An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Int J Prev Med

Qualitative Methods in Health Care Research
Vishnu renjith.
School of Nursing and Midwifery, Royal College of Surgeons Ireland - Bahrain (RCSI Bahrain), Al Sayh Muharraq Governorate, Bahrain
Renjulal Yesodharan
1 Department of Mental Health Nursing, Manipal College of Nursing Manipal, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India
Judith A. Noronha
2 Department of OBG Nursing, Manipal College of Nursing Manipal, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India
Elissa Ladd
3 School of Nursing, MGH Institute of Health Professions, Boston, USA
Anice George
4 Department of Child Health Nursing, Manipal College of Nursing Manipal, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India
Healthcare research is a systematic inquiry intended to generate robust evidence about important issues in the fields of medicine and healthcare. Qualitative research has ample possibilities within the arena of healthcare research. This article aims to inform healthcare professionals regarding qualitative research, its significance, and applicability in the field of healthcare. A wide variety of phenomena that cannot be explained using the quantitative approach can be explored and conveyed using a qualitative method. The major types of qualitative research designs are narrative research, phenomenological research, grounded theory research, ethnographic research, historical research, and case study research. The greatest strength of the qualitative research approach lies in the richness and depth of the healthcare exploration and description it makes. In health research, these methods are considered as the most humanistic and person-centered way of discovering and uncovering thoughts and actions of human beings.
Introduction
Healthcare research is a systematic inquiry intended to generate trustworthy evidence about issues in the field of medicine and healthcare. The three principal approaches to health research are the quantitative, the qualitative, and the mixed methods approach. The quantitative research method uses data, which are measures of values and counts and are often described using statistical methods which in turn aids the researcher to draw inferences. Qualitative research incorporates the recording, interpreting, and analyzing of non-numeric data with an attempt to uncover the deeper meanings of human experiences and behaviors. Mixed methods research, the third methodological approach, involves collection and analysis of both qualitative and quantitative information with an objective to solve different but related questions, or at times the same questions.[ 1 , 2 ]
In healthcare, qualitative research is widely used to understand patterns of health behaviors, describe lived experiences, develop behavioral theories, explore healthcare needs, and design interventions.[ 1 , 2 , 3 ] Because of its ample applications in healthcare, there has been a tremendous increase in the number of health research studies undertaken using qualitative methodology.[ 4 , 5 ] This article discusses qualitative research methods, their significance, and applicability in the arena of healthcare.
Qualitative Research
Diverse academic and non-academic disciplines utilize qualitative research as a method of inquiry to understand human behavior and experiences.[ 6 , 7 ] According to Munhall, “Qualitative research involves broadly stated questions about human experiences and realities, studied through sustained contact with the individual in their natural environments and producing rich, descriptive data that will help us to understand those individual's experiences.”[ 8 ]
Significance of Qualitative Research
The qualitative method of inquiry examines the 'how' and 'why' of decision making, rather than the 'when,' 'what,' and 'where.'[ 7 ] Unlike quantitative methods, the objective of qualitative inquiry is to explore, narrate, and explain the phenomena and make sense of the complex reality. Health interventions, explanatory health models, and medical-social theories could be developed as an outcome of qualitative research.[ 9 ] Understanding the richness and complexity of human behavior is the crux of qualitative research.
Differences between Quantitative and Qualitative Research
The quantitative and qualitative forms of inquiry vary based on their underlying objectives. They are in no way opposed to each other; instead, these two methods are like two sides of a coin. The critical differences between quantitative and qualitative research are summarized in Table 1 .[ 1 , 10 , 11 ]
Differences between quantitative and qualitative research
Qualitative Research Questions and Purpose Statements
Qualitative questions are exploratory and are open-ended. A well-formulated study question forms the basis for developing a protocol, guides the selection of design, and data collection methods. Qualitative research questions generally involve two parts, a central question and related subquestions. The central question is directed towards the primary phenomenon under study, whereas the subquestions explore the subareas of focus. It is advised not to have more than five to seven subquestions. A commonly used framework for designing a qualitative research question is the 'PCO framework' wherein, P stands for the population under study, C stands for the context of exploration, and O stands for the outcome/s of interest.[ 12 ] The PCO framework guides researchers in crafting a focused study question.
Example: In the question, “What are the experiences of mothers on parenting children with Thalassemia?”, the population is “mothers of children with Thalassemia,” the context is “parenting children with Thalassemia,” and the outcome of interest is “experiences.”
The purpose statement specifies the broad focus of the study, identifies the approach, and provides direction for the overall goal of the study. The major components of a purpose statement include the central phenomenon under investigation, the study design and the population of interest. Qualitative research does not require a-priori hypothesis.[ 13 , 14 , 15 ]
Example: Borimnejad et al . undertook a qualitative research on the lived experiences of women suffering from vitiligo. The purpose of this study was, “to explore lived experiences of women suffering from vitiligo using a hermeneutic phenomenological approach.” [ 16 ]
Review of the Literature
In quantitative research, the researchers do an extensive review of scientific literature prior to the commencement of the study. However, in qualitative research, only a minimal literature search is conducted at the beginning of the study. This is to ensure that the researcher is not influenced by the existing understanding of the phenomenon under the study. The minimal literature review will help the researchers to avoid the conceptual pollution of the phenomenon being studied. Nonetheless, an extensive review of the literature is conducted after data collection and analysis.[ 15 ]
Reflexivity
Reflexivity refers to critical self-appraisal about one's own biases, values, preferences, and preconceptions about the phenomenon under investigation. Maintaining a reflexive diary/journal is a widely recognized way to foster reflexivity. According to Creswell, “Reflexivity increases the credibility of the study by enhancing more neutral interpretations.”[ 7 ]
Types of Qualitative Research Designs
The qualitative research approach encompasses a wide array of research designs. The words such as types, traditions, designs, strategies of inquiry, varieties, and methods are used interchangeably. The major types of qualitative research designs are narrative research, phenomenological research, grounded theory research, ethnographic research, historical research, and case study research.[ 1 , 7 , 10 ]
Narrative research
Narrative research focuses on exploring the life of an individual and is ideally suited to tell the stories of individual experiences.[ 17 ] The purpose of narrative research is to utilize 'story telling' as a method in communicating an individual's experience to a larger audience.[ 18 ] The roots of narrative inquiry extend to humanities including anthropology, literature, psychology, education, history, and sociology. Narrative research encompasses the study of individual experiences and learning the significance of those experiences. The data collection procedures include mainly interviews, field notes, letters, photographs, diaries, and documents collected from one or more individuals. Data analysis involves the analysis of the stories or experiences through “re-storying of stories” and developing themes usually in chronological order of events. Rolls and Payne argued that narrative research is a valuable approach in health care research, to gain deeper insight into patient's experiences.[ 19 ]
Example: Karlsson et al . undertook a narrative inquiry to “explore how people with Alzheimer's disease present their life story.” Data were collected from nine participants. They were asked to describe about their life experiences from childhood to adulthood, then to current life and their views about the future life. [ 20 ]
Phenomenological research
Phenomenology is a philosophical tradition developed by German philosopher Edmond Husserl. His student Martin Heidegger did further developments in this methodology. It defines the 'essence' of individual's experiences regarding a certain phenomenon.[ 1 ] The methodology has its origin from philosophy, psychology, and education. The purpose of qualitative research is to understand the people's everyday life experiences and reduce it into the central meaning or the 'essence of the experience'.[ 21 , 22 ] The unit of analysis of phenomenology is the individuals who have had similar experiences of the phenomenon. Interviews with individuals are mainly considered for the data collection, though, documents and observations are also useful. Data analysis includes identification of significant meaning elements, textural description (what was experienced), structural description (how was it experienced), and description of 'essence' of experience.[ 1 , 7 , 21 ] The phenomenological approach is further divided into descriptive and interpretive phenomenology. Descriptive phenomenology focuses on the understanding of the essence of experiences and is best suited in situations that need to describe the lived phenomenon. Hermeneutic phenomenology or Interpretive phenomenology moves beyond the description to uncover the meanings that are not explicitly evident. The researcher tries to interpret the phenomenon, based on their judgment rather than just describing it.[ 7 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 ]
Example: A phenomenological study conducted by Cornelio et al . aimed at describing the lived experiences of mothers in parenting children with leukemia. Data from ten mothers were collected using in-depth semi-structured interviews and were analyzed using Husserl's method of phenomenology. Themes such as “pivotal moment in life”, “the experience of being with a seriously ill child”, “having to keep distance with the relatives”, “overcoming the financial and social commitments”, “responding to challenges”, “experience of faith as being key to survival”, “health concerns of the present and future”, and “optimism” were derived. The researchers reported the essence of the study as “chronic illness such as leukemia in children results in a negative impact on the child and on the mother.” [ 25 ]
Grounded Theory Research
Grounded theory has its base in sociology and propagated by two sociologists, Barney Glaser, and Anselm Strauss.[ 26 ] The primary purpose of grounded theory is to discover or generate theory in the context of the social process being studied. The major difference between grounded theory and other approaches lies in its emphasis on theory generation and development. The name grounded theory comes from its ability to induce a theory grounded in the reality of study participants.[ 7 , 27 ] Data collection in grounded theory research involves recording interviews from many individuals until data saturation. Constant comparative analysis, theoretical sampling, theoretical coding, and theoretical saturation are unique features of grounded theory research.[ 26 , 27 , 28 ] Data analysis includes analyzing data through 'open coding,' 'axial coding,' and 'selective coding.'[ 1 , 7 ] Open coding is the first level of abstraction, and it refers to the creation of a broad initial range of categories, axial coding is the procedure of understanding connections between the open codes, whereas selective coding relates to the process of connecting the axial codes to formulate a theory.[ 1 , 7 ] Results of the grounded theory analysis are supplemented with a visual representation of major constructs usually in the form of flow charts or framework diagrams. Quotations from the participants are used in a supportive capacity to substantiate the findings. Strauss and Corbin highlights that “the value of the grounded theory lies not only in its ability to generate a theory but also to ground that theory in the data.”[ 27 ]
Example: Williams et al . conducted a grounded theory research to explore the nature of relationship between the sense of self and the eating disorders. Data were collected form 11 women with a lifetime history of Anorexia Nervosa and were analyzed using the grounded theory methodology. Analysis led to the development of a theoretical framework on the nature of the relationship between the self and Anorexia Nervosa. [ 29 ]
Ethnographic research
Ethnography has its base in anthropology, where the anthropologists used it for understanding the culture-specific knowledge and behaviors. In health sciences research, ethnography focuses on narrating and interpreting the health behaviors of a culture-sharing group. 'Culture-sharing group' in an ethnography represents any 'group of people who share common meanings, customs or experiences.' In health research, it could be a group of physicians working in rural care, a group of medical students, or it could be a group of patients who receive home-based rehabilitation. To understand the cultural patterns, researchers primarily observe the individuals or group of individuals for a prolonged period of time.[ 1 , 7 , 30 ] The scope of ethnography can be broad or narrow depending on the aim. The study of more general cultural groups is termed as macro-ethnography, whereas micro-ethnography focuses on more narrowly defined cultures. Ethnography is usually conducted in a single setting. Ethnographers collect data using a variety of methods such as observation, interviews, audio-video records, and document reviews. A written report includes a detailed description of the culture sharing group with emic and etic perspectives. When the researcher reports the views of the participants it is called emic perspectives and when the researcher reports his or her views about the culture, the term is called etic.[ 7 ]
Example: The aim of the ethnographic study by LeBaron et al . was to explore the barriers to opioid availability and cancer pain management in India. The researchers collected data from fifty-nine participants using in-depth semi-structured interviews, participant observation, and document review. The researchers identified significant barriers by open coding and thematic analysis of the formal interview. [ 31 ]
Historical research
Historical research is the “systematic collection, critical evaluation, and interpretation of historical evidence”.[ 1 ] The purpose of historical research is to gain insights from the past and involves interpreting past events in the light of the present. The data for historical research are usually collected from primary and secondary sources. The primary source mainly includes diaries, first hand information, and writings. The secondary sources are textbooks, newspapers, second or third-hand accounts of historical events and medical/legal documents. The data gathered from these various sources are synthesized and reported as biographical narratives or developmental perspectives in chronological order. The ideas are interpreted in terms of the historical context and significance. The written report describes 'what happened', 'how it happened', 'why it happened', and its significance and implications to current clinical practice.[ 1 , 10 ]
Example: Lubold (2019) analyzed the breastfeeding trends in three countries (Sweden, Ireland, and the United States) using a historical qualitative method. Through analysis of historical data, the researcher found that strong family policies, adherence to international recommendations and adoption of baby-friendly hospital initiative could greatly enhance the breastfeeding rates. [ 32 ]
Case study research
Case study research focuses on the description and in-depth analysis of the case(s) or issues illustrated by the case(s). The design has its origin from psychology, law, and medicine. Case studies are best suited for the understanding of case(s), thus reducing the unit of analysis into studying an event, a program, an activity or an illness. Observations, one to one interviews, artifacts, and documents are used for collecting the data, and the analysis is done through the description of the case. From this, themes and cross-case themes are derived. A written case study report includes a detailed description of one or more cases.[ 7 , 10 ]
Example: Perceptions of poststroke sexuality in a woman of childbearing age was explored using a qualitative case study approach by Beal and Millenbrunch. Semi structured interview was conducted with a 36- year mother of two children with a history of Acute ischemic stroke. The data were analyzed using an inductive approach. The authors concluded that “stroke during childbearing years may affect a woman's perception of herself as a sexual being and her ability to carry out gender roles”. [ 33 ]
Sampling in Qualitative Research
Qualitative researchers widely use non-probability sampling techniques such as purposive sampling, convenience sampling, quota sampling, snowball sampling, homogeneous sampling, maximum variation sampling, extreme (deviant) case sampling, typical case sampling, and intensity sampling. The selection of a sampling technique depends on the nature and needs of the study.[ 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 ] The four widely used sampling techniques are convenience sampling, purposive sampling, snowball sampling, and intensity sampling.
Convenience sampling
It is otherwise called accidental sampling, where the researchers collect data from the subjects who are selected based on accessibility, geographical proximity, ease, speed, and or low cost.[ 34 ] Convenience sampling offers a significant benefit of convenience but often accompanies the issues of sample representation.
Purposive sampling
Purposive or purposeful sampling is a widely used sampling technique.[ 35 ] It involves identifying a population based on already established sampling criteria and then selecting subjects who fulfill that criteria to increase the credibility. However, choosing information-rich cases is the key to determine the power and logic of purposive sampling in a qualitative study.[ 1 ]
Snowball sampling
The method is also known as 'chain referral sampling' or 'network sampling.' The sampling starts by having a few initial participants, and the researcher relies on these early participants to identify additional study participants. It is best adopted when the researcher wishes to study the stigmatized group, or in cases, where findings of participants are likely to be difficult by ordinary means. Respondent ridden sampling is an improvised version of snowball sampling used to find out the participant from a hard-to-find or hard-to-study population.[ 37 , 38 ]
Intensity sampling
The process of identifying information-rich cases that manifest the phenomenon of interest is referred to as intensity sampling. It requires prior information, and considerable judgment about the phenomenon of interest and the researcher should do some preliminary investigations to determine the nature of the variation. Intensity sampling will be done once the researcher identifies the variation across the cases (extreme, average and intense) and picks the intense cases from them.[ 40 ]
Deciding the Sample Size
A-priori sample size calculation is not undertaken in the case of qualitative research. Researchers collect the data from as many participants as possible until they reach the point of data saturation. Data saturation or the point of redundancy is the stage where the researcher no longer sees or hears any new information. Data saturation gives the idea that the researcher has captured all possible information about the phenomenon of interest. Since no further information is being uncovered as redundancy is achieved, at this point the data collection can be stopped. The objective here is to get an overall picture of the chronicle of the phenomenon under the study rather than generalization.[ 1 , 7 , 41 ]
Data Collection in Qualitative Research
The various strategies used for data collection in qualitative research includes in-depth interviews (individual or group), focus group discussions (FGDs), participant observation, narrative life history, document analysis, audio materials, videos or video footage, text analysis, and simple observation. Among all these, the three popular methods are the FGDs, one to one in-depth interviews and the participant observation.
FGDs are useful in eliciting data from a group of individuals. They are normally built around a specific topic and are considered as the best approach to gather data on an entire range of responses to a topic.[ 42 Group size in an FGD ranges from 6 to 12. Depending upon the nature of participants, FGDs could be homogeneous or heterogeneous.[ 1 , 14 ] One to one in-depth interviews are best suited to obtain individuals' life histories, lived experiences, perceptions, and views, particularly while exporting topics of sensitive nature. In-depth interviews can be structured, unstructured, or semi-structured. However, semi-structured interviews are widely used in qualitative research. Participant observations are suitable for gathering data regarding naturally occurring behaviors.[ 1 ]
Data Analysis in Qualitative Research
Various strategies are employed by researchers to analyze data in qualitative research. Data analytic strategies differ according to the type of inquiry. A general content analysis approach is described herewith. Data analysis begins by transcription of the interview data. The researcher carefully reads data and gets a sense of the whole. Once the researcher is familiarized with the data, the researcher strives to identify small meaning units called the 'codes.' The codes are then grouped based on their shared concepts to form the primary categories. Based on the relationship between the primary categories, they are then clustered into secondary categories. The next step involves the identification of themes and interpretation to make meaning out of data. In the results section of the manuscript, the researcher describes the key findings/themes that emerged. The themes can be supported by participants' quotes. The analytical framework used should be explained in sufficient detail, and the analytic framework must be well referenced. The study findings are usually represented in a schematic form for better conceptualization.[ 1 , 7 ] Even though the overall analytical process remains the same across different qualitative designs, each design such as phenomenology, ethnography, and grounded theory has design specific analytical procedures, the details of which are out of the scope of this article.
Computer-Assisted Qualitative Data Analysis Software (CAQDAS)
Until recently, qualitative analysis was done either manually or with the help of a spreadsheet application. Currently, there are various software programs available which aid researchers to manage qualitative data. CAQDAS is basically data management tools and cannot analyze the qualitative data as it lacks the ability to think, reflect, and conceptualize. Nonetheless, CAQDAS helps researchers to manage, shape, and make sense of unstructured information. Open Code, MAXQDA, NVivo, Atlas.ti, and Hyper Research are some of the widely used qualitative data analysis software.[ 14 , 43 ]
Reporting Guidelines
Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) is the widely used reporting guideline for qualitative research. This 32-item checklist assists researchers in reporting all the major aspects related to the study. The three major domains of COREQ are the 'research team and reflexivity', 'study design', and 'analysis and findings'.[ 44 , 45 ]
Critical Appraisal of Qualitative Research
Various scales are available to critical appraisal of qualitative research. The widely used one is the Critical Appraisal Skills Program (CASP) Qualitative Checklist developed by CASP network, UK. This 10-item checklist evaluates the quality of the study under areas such as aims, methodology, research design, ethical considerations, data collection, data analysis, and findings.[ 46 ]
Ethical Issues in Qualitative Research
A qualitative study must be undertaken by grounding it in the principles of bioethics such as beneficence, non-maleficence, autonomy, and justice. Protecting the participants is of utmost importance, and the greatest care has to be taken while collecting data from a vulnerable research population. The researcher must respect individuals, families, and communities and must make sure that the participants are not identifiable by their quotations that the researchers include when publishing the data. Consent for audio/video recordings must be obtained. Approval to be in FGDs must be obtained from the participants. Researchers must ensure the confidentiality and anonymity of the transcripts/audio-video records/photographs/other data collected as a part of the study. The researchers must confirm their role as advocates and proceed in the best interest of all participants.[ 42 , 47 , 48 ]
Rigor in Qualitative Research
The demonstration of rigor or quality in the conduct of the study is essential for every research method. However, the criteria used to evaluate the rigor of quantitative studies are not be appropriate for qualitative methods. Lincoln and Guba (1985) first outlined the criteria for evaluating the qualitative research often referred to as “standards of trustworthiness of qualitative research”.[ 49 ] The four components of the criteria are credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability.
Credibility refers to confidence in the 'truth value' of the data and its interpretation. It is used to establish that the findings are true, credible and believable. Credibility is similar to the internal validity in quantitative research.[ 1 , 50 , 51 ] The second criterion to establish the trustworthiness of the qualitative research is transferability, Transferability refers to the degree to which the qualitative results are applicability to other settings, population or contexts. This is analogous to the external validity in quantitative research.[ 1 , 50 , 51 ] Lincoln and Guba recommend authors provide enough details so that the users will be able to evaluate the applicability of data in other contexts.[ 49 ] The criterion of dependability refers to the assumption of repeatability or replicability of the study findings and is similar to that of reliability in quantitative research. The dependability question is 'Whether the study findings be repeated of the study is replicated with the same (similar) cohort of participants, data coders, and context?'[ 1 , 50 , 51 ] Confirmability, the fourth criteria is analogous to the objectivity of the study and refers the degree to which the study findings could be confirmed or corroborated by others. To ensure confirmability the data should directly reflect the participants' experiences and not the bias, motivations, or imaginations of the inquirer.[ 1 , 50 , 51 ] Qualitative researchers should ensure that the study is conducted with enough rigor and should report the measures undertaken to enhance the trustworthiness of the study.
Conclusions
Qualitative research studies are being widely acknowledged and recognized in health care practice. This overview illustrates various qualitative methods and shows how these methods can be used to generate evidence that informs clinical practice. Qualitative research helps to understand the patterns of health behaviors, describe illness experiences, design health interventions, and develop healthcare theories. The ultimate strength of the qualitative research approach lies in the richness of the data and the descriptions and depth of exploration it makes. Hence, qualitative methods are considered as the most humanistic and person-centered way of discovering and uncovering thoughts and actions of human beings.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
- Open access
- Published: 27 May 2020
How to use and assess qualitative research methods
- Loraine Busetto ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9228-7875 1 ,
- Wolfgang Wick 1 , 2 &
- Christoph Gumbinger 1
Neurological Research and Practice volume 2 , Article number: 14 ( 2020 ) Cite this article
732k Accesses
296 Citations
84 Altmetric
Metrics details
This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions, and focussing on intervention improvement. The most common methods of data collection are document study, (non-) participant observations, semi-structured interviews and focus groups. For data analysis, field-notes and audio-recordings are transcribed into protocols and transcripts, and coded using qualitative data management software. Criteria such as checklists, reflexivity, sampling strategies, piloting, co-coding, member-checking and stakeholder involvement can be used to enhance and assess the quality of the research conducted. Using qualitative in addition to quantitative designs will equip us with better tools to address a greater range of research problems, and to fill in blind spots in current neurological research and practice.
The aim of this paper is to provide an overview of qualitative research methods, including hands-on information on how they can be used, reported and assessed. This article is intended for beginning qualitative researchers in the health sciences as well as experienced quantitative researchers who wish to broaden their understanding of qualitative research.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is defined as “the study of the nature of phenomena”, including “their quality, different manifestations, the context in which they appear or the perspectives from which they can be perceived” , but excluding “their range, frequency and place in an objectively determined chain of cause and effect” [ 1 ]. This formal definition can be complemented with a more pragmatic rule of thumb: qualitative research generally includes data in form of words rather than numbers [ 2 ].
Why conduct qualitative research?
Because some research questions cannot be answered using (only) quantitative methods. For example, one Australian study addressed the issue of why patients from Aboriginal communities often present late or not at all to specialist services offered by tertiary care hospitals. Using qualitative interviews with patients and staff, it found one of the most significant access barriers to be transportation problems, including some towns and communities simply not having a bus service to the hospital [ 3 ]. A quantitative study could have measured the number of patients over time or even looked at possible explanatory factors – but only those previously known or suspected to be of relevance. To discover reasons for observed patterns, especially the invisible or surprising ones, qualitative designs are needed.
While qualitative research is common in other fields, it is still relatively underrepresented in health services research. The latter field is more traditionally rooted in the evidence-based-medicine paradigm, as seen in " research that involves testing the effectiveness of various strategies to achieve changes in clinical practice, preferably applying randomised controlled trial study designs (...) " [ 4 ]. This focus on quantitative research and specifically randomised controlled trials (RCT) is visible in the idea of a hierarchy of research evidence which assumes that some research designs are objectively better than others, and that choosing a "lesser" design is only acceptable when the better ones are not practically or ethically feasible [ 5 , 6 ]. Others, however, argue that an objective hierarchy does not exist, and that, instead, the research design and methods should be chosen to fit the specific research question at hand – "questions before methods" [ 2 , 7 , 8 , 9 ]. This means that even when an RCT is possible, some research problems require a different design that is better suited to addressing them. Arguing in JAMA, Berwick uses the example of rapid response teams in hospitals, which he describes as " a complex, multicomponent intervention – essentially a process of social change" susceptible to a range of different context factors including leadership or organisation history. According to him, "[in] such complex terrain, the RCT is an impoverished way to learn. Critics who use it as a truth standard in this context are incorrect" [ 8 ] . Instead of limiting oneself to RCTs, Berwick recommends embracing a wider range of methods , including qualitative ones, which for "these specific applications, (...) are not compromises in learning how to improve; they are superior" [ 8 ].
Research problems that can be approached particularly well using qualitative methods include assessing complex multi-component interventions or systems (of change), addressing questions beyond “what works”, towards “what works for whom when, how and why”, and focussing on intervention improvement rather than accreditation [ 7 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 ]. Using qualitative methods can also help shed light on the “softer” side of medical treatment. For example, while quantitative trials can measure the costs and benefits of neuro-oncological treatment in terms of survival rates or adverse effects, qualitative research can help provide a better understanding of patient or caregiver stress, visibility of illness or out-of-pocket expenses.
How to conduct qualitative research?
Given that qualitative research is characterised by flexibility, openness and responsivity to context, the steps of data collection and analysis are not as separate and consecutive as they tend to be in quantitative research [ 13 , 14 ]. As Fossey puts it : “sampling, data collection, analysis and interpretation are related to each other in a cyclical (iterative) manner, rather than following one after another in a stepwise approach” [ 15 ]. The researcher can make educated decisions with regard to the choice of method, how they are implemented, and to which and how many units they are applied [ 13 ]. As shown in Fig. 1 , this can involve several back-and-forth steps between data collection and analysis where new insights and experiences can lead to adaption and expansion of the original plan. Some insights may also necessitate a revision of the research question and/or the research design as a whole. The process ends when saturation is achieved, i.e. when no relevant new information can be found (see also below: sampling and saturation). For reasons of transparency, it is essential for all decisions as well as the underlying reasoning to be well-documented.
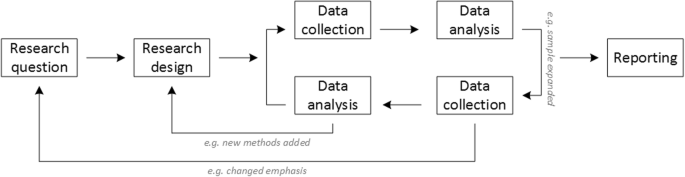
Iterative research process
While it is not always explicitly addressed, qualitative methods reflect a different underlying research paradigm than quantitative research (e.g. constructivism or interpretivism as opposed to positivism). The choice of methods can be based on the respective underlying substantive theory or theoretical framework used by the researcher [ 2 ].
Data collection
The methods of qualitative data collection most commonly used in health research are document study, observations, semi-structured interviews and focus groups [ 1 , 14 , 16 , 17 ].
Document study
Document study (also called document analysis) refers to the review by the researcher of written materials [ 14 ]. These can include personal and non-personal documents such as archives, annual reports, guidelines, policy documents, diaries or letters.
Observations
Observations are particularly useful to gain insights into a certain setting and actual behaviour – as opposed to reported behaviour or opinions [ 13 ]. Qualitative observations can be either participant or non-participant in nature. In participant observations, the observer is part of the observed setting, for example a nurse working in an intensive care unit [ 18 ]. In non-participant observations, the observer is “on the outside looking in”, i.e. present in but not part of the situation, trying not to influence the setting by their presence. Observations can be planned (e.g. for 3 h during the day or night shift) or ad hoc (e.g. as soon as a stroke patient arrives at the emergency room). During the observation, the observer takes notes on everything or certain pre-determined parts of what is happening around them, for example focusing on physician-patient interactions or communication between different professional groups. Written notes can be taken during or after the observations, depending on feasibility (which is usually lower during participant observations) and acceptability (e.g. when the observer is perceived to be judging the observed). Afterwards, these field notes are transcribed into observation protocols. If more than one observer was involved, field notes are taken independently, but notes can be consolidated into one protocol after discussions. Advantages of conducting observations include minimising the distance between the researcher and the researched, the potential discovery of topics that the researcher did not realise were relevant and gaining deeper insights into the real-world dimensions of the research problem at hand [ 18 ].
Semi-structured interviews
Hijmans & Kuyper describe qualitative interviews as “an exchange with an informal character, a conversation with a goal” [ 19 ]. Interviews are used to gain insights into a person’s subjective experiences, opinions and motivations – as opposed to facts or behaviours [ 13 ]. Interviews can be distinguished by the degree to which they are structured (i.e. a questionnaire), open (e.g. free conversation or autobiographical interviews) or semi-structured [ 2 , 13 ]. Semi-structured interviews are characterized by open-ended questions and the use of an interview guide (or topic guide/list) in which the broad areas of interest, sometimes including sub-questions, are defined [ 19 ]. The pre-defined topics in the interview guide can be derived from the literature, previous research or a preliminary method of data collection, e.g. document study or observations. The topic list is usually adapted and improved at the start of the data collection process as the interviewer learns more about the field [ 20 ]. Across interviews the focus on the different (blocks of) questions may differ and some questions may be skipped altogether (e.g. if the interviewee is not able or willing to answer the questions or for concerns about the total length of the interview) [ 20 ]. Qualitative interviews are usually not conducted in written format as it impedes on the interactive component of the method [ 20 ]. In comparison to written surveys, qualitative interviews have the advantage of being interactive and allowing for unexpected topics to emerge and to be taken up by the researcher. This can also help overcome a provider or researcher-centred bias often found in written surveys, which by nature, can only measure what is already known or expected to be of relevance to the researcher. Interviews can be audio- or video-taped; but sometimes it is only feasible or acceptable for the interviewer to take written notes [ 14 , 16 , 20 ].
Focus groups
Focus groups are group interviews to explore participants’ expertise and experiences, including explorations of how and why people behave in certain ways [ 1 ]. Focus groups usually consist of 6–8 people and are led by an experienced moderator following a topic guide or “script” [ 21 ]. They can involve an observer who takes note of the non-verbal aspects of the situation, possibly using an observation guide [ 21 ]. Depending on researchers’ and participants’ preferences, the discussions can be audio- or video-taped and transcribed afterwards [ 21 ]. Focus groups are useful for bringing together homogeneous (to a lesser extent heterogeneous) groups of participants with relevant expertise and experience on a given topic on which they can share detailed information [ 21 ]. Focus groups are a relatively easy, fast and inexpensive method to gain access to information on interactions in a given group, i.e. “the sharing and comparing” among participants [ 21 ]. Disadvantages include less control over the process and a lesser extent to which each individual may participate. Moreover, focus group moderators need experience, as do those tasked with the analysis of the resulting data. Focus groups can be less appropriate for discussing sensitive topics that participants might be reluctant to disclose in a group setting [ 13 ]. Moreover, attention must be paid to the emergence of “groupthink” as well as possible power dynamics within the group, e.g. when patients are awed or intimidated by health professionals.
Choosing the “right” method
As explained above, the school of thought underlying qualitative research assumes no objective hierarchy of evidence and methods. This means that each choice of single or combined methods has to be based on the research question that needs to be answered and a critical assessment with regard to whether or to what extent the chosen method can accomplish this – i.e. the “fit” between question and method [ 14 ]. It is necessary for these decisions to be documented when they are being made, and to be critically discussed when reporting methods and results.
Let us assume that our research aim is to examine the (clinical) processes around acute endovascular treatment (EVT), from the patient’s arrival at the emergency room to recanalization, with the aim to identify possible causes for delay and/or other causes for sub-optimal treatment outcome. As a first step, we could conduct a document study of the relevant standard operating procedures (SOPs) for this phase of care – are they up-to-date and in line with current guidelines? Do they contain any mistakes, irregularities or uncertainties that could cause delays or other problems? Regardless of the answers to these questions, the results have to be interpreted based on what they are: a written outline of what care processes in this hospital should look like. If we want to know what they actually look like in practice, we can conduct observations of the processes described in the SOPs. These results can (and should) be analysed in themselves, but also in comparison to the results of the document analysis, especially as regards relevant discrepancies. Do the SOPs outline specific tests for which no equipment can be observed or tasks to be performed by specialized nurses who are not present during the observation? It might also be possible that the written SOP is outdated, but the actual care provided is in line with current best practice. In order to find out why these discrepancies exist, it can be useful to conduct interviews. Are the physicians simply not aware of the SOPs (because their existence is limited to the hospital’s intranet) or do they actively disagree with them or does the infrastructure make it impossible to provide the care as described? Another rationale for adding interviews is that some situations (or all of their possible variations for different patient groups or the day, night or weekend shift) cannot practically or ethically be observed. In this case, it is possible to ask those involved to report on their actions – being aware that this is not the same as the actual observation. A senior physician’s or hospital manager’s description of certain situations might differ from a nurse’s or junior physician’s one, maybe because they intentionally misrepresent facts or maybe because different aspects of the process are visible or important to them. In some cases, it can also be relevant to consider to whom the interviewee is disclosing this information – someone they trust, someone they are otherwise not connected to, or someone they suspect or are aware of being in a potentially “dangerous” power relationship to them. Lastly, a focus group could be conducted with representatives of the relevant professional groups to explore how and why exactly they provide care around EVT. The discussion might reveal discrepancies (between SOPs and actual care or between different physicians) and motivations to the researchers as well as to the focus group members that they might not have been aware of themselves. For the focus group to deliver relevant information, attention has to be paid to its composition and conduct, for example, to make sure that all participants feel safe to disclose sensitive or potentially problematic information or that the discussion is not dominated by (senior) physicians only. The resulting combination of data collection methods is shown in Fig. 2 .
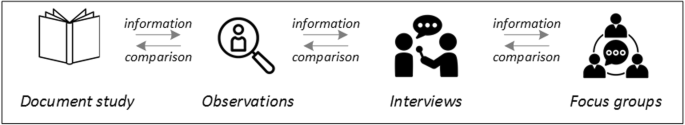
Possible combination of data collection methods
Attributions for icons: “Book” by Serhii Smirnov, “Interview” by Adrien Coquet, FR, “Magnifying Glass” by anggun, ID, “Business communication” by Vectors Market; all from the Noun Project
The combination of multiple data source as described for this example can be referred to as “triangulation”, in which multiple measurements are carried out from different angles to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of the phenomenon under study [ 22 , 23 ].
Data analysis
To analyse the data collected through observations, interviews and focus groups these need to be transcribed into protocols and transcripts (see Fig. 3 ). Interviews and focus groups can be transcribed verbatim , with or without annotations for behaviour (e.g. laughing, crying, pausing) and with or without phonetic transcription of dialects and filler words, depending on what is expected or known to be relevant for the analysis. In the next step, the protocols and transcripts are coded , that is, marked (or tagged, labelled) with one or more short descriptors of the content of a sentence or paragraph [ 2 , 15 , 23 ]. Jansen describes coding as “connecting the raw data with “theoretical” terms” [ 20 ]. In a more practical sense, coding makes raw data sortable. This makes it possible to extract and examine all segments describing, say, a tele-neurology consultation from multiple data sources (e.g. SOPs, emergency room observations, staff and patient interview). In a process of synthesis and abstraction, the codes are then grouped, summarised and/or categorised [ 15 , 20 ]. The end product of the coding or analysis process is a descriptive theory of the behavioural pattern under investigation [ 20 ]. The coding process is performed using qualitative data management software, the most common ones being InVivo, MaxQDA and Atlas.ti. It should be noted that these are data management tools which support the analysis performed by the researcher(s) [ 14 ].
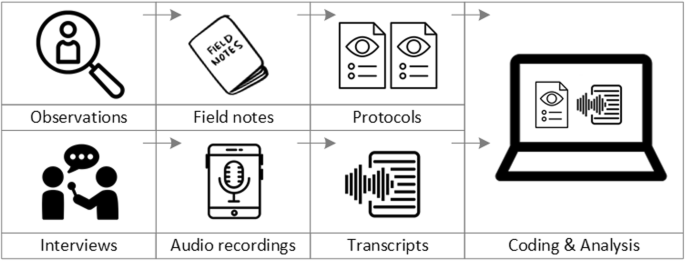
From data collection to data analysis
Attributions for icons: see Fig. 2 , also “Speech to text” by Trevor Dsouza, “Field Notes” by Mike O’Brien, US, “Voice Record” by ProSymbols, US, “Inspection” by Made, AU, and “Cloud” by Graphic Tigers; all from the Noun Project
How to report qualitative research?
Protocols of qualitative research can be published separately and in advance of the study results. However, the aim is not the same as in RCT protocols, i.e. to pre-define and set in stone the research questions and primary or secondary endpoints. Rather, it is a way to describe the research methods in detail, which might not be possible in the results paper given journals’ word limits. Qualitative research papers are usually longer than their quantitative counterparts to allow for deep understanding and so-called “thick description”. In the methods section, the focus is on transparency of the methods used, including why, how and by whom they were implemented in the specific study setting, so as to enable a discussion of whether and how this may have influenced data collection, analysis and interpretation. The results section usually starts with a paragraph outlining the main findings, followed by more detailed descriptions of, for example, the commonalities, discrepancies or exceptions per category [ 20 ]. Here it is important to support main findings by relevant quotations, which may add information, context, emphasis or real-life examples [ 20 , 23 ]. It is subject to debate in the field whether it is relevant to state the exact number or percentage of respondents supporting a certain statement (e.g. “Five interviewees expressed negative feelings towards XYZ”) [ 21 ].
How to combine qualitative with quantitative research?
Qualitative methods can be combined with other methods in multi- or mixed methods designs, which “[employ] two or more different methods [ …] within the same study or research program rather than confining the research to one single method” [ 24 ]. Reasons for combining methods can be diverse, including triangulation for corroboration of findings, complementarity for illustration and clarification of results, expansion to extend the breadth and range of the study, explanation of (unexpected) results generated with one method with the help of another, or offsetting the weakness of one method with the strength of another [ 1 , 17 , 24 , 25 , 26 ]. The resulting designs can be classified according to when, why and how the different quantitative and/or qualitative data strands are combined. The three most common types of mixed method designs are the convergent parallel design , the explanatory sequential design and the exploratory sequential design. The designs with examples are shown in Fig. 4 .
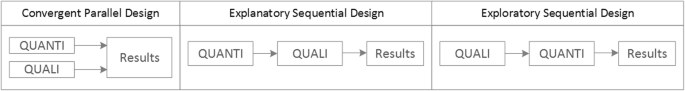
Three common mixed methods designs
In the convergent parallel design, a qualitative study is conducted in parallel to and independently of a quantitative study, and the results of both studies are compared and combined at the stage of interpretation of results. Using the above example of EVT provision, this could entail setting up a quantitative EVT registry to measure process times and patient outcomes in parallel to conducting the qualitative research outlined above, and then comparing results. Amongst other things, this would make it possible to assess whether interview respondents’ subjective impressions of patients receiving good care match modified Rankin Scores at follow-up, or whether observed delays in care provision are exceptions or the rule when compared to door-to-needle times as documented in the registry. In the explanatory sequential design, a quantitative study is carried out first, followed by a qualitative study to help explain the results from the quantitative study. This would be an appropriate design if the registry alone had revealed relevant delays in door-to-needle times and the qualitative study would be used to understand where and why these occurred, and how they could be improved. In the exploratory design, the qualitative study is carried out first and its results help informing and building the quantitative study in the next step [ 26 ]. If the qualitative study around EVT provision had shown a high level of dissatisfaction among the staff members involved, a quantitative questionnaire investigating staff satisfaction could be set up in the next step, informed by the qualitative study on which topics dissatisfaction had been expressed. Amongst other things, the questionnaire design would make it possible to widen the reach of the research to more respondents from different (types of) hospitals, regions, countries or settings, and to conduct sub-group analyses for different professional groups.
How to assess qualitative research?
A variety of assessment criteria and lists have been developed for qualitative research, ranging in their focus and comprehensiveness [ 14 , 17 , 27 ]. However, none of these has been elevated to the “gold standard” in the field. In the following, we therefore focus on a set of commonly used assessment criteria that, from a practical standpoint, a researcher can look for when assessing a qualitative research report or paper.
Assessors should check the authors’ use of and adherence to the relevant reporting checklists (e.g. Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR)) to make sure all items that are relevant for this type of research are addressed [ 23 , 28 ]. Discussions of quantitative measures in addition to or instead of these qualitative measures can be a sign of lower quality of the research (paper). Providing and adhering to a checklist for qualitative research contributes to an important quality criterion for qualitative research, namely transparency [ 15 , 17 , 23 ].
Reflexivity
While methodological transparency and complete reporting is relevant for all types of research, some additional criteria must be taken into account for qualitative research. This includes what is called reflexivity, i.e. sensitivity to the relationship between the researcher and the researched, including how contact was established and maintained, or the background and experience of the researcher(s) involved in data collection and analysis. Depending on the research question and population to be researched this can be limited to professional experience, but it may also include gender, age or ethnicity [ 17 , 27 ]. These details are relevant because in qualitative research, as opposed to quantitative research, the researcher as a person cannot be isolated from the research process [ 23 ]. It may influence the conversation when an interviewed patient speaks to an interviewer who is a physician, or when an interviewee is asked to discuss a gynaecological procedure with a male interviewer, and therefore the reader must be made aware of these details [ 19 ].
Sampling and saturation
The aim of qualitative sampling is for all variants of the objects of observation that are deemed relevant for the study to be present in the sample “ to see the issue and its meanings from as many angles as possible” [ 1 , 16 , 19 , 20 , 27 ] , and to ensure “information-richness [ 15 ]. An iterative sampling approach is advised, in which data collection (e.g. five interviews) is followed by data analysis, followed by more data collection to find variants that are lacking in the current sample. This process continues until no new (relevant) information can be found and further sampling becomes redundant – which is called saturation [ 1 , 15 ] . In other words: qualitative data collection finds its end point not a priori , but when the research team determines that saturation has been reached [ 29 , 30 ].
This is also the reason why most qualitative studies use deliberate instead of random sampling strategies. This is generally referred to as “ purposive sampling” , in which researchers pre-define which types of participants or cases they need to include so as to cover all variations that are expected to be of relevance, based on the literature, previous experience or theory (i.e. theoretical sampling) [ 14 , 20 ]. Other types of purposive sampling include (but are not limited to) maximum variation sampling, critical case sampling or extreme or deviant case sampling [ 2 ]. In the above EVT example, a purposive sample could include all relevant professional groups and/or all relevant stakeholders (patients, relatives) and/or all relevant times of observation (day, night and weekend shift).
Assessors of qualitative research should check whether the considerations underlying the sampling strategy were sound and whether or how researchers tried to adapt and improve their strategies in stepwise or cyclical approaches between data collection and analysis to achieve saturation [ 14 ].
Good qualitative research is iterative in nature, i.e. it goes back and forth between data collection and analysis, revising and improving the approach where necessary. One example of this are pilot interviews, where different aspects of the interview (especially the interview guide, but also, for example, the site of the interview or whether the interview can be audio-recorded) are tested with a small number of respondents, evaluated and revised [ 19 ]. In doing so, the interviewer learns which wording or types of questions work best, or which is the best length of an interview with patients who have trouble concentrating for an extended time. Of course, the same reasoning applies to observations or focus groups which can also be piloted.
Ideally, coding should be performed by at least two researchers, especially at the beginning of the coding process when a common approach must be defined, including the establishment of a useful coding list (or tree), and when a common meaning of individual codes must be established [ 23 ]. An initial sub-set or all transcripts can be coded independently by the coders and then compared and consolidated after regular discussions in the research team. This is to make sure that codes are applied consistently to the research data.
Member checking
Member checking, also called respondent validation , refers to the practice of checking back with study respondents to see if the research is in line with their views [ 14 , 27 ]. This can happen after data collection or analysis or when first results are available [ 23 ]. For example, interviewees can be provided with (summaries of) their transcripts and asked whether they believe this to be a complete representation of their views or whether they would like to clarify or elaborate on their responses [ 17 ]. Respondents’ feedback on these issues then becomes part of the data collection and analysis [ 27 ].
Stakeholder involvement
In those niches where qualitative approaches have been able to evolve and grow, a new trend has seen the inclusion of patients and their representatives not only as study participants (i.e. “members”, see above) but as consultants to and active participants in the broader research process [ 31 , 32 , 33 ]. The underlying assumption is that patients and other stakeholders hold unique perspectives and experiences that add value beyond their own single story, making the research more relevant and beneficial to researchers, study participants and (future) patients alike [ 34 , 35 ]. Using the example of patients on or nearing dialysis, a recent scoping review found that 80% of clinical research did not address the top 10 research priorities identified by patients and caregivers [ 32 , 36 ]. In this sense, the involvement of the relevant stakeholders, especially patients and relatives, is increasingly being seen as a quality indicator in and of itself.
How not to assess qualitative research
The above overview does not include certain items that are routine in assessments of quantitative research. What follows is a non-exhaustive, non-representative, experience-based list of the quantitative criteria often applied to the assessment of qualitative research, as well as an explanation of the limited usefulness of these endeavours.
Protocol adherence
Given the openness and flexibility of qualitative research, it should not be assessed by how well it adheres to pre-determined and fixed strategies – in other words: its rigidity. Instead, the assessor should look for signs of adaptation and refinement based on lessons learned from earlier steps in the research process.
Sample size
For the reasons explained above, qualitative research does not require specific sample sizes, nor does it require that the sample size be determined a priori [ 1 , 14 , 27 , 37 , 38 , 39 ]. Sample size can only be a useful quality indicator when related to the research purpose, the chosen methodology and the composition of the sample, i.e. who was included and why.
Randomisation
While some authors argue that randomisation can be used in qualitative research, this is not commonly the case, as neither its feasibility nor its necessity or usefulness has been convincingly established for qualitative research [ 13 , 27 ]. Relevant disadvantages include the negative impact of a too large sample size as well as the possibility (or probability) of selecting “ quiet, uncooperative or inarticulate individuals ” [ 17 ]. Qualitative studies do not use control groups, either.
Interrater reliability, variability and other “objectivity checks”
The concept of “interrater reliability” is sometimes used in qualitative research to assess to which extent the coding approach overlaps between the two co-coders. However, it is not clear what this measure tells us about the quality of the analysis [ 23 ]. This means that these scores can be included in qualitative research reports, preferably with some additional information on what the score means for the analysis, but it is not a requirement. Relatedly, it is not relevant for the quality or “objectivity” of qualitative research to separate those who recruited the study participants and collected and analysed the data. Experiences even show that it might be better to have the same person or team perform all of these tasks [ 20 ]. First, when researchers introduce themselves during recruitment this can enhance trust when the interview takes place days or weeks later with the same researcher. Second, when the audio-recording is transcribed for analysis, the researcher conducting the interviews will usually remember the interviewee and the specific interview situation during data analysis. This might be helpful in providing additional context information for interpretation of data, e.g. on whether something might have been meant as a joke [ 18 ].
Not being quantitative research
Being qualitative research instead of quantitative research should not be used as an assessment criterion if it is used irrespectively of the research problem at hand. Similarly, qualitative research should not be required to be combined with quantitative research per se – unless mixed methods research is judged as inherently better than single-method research. In this case, the same criterion should be applied for quantitative studies without a qualitative component.
The main take-away points of this paper are summarised in Table 1 . We aimed to show that, if conducted well, qualitative research can answer specific research questions that cannot to be adequately answered using (only) quantitative designs. Seeing qualitative and quantitative methods as equal will help us become more aware and critical of the “fit” between the research problem and our chosen methods: I can conduct an RCT to determine the reasons for transportation delays of acute stroke patients – but should I? It also provides us with a greater range of tools to tackle a greater range of research problems more appropriately and successfully, filling in the blind spots on one half of the methodological spectrum to better address the whole complexity of neurological research and practice.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
Endovascular treatment
Randomised Controlled Trial
Standard Operating Procedure
Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research
Philipsen, H., & Vernooij-Dassen, M. (2007). Kwalitatief onderzoek: nuttig, onmisbaar en uitdagend. In L. PLBJ & H. TCo (Eds.), Kwalitatief onderzoek: Praktische methoden voor de medische praktijk . [Qualitative research: useful, indispensable and challenging. In: Qualitative research: Practical methods for medical practice (pp. 5–12). Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.
Chapter Google Scholar
Punch, K. F. (2013). Introduction to social research: Quantitative and qualitative approaches . London: Sage.
Kelly, J., Dwyer, J., Willis, E., & Pekarsky, B. (2014). Travelling to the city for hospital care: Access factors in country aboriginal patient journeys. Australian Journal of Rural Health, 22 (3), 109–113.
Article Google Scholar
Nilsen, P., Ståhl, C., Roback, K., & Cairney, P. (2013). Never the twain shall meet? - a comparison of implementation science and policy implementation research. Implementation Science, 8 (1), 1–12.
Howick J, Chalmers I, Glasziou, P., Greenhalgh, T., Heneghan, C., Liberati, A., Moschetti, I., Phillips, B., & Thornton, H. (2011). The 2011 Oxford CEBM evidence levels of evidence (introductory document) . Oxford Center for Evidence Based Medicine. https://www.cebm.net/2011/06/2011-oxford-cebm-levels-evidence-introductory-document/ .
Eakin, J. M. (2016). Educating critical qualitative health researchers in the land of the randomized controlled trial. Qualitative Inquiry, 22 (2), 107–118.
May, A., & Mathijssen, J. (2015). Alternatieven voor RCT bij de evaluatie van effectiviteit van interventies!? Eindrapportage. In Alternatives for RCTs in the evaluation of effectiveness of interventions!? Final report .
Google Scholar
Berwick, D. M. (2008). The science of improvement. Journal of the American Medical Association, 299 (10), 1182–1184.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Christ, T. W. (2014). Scientific-based research and randomized controlled trials, the “gold” standard? Alternative paradigms and mixed methodologies. Qualitative Inquiry, 20 (1), 72–80.
Lamont, T., Barber, N., Jd, P., Fulop, N., Garfield-Birkbeck, S., Lilford, R., Mear, L., Raine, R., & Fitzpatrick, R. (2016). New approaches to evaluating complex health and care systems. BMJ, 352:i154.
Drabble, S. J., & O’Cathain, A. (2015). Moving from Randomized Controlled Trials to Mixed Methods Intervention Evaluation. In S. Hesse-Biber & R. B. Johnson (Eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Multimethod and Mixed Methods Research Inquiry (pp. 406–425). London: Oxford University Press.
Chambers, D. A., Glasgow, R. E., & Stange, K. C. (2013). The dynamic sustainability framework: Addressing the paradox of sustainment amid ongoing change. Implementation Science : IS, 8 , 117.
Hak, T. (2007). Waarnemingsmethoden in kwalitatief onderzoek. In L. PLBJ & H. TCo (Eds.), Kwalitatief onderzoek: Praktische methoden voor de medische praktijk . [Observation methods in qualitative research] (pp. 13–25). Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.
Russell, C. K., & Gregory, D. M. (2003). Evaluation of qualitative research studies. Evidence Based Nursing, 6 (2), 36–40.
Fossey, E., Harvey, C., McDermott, F., & Davidson, L. (2002). Understanding and evaluating qualitative research. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 36 , 717–732.
Yanow, D. (2000). Conducting interpretive policy analysis (Vol. 47). Thousand Oaks: Sage University Papers Series on Qualitative Research Methods.
Shenton, A. K. (2004). Strategies for ensuring trustworthiness in qualitative research projects. Education for Information, 22 , 63–75.
van der Geest, S. (2006). Participeren in ziekte en zorg: meer over kwalitatief onderzoek. Huisarts en Wetenschap, 49 (4), 283–287.
Hijmans, E., & Kuyper, M. (2007). Het halfopen interview als onderzoeksmethode. In L. PLBJ & H. TCo (Eds.), Kwalitatief onderzoek: Praktische methoden voor de medische praktijk . [The half-open interview as research method (pp. 43–51). Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.
Jansen, H. (2007). Systematiek en toepassing van de kwalitatieve survey. In L. PLBJ & H. TCo (Eds.), Kwalitatief onderzoek: Praktische methoden voor de medische praktijk . [Systematics and implementation of the qualitative survey (pp. 27–41). Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.
Pv, R., & Peremans, L. (2007). Exploreren met focusgroepgesprekken: de ‘stem’ van de groep onder de loep. In L. PLBJ & H. TCo (Eds.), Kwalitatief onderzoek: Praktische methoden voor de medische praktijk . [Exploring with focus group conversations: the “voice” of the group under the magnifying glass (pp. 53–64). Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.
Carter, N., Bryant-Lukosius, D., DiCenso, A., Blythe, J., & Neville, A. J. (2014). The use of triangulation in qualitative research. Oncology Nursing Forum, 41 (5), 545–547.
Boeije H: Analyseren in kwalitatief onderzoek: Denken en doen, [Analysis in qualitative research: Thinking and doing] vol. Den Haag Boom Lemma uitgevers; 2012.
Hunter, A., & Brewer, J. (2015). Designing Multimethod Research. In S. Hesse-Biber & R. B. Johnson (Eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Multimethod and Mixed Methods Research Inquiry (pp. 185–205). London: Oxford University Press.
Archibald, M. M., Radil, A. I., Zhang, X., & Hanson, W. E. (2015). Current mixed methods practices in qualitative research: A content analysis of leading journals. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 14 (2), 5–33.
Creswell, J. W., & Plano Clark, V. L. (2011). Choosing a Mixed Methods Design. In Designing and Conducting Mixed Methods Research . Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Mays, N., & Pope, C. (2000). Assessing quality in qualitative research. BMJ, 320 (7226), 50–52.
O'Brien, B. C., Harris, I. B., Beckman, T. J., Reed, D. A., & Cook, D. A. (2014). Standards for reporting qualitative research: A synthesis of recommendations. Academic Medicine : Journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges, 89 (9), 1245–1251.
Saunders, B., Sim, J., Kingstone, T., Baker, S., Waterfield, J., Bartlam, B., Burroughs, H., & Jinks, C. (2018). Saturation in qualitative research: Exploring its conceptualization and operationalization. Quality and Quantity, 52 (4), 1893–1907.
Moser, A., & Korstjens, I. (2018). Series: Practical guidance to qualitative research. Part 3: Sampling, data collection and analysis. European Journal of General Practice, 24 (1), 9–18.
Marlett, N., Shklarov, S., Marshall, D., Santana, M. J., & Wasylak, T. (2015). Building new roles and relationships in research: A model of patient engagement research. Quality of Life Research : an international journal of quality of life aspects of treatment, care and rehabilitation, 24 (5), 1057–1067.
Demian, M. N., Lam, N. N., Mac-Way, F., Sapir-Pichhadze, R., & Fernandez, N. (2017). Opportunities for engaging patients in kidney research. Canadian Journal of Kidney Health and Disease, 4 , 2054358117703070–2054358117703070.
Noyes, J., McLaughlin, L., Morgan, K., Roberts, A., Stephens, M., Bourne, J., Houlston, M., Houlston, J., Thomas, S., Rhys, R. G., et al. (2019). Designing a co-productive study to overcome known methodological challenges in organ donation research with bereaved family members. Health Expectations . 22(4):824–35.
Piil, K., Jarden, M., & Pii, K. H. (2019). Research agenda for life-threatening cancer. European Journal Cancer Care (Engl), 28 (1), e12935.
Hofmann, D., Ibrahim, F., Rose, D., Scott, D. L., Cope, A., Wykes, T., & Lempp, H. (2015). Expectations of new treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: Developing a patient-generated questionnaire. Health Expectations : an international journal of public participation in health care and health policy, 18 (5), 995–1008.
Jun, M., Manns, B., Laupacis, A., Manns, L., Rehal, B., Crowe, S., & Hemmelgarn, B. R. (2015). Assessing the extent to which current clinical research is consistent with patient priorities: A scoping review using a case study in patients on or nearing dialysis. Canadian Journal of Kidney Health and Disease, 2 , 35.
Elsie Baker, S., & Edwards, R. (2012). How many qualitative interviews is enough? In National Centre for Research Methods Review Paper . National Centre for Research Methods. http://eprints.ncrm.ac.uk/2273/4/how_many_interviews.pdf .
Sandelowski, M. (1995). Sample size in qualitative research. Research in Nursing & Health, 18 (2), 179–183.
Sim, J., Saunders, B., Waterfield, J., & Kingstone, T. (2018). Can sample size in qualitative research be determined a priori? International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 21 (5), 619–634.
Download references
Acknowledgements
no external funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Neurology, Heidelberg University Hospital, Im Neuenheimer Feld 400, 69120, Heidelberg, Germany
Loraine Busetto, Wolfgang Wick & Christoph Gumbinger
Clinical Cooperation Unit Neuro-Oncology, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany
Wolfgang Wick
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
LB drafted the manuscript; WW and CG revised the manuscript; all authors approved the final versions.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Loraine Busetto .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Busetto, L., Wick, W. & Gumbinger, C. How to use and assess qualitative research methods. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2 , 14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42466-020-00059-z
Download citation
Received : 30 January 2020
Accepted : 22 April 2020
Published : 27 May 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s42466-020-00059-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Mixed methods
- Quality assessment
Neurological Research and Practice
ISSN: 2524-3489
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Loading metrics
Open Access
Qualitative Research: Understanding Patients' Needs and Experiences
- The PLoS Medicine Editors

Published: August 28, 2007
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0040258
- Reader Comments
Citation: The PLoS Medicine Editors (2007) Qualitative Research: Understanding Patients' Needs and Experiences. PLoS Med 4(8): e258. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0040258
Copyright: © 2007 The PLoS Medicine Editors. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Why do up to half of all patients with tuberculosis (TB) fail to adhere to drug treatment [ 1 ]? The answer to this question is a matter of life and death, since nonadherence contributes to disease relapse and mortality [ 2 ]. In last month's PLoS Medicine, Salla Munro and colleagues argue that qualitative studies—in which researchers listen to what patients, care givers, and health care providers have to say—can provide important insights into why nonadherence occurs [ 3 ]. Their paper is a “meta-ethnography” [ 4 ], a systematic review and synthesis of qualitative studies on adherence to TB medication. The review found a wide array of factors to explain nonadherence, such as the belief that if one's symptoms have disappeared there is no need to finish a course of treatment. We published this review because we thought it would play a role in improving the delivery of TB treatment and ultimately in reducing the enormous global burden of the disease.
PLoS Medicine has now published two such meta-ethnographies (the first looked at adherence to HIV medication [ 5 ]). We have also published a small number of individual qualitative studies. For example, in our special issue on social medicine ( http://collections.plos.org/plosmedicine/socialmedicine-2006.php ), we published a qualitative study of migrant workers in the US that found that farm working and housing conditions are organized according to ethnicity and citizenship and that this hierarchy determines health disparities [ 6 ]. We have been very selective in our editorial decisions about which qualitative studies to publish. In our decision-making process, we have been guided by two crucial questions.
The first question is whether a qualitative approach was the right way to answer the research question. Quantitative research strives to be objective: human beings, health, and illness are the objects of investigation. Such investigation has led to extraordinary biomedical advances—yet patients often fail to reap the benefits because health professionals may not understand how best to deliver them in the context of patients' multifaceted lives. The academic editor of Salla Munro and colleagues' study commented that thinking of TB drugs simply as a “biomedical intervention” without factoring in patients' needs and broader social contexts creates circumstances that increase the likelihood of poor adherence to treatment. Qualitative research is the best way to understand these needs and contexts.
Astrid Fletcher and colleagues, for example, used quantitative methods to objectively determine who (in terms of age, sex, and education level) did not use the eye-care services available in India [ 7 ]. But they adopted a qualitative approach to answer the question of why people did not use these services. David Leon and colleagues, during a quantitative study on hazardous alcohol drinking in Russia, learned that much alcohol was consumed in the form of what were described as “surrogates” [ 8 ]. Qualitative research helped to identify what these surrogates were—they included eau de Cologne and over-the-counter medications.
When researchers investigate the experiences of people receiving or failing to receive health care, identify themes in these subjective stories, and integrate these themes into the greater context of human life experience, the results are informative to care providers. The usefulness of these results lies precisely in their subjectivity: the subjects are telling us, or we are finding out through more subtle observation, what matters to them.
The results of qualitative research can also help to inform the very process of research itself. Qualitative approaches can help us to understand, for example, why some patients decline to participate in clinical trials [ 9 ], or how patients experience the trial process itself. They can even be used to refine or improve a clinical trial in “real time.” In a trial of a computerized decision support tool for patients with atrial fibrillation being considered for anticoagulation treatment, Madeleine Murtagh and colleagues used qualitative evidence in deciding to discontinue one arm of the trial (the intervention in that arm was causing confusion amongst the patients and was unlikely to produce valid data) [ 10 ]. When a quantitative study is assessing the effectiveness of a complex multifaceted intervention, qualitative methods can help to tease out why such an intervention works or fails [ 11 ]. Qualitative approaches can also help to identify which of many possible research questions should receive priority for investigation, often by asking the research participants themselves. For example, patients with asthma may value easy-to-use inhalers more highly than a new class of drug.
Once it is clear that qualitative methods constitute the right approach for a study submitted to PLoS Medicine, the second question is whether the study meets our criteria for rigor and relevance. For a study to be suitable, regardless of the methodology, it should address an important topic in clinical medicine or public health and it should have the potential to transform our understanding of the causes or treatment of disease. In assessing any study, quantitative or qualitative, we are always on the lookout for biases, poorly described methods, and limited generalizability or overinterpretation of the data. In specifically assessing qualitative studies, we additionally wish to be reassured that the researchers used some type of “quality control” in analyzing the data—for example, were the data independently analyzed by at least two researchers and did consistent themes emerge from the data each time?
One characteristic of PLoS Medicine is the very broad range of research that we have published to date. We feel that such a range is appropriate for a medical journal, since understanding the complex nature of illness and health care requires a variety of different research approaches. “What is involved is not a crossroads where we have to go left or right,” Martyn Hammersley has argued in a discussion of the false dichotomy between quantitative and qualitative research. “A better analogy is a complex maze where we are repeatedly faced with decisions, and where paths wind back on one another” [ 12 ].
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- 2. Volmink J, Garner P (2006) Directly observed therapy for treating tuberculosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2, CD003343.
- 4. Noblit GW, Hare RD (1988) Meta-ethnography: Synthesizing qualitative studies. Newbury Park (CA): Sage. 88 p.
- 12. (1992) Deconstructing the qualitative–quantitative divide. In: Brannen J, editor. Mixing methods: Qualitative and quantitative research. Aldershot (United Kingdom): Avebury. pp. 39–55. editor.
Qualitative Research : Definition
Qualitative research is the naturalistic study of social meanings and processes, using interviews, observations, and the analysis of texts and images. In contrast to quantitative researchers, whose statistical methods enable broad generalizations about populations (for example, comparisons of the percentages of U.S. demographic groups who vote in particular ways), qualitative researchers use in-depth studies of the social world to analyze how and why groups think and act in particular ways (for instance, case studies of the experiences that shape political views).
Events and Workshops
- Introduction to NVivo Have you just collected your data and wondered what to do next? Come join us for an introductory session on utilizing NVivo to support your analytical process. This session will only cover features of the software and how to import your records. Please feel free to attend any of the following sessions below: April 25th, 2024 12:30 pm - 1:45 pm Green Library - SVA Conference Room 125 May 9th, 2024 12:30 pm - 1:45 pm Green Library - SVA Conference Room 125 May 30th, 2024 12:30 pm - 1:45 pm Green Library - SVA Conference Room 125
- Next: Choose an approach >>
- Choose an approach
- Find studies
- Learn methods
- Get software
- Get data for secondary analysis
- Network with researchers

- Last Updated: Apr 2, 2024 10:41 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.stanford.edu/qualitative_research
- Open access
- Published: 13 December 2018
Using qualitative Health Research methods to improve patient and public involvement and engagement in research
- Danielle E. Rolfe 1 ,
- Vivian R. Ramsden 2 ,
- Davina Banner 3 &
- Ian D. Graham 1
Research Involvement and Engagement volume 4 , Article number: 49 ( 2018 ) Cite this article
43k Accesses
58 Citations
23 Altmetric
Metrics details
Plain English summary
Patient engagement (or patient and public involvement) in health research is becoming a requirement for many health research funders, yet many researchers have little or no experience in engaging patients as partners as opposed to research subjects. Additionally, many patients have no experience providing input on the research design or acting as a decision-making partner on a research team. Several potential risks exist when patient engagement is done poorly, despite best intentions. Some of these risks are that: (1) patients’ involvement is merely tokenism (patients are involved but their suggestions have little influence on how research is conducted); (2) engaged patients do not represent the diversity of people affected by the research; and, (3) research outcomes lack relevance to patients’ lives and experiences.
Qualitative health research (the collection and systematic analysis of non-quantitative data about peoples’ experiences of health or illness and the healthcare system) offers several approaches that can help to mitigate these risks. Several qualitative health research methods, when done well, can help research teams to: (1) accurately incorporate patients’ perspectives and experiences into the design and conduct of research; (2) engage diverse patient perspectives; and, (3) treat patients as equal and ongoing partners on the research team.
This commentary presents several established qualitative health research methods that are relevant to patient engagement in research. The hope is that this paper will inspire readers to seek more information about qualitative health research, and consider how its established methods may help improve the quality and ethical conduct of patient engagement for health research.
Research funders in several countries have posited a new vision for research that involves patients and the public as co-applicants for the funding, and as collaborative partners in decision-making at various stages and/or throughout the research process. Patient engagement (or patient and public involvement) in health research is presented as a more democratic approach that leads to research that is relevant to the lives of the people affected by its outcomes. What is missing from the recent proliferation of resources and publications detailing the practical aspects of patient engagement is a recognition of how existing research methods can inform patient engagement initiatives. Qualitative health research, for example, has established methods of collecting and analyzing non-quantitative data about individuals’ and communities’ lived experiences with health, illness and/or the healthcare system. Included in the paradigm of qualitative health research is participatory health research, which offers approaches to partnering with individuals and communities to design and conduct research that addresses their needs and priorities.
The purpose of this commentary is to explore how qualitative health research methods can inform and support meaningful engagement with patients as partners. Specifically, this paper addresses issues of: rigour (how can patient engagement in research be done well?); representation (are the right patients being engaged?); and, reflexivity (is engagement being done in ways that are meaningful, ethical and equitable?). Various qualitative research methods are presented to increase the rigour found within patient engagement. Approaches to engage more diverse patient perspectives are presented to improve representation beyond the common practice of engaging only one or two patients. Reflexivity, or the practice of identifying and articulating how research processes and outcomes are constructed by the respective personal and professional experiences of researchers and patients, is presented to support the development of authentic, sustainable, equitable and meaningful engagement of patients as partners in health research.
Conclusions
Researchers will need to engage patients as stakeholders in order to satisfy the overlapping mandate in health policy, care and research for engaging patients as partners in decision-making. This paper presents several suggestions to ground patient engagement approaches in established research designs and methods.
Peer Review reports
Patient engagement (or patient and public involvement) in research involves partnering with ‘patients’ (a term more often used in Canada and the US, that is inclusive of individuals, caregivers, and/or members of the public) to facilitate research related to health or healthcare services. Rather than research subjects or participants, patients are engaged as partners in the research process. This partnership is intended to be meaningful and ongoing, from the outset of planning a research project, and/or at various stages throughout the research process. Engagement can include the involvement of patients in defining a research question, identifying appropriate outcomes and methods, collecting and interpreting data, and developing and delivering a knowledge translation strategy [ 1 ].
The concept of engaging non-researchers throughout the research process is not new to participatory health researchers, or integrated knowledge translation researchers, as the latter involves ongoing collaboration with clinicians, health planners and policy makers throughout the research process in order to generate new knowledge [ 2 , 3 ]. Patients, however, are less frequently included as partners on health research teams, or as knowledge users in integrated knowledge translation research teams compared to clinicians, healthcare managers and policy-makers, as these individuals are perceived as having “the authority to invoke change in the practice or policy setting.” (p.2) [ 2 ] Recent requirements for patient engagement by health research funders [ 4 , 5 , 6 ], ,and mandates by most healthcare planners and organizations to engage patients in healthcare improvement initiatives, suggest that it would be prudent for integrated knowledge translation (and indeed all) health researchers to begin engaging patients as knowledge users in many, if not all, of their research projects.
Training and tools for patient engagement are being developed and implemented in Canada via the Canadian Institutes for Health Research (CIHR) Strategy for Patient Oriented Research (SPOR) initiative, in the US via Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI), and very practical resources are already available from the UK’s more established INVOLVE Advisory Group [ 5 , 6 , 7 ]. What is seldom provided by these ‘get started’ guides, however, are rigorous methods and evidence-based approaches to engaging diverse patient perspectives, and ensuring that their experiences, values and advice are appropriately incorporated into the research process.
The purpose of this commentary is to stimulate readers’ further discussion and inquiry into qualitative health research methods as a means of fostering the more meaningfully engagement of patients as partners for research. Specifically, this paper will address issues of: rigour (how do we know that the interpretation of patients’ perspectives has been done well and is applicable to other patients?); representation (are multiple and diverse patient perspectives being sought?); and, reflexivity (is engagement being done ethically and equitably?). This commentary alone is insufficient to guide researchers and patient partners to use the methods presented as part of their patient engagement efforts. However, with increased understanding of these approaches and perhaps guidance from experienced qualitative health researchers, integrated knowledge translation and health researchers alike may be better prepared to engage patients in a meaningful way in research that has the potential to improve health and healthcare experiences and outcomes.
What can be learned from methods utilized in qualitative health research?
There is wide variation in researchers’ and healthcare providers’ openness to engaging patients [ 8 ]. Often, the patients that are engaged are a select group of individuals known to the research team, sometimes do not reflect the target population of the research, are involved at a consultative rather than a partnership level, and are more likely to be involved in the planning rather than the dissemination of research [ 9 , 10 , 11 ]. As a result, patient engagement can be seen as tokenistic and the antithesis of the intention of most patient engagement initiatives, which is to have patients’ diverse experiences and perspectives help to shape what and how research is done. The principles, values, and practices of qualitative health research (e.g., relativism, social equity, inductive reasoning) have rich epistemological traditions that align with the conceptual and practical spirit of patient engagement. It is beyond the scope of this commentary, however, to describe in detail the qualitative research paradigm, and readers are encouraged to gain greater knowledge of this topic via relevant courses and texts. Nevertheless, several qualitative research considerations and methods can be applied to the practice of patient engagement, and the following sections describe three of these: rigour, representation and reflexivity.
Rigour: Interpreting and incorporating patients’ experiences into the design and conduct of research
When patient engagement strategies go beyond the inclusion of a few patient partners on the research team, for example, by using focus groups, interviews, community forums, or other methods of seeking input from a broad range of patient perspectives, the diversity of patients’ experiences or perspectives may be a challenge to quickly draw conclusions from in order to make decisions about the study design. To make these decisions, members of the research team (which should include patient partners) may discuss what they heard about patients’ perspectives and suggestions, and then unsystematically incorporate these suggestions, or they may take a vote, try to achieve consensus, implement a Delphi technique [ 12 ], or use another approach designed specifically for patient engagement like the James Lind Alliance technique for priority setting [ 13 ]. Although the information gathered from patients is not data (and indeed would require ethical review to be used as such), a number of qualitative research practices designed to increase rigour can be employed to help ensure that the interpretation and incorporation of patients’ experiences and perspectives has been done systematically and could be reproduced [ 14 ]. These practices include member checking , dense description , and constant comparative analysis . To borrow key descriptors of rigour from qualitative research, these techniques improve “credibility” (i.e., accurate representations of patients’ experiences and preferences that are likely to be understood or recognized by other patients in similar situations – known in quantitative research as internal validity), and “transferability” (or the ability to apply what was found among a group of engaged patients to other patients in similar contexts – known in quantitative research as external validity) [ 15 ].
Member checking
Member checking in qualitative research involves “taking ideas back to the research participants for their confirmation” (p. 111) [ 16 ]. The objective of member checking is to ensure that a researcher’s interpretation of the data (whether a single interview with a participant, or after analyzing several interviews with participants) accurately reflects the participants’ intended meaning (in the case of a member check with a single participant about their interview), or their lived experience (in the case of sharing an overall finding about several individuals with one or more participants) [ 16 ]. For research involving patient engagement, member checking can be utilized to follow-up with patients who may have been engaged at one or only a few time points, or on an on-going basis with patient partners. A summary of what was understood and what decisions were made based on patients’ recommendations could be used to initiate this discussion and followed up with questions such as, “have I understood correctly what you intended to communicate to me?” or “do you see yourself or your experience(s) reflected in these findings or suggestions for the design of the study?”
Dense description
As with quantitative research, detailed information about qualitative research methods and study participants is needed to enable other researchers to understand the context and focus of the research and to establish how these findings relate more broadly. This helps researchers to not only potentially repeat the study, but to extend its findings to similar participants in similar contexts. Dense description provides details of the social, demographic and health profile of participants (e.g., gender, education, health conditions, etc.), as well as the setting and context of their experiences (i.e., where they live, what access to healthcare they have). In this way, dense description improves the transferability of study findings to similar individuals in similar situations [ 15 ]. To date, most studies involving patient engagement provide limited details about their engagement processes and who was engaged [ 17 ]. This omission may be done intentionally (e.g., to protect the privacy of engaged patients, particularly those with stigmatizing health conditions), or as a practical constraint such as publication word limits. Nonetheless, reporting of patient engagement using some aspects of dense description of participants (as appropriate), the ways that they were engaged, and recommendations that emanated from engaged patients can also contribute to greater transferability and understanding of how patient engagement influenced the design of a research study.
Constant comparative analysis
Constant comparative analysis is a method commonly used in grounded theory qualitative research [ 18 ]. Put simply, the understanding of a phenomenon or experience that a researcher acquires through engaging with participants is constantly redeveloped and refined based on subsequent participant interactions. This process of adapting to new information in order to make it more relevant is similar to processes used in rapid cycle evaluation during implementation research [ 19 ]. This method can be usefully adapted and applied to research involving ongoing collaboration and partnership with several engaged patient partners, and/or engagement strategies that seek the perspectives of many patients at various points in the research process. For example, if, in addition to having ongoing patient partners, a larger group of patients provides input and advice (e.g., a steering or advisory committee) at different stages in the research process, their input may result in multiple course corrections during the design and conduct of the research processes to incorporate their suggestions. These suggestions may result in refinement of earlier decisions made about study design or conduct, and as such, the research process becomes more iterative rather than linear. In this way, engaged patients and patient partners are able to provide their input and experience to improve each step of the research process from formulating an appropriate research question or objective, determining best approaches to conducting the research and sharing it with those most affected by the outcomes.
Representation: Gathering diverse perspectives to design relevant and appropriate research studies
The intention of engaging patients is to have their lived experience of health care or a health condition contribute to the optimization of a research project design [ 20 ]. Development of a meaningful and sustainable relationship with patient partners requires considerable time, a demonstrated commitment to partnership by both the patient partners and the researcher(s), resources to facilitate patient partners’ engagement, and often, an individual designated to support the development of this relationship [ 17 , 21 ]. This may lead some research teams to sustain this relationship with only one or two patients who are often previously known to the research team [ 17 ]. The limitation of this approach is that the experiences of these one or two individuals may not adequately reflect the diverse perspectives of patients that may be affected by the research or its outcomes. The notion of gaining ‘ the patient perspective’ from a single or only a few individuals has already been problematized [ 22 , 23 ]. To be sure, the engagement of a single patient is better than none at all, but the engagement of a broader and diverse population of patients should be considered to better inform the research design, and to help prevent further perpetuation of health disparities. Key issues to be considered include (1) how engagement can be made accessible to patients from diverse backgrounds, and (2) which engagement strategies (e.g., ranging from a community information forum to full partnership on the research team) are most appropriate to reach the target population [ 24 ].
Making engagement accessible
Expecting patient partner(s) to attend regular research team meetings held during working hours in a boardroom setting in a hospital, research institute or university limits the participation of many individuals. To support the participation and diversity of engaged patients, effort should be made to increase the accessibility and emotional safety of engagement initiatives [ 25 ]. A budget must be allocated for patient partners’ transportation, childcare or caregiving support, remuneration for time or time taken off work and, at the very least, covering expenses related to their engagement. Another consideration that is often made by qualitative health researchers is whether brief counselling support can be provided to patients should the sharing of their experiences result in emotional distress. There are some resources that can help with planning for costs [ 26 ], including an online cost calculator [ 27 ].
Engagement strategies
Patient partners can be coached to consider the needs and experiences of people unlike them, but there are other methods of engagement that can help to gain a more fulsome perspective of what is likely a diverse patient population that is the focus of the research study. In qualitative health research, this is known as purposeful or purposive sampling: finding people who can provide information-rich descriptions of the phenomenon under study [ 28 ]. Engagement may require different approaches (e.g., deliberative group processes, community forums, focus groups, and patient partners on the research team), at different times in the research process to reach different individuals or populations (e.g., marginalized patients, or patients or caregivers experiencing illnesses that inhibit their ability to maintain an ongoing relationship with the research team). Engagement strategies of different forms at different times may be required. For example, ongoing engagement may occur with patient partners who are members of the research team (e.g., co-applicants on a research grant), and intermittent engagement may be sought from other patients through other methods that may be more time-limited or accessible to a diverse population of patients (e.g., a one-time focus group, community forum, or ongoing online discussion) to address issues that may arise during various stages of the research or dissemination processes. The result of this approach is that patients are not only consulted or involved (one-time or low commitment methods), but are also members of the research team and have the ability to help make decisions about the research being undertaken.
Engagement can generate a wealth of information from very diverse perspectives. Each iteration of engagement may yield new information. Knowing when enough information has been gathered to make decisions with the research team (that includes patient partners) about how the research may be designed or conducted can be challenging. One approach from qualitative research that can be adapted for patient engagement initiatives is theoretical saturation [ 29 ], or “the point in analysis when…further data gathering and analysis add little new to the conceptualization, though variations can always be discovered.” (p. 263) [ 18 ]. That is, a one-time engagement strategy (e.g., a discussion with a single patient partner) may be insufficient to acquire the diverse perspectives of the individuals that will be affected by the research or its outcomes. Additional strategies (e.g., focus groups or interviews with several individuals) may be initiated until many patients identify similar issues or recommendations.
Engagement approaches should also consider: how patients are initially engaged (e.g., through known or new networks, posted notices, telephone or in-person recruitment) and whether involvement has been offered widely enough to garner multiple perspectives; how patients’ experiences are shared (e.g., community forums, formal meetings, individual or group discussions) and whether facilitation enables broad participation; and finally, how patients’ participation and experiences are incorporated into the research planning and design, with patients having equal decision-making capacity to other research team members. Several publications and tools are available that can help guide researchers who are new to processes of engaging patients in research [ 24 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 ], but unfortunately few address how to evaluate the effectiveness of engagement [ 35 ].
Reflexivity: Ensuring meaningful and authentic engagement
In qualitative research, reflexivity is an ongoing process of “the researcher’s scrutiny of his or her research experience, decisions, and interpretations in ways that bring the researcher into the process and allow the reader to assess how and to what extent the researcher’s interests, positions, and assumptions influenced inquiry. A reflexive stance informs how the researcher conducts his or her research, relates to the research participants, and represents them in written reports,” (p.188–189) [ 16 ]. The concept of reflexivity can be applied to research involving patient engagement by continually and explicitly considering how decisions about the research study were made. All members of the research team must consider (and perhaps discuss): (1) how patient partners are invited to participate in research planning and decision-making; (2) how their input is received relative to other team members (i.e., do their suggestions garner the same respect as researchers’ or providers’?); and, (3) whether engaged patients or patient partners feel sufficiently safe, able and respected to share their experiences, preferences and recommendations with the research team.
Ideally, reflexivity becomes a practice within the research team and may be operationalized through regular check-ins with patients and researchers about their comfort in sharing their views, and whether they feel that their views have been considered and taken onboard. Power dynamics should also be considered during patient engagement initiatives. For example, reflecting on how community forums, focus groups or interviews are to be facilitated, including a consideration of who is at the table/who is not, who speaks/who does not, whose suggestions are implemented/whose are not? Reflexivity can be practiced through informal discussions, or using methods that may allow more candid responses by engaged patients (e.g., anonymous online survey or feedback forms). At the very least, if these practices were not conducted throughout the research process, the research team (including patient partners) should endeavor to reflect upon team dynamics and consider how these may have contributed to the research design or outcomes. For example, were physicians and researchers seen as experts and patients felt less welcome or able to share their personal experiences? Were patients only engaged by telephone rather than in-person and did this influence their ability to easily engage in decision-making? Reflexive practices may be usefully supplemented by formal evaluation of the process of patient engagement from the perspective of patients and other research team members [ 36 , 37 ], and some tools are available to do this [ 35 ].

A note about language
One way to address the team dynamic between researchers, professional knowledge users (such as clinicians or health policy planners) and patients is to consider the language used to engage with patients in the planning of patient engagement strategies. That is, the term ‘patient engagement’ is a construction of an individual’s identity that exists only within the healthcare setting, and in the context of a patient-provider dynamic. This term does not consider how people make decisions about their health and healthcare within a broader context of their family, community, and culture [ 22 , 38 ]. This may be why research communities in some countries (e.g., the United Kingdom) use the term ‘patient and public involvement’. Additionally, research that involves communities defined by geography, shared experiences, cultural or ethnic identity, as is the case with participatory health research, may refer to ‘community engagement.’ Regardless of the term used, partnerships with patients, the public, or with communities need to be conceived instead as person-to-person interactions between researchers and individuals who are most affected by the research. Discussions with engaged patients should be conducted early on to determine how to best describe their role on the team or during engagement initiatives (e.g., as patient partners, community members, or people with lived experience).
Tokenism is the “difference between…the empty ritual of participation and having the real power needed to affect the outcome,” (p.2) [ 39 ]. Ongoing reflection on the power dynamic between researchers and engaged patients, a central tenet of critical qualitative health research [ 40 , 41 ], can increase the likelihood that engagement involves equitable processes and will result in meaningful engagement experiences by patients rather than tokenism [ 36 , 42 ]. Patient engagement initiatives should strive for “partnership” amongst all team members, and not just reflect a patient-clinician or researcher-subject dynamic [ 43 ]. To develop meaningful, authentic and sustainable relationships with engaged patients, methods used for participatory, action or community-based research (approaches that fall under the paradigm of qualitative inquiry) provide detailed experiential guidance [ 44 ]. For example, a realist review of community-based participatory research projects reported that gaining and maintaining trust with patient or community partners, although time-intensive, is foundational to equitable and sustainable partnerships that benefit communities and individuals [ 45 , 46 ]. Additionally, Chapter Nine of the Canadian Tri-Council Policy Statement on Research involving Humans, which has to date been applied to research involving First Nations, Inuit and, Métis Peoples in Canada [ 47 ], provides useful information and direction that can be applied to working with patient partners on research [ 48 ].
Authentic patient engagement should include their involvement at all stages of the research process [ 49 , 50 ], but this is often not the case [ 10 ]. .Since patient partners are not research subjects or participants, their engagement does not (usually) require ethics approval, and they can be engaged as partners as early as during the submission of grant applications [ 49 ]. This early engagement helps to incorporate patients’ perspectives into the proposed research before the project is wedded to particular objectives, outcomes and methods, and can also serve to allocate needed resources to support patient engagement (including remuneration for patient partners’ time). Training in research for patient partners can also support their meaningful engagement by increasing their ability to fully engage in decision-making with other members of the research team [ 51 , 52 ]. Patient partners may also thrive in co-leading the dissemination of findings to healthcare providers, researchers, patients or communities most affected by the research [ 53 ].
Patient engagement has gained increasing popularity, but many research organizations are still at the early stages of developing approaches and methods, many of which are based on experience rather than evidence. As health researchers and members of the public will increasingly need to partner for research to satisfy the overlapping mandate of patient engagement in health policy, healthcare and research, the qualitative research methods highlighted in this commentary provide some suggestions to foster rigorous, meaningful and sustained engagement initiatives while addressing broader issues of power and representation. By incorporating evidence-based methods of gathering and learning from multiple and diverse patient perspectives, we will hopefully conduct better patient engaged research, live out the democratic ideals of patient engagement, and ultimately contribute to research that is more relevant to the lives of patients; as well as, contribute to the improved delivery of healthcare services. In addition to the references provided in this paper, readers are encouraged to learn more about the meaningful engagement of patients in research from several key texts [ 54 , 55 , 56 ].
Abbreviations
Canadian Institutes for Health Research
Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute
Strategy for Patient Oriented Research
Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Strategy for Patient-Oriented Research. 2014. http://www.cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/documents/spor_framework-en.pdf . Accessed 27 Sep 2017.
Google Scholar
Kothari A, Wathen CN. Integrated knowledge translation: digging deeper, moving forward. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2017;71:619–23. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech-2016-208490 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Gagliardi AR, Berta W, Kothari A, Boyko J, Urquhart R. Integrated knowledge translation (IKT) in health care: a scoping review. Implement Sci. 2016;11:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-016-0399-1 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Strategy for Patient-Oriented Research - CIHR. http://www.cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/41204.html . Accessed 20 Sep 2017.
Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute website. https://www.pcori.org/ . Accessed 20 Sep 2017.
National Institute for Health Research. INVOLVE | INVOLVE Supporting public involvement in NHS, public health and social care research. http://www.invo.org.uk/ . Accessed 27 Sep 2017.
Canadian Institutes of Health Research. SPOR SUPPORT Units - CIHR. http://www.cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/45859.html . Accessed 27 Sep 2017.
Ocloo J, Matthews R. From tokenism to empowerment: progressing patient and public involvement in healthcare improvement. BMJ Qual Saf. 2016;25:626–32.
Hearld KR, Hearld LR, Hall AG. Engaging patients as partners in research: factors associated with awareness, interest, and engagement as research partners. SAGE open Med. 2017;5:2050312116686709. https://doi.org/10.1177/2050312116686709.
Domecq JP, Prutsky G, Elraiyah T, Wang Z, Nabhan M, Shippee N, et al. Patient engagement in research: a systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014;14:89. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-14-89 .
Concannon TW, Fuster M, Saunders T, Patel K, Wong JB, Leslie LK, et al. A systematic review of stakeholder engagement in comparative effectiveness and patient-centered outcomes research. J Gen Intern Med. 2014;29:1692–701.
Oostendorp LJM, Durand M-A, Lloyd A, Elwyn G. Measuring organisational readiness for patient engagement (MORE): an international online Delphi consensus study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2015;15:61. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-015-0717-3 .
Boddy K, Cowan K, Gibson A, Britten N. Does funded research reflect the priorities of people living with type 1 diabetes? A secondary analysis of research questions. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e016540. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016540 .
Mays N, Pope C. Rigour and qualitative research. BMJ Br Med J. 1995;311:109–12.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Krefting L. Rigor in qualitative research: the assessment of trustworthiness. Am J Occup Ther. 1991;45:214–22.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Charmaz K. Constructing grounded theory : a practical guide through qualitative analysis. London: Sage Publications; 2006.
Wilson P, Mathie E, Keenan J, McNeilly E, Goodman C, Howe A, et al. ReseArch with patient and public invOlvement: a RealisT evaluation – the RAPPORT study. Heal Serv Deliv Res. 2015;3:1–176. https://doi.org/10.3310/hsdr03380 .
Corbin JM, Strauss AL, Strauss AL. Basics of qualitative research : techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications; 2008.
Keith RE, Crosson JC, O’Malley AS, Cromp D, Taylor EF. Using the consolidated framework for implementation research (CFIR) to produce actionable findings: a rapid-cycle evaluation approach to improving implementation. Implement Sci. 2017;12:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-017-0550-7 .
Esmail L, Moore E. Evaluating patient and stakeholder engagement in research: moving from theory to practice. J Comp Eff Res. 2015;4:133–45. https://doi.org/10.2217/cer.14.79 .
Brett J, Staniszewska S, Mockford C, Herron-Marx S, Hughes J, Tysall C, et al. A systematic review of the impact of patient and public involvement on service users, researchers and communities. Patient. 2014;7:387–95.
Rowland P, McMillan S, McGillicuddy P, Richards J. What is “the patient perspective” in patient engagement programs? Implicit logics and parallels to feminist theories. Heal An Interdiscip J Soc Study Heal Illn Med. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1177/1363459316644494 .
Article Google Scholar
Martin GP. “Ordinary people only”: knowledge, representativeness, and the publics of public participation in healthcare. Sociol Health Illn. 2008;30:35–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9566.2007.01027.x .
Snow B, Tweedie K, Pederson A, Shrestha H, Bachmann L. Patient Engagement: Heard and valued. 2013. http://www.cfhi-fcass.ca/sf-docs/default-source/patient-engagement/awesome_workbook-fraserhealth.pdf . Accessed 24 Jan 2018.
Montesanti SR, Abelson J, Lavis JN, Dunn JR. Enabling the participation of marginalized populations: case studies from a health service organization in Ontario. Canada Health Promot Int. 2017;32(4):636–49. https://doi.org/10.1093/heapro/dav118.
The Change Foundation. Should Money Come into It? A Tool for Deciding Whether to Pay Patient- Engagement Participants. Toronto; 2015. http://www.changefoundation.ca/site/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Should-money-come-into-it.pdf . Accessed 18 June 2018
INVOLVE. Involvement Cost Calculator | INVOLVE. http://www.invo.org.uk/resource-centre/payment-and-recognition-for-public-involvement/involvement-cost-calculator/ . Accessed 11 Oct 2017.
Patton MQ. Qualitative research and evaluation methods. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications; 2002.
Kerr C, Nixon A, Wild D. Assessing and demonstrating data saturation in qualitative inquiry supporting patient-reported outcomes research. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2010;10(3):269–81. https://doi.org/10.1586/erp.10.30 .
Canadian Institutes of Health Research. CIHR’S Citizen Engagement Handbook. http://www.cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/documents/ce_handbook_e.pdf . Accessed 18 June 2018.
Elliott J, Heesterbeek S, Lukensmeyer CJ, Slocum N. Participatory and deliberative methods toolkit how to connect with citizens: a practitioner’s manual. King Baudouin Foundation; 2005. https://www.kbs-frb.be/en/Virtual-Library/2006/294864 . Accessed 28 Sep 2017.
Robbins M, Tufte J, Hsu C. Learning to “swim” with the experts: experiences of two patient co-investigators for a project funded by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Perm J. 2016;20:85–8.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Gauvin F-P, Abelson J, Lavis JN. Strengthening public and patient engagement in health technology assessment in Ontario. 2014. https://www.mcmasterforum.org/docs/default-source/product-documents/evidence-briefs/public-engagement-in-health-technology-assessement-in-ontario-eb.pdf?sfvrsn=2 . Accessed 18 June 2018.
Abelson J, Montesanti S, Li K, Gauvin F-P, Martin E. Effective strategies for interactive public engagement in the development of healthcare policies and Programs. 2010; https://www.cfhi-fcass.ca/sf-docs/default-source/commissionedresearch-reports/Abelson_EN_FINAL.pdf?sfvrsn=0. . Accessed 16 Nov 2018.
Abelson J. Public and patient engagement evaluation tool (version 1.0), vol. 0; 2015. https://www.fhs.mcmaster.ca/publicandpatientengagement/ppeet_request_form.html ! Accessed 18 June 2018
Johnson DS, Bush MT, Brandzel S, Wernli KJ. The patient voice in research—evolution of a role. Res Involv Engagem. 2016;2:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40900-016-0020-4 .
Crocker JC, Boylan AM, Bostock J, Locock L. Is it worth it? Patient and public views on the impact of their involvement in health research and its assessment: a UK-based qualitative interview study. Health Expect. 2017;20(3):519–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/hex.12479 .
Renedo A, Marston C. Healthcare professionals’ representations of “patient and public involvement” and creation of “public participant” identities: implications for the development of inclusive and bottom-up community participation initiatives. J Community Appl Soc Psychol. 2011;21:268–80. https://doi.org/10.1002/casp.1092 .
Hahn DL, Hoffmann AE, Felzien M, LeMaster JW, Xu J, Fagnan LJ. Tokenism in patient engagement. Fam Pract. 2017;34(3):290–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/fampra/cmw097.
Hart C, Poole JM, Facey ME, Parsons JA. Holding firm: power, push-Back, and opportunities in navigating the liminal space of critical qualitative Health Research. Qual Health Res. 2017;27:1765–74. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732317715631 .
Eakin JM. Educating critical qualitative health researchers in the land of the randomized controlled trial. Qual Inq. 2016;22:107–18. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077800415617207 .
Safo S, Cunningham C, Beckman A, Haughton L, Starrels JL. “A place at the table:” a qualitative analysis of community board members’ experiences with academic HIV/AIDS research. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2016;16:80. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-016-0181-8 .
Thompson J, Bissell P, Cooper C, Armitage CJ, Barber R, Walker S, et al. Credibility and the “professionalized” lay expert: reflections on the dilemmas and opportunities of public involvement in health research. Heal Interdiscip J Soc Study Heal Illn Med. 2012;16:602–18. https://doi.org/10.1177/1363459312441008 .
Burke JG, Jones J, Yonas M, Guizzetti L, Virata MC, Costlow M, et al. PCOR, CER, and CBPR: alphabet soup or complementary fields of Health Research? Clin Transl Sci. 2013;6:493–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/cts.12064 .
Jagosh J, Bush PL, Salsberg J, Macaulay AC, Greenhalgh T, Wong G, et al. A realist evaluation of community-based participatory research: partnership synergy, trust building and related ripple effects. BMC Public Health. 2015;15:725. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-015-1949-1 .
Jagosh J, Macaulay AC, Pluye P, Salsberg J, Bush PL, Henderson J, et al. Uncovering the benefits of participatory research: implications of a realist review for health research and practice. Milbank Q. 2012;90:311–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0009.2012.00665.x .
Government of Canada IAP on RE. TCPS 2 - Chapter 9 Research Involving the First Nations, Inuit and Métis Peoples of Canada. http://www.pre.ethics.gc.ca/eng/policy-politique/initiatives/tcps2-eptc2/chapter9-chapitre9/ . Accessed 16 Oct 2017.
Ramsden VR, Crowe J, Rabbitskin N, Rolfe D, Macaulay A. Authentic engagement, co-creation and action research. In: Goodyear-smith F, Mash B, editors. How to do primary care research. Boca Raton: CRC press, medicine, Taylor & Francis Group; 2019.
Ramsden VR, Salsberg J, Herbert CP, Westfall JM, LeMaster J, Macaulay AC. Patient- and community-oriented research: how is authentic engagement identified in grant applications? Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:74–6.
Woolf SH, Zimmerman E, Haley A, Krist AH. Authentic engagement of patients and communities can transform research, practice, and policy. Health Aff. 2016;35:590–4.
Parkes JH, Pyer M, Wray P, Taylor J. Partners in projects: preparing for public involvement in health and social care research. Health Policy. 2014;117:399–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2014.04.014 .
Norman N, Bennett C, Cowart S, Felzien M, Flores M, Flores R, et al. Boot camp translation: a method for building a community of solution. J Am Board Fam Med. 2013;26:254–63. https://doi.org/10.3122/jabfm.2013.03.120253 .
Ramsden VR, Rabbitskin N, Westfall JM, Felzien M, Braden J, Sand J. Is knowledge translation without patient or community engagement flawed. Fam Pract. 2016:1–3.
Denzin NK, Lincoln YS. SAGE Handbook of qualitative research. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications; 2005.
Pearce V, Baraitser P, Smith G, Greenhalgh T. Experience-based co-design. In: User involvement in health care. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010. p. 28–51. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444325164.ch3 .
Chapter Google Scholar
Hulatt I, Lowes L. Involving service users in health and social care research: Routledge; 2005. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203865651.
Book Google Scholar
Download references
Acknowledgements
This paper was drafted in response to a call for concept papers related to integrated knowledge translation issued by the Integrated Knowledge Translation Research Network (CIHR FDN #143237).
This paper was commissioned by the Integrated Knowledge Translation Network (IKTRN). The IKTRN brings together knowledge users and researchers to advance the science and practice of integrated knowledge translation and train the next generation of integrated knowledge translation researchers. Honorariums were provided for completed papers. The IKTRN is funded by a Canadian Institutes of Health Research Foundation Grant (FDN #143247).
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Epidemiology and Public Health, University of Ottawa, 307D- 600 Peter Morand Crescent, Ottawa, ON, K1G 5Z3, Canada
Danielle E. Rolfe & Ian D. Graham
Department of Academic Family Medicine, University of Saskatchewan, West Winds Primary Health Centre, 3311 Fairlight Drive, Saskatoon, SK, S7M 3Y5, Canada
Vivian R. Ramsden
School of Nursing, University of Northern British Columbia, 3333 University Way, Prince George, BC, V2K4C6, Canada
Davina Banner
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
DR conceived and drafted this paper. All authors were involved in critiquing and revising the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Danielle E. Rolfe .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Rolfe, D.E., Ramsden, V.R., Banner, D. et al. Using qualitative Health Research methods to improve patient and public involvement and engagement in research. Res Involv Engagem 4 , 49 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40900-018-0129-8
Download citation
Received : 18 June 2018
Accepted : 09 November 2018
Published : 13 December 2018
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40900-018-0129-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative methods
- Qualitative health research
- Patient-oriented research
- Integrated knowledge translation
- Patient engagement
- Patient partners
- Patient and public involvement
Research Involvement and Engagement
ISSN: 2056-7529
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 01 October 2022
Qualitative longitudinal research in health research: a method study
- Åsa Audulv 1 ,
- Elisabeth O. C. Hall 2 , 3 ,
- Åsa Kneck 4 ,
- Thomas Westergren 5 , 6 ,
- Liv Fegran 5 ,
- Mona Kyndi Pedersen 7 , 8 ,
- Hanne Aagaard 9 ,
- Kristianna Lund Dam 3 &
- Mette Spliid Ludvigsen 10 , 11
BMC Medical Research Methodology volume 22 , Article number: 255 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
11k Accesses
20 Citations
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
Qualitative longitudinal research (QLR) comprises qualitative studies, with repeated data collection, that focus on the temporality (e.g., time and change) of a phenomenon. The use of QLR is increasing in health research since many topics within health involve change (e.g., progressive illness, rehabilitation). A method study can provide an insightful understanding of the use, trends and variations within this approach. The aim of this study was to map how QLR articles within the existing health research literature are designed to capture aspects of time and/or change.
This method study used an adapted scoping review design. Articles were eligible if they were written in English, published between 2017 and 2019, and reported results from qualitative data collected at different time points/time waves with the same sample or in the same setting. Articles were identified using EBSCOhost. Two independent reviewers performed the screening, selection and charting.
A total of 299 articles were included. There was great variation among the articles in the use of methodological traditions, type of data, length of data collection, and components of longitudinal data collection. However, the majority of articles represented large studies and were based on individual interview data. Approximately half of the articles self-identified as QLR studies or as following a QLR design, although slightly less than 20% of them included QLR method literature in their method sections.
Conclusions
QLR is often used in large complex studies. Some articles were thoroughly designed to capture time/change throughout the methodology, aim and data collection, while other articles included few elements of QLR. Longitudinal data collection includes several components, such as what entities are followed across time, the tempo of data collection, and to what extent the data collection is preplanned or adapted across time. Therefore, there are several practices and possibilities researchers should consider before starting a QLR project.
Peer Review reports
Health research is focused on areas and topics where time and change are relevant. For example, processes such as recovery or changes in health status. However, relating time and change can be complicated in research, as the representation of reality in research publications is often collected at one point in time and fixed in its presentation, although time and change are always present in human life and experiences. Qualitative longitudinal research (QLR; also called longitudinal qualitative research, LQR) has been developed to focus on subjective experiences of time or change using qualitative data materials (e.g., interviews, observations and/or text documents) collected across a time span with the same participants and/or in the same setting [ 1 , 2 ]. QLR within health research may have many benefits. Firstly, human experiences are not fixed and consistent, but changing and diverse, therefore people’s experiences in relation to a health phenomenon may be more comprehensively described by repeated interviews or observations over time. Secondly, experiences, behaviors, and social norms unfold over time. By using QLR, researchers can collect empirical data that represents not only recalled human conceptions but also serial and instant situations reflecting transitions, trajectories and changes in people’s health experiences, personal development or health care organizations [ 3 , 4 , 5 ].
Key features of QLR
Whether QLR is a methodological approach in its own right or a design element of a particular study within a traditional methodological approach (e.g., ethnography or grounded theory) is debated [ 1 , 6 ]. For example, Bennett et al. [ 7 ] describe QLR as untied to methodology, giving researchers the flexibility to develop a suitable design for each study. McCoy [ 6 ] suggests that epistemological and ontological standpoints from interpretative phenomenological analysis (IPA) align with QLR traditions, thus making longitudinal IPA a suitable methodology. Plano-Clark et al. [ 8 ] described how longitudinal qualitative elements can be used in mixed methods studies, thus creating longitudinal mixed methods. In contrast, several researchers have argued that QLR is an emerging methodology [ 1 , 5 , 9 , 10 ]. For example, Thomson et al. [ 9 ] have stated “What distinguishes longitudinal qualitative research is the deliberate way in which temporality is designed into the research process, making change a central focus of analytic attention” (p. 185). Tuthill et al. [ 5 ] concluded that some of the confusion might have arisen from the diversity of data collection methods and data materials used within QLR research. However, there are no investigations showing to what extent QLR studies use QLR as a distinct methodology versus using a longitudinal data collection as a more flexible design element in combination with other qualitative methodologies.
QLR research should focus on aspects of temporality, time and/or change [ 11 , 12 , 13 ]. The concepts of time and change are seen as inseparable since change is happening with the passing of time [ 13 ]. However, time can be conceptualized in different ways. Time is often understood from a chronological perspective, and is viewed as fixed, objective, continuous and measurable (e.g., clock time, duration of time). However, time can also be understood from within, as the experience of the passing of time and/or the perspective from the current moment into the constructed conception of a history or future. From this perspective, time is seen as fluid, meaning that events, contexts and understandings create a subjective experience of time and change. Both the chronological and fluid understanding of time influence QLR research [ 11 ]. Furthermore, there is a distinction between over-time, which constitutes a comparison of the difference between points in time, often with a focus on the latter point or destination, and through-time, which means following an aspect across time while trying to understand the change that occurs [ 11 ]. In this article, we will mostly use the concept of across time to include both perspectives.
Some authors assert that QLR studies should include a qualitative data collection with the same sample across time [ 11 , 13 ], whereas Thomson et al. [ 9 ] also suggest the possibility of returning to the same data collection site with the same or different participants. When a QLR study involves data collection in shorter engagements, such as serial interviews, these engagements are often referred to as data collection time points. Data collection in time waves relates to longer engagements, such as field work/observation periods. There is no clear-cut definition for the minimum time span of a QLR study; instead, the length of the data collection period must be decided based upon what processes or changes are the focus of the study [ 13 ].
Most literature describing QLR methods originates from the social sciences, where the approach has a long tradition [ 1 , 10 , 14 ]. In health research, one-time-data collection studies have been the norm within qualitative methods [ 15 ], although health research using QLR methods has increased in recent years [ 2 , 5 , 16 , 17 ]. However, collecting and managing longitudinal data has its own sets of challenges, especially regarding how to integrate perspectives of time and/or change in the data collection and subsequent analysis [ 1 ]. Therefore, a study of QLR articles from the health research literature can provide an insightful understanding of the use, trends and variations of how methods are used and how elements of time/change are integrated in QLR studies. This could, in turn, provide inspiration for using different possibilities of collecting data across time when using QLR in health research. The aim of this study was to map how QLR articles within the existing health research literature are designed to capture aspects of time and/or change.
More specifically, the research questions were:
What methodological approaches are described to inform QLR research?
What methodological references are used to inform QLR research?
How are longitudinal perspectives articulated in article aims?
How is longitudinal data collection conducted?
In this method study, we used an adapted scoping review method [ 18 , 19 , 20 ]. Method studies are research conducted on research studies to investigate how research design elements are applied across a field [ 21 ]. However, since there are no clear guidelines for method studies, they often use adapted versions of systematic reviews or scoping review methods [ 21 ]. The adaptations of the scoping review method consisted of 1) using a large subsample of studies (publications from a three-year period) instead of including all QLR articles published, and 2) not including grey literature. The reporting of this study was guided by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) checklist [ 20 , 22 ] (see Additional file 1 ). A (unpublished) protocol was developed by the research team during the spring of 2019.
Eligibility criteria
In line with method study recommendations [ 21 ], we decided to draw on a manageable subsample of published QLR research. Articles that were eligible for inclusion were health research primary studies written in English, published between 2017 and 2019, and with a longitudinal qualitative data collection. Our operating definition for qualitative longitudinal data collection was data collected at different time points (e.g., repeated interviews) or time waves (e.g., periods of field work) involving the same sample or conducted in the same setting(s). We intentionally selected a broad inclusion criterion for QLR since we wanted a wide variety of articles. The selected time period was chosen because the first QLR method article directed towards health research was published in 2013 [ 1 ] and during the following years the methodological resources for QLR increased [ 3 , 8 , 17 , 23 , 24 , 25 ], thus we could expect that researchers publishing QLR in 2017–2019 should be well-grounded in QLR methods. Further, we found that from 2012 to 2019 the rate of published QLR articles were steady at around 100 publications per year, so including those from a three-year period would give a sufficient number of articles (~ 300 articles) for providing an overview of the field. Published conference abstracts, protocols, articles describing methodological issues, review articles, and non-research articles (e.g., editorials) were excluded.
Search strategy
Relevant articles were identified through systematic searches in EBSCOhost, including biomedical and life science research and nursing and allied health literature. A librarian who specialized in systematic review searches developed and performed the searches, in collaboration with the author team (LF, TW & ÅA). In the search, the term “longitudinal” was combined with terms for qualitative research (for the search strategy see Additional file 2 ). The searches were conducted in the autumn of 2019 (last search 2019-09-10).
Study selection
All identified citations were imported into EndNote X9 ( www.endnote.com ) and further imported into Rayyan QCRI online software [ 26 ], and duplicates were removed. All titles and abstracts were screened against the eligibility criteria by two independent reviewers (ÅA & EH), and conflicting decisions were discussed until resolved. After discussions by the team, we decided to include articles published between 2017 and 2019, that selection alone included 350 records with diverse methods and designs. The full texts of articles that were eligible for inclusion were retrieved. In the next stage, two independent reviewers reviewed each full text article to make final decisions regarding inclusion (ÅA, EH, Julia Andersson). In total, disagreements occurred in 8% of the decisions, and were resolved through discussion. Critical appraisal was not assessed since the study aimed to describe the range of how QLR is applied and not aggregate research findings [ 21 , 22 ].
Data charting and analysis
A standardized charting form was developed in Excel (Excel 2016). The charting form was reviewed by the research team and pretested in two stages. The tests were performed to increase internal consistency and reduce the risk of bias. First, four articles were reviewed by all the reviewers, and modifications were made to the form and charting instructions. In the next stage, all reviewers used the charting form on four other articles, and the convergence in ratings was 88%. Since the convergence was under 90%, charting was performed in duplicate to reduce errors in the data. At the end of the charting process, the convergence among the reviewers was 95%. The charting was examined by the first author, who revised the charting in cases of differences.
Data items that were charted included 1) the article characteristics (e.g., authors, publication year, journal, country), 2) the aim and scope (e.g., phenomenon of interest, population, contexts), 3) the stated methodology and analysis method, 4) text describing the data collection (e.g., type of data material, number of participants, time frame of data collection, total amount of data material), and 5) the qualitative methodological references used in the methods section. Extracted text describing data collection could consist of a few sentences or several sections from the articles (and sometimes figures) concerning data collection practices, rational for time periods and research engagement in the field. This was later used to analyze how the longitudinal data collection was conducted and elements of longitudinal design. To categorize the qualitative methodology approaches, a framework from Cresswell [ 27 ] was used (including the categories for grounded theory, phenomenology, ethnography, case study and narrative research). Overall, data items needed to be explicitly stated in the articles in order to be charted. For example, an article was categorized as grounded theory if it explicitly stated “in this grounded theory study” but not if it referred to the literature by Glaser and Strauss without situating itself as a grounded theory study (See Additional file 3 for the full instructions for charting).
All charting forms were compiled into a single Microsoft Excel spreadsheet (see Supplementary files for an overview of the articles). Descriptive statistics with frequencies and percentages were calculated to summarize the data. Furthermore, an iterative coding process was used to group the articles and investigate patterns of, for example, research topics, words in the aims, or data collection practices. Alternative ways of grouping and presenting the data were discussed by the research team.
Search and selection
A total of 2179 titles and abstracts were screened against the eligibility criteria (see Fig. 1 ). The full text of one article could not be found and the article was excluded [ 28 ]. Fifty full text articles were excluded. Finally, 299 articles, representing 271 individual studies, were included in this study (see additional files 4 and 5 respectively for tables of excluded and included articles).
PRISMA diagram of study selection]
General characteristics and research areas of the included articles
The articles were published in many journals ( n = 193), and 138 of these journals were represented with one article each. BMJ Open was the most prevalent journal ( n = 11), followed by the Journal of Clinical Nursing ( n = 8). Similarly, the articles represented many countries ( n = 41) and all the continents; however, a large part of the studies originated from the US or UK ( n = 71, 23.7% and n = 70, 23.4%, respectively). The articles focused on the following types of populations: patients, families−/caregivers, health care providers, students, community members, or policy makers. Approximately 20% ( n = 63, 21.1%) of the articles collected data from two or more of these types of population(s) (see Table 1 ).
Approximately half of the articles ( n = 158, 52.8%) articulated being part of a larger research project. Of them, 95 described a project with both quantitative and qualitative methods. They represented either 1) a qualitative study embedded in an intervention, evaluation or implementation study ( n = 66, 22.1%), 2) a longitudinal cohort study collecting both quantitative and qualitative material ( n = 23, 7.7%), or 3) qualitative longitudinal material collected together with a cross sectional survey (n = 6, 2.0%). Forty-eight articles (16.1%) described belonging to a larger qualitative project presented in several research articles.
Methodological traditions
Approximately one-third ( n = 109, 36.5%) of the included articles self-identified with one of the qualitative traditions recognized by Cresswell [ 27 ] (case study: n = 36, 12.0%; phenomenology: n = 35, 11.7%; grounded theory: n = 22, 7.4%; ethnography: n = 13, 4.3%; narrative method: n = 3, 1.0%). In nine articles, the authors described using a mix of two or more of these qualitative traditions. In addition, 19 articles (6.4%) self-identified as mixed methods research.
Every second article self-identified as having a qualitative longitudinal design ( n = 156, 52.2%); either they self-identified as “a longitudinal qualitative study” or “using a longitudinal qualitative research design”. However, in some articles, this was stated in the title and/or abstract and nowhere else in the article. Fifty-two articles (17.4%) self-identified both as having a QLR design and following one of the methodological approaches (case study: n = 8; phenomenology: n = 23; grounded theory: n = 9; ethnography: n = 6; narrative method: n = 2; mixed methods: n = 4).
The other 143 articles used various terms to situate themselves in relation to a longitudinal design. Twenty-seven articles described themselves as a longitudinal study (9.0%) or a longitudinal study within a specific qualitative tradition (e.g., a longitudinal grounded theory study or a longitudinal mixed method study) ( n = 64, 21.4%). Furthermore, 36 articles (12.0%) referred to using longitudinal data materials (e.g., longitudinal data or longitudinal interviews). Nine of the articles (3.0%) used the term longitudinal in relation to the data analysis or aim (e.g., the aim was to longitudinally describe), used terms such as serial or repeated in relation to the data collection design ( n = 2, 0.7%), or did not use any term to address the longitudinal nature of their design ( n = 5, 1.7%).
Use of methodological references
The mean number of qualitative method references in the methods sections was 3.7 (range 0 to 16), and 20 articles did not have any qualitative method reference in their methods sections. Footnote 1 Commonly used method references were generic books on qualitative methods, seminal works within qualitative traditions, and references specializing in qualitative analysis methods (see Table 2 ). It should be noted that some references were comprehensive books and thus could include sections about QLR without being focused on the QLR method. For example, Miles et al. [ 31 ] is all about analysis and coding and includes a chapter regarding analyzing change.
Only approximately 20% ( n = 58) of the articles referred to the QLR method literature in their methods sections. Footnote 2 The mean number of QLR method references (counted for articles using such sources) was 1.7 (range 1 to 6). Most articles using the QLR method literature also used other qualitative methods literature (except two articles using one QLR literature reference each [ 39 , 40 ]). In total, 37 QLR method references were used, and 24 of the QLR method references were only referred to by one article each.
Longitudinal perspectives in article aims
In total, 231 (77.3%) articles had one or several terms related to time or change in their aims, whereas 68 articles (22.7%) had none. Over one hundred different words related to time or change were identified. Longitudinally oriented terms could focus on changes across time (process, trajectory, transition, pathway or journey), patterns of how something changed (maintenance, continuity, stability, shifts), or phenomena that by nature included change (learning or implementation). Other types of terms emphasized the data collection time period (e.g., over 6 months) or a specific changing situation (e.g., during pregnancy, through the intervention period, or moving into a nursing home). The most common terms used for the longitudinal perspective were change ( n = 63), over time ( n = 52), process ( n = 36), transition ( n = 24), implementation ( n = 14), development ( n = 13), and longitudinal (n = 13). Footnote 3
Furthermore, the articles varied in what ways their aims focused on time/change, e.g., the longitudinal perspectives in the aims (see Table 3 ). In 71 articles, the change across time was the phenomenon of interest of the article : for example, articles investigating the process of learning or trajectories of diseases. In contrast, 46 articles investigated change or factors impacting change in relation to a defined outcome : for example, articles investigating factors influencing participants continuing in a physical activity trial. The longitudinal perspective could also be embedded in an article’s context . In such cases, the focus of the article was on experiences that happened during a certain time frame or in a time-related context (e.g., described experiences of the patient-provider relationship during 6 months of rehabilitation).
Types of data and length of data collection
The QLR articles were often large and complex in their data collection methods. The median number of participants was 20 (range from one to 1366, the latter being an article with open-ended questions in questionnaires [ 46 ]). Most articles used individual interviews as the data material ( n = 167, 55.9%) or a combination of data materials ( n = 98, 32.8%) (e.g., interviews and observations, individual interviews and focus group interviews, or interviews and questionnaires). Forty-five articles (15.1%) presented quantitative and qualitative results. The median number of interviews was 46 (range three to 507), which is large in comparison to many qualitative studies. The observation materials were also comprehensive and could include several hundred hours of observations. Documents were often used as complementary material and included official documents, newspaper articles, diaries, and/or patient records.
The articles’ time spans Footnote 4 for data collection varied between a few days and over 20 years, with 60% of the articles’ time spans being 1 year or shorter ( n = 180) (see Fig. 2 ). The variation in time spans might be explained by the different kinds of phenomena that were investigated. For example, Jensen et al. [ 47 ] investigated hospital care delivery and followed each participant, with observations lasting between four and 14 days. Smithbattle [ 48 ] described the housing trajectories of teen mothers, and collected data in seven waves over 28 years.
Number of articles in relation to the time span of data collection. The time span of data collection is given in months
Three components of longitudinal data collection
In the articles, the data collection was conducted in relation to three different longitudinal data collection components (see Table 4 ).
Entities followed across time
Four different types of entities were followed across time: 1) individuals, 2) individual cases or dyads, 3) groups, and 4) settings. Every second article ( n = 170, 56.9%) followed individuals across time, thus following the same participants through the whole data collection period. In contrast, when individual cases were followed across time, the data collection was centered on the primary participants (e.g., people with progressive neurological conditions) who were followed over time, and secondary participants (e.g., family caregivers) might provide complementary data at several time points or only at one-time point. When settings were followed over time, the participating individuals were sometimes the same, and sometimes changed across the data collection period. Typical settings were hospital wards, hospitals, smaller communities or intervention trials. The type of collected data corresponded with what kind of entities were followed longitudinally. Individuals were often followed with serial interviews, whereas groups were commonly followed with focus group interviews complemented with individual interviews, observations and/or questionnaires. Overall, the lengths of data collection periods seemed to be chosen based upon expected changes in the chosen entities. For example, the articles following an intervention setting were structured around the intervention timeline, collecting data before, after and sometimes during the intervention.
Tempo of data collection
The data collection tempo differed among the articles (e.g., the frequency and mode of the data collection). Approximately half ( n = 154, 51.5%) of the articles used serial time points, collecting data at several reoccurring but shorter sequences (e.g., through serial interviews or open-ended questions in questionnaires). When data were collected in time waves ( n = 50, 16.7%), the periods of data collection were longer, usually including both interviews and observations; often, time waves included observations of a setting and/or interviews at the same location over several days or weeks.
When comparing the tempo with the type of entities, some patterns were detected (see Fig. 3 ). When individuals were followed, data were often collected at time points, mirroring the use of individual interviews and/or short observations. For research in settings, data were commonly collected in time waves (e.g., observation periods over a few weeks or months). In studies exploring settings across time, time waves were commonly used and combined several types of data, particularly from interviews and observations. Groups were the least common studied entity ( n = 9, 3.0%), so the numbers should be interpreted with caution, but continuous data collection was used in five of the nine studies. The continuous data collection mode was, for example, collecting electronic diaries [ 62 ] or minutes from committee meetings during a time period [ 63 ].
Tempo of data collection in relation to entities followed over time
Preplanned or adapted data collection
A large majority ( n = 224, 74.9%) of the articles used preplanned data collection (e.g., in preplanned data collection, all participants were followed across time according to the same data collection plan). For example, all participants were interviewed one, six and twelve months’ post-diagnosis. In contrast to the preplanned data collection approach, 44 articles had a participant-adapted data collection (14.7%), and participants were followed at different frequencies and/or over various lengths of time depending on each participant’s situation. Participant-adapted data collection was more common among articles following individuals or individual cases (see Fig. 4 ). To adapt the data collection to the participants, the researchers created strategies to reach participants when crucial events were happening. Eleven articles used a participant entry approach to data collection ( n = 11, 6.7%), and the whole or parts of the data were independently sent in by participants in the form of diaries, questionnaires, or blogs. Another approach to data collection was using theoretical or analysis-driven ideas to guide the data collection ( n = 19, 6.4%). In these articles, the analysis and data collection were conducted simultaneously, and ideas arising in the analysis could be followed up, for example, returning to some participants, recruiting participants with specific experiences, or collecting complementary types of data materials. This approach was most common in the articles following settings across time, which often included observations and interviews with different types of populations. Articles using theoretical or analysis driven data collection were not associated with grounded theory to a greater extent than the other articles in the sample (e.g., did not self-identify as grounded theory or referred to methodological literature within grounded theory traditions to a greater proportion).
Preplanned or adapted data collection in relation to entities followed over time
According to our results, some researchers used QLR as a methodological approach and other researchers used a longitudinal qualitative data collection without aiming to investigate change. Adding to the debate on whether QLR is a methodological approach in its own right or a design element in a particular study we suggest that the use of QLR can be described as layered (see Fig. 5 ). Namely, articles must fulfill several criteria in order to use QLR as a methodological approach, and that is done in some articles. In those articles QLR method references were used, the aim was to investigate change of a phenomenon and the longitudinal elements of the data collection were thoroughly integrated into the method section. On the other hand, some articles using a longitudinal qualitative data collection were just collecting data over time, without addressing time and/or change in the aim. These articles can still be interesting research studies with valuable results, but they are not using the full potential of QLR as a methodological approach. In all, around 40% of the articles had an aim that focused on describing or understanding change (either as phenomenon or outcome); but only about 24% of the articles set out to investigate change across time as their phenomenon of interest.
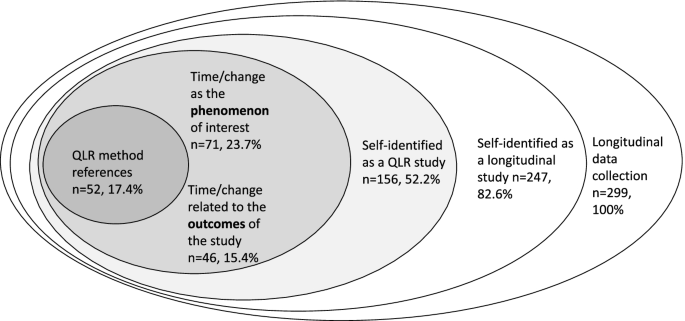
The QLR onion. The use of QLR design can be described as layered, where researchers use more or less elements of a QLR design. The two inmost layers represents articles using QLR as a methodological approach
Regarding methodological influences, about one-third of the articles self-identify with any of the traditional qualitative methodologies. Using a longitudinal qualitative data collection as an element integrated with another methodological tradition can therefore be seen as one way of working with longitudinal qualitative materials. In our results, the articles referring to methodologies other than QLR preferably used case study, phenomenology and grounded theory methodologies. This was surprising since Neale [ 10 ] identified ethnography, case studies and narrative methods as the main methodological influences on QLR. Our findings might mirror the profound impacts that phenomenology and grounded theory have had on the qualitative field of health research. Regarding phenomenology, the findings can also be influenced by more recent discussions of combining interpretative phenomenological analysis with QLR [ 6 ].
Half of the articles self-identified as QLR studies, but QLR method references were used in less than 20% of the identified articles. This is both surprising and troublesome since use of appropriate method literature might have supported researchers who were struggling with for example a large quantity of materials and complex analysis. A possible explanation for the lack of use of QLR method literature is that QLR as a methodological approach is not well known, and authors might not be aware that method literature exists. It is quite understandable that researchers can describe a qualitative project with longitudinal data collection as a qualitative longitudinal study, without being aware that QLR is a specific form of study. Balmer [ 64 ] described how their group conducted serial interviews with medical students over several years before they became aware of QLR as a method of study. Within our networks, we have met researchers with similar experiences. Likewise, peer reviewers and editorial boards might not be accustomed to evaluating QLR manuscripts. In our results, 138 journals published one article between 2017 and 2019, and that might not be enough for editorial boards and peer reviewers to develop knowledge to enable them to closely evaluate manuscripts with a QLR method.
In 2007, Holland and colleagues [ 65 ] mapped QLR in the UK and described the following four categories of QLR: 1) mixed methods approaches with a QLR component; 2) planned prospective longitudinal studies; 3) follow-up studies complementing a previous data collection with follow-up; and 4) evaluation studies. Examples of all these categories can be found among the articles in this method study; however, our results do paint a more complex picture. According to our results, Holland’s categories are not multi-exclusive. For example, studies with intentions to evaluate or implement practices often used a mixed methods design and were therefore eligible for both categories one and four described above. Additionally, regarding the follow-up studies, it was seldom clearly described if they were planned as a two-time-point study or if researchers had gained an opportunity to follow up on previous data collection. When we tried to categorize QLR articles according to the data collection design, we could not identify multi-exclusive categories. Instead, we identified the following three components of longitudinal data collection: 1) entities followed across time; 2) tempo; and 3) preplanned or adapted data collection approaches. However, the most common combination was preplanned studies that followed individuals longitudinally with three or more time points.
The use of QLR differs between disciplines [ 14 ]. Our results show some patterns for QLR within health research. Firstly, the QLR projects were large and complex; they often included several types of populations and various data materials, and were presented in several articles. Secondly, most studies focused upon the individual perspective, following individuals across time, and using individual interviews. Thirdly, the data collection periods varied, but 53% of the articles had a data collection period of 1 year or shorter. Finally, patients were the most prevalent population, even though topics varied greatly. Previously, two other reviews that focused on QLR in different parts of health research (e.g., nursing [ 4 ] and gerontology [ 66 ]) pointed in the same direction. For example, individual interviews or a combination of data materials were commonly used, and most studies were shorter than 1 year but a wide range existed [ 4 , 66 ].
Considerations when planning a QLR project
Based on our results, we argue that when health researchers plan a QLR study, they should reflect upon their perspective of time/change and decide what part change should play in their QLR study. If researchers decide that change should play the main role in their project, then they should aim to focus on change as the phenomenon of interest. However, in some research, change might be an important part of the plot, without having the main role, and change in relation to the outcomes might be a better perspective. In such studies, participants with change, no change or different kinds of change are compared to explore possible explanations for the change. In our results, change in relation to the outcomes was often used in relation to intervention studies where participants who reached a desired outcome were compared to individuals who did not. Furthermore, for some research studies, change is part of the context in which the research takes place. This can be the case when certain experiences happen during a period of change; for example, when the aim is to explore the experience of everyday life during rehabilitation after stroke. In such cases a longitudinal data collection could be advisable (e.g., repeated interviews often give a deep relationship between interviewer and participants as well as the possibility of gaining greater depth in interview answers during follow-up interviews [ 15 ]), but the study might not be called a QLR study since it does not focus upon change [ 13 ]. We suggest that researchers make informed decisions of what kind of longitudinal perspective they set out to investigate and are transparent with their sources of methodological inspiration.
We would argue that length of data collection period, type of entities, and data materials should be in accordance with the type of change/changing processes that a study focuses on. Individual change is important in health research, but researchers should also remember the possibility of investigating changes in families, working groups, organizations and wider communities. Using these types of entities were less common in our material and could probably grant new perspectives to many research topics within health. Similarly, using several types of data materials can complement the insights that individual interviews can give. A large majority of the articles in our results had a preplanned data collection. Participant-adapted data collection can be a way to work in alignment with a “time-as-fluid” conceptualization of time because the events of subjective importance to participants can be more in focus and participants (or other entities) change processes can differ substantially across cases. In studies with lengthy and spaced-out data collection periods and/or uncertainty in trajectories, researchers should consider participant-adapted or participant entry data collection. For example, some participants can be followed for longer periods and/or with more frequency.
Finally, researchers should consider how to best publish and disseminate their results. Many QLR projects are large, and the results are divided across several articles when they are published. In our results, 21 papers self-identified as a mixed methods project or as part of a larger mixed methods project, but most of these did not include quantitative data in the article. This raises the question of how to best divide a large research project into suitable pieces for publication. It is an evident risk that the more interesting aspects of a mixed methods project are lost when the qualitative and quantitative parts are analyzed and published separately. Similar risks occur, for example, when data have been collected from several types of populations but are then presented per population type (e.g., one article with patient data and another with caregiver data). During the work with our study, we also came across studies where data were collected longitudinally, but the results were divided into publications per time point. We do not argue that these examples are always wrong, there are situations when these practices are appropriate. However, it often appears that data have been divided without much consideration. Instead, we suggest a thematic approach to dividing projects into publications, crafting the individual publications around certain ideas or themes and thus using the data that is most suitable for the particular research question. Combining several types of data and/or several populations in an analysis across time is in fact what makes QLR an interesting approach.
Strengths and limitations
This method study intended to paint a broad picture regarding how longitudinal qualitative methods are used within the health research field by investigating 299 published articles. Method research is an emerging field, currently with limited methodological guidelines [ 21 ], therefore we used scoping review method to support this study. In accordance with scoping review method we did not use quality assessment as a criterion for inclusion [ 18 , 19 , 20 ]. This can be seen as a limitation because we made conclusions based upon a set of articles with varying quality. However, we believe that learning can be achieved by looking at both good and bad examples, and innovation may appear when looking beyond established knowledge, or assessing methods from different angles. It should also be noted that the results given in percentages hold no value for what procedures that are better or more in accordance with QLR, the percentages simply state how common a particular procedure was among the articles.
As described, the included articles showed much variation in the method descriptions. As the basis for our results, we have only charted explicitly written text from the articles, which might have led to an underestimation of some results. The researchers might have had a clearer rationale than described in the reports. Issues, such as word restrictions or the journal’s scope, could also have influenced the amount of detail that was provided. Similarly, when charting how articles drew on a traditional methodology, only data from the articles that clearly stated the methodologies they used (e.g., phenomenology) were charted. In some articles, literature choices or particular research strategies could implicitly indicate that the researchers had been inspired by certain methodologies (e.g., referring to grounded theory literature and describing the use of simultaneous data collection and analysis could indicate that the researchers were influenced by grounded theory), but these were not charted as using a particular methodological tradition. We used the articles’ aims and objectives/research questions to investigate their longitudinal perspectives. However, as researchers have different writing styles, information regarding the longitudinal perspectives could have been described in surrounding text rather than in the aim, which might have led to an underestimation of the longitudinal perspectives.
The experience and diversity of the research team in our study was a strength. The nine authors on the team represent ten universities and three countries, and have extensive experience in different types of qualitative research, QLR and review methods. The different level of experiences with QLR within the team (some authors have worked with QLR in several projects and others have qualitative experience but no experience in QLR) resulted in interesting discussions that helped drive the project forward. These experiences have been useful for understanding the field.
Based on a method study of 299 articles, we can conclude that QLR in health research articles published between 2017 and 2019 often contain comprehensive complex studies with a large variation in topics. Some research was thoroughly designed to capture time/change throughout the methodology, focus and data collection, while other articles included a few elements of QLR. Longitudinal data collection included several components, such as what entities were followed across time, the tempo of data collection, and to what extent the data collection was preplanned or adapted across time. In sum, health researchers need to be considerate and make informed choices when designing QLR projects. Further research should delve deeper into what kind of research questions go well with QLR and investigate the best practice examples of presenting QLR findings.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analyzed in this current study are available in supplementary file 6 .
Qualitative method references were defined as a journal article or book with a title that indicated an aim to guide researchers in qualitative research methods and/or research theories. Primary studies, theoretical works related to the articles’ research topics, protocols, and quantitative method literature were excluded. References written in a language other than English was also excluded since the authors could not evaluate their content.
QLR method references were defined as a journal article or book that 1) focused on qualitative methodological questions, 2) used terms such as ‘longitudinal’ or ‘time’ in the title so it was evident that the focus was on longitudinal qualitative research. Referring to another original QLR study was not counted as using QLR method literature.
Words were charted depending on their word stem, e.g., change, changes and changing were all charted as change.
It should be noted that here time span refers to the data collection related to each participant or case. Researchers could collect data for 2 years but follow each participant for 6 months.
Calman L, Brunton L, Molassiotis A. Developing longitudinal qualitative designs: lessons learned and recommendations for health services research. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2013;13:14.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Solomon P, Nixon S, Bond V, Cameron C, Gervais N. Two approaches to longitudinal qualitative analyses in rehabilitation and disability research. Disabil Rehabil. 2020;42:3566–72.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Grossoehme D, Lipstein E. Analyzing longitudinal qualitative data: the application of trajectory and recurrent cross-sectional approaches. BMC Res Notes. 2016;9:136.
SmithBattle L, Lorenz R, Reangsing C, Palmer JL, Pitroff G. A methodological review of qualitative longitudinal research in nursing. Nurs Inq. 2018;25:e12248.
Tuthill EL, Maltby AE, DiClemente K, Pellowski JA. Longitudinal qualitative methods in health behavior and nursing research: assumptions, design, analysis and lessons learned. Int J Qual Methods. 2020;19:10.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
McCoy LK. Longitudinal qualitative research and interpretative phenomenological analysis: philosophical connections and practical considerations. Qual Res Psychol. 2017;14:442–58.
Article Google Scholar
Bennett D, Kajamaa A, Johnston J. How to... Do longitudinal qualitative research. Clin Teach. 2020;17:489–92.
Plano Clark V, Anderson N, Wertz JA, Zhou Y, Schumacher K, Miaskowski C. Conceptualizing longitudinal mixed methods designs: a methodological review of health sciences research. J Mix Methods Res. 2014;23:1–23.
Google Scholar
Thomson R, Plumridge L, Holland J. Longitudinal qualitative research: a developing methodology. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2003;6:185–7.
Neale B. The craft of qualitative longitudinal research: thousand oaks. Sage. 2021.
Balmer DF, Varpio L, Bennett D, Teunissen PW. Longitudinal qualitative research in medical education: time to conceptualise time. Med Educ. 2021;55:1253–60.
Smith N. Cross-sectional profiling and longitudinal analysis: research notes on analysis in the longitudinal qualitative study, 'Negotiating transitions to Citizenship'. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2003;6:273–7.
Saldaña J. Longitudinal qualitative research - analyzing change through time. Walnut Creek: AltaMira Press; 2003.
Corden A, Millar J. Time and change: a review of the qualitative longitudinal research literature for social policy. Soc Policy Soc. 2007;6:583–92.
Thorne S. Interpretive description: qualitative research for applied practice (2nd ed): Routledge; 2016.
Book Google Scholar
Kneck Å, Audulv Å. Analyzing variations in changes over time: development of the pattern-oriented longitudinal analysis approach. Nurs Inq. 2019;26:e12288.
Whiffin CJ, Bailey C, Ellis-Hill C, Jarrett N. Challenges and solutions during analysis in a longitudinal narrative case study. Nurse Res. 2014;21:20–62.
Arksey H, O'Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8:19–32.
Levac D, Colquhoun H, O’Brien KK. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implement Sci. 2010;5:69.
Peters MDJ, Marnie C, Tricco AC, Pollock D, Munn Z, Alexander L, et al. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evidence Implementation. 2021;19:3–10.
Mbuagbaw L, Lawson DO, Puljak L, Allison DB, Thabane L. A tutorial on methodological studies: the what, when, how and why. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020;20:226.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern. 2018;169:467–73.
Neale B. Adding time into the mix: stakeholder ethics in qualitative longitudinal research. Methodological Innovations Online. 2013;8:6–20.
Henderson S, Holland J, McGrellis S, Sharpe S, Thomson R. Storying qualitative longitudinal research: sequence, voice and motif. Qual Res. 2016;12:16–34.
Balmer DF, Richards BF. Longitudinal qualitative research in medical education. Perspect Med Educ. 2017;6:306–10.
Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, Elmagarmid A. Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016;5:210.
Creswell JW. Qualitative inquiry and research design: choosing among five approaches. 3rd ed: SAGE Publications; 2012.
McIntyre H, Fraser D. 'Hands-off' breastfeeding skill development in a UK, UNICEF baby friendly initiative pre-registration midwifery programme. MIDIRS Midwifery Digest. 2018;28:98–102.
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3:77–101.
Patton MQ. Qualitative research and evaluation methods: integrating theory and practice. Sage. 2015.
Miles M, Huberman A, Saldaña J. Qualitative data analysis: a methods sourcebook. 4th ed: Sage Publications; 2020.
Miles MB, Huberman AM. Qualitative data analysis: an expanded sourcebook (2nd ed): Sage Publications; 1994.
Smith JA, Flowers P, Larkin M. Interpretative phenomenological analysis: theory, method and research. Sage. 2009.
Hsieh HF, Shannon SE. Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qual Health Res. 2005;15:1277–88.
Glaser B, Strauss A. The discovery of grounded theory: strategies for qualitative research. Aldine De Gruyter. 1967.
Tong A, Sainsbury P, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007;19:349–57.
Murray SA, Kendall M, Carduff E, Worth A, Harris FM, Lloyd A, et al. Use of serial qualitative interviews to understand patients' evolving experiences and needs. BMJ. 2009;339:b3702.
Thomson R, Holland J. Hindsight, foresight and insight: the challenges of longitudinal qualitative research. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2003;6:233–44.
Morrow V, Tafere Y, Chuta N, Zharkevich I. "I started working because I was hungry": the consequences of food insecurity for children's well-being in rural Ethiopia. Soc Sci Med. 2017;182:1–9.
Solomon P, O'Brien KK, Nixon S, Letts L, Baxter L, Gervais N. Qualitative longitudinal study of episodic disability experiences of older women living with HIV in Ontario, Canada. BMJ Open. 2018;8:e021507.
Coombs MA, Parker R, de Vries K. Managing risk during care transitions when approaching end of life: a qualitative study of patients’ and health care professionals’ decision making. Palliat Med. 2017;31:617–24.
Vaghefi I, Tulu B. The continued use of mobile health apps: insights from a longitudinal study. JMIR Mhealth And Uhealth. 2019;7:e12983.
Andersen IC, Thomsen TG, Bruun P, Bødtger U, Hounsgaard L. Patients' and their family members' experiences of participation in care following an acute exacerbation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a phenomenological-hermeneutic study. J Clin Nurs. 2017;26:4877–89.
Albrecht TA, Keim-Malpass J, Boyiadzis M, Rosenzweig M. Psychosocial experiences of young adults diagnosed with acute leukemia during hospitalization for induction chemotherapy treatment. JHPN. 2019;21:167–73.
PubMed Google Scholar
Corepal R, Best P, O'Neill R, Tully MA, Edwards M, Jago R, et al. Exploring the use of a gamified intervention for encouraging physical activity in adolescents: a qualitative longitudinal study in Northern Ireland. BMJ Open. 2018;8:e019663.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Malin H, Liauw I, Damon W. Purpose and character development in early adolescence. J Youth Adolesc. 2017;46:1200–15.
Jensen AM, Pedersen BD, Olsen RB, Hounsgaard L. Medication and care in Alzheimer's patients in the acute care setting: a qualitative analysis. Dementia. 2019;18:2173–88.
SmithBattle L. Housing trajectories of teen mothers and their families over 28 years. Am J Orthop. 2019;89:258–67.
Denney-Koelsch EM, Côté-Arsenault D, Jenkins Hall W. Feeling cared for versus experiencing added burden: Parents' interactions with health-care providers in pregnancy with a lethal fetal diagnosis. Illn Crisis Loss. 2018;26:293–315.
Pyörälä E, Mäenpää S, Heinonen L, Folger D, Masalin T, Hervonen H. The art of note taking with mobile devices in medical education. BMC Med Educ. 2019;19:96.
Lindberg K, Mørk BE, Walter L. Emergent coordination and situated learning in a hybrid OR: the mixed blessing of using radiation. Soc Science Med. 2019;228:232–9.
Frost J, Wingham J, Britten N, Greaves C, Abraham C, Warren FC, et al. Home-based rehabilitation for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: mixed methods process evaluation of the REACH-HF multicentre randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e026039.
Young JL, Werner-Lin A, Mueller R, Hoskins L, Epstein N, Greene MH. Longitudinal cancer risk management trajectories of BRCA1/2 mutation-positive reproductive-age women. J Psych Oncology. 2017;35:393–408.
Lewis M, Jones A, Hunter B. Women's experience of trust within the midwife-mother relationship. Int J Childbirth. 2017;7:40–52.
Mozaffar H, Cresswell KM, Williams R, Bates DW, Sheikh A. Exploring the roots of unintended safety threats associated with the introduction of hospital ePrescribing systems and candidate avoidance and/or mitigation strategies: a qualitative study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2017;26:722–33.
Castro A, Andrews G. Nursing lives in the blogosphere: a thematic analysis of anonymous online nursing narratives. J Adv Nurs. 2018;74:329–38.
Jensen AM, Pedersen BD, Olsen RB, Wilson RL, Hounsgaard L. "if only they could understand me!" acute hospital care experiences of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Dementia. 2018;19:2332–53.
Nash BH, Mitchell AW. Longitudinal study of changes in occupational therapy students' perspectives on frames of reference. Am J Occup Ther. 2017;71:7105230010p1–7.
Bright FAS, Kayes NM, McPherson KM, Worrall LE. Engaging people experiencing communication disability in stroke rehabilitation: a qualitative study. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2018;53:981–94.
Superdock AK, Barfield RC, Brandon DH, Docherty SL. Exploring the vagueness of religion & spirituality in complex pediatric decision-making: a qualitative study. BMC Palliat. 2018;17:107.
Gordon L, Jindal-Snape D, Morrison J, Muldoon J, Needham G, Siebert S, et al. Multiple and multidimensional transitions from trainee to trained doctor: a qualitative longitudinal study in the UK. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e018583.
Cain CL, Frazer M, Kilaberia TR. Identity work within attempts to transform healthcare: invisible team processes. Hum Relat. 2019;72:370–96.
Klinga C, Hasson H, Andreen Sachs M, Hansson J. Understanding the dynamics of sustainable change: a 20-year case study of integrated health and social care. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18:400.
Balmer DF, Richards BF. Conducting qualitative research through time: how might theory be useful in longitudinal qualitative research? Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2021;27:277–88.
Holland J. Qualitative longitudinal research: exploring ways of researching lives through time. ESRC National Centre for Research Methods Workshop; London: London South Bank University; 2007.
Nevedal AL, Ayalon L, Briller SH. A qualitative evidence synthesis review of longitudinal qualitative research in gerontology. Gerontologist. 2019;59:e791–801.
Download references
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Ellen Sejersted, librarian at the University of Agder, Kristiansand, Norway, who conducted the literature searches and Julia Andersson, research assistant at the Department of Nursing, Umeå University, Sweden, who supported the data management and took part in the initial screening phases of the project.
Open access funding provided by Umea University. This project was conducted within the authors’ positions and did not receive any specific funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Nursing, Umeå University, Umeå, Sweden
Faculty of Health, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark
Elisabeth O. C. Hall
Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Faroe Islands, Thorshavn, Faroe Islands, Denmark
Elisabeth O. C. Hall & Kristianna Lund Dam
Department of Health Care Sciences, Ersta Sköndal Bräcke University College, Stockholm, Sweden
Department of Health and Nursing Science, University of Agder, Kristiansand, Norway
Thomas Westergren & Liv Fegran
Department of Public Health, University of Stavanger, Stavanger, Norway
Thomas Westergren
Center for Clinical Research, North Denmark Regional Hospital, Hjørring, Denmark
Mona Kyndi Pedersen
Department of Clinical Medicine, Aalborg University, Aalborg, Denmark
Lovisenberg Diaconale Univeristy of College, Oslo, Norway
Hanne Aagaard
Department of Clinical Medicine-Randers Regional Hospital, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark
Mette Spliid Ludvigsen
Faculty of Nursing and Health Sciences, Nord University, Bodø, Norway
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
ÅA conceived the study. ÅA, EH, TW, LF, MKP, HA, and MSL designed the study. ÅA, TW, and LF were involved in literature searches together with the librarian. ÅA and EH performed the screening of the articles. All authors (ÅA, EH, TW, LF, ÅK, MKP, KLD, HA, MSL) took part in the data charting. ÅA performed the data analysis and discussed the preliminary results with the rest of the team. ÅA wrote the 1st manuscript draft, and ÅK, MSL and EH edited. All authors (ÅA, EH, TW, LF, ÅK, MKP, KLD, HA, MSL) contributed to editing the 2nd draft. MSL and LF provided overall supervision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
All authors represent the nursing discipline, but their research topics differ. ÅA and ÅK have previously worked together with QLR method development. ÅA, EH, TW, LF, MKP, HA, KLD and MSL work together in the Nordic research group PRANSIT, focusing on nursing topics connected to transition theory using a systematic review method, preferably meta synthesis. All authors have extensive experience with qualitative research but various experience with QLR.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Åsa Audulv .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
PRISMA-ScR checklist.
Additional file 2.
Data base searches.
Additional file 3.
Guidelines for data charting
Additional file 4.
List of excluded articles
Additional file 5.
Table of included articles (author(s), year of publication, reference, country, aims and research questions, methodology, type of data material, length of data collection period, number of participants)
Additional file 6.
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Audulv, Å., Hall, E.O.C., Kneck, Å. et al. Qualitative longitudinal research in health research: a method study. BMC Med Res Methodol 22 , 255 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-022-01732-4
Download citation
Received : 13 January 2022
Accepted : 22 September 2022
Published : 01 October 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-022-01732-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative longitudinal research
- Method development
- Repeated data collection
BMC Medical Research Methodology
ISSN: 1471-2288
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Advertisement

- Previous Issue
- Previous Article
- Next Article
- Box 1. What to Look for in Research Using This Method
What Is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative versus quantitative research, conducting and appraising qualitative research, conclusions, research support, competing interests, qualitative research methods in medical education.
Submitted for publication January 5, 2018. Accepted for publication November 29, 2018.
- Split-Screen
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
- Peer Review
- Open the PDF for in another window
- Cite Icon Cite
- Get Permissions
- Search Site
Adam P. Sawatsky , John T. Ratelle , Thomas J. Beckman; Qualitative Research Methods in Medical Education. Anesthesiology 2019; 131:14–22 doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000002728
Download citation file:
- Ris (Zotero)
- Reference Manager
Qualitative research was originally developed within the social sciences. Medical education is a field that comprises multiple disciplines, including the social sciences, and utilizes qualitative research to gain a broader understanding of key phenomena within the field. Many clinician educators are unfamiliar with qualitative research. This article provides a primer for clinician educators who want to appraise or conduct qualitative research in medical education. This article discusses a definition and the philosophical underpinnings for qualitative research. Using the Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research as a guide, this article provides a step-wise approach for conducting and evaluating qualitative research in medical education. This review will enable the reader to understand when to utilize qualitative research in medical education and how to interpret reports using qualitative approaches.

Image: J. P. Rathmell and Terri Navarette.
Qualitative research provides approaches to explore and characterize the education of future anesthesiologists. For example, the practice of anesthesiology is increasingly team-based; core members of the anesthesia care team include physicians, trainees, nurse anesthetists, anesthesiologist assistants, and other healthcare team members. 1 Understanding how to work within and how to teach learners about anesthesia care teams requires the ability to conceptualize the complexity of individual psychology and social interactions that occur within teams. Qualitative research is well suited to investigate complex issues like team-based care. For example, one qualitative study observed the interactions between members of the anesthesia care team during simulated stressful situations and conducted interviews of team members; they described limited understanding of each team member’s role and perceptions about appropriate roles and responsibilities, which provided insight for interprofessional team training. 2 Another qualitative study explored the hierarchy within the anesthesia care team, highlighting residents’ reluctance to challenge the established hierarchy and outlining the strategies they use to cope with fear and intimidation. 3 Key issues in medical education and anesthesiology, particularly when exploring human experience and social interactions, may be best studied using qualitative research methodologies and methods.
Medical education is a complex field, and medical education research and practice fittingly draws from many disciplines ( e.g. , medicine, psychology, sociology, education) and synthesizes multiple perspectives to explain how people learn and how medicine should be taught. 4 , 5 The concept of a field was well described by Cristancho and Varpio 5 in their tips for early career medical educators: “A discipline is usually guided by shared paradigms, assumptions, rules and methods to present their knowledge claims— i.e. , people from the same discipline speak the same language. A field brings people from multiple disciplines together.” Qualitative research draws from the perspectives of multiple disciplines and has provided methodologies to explore the complex research questions inherent to medical education.
When appraising qualitative research in medical education, do the authors:
Clearly state the study purpose and research question?
Describe the conceptual framework that inform the study and guide analysis?
Identify their qualitative methodology and research paradigm?
Demonstrate adequate reflexivity, conveying to the reader their values, assumptions and way of thinking, being explicit about the effects these ways of thinking have on the research process?
Choose data collection methods that are congruent with the research purpose and qualitative methodology?
Select an appropriate sampling strategy, choosing participants whose perspectives or experiences are relevant to the study question?
Define their method for determining saturation, how they decided to stop data collection?
Outline their process for data processing, including the management and coding of study data?
Conduct data analysis consistent with their chosen methodology?
Consider techniques to enhance trustworthiness of their study findings?
Synthesize and interpret their data with sufficient detail and supporting quotations to explain the phenomenon of study?
Current medical training is heavily influenced by the practice of evidence-based medicine. 6 Trainees are taught the “hierarchy of evidence” for evaluating studies of clinical interventions. 7 This hierarchy prioritizes knowledge gained through systematic reviews and meta-analyses, randomized controlled trials, and observational studies, but it does not include qualitative research methodologies. This means that because of their medical training and exposure to quantitative medical literature, clinician educators may be more familiar with quantitative research and feel more comfortable engaging in studies utilizing quantitative methodologies. However, many clinician educators are not familiar with the language and application of qualitative research and feel less comfortable engaging in studies using qualitative methodologies.
Because medical education is a diverse and complex field, qualitative research is a common approach in medical education research. Clinician educators who wish to understand the medical education literature need to be familiar with qualitative research. Clinician educators involved in research may also find themselves asking questions best answered by qualitative methodologies. Our goal is to provide a broad, practical overview of qualitative research in medical education. Our objectives are to:
1) Define qualitative research.
2) Compare and contrast qualitative and quantitative research.
3) Provide a framework for conducting and appraising qualitative research in medical education.
Qualitative research in medical education has a distinct vocabulary with terminology not commonly used in other biomedical research fields. Therefore, we have provided a glossary and definitions of the common terms that are used throughout this article ( table 1 ).
Glossary of Common Terms Used in Qualitative Research

Of the many attempts to provide a comprehensive definition of qualitative research, our favorite definition comes from Denzin and Lincoln:
“Qualitative research is a situated activity that locates the observer in the world. Qualitative research consists of a set of interpretive, material practices that make the world visible. These practices…turn the world into a series of representations, including field notes, interviews, conversations, photographs, recordings, and memos to the self. At this level, qualitative research involves an interpretive, naturalistic approach to the world. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of or interpret phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them.” 12
This definition reveals the following points: first, qualitative research is a “situated activity,” meaning that the research and observations are made in the real world, in this case a real life clinical or educational situation. Second, qualitative research “turns the world into a series of representations” by representing the observations, in this case of a clinical or educational situation, with qualitative data, usually taking the form of words, pictures, documents, and other symbols. Last, qualitative researchers seek to “make sense” of the meanings that research participants bring to different phenomena to allow for a greater understanding of those phenomena. Through qualitative research, observers comprehend participants’ beliefs and values and the way these beliefs and values are shaped by the context in which they are studied.
Because most clinician educators are familiar with quantitative methods, we will start by comparing qualitative and quantitative methods to gain a better understanding of qualitative research ( table 2 ). To illustrate the difference between qualitative and quantitative research in medical education, we pose the question: “What makes noon conference lectures effective for resident learning?” A qualitative approach might explore the learner perspective on learning in noon conference lectures during residency and conduct an exploratory thematic analysis to better understand what the learner thinks is effective. 13 A qualitative approach is useful to answer this question, especially if the phenomenon of interest is incompletely understood. If we wanted to compare types or attributes of conferences to assess the most effective methods of teaching in a noon conference setting, then a quantitative approach might be more appropriate, though a qualitative approach could be helpful as well. We could use qualitative data to inform the design of a survey 14 or even inform the design of a randomized control trial to compare two types of learning during noon conference. 15 Therefore, when discussing qualitative and quantitative research, the issue is not which research approach is stronger, because it is understood that each approach yields different types of knowledge when answering the research question.
Comparisons of Quantitative and Qualitative Research in Medical Education

Similarities
The first step of any research project, qualitative or quantitative, is to determine and refine the study question; this includes conducting a thorough literature review, crafting a problem statement, establishing a conceptual framework for the study, and declaring a statement of intent. 16 A common pitfall in medical education research is to start by identifying the desired methods ( e.g. , “I want to do a focus group study with medical students.”) without having a clearly refined research question, which is like putting the cart before the horse. In other words, the research question should guide the methodology and methods for both qualitative and quantitative research.
Acknowledging the conceptual framework for a study is equally important for both qualitative and quantitative research. In a systematic review of medical education research, only 55% of studies provided a conceptual framework, limiting the interpretation and meaning of the results. 17 Conceptual frameworks are often theories that represent a way of thinking about the phenomenon being studied. Conceptual frameworks guide the interpretation of data and situate the study within the larger body of literature on a specific topic. 9 Because qualitative research was developed within the social sciences, many qualitative research studies in medical education are framed by theories from social sciences. Theories from social science disciplines have the ability to “open up new ways of seeing the world and, in turn, new questions to ask, new assumptions to unearth, and new possibilities for change.” 18 Qualitative research in medical education has benefitted from these new perspectives to help understand fundamental and complex problems within medical education such as culture, power, identity, and meaning.
Differences
The fundamental difference between qualitative and quantitative methodologies centers on epistemology ( i.e. , differing views on truth and knowledge). Cleland 19 describes the differences between qualitative and quantitative philosophies of scientific inquiry: “quantitative and qualitative approaches make different assumptions about the world, about how science should be conducted and about what constitutes legitimate problems, solutions and criteria of ‘proof.’”
Quantitative research comes from objectivism , an epistemology asserting that there is an absolute truth that can be discovered; this way of thinking about knowledge leads researchers to conduct experimental study designs aimed to test hypotheses about cause and effect. 10 Qualitative research, on the other hand, comes from constructivism , an epistemology asserting that reality is constructed by our social, historical, and individual contexts, and leads researchers to utilize more naturalistic or exploratory study designs to provide explanations about phenomenon in the context that they are being studied. 10 This leads researchers to ask fundamentally different questions about a given phenomenon; quantitative research often asks questions of “What?” and “Why?” to understand causation, whereas qualitative research often asks the questions “Why?” and “How?” to understand explanations. Cook et al. 20 provide a framework for classifying the purpose of medical education research to reflect the steps in the scientific method—description (“What was done?”), justification (“Did it work?”), and clarification (“Why or how did it work?”). Qualitative research nicely fits into the categories of “description” and “clarification” by describing observations in natural settings and developing models or theories to help explain “how” and “why” educational methods work. 20
Another difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the role of the researcher in the research process. Experimental studies have explicitly stated methods for creating an “unbiased” study in which the researcher is detached ( i.e. , “blinded”) from the analysis process so that their biases do not shape the outcome of the research. 21 The term “bias” comes from the positivist paradigm underpinning quantitative research. Assessing and addressing “bias” in qualitative research is incongruous. 22 Qualitative research, based largely on a constructivist paradigm, acknowledges the role of the researcher as a “coconstructer” of knowledge and utilizes the concept of “reflexivity.” Because researchers act as coconstructors of knowledge, they must be explicit about the perspectives they bring to the research process. A reflexive researcher is one who challenges their own values, assumptions, and way of thinking and who is explicit about the effects these ways of thinking have on the research process. 23 For example, when we conducted a study on self-directed learning in residency training, we were overt regarding our roles in the residency program as core faculty, our belief in the importance of self-directed learning, and our assumptions that residents actually engaged in self-directed learning. 24 , 25 We also needed to challenge these assumptions and open ourselves to alternative questions, methods of data collection, and interpretations of the data, to ultimately ensure that we created a research team with varied perspectives. Therefore, qualitative researchers do not strive for “unbiased” research but to understand their own roles in the coconstruction of knowledge. When assessing reflexivity, it is important for the authors to define their roles, explain how those roles may affect the collection and analysis of data, and how the researchers accounted for that effect and, if needed, challenged any assumptions during the research process. Because of the role of the researcher in qualitative research, it is vital to have a member of the research team with qualitative research experience.
A Word on Mixed Methods
In mixed methods research, the researcher collects and analyzes both qualitative and quantitative data rigorously and integrates both forms of data in the results of the study. 26 Medical education research often involves complex questions that may be best addressed through both quantitative and qualitative approaches. Combining methods can complement the strengths and limitations of each method and provide data from multiple sources to create a more detailed understanding of the phenomenon of interest. Examples of uses of mixed methods that would be applicable to medical education research include: collecting qualitative and quantitative data for more complete program evaluation, collecting qualitative data to inform the research design or instrument development of a quantitative study, or collecting qualitative data to explain the meaning behind the results of a quantitative study. 26 The keys to conducting mixed methods studies are to clearly articulate your research questions, explain your rationale for use of each approach, build an appropriate research team, and carefully follow guidelines for methodologic rigor for each approach. 27
Toward Asking More “Why” Questions
We presented similarities and differences between qualitative and quantitative research to introduce the clinician educator to qualitative research but not to suggest the relative value of one these research methods over the other. Whether conducting qualitative or quantitative research in medical education, researchers should move toward asking more “why” questions to gain deeper understanding of the key phenomena and theories in medical education to move the field of medical education forward. 28 By understanding the theories and assumptions behind qualitative and quantitative research, clinicians can decide how to use these approaches to answer important questions in medical education.
There are substantial differences between qualitative and quantitative research with respect to the assessment of rigor; here we provide a framework for reading, understanding, and assessing the quality of qualitative research. O’Brien et al. 29 created a useful 21-item guide for reporting qualitative research in medical education, based upon a systematic review of reporting standards for qualitative research—the Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research. It should be noted, however, that just performing and reporting each step in these standards do not ensure research quality.
Using the Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research as a backdrop, we will highlight basic steps for clinician educators wanting to engage with qualitative research. If you use this framework to conduct qualitative research in medical education, then you should address these steps; if you are evaluating qualitative research in medical education, then you can assess whether the study investigators addressed these steps. Table 3 underscores each step and provides examples from our research in resident self-directed learning. 25
Components of Qualitative Research: Examples from a Single Research Study

Refine the study question. As with any research project, investigators should clearly define the topic of research, describe what is already known about the phenomenon that is being studied, identify gaps in the literature, and clearly state how the study will fill that gap. Considering theoretical underpinnings of qualitative research in medical education often means searching for sources outside of the biomedical literature and utilizing theories from education, sociology, psychology, or other disciplines. This is also a critical time to engage people from other disciplines to identify theories or sources of information that can help define the problem and theoretical frameworks for data collection and analysis. When evaluating the introduction of a qualitative study, the researchers should demonstrate a clear understanding of the phenomenon being studied, the previous research on the phenomenon, and conceptual frameworks that contextualize the study. Last, the problem statement and purpose of the study should be clearly stated.
Identify the qualitative methodology and research paradigm. The qualitative methodology should be chosen based on the stated purpose of the research. The qualitative methodology represents the overarching philosophy guiding the collection and analysis of data and is distinct from the research methods ( i.e. , how the data will be collected). There are a number of qualitative methodologies; we have included a list of some of the most common methodologies in table 4 . Choosing a qualitative methodology involves examining the existing literature, involving colleagues with qualitative research expertise, and considering the goals of each approach. 32 For example, explaining the processes, relationships, and theoretical understanding of a phenomenon would point the researcher to grounded theory as an appropriate approach to conducting research. Alternatively, describing the lived experiences of participants may point the researcher to a phenomenological approach. Ultimately, qualitative research should explicitly state the qualitative methodology along with the supporting rationale. Qualitative research is challenging, and you should consult or collaborate with a qualitative research expert as you shape your research question and choose an appropriate methodology. 32
Choose data collection methods. The choice of data collection methods is driven by the research question, methodology, and practical considerations. Sources of data for qualitative studies would include open-ended survey questions, interviews, focus groups, observations, and documents. Among the most important aspects of choosing the data collection method is alignment with the chosen methodology and study purpose. 33 For interviews and focus groups, there are specific methods for designing the instruments. 34 , 35 Remarkably, these instruments can change throughout the course of the study, because data analysis often informs future data collection in an iterative fashion.
Select a sampling strategy. After identifying the types of data to be collected, the next step is deciding how to sample the data sources to obtain a representative sample. Most qualitative methodologies utilize purposive sampling, which is choosing participants whose perspectives or experiences are relevant to the study question. 11 Although random sampling and convenience sampling may be simpler and less costly for the researcher than purposeful sampling, these approaches often do not provide sufficient information to answer the study question. 36 For example, in grounded theory, theoretical sampling means that the choice of subsequent participants is purposeful to aid in the building and refinement of developing theory. The criteria for selecting participants should be stated clearly. One key difference between qualitative and quantitative research is sample size: in qualitative research, sample size is usually determined during the data collection process, whereas in quantitative research, the sample size is determined a priori . Saturation is verified when the analysis of newly collected data no longer provides additional insights into the data analysis process. 10
Plan and outline a strategy for data processing. Data processing refers to how the researcher organizes, manages, and dissects the study data. Although data processing serves data analysis, it is not the analysis itself. Data processing includes practical aspects of data management, like transcribing interviews, collecting field notes, and organizing data for analysis. The next step is coding the data, which begins with organizing the raw data into chunks to allow for the identification of themes and patterns. A code is a “word or short phrase that symbolically assigns a summative, salient, essence-capturing, and/or evocative attribute for a portion of language-based or visual data.” 8 There is an artificial breakdown between data processing and analysis, because these steps may be conducted simultaneously; many consider coding as different from—yet a necessary step to facilitating—the analysis of data. 8 Qualitative software can support this process, by making it easier to organize, access, search, and code your data. However, it is noteworthy that these programs do not do the work for you, they are merely tools for supporting data processing and analysis.
Conduct the data analysis. When analyzing the data, there are several factors to consider. First, the process of data analysis begins with the initial data collection, which often informs future data collection. Researchers should be intentional when reading, reviewing, and analyzing data as it is collected, so that they can shape and enrich subsequent data collection ( e.g. , modify the interview questions). Second, data analysis is often conducted by a research team that should have the appropriate expertise and perspectives to bring to the analysis process. Therefore, when evaluating a qualitative study, you should consider the team’s composition and their reflexivity with respect to their potential biases and influences on their study subjects. Third, the overall goal is to move from the raw data to abstractions of the data that answer the research question. For example, in grounded theory, the research moves from the raw data, to the identification of themes, to categorization of themes, to identifying relationships between themes, and ultimately to the development of theoretical explanations of the phenomenon. 30 Consequently, the primary researcher or research team should be intimately involved with the data analysis, interrogating the data, writing analytic memos, and ultimately make meaning out of the data. There are differing opinions about the use of “counting” of codes or themes in qualitative research. In general, counting of themes is used during the analysis process to recognize patterns and themes; often these are not reported as numbers and percentages as in quantitative research, but may be represented by words like few , some , or many . 37
Recognize techniques to enhance trustworthiness of your study findings. Ensuring consistency between the data and the results of data analysis, along with ensuring that the data and results accurately represent the perspectives and contexts related to the data source, are crucial to ensuring trustworthiness of study findings. Methods for enhancing trustworthiness include triangulation , which is comparing findings from different methods or perspectives, and member-checking , which is presenting research findings to study participants to provide opportunities to ensure that the analysis is representative. 10
Synthesize and interpret your data. Synthesis of qualitative research is determined by the depth of the analysis and involves moving beyond description of the data to explaining the findings and situating the results within the larger body of literature on the phenomenon of interest. The reporting of data synthesis should match the research methodology. For instance, if the study is using grounded theory, does the study advance the theoretical understanding of the phenomenon being studied? It is also important to acknowledge that clarity and organization are paramount. 10 Qualitative data are rich and extensive; therefore, researchers must organize and tell a compelling story from the data. 38 This process includes the selection of representative data ( e.g. , quotations from interviews) to substantiate claims made by the research team.
Common Methodologies Used in Qualitative Research

For more information on qualitative research in medical education:
Qualitative Research and Evaluation Methods: Integrating Theory and Practice, by Michael Q. Patton (SAGE Publications, Inc., 2014)
Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing Among Five Approaches, by John W. Cresswell (SAGE Publications, Inc. 2017)
Researching Medical Education, by Jennifer Cleland and Steven J. Durning (Wiley-Blackwell, 2015)
Qualitative Research in Medical Education, by Patricia McNally, in Oxford Textbook of Medical Education, edited by Kieren Walsh (Oxford University Press, 2013)
The Journal of Graduate Medical Education “Qualitative Rip Out Series” (Available at: http://www.jgme.org/page/ripouts )
The Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (O'Brien BC, Harris IB, Beckman TJ, Reed DA, Cook DA. Standards for reporting qualitative research: a synthesis of recommendations. Acad Med. 2014;89(9):1245-51.)
The Wilson Centre Qualitative Atelier (For more information: http://thewilsoncentre.ca/atelier/ )
Qualitative research is commonly used in medical education but may be unfamiliar to many clinician educators. In this article, we provided a definition of qualitative research, explored the similarities and differences between qualitative and quantitative research, and outlined a framework for conducting or appraising qualitative research in medical education. Even with advanced training, it can be difficult for clinician educators to understand and conduct qualitative research. Leaders in medical education research have proposed the following advice to clinician educators wanting to engage in qualitative medical education research: (1) clinician educators should find collaborators with knowledge of theories from other disciplines ( e.g. , sociology, cognitive psychology) and experience in qualitative research to utilize their complementary knowledge and experience to conduct research—in this way, clinician educators can identify important research questions; collaborators can inform research methodology and theoretical perspectives; and (2) clinician educators should engage with a diverse range disciplines to generate new questions and perspectives on research. 4
Support was provided solely from institutional and/or departmental sources.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Citing articles via
Most viewed, email alerts, related articles, social media, affiliations.
- ASA Practice Parameters
- Online First
- Author Resource Center
- About the Journal
- Editorial Board
- Rights & Permissions
- Online ISSN 1528-1175
- Print ISSN 0003-3022
- Anesthesiology
- ASA Monitor

- Terms & Conditions Privacy Policy
- Manage Cookie Preferences
- © Copyright 2024 American Society of Anesthesiologists
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
- Research Note
- Open access
- Published: 15 May 2024
Concepts of lines of therapy in cancer treatment: findings from an expert interview-based study
- Lisa Falchetto 1 na1 ,
- Bernd Bender 1 , 2 na1 ,
- Ian Erhard 1 , 2 ,
- Kim N. Zeiner 3 ,
- Jan A. Stratmann 11 ,
- Florestan J. Koll 4 ,
- Sebastian Wagner 11 ,
- Marcel Reiser 5 ,
- Khayal Gasimli 6 ,
- Angelika Stehle 7 ,
- Martin Voss 8 ,
- Olivier Ballo 11 ,
- Jörg Janne Vehreschild 1 , 9 , 10 &
- Daniel Maier 1 , 2
BMC Research Notes volume 17 , Article number: 137 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
The concept of lines of therapy (LOT) in cancer treatment is often considered for decision making in tumor boards and clinical management, but lacks a common definition across medical specialties. The complexity and heterogeneity of malignancies and treatment modalities contribute to an inconsistent understanding of LOT among physicians. This study assesses the heterogeneity of understandings of the LOT concept, its major dimensions, and criteria from the perspective of physicians of different specialties with an oncological focus in Germany. Semi-structured expert interviews with nine physicians were conducted and evaluated using qualitative content analysis.
Most interviewees agreed that there is no single definition for LOT and found it difficult to explicate their understanding. A majority of experts stated that they had already encountered misunderstandings with colleagues regarding LOT and that they had problems with deciphering LOT from the medical records of their patients. Disagreement emerged about the roles of the following within the LOT concept: maintenance therapy, treatment intention, different therapy modalities, changing pharmaceutical agents, and therapy breaks. Respondents predominantly considered the same criteria as decisive for the definition of LOT as for a change in LOT (e.g., the occurrence of a progression event or tumor recurrence).
Peer Review reports
Introduction
While clinical oncology considers line of therapy (LOT) essential information for therapy planning, the field lacks a homogeneous understanding of the concept, as well as clear and consistent criteria for its classification [ 1 ]. Especially in real-world data-based research, it is often unclear whether a certain therapy is still part of an LOT; and often, conflicting interpretations lead to misunderstandings in information exchange about therapy progression [ 1 ]. Existing approaches, for standardizing the classification of LOT either focus on patterns proposed by guidelines (e.g., drug administration period, first-line termination) or on drug administration sequences [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 ]. However, other issues related to the LOT concept remain largely unclear. For example, the roles of maintenance therapies and local therapy modalities have not yet been discussed [ 1 ].
This expert-interview study aims to provide a better conceptual understanding of the defining criteria of LOT for solid and non-solid cancers. Therefore, it may contribute to identifying unclear aspects of the LOT concept and avoiding misunderstandings in communication about LOTs, especially between physicians of different medical disciplines. Concerning the rapidly developing field of real-world cancer research, data augmentation strategies and feature engineering require empirically validated concepts to obtain reliable evidence from observational data. More specifically, investigating the conceptual understanding of LOTs will help us build a rule-based framework for LOT classification within the Clinical Communication Platform of the German Cancer Consortium (DKTK).
The study’s target group was physicians from various specialties with an oncological focus, working in either university hospitals or private practice. Physicians from the University Hospital Frankfurt and private practices were contacted by e-mail. In total, nine were interviewed. Their varied specialties included neuro-oncology, pulmonology, hematology and medical oncology, urology, dermatology, and gynecological oncology, as well as one resident specialist in internal medicine with a focus on hematology and oncology. The interviewees’ professional experience ranged from 3.5 to 29 years and most had experience in treating both solid and non-solid malignancies.
Qualitative expert interviews [ 7 , 8 ] were conducted by posing open questions within a semi-structured framework [ 9 ]. An interview manual delineated this framework and was developed based on existing literature about oncological LOTs and associated concepts (see Additional File 1 ). Before the interviews, the interview manual was pre-tested with an experienced oncologist and adjusted accordingly. Each participant declared their consent before the interview. Confidentiality and anonymity of participants’ responses and information were assured. The first part of the interview manual asked about the interviewee’s underlying understanding of LOTs and the relevant criteria for their definition. Subsequently, questions concerning misunderstandings in interactions with colleagues were posed to determine whether there are frequent uncertainties in the use of the LOT concept and, if so, what reasons may underlie this situation. Next, the interviewer asked about how specific criteria, picked out of the literature, related to the definition of LOT. These included the influence of treatment intention, the role of maintenance therapy, and local therapies. Another focus of the interviews was how the interviewees judged the relationship of both changes in drug regimen and therapy breaks to the definition of LOT.
Data collection/conduct of interviews
The expert interviews were conducted between June 1 and July 17, 2022 via video conference and in German. They lasted between 10 and 25 minutes with an average duration of approximately 18 minutes. The interviews were recorded and transcribed using the ExpressScribe Pro software (Version 10.17).
Data analysis
The interviews were analyzed using methods of qualitative content analysis as described in Mayring [ 10 ] and the software MaxQDA Analytics Pro 2022 (release 22.2.0). A system for coding the interview material was developed based on literature research conducted before the interviews.
Since the interviews were conducted in German, we provide an English translation of selected quotes. Table 1 contains the main topics and sub-topics of the interview, as well as exemplary quotes from the interviewees.
LOT definition and misunderstandings
Most interviewees confirmed that there was no common understanding of LOT and that they had difficulties explicating their own understanding of the concept. Furthermore, four of the interviewees reported misunderstandings with colleagues regarding LOTs and seven reported that they experienced uncertainties in their clinical practice when defining an LOT. For instance, if care for a patient was delivered by multiple centers, misunderstandings concerning LOT progression frequently occurred, because involved persons lacked a common understanding:
“[…] when it comes to categorizing it somehow so that it is standardized and applicable across multiple centers, yes there existed discrepancies in the particular considerations.” (Expert interview (E)05).
Treatment intention
Six interviewees said that treatment intention (curative vs. palliative) is important in the choice of therapy. Consequently, treatment intention is also relevant to LOT planning. Three experts expressed that LOT is especially relevant and established in the palliative setting:
“With a curative therapy option, […] you shouldn’t have any progression under therapy, after all. So that’s why the definition [of the line of therapy] does differ somewhat – palliative versus curative.” (E03).
Maintenance therapy
Starting a maintenance therapy to control a tumor after chemotherapy was predominantly not considered an indicator for a change in LOT, since usually only part of the medication regimen is discontinued for maintenance, while the rest remains the same. However, interviewees also said that maintenance therapy can include an entirely new pharmaceutical agent, which would, in turn, complicate the delineation between LOT:
“Yes, that’s difficult, too. I would probably count maintenance therapy as part of that – if it’s sort of quasi-logically linked to the therapy that was administered before it. But if it’s a completely different type of substance now, then it becomes more difficult again.” (E03).
Local therapies vs. systemic therapies
Six of the physicians interviewed opined that a LOT can contain both local and systemic therapies. However, some participants stated that beginning a new local therapy would not lead to a change of LOT, in contrast to beginning a new systemic therapy. Meanwhile, in contrast to the other six, three physicians emphasized that only systemic therapies can constitute a LOT:
“In my opinion, the therapy line is primarily defined by the systemic therapies. The local therapies are rather something supplementary that is carried out additionally, or – as the case may be – primarily in addition to symptom relief. Local therapies can also be used to achieve a response, but are not usually mentioned as a line of therapy.” (E06).
Change of LOT
All interviewees said that the LOT must be changed if tumor progression or disease relapse occurs or if therapy response fails. Six interviewees considered the occurrence of adverse effects (e.g., severe toxicity) a significant criterion for the decision to change an LOT. Only three interviewees saw the addition of a new pharmaceutical agent as resulting in a change of LOT:
“Dropping an active substance, I would always see as being due to toxicity or at the patient’s request – so actually owed to toxicity. That is, I would never call that a new line of therapy, whereas the addition of a new agent – strictly speaking, it would have to be considered a new line of therapy, although it is also difficult in terms of definition.” (E09).
The other seven interviewees only considered the introduction of new pharmaceutical agents a change in LOT if the treatment intention changed as well, or if a recurrence or progression occurred. Only the replacement of one drug with another of the same class (e.g., cisplatin with carboplatin) was not considered a change of LOT by anyone.
Therapy breaks
There were also ambiguous opinions regarding the role of breaks in therapy for the classification of LOT. On the one hand, the length of the break was considered decisive, whereas on the other hand, it was said that the therapy following the break was more important. Additionally, some viewed breaks in therapy as important for the classification of LOT in the event of a relapse or progression:
“[…] In principle, if no recurrence has occurred and it is perhaps even the same substance […] then I would consider it one line of therapy, regardless of how long the break was.” (E01).
If the break was unplanned, it was considered a significantly more important criterion for a change in LOT than if it was part of the therapy concept.
The expert interviews in this study largely confirmed that there is no common understanding of the LOT concept or its defining criteria. The interview material suggests that individual backgrounds in differing medical disciplines may influence views on and understandings of LOT. This potential context dependency of the LOT concept also appears consistent with heterogeneous working definitions of LOT in different real-world studies of distinct cancer entities [ 1 , 11 , 12 ].
However, it appeared that a LOT was considered a therapeutic concept with start- and endpoints that is focused on systemic therapies, although it may also contain additional treatment modalities. If included in the LOT, such non-systemic modalities would be selected based on individual patient and disease characteristics, and terminated if certain events (e.g., tumor progression) occurred.
There was evident uncertainty about the role of adjuvant and maintenance therapy and whether they should be regarded as an LOT together with the preceding (systemic) therapy. Also, no prevailing opinion could be identified on the questions of whether treatment intention (curative vs. palliative) and therapy breaks were integral to defining LOTs. Furthermore, experts held differing opinions on which changes in the administered drug regimen would initiate a change in LOT.
In the literature, however, individual approaches for standardizing the criteria for a change in LOT exist in the following cases: the termination of a LOT is indicated in the event of treatment discontinuation, addition of a new, non-equivalent agent, interruption of treatment, clinical progression of the disease, or death of the patient [ 2 , 3 ]. The interviewees were also nearly unanimous on these criteria: all considered tumor progression and recurrence decisive for a change in LOT; six experts highlighted the occurrence of side effects or relevant toxicity; three mentioned the scheduled end of therapy; and one cited patients’ wishes. Only some of the interviewees considered a change in pharmaceutical regimen a factor in identifying a change in LOT, while replacement of one drug with another from the same class was not viewed as altering the LOT.
The interviews both identified tumor recurrence and progression as LOT-relevant events and raised questions about the nature of their role. Recurrence and progression during therapy breaks, as well as the length of the break and the treatment thereafter, were considered relevant factors for a change in LOT. In two interviews, although the participants initially identified recurrence and progression as indicators for a change in LOT, their further comments appeared to contradict this standpoint. This apparent inconsistency should be investigated in future research.
Seven interviewees considered treatment intention relevant to LOT. Predominantly, interviewees considered the adoption of maintenance therapy as a continuation of an ongoing LOT. However, it remains unclear whether changes in the dosage or interval of drug administration during maintenance therapy imply a change in LOT. Six interviewees said that both local and systemic therapy modalities should be included in characterizations of LOT, although previous research excluded local modalities [ 1 , 13 , 14 , 15 ].
While similar approaches to standardizing the duration of a LOT [ 2 ] and first-line therapy [ 2 , 3 ] exist, it is not clear whether the definition of LOT can be standardized across disciplines as well as tumor entities. Nevertheless, a cross-disciplinary standard definition of the LOT concept should be targeted.
Limitations
This study exhibits the following limitations:
Qualitative expert interviews were only feasible for a small sample ( n = 9) of oncological experts, most of whom were located at a single center (eight out of nine). While the study delivers highly granular insights, this approach precludes generalization of the findings. Therefore, subsequent research must evaluate the qualitative insights leaned from this study in larger and more representative samples.
The interviewees had varying degrees of professional experience and different specialties, making direct comparisons of experience and assessments regarding oncological LOT difficult. However, this was intentional to obtain the widest possible range of assessments regarding the broad topic under investigation.
No triangulation in the form of using multiple and diverse data sources, perspectives, locations, or theories took place in conducting the study. Such methods can help to mitigate subjective bias resulting from the explicit focus on one’s own data [ 16 ].
Data availability
Details on the data and materials related to the study may be available upon reasonable request from Bernd Bender ([email protected]).
Abbreviations
German Cancer Consortium
- Expert interview
Line of therapy
Saini KS, Twelves C. Determining lines of therapy in patients with solid cancers: a proposed new systematic and comprehensive framework. Br J Canc. 2021;125(2):155–63.
Article Google Scholar
OPTUM. Determining lines of therapy (LOT) in oncology in claims databases. 2018. https://www.optum.com/content/dam/optum3/optum/en/resources/white-papers/guidelines-for-determining-lines-of-therapy-whitepaper.pdf . Accessed 28 March 2023.
Hess LM, Li X, Wu Y, Goodloe RJ, Cui ZL. Defining treatment regimens and lines of therapy using real-world data in oncology. Future Oncol. 2021;17(15):1865–77.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Rajkumar SV, Richardson P, San Miguel JF. Guidelines for determination of the number of prior lines of therapy in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2015;126(7):921–2.
Carroll NM, Burniece KM, Holzman J, McQuillan DB, Plata A, Ritzwoller DP. Algorithm to identify systemic cancer therapy treatment using structured electronic data. JCO Clin Cancer Inf. 2017;1:1–9.
Google Scholar
Weymann D, Costa S, Regier DA. Validation of a cyclic algorithm to proxy number of lines of systemic cancer therapy using administrative data. JCO Clin Cancer Inf. 2019;3:1–10.
Döringer S. The problem-centred expert interview’. Combining qualitative interviewing approaches for investigating implicit expert knowledge. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2021;24(3):265–78.
Cooke NM, McDonald JE. A formal methodology for acquiring and representing expert knowledge. Proc IEEE Inst Electr Electron Eng. 1986;74(10):1422–30.
Kallio H, Pietilä AM, Johnson M, Kangasniemi M. Systematic methodological review: developing a framework for a qualitative semi-structured interview guide. J Adv Nurs. 2016;72(12):2954–65.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Mayring P. Qualitative content analysis: demarcation, varieties, developments. Forum Qual Social Res. 2019;20(3):1–26.
Abrams T, Hess LM, Zhu YE, Schelman W, Liepa AM, Fuchs C. Predictors of heterogeneity in the first-line treatment of patients with advanced/metastatic gastric cancer in the US. Gastric Cancer. 2018;21:738–44.
Meng W, Ou W, Chandwani S, Chen X, Black W, Cai Z. Temporal phenotyping by mining healthcare data to derive lines of therapy for cancer. J Biomed Inf. 2019;100:103335.
Shah S, Raskin L, Cohan D, Freeman M, Hamid O. Treatment patterns of malignant melanoma in the United States from 2011 to 2016: a retrospective cohort study. CMRO. 2020;36:63–72.
CAS Google Scholar
Hess GP, Wang PF, Quach D, Barber B, Zhao Z. Systemic therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer: patterns of chemotherapy and biologic therapy use in US medical oncology practice. J Oncol Pract. 2010;6(6):301–7.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Fonseca R, Usmani SZ, Mehra M, Slavcev M, He J, Cote S, Lam A, Ukropec J, Maiese EM, Nair S, Potluri R, Voorhees PM. Frontline treatment patterns and attrition rates by subsequent lines of therapy in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. BMC Cancer. 2020;20:1087.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cho J, Lee EH. Reducing confusion about grounded theory and qualitative content analysis: similarities and differences. Qual Rep. 2014;19(64):1–20.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the expert physicians who participated in the interviews for their time and willingness to share their experiences and perspectives. Furthermore, we would like to thank the German Cancer Consortium’s Clinical Data Science Group for the support in realizing the study.
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL. This research is partly funded by the German Cancer Consortium (DKTK).
Author information
Lisa Falchetto and Bernd Bender contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Institute for Digital Medicine and Clinical Data Science, Goethe University Frankfurt, Faculty of Medicine, Frankfurt, Germany
Lisa Falchetto, Bernd Bender, Ian Erhard, Jörg Janne Vehreschild & Daniel Maier
German Cancer Consortium (DKTK), partner site Frankfurt/Mainz and German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany
Bernd Bender, Ian Erhard & Daniel Maier
Department for Dermatology, Venerology and Allergology, University Hospital Frankfurt, Frankfurt, Germany
Kim N. Zeiner
Department of Urology, University Hospital Frankfurt, Frankfurt, Germany
Florestan J. Koll
PIOH Praxis Internistischer Onkologie und Hämatologie, Cologne, Germany
Marcel Reiser
Clinic for Gynecology and Obstetrics, University Hospital Frankfurt, Frankfurt, Germany
Khayal Gasimli
Department for Internal Medicine 1, University Hospital Frankfurt, Frankfurt, Germany
Angelika Stehle
Department Neuro-Oncology, University Hospital Frankfurt, Frankfurt, Germany
Martin Voss
Department I of Internal Medicine, University Hospital of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
Jörg Janne Vehreschild
German Center for Infection Research (DZIF) partner site Bonn Cologne, Cologne, Germany
Medical Department 2 (Hematology/Oncology), Center for Internal Medicine, University Hospital Frankfurt, Goethe University Frankfurt, Frankfurt, Germany
Jan A. Stratmann, Sebastian Wagner & Olivier Ballo
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
BB, LF, and DM contributed to the writing of this article. LF and DM created the interview manual. LF conducted the interviews with the oncological experts and analyzed the interview material collected. DM and JJV were substantially involved in the conception of the study and in the acquisition of the interviewed experts. JJV also supported the piloting of the interview manual. IE edited the manuscript. KNZ, JAS, FJK, SW, MR, KG, AS, MV and OB participated in the study and provided the substantive statements and findings.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Bernd Bender .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
All subjects provided written informed consent to participate and this study was conducted according to all relevant ethical and regulatory guidelines. The project was approved by the ethics committee of the department of medicine of the Goethe University Frankfurt (ethical code number: 274/18).
Consent for publication
All interviewees permitted the use of the interview material and consented to publication.
Competing interests
Kim N. Zeiner (KNZ) received an honorarium for presentation from Bristol-Myers Squibb. Jan A. Stratmann (JAS) has personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Roche, BMS, Amgen, LEO pharma, Novartis and Takeda. Florestan J. Koll (FJK) received grants from the German Cancer Aid and the German Cancer Consortium (DKTK). Marcel Reiser (MR) received consulting fees from Amgen, Abbvie, Stemline, Novartis and honoria from Roche. Jörg Janne Vehreschild (JJV) has personal fees from Merck / MSD, Gilead, Pfizer, Astellas Pharma, Basilea, German Centre for Infection Research (DZIF), University Hospital Freiburg/ Congress and Communication, Academy for Infectious Medicine, University Manchester, German Society for Infectious Diseases (DGI), Ärztekammer Nordrhein, University Hospital Aachen, Back Bay Strategies, German Society for Internal Medicine (DGIM), Shionogi, Molecular Health, Netzwerk Universitätsmedizin, Janssen, NordForsk, Biontech, APOGEPHA and grants from Merck / MSD, Gilead, Pfizer, Astellas Pharma, Basilea, German Centre for Infection Research (DZIF), German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR), University of Bristol, Rigshospitalet Copenhagen. Daniel Maier (DM) received speaker honoraria from Free University Berlin and travel compensation from IQVIA. Lisa Falchetto (LF), Bernd Bender (BB), Ian Erhard (IE), Sebastian Wagner (SW), Khayal Gasimli (KG), Angelika Stehle (AS), Martin Voss (MV) and Olivier Ballo (OB) have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Additional file 1.
Interview manual with all instructions and questions.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Falchetto, L., Bender, B., Erhard, I. et al. Concepts of lines of therapy in cancer treatment: findings from an expert interview-based study. BMC Res Notes 17 , 137 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-024-06789-6
Download citation
Received : 28 July 2023
Accepted : 25 April 2024
Published : 15 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-024-06789-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Lines of therapy
- cancer treatment
- Therapy planning
BMC Research Notes
ISSN: 1756-0500
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Significance of Qualitative Research. The qualitative method of inquiry examines the 'how' and 'why' of decision making, rather than the 'when,' 'what,' and 'where.'[] Unlike quantitative methods, the objective of qualitative inquiry is to explore, narrate, and explain the phenomena and make sense of the complex reality.Health interventions, explanatory health models, and medical-social ...
Qualitative studies are often used to research phenomena that are difficult to quantify numerically.1,2 These may include concepts, feelings, opinions, interpretations and meanings, or why people behave in a certain way. Although qualitative research is often described in opposition to quantitative research, the approaches are complementary, and many researchers use mixed methods in their ...
Qualitative research is defined as "the study of the nature of phenomena", including "their quality, different manifestations, the context in which they appear or the perspectives from which they can be perceived", but excluding "their range, frequency and place in an objectively determined chain of cause and effect" [].This formal definition can be complemented with a more ...
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Qualitative research is the best way to understand these needs and contexts. Astrid Fletcher and colleagues, for example, used quantitative methods to objectively determine who (in terms of age, sex, and education level) did not use the eye-care services available in India ... We feel that such a range is appropriate for a medical journal ...
Qualitative research is the naturalistic study of social meanings and processes, using interviews, observations, and the analysis of texts and images. In contrast to quantitative researchers, whose statistical methods enable broad generalizations about populations (for example, comparisons of the percentages of U.S. demographic groups who vote in particular ways), qualitative researchers use ...
Qualitative research relies on nuanced judgements that require researcher reflexivity, yet reflexivity is often addressed superficially or overlooked completely during the research process. In this AMEE Guide, we define reflexivity as a set of continuous, collaborative, and multifaceted practices through which researchers self-consciously ...
Plain English summary Patient engagement (or patient and public involvement) in health research is becoming a requirement for many health research funders, yet many researchers have little or no experience in engaging patients as partners as opposed to research subjects. Additionally, many patients have no experience providing input on the research design or acting as a decision-making partner ...
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
1 Often begins with a single case, chosen because of its convenience or interest. 2 Often studies phenomena in the contexts in which they arise through observation and/or recording or the analysis of printed and Internet material. 3 Hypotheses are often generated from the analysis rather than stated at the outset.
Qualitative research is defined as an exploratory method that aims to understand complex phenomena, often within their natural settings, by examining subjective experiences, beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical measurements and statistical analysis, qualitative research employs a range of ...
Qualitative longitudinal research (QLR) comprises qualitative studies, with repeated data collection, that focus on the temporality (e.g., time and change) of a phenomenon. The use of QLR is increasing in health research since many topics within health involve change (e.g., progressive illness, rehabilitation). A method study can provide an insightful understanding of the use, trends and ...
Qualitative Research. Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people's beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus ...
Medical education is a complex field, and medical education research and practice fittingly draws from many disciplines (e.g., medicine, psychology, sociology, education) and synthesizes multiple perspectives to explain how people learn and how medicine should be taught. 4,5 The concept of a field was well described by Cristancho and Varpio 5 in their tips for early career medical educators ...
research. the systematic, rigorous investigation of a situation or problem in order to generate new knowledge or validate existing knowledge. Research in health care takes place in a variety of areas and has many potential benefits; the areas include professional practice, environmental issues affecting health, vitality, treatments, theory ...
The concept of lines of therapy (LOT) in cancer treatment is often considered for decision making in tumor boards and clinical management, but lacks a common definition across medical specialties. The complexity and heterogeneity of malignancies and treatment modalities contribute to an inconsistent understanding of LOT among physicians. This study assesses the heterogeneity of understandings ...