray the world as well as words or pictures. A naive thinker who believes that the creative economy is the most powerful force in the world!
Get practical strategies that drive consistent growth
12 Tips for Developing a Successful Data Analytics Strategy

What Is Data Reporting and How to Create Data Reports for Your Business

What Is KPI Reporting? KPI Report Examples, Tips, and Best Practices
Build your first dashboard in 5 minutes or less
Latest from our blog
- BTB: Mastering Data-Driven Legal Marketing Success (w/ Guy Alvarez, Good2BSocial) May 15, 2024
- The State of B2B Content Creation: Navigating the Future of In-House Marketing Innovation May 9, 2024
- Metrics & KPIs
- vs. Tableau
- vs. Looker Studio
- vs. Klipfolio
- vs. Power BI
- vs. Whatagraph
- vs. AgencyAnalytics
- Product & Engineering
- Inside Databox
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Talent Resources
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- API Documentation
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Table of Contents

Research Report
Definition:
Research Report is a written document that presents the results of a research project or study, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions, in a clear and objective manner.
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the findings of the research to the intended audience, which could be other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public.
Components of Research Report
Components of Research Report are as follows:
Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the research report and provides a brief overview of the research question or problem being investigated. It should include a clear statement of the purpose of the study and its significance or relevance to the field of research. It may also provide background information or a literature review to help contextualize the research.
Literature Review
The literature review provides a critical analysis and synthesis of the existing research and scholarship relevant to the research question or problem. It should identify the gaps, inconsistencies, and contradictions in the literature and show how the current study addresses these issues. The literature review also establishes the theoretical framework or conceptual model that guides the research.
Methodology
The methodology section describes the research design, methods, and procedures used to collect and analyze data. It should include information on the sample or participants, data collection instruments, data collection procedures, and data analysis techniques. The methodology should be clear and detailed enough to allow other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the study in a clear and objective manner. It should provide a detailed description of the data and statistics used to answer the research question or test the hypothesis. Tables, graphs, and figures may be included to help visualize the data and illustrate the key findings.
The discussion section interprets the results of the study and explains their significance or relevance to the research question or problem. It should also compare the current findings with those of previous studies and identify the implications for future research or practice. The discussion should be based on the results presented in the previous section and should avoid speculation or unfounded conclusions.
The conclusion summarizes the key findings of the study and restates the main argument or thesis presented in the introduction. It should also provide a brief overview of the contributions of the study to the field of research and the implications for practice or policy.
The references section lists all the sources cited in the research report, following a specific citation style, such as APA or MLA.
The appendices section includes any additional material, such as data tables, figures, or instruments used in the study, that could not be included in the main text due to space limitations.
Types of Research Report
Types of Research Report are as follows:
Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master’s or Doctoral degree, although it can also be written by researchers or scholars in other fields.
Research Paper
Research paper is a type of research report. A research paper is a document that presents the results of a research study or investigation. Research papers can be written in a variety of fields, including science, social science, humanities, and business. They typically follow a standard format that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion sections.
Technical Report
A technical report is a detailed report that provides information about a specific technical or scientific problem or project. Technical reports are often used in engineering, science, and other technical fields to document research and development work.
Progress Report
A progress report provides an update on the progress of a research project or program over a specific period of time. Progress reports are typically used to communicate the status of a project to stakeholders, funders, or project managers.
Feasibility Report
A feasibility report assesses the feasibility of a proposed project or plan, providing an analysis of the potential risks, benefits, and costs associated with the project. Feasibility reports are often used in business, engineering, and other fields to determine the viability of a project before it is undertaken.
Field Report
A field report documents observations and findings from fieldwork, which is research conducted in the natural environment or setting. Field reports are often used in anthropology, ecology, and other social and natural sciences.
Experimental Report
An experimental report documents the results of a scientific experiment, including the hypothesis, methods, results, and conclusions. Experimental reports are often used in biology, chemistry, and other sciences to communicate the results of laboratory experiments.
Case Study Report
A case study report provides an in-depth analysis of a specific case or situation, often used in psychology, social work, and other fields to document and understand complex cases or phenomena.
Literature Review Report
A literature review report synthesizes and summarizes existing research on a specific topic, providing an overview of the current state of knowledge on the subject. Literature review reports are often used in social sciences, education, and other fields to identify gaps in the literature and guide future research.
Research Report Example
Following is a Research Report Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance among High School Students
This study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students. The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The findings indicate that there is a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students. The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers, as they highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities.
Introduction:
Social media has become an integral part of the lives of high school students. With the widespread use of social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Snapchat, students can connect with friends, share photos and videos, and engage in discussions on a range of topics. While social media offers many benefits, concerns have been raised about its impact on academic performance. Many studies have found a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance among high school students (Kirschner & Karpinski, 2010; Paul, Baker, & Cochran, 2012).
Given the growing importance of social media in the lives of high school students, it is important to investigate its impact on academic performance. This study aims to address this gap by examining the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students.
Methodology:
The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The questionnaire was developed based on previous studies and was designed to measure the frequency and duration of social media use, as well as academic performance.
The participants were selected using a convenience sampling technique, and the survey questionnaire was distributed in the classroom during regular school hours. The data collected were analyzed using descriptive statistics and correlation analysis.
The findings indicate that the majority of high school students use social media platforms on a daily basis, with Facebook being the most popular platform. The results also show a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students.
Discussion:
The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. The negative correlation between social media use and academic performance suggests that strategies should be put in place to help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. For example, educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, this study provides evidence of the negative impact of social media on academic performance among high school students. The findings highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. Further research is needed to explore the specific mechanisms by which social media use affects academic performance and to develop effective strategies for addressing this issue.
Limitations:
One limitation of this study is the use of convenience sampling, which limits the generalizability of the findings to other populations. Future studies should use random sampling techniques to increase the representativeness of the sample. Another limitation is the use of self-reported measures, which may be subject to social desirability bias. Future studies could use objective measures of social media use and academic performance, such as tracking software and school records.
Implications:
The findings of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. Educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. For example, teachers could use social media platforms to share relevant educational resources and facilitate online discussions. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. They could also engage in open communication with their children to understand their social media use and its impact on their academic performance. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students. For example, schools could implement social media policies that restrict access during class time and encourage responsible use.
References:
- Kirschner, P. A., & Karpinski, A. C. (2010). Facebook® and academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(6), 1237-1245.
- Paul, J. A., Baker, H. M., & Cochran, J. D. (2012). Effect of online social networking on student academic performance. Journal of the Research Center for Educational Technology, 8(1), 1-19.
- Pantic, I. (2014). Online social networking and mental health. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 17(10), 652-657.
- Rosen, L. D., Carrier, L. M., & Cheever, N. A. (2013). Facebook and texting made me do it: Media-induced task-switching while studying. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(3), 948-958.
Note*: Above mention, Example is just a sample for the students’ guide. Do not directly copy and paste as your College or University assignment. Kindly do some research and Write your own.
Applications of Research Report
Research reports have many applications, including:
- Communicating research findings: The primary application of a research report is to communicate the results of a study to other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public. The report serves as a way to share new knowledge, insights, and discoveries with others in the field.
- Informing policy and practice : Research reports can inform policy and practice by providing evidence-based recommendations for decision-makers. For example, a research report on the effectiveness of a new drug could inform regulatory agencies in their decision-making process.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research in a particular area. Other researchers may use the findings and methodology of a report to develop new research questions or to build on existing research.
- Evaluating programs and interventions : Research reports can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and interventions in achieving their intended outcomes. For example, a research report on a new educational program could provide evidence of its impact on student performance.
- Demonstrating impact : Research reports can be used to demonstrate the impact of research funding or to evaluate the success of research projects. By presenting the findings and outcomes of a study, research reports can show the value of research to funders and stakeholders.
- Enhancing professional development : Research reports can be used to enhance professional development by providing a source of information and learning for researchers and practitioners in a particular field. For example, a research report on a new teaching methodology could provide insights and ideas for educators to incorporate into their own practice.
How to write Research Report
Here are some steps you can follow to write a research report:
- Identify the research question: The first step in writing a research report is to identify your research question. This will help you focus your research and organize your findings.
- Conduct research : Once you have identified your research question, you will need to conduct research to gather relevant data and information. This can involve conducting experiments, reviewing literature, or analyzing data.
- Organize your findings: Once you have gathered all of your data, you will need to organize your findings in a way that is clear and understandable. This can involve creating tables, graphs, or charts to illustrate your results.
- Write the report: Once you have organized your findings, you can begin writing the report. Start with an introduction that provides background information and explains the purpose of your research. Next, provide a detailed description of your research methods and findings. Finally, summarize your results and draw conclusions based on your findings.
- Proofread and edit: After you have written your report, be sure to proofread and edit it carefully. Check for grammar and spelling errors, and make sure that your report is well-organized and easy to read.
- Include a reference list: Be sure to include a list of references that you used in your research. This will give credit to your sources and allow readers to further explore the topic if they choose.
- Format your report: Finally, format your report according to the guidelines provided by your instructor or organization. This may include formatting requirements for headings, margins, fonts, and spacing.

Purpose of Research Report
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the results of a research study to a specific audience, such as peers in the same field, stakeholders, or the general public. The report provides a detailed description of the research methods, findings, and conclusions.
Some common purposes of a research report include:
- Sharing knowledge: A research report allows researchers to share their findings and knowledge with others in their field. This helps to advance the field and improve the understanding of a particular topic.
- Identifying trends: A research report can identify trends and patterns in data, which can help guide future research and inform decision-making.
- Addressing problems: A research report can provide insights into problems or issues and suggest solutions or recommendations for addressing them.
- Evaluating programs or interventions : A research report can evaluate the effectiveness of programs or interventions, which can inform decision-making about whether to continue, modify, or discontinue them.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies.
When to Write Research Report
A research report should be written after completing the research study. This includes collecting data, analyzing the results, and drawing conclusions based on the findings. Once the research is complete, the report should be written in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
In academic settings, research reports are often required as part of coursework or as part of a thesis or dissertation. In this case, the report should be written according to the guidelines provided by the instructor or institution.
In other settings, such as in industry or government, research reports may be required to inform decision-making or to comply with regulatory requirements. In these cases, the report should be written as soon as possible after the research is completed in order to inform decision-making in a timely manner.
Overall, the timing of when to write a research report depends on the purpose of the research, the expectations of the audience, and any regulatory requirements that need to be met. However, it is important to complete the report in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
Characteristics of Research Report
There are several characteristics of a research report that distinguish it from other types of writing. These characteristics include:
- Objective: A research report should be written in an objective and unbiased manner. It should present the facts and findings of the research study without any personal opinions or biases.
- Systematic: A research report should be written in a systematic manner. It should follow a clear and logical structure, and the information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand and follow.
- Detailed: A research report should be detailed and comprehensive. It should provide a thorough description of the research methods, results, and conclusions.
- Accurate : A research report should be accurate and based on sound research methods. The findings and conclusions should be supported by data and evidence.
- Organized: A research report should be well-organized. It should include headings and subheadings to help the reader navigate the report and understand the main points.
- Clear and concise: A research report should be written in clear and concise language. The information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand, and unnecessary jargon should be avoided.
- Citations and references: A research report should include citations and references to support the findings and conclusions. This helps to give credit to other researchers and to provide readers with the opportunity to further explore the topic.
Advantages of Research Report
Research reports have several advantages, including:
- Communicating research findings: Research reports allow researchers to communicate their findings to a wider audience, including other researchers, stakeholders, and the general public. This helps to disseminate knowledge and advance the understanding of a particular topic.
- Providing evidence for decision-making : Research reports can provide evidence to inform decision-making, such as in the case of policy-making, program planning, or product development. The findings and conclusions can help guide decisions and improve outcomes.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research on a particular topic. Other researchers can build on the findings and conclusions of the report, which can lead to further discoveries and advancements in the field.
- Demonstrating expertise: Research reports can demonstrate the expertise of the researchers and their ability to conduct rigorous and high-quality research. This can be important for securing funding, promotions, and other professional opportunities.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies. Producing a high-quality research report can help ensure compliance with these requirements.
Limitations of Research Report
Despite their advantages, research reports also have some limitations, including:
- Time-consuming: Conducting research and writing a report can be a time-consuming process, particularly for large-scale studies. This can limit the frequency and speed of producing research reports.
- Expensive: Conducting research and producing a report can be expensive, particularly for studies that require specialized equipment, personnel, or data. This can limit the scope and feasibility of some research studies.
- Limited generalizability: Research studies often focus on a specific population or context, which can limit the generalizability of the findings to other populations or contexts.
- Potential bias : Researchers may have biases or conflicts of interest that can influence the findings and conclusions of the research study. Additionally, participants may also have biases or may not be representative of the larger population, which can limit the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Accessibility: Research reports may be written in technical or academic language, which can limit their accessibility to a wider audience. Additionally, some research may be behind paywalls or require specialized access, which can limit the ability of others to read and use the findings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Marketing 50+ Essential Business Report Examples with Templates
50+ Essential Business Report Examples with Templates
Written by: Sara McGuire May 29, 2023

Reports may not be the most exciting communication format. But they’re important.
To make smart decisions about budgeting, marketing strategies, product development and growth strategies, you can’t rely on gut feeling alone.
And if you’re trying to sway stakeholders, creating a report with a simple, elegant design and creative data visualizations is guaranteed to impress.
This guide will deliver the most essential business report templates you can edit with Venngage, plus design tips and best practices.
Top business report templates (click to jump ahead):
What is a business report?
- Annual reports
- Project status reports
- Budget reports
- Sales reports
- Marketing reports
- Case studies
- White papers
- How to create a business report in 6 steps
- What are the types of business reports
- Business report template FAQs
A business report is a document that delivers important information about a company’s performance, financial health, a particular project, or other aspects that influence its decision-making process.
Business reports come in various formats, such as PowerPoint presentations and online dashboards, offering more than just traditional files and spreadsheets.
They are crucial for organizations as they provide vital details that guide decision-making for business owners and managers.
They act as GPS, highlighting essential aspects like customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and financial figures. Business reports serve different audiences and purposes, delivering information in a clear and engaging format for both internal and external stakeholders.
Want a quick rundown of some of the business report templates in this blog? Check out this video tutorial:
1. Annual Report Templates
An annual report is an all-encompassing document that allows you to reflect on your company’s past year, including:
- Your company’s mission statement
- Your company’s growth (financially, product-wise, culture-wise)
- Your statement of income and cash flow
- Your various business segments
- Information about the company’s directors and executive officers
- Information about your company’s stock and dividends
- Wins and success stories
A lot of that sounds pretty dry, doesn’t it?
There’s actually a lot to be excited about in that list. You’re talking about how your company has grown, your wins (and maybe a few losses), and what’s on the horizon for the coming year.
You can bring that story to life in your annual report design and we have business report samples to inspire you.
This annual business report example uses a variety of charts and unique sections like “program highlights” to tell the agency’s story:

Think about how you can represent your company visually:
- Are there photos you can include of your business in action?
- What fonts and colors reflect your business’s personality?
- Are there icons you can use to illustrate certain concepts?
The below annual report design uses an energizing orange and yellow color scheme and cute icons. The format is highly visual and modern. All this reflects a dynamic company that’s optimistic about the future.
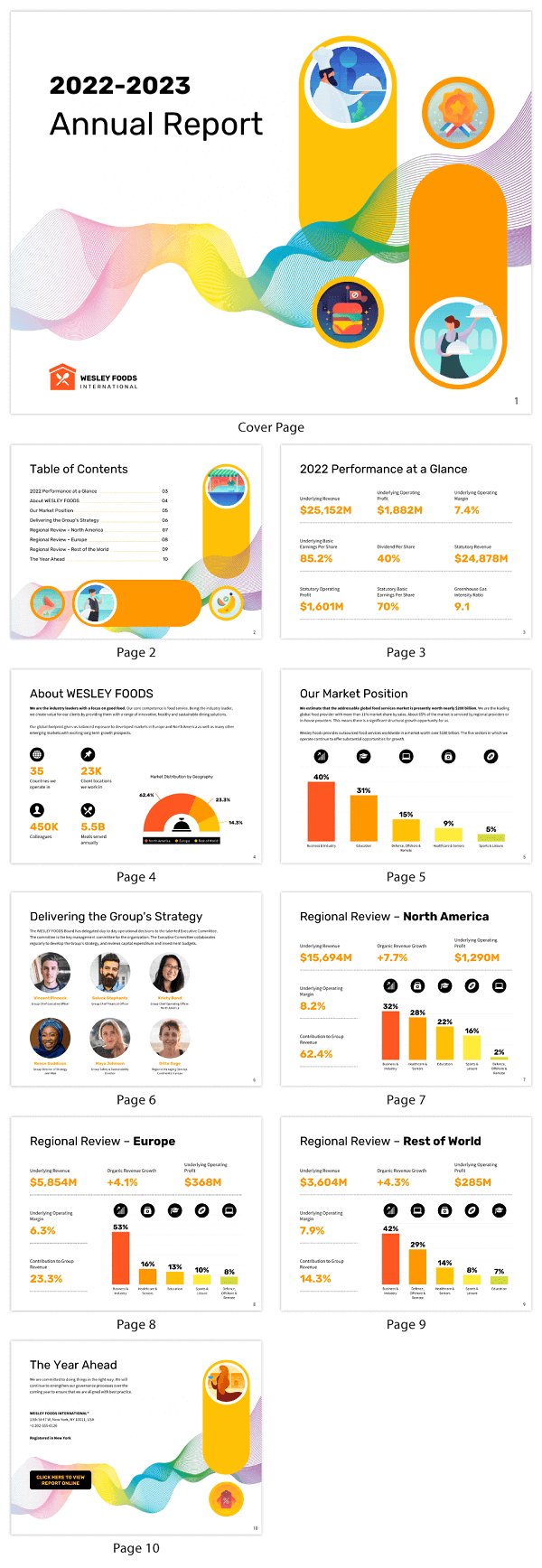
This company annual report template uses a mountain motif to reflect the company’s ambitious goals. Take a look at how the different sections of the report (“Strategy”, “Finance” and “Performance”) are color-coded to make the report easier to scan:

In the business report example below, the sleek, modern design with bold color accents reflects design trends in the games industry, which would appeal to stakeholders.

The same design ideas can be applied to an annual report presentation.
Take this annual report presentation for a coffee shop company. The whole design reflects the coziness of a coffee shop, from the softly filtered photos to the old-fashioned font:

A few annual report best practices:
- Create an eye-catching cover for your report
- Tell your company’s story in your annual report design by using thematic visuals, like background images and icons
- Pick a decorative font for headers and pair it with a more minimalist font for body text
- Look for opportunities to visualize data using infographics , charts and pictograms
Related : Our blog post with 55+ annual report templates , plus design tips and best practices.
2. Project Status Report Templates
Communication is central in any project. Consultants, agencies and freelancers especially want to be as transparent as possible. That is why a project status report template is one of the business report examples we are sharing in the article.
A project status report is crucial for communicating updates on what you’ve accomplished and what’s still pending. It also helps you flag any issues, either current or on the horizon. This helps build trust with the client.
The project status report template below communicates key information in an easy-to-understand format.

The above template lets you alert the client if the project is:
- Suffering from budget or scope creep
- On track in terms of schedule
- Healthy or not i.e. milestones completed on schedule, issues resolved
You can add bullet points on the second page to quickly flag key issues that are impacting project success.
Related : Our post on how to write a project management plan .
Simple Project Status Report Templates
Avoid ad-hoc emails or meetings. Use a simple project status report template to present your latest work and keep everyone on the same page, without endless back and forth.

The project status report below would work well for weekly updates.
This template lets you quickly provide an overview to busy stakeholders, who’ll be able to spot key project issues and progress at a glance.

Project Status Report Template PPT
Big updates might require consultants to communicate the status of a project in person. The below presentation template uses charts and data visualization to get your key points across immediately.
Clients or other stakeholders can see what’s been accomplished and when, while the last slide leaves room for what’s still pending.

A few project status report best practices:
- Include a summary of all important tasks currently in progress. If you have a weekly meeting with the client, this section will probably serve as the jumping-off point for your conversation.
- Stakeholders should be able to tell at a glance if the project is way off schedule or there are too many unresolved issues.
- Document all outstanding problems and concerns. It’s important to have a record in case you run into issues with the client later on.
Related : Our post with 30+ project plan examples plus design tips.
3. Budget Report Templates
This is Business 101: on a quarterly or yearly basis, you should be analyzing your budget, expenses and revenue.
A budget report typically breaks down:
- The different categories of your budget
- The last year or quarter’s spending for each category of your budget
- Areas where you may need to cut or increase spending
- Forecasts for the coming year or quarter
Business Monthly Expenses Template
A full budget report is a bit too dense to pass around a room during a meeting.
But, a visually engaging presentation or one-page summary, like the business report example below, is perfect for keeping your team and stakeholders up to speed.

You can provide an overview of the last period’s spending by category, and highlight the amount you saved or exceeded the budget by.
For example, take a look at this summary budget report slide that uses a thematic background image to make it more engaging:
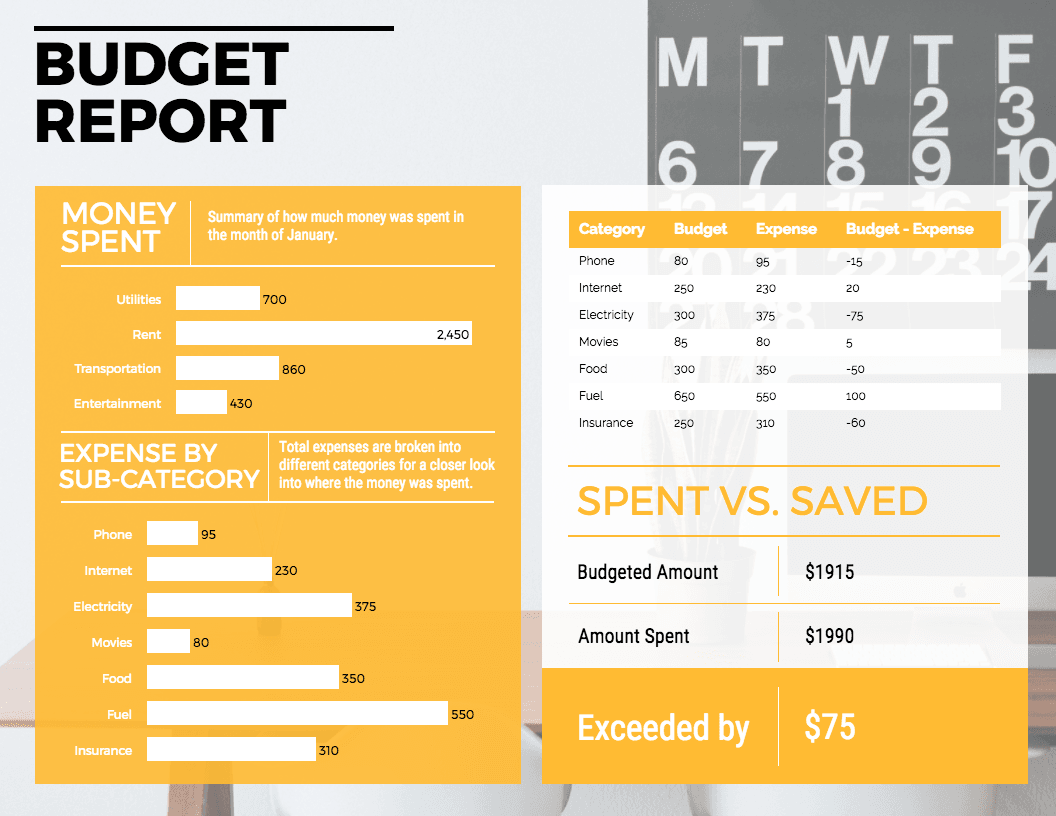
A quick summary page is also the perfect opportunity to creatively visualize data.
While tables are certainly efficient for comparing amounts spent, you could also use a more unusual visual like a bubble chart. This is because unique visuals make memorable business report examples.
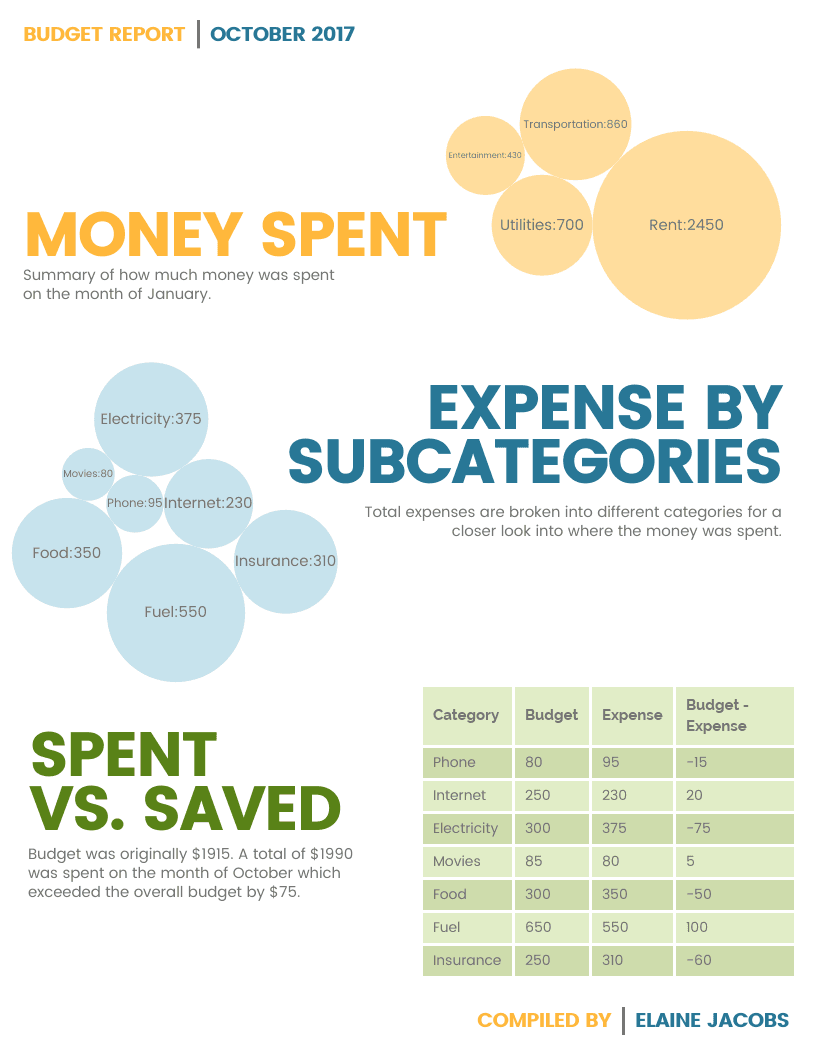
Forecast Budget Template
A forecast is an essential business report that shows where a business is headed financially. It’s not a plan for the future, but rather its current short-term direction .
Use this forecast template to project your businesses’ revenue, and take appropriate action.

A few budget report best practices:
- Clearly label the period the report covers (monthly, quarterly, yearly)
- Provide a brief description of each section of your report, to highlight important insights
- Use a table to compare amounts of money saved vs. spent
- Use bar charts, pie charts and bubble charts to visualize budget allotment
- Highlight important insights using contrasting colors, bold fonts and icons
4. Sales Report Templates
If you aren’t tracking your sales on a weekly, monthly, quarterly and yearly basis, it’s time to start.
Creating a sales report for different time periods can help you identify trends, as well as an opportunity for growth. Regularly reporting on your sales can also help your team stay focused on your goals.
What should be included in a sales report?
A sales report typically covers any of the following data:
- An overview of sales goals and whether or not those goals are being met
- Revenue and expenses
- Sales forecasts for the upcoming periods (month, quarter, year)
- Products and services that are selling the most and ones that are lagging
- Number of leads and conversion rates for a given period
- Any challenges or roadblocks
Weekly sales report template
Consider making sales reporting a segment of your weekly team meetings. You may want to provide a quick update for company-wide meetings and a more in-depth report for sales and marketing team meetings.
Here’s an example of what a quick weekly sales report could look like:

The slide simply covers the total sales for the week and compares them to previous weeks to highlight growth.
While this sales report presentation digs deeper into KPIs (key performance indicators) and conversions :
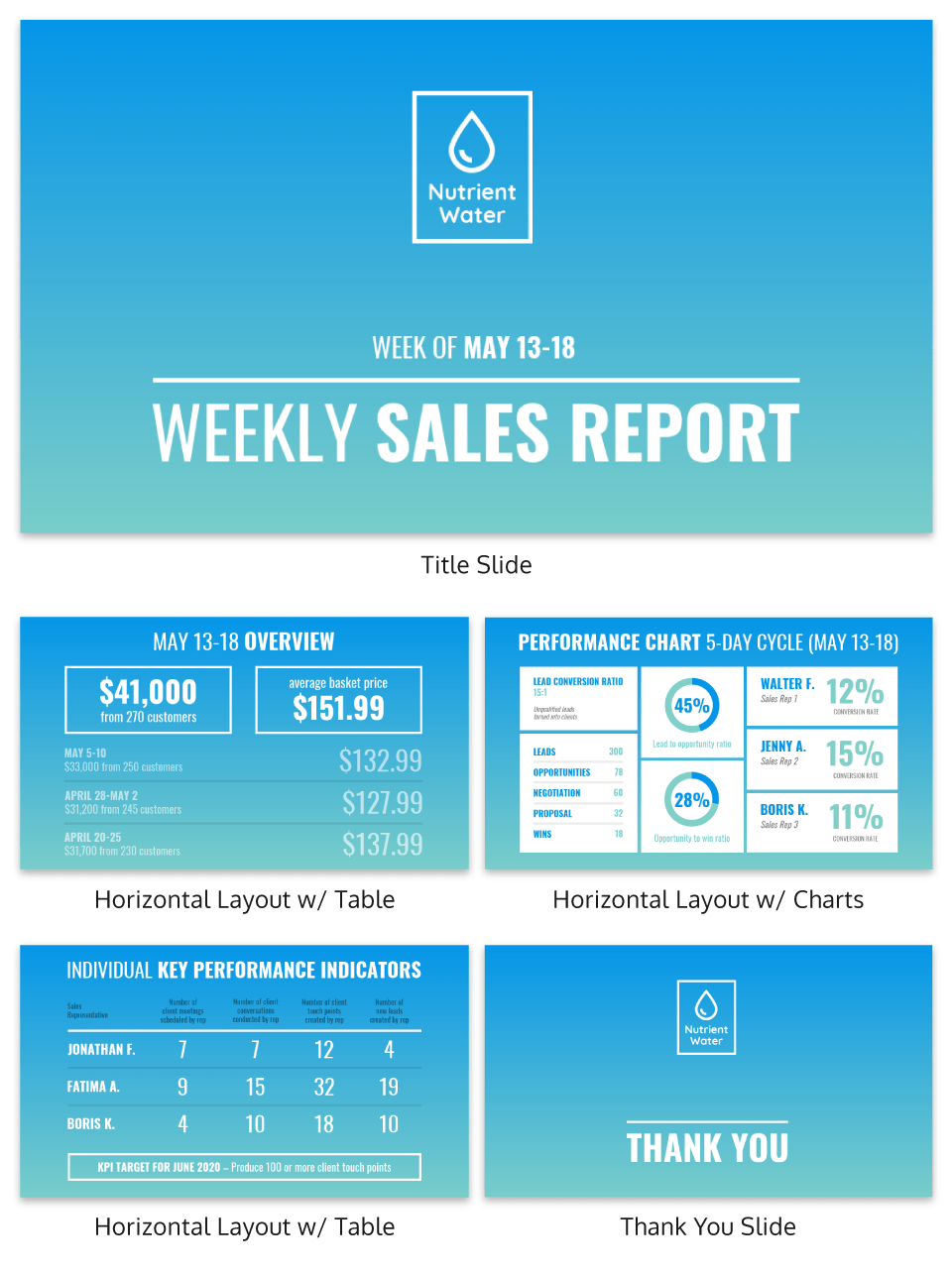
Monthly sales report template
For a monthly, quarterly or yearly sales report, you will probably want to go more in-depth into your metrics as you plan for upcoming periods.
That said, you don’t want to produce a 62-page text-heavy document no one will read. Surprise your client or boss with a fresh new way of doing things that are engaging and concise. You’ll differentiate yourself as an innovator.
For example, the following monthly sales report template uses a variety of charts and tables to keep the data fresh:

The below sales report template will help you visualize key sales metrics using pie charts, bar graphs and tables. The weighted text and icons help organize information in an easily digestible way.
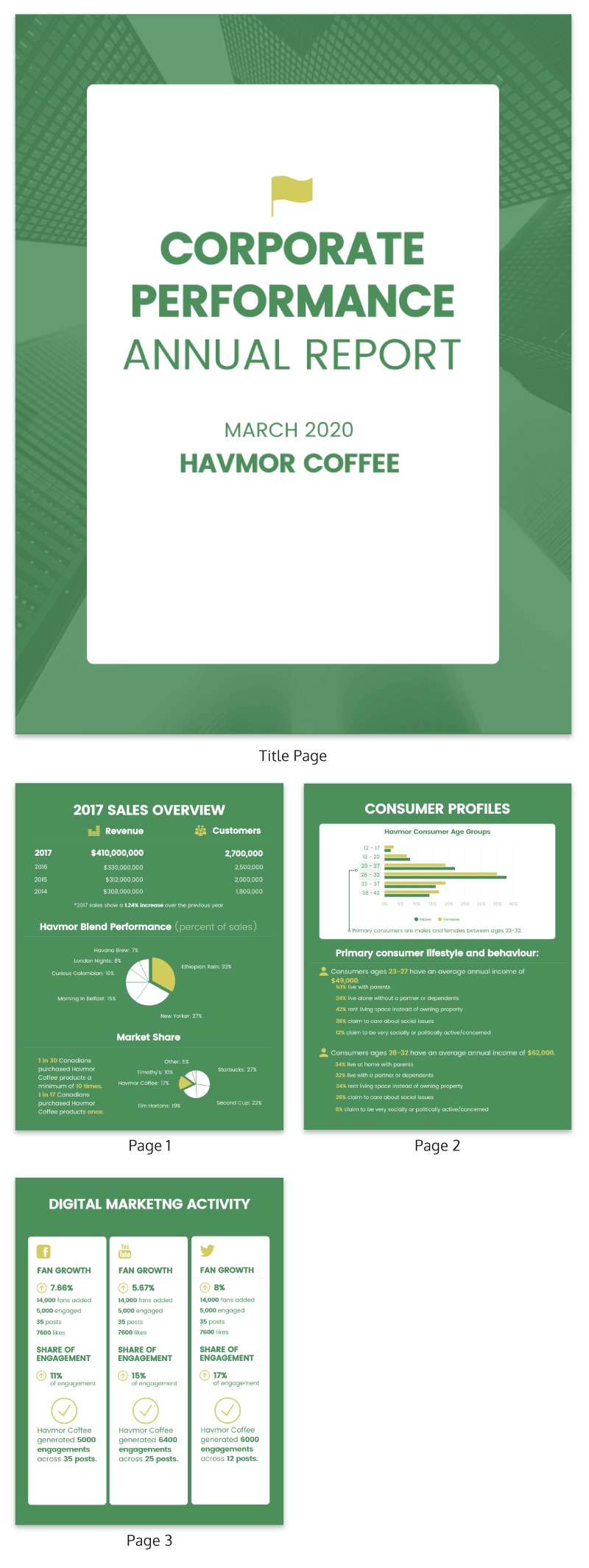
Making your sales report easily accessible will help build your reputation as someone who’s transparent and trustworthy.
A few sales report best practices:
- Clearly identify the time period you are reporting on
- Use descriptive section headers and include descriptions for any charts or tables that need more clarification
- Provide context for readers, explain any major trends they should be aware of, any challenges your team encountered, and how the goals have been impacted
- Use line charts and bar graphs to show changes over time and highlight trends
- Emphasize key metrics in big, bold fonts (for example, the total sales for a given week)
- Use contrasting colors to emphasize keywords or one point on a graph
Related : 5 ways to host a more successful sales demo by using images.
5. Digital Marketing Report Templates
If you’re a SaaS or e-commerce business, I don’t have to tell you how important digital marketing is. It’s the thing that can make or break many small businesses.
In order to scale and grow your business , it’s important to make informed, deliberate digital marketing decisions.
That means always looking for ways to improve your search rankings, grow your social media engagement, and optimize your ad campaigns.
A ‘ digital marketing report ‘ is a pretty broad term for a report that could be an overview of all your digital marketing channels or one particular channel.
A digital marketing report that covers all your main marketing channels could include any (or all) of the following data:
- An overview of your current digital marketing strategy
- Your main marketing goals and whether or not they are being met
- An overview of your conversion metrics, including the number of leads, paid vs. organic leads, and your cost per conversion
- An overview of your traffic metrics, organized by channel
- An SEO overview , including any chhttps://growthbarseo.com/anges in rankings for target keywords
- An overview of PPC campaigns you’re running, including clickthrough rate, ROI and cost per click
- An overview of your social media channels, including engagement metrics and leads from specific channels
For example, take a look at this digital marketing report template that dedicates one page to each channel. Note how the company’s branding has also been incorporated into the design by using the brand’s colors and visuals that reflect the computer theme:

In a digital marketing report that focuses on one specific marketing channel, you will probably want to go more in-depth into each metric.
For example, in a social media report, you should cover:
- A comparison of your performance on specific social media channels like Facebook, Twitter and YouTube (you could try visualizing it with a comparison infographic )
- Specific engagement metrics like impressions, clicks, subscriber count, likes and comments
- An overview of your followers, including demographic information like age, gender and profession
- Conversion metrics from each specific social media channel
The below social media report visualizes some of these key metrics.
As a consultant, you may be gifted in social media marketing but totally flummoxed by all things design. Look better than you are by using the above template. It’ll help you present your findings in a way that’s effective and professional, while still managing to be playful and engaging.
If you’re concerned about organizing information by channel, here’s an example of a social media marketing report presentation that uses colored columns to make it easy to scan for a specific channel’s metrics:

A few digital marketing report best practices:
- Provide an overview of the performance of all your channels, or a particular channel
- Organize your report by channel (“Organic Search”, “Social Media”, “PPC”) or by specific campaigns/projects
- If your report is long enough, include a table of content to make it easier for readers to navigate your report
- Use bar charts and tables to compare your performance on different marketing channels
- Use icons to emphasize key information and visualize different channels (for example, different social media networks)
- Try to communicate your information concisely and focus on only one topic per page or slide
Related : Our post on what is a marketing plan and how to write and design one for maximum effectiveness.
6. Competitor Analysis Templates
Get the attention of marketers with a competitor analysis report. The best reports show exactly what a company must face off (and beat) to be successful.
A competitor analysis report usually has the following sections:
- Product summary
- Competitor strengths and weaknesses
- Competitor strategies and objectives
- Outlook: is the market growing? Flat? Splintering into niche segments?
The following competitor analysis template neatly organizes these categories into compact sections and highlights important stats. Stakeholders can quickly compare them with their own company’s numbers and get an immediate sense of how they measure up.

Using a pre-designed competitor analysis template is also a great idea for consultants who want to set themselves apart from big consulting firms or boutiques. Visualizing data is a way to set yourself apart as numbers-focused, unique and innovative, as in this business report example.

A few competitor analysis report best practices:
- If you’re listing all competitors, add those entering the market in the next year as well as indirect competitors who sell to the same customers as yours.
- Find customer satisfaction surveys for competitors (usually carried out by trade press) and include their findings.
- Talk to the sales department to get a sense of the competitor’s customers.
- Do informal research on the competitor’s strengths and weaknesses. Talk to journalists who cover this specific industry. Don’t just rely on online information.
Related : Our post on how to create a competitor analysis report (with templates).
7. Case Study Templates
One of the business report examples on our list is the business case study. Though not a report exactly, a case study analyzes a particular aspect of a company or a situation it faced. A consultant may need to write one as part of a corporate training program they’re developing.
Case studies usually focus on one of these situations:
- Startup or early-stage venture
- Merger, joint venture, acquisition
- Market entry or expansion
- New project or product
- Pricing optimization
- Profitability
- Industry landscape
- Growth strategy
What makes case studies unique is how they tell a story. They include background information on the company, a protagonist or key players, the situation and outcomes.
The below case study template has plenty of space for this narrative while using icons and numbers to highlight key details.

Make sure to include a conclusion that contains your key findings. Why did the protagonist make the decisions she made? What were the outcomes? What can we learn from this? Circle back to the key question the case study raises and answer it.
Business case study template
Business case studies are usually teaching tools to show how real companies approached a particular scenario or problem. The case study usually reflects a business theory and demonstrates its real-life application.
For example, the following business case study template shows how a crafts retailer uses earned media to drive engagement-heavy traffic.

This is another version of the above case study. Notice the changes in branding in this business report example that sets it apart from the previous template.

Marketing case study template
Case studies are a powerful form of marketing as they show a potential customer how existing customers are already using your product or service to meet their goals.
For example, this social media marketing case study illustrates how Toy Crates used content marketing to radically increase their sales:

A few case study best practices:
- Outline any constraints and challenges the protagonist of the case study faced that affected her decision (such as a tight deadline).
- Attach supporting documentation, such as financial statements.
- Include an original title, such as “Design Thinking and Innovation at Apple.” The title should mention the company and the subject of the case study.
Related : Our post on how to write and design a case study .
8. Growth Strategy Templates
Setting goals for your business might seem easy in theory… but setting ambitious yet realistic goals can actually be quite challenging.
At Venngage, we follow these 5 steps to set our goals:
- Identifying and set high-level goals.
- Understand which inputs and outputs impact those goals.
- Run experiments to impact those inputs.
- Validate those experiments.
- Foster accountability for the results within the team.
For a more in-depth look at this process read our growth strategy guide .
For example, if you’re a SaaS company, your high-level goals would probably be a specific number for revenue, a number of daily active users or employee count, like in the business report template below:

Once you’ve identified your high-level goals, the next step is to identify your OKRs (Objective Key Results), the metrics that impact your goals. Generally, you will probably want to break down your OKRs by channel.
So, if one of your goals is to hit a certain number of daily active users, your OKRs could be organized by:
- Acquisition OKRs, like organic traffic and paid traffic
- Conversion OKRs, like conversion rate
- Retention OKRs, like retention rate
Once you’ve identified your OKRs, you can come up with experiments to run that will impact those OKRs.
At Venngage, we use a weekly sprint to plan, execute and analyze our growth experiments. But I know other companies that use longer sprints, like two-week or month-long sprints.
Before you run an experiment, you should validate that it’s an experiment worth running. You can do that by identifying which goal it impacts, what resources the experiment will require, and how much effort you anticipate it will take to run the experiment.
This is the exact marketing sprint validator template that our marketing team uses when we schedule growth experiments:
After you’ve run a growth experiment, it’s extremely important to track your results.
At the end of every sprint, take a good chunk of time to analyze your experiments to see what learnings you can take from them. Then, classify an experiment as a “Winner” or “Loser” based on whether or not the results lined up with your hypothesis.
You can use your results from the sprint that just ended to inform your experiments in the upcoming print.
Here’s an example of a sprint release and results template that you could use. Note how each experiment is owned by a team member to foster accountability for the process and results:

A few growth strategy report best practices:
- Divide your growth strategy reports into color-coded columns based on goals, OKRs, or stages in a sprint
- Use icons like checkmarks and x’s to identify winning experiments and losing experiments
- Include brief descriptions on each template, to make it easy to understand
- Attribute each growth experiment to a team member, to foster accountability for the process and results
- Use your company colors, fonts and logo to maintain consistent branding across all of your communications
Related : Our complete guide to developing a growth strategy checklist.

9. Market Research Report Templates
Even after you’ve launched your business, it’s a good idea to do regular market research. You can use your research to plan and refine your marketing strategies, to identify new prospective customers and product plan.
Market research generally involves gathering information about the needs, problems and wants of your customers. This research can help you come up with your customer personas and specific problems you want to solve with your product or service.
You can conduct market research in two ways:
- Qualitative research (calls, focus groups)
- Survey research
For example, many consultants struggle to get buy-in from various stakeholders. The boss may be constantly changing the scope of the project based on a whim, such as the latest article he’s scoured from the internet! Employees may be set in their ways and resistant to incorporate consultants into their workflow.
One way to get clients on board and build trust is to provide stats and research that support your recommendations.
Here’s a market research business report example that lays out the industry landscape and gives clear guidance on the way forward, all backed up by facts.

This cheerful, icon-heavy market research report should help energize reluctant stakeholders. Packaging new (and sometimes daunting) information in fresh ways can help break through resistance.

You may also want to look at competitor statistics and industry trends. This template includes a competitor case study, including website analytics, and a SWOT analysis :

When it comes to creating your market research report, you may want to do an in-depth overview of all of your market research. Or you may want to focus on one area of your research, such as your survey results.
Survey Report Template
This survey report template helps visualize your findings; the pictogram and chart make the findings easy to understand.
The one-slide market research report identifies the demographics of the survey participants. The report categorizes participants by their jobs, locations, and the topics that they find most engaging. Note how each persona is visualized using an icon:

This business report example highlights how you can give your team and stakeholders a quick overview of your main market and what topics they’re interested in.
One of the purposes of a market research report is to present any conclusions that you came to after analyzing the data.
These could be conclusions about who your target customers are, areas where you can expand your business, and customer needs that aren’t currently being met. The below business report example visualizes this data and also provides space to draw your own conclusions.

Here’s an example of a market research report template that emphasizes key findings in the larger text before providing supporting data:
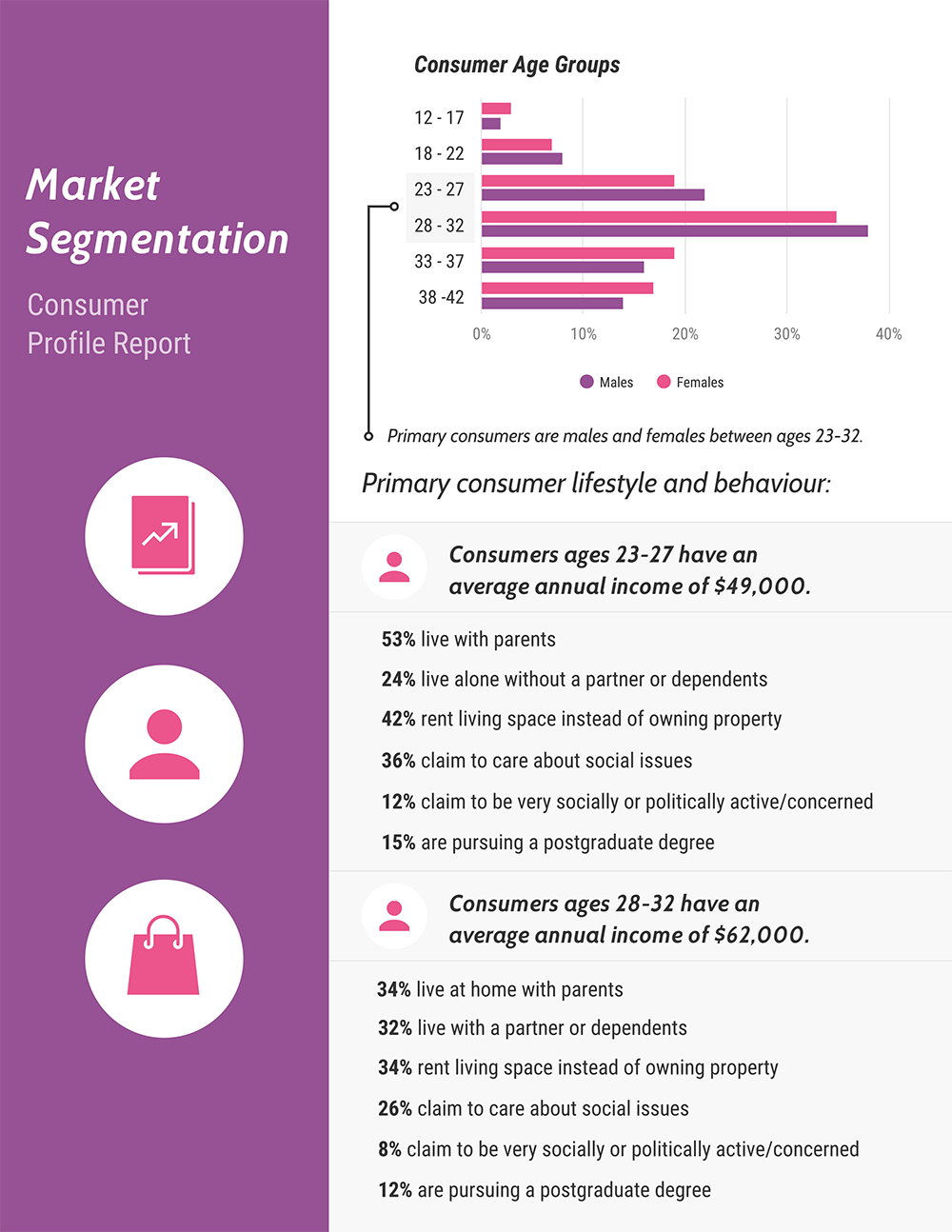
A few market research report best practices:
- Use icons to illustrate your customer personas
- Use charts and graphs to compare demographic information like customer age, gender, location, and occupations
- Include the main conclusions you came from after analyzing your data
- If your market research report is long enough, include a table of contents
- Include a brief summary of your data collection methods , including the sample size
10. White Paper Templates
White papers are great tools to educate and persuade stakeholders. Consultants can also use them to improve their reputation vis-a-vis big consulting firms and boutique firms or use them as lead magnets in Facebook ads etc.
As always, a polished design is much more likely to engage senior leaders or potential clients.
A business report template or consulting report template is the fastest way to produce something that’s both attractive and easy to understand.
The below consulting report example has a full page dedicated to visuals. It’s the perfect way to break up the text and let it breathe. It also reinforces the information.

Browse our library of thousands of professional, free stock photos to swap in images that suit your topic best. Or upload your own.
Our editor makes it simple to adapt any of our business and consulting report templates to your needs. Change the text, fonts, photos, icons, colors, anything you want.
The next business report template is perfect for marketers and marketing consultants. It has an inviting and fun (but still professional) cover page that quickly communicates the content marketing process using icons.

Venngage has an extensive library of thousands of custom, modern and diverse icons you can swap into the above consulting report example. For instance, you could add the Twitter or Facebook logo or a “thumbs up” icon.
Then, click on the template’s chart or graph (pages four and five) to add your own data.
Struggling with organizing information in your reports? It’s important for consultants and marketers to find a way to communicate key takeaways, and not overwhelm your reader with data.
The below consulting report template uses filled text boxes and icons on the third page to highlight top findings.

Different-colored headers also help create a hierarchy of information and add more variety to the design.
A few white paper best practices:
- Create an eye-catching white paper cover page using a background in bold color, photos or icons.
- Add a key takeaways section, with a header and bullet points.
- Visualize data using charts and pictograms in order to highlight key data.
- Incorporate your branding into your white paper template (brand colors and logo).
Related : Our blog post with 20+ white paper examples for even more templates and design tips.
11. Project Plan Templates
A project plan is the best way to keep a project on track.
But, showcasing the steps towards completing a project and showing how each step is actionable and measurable can be tough.
This is especially difficult if you’re a consultant and you don’t have company templates to rely on.
The below project plan template is a simple way to visualize what needs to happen, and when.

The above highly organized project plan template uses bar graphs, icons and color-coding to present information in an accessible way. Once you enter the editor, click on the bar graph to customize the schedule.
The project timeline below also uses icons and color-coding to organize information, though in a slightly different way.
Projects suffer when there’s confusion about deadlines and what’s required at each step. This timeline from a business report sample makes it crystal clear what tasks belong to what step and how long each step should take.

A timeline is a perfect way for your team or client to refer back to the project schedule without having to read through tons of text.
You can also revise your timeline as the project progresses to reflect changes in the schedule.
The below consulting report template has a more traditional format for a project plan. Still, like the timelines, this business report sample relies heavily on visuals to create an easily scannable and understandable project overview.

Scope creep is the enemy of any project’s success (and the bane of many consultant’s existence). That’s why it’s so important to define the project from the very beginning. The consulting report template above has a section to do just that.
Of course, projects change and evolve. The project report below will help you raise any issues as soon as they happen and present solutions. That way, stakeholders can make a decision before the project schedule is seriously derailed.

Check out our blog post with 15+ project plan templates for even more examples and design tips.
A few project plan best practices:
- Plot your project schedule visually using a timeline.
- Use color to categorize tasks and milestones.
- Use icons to illustrate steps in a process.
- Insert charts to track the duration of each phase of a project.
- Pick a flexible template that you can update as the project progresses and things change.
Related : Our post on the four phases of the project life cycle .
12. Business Proposal Templates
A business proposal is a document that presents your product or service as the solution to a client’s problem. The goal of a business proposal is to persuade a prospective client to buy your product or service. These proposals can be either solicited or unsolicited.
The contents of a business proposal report will vary depending on the problem.
Typically, a business proposal will include these sections:
- Information about your company (mission, qualifications, competitive edge)
- A detailed description of your client’s problem
- The cost of your product/service
- The methodology of how you propose to solve the client’s problem
- A timeline of your approach to solving the problem
A few business report examples and design tips:
Create an engaging title page for your business proposal. Think of it as the cover of a book or a movie poster. This will be your prospective client’s first impression of your business.
Use a design that tells a story about your company’s mission and the people you serve. For example, the cover for this business proposal template shows a happy team working together:

Meanwhile, this simple business proposal example uses icons to illustrate what the company does. The motif is carried throughout the rest of the proposal design:

Use visuals to highlight the emotion behind the problem
Businesses are made up of people, and people are emotionally charged. When identifying the problem, use imagery to highlight the frustration, confusion, or dissatisfaction behind the problem. This will show empathy towards the people you’re proposing your solution to.
This business report sample page from a business proposal contrasts one image to illustrate the “problem” with a more cheerful image for the “solution”:

This marketing business proposal uses a variety of visuals like icons, bold typography and photos to tell a story:

Related : Our post on consulting proposal templates or our guide to creating a business proposal .
How to create a business report in 6 steps?
Creating a business report can seem daunting, especially if you’ve never done it before. don’t let the word “business” intimidate you – these steps can be used for writing a report in any field!
Step 1: Define the purpose and scope of your report
Know the purpose of your report. Are you aiming to share the results of a project? Analyze performance? Recommend specific actions? Whatever the goal, keep it in mind as you go through the process. Also, consider the scope of your report. Decide what information you’ll be including, as well as what you can leave out.
Example: Let’s say your boss wants a report on your team’s sales performance during the last quarter. Your purpose might be to analyze the numbers and identify trends, areas for improvement, or opportunities for growth.
Step 2: Gather relevant data and information
Now that you know what you’re aiming for, it’s time to gather the information you’ll need. This might involve pulling data from internal systems, interviewing colleagues, or even conducting your research. Remember, the quality of your report depends on the accuracy and relevance of the information you provide, so double-check your sources and make sure you’ve got everything you need.
Example: For our sales performance report, you’ll need to collect data on product sales, individual and team performance, and any factors that may have influenced sales during the quarter.
Step 3: Organize your content
Next up is organizing all that information into a logical and easy-to-follow structure. This will depend on the specific requirements of your report, but some common components are an introduction, executive summary, main body, conclusion, and recommendations. A clear and logical structure helps readers easily understand and follow your report.
Example: In a sales performance report, you might start with an executive summary highlighting sales growth (or declines), outline individual team member’s performance, and then delve into a more detailed analysis of factors and trends.
Step 4: Write the report
When writing your report, start by developing a clear and concise writing style, avoiding jargon and buzzwords. Keep your audience in mind – make sure your report is easily digestible for your intended readers.
Example: When writing about sales performance, share facts and figures in simple terms that everyone can understand. Instead of saying, “Our sales team demonstrated a 12.3% compound annual growth rate,” say, “Our sales team increased their sales by 12.3% each year.”
Step 5: Add visual aids
To make your report more engaging and easier to understand, consider adding visual aids like graphs, charts, or images. These can help break up large blocks of text and highlight key findings or trends.
Example: For your sales performance report, you might create a bar chart showing sales growth over time or a pie chart displaying individual team members’ contributions.
Step 6: Review and refine
Last but not least, review your report. Does it achieve the purpose you set at the beginning? Are there any gaps in the information? Are there areas that could be clearer or more concise? Address any issues you find and refine your report until it meets your goals and is easy to understand for your target audience.
Example: In your sales performance report, if you find that you haven’t adequately explored the impact of a new product launch on sales, go back and add that analysis to provide a more comprehensive view.
What are the types of business reports?
Different types of business reports cater to various purposes, including monitoring performance, making decisions, and more, offering a range of options beyond standard reports.
1. Informational reports
The primary purpose of informational reports is, well, to inform. These reports provide all the nitty-gritty details of specific aspects of your business without any conclusions or opinions.
Examples include daily sales reports, inventory levels, or even project updates. This is the essential “just the facts, ma’am” type of report you need to stay in the loop.
2. Analytical reports
Analytical reports give you a more in-depth look at the data to help you make decisions. These reports come with all the bells and whistles – charts, graphs, and recommendations based on thorough analysis. Analytical reports are what you whip out when you need to decide whether to invest in a new project, evaluate your marketing efforts, or diagnose challenges within the company. The goal of such a report is to help you make smarter decisions for the growth and development of your business.
3. Summaries & reviews:
If you’re a little short on time and need a quick overview of your business’s performance, summary reports are your best bet. These reports condense the crucial details from other reports at regular intervals (monthly, quarterly, or annually) and present them in a digestible format.
4. Research reports
As the name suggests, these in-depth reports dig into specific topics or issues relevant to your business. Research reports are great when exploring new markets, considering new product development, or requiring a detailed evaluation of business practices. These reports act as guides for making major decisions that could significantly impact your company’s direction and success.
5. Progress reports
Let’s say you’ve got a fantastic project idea underway. You’ll need to keep track of every stage of it to ensure it’s smooth sailing ahead. Enter progress reports. They track the achievements, setbacks, and future plans of ongoing projects. These are essential for keeping everyone – from employees to investors – in the loop.
Business report template FAQs
1. what are the best practices for creating a business report.
You could open up Google doc, record your metrics and make a few points of analysis, send it to your team and call it a day. But is that the most effective way to report on your findings?
Many people may not even read those types of reports. Not to mention, a plain old report probably won’t impress stakeholders.
It’s important to brand yourself (and stand out from your competition). And then there’s the ever-important need to create buy-in from stakeholders and convince them of your recommendations.
That’s why it pays to make your reports as engaging as possible. That means visualizing data , processes , and concepts to make them easier to understand and more fun to look at, as you’ve seen from the business report examples in this post.

You can do that easily by getting started with a business report template or consulting report template .
There are two big reasons why it’s a good idea to create a highly visual business report:
- You will be able to organize, analyze and summarize your findings .
- You will be able to communicate your reports more effectively with your team, stakeholders and customers.
For example, the below business report template shows four different ways you can visualize information. It’s much more captivating and easily digested than a block of text.
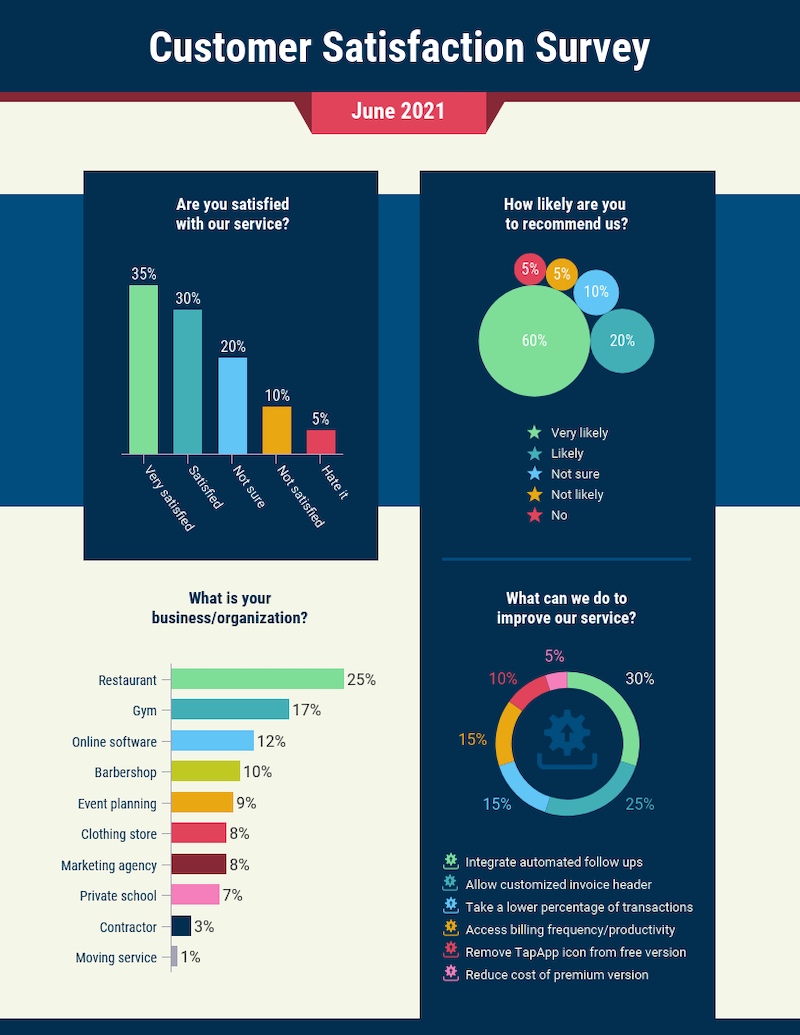
And don’t worry about how time-consuming designing a report might be. If you start with a solid business report template, you can repurpose that template over and over again.
Use the template as a framework, then customize your information and design to fit your specific needs. Then, use a chart tool to convert cumbersome data into clear visuals.
Just like in the above business report sample, you’ll have a succinct, powerful (and polished) report that stakeholders can understand at a glance.
2. How do you design a business report template?
Incorporate your branding into the design
Part of building a strong brand is using consistent branding across all of your content, both internal and public-facing. You can incorporate your branding into your business report design by importing your logo and using your brand colors and fonts.
Our My Brand Kit feature automatically imports company logos and fonts from any website. You can then apply them to your design with one click.
Stick to only one topic per page or slide
When creating a report, it’s easy to try and cram a bunch of text onto one page. But then you run the risk of creating an impenetrable wall of text.
Instead, focus on only one topic per page or slide. If you find that even that makes your page look too cramped, then try breaking up your information into two pages or looking for ways to better summarize your information .
Put functionality first
When you’re designing a business report, you should look for opportunities to visualize data and creatively present information. That being said, the primary goal of your business report should still be to communicate information clearly.
Use design elements such as icons or fonts in different sizes, weights and colors to highlight, emphasize and categorize information, not obscure it. If a page you’re working on looks cluttered or confusing, take another stab at it.
Remember that functionality comes first, and that includes using the right visuals for your information.
3. What is the best business report maker?
You can make a business report online using a number of tools. As we have mentioned, a great business report is visually appealing, includes icons, images, clear fonts, easy-to-understand charts and graphs, as well as being branded.
Venngage is the one-stop design solution when it comes to creating reports. The business report examples in this article highlight how easy it is to design a variety of reports for every type of organization and activity. Make design simple by using Venngage.
More business communication guides:
- The Ultimate Guide to Consulting Proposals (2024)
- 20+ White Paper Examples [Design Guide + White Paper Templates]
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
How To Present Your Market Research Results And Reports In An Efficient Way

Table of Contents
1) What Is A Market Research Report?
2) Market Research Reports Examples
3) Why Do You Need Market Research Reports
4) How To Make A Market Research Report?
5) Types Of Market Research Reports
6) Challenges & Mistakes Market Research Reports
Market research analyses are the go-to solution for many professionals, and for good reason: they save time, offer fresh insights, and provide clarity on your business. In turn, market research reports will help you to refine and polish your strategy. Plus, a well-crafted report will give your work more credibility while adding weight to any marketing recommendations you offer a client or executive.
But, while this is the case, today’s business world still lacks a way to present market-based research results efficiently. The static, antiquated nature of PowerPoint makes it a bad choice for presenting research discoveries, yet it is still widely used to present results.
Fortunately, things are moving in the right direction. There are online data visualization tools that make it easy and fast to build powerful market research dashboards. They come in handy to manage the outcomes, but also the most important aspect of any analysis: the presentation of said outcomes, without which it becomes hard to make accurate, sound decisions.
Here, we consider the benefits of conducting research analyses while looking at how to write and present market research reports, exploring their value, and, ultimately, getting the very most from your research results by using professional market research software .
Let’s get started.
What Is a Market Research Report?
A market research report is an online reporting tool used to analyze the public perception or viability of a company, product, or service. These reports contain valuable and digestible information like customer survey responses and social, economic, and geographical insights.
On a typical market research results example, you can interact with valuable trends and gain insight into consumer behavior and visualizations that will empower you to conduct effective competitor analysis. Rather than adding streams of tenuous data to a static spreadsheet, a full market research report template brings the outcomes of market-driven research to life, giving users a data analysis tool to create actionable strategies from a range of consumer-driven insights.
With digital market analysis reports, you can make your business more intelligent more efficient, and, ultimately, meet the needs of your target audience head-on. This, in turn, will accelerate your commercial success significantly.
Your Chance: Want to test a market research reporting software? Explore our 14-day free trial & benefit from interactive research reports!
How To Present Your Results: 4 Essential Market Research Report Templates
When it comes to sharing rafts of invaluable information, research dashboards are invaluable.
Any market analysis report example worth its salt will allow everyone to get a firm grip on their results and discoveries on a single page with ease. These dynamic online dashboards also boast interactive features that empower the user to drill down deep into specific pockets of information while changing demographic parameters, including gender, age, and region, filtering the results swiftly to focus on the most relevant insights for the task at hand.
These four market research report examples are different but equally essential and cover key elements required for market survey report success. You can also modify each and use it as a client dashboard .
While there are numerous types of dashboards that you can choose from to adjust and optimize your results, we have selected the top 3 that will tell you more about the story behind them. Let’s take a closer look.
1. Market Research Report: Brand Analysis
Our first example shares the results of a brand study. To do so, a survey has been performed on a sample of 1333 people, information that we can see in detail on the left side of the board, summarizing the gender, age groups, and geolocation.
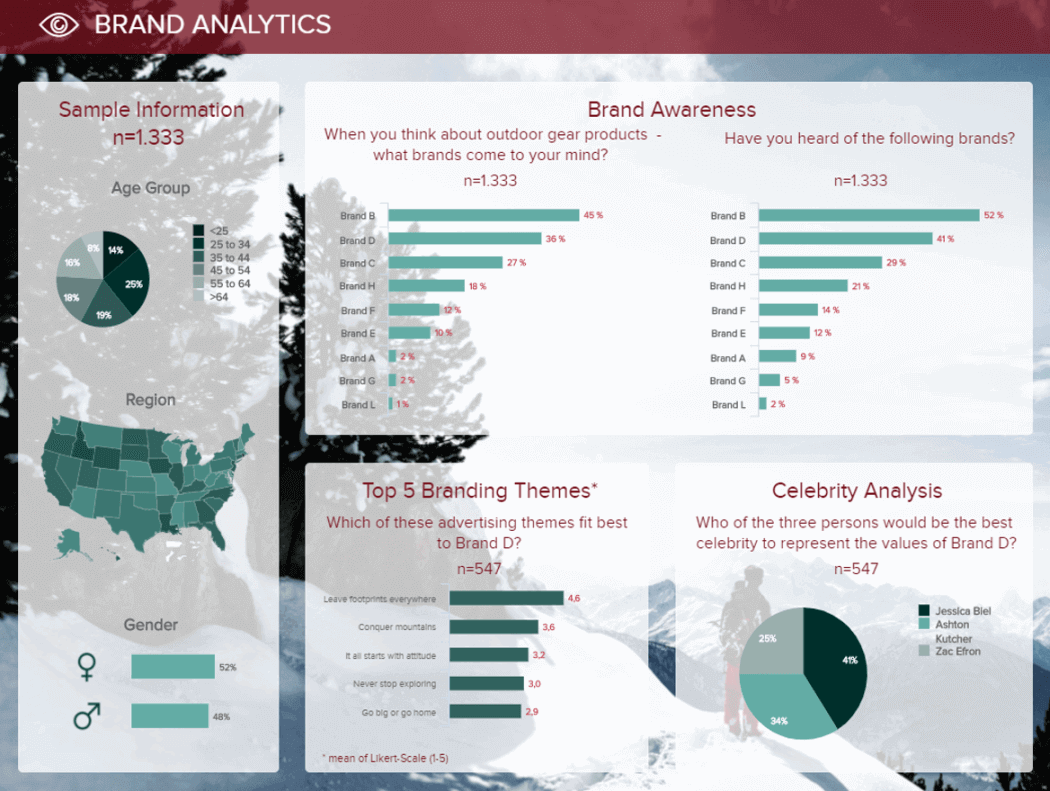
**click to enlarge**
At the dashboard's center, we can see the market-driven research discoveries concerning first brand awareness with and without help, as well as themes and celebrity suggestions, to know which image the audience associates with the brand.
Such dashboards are extremely convenient to share the most important information in a snapshot. Besides being interactive (but it cannot be seen on an image), it is even easier to filter the results according to certain criteria without producing dozens of PowerPoint slides. For instance, I could easily filter the report by choosing only the female answers, only the people aged between 25 and 34, or only the 25-34 males if that is my target audience.
Primary KPIs:
a) Unaided Brand Awareness
The first market research KPI in this most powerful report example comes in the form of unaided brand awareness. Presented in a logical line-style chart, this particular market study report sample KPI is invaluable, as it will give you a clear-cut insight into how people affiliate your brand within their niche.
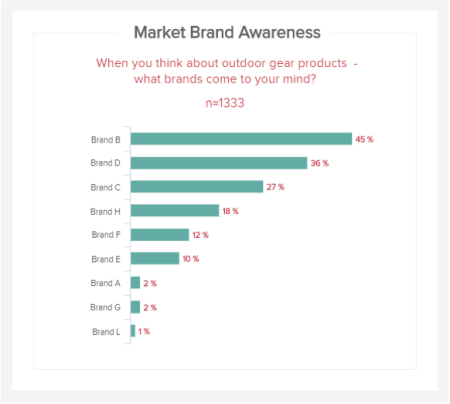
As you can see from our example, based on a specific survey question, you can see how your brand stacks up against your competitors regarding awareness. Based on these outcomes, you can formulate strategies to help you stand out more in your sector and, ultimately, expand your audience.
b) Aided Brand Awareness
This market survey report sample KPI focuses on aided brand awareness. A visualization that offers a great deal of insight into which brands come to mind in certain niches or categories, here, you will find out which campaigns and messaging your target consumers are paying attention to and engaging with.

By gaining access to this level of insight, you can conduct effective competitor research and gain valuable inspiration for your products, promotional campaigns, and marketing messages.
c) Brand image
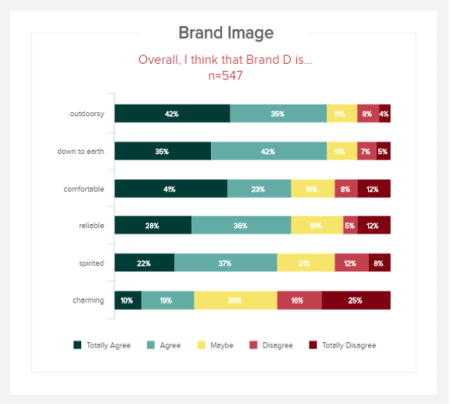
When it comes to research reporting, understanding how others perceive your brand is one of the most golden pieces of information you could acquire. If you know how people feel about your brand image, you can take informed and very specific actions that will enhance the way people view and interact with your business.
By asking a focused question, this visual of KPIs will give you a definitive idea of whether respondents agree, disagree, or are undecided on particular descriptions or perceptions related to your brand image. If you’re looking to present yourself and your message in a certain way (reliable, charming, spirited, etc.), you can see how you stack up against the competition and find out if you need to tweak your imagery or tone of voice - invaluable information for any modern business.
d) Celebrity analysis
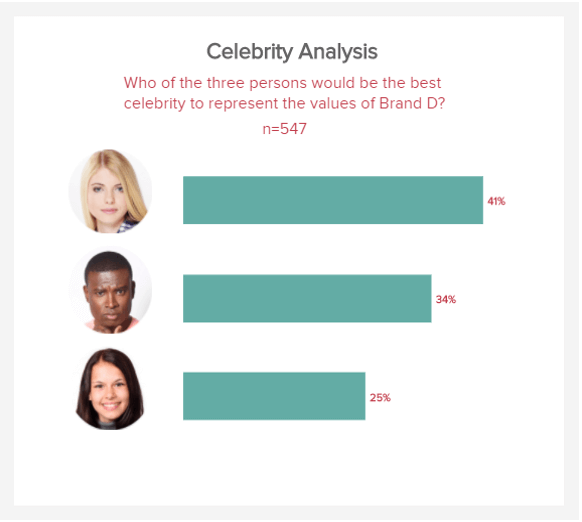
This indicator is a powerful part of our research KPI dashboard on top, as it will give you a direct insight into the celebrities, influencers, or public figures that your most valued consumers consider when thinking about (or interacting with) your brand.
Displayed in a digestible bar chart-style format, this useful metric will not only give you a solid idea of how your brand messaging is perceived by consumers (depending on the type of celebrity they associate with your brand) but also guide you on which celebrities or influencers you should contact.
By working with the right influencers in your niche, you will boost the impact and reach of your marketing campaigns significantly, improving your commercial awareness in the process. And this is the KPI that will make it happen.
2. Market Research Results On Customer Satisfaction
Here, we have some of the most important data a company should care about: their already-existing customers and their perception of their relationship with the brand. It is crucial when we know that it is five times more expensive to acquire a new consumer than to retain one.
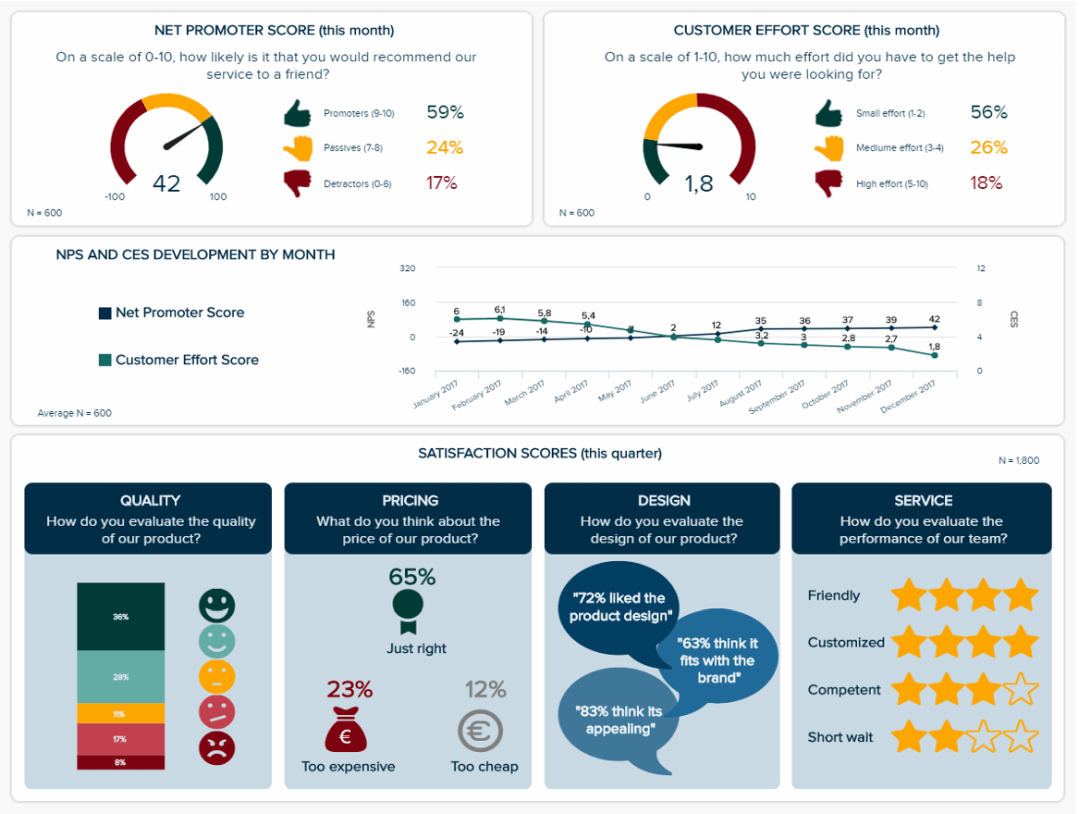
This is why tracking metrics like the customer effort score or the net promoter score (how likely consumers are to recommend your products and services) is essential, especially over time. You need to improve these scores to have happy customers who will always have a much bigger impact on their friends and relatives than any of your amazing ad campaigns. Looking at other satisfaction indicators like the quality, pricing, and design, or the service they received is also a best practice: you want a global view of your performance regarding customer satisfaction metrics .
Such research results reports are a great tool for managers who do not have much time and hence need to use them effectively. Thanks to these dashboards, they can control data for long-running projects anytime.
Primary KPIs :
a) Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Another pivotal part of any informative research presentation is your NPS score, which will tell you how likely a customer is to recommend your brand to their peers.
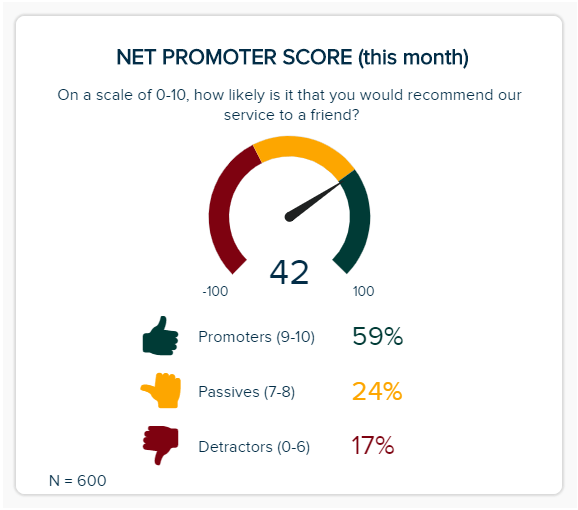
Centered on overall customer satisfaction, your NPS Score can cover the functions and output of many departments, including marketing, sales, and customer service, but also serve as a building block for a call center dashboard . When you’re considering how to present your research effectively, this balanced KPI offers a masterclass. It’s logical, it has a cohesive color scheme, and it offers access to vital information at a swift glance. With an NPS Score, customers are split into three categories: promoters (those scoring your service 9 or 10), passives (those scoring your service 7 or 8), and detractors (those scoring your service 0 to 6). The aim of the game is to gain more promoters. By gaining an accurate snapshot of your NPS Score, you can create intelligent strategies that will boost your results over time.
b) Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
The next in our examples of market research reports KPIs comes in the form of the CSAT. The vast majority of consumers that have a bad experience will not return. Honing in on your CSAT is essential if you want to keep your audience happy and encourage long-term consumer loyalty.
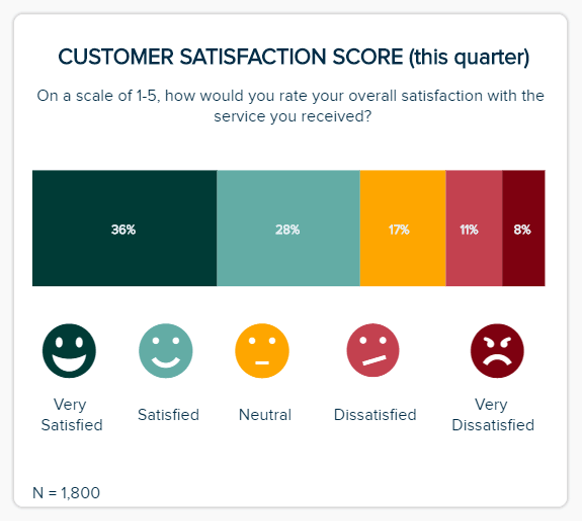
This magnificent, full report KPI will show how satisfied customers are with specific elements of your products or services. Getting to grips with these scores will allow you to pinpoint very specific issues while capitalizing on your existing strengths. As a result, you can take measures to improve your CSAT score while sharing positive testimonials on your social media platforms and website to build trust.
c) Customer Effort Score (CES)
When it comes to presenting research findings, keeping track of your CES Score is essential. The CES Score KPI will give you instant access to information on how easy or difficult your audience can interact with or discover your company based on a simple scale of one to ten.
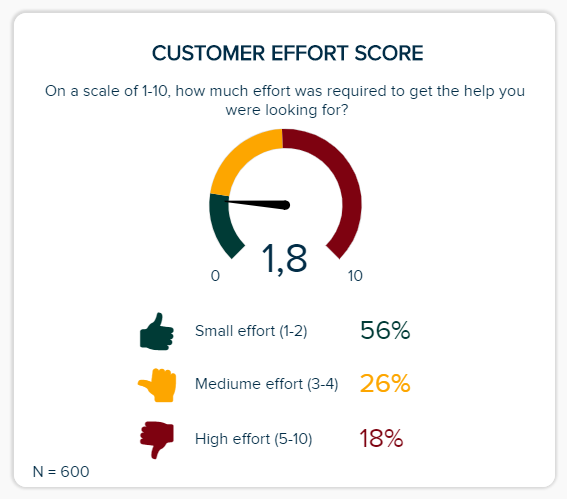
By getting a clear-cut gauge of how your customers find engagement with your brand, you can iron out any weaknesses in your user experience (UX) offerings while spotting any friction, bottlenecks, or misleading messaging. In doing so, you can boost your CES score, satisfy your audience, and boost your bottom line.
3. Market Research Results On Product Innovation
This final market-driven research example report focuses on the product itself and its innovation. It is a useful report for future product development and market potential, as well as pricing decisions.
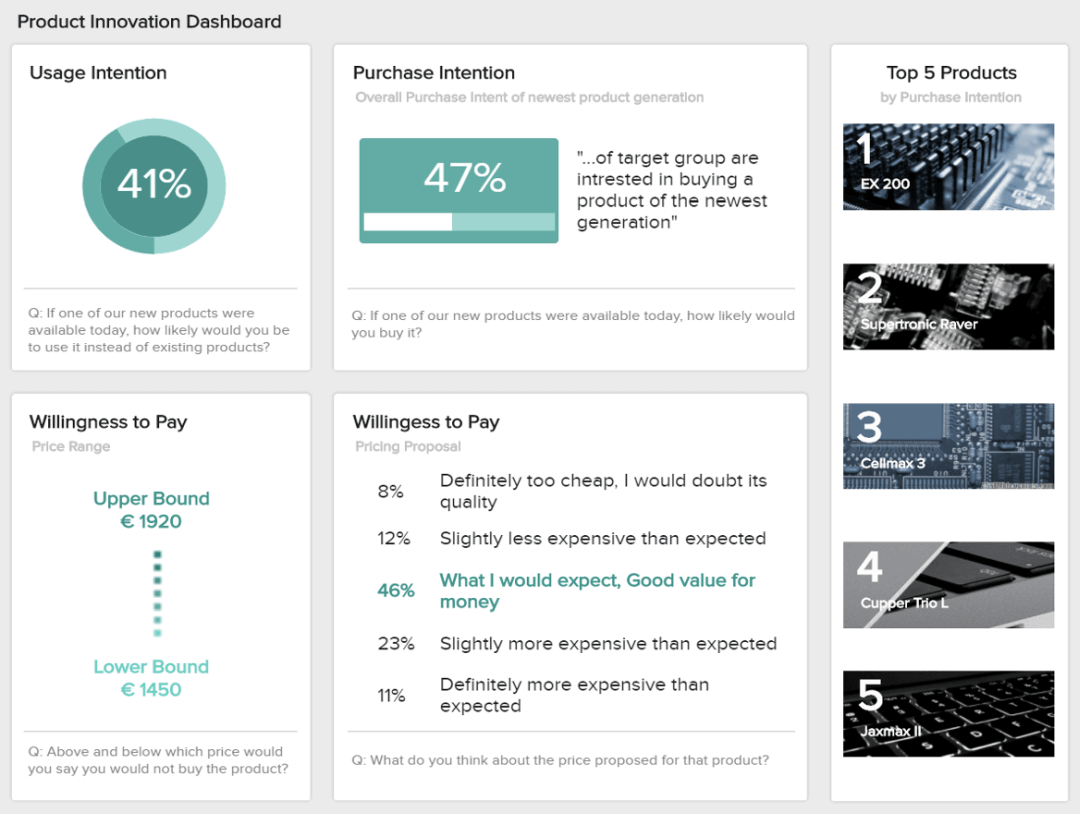
Using the same sample of surveyed people as for the first market-focused analytical report , they answer questions about their potential usage and purchase of the said product. It is good primary feedback on how the market would receive the new product you would launch. Then comes the willingness to pay, which helps set a price range that will not be too cheap to be trusted nor too expensive for what it is. That will be the main information for your pricing strategy.
a) Usage Intention
The first of our product innovation KPI-based examples comes in the form of usage intention. When you’re considering how to write a market research report, including metrics centered on consumer intent is critical.
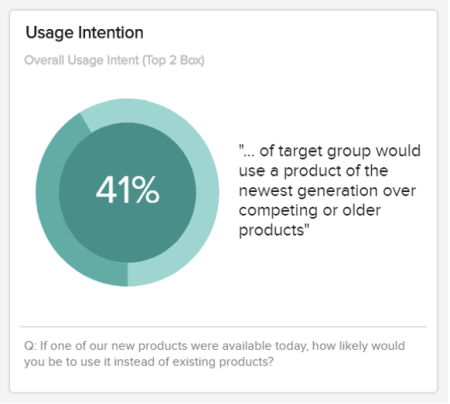
This simple yet effective visualization will allow you to understand not only how users see your product but also whether they prefer previous models or competitor versions . While you shouldn’t base all of your product-based research on this KPI, it is very valuable, and you should use it to your advantage frequently.
b) Purchase Intention
Another aspect to consider when looking at how to present market research data is your audience’s willingness or motivation to purchase your product. Offering percentage-based information, this effective KPI provides a wealth of at-a-glance information to help you make accurate forecasts centered on your product and service offerings.
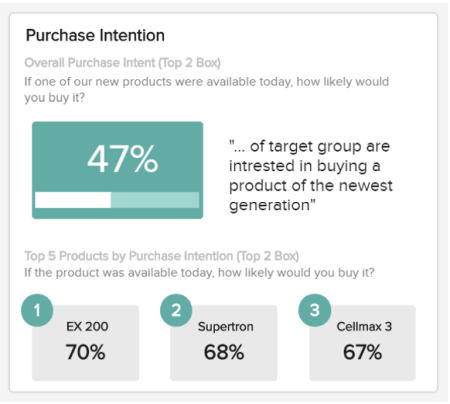
Analyzing this information regularly will give you the confidence and direction to develop strategies that will steer you to a more prosperous future, meeting the ever-changing needs of your audience on an ongoing basis.
c) Willingness To Pay (WPS)
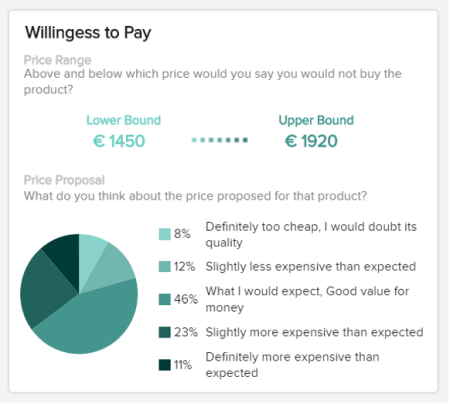
Our final market research example KPI is based on how willing customers are to pay for a particular service or product based on a specific set of parameters. This dynamic visualization, represented in an easy-to-follow pie chart, will allow you to realign the value of your product (USPs, functions, etc.) while setting price points that are most likely to result in conversions. This is a market research presentation template that every modern organization should use to its advantage.
4. Market Research Report On Customer Demographics
This particular example of market research report, generated with a modern dashboard creator , is a powerful tool, as it displays a cohesive mix of key demographic information in one intuitive space.
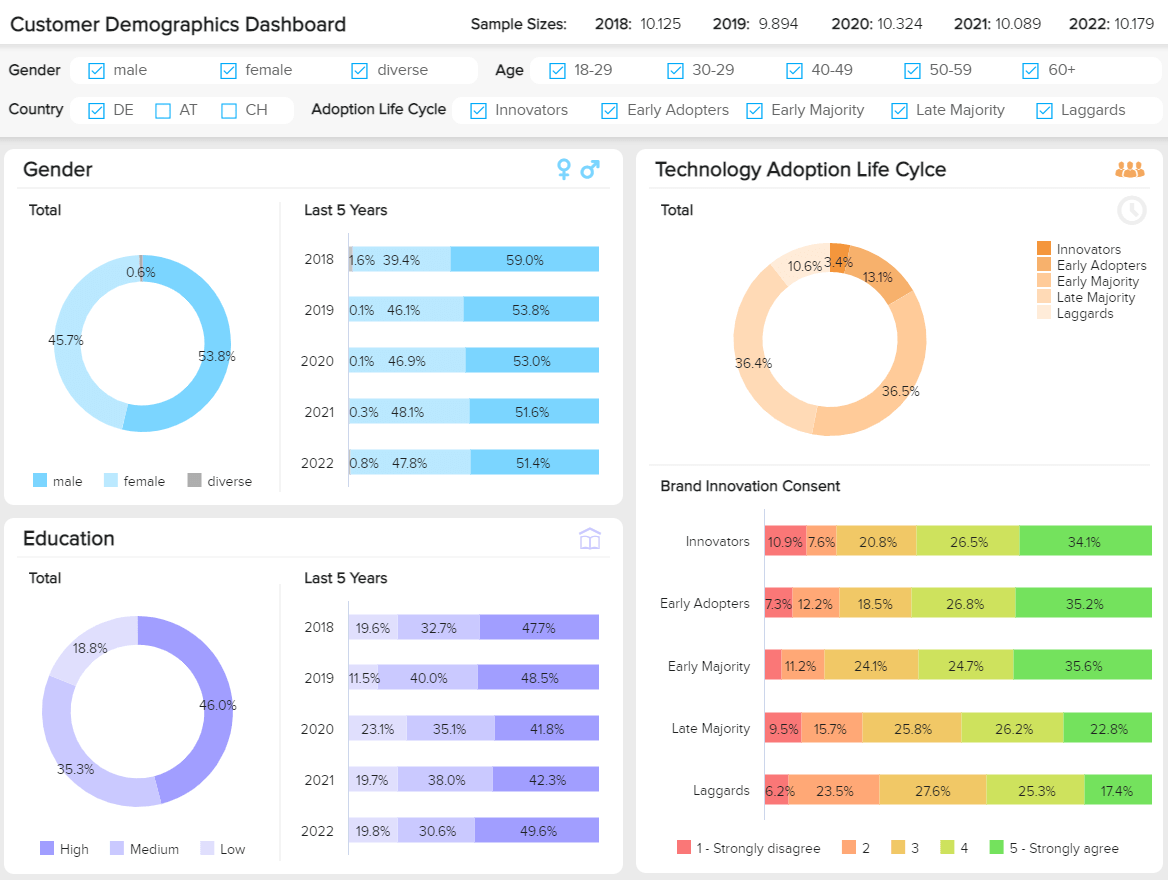
By breaking down these deep pockets of consumer-centric information, you can gain the power to develop more impactful customer communications while personalizing every aspect of your target audience’s journey across every channel or touchpoint. As a result, you can transform theoretical insights into actionable strategies that will result in significant commercial growth.
Every section of this responsive marketing research report works in unison to build a profile of your core audience in a way that will guide your company’s consumer-facing strategies with confidence. With in-depth visuals based on gender, education level, and tech adoption, you have everything you need to speak directly to your audience at your fingertips.
Let’s look at the key performance indicators (KPIs) of this invaluable market research report example in more detail.
a) Customer By Gender
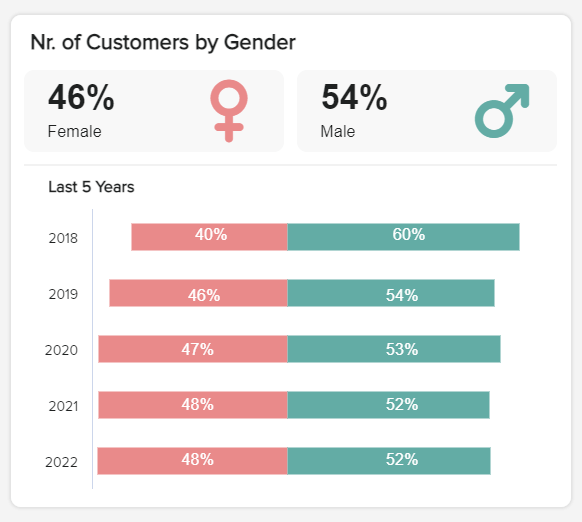
This KPI is highly visual and offers a clear-cut representation of your company’s gender share over time. By gaining access to this vital information, you can deliver a more personalized experience to specific audience segments while ensuring your messaging is fair, engaging, and inclusive.
b) Customers by education level
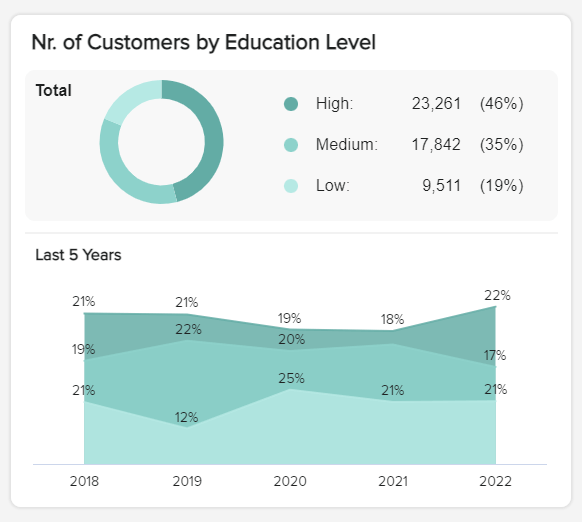
The next market analysis report template is a KPI that provides a logical breakdown of your customers’ level of education. By using this as a demographic marker, you can refine your products to suit the needs of your audience while crafting your content in a way that truly resonates with different customer groups.
c) Customers by technology adoption
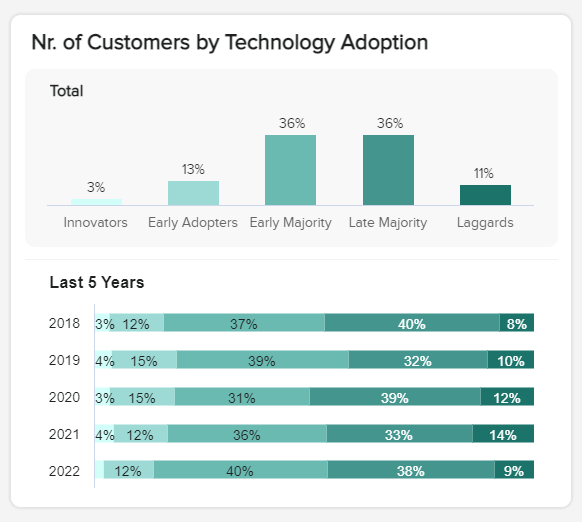
Particularly valuable if you’re a company that sells tech goods or services, this linear KPI will show you where your customers are in terms of technological know-how or usage. By getting to grips with this information over time, you can develop your products or services in a way that offers direct value to your consumers while making your launches or promotions as successful as possible.
d) Customer age groups
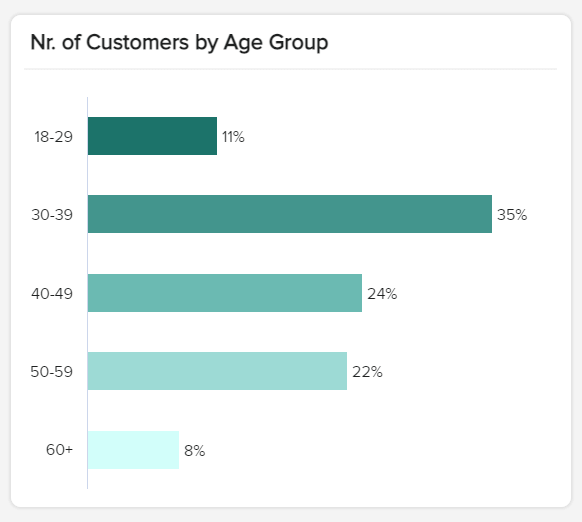
By understanding your customers’ age distribution in detail, you can gain a deep understanding of their preferences. And that’s exactly what this market research report sample KPI does. Presented in a bar chart format, this KPI will give you a full breakdown of your customers’ age ranges, allowing you to build detailed buyer personas and segment your audience effectively.
Why Do You Need Market Research Reports?
As the adage goes, “Look before you leap“ – which is exactly what a research report is here for. As the headlights of a car, they will show you the pitfalls and fast lanes on your road to success: likes and dislikes of a specific market segment in a certain geographical area, their expectations, and readiness. Among other things, a research report will let you:
- Get a holistic view of the market : learn more about the target market and understand the various factors involved in the buying decisions. A broader view of the market lets you benchmark other companies you do not focus on. This, in turn, will empower you to gather the industry data that counts most. This brings us to our next point.
- Curate industry information with momentum: Whether you’re looking to rebrand, improve on an existing service, or launch a new product, time is of the essence. By working with the best market research reports created with modern BI reporting tools , you can visualize your discoveries and data, formatting them in a way that not only unearths hidden insights but also tells a story - a narrative that will gain a deeper level of understanding into your niche or industry. The features and functionality of a market analysis report will help you grasp the information that is most valuable to your organization, pushing you ahead of the pack in the process.
- Validate internal research: Doing the internal analysis is one thing, but double-checking with a third party also greatly helps avoid getting blinded by your own data.
- Use actionable data and make informed decisions: Once you understand consumer behavior as well as the market, your competitors, and the issues that will affect the industry in the future, you are better armed to position your brand. Combining all of it with the quantitative data collected will allow you to more successful product development. To learn more about different methods, we suggest you read our guide on data analysis techniques .
- Strategic planning: When you want to map out big-picture organizational goals, launch a new product development, plan a geographic market expansion, or even a merger and acquisition – all of this strategic thinking needs solid foundations to fulfill the variety of challenges that come along.
- Consistency across the board: Collecting, presenting, and analyzing your results in a way that’s smarter, more interactive, and more cohesive will ensure your customer communications, marketing campaigns, user journey, and offerings meet your audience’s needs consistently across the board. The result? Faster growth, increased customer loyalty, and more profit.
- Better communication: The right market research analysis template (or templates) will empower everyone in the company with access to valuable information - the kind that is relevant and comprehensible. When everyone is moving to the beat of the same drum, they will collaborate more effectively and, ultimately, push the venture forward thanks to powerful online data analysis techniques.
- Centralization: Building on the last point, using a powerful market research report template in the form of a business intelligence dashboard will make presenting your findings to external stakeholders and clients far more effective, as you can showcase a wealth of metrics, information, insights, and invaluable feedback from one centralized, highly visual interactive screen.
- Brand reputation: In the digital age, brand reputation is everything. By making vital improvements in all of the key areas above, you will meet your customers’ needs head-on with consistency while finding innovative ways to stand out from your competitors. These are the key ingredients of long-term success.
How To Present Market Research Analysis Results?

Here we look at how you should present your research reports, considering the steps it takes to connect with the outcomes you need to succeed:
- Collect your data
As with any reporting process, you first and foremost need to collect the data you’ll use to conduct your studies. Businesses conduct research studies to analyze their brand awareness, identity, and influence in the market. For product development and pricing decisions, among many others. That said, there are many ways to collect information for a market research report. Among some of the most popular ones, we find:
- Surveys: Probably the most common way to collect research data, surveys can come in the form of open or closed questions that can be answered anonymously. They are the cheapest and fastest way to collect insights about your customers and business.
- Interviews : These are face-to-face discussions that allow the researcher to analyze responses as well as the body language of the interviewees. This method is often used to define buyer personas by analyzing the subject's budget, job title, lifestyle, wants, and needs, among other things.
- Focus groups : This method involves a group of people discussing a topic with a mediator. It is often used to evaluate a new product or new feature or to answer a specific question that the researcher might have.
- Observation-based research : In this type of research, the researcher or business sits back and watches customers interact with the product without any instructions or help. It allows us to identify pain points as well as strong features.
- Market segmentation : This study allows you to identify and analyze potential market segments to target. Businesses use it to expand into new markets and audiences.
These are just a few of the many ways in which you can gather your information. The important point is to keep the research objective as straightforward as possible. Supporting yourself with professional BI solutions to clean, manage, and present your insights is probably the smartest choice.
2. Hone in on your research:
When looking at how to source consumer research in a presentation, you should focus on two areas: primary and secondary research. Primary research comes from your internal data, monitoring existing organizational practices, the effectiveness of sales, and the tools used for communication, for instance. Primary research also assesses market competition by evaluating the company plans of the competitors. Secondary research focuses on existing data collected by a third party, information used to perform benchmarking and market analysis. Such metrics help in deciding which market segments are the ones the company should focus its efforts on or where the brand is standing in the minds of consumers. Before you start the reporting process, you should set your goals, segmenting your research into primary and secondary segments to get to grips with the kind of information you need to work with to achieve effective results.
3. Segment your customers:
To give your market research efforts more context, you should segment your customers into different groups according to the preferences outlined in the survey or feedback results or by examining behavioral or demographic data.
If you segment your customers, you can tailor your market research and analysis reports to display only the information, charts, or graphics that will provide actionable insights into their wants, needs, or industry-based pain points.
- Identify your stakeholders:
Once you’ve drilled down into your results and segmented your consumer groups, it’s important to consider the key stakeholders within the organization that will benefit from your information the most.
By looking at both internal and external stakeholders, you will give your results a path to effective presentation, gaining the tools to understand which areas of feedback or data are most valuable, as well as most redundant. As a consequence, you will ensure your results are concise and meet the exact information needs of every stakeholder involved in the process.
- Set your KPIs:
First, remember that your reports should be concise and accurate - straight to the point without omitting any essential information. Work to ensure your insights are clean and organized, with participants grouped into relevant categories (demographics, profession, industry, education, etc.). Once you’ve organized your research, set your goals, and cleaned your data, you should set your KPIs to ensure your report is populated with the right visualizations to get the job done. Explore our full library of interactive KPI examples for inspiration.
- Include competitor’s analysis
Whether you are doing product innovation research, customer demographics, pricing, or any other, including some level of insights about competitors in your reports is always recommended as it can help your business or client better understand where they stand in the market. That being said, competitor analysis is not as easy as picking a list of companies in the same industry and listing them. Your main competitor can be just a company's division in an entirely different industry. For example, Apple Music competes with Spotify even though Apple is a technology company. Therefore, it is important to carefully analyze competitors from a general but detailed level.
Providing this kind of information in your reports can also help you find areas that competitors are not exploiting or that are weaker and use them to your advantage to become a market leader.
- Produce your summary:
To complement your previous efforts, writing an executive summary of one or two pages that will explain the general idea of the report is advisable. Then come the usual body parts:
- An introduction providing background information, target audience, and objectives;
- The qualitative research describes the participants in the research and why they are relevant to the business;
- The survey research outlines the questions asked and answered;
- A summary of the insights and metrics used to draw the conclusions, the research methods chosen, and why;
- A presentation of the findings based on your research and an in-depth explanation of these conclusions.
- Use a mix of visualizations:
When presenting your results and discoveries, you should aim to use a balanced mix of text, graphs, charts, and interactive visualizations.
Using your summary as a guide, you should decide which type of visualization will present each specific piece of market research data most effectively (often, the easier to understand and more accessible, the better).
Doing so will allow you to create a story that will put your research information into a living, breathing context, providing a level of insight you need to transform industry, competitor, or consumer info or feedback into actionable strategies and initiatives.
- Be careful not to mislead
Expanding on the point above, using a mix of visuals can prove highly valuable in presenting your results in an engaging and understandable way. That being said, when not used correctly, graphs and charts can also become misleading. This is a popular practice in the media, news, and politics, where designers tweak the visuals to manipulate the masses into believing a certain conclusion. This is a very unethical practice that can also happen by mistake when you don’t pick the right chart or are not using it in the correct way. Therefore, it is important to outline the message you are trying to convey and pick the chart type that will best suit those needs.
Additionally, you should also be careful with the data you choose to display, as it can also become misleading. This can happen if you, for example, cherry-pick data, which means only showing insights that prove a conclusion instead of the bigger picture. Or confusing correlation with causation, which means assuming that because two events happened simultaneously, one caused the other.
Being aware of these practices is of utmost importance as objectivity is crucial when it comes to dealing with data analytics, especially if you are presenting results to clients. Our guides on misleading statistics and misleading data visualizations can help you learn more about this important topic.
- Use professional dashboards:
To optimize your market research discoveries, you must work with a dynamic business dashboard . Not only are modern dashboards presentable and customizable, but they will offer you past, predictive, and real-time insights that are accurate, interactive, and yield long-lasting results.
All market research reports companies or businesses gathering industry or consumer-based information will benefit from professional dashboards, as they offer a highly powerful means of presenting your data in a way everyone can understand. And when that happens, everyone wins.
Did you know? The interactive nature of modern dashboards like datapine also offers the ability to quickly filter specific pockets of information with ease, offering swift access to invaluable insights.
- Prioritize interactivity
The times when reports were static are long gone. Today, to extract the maximum value out of your research data, you need to be able to explore the information and answer any critical questions that arise during the presentation of results. To do so, modern reporting tools provide multiple interactivity features to help you bring your research results to life.
For instance, a drill-down filter lets you go into lower levels of hierarchical data without generating another graph. For example, imagine you surveyed customers from 10 different countries. In your report, you have a chart displaying the number of customers by country, but you want to analyze a specific country in detail. A drill down filter would enable you to click on a specific country and display data by city on that same chart. Even better, a global filter would allow you to filter the entire report to show only results for that specific country.
Through the use of interactive filters, such as the one we just mentioned, you’ll not only make the presentation of results more efficient and profound, but you’ll also avoid generating pages-long reports to display static results. All your information will be displayed in a single interactive page that can be filtered and explored upon need.
- Customize the reports
This is a tip that is valuable for any kind of research report, especially when it comes to agencies that are reporting to external clients. Customizing the report to match your client’s colors, logo, font, and overall branding will help them grasp the data better, thanks to a familiar environment. This is an invaluable tip as often your audience will not feel comfortable dealing with data and might find it hard to understand or intimidating. Therefore, providing a familiar look that is also interactive and easier to understand will keep them engaged and collaborative throughout the process.
Plus, customizing the overall appearance of the report will also make your agency look more professional, adding extra value to your service.
- Know your design essentials
When you’re presenting your market research reports sample to internal or external stakeholders, having a firm grasp on fundamental design principles will make your metrics and insights far more persuasive and compelling.
By arranging your metrics in a balanced and logical format, you can guide users toward key pockets of information exactly when needed. In turn, this will improve decision-making and navigation, making your reports as impactful as possible.
For essential tips, read our 23 dashboard design principles & best practices to enhance your analytics process.
- Think of security and privacy
Cyberattacks are increasing at a concerning pace, making security a huge priority for organizations of all sizes today. The costs of having your sensitive information leaked are not only financial but also reputational, as customers might not trust you again if their data ends up in the wrong hands. Given that market research analysis is often performed by agencies that handle data from clients, security and privacy should be a top priority.
To ensure the required security and privacy, it is necessary to invest in the right tools to present your research results. For instance, tools such as datapine offer enterprise-level security protocols that ensure your information is encrypted and protected at all times. Plus, the tool also offers additional security features, such as being able to share your reports through a password-protected URL or to set viewer rights to ensure only the right people can access and manipulate the data.
- Keep on improving & evolving
Each time you gather or gain new marketing research reports or market research analysis report intel, you should aim to refine your existing dashboards to reflect the ever-changing landscape around you.
If you update your reports and dashboards according to the new research you conduct and new insights you connect with, you will squeeze maximum value from your metrics, enjoying consistent development in the process.
Types of Market Research Reports: Primary & Secondary Research
With so many market research examples and such little time, knowing how to best present your insights under pressure can prove tricky.
To squeeze every last drop of value from your market research efforts and empower everyone with access to the right information, you should arrange your information into two main groups: primary research and secondary research.
A. Primary research
Primary research is based on acquiring direct or first-hand information related to your industry or sector and the customers linked to it.
Exploratory primary research is an initial form of information collection where your team might set out to identify potential issues, opportunities, and pain points related to your business or industry. This type of research is usually carried out in the form of general surveys or open-ended consumer Q&As, which nowadays are often performed online rather than offline .
Specific primary research is definitive, with information gathered based on the issues, information, opportunities, or pain points your business has already uncovered. When doing this kind of research, you can drill down into a specific segment of your customers and seek answers to the opportunities, issues, or pain points in question.
When you’re conducting primary research to feed into your market research reporting efforts, it’s important to find reliable information sources. The most effective primary research sources include:
- Consumer-based statistical data
- Social media content
- Polls and Q&A
- Trend-based insights
- Competitor research
- First-hand interviews
B. Secondary research
Secondary research refers to every strand of relevant data or public records you have to gain a deeper insight into your market and target consumers. These sources include trend reports, market stats, industry-centric content, and sales insights you have at your disposal. Secondary research is an effective way of gathering valuable intelligence about your competitors.
You can gather very precise, insightful secondary market research insights from:
- Public records and resources like Census data, governmental reports, or labor stats
- Commercial resources like Gartner, Statista, or Forrester
- Articles, documentaries, and interview transcripts
Another essential branch of both primary and secondary research is internal intelligence. When it comes to efficient market research reporting examples that will benefit your organization, looking inward is a powerful move.
Existing sales, demographic, or marketing performance insights will lead you to valuable conclusions. Curating internal information will ensure your market research discoveries are well-rounded while helping you connect with the information that will ultimately give you a panoramic view of your target market.
By understanding both types of research and how they can offer value to your business, you can carefully choose the right informational sources, gather a wide range of intelligence related to your specific niche, and, ultimately, choose the right market research report sample for your specific needs.
If you tailor your market research report format to the type of research you conduct, you will present your visualizations in a way that provides the right people with the right insights, rather than throwing bundles of facts and figures on the wall, hoping that some of them stick.
Taking ample time to explore a range of primary and secondary sources will give your discoveries genuine context. By doing so, you will have a wealth of actionable consumer and competitor insights at your disposal at every stage of your organization’s development (a priceless weapon in an increasingly competitive digital age).
Dynamic market research is the cornerstone of business development, and a dashboard builder is the vessel that brings these all-important insights to life. Once you get into that mindset, you will ensure that your research results always deliver maximum value.
Common Challenges & Mistakes Of Market Research Reporting & Analysis
We’ve explored different types of market research analysis examples and considered how to conduct effective research. Now, it’s time to look at the key mistakes of market research reporting. Let’s start with the mistakes.
The mistakes
One of the biggest mistakes that stunt the success of a company’s market research efforts is strategy. Without taking the time to gather an adequate mix of insights from various sources and define your key aims or goals, your processes will become disjointed. You will also suffer from a severe lack of organizational vision.
For your market research-centric strategy to work, everyone within the company must be on the same page. Your core aims and objectives must align throughout the business, and everyone must be clear on their specific role. If you try to craft a collaborative strategy and decide on your informational sources from the very start of your journey, your strategy will deliver true growth and intelligence.
- Measurement
Another classic market research mistake is measurement – or, more accurately, a lack of precise measurement. When embarking on market intelligence gathering processes, many companies fail to select the right KPIs and set the correct benchmarks for the task at hand. Without clearly defined goals, many organizations end up with a market analysis report format that offers little or no value in terms of decision-making or market insights.
To drive growth with your market research efforts, you must set clearly defined KPIs that align with your specific goals, aims, and desired outcomes.
- Competition
A common mistake among many new or scaling companies is failing to explore and examine the competition. This will leave you with gaping informational blindspots. To truly benefit from market research, you must gather valuable nuggets of information from every key source available. Rather than solely looking at your consumers and the wider market (which is incredibly important), you should take the time to see what approach your direct competitors have adopted while getting to grips with the content and communications.
One of the most effective ways of doing so (and avoiding such a monumental market research mistake) is by signing up for your competitors’ mailing lists, downloading their apps, and examining their social media content. This will give you inspiration for your own efforts while allowing you to exploit any gaps in the market that your competitors are failing to fill.
The challenges
- Informational quality
We may have an almost infinite wealth of informational insights at our fingertips, but when it comes to market research, knowing which information to trust can prove an uphill struggle.
When working with metrics, many companies risk connecting with inaccurate insights or leading to a fruitless informational rabbit hole, wasting valuable time and resources in the process. To avoid such a mishap, working with a trusted modern market research and analysis sample is the only way forward.
- Senior buy-in
Another pressing market research challenge that stunts organizational growth is the simple case of senior buy-in. While almost every senior decision-maker knows that market research is an essential component of a successful commercial strategy, many are reluctant to invest an ample amount of time or money in the pursuit.
The best way to overcome such a challenge is by building a case that defines exactly how your market research strategies will offer a healthy ROI to every key aspect of the organization, from marketing and sales to customer experience (CX) and beyond.
- Response rates
Low interview, focus group, or poll response rates can have a serious impact on the success and value of your market research strategy. Even with adequate senior buy-in, you can’t always guarantee that you will get enough responses from early-round interviews or poll requests. If you don’t, your market research discoveries run the risk of being shallow or offering little in the way of actionable insight.
To overcome this common challenge, you can improve the incentive you offer your market research prospects while networking across various platforms to discover new contact opportunities. Changing the tone of voice of your ads or emails will also help boost your consumer or client response rates.
Bringing Your Reports a Step Further
Even if it is still widespread for market-style research results presentation, using PowerPoint at this stage is a hassle and presents many downsides and complications. When busy managers or short-on-time top executives grab a report, they want a quick overview that gives them an idea of the results and the big picture that addresses the objectives: they need a dashboard. This can be applied to all areas of a business that need fast and interactive data visualizations to support their decision-making.
We all know that a picture conveys more information than simple text or figures, so managing to bring it all together on an actionable dashboard will convey your message more efficiently. Besides, market research dashboards have the incredible advantage of always being up-to-date since they work with real-time insights: the synchronization/updating nightmare of dozens of PowerPoint slides doesn’t exist for you anymore. This is particularly helpful for tracking studies performed over time that recurrently need their data to be updated with more recent ones.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, companies must identify and grab new opportunities as they arise while staying away from threats and adapting quickly. In order to always be a step further and make the right decisions, it is critical to perform market research studies to get the information needed and make important decisions with confidence.
We’ve asked the question, “What is a market research report?”, and examined the dynamics of a modern market research report example, and one thing’s for sure: a visual market research report is the best way to understand your customer and thus increase their satisfaction by meeting their expectations head-on.
From looking at a sample of a market research report, it’s also clear that modern dashboards help you see what is influencing your business with clarity, understand where your brand is situated in the market, and gauge the temperature of your niche or industry before a product or service launch. Once all the studies are done, you must present them efficiently to ensure everyone in the business can make the right decisions that result in real progress. Market research reports are your key allies in the matter.
To start presenting your results with efficient, interactive, dynamic research reports and win on tomorrow’s commercial battlefield, try our dashboard reporting software and test every feature with our 14-day free trial !

How to Write a Research Paper
- Smodin Editorial Team
- Updated: May 17, 2024
Most students hate writing research papers. The process can often feel long, tedious, and sometimes outright boring. Nevertheless, these assignments are vital to a student’s academic journey. Want to learn how to write a research paper that captures the depth of the subject and maintains the reader’s interest? If so, this guide is for you.
Today, we’ll show you how to assemble a well-organized research paper to help you make the grade. You can transform any topic into a compelling research paper with a thoughtful approach to your research and a persuasive argument.
In this guide, we’ll provide seven simple but practical tips to help demystify the process and guide you on your way. We’ll also explain how AI tools can expedite the research and writing process so you can focus on critical thinking.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear roadmap for tackling these essays. You will also learn how to tackle them quickly and efficiently. With time and dedication, you’ll soon master the art of research paper writing.
Ready to get started?
What Is a Research Paper?
A research paper is a comprehensive essay that gives a detailed analysis, interpretation, or argument based on your own independent research. In higher-level academic settings, it goes beyond a simple summarization and includes a deep inquiry into the topic or topics.
The term “research paper” is a broad term that can be applied to many different forms of academic writing. The goal is to combine your thoughts with the findings from peer-reviewed scholarly literature.
By the time your essay is done, you should have provided your reader with a new perspective or challenged existing findings. This demonstrates your mastery of the subject and contributes to ongoing scholarly debates.
7 Tips for Writing a Research Paper
Often, getting started is the most challenging part of a research paper. While the process can seem daunting, breaking it down into manageable steps can make it easier to manage. The following are seven tips for getting your ideas out of your head and onto the page.
1. Understand Your Assignment
It may sound simple, but the first step in writing a successful research paper is to read the assignment. Sit down, take a few moments of your time, and go through the instructions so you fully understand your assignment.
Misinterpreting the assignment can not only lead to a significant waste of time but also affect your grade. No matter how patient your teacher or professor may be, ignoring basic instructions is often inexcusable.
If you read the instructions and are still confused, ask for clarification before you start writing. If that’s impossible, you can use tools like Smodin’s AI chat to help. Smodin can help highlight critical requirements that you may overlook.
This initial investment ensures that all your future efforts will be focused and efficient. Remember, thinking is just as important as actually writing the essay, and it can also pave the wave for a smoother writing process.
2. Gather Research Materials
Now comes the fun part: doing the research. As you gather research materials, always use credible sources, such as academic journals or peer-reviewed papers. Only use search engines that filter for accredited sources and academic databases so you can ensure your information is reliable.
To optimize your time, you must learn to master the art of skimming. If a source seems relevant and valuable, save it and review it later. The last thing you want to do is waste time on material that won’t make it into the final paper.
To speed up the process even more, consider using Smodin’s AI summarizer . This tool can help summarize large texts, highlighting key information relevant to your topic. By systematically gathering and filing research materials early in the writing process, you build a strong foundation for your thesis.
3. Write Your Thesis
Creating a solid thesis statement is the most important thing you can do to bring structure and focus to your research paper. Your thesis should express the main point of your argument in one or two simple sentences. Remember, when you create your thesis, you’re setting the tone and direction for the entire paper.
Of course, you can’t just pull a winning thesis out of thin air. Start by brainstorming potential thesis ideas based on your preliminary research. And don’t overthink things; sometimes, the most straightforward ideas are often the best.
You want a thesis that is specific enough to be manageable within the scope of your paper but broad enough to allow for a unique discussion. Your thesis should challenge existing expectations and provide the reader with fresh insight into the topic. Use your thesis to hook the reader in the opening paragraph and keep them engaged until the very last word.
4. Write Your Outline
An outline is an often overlooked but essential tool for organizing your thoughts and structuring your paper. Many students skip the outline because it feels like doing double work, but a strong outline will save you work in the long run.
Here’s how to effectively structure your outline.
- Introduction: List your thesis statement and outline the main questions your essay will answer.
- Literature Review: Outline the key literature you plan to discuss and explain how it will relate to your thesis.
- Methodology: Explain the research methods you will use to gather and analyze the information.
- Discussion: Plan how you will interpret the results and their implications for your thesis.
- Conclusion: Summarize the content above to elucidate your thesis fully.
To further streamline this process, consider using Smodin’s Research Writer. This tool offers a feature that allows you to generate and tweak an outline to your liking based on the initial input you provide. You can adjust this outline to fit your research findings better and ensure that your paper remains well-organized and focused.
5. Write a Rough Draft
Once your outline is in place, you can begin the writing process. Remember, when you write a rough draft, it isn’t meant to be perfect. Instead, use it as a working document where you can experiment with and rearrange your arguments and evidence.
Don’t worry too much about grammar, style, or syntax as you write your rough draft. Focus on getting your ideas down on paper and flush out your thesis arguments. You can always refine and rearrange the content the next time around.
Follow the basic structure of your outline but with the freedom to explore different ways of expressing your thoughts. Smodin’s Essay Writer offers a powerful solution for those struggling with starting or structuring their drafts.
After you approve the outline, Smodin can generate an essay based on your initial inputs. This feature can help you quickly create a comprehensive draft, which you can then review and refine. You can even use the power of AI to create multiple rough drafts from which to choose.
6. Add or Subtract Supporting Evidence
Once you have a rough draft, but before you start the final revision, it’s time to do a little cleanup. In this phase, you need to review all your supporting evidence. You want to ensure that there is nothing redundant and that you haven’t overlooked any crucial details.
Many students struggle to make the required word count for an essay and resort to padding their writing with redundant statements. Instead of adding unnecessary content, focus on expanding your analysis to provide deeper insights.
A good essay, regardless of the topic or format, needs to be streamlined. It should convey clear, convincing, relevant information supporting your thesis. If you find some information doesn’t do that, consider tweaking your sources.
Include a variety of sources, including studies, data, and quotes from scholars or other experts. Remember, you’re not just strengthening your argument but demonstrating the depth of your research.
If you want comprehensive feedback on your essay without going to a writing center or pestering your professor, use Smodin. The AI Chat can look at your draft and offer suggestions for improvement.
7. Revise, Cite, and Submit
The final stages of crafting a research paper involve revision, citation, and final review. You must ensure your paper is polished, professionally presented, and plagiarism-free. Of course, integrating Smodin’s AI tools can significantly streamline this process and enhance the quality of your final submission.
Start by using Smodin’s Rewriter tool. This AI-powered feature can help rephrase and refine your draft to improve overall readability. If a specific section of your essay just “doesn’t sound right,” the AI can suggest alternative sentence structures and word choices.
Proper citation is a must for all academic papers. Thankfully, thanks to Smodin’s Research Paper app, this once tedious process is easier than ever. The AI ensures all sources are accurately cited according to the required style guide (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
Plagiarism Checker:
All students need to realize that accidental plagiarism can happen. That’s why using a Plagiarism Checker to scan your essay before you submit it is always useful. Smodin’s Plagiarism Checker can highlight areas of concern so you can adjust accordingly.
Final Submission
After revising, rephrasing, and ensuring all citations are in order, use Smodin’s AI Content Detector to give your paper one last review. This tool can help you analyze your paper’s overall quality and readability so you can make any final tweaks or improvements.
Mastering Research Papers
Mastering the art of the research paper cannot be overstated, whether you’re in high school, college, or postgraduate studies. You can confidently prepare your research paper for submission by leveraging the AI tools listed above.
Research papers help refine your abilities to think critically and write persuasively. The skills you develop here will serve you well beyond the walls of the classroom. Communicating complex ideas clearly and effectively is one of the most powerful tools you can possess.
With the advancements of AI tools like Smodin , writing a research paper has become more accessible than ever before. These technologies streamline the process of organizing, writing, and revising your work. Write with confidence, knowing your best work is yet to come!
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Research: Negotiating Is Unlikely to Jeopardize Your Job Offer
- Einav Hart,
- Julia Bear,
- Zhiying (Bella) Ren

A series of seven studies found that candidates have more power than they assume.
Job seekers worry about negotiating an offer for many reasons, including the worst-case scenario that the offer will be rescinded. Across a series of seven studies, researchers found that these fears are consistently exaggerated: Candidates think they are much more likely to jeopardize a deal than managers report they are. This fear can lead candidates to avoid negotiating altogether. The authors explore two reasons driving this fear and offer research-backed advice on how anxious candidates can approach job negotiations.
Imagine that you just received a job offer for a position you are excited about. Now what? You might consider negotiating for a higher salary, job flexibility, or other benefits , but you’re apprehensive. You can’t help thinking: What if I don’t get what I ask for? Or, in the worst-case scenario, what if the hiring manager decides to withdraw the offer?
- Einav Hart is an assistant professor of management at George Mason University’s Costello College of Business, and a visiting scholar at the Wharton School. Her research interests include conflict management, negotiations, and organizational behavior.
- Julia Bear is a professor of organizational behavior at the College of Business at Stony Brook University (SUNY). Her research interests include the influence of gender on negotiation, as well as understanding gender gaps in organizations more broadly.
- Zhiying (Bella) Ren is a doctoral student at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania. Her research focuses on conversational dynamics in organizations and negotiations.
Partner Center

Global Wine Market to Reach $528.3 Billion by 2030
The global market for Wine estimated at US$385 Billion in the year 2023, is projected to reach a revised size of US$528.3 Billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 4.6% over the analysis period 2023-2030.
The wine sector, although niche within the global alcoholic beverages sector, is influenced by a multitude of factors shaping its consumption patterns. While Europe remains a core region for the industry, substantial opportunities are identified outside of Europe. However, the sector faces several challenges, including a declining image among health-conscious consumers, climate extremes affecting production, counterfeit wines, and anti-alcohol campaigns and legislations.
Still Wine, one of the segments analyzed in the report, is expected to record a 4.5% CAGR and reach US$273.7 Billion by the end of the analysis period. Growth in the Sparkling Wine segment is estimated at 4.9% CAGR for the next 7-year period.
Competition is fierce, with wineries deploying various strategies such as collaborations, aggressive marketing, and new product launches to succeed in the market. Enhancing taste, flavor, and quality remains a priority, while private label wines pose stiff competition to industry leaders in matured markets. The global key competitors' percentage market share in 2024 provides insights into the market structure and competitive dynamics.
The U.S. Market is Estimated at $101.5 Billion, While China is Forecast to Grow at 7.2% CAGR
The Wine market in the U.S. is estimated at US$101.5 Billion in the year 2023. China, the world's second largest economy, is forecast to reach a projected market size of US$116 Billion by the year 2030 trailing a CAGR of 7.2% over the analysis period 2023 to 2030. Among the other noteworthy geographic markets are Japan and Canada, each forecast to grow at 2.6% and 3.5% respectively over the 2023-2030 period. Within Europe, Germany is forecast to grow at approximately 3.4% CAGR. Led by countries such as Australia, India, and South Korea, the market in Asia-Pacific is forecast to reach US$73 Billion by the year 2030.
Key Attributes:
MARKET OVERVIEW
- Influencer Market Insights
- World Market Trajectories
- Alcoholic Beverages: An Introductory Prelude
- Recent Market Activity
- Wine: A Niche Category within the Global Alcoholic Beverages Sector
- Wine Sector - Influenced by Myriad Factors
- Mixed Trend in Wine Consumption Patterns
- Diverse Range of Products Enhance the Addressable Market
- Europe: Core Region for the Global Wine Industry
- Wine Sector Identifies Substantial Opportunities Outside Europe
- Global Market Outlook
- Issues & Challenges
- Declining Image of Alcohol Drinks among Health-Conscious Consumers
- Climate Extremes Influence Wine Production
- Counterfeit Wines
- Anti-Alcohol Campaigns and Legislations
- Competition
- Market Structure
- Wineries Deploy Various Different Strategies
- Collaborations - Key to Market Success
- Aggressive Marketing & Promotional Campaigns
- New Product Launches: A Key Business Strategy
- Enhancing Taste, Flavor and Quality Remains a Top Priority
- Private Label Wines Give Stiff Competition to Leaders in Matured Markets
- Wine - Global Key Competitors Percentage Market Share in 2024 (E)
- Competitive Market Presence - Strong/Active/Niche/Trivial for Players Worldwide in 2024 (E)
- Global Economic Update
MARKET TRENDS & DRIVERS
- New World Wines Make Robust Gains
- Old World Wines Remain Major Segment
- Still Wines: The Dominant Segment
- Sparkling Wine Evolves into A Niche Category
- Diverse Line of Products: Key Trait of Sparkling Wine Market
- Champagne: Highly Distinguished Sparkling Wine
- Prosecco's Phenomenal Performance
- New Variants Aim to Penetrate the Market
- Rose Wine Set to Expand Market Share
- Natural Wines Gain Traction
- Organic Wine: The New Growth Vertical
- Rice Wine Seeks Global Audience
- Fortified Wines Gain Traction among Heavy Drinkers
- Preference for Premium Wines Soars
- On-Trade Channel: A Potential Revenue Generator
- Wine Sales Remain High in Off-Trade Channel
- Retail Stores: The High-Volume Distribution Medium
- E-Commerce Evolves into High-Potential Sales Vertical
- Social Media Emerges as New Promotion Tool
- Wine Market Sees Packaging Diversification
- Bag-in-Box for Extended Shelf Life
- Canned Wine: The New Fad
- Bourbon Barrels: The Upcoming Wine Aging Method
- Precision Agriculture Methods & 'Tech' Innovations to Aid Wine Grape Growers
- Lifestyle Trends & Cultural Issues Favor Wine Market
- Busy Lifestyles
- Disposable Incomes
- Urban Population
- Wine-Drinking Occasions
- Desire for Trendy Drinks
- Demand for Drinks Considered as Healthy
FOCUS ON SELECT PLAYERS (Total 398 Featured)
- Accolade Wines Australia Limited (Australia)
- Bacardi Limited (Bermuda)
- Brown-Forman Corporation (USA)
- Cantine Riunite & CIV S.C.Agr. (Italy)
- Castel Group (France)
- Caviro s.c.a (Italy)
- Codorniu, S.A. (Spain)
- Constellation Brands, Inc. (USA)
- E. & J. Gallo Winery (USA)
- Freixenet S.A. (Spain)
- Grupo Penaflor S.A. (Argentina)
- Gruppo Italiano Vini S.P.A. (Italy)
- Henkell & Co. Sektkellerei KG (Germany)
- J. Garcia Carrion S.A (Spain)
- Kendall-Jackson Wine Estates, Ltd. (USA)
- LANSON-BCC (France)
- LVMH Moet Hennessy Louis Vuitton S.E. (France)
- Miguel Torres S. A (Spain)
- Pernod Ricard Groupe (France)
- Remy Cointreau Group (France)
- The Schenk Group (Switzerland)
- Treasury Wine Estates Limited (Australia)
- Vina Concha y Toro S.A. (Chile)
- The Wine Group LLC (USA)
For more information about this report visit https://www.researchandmarkets.com/r/74sqht
About ResearchAndMarkets.com
ResearchAndMarkets.com is the world's leading source for international market research reports and market data. We provide you with the latest data on international and regional markets, key industries, the top companies, new products and the latest trends.
ResearchAndMarkets.com Laura Wood, Senior Press Manager [email protected] For E.S.T Office Hours Call 1-917-300-0470 For U.S./ CAN Toll Free Call 1-800-526-8630 For GMT Office Hours Call +353-1-416-8900


Senators urge $32 billion in emergency spending on AI after finishing yearlong review
W ASHINGTON (AP) — A bipartisan group of four senators led by Majority Leader Chuck Schumer is recommending that Congress spend at least $32 billion over the next three years to develop artificial intelligence and place safeguards around it, writing in a report released Wednesday that the U.S. needs to “harness the opportunities and address the risks” of the quickly developing technology.
The group of two Democrats and two Republicans said in an interview Tuesday that while they sometimes disagreed on the best paths forward, they felt it was imperative to find consensus with the technology taking off and other countries like China investing heavily in its development. They settled on a raft of broad policy recommendations that were included in their 33-page report.
While any legislation related to AI will be difficult to pass, especially in an election year and in a divided Congress, the senators said that regulation and incentives for innovation are urgently needed.
“It’s complicated, it’s difficult, but we can’t afford to put our head in the sand,” said Schumer, D-N.Y., who convened the group last year after AI chatbot ChatGPT entered the marketplace and showed that it could in many ways mimic human behavior.
The group recommends in the report that Congress draft emergency spending legislation to boost U.S. investments in artificial intelligence, including new research and development and new testing standards to try to understand the potential harms of the technology. The group also recommended new requirements for transparency as artificial intelligence products are rolled out and that studies be conducted into the potential impact of AI on jobs and the U.S. workforce .
Republican Sen. Mike Rounds, a member of the group, said the money would be well spent not only to compete with other countries who are racing into the AI space but also to improve Americans’ quality of life — supporting technology that could help cure some cancers or chronic illnesses, he said, or improvements in weapons systems could help the country avoid a war.
“This is a time in which the dollars we put into this particular investment will pay dividends for the taxpayers of this country long term,” he said.
The group came together a year ago after Schumer made the issue a priority — an unusual posture for a majority leader — and brought in Democratic Sen. Martin Heinrich of New Mexico, Republican Sen. Todd Young of Indiana and Rounds of South Dakota.
As the four senators began meeting with tech executives and experts, Schumer said in a speech over the summer that the rapid growth of artificial intelligence tools was a “moment of revolution” and that the government must act quickly to regulate companies that are developing it.
Young said the development of ChatGPT, along with other similar models, made them realize that “we’re going to have to figure out collectively as an institution” how to deal with the technology.
“In the same breath that people marveled at the possibilities of just that one generative AI platform, they began to hypothesize about future risks that might be associated with future developments of artificial intelligence,” Young said.
While passing legislation will be tough, the group’s recommendations lay out the first comprehensive road map on an issue that is complex and has little precedent for consideration in Congress. The group spent almost a year compiling the list of policy suggestions after talking privately and publicly to a range of technology companies and other stakeholders, including in eight forums to which the entire Senate was invited.
The first forum in September included X owner and Tesla CEO Elon Musk, Meta’s Mark Zuckerberg, former Microsoft CEO Bill Gates and Google CEO Sundar Pichai.
Schumer said after the private meeting that he had asked everyone in the room — including almost two dozen tech executives, advocates and skeptics — whether government should have a role in the oversight of artificial intelligence, and “every single person raised their hand.”
Still, there are diverse views in the tech industry about the future of AI. Musk has voiced dire concerns evoking popular science fiction about the possibility of humanity losing control to advanced AI systems if the right safeguards are not in place. Others are more concerned about the details of how proposed regulations could affect their business, from possible government oversight over the most capable AI systems to tracking of highly sought-after AI computer chips for national security.
The four senators are pitching their recommendations to Senate committees, which are then tasked with reviewing them and trying to figure out what is possible. The Senate Rules Committee is already moving forward with legislation, on Wednesday approving three bills that would ban deceptive AI content used to influence federal elections, require AI disclaimers on political ads and create voluntary guidelines for state election offices that oversee candidates.
Schumer, who controls the Senate’s schedule, said those election bills were among the chamber’s “highest priorities” this year. He also said he planned to sit down with House Speaker Mike Johnson, who has expressed interest in looking at AI policy but has not said how he would do that.
Still, winning enough votes on the legislation may be not be easy. The bills that would ban deceptive AI election content and require AI disclaimers on political ads were approved by the Rules panel on party line votes, with no GOP support. Republicans argued that the legislation would usurp states that are already acting on the issue and potentially violate political candidates' rights to free speech.
Senate Rules Committee Chairwoman Amy Klobuchar, a Democrat from Minnesota, said that the rapid development of AI is a “hair on fire” moment for elections. And while states may be passing similar bills, she said the country is "unguarded on the federal level.”
Some experts warn that the U.S. is behind many other countries on the issue, including the EU which took the lead in March when they gave final approval to a sweeping new law governing artificial intelligence in the 27-nation bloc. Europe’s AI Act sets tighter rules for the AI products and services deemed to pose the highest risks, such as in medicine, critical infrastructure or policing. But it also includes provisions regulating the new class of generative AI systems like ChatGPT that have rapidly advanced in recent years.
“It’s time for Congress to act,” said Alexandra Reeve Givens, CEO of the Center for Democracy & Technology. “It’s not enough to focus on investment and innovation. We need guardrails to ensure the responsible development of AI.”
Others said the senators' road map wasn't tough enough on tech companies. Some groups calling for tighter AI safeguards and civil rights protections said it showed too much deference to industry priorities.
Alix Dunn is a senior adviser at AI Now, a policy research center that pushes for more accountability around AI technology. She criticized the closed door sessions with tech CEOs. “I don’t see how it got us even an inch closer to meaningful government action on AI,” she said.
The senators emphasized balance between innovation and safeguards, and also the urgency of action.
“We have the lead at this moment in time on this issue, and it will define the relationship between the United States and our allies and other competing powers in the world for a long time to come,” Heinrich said.
O'Brien reported from Providence, R.I. Associated Press writer Dan Merica in Washington contributed to this report.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 2: Create an Outline. Once you've gathered the resources, it's time to plan the report. Before you start writing, create an outline that will help you stick to the right structure. A business report is complex writing in which you can get lost very easily if you don't have a clear plan.
This tutorial explains how to write a business report for post-graduate level students. It covers the introduction, report structure and organisation, writin...
A business analysis report examines the structure of a company, including its management, staff, departments, divisions, and supply chain. It also evaluates how well-managed the company is and how efficient its supply chain is. In order to develop a strong strategy, you need to be able to analyze your business structure.
Front matter: List your name, job title, contact information, and the date of submission. You can also create a title for the report. Background: State the background of the topic you'll be addressing, along with the purpose of the report itself. Key findings: Provide facts, data, and key findings that are relevant to the purpose stated in ...
Research reports. Next in our types of business reports that we will discuss is a research report. Companies often use these kinds of reports to test the viability of a new product, study a new geographical area to sell, or understand their customer's perception of their brand image. ... When you write a business-style report, you should ...
In this post, then, we'll look at how to structure a business report for maximum clarity and professionalism. 1. Title Page. Every business report should feature a title page. The title itself should clearly set out what the report is about. Typically, you should also include your name and the date of the report. 2.
Writing a business research report. This video explains how to write a business report for postgraduate level students. It covers the introduction, report structure and organisation, writing the report, and business writing. Writing a business research report. Watch on.
To achieve this, the report must present a clear and logical case that demonstrates the subject knowledge and authority of the author and will lead the reader to understand and appreciate the value of the recommended actions. This guide offers advice on the report-writing process and sets out key steps to improve the quality of business reports.
Writing a Business Report Writing Centre Learning Guide Overview 1. Start your report with the main point. Why is this report important? Why was it requested? What has it found? 2. Organise your content. Divide your information to blocks of topics. 3. Give each block a title/heading. 4. Begin each block with the main point.
3.3 Presentation of the Research Report. A business researcher can present the findings of the research either in an electronic format or as a printout. Irrespective of the medium the researcher chooses to present his report, he should ensure that the findings are presented in a professional manner to the end-user.
Write up a state-of-the-art research report. Understand how to use scientific language in research reports. Develop a structure for your research report that comprises all relevant sections. Assess the consistency of your research design. Avoid dumbfounding your reader with surprising information.
Research reports are recorded data prepared by researchers or statisticians after analyzing the information gathered by conducting organized research, typically in the form of surveys or qualitative methods. A research report is a reliable source to recount details about a conducted research. It is most often considered to be a true testimony ...
3.5 Use white space and well-chosen fonts. White space refers to the empty space on the page. Business reports which have a more balanced use of white space and text are easier to read and more effectively communicate main points and subordinate ideas. Create white space by:
Make sure the title is clear and visible at the beginning of the report. You should also add your name and the names of others who have worked on the report and the date you wrote it. 4. Write a table of contents. The table of contents page should follow the title and authors.
The purpose of creating a market research report is to make calculated decisions about business ideas. Market research is done to evaluate the feasibility of a new product or service, through research conducted with potential consumers. ... Here are some best practices you should keep in mind when writing a research report. Objectives - The ...
Thesis. Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master's or Doctoral degree, although it ...
A sound report structure, along with "story-like" writing is crucial to case study reporting. The following points should be taken into consideration while reporting a case study. ... Qualitative methods in business research: A practical guide to social research. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. Google Scholar. Flick U., Kardorff E., Steinke I. (2004).
Add your name, the names of the other people who worked on it and the date under the title. Write an index or table of contents: A table of contents or index is essential in any business report, especially if the document is long and complex. Add a list of each section of the document under the title and ensure the page numbers accurately match ...
Here's a market research business report example that lays out the industry landscape and gives clear guidance on the way forward, all backed up by facts. ... Step 4: Write the report. When writing your report, start by developing a clear and concise writing style, avoiding jargon and buzzwords. Keep your audience in mind - make sure your ...
1. Market Research Report: Brand Analysis. Our first example shares the results of a brand study. To do so, a survey has been performed on a sample of 1333 people, information that we can see in detail on the left side of the board, summarizing the gender, age groups, and geolocation. **click to enlarge**.
Use the section headings (outlined above) to assist with your rough plan. Write a thesis statement that clarifies the overall purpose of your report. Jot down anything you already know about the topic in the relevant sections. 3 Do the Research. Steps 1 and 2 will guide your research for this report.
Abstract. This guide for writers of research reports consists of practical suggestions for writing a report that is clear, concise, readable, and understandable. It includes suggestions for terminology and notation and for writing each section of the report—introduction, method, results, and discussion. Much of the guide consists of ...
2. Follow the Right Report Writing Format: Adhere to a structured format, including a clear title, table of contents, summary, introduction, body, conclusion, recommendations, and appendices. This ensures clarity and coherence. Follow the format suggestions in this article to start off on the right foot. 3.
5 Weekly / Monthly / Quarterly Report Examples. Similar to daily progress reports, weekly, monthly and quarterly reports are constants in a business setting.They're usually more generalized than a progress report, which is about a specific project. Weekly and monthly reports are sometimes condensed sections of different analytics reports put together into one document.
1. Understand Your Assignment. It may sound simple, but the first step in writing a successful research paper is to read the assignment. Sit down, take a few moments of your time, and go through the instructions so you fully understand your assignment.
Six steps to writing a project proposal: write the executive summary, explain the project background, present a solution, and define the project deliverables and resources needed. Top tips for writing a persuasive project proposal: know your audience, keep it simple and make it persuasive, do you research, use a template and cover letter.
Across a series of seven studies, researchers found that these fears are consistently exaggerated: Candidates think they are much more likely to jeopardize a deal than managers report they are.
Inside this detailed 43-page report, Social Media Examiner uncovers: Most used social media platforms for B2B vs. B2C. Current and future organic social plans. Video marketing use and future plans. Platforms that deliver the most exposure, sales, and leads. How marketers are responding to AI.
DUBLIN--(BUSINESS WIRE)--The "Wine - Global Strategic Business Report" has been added to ResearchAndMarkets.com's offering.Global Wine Market to Reach $528.3 Billion by 2030. The global market for ...
The group recommends in the report that Congress draft emergency spending legislation to boost U.S. investments in artificial intelligence, including new research and development and new testing ...