

Health and Social Care
- Getting Started
- Journals & Databases
- NHS Scotland Knowledge Network
- Literature Reviewing
Literature reviewing - the overview
- What is a literature review?
- How are literature reviews relevant to health and social care?
- Types of Literature Review
- Reporting and Conducting Guidance
- What's in a good literature review?
- Common mistakes?
A literature review:
- Finds existing literature/sources published on a specific topic/to answer a review question.
- Brings together the literature sources into a single body of literature.
- Makes comparisons between the different included sources to identify both patterns/similarities and conflicts/differences.
Within healthcare literature reviews are often known as 'evidence synthesis reviews' and usually have specific methods and processes which are detailed in more depth in the section below titled 'Literature reviewing - the process'. This can differ from other field areas so if you have not done a healthcare evidence synthesis review before you may find it very different to previous expectations or experiences.
There are also a number of different types of evidence synthesis reviews within healthcare and the type of review impacts the purpose and methods. The next tab gives more information about different types of review. If you are doing a review as part of an academic assignment then please ensure you follow the requirements and any methods set out in your assignment brief.
Taking a Systematic Approach
Within healthcare evidence synthesis reviews there is an expectation that the approach taken, no matter what type of review is being done, is systematic. Whilst a systematic review is a specific review type, any review type can still take a systematic approach which strengths the quality of the methods, and therefore also strengthens the quality of the findings, write up, and usefulness/applicability of the review.
- Wakefield, A.(2014). Searching and critiquing the research literature. Nursing Standard, 28(39), 49-57
- Kable, A. K., Pich, J., & Maslin-Prothero, S. E. (2012). A structured approach to documenting a search strategy for publication: a 12 step guideline for authors. Nurse Education Today, 32(8), 878-886
- Smith, J., Noble, H. (2016) Reviewing the literature. Evidence Based Nursing, 19 (1), 2-3.
In health and social care there are a number of different types of review. The resources below give an outline of the different types and outline the differences between them:
Grant, M. J., & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information and Libraries Journal , 26 (2), 91–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
Sutton, A., Clowes, M., Preston, L., & Booth, A. (2019). Meeting the review family: exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements. Health Information and Libraries Journal , 36 (3), 202–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/hir.12276
If you are doing a literature review as part of an academic assignment then please ensure you follow the requirements and any methods set out in your assignment brief. You may be advised to do a specific type of review, but when reading the guidance of how to conduct one find that it differs from your assignment brief. If so, discuss this with your supervisor or module leader.
Choosing a Review Type
You need to understand the purpose of different review types and match this up with what you are intending to achieve from carrying out your review in order to select the most appropriate type. You can include this explanation and justification within your write up. As well as the guidance above please see some further resources below to support your decision making.
Munn, Z., Peters, M. D. J., Stern, C., Tufanaru, C., McArthur, A., & Aromataris, E. (2018). Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Medical Research Methodology , 18 (1), 143–143. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-018-0611-x
Jonkoping University. (n.d.). Which review is right for you? https://guides.library.ju.se/c.php?g=690269&p=4943634
Right Review. (2024). Right Review Tool. https://rightreview.knowledgetranslation.net/
There are a number of published reporting and conducting guidelines and handbooks to support you in both carrying out and writing up your review. These help to ensure the quality and transparency of your review by ensuring you have included and conducted your review in a way that meets established methodological expectations.
Reporting guidelines give information on what you need to include in the write up of the review. Conducting guidelines provide more methodological guidance on how to carry out and undertake each stage of a review, not just stating what you need to include/report. When using these they need to be cited and referenced and the wording you would use needs to distinguish if it is a reporting or conducting resource, and therefore how it has been used. Examples:
'this review/protocol was reported using . . . '
'the conducting of this review was guided by . . . '
A lot of these were designed for quantitative systematic reviews of interventions, however a number of resources now exist for different types of evidence synthesis reviews. Below are resources of some of the most commonly used guidelines.
The PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) statement consists of a 27-item checklist that covers the elements needed in the write up of a systematic review, and a flow diagram.
There is an article giving further explanation of every element of the checklist and a glossary of terms .
PRISMA also have guidance for reporting protocols, known as the PRISMA-P extension.
There is also a checklist extension for Scoping Reviews called PRISMA- ScR , which is very similar to the Systematic Review checklist but with some key differences.
Also a more in-depth explanatory paper for this checklist as well.
The Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions needs to be followed if you were to publish a review or review protocol in the Cochrane Library of Systematic Reviews.
There are a set a reporting guidelines for both review protocols and full reviews .
Key aspects of the Cochrane handbook are collated as the Methodological Expectations for Cochrane Intervention Reviews – takes you through steps needed to conduct.
The Cochrane Handbook Chapter V also details methodology for conducting Overviews of Reviews.
The Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group have published a series of 6 papers covering qualitative evidence synthesis methods .
Other Guides
The JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis separates SRs out by types of evidence included, as well as having chapters on Mixed Methods Reviews, Scoping Reviews and Umbrella Reviews.
RAMSES reporting can be used for realist reviews and meta-narrative reviews.
The ENTREQ checklist can be used to report reviews of qualitative literature, alongside a fuller article explaining the development of the checklist .
Further reporting and conducting guidelines can be found on this useful page from the University of Illinois .
Booth, A. (2016). EVIDENT Guidance for reviewing the evidence: a compendium of methodological literature and websites. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/292991575_EVIDENT_Guidance_for_Reviewing_the_Evidence_a_compendium_of_methodological_literature_and_websites
A good literature review should:
- Address a focused, explicit research question.
- Take a systematic approach to the searching of the literature.
- Document the search process so that it is replicable by others (often a requirement for publication within many academic journals)
- Demonstrate that a wide range of sources have been searched.
- Undertake a critical analysis of the retrieved literature, not merely describe what has been read.
- Justify why particular items of literature are being referred to. They should summarise the current state of research, perhaps debates that have taken place over a period of time within that topic or arguments for and against a particular aspect of the topic.
- Relate the question to the larger body of knowledge within which your topic sits, and to put your work into context.
- Summarise the current state of the research evidence.
- Identify the gap in the literature that your research question is going to answer.
Common Mistakes
- Review is too descriptive. No critiquing or critical evaluation of the evidence. No identification of strengths and weaknesses. It becomes an essay, not a review. It does not set the foundation for your own research process.
- It becomes a dumping ground to write down everything you know about the topic or is presented as a series of quotes from the papers you have read.
- Not enough time has been allocated to searching and reviewing the literature. Do your literature reviewing early. It helps inform your final research question, future methodologies and identifies whether there is indeed a "gap" in the current research literature that your queston is going to answer.
- Literature used is not from scholarly peer reviewed sources.
- There is no documentation or explanation of how the search was undertaken and the key terms used. No explanation of inclusion/exclusion criteria.
- Referencing does not follow the School guidelines. It is not consistent in style or presentation.
- There has been no revision or proof reading. Thinking develops as you write. Go back over what you have written a few days after you have done it. Check grammar and language – give it to someone else to proof read.
Here are 5 top tips towards a stress free literature review
- Top tips for literature reviewing
Literature reviewing - the process
- Question Development
- Eligibility Criteria
- Planning the Search Strategy
- Searching the Literature
- Selecting the Literature
- Keeping track of your literature
- Critical Appraisal
- Analysing and Discussing the Literature
Formulating a review question is a key stage of the review process as this impacts the development of the outcomes of the review, the eligibility criteria for selection, and the development of the search strategy. If you make changes to your review question after already moving on to other stages of the review you may need to go back and make changes to these other steps.
Ideally a review should add new knowledge to that topic or field, so you want to develop a question that has a new focus or outcomes that has not previously been explored. Sometimes it is appropriate to update a previous review using the same question and outcomes to see if the findings of the review have changed with the inclusion of new literature since the previous one was published.
If you are a Masters student it is particularly important that you choose a topic that is both viable and manageable within the word count and timescales for completion. Viable means a topic where there is published literature, you cannot do a literature review on a question where there is no available literature. Manageable means selecting a focused topic where there will not be too vast an amount of literature to include as you have a word count limit and a timescale in which to submit the assignment.
To help you develop a question try and identify an area from practice that you are interested in – ideally something the practice area can benefit from which will give value to your review findings.
The question you develop from this topic should be focused, manageable and answerable within the timescales you have.
Scoping the Literature
This is where we run initial literature searches around our topic of interest to get an initial idea of what literature is out there. This will help us to:
- Check what reviews have already been done on this topic.
- Check our topic is viable - there is enough literature out there.
- Check our topic is not too broad - too much literature out there.
From these initial searches of the literature you can start to refine your review question, broadening or focusing as necessary. Please see the following video on Scoping Searches to Refine Your Topic for an example of how this works in practice.
- Question Formulation Frameworks
Question formulation frameworks are used particularly within healthcare to help you identify the key concepts of your topic, to then structure into a research or review question. The following document shows you examples of the most commonly used ones in healthcare, breaking down each framework into what the concepts mean, giving examples in practice of questions structured using that framework, and suggestions of review outcomes and types best suited to each framework.
The eligibility criteria can also be referred to as the inclusion and exclusion criteria. This is a set of criteria you will develop which you will use during the selection process of the review to decide which sources of literature to include and exclude. This criteria helps to reduce selection bias, because every decision you make should be based on this pre-determined set of criteria.
When take a systematic approach to searching and selecting the literature your eligibility criteria needs to be very detailed, both for you to be able to make decisions for each of the pieces of literature you have found, but also for someone else to be able to use the criteria with the same set of literature and make the same decisions as you. If you are doing a review as part of a review team for publication then there should be a minimum of two people involved in the selection of the literature, both using the same criteria to make selection decisions. This aligns to the systematic criteria of transparency .
When developing your eligibility criteria think about the following elements:
- Each of your question concepts from your question formulation framework and detail exactly what criteria would mean a source would be included or excluded in relation to each question concept.
E.g. your population group is people with dementia, so as inclusion criteria you would state that each literature source needs this population group and any source without this population group would be excluded. But what about literature where participants and both people with dementia and people with Parkinsons. Would this be included or excluded? Your criteria needs to be detailed enough to capture all of the potential decisions you would need to make.
- The study criteria for research literature, so the methodology, design and any further details. Depending on your review question there will sometimes be specific types of data most suited to answer the question, so sometimes either quantitative or qualitative data only would be appropriate, and sometimes only specific study designs like randomised controlled trials
E.g. you're question is exploring the experiences and views of a particular group of participants, therefore the data most appropriate to 'answer' this question would be qualitative.
- Types of publications, so are you only including primary research or wider sources of literature? Even with primary research there are a number of different source types this could be presented in such as journal articles, theses, conference proceedings.
- Publication dates, so is there a specific date range you will only be including literature from? Try to think about the context of your specific topic/question and what would make something too old.
E.g. there has been a new guideline in your topic area published in a specific year with major changes to how a specific procedure is done in practice, meaning that older literature is not relevant to the current guideline. Topics related to technology could be outdated more easily due to specific technological developments in a specific field or equipment.
A search strategy includes where and how you are searching. Can someone else use your process to find what you found? This aligns with the systematic criteria of being transparent.
You need to plan and include the following detail in your write up to allow someone else to replicate your search:
- Search Strategy Planning Template
When searching in databases most of the time you want to use the advanced search feature to build a search that will find a more relevant set of search results. To do this you need to be able to plan effective search strategies, using appropriate keyword search terms, and inputting these into the database in the most effective combination.
The videos below demonstrate how to input a planned systematic search strategy into a database. Different database platforms will look slightly different, but the principles for doing an advanced search are the same across them all, but differences are demonstrated.
Searching in EBSCO databases (CINAHL, Medline, APA PsycInfo etc.)
Searching in PubMed
Searching in Ovid
Searching in Web of Science
Searching in Proquest
The selection process is where you will use your eligibility criteria to select the literature for inclusion in your review. Considerations needed are:
Keeping track of literature
Writing a literature review will mean that you will collect a large number of pieces of information from many sources. Before you begin searching, give some thought as to how you are going to manage this information.
Reference management software will enable you to automatically export references you collect from database searches and store them in the reference manager. Once you have read each paper you can then make personal research notes and store these within each reference inside the reference manager.
Use the software to format the citations within the text of your review. It will also produce the reference list at the end of your document formatted in a style of your choosing e.g. APA 7th.
See our Reference Management LibGuide on how to get started with Endnote or Mendeley, Edinburgh Napier’s referencing management software.
NHS Scotland users can also use the Refworks ref management software supplied on the NHS Knowledge network site instead of Endnote, if they would prefer.
What is critical appraisal?
Critical appraisal/quality assessment is a specific aspect of critical analysis where you examine and assess research in order to judge its:
You are evaluating the quality of the research and how it has been conducted, as well as the findings themselves and how it has been reported. Please see the following video by Cochrane on an Introduction to Critical Appraisal for a more in depth description.
Why do we do it?
Critical appraisal is often carried out using checklists that help signpost areas to look for while reading a paper. There are different types of checklist depending on the type of research you are reviewing.
The following document lists some of the main appraisal tools used in published reviews and would be a good place to start when deciding on which tool to use.
- Critical Appraisal/Quality Assessment Tools
Further Critical Appraisal Resources

Two excellent videos from Andrew Booth at SCHARR at the University of Sheffield. These take you through the actual process of appraising papers using the CASP tool.
Appraising a Quantitative Study [13 mins]
Critical Appraisal of a Qualitative Study [12 mins]
Data Extraction and Charting
Your literature findings need to be presented and discussed both descriptively and analytically. It is usually to present a summary of the included sources in the form of a data extraction or study characteristics table, a process also referred to as data extraction and charting your results. The video below covers how to present your findings in this way.
- Presenting Your Results in a Study Characteristics Table
Analysing and Synthesising the Findings of the Literature
Depending on the type of review you are doing and also whether the review is being done as an assignment, there may be differing expectations of how you analyse the included literature sources.
At Masters dissertation level you would be expected as a minimum to provide a narrative thematic analysis, where you compare and contrast the literature to identify patterns and themes and interpret these in relation to your review question. You can use a deductive approach where you start with a pre-existing framework of themes, or an inductive approach where themes are generated from reading the literature.
At PhD or researcher for publication level there would be an expectation of a more complex analysis of the literature, appropriate to the literature sources. A scoping review including a wide range of source types would likely best be suited to a narrative analysis, but if the review literature is all research then an appropriate quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods form of analysis of the data would be expected.
Most Systematic Review conduction and reporting guidelines are designed around an analysis of quantitative data, so if this does not fit the data of your literature you may need to use different analysis and synthesis guidance. There are a number of different analysis methods, some examples and resources are listed below as a starting point but you may also want to look at examples of similar reviews fur further methods.
- Chapters 10 and 11 of the Cochrane Handbook covers quantitative meta-analysis.
- Chapter 12 covers over methods, however these are all still mainly quantitative methods.
- The eMergE reporting guidance covers meta-ethnography qualitative synthesis, and the ENTREQ statement can also be used for qualitative synthesis.
Recommended Reading
- << Previous: NHS Scotland Knowledge Network
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 1:35 PM
- URL: https://libguides.napier.ac.uk/shsc
- Find My Rep
You are here
Doing a Literature Review in Nursing, Health and Social Care
- Michael Coughlan - Trinity College Dublin, Ireland
- Patricia Cronin - Trinity College Dublin, Ireland
- Description
A clear and practical guide to completing a literature review in nursing and healthcare studies.
Providing students with straightforward guidance on how to successfully carry out a literature review as part of a research project or dissertation, this book uses examples and activities to demonstrate how to complete each step correctly, from start to finish, and highlights how to avoid common mistakes.
The third edition includes:
- Expert advice on selecting and researching a topic
- A chapter outlining the different types of literature review
- Increased focus on Critical Appraisal Tools and how to use them effectively
- New real-world examples presenting best practice
- Instructions on writing up and presenting the final piece of work
Perfect for any nursing or healthcare student new to literature reviews and for anyone who needs a refresher in this important topic.
Praise for the previous edition:
'This book is an excellent resource for practitioners wishing to develop their knowledge and understanding of reviewing literature and the processes involved. It uses uncomplicated language to signpost the reader effortlessly through key aspects of research processes. Practitioners will find this an invaluable companion for navigating through evidence to identify quality literature applicable to health and social care practice.'
'Students often struggle with writing an effective literature review and this invaluable guide will help to allay their concerns. Key terms are clearly explained, and the inclusion of learning outcomes is a helpful feature for students and lecturers alike. The examples are also very helpful, particularly for less confident students. This is an accessible yet authoritative guide which I can thoroughly recommend.'
'A must have - this book provides useful information and guidance to students and professionals alike. It guides the reader through various research methods in a theoretical and pragmatic manner.'
' It's a very readable, concise, and accessible introduction to undertaking a literature review in the field of healthcare. The book’s layout has a logical format which really helped me to think methodically about my research question. An excellent reference for undergraduates who are about to undertake their first literature review.'
'This book is an essential resource for students. Clearly written and excellently structured, with helpful study tools throughout, it takes the reader step by step through the literature review process in an easy, informative and accessible manner. This text gives students the skills they need to successfully complete their own review.'
'The updating of the chapters will be exceptionally helpful given the rapid changes in online availability of resources and open-access literature.'
Excellent resource. Useful for any stage of studying
Excellent text for masters and doctoral level students
An excellent primer to help the level 7 students write their systemised review for the assignment.
This book provides a comprehensive overview of the practical process of literature review in healthcare. It contains all details required to conduct a review by students.
This is an excellent clear and concise book on undertaking literature reviews being particularly good at demystifying jargon. It is timely given the move to student dissertations being primarily literature reviews in the current Covid pandemic. However nearly all the examples are drawn from nursing and health making the text less useful for social care and social work. A little disappointing given the title. SW students are likely to gravitate to texts where their subject is more prominent for a primary text.
Accessible, informative, step to step guide
This is a really helpful, accessible text for students and academic staff alike.
A really good addition to the repertoire of skills and techniques for understanding the essential process of literature reviewing.
Preview this book
For instructors.
Please select a format:
Select a Purchasing Option
- Electronic Order Options VitalSource Amazon Kindle Google Play eBooks.com Kobo
Related Products

Health (Nursing, Medicine, Allied Health)
- Find Articles/Databases
- Reference Resources
- Evidence Summaries & Clinical Guidelines
- Drug Information
- Health Data & Statistics
- Patient/Consumer Facing Materials
- Images and Streaming Video
- Grey Literature
- Mobile Apps & "Point of Care" Tools
- Tests & Measures This link opens in a new window
- Citing Sources
- Selecting Databases
- Framing Research Questions
- Crafting a Search
- Narrowing / Filtering a Search
- Expanding a Search
- Cited Reference Searching
- Saving Searches
- Term Glossary
- Critical Appraisal Resources
- What are Literature Reviews?
- Conducting & Reporting Systematic Reviews
- Finding Systematic Reviews
- Tutorials & Tools for Literature Reviews
- Finding Full Text
What are Systematic Reviews? (3 minutes, 24 second YouTube Video)
Systematic Literature Reviews: Steps & Resources
These steps for conducting a systematic literature review are listed below .
Also see subpages for more information about:
- The different types of literature reviews, including systematic reviews and other evidence synthesis methods
- Tools & Tutorials
Literature Review & Systematic Review Steps
- Develop a Focused Question
- Scope the Literature (Initial Search)
- Refine & Expand the Search
- Limit the Results
- Download Citations
- Abstract & Analyze
- Create Flow Diagram
- Synthesize & Report Results
1. Develop a Focused Question
Consider the PICO Format: Population/Problem, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome
Focus on defining the Population or Problem and Intervention (don't narrow by Comparison or Outcome just yet!)
"What are the effects of the Pilates method for patients with low back pain?"
Tools & Additional Resources:
- PICO Question Help
- Stillwell, Susan B., DNP, RN, CNE; Fineout-Overholt, Ellen, PhD, RN, FNAP, FAAN; Melnyk, Bernadette Mazurek, PhD, RN, CPNP/PMHNP, FNAP, FAAN; Williamson, Kathleen M., PhD, RN Evidence-Based Practice, Step by Step: Asking the Clinical Question, AJN The American Journal of Nursing : March 2010 - Volume 110 - Issue 3 - p 58-61 doi: 10.1097/01.NAJ.0000368959.11129.79
2. Scope the Literature
A "scoping search" investigates the breadth and/or depth of the initial question or may identify a gap in the literature.
Eligible studies may be located by searching in:
- Background sources (books, point-of-care tools)
- Article databases
- Trial registries
- Grey literature
- Cited references
- Reference lists
When searching, if possible, translate terms to controlled vocabulary of the database. Use text word searching when necessary.
Use Boolean operators to connect search terms:
- Combine separate concepts with AND (resulting in a narrower search)
- Connecting synonyms with OR (resulting in an expanded search)
Search: pilates AND ("low back pain" OR backache )
Video Tutorials - Translating PICO Questions into Search Queries
- Translate Your PICO Into a Search in PubMed (YouTube, Carrie Price, 5:11)
- Translate Your PICO Into a Search in CINAHL (YouTube, Carrie Price, 4:56)
3. Refine & Expand Your Search
Expand your search strategy with synonymous search terms harvested from:
- database thesauri
- reference lists
- relevant studies
Example:
(pilates OR exercise movement techniques) AND ("low back pain" OR backache* OR sciatica OR lumbago OR spondylosis)
As you develop a final, reproducible strategy for each database, save your strategies in a:
- a personal database account (e.g., MyNCBI for PubMed)
- Log in with your NYU credentials
- Open and "Make a Copy" to create your own tracker for your literature search strategies
4. Limit Your Results
Use database filters to limit your results based on your defined inclusion/exclusion criteria. In addition to relying on the databases' categorical filters, you may also need to manually screen results.
- Limit to Article type, e.g.,: "randomized controlled trial" OR multicenter study
- Limit by publication years, age groups, language, etc.
NOTE: Many databases allow you to filter to "Full Text Only". This filter is not recommended . It excludes articles if their full text is not available in that particular database (CINAHL, PubMed, etc), but if the article is relevant, it is important that you are able to read its title and abstract, regardless of 'full text' status. The full text is likely to be accessible through another source (a different database, or Interlibrary Loan).
- Filters in PubMed
- CINAHL Advanced Searching Tutorial
5. Download Citations
Selected citations and/or entire sets of search results can be downloaded from the database into a citation management tool. If you are conducting a systematic review that will require reporting according to PRISMA standards, a citation manager can help you keep track of the number of articles that came from each database, as well as the number of duplicate records.
In Zotero, you can create a Collection for the combined results set, and sub-collections for the results from each database you search. You can then use Zotero's 'Duplicate Items" function to find and merge duplicate records.

- Citation Managers - General Guide
6. Abstract and Analyze
- Migrate citations to data collection/extraction tool
- Screen Title/Abstracts for inclusion/exclusion
- Screen and appraise full text for relevance, methods,
- Resolve disagreements by consensus
Covidence is a web-based tool that enables you to work with a team to screen titles/abstracts and full text for inclusion in your review, as well as extract data from the included studies.

- Covidence Support
- Critical Appraisal Tools
- Data Extraction Tools
7. Create Flow Diagram
The PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses) flow diagram is a visual representation of the flow of records through different phases of a systematic review. It depicts the number of records identified, included and excluded. It is best used in conjunction with the PRISMA checklist .

Example from: Stotz, S. A., McNealy, K., Begay, R. L., DeSanto, K., Manson, S. M., & Moore, K. R. (2021). Multi-level diabetes prevention and treatment interventions for Native people in the USA and Canada: A scoping review. Current Diabetes Reports, 2 (11), 46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-021-01414-3
- PRISMA Flow Diagram Generator (ShinyApp.io, Haddaway et al. )
- PRISMA Diagram Templates (Word and PDF)
- Make a copy of the file to fill out the template
- Image can be downloaded as PDF, PNG, JPG, or SVG
- Covidence generates a PRISMA diagram that is automatically updated as records move through the review phases
8. Synthesize & Report Results
There are a number of reporting guideline available to guide the synthesis and reporting of results in systematic literature reviews.
It is common to organize findings in a matrix, also known as a Table of Evidence (ToE).

- Reporting Guidelines for Systematic Reviews
- Download a sample template of a health sciences review matrix (GoogleSheets)
The implementation of person-centred plans in the community-care sector: a qualitative study of organizations in Ontario, Canada
- Samina Idrees 1 ,
- Gillian Young 1 ,
- Brian Dunne 2 ,
- Donnie Antony 2 ,
- Leslie Meredith 1 &
- Maria Mathews 1
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 680 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
324 Accesses
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
Person-centred planning refers to a model of care in which programs and services are developed in collaboration with persons receiving care (i.e., persons-supported) and tailored to their unique needs and goals. In recent decades, governments around the world have enacted policies requiring community-care agencies to adopt an individualized or person-centred approach to service delivery. Although regional mandates provide a framework for directing care, it is unclear how this guidance is implemented in practice given the diversity and range of organizations within the sector. This study aims to address a gap in the literature by describing how person-centred care plans are implemented in community-care organizations.
We conducted semi-structured interviews with administrators from community-care organizations in Ontario, Canada. We asked participants about their organization’s approach to developing and updating person-centred care plans, including relevant supports and barriers. We analyzed the data thematically using a pragmatic, qualitative, descriptive approach.
We interviewed administrators from 12 community-care organizations. We identified three overarching categories or processes related to organizational characteristics and person-centred planning: (1) organizational context, (2) organizational culture, and (3) the design and delivery of person-centred care plans. The context of care and the types of services offered by the organization were directly informed by the needs and characteristics of the population served. The culture of the organization (e.g., their values, attitudes and beliefs surrounding persons-supported) was a key influence in the development and implementation of person-centred care plans. Participants described the person-centred planning process as being iterative and collaborative, involving initial and continued consultations with persons-supported and their close family and friends, while also citing implementation challenges in cases where persons had difficulty communicating, and in cases where they preferred not to have a formal plan in place.
Conclusions
The person-centred planning process is largely informed by organizational context and culture. There are ongoing challenges in the implementation of person-centred care plans, highlighting a gap between policy and practice and suggesting a need for comprehensive guidance and enhanced adaptability in current regulations. Policymakers, administrators, and service providers can leverage these insights to refine policies, advocating for inclusive, flexible approaches that better align with diverse community needs.
Peer Review reports
The community-care sector facilitates the coordination and administration of in-home and community-based health and social services. Community-care services include supports for independent living, residential services, complex medical care, and community-participation services to support personal and professional goals (e.g., education, employment, and recreation-based supports) [ 1 ]. There is substantial heterogeneity in the clinical and demographic characteristics of the community-care population, including individuals with physical and developmental disabilities, and complex medical needs [ 2 ]. We refer to the individuals served by these organizations as ‘persons-supported’ in line with person-first language conventions [ 3 , 4 ].
In recent decades, governments across the world have enacted policies requiring community-care agencies to adopt an individualized or person-centred approach to service delivery [ 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 ]. Person-centred care encompasses a broad framework designed to direct care delivery, as opposed to a singular standardized process. In the context of community-care, person-centred planning refers to a model of care provision in which programs and services are developed in collaboration with persons-supported and tailored to their unique needs and desired outcomes [ 9 , 10 ].
In Ontario, Canada, community-care services are funded by the Ministry of Health (MOH) and the Ministry of Children, Community and Social Services (MCCSS). Service agreements between these ministries and individual agencies can be complex and contingent on different factors including compliance with a number of regulatory items and policies [ 7 , 11 ]. MOH provides funding for health-based services including in-home physiotherapy, respiratory therapy, and personal support services, among several others. MOH funds Home and Community Care Support Services (HCCSS), a network of organizations responsible for coordinating the delivery of in-home and community-based care in the province. MCCSS funds social service agencies including those providing community participation and residential support for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities (IDDs).
Several tools and resources have been developed to aid organizations in providing person-centred care and organizations may differ in their use of these tools and their specific approach. Although regional mandates provide a framework for directing care delivery, it is unclear how this guidance is implemented in practice given the diversity and range of organizations within the sector. In addition, as noted by a recent scoping review, there is limited literature on the implementation process and impact of person-centred planning on individual outcomes [ 12 ]. Using a pragmatic, qualitative, descriptive approach [ 13 ], we outline how community-care organizations enact a person-centred approach to care and the factors that shape their enactment. By describing existing practices in the context of the community-care sector, we aim to provide insight on how to optimize care delivery to improve outcomes and inform current policy. This study is part of a larger, multi-methods project examining the implementation of person-centred care plans in the community-care sector. This project encompasses qualitative interviews with representatives from different community-care organizations, as well as staff and persons-supported at a partner community-care organization. This paper focuses on analyzing data from interviews with representatives from different community-care organizations.
We conducted semi-structured interviews with administrators from community-care organizations in Southwestern Ontario (roughly the Ontario Health West Region) between October 2022 and January 2023. We included community-care organizations funded by MOH or MCCSS. We excluded organizations that did not provide services in Southwestern Ontario. We identified eligible organizations and participants by searching online databases, including community resource lists, as well as through consultation with members of the research team.
We used maximum variation sampling [ 14 ], to recruit participants from organizations with a wide range of characteristics including location (i.e., urban, rural), organization type (i.e., for-profit, not-for-profit), and types of services provided (e.g., residential, recreation, transportation, etc.) We contacted eligible organizations via email, providing them with study information and inviting them to participate. We recruited until the data reached saturation, defined as the point at which there was sufficient data to enable rigorous analysis [ 14 , 15 ].
In each interview, we asked participants about their organization’s approach to developing and updating individual service agreements or person-centred care plans, and the supports and barriers (e.g., organizational, funding, staffing, etc.) that facilitate or hinder the implementation of these plans (Supplementary Material 1 : Interview Guide). We also collected information on relevant participant and organizational characteristics, including participant gender, position, years of experience, organization location, type (i.e., for-profit, not-for-profit), services offered, years in operation, and client load. The interviews were approximately one hour in length and conducted virtually via Zoom (Zoom Video Communications Inc.) or by telephone. The interviews were audio-recorded and transcribed verbatim. Interviewer field notes were also used in data analysis.
We analyzed the data thematically [ 16 ]. The coding process followed a collaborative and multi-step approach. Initially, three members of the research team independently reviewed and coded a selection of transcripts to identify key ideas and patterns in the data, and form a preliminary coding template. We then met to consolidate individual coding efforts. We compared coding of each transcript, resolving conflicts through discussion and consensus. In coding subsequent transcripts and through a series of meetings, we worked together to finalize the codebook to reflect more analytic codes. We used the finalized template to code all interview transcripts in NVivo (QSR International), a software designed to facilitate qualitative data analysis. We refined the codebook on an as-needed basis by incorporating novel insights gleaned from the coding of additional transcripts, reflecting the iterative nature of the analysis.
We increased the robustness of our methodology by pre-testing interview questions, documenting interview and transcription protocols, using experienced interviewers, and confirming meaning with participants in interviews [ 14 , 15 , 16 ]. We kept detailed records of interviews, field notes, and drafts of the coding template. We made efforts to identify negative cases and provided rich descriptions and illustrative quotes [ 17 ]. We included individuals directly involved in the administration of community-care services on our research team. These individuals provided important context and feedback at each stage of the research process.
This study was approved by the research ethics board at Western University. We obtained informed consent from participants prior to the onset of interviews. We maintained confidentiality through secure storage of interview data (e.g., audio recordings), password-protection of sensitive documents, and the de-identification of transcripts.
Positionality
The authors represent a multidisciplinary team of researchers, clinicians, and community-care leaders. The community-care leaders and clinicians on our team provided key practical expertise to inform the development of interview questions and the analysis of study findings.
We interviewed administrators across 12 community-care organizations in Southwestern Ontario. The sample included representatives from seven organizations that received funding from MCCSS, three organizations that received funding from MOH, and two organizations that received funding from both MCCSS and MOH (Table 1 ). Eleven organizations were not-for-profit, one was a for-profit agency. The organizations provided care in rural ( n = 3), urban ( n = 4), or both rural and urban populations ( n = 5). Seven of the 12 participants were women, nine had been working with their organization for more than 11 years, and all had been working in the community-care sector for more than 12 years (Table 2 ).
We identified three key categories or processes relating to organizational characteristics and their impact on the design and delivery of person-centred care plans: (1) organizational context, (2) organizational culture, and (3) the development and implementation of person-centred care plans.
Organizational context
Organizational context refers to the characteristics of persons-supported, and the nature of services provided. Organizational context accounts for the considerable heterogeneity across organizations in the community-care sector and their approach to person-centred care plans.
Populations served
The majority of organizations included in the study supported individuals with IDDs: “all of the people have been identified as having a developmental disability. That’s part of the eligibility criteria for any funded developmental service in Ontario.” [P10]. Participants described how eligibility was ascertained through the referral process: “ the DSO [Developmental Services Ontario] figures all of that out and then refers them to us .” [P08]. These descriptions highlighted a common access point for publicly-funded adult developmental services in the province. Accordingly, these organizations were primarily funded by MCCSS. Other organizations focused on medically complex individuals including those with acquired brain injuries or those unable to access out-patient services due to physical disabilities: “the typical reason for referral is going to be around a physical impairment… But, with this medically complex population, you’re often seeing comorbidities where there may be some cognitive impairment, early dementia.” [P04]. In these organizations, eligibility and referral were usually coordinated by HCCSS. These insights highlighted the diverse characteristics of community-care populations, emphasizing the need to consider both physical and cognitive health challenges in care provision approaches.
Services offered
The characteristics of persons-supported informed the context of care and the type of services offered by the organization. The different dimensions of services offered within this sector include social and medical care, short and long-term care provision, in-home and community-care, and full and part-time care.
Nature of care: social vs. medical
Many organizations serving individuals with IDDs employed a holistic, psychosocial model of care, designed to support all areas of an individual’s life including supports for independent-living, and community-based education, employment, and recreation services to support personal and professional goals: “we support people in their homes, so residential supports. We also support people in the community, to be a part of the community, participate in the community and also to work in the community.” [P06]. These descriptions reflect a comprehensive approach to care, aiming to address needs within and beyond residential settings to promote active participation within the broader community. In contrast, some organizations followed a biomedical model of care, designed to support specific health needs: “We provide all five therapies… physiotherapy, occupational therapy, speech, social work, and nutrition. In some locations we provide visiting nursing, at some locations shift nursing. We have some clinic-nursing… and we provide personal support and home-making services in a number of locations as well.” [P04]. These organizations adopted a more clinically-focused approach to care. In either instance, the care model and the nature of services offered were largely determined by an organization’s mandate including which gaps they aimed to fill within the community. Many organizations described providing a mixture of social and medical care for individuals with complex needs. However, the implementation of care plans could be impacted by the lack of integration between social and medical care sectors, as some participants spoke to the importance of “[integrating] all of the different healthcare sector services… [including] acute care and public health and home and community care and primary care, and mental health and addictions.” [P04].
Duration of care: short-term vs. long-term
The duration of care also varied based on the needs of persons-supported. Organizations serving individuals with IDDs usually offered support across the lifespan: “We support adults with developmental disabilities and we support them from 18 [years] up until the end of their life.” [P06]. Some organizations provided temporary supports aimed at addressing specific health needs: “For therapies – these are all short-term interventions and typically they’re very specific and focused on certain goals. And so, you may get a referral for physiotherapy that is authorized for three visits or five visits” [P04], or crisis situations (e.g., homelessness): “Our services are then brought in to help provide some level of support, guidance, stabilization resource, and once essentially sustainability and positive outcomes are achieved—then our services are immediately withdrawn.” [P12]. One organization employed a model of care with two service streams, an initial rehabilitation stream that was intended to be short-term and an ongoing service stream for individuals requiring continuing support.
In-home vs. community-based care
Many organizations provided in-home care and community-based supports, where residential supports were designed to help individuals lead independent lives, and community-based supports encouraged participation in community activities to further inclusion and address personal and professional goals. One participant spoke about the range of services offered in the home and community:
“There’s probably two big categories of [services we offer]: community support services—so that includes things like adult day programs, assisted living, meals on wheels, transportation, friendly visiting … and things like blood pressure clinics, exercise programs… and then on the other side we do home care services. In the home care basket, we provide personal support, and we also provide social work support.” [P05].
Likewise, another participant spoke in further detail on the types of services that allow individuals to live independently within their homes, or in community-based residential settings (e.g., long-term care facilities):
“We provide accommodation supports to about 100 people living in our community—which means that we will provide support to them in their own homes. So, anywhere from an hour a week to 24 hours a day. And that service can include things from personal care to home management to money management, cooking, cleaning, and being out and about in communities—so community participation. We also provide supports for about 50 people living in long-term care facilities and that is all community participation support. So, minus the last 2 and a half years because of the pandemic, what that means is that a person living in a long-term care facility with a developmental disability can have our support to get out and about for 2 or 3 hours a week, on average.” [P10].
Full-time vs. part-time support
The person-supported’s needs also determined whether they would receive care within their homes and if they would be supported on a full-time (i.e., 24 h a day, 7 days a week) or part-time basis:
“ It really does range from that intensive 24- hour/7 day a week support, which we actually do provide that level of intense support in the family home, if that’s needed. And then, all the way through to just occasional advocacy support and phone check-in.” [P01].
Organizational Culture
Organizational culture was described as a key influence in the development and implementation of person-centred care plans. The culture of the organization includes their perceptions, attitudes and beliefs surrounding persons-supported; their model of care provision; as well as their willingness to evolve and adapt service provision to optimize care delivery.
Perceptions, attitudes, and beliefs regarding persons-supported
Participants described their organization’s view of persons-supported, with many organizations adopting an inclusionary framework where persons-supported were afforded the same rights and dignities as others in the community. This organizational philosophy was described as being deeply intertwined with an organization’s approach to personalizing programs and services:
“…an organization needs to be able to listen to the people who are receiving the service… and support them, to learn more, figure out, articulate, whatever it is, the service or the supports that they need in order to get and move forward with their life.” [P10].
The focus on the person-supported, their needs, likes, and dislikes, was echoed across organizations, with an emphasis on the impact of “culture and trying to embed for each person who delivers service the importance of understanding the individual.” [P05]. Participants also described their organization’s approach to allowing persons-supported to take risks, make mistakes, and live life on their own terms:
“You have to go and venture out and take some [risks]… We try to exercise that philosophy - people with disabilities should have the same rights and responsibilities as other people in the community. Whether that’s birthing or education, getting a job, having a house they can be proud of, accessing community supports, whether that be [a] library or community centre, or service club, whatever that is.” [P03].
Model of care provision
The model of care provision was heavily influenced by the organization’s values and philosophy. Several organizations employed a flexible model of care where supports were developed around the needs, preferences, and desired outcomes of the person-supported:
“…if we don’t offer [the program they want], we certainly build it. Honestly, most of our programs were either created or built by someone coming to us [and] saying ‘I want to do this with my life,’ or …‘my son would like to do art.’” [P02].
Although there were similarities in models across the different organizations, one participant noted that flexibility can be limited in the congregate care setting as staff must tend to the needs of a group as opposed to an individual:
“Our typical plan of operation outside of the congregate setting is we design services around the needs of the person. We don’t ask them to fit into what we need, we build services for what they need. Within the congregate care setting, we have a specific set of rules and regulations for safety and well-being of the other people that are here.” [P11].
Evolving service orientation
In organizations serving individuals with IDDs, many described shifting from program-based services to more individualized and community-based supports: “The goal was always to get people involved in their community and build in some of those natural supports … [we] are looking to support people in their own communities based on their individual plans.” [P07]. One participant described this model as a person-directed approach as opposed to person-centred, citing the limitations of program-based services in meeting individual needs:
“[Persons-supported] couldn’t [do] what they wanted because they were part of a bigger group. We would listen to the bigger group, but if one person didn’t want to go bowling … we couldn’t support them because everybody had to go bowling.” [P06].
The focus on individualized support could potentially lead to increased inclusion for persons-supported in their communities:
“… people go to Tim Horton’s, and if they go every day at 9 they probably, eventually will meet other people that go at 9 o’clock and maybe strike up a conversation and get to know somebody and join a table … and meet people in the community.” [P02].
By creating routines centred on individual preferences, the person-supported becomes a part of a community with shared interests and values.
Person-centred care plans
Community-care organizations enacted a person-centred approach by creating person-centred care plans for each person-supported. Although all participants said their organization provided person-centred services, there was considerable variation in the specific processes for developing, implementing, and updating care plans.
Developing a person-centred care plan
The development of a care plan includes assessment, consultation, and prioritization. The initial development of the care plan usually involved an assessment of an individual’s needs and goals. Participants described agency-specific assessment processes that often incorporated information from service referrals: “ In addition to the material we get from the DSO [Disability Services Ontario] we facilitate the delivery of an intake package specifically for our services. And that intake package helps to further understand the nature and needs of an individual.” [P12]. Agency-specific assessment processes differed by the nature of services provided and the characteristics of the population. However, most organizations included assessments of “not only physical functioning capabilities, but also cognitive.” [P01]. Assessment also included an appraisal of the suitability of the organization’s services. In instances where persons-supported were seeking residential placements or independent-living support, organizations assessed their ability to carry out the activities of daily living:
“[Our internal assessment] is an overview of all areas of their life. From, ‘do they need assistance with baking, cooking, groceries, cleaning, laundry? Is there going to be day program opportunities included in that residential request for placement? What the medical needs are?’” [P02].
In contrast, the person-supported’s community-based activities were primarily informed by their interests and desired outcomes: “We talk about what kinds of goals they want to work on. What kind of outcomes we’re looking for…” [P06].
The development of the care plan also included a consultation phase, involving conversations with the person-supported, their family members, and potentially external care providers: “We would use the application information, we’d use the supports intensity scale, but we’d also spend time with the person and their connections, their family and friends, in their home to figure out what are the kinds of things that this person needs assistance with.” [P10]. Participants described the person-supported’s view as taking precedence in these meetings: “We definitely include the family or [alternate] decision-maker in that plan, but the person-supported ultimately has the final stamp of approval.” [P08]. Many participants also acknowledged the difficulty of identifying and incorporating the person-supported’s view in cases where opinions clash and the person-supported has difficulty communicating and/or is non-verbal: “Some of the people we support are very good at expressing what they want. Some people are not. Some of our staff are really strong in expressing what they support. …And some of the family members are very strong. So you have to be very careful that the [person-supported] is not being lost in the middle of it.” [P06].
Participants also noted that some persons-supported preferred not to have a care plan:
“Some of the people say ‘I hate [the plans] I don’t want to do them’…. we look at it in a different way then. We’ll use graphic art, we’ll use video, we’ll think outside the box to get them to somehow—because at the end of the day when we’re audited by MCCSS every [person-supported] either has to have [a plan]… or there has to be [an approval of] why it wasn’t completed.” [P02].
Plan development may also include a prioritization process, particularly in cases where resources are limited. A person-supported’s goals could be prioritized using different schemas. One participant noted that “the support coordinator takes the cue from the person-supported - … what they’ve identified as ‘have to have’ and ‘nice to have’. … because the ‘have to haves’ are prioritized.” [P09]. Likewise, the person-supported’s preference could also be identified through “[an] exercise, called ‘what’s important for and what’s important to .’” [P06]. This model, based on a Helen Sanderson approach [ 18 ], was described as being helpful in highlighting what is important to the person-supported, as opposed to what others (i.e., friends, family, staff, etc.) feel is important for them.
Several organizations updated care plans throughout the year, to document progress towards goals, adapt to changing needs and plan for future goals: “We revisit the plan periodically through the year. And if they say the goal is done, we may set another goal.” [P06]. Organizations may also change plans to adapt to the person-supported’s changing health status or personal capacity.
Implementing a person-centred care plan
The implementation of care plans differed based on the nature of services provided by the organization. The delivery of health-based or personal support services often involved matching the length and intensity of care with the individual’s needs and capacity:
“Sometimes that is a long time, sometimes it’s a short time, sometimes it’s an intervention that’s needed for a bit, and then the person is able to function.” [P05].
In contrast, the delivery of community-based services involved matching activities and staff by interests: “[if] a person-supported wants to go out and be involved in the music community, then we pull the staff pool in and match them up according to interest.” [P06].
Broad personal goals were broken down into smaller, specific activities. For example, one participant described their organization’s plan in helping a person-supported achieve his professional goal of securing employment:
“[The person-supported] said ‘Okay, I want a job.’ So for three weeks he was matched up with a facilitator. They came up with an action plan in terms of how to get a job, what kind of job he’s looking for, where he wants to go, where he wants to apply, how to conduct an interview. And after three weeks he got a job.” [P09].
Organizations that provided residential services focused on developing independent-living skills. One participant described their organization’s plan to empowering persons-supported by allowing them to make their own financial decisions:
“If one month they’re looking after their own finances, and they’ve overspent. Well, maybe we help them out with a grocery card or something and say ‘okay, next month how are you going to do this?’ [The person-supported may say], ‘well, maybe I’ll put so much money aside each week rather than doing a big grocery shop the first week and not having enough money left at the end of the month.’” [P03].
The participant noted that “a tremendous amount of learning [happens] when a person is allowed to [take] risks and make their own decisions.” [P03].
Likewise, participants representing organizations that provided residential services described tailoring care to the persons-supported’s sleeping schedule and daily routine:
“We develop a plan and tweak it as we go. With [the person-supported] coming to the home, what worked well was, we found that he wanted to sleep in, so we adjusted the [staff] time. We took a look at his [medication] times in the morning… and [changed] his [medication] times. We found that he wanted to sleep [until] later in the day, so he would get up at 10 o’clock, so then instead of having breakfast, lunch, and supper he would just have a bigger brunch. Just really tailoring the plan around the person-supported, and it’s worked out well.” [P08].
These examples highlight how organizational context and culture influence how organizations operationalize person-centred care plans; the same individual may experience different approaches to care and engage in different activities depending on the organization they receive services from.
In this paper, we described key elements of the person-centred planning process across different community-care organizations in Southwestern Ontario. We also identified that the context and culture of an organization play a central role in informing the process by which services are personalized to an individual’s needs. These findings shed light on the diversity of factors that influence the implementation of person-centred care plans and the degree to which organizations are able to address medical and social needs in an integrated fashion. They also inform future evaluations of person and system-related outcomes of person-centred planning.
There are regulations around individualizing services delivered by community-care organizations, whereby care providers must allow persons-supported to participate in the development and evaluation of their care plans. HCCSS or MOH-funded services are largely focused on in-home rehabilitation or medical care. In contrast, MCCSS-funded organizations often focus on developing independent living skills or promoting community participation, thus highlighting the role of the funding agency in determining organizational context as well as the nature of services and personalization of care plans.
We also identified organizational culture as a key influence in the person-centred planning process. In previous reports, organizational culture, and specifically the way in which staff perceive and view persons-supported and their decision-making capabilities can impact the effective delivery of person-centred care [ 19 ]. Staff support, including their commitment to persons-supported and the person-centred process, has been regarded as one of the most powerful predictors of positive outcomes and goal attainment in the developmental services sector [ 20 , 21 ]. Moreover, in order to be successful, commitment to this process should extend across all levels of the organization, be fully integrated into organizational service delivery, and be reflected in organizational philosophy, values and views of persons-supported [ 22 , 23 , 24 ].
MCCSS mandates that agencies serving individuals with IDDs develop an individual service plan (ISP) for each person-supported, one “that address[es] the person’s goals, preferences and needs.” [ 7 ]. We reference ISPs as person-centred care plans, as is in line with the view of participants in interviews. There are a series of checklists designed to measure compliance with these policies, and the process is iterative, with mandated annual reviews of care plans and active participation by the person-supported [ 25 ]. In our study, the agencies funded by MCCSS adhered to the general framework outlined by these regulations and informed service delivery accordingly. However, participants also described areas for improvement with respect to the implementation of these policies in practice. These policies, while well-intentioned, may imply a one-size-fits-all approach and appear more as an administrative exercise as opposed to a meaningful endeavor designed to optimize care. Participants spoke about individuals who preferred not to have an ISP, and how that in and of itself is a person-centred approach, respecting the person’s wishes. Additionally, we heard about how the goal-setting process may not be realistic as it can be perceived as unnatural to have goals at each point in one’s life. Moreover, participants noted challenges in implementing person-centred care in shared residential settings (e.g., group homes) or in cases where persons-supported had difficulty communicating.
Prior research indicates that individuals living in semi-independent settings fare better across several quality-of-life measures relative to individuals living in group homes, including decreased social dissatisfaction, increased community participation, increased participation in activities of daily living, and increased empowerment [ 26 ]. Furthermore, a recent study by İsvan et al. (2023) found that individuals living in the community (e.g., own home, family home, or foster home) exhibit greater autonomy in making everyday and life decisions, and greater satisfaction with their inclusion in the community [ 27 ]. These findings may be indicative of a reduced focus on person-centred care plan development and implementation in congregate care settings, where limited staff capacity can make it difficult to tend to the needs of everyone in the home. However, poor outcomes may also be explained by potentially more complex health challenges or more severe disability in persons-supported living in congregate care settings. The challenges described in our study are consistent with calls to improve the quality of care provided in residential group home settings [ 28 , 29 ].
In line with our findings, previous literature also describes challenges in implementing person-centred planning for individuals who have difficulty communicating or are non-verbal [ 19 , 30 , 31 , 32 ]. Communication has also been identified as a barrier to patient-centred care for adults with IDDs in healthcare settings [ 33 , 34 ]. Other reports have identified a need for increased training and awareness of diverse communication styles (including careful observation of non-verbal cues) to aid staff in including persons-supported in the development of care plans [ 35 , 36 , 37 ]. Importantly, these methods take substantial time which is often limited, and compounded by staffing shortages that are widespread across the sector [ 38 ]. Similar barriers were identified in interviews with staff and persons-supported at a partner community-care agency within our larger project [ 39 ]; other papers from the project examine strategies used by the organization to overcome these barriers.
Limitations
The findings from this study should be interpreted in the context of the following limitations. There is a risk for social desirability bias, whereby participants may feel pressure to present their care plan process in a more positive light due to societal norms and expectations [ 40 ]. Additionally, the experiences and views of community-care organizations may vary by region and organization type (i.e., for-profit vs. not-for-profit). In this study, we limited participation to agencies providing services in Southwestern Ontario and we were only able to interview one for-profit agency, despite concerted recruitment efforts. Consequently, we may not have fully captured how financial pressures, or different contextual and cultural components of an organization impact their implementation of care plans.
The person-centred planning process in community-care organizations is largely informed by the characteristics of the population served and the nature of services offered (i.e., organizational context). This process usually involves initial and continued consultations with persons-supported to tailor plans to their specific needs and desired outcomes. There are ongoing challenges in the implementation of person-centred planning, including a need for increased adaptability and clarity in current regulations. In some areas, there may be benefit to incorporating nuance in the application of policies (e.g., in cases where a person-supported does not want to have a formal plan in place). In other areas, it may be helpful to have increased guidance on how to optimize care delivery to improve outcomes (e.g., in cases where a person-supported has difficulty communicating, or is residing in a group home). Policymakers, administrators, and service providers can leverage these insights to refine policies, advocating for inclusive, flexible approaches that better align with diverse community needs.
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed in the current study are not publicly available to maintain participant confidentiality, however access may be granted by the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Acquired Brain Injury
Disability Services Ontario
Home and Community Care Support Services
Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities
Individual Service Plan
Ministry of Children, Community and Social Services
Ministry of Health
Purbhoo D, Wojtak A. Patient and family-centred home and community care: realizing the opportunity. Nurs Leadersh Tor Ont. 2018;31(2):40–51.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lin E, Balogh RS, Durbin A, Holder L, Gupta N, Volpe T et al. Addressing gaps in the health care services used by adults with developmental disabilities in Ontario. ICES. 2019 [cited 2023 Aug 30]. https://www.ices.on.ca/publications/research-reports/addressing-gaps-in-the-health-care-services-used-by-adults-with-developmental-disabilities-in-ontario/
American Psychological Association. APA Guidelines for Assessment and Intervention with Persons with Disabilities: (502822022-001). 2022 [cited 2023 Aug 30]; http://doi.apa.org/get-pe-doi.cfm?doi=10.1037/e502822022-001
Dunn DS, Andrews EE. Person-first and identity-first language: developing psychologists’ cultural competence using disability language. Am Psychol. 2015;70(3):255–64.
Burke C. Building a stronger system for people with developmental disabilities: a six-month progress report from Commissioner Courtney Burke. New York Office for People with Developmental Disabilities; 2011. https://opwdd.ny.gov/system/files/documents/2019/12/6_month_progress_report_0.pdf
Government of Manitoba. Agency service coordination manual: 5.1 person-centred planning. 2021. https://www.gov.mb.ca/fs/clds/asc-manual/pubs/5.1-person-centred-planning.pdf
Government of Ontario. Services and supports to promote the social inclusion of Persons with Developmental Disabilities Act, 2008. 2008 [cited 2023 Aug 30]. https://www.ontario.ca/laws/regulation/100299#:~:text=O.-,Reg.,and other relevant clinical assessments
State of Michigan. Person Centered Planning.pdf. 2018.
O’Brien CL, O’Brien J. The origins of person-centered planning: a community of practice perspective.
Sanderson H. Person Centred Planning. York, Joseph Rowntree Foundation; 2000.
Government of Ontario. Ontario.ca. 2019 [cited 2023 Sep 4]. Connecting Care Act, 2019: Home and Community Care Services. https://www.ontario.ca/laws/regulation/220187#BK17
Dong M. Examining individualized participatory approaches to care for individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities. University of Western Ontario; 2023. https://ir.lib.uwo.ca/etd/9517
Doyle L, McCabe C, Keogh B, Brady A, McCann M. An overview of the qualitative descriptive design within nursing research. J Res Nurs. 2020;25(5):443–55.
Creswell JW. Research design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. SAGE; 2014. p. 305.
Berg BL. Qualitative research methods for the social sciences: 2nd ed. Bostan, MA: Allyn and Bacon; 1995. p. 421.
Google Scholar
Guest G, MacQueen KM, Namey EE. Applied Thematic Analysis. SAGE; 2012. p. 321.
Yin RK. Case study research design and methods. 5th ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE; 2014. p. 282.
Helen Sanderson Associates. Helen Sanderson Associates. [cited 2023 Oct 31]. Sorting important to/for. http://helensandersonassociates.co.uk/person-centred-practice/person-centred-thinking-tools/sorting-important-tofor/
Hughes CA. The benefits and barriers to person centered planning for adults with developmental disabilities. [Saint Paul, Minnesota, USA]: St. Catherine University; 2013. https://sophia.stkate.edu/msw_papers/191
Heller T, Miller AB, Hsieh K, Sterns H. Later-life planning: promoting knowledge of options and choice-making. Ment Retard. 2000;38(5):395–406.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Ratti V, Hassiotis A, Crabtree J, Deb S, Gallagher P, Unwin G. The effectiveness of person-centred planning for people with intellectual disabilities: a systematic review. Res Dev Disabil. 2016;57:63–84.
Kaehne A, Beyer S. Person-centred reviews as a mechanism for planning the post-school transition of young people with intellectual disability. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2014;58(7):603–13.
Parley FF. Person-centred outcomes: are outcomes improved where a person-centred care model is used? J Learn Disabil. 2001;5(4):299–308.
Article Google Scholar
Sanderson H, Thompson J, Kilbane J. The emergence of person-centred planning as evidence‐based practice. J Integr Care. 2006;14(2):18–25.
Government of Ontario. Ministry of Children, Community and Social Services. Developmental service (DS) compliance inspection: indicator list. 2021 [cited 2023 Sep 4]. https://www.mcss.gov.on.ca/documents/en/mcss/developmental/EN_DS_Indicator_List.pdf
Stancliffe RJ, Keane S. Outcomes and costs of community living: a matched comparison of group homes and semi-independent living. J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2000;25(4):281–305.
İsvan N, Bonardi A, Hiersteiner D. Effects of person-centred planning and practices on the health and well-being of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: a multilevel analysis of linked administrative and survey data. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2023 [cited 2023 Sep 4]; https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/ https://doi.org/10.1111/jir.13015
Office of the Auditor General of Ontario. 3.10: residential services for people with developmental disabilities. 2014. https://www.auditor.on.ca/en/content/annualreports/arreports/en14/310en14.pdf
Office of the Auditor General of Ontario. 1.10 residential services for people with developmental disabilities. 2016. https://www.auditor.on.ca/en/content/annualreports/arreports/en16/v2_110en16.pdf
Robertson J, Emerson E, Hatton C, Elliott J, McIntosh B, Swift P, et al. Person-centred planning: factors associated with successful outcomes for people with intellectual disabilities. J Intellect Disabil Res JIDR. 2007;51(Pt 3):232–43.
Everson JM, Zhang D, Person-Centered Planning. Characteristics, inhibitors, and supports. Educ Train Ment Retard Dev Disabil. 2000;35(1):36–43.
Claes C, Van Hove G, Vandevelde S, van Loon J, Schalock RL. Person-centered planning: analysis of research and effectiveness. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2010;48(6):432–53.
Stringer K, Terry AL, Ryan BL, Pike A. Patient-centred primary care of adults with severe and profound intellectual and developmental disabilities. Can Fam Physician. 2018;64(Suppl 2):S63–9.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Badcock E, Sakellariou D. Treating him… like a piece of meat: poor communication as a barrier to care for people with learning disabilities. Disabil Stud Q. 2022 [cited 2023 Sep 4];42(1). https://dsq-sds.org/index.php/dsq/article/view/7408
Mansell J, Beadle-Brown J. Person-centred planning or person-centred action? Policy and Practice in Intellectual Disability Services. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2004;17(1):1–9.
Bigby C, Frawley P. Social work practice and intellectual disability: working to support change. Bloomsbury Publishing; 2018. p. 253.
Taylor JE, Taylor JA. Person-centered planning: evidence-based practice, challenges, and potential for the 21st century. J Soc Work Disabil Rehabil. 2013;12(3):213–35.
Zijlstra R, Vlaskamp C, Buntinx W. Direct-care staff turnover: an indicator of the quality of life of individuals with profound multiple disabilities. Eur J Mental Disabil. 2001;(22):39–55.
Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), CIHR-Institute of Health Services and Policy Research (CIHR-IHSPR) and partners. Evidence brief booklet: quadruple aim & equity catalyst grants. 2024 [cited 2024 Apr 2]. https://face2face.events/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Evidence-Brief-Booklet-Quadruple-Aim-and-Equity-EN.pdf
Bergen N, Labonté R. Everything is perfect, and we have no problems: detecting and limiting social desirability bias in qualitative research. Qual Health Res. 2020;30(5):783–92.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ruth Armstrong, from PHSS - Medical & Complex Care in Community, for her valuable feedback and support throughout the research process.
This research was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The funding agency had no role in the conceptualization, design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Family Medicine, Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, Western University, 1151 Richmond St, London, ON, N6A 5C1, Canada
Samina Idrees, Gillian Young, Leslie Meredith & Maria Mathews
PHSS - Medical & Complex Care in Community, 620 Colborne St, London, ON, N6B 3R9, Canada
Brian Dunne & Donnie Antony
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
S.I. conducted the interviews, developed the coding template, coded the data, thematically analyzed the data, and prepared the manuscript. G.Y. helped develop the coding template, and reviewed and approved the final manuscript. B.D. and D.A. helped conceptualize the study, aided in the interpretation and analysis of study findings, and reviewed and approved the final manuscript. L.M. coordinated research activities, aided in the interpretation and analysis of study findings, and reviewed and approved the final manuscript. M.M. conceptualized the study, supervised its implementation, and was a major contributor in reviewing and editing the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Maria Mathews .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study was approved by the research ethics board at Western University. We obtained informed consent from participants prior to the onset of interviews.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Idrees, S., Young, G., Dunne, B. et al. The implementation of person-centred plans in the community-care sector: a qualitative study of organizations in Ontario, Canada. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 680 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11089-7
Download citation
Received : 14 February 2024
Accepted : 08 May 2024
Published : 29 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11089-7

Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Person-centred planning
- Community-based care
- Integrated care
- Social services
- Health services
- Organizational culture
- Qualitative study
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Life story work in health and social care: systematic literature review
Affiliation.
- 1 Older Adult Care Group, Sheffield Care Trust, Sheffield, UK. [email protected]
- PMID: 16866815
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2006.03897.x
Aim: The aim of this paper is to review the literature on life story work in health and social care practice.
Background: Life story work as an intervention has been used with a number of health and social care clients, such as children people with learning disabilities, older people on medical wards and with older people who have dementia. It may help challenge ageist attitudes and assumptions, be used as a basis for individualized care, improve assessment, assist in transitions between different care environments, and help to develop improved relationships between care staff and family carers. However, to date there has been no attempt to collate the findings from published accounts.
Methods: A systematic search of the literature on life story work was conducted in February 2004, using nursing, medical and social science databases and a combination of thesaurus and free text search terms. This revealed over 1000 publications; the use of carefully constructed inclusion and exclusion criteria identified 51 relevant items. Fourteen were subsequently selected and reviewed using a set of reflective critical appraisal questions.
Findings: A range of methodological approaches has been adopted to explore the use of life story work with no one specific methodology prevailing. The work has been most frequently used with older people and people with a learning disability and life story books are the most common approach. Staff perceptions of life story work have been explored, but patient and carer views are less frequently reported. The findings of the studies are discussed in broad themes, offering some tentative recommendations for using life story work in practice.
Conclusion: Evidence on the use of life story work is immature, leading to the recommendation for more research. Although appraising literature from a range of approaches is complex, there are some potentially far-reaching benefits of life story work in health and social care practice.
Publication types
- Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
- Systematic Review
- Attitude of Health Personnel
- Attitude to Health
- Autobiographies as Topic
- Family / psychology
- Health Personnel / psychology
- Patients / psychology
- Professional-Patient Relations
- Psychotherapy / ethics
- Psychotherapy / methods*
- Qualitative Research
- Research Design
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Behav Neurosci
- PMC10317209
Understanding health behavior change by motivation and reward mechanisms: a review of the literature
The global rise of lifestyle-related chronic diseases has engendered growing interest among various stakeholders including policymakers, scientists, healthcare professionals, and patients, regarding the effective management of health behavior change and the development of interventions that facilitate lifestyle modification. Consequently, a plethora of health behavior change theories has been developed with the intention of elucidating the mechanisms underlying health behavior change and identifying key domains that enhance the likelihood of successful outcomes. Until now, only few studies have taken into account neurobiological correlates underlying health behavior change processes. Recent progress in the neuroscience of motivation and reward systems has provided further insights into the relevance of such domains. The aim of this contribution is to review the latest explanations of health behavior change initiation and maintenance based on novel insights into motivation and reward mechanisms. Based on a systematic literature search in PubMed, PsycInfo, and Google Scholar, four articles were reviewed. As a result, a description of motivation and reward systems (approach/wanting = pleasure; aversion/avoiding = relief; assertion/non-wanting = quiescence) and their role in health behavior change processes is presented. Three central findings are discussed: (1) motivation and reward processes allow to distinguish between goal-oriented and stimulus-driven behavior, (2) approach motivation is the key driver of the individual process of behavior change until a new behavior is maintained and assertion motivation takes over, (3) behavior change techniques can be clustered based on motivation and reward processes according to their functional mechanisms into facilitating (= providing external resources), boosting (= strengthening internal reflective resources) and nudging (= activating internal affective resources). The strengths and limitations of these advances for intervention planning are highlighted and an agenda for testing the models as well as future research is proposed.
1. Introduction
The prevalence of lifestyle-related chronic diseases has increased dramatically in the last decades. Chronic diseases were responsible for 71% of all deaths occurring worldwide in 2019 ( World Health Organisation [WHO], 2022a ), of which about one third are premature deaths, i.e., happening to people aged between 30 and 69 years ( World Health Organisation [WHO], 2022a ). Diseases of the circulatory system like stroke and ischaemic heart disease accounted for 30% of all deaths in 2019 in OECD countries, followed by cancer (24%), diseases of the respiratory system (10%) and diabetes (3%) ( Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development [OECD], 2021 ). Individuals living with these conditions also face a major stress burden due to disability, in some cases already at young ages. Indeed, averaged across 26 OECD countries, more than one third of individuals aged 16 and over have been found to be living with longstanding illness or health problems ( Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development [OECD], 2021 ). In addition, comorbidities (multimorbidity) as well as individual physical and emotional suffering frequently occur ( Stewart et al., 1989 ; Moussavi et al., 2007 ; de Ridder et al., 2008 ), reducing overall quality of life ( Maresova et al., 2019 ).
These numbers and trends can in part be traced back to rising rates of obesity, sedentary behavior and poor nutrition, as well as other metabolic risk factors for chronic diseases including tobacco use and harmful alcohol intake. In addition, as diseases and comorbidities accumulate in older age, countries’ aging populations further influence these numbers ( Zhou et al., 2016 ). Indeed, most countries in the world have experienced, and will experience great demographic transitions. It has been estimated that between 2015 and 2050, the number of individuals aged 60 years and older will nearly double from 12 to 22%, with two billion people aged above 60 years by 2050 ( World Health Organisation [WHO], 2022b ). At the same time, life expectancy has risen from 67.5 years in 2000 to 72.9 years in 2020 at the world’s average ( The World Bank, 2022 ). Based on these projections, it can be assumed that the total number of individuals with longstanding illnesses or health problems will continue to rise.
The treatment of chronic diseases is often lengthy and intense, and is frequently accompanied by a reduced ability to work ( Seuring et al., 2015 ). While this can reduce the quality of life in patients further ( Jing et al., 2018 ), it can also affect an individual’s household financial resources ( Seuring et al., 2015 ). In low income settings, tremendous costs for treatment can quickly drain savings ( World Health Organisation [WHO], 2022a ). This, in return, may perpetuate people’s conditions, as it has been found that poverty is closely linked with the prevalence of chronic diseases: vulnerable and socially disadvantaged people tend to get ill quicker and have lower life expectancy than people of higher social positions ( World Health Organisation [WHO], 2022a ). The main reasons for this phenomenon are that economically vulnerable individuals are at greater risk of being exposed to harmful products, such as tobacco, tend to have unhealthy diets, and, in some countries, cities or neighborhoods, have limited access to health services. In fact, the average life expectancy at birth of people with low income is 4.4 (women) to 8.6 (men) years lower than of people in the highest of five income groups ( Lampert et al., 2019 ).
These costs on individuals are accompanied by costs for the healthcare system and society as a whole. Health expenditure related to diabetes, for example, is at least 966 billion USD per year worldwide, which represents a 316% increase over the last 15 years ( International Diabetes Federation [IDF], 2021 ). In Germany, the cost burden for diabetes type 2 treatment has been calculated to be on average 1.8 times higher than for other diseases ( Ulrich et al., 2016 ). Multimorbidity typically incurs greater health care costs ( Rizzo et al., 2015 ), measured by the use of medication as well as emergency department presentations and hospital admissions ( Chan et al., 2002 ). For example, Schneider et al. (2009) found that older adults in the United States with three or more chronic conditions utilized on average 25 times more hospital bed-days and had on average 14.6 times more hospital admissions than older adults without any chronic condition. Furthermore, with one additional chronic condition in older adults, the health care utilization costs increase near exponentially ( Lehnert et al., 2011 ). In addition to these financial impacts, chronic conditions tend to dwell on non-tangible resources, e.g., through time and energy spent on disease management by the patient and family members ( Ellrodt et al., 1997 ; Korff et al., 1998 ; Wagner, 2000 ). These circumstances call for shifting the focus to health care measures that help to prevent and improve chronic conditions according to patient needs in a cost-effective way.
There is compelling evidence to suggest that lifestyle changes can significantly improve the conditions of chronic diseases. Studies have demonstrated the positive impact of increased exercise, healthier nutrition, reduced alcohol intake, smoking cessation, and relaxation techniques on a range of chronic conditions ( Ornish et al., 1990 ; Knowler et al., 2002 ; Savoye et al., 2007 ; Alert et al., 2013 ; Cramer et al., 2014 ; Morris et al., 2019 ). These health behaviors can decrease the major metabolic risk factors for chronic diseases and premature deaths, including blood pressure, blood glucose, blood lipids, and obesity ( World Health Organisation [WHO], 2022a ). Remarkably, the risk of developing type 2 diabetes is predominantly attributable to lifestyle-related factors rather than genetic risks ( Langenberg et al., 2014 ). Moreover, lifestyle changes could prevent up to 70% of strokes and cases of colon cancer, 80% of coronary heart diseases, and 90% of diabetes cases ( Willett, 2002 ). Such findings highlight the tremendous potential of lifestyle modification interventions for public health outcomes.
It is widely recognized that individuals encounter challenges when endeavoring to attain their lifestyle goals. This is not unexpected, given that lifestyle change necessitates a series of individual choices that often require postponement of immediate pleasure in favor of prospective long-term health gains (a.k.a. delayed gratification, present bias, hyperbolic discounting, etc., see Stroebe et al., 2008 , 2013 ; Hall and Fong, 2015 ). Despite these obvious difficulties, practitioners, politicians and stakeholders aim to engage patients in health behavior change ( Esch, 2018 ). How consistently individuals pursue health behavior changes depends largely on how well they can overcome their innate present bias and on their endowment with other resources, such as their knowledge about health behavior change consequences, their beliefs in their ability to succeed, their self-regulation skills, self-efficacy, internal locus of control, engagement and empowerment ( Cane et al., 2012 ; Cheng et al., 2016 ; Sheeran et al., 2016 ; Ludwig et al., 2020 ; Cardoso Barbosa et al., 2021 ). Hence, a thorough understanding of health behavior change and interventions to support health behavior change taking into account individuals’ resources are necessary.
Numerous health behavior change theories have been devised, with a primary emphasis on reflective resources and willpower ( Kwasnicka et al., 2016 ). However, there is a scarcity of research on domains that are supported by, or rooted in, neuroscientific evidence. Notably, recent advances in the neuroscience of motivation and reward systems have revealed new insights into the importance of such domains ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2021 , 2022 ).
The aim of this contribution is to provide an overview of the latest explanations of health behavior change initiation and maintenance based on novel insights to motivation and reward mechanisms. Based on a literature search in PubMed (22 hits), PsycInfo (39 hits), and Google Scholar using the term “motivation AND reward AND (‘behavior change’ OR ‘behavior modification’)” in titles and abstracts in January 2023, we identified four articles which discuss neurobiological mechanisms of reward and motivation in relation to health behavior change ( Letzen et al., 2019 ; Ludwig et al., 2020 ; Michaelsen and Esch, 2021 , 2022 ). These are integrated into the social psychological literature on behavior change, previously reviewed in Michaelsen and Esch (2021 , 2022) . The review is structured as follows: the next chapter presents a summary of behavior change theories as discussed in social and health psychology in order to provide thorough ground for the discussion of the role of motivation and reward processes in health behavior change. This is followed by a description of motivation and reward processes as recently discussed in neurobiological science. After this, three models are presented which take into account motivation and reward mechanisms in health behavior change and thereby combine the two strands of literature and present interesting avenues for future health behavior change intervention planning and implementation. A discussion of the review and future research is presented at the end of the article.
2. Behavior change theories in social and health psychology
A large number of theories aiming to explain health behavior change have been published in recent decades, most of them grounded in social and health psychology. These theories differ in the views of human nature they hold ( Bandura, 1989 ) as well as in what they consider to be the fundamental drivers of behavior and the resources necessary for behavior change.
Established theories are concerned with the determinants of and motives for initiation of behavior change, and some also take into account the domains that enhance the likelihood of maintaining a new behavior after initiation ( Kwasnicka et al., 2016 ). Among the leading theories are Bandura’s Social Cognitive Theory ( Bandura, 1989 ), Gollwitzer’s theory on Implementation Intentions ( Gollwitzer, 1999 ), and the Social Determination Theory by Ryan and Deci (2000) and Deci and Ryan (2008) . In Bandura’s Social Cognitive Theory, individuals are assumed to learn new behaviors not only through trial-and-error but also through copying the behavior of others. Based on the existence of role models, the performance of the new behavior is enhanced by outcome expectancies (individuals understand the potential outcomes of their behavior), self-efficacy (individuals believe that they can achieve their desired behavioral goal), and identification (individuals identify with certain aspects of the role model) ( Bandura, 1989 ). In Gollwitzer’s (1999) theory on Implementation Intentions, individuals are suggested to make plans for anticipated situations, in which their desired behavior is at risk. These plans (implementation intentions) are assumed to delegate the control of goal-directed responses over these critical situations when encountered. Another prominent behavior change theory has been published by Ryan and Deci (2000) and Deci and Ryan (2008) . According to their Self-Determination Theory, for behavior change to be successful, three basic psychological needs require fulfillment: autonomy (being the causal agent of one’s own life), competence (ability to master skills important to oneself) and relatedness (feeling connected to others). A number of other theories have each determined a small, inconsistent number of domains supposedly relevant for behavior change initiation.
In a systematic review on 100 behavior change maintenance theories, Kwasnicka et al. (2016) highlight a deficiency in theoretical elaboration regarding the process of maintenance after initial change present in the literature. Theories that are concerned with the behavior change maintenance describe several stages of a behavior change process and the resources necessary to progress from one stage to another. A widely used theory is the Transtheoretical Model ( Prochaska et al., 2008 ), according to which an individual’s change process starts at a precontemplation stage, and continues with the contemplation, planning, implementation, maintenance and termination stages. Similar processes have been suggested by other authors ( Weinstein and Sandman, 1992 , 2002 ; Gollwitzer, 1999 ; Rothman et al., 2004 ; Schwarzer et al., 2011 ). For example, Weinstein and Sandman (2002) emphasize the stage before precontemplation where individuals may be unaware of the issue (e.g., that change in diet could improve their health conditions) and Rothman et al.’s (2004) model adds a habit stage where individuals have automated the new behavior. Michaelsen and Esch (2021) have provided the first comprehensive synthesis of behavior change models, a flexible seven-stage behavior change process, which allows to systematically relate motivation and reward mechanisms to these stages. In their process, individuals may experience the stages unawareness, awareness, contemplation, planning, initiation, continued action, and maintenance. These stages are categorized into three phases of engagement, namely, non-engagement, motivational engagement, and executive engagement, in which individuals’ actions are driven by different types of motivation and reward processes ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2021 , 2022 ), as explained in more detail below.
3. Motivation and reward systems involved in behavior change processes
Michaelsen and Esch (2021) have described three types of motivational states (approach motivation, avoidance motivation, and assertion motivation) and their corresponding rewards (pleasure, relief, and quiescence) that seem to play key roles in health behavior change processes (see Figure 1 ).

Three types of motivation and reward. Esch (2022) ; copyright: ©2022 by the author (TE). Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland.
3.1. Approach motivation
Approach motivation, also known as appetitive or incentive salience, is focused on stimuli or goals that are associated with positive and pleasurable experiences ( Bozarth, 1994 ; Esch and Stefano, 2004 ; Elliot et al., 2013 ). This type of motivation is linked to the wanting-system, reward expectation, performance, and action ( Esch, 2022 ). The attainment of a desired stimulus or goal typically produces a sense of pleasure or reward, which may or may not be noticeable depending on the intensity of the experience. The reward is not derived from the stimulus or goal itself, but from the psychological and neurobiological processes that occur when there is a positive anticipation and response to a stimulus or goal ( Berridge and Kringelbach, 2008 ; Schultz, 2015 ). While it is challenging to categorize experiences into specific types of motivational processes, it is generally agreed that individuals tend to assess stimuli as positive or negative ( Elliot et al., 2013 ). These assessments are frequently referred to as fundamental affective experiences and include emotions such as joy, pleasure, and excitement ( Schneirla, 1959 ; Cacioppo et al., 1999 ; Elliot et al., 2013 ; Lang and Bradley, 2013 ; Rolls, 2013 ). Therefore, the essence of approach motivation lies in the anticipation of obtaining a reward that is characterized by positive emotions.
The underlying physiological mechanisms of motivation occur in specific brain areas distinct from other sensory and cognitive areas ( Kringelbach, 2005 ; Esch, 2022 ). The approach motivation and reward system is commonly described as being embedded in the central nervous system (CNS), involves nerve cells that originate in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and send projections to the frontal brain, specifically the nucleus accumbens (NAC), via the neurotransmitter dopamine ( Nestler, 2001 ; Nestler et al., 2001 ; Esch and Stefano, 2004 , 2010 ). The nucleus accumbens (NAC) plays a crucial role in the neural regulation of reward-seeking behavior by signaling the degree of effort necessary to acquire a reward and the desire to obtain it, thereby determining the appetitive motivational salience. Additionally, the ventral tegmental area-nucleus accumbens (VTA-NAC) pathway is responsible for measuring and regulating the rewarding aspects of an activity, transmitting pertinent information to other brain regions ( Esch and Stefano, 2004 ; Berridge, 2007 ; Smith et al., 2011 ; Esch, 2022 ). The magnitude of expected reward has been found to significantly influence the likelihood of an individual to retain and repeat a behavior ( Esch and Stefano, 2010 ). Furthermore, the hippocampus and amygdala have been identified as crucial components of the reward system, with the hippocampus serving as a gatekeeper for experiences to be recognized and stored in memory, while the amygdala assesses these experiences as either pleasurable or detrimental ( Esch and Stefano, 2004 ; Nestler and Malenka, 2004 ). The mesocortical dopamine pathway in the frontal cortex is also known to be involved in the evaluation of the “costs” and risks associated with the pursuit of rewards, ultimately shaping an individual’s behavioral response ( Esch and Stefano, 2010 ).
3.2. Avoidance motivation
The construct of avoidance motivation, also referred to as negatively-valenced fearful salience, pertains to the motivational system that drives the avoidance of punishment or potential harm, rather than the pursuit of reward. This type of motivation is intricately linked to the fight-flight-freeze response, which encompasses physiological and behavioral changes in response to perceived threat ( Bozarth, 1994 ; Esch and Stefano, 2004 ; Seymour et al., 2007 ; Esch, 2022 ). The phenomenon commonly known as avoidance behavior is typically evoked by an aversive or challenging stimulus, and elicits a motivated reaction of withdrawal, commonly manifested as the act of moving away from unpleasant conditions. It is noteworthy that avoidance behavior can be differentiated from punishment, which exerts a suppressing effect on the strength of the behavioral response (passive avoidance), and from negative reinforcement, which engenders an augmenting effect on the strength of the behavioral response (active avoidance) ( Schultz, 2015 ). In contrast to active reactions such as fighting or fleeing in response to a fear-inducing stimulus, there can also be the passive reactions of freezing ( Berridge, 2018 ). Emotions associated with avoidance motivation include anxiety, fear, and disgust ( Lang, 1995 ; Cacioppo et al., 1999 ; Watson et al., 1999 ; Elliot et al., 2013 ; Hirschberg and Manning, 2015 ; Esch, 2022 ).
Avoidance motivation is embedded in the stress system and involves increased sympathetic activity and the release of cortisol, adrenaline, opioids, and vasopressin ( Esch, 2022 ). This type of motivation is rooted in the lower limbic system, specifically the amygdala and hypothalamus. Upon the anticipation of an actual or imagined threat, two distinct pathways are instigated: one through the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, leading to the release of cortisol, and the other through the sympathetic nervous system, leading to the release of adrenaline ( Esch, 2022 ). The freeze reaction is also connected to the amygdala ( LeDoux, 1998 ). Successful avoidance can lead to relief, a positive, low-arousal emotion that can be experienced as relaxation or reward ( Levenson, 2011 ; Krisam et al., 2017 ; Esch, 2022 ). An incontrovertible interdependence between the approach and avoidance motivation systems exists, as akin brain regions are triggered during both relief and other positive affects ( Kim et al., 2007 ; Sangha, 2015 ).
3.3. Assertion motivation
The majority of research on motivation and reward does not differentiate between behavior driven by approach motivation and behavior driven by assertion motivation. In point of fact, these two categories of motivation are frequently confounded or amalgamated ( McCall and Singer, 2012 ), despite the divergent neurobiological mechanisms underlying them, their distinct loci in the brain, and their discrepant behavioral outcomes. Assertion motivation, or assertive salience, is linked to the “non-wanting” system and associated with inaction, acceptance, or contentment, homeostasis, and quiescence. It describes the motivation to maintain a certain condition or state ( McCall and Singer, 2012 ; Esch, 2022 ). Assertion motivation is different from approach motivation in terms of the emotions it evokes and the types of behavior it leads to McCall and Singer (2012) and Esch (2022) . Assertion motivation is associated with a lack of desire to change or move away from the current state, while approach motivation is associated with a desire to move toward something. Assertion motivation can be seen in instances where a person is content with their current situation, such as a newly habituated health behavior, and there is no inclination to change or move away from it.
Assertion motivation is linked to increased activity in the parasympathetic autonomous nervous system and is associated with neurotransmitters such as endogenous opiates, oxytocin, acetylcholine, serotonin, and endocannabinoids ( Esch, 2022 ). Brain areas involved in the activation of assertive motivation include the midbrain, vagus areas, cingulum, hippocampus, ventral striatum, hypothalamus, and pituitary gland ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2021 ). It is different from approach and avoidance motivation in terms of related affective qualities and behavioral outcomes and is not characterized by activation of dopaminergic activity.
4. Weaving together motivation and reward mechanisms with health behavior change theories
Weaving together psychological explanations of behavior change with neurobiological understandings of motivation and reward processes has produced three models explaining different aspects of behavior change. First, a model differentiating goal-directed and stimulus-driven behavior ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2021 ) will be explained. This is followed by the description of the Model of Engagement, that illustrates the role of the three types of motivation during a behavior change process ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2021 ). Finally, the behavior change resource model ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2022 ) that integrates the differentiation between goal-directed and stimulus-driven behavior with the Model of Engagement to explain the functional mechanisms of behavior change techniques is presented. The elaborations of Ludwig et al. (2020) concerning reward valuation and Letzen et al. (2019) on mesocorticolimbic function in behavior change are discussed within these sections.
4.1. Goal-directed and stimulus-driven behavior
Kwasnicka et al.’s (2016) systematic review revealed that existing health behavior change theories largely focus on cognitive resources deemed necessary for achieving behavior change. Their findings indicated that only 10% of the theories reviewed took into account the relevance of automatic responses to relevant cues or stimuli, which has been identified as a limitation to existing theories ( Van Cappellen et al., 2018 ). This is because the manifestation of health behaviors in daily life is often influenced by implicit emotions and non-cognitive motives, rather than reflective cognitive willpower, as various dual-process models have emphasized (e.g., Kahneman and Tversky, 1982 ; Strack and Deutsch, 2004 ; Hall and Fong, 2007 ; Marteau et al., 2012 ; Sheeran et al., 2013 ). Dual-process models of decision-making have been developed to differentiate between two regulatory systems in the brain: reflective (cognitive, conscious) and affective (impulsive, intuitive, automatic) antecedents of behavior ( Chaiken, 1980 ; Petty and Cacioppo, 2012 ). The reflective system is based on conscious deliberation and control, which requires subjective effort. It draws upon an individual’s knowledge of probabilities and values and is based on rules of language and logic. The key processes of the reflective system are volition and reasoning, which can be intentionally accessed. However, the reflective process is relatively slow ( Strack and Deutsch, 2004 ; Sheeran et al., 2013 ). The reflective system typically supersedes the automatic system, which is quicker and more effortless, and operates by utilizing stored associations acquired through experiences, responding to habits and impulses. Strack and Deutsch (2004) posit that the automatic system is a significant impulsive process that engenders activation, in which perceptual inputs stimulate elements in the associative memory, subsequently activating other related elements. This form of information processing is characterized by its rapidity and operation beyond conscious awareness, as noted in the extant literature ( Strack and Deutsch, 2004 ; Evans, 2010 ; Sheeran et al., 2013 ). While this view has garnered both commendation and condemnation from scholars ( Evans, 2018 ), it nevertheless represents a significant contribution to the comprehension of health behavior and behavior change. Furthermore, a widespread view stemming from dual-process models is that the more rapid component governs behavior.
In reference to dual-process models and the differentiation between controlled goals and autonomous goals (or unnoticed stimuli), Michaelsen and Esch (2021) present a neurobiologically informed model of stimulus-driven and goal-directed behavior. In stimulus-driven behavior, a stimulus activates automatic processes and leads to behavior without the individual having noticed the stimulus. Once a stimulus has undergone cognitive processing and been transformed into a goal, the ensuing behavior is referred to as goal-directed behavior. The authors posit that both varieties of stimuli are capable of inciting appetitive, aversive, or assertive salience by means of reward anticipation. In this way, motivational salience, or the ability to attract and hold attention, can lead to action and engagement without conscious thought or planning ( Ryan and Deci, 2000 ; Carver, 2009 ; Kruglanski et al., 2014 ; Berridge, 2018 ). Both unnoticed stimuli and those that are deliberately processed can result in the same actions and engagement. However, in goal-directed behavior, the individual is aware of their actions and is actively involved in the process, as noted by Michaelsen and Esch (2021) . Figure 2 illustrates the difference between stimulus-driven and goal-directed behavior in a simplified way.

Goal-directed and stimulus-driven behavior ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2021 ).
The model can be expanded by the theory proposed by Ludwig et al. (2020) , who propose an approach to achieve sustainable behavior change through a combination of theories and research on autonomous motivation, reinforcement learning and mindfulness. The authors argue that behavior change can occur through increased awareness of the reward value of specific actions, which drives future behavior, in addition to the commonly proposed “mental gap” mechanism. The stability of a behavior depends on changes in its reward value over time and the accessibility of more rewarding behaviors. The reward value of a behavior may depend on both external and internal factors, such as subjective experience and goal achievement. The authors suggest that bringing present-moment or mindful awareness to current behavior can update the reward value of habitual behaviors and lead to new learning. This approach involves direct, in-the-moment, curious awareness and is not reliant on reflective thought processes. An increased awareness about stimuli that engender change through increased reward value would shift individuals, in the above model, from stimulus-driven to goal-directed behavior.
4.2. Motivational engagement in behavior change processes
Based on the synthesis of multi-stage behavior change theories, Michaelsen and Esch (2021) have derived three different phases of engagement, based on the role of motivational processes involved during the stages of behavior change. During the first phase, called non-engagement phase, individuals are either unaware that behavior change may improve their health conditions, or they are aware but have no intention to change an aspect of their health behavior. During this phase, any motivational mechanisms are yet absent. Stimuli like new information about the health benefits of a certain behavior change may activate motivational processes so that individuals progress into the motivational engagement phase, which is comprised of the contemplation and planning stages.
The nature of the contemplative phase is contingent on the sort of motivational salience that is evoked by the stimulus. Should an individual be satisfied with their present state, assertive salience becomes operational. Here, the likelihood of perpetuating the present condition is linked to positive valence that instigates sensations of quiescence, stillness, and/or relaxation stemming from the discharge, such as that of endogenous opiates, oxytocin and related neurotransmitters, as well as parasympathetic activity. Such a state leads to a lack of behavioral activity, resulting in the cessation of the process of behavior change. In the event that an individual desires a change, either appetitive or aversive salience is elicited. When appetitive salience is activated, information undergoes processing by the mesocortical dopamine pathway in the frontal cortex, and a preference for a new behavior is set ( Esch and Stefano, 2010 ; Michaelsen and Esch, 2021 ). On the other hand, should aversive salience be activated, information is routed through the stress response pathways, namely, the hypothalamic-pituitary (-adrenal) axis and the (amygdalar-) sympathetic nervous system axis ( Esch and Stefano, 2010 ).
The planning stage is defined by cognitive, goal-directed action (see Figure 3 ). In order to plan, the actions of thinking, reflecting, and evaluating are involved, and, neurobiologically, the upper limbic level. The cognitive task of planning is propelled by either appetitive or aversive motivational salience and may culminate in an intention, or a series of intentions (a plan). Michaelsen and Esch (2021) contend that, owing to its cognitive underpinnings, planning can only transpire in goal-directed behavioral processes, and not in stimulus-driven behavioral processes. They posit that both stages of motivational engagement can be bypassed if the presented stimulus and the evoked motivational salience go unnoticed (i.e., are stimulus-driven).

Model of Engagement ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2021 ).
The third engagement phase is called executive engagement and consists of the stages initiation, continued action and maintenance ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2021 ). According to the authors, initiation is the behavioral consequence of a response-outcome mechanism, whereby an individual actively reacts to the appetitive or aversive motivational salience that ensues from the encounter (and processing) of a stimulus. This reaction is propelled by the anticipation of pleasurable feelings (in the case of positive stimuli) or relief (in the case of negative stimuli). The appraisal of experiences as pleasurable or unpleasurable takes place within the endogenous reward system (such as the amygdala), which also encompasses the establishment of associations between an experience and other stimuli ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2021 ). Upon fulfillment of the expectation of a positive experience, said experience engenders a memory that, in turn, spawns an anticipation of a reward from the same activity, thereby enhancing the likelihood of the behavior being reiterated ( Van Cappellen et al., 2018 ). This phenomenon is referred to as reward responsiveness ( Carver and White, 1994 ).
The process of recording memories of experiences, which includes the context in which they occurred, such as the location, time, and social companionship, entails the involvement of the hippocampus ( Nestler, 2001 ; Nestler et al., 2001 ; Esch and Stefano, 2004 , 2010 ). This type of learning can lead to a reciprocal effect: as time passes, associations between positive affect and stimuli that predict it, and memories of it, may endow those stimuli with appetitive salience, making them more likely to capture attention in the future ( Fredrickson and Joiner, 2018 ; Van Cappellen et al., 2018 ). The phenomenon of learning encompasses two critical components, namely conditioning and expectation. In the context of stimulus-driven and goal-directed behavior, the experience of reward is not contingent on whether the stimulus was subjected to cognitive processing to be transformed into a goal. According to Michaelsen and Esch (2021) , the initiation of a new behavior through the activation of endogenous reward triggers a learning process, wherein the association between the new behavior and the experienced positive affect fosters reward expectancy, potentially resulting in continued action. The present study posits that the maintenance of response-outcome associations between pleasurable stimuli and their predictive cues is enhanced by sustained behavioral engagement. In this context, the authors assert that the probability of repetitive behavior, and consequently the degree of engagement therein, is contingent upon the magnitude of endogenous reward elicited by the new behavior ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2021 ). Following the repeated enactment of stimulus-driven or goal-directed behavioral actions, individuals ultimately transition into a maintenance stage, characterized by a sustained operant learning process that leads to habit formation ( Schultz, 2015 ). During this stage, the behavior is executed with regularity, and the assertive salience driven by the motivation and reward systems remains active, thereby strengthening the habitually performed action ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2021 ). The experience of quiescence, calm or contentment associated with the activation of the parasympathetic nervous system and other down-regulatory pathways serves as a powerful motivator for the maintenance of newly adopted behaviors. This state of contentment engenders a state of “non-wanting” with regard to further modifications of behavior ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2021 ). This Model of Engagement is presented in Figure 3 .
The findings can be integrated with the idea of Letzen et al. (2019) , who incorporate putative neurobiological mechanisms contributing to motivation for pain self-management into the Motivational Model for Pain Self-Management ( Jensen et al., 2003 ). The authors propose that an altered function in the mesocorticolimbic function would inhibit behavior change. The goal of this updated model is to determine whether potential neurobiological deficiencies contributing to poor motivation feed into observed non-adherence among patients with chronic pain. The authors hypothesize that mesocorticolimbic function subserves treatment-related learning history, contingency processing, and cost/benefit analysis, and individuals with mesocorticolimbic dysfunction will have lower perceived importance of symptom self-management and poorer self-efficacy for symptom self-management. They also suggest that magnitude of mesocorticolimbic dysfunction will correlate with reported treatment motivation, so that greater dysfunction is associated with poorer readiness for change, and that self-reported treatment motivation moderates the relationship between pre-treatment mesocorticolimbic function and adherence ( Letzen et al., 2019 ). The article also suggests that practice of a pain management strategy will be associated with mesocorticolimbic activity via reinforcement, and individuals with high reinforcement from this practice will have greater motivation for future practice, leading to better adherence ( Letzen et al., 2019 ). While the authors do not discuss pain management behavior as a process, by relating their hypothesis to the Model of Engagement, we can derive that mesocorticolimbic dysfunction would inhibit the progress to the stages contemplation, planning, initiation and/or continued action, and individuals with mesocorticolimbic dysfunction facing these stages within their health behavior change process would need specific support to progress.
4.3. The behavior change resource model
4.3.1. three types of behavior change resources.
The resources individuals need to progress from one health behavior change stage to another, as suggested in a number of health behavior change theories, have been summarized by Cane et al. (2012) , Kwasnicka et al. (2016) , and Carey et al. (2019) . Recently, the resources that facilitate changes in health behavior have been classified by Michaelsen and Esch (2022) into two broad categories, namely the socio-environmental resources external to the individual, and the bio-psychological resources that pertain to the internal state of the individual, with both types being characterized by changeable and non-changeable factors. While behavior change techniques (BCTs) cannot be leveraged to address non-changeable factors such as the weather, their utility is geared to targeting changeable resources ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2022 ).
Based on the distinction between reflective and affective aspects, Michaelsen and Esch (2022) have established a categorization of resources according to how these resources are accessed or generated in the brain. As such, resources are either external (socio-environmental), or internal (bio-psychological), whereby the latter can be either reflective or affective. Reflective resources are accessed, generated or refined through deliberate and effortful cognitive processing, including but not limited to goal-setting and behavioral regulation. In contrast, affective resources, such as emotions and their reinforcing valences, may be promptly elicited by environmental stimuli without the need for volitional engagement. External resources, such as environmental context and material resources, can be externally provided ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2022 ). These three types of changeable resources are depicted in Figure 4 .

Three types of changeable resources ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2022 ).
4.3.2. Behavior change techniques
Behavior change theories provide a foundation for developing effective behavior change techniques (BCTs) to support individuals in modifying their behaviors. Such theories have been employed in diverse ways, including the integration of social interactions based on Bandura’s (1989) Social Cognitive Theory, and assisting patients in generating implementation intentions, drawing on Gollwitzer’s (1999) theory on Implementation Intentions [see Bélanger-Gravel et al. (2013) for a meta-analysis of BCTs based on Gollwitzer’s (1999) theory on Implementation Intentions]. The extant literature has primarily focused on employing behavior change techniques (BCTs) that enhance cognitive resources, such as nutritional or psychological counseling ( Ball et al., 2013 ), or create situations that promote behavior modification, such as supervised walking groups ( Kassavou et al., 2013 ) or financial incentives ( Lee et al., 2019 ). However, these techniques often fail to account for patients’ individual differences in needs and circumstances ( Cecchini et al., 2010 ). The majority of interventions geared toward behavioral change tend to be financially costly and hence, not sustainable over a prolonged period of time or feasible to offer to a wide populace ( Forster et al., 2011 ). Some interventions have also yielded adverse side effects. For instance, monetary rewards for weight loss have been shown to be effective until the remuneration is obtained; however, subsequent weeks have reported higher odds of weight gain ( Paul-Ebhohimhen and Avenell, 2008 ). In contrast to BCTs that mainly, or solely, address cognitive, rational, or circumstantial/environmental resources and domains, modern BCTs primarily build on individual behavioral responses to various motivational stimuli, including affective components of a behavioral decision. Examples are the use of wearables (e.g., Piwek et al., 2016 ) and other digital innovations (e.g., Priesterroth et al., 2019 ) as well as reminders (e.g., Orr and King, 2015 ) among various forms of nudging. Nudging can be understood as shaping decision contexts in a way that encourages a particular behavior (e.g., Hansen and Jespersen, 2013 ) in a playful way through the activation of affective processes in the brain ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2022 ).
Despite a rapid growth in the implementation of interventions, most of these interventions are only successful in the short term, and often fail to demonstrate a significant improvement in the medium and long term (e.g., Marteau et al., 2012 ; International Diabetes Federation [IDF], 2013 ; Ulrich et al., 2016 ; Sainsbury et al., 2019 ). One reason for this may be the lack of comprehensive theories that allow developing successful BCTs. Another reason may be the insufficient use of theories in intervention development. In a scoping review pertaining to nudging interventions, it was discovered that only a quarter of the studies under review took into consideration the purported working mechanisms underlying the effectiveness of the intervention, while three-quarters focused solely on demonstrating its efficacy ( Szaszi et al., 2018 ). The working mechanisms, which involve the connections between BCTs and the targeted domains or resources, i.e., the specific BCT that addresses a particular resource, were elucidated upon by Carey et al. (2019) . A detailed list of resources relevant to behavior change initiation is presented by Michie et al. (2005) , who identified 112 behavior change theories and clustered the domains of behavior change mentioned therein into 12 categories. This Theoretical Domains Framework has been validated by Cane et al. (2012) , who extended the number of categories to 14 domains: “knowledge,” “skills,” “social/professional role and identity,” “beliefs about capabilities,” “optimism,” “beliefs about consequences,” “reinforcement,” “intentions,” “goals,” “memory,” “attention and decision processes,” “environmental context and resources,” “social influences,” “emotion,” and “self-regulation”. Kwasnicka et al. (2016) have summarized the domains that have been presented relevant for behavior change maintenance in their reviewed maintenance theories into five overarching categories; “maintenance motives,” “self-regulation,” “resources,” “habit,” and “environmental and social influences.” These inhibit significant overlaps with Cane et al.’s (2012) 14 domains. An analysis of these resources and the BCTs they are targeted by is presented by Michaelsen and Esch (2022) , as is further explained below.
4.3.3. Clustering BCTs
Based on the triad of behavior change resources, BCTs can be clustered according to how they address these resources and can thereby be described as the functional mechanisms of BCTs. In this way, Michaelsen and Esch (2022) derived three types of BCTs, namely those, that provide external resources (facilitating), those which strengthen internal reflective resources (boosting) and those that activate internal affective resources (nudging).
4.3.3.1. Facilitating
BCTs that focus on providing external resources enable individuals to engage in a desired behavior. These resources, which fall under categories such as “environmental context and resources” and “social influences” in the Theoretical Domains Framework ( Michie et al., 2005 ; Cane et al., 2012 ), can be provided by the individual, another person, or an organization. Illustrative of the aforementioned interventions are strategies that enhance the availability of healthy food alternatives within workplace canteens ( Geaney et al., 2013 ), incentivization programs that offer monetary rewards ( Petry et al., 2013 ), modification of the physical environment through initiatives such as the establishment of public fitness trails ( Cohen et al., 2012 ), and social support mechanisms including the facilitation of assisted walking groups ( Kassavou et al., 2013 ). These techniques can help facilitate behavior change, but the new behavior may not be sustained once the external resources are removed. However, when an individual has established a routine or habit of a specific new behavior, and their motivation to continue is strong, the end of the availability of the BCT may lead to a similar behavior that can be implemented independently of the original BCT. As an example, the termination of an organized walking group may prompt the participants to either sustain their walking activity on an individual basis or establish autonomous walking groups.
4.3.3.2. Boosting
Internal reflective resources can be addressed by involving cognitive processes. BCTs which target theses resources are called boosts. These enjoyable tasks foster the building up or strengthening of internal reflective resources that can support health behavior change. Examples are “beliefs about capabilities,” “beliefs about consequences,” “intentions,” “goals,” and “behavioral regulation” ( Cane et al., 2012 ). These types of interventions may include self-monitoring techniques, such as keeping a diary or practicing mindfulness ( Shomaker et al., 2019 ) to improve attention and awareness. Additionally, interventions like health education ( Gigerenzer et al., 2007 ) and nutritional counseling ( Ball et al., 2013 ) can increase an individual’s understanding of the consequences of their behavior and lead to a willingness to change. There are also other examples of boosting interventions (see, e.g., Grüne-Yanoff and Hertwig, 2016 ) that can similarly lead to an increased readiness to change and intentional implementation of a desired behavior ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2022 ). Having executed the desired behavior by means of one’s own effort, thus, leads to an experience of self-efficacy and the related positive affect. This in turn, can act as a reinforcement to pursue the behavior again. The generated effects potentially persist beyond the intervention, if those resources have become sufficiently strong or stable ( Hertwig and Grüne-Yanoff, 2017 ) and the reward, e.g., through the self-efficacy experience, has been sufficiently intense and therefore been stored in memory.
4.3.3.3. Nudging
Nudges are interventions that guide people toward a certain behavior without limiting their freedom of choice (e.g., Thaler and Sunstein, 2008 ; Alemanno and Sibony, 2015 ; Halpern and Sanders, 2016 ). This is achieved by manipulating aspects of the environment to create cues, stimuli, or triggers that make the desired behavior more appealing. Nudging activates the emotional aspects of decision-making, making the behavior more attractive, enjoyable and intrinsically rewarding, while still allowing individuals to make their own choices ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2021 , 2022 ). Nudging does not require cognitive skills or external resources, but it activates non-conscious or automatic resources to compensate for the lack of external or reflective resources needed for behavior change ( van Gestel et al., 2020 ). Felsen and Reiner (2015) provided a neuroscientific explanation of how nudges exert their effects based on diffusion-to-bound models. In diffusion-to-bound models, it is assumed that a decision is made within a decision space bounded by the available choices. A decision variable that is comprised of multiple factors that influence the decision including current sensory stimulation, stored memory about past experience, and the subjective value of each option, moves further or closer to each bound depending on the strength of these factors until one bound is reached and the corresponding decision is made ( Felsen and Reiner, 2015 ). Nudges can be considered to shift the decision variable toward the bound of the preferred choice, i.e., making the preferred choice more likely ( Felsen and Reiner, 2015 ).
In a systematic review, nudging interventions have been shown to lead to medium size effects in behavior change ( Mertens et al., 2022 ). Examples are variations in the manner of presenting food items ( Bucher et al., 2016 ; Broers et al., 2017 ; van Gestel et al., 2020 ), reminders or reinforcement-based learning schemes ( Orr and King, 2015 ; Yom-Tov et al., 2017 ), lotteries ( Volpp et al., 2008 ), and point systems ( Priesterroth et al., 2019 ), all of which serve to augment the expectation of rewards. The underlying premise is that the magnitude of the anticipated reward is positively correlated with the likelihood of remembering and repeating it ( Esch and Stefano, 2004 ). These nudges are believed to only have temporary effects on behavior, as the increased motivation from the nudge is not sustained once the nudge is removed. For example, a study that used point-of-decision prompts to encourage stair use in a university dormitory found that the effects were not sustained once the prompts were removed ( Howie and Young, 2011 ). However, with frequent repetition, the behavior being nudged may become a habit that continues even after the nudge is removed because of neurobiological learning processes ( Verplanken and Aarts, 1999 ; Lieberoth et al., 2018 ; van Rookhuijzen et al., 2021 ).
4.3.4. Summary of the behavior change resource model
The classification of BCTs based on the behavior change resources they address, may be sufficient to define all existing BCTs and explain their functional mechanism. This means that any BCT, such as those listed in Michie et al. (2013) can be categorized as facilitating, boosting, or nudging. Michaelsen and Esch (2022) have defined resource-driven behavior change as a process that increases the likelihood of a preferred behavior by focusing on the resources needed for that particular behavior to occur. Resource-driven behavior change is accomplished via the implementation of one or a blend of three BCT types that provide external resources (facilitating), build up internal reflective resources (boosting) or activate internal affective resources (nudging). Upon achieving a certain level of efficacy, the BCTs can prompt the initiation or maintenance of a new behavior, which can subsequently yield a positive response (affect) as a reward. Such reward can serve as a cue or stimulus to augment resources, known as vantage resources ( Van Cappellen et al., 2018 ). Exemplifying this notion, a positive affect can function as a reinforcement, thereby acting as a subtle prompting mechanism (nudging), as the experience of a pleasurable affect is deemed vital in predicting the likelihood of subsequent behavioral engagement ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2022 ). Furthermore, successful implementation or repetition of the desired behavior can also reinforce other desirable cognitive and affective states, such as strengthening one’s belief in one’s own abilities (i.e., self-efficacy), which can serve as a boosting strategy. Neurobiologically, these emotional influences on reward experiences and subsequent decisions are mediated in the medial prefrontal cortex, as evidence from human and animal model studies indicates ( Euston et al., 2012 ). Therefore, the functional mechanisms of BCTs are not independent, but interrelated with neurobiological motivation and reward proceedings. Recognizing these multidirectional causal relationships, Michaelsen and Esch (2022) propose a new framework for understanding the functional mechanisms of BCTs, called the behavior change resource model (BCRM). The BCRM and its relation to the Model of Engagement is illustrated in Figure 5 .

Behavior change resource model and its relation to the Model of Engagement ( Michaelsen and Esch, 2021 , 2022 ).
5. Discussion
5.1. understanding health behavior change by motivation and reward mechanisms.
Despite being essential to enhance health, behavior change support is rarely covered by health care systems around the world ( Chauhan et al., 2017 ; Grabovac et al., 2019 ). It is therefore even more important to support the development of interventions, which are powerful in terms of efficiency and preservation of individuals’ autonomy in order to be applied in low-resource settings or independently of political decision-makers. Behavior change has been studied primarily from a social psychology perspective, focusing on cognitive, or reflective, resources and domains relevant to behavior change, including circumstantial/environmental aspects. Neurobiological advances in automatic functioning as well as motivation and reward systems, however, fit neatly into the discussion of how humans act and how behavior can be changed. Integrating motivation and reward mechanisms into the behavior change literature and presenting new models to understand behavior change potentially helps policy makers to identify the necessary and sufficient environmental, economic, and psychological conditions that make healthy choices possible and easy.
A framework with a similar purpose as the behavior change resource model is the behavior change wheel (BCW) ( Michie et al., 2011 ). The BCW is based on a review of 19 behavior change frameworks from various fields (e.g., health, environmental behavior). Its core is a “behavior system” with three essential conditions: capability, opportunity, and motivation. These three conditions can be interpreted as attributes of behavior change resources. They overlap slightly with the categorization of resources made by Michaelsen and Esch (2022) , in the sense that opportunity to behavior change is present when external resources are available, capability is fulfilled when the necessary internal reflective resources are strong enough, and motivation can be seen as an internal affective resource. In the BCW, motivation represents a psychological resource (referring to intrinsic vs. extrinsic motivation) and is not discussed or integrated in terms of its neurobiological underpinnings. In a second step, Michie et al. (2011) developed intervention functions, which are essentially a categorization of BCTs into nine groups: education, persuasion, incentivization, coercion, training, restriction, environmental restructuring, modeling and enablement. The three conditions are then linked to the intervention’s functions without a specific explanation of how the conditions relate to the interventions, i.e., their functional mechanisms are not explained.
5.2. Practical implications of the presented literature
The understanding of the role of motivational salience in health behavior change processes presented by the Model of Engagement could be applied to develop suitable cues and stimuli, e.g., nudges that direct people’s actions into their desired outcome. General examples are fruit placement experiments ( Wansink et al., 2011 ; Hansen et al., 2016 ) or goal formation through social comparison ( Custers and Aarts, 2005 , 2010 ). The findings can also be used in a more differentiated way. Considering the seven stages of the behavior change process, findings imply that different BCTs are required depending on where at the change process an individual is. At the unawareness stage, individuals are not aware that behavior change could contribute to their health status. Therefore, to move to the next stage, individuals require knowledge, insight or possibly a shift in health locus of control from external to more internal (i.e., perceiving the reward from one’s behavior as contingent on one’s own behavior, see Rotter, 1966 , or Cheng et al., 2016 for a meta-analysis on health locus of control and specific health behaviors). Knowledge can be provided, for example, through large-scale policy campaigns. Once an individual is aware that a change in behavior could positively affect their current or future health, a number of other resources may be required to spike interest in behavior change and to move into the motivational engagement phase. For example, hearing or reading about personal experiences from peers (e.g., friends, colleagues) could lead to goal formation. Thus, an individual could be incentivized to talk with peers about their health behavior goals and achievements. To move from the contemplation to the planning stage, information about various offers of health promotion courses could be beneficial. In general, the findings can be applied using these three steps:
- 1. Determining at which stage of their individual change process an individual is.
- 2. Identifying the resource(s) needed to reach the next relevant stage.
- 3. Selecting a BCT that targets the lacking, weak or inactive resource.
Step 1 can be done by applying motivational interviewing ( Rollnick and Miller, 1995 ) or the set of questions developed by Michie et al. (2005) . For step 2, the Theoretical Domains Framework by Cane et al. (2012) or any other framework that lists health behavior change resources, can be used. Once the lacking, weak or inactive resources for successful behavior change have been identified, one or more suitable BCTs can be selected and applied (step 3). Michaelsen and Esch (2022) provide guidance for the third step in their application guide of the BCRM. In this table, the potential target groups for each type of BCT, based on the seven-stage behavior change process described above, are explained and numerous examples for various settings and stakeholders are given. This can assist health/behavior therapists, intervention planners and patients in selecting appropriate measures to achieve the desired health behavior change.
From a public health perspective, the findings of the studies can also contribute to improve health literacy of specific patient groups, e.g., the chronically ill, or specific populations, such as vulnerable families, e.g., in low-income settings. By identifying the needs of these groups in relation to their health, knowing which type of motivation to foster and which resource to provide, strengthen, or activate with which measures, health behavior (e.g., diet) and disease management (e.g., regularly measuring blood sugar) can be improved. Thus, the findings can also be used in prevention and health promotion contexts and potentially help to close the gap in life expectancy between low- and high-income communities.
Furthermore, the findings have the potential to improve intervention effectiveness by better matching the goals of the intervention and the goals of the patients or individuals for whom they are developed. Interventions with a better fit promise better outcomes ( Michie and Prestwich, 2010 ; Prestwich et al., 2014 ; Beard et al., 2019 ; Carey et al., 2019 ) and could therefore be more cost-effective, thereby relying less on scarce financial resources of providers, such as health insurances, local governments, or states.
5.3. Avenues for future research
The results presented in this review are theoretical in nature and therefore require empirical verification. In addition, a number of aspects contained in the studies need to be explored further or discussed in more detail. Some of these points for future research are highlighted in the following.
First, for a number of research strands processed in this review, systematic rather than convenience literature searches could help to substantiate the claims made. While systematic literature searches have been conducted and reviews published on behavior change resources and BCTs (e.g., Cane et al., 2012 ; Prestwich et al., 2014 ; Kwasnicka et al., 2016 ), as well as on behavior change frameworks that served as a basis in the presented analyses (e.g., Kwasnicka et al., 2016 ; Carey et al., 2019 ), conducting new systematic searches and reviews could help to integrate the knowledge gained since the reviews were published. Especially the growing literature on single- or multi-system models (as alternatives to dual-process models) of behavior would benefit from a systematic overview and discussion of the advantages and disadvantages of the views published so far. On this basis, the BCRM potentially requires refinement. The literature on health promotion and behavior change is growing rapidly, so more up-to-date reviews could help to increase the granularity and accuracy of the findings. For example, a future systematic search of the behavior change resource literature could be done to map the resources identified in the literature to the three types of resources generated in this review. A comprehensive list of internal affective, internal reflective and external resources could be the result. This list could then be augmented by neurobiological analyses of the functional mechanisms proposed. In addition, a systematic search and analysis of empirically tested BCTs can result in a list and discussion of BCTs in the light of their functional mechanisms. Providing such lists would facilitate the application of the BCRM such that users could easily identify resources they need and the BCTs that help to address them.
Second, the Model of Engagement could be tested in the “real world” with patients, e.g., in primary care settings, through interviews that help patients to describe how they perceive their own behavior change process, at which stage they assume to be and what they require to move forwards. These descriptions are presumably very diverse and depend on patient characteristics, such as age, disease or cultural background. Qualitative interviews are potentially the right starting point for the development of a more general questionnaire to test the model in a larger population and with specific target groups.
Third, the BCRM, and aspects of it, is proposed based on several implicit hypotheses that need empirical verification. The first hypothesis is that it is possible to determine uniquely the stage in the behavior change process for each individual patient. This hypothesis could be tested through a new questionnaire that builds upon motivational interviewing ( Rollnick and Miller, 1995 ) or the set of questions developed by Michie et al. (2005) with specific reference to the stages developed in the Model of Engagement. The second hypothesis is that motivation and reward systems are required to process along the stages. This could be tested by interviewing individuals who have successfully progressed along their stage process with respect to their own description of their affective states (pleasure, relief, quiescence) that were present while progressing. The third hypothesis is that resources can uniquely be classified into internal affective, internal reflective and external resources. Neuroscientific methods such as brain imaging could be used to analyze the affective and motivational components associated with these resources and potentially involved in various BCTs. The fourth hypothesis is that certain BCTs influence resources through the three described functional mechanisms of facilitating, boosting, or nudging. Qualitative research methodologies may provide a means to expound upon the perceptions of individuals who have undergone specific interventions, in relation to the mechanisms that either support or impede their engagement in behavior change processes.
Future research should explore the specific functional mechanisms of BCTs in more detail. So far, the literature presents only a general understanding of the functional mechanisms of BCTs. The BCRM should be subject to further scrutiny by investigating the intricate affective processes that underlie nudging interventions, through the assessment of affective states before, during, and after decision-making. Gaining insight into the neurobiological mechanisms that underpin the three functional components of the BCRM, and their respective roles in determining motivational salience and reward intensity, would undoubtedly enhance the scientific knowledge base and prove invaluable in the development and implementation of future interventions in everyday settings.
Finally, the application process of the three steps with patients or communities could be accompanied by research on its applicability, feasibility and effectiveness to optimize the model and its features for future use.
6. Conclusion
Previous theories of health behavior change have overemphasized either cognitive, rational, or relational aspects, while largely neglecting the emotional-affective or motivational processes involved in behavior change. Recent literature has integrated neuroscientific evidence and evidence-informed models into the explanations of how health behavior can be changed, short-term and long-term. Thereby, classifications of behavior change resources and behavior change techniques have been developed and the mechanisms of behavior change techniques have been explained. All in all, the literature has potential to be enriched by more neuroscientific evidence, e.g., more details of the functional mechanisms of health behavior change techniques for particular behavior change resources. Other interesting avenues for future research have been described in this review.
Author contributions
MM was responsible for initial literature search, article screening, interpretation of the existing research, conducting the analysis, as well as writing, and critical revision of the manuscript. TE provided support from the idea through the conception and design of the review and also provided suggestions for revising the manuscript. Both authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- Alemanno A., Sibony A. -L. (2015). Nudge and the law: A European perspective. London: Bloomsbury Publishing. [ Google Scholar ]
- Alert M. D., Rastegar S., Foret M., Slipp L., Jacquart J., Macklin E., et al. (2013). The effectiveness of a comprehensive mind body weight loss intervention for overweight and obese adults: A pilot study. Complement. Ther. Med. 21 286–293. 10.1016/j.ctim.2013.05.005 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ball L., Johnson C., Desbrow B., Leveritt M. (2013). General practitioners can offer effective nutrition care to patients with lifestyle-related chronic disease. J. Prim. Health Care 5 59–69. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bandura A. (1989). “ Social cognitive theory ,” in Annals of child development: Vol. 6. Six theories of child development , ed. Vasta R. (Stamford, CT: JAI Press; ), 1–60. [ Google Scholar ]
- Beard E., West R., Lorencatto F., Gardner B., Michie S., Owens L., et al. (2019). What do cost-effective health behaviour-change interventions contain? A comparison of six domains. PLoS One 14 : e0213983 . 10.1371/journal.pone.0213983 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bélanger-Gravel A., Godin G., Amireault S. (2013). A meta-analytic review of the effect of implementation intentions on physical activity. Health Psychol. Rev. 7 23–54. 10.1080/17437199.2011.560095 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berridge K. C. (2007). The debate over dopamine’s role in reward: The case for incentive salience. Psychopharmacology 191 391–431. 10.1007/s00213-006-0578-x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berridge K. C. (2018). Evolving concepts of emotion and motivation. Front. Psychol. 9 : 1647 . 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01647 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berridge K. C., Kringelbach M. L. (2008). Affective neuroscience of pleasure: Reward in humans and animals. Psychopharmacology 199 457–480. 10.1007/s00213-008-1099-6 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bozarth M. (1994). “ Pleasure systems in the brain ,” in Pleasure: The politics and the reality , ed. Warburton D. M. (Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons; ). [ Google Scholar ]
- Broers V. J. V., de Breucker C., van den Broucke S., Luminet O. (2017). A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effectiveness of nudging to increase fruit and vegetable choice. Eur. J. Public Health 27 912–920. 10.1093/eurpub/ckx085 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bucher T., Collins C., Rollo M. E., McCaffrey T. A., Vlieger N., de, et al. (2016). Nudging consumers towards healthier choices: A systematic review of positional influences on food choice. Br. J. Nutr. 115 2252–2263. 10.1017/S0007114516001653 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cacioppo J. T., Gardner W. L., Berntson G. G. (1999). The affect system has parallel and integrative processing components: Form follows function. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 76 839–855. 10.1037/0022-3514.76.5.839 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cane J., O’Connor D., Michie S. (2012). Validation of the theoretical domains framework for use in behaviour change and implementation research. Implement. Sci. 7 : 37 . 10.1186/1748-5908-7-37 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cardoso Barbosa H., de Queiroz Oliveira J. A., Moreira da Costa J., Melo Santos R. P., et al. (2021). Empowerment-oriented strategies to identify behavior change in patients with chronic diseases: An integrative review of the literature. Patient Educ. Counsel. 104 689–702. 10.1016/j.pec.2021.01.011 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carey R. N., Connell L. E., Johnston M., Rothman A. J., de Bruin M., Kelly M. P., et al. (2019). Behavior change techniques and their mechanisms of action: A synthesis of links described in published intervention literature. Ann. Behav. Med. 53 693–707. 10.1093/abm/kay078 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carver C. S. (2009). Threat sensitivity, incentive sensitivity, and the experience of relief. J. Pers. 77 125–138. 10.1111/j.1467-6494.2008.00540.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carver C. S., White T. L. (1994). Behavioral inhibition, behavioral activation, and affective responses to impending reward and punishment: The BIS/BAS scales. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 67 319–333. 10.1037//0022-3514.67.2.319 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cecchini M., Sassi F., Lauer J. A., Lee Y. Y., Guajardo-Barron V., Chisholm D. (2010). Tackling of unhealthy diets, physical inactivity, and obesity: Health effects and cost-effectiveness. Lancet 376 1775–1784. 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61514-0 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chaiken S. (1980). Heuristic versus systematic information processing and the use of source versus message cues in persuasion. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 39 752–766. 10.1037/0022-3514.39.5.752 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chan D. K. Y., Chong R., Basilikas J., Mathie M., Hung W. T. (2002). Survey of major chronic iIlnesses and hospital admissions via the emergency department in a randomized older population in Randwick, Australia. Emerg. Med. 14 387–392. 10.1046/j.1442-2026.2002.00343.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chauhan B. F., Jeyaraman M. M., Mann A. S., Lys J., Skidmore B., Sibley K. M., et al. (2017). Behavior change interventions and policies influencing primary healthcare professionals’ practice-an overview of reviews. Implement. Sci. 12 : 3 . 10.1186/s13012-016-0538-8 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cheng C., Cheung M. W. L., Lo B. C. Y. (2016). Relationship of health locus of control with specific health behaviours and global health appraisal: A meta-analysis and effects of moderators. Health Psychol. Rev. 10 460–477. 10.1080/17437199.2016.1219672 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cohen D., Marsh T., Williamson S., Golinelli D., McKenzie T. L. (2012). Impact and cost-effectiveness of family fitness zones: A natural experiment in urban public parks. Health Place 18 39–45. 10.1016/j.healthplace.2011.09.008 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cramer H., Lauche R., Haller H., Steckhan N., Michalsen A., Dobos G. (2014). Effects of yoga on cardiovascular disease risk factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 173 170–183. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.02.017 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Custers R., Aarts H. (2005). Positive affect as implicit motivator: On the nonconscious operation of behavioral goals. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 89 129–142. 10.1037/0022-3514.89.2.129 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Custers R., Aarts H. (2010). The unconscious will: How the pursuit of goals operates outside of conscious awareness. Science 329 47–50. 10.1126/science.1188595 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- de Ridder D., Geenen R., Kuijer R., van Middendorp H. (2008). Psychological adjustment to chronic disease. Lancet 372 246–255. 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61078-8 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Deci E. L., Ryan R. M. (2008). Self-determination theory: A macrotheory of human motivation, development, and health. Can. Psychol. 49 182–185. 10.1037/a0012801 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elliot A. J., Eder A. B., Harmon-Jones E. (2013). Approach–avoidance motivation and emotion: Convergence and divergence. Emot. Rev. 5 308–311. 10.1177/1754073913477517 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ellrodt G., Cook D. J., Lee J., Cho M., Hunt D., Weingarten S. (1997). Evidence-based disease management. JAMA 278 1687–1692. 10.1001/jama.1997.03550200063033 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Esch T. (2018). OpenNotes, patient narratives, and their transformative effects on patient-centered care. NEJM (Catalyst). Available online at: https://catalyst.nejm.org/doi/abs/10.1056/CAT.18.0078 (accessed January 25, 2023). [ Google Scholar ]
- Esch T. (2022). The ABC model of happiness-neurobiological aspects of motivation and positive mood, and their dynamic changes through practice, the course of life . Biology 11 : 843 . 10.3390/biology11060843 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Esch T., Stefano G. B. (2004). The neurobiology of pleasure, reward processes, addiction and their health implications. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 25 235–251. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Esch T., Stefano G. B. (2010). Endogenous reward mechanisms and their importance in stress reduction, exercise and the brain. AMS 6 447–455. 10.5114/aoms.2010.14269 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Euston D. R., Gruber A. J., McNaughton B. L. (2012). The role of medial prefrontal cortex in memory and decision making. Neuron 76 1057–1070. 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.12.002 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Evans J. (2010). Intuition and reasoning: A dual-process perspective. Psychol. Inq. 21 313–326. [ Google Scholar ]
- Evans J. (2018). “ Dual process theory: Perspectives and problems ,” in Dual process theory 2.0 , ed. De Neys W. (Oxforshire: Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group; ), 137–155. [ Google Scholar ]
- Felsen G., Reiner P. B. (2015). What can neuroscience contribute to the debate over nudging? Rev. Philos. Psychol. 6 469–479. 10.1007/s13164-015-0240-9 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Forster M., Veerman J. L., Barendregt J. J., Vos T. (2011). Cost-effectiveness of diet and exercise interventions to reduce overweight and obesity. Int. J. Obes. 35 1071–1078. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fredrickson B. L., Joiner T. (2018). Reflections on positive emotions and upward spirals. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 13 194–199. 10.1177/1745691617692106 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Geaney F., Di Scotto Marrazzo J., Kelly C., Fitzgerald A. P., Harrington J. M., Kirby A., et al. (2013). The food choice at work study: Effectiveness of complex workplace dietary interventions on dietary behaviours and diet-related disease risk - study protocol for a clustered controlled trial. Trials 14 : 370 . 10.1186/1745-6215-14-370 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gigerenzer G., Gaissmaier W., Kurz-Milcke E., Schwartz L. M., Woloshin S. (2007). Helping doctors and patients make sense of health statistics. Psychol. Sci. Public Interest 8 53–96. 10.1111/j.1539-6053.2008.00033.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gollwitzer P. M. (1999). Implementation intentions: Strong effects of simple plans. Am. Psychol. 54 493–503. 10.1037/0003-066X.54.7.493 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Grabovac I., Smith L., Stefanac S., Haider S., Cao C., Waldhoer T., et al. (2019). Health care providers’ advice on lifestyle modification in the US population: Results from the NHANES 2011-2016. Am. J. Med. 132 489–497.e1. 10.1016/j.amjmed.2018.11.021 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Grüne-Yanoff T., Hertwig R. (2016). Nudge versus boost: How coherent are policy and theory? Minds Mach. 26 149–183. 10.1007/s11023-015-9367-9 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hall P. A., Fong G. T. (2007). Temporal self-regulation theory: A model for individual health behavior. Health Psychol. Rev. 1 6–52. 10.1080/17437190701492437 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hall P. A., Fong G. T. (2015). Temporal self-regulation theory: A neurobiologically informed model for physical activity behavior. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 9 : 117 . 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00117 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Halpern D., Sanders M. (2016). Nudging by government: Progress, impact, & lessons learned. Behav. Sci. Policy 2 52–65. 10.1353/bsp.2016.0015 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hansen P. G., Jespersen A. M. (2013). Nudge and the manipulation of choice: A framework for the responsible use of the nudge approach to behaviour change in public policy. Eur. J. Risk Regul. 4 3–28. 10.1017/S1867299X00002762 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hansen P. G., Skov L. R., Jespersen A. M., Skov K. L., Schmidt K. (2016). Apples versus brownies: A field experiment in rearranging conference snacking buffets to reduce short-term energy intake. J. Foodserv. Bus. Res. 19 122–130. 10.1080/15378020.2016.1129227 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hertwig R., Grüne-Yanoff T. (2017). Nudging and boosting: Steering or empowering good decisions. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 12 973–986. 10.1177/1745691617702496 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hirschberg J., Manning C. D. (2015). Advances in natural language processing. Science 349 261–266. 10.1126/science.aaa8685 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Howie E. K., Young D. R. (2011). Step it up: A multicomponent intervention to increase stair use in a university residence building. Am. J. Health Promot. 26 2–5. 10.4278/ajhp.091106-ARB-357 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- International Diabetes Federation [IDF] (2013). IDF diabetes , 6th Edn. Belgium: International Diabetes Federation. [ Google Scholar ]
- International Diabetes Federation [IDF] (2021). IDF diabetes , 10th Edn. Belgium: International Diabetes Federation. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jensen M. P., Nielson W. R., Kerns R. D. (2003). Toward the development of a motivational model of pain self-management. J. Pain 4 477–492. 10.1016/S1526-5900(03)00779-X [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jing X., Chen J., Dong Y., Han D., Zhao H., Wang X., et al. (2018). Related factors of quality of life of type 2 diabetes patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 16 : 189 . 10.1186/s12955-018-1021-9 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kahneman D., Tversky A. (1982). The psychology of preferences. Sci. Am. 246 160–173. 10.1038/scientificamerican0182-160 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kassavou K., Turner A., French D. (2013). Do interventions to promote walking in groups increase physical activity? A meta-analysis. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 10 : 18 . 10.1186/1479-5868-10-18 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim J., Lee S., Park K., Hong I., Song B., Son G., et al. (2007). Amygdala depotentiation and fear extinction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104 20955–20960. 10.1073/pnas.0710548105 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Knowler W. C., Barrett-Connor E., Fowler S. E., Hamman R. F., Lachin J. M., Walker E. A., et al. (2002). Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Eng. J. Med. 346 393–403. 10.1056/NEJMoa012512 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Korff M., Gruman J., Schaefer J., Curry S. J., Wagner E. H. (1998). Collaborative management of chronic illness. Ann. Int. Med. 127 1097–1102. 10.7326/0003-4819-127-12-199712150-00008 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kringelbach M. L. (2005). The human orbitofrontal cortex: Linking reward to hedonic experience. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6 691–702. 10.1038/nrn1747 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krisam M., Meder B., Philipsborn P., von (2017). Nudging in der primärprävention: Eine übersicht und perspektiven für deutschland. Gesundheitswesen 79 117–123. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kruglanski A. W., Chernikova M., Rosenzweig E., Kopetz C. (2014). On motivational readiness. Psychol. Rev. 121 367–388. 10.1037/a0037013 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kwasnicka D., Dombrowski S. U., White M., Sniehotta F. F. (2016). Theoretical explanations for maintenance of behavior change: A systematic review of behavior theories. Health Psychol. Rev. 10 1–39. 10.1080/17437199.2016.1151372 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lampert T., Hoebel J., Kroll L. E. (2019). Soziale unterschiede in der mortalität und lebenserwartung in deutschland. Aktuelle situation und trends. J. Health Monit. 4 3–15. 10.25646/5868 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lang P. J. (1995). The emotion probe: Studies of motivation and attention. Am. Psychol. 50 372–385. 10.1037/0003-066X.50.5.372 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lang P. J., Bradley M. M. (2013). Appetitive and defensive motivation: Goal-directed or goal-determined? Emot. Rev. 5 230–234. 10.1177/1754073913477511 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Langenberg C., Sharp S. J., Franks P. W., Scott R. A., Deloukas P., Forouhi N. G., et al. (2014). Gene-lifestyle interaction and type 2 diabetes: The EPIC interact case-cohort study. PLoS Med. 11 : e1001647 . 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001647 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- LeDoux J. (1998). Fear and the brain: Where have we been, and where are we going? Biol. Psychiatry 44 1229–1238. 10.1016/S0006-3223(98)00282-0 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee Y., Mozaffarian D., Sy S., Huang Y., Liu J., Wilde P. E., et al. (2019). Cost-effectiveness of financial incentives for improving diet and health through medicare and medicaid: A microsimulation study. PLoS Med. 16 : e1002761 . 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002761 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lehnert T., Heider D., Leicht H., Heinrich S., Corrieri S., Luppa M., et al. (2011). Review: Health care utilization and costs of elderly persons with multiple chronic conditions. Med. Care Res. Rev. 68 387–420. 10.1177/1077558711399580 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Letzen J. E., Seminowicz D. A., Campbell C. M., Finan P. H. (2019). Exploring the potential role of mesocorticolimbic circuitry in motivation for and adherence to chronic pain self-management interventions. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 98 10–17. 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.12.011 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Levenson R. W. (2011). Basic emotion questions. Emot. Rev. 3 379–386. 10.1177/1754073911410743 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lieberoth A., Holm Jensen N., Bredahl T. (2018). Selective psychological effects of nudging, gamification and rational information in converting commuters from cars to buses: A controlled field experiment. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 55 246–261. 10.1016/j.trf.2018.02.016 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ludwig V. U., Brown K. W., Brewer J. A. (2020). Self-regulation without force: Can awareness leverage reward to drive behavior change? Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 15 1382–1399. 10.1177/1745691620931460 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Maresova P., Javanmardi E., Barakovic S., Barakovic Husic J., Tomsone S., Krejcar O., et al. (2019). Consequences of chronic diseases and other limitations associated with old age - a scoping review. BMC Public Health 19 : 1431 . 10.1186/s12889-019-7762-5 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marteau T. M., Hollands G. J., Fletcher P. C. (2012). Changing human behavior to prevent disease: The importance of targeting automatic processes. Science 337 1492–1495. 10.1126/science.1226918 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McCall C., Singer T. (2012). The animal and human neuroendocrinology of social cognition, motivation and behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 15 681–688. 10.1038/nn.3084 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mertens S., Herberz M., Hahnel U. J. J., Brosch T. (2022). The effectiveness of nudging: A meta-analysis of choice architecture interventions across behavioral domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 119 : e2107346118 . 10.1073/pnas.2107346118 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Michaelsen M. M., Esch T. (2021). Motivation and reward mechanisms in health behavior change processes. Brain Res. 1757 : 147309 . 10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147309 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Michaelsen M. M., Esch T. (2022). Functional mechanisms of health behavior change techniques: A conceptual review. Front. Psychol. 13 : 725644 . 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.725644 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Michie S., Prestwich A. (2010). Are interventions theory-based? Development of a theory coding scheme. Health Psychol. 29 1–8. 10.1037/a0016939 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Michie S., Johnston M., Abraham C., Lawton R., Parker D., Walker A. (2005). Making psychological theory useful for implementing evidence based practice: A consensus approach. BMJ Qual. Saf. 14 26–33. 10.1136/qshc.2004.011155 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Michie S., Richardson M., Johnston M., Abraham C., Francis J., Hardeman W., et al. (2013). The behavior change technique taxonomy (v1) of 93 hierarchically clustered techniques: Building an international consensus for the reporting of behavior change interventions. Ann. Behav. Med. 46 81–95. 10.1007/s12160-013-9486-6 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Michie S., van Stralen M. M., West R. (2011). The behaviour change wheel: A new method for characterising and designing behaviour change interventions. Implement. Sci. 6 : 42 . 10.1186/1748-5908-6-42 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morris E., Jebb S., Aveyard P. (2019). Type 2 diabetes: Treating not managing. Lancet Diab. Endocrinol. 7 326–327. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Moussavi S., Chatterji S., Verdes E., Tandon A., Patel V., Ustun B. (2007). Depression, chronic diseases, and decrements in health: Results from the world health surveys. Lancet 370 851–858. 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61415-9 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nestler E. J. (2001). Molecular basis of long-term plasticity underlying addiction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2 119–128. 10.1038/35053570 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nestler E. J., Malenka R. C. (2004). The addicted brain. Sci. Am. 290 78–85. 10.1038/scientificamerican0304-78 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nestler E. J., Malenka R. C., Hyman S. (2001). Molecular basis of neuropharmacology. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Medical. [ Google Scholar ]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development [OECD] (2021). Health at a glance 2021. Berlin: OECD Publishing. 10.1787/ae3016b9-en [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ornish D., Brown S. E., Billings J. H., Scherwitz L. W., Armstrong W. T., Ports T. A., et al. (1990). Can lifestyle changes reverse coronary heart disease? The lifestyle heart trial. Lancet 336 129–133. 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91656-U [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Orr J. A., King R. J. (2015). Mobile phone SMS messages can enhance healthy behaviour: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Health Psychol. Rev. 9 397–416. 10.1080/17437199.2015.1022847 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paul-Ebhohimhen V., Avenell A. (2008). Systematic review of the use of financial incentives in treatments for obesity and overweight. Obes. Rev. 9 355–367. 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2007.00409.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Petry N. M., Cengiz E., Wagner J. A., Hood K. K., Carria L., Tamborlane W. V. (2013). Incentivizing behaviour change to improve diabetes care. Diab. Obes. Metab. 15 1071–1076. 10.1111/dom.12111 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Petty R. E., Cacioppo J. T. (2012). “ The elaboration likelihood model of persuasion ,” in Communication and persuasion: Central and peripheral routes to attitude change , ed. Petty R. E. (Berlin: Springer; ), 1–24. 10.1007/978-1-4612-4964-1_1 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Piwek L., Ellis D. A., Andrews S., Joinson A. (2016). The rise of consumer health wearables: Promises and barriers. PLoS Med. 13 : e1001953 . 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001953 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Prestwich A., Sniehotta F. F., Whittington C., Dombrowski S. U., Rogers L., Michie S. (2014). Does theory influence the effectiveness of health behavior interventions? Meta-analysis. Health Psychol. 33 465–474. 10.1037/a0032853 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Priesterroth L., Grammes J., Holtz K., Reinwarth A., Kubiak T. (2019). Gamification and behavior change techniques in diabetes self-management apps. J. Diab. Sci. Technol. 13 954–958. 10.1177/1932296818822998 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Prochaska J. O., Redding C. A., Evers K. E. (2008). “ The transtheoretical model and stages of change ,” in Health behavior and health education: Theory, research, and practice , 4th Edn, eds Glanz K., Rimer B. K., Viswanath K. (Hoboken, NJ: Jossey-Bass; ), 97–121. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rizzo J. A., Chen J., Gunnarsson C. L., Naim A., Lofland J. H. (2015). Adjusting for comorbidities in cost of illness studies. J. Med. Econ. 18 12–28. 10.3111/13696998.2014.969434 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rollnick S., Miller W. R. (1995). What is motivational interviewing? Behav. Cogn. Psychother. 23 325–334. 10.1017/S135246580001643X [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rolls E. T. (2013). What are emotional states, and why do we have them? Emot. Rev. 5 241–247. 10.1177/1754073913477514 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rothman A. J., Baldwin A. S., Hertel A. W. (2004). “ Self-regulation and behavior change: Disentangling behavioral initiation and behavioral maintenance ,” in Handbook of self-regulation: Research, theory, and applications , eds Baumeister R. F., Vohs K. D. (New York, NY: Guilford Press; ), 130–148. 10.1186/s12889-020-09111-8 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rotter J. B. (1966). Generalized expectancies for internal versus external control of reinforcement (No. 1). Psychol. Monogr. Gen. Appl. 80 1–28. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryan R. M., Deci E. L. (2000). Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. Am. Psychol. 55 68–78. 10.1037//0003-066x.55.1.68 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sainsbury K., Evans E. H., Pedersen S., Marques M. M., Teixeira P. J., Lähteenmäki L., et al. (2019). Attribution of weight regain to emotional reasons amongst European adults with overweight and obesity who regained weight following a weight loss attempt. Eat. Weight Disord. 24 351–361. 10.1007/s40519-018-0487-0 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sangha S. (2015). Plasticity of fear and safety neurons of the amygdala in response to fear extinction. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 9 : 354 . 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00354 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Savoye M., Shaw M., Dziura J., Tamborlane W. V., Rose P., Guandalini C., et al. (2007). Effects of a weight management program on body composition and metabolic parameters in overweight children a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 297 2697–2704. 10.1001/jama.297.24.2697 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schneider K. M., O’Donnell B. E., Dean D. (2009). Prevalence of multiple chronic conditions in the United States’ medicare population. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 7 : 82 . 10.1186/1477-7525-7-82 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schneirla T. C. (1959). “ An evolutionary and developmental theory of biphasic processes underlying approach and withdrawal ,” in Nebraska symposium on motivation , Vol. 7 ed. Jones M. R. (Lincoln, NE: University Nebraska Press; ), 1–42. 10.1177/000306517001800210 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schultz W. (2015). Neuronal reward and decision signals: From theories to data. Physiol. Rev. 95 853–951. 10.1152/physrev.00023.2014 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schwarzer R., Lippke S., Luszczynska A. (2011). Mechanisms of health behavior change in persons with chronic illness or disability: The health action process approach (HAPA). Rehabil. Psychol. 56 161–170. 10.1037/a0024509 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Seuring T., Archangelidi O., Suhrcke M. (2015). The economic costs of type 2 diabetes: A global systematic review. Pharmacoeconomics 33 811–831. 10.1007/s40273-015-0268-9 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Seymour B., Singer T., Dolan R. (2007). The neurobiology of punishment. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8 300–311. 10.1038/nrn2119 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheeran P., Gollwitzer P. M., Bargh J. A. (2013). Nonconscious processes and health. Health Psychol. 32 460–473. 10.1037/a0029203 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheeran P., Maki A., Montanaro E., Avishai A., Bryan A., Klein W., et al. (2016). The impact of changing attitudes, norms, and self-efficacy on health-related intentions and behavior: A meta-analysis. Health Psychol. 35 1178–1188. 10.1037/hea0000387 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shomaker L. B., Pivarunas B., Annameier S. K., Gulley L., Quaglia J., Brown K. W., et al. (2019). One-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial piloting a mindfulness-based group intervention for adolescent insulin resistance. Front. Psychol. 10 : 1040 . 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01040 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith K. S., Berridge K. C., Aldridge J. W. (2011). Disentangling pleasure from incentive salience and learning signals in brain reward circuitry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108 E255–E264. 10.1073/pnas.1101920108 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stewart A. L., Greenfield S., Hays R. D., Wells K., Rogers W. H., Berry S. D., et al. (1989). Functional status and well-being of patients with chronic conditions. Results from the medical outcomes study. JAMA 262 907–913. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Strack F., Deutsch R. (2004). Reflective and impulsive determinants of social behavior. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 8 220–247. 10.1207/s15327957pspr0803_1 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stroebe W., Mensink W., Aarts H., Schut H., Kruglanski A. W. (2008). Why dieters fail: Testing the goal conflict model of eating. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 44 26–36. 10.1016/j.jesp.2007.01.005 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stroebe W., van Koningsbruggen G. M., Papies E. K., Aarts H. (2013). Why most dieters fail but some succeed: A goal conflict model of eating behavior. Psychol. Rev. 120 110–138. 10.1037/a0030849 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Szaszi B., Palinkas A., Palfi B., Szollosi A., Aczel B. (2018). A systematic scoping review of the choice architecture movement: Toward understanding when and why nudges work. J. Behav. Decis. Mak. 31 355–366. 10.1002/bdm.2035 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thaler R. H., Sunstein C. R. (2008). Nudge: Improving decisions about health, wealth, and happiness. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- The World Bank (2022). Data - Life expectancy at birth. Available online at: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.DYN.LE00.IN (accessed January 25, 2023). [ Google Scholar ]
- Ulrich S., Holle R., Wacker M., Stark R., Icks A., Thorand B., et al. (2016). Cost burden of type 2 diabetes in Germany: Results from the population-based KORA studies. BMJ Open 6 : e012527 . 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012527 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Van Cappellen P., Rice E. L., Catalino L. I., Fredrickson B. L. (2018). Positive affective processes underlie positive health behaviour change. Psychol. Health 33 77–97. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- van Gestel L. C., Adriaanse M. A., de Ridder D. T. D. (2020). Beyond discrete choices - investigating the effectiveness of a proximity nudge with multiple alternative options. Front. Psychol. 11 : 1211 . 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01211 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- van Rookhuijzen M., de Vet E., Adriaanse M. A. (2021). The effects of nudges: One-shot only? Exploring the temporal spillover effects of a default nudge. Front. Psychol. 12 : 683262 . 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.683262 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Verplanken B., Aarts H. (1999). Habit, attitude, and planned behaviour: Is habit an empty construct or an interesting case of goal-directed automaticity? Eur. Rev. Soc. Psychol. 10 101–134. 10.1080/14792779943000035 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Volpp K. G., John L. K., Troxel A. B., Norton L., Fassbender J., Loewenstein G. (2008). Financial incentive–based approaches for weight loss: A randomized trial. JAMA 300 2631–7. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wagner E. H. (2000). The role of patient care teams in chronic disease management. BMJ 320 569–572. 10.1136/bmj.320.7234.569 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wansink B., Just D., Smith L. (2011). Move the fruit: Putting fruit in new bowls and new places doubles lunchroom sales. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 43 : S1 . 10.1016/j.jneb.2011.03.013 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Watson D., Wiese D., Vaidya J., Tellegen A. (1999). The two general activation systems of affect: Structural findings, evolutionary considerations, and psychobiological evidence. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 76 820–838. 10.1037/0022-3514.76.5.820 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weinstein N. D., Sandman P. M. (1992). A model of the precaution adoption process: Evidence from home radon testing. Health Psychol. 11 170–180. 10.1037/0278-6133.11.3.170 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weinstein N. D., Sandman P. M. (2002). “ The precaution adoption process model and its application ,” in Emerging Theories in Health Promotion Practice and Research , eds DiClemente R. J., Crosby R. A., Kegler Michelle C. (Hoboken, NJ: Jossey-Bass; ), 16–39. [ Google Scholar ]
- Willett W. C. (2002). Balancing life-style and genomics research for disease prevention. Science 296 695–698. 10.1126/science.1071055 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- World Health Organisation [WHO] (2022a). Fact sheets - noncommunicable diseases. Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases (accessed January 25, 2023). [ Google Scholar ]
- World Health Organisation [WHO] (2022b). Fact sheets - aging and health. Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health (accessed January 25, 2023). [ Google Scholar ]
- Yom-Tov E., Feraru G., Kozdoba M., Mannor S., Tennenholtz M., Hochberg I. (2017). Encouraging physical activity in patients with diabetes: Intervention using a reinforcement learning system. J. Med. Int. Res. 19 : e338 . 10.2196/jmir.7994 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhou B., Lu Y., Hajifathalian K., Bentham J., Di Cesare M., Danaei G., et al. (2016). Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: A pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4⋅4 million participants. Lancet 387 1513–1530. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00618-8 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 05 June 2024
Understanding variation in catastrophic health expenditure from socio-ecological aspect: a systematic review
- Kaniz Fatima Mohsin ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6009-9896 1 ,
- Md. Nasif Ahsan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8633-6303 1 &
- Mohammed Ziaul Haider ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1520-0633 1
BMC Public Health volume 24 , Article number: 1504 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Out-of-pocket (OOP) payment is one of many countries’ main financing options for health care. High OOP payments push them into financial catastrophe and the resultant impoverishment. The infrastructure, society, culture, economic condition, political structure, and every element of the physical and social environment influence the intensity of financial catastrophes in health expenditure. Hence, the incidence of Catastrophic Health Expenditure (CHE) must be studied more intensively, specifically from regional aspects. This systematic review aims to make a socio-ecological synthesis of the predictors of CHE.
We retrieved data from Scopus and Web of Science. This review followed PRISMA guidelines. The interest outcomes of the included literature were the incidence and the determinants of CHE. This review analyzed the predictors in light of the socio-ecological model.
Out of 1436 screened documents, fifty-one met the inclusion criteria. The selected studies were quantitative. The studies analyzed the socioeconomic determinants from the demand side, primarily focused on general health care, while few were disease-specific and focused on utilized care. The included studies analyzed the interpersonal, relational, and institutional predictors more intensively. In contrast, the community and policy-level predictors are scarce. Moreover, neither of the studies analyzed the supply-side predictors. Each CHE incidence has different reasons and different outcomes. We must go with those case-specific studies. Without the supply-side response, it is difficult to find any effective solution to combat CHE.
Financial protection against CHE is one of the targets of sustainable development goal 3 and a tool to achieve universal health coverage. Each country has to formulate its policy and enact laws that consider its requirements to preserve health rights. That is why the community and policy-level predictors must be studied more intensively. Proper screening of the cause of CHE, especially from the perspective of the health care provider’s perspective is required to identify the individual, organizational, community, and policy-level barriers in healthcare delivery.
Peer Review reports
Health expenditure becomes catastrophic if the out-of-pocket (OOP) payment for healthcare exceeds a specified threshold, which can be determined based on income or ability to pay [ 1 ]. Measuring the Catastrophic Health Expenditure (CHE) may seem simple, but the outcome is challenging. High OOP makes health care inaccessible to needy people and may result in impoverishment. Impoverishment occurs when a health event compels a household to divert the expenditure on basic needs to such an extent that the spending on basic needs is reduced below the poverty line [ 2 ]. The incidence of CHE is showing a rising trend. Lots of factors are responsible for that rise. Disease prevalence is in a transitional phase, with non-communicable disease (NCD) spreading at an alarming rate due to changes in lifestyle [ 3 ]. Communicable diseases are still not controlled in many parts of the world, and climatic factors also change the disease type and severity [ 4 ]. The prevalence of NCD is increasing in middle and low-income countries, putting pressure on already stretched health systems [ 5 ]. If we consider the physical and financial burden of NCDs, they have a significant negative impact at the household level [ 6 ]. This is because OOP payment is the main financing option for most low- and middle-income countries to pay for health care [ 4 ]. According to a study, globally, 150 million people are facing CHE, with 90% coming from low-income countries [ 7 ]. According to the global monitoring report on tracking universal health coverage by the World Health Organization (WHO), each year, CHE causes 100 million people to become impoverished [ 8 ].
As per World Bank data, the global average of OOP expenditure is 16.36% of total health expenditure. For high-income groups, the average OOP expenditure is 12.12%, while for Lower Middle-Income Countries (LMIC), OOP expenditure is 41.96%. The gap is larger if we consider the country-specific data. Being part of the same sub-continent, OOP expenditure in Bangladesh is 74%, while in India, it is 50.59%, and in Pakistan, it is 55.44%. If we compare the situation with African nations, OOP expenditure in Ghana is 33.44%, while in Nigeria, it is 74.68% (World Bank, 2023). Like OOP, the incidence of CHE also varies across the region. According to WHO, the global average CHE incidence is 13%, suggesting that 13% of the world’s population has to cut off their consumption expenditure to pay for health. Whereas for LMICs, the incidence of CHE is 16%. Among the countries in the Indian subcontinent and sub-Saharan Africa, there is a significant difference in the incidence of CHE. In India, the incidence of CHE is 17%, whereas in Bangladesh, the percentage is 24. CHE incidence in Nigeria is 16%, whereas in Ghana and Rwanda, CHE incidence is only 1% (WHO, 2023). African nations are mostly war-torn and poverty-ridden countries. However, the countries in South Asia are relatively politically stable regions. Still, African nations are making progress in saving people from CHE. Despite their close geographical proximity and socioeconomic and cultural resemblance, significant variations exist across the countries. CHE needs to be understood more comprehensively to find the reason for this variation.
A systematic review combines evidence from existing literature with a focus on structure and methodology. A review of CHE is common in the available literature; nonetheless, the authors highlight the incidence and determinants. However, there is a dearth of synthesis of the predictors of CHE with the socio-ecological model in the existing literature. Synthesizing the predictors with the socio-ecological model will help to identify the gaps more precisely. Detection of the gaps will facilitate underlining the loopholes both from the demand and supply sides, based on which the policymakers would devise policy and bring necessary modifications to the existing health system. The WHO South-East Asia Journal of Public Health reported that financial protection is a global priority outlined in Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3 [ 9 ]. Most of the LMICs are lagging in providing financial protection against CHE. The reasons for CHE have to be analyzed in a more meaningful way.
The guiding framework: the socio-ecological model
When confronted with a health issue, seeking medical assistance is contingent upon the individual’s social and environmental context. Whether a patient will encounter a qualified medical professional or an unqualified individual depends on various factors, including the patient’s knowledge, beliefs, attitudes, familial environment, and the characteristics of the healthcare system. Sarker et al. [ 10 ] concluded that this phenomenon can attribute to a lower OOP expenditure associated with a higher prevalence of CHE, which is frequently observed in most LMICs, where it is challenging to ensure the physical accessibility of healthcare services to patients requiring them.
Nevertheless, without addressing these socioeconomic, religious, and cultural concerns, making health care physically available alone would not ensure accessibility. The physical environment, including ecological and natural phenomena and the social environment in which individuals undergo their developmental years, influence health [ 11 ]. Urie Bronfenbrenner introduced the socio-ecological model in 1979 to explain how the surrounding ecology and socioeconomic environment influence a child’s development [ 12 ]. Further, McLeroy and colleagues updated the model to explain health-seeking behavior and identified five levels influencing health behavior, practices, and conditions [ 13 ]. These five levels are interpersonal, relational, institutional, community, and policy [ 14 ]. Interpersonal factors encompass personal attributes, knowledge, and beliefs governing people’s behavior and practices. The relational factors encompass the impact of familial dynamics, peer relations, and social networks. Institutional factors like educational institutions, diverse commercial enterprises, religious institutions, and healthcare management, substantially influence individuals’ proclivity to pursue healthcare services. Community-level factors primarily encompass the dynamic interplay between institutional factors and organizations. Policy-level factors contain laws and regulations at the international, national, and local levels that govern healthcare administration and other affiliated entities. The model comprehensively incorporates various socioeconomic, political, and cultural dimensions.
This paper intends to synthesize the predictors of CHE with the socio-ecological model to find out the gap in the existing literature. Figure 1 presents the main themes. This paper first sorted out the predictors of CHE, then categorized the predictors according to the five levels of the socio-ecological model: interpersonal, relational, intuitional, community, and at the policy level, and finally tried to find out which level of the model has been less focused, where is the gap. Pulling the poor out of CHE requires a holistic effort, and all the loopholes in the health system must be identified carefully from each level.
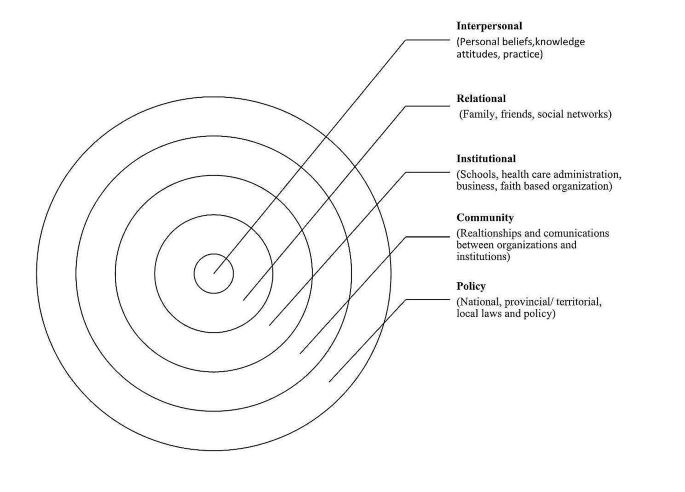
Socio-ecological model, Adapted from McLaren L, Hawe P. Ecological perspectives in health research. Journal of epidemiology and community health. 2005 Jan; 59 [ 15 ]:6
This review followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guideline in deciding the mandatory components of a systematic review. Figure 2 presents the sequential flow chart of screening the literature following PRISMA.
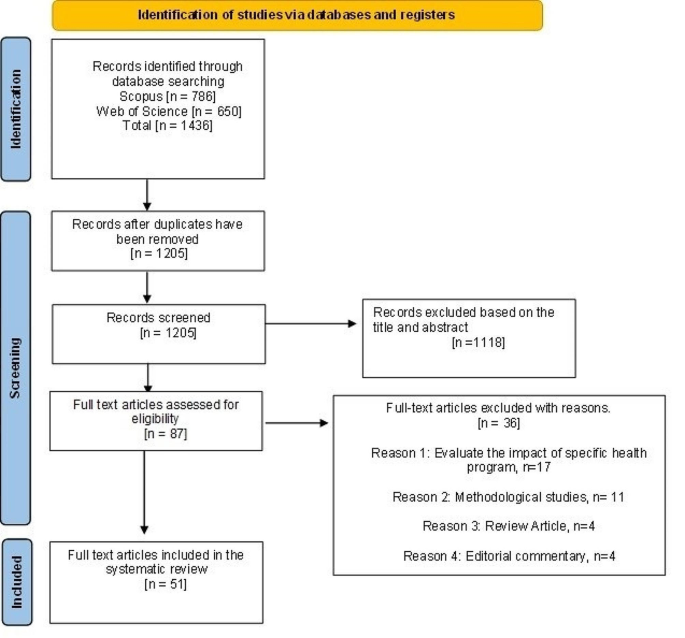
PRISMA flow chart
Search strategy and inclusion criteria
We retrieved data from Scopus and Web of Science electronic databases. The time frame of the included publications was from 2011 to 2023. We did a systematic search with the combination of text words with the thesaurus terms ‘catastrophic health expenditure’ with ‘incidence’, ‘impact’, ‘impoverishment’, ‘determinant’, ‘predictors’, ‘economic impact’, ‘financial burden’, ‘coping mechanism, and ‘source of finance’. The subject area of the search was confined to health, biomedical science, arts, and social science, and the language was restricted to English. We present the inclusion and exclusion criteria in Table 1 .
Data extraction and analysis
Consulting with the co-authors, the second author extracted the data. With the search key, 1,436 documents were identified. The inclusion and exclusion criteria were decided based on the discussion of the three authors. Analyzing the title and abstract, the first and second authors excluded 1,118 documents as per the exclusion criteria. We finally selected eighty-seven documents for full-text review in consultation with the third author. The first and second authors reviewed eighty-seven documents for full-text assessment. After assessing eighty-seven documents, thirty-six articles were excluded, seventeen focused on some health program evaluation, twelve documents evaluated the methodological appropriateness, four were review articles, and four documents were editorial commentary. Assessing the full text, three authors finally agreed to include fifty-one articles in the review.
The primary focused information includes the study context (i.e., publication year and country), features of the study population, and methodology (i.e., data source, research approach, study focus, utilized care). The focus of the included literature was the determinants of CHE.
Fifty-one studies from fifteen countries have been analyzed, where Bangladesh (sixteen documents) and China (eleven documents) had dominations. Among the sixteen papers from Bangladesh, seven studies used Household Income and Expenditure Survey data. China used different databases as they have versatile data sources like the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study, National Health Service Survey, China Family Panel Studies, and Health Services Survey in different provinces. Five studies used the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study, which depicts China concentrating on the age-specific health needs of its population, as age is a strong predictor of health status and CHE. Bangladesh has no age-specific database, so their studies do not consider age-differential health needs.
Quality appraisal of the included literature
The quality of the included articles has been assessed following the Crombie critical appraisal guideline. The first two authors independently assessed the quality of the included literature. This is a tool used to appraise the quality of quantitative analysis using cross-sectional data. All the included literature was quantitative and mainly used cross-sectional data. The procedure contains 11 questions presented in Table 2 with three probable responses: ‘Yes,’ ‘No,’ and ‘Can’t tell.’ Among the 11 criteria, the included pieces of literature fulfilled 6–10 criteria. A single study met ten criteria; forty-three studies met nine criteria; six studies met seven criteria; and a single study met six criteria. Forty-seven studies used random sampling, whereas a single study used convenience sampling. Three documents did not report the sampling procedure. Sixteen documents reported the response rate. Based on the Crombie score, forty-four studies were of high quality, and the quality of seven studies was poor. Details of the critical appraisal have been presented in Table 2 .
Characteristics of the included literature
Among the fifty-one documents, sixteen studies were from Bangladesh, eleven were from China, four were from India, and three were from South Korea and Malaysia each; two were from Kenya, Nigeria, Vietnam, and Pakistan. Single papers were selected from Brazil, Iran, Malawi, Mongolia, Nepal, and South Africa. The merit of selecting the literature from countries with different development statuses was to capture the variation in the predictors of CHE. Seventeen papers were primary data-based, and thirty-four papers were based on secondary data. The secondary data-based studies used sources like the National Database, Household Income and Expenditure Survey, Family Panel data, and Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. Of eleven studies from China, nine papers used secondary data; out of sixteen papers from Bangladesh, nine used primary data. The study sample covered in the selected literature includes general households, the elderly (aged 65+), and persons with disabilities, children, and mothers. Twenty-three studies were disease-specific (encompassed NCD, cancer, diabetes, hypertension, chronic illness, chronic liver disease, spinal cord injury, rotavirus infection, diarrhea, and tuberculosis), whereas twenty-six studies concentrated on general health care, and two papers focused on multiple diseases. Forty-one studies used cross-sectional data, while seven studies used longitudinal data. Forty-six papers have considered both inpatient and outpatient care; three papers concentrated on the utilization of inpatient care, and two papers focused on medication and community-based home care. Detailed information, along with the predictors of CHE, has been summed up in Table 3 .
Before synthesizing the predictors of CHE with the socio-ecological model, we present some numerics from the World Bank related to financial protection against catastrophic health expenditure in Table 4 . We have presented the data of the countries in which we have included literature in this review.
If we concentrate on the numerics, the World Bank data on the countries included in the literature shows that Nigeria has the highest OOP. Patients have to pay 75% of their current health expenditures out of their pocket. Bangladesh has the second highest OOP (74%). Conversely, South Africa has the lowest OOP (5%) and Malawi has the second lowest (20%). Brazil spends 10% of its GDP on health, whereas India and Bangladesh spend only 3% on health. To achieve universal health coverage, nations must invest at least four to five% of their GDP in health [ 16 ]. The data depicts that countries investing more in health have lower OOP. Social health insurance coverage in current health expenditure is 35, 34, and 30% for China, Vietnam, and Iran, respectively. However, in Bangladesh, the social health insurance coverage is 0%. According to the World Bank data, countries with higher social health insurance coverage have lower OOP.
Primary health care expenditure by government and donors as a percentage of current health expenditure is 3% for South Africa and Malawi but 0% for Bangladesh and Nigeria [ 17 ]. Nevertheless, to combat NCDs, resource-poor countries have no other way but to follow the proverb ‘prevention is better than cure’ as the health system is lagging in technology, health professionals, and financial ability to provide curative care for NCDs like cancer [ 18 ]. Preventive care is a part of primary health care. But here data from Bangladesh and Nigeria revealed that the government or donor support on primary health care is zero. In China, 14% of the population are aged 65+. In Brazil, it is 10%, for Malaysia and Bangladesh, the percentage is eight, and six respectively. We have to concentrate to face the challenges of aging, have to prepare to meet the health needs of the senior citizens. These are only a glimpse of the neglected health sector investment of the countries that have been reviewed.
Socio-ecological synthesis
We classified the determinants of CHE and analyzed them in a precise way. We classified the determinants as the demographic, cost-related, and utilized care-related variables, variables that are the constructs of the health belief model, like perceived severity of illness. There were also some healthcare regulation-related variables. Now, we will make a socio-ecological synthesis of the predictors of CHE. If we want a sustainable solution, any problem must be studied from upstream, not downstream. In that case, the socio-ecological model could facilitate the identification of the predictors of CHE from the upstream, as this model encompasses a holistic view of any health problem.
Interpersonal predictors
Among the personal attributes, age, sex, education, income, and place of residence are consistent demographic predictors of CHE. With age, susceptibility to disease increases [ 10 , 19 ]. Old age dependency makes the situation difficult for senior citizens, especially where the social safety nets are unavailable or poor [ 20 , 21 ]. The patient’s gender is another deciding factor in accessing health care and significantly impacts CHE [ 3 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 ]. A study from Bangladesh denotes that the health needs of women are often neglected by their families [ 25 , 26 ]. In the case of pregnancy-related care, a study from Bangladesh found that facing any health complexity during delivery considerably incurs CHE [ 27 ]. Education is associated with CHE as education impacts health-seeking behavior like food habits, health precautions, preventive measures, and choice of care [ 4 , 18 , 19 , 23 , 28 ].
As a predictor of CHE, income has been studied for different quintiles, and the extent of the relationship varied for different quintiles. A study from Malawi and Nigeria concluded that the better off face higher CHE than people with low incomes [ 5 , 29 ]. On the other hand, studies from India and Bangladesh concluded that the poor face higher CHE than the rich [ 21 , 30 , 31 ]. Economic status highly dictates the care utilization pattern, but this variable also gave an assorted result. Studies from China, Vietnam, and Nigeria revealed that people with high economic status faced higher CHE than those with lower economic status [ 29 , 32 , 33 , 34 ]. In contrast, a study from China concluded that people with lower economic status faced higher CHE [ 35 ]. The susceptibility to chronic diseases increases with age, which requires regular and long-term care [ 35 ]. Nevertheless, the elderly who do not have any earning source at this age, and this dependency pushes them into CHE [ 36 ]. Again, several studies from Bangladesh and South Korea found that the loss of income due to disease, an indirect cost of illness, increases CHE incidence [ 13 , 15 , 37 , 38 ]. With the increase in sick days, this indirect loss increases, which worsens the financial catastrophe [ 30 ].
Now, let us move on to disease-specific factors. Type of illness is a significant predictor of CHE [ 7 , 22 , 39 ]. Studies from Bangladesh, South Korea, India, and China found that diseases that require inpatient care have higher CHE incidence as with the increase in hospitalization, the direct cost and indirect income loss due to disease increases the financial burden [ 13 , 15 , 18 , 26 , 30 , 37 , 38 , 40 ]. Studies from Bangladesh, China, Vietnam, and Malaysia concluded that NCD, Cancer, and Chronic disease have higher CHE incidence as these diseases demand long-term care and the treatment is expensive [ 4 , 18 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 32 , 41 ]. Perceived severity of illness and patients/diagnostic delay are two health belief model constructs. Studies from China and Vietnam identified these two as significant predictors of CHE [ 36 , 42 ]. A study from China on tuberculosis depicted that patient/diagnostic delay, which is the gap between the onset of the symptoms of the disease to the clinical diagnosis, considerably deteriorates treatment outcomes, demands inpatient care, and results in CHE [ 43 ].
Rural-urban differences in availability and quality of health care are significant, so the place of residence has been identified as the most consistent predictor of CHE in studies from China, Bangladesh, India, Nepal, Malaysia, Malawi, and Nigeria [ 4 , 5 , 13 , 14 , 21 , 22 , 26 , 27 , 31 , 41 , 42 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 ]. Disease pattern highly influences the health care utilization pattern and has CHE impact. For instance, type of illness. Studies from China, Bangladesh, Malaysia, and Kenya showed that patients having chronic disease, NCD and cancer face higher CHE [ 25 , 26 , 31 , 32 , 41 , 48 , 49 ].
Relational predictors
Household composition highly influences the health-seeking behavior of a patient. First comes the type of family, nuclear or extended. Two studies from Bangladesh and South Africa concluded that nuclear families face higher CHE incidence than extended families [ 3 , 44 ]. The household size gives mixed findings. Studies from China and Vietnam showed that CHE is lower among families with large households [ 4 , 19 , 35 , 36 ]. However, a study from Bangladesh found that larger households face higher CHE than smaller ones [ 31 , 37 ]. The characteristics of the household head are consistent determinants of CHE. Studies from Nigeria, Kenya, India, and Vietnam concluded that the family faces lower CHE if the household head is male, employed, and educated [ 20 , 22 , 36 , 50 ]. A comperative study among two provinces of China concluded that if the household head is unemployed, the family faces a highe CHE [ 51 ]. On the contrary, families where a female is the breadwinner face higher CHE [ 4 , 20 , 22 , 50 ]. Studies from China, Pakistan, Iran, and Vietnam revealed that families with elderly (aged 65+) have higher CHE incidence [ 4 , 32 , 33 , 47 , 52 ]. However, a study from Nigeria identified having the elderly as a weak predictor of CHE [ 22 ]. Studies from China, Nepal, Korea, and Kenya concluded that families having members with chronic disease face higher CHE [ 20 , 34 , 42 , 53 , 54 ]. Again, the study from Kenya, Pakistan, and South Africa found that families with children have higher CHE incidence [ 3 , 20 , 52 ]. However, a study from Nigeria concluded that the number of elderly or children is a weak predictor of CHE [ 22 ]. Social networks have been identified as a defending factor against CHE in studies from Bangladesh, Vietnam, and South Africa [ 3 , 36 , 37 ]. Membership in any social safety net could save people from CHE in Kenya [ 20 ].
Institutional predictors
Institutional factors attract the highest concentration in the existing literature, where the cost and utilization pattern got priority. OOP is the dominant CHE predictor and is consistent in the existing literature. Studies from China, Mongolia, and Bangladesh concluded that high OOP is the leading cause of CHE [ 7 , 13 , 14 , 55 ]. OOP is the payment that the care receivers must pay at the point of care, which no third party reimburses. Two studies from Bangladesh found OOP regressive [ 13 , 14 ]. Different studies chalked out different causes of high OOP. Physician fees are a significant predictor of CHE in Bangladesh. In contrast, outpatient visits have been identified as an important predictor of CHE in China [ 14 , 40 ]. The cost of medicine is the main contributor to OOP in Bangladesh, China, and Vietnam [ 14 , 25 , 32 , 37 , 43 , 56 ]. Diagnostic costs considerably increase OOP in Bangladesh and China [ 37 , 43 , 56 ].
Apart from those direct costs, a study in Bangladesh identified indirect costs like food, lodging, and transport costs as significant predictors of CHE [ 57 ]. Health-related income loss is another indirect cost that notably impacts impoverishment in South Korea and Bangladesh [ 13 , 15 , 37 , 38 ]. The included literature identified predictors related to utilized care. The type of provider plays a dominating role in CHE. Public providers offer treatment at a considerably lower cost than private providers. Studies from Nigeria, Kenya, Bangladesh, and India found that patients accessing care from public providers have a lower risk of CHE than those accessing care from private providers [ 7 , 20 , 22 , 26 , 29 , 31 , 50 , 57 ]. Again, accessed care is another influential predictor of CHE. Studies from Iran, China, and Vietnam concluded that those who are taking inpatient care very likely face CHE [ 4 , 36 , 47 , 48 , 54 ]. Moreover, diseases for which the treatment cost is higher have higher CHE. Two studies from China and one from Malaysia found that the cost of chemotherapy and surgery incurs a two-fold increased risk of CHE [ 40 , 47 , 58 ]. A study on tuberculosis in China found that the cost of ancillary services for liver protection increases the threat of CHE [ 43 ].
The review identified three spots at the institutional level. Studies from Bangladesh, India, Nigeria, and Kenya found a significant gap in treatment costs between public and private providers [ 7 , 20 , 29 , 31 , 50 ]. Again, a study from Bangladesh revealed that the public sector needs to be more functional, especially in the underserved areas, which significantly impact CHE [ 39 ]. Again, the same study found that private facilities were unavailable in rural coastal areas, which made health care inaccessible to many. Health insurance has been identified as a protector against CHE in several studies from China, Bangladesh, Malaysia, Kenya, and Vietnam [ 4 , 20 , 24 , 48 ]. On the contrary, studies from China found that delayed or ignored inpatient treatment coverage often fails to protect patients from CHE [ 43 ]. Another study from Pakistan found that the sub-performance of drug regulatory authority is one of the leading causes of the high price of medicine, which is a risk factor for CHE [ 14 , 59 ].
Community predictors
The review found three community-level factors: comorbidity, poverty, and social stigma. A study from Bangladesh argued that the poor cannot pay for the health shocks. Moreover, the income loss due to illness makes them more vulnerable as they have no other source but to go for distress financing, which increases the intensity of poverty [ 13 , 14 ]. Studies from Bangladesh and Vietnam found that due to poverty, the incidence of forgone care is significant, especially for NCDs and cancer [ 14 , 25 , 31 , 32 ]. Social stigma about disease increases the risk of facing CHE, which has been concluded in studies from Bangladesh and Vietnam [ 36 , 37 ]. The relative prevalence of natural disasters has been found to significantly impact the incidence of CHE in Bangladesh [ 39 ].
Policy level predictors
At the policy level, this review has found only a single predictor. Studies from Bangladesh concluded that due to the lack of regulation of health care market, OOP is considerably high, resulting in CHE [ 10 , 39 ]. The predictors of different levels are summed up in Fig. 3 . The details of the predictors and their occurrence in the included literature are summed up in Table 5 , where the number in the parentheses refers to the number of the literature as of cited in the reference. Figure 3 presents the gap in the reviewed literature to understand the socio-ecological synthesis better.
Socio-ecological synthesis of the predictors of CHE
We presented a word cloud based on all the articles included in the study using NVivo 12. Figure 4 presents the word cloud. The word cloud is a frequently used tool in qualitative studies to visualize the respondents’ responses and facilitate thematic analysis. This is not so suitable to quantitative studies.

Word cloud depicting word’s relative relevance in the reviewed papers
In this review, our motivation of using word cloud is different. We first used the word cloud to figure out the relevance of the searched literature with the study objective and to show the relative relevance of the words that occurred in the included literature. Bigger and bolder words have a higher frequency in the reviewed documents. ‘Household’, ‘type’, ‘head’, ‘prevalence’, ‘illness’, ‘health’, ‘income’, and ‘social’ largely occurred in the included literature. The main query of the included papers was to identify the predictors of CHE. The word cloud depicts that the search was quite relevant to the study objective, as all the words that have been visualized in the cloud have close relevance with the predictors of CHE. The bigger and bolder words are mainly relational, interpersonal, and institutional factors, the policy-level factors were smaller.
The objective of this review is to make a socio-ecological synthesis of the predictors of CHE. The included literature mainly dealt with the interpersonal, relational, and institutional predictors and the papers put nominal concentration on community and policy-level factors. The institutional level yielded the greatest number of predictors; however, all of them were solely based on patient responses from the demand side. The supply side predictors, i.e., the providers’ response, were completely missing in the included literature. However, the studies presented altered dimensions of CHE. A study from South Korea revealed many blind spots in the country’s healthcare system, such as chronic kidney disease [ 53 ]. The prevalence of such diseases is considerably increasing. Nonetheless, the treatment is minimal against demand and highly expensive, having a high CHE impact. However, most countries’ health systems failed to identify the financial catastrophe and the urgency of treating such fatal diseases at a lower cost.
A study from Vietnam concluded that households with higher socioeconomic status utilized care for NCDs, but patients from lower economic status often forgo care as treatment is expensive [ 32 ]. Studies from China and Malaysia showed that in the case of surgery and chemotherapy, patients have a two-fold high risk of facing CHE [ 40 , 58 ]. Complications during birth have a high incidence of CHE in Bangladesh. Families rarely go for distress financing (donation, sale of assets, loan). Instead, they try to mitigate from their income or savings. The authors implicate these findings in an assorted way [ 27 ]. The study argued that this finding might have two reasons. Family ties work positively here, and the family saves money for the upcoming birth event. Conversely, there are also incidents where even if birth becomes complicated, the family does not go to the clinics, and the result might be the loss of life of the mother or the newborn.
A study from Bangladesh found that if the patient is male and earning, distress financing is common for NCDs. However, suppose the patient is female or elderly or unemployed. In that case, the family rarely goes for distress financing instead of forgoing care [ 25 ]. A study from China concluded that the assessment of a household head regarding family member’s health status plays a pivotal role in the healthcare utilization pattern of family members [ 45 ]. A study from Bangladesh showed that women often could not access formal care due to the lack of financial support, absence of peers to accompany them, or lack of permission from the family, even in cases of NCDs like cancer [ 25 ]. Studies on tuberculosis in Bangladesh and China concluded that the delay from symptom to diagnosis (patients/diagnostic delay) deteriorates the treatment outcome [ 37 , 43 ].
Social stigma is a predictor of CHE. A study from Bangladesh found that in fear of losing a job or being marginalized, tuberculosis patients do not go for clinical diagnosis. Studies from China, India, and Bangladesh concluded that delayed diagnosis increases the risk of hospitalization, a consistent contributor to OOP and the resultant CHE [ 18 , 26 , 30 , 40 ]. The literature gave mixed results on economic status and poverty in CHE. Studies from Malawi and Nigeria showed that CHE incidence is higher among the better off as they are more cautious, and their healthcare utilization rate is higher than that of those with low economic status [ 5 , 29 ]. A study from Bangladesh also concluded that people from lower income quintiles have lower CHE as the utilization of formal care is low [ 31 ]. Conversely, poverty consistently predicts CHE, indicating that poor people have higher CHE [ 13 , 18 , 21 , 27 , 28 , 37 , 46 , 48 , 54 , 58 ]. To safeguard poor people from financial catastrophe, several studies from China, Kenya, and Malaysia emphasized on health insurance [ 19 , 20 , 36 , 54 ]. However, countries where health insurance is available reported that due to insufficient coverage and the delay in reimbursement, health insurance could not save people from CHE [ 43 ]. Again, in Mongolia, despite having high social health insurance coverage, the incidence of CHE is high as social health insurance can not cover the treatment cost of the elderly, especially those with chronic diseases [ 55 ]. The study from China concluded that basic health insurance has an insignificant impact on CHE, especially for poor people with chronic disease [ 34 ]. Another study from China concluded that social health insurance coverage could not save the elderly from facing catastrophic health expenditures [ 62 ].
Studies from China and Vietnam identified family ties as a protector against CHE [ 35 , 36 ]. The papers argued that in large families, family members care for each other, give mental and spiritual support, and have a more extensive social support network and better risk management capacities against CHE.
OOP is the crucial determinant of CHE, and utilized care is the key contributor. Only three studies from Bangladesh and South Korea concentrated on inpatient care, and a study from Pakistan worked on medication [ 15 , 26 , 38 , 59 ]. One paper from Bangladesh on spinal cord injury worked on community-based home care [ 57 ]. The rest of the paper does not consider the utilized care. Instead, they consider general health care. This is a considerable gap. The existing literature lacks an analysis of the institutional factors contributing to increased diagnosis and medicine costs, as well as the vulnerabilities faced by the poor due to the utilization of care. The reasons behind these issues, particularly in the context of Bangladesh, have received minimal attention in research.
Most papers used secondary data, whereas disease-specific studies used primary data. Studies using secondary data on general health care poorly apprehended the vulnerabilities of a disease. Instead, concentrating on disease and using primary data could help to capture disease-specific vulnerabilities more intensively. Suppose the countries want to identify the causes of high OOP. In that case, they must concentrate more on the healthcare utilization pattern with age, income, and disease prevalence. If we focus on similar studies from the developed world, like Canada, the USA, the UK, or Australia, the authors are concentrating more on supply-side predictors. They emphasize health rights and health-related laws and concentrate more on the community, institutional, and policy levels. However, these aspects are almost absent in the included literature. Only two studies from Bangladesh identified a lack of regulation in the healthcare market, nonfunctional public facilities, and the unavailability of private facilities as predictors of CHE [ 14 , 39 ].
The WHO proposed health insurance as a safeguard against CHE, which is largely overlooked in the studies from Bangladesh as her insurance coverage is only 2% [ 63 ]. On the contrary, studies from China, South Korea, Vietnam, and African countries like Nigeria or Kenya concentrated more on finding a suitable health insurance package based on age or disease prevalence. Social stigma or the need for social networks is studied in countries like South Korea, China, Vietnam, Kenya, and Nigeria. However, Bangladesh is lagging behind in addressing community predictors.
The review found sufficient predictors from the demand side in explaining why does CHE vary across the regions. However, the supply side predictors, more specifically the community and policy level factors, are rare in the included literature. The world bank data revealed that, in the countries of the reviewed literature, OOP varies on an extensive range; domestic general government health expenditure or government and donors support for primary health care vary. Some countries have no or minimal social health insurance coverage. Thus, it is worth investigating the reasons behind such variation. Results from our review suggest that the determinants behind the variations are originated from the loopholes in the supply side determinants at policy level, which are understudied. Furthermore, the difference in government health expenditure is the primary cause of the variation in financial protection against CHE [ 31 ]. We have to find out the reasons behind this deficiency. The reasons for high OOP or CHE are partially examined. We have to conentrate on the supply side predictors of CHE. If we concentrate on China, India, South Korea, the studies from those countries used different registers to study the health needs at different ages or diseases. However, many other countries like Bangladesh do not have any age- or disease-specific data sources that the researchers could use. That might be the primary cause of high CHE incidence in the LMICs [ 9 ].
The health-seeking behavior of a person is influenced by his attributes, the family and peers with whom he lives, the institutions with whom he/she interacts, the community where he/she belongs, that shapes his/her culture and values, and the policies that control and, at the same time, facilitate his/her deeds. The health system must consistently address the factors encompassing the five levels and keep coherence among different levels. Any gap among the different levels will worsen the CHE scenario. Nevertheless, this study found significant gap in the studies of the predictors of CHE from two specific aspects. First, the studies mainly concentrated on interpersonal, relational and institutional factors. The community and policy-level factors are rarely studied. The second gap is that the predictors have been studied from the demand side. A study on supply-side predictors is missing in the review; all the studies were on patients, and there is not a single study from the provider side. Saving people with low incomes from financial catastrophes is one of the targets of SDG 3. To achieve this target, countries must fill the gap.
Implication for research
The review found that authors from resource-poor countries concentrate less on community and policy-level factors. Along with the community and policy level factors, the institutional factors must be examined from the supply side. Health professionals like doctors, nurses, and hospital administrators would better explain the cause of high consultation fees, high price of medicine and diagnosis, high hospital charges, high cost of chemotherapy or surgery, or the reasons for the unavailability of treatment in underserved areas, or, why the access of a patient is denied due to the lack of financial ability, definitely in a more comprehensive way than a patient. The demand for health care is supplier-induced. The patient does not know what they need, and they do not know the utility that they will gain from treatment. So, we have to get the supply-side response.
Policy implications
To safeguard people experiencing poverty from CHE, the WHO promoted health insurance to protect against financial catastrophe. However, study findings from different countries concluded that insurance coverage is insufficient for many countries, especially to cover the treatment cost of chronic diseases like chronic kidney disease, especially for the elderly. Again, many studies found that large family sizes act as the first line of defense against CHE. Strengthening the family bondage could save people from CHE. The social stigma of the disease has a more significant mental effect with visible physical complexity. The studies do not care much about the social stigma of a disease. However, the cost of CHE is not only a financial issue but also has immense social implications. Countries must increase coverage and design insurance benefit packages that consider age, income, disease, and treatment type. Again, the impact of social capital must be recognized by the policymakers as a shield against CHE and how this could be better utilized against CHE.
Limitations of the study
To the best of our knowledge, this paper is the first attempt to synthesize the predictors of CHE with the socio-ecolofgical model. The findings may be helpful to chalk out the loopholes of the health system more precisely that pushes people to catastrophic health expenditure.
The study has some limitations. Most of the included documents used secondary data sources and worked on general health care to measure the incidence of CHE. We have to concentrate more on primary data-based and disease-specific studies to capture the accurate predictors. In the online data sources, such literature is limited on LMICs. That is why this systematic review’s proportion of secondary data-based studies was higher. This is a limitation of the study. Again, we excluded non-English documents from the review, and the data search did not cover the data from some other related electronic data sources like Pub-med. We did not go for any open search like google scholar. Our study was also confined to LMICs. The inclusion of data from more data bases and open sources, and the non-English sources may produce more comprehensive results and may be a scope for future research.
Data availability
The dataset analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Catastrophic Health Expenditure
Gross Domestic Product
Lower Middle-Income Country
Non-communicable Disease
Out-of-Pocket
Primary Health Care
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis
Sustainable Development Goal
World Health Organization
Amaya Lara JL, Ruiz Gómez F. Determining factors of catastrophic health spending in Bogota. Colombia Int J Health care Finance Econ. 2011;11:83–100.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
World Health Organization. Primary health care on the road to universal health coverage. Global Monit Rep. 2019;22.
Mutyambizi C, Pavlova M, Hongoro C, Booysen F, Groot W. Incidence, socioeconomic inequalities and determinants of catastrophic health expenditure and impoverishment for diabetes care in South Africa: a study at two public hospitals in Tshwane. Int J Equity Health. 2019;18:1–5.
Article Google Scholar
Liu C, Liu ZM, Nicholas S, Wang J. Trends and determinants of catastrophic health expenditure in China 2010–2018: a national panel data analysis. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):526.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mchenga M, Chirwa GC, Chiwaula LS. Impoverishing effects of catastrophic health expenditures in Malawi. Int J Equity Health. 2017;16(1):1–8.
Lee JT, Hamid F, Pati S, Atun R, Millett C. Impact of non-communicable disease multimorbidity on healthcare utilization and out-of-pocket expenditures in middle-income countries: cross sectional analysis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(7):e0127199.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Xu K, Evans D, Carrin G, Aguilar-Rivera AM. Designing health financing systems to reduce catastrophic health expenditure.
World Health Organization. World Bank. Tracking Universal Health Coverage: 2023 Global Monitoring Report.
World Health Organization. A Stakeholder Analysis of Non-communicable Diseases’ Multisectoral Action Plan in Bangladesh. WHO South-East Asia Journal of Public Health, Volume 10, Issue 1, January-June 2021. 2021;10(1):1– 0.
Sarker AR, Sultana M, Alam K, Ali N, Sheikh N, Akram R, Morton A. Households’ out-of‐pocket expenditure for healthcare in Bangladesh: a health financing incidence analysis. Int J Health Plann Manag. 2021;36(6):2106–17.
McLaren L, Hawe P. Ecological perspectives in health research. J Epidemiol Commun Health. 2005;59(1):6.
Chung J, Seo JY, Lee J. Using the socioecological model to explore factors affecting health-seeking behaviours of older Korean immigrants. Int J Older People Nurs. 2018;13(2):e12179. https://doi.org/10.1111/opn.12179 . Epub 2017 Oct 30. PMID: 29083091.
Rimer BK, Glanz K. Theory at a glance: a guide for health promotion practice. US Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute; 2005.
Sarker AR, Ali SZ, Ahmed M, Chowdhury SZ, Ali N. Out-of-pocket payment for healthcare among urban citizens in Dhaka, Bangladesh. PLoS ONE. 2022;17(1):e0262900.
Ahmed S, Dorin F, Satter SM, Sarker AR, Sultana M, Gastanaduy PA, Parashar U, Tate JE, Heffelfinger JD, Gurley ES, Khan JA. The economic burden of rotavirus hospitalization among children < 5 years of age in selected hospitals in Bangladesh. Vaccine. 2021;39(48):7082–90.
Awoyemi BO, Makanju AA, Mpapalika J, Ekpeyo RS. A time series analysis of government expenditure and health outcomes in Nigeria. J Public Health Afr. 2023;14(7).
The World Bank Group. Health-nutrition-and-population-statistics. https://databank.worldbank.org/source/health-nutrition-and-population-statistics (2022). Accessed Jan 01 2023.
Rahman MM, Gilmour S, Saito E, Sultana P, Shibuya K. Health-related financial catastrophe, inequality and chronic illness in Bangladesh. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(2):e56873.
Sarker AR, Sultana M, Mahumud RA, Ali N, Huda TM, Salim Uzzaman M, Haider S, Rahman H, Islam Z, Khan JA, Van Der Meer R. Economic costs of hospitalized diarrheal disease in Bangladesh: a societal perspective. Global Health Res Policy. 2018;3:1–2.
Buigut S, Ettarh R, Amendah DD. Catastrophic health expenditure and its determinants in Kenya slum communities. Int J Equity Health. 2015;14(1):1–2.
Mohanty SK, Sahoo U, Rashmi R. Old-age dependency, and catastrophic health expenditure: evidence from Longitudinal Ageing Study in India. Int J Health Plann Manag. 2022;37(6):3148–71.
Aregbeshola BS, Khan SM. Out-of-pocket payments, catastrophic health expenditure and poverty among households in Nigeria 2010. Int J Health Policy Manage. 2018;7(9):798.
Fu XZ, Sun QW, Sun CQ, Xu F, He JJ. Urban-rural differences in catastrophic health expenditure among households with chronic non-communicable disease patients: evidence from China family panel studies. BMC Public Health. 2021;21(1):874.
Molla AA, Chi C, Mondaca AL. Predictors of high out-of-pocket healthcare expenditure: an analysis using Bangladesh household income and expenditure survey, 2010. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):1–8.
Rahman MM, Islam MR, Rahman MS, Hossain F, Alam A, Rahman MO, Jung J, Akter S. Forgone healthcare and financial burden due to out-of-pocket payments in Bangladesh: a multilevel analysis. Health Econ Rev. 2022;12(1):1–1.
Sayuti M, Sukeri S. Assessing progress towards sustainable development goal 3.8. 2 and determinants of catastrophic health expenditures in Malaysia. PLoS ONE. 2022;17(2):e0264422.
Hoque ME, Dasgupta SK, Naznin E, Al Mamun A. Household coping strategies for delivery and related healthcare cost: findings from rural Bangladesh. Tropical Med Int Health. 2015;20(10):1368–75.
Boing AC, Bertoldi AD, Barros AJ, Posenato LG, Peres KG. Socioeconomic inequality in catastrophic health expenditure in Brazil. Rev Saude Publica. 2014;48:632–41.
Aregbeshola BS, Khan SM. Determinants of catastrophic health expenditure in Nigeria. Eur J Health Econ. 2018;19:521–32.
Misra S, Awasthi S, Singh JV, Agarwal M, Kumar V. Assessing the magnitude, distribution, and determinants of catastrophic health expenditure in urban Lucknow, North India. Clin Epidemiol Global Health. 2015;3(1):10–6.
Rahman T, Gasbarro D, Alam K. Financial risk protection against non-communicable diseases: trends and patterns in Bangladesh. BMC Public Health. 2022;22(1):1835.
Kien VD, Minh HV, Ngoc NB, Phuong TB, Ngan TT, Quam MB. Inequalities in household catastrophic health expenditure and impoverishment associated with non-communicable diseases in Chi Linh, Hai Duong, Vietnam. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2017;29(5suppl):S35–44.
Sheikh N, Sarker AR, Sultana M, Mahumud RA, Ahmed S, Islam MT, Howick S, Morton A. Disease-specific distress healthcare financing and catastrophic out-of-pocket expenditure for hospitalization in Bangladesh. Int J Equity Health. 2022;21(1):114.
Zhao Y, Tang S, Mao W, Akinyemiju T. Socioeconomic and rural-urban differences in healthcare and catastrophic health expenditure among cancer patients in China: analysis of the China health and retirement longitudinal study. Front Public Health. 2022;9:779285.
Dang Y, Yang Y, Yang A, Cao S, Zhang J, Wang X, Lu J, Hu X. Factors influencing catastrophic health expenditure of households with people with diabetes in Northwest China-an example from Gansu Province. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023;23(1):1–4.
Si Y, Zhou Z, Su M, Wang X, Lan X, Wang D, Gong S, Xiao X, Shen C, Ren Y, Zhao D. Decomposing inequality in catastrophic health expenditure for self-reported hypertension household in Urban Shaanxi, China from 2008 to 2013: two waves’ cross-sectional study. Bmj Open. 2019;9(5):e023033.
Chowdhury AS, Ahmed MS, Ahmed S, Khanam F, Farjana F, Reza S, Islam S, Islam A, Khan JA, Rahman M. Estimating catastrophic costs due to pulmonary tuberculosis in Bangladesh. J Epidemiol Global Health. 2021;11(1):83.
Jung H, Yang J, Kim E, Lee J. The effect of mid-to-long-term hospitalization on the catastrophic health expenditure: focusing on the mediating effect of earned income loss. In Healthcare 2021 Aug 7 (Vol. 9, No. 8, p. 1013). MDPI.
Begum A, Hamid SA. Impoverishment impact of out-of-pocket payments for healthcare in rural Bangladesh: do the regions facing different climate change risks matter? PLoS ONE. 2021;16(6):e0252706.
Yazdi-Feyzabadi V, Bahrampour M, Rashidian A, Haghdoost AA, Akbari Javar M, Mehrolhassani MH. Prevalence and intensity of catastrophic health care expenditures in Iran from 2008 to 2015: a study on Iranian household income and expenditure survey. Int J Equity Health. 2018;17:1–3.
Koris R, Nor NM, Haron SA, Ismail NW, Junid SM, Nur AM, Shafie AA, Yusoff S, Maimaiti N. Socio-demographic, cognitive status and Comorbidity Determinants of Catastrophic Health expenditure among Elderly in Malaysia. Int J Econ Manage. 2017;11.
Ghimire M, Ayer R, Kondo M. Cumulative incidence, distribution, and determinants of catastrophic health expenditure in Nepal: results from the living standards survey. Int J Equity Health. 2018;17(1):1–2.
Duan W, Zhang W, Wu C, Wang Q, Yu Y, Lin H, Liu Y, Hu D. Extent and determinants of catastrophic health expenditure for tuberculosis care in Chongqing municipality, China: a cross-sectional study. BMJ open. 2019;9(4):e026638.
Ahmed S, Ahmed MW, Hasan MZ, Mehdi GG, Islam Z, Rehnberg C, Niessen LW, Khan JA. Assessing the incidence of catastrophic health expenditure and impoverishment from out-of-pocket payments and their determinants in Bangladesh: evidence from the nationwide Household Income and Expenditure Survey 2016. Int Health. 2022;14(1):84–96.
Fu Y, Chen M, Si L. Multimorbidity and catastrophic health expenditure among patients with diabetes in China: a nationwide population-based study. BMJ Global Health. 2022;7(2):e007714.
Khan JA, Ahmed S, Evans TG. Catastrophic healthcare expenditure and poverty related to out-of-pocket payments for healthcare in Bangladesh—an estimation of financial risk protection of universal health coverage. Health Policy Plann. 2017;32(8):1102–10.
Yadav J, Menon GR, John D. Disease-specific out-of-pocket payments, catastrophic health expenditure and impoverishment effects in India: an analysis of National Health Survey data. Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2021;19:769–82.
Miao W, Zhang X, Shi B, Tian W, Wu B, Lai Y, Li Y, Huang Z, Xia Q, Yang H, Ding F. Multi-dimensional vulnerability analysis on catastrophic health expenditure among middle-aged and older adults with chronic diseases in China. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2022;22(1):151.
Mwai D, Muriithi M. Catastrophic health expenditure and household impoverishment: a case of NCDs prevalence in Kenya. Epidemiol Biostatistics Public Health. 2016;13(1).
Dalui A, Banerjee S, Roy R. Determinants of out-of-pocket and catastrophic health expenditure in rural population: a community-based study in a block of Purba Barddhaman, West Bengal. Indian J Public Health. 2020;64(3):223.
Zhen X, Zhang H, Hu X, Gu S, Li Y, Gu Y, Huang M, Sun X, Wei J, Dong H. A comparative study of catastrophic health expenditure in Zhejiang and Qinghai province, China. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18:1–8.
Bashir S, Kishwar S. Incidence and determinants of catastrophic health expenditures and impoverishment in Pakistan. Public Health. 2021;197:42–7.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Choi JW, Choi JW, Kim JH, Yoo KB, Park EC. Association between chronic disease and catastrophic health expenditure in Korea. BMC Health Serv Res. 2015;15:1–8.
Wang Y, Du M, Qin C, Liu Q, Yan W, Liang W, Liu M, Liu J. Associations among socioeconomic status, multimorbidity of non-communicable diseases, and the risk of household catastrophic health expenditure in China: a population-based cohort study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023;23(1):1–1.
Dorjdagva J, Batbaatar E, Svensson M, Dorjsuren B, Kauhanen J. Catastrophic health expenditure and impoverishment in Mongolia. Int J Equity Health. 2016;15(1):1–9.
Haque MF, Islam AN, Pervin S, Akter E, Hasan MM. Catastrophic Health Expenditure, Distress Financing and Impoverishment due to out-of-Pocket expenses for Healthcare among patients with chronic liver disease: a cross-sectional study among hospitalized patients in Bangladesh. J Health Med Sci. 2021;4(1).
Islam MS, Harvey LA, Hossain MS, Rahman MA, Costa PD, Liu H, Muldoon S, Taylor V, Billot L, Lindley RI, Biering-Sorensen F. The cost of providing a community-based model of care to people with spinal cord injury, and the healthcare costs and economic burden to households of spinal cord injury in Bangladesh. Spinal Cord. 2021;59(8):833–41.
Azzani M, Yahya A, Roslani AC, Su TT. Catastrophic health expenditure among colorectal cancer patients and families: a case of Malaysia. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2017;29(6):485–94.
Datta BK, Husain MJ, Asma S. Assessing the relationship between out-of-pocket spending on blood pressure and diabetes medication and household catastrophic health expenditure: evidence from Pakistan. Int J Equity Health. 2019;18(1):1–2.
Thu Thuong NT, Van Den Berg Y, Huy TQ, Tai DA, Anh BN. Determinants of catastrophic health expenditure in Vietnam. Int J Health Plann Manag. 2021;36(2):316–33.
Kim Y, Yang B. Relationship between catastrophic health expenditures and household incomes and expenditure patterns in South Korea. Health Policy. 2011;100(2–3):239–46.
Wang Z, Li X, Chen M. Catastrophic health expenditures and its inequality in elderly households with chronic disease patients in China. Int J Equity Health. 2015;14:1–1.
World Health Organization. Bangladesh health system review. WHO Regional Office for the Western Pacific; 2015.
Download references
The authors are expressing gratitude toward the Prime Minister’s Education Assistance Trust for supporting the Doctoral research of the first author under the supervision of the other authors. The authors are also thankful to Khulna University for providing the article processing charge through the High Impact Factor Journal Publication Grants scheme (Number: HIFJPG_e01_01/2024).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Economics Discipline, Khulna University, Khulna, Bangladesh
Kaniz Fatima Mohsin, Md. Nasif Ahsan & Mohammed Ziaul Haider
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conception and design: KFM, NA; Data extraction: NA; Assessing full text articles: KFM, NA; Inclusion of literatures: KFM, NA, ZH; Analysis and interpretation: KFM, NA, ZH; Drafting of the article: KFM, NA, ZH; Final approval of the article: KFM, NA, ZH.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Kaniz Fatima Mohsin or Md. Nasif Ahsan .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Mohsin, K.F., Ahsan, M.N. & Haider, M.Z. Understanding variation in catastrophic health expenditure from socio-ecological aspect: a systematic review. BMC Public Health 24 , 1504 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18579-7
Download citation
Received : 06 January 2024
Accepted : 12 April 2024
Published : 05 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18579-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Socio-ecological
- Out-of-Pocket payment
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The systematic review of the literature in health and social care has a differ-ent focus. It aims to contribute to clinical practice through an assessment of the efficacy of a particular health care intervention and, with the emphasis on evidence-based practice, has become increasingly important. A basic overview
This best-selling book is a step-by-step guide to doing a literaturereview for students in all areas of health and social care. It is vitalreading for all those doing their undergraduate dissertation or anystudy that involves doing a literature review.This book provides a practical guide to doing a literature reviewfrom start to finish. This fourth edition includes:• A broad range of real ...
This step-by-step guide takes the reader logically through the process of undertaking a literature review, from determining when this methodology might be useful, through to publishing the findings. It is designed particularly for students undertaking a dissertation using literature review methodology. However, it also caters to practitioners ...
This best-selling book, now in its fifth edition, is a step-by-step guide to doing a literature review for students in all areas of health and social care. It is essential reading for all those doing their undergraduate dissertation or any study that involves doing a literature review. The new edition maintains its signature 'can do ...
LITERATURE REVIEWS are an important preliminary step towards a research project or dissertation, as well as being an important source of information in their own right. ... Doing a Literature Review in Health and Social Care A Practical Guide Second edition Helen Aveyard Doing a Literature Review in Health and Social Care A Practical Guide ...
A literature review: Finds existing literature/sources published on a specific topic/to answer a review question. Brings together the literature sources into a single body of literature. Makes comparisons between the different included sources to identify both patterns/similarities and conflicts/differences. Within healthcare literature reviews ...
A literature review differs from a systematic review, which addresses a specific clinical question by combining the results of multiple clinical trials (an article on this topic will follow as part of this series of publications). ... Your Undergraduate Dissertation in Health and Social Care: The Essential Guide for Success. 2009. SAGE Research ...
78 Doing a literature review in nursing, health anD soCial Care include studies not directly related to that subheading and find they have moved away from the original theme. It is important, therefore, to constantly check that the findings being discussed are connected to the title of that theme.
Third Edition. A clear and practical guide to completing a literature review in nursing and healthcare studies. Providing students with straightforward guidance on how to successfully carry out a literature review as part of a research project or dissertation, this book uses examples and activities to demonstrate how to complete each step ...
Books. Doing a Literature Review in Health and Social Care. Helen Aveyard. McGraw-Hill Companies,Incorporated, Aug 1, 2007 - Reference - 148 pages. Why do a literature review? What literature is relevant? How do I appraise my findings? How do I present my literature review? This step-by-step guide simplifies the process of reviewing published ...
This book provides a concise and informative guide to the process of literature review in nursing, health and social care, and is applicable to students and professionals. ... Doing a Literature Review in Nursing, Health and Social Care (Second edition) Coughlan Michael and Cronin Patricia Doing a Literature Review in Nursing, Health and Social ...
2. Scope the Literature. A "scoping search" investigates the breadth and/or depth of the initial question or may identify a gap in the literature. Eligible studies may be located by searching in: Background sources (books, point-of-care tools) Article databases; Trial registries; Grey literature; Cited references; Reference lists
Doing a Literature Review in Health and Social Care, 3rd Edition is essential reading for students at all levels within the health and social care field and a useful text for anyone new to reviewing and appraising evidence. Amazon reviews for the 2nd edition: "This really helped me complete my dissertation. Well set out, easy to understand and ...
Purpose and Importance of the Literature Review. An understanding of the current literature is critical for all phases of a research study. Lingard 9 recently invoked the "journal-as-conversation" metaphor as a way of understanding how one's research fits into the larger medical education conversation. As she described it: "Imagine yourself joining a conversation at a social event.
Published 21 September 2015. Medicine, Education. This bestselling book is a step-by-step guide to doing a literature review in health and social care. It is vital reading for all those undertaking their undergraduate or postgraduate dissertation or any research module which involves a literature review. No Paper Link Available. Save to Library.
Prior to that she completed her doctoral study at King's College University of London. She is co-author of two other books: A Beginner's Guide to Evidence-Based Practice in Health and Social Care, 2nd edition and A Beginner's Guide to Critical Thinking and Writing in Health and Social Care.
"Doing a Literature Review in Health and Social Care: A Practical Guide." Social Work Education, 31(8), pp. 1105-1106
This text is a comprehensive, highly readable guide to how to undertake a literature review in health and social care, tailored specifically for postgraduate study. Essential reading for all those undertaking any study at post-graduate level, the book provides clarity and a step by step approach to doing a literature review from start to finish which will enable you to:• Identify which type ...
Systematic reviews that summarize the available information on a topic are an important part of evidence-based health care. There are both research and non-research reasons for undertaking a literature review. It is important to systematically review the literature when one would like to justify the need for a study, to update personal ...
In short, a literature review is the comprehensive study and interpretation of litera-ture that relates to a particular topic. When you undertake a literature review, you identify a research question then seek to answer this ques-tion by searching for and analysing relevant literature. This review leads you to the development of new insights ...
To ensure that this literature review would be sensitive to picking up studies pertaining to relevant IHSC services, ... For the purpose of this review, 'integrated health and social care' is defined as 'two or more organisations, each from a separate sector, work together to deliver health and social care well-being services (e.g. healthcare ...
Remember, the literature review is an iterative process. You may need to revisit parts of this search, find new or additional information, or update your research question based on what you find. 7. Provide a synthesis and overview of the literature; this can be organized by themes or chronologically.
The community-care sector facilitates the coordination and administration of in-home and community-based health and social services. Community-care services include supports for independent living, residential services, complex medical care, and community-participation services to support personal and professional goals (e.g., education, employment, and recreation-based supports) [].
The literature review in healthcare provides valuable insights into various aspects of hospital management strategy and organization. ... aims to systematically collect social information in ...
Abstract. Aim: The aim of this paper is to review the literature on life story work in health and social care practice. Background: Life story work as an intervention has been used with a number of health and social care clients, such as children people with learning disabilities, older people on medical wards and with older people who have ...
The aim of this contribution is to review the latest explanations of health behavior change initiation and maintenance based on novel insights into motivation and reward mechanisms. Based on a systematic literature search in PubMed, PsycInfo, and Google Scholar, four articles were reviewed.
This scoping review aims to identify intersectoral health interventions implemented in primary care and community settings to improve the well-being and health of people living with type 2 diabetes. Introduction Intersectoral collaboration is a collaborative approach between the health sectors and other sectors to address the interdependent nature of the social determinants of health ...
This gave families little hope or relief in placing their children in out-of-home care. A literature review by Brien , which demonstrates the competency and agency of children and young people with disabilities to make choices in their own lives, contradicts the deficit-based assumption in care arrangements about children and young people's ...
Out-of-pocket (OOP) payment is one of many countries' main financing options for health care. High OOP payments push them into financial catastrophe and the resultant impoverishment. The infrastructure, society, culture, economic condition, political structure, and every element of the physical and social environment influence the intensity of financial catastrophes in health expenditure.