Jump to navigation

- Undergraduate Admissions
- Transfer Admissions
- Graduate Admissions
- Honors and Scholars Admissions
- International Admissions
- Law Admissions
- Office of Financial Aid
- Orientation
- Pre-College Programs
- Scholarships
- Tuition & Fees
- Academic Calendar
- Academic Colleges
- Degree Programs
- Online Programs
- Class Schedule
- Workforce Development
- Sponsored Programs and Research Services
- Technology Transfer
- Faculty Expertise Database
- Research Centers
- College of Graduate Studies
- Institutional Research and Analysis
- At a Glance
- Concerned Vikes
- Free Speech on Campus
- Policies and Procedures
- Messages & Updates
- In the News
- Board of Trustees
- Senior Leadership Team
- Services Near CSU


Cleveland State University
Search this site
Critical reading: what is critical reading, and why do i need to do it.
Critical reading means that a reader applies certain processes, models, questions, and theories that result in enhanced clarity and comprehension. There is more involved, both in effort and understanding, in a critical reading than in a mere "skimming" of the text. What is the difference? If a reader "skims" the text, superficial characteristics and information are as far as the reader goes. A critical reading gets at "deep structure" (if there is such a thing apart from the superficial text!), that is, logical consistency, tone, organization, and a number of other very important sounding terms.
What does it take to be a critical reader? There are a variety of answers available to this question; here are some suggested steps:
1. Prepare to become part of the writer's audience.
After all, authors design texts for specific audiences, and becoming a member of the target audience makes it easier to get at the author's purpose. Learn about the author, the history of the author and the text, the author's anticipated audience; read introductions and notes.
2. Prepare to read with an open mind.
Critical readers seek knowledge; they do not "rewrite" a work to suit their own personalities. Your task as an enlightened critical reader is to read what is on the page, giving the writer a fair chance to develop ideas and allowing yourself to reflect thoughtfully, objectively, on the text.
3. Consider the title.
This may seem obvious, but the title may provide clues to the writer's attitude, goals, personal viewpoint, or approach.
4. Read slowly.
Again, this appears obvious, but it is a factor in a "close reading." By slowing down, you will make more connections within the text.
5. Use the dictionary and other appropriate reference works.
If there is a word in the text that is not clear or difficult to define in context: look it up. Every word is important, and if part of the text is thick with technical terms, it is doubly important to know how the author is using them.
6. Make notes.
Jot down marginal notes, underline and highlight, write down ideas in a notebook, do whatever works for your own personal taste. Note for yourself the main ideas, the thesis, the author's main points to support the theory. Writing while reading aids your memory in many ways, especially by making a link that is unclear in the text concrete in your own writing.
7. Keep a reading journal
In addition to note-taking, it is often helpful to regularly record your responses and thoughts in a more permanent place that is yours to consult. By developing a habit of reading and writing in conjunction, both skills will improve.
Critical reading involves using logical and rhetorical skills. Identifying the author's thesis is a good place to start, but to grasp how the author intends to support it is a difficult task. More often than not an author will make a claim (most commonly in the form of the thesis) and support it in the body of the text. The support for the author's claim is in the evidence provided to suggest that the author's intended argument is sound, or reasonably acceptable. What ties these two together is a series of logical links that convinces the reader of the coherence of the author's argument: this is the warrant. If the author's premise is not supportable, a critical reading will uncover the lapses in the text that show it to be unsound.
Questions, comments, and other sundry things may be sent to [email protected]
[Top of Page]
©2024 Cleveland State University | 2121 Euclid Avenue, Cleveland, OH 44115-2214 | (216) 687-2000. Cleveland State University is an equal opportunity educator and employer. Affirmative Action | Diversity | Employment | Tobacco Free | Non-Discrimination Statement | Web Privacy Statement | Accreditations

Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research
In Between the Lines: A Guide to Reading Critically
I often find that Princeton professors assume that we all know how to “read critically.” It’s a phrase often included in essay prompts, and a skill necessary to academic writing. Maybe we’re familiar with its definition: close examination of a text’s logic, arguments, style, and other content in order to better understand the author’s intent. Reading non-critically would be identifying a metaphor in a passage, whereas the critical reader would question why the author used that specific metaphor in the first place. Now that the terminology is clarified, what does critical reading look like in practice? I’ve put together a short guide on how I approach my readings to help demystify the process.
- Put on your scholar hat. Critical reading starts before the first page. You should assume that the reading in front of you was the product of several choices made by the author, and that each of these choices is subject to analysis. This is a critical mindset, but importantly, not a negative one. Not taking a reading at face value doesn’t mean approaching the reading hoping to find everything that’s wrong, but rather what could be improved .
- Revisit Writing Sem : Motive and thesis are incredibly helpful guides to understanding tough academic texts. Examining why the author is writing this text (motive), provides a context for the work that follows. The thesis should be in the back of your mind at all times to understand how the evidence presented proves it, but simultaneously thinking about the motive allows you to think about what opponents to the author might say, and then question how the evidence would stand up to these potential rebuttals.
- Get physical . Take notes! Critical reading involves making observations and insights—track them! My process involves underlining, especially as I see recurring terms, images, or themes. As I read, I also like to turn back and forth constantly between pages to link up arguments. I was reading a longer legal text for a class and found that flipping back and forth helped me clarify the ideas presented in the beginning of the text so I could track their development in later pages.
- Play Professor. While I’m reading, I like to imagine potential discussion or essay topics I would come up with if I were a professor. These usually involves examining the themes of the text, placing this text in comparison or contrast with another one we have read in the class, and paying close attention to how the evidence attempts to prove the thesis.
- Form an (informed) opinion. After much work, underlining, and debating, it’s safe to make your own judgments about the author’s work. In forming this opinion, I like to mentally prepare to have this opinion debated, which helps me complicate my own conclusions—a great start to a potential essay!
Critical reading is an important prerequisite for the academic writing that Princeton professors expect. The best papers don’t start with the first word you type, but rather how you approach the texts composing your essay subject. Hopefully, this guide to reading critically will help you write critically as well!
–Elise Freeman, Social Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr


- LEARNING SKILLS
- Study Skills
- Critical Reading
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Learning Skills:
- A - Z List of Learning Skills
- What is Learning?
- Learning Approaches
- Learning Styles
- 8 Types of Learning Styles
- Understanding Your Preferences to Aid Learning
- Lifelong Learning
- Decisions to Make Before Applying to University
- Top Tips for Surviving Student Life
- Living Online: Education and Learning
- 8 Ways to Embrace Technology-Based Learning Approaches
- Critical Thinking Skills
- Critical Thinking and Fake News
- Understanding and Addressing Conspiracy Theories
- Critical Analysis
- Top Tips for Study
- Staying Motivated When Studying
- Student Budgeting and Economic Skills
- Getting Organised for Study
- Finding Time to Study
- Sources of Information
- Assessing Internet Information
- Using Apps to Support Study
- What is Theory?
- Styles of Writing
- Effective Reading
- Note-Taking from Reading
- Note-Taking for Verbal Exchanges
- Planning an Essay
- How to Write an Essay
- The Do’s and Don’ts of Essay Writing
- How to Write a Report
- Academic Referencing
- Assignment Finishing Touches
- Reflecting on Marked Work
- 6 Skills You Learn in School That You Use in Real Life
- Top 10 Tips on How to Study While Working
- Exam Skills
Get the SkillsYouNeed Study Skills eBook

Part of the Skills You Need Guide for Students .
- Writing a Dissertation or Thesis
- Research Methods
- Teaching, Coaching, Mentoring and Counselling
- Employability Skills for Graduates
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Critical Reading and Reading Strategy
What is critical reading.
Reading critically does not, necessarily, mean being critical of what you read.
Both reading and thinking critically don’t mean being ‘ critical ’ about some idea, argument, or piece of writing - claiming that it is somehow faulty or flawed.
Critical reading means engaging in what you read by asking yourself questions such as, ‘ what is the author trying to say? ’ or ‘ what is the main argument being presented? ’
Critical reading involves presenting a reasoned argument that evaluates and analyses what you have read. Being critical, therefore - in an academic sense - means advancing your understanding , not dismissing and therefore closing off learning.
See also: Listening Types to learn about the importance of critical listening skills.
To read critically is to exercise your judgement about what you are reading – that is, not taking anything you read at face value.
When reading academic material you will be faced with the author’s interpretation and opinion. Different authors will, naturally, have different slants. You should always examine what you are reading critically and look for limitations, omissions, inconsistencies, oversights and arguments against what you are reading.
In academic circles, whilst you are a student, you will be expected to understand different viewpoints and make your own judgements based on what you have read.
Critical reading goes further than just being satisfied with what a text says, it also involves reflecting on what the text describes, and analysing what the text actually means, in the context of your studies.
As a critical reader you should reflect on:
- What the text says: after critically reading a piece you should be able to take notes, paraphrasing - in your own words - the key points.
- What the text describes: you should be confident that you have understood the text sufficiently to be able to use your own examples and compare and contrast with other writing on the subject in hand.
- Interpretation of the text: this means that you should be able to fully analyse the text and state a meaning for the text as a whole.
Critical reading means being able to reflect on what a text says, what it describes and what it means by scrutinising the style and structure of the writing, the language used as well as the content.
Critical Thinking is an Extension of Critical Reading
Thinking critically, in the academic sense, involves being open-minded - using judgement and discipline to process what you are learning about without letting your personal bias or opinion detract from the arguments.
Critical thinking involves being rational and aware of your own feelings on the subject – being able to reorganise your thoughts, prior knowledge and understanding to accommodate new ideas or viewpoints.
Critical reading and critical thinking are therefore the very foundations of true learning and personal development.
See our page: Critical Thinking for more.
Developing a Reading Strategy
You will, in formal learning situations, be required to read and critically think about a lot of information from different sources.
It is important therefore, that you not only learn to read critically but also efficiently.
The first step to efficient reading is to become selective.
If you cannot read all of the books on a recommended reading list, you need to find a way of selecting the best texts for you. To start with, you need to know what you are looking for. You can then examine the contents page and/or index of a book or journal to ascertain whether a chapter or article is worth pursuing further.
Once you have selected a suitable piece the next step is to speed-read.
Speed reading is also often referred to as skim-reading or scanning. Once you have identified a relevant piece of text, like a chapter in a book, you should scan the first few sentences of each paragraph to gain an overall impression of subject areas it covers. Scan-reading essentially means that you know what you are looking for, you identify the chapters or sections most relevant to you and ignore the rest.
When you speed-read you are not aiming to gain a full understanding of the arguments or topics raised in the text. It is simply a way of determining what the text is about.
When you find a relevant or interesting section you will need to slow your reading speed dramatically, allowing you to gain a more in-depth understanding of the arguments raised. Even when you slow your reading down it may well be necessary to read passages several times to gain a full understanding.
See also: Speed-Reading for Professionals .
Following SQ3R
SQ3R is a well-known strategy for reading. SQ3R can be applied to a whole range of reading purposes as it is flexible and takes into account the need to change reading speeds.
SQ3R is an acronym and stands for:
This relates to speed-reading, scanning and skimming the text. At this initial stage you will be attempting to gain the general gist of the material in question.
It is important that, before you begin to read, you have a question or set of questions that will guide you - why am I reading this? When you have a purpose to your reading you want to learn and retain certain information. Having questions changes reading from a passive to an active pursuit. Examples of possible questions include:
- What do I already know about this subject?
- How does this chapter relate to the assignment question?
- How can I relate what I read to my own experiences?
Now you will be ready for the main activity of reading. This involves careful consideration of the meaning of what the author is trying to convey and involves being critical as well as active.
Regardless of how interesting an article or chapter is, unless you make a concerted effort to recall what you have just read, you will forget a lot of the important points. Recalling from time to time allows you to focus upon the main points – which in turn aids concentration. Recalling gives you the chance to think about and assimilate what you have just read, keeping you active. A significant element in being active is to write down, in your own words, the key points.
The final step is to review the material that you have recalled in your notes. Did you understand the main principles of the argument? Did you identify all the main points? Are there any gaps? Do not take for granted that you have recalled everything you need correctly – review the text again to make sure and clarify.
Continue to: Effective Reading Critical Thinking
See also: Critical Analysis Writing a Dissertation Critical Thinking and Fake News

2a. Critical Reading
An introduction to reading in college.
While the best way to develop your skills as a writer is to actually practice by writing, practicing critical reading skills is crucial to becoming a better college writer. Careful and skilled readers develop a stronger understanding of topics, learn to better anticipate the needs of the audience, and pick up sophisticated writing “maneuvers” and strategies from professional writing. A good reading practice requires reading text and context, which you’ll learn more about in the next section. Writing a successful academic essay also begins with critical reading as you explore ideas and consider how to make use of sources to provide support for your writing.
Questions to ask as you read
If you consider yourself a particularly strong reader or want to improve your reading comprehension skills, writing out notes about a text—even if it’s in shorthand—helps you to commit the answers to memory more easily. Even if you don’t write out all these notes, answering these basic questions about any text or reading you encounter in college will help you get the most out of the time you put into your reading. It will also give you more confidence to understand and question the text while you read.
- Is there context provided about the author and/or essay? If so, what stands out as important?
Context in this instance means things like dates of publication, where the piece was originally published, and any biographical information about the author. All of that information will be important for developing a critical reading of the piece, so track what’s available as you read.
- If you had to guess, who is the author’s intended audience ? Describe them in as much detail as possible.
Sometimes the author will state who the audience is, but sometimes you have to figure it out by context clues, such as those you tracked above. For instance, the audience for a writer on Buzzfeed is very different from the audience for a writer for the Wall Street Journal —and both writers know that, which means they’re more effective at reaching their readers. Learning how to identify your audience is a crucial writing skill for all genres of writing.
- In your own words, what is the question the author is trying to answer in this piece? What seems to have caused them to write in the first place?
In nonfiction writing of the kind we read in Writing 121, writers set out to answer a question. Their thesis/main argument is usually the answer to the question, so sometimes you can “reverse engineer” the question from that. Often, the question is asked in the title of the piece.
- In your own words, what’s the author’s main idea or argument ? If you had to distill it down to one or two sentences, what does the author want you, the reader, to agree with?
If you’ve ever had to write a paper for a class, you’re probably familiar with a thesis or main argument. Published writers also have a thesis (or else they don’t get published!), but sometimes it can be tricky to find in a more sophisticated piece of writing. Trying to put the main argument into your own words can help.
- How many examples and types of evidence did the author provide to support the main argument? Which examples/evidence stood out to you as persuasive?
It’s never enough to just make a claim and expect people to believe it—we have to support that claim with evidence. The types of evidence and examples that will be persuasive to readers depends on the audience, though, which is why it’s important to have some idea of your readers and their expectations.
- Did the author raise any points of skepticism (also known as counterarguments)? Can you identify exactly what page or paragraph where the author does this?
As we’ll see later when the writing process, respectfully engaging with points of skepticism and counterarguments builds trust with the reader because it shows that the writer has thought about the issue from multiple perspectives before arriving at the main argument. Raising a counterargument is not enough, though. Pay careful attention to how the writer responds to that counterargument—is it an effective and persuasive response? If not, perhaps the counterargument has more merit for you than the author’s main argument.
- In your own words, how does the essay conclude ? What does the author “want” from us, the readers?
A conclusion usually offers a brief summary of the main argument and some kind of “what’s next?” appeal from the writer to the audience. The “what’s next?” appeal can take many forms, but it’s usually a question for readers to ponder, actions the author thinks people should take, or areas related to the main topic that need more investigation or research. When you read the conclusion, ask yourself, “What does the author want from me now that I’ve read their essay?”
Reading Like Writers: Critical Reading
Reading as a creative act.
“The theory of books is noble. The scholar of the first age received into him the world around; brooded thereon; gave it the new arrangement of his own mind, and uttered it again. It came into him life; it went out from him truth. It came to him short-lived actions; it went out from him immortal thoughts. It came to him business; it went from him poetry. It was dead fact; now, it is quick thought. It can stand, and it can go. It now endures, it now flies, it now inspires. Precisely in proportion to the depth of mind from which it issued, so high does it soar, so long does it sing.” ~Ralph Waldo Emerson, “The American Scholar”
- Consider the discourse community when you read and write in your college classes
- Analyze any reading for text and context
- Read like a writer so you can write for your readers

By the end of this lesson, you’ll be able to apply the concept of discourse community to honing your college-level critical reading skills.
Good writers are good readers, so let’s start there. When you can confidently identify the audience, context, and purpose of a text —position it within its discourse community—you’ll be a stronger, savvier reader.
Strong, savvy readers are more effective writers because they consider their own audience, context, and purpose when they write and communicate, which makes their writing clearer and to the point.
So the goal of this lesson is to help you read like a writer!
The Savvy Reader
Good writers are good readers! And good readers. . .

- get to know the author
- get to know the author’s community + audience
- accurately summarize the author’s argument
- look up terms you don’t know
- “listen” respectfully to the author’s point of view
- have a sense of the larger conversation
- think about other issues related to the conversation
- put it in current context
- analyze and assess the author’s reasoning, evidence, and assumptions
Why read critically? While the best way to develop your skills as a writer is to actually practice by writing, practicing critical reading skills is crucial to becoming a better writer. Careful and skilled readers develop a stronger understanding of topics, learn to better anticipate the needs of the audience, and pick up writing “maneuvers” and strategies from professional writing.
Reading Like Writers
How do you read like a writer? When you read like a writer, you are practicing deeper reading comprehension. In order to understand a text, you are reading not just what’s in it but what’s around it, too: text and context.
Practice: Reading Like Writers
In-class discussion : Advertisements are helpful for practicing reading like writers because advertisers make deliberate choices with text and images based on audience (target consumer), context (where they are reaching them), and purpose (buy this product).
- But I’m not trying to sell a product! How can I use my newfound understanding of audience, context, and purpose to improve my writing?
It’s true! You aren’t selling a product. You aren’t (I hope) trying to manipulate your audience. You aren’t relying on discriminatory assumptions or stereotypes to appeal to your audience. But when you write, let’s say, an essay, you are asking readers to “buy into” your point of view. The goal doesn’t have to be for them to agree with you; it can be for your readers to respectfully consider, understand, or sympathize with your point of view or analysis of an issue. The point is you’re thinking of your reader when you write, and that will make your writing process smoother and your writing clearer.
Writing for Your Readers
When you write for your readers, you. . .
- Learn from your reading and communication experience: What makes texts work? How are ideas conveyed clearly?
- Analyze the writing situation: What are the goals and purpose for a writing project? Who is your audience?
- Explore and play as you draft: What are different ways to respond? Can you use a better word or phrase?
- Consider your audience: What might a reader expect to see? What does your reader need to understand your point of view? What questions might a reader have?

Writing as a process of inquiry
Just as you want your readers to take you seriously, you want to approach texts with an open and curious mind. Whatever the topic, it was important enough for this person to want to write on it. While we don’t have to agree with the point someone is making, we can respect their opinion and appreciate reading a different perspective.
Approach reading and writing in college in a learning zone. Be open, be curious, ask questions, seek answers. Share, stretch, experiment.
Guides and Worksheets
- Use this guide for any of your college reading!
- Learn a basic study skill–annotating or taking notes on your readings
Critical Reading Guide: Text + Context
Title of the text: Author:
Reading the text: Comprehension
Main idea . In one sentence, summarize the main point or argument of the text.
Claim . Identify one claim in the text.
Key points . Paraphrase a key point, example, or passage that interested you.
Evidence . In your own words, describe 1-2 compelling examples or pieces of evidence that support the point/argument of the text.
Conclusion . What is the ultimate takeaway the text gives us on the topic/issue?
Personal experience . What is your experience of the topic? Have you had problems related to it?
Vocabulary . What is a word or phrase in the text you didn’t know? Look it up. What does it mean?
Inquiry . What is one thing you need more information about? Or, what is one question you have about the content of the text?
Reading for context: Rhetorical analysis
The author . Do an internet search on the author. What did you find out?
Ethos . Do you trust the author on the topic/issue? Why or why not?
Container . When and where was the text first published? Who will read/see it?
Audience . How does the author address or appeal to their readers? What tone does the author use in the text?
Bias . What knowledge, values, or beliefs does the author assume the reader shares?
Types of evidence . What types of evidence does the author use? Types of evidence include facts, examples, statistics, statements by authorities (references to or quotes from other sources), interviews, observations, logical reasoning, and personal experience
Structure . How does the author organize the text?
Purpose . What question does the author seek to answer in the text? In other words, why do you think they wrote this piece?
Mark-up Assignment: The Savvy Reader Practice
The object is to fill the empty space of the margins with your thoughts and questions to the text. By reading sympathetically (reading to understand what the writer is saying) and critically (reading to analyze and critique what the writer is saying), you are reading mindfully and creatively. You are finding those passages that you are drawn to, asking questions that you have, and beginning to develop your reaction, response, and ideas about a topic or issue. It’s a useful tool in the “getting started” phase of the writing process. Learning how to read effectively will be an invaluable skill in your college career and beyond because it means engaging in a task actively rather than passively.
Choose 1-2 paragraphs from READING X to fully annotate. This passage should be one that interests you, i.e. seems important, confusing, and/or prompted agreement, disagreement, or questions for you.
- Circle any word you think is crucial for the passage, including ones you cannot easily define.
- Underline phrases or images you think crucial for the meaning of the passage/essay.
- Put a bracket around ideas or assertions you find puzzling or questionable.
- Then write notes around the margins of the passage defining these terms, identifying the important ideas, or raising questions with the bracketed phrases. For each item you have circled, underlined, or bracketed, there should be a margin note. For this assignment, your margin notes should be substantive: they should meaty statements and full questions.
Photocopy or clear, legible photograph of paragraphs with your annotations or type up the paragraphs and annotate.
Writing as Inquiry Copyright © 2021 by Kara Clevinger and Stephen Rust is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Reading Critically and Actively
Critical reading is a vital part of the writing process. In fact, reading and writing processes are alike. In both, you make meaning by actively engaging a text. As a reader, you are not a passive participant, but an active constructor of meaning. Exhibiting an inquisitive, "critical" attitude towards what you read will make anything you read richer and more useful to you in your classes and your life. This guide is designed to help you to understand and engage this active reading process more effectively so that you can become a better critical reader.
Reading a Text--Some Definitions
You might think that reading a text means curling up with a good book, or forcing yourself to study a textbook. Actually, reading a text can mean much more. First of all, let's define the two terms of interest here--"reading" and "text."
What Counts as Reading?
Reading is something we do with books and other print materials, certainly, but we also read things like the sky when we want to know what the weather is doing, someone's expression or body language when we want to know what someone is thinking or feeling, or an unpredictable situation so we'll know what the best course of action is. As well as reading to gather information, "reading" can mean such diverse things as interpreting, analyzing, or attempting to make predictions.
What Counts as a Text?
When we think of a text, we may think of words in print, but a text can be anything from a road map to a movie. Some have expanded the meaning of "text" to include anything that can be read, interpreted or analyzed. So a painting can be a text to interpret for some meaning it holds, and a mall can be a text to be analyzed to find out how modern Americans behave in their free time.
How Do Readers Read?
Those who study the way readers read have come up with some different theories about how readers make meaning from the texts they read.
Being aware of how readers read is important so that you can become a more critical reader. In fact, you may discover that you are already a critical reader.
The Reading Equation
Prior Knowledge + Predictions = Comprehension
When we read, we don't decipher every word on the page for its individual meaning. We process text in chunks, and we also employ other "tricks" to help us make meaning out of so many individual words in a text we are reading. First, we bring prior knowledge to everything we read, whether we are aware of it or not. Titles of texts, authors' names, and the topic of the piece all trigger prior knowledge in us. The more prior knowledge we have, the better prepared we are to make meaning of the text. With prior knowledge we make predictions, or guesses about how what we are reading relates to our prior experience. We also make predictions about what meaning the text will convey.
Related Information: How can Reaching Comprehension Make Us Better Writers?
When you have successfully comprehended the text you are reading, you should take this comprehension one step further and try to apply it to your writing process. Good writers know that readers have to work to make meaning of texts, so they will try to make the reader's journey through the text as effortless as possible. As a writer you can help readers tap into prior knowledge by clearly outlining your intent in the introduction of your paper and making use of your own personal experience. You can help readers make accurate guesses by employing clear organization and using clear transitions in your paper.
Related Information: Making Predictions
Whether you realize it or not, you are always making guesses about what you will encounter next in a text. Making predictions about where a text is headed is an important part of the comprehension equation. It's alright to make wrong guesses about what a text will do--wrong guesses are just as much a part of the meaning-making process of reading as right guesses are.
Related Information: Tapping into Prior Knowledge
It's important to tap into your prior knowledge of subject before you read about it. Writing an entry in your writer's notebook may be a good way to access this prior knowledge. Discussing the subject with classmates before you read is also a good idea. Tapping into prior knowledge will allow you to approach a piece of writing with more ways to create comprehension than if you start reading "cold."
Cognitive Reading Theory
When you read, you may think you are decoding a message that a writer has encoded into a text. Error in reading comprehension, in this model, would occur if you as a reader were not decoding the message correctly, or if the writer was not encoding the message accurately or clearly. The writer, however, would have the responsibility of getting the message into the text, and the reader would assume a passive role.
Related Information: Reading has a Model
Let's look at a more recent and widely accepted model of reading that is based on cognitive psychology and schema theory. In this model, the reader is an active participant who has an important interpretive function in the reading process. In other words, in the cognitive model you as a reader are more than a passive participant who receives information while an active text makes itself and its meanings known to you. Actually, the act of reading is a push and pull between reader and text. As a reader, you actively make, or construct, meaning; what you bring to the text is at least as important as the text itself.
Related Information: Reading is an active, constuctive, meaning-making process
Readers construct a meaning they can create from a text, so that "what a text means" can differ from reader to reader. Readers construct meaning based not only on the visual cues in the text (the words and format of the page itself) but also based on non-visual information such as all the knowledge readers already have in their heads about the world, their experience with reading as an activity, and, especially, what they know about reading different kinds of writing. This kind of non-visual information that readers bring with them before they even encounter the text is far more potent than the actual words on the page.
Related Information: Reading is hypothesis based
In yet another layer of complexity, readers also create for themselves an idea of what the text is about before they read it. In reading, prediction is much more important than decoding. In fact, if we had to read each letter and word, we couldn't possibly remember the letters and words long enough to put them all together to make sense of a sentence. And reading larger chunks than sentences would be absolutely impossible with our limited short-term memories.
So, instead of looking at each word and figuring out what it "means," readers rely on all their language and discourse knowledge to predict what a text is about. Then we sample the text to confirm, revise, or discard that hypothesis. More highly structured texts with topic sentences and lots of forecasting features are easier to hypothesize about; they're also easier to learn information from. Less structured texts that allow lots of room for predictions (and revised and discarded hypotheses) give more room for creative meanings constructed by readers. Thus we get office memos or textbooks or entertaining novels.
Related Information: Reading is multi-level
When we read a text, we pick up visual cues based on font size and clarity, the presence or absence of "pictures," spelling, syntax, discourse cues, and topic. In other words, we integrate data from a text including its smallest and most discrete features as well as its largest, most abstract features. Usually, we don't even know we're integrating data from all these levels. In addition, data from the text is being integrated with what we already know from our experience in the world about all fonts, pictures, spelling, syntax, discourse, and the topic more generally. No wonder reading is so complex!
Related Information: Reading is Strategic
We change our reading strategies (processes) depending on why we're reading. If we are reading an instruction manual, we usually read one step at a time and then try to do whatever the instructions tell us. If we are reading a novel, we don't tend to read for informative details. If we a reading a biology textbook, we read for understanding both of concepts and details (particularly if we expected to be tested over our comprehension of the material.)
Our goals for reading will affect the way we read a text. Not only do we read for the intended message, but we also construct a meaning that is valuable in terms of our purpose for reading the text.
Strategic reading also allows us to speed up or slow down, depending on our goals for reading (e.g. scanning newspaper headlines v. Carefully perusing a feature story).
Strategies for Reading More Critically
Although you probably already read critically in some respects, here are some things you can do when you read a text to improve your critical reading skills.
Most successful critical readers do some combination of the following strategies:
Summarizing
Previewing a text means gathering as much information about the text as you can before you actually read it. You can ask yourself the following questions:
What is my Purpose for Reading?
If you are being asked to summarize a particular piece of writing, you will want to look for the thesis and main points. Are you being asked to respond to a piece? If so, you may want to be conscious of what you already know about the topic and how you arrived at that opinion.
What can the Title Tell Me About the Text?
Before you read, look at the title of the text. What clues does it give you about the piece of writing? It may reveal the author's stance, or make a claim the piece will try to support. Good writers usually try to make their titles do work to help readers make meaning of the text from the reader's first glance at it.
Who is the Author?
If you have heard the author's name before, what comes to your mind in terms of their reputation and/or stance on the issue you are reading about? Has the author written other things of which you are aware? How does the piece in front of you fit into to the author's body of work? What is the author's political position on the issue they are writing about? Are they liberal, conservative, or do you know anything about what prompted them to write in the first place?
How is the Text Structured?
Sometimes the structure of a piece can give you important clues to its meaning. Be sure to read all section headings carefully. Also, reading the opening sentences of paragraphs should give you a good idea of the main ideas contained in the piece.
Annotating is an important skill to employ if you want to read critically. Successful critical readers read with a pencil in their hand, making notes in the text as they read. Instead of reading passively, they create an active relationship with what they are reading by "talking back" to the text in its margins. You may want to make the following annotations as you read:
Mark the Thesis and Main Points of the Piece
Mark key terms and unfamiliar words, underline important ideas and memorable images, write your questions and/or comments in the margins of the piece, write any personal experience related to the piece, mark confusing parts of the piece, or sections that warrant a reread, underline the sources, if any, the author has used.
Mark the thesis and main points of the piece. The thesis is the main idea or claim of the text, and relates to the author's purpose for writing. Sometimes the thesis is not explicitly stated, but is implied in the text, but you should still be able to paraphrase an overall idea the author is interested in exploring in the text. The thesis can be thought of as a promise the writer makes to the reader that the rest of the essay attempts to fulfill.
The main points are the major subtopics, or sub-ideas the author wants to explore. Main points make up the body of the text, and are often signaled by major divisions in the structure of the text.
Marking the thesis and main points will help you understand the overall idea of the text, and the way the author has chosen to develop her or his thesis through the main points s/he has chosen.
While you are annotating the text you are reading, be sure to circle unfamiliar words and take the time to look them up in the dictionary. Making meaning of some discussions in texts depends on your understanding of pivotal words. You should also annotate key terms that keep popping up in your reading. The fact that the author uses key terms to signal important and/or recurring ideas means that you should have a firm grasp of what they mean.
You will want to underline important ideas and memorable images so that you can go back to the piece and find them easily. Marking these things will also help you relate to the author's position in the piece more readily. Writers may try to signal important ideas with the use of descriptive language or images, and where you find these stylistic devices, there may be a key concept the writer is trying to convey.
Writing your own questions and responses to the text in its margins may be the most important aspect of annotating. "Talking back" to the text is an important meaning-making activity for critical readers. Think about what thoughts and feelings the text arouses in you. Do you agree or disagree with what the author is saying? Are you confused by a certain section of the text? Write your reactions to the reading in the margins of the text itself so you can refer to it again easily. This will not only make your reading more active and memorable, but it may be material you can use in your own writing later on.
One way to make a meaningful connection to a text is to connect the ideas in the text to your own personal experience. Where can you identify with what the author is saying? Where do you differ in terms of personal experience? Identifying personally with the piece will enable you to get more out of your reading because it will become more relevant to your life, and you will be able to remember what you read more easily.
Be sure to mark confusing parts of the piece you are reading, or sections that warrant a reread. It is tempting to glide over confusing parts of a text, probably because they cause frustration in us as readers. But it is important to go back to confusing sections to try to understand as much as you can about them. Annotating these sections may also remind you to bring up the confusing section in class or to your instructor.
Good critical readers are always aware of the sources an author uses in her or his text. You should mark sources in the text and ask yourself the following questions:
- Is the source relevant? In other words, does the source work to support what the author is trying to say?
- Is the source credible? What is his or her reputation? Is the source authoritative? What is the source's bias on the issue? What is the source's political and/or personal stance on the issue?
- Is the source current? Is there new information that refutes what the source is asserting? Is the writer of the text using source material that is outdated?
Summarizing the text you've read is an valuable way to check your understanding of the text. When you summarize, you should be able to find and write down the thesis and main points of the text.
Annotating the thesis and main points
Analyzing a text means breaking it down into its parts to find out how these parts relate to one another. Being aware of the functions of various parts of a piece of writing and their relationship to one another and the overall piece can help you better understand a text's meaning. To analyze a text, you can look at the following things:
- Assumptions
- Author Bias
Analyzing Evidence
Consider the evidence the author presents. Is there enough evidence to support the point the author is trying to make? Does the evidence relate to the main point in a logical way? In other words, does the evidence work to prove the point, or does is contradict the point, or show itself to be irrelevant to the point the author is trying to make?
Related Information: Source Evaluation
Analyzing Assumptions
Consider any assumptions the author is making. Assumptions may be unstated in the piece of writing you are assessing, but the writer may be basing her or his thesis on them. What does the author have to believe is true before the rest of her or his essay makes sense?
Example: "[I]f a college recruiter argues that the school is superior to most others because its ratio of students to teachers is low, the unstated assumptions are (1) that students there will get more attention, and (2) that more attention results in a better education" (Crusius and Channell, The Aims of Argument , Mayfield Publishing Co., 1995).
Analyzing Sources
If an author uses outside sources to back up what s/he is saying, analyzing those sources is an important critical reading activity. Not all sources are created equal. There are at least three criteria to keep in mind when you are evaluating a source:
- Is the Source Relevant?
- Is the Source Credible?
- Is the Source Current?
Analyzing Author Bias
Taking a close look at the author's bias can tell you a lot about a text. Ask yourself what experiences in the author's background may have led him or her to hold the position s/he does. What does s/he hope to gain from taking this position? How does the author's position stand up in comparison to other positions on the issue? Knowing where the author is "coming from" can help you to more easily make meaning from a text.
Re-reading is a crucial part of the critical reading process. Good readers will reread a piece several times, until they are satisfied they know it inside and out. It is recommended that you read a text three times to make as much meaning as you can.
The First Reading
The first time you read a text, skim it quickly for its main ideas. Pay attention to the introduction, the opening sentences of paragraphs, and section headings, if there are any. Previewing the text in this way gets you off to a good start when you have to read critically.
The Second Reading
The second reading should be a slow, meditative read, and you should have your pencil in your hand so you can annotate the text. Taking time to annotate your text during the second reading may be the most important strategy to master if you want to become a critical reader.
The Third Reading
The third reading should take into account any questions you asked yourself by annotating the margins. You should use this reading to look up any unfamiliar words, and to make sure you have understood any confusing or complicated sections of the text.
Responding to what you read is an important step in understanding what you read. You can respond in writing, or by talking about what you've read to others. Here are several ways you can respond critically to a piece of writing:
- Writing a Response in Your Writer's Notebook
- Discussing the Text with Others
Writing a response in your writer's notebook
One way to make sure you have understood a piece of writing is to write a response to it. It may be beneficial to first write a summary of the text, covering the thesis and main points in an unbiased way. Pretend you are reporting on the "facts" of the piece to a friend who has not read it, the point being to keep your own opinion out of the summary. Once you have summarized the author's ideas objectively, you can respond to them in your writer's notebook. You can agree or disagree with the text, interpret it, or analyze it. Working with your reading of the text by responding in writing is a good way to read critically.
Keeping a writer's notebook
A writer's notebook, or journal, is a place in which you can respond to your reading. You should feel free to say what you really think about the piece you are reading, to ask questions, and to express frustration or confusion about the piece. The writer's notebook is a place you can come back to when it is time to write an assignment, to look for your initial reactions to your readings, or to pull support for an essay from personal experience you may have recorded. Writing about what you are reading is a way to become actively engaged in the critical reading process.
Discussing the text with others
Cooperative activities are important to critical reading just as they are to the writing process. Sharing your knowledge of a text with others reading the same text is a good way to check your understanding and open up new avenues of comprehension. You can annotate a text on your own first, and then confer with a group of classmates about how they annotated their texts. Or, you can be sure to participate in class discussion of a shared text--verbalizing your ideas about a text will reinforce your reading process.
Critically Reading Assignment Sheets
It is important to have read your assignment sheet critically before you begin to write. Consider the following things:
Analyze your Assignment Sheet Carefully
Pay attention to the length of the essay, and other requirements, plan your time well.
You may want to annotate your assignment sheet like you would any other piece of writing. Look for key terms like analyze, interpret, argue, summarize, compare, contrast, explain, etc. These terms will tell you your purpose for writing. Be sure to know how your instructor is using key words on the assignment sheet. If you don't understand something about the assignment, be sure to ask your instructor. It's vital to understand the assignment completely before you begin writing.
Be sure to have a firm grasp on what you must do to meet the requirements of the assignment. Know how long the essay must be, because this will affect the thesis and focus of the paper. Short papers dictate a narrow focus, whereas longer paper allow for a larger focus.
Know also what formatting requirements are in place, such as font size, margins and other constraints.
Know when the assignment due date is and be sure to allow enough time for all thinking, reading, researching , drafting and revising. Be aware of your instructor's policy on due dates. Most instructors do not accept late papers.
Reading for Meaning
After you've read an essay once, use the following set of questions to guide your re-readings of the text. The question on the left-hand side will help you describe and analyze the text; the question on the right hand side will help focus your response(s).
Remember that not all these questions will be relevant to any given essay or text, but one or two of them may suggest a direction or give a focus to your overall response.
When one of these questions suggests a focus for your response to the essay, go back to the text to gather evidence to support your response.
Walker, Debra, Kate Kiefer, & Stephen Reid. (1995). Critical Reading. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guide,cfm?guideid=31

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: What is Critical Reading?
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 107737
Reading critically does not simply mean being moved, affected, informed, influenced, and persuaded by a piece of writing. It refers to analyzing and understanding the overall composition of the writing as well as how the writing has achieved its effect on the audience. This level of understanding begins with thinking critically about the texts you are reading. In this case, “critically” does not mean that you are looking for what is wrong with a work (although during your critical process, you may well do that). Instead, thinking critically means approaching a work as if you were a critic or commentator whose job it is to analyze a text beyond its surface.
A text is simply a piece of writing, or as Merriam-Webster defines it, “the main body of printed or written matter on a page.” In English classes, the term “text” is often used interchangeably with the words “reading” or “work.”
This step is essential in analyzing a text, and it requires you to consider many different aspects of a writer’s work. Do not just consider what the text says; think about what effect the author intends to produce in a reader or what effect the text has had on you as the reader. For example, does the author want to persuade, inspire, provoke humor, or simply inform his audience? Look at the process through which the writer achieves (or does not achieve) the desired effect and which rhetorical strategies he uses. If you disagree with a text, what is the point of contention? If you agree with it, how do you think you can expand or build upon the argument put forth?
Consider this example: Which of the following tweets below are critical and which are uncritical?
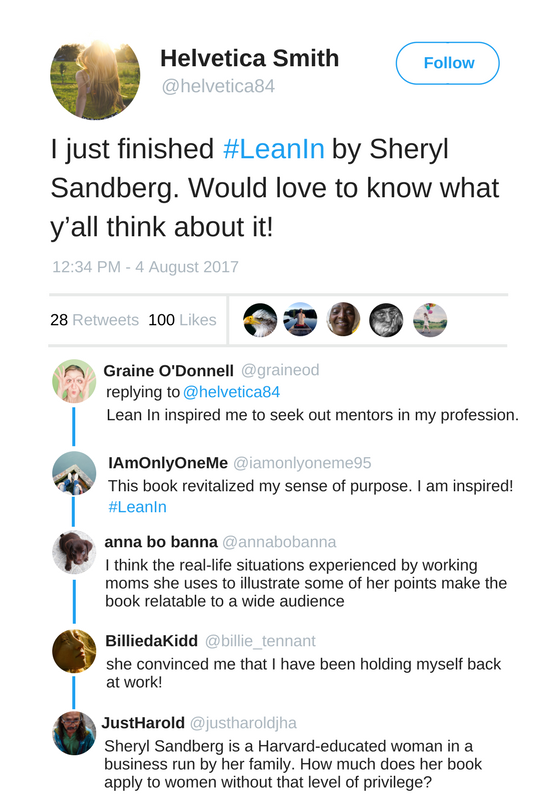
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Finding an error in someone else’s argument can be the point of destabilization you need to make a worthy argument of your own, illustrated in the final tweet from the previous image. Critical reading has many uses. If applied to a work of literature, for example, it can become the foundation for a detailed textual analysis. With scholarly articles, critical reading can help you evaluate their potential reliability as future sources. Critical reading can even help you hone your own argumentation skills because it requires you to think carefully about which strategies are effective for making arguments, and in this age of social media and instant publication, thinking carefully about what we say is a necessity.
Contributors and Attributions
Adapted from Let's Get Writing (Browning, DeVries, Boylan, Kurtz and Burton) . Sourced from LibreTexts , licensed under CC BY-NC-SA

Research and Critical Reading
Pavel Zemilansky
Learning Objectives
- Read critically to discover the meaning, purpose, and content of a piece
- Respond critically to written works using reading strategy
INTRODUCTION
Good researchers and writers examine their sources critically and actively. They do not just compile and summarize these research sources in their writing, but use them to create their own ideas, theories, and, ultimately, their own, new understanding of the topic they are researching. Such an approach means not taking the information and opinions that the sources contain at face value and for granted, but to investigate, test, and even doubt every claim, every example, every story, and every conclusion. It means not to sit back and let your sources control you, but to engage in active conversation with them and their authors. In order to be a good researcher and writer, one needs to be a critical and active reader.
This chapter is about the importance of critical and active reading. It is also about the connection between critical reading and active, strong writing. Much of the discussion you will find in this chapter in fundamental to research and writing, no matter what writing genre, medium, or academic discipline you read and write in. Every other approach to research writing, every other research method and assignment offered elsewhere in this book is, in some way, based upon the principles discussed in this chapter.
Reading is at the heart of the research process. No matter what kinds of research sources and, methods you use, you are always reading and interpreting text. Most of us are used to hearing the word “reading” in relation to secondary sources, such as books, journals, magazines, websites, and so on. But even if you are using other research methods and sources, such as interviewing someone or surveying a group of people, you are reading. You are reading their subjects’ ideas and views on the topic you are investigating. Even if you are studying photographs, cultural artifacts, and other non-verbal research sources, you are reading them, too by trying to connect them to their cultural and social contexts and to understand their meaning. Principles of critical reading which we are about to discuss in this chapter apply to those research situations as well.
I like to think about reading and writing as not two separate activities but as two tightly connected parts of the same whole. That whole is the process of learning and making of new meaning. It may seem that reading and writing are complete opposite of one another. According to the popular view, when we read, we “consume” texts, and when we write, we “produce” texts. But this view of reading and writing is true only if you see reading as a passive process of taking in information from the text and not as an active and energetic process of making new meaning and new knowledge. Similarly, good writing does not come from nowhere but is usually based upon, or at least influenced by ideas, theories, and stories that come from reading. So, if, as a college student, you have ever wondered why your writing teachers have asked you to read books and articles and write responses to them, it is because writers who do not read and do not actively engage with their reading, have little to say to others.
We will begin this chapter with the definition of the term “critical reading.” We will consider its main characteristics and briefly touch upon ways to become an active and critical reader. Next, we will discuss the importance of critical reading for research and how reading critically can help you become a better researcher and make the research process more enjoyable. Also in this chapter, a student-writer offers us an insight into his critical reading and writing processes. This chapter also shows how critical reading can and should be used for critical and strong writing. And, as all other chapters, this one offers you activities and projects designed to help you implement the advice presented here into practice.
WHAT KIND OF READER ARE YOU?
You read a lot, probably more that you think. You read school textbooks, lecture notes, your classmates’ papers, and class websites. When school ends, you probably read some fiction, magazines. But you also read other texts. These may include CD liner notes, product reviews, grocery lists, maps, driving directions, road signs, and the list can go on and on. And you don’t read all these texts in the same way. You read them with different purposes and using different reading strategies and techniques. The first step towards becoming a critical and active reader is examining your reading process and your reading preferences. Therefore, you are invited to complete the following exploration activity.
Writing Activity: Analyzing Your Reading Habits
List all the reading you have done in the last week. Include both “school” and “out-of school” reading. Try to list as many texts as you can think of, no matter how short and unimportant they might seem. Now, answer the following questions.
• What was your purpose in reading each of those texts? Did you read for information, to pass a test, for enjoyment, to decide on a product you wanted to buy, and so on? Or, did you read to figure out some complex problem that keeps you awake at night?
• You have probably come up with a list of different purposes. How did each of those purposes influence your reading strategies? Did you take notes or try to memorize what you read? How long did it take you to read different texts? Did you begin at the beginning and read till you reached the end, or did you browse some texts? Consider the time of day you were reading. Consider even whether some texts tired you out or whether you thought they were “boring.” Why?
• What did you do with the results of your reading? Did you use them for some practical purpose, such as buying a new product or finding directions, or did you use them for a less practical purpose, such as understanding some topic better r learning something about yourself and others?
When you finish, share your results with the rest of the class and with your instructor.
Having answered the questions above, you have probably noticed that your reading strategies differed depending on the reading task you were facing and on what you planned to do with the results of the reading. If, for example, you read lecture notes in order to pass a test, chances are you “read for information,” or “for the main” point, trying to remember as much material as possible and anticipating possible test questions. If, on the other hand, you read a good novel, you probably just focused on following the story. Finally, if you were reading something that you hoped would help you answer some personal question or solve some personal problem, it is likely that you kept comparing and contrasting the information that you read your own life and your own experiences.
You may have spent more time on some reading tasks than others. For example, when we are interested in one particular piece of information or fact from a text, we usually put that text aside once we have located the information we were looking for. In other cases, you may have been reading for hours on end taking careful notes and asking questions.
If you share the results of your investigation into your reading habits with your classmates, you may also notice that some of their reading habits and strategies were different from yours. Like writing strategies, approaches to reading may vary from person to person depending on our previous experiences with different topics and types of reading materials, expectations we have of different texts, and, of course, the purpose with which we are reading.
Life presents us with a variety of reading situations which demand different reading strategies and techniques. Sometimes, it is important to be as efficient as possible and read purely for information or “the main point.” At other times, it is important to just “let go” and turn the pages following a good story, although this means not thinking about the story you are reading. At the heart of writing and research, however, lies the kind of reading known as critical reading. Critical examination of sources is what makes their use in research possible and what allows writers to create rhetorically effective and engaging texts.
KEY FEATURES OF CRITICAL READING
Critical readers are able to interact with the texts they read through carefully listening, writing, conversation, and questioning. They do not sit back and wait for the meaning of a text to come to them, but work hard in order to create such meaning. Critical readers are not made overnight. Becoming a critical reader will take a lot of practice and patience. Depending on your current reading philosophy and experiences with reading, becoming a critical reader may require a significant change in your whole understanding of the reading process. The trade-off is worth it, however. By becoming a more critical and active reader, you will also become a better researcher and a better writer. Last but not least, you will enjoy reading and writing a whole lot more because you will become actively engaged in both.
One of my favorite passages describing the substance of critical and active reading comes from the introduction to their book Ways of Reading , whose authors David Bartholomae and Anthony Petrosky write:
Reading involves a fair measure of push and shove. You make your mark on the book and it makes its mark on you. Reading is not simply a matter of hanging back and waiting for a piece, or its author, to tell you what the writing has to say. In fact, one of the difficult things about reading is that the pages before you will begin to speak only when the authors are silent and you begin to speak in their place, sometimes for them—doing their work, continuing their projects—and sometimes for yourself, following your own agenda (1).
Notice that Bartholomae and Petrosky describe reading process in pro-active terms. Meaning of every text is “made,” not received. Readers need to “push and shove” in order to create their own, unique content of every text they read. It is up the you as a reader to make the pages in front of you “speak” by talking with and against the text, by questioning and expanding it.
Critical reading, then, is a two-way process. As reader, you are not a consumer of words, waiting patiently for ideas from the printed page or a web-site to fill your head and make you smarter. Instead, as a critical reader, you need to interact with what you read, asking questions of the author, testing every assertion, fact, or idea, and extending the text by adding your own understanding of the subject and your own personal experiences to your reading.
The following are key features of the critical approach to reading:
- No text, however well written and authoritative, contains its own, pre-determined meaning.
- Readers must work hard to create meaning from every text.
- Critical readers interact with the texts they read by questioning them, responding to them, and expanding them, usually in writing.
- To create meaning, critical readers use a variety of approaches, strategies, and techniques which include applying their personal experiences and existing knowledge to the reading process.
- Critical readers seek actively out other texts, related to the topic of their investigation.
The following section is an examination of these claims about critical reading in more detail.
TEXTS PRESENT IDEAS, NOT ABSOLUTE TRUTHS
In order to understand the mechanisms and intellectual challenges of critical reading, we need to examine some of our deepest and long-lasting assumptions about reading. Perhaps the two most significant challenges facing anyone who wants to become a more active and analytical reader is understanding that printed texts doe not contain inarguable truths and learning to questions and talk back to those texts. Students in my writing classes often tell me that the biggest challenge they face in trying to become critical readers is getting away from the idea that they have to believe everything they read on a printed page. Years of schooling have taught many of us to believe that published texts present inarguable, almost absolute truths. The printed page has authority because, before publishing his or her work, every writer goes through a lengthy process of approval, review, revision, fact-checking, and so on. Consequently, this theory goes, what gets published must be true. And if it is true, it must be taken at face value, not questioned, challenged, or extended in any way.
Perhaps, the ultimate authority among the readings materials encountered by college belongs to the textbook. As students, we all have had to read and almost memorize textbook chapters in order to pass an exam. We read textbooks “for information,” summarizing their chapters, trying to find “the main points” and then reproducing these main points during exams. I have nothing against textbook as such, in fact, I am writing one right now. And it is certainly possible to read textbooks critically and actively. But, as I think about the challenges which many college students face trying to become active and critical readers, I come to the conclusion that the habit to read every text as if they were preparing for an exam on it, as if it was a source of unquestionable truth and knowledge prevents many from becoming active readers.
Treating texts as if they were sources of ultimate and unquestionable knowledge and truth represents the view of reading as consumption. According to this view, writers produce ideas and knowledge, and we, readers, consume them. Of course, sometimes we have to assume this stance and read for information or the “main point” of a text. But it is critical reading that allows us to create new ideas from what we read and to become independent and creative learners.
Critical reading is a collaboration between the reader and the writer. It offers readers the ability to be active participants in the construction of meaning of every text they read and to use that meaning for their own learning and self-fulfillment. Not even the best researched and written text is absolutely complete and finished. Granted, most fields of knowledge have texts which are called “definitive.” Such texts usually represent our best current knowledge on their subjects. However, even the definitive works get revised over time and they are always open to questioning and different interpretations.
READING IS A RHETORICAL TOOL
To understand how the claim that every reader makes his or her meaning from texts works, it is necessary to examine what is know as the rhetorical theory of reading. The work that best describes and justifies the rhetorical reading theory is Douglas Brent’s 1992 book Reading as Rhetorical Invention: Knowledge, Persuasion, and the Teaching of Research-Based Writing . I like to apply Brent’s ideas to my discussions of critical reading because I think that they do a good job demystifying critical reading’s main claims. Brent’s theory of reading is a rhetorical device puts significant substance behind the somewhat abstract ideas of active and critical reading, explaining how the mechanisms of active interaction between readers and texts actually work.
Briefly explained, Brent treats reading not only as a vehicle for transmitting information and knowledge, but also as a means of persuasion. In fact, according to Brent, knowledge equals persuasion because, in his words, “Knowledge is not simply what one has been told. Knowledge is what one believes, what one accepts as being at least provisionally true.” (xi). This short passage contains two assertions which are key to the understanding of mechanisms of critical reading. Firstly, notice that simply reading “for the main point” will not necessarily make you “believe” what you read. Surely, such reading can fill our heads with information, but will that information become our knowledge in a true sense, will we be persuaded by it, or will we simply memorize it to pass the test and forget it as soon as we pass it? Of course not! All of us can probably recall many instances in which we read a lot to pass a test only to forget, with relief, what we read as soon as we left the classroom where that test was held. The purpose of reading and research, then, is not to get as much as information out of a text as possible but to change and update one’s system of beliefs on a given subject (Brent 55-57).
Brent further states:
The way we believe or disbelieve certain texts clearly varies from one individual to the next. If you present a text that is remotely controversial to a group of people, some will be convinced by it and some not, and those who are convinced will be convinced in different degrees. The task of a rhetoric of reading is to explain systematically how these differences arise— how people are persuaded differently by texts (18).
Critical and active readers not only accept the possibility that the same texts will have different meanings for different people, but welcome this possibility as an inherent and indispensable feature of strong, engaged, and enjoyable reading process. To answer his own questions about what factors contribute to different readers’ different interpretations of the same texts, Brent offers us the following principles that I have summarized from his book:
• Readers are guided by personal beliefs, assumptions, and pre-existing knowledge when interpreting texts. You can read more on the role of the reader’s pre-existing knowledge in the construction of meaning later on in this chapter.
• Readers react differently to the logical proofs presented by the writers of texts.
• Readers react differently to emotional and ethical proofs presented by writers. For example, an emotional story told by a writer may resonate with one person more than with another because the first person lived through a similar experience and the second one did not, and so on.
The idea behind the rhetorical theory of reading is that when we read, we not only take in ideas, information, and facts, but instead we “update our view of the world.” You cannot force someone to update their worldview, and therefore, the purpose of writing is persuasion and the purpose of reading is being persuaded. Persuasion is possible only when the reader is actively engaged with the text and understands that much more than simple retrieval of information is at stake when reading.
One of the primary factors that influence our decision to accept or not to accept an argument is what Douglas Brent calls our “repertoire of experience, much of [which] is gained through prior interaction with texts” (56). What this means is that when we read a new text, we do not begin with a clean slate, an empty mind. However unfamiliar the topic of this new reading may seem to us, we approach it with a large baggage of previous knowledge, experiences, points of view, and so on. When an argument “comes in” into our minds from a text, this text, by itself, cannot change our view on the subject. Our prior opinions and knowledge about the topic of the text we are reading will necessarily “filter out” what is incompatible with those views (Brent 56-57). This, of course, does not mean that, as readers, we should persist in keeping our old ideas about everything and actively resist learning new things. Rather, it suggests that the reading process is an interaction between the ideas in the text in front of us and our own ideas and pre-conceptions about the subject of our reading. We do not always consciously measure what we read according to our existing systems of knowledge and beliefs, but we measure it nevertheless. Reading, according to Brent, is judgment, and, like in life where we do not always consciously examine and analyze the reasons for which we make various decisions, evaluating a text often happens automatically or subconsciously (59).
Applied to research writing, Brent’s theory or reading means the following:
- The purpose of research is not simply to retrieve data, but to participate in a conversation about it. Simple summaries of sources is not research, and writers should be aiming for active interpretation of sources instead
- There is no such thing as an unbiased source. Writers make claims for personal reasons that critical readers need to learn to understand and evaluate.
- Feelings can be a source of shareable good reason for belief. Readers and writers need to use, judiciously, ethical and pathetic proofs in interpreting texts and in creating their own.
- Research is recursive. Critical readers and researchers never stop asking questions about their topic and never consider their research finished.
ACTIVE READERS LOOK FOR CONNECTIONS BETWEEN TEXTS
Earlier on, I mentioned that one of the traits of active readers is their willingness to seek out other texts and people who may be able to help them in their research and learning. I find that for many beginning researchers and writers, the inability to seek out such connections often turns into a roadblock on their research route. Here is what I am talking about.
Recently, I asked my writing students to investigate some problem on campus and to propose a solution to it. I asked them to use both primary (interviews, surveys, etc.) and secondary (library, Internet, etc.) research. Conducting secondary research allows a writer to connect a local problem he or she is investigating and a local solution he or she is proposing with a national and even global context, and to see whether the local situation is typical or a-typical.
One group of students decided to investigate the issue of racial and ethnic diversity on our campus. The lack of diversity is a “hot” issue on our campus, and recently an institutional task force was created to investigate possible ways of making our university more diverse.
The students had no trouble designing research questions and finding people to interview and survey. Their subjects included students and faculty as well as the university vice-president who was changed with overseeing the work of the diversity task force. Overall, these authors have little trouble conducting and interpreting primary research that led them to conclude that, indeed, our campus is not diverse enough and that most students would like to see the situation change.
The next step these writers took was to look at the websites of some other schools similar in size and nature to ours, to see how our university compared on the issue of campus diversity with others. They were able to find some statistics on the numbers of minorities at other colleges and universities that allowed them to create a certain backdrop for their primary research that they had conducted earlier.
But good writing goes beyond the local situation. Good writing tries to connect the local and the national and the global. It tries to look beyond the surface of the problem, beyond simply comparing numbers and other statistics. It seeks to understand the roots of a problem and propose a solution based on a local and well as a global situation and research. The primary and secondary research conducted by these students was not allowing them to make that step from analyzing local data to understanding their problem in context. They needed some other type of research sources.
At that point, however, those writers hit an obstacle. How and where, they reasoned, would we find other secondary sources, such as books, journals, and websites, about the lack of diversity on our campus? The answer to that question was that, at this stage in their research and writing, they did not need to look for more sources about our local problem with the lack of diversity. They needed to look at diversity and ways to increase it as a national and global issue. They needed to generalize the problem and, instead of looking at a local example, to consider its implications for the issue they were studying overall. Such research would not only have allowed these writers to examine the problem as a whole but also to see how it was being solved in other places. This, in turn, might have helped them to propose a local solution.
Critical readers and researchers understand that it is not enough to look at the research question locally or narrowly. After conducting research and understanding their problem locally, or as it applies specifically to them, active researchers contextualize their investigation by seeking out texts and other sources which would allow them to see the big picture.
Sometimes, it is hard to understand how external texts which do not seem to talk directly about you can help you research and write about questions, problems, and issues in your own life. In her 2004 essay, “Developing ‘Interesting Thoughts’: Reading for Research,” writing teacher and my former colleague Janette Martin tells a story of a student who was writing a paper about what it is like to be a collegiate athlete. The emerging theme in that paper was that of discipline and sacrifice required of student athletes. Simultaneously, that student was reading a chapter from the book by the French philosopher Michel Foucault called Discipline and Punish. Foucault’s work is a study of the western penitentiary system, which, of course cannot be directly compared to experiences of a student athlete. At the same time, one of the leading themes in Foucault’s work is discipline. Martin states that the student was able to see some connection between Foucault and her own life and use the reading for her research and writing (6). In addition to showing how related texts can be used to explore various aspects of the writer’s own life, this example highlights the need to read texts critically and interpret them creatively. Such reading and research goes beyond simply comparing of facts and numbers and towards relating ideas and concepts with one another.
FROM READING TO WRITING
Reading and writing are the two essential tools of learning. Critical reading is not a process of passive consumption, but one of interaction and engagement between the reader and the text. Therefore, when reading critically and actively, it is important not only to take in the words on the page, but also to interpret and to reflect upon what you read through writing and discussing it with others.
CRITICAL READERS UNDERSTAND THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN REACTING AND RESPONDING TO A TEXT
As stated earlier in this chapter, actively responding to difficult texts, posing questions, and analyzing ideas presented in them is the key to successful reading. The goal of an active reader is to engage in a conversation with the text he or she is reading. In order to fulfill this goal, it is important to understand the difference between reacting to the text and responding to it.
Reacting to a text is often done on an emotional, rather than on an intellectual level. It is quick and shallow. For example, if we encounter a text that advances arguments with which we strongly disagree, it is natural to dismiss those ideas out of hand as not wrong and not worthy of our attention. Doing so would be reacting to the text based only on emotions and on our pre-set opinions about its arguments. It is easy to see that reacting in this way does not take the reader any closer to understanding the text. A wall of disagreement that existed between the reader and the text before the reading continues to exist after the reading.
Responding to a text, on the other hand, requires a careful study of the ideas presented and arguments advanced in it. Critical readers who possess this skill are not willing to simply reject or accept the arguments presented in the text after the first reading right away. To continue with our example from the preceding paragraph, a reader who responds to a controversial text rather than reacting to it might apply several of the following strategies before forming and expressing an opinion about that text.
- Read the text several times, taking notes, asking questions, and underlining key places.
- Study why the author of the text advances ideas, arguments, and convictions, so different from the reader’s own. For example, is the text’s author advancing an agenda of some social, political, religious, or economic group of which he or she is a member?
- Study the purpose and the intended audience of the text.
- Study the history of the argument presented in the text as much as possible. For example, modern texts on highly controversial issues such as the death penalty, abortion, or euthanasia often use past events, court cases, and other evidence to advance their claims. Knowing the history of the problem will help you to construct meaning of a difficult text.
- Study the social, political, and intellectual context in which the text was written. Good writers use social conditions to advance controversial ideas. Compare the context in which the text was written to the one in which it is read. For example, have social conditions changed, thus invalidating the argument or making it stronger?
- Consider the author’s (and your own) previous knowledge of the issue at the center of the text and your experiences with it. How might such knowledge or experience have influenced your reception of the argument?
Taking all these steps will help you to move away from simply reacting to a text and towards constructing informed and critical response to it.
CRITICAL READERS RESIST OVERSIMPLIFIED BINARY RESPONSES
Critical readers learn to avoid simple “agree-disagree” responses to complex texts. Such way of thinking and arguing is often called “binary” because is allows only two answers to every statement and every questions. But the world of ideas is complex and, a much more nuanced approach is needed when dealing with complex arguments.
When you are asked to “critique” a text, which readers are often asked to do, it does not mean that you have to “criticize” it and reject its argument out of hand. What you are being asked to do instead is to carefully evaluate and analyze the text’s ideas, to understand how and why they are constructed and presented, and only then develop a response to that text. Not every text asks for an outright agreement or disagreement. Sometimes, we as readers are not in a position to either simply support an argument or reject it. What we can do in such cases, though, is to learn more about the text’s arguments by carefully considering all of their aspects and to construct a nuanced, sophisticated response to them. After you have done all that, it will still be possible to disagree with the arguments presented in the reading, but your opinion about the text will be much more informed and nuanced than if you have taken the binary approach from the start.
TWO SAMPLE STUDENT RESPONSES
To illustrate the principles laid out in this section, consider the following two reading responses. Both texts respond to a very well known piece, “A Letter from Birmingham Jail,” by Martin Luther King, Jr. In the letter, King responds to criticism from other clergymen who had called his methods of civil rights struggle “unwise and untimely.” Both student writers were given the same response prompt:
Example: Student A
Martin Luther King Jr’s “Letter from Birmingham Jail” is a very powerful text. At the time when minorities in America were silenced and persecuted, King had the courage to lead his people in the struggle for equality. After being jailed in Birmingham, Alabama, King wrote a letter to his “fellow clergymen” describing his struggle for civil rights. In the letter, King recounts a brief history of that struggle and rejects the accusation that it is “unwise and untimely.” Overall, I think that King’s letter is a very rhetorically effective text, one that greatly helped Americans to understand the civil rights movement.
Example: Student B
King begins his “Letter from Birmingham Jail” by addressing it to his “fellow clergymen.” Thus, he immediately sets the tone of inclusion rather than exclusion. By using the word “fellow” in the address, I think he is trying to do two things. First of all, he presents himself as a colleague and a spiritual brother of his audience. That, in effect, says “you can trust me,” “I am one of your kind.” Secondly, by addressing his readers in that way, King suggests that everyone, even those Americans who are not directly involved in the struggle for civil rights, should be concerned with it. Hence the word “fellow.” King’s opening almost invokes the phrase “My fellow Americans” or “My fellow citizens” used so often by American Presidents when they address the nation.
King then proceeds to give a brief background of his actions as a civil rights leader. As I read this part of the letter, I was wondering whether his readers would really have not known what he had accomplished as a civil rights leader. Then I realized that perhaps he gives all that background information as a rhetorical move. His immediate goal is to keep reminding his readers about his activities. His ultimate goal is to show to his audience that his actions were non-violent but peaceful. In reading this passage by King, I remembered once again that it is important not to assume that your audience knows anything about the subject of the writing. I will try to use this strategy more in my own papers.
In the middle of the letter, King states: “The purpose of our direct-action program is to create a situation so crisis-packed that it will inevitably open the door to negotiation.” This sentence looks like a thesis statement and I wonder why he did not place it towards the beginning of the text, to get his point across right away. After thinking about this for a few minutes and re- reading several pages from our class textbook, I think he leaves his “thesis” till later in his piece because he is facing a not- so-friendly (if not hostile) audience. Delaying the thesis and laying out some background information and evidence first helps a writer to prepare his or her audience for the coming argument. That is another strategy I should probably use more often in my own writing, depending on the audience I am facing.
REFLECTING ON THE RESPONSES
To be sure, much more can be said about King’s letter than either of these writers have said. However, these two responses allow us to see two dramatically different approaches to reading. After studying both responses, consider the questions below.
- Which response fulfills the goals set in the prompt better and why?
- Which responses shows a deeper understanding of the texts by the reader and why?
- Which writer does a better job at avoiding binary thinking and creating a sophisticated reading of King’s text and why?
- Which writer is more likely to use the results of the reading in his or her own writing in the future and why?
- Which writer leaves room for response to his text by others and why?
CRITICAL READERS DO NOT READ ALONE AND IN SILENCE
One of the key principles of critical reading is that active readers do not read silently and by themselves. By this I mean that they take notes and write about what they read. They also discuss the texts they are working with, with others and compare their own interpretations of those texts with the interpretations constructed by their colleagues.
As a college student, you are probably used to taking notes of what you read. When I was in college, my favorite way of preparing for a test was reading a chapter or two from my textbook, then closing the book, then trying to summarize what I have read on a piece of paper. I tried to get the main points of the chapters down and the explanations and proofs that the textbooks’ authors used. Sometimes, I wrote a summary of every chapter in the textbook and then studied for the test from those summaries rather than from the textbook itself. I am sure you have favorite methods of note taking and studying from your notes, too.
But now it strikes me that what I did with those notes was not critical reading. I simply summarized my textbooks in a more concise, manageable form and then tried to memorize those summaries before the test. I did not take my reading of the textbooks any further than what was already on their pages. Reading for information and trying to extract the main points, I did not talk back to the texts, did not question them, and did not try to extend the knowledge which they offered in any way. I also did not try to connect my reading with my personal experiences or pre-existing knowledge in any way. I also read in silence, without exchanging ideas with other readers of the same texts. Of course, my reading strategies and techniques were dictated by my goal, which was to pass the test.
Critical reading has other goals, one of which is entering an on-going intellectual exchange. Therefore it demands different reading strategies, approaches, and techniques. One of these new approaches is not reading in silence and alone. Instead, critical readers read with a pen or pencil in hand. They also discuss what they read with others.
STRATEGIES FOR CONNECTING READING AND WRITING
If you want to become a critical reader, you need to get into a habit of writing as you read. You also need to understand that complex texts cannot be read just once. Instead, they require multiple readings, the first of which may be a more general one during which you get acquainted with the ideas presented in the text, its structure and style. During the second and any subsequent readings, however, you will need to write, and write a lot. The following are some critical reading and writing techniques which active readers employ as they work to create meanings from texts they read.
UNDERLINE INTERESTING AND IMPORTANT PLACES IN THE TEXT
Underline words, sentences, and passages that stand out, for whatever reason. Underline the key arguments that you believe the author of the text is making as well as any evidence, examples, and stories that seem interesting or important. Don’t be afraid to “get it wrong.” There is no right or wrong here. The places in the text that you underline may be the same or different from those noticed by your classmates, and this difference of interpretation is the essence of critical reading.
Take notes on the margins. If you do not want to write on your book or journal, attach post-it notes with your comments to the text. Do not be afraid to write too much. This is the stage of the reading process during which you are actively making meaning. Writing about what you read is the best way to make sense of it, especially, if the text is difficult.
Do not be afraid to write too much. This is the stage of the reading process during which you are actively making meaning. Writing about what you read will help you not only to remember the argument which the author of the text is trying to advance (less important for critical reading), but to create your own interpretations of the text you are reading (more important).
Here are some things you can do in your comments
- Ask questions.
- Agree or disagree with the author.
- Question the evidence presented in the text
- Offer counter-evidence
- Offer additional evidence, examples, stories, and so on that support the author’s argument
- Mention other texts which advance the same or similar arguments
- Mention personal experiences that enhance your reading of the text
WRITE EXPLORATORY RESPONSES
Write extended responses to readings. Writing students are often asked to write one or two page exploratory responses to readings, but they are not always clear on the purpose of these responses and on how to approach writing them. By writing reading responses, you are continuing the important work of critical reading which you began when you underlined interesting passages and took notes on the margins. You are extending the meaning of the text by creating your own commentary to it and perhaps even branching off into creating your own argument inspired by your reading. Your teacher may give you a writing prompt, or ask you to come up with your own topic for a response. In either case, realize that reading responses are supposed to be exploratory, designed to help you delve deeper into the text you are reading than note-taking or underlining will allow.
When writing extended responses to the readings, it is important to keep one thing in mind, and that is their purpose. The purpose of these exploratory responses, which are often rather informal, is not to produce a complete argument, with an introduction, thesis, body, and conclusion. It is not to impress your classmates and your teacher with “big” words and complex sentences. On the contrary, it is to help you understand the text you are working with at a deeper level. The verb “explore” means to investigate something by looking at it more closely. Investigators get leads, some of which are fruitful and useful and some of which are dead-ends. As you investigate and create the meaning of the text you are working with, do not be afraid to take different directions with your reading response. In fact, it is important resist the urge to make conclusions or think that you have found out everything about your reading. When it comes to exploratory reading responses, lack of closure and presence of more leads at the end of the piece is usually a good thing. Of course, you should always check with your teacher for standards and format of reading responses.
Try the following guidelines to write a successful response to a reading:
Remember your goal—exploration. The purpose of writing a response is to construct the meaning of a difficult text. It is not to get the job done as quickly as possible and in as few words as possible.
As you write, “talk back to the text.” Make comments, ask questions, and elaborate on complex thoughts. This part of the writing becomes much easier if, prior to writing your response, you had read the assignment with a pen in hand and marked important places in the reading.
If your teacher provides a response prompt, make sure you understand it. Then try to answer the questions in the prompt to the best of your ability. While you are doing that, do not be afraid of bringing in related texts, examples, or experiences. Active reading is about making connections, and your readers will appreciate your work because it will help them understand the text better.
While your primary goal is exploration and questioning, make sure that others can understand your response. While it is OK to be informal in your response, make every effort to write in a clear, error-free language.
Involve your audience in the discussion of the reading by asking questions, expressing opinions, and connecting to responses made by others.
USE READING FOR INVENTION
Use reading and your responses to start your own formal writing projects. Reading is a powerful invention tool. While preparing to start a new writing project, go back to the readings you have completed and your responses to those readings in search for possible topics and ideas. Also look through responses your classmates gave to your ideas about the text. Another excellent way to start your own writing projects and to begin research for them is to look through the list of references and sources at the end of the reading that you are working with. They can provide excellent topic-generating and research leads.
KEEP A DOUBLE-ENTRY JOURNAL
Many writers like double-entry journals because they allow us to make that leap from summary of a source to interpretation and persuasion. To start a double-entry journal, divide a page into two columns. As you read, in the left column write down interesting and important words, sentences, quotations, and passages from the text. In the right column, right your reaction and responses to them. Be as formal or informal as you want. Record words, passages, and ideas from the text that you find useful for your paper, interesting, or, in any, way striking or unusual. Quote or summarize in full, accurately, and fairly. In the right-hand side column, ask the kinds of questions and provide the kinds of responses that will later enable you to create an original reading of the text you are working with and use that reading to create your own paper.
DON’T GIVE UP
If the text you are reading seems too complicated or “boring,” that might mean that you have not attacked it aggressively and critically enough. Complex texts are the ones worth pursuing and investigating because they present the most interesting ideas. Critical reading is a liberating practice because you do not have to worry about “getting it right.” As long as you make an effort to engage with the text and as long as you are willing to work hard on creating a meaning out of what you read, the interpretation of the text you are working with will be valid.
IMPORTANT: So far, we have established that no pre-existing meaning is possible in written texts and that critical and active readers work hard to create such meaning. We have also established that interpretations differ from reader to reader and that there is no “right” or “wrong” during the critical reading process. So, you may ask, does this mean that any reading of a text that I create will be a valid and persuasive one? With the exception of the most outlandish and purposely-irrelevant readings that have nothing to do with the sources text, the answer is “yes.” However, remember that reading and interpreting texts, as well as sharing your interpretations with others are rhetorical acts. First of all, in order to learn something from your critical reading experience, you, the reader, need to be persuaded by your own reading of the text. Secondly, for your reading to be accepted by others, they need to be persuaded by it, too. It does not mean, however, that in order to make your reading of a text persuasive, you simply have to find “proof” in the text for your point of view. Doing that would mean reverting to reading “for the main point,” reading as consumption. Critical reading, on the other hand, requires a different approach. One of the components of this approach is the use of personal experiences, examples, stories, and knowledge for interpretive and persuasive purposes. This is the subject of the next section of this chapter.
ONE CRITICAL READER’S PATH TO CREATING A MEANING: A CASE STUDY
Earlier on in this chapter, we discussed the importance of using your existing knowledge and prior experience to create new meaning out of unfamiliar and difficult texts. In this section, I’d like to offer you one student writer’s account of his meaning- making process. Before I do that, however, it is important for me to tell you a little about the class and the kinds of reading and writing assignments that its members worked on.
All the writing projects offered to the members of the class were promoted by readings, and students were expected to actively develop their own ideas and provide their own readings of assigned texts in their essays. The main text for the class was the anthology Ways of Reading edited by David Bartholomae and Anthony Petrosky that contains challenging and complex texts. Like for most of his classmates, this approach to reading and writing was new to Alex who had told me earlier that he was used to reading “for information” or “for the main point”.
In preparation for the first writing project, the class read Adrienne Rich’s essay “When We Dead Awaken: Writing as Revision.” In her essay, Rich offers a moving account of her journey to becoming a writer. She makes the case for constantly “revising” one’s life in the light of all new events and experiences. Rich blends voices and genres throughout the essay, using personal narrative, academic argument, and even poetry. As a result, Rich creates the kind of personal-public argument which, on the one hand, highlights her own life, and on the other, illustrates that Rich’s life is typical for her time and her environment and that her readers can also learn from her experiences.
To many beginning readers and writers, who are used to a neat separation of “personal” and “academic” argument, such a blend of genres and styles may seem odd. In fact, on of the challenges that many of the students in the class faced was understanding why Rich chooses to blend personal writing with academic and what rhetorical effects she achieves by doing so. After writing informal responses to the essay and discussing it in class, the students were offered the following writing assignment:
Although Rich tells a story of her own, she does so to provide an illustration of an even larger story—one about what it means to be a woman and a writer. Tell a story of your own about the ways you might be said to have been named or shaped or positioned by an established or powerful culture. Like Rich (and perhaps with similar hesitation), use your own experience as an illustration of both your own situation and the situation of people like you. You should imagine that the assignment is a way for you to use (and put to the test) some of Rich’s terms, words like “re-vision,” “renaming,” and “structure.” (Bartholomae and Petrosky 648).
Notice that this assignment does not ask students to simply analyze Rich’s essay, to dissect its argument or “main points.” Instead, writers are asked to work with their own experiences and events of their own lives in order to provide a reading of Rich which is affected and informed by the writers’ own lives and own knowledge of life. This is critical reading in action when a reader creates his or her one’s own meaning of a complex text by reflecting on the relationship between the content of that text and one’s own life.
In response to the assignment, one of the class members, Alex Cimino-Hurt, wrote a paper that re-examined and re- evaluated his upbringing and how those factors have influenced his political and social views. In particular, Alex was trying to reconcile his own and his parents’ anti-war views with the fact than a close relative of his was fighting in the war in Iraq as he worked on the paper. Alex used such terms as “revision” and “hesitation” to develop his piece.
Like most other writers in the class, initially Alex seemed a little puzzled, even confused by the requirement to read someone else’s text through the prism of his own life and his own experiences. However, as he drafted, revised, and discussed his writing with his classmates and his instructor, the new approach to reading and writing became clearer to him. After finishing the paper, Alex commented on his reading strategies and techniques and on what he learned about critical reading during the project:
ON PREVIOUS READING HABITS AND TECHNIQUES
Previously when working on any project whether it be for a History, English, or any other class that involved reading and research, there was a certain amount of minimalism. As a student I tried to balance the least amount of effort with the best grade. I distinctly remember that before, being taught to skim over writing and reading so that I found “main” points and highlighted them. The value of thoroughly reading a piece was not taught because all that was needed was a shallow interpretation of whatever information that was provided followed by a regurgitation. [Critical reading] provided a dramatic difference in perspective and helped me learn to not only dissect the meaning of a piece, but also to see why the writer is using certain techniques or how the reading applies to my life.
ON DEVELOPING CRITICAL READING STRATEGIES
When reading critically I found that the most important thing for me was to set aside a block of time in which I would’t have to hurry my reading or skip parts to “Get the gist of it.” Developing an eye for…detail came in two ways. The first method is to read the text several times, and the second is to discuss it with my classmates and my teacher. It quickly became clear to me that the more I read a certain piece, the more I got from it as I became more comfortable with the prose and writing style. With respect to the second way, there is always something that you can miss and there is always a different perspective that can be brought to the table by either the teacher or a classmate.
ON READING RICH’S ESSAY
In reading Adrienne Rich’s essay, the problem for me was’t necessarily relating to her work but instead just finding the right perspective from which to read it. I was raised in a very open family so being able to relate to others was learned early in my life. Once I was able to parallel my perspective to hers, it was just a matter of composing my own story. Mine was my liberalism in conservative environments—the fact that frustrates me sometimes. I felt that her struggle frustrated her, too. By using quotations from her work, I was able to show my own situation to my readers.
ON WRITING THE PAPER
The process that I went through to write an essay consisted of three stages. During the first stage, I wrote down every coherent idea I had for the essay as well as a few incoherent ones. This helped me create a lot of material to work with. While this initial material doesn’t always have direction it provides a foundation for writing. The second stage involved rereading Rich’s essay and deciding which parts of it might be relevant to my own story. Looking at my own life and at Rich’s work together helped me consolidate my paper. The third and final stage involved taking what is left and refining the style of the paper and taking care of the mechanics.
ADVICE FOR CRITICAL READERS
The first key to being a critical and active reader is to find something in the piece that interests, bothers, encourages, or just confuses you. Use this to drive your analysis. Remember there is no such thing as a boring essay, only a boring reader.
- Reading something once is never enough so reading it quickly before class just won’t cut it. Read it once to get your brain comfortable with the work, then read it again and actually try to understand what’s going on in it. You can’t read it too many times.
- Ask questions. It seems like a simple suggestion but if you never ask questions you’ll never get any answers. So, while you’re reading, think of questions and just write them down on a piece of paper lest you forget them after about a line and a half of reading.
Reading and writing are rhetorical processes, and one does not exist without the other. The goal of a good writer is to engage his or her readers into a dialog presented in the piece of writing. Similarly, the goal of a critical and active reader is to participate in that dialog and to have something to say back to the writer and to others. Writing leads to reading and reading leads to writing. We write because we have something to say and we read because we are interested in ideas of others.
Reading what others have to say and responding to them help us make that all-important transition from simply having opinions about something to having ideas. Opinions are often over-simplified and fixed. They are not very useful because, if different people have different opinions that they are not willing to change or adjust, such people cannot work or think together. Ideas, on the other hand, are ever evolving, fluid, and flexible. Our ideas are informed and shaped by our interactions with others, both in person and through written texts. In a world where thought and action count, it is not enough to simply “agree to disagree.” Reading and writing, used together, allow us to discuss complex and difficult issues with others, to persuade and be persuaded, and, most importantly, to act.
Reading and writing are inextricably connected, and I hope that this chapter has shown you ways to use reading to inform and enrich you writing and your learning in general. The key to becoming an active, critical, and interested reader is the development of varied and effective reading techniques and strategies. I’d like to close this chapter with the words from the writer Alex Cimino-Hurt: “Being able to read critically is important no matter what you plan on doing with your career or life because it allows you to understand the world around you.”
Bartholomae, David and Anthony Petrosky, Eds. Introduction. Ways of Reading . 8th Ed. New York: Bedford/St. Martin’s, 2008.
Brent, Douglas. 1992. Reading as Rhetorical Invention. NCTE , Urbana, Illinois. Cimino-Hurt, Alex. Personal Interview. 2003.
Martin, Janette. 2004. “Developing ‘Interesting Thoughts:’ Reading for Research.” In Research Writing Revisited: A Sourcebook for Teachers , eds. Pavel Zemliansky and Wendy Bishop, Heinemann, Portsmouth, NH. (3-13).
Rich, Adrienne. 2002. “When We Dead Awaken: Writing as Re-vision.” In Ways of Reading , 6th ed. Eds. Bartholomae, David and Anthony Petrosky. Bedford/St. Martin’s Boston, (627-645).
Research and Critical Reading Copyright © 2016 by Pavel Zemilansky is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Feedback/errata.
Comments are closed.
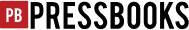
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1 Critical Reading
Elizabeth Browning; Karen Kyger; and Cate Bombick
Reading as a Conversation
What would happen if you walked by the tables in front of Duncan Hall on your first day at HCC, approached a group of strangers quietly chatting, and proceeded to announce to the group exactly what you were thinking at the moment? Most likely, the group would stop talking, look at you, laugh, and slowly move away. Let’s try another approach.
This time, you walk up and quietly join the group. You listen for a few minutes to figure out the topic being discussed and to understand the group members’ different perspectives before adding your own voice to the conversation. You have probably used this method many times throughout your life and have found it to work well, especially when joining a group of people you do not know very well. This method is the very same way to approach reading in your college courses.
To be a successful reader in college, you will need to move beyond simply understanding what the author is trying to say and think about the conversation in which the author is participating.
By thinking about reading and writing as a conversation, you will want to consider:
- Who else has written about this topic?
- Who are they?
- What is their perspective or argument on this topic?
- What type of evidence do they use to support their point of view?
In this chapter, we will introduce expectations for college reading, identify key strategies of skilled readers, and review the active reading process. Throughout the chapter, you will find links to samples, examples, and materials you may use.
We will also be introducing the concept of critical reading. Critical reading is moving beyond just understanding the author’s meaning of a text to consider the choices the author makes to communicate their message.
By learning to read critically, you will not only improve your comprehension of college-level texts, but also improve your writing by learning about the choices other writers have make to communicate their ideas. Honing your writing, reading, and critical thinking skills will give you a more solid foundation for success, both academically and professionally.
Understanding and using the strategies outlined in this chapter is an important part of your success in your ENGL-121 College Composition course. You will need strong reading skills in order to understand assignments, write papers and participate in class discussion. Here are the ENGL-121 objectives that are relevant to the reading process:
4) Maintain a controlling purpose for research and writing that emerges from a clearly-defined research question.
5) Locate, evaluate, and integrate appropriate sources accurately and fairly through paraphrase and direct quotation.
6) Critically engage sources through interpretation, analysis, and/or critique in service of developing and supporting logical, well-defined claims.
Taken together, these objectives prescribe an approach to reading that is driven by questions, that is sensitive to authors’ meaning, credibility, and relevance, and that does not take sources’ perspectives for granted but that evaluates the reliability of their claims.
In This Chapter
1. Expectations for Reading in College
2. What is critical reading?
3. Why do we read critically?
4. How do we read critically?
4.1 Start with Questions
4.2 Identify the Main Idea and Supporting Details
4.3 Decode Vocabulary
4.4 Utilize Metacognitive Strategies
4.5 read recursively, 5. the active reading process, 5.1 before you read, 5.2 while you read, 5.3 after you read.
6. Now what?
1. Expectations for Reading in College
How does reading in college differ from reading in high school.
In college, academic expectations change from what you may have experienced in high school. As the quantity of work expected of you increases, the quality of the work also changes. You must do more than just understand course material and summarize it on an exam. You will be expected to engage seriously with new ideas by reflecting on them, analyzing them, critiquing them, making connections, drawing conclusions, or finding new ways of thinking about them. Educationally, you are moving into deeper waters. Learning how to read and write strategically and critically will help you swim.
2. What is critical reading?
Reading critically does not simply mean being moved, affected, informed, influenced, and persuaded by a piece of writing. It refers to analyzing and understanding the overall composition of the writing as well as how the writing has achieved its effect on the audience.
This level of understanding begins with thinking critically about the texts you are reading. In this case, “critically” does not mean that you are looking for what is wrong with a work (although during your critical process, you may well do that). Instead, thinking critically means approaching a work as if you were a critic or commentator whose job it is to analyze a text beyond its surface.
These rhetorical strategies are covered in the next chapter . If you disagree with a text, what is the point of contention? If you agree with it, how do you think you can expand or build upon the argument put forth?
Consider the example below. Which of the following tweets below are critical and which are uncritical?
3. Why do we read critically?
Critical reading has many uses. If applied to a work of literature, for example, it can become the foundation for a detailed textual analysis. With scholarly articles, critical reading can help you evaluate their potential reliability as future sources.
Finding an error in someone else’s argument can be the point of destabilization you need to make a worthy argument of your own, illustrated in the final tweet from the previous image, for example. Critical reading can help you hone your own argumentation skills because it requires you to think carefully about which strategies are effective for making arguments, and in this age of social media and instant publication, thinking carefully about what we say is a necessity.
4. How to read critically
Reading does not come naturally. It is not an instinct that you were born with — rather, it is a cultural development that began 6,000 years ago when humans began to use symbols to represent ideas. The process of reading is learned through instruction and recruits brain mechanisms that evolved for other purposes.
In other words, you weren’t born to read. Reading is a learned skill that relies on interaction nature, nurture, and culture. It is a cognitive tool that is developed through learning and practice. So what reading strategies are already in your toolbox? What strategies can you add to your toolbox to become a more efficient and effective college reader?
4.1 Start with Questions
Questions to ask a text.
Inquiry-based learning methods, or question-based investigations, are often the basis for writing and research at the college level. Specific questions generated about the text can guide your critical reading process and help you when writing a formal analysis.
When reading critically, you should begin with broad questions and then work towards more specific questions; after all, the ultimate purpose of engaging in critical reading is to turn you into an analyzer who asks questions that work to develop the purpose of the text
In order to develop good questions before reading a text, you will want to think about your purpose for reading. As a college student, you’ll want to think about why your professor assigned this particular text? How does this text connect to topics you have been discussing in class or to other assigned readings?
For example, if you have been assigned to read UMBC President, Freeman Hrabowski’s essay entitled, “Colleges Prepare People for Life,” ask yourself why your professor assigned that particular text. Perhaps your professor wants you to read a variety of perspectives on the purpose of college. In that case, you’ll want to ask a question such as, What is Hrabowski’s view on the purpose of college? Perhaps, your professor is preparing you to write an argument essay and would like students to see how other authors have crafted their arguments. In that case, a good question might be, How does Hrabowski introduce other people’s views on this topic and how can that help me in my own writing?
Another effective questioning strategy is to turn the title or a sub-heading into a question by adding what, how, or why to the title or heading. You can turn the title into a question by adding how. The question becomes “How do colleges prepare people for life?” Once you have finished reading the essay, return to that question to see how well you can answer it using the information you learned from the text.

Questions For Further Inquiry
In addition to asking questions of the text and author, you will want to use a text to develop additional questions about the topic. This is a crucial step in the process of entering into an academic conversation. To develop questions for further inquiry, you should focus on open-ended questions that cannot be easily answered by a quick Internet search.
For example, if you are reading a text about changing the name of Washington’s NFL team, a question for future inquiry could be “What are the effects of media stereotypes?” A closed-ended question such as “What other NFL teams use Native Americans as a mascot?” would close the door to inquiry. The answer to the second question can be easily found using a quick search that ends your line of inquiry. Conversely, the first question can lead to a much deeper level of critical thinking about the topic.
As you read and learn more about the topic, you may want to develop additional questions even if this line of inquiry goes in a completely different direction from where you started. To develop questions for inquiry consider asking these types of questions:
- Where are there holes or gaps in the logic or evidence in this text?
- What else would you like to know about this topic beyond this text?
- How are other authors writing about this topic?
- Where are the disagreements between texts?
More on Starting with a Question
- Asking Questions as a Reading Comprehension Strategy
- Critical Reading Questionnaire
- K-W-L Guide
Your college professors will expect you to be able to read independently to understand all the information you are expected to process in your college texts. Some of your reading assignments will be fairly straightforward. Others will be longer and more complex, so you will need a plan for how to handle them.
For any expository writing—that is, nonfiction, informational writing—your first comprehension goal is to identify the main points and relate any details to those main points. Regardless of what type of expository text you are assigned to read, the primary comprehension goal is to identify the main point: the most important idea that the writer wants to communicate. This idea is often stated early on in the introduction and re-emphasized in the conclusion.
Finding the main point gives you a framework to organize the details presented in the reading and to relate the reading to concepts you learned in class or through other reading assignments. After identifying the main point, find the supporting points: the details, facts, and explanations that develop and clarify the main point.
More on Identifying the Main Idea and Supporting Details
- Finding the Main Idea
- Implied Main Idea
- Supporting Details and Patterns in Reading
- Notes Outline
- Notes Organizer
- Argument Organizer
4.3 Decode Vocabulary
Understanding the vocabulary used in your college texts is a critical component of reading comprehension. Having strategies to use when you come across unfamiliar words will help you build and improve your vocabulary. You can sometimes determine the meaning of a word by looking within the word (at its root, prefix, or suffix) or around the word (at the clues given in the sentence or paragraph in which the word appears). If you are unable to determine the meaning of word in context, you may look up the definition.
Each academic discipline has its own terminology, and part of your success in all of your college courses will require you to move beyond simple memorization of word meanings to using these terms appropriately within the context of the situation. This means being aware that words have different meanings and connotations associated with them, and these meanings and connotations can change depending upon the situation in which they are being used.
Context Determines Meaning
Match the correct meaning of the word synthesis to the context in which it is being used:
Definition #1: the combination of ideas to form a theory or system.
Definition #2: the production of chemical compounds by reaction from simpler materials.
Context: Your English professor would like to see you use more synthesis within the body of your essay.
Answer: You may get a failing grade on your essay if you combine chemicals to form an explosion, so you better go with definition #1!
More on Decoding Vocabulary
- Using Context Clues
- Context Clues and Practice
- Denote or Connote?
- Developing Strategies for Building Vocabulary
Because college-level texts can be challenging, you will also need to monitor your reading comprehension. That is, you will need to stop periodically and assess how well you understand what you are reading. You can improve comprehension by taking time to determine which strategies work best for you and putting those strategies into practice.
Finding the main idea and paying attention to text features as you read helps you figure out what you should know. Just as important, however, is being able to figure out what you do not know and developing a strategy to deal with it.
Textbooks often include comprehension questions in the margins or at the end of a section or chapter. As you read, stop occasionally to answer these questions on paper or in your head. Use them to identify sections you may need to reread, read more carefully, or ask your instructor about later. Even when a text does not have built-in comprehension features, you can actively monitor your own comprehension.
Try these strategies, adapting them as needed to suit different kinds of texts:
- Summarize. At the end of each section, pause to summarize the main points in a few sentences. If you have trouble doing so, revisit that section.
- Ask and answer questions. When you begin reading a section, try to identify two to three questions you should be able to answer after you finish it. Write down your questions and use them to test yourself on the reading. If you cannot answer a question, try to determine why.
- Don’t read in a vacuum. Look for opportunities to discuss the reading with your classmates. Many instructors set up online discussion forums or blogs specifically for that purpose. Participating in these discussions can help you determine whether your understanding of the main points is the same as that of your peers.
More on Metacognitive Strategies
- What is Metacognition?
- Setting a Purpose for Reading
- Cornell Notes
Reading is a recursive, rather than linear, activity. It is rare that you will read a text in college once, straight through from beginning to end. You may need to read a sentence or paragraph several times to understand it. Your reading will slow down or speed up as you encounter novel or familiar information. You may get “lost” in an example and need to double back or skip ahead to understand the point the author is trying to make.
You should plan on reading a text more than once: first for general understanding, and then to analyze and synthesize the material. Reading actively and recursively is the secret to becoming an effective reader.
- First Reading – Focus on the literal meaning of the text. What is the author “saying”? Annotate the text or take notes to keep track of the thesis and key points. Use strategies for unfamiliar vocabulary.
- Second Reading – Focus on “how” the author is communicating. What literary or rhetorical techniques does the author use? Pretend you are having a conversation with the author. What questions do you have? Are there any gaps in the narrative, evidence, or conclusions?
- What ideas/passages did you find most/least interesting?
- What did you learn from the reading that you did not know before?
- Did the author succeed in changing your view on the topic? Why or why not?
- What elements of the text did you connect with the most?
- What problems do you have with the text?
More on Reading Recursively
- Active Reading
- Active Reading In Action
- Active Reading with a Digital Source

What strategies do I use when I read? What strategies do I need to add?
How many times have you read a page in a book, or even just a paragraph, and by the end of it thought to yourself, “I have no idea what I just read; I can’t remember any of it?” Almost everyone has done it, and it’s particularly easy to do when you don’t care about the material, are not interested in the material, or if the material is full of difficult or new concepts. If you don’t feel engaged with a text, then you will passively read it, failing to pay attention to substance and structure. Passive reading results in zero gains; you will get nothing from what you have just read.
On the other hand, critical reading is based on active reading because you actively engage with the text, which means thinking about the text before you begin to read it, asking yourself questions as you read it as well as after you have read it, taking notes or annotating the text, summarizing what you have read, and, finally, evaluating the text.
Completing these steps will help you to engage with a text, even if you don’t find it particularly interesting, which may be the case when it comes to assigned readings for some of your classes. In fact, active reading may even help you to develop an interest in the text even when you thought that you initially had none.
By taking an actively critical approach to reading, you will be able to do the following:
- Stay focused while you read the text
- Understand the main idea of the text
- Understand the overall structure or organization of the text
- Retain what you have read
- Pose informed and thoughtful questions about the text
- Evaluate the effectiveness of ideas in the text
Establish Your Purpose
Establishing why you read something helps you decide how to read it, which saves time and improves comprehension. Before you start to read, remind yourself what questions you want to keep in mind. (Review Start with a Question section in this chapter). Then establish your purpose for reading.
In college and in your profession, you will read a variety of texts to gain and use information (e.g., scholarly articles, textbooks, reviews). Some purposes for reading might include the following:
- to scan for specific information
- to skim to get an overview of the text
- to relate new content to existing knowledge
- to write something (often depends on a prompt)
- to discuss in class
- to critique an argument
- to learn something
- for general comprehension
Strategies differ from reader to reader. The same reader may use different strategies for different contexts because her purpose for reading changes. Ask yourself “why am I reading?” and “what am I reading?” when deciding which strategies work best.
Preview the Text
Once you have established your purpose for reading, the next step is to preview the text. Previewing a text involves skimming over it and noticing what stands out so that you not only get an overall sense of the text, but you also learn the author’s main ideas before reading for details. Thus, because previewing a text helps you better understand it, you will have better success analyzing it.
Questions to ask when previewing may include the following:
- What is the title of the text? Does it give a clear indication of the text’s subject?
- Who is the author? Is the author familiar to you? Is any biographical information about the author included?
- If previewing a book, is there a summary on the back or inside the front of the book?
- What main idea emerges from the introductory paragraph? From the concluding paragraph?
- Are there any organizational elements that stand out, such as section headings, numbering, bullet points, or other types of lists?
- Are there any editorial elements that stand out, such as words in italics, bold print, or in a large font size?
- Are there any visual elements that give a sense of the subject, such as photos or illustrations?
Once you have formed a general idea about the text by previewing it, the next preparatory step for critical reading is to speculate about the author’s purpose for writing.
- What do you think the author’s aim might be in writing this text?
- What sort of questions do you think the author might raise?
Activate Your Background Knowledge on the Topic
All of us have a library of life experiences and previous reading knowledge stored in our brains, but this stored knowledge will sit unused unless we consciously take steps to connect to it or “activate” this knowledge.
After previewing a text, ask yourself, “What do I already know about this topic?” If you realize that you know very little about the topic or have some gaps, you may want to pause and do some quick Internet searches to fill in those gaps.
Although Wikipedia is usually not considered a credible source for an academic essay, it can be a helpful tool to discover what other people are saying about the topic, author, or publisher of a text. Internet searches, online encyclopedias, news websites may all be used to help you quickly learn some of the key issues related to the topic.
As you read, you should consider what new information you have learned and how it connects to what you already know. Making connections between prior knowledge and new information is a critical step in reading, thinking, and learning.
- Reading with Purpose
Improve Comprehension through Annotation
Annotating a text means that you actively engage with it by taking notes as you read, usually by marking the text in some way (underlining, highlighting, using symbols such as asterisks) as well as by writing down brief summaries, thoughts, or questions in the margins of the page. If you are working with a textbook and prefer not to write in it, annotations can be made on sticky notes or on a separate sheet of paper.
Regardless of what method you choose, annotating not only directs your focus, but it also helps you retain that information. Furthermore, annotating helps you to recall where important points are in the text if you must return to it for a writing assignment or class discussion.

More on Active Reading Strategies
- Be an Active Reader
- 10 Active Reading Strategies
- How to Take Notes
- Says/Does In Action
- UNC Annotated Journal Article
- UNC Annotated Book Chapter Excerpt
- Annotation Checklist
Consider the Unique Qualities of the Text
The way you approach a text should vary based on the type of text you encounter. Reading a poem is very different from reading a chapter in a textbook. There are unique structures, elements, and purposes to the various texts you will encounter in college.
Below are some examples of active reading strategies employed with a variety of “texts” you might encounter in college including textbooks, scientific research, online media, artwork, and more. Notice how the readers approach the text differently based on the length, format, subject matter, and the reader’s own purpose for reading.
Once you’ve finished reading, take time to review your initial reactions from your first preview of the text. Were any of your earlier questions answered within the text? Was the author’s purpose similar to what you had speculated it would be?
The following steps will help you process what you have read so that you can move onto the next step of analyzing the text.
- Summarize the text in your own words (note your impressions, reactions, and what you learned)
- Talk to someone about the author’s ideas to check your comprehension
- Identify and reread difficult parts of the text
- Review your annotations
- Try to answer some of your own questions from your annotations
- Connect the text to others you have read or researched on the topic
Once you understand the text, the next steps will be to analyze and synthesize the information with other sources and with your own knowledge. You will be ready to add your perspective, especially if you can provide evidence to support your viewpoint.
Just like with any new skill, developing your ability to read critically will require focus and dedication. With practice, you will gain confidence and fluency in your ability to read critically. You will be ready to join the academic conversations that surround you at HCC and beyond.
More on After-Reading Strategies
- Summary/Response Organizer
- Cause Effect Organizer
- Problem Solution Organizer
6. Now What?
After you have taken the time to read a text critically, the next step, which is covered in the next chapter , is to analyze the text rhetorically to establish a clear idea of what the author wrote and how the author wrote it, as well as how effectively the author communicated the overall message of the text.
Key Takeaways
- College-level reading and writing assignments differ from high school assignments in quantity, quality, and purpose.
- Managing college reading assignments successfully requires you to plan and manage your time, set a purpose for reading, implement effective comprehension skills, and use active reading strategies to deepen your understanding of the text.
- Finding the main idea and paying attention to textual features as you read helps you figure out what you should know. Just as important, however, is being able to figure out what you do not know and developing a strategy to deal with it.
- Ask and answer questions. When you begin reading a section, try to identify two to three questions you should be able to answer after you finish it. If you cannot answer a question, try to determine why. Active engagement in the inquiry process is critical to success in college.
- College writing assignments place greater emphasis on learning to think critically about a particular discipline and less emphasis on personal and creative writing. Your focus becomes analyzing and synthesizing information to enter into academic conversations.
- Do not read in a vacuum. Simply put, don’t rely solely on your own interpretation. Look for opportunities to discuss the reading in and out of class to help clarify and deepen your understanding.
Additional Instructional Overviews
- The Reading Process
- Close Reading in College
- Student Success and Metacognition
CC Licensed Content, Shared Previously
English Composition I , Lumen Learning, CC-BY 4.0.
Rhetoric and Composition , John Barrett, et al., CC-BY-SA 3.0.
Writing for Success , CC-BY-NC-SA 3.0.
Rhetoric and Composition , Bay College , CC-BY 4.0
Image Credits
Figure 1.1 “High School versus College Assignments,” Cate Bombick, Howard Community College, CC -0, derivative image from “High School Versus College Assignments,” Writing for Success , CC-BY-NC-SA 3.0.
Figure 1.2 “Lean In Tweets,” Kalyca Schultz, Virginia Western Community College, CC-0.
Figure 1.3 “Example Questions to Ask a Text,” Kalyca Schultz, Virginia Western Community College, CC-0 .
Figure 1.4 “Sample Says/Does Annotation,” Karen Kyger, Howard Community College, CC-0.
Originally Composed by Elizabeth Browning; revised by Karen Kyger and Cate Bombick, Howard Community College Faculty
Critical Reading Copyright © 2021 by Elizabeth Browning; Karen Kyger; and Cate Bombick is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- Subject Guides
Being critical: a practical guide
Critical reading.
- Being critical
- Critical thinking
- Evaluating information
- Reading academic articles
- Critical writing
The purposes and practices of reading
The way we read depends on what we’re reading and why we’re reading it. The way we read a novel is different to the way we read a menu . Perhaps we are reading to understand a subject, to increase our knowledge, to analyse data, to retrieve information, or maybe even to have fun! The purpose of our reading will determine the approach we take.
Reading for information
Suppose we were trying to find some directions or opening hours... We would need to scan the text for key words or phrases that answer our question, and then we would move on.
It's a bit like doing a Google search and then just reading the results page rather than accessing the website.
Reading for understanding
When we're reading for pleasure or doing background reading on a topic, we'll generally read the text once, from start to finish . We might apply skimming techniques to look through the text quickly and get the general gist. Our engagement with the text might therefore be quite passive: we're looking for a general understanding of what's being written, perhaps only taking in the bits that seem important.
Reading for analysis
When we're doing reading for an essay, dissertation, or thesis, we're going to need to actively read the text multiple times . All the while we'll engage our prior knowledge and actively apply it to our reading, asking questions of what's been written.
This is critical reading !
Reading strategies
When you’re reading you don’t have to read everything with the same amount of care and attention. Sometimes you need to be able to read a text very quickly.
There are three different techniques for reading:
- Scanning — looking over material quite quickly in order to pick out specific information;
- Skimming — reading something fairly quickly to get the general idea;
- Close reading — reading something in detail.
You'll need to use a combination of these methods when you are reading an academic text: generally, you would scan to determine the scope and relevance of the piece, skim to pick out the key facts and the parts to explore further, then read more closely to understand in more detail and think critically about what is being written.
These strategies are part of your filtering strategy before deciding what to read in more depth. They will save you time in the long run as they will help you focus your time on the most relevant texts!
You might scan when you are...
- ...browsing a database for texts on a specific topic;
- ...looking for a specific word or phrase in a text;
- ...determining the relevance of an article;
- ...looking back over material to check something;
- ...first looking at an article to get an idea of its shape.
Scan-reading essentially means that you know what you are looking for. You identify the chapters or sections most relevant to you and ignore the rest. You're scanning for pieces of information that will give you a general impression of it rather than trying to understand its detailed arguments.
You're mostly on the look-out for any relevant words or phrases that will help you answer whatever task you're working on. For instance, can you spot the word "orange" in the following paragraph?
Being able to spot a word by sight is a useful skill, but it's not always straightforward. Fortunately there are things to help you. A book might have an index, which might at least get you to the right page. An electronic text will let you search for a specific word or phrase. But context will also help. It might be that the word you're looking for is surrounded by similar words, or a range of words associated with that one. I might be looking for something about colour, and see reference to pigment, light, or spectra, or specific colours being called out, like red or green. I might be looking for something about fruit and come across a sentence talking about apples, grapes and plums. Try to keep this broader context in mind as you scan the page. That way, you're never really just going to be looking for a single word or orange on its own. There will normally be other clues to follow to help guide your eye.
Approaches to scanning articles:
- Make a note of any questions you might want to answer – this will help you focus;
- Pick out any relevant information from the title and abstract – Does it look like it relates to what you're wanting? If so, carry on...
- Flick or scroll through the article to get an understanding of its structure (the headings in the article will help you with this) – Where are certain topics covered?
- Scan the text for any facts , illustrations , figures , or discussion points that may be relevant – Which parts do you need to read more carefully? Which can be read quickly?
- Look out for specific key words . You can search an electronic text for key words and phrases using Ctrl+F / Cmd+F. If your text is a book, there might even be an index to consult. In either case, clumps of results could indicate an area where that topic is being discussed at length.
Once you've scanned a text you might feel able to reject it as irrelevant, or you may need to skim-read it to get more information.
You might skim when you are...
- ...jumping to specific parts such as the introduction or conclusion;
- ...going over the whole text fairly quickly without reading every word;
Skim-reading, or speed-reading, is about reading superficially to get a gist rather than a deep understanding. You're looking to get a feel for the content and the way the topic is being discussed.
Skim-reading is easier to do if the text is in a language that's very familiar to you, because you will have more of an awareness of the conventions being employed and the parts of speech and writing that you can gloss over. Not only will there be whole sections of a text that you can pretty-much ignore, but also whole sections of paragraphs. For instance, the important sentence in this paragraph is the one right here where I announce that the important part of the paragraph might just be one sentence somewhere in the middle. The rest of the paragraph could just be a framework to hang around this point in order to stop the article from just being a list.
However, it may more often be that the important point for your purposes comes at the start of the paragraph. Very often a paragraph will declare what it's going to be about early on, and will then start to go into more detail. Maybe you'll want to do some closer reading of that detail, or maybe you won't. If the first paragraph makes it clear that this paragraph isn't going to be of much use to you, then you can probably just stop reading it. Or maybe the paragraph meanders and heads down a different route at some point in the middle. But if that's the case then it will probably end up summarising that second point towards the end of the paragraph. You might therefore want to skim-read the last sentence of a paragraph too, just in case it offers up any pithy conclusions, or indicates anything else that might've been covered in the paragraph!
For example, this paragraph is just about the 1980s TV gameshow "Treasure Hunt", which is something completely irrelevant to the topic of how to read an article. "Treasure Hunt" saw two members of the public (aided by TV newsreader Kenneth Kendall) using a library of books and tourist brochures to solve a series of five clues (provided, for the most part, by TV weather presenter Wincey Willis). These clues would generally be hidden at various tourist attractions within a specific county of the British Isles. The contestants would be in radio contact with a 'skyrunner' (Anneka Rice) who had a map and the use of a helicopter (piloted by Keith Thompson). Solving a clue would give the contestants the information they needed to direct the skyrunner (and her crew of camera operator Graham Berry and video engineer Frank Meyburgh) to the location of the next clue, and, ultimately, to the 'treasure' (a token object such as a little silver brooch). All of this was done against the clock, the contestants having only 45' to solve the clues and find the treasure. This, necessarily, required the contestants to be able to find relevant information quickly: they would have to select the right book from the shelves, and then navigate that text to find the information they needed. This, inevitably, involved a considerable amount of skim-reading. So maybe this paragraph was slightly relevant after all? No, probably not...
Skim-reading, then, is all about picking out the bits of a text that look like they need to be read, and ignoring other bits. It's about understanding the structure of a sentence or paragraph, and knowing where the important words like the verbs and nouns might be. You'll need to take in and consider the meaning of the text without reading every single word...
Approaches to skim-reading articles:
- Pick out the most relevant information from the title and abstract – What type of article is it? What are the concepts? What are the findings?;
- Scan through the article and note the headings to get an understanding of structure;
- Look more closely at the illustrations or figures ;
- Read the conclusion ;
- Read the first and last sentences in a paragraph to see whether the rest is worth reading.
After skimming, you may still decide to reject the text, or you may identify sections to read in more detail.
Close reading
You might read closely when you are...
- ...doing background reading;
- ...trying to get into a new or difficult topic;
- ...examining the discussions or data presented;
- ...following the details or the argument.
Again, close reading isn't necessarily about reading every single word of the text, but it is about reading deeply within specific sections of it to find the meaning of what the author is trying to convey. There will be parts that you will need to read more than once, as you'll need to consider the text in great detail in order to properly take in and assess what has been written.
Approaches to the close reading of articles:
- Focus on particular passages or a section of the text as a whole and read all of its content – your aim is to identify all the features of the text;
- Make notes and annotate the text as you read – note significant information and questions raised by the text;
- Re-read sections to improve understanding;
- Look up any concepts or terms that you don’t understand.

Questioning
Questioning goes hand-in-hand with reading for analysis. Before you begin to read, you should have a question or set of questions that will guide you. This will give purpose to your reading, and focus you; it will change your reading from a passive pursuit to an active one, and make it easier for you to retain the information you find. Think about what you want to achieve and keep the purpose in mind as you're reading.
Ask yourself...
- Why am I reading this? — What is my task or assignment question, and how is this source helping to answer it?
- What do I already know about the subject? — How can I relate what I'm reading to my own experiences?
You'll need to ask questions of the text too:
- Examine the evidence or arguments presented;
- Check out any influences on the evidence or arguments;
- Check the limitations of study design or focus;
- Examine the interpretations made.
Are you prepared to accept the authors’ arguments, opinions, or conclusions?
Critical reading: why, what, and how
Blocks to critical reading.
Certain habits or approaches we have to life can hold us back from really thinking objectively about issues. We may not realise it, but often we're our own worst enemies when it comes to being critical...
Select a student to reveal the statement they've made.

I have been asked to work on an area that is completely new. Where do I start in terms of finding relevant texts?
Ask for guidance:
ask your tutor or module leader
use your module reading lists
make use of the Skills Guides (oh... you are! Excellent!)
ask your Faculty Librarians
Take a look at our contextagon and begin to consider sources of information .

I don’t understand what I'm reading – It's too difficult!
If the text is difficult, don’t panic!
If it is a journal article, scan the text first – look at the contents, abstract, introduction, conclusion and subheadings to try to make sense of the argument.
Then read through the whole text to try to understand the key messages, rather than every single word or section. On a second reading, you will find it easier to understand more.
If you are struggling to get to grips with theories or concepts, you might find it useful to look at a summary as a way in -- for example, in an online subject encyclopaedia .
If you are struggling with difficult vocabulary, it may be useful to keep a glossary of key vocabulary, particularly if it is specialist or technical.
Remember, the more you read, the more you will understand it and be able to use it yourself.
Take a look at our Academic sources Skills Guide .

Help! There is too much to read and too little time!
University study involves a large amount of reading. However, some texts on your reading lists are core texts and some are more optional.
You will generally need to read the core text, but on the optional list there may be a range of texts which deal with the same topic from different perspectives. You will need to decide which are the most relevant to your interests and assignments.
Keep in mind the questions you want the text to answer and look for what is relevant to those questions. Prioritise and read only as much as you need to get the information you need (if it's a book, use the index; if it's an article, concentrate on the relevant parts).
Improve your note-taking skills by keeping them brief and selective.
If in doubt, ask your tutor or Faculty Librarians for guidance.
Take a look at the Organise and Analyse section of the Skills Guides.

I am struggling to remember what I have read.
To remember what you have read, you need to interact with the material. If you have questioned and evaluated the material you are reading, you will find it easier to remember.
Improve your active note-taking skills using a method like Cornell or Survey, Question, Read, Recite, Review (SQR3).
Annotate your pdfs and use a note-taking app .
Make time to consolidate your reading periodically. You could do this by summarising key points from memory or connecting ideas using mindmapping.
Consider using a reference management program to keep on top of reading, and mind-mapping software like Mindgenius to connect ideas.

Where did I read that thing?
Make sure you have a good system for taking notes and try to keep your notes organised/in one place, whether that is using an app or taking notes by hand. There is no right way to do this - find a system that works for you.
Logically label and file your notes, linking new information with what you already know and cross-reference with any handouts.
Make sure you make a note of information for referencing sources.
Where possible, save resources you have used to Google Drive or your University filestore , and organise these (e.g. by module, assessment, topic etc.).
Many of the above tips can be achieved with reference management software .

I have strong opinions about the argument being presented in the reading – why can’t I just put this side forward?
Truth is a complicated business. Core texts or texts by highly respected authors are an author’s interpretation, and that interpretation is not above question. Any single text only provides a perspective. Even a scientific observation may be modified by further evidence. Critical writing means making sure your argument is balanced, considering and critiquing a range of perspectives.
Read texts objectively and assess their value in terms of what they can bring to your work, rather than whether you agree with them or not.
If you agree or disagree strongly with an author, you still need to analyse their argument and justify why it is sound or unsound, reliable or unreliable, and valid or lacking validity.
Ignoring opposing views can be a mistake. Your reader may think you are unaware of the different views or are not willing to think the ideas through and challenge them.
Be careful not to be blinded by your own views about a topic or an author. Engaging actively with a text which you initially don’t agree with can mean you have to rethink or adjust your own position, making your final argument stronger.
Take a look at the other parts of the Being critical Skills Guides .
That's not right. Try again.
Being actively critical
Active reading is about making a conscious effort to understand and evaluate a text for its relevance to your studies. You would actively try to think about what the text is trying to say, for example by making notes or summaries.
Critical reading is about engaging with the text by asking questions rather than passively accepting what it says. Is the methodology sound? What was the purpose? Do ideas flow logically? Are arguments properly formulated? Is the evidence there to support what is being claimed?
When you're reading critically, you're looking to...
- ...link evidence to your own research;
- ...compare and contrast different sources effectively;
- ...focus research and sources;
- ...synthesise the information you've found;
- ...justify your own arguments with reference to other sources.
You're going beyond just an understanding of a text. You're asking questions of it; making judgements about it... What you're reading is no longer undisputed 'fact': it's an argument put forward by an author. And you need to determine whether that argument is a valid one.
"Reading without reflecting is like eating without digesting"
– Edmund Burke
"Feel free to reflect on the merits (or not) of that quote..."
– anon.
Critical reading involves understanding the content of the text as well as how the subject matter is developed...
- How true is what's being written?
- How significant are the statements that are being made?
Regardless of how objective, technical, or scientific the text may be, the authors will have made certain decisions during the writing process, and it is these decisions that we will need to examine.
Two models of critical reading
There are several approaches to critical reading. Here's a couple of models you might want to try:
Choose a chapter or article relevant to your assessment (or pick something from your reading list).
Then do the following:
Determine broadly what the text is about.
Look at the front and back covers
Scan the table of contents
Look at the title, headings, and subheadings
Read the abstract, introduction and conclusion
Are there any images, charts, data or graphs?
What are the questions the text will answer? Write some down.
Use the title, headings and subheadings to write questions
What questions do the abstract, introduction and conclusion prompt?
What do you already know about the topic? What do you need to know?
Do a first reading. Read selectively.
Read a section at a time
Answer your questions
Summarise or make brief notes
Underline or highlight any key points
Recite (in your own words)
Recall the key points.
Summarise key points from memory
Try to answer the questions you asked orally, without looking at the text or your notes
Use diagrams or mindmaps to recall the information
After you have completed the reading…
Go back over your notes and check they are clear
Check that you have answered all your questions
At a later date, review your notes to check that they make sense
At a later date, review the questions and see how much you can recall from memory
Choose a relevant article from your reading list and make brief notes on it using the prompts below.
Choose an article you have read earlier in your course and re-read it, applying the prompts below.
Compare your comments and the notes you have made. What are the differences?
Who is the text by? Who is the text aimed at? Who is described in the text?
What is the text about? What is the main point, problem or topic? What is the text's purpose?
Where is the problem/topic/issue situated?, and in what context?
When does the problem/topic/issue occur, and what is its context? When was the text written?
How did the topic/problem/issue occur? How does something work? How does one factor affect another? How does this fit into the bigger picture?
Why did the topic/problem/issue occur? Why was this argument/theory/solution used? Why not something else?
What if this or that factor were added/removed/altered? What if there are alternatives?
So what makes it significant? So what are the implications? So what makes it successful?
What next in terms of how and where else it's applied? What next in terms of what can be learnt? What next in terms of what needs doing now?
Here's a template for use with the model.
Go to File > Make a copy... to create your own version of the template that you can edit.
CC BY-NC-SA Learnhigher
Arguments & evidence
Academic reading can be a trial. In more ways than one...
It might help to think of every text you read as a witness in a court case. And you're the judge ! You're going to need to examine the testimony...
- What’s being claimed ?
- What are the reasons for making that claim?
- Are there gaps in the evidence?
- Do other witnesses support and corroborate their testimony?
- Does the testimony support the overall case ?
- How does the testimony relate to the other witnesses?
You're going to need to consider all sides of the case...
Considering the argument
An argument explains a position on something. A lot of academic writing is about gathering those claims and explaining your own position through their explanations.
You'll need to question...
- ...the author's claims ;
- ...the arguments they use — are their claims well documented ?;
- ...the counter-arguments presented;
- ...any bias in the source;
- ...the research method being used;
- ...how the author qualifies their arguments.
You'll also need to develop your own reasoned arguments, based on a logical interpretation of reliable sources of information.
What's the evidence?
Evidence isn't just the results of research or a reference to an academic study. You might use other authors' opinions to back up your argument. Keep in mind that some evidence is stronger than others:
You can get an idea of an author's certainty through the language they use, too:
Linking evidence to argument
- Why did the author select the evidence they did? — Why did they decide to use a particular methodology, choose a specific method, or conduct the work in the way they did?
- How does the author interpret the evidence?
- How does the evidence prove or help the argument?
Even in the most technical and scientific disciplines, the presentation of argument will always involve elements that can be examined and questioned. For example, you could ask:
- Why did the author select that particular topic of enquiry in the first place?
- Why did the author select that particular process of analysis?
Synthesis :
"the combination of components or elements to form a connected whole."
You'll need to make logical connections between the different sources you encounter, pulling together their findings. Are there any patterns that emerge?
Analyse the texts you've found, and how meaningful they are in context of your studies...
- How do they compare to each other and to any other knowledge you are gathering about the subject? Do some ideas complement or conflict with each other?
- How will you synthesise the different sources to serve an idea you are constructing? Are there any inferences you can draw from the material?
Embracing other perspectives
Good critical research seeks to be impartial, and will embrace (or, at the very least, address) conflicting opinions. Try to bring these into your research to show comprehensive searching and knowledge of the subject.
You can strengthen your argument by explaining, critically, why one source is more persuasive than another.
Recall & review
Synthesising research is much easier if you take notes. When you know an article is relevant to your area of research, read it and make notes which are relevant to you. Consider keeping a spreadsheet or something similar , to make a note of what you have read and how it relates to the task.
You don't need elaborate notes; just a summary of the relevant details. But you can use your notes to help with the process of analysing and synthesising the texts. One method you could try is the recall & review approach:
Try to summarise key words and elements of the text:
- Sketch a rough diagram of the text from memory — test what you can recall from your reading of the text;
- Make headings of the main ideas and note the supporting evidence;
- Include your evaluation — what were the strengths and weaknesses?
- Identify any gaps in your memory.
Go over your notes, focusing on the parts you found difficult. Organise your notes, re-read parts, and start to bring everything together...
- Summarise the text in preparation for writing;
- Be creative: use colour and arrows; make it easy to visualise;
- Highlight the ideas you may want to make use of;
- Identify areas for further research.
Critical analysis vs criticism
The aim of critical reading and critical writing is not to find fault; it's not about focusing on the negative or being derogatory. Rather it's about assessing the strength of the evidence and the argument. It's just as useful to conclude that a study or an article presents very strong evidence and a well-reasoned argument as it is to identify weak evidence and poorly formed arguments.
Criticising
The author's argument is poor because it is badly written.
Critical analysis
The author's argument is unconvincing without further supporting evidence.
Academic reading: What it is and how to do it
Struggling with academic reading? This bitesize workshop breaks it down for you! Discover how to read faster, smarter, and make those academic texts work for you:
Think critically about what you read...
- examine the evidence or arguments presented
- check out any influences on the evidence or arguments
- check out the limitations of study design or focus
- examine the interpretations made

Active critical reading
It's important to take an analytical approach to reading the texts you encounter. In the concluding part of our " Being critical " theme, we look at how to evaluate sources effectively, and how to develop practical strategies for reading in an efficient and critical manner.

Forthcoming training sessions
Forthcoming sessions on :
CITY College
Please ensure you sign up at least one working day before the start of the session to be sure of receiving joining instructions.
If you're based at CITY College you can book onto the following sessions by sending an email with the session details to your Faculty Librarian:
There's more training events at:
- << Previous: Reading academic articles
- Next: Critical writing >>
- Last Updated: Mar 25, 2024 5:46 PM
- URL: https://subjectguides.york.ac.uk/critical
Critical Reading Is Important: Why?

Reading is a proven way to improve knowledge and increase mental abilities. These benefits are enjoyed by those who read for pleasure and those studying in school. It has been shown that those who engage in critical reading have an increase in these benefits.
So, why is critical reading important? It plays a crucial role in your development as a reader and is an excellent workout for the brain. Reading has critical effects on mental development. If you are looking for how to improve critical reading skills, we have an article dedicated to that topic . It offers valuable tips and provides detailed information on why critical thinking is essential to reading.
What Does Reading Critically Mean?
Critical reading refers to the ability to read content and understand the material while determining whether it is fact or fiction. It involves analyzing and evaluating all content. You will have to judge the credibility of what has been written instead of simply assuming it is true. The process involves reading content and then questioning what has been said so you can determine validity. This is an essential skill that will be needed if you are a student who needs to conduct research. It can help in selecting different sources that will be referenced in your own research.
How Is This Important and Effective?
Having the ability to comprehend and understand what is being read is a skill that all students will require. Why is critical viewing, listening, and reading important? It can help enhance the ability to understand and is essential for higher earning. Successful students will not take things at face value. They will use these skills to assess what information is essential and whether it has the appropriate facts.
What is the most crucial requirement for critical reading and writing? This is a question that all students should be able to answer. The main requirement is identifying fact from fiction. You also must be able to look at any arguments presented and determine whether they are supported by valid research.
Beyond mastering the art of critical reading, learning about services like Babbel and the associated Babbel cost could also be beneficial. Babbel offers a wide range of language learning courses, which could help in developing your critical reading skills in multiple languages.
Why Do I Need Critical Reading Skills?
As a reader, having specific skills will help you better understand the text. Instead of simply skimming words, you will benefit from enhanced comprehension. Those who are critical thinkers and readers will seek knowledge. Why is it important to have critical reading skills? As a student, you can raise questions from the content and then be able to evaluate and solve any problems. You will also be able to base all judgments on evidence.
These skills will also help readers identify various arguments and ask thought-provoking questions. This later allows you to develop ideas based on analysis. Instead of simply accepting the information that is presented, having these skills allows for the development of an individualized interpretation of ideas.
As a student applying for college, critical reading will be part of your SAT exam. After completing the exam, you will start the application process for getting into the desired school. One thing that is important at this time is deadlines. Some schools will have a priority deadline. What is a priority deadline ? This is the time in which you must submit an application for consideration.
When it comes to college admissions, there is a difference between rolling admission and standard decisions. If you do not meet the priority deadline, your application will be considered on a rolling basis.
Is rolling admission the same as a regular decision? No. Rolling admission refers to the review of applications as they are sent in. There are no specific deadlines in place. With a regular decision process, you have to submit an application within a specific time frame. We have more detailed information on rolling admissions and priority deadlines on our blog .
Important to Determine Arguments

As a student, critical reading will be important when completing academic assignments. You have to develop your own arguments when writing papers and these skills allow this to be done. By reading texts multiple times, focus can be placed on different aspects. The information that is presented can be analyzed and evidence can be used to support your argument.
When reading, you will have to determine whether the information included can support an argument with facts and data. Why are critical reading skills important? Instead of accepting a claim that is made by another, critical readers will have the skills to examine arguments and see things from both sides. By being able to constantly evaluate what is being read, you can determine if an argument is logical and backed by proper research.
Improving critical reading skills can be an asset for every student. In addition to understanding why critical reading is important, explore strategies on how to improve critical reading . The skills you’ll gain are not only applicable in academic contexts but also invaluable for everyday life.
Critical Reading and Assumptions and Values
When reading any content, it is important to analyze any assumptions that are made by an author. An Assumption is something that an author believes is true in order for them to make an argument. One must have the ability to question any assumptions and determine if it has value. Value is something that one person thinks has importance. Why are values important to known in critical reading? One must understand an argument of an author and use their values to determine whether the standpoint is factual.
Uses in Conducting Scientific Research
When conducting research and completing scientific research papers, this form of thinking will be essential. No matter how technical the subject matter may be, a writer will ace to make a variety of decisions during the research process. This will include determining what information to include in a paper. If you are wondering why is critical reading and thinking important, you will quickly see how effective it is when conducting research.
As you prepare to conduct research, you will have to make use of different sources and the writings of other people. Having appropriate skills will enable one to perform good research and know exactly what to include to make a strong argument. Some features of critical reading that will be used when performing research include:
- Examining evidence or current arguments
- Checking the influence of such evidence
- Learning the limitations of focus
- Examining interpretations
- Deciding how to use researched arguments or opinions
As we delve into the importance of critical reading, considering the safety of online tutoring platforms becomes pertinent. Assessing the question, is online tutoring safe , helps ensure that the learning environment is conducive and secure, adding another layer of confidence as you engage in the learning process.
Critical Thinking and Writing
Critical thinking is a life skill that is learned and it is the ability to understand and evaluate information that is read. Why is reading an important critical thinking skill? The more you read, the more you can analyze information and filter that using your own thought process. This can be a powerful tool in the development of being a critical thinker. As a writer, this skill can help you present ideas and concepts that will stimulate readers.
Critical thinking is what will define your writing style . The best writers are those who have the ability to think critically. If you are wondering why is critical thinking important in reading and writing, it is because it paves the road for a writer to create a story or article that presents an argument clearly. It allows writers to choose appropriate words and ideas that will convey the message with the greatest impact.
Why Ambiguity is Important
Ambiguity plays a key role in being a critical thinker or reader. This refers to words or phrases having various meanings. One must force themselves to look for ambiguity. Any term will be ambiguous when it has a meaning that is uncertain and will require further clarification before any judgment can be made. When making an argument, ambiguity should be avoided. You want clear and concise information that will support a view or an opinion.
If any words or phrases need clarification, they will be considered to be ambiguous. It is essential to take the time to read content and examine it carefully so you can determine the meaning of any phrases. If that meaning is still uncertain, an important ambiguity has been detected. As a student, this will require an extensive vocabulary. You need to know the different meanings of words and determine whether the information supports an argument.
If you need help with improving your critical reading skills, consider hiring an online tutor. We have a list of the top ones here .
The most effective communicators will ensure clarity. They will review what has been written to make sure no cases of ambiguity are present. This allows for a strong argument to be presented and removes any doubt a reader may have.
Writer & Editor
Born and raised with French heritage, our featured author brings a unique European flair to his writing. With years of experience, he has honed his skills as a professional copywriter, mastering not only his native French but also English, ...
Relevant articles

Let’s assume you have registered for this exam and it turns out you don’t feel quite ready to take it. Maybe you wish to postpone it, or don’t take it at all and instead take a different exam. After all, if you are not required by the college to submit your score, then there is…

One of the hardest periods a teenager could experience is probably his or her high school life. When you have to start thinking about your future – what course you want to take, where you want to study, and what your career plans would be ten to twenty years from now. But to get into…
Featured Photo by Nguyen Dang Hoang Nhu on Unsplash “Without continual growth and progress, such words as improvement, achievement, and success have no meaning”, – Benjamin Franklin Knowing how to raise SAT score 200 points in a week can definitely come in handy. At first, it may sound impossible, but with the right strategy and…
Critical reading is a valuable tool for educational growth. It opens our minds better to understand articles and written works such as novels. Critical thinking is essential as it allows us to engage in critical thinking and writing. You need to read with a purpose and value to develop good critical reading skills.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Resume Writing CompTIA Certification on Resume: How to Put It [+Examples]
Resume Writing Can You Put Udemy On Resume?
Admission Consulting The Five Best Graduate School Admissions Consultants Reviewed

Get free insights for your resumes. Get 10% OFF all orders.
OFF on lessons
Critical Reading: Critical Reading
- Critical Reading
- Tools to Aid Reading Comprehension
- Tools for Film Analysis
Resources for Critical Reading
Source: Knott, Deborah. Critical Reading Towards Critical Writing. New College Writing Centre. University of Toronto. http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/reading-and-researching/critical-reading
For a nicely formatted pdf of this page, visit http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/images/stories/Documents/critical-reading.pdf
CRITICAL READING TOWARD CRITICAL WRITING Critical writing depends on critical reading. Most of the essays you write will involve reflection on written texts -- the thinking and research that have already been done on your subject. In order to write your own analysis of this subject, you will need to do careful critical reading of sources and to use them critically to make your own argument. The judgments and interpretations you make of the texts you read are the first steps towards formulating your own approach. CRITICAL READING: WHAT IS IT? To read critically is to make judgments about how a text is argued. This is a highly reflective skill requiring you to “stand back” and gain some distance from the text you are reading. (You might have to read a text through once to get a basic grasp of content before you launch into an intensive critical reading.) THE KEY IS THIS: -- don’t read looking only or primarily for information -- do read looking for ways of thinking about the subject matter When you are reading, highlighting, or taking notes, avoid extracting and compiling lists of evidence, lists of facts and examples. Avoid approaching a text by asking “What information can I get out of it?” Rather ask “How does this text work? How is it argued? How is the evidence (the facts, examples, etc.) used and interpreted? How does the text reach its conclusions? HOW DO I READ LOOKING FOR WAYS OF THINKING? 1. First determine the central claims or purpose of the text (its thesis). A critical reading attempts to identify and assess how these central claims are developed or argued. 2. Begin to make some judgments about context. What audience is the text written for? Who is it in dialogue with? (This will probably be other scholars or authors with differing viewpoints.) In what historical context is it written? All these matters of context can contribute to your assessment of what is going on in a text. 3. Distinguish the kinds of reasoning the text employs. What concepts are defined and used? Does the text appeal to a theory or theories? Is any specific methodology laid out? If there is an appeal to a particular concept, theory, or method, how is that concept, theory, or method then used to organize and interpret the data? You might also examine how the text is organized: how has the author analyzed (broken down) the material? Be aware that different disciplines (i.e. history, sociology, philosophy, biology) will have different ways of arguing.
4. Examine the evidence (the supporting facts, examples, etc) the text employs. Supporting evidence is indispensable to an argument. Having worked through Steps 1-3, you are now in a position to grasp how the evidence is used to develop the argument and its controlling claims and concepts. Steps 1-3 allow you to see evidence in its context. Consider the kinds of evidence that are used. What counts as evidence in this argument? Is the evidence statistical? literary? historical? etc. From what sources is the evidence taken? Are these sources primary or secondary? 5. Critical reading may involve evaluation. Your reading of a text is already critical if it accounts for and makes a series of judgments about how a text is argued. However, some essays may also require you to assess the strengths and weaknesses of an argument. If the argument is strong, why? Could it be better or differently supported? Are there gaps, leaps, or inconsistencies in the argument? Is the method of analysis problematic? Could the evidence be interpreted differently? Are the conclusions warranted by the evidence presented? What are the unargued assumptions? Are they problematic? What might an opposing argument be? SOME PRACTICAL TIPS: 1. Critical reading occurs after some preliminary processes of reading. Begin by skimming research materials, especially introductions and conclusions, in order to strategically choose where to focus your critical efforts. 2. When highlighting a text or taking notes from it, teach yourself to highlight argument: those places in a text where an author explains her analytical moves, the concepts she uses, how she uses them, how she arrives at conclusions. Don’t let yourself foreground and isolate facts and examples, no matter how interesting they may be. First, look for the large patterns that give purpose, order, and meaning to those examples. The opening sentences of paragraphs can be important to this task. 3. When you begin to think about how you might use a portion of a text in the argument you are forging in your own paper, try to remain aware of how this portion fits into the whole argument from which it is taken. Paying attention to context is a fundamental critical move. 4. When you quote directly from a source, use the quotation critically. This means that you should not substitute the quotation for your own articulation of a point. Rather, introduce the quotation by laying out the judgments you are making about it, and the reasons why you are using it. Often a quotation is followed by some further analysis. 5. Critical reading skills are also critical listening skills. In your lectures, listen not only for information but also for ways of thinking. Your instructor will often explicate and model ways of thinking appropriate to a discipline.
Prepared by Deborah Knott, Director of the New College Writing Centre Over 50 other files giving advice on university writing are available at www.writing.utoronto.ca
Reprinted with permission from D. Knott, 2014
Skimming and Scanning
Source: Freedman, Leora. English Language Learning, Arts and Sciences. University of Toronto. http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/reading-and-researching/skim-and-scan
For a nicely printable pdf version of this, visit: http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/images/stories/Documents/skim-and-scan.pdf
Reading to Write: About Skimming and Scanning Your perceptions of any written text are deepened through familiarity. One of the most effective methods for beginning the kind of thoughtful reading necessary for academic work is to get a general overview of the text before beginning to read it in detail. By first skimming a text, you can get a sense of its overall logical progression. Skimming can also help you make decisions about where to place your greatest focus when you have limited time for your reading. Here is one technique for skimming a text. You may need to modify it to suit your own reading style.
a. First, prior to skimming, use some of the previewing techniques. b. Then, read carefully the introductory paragraph, or perhaps the first two paragraphs. As yourself what the focus of the text appears to be, and try to predict the direction of the coming explanations or arguments. c. Read carefully the first one or two sentences of each paragraph, as well as the concluding sentence or sentences. d. In between these opening and closing sentences, keep your eyes moving and try to avoid looking up unfamiliar words or terminology. Your goal is to pick up the larger concepts and something of the overall pattern and significance of the text. e. Read carefully the concluding paragraph or paragraphs. What does the author’s overall purpose seem to be? Remember that you may be mistaken, so be prepared to modify your answer. f. Finally, return to the beginning and read through the text carefully, noting the complexities you missed in your skimming and filling in the gaps in your understanding. Think about your purpose in reading this text and what you need to retain from it, and adjust your focus accordingly. Look up the terms you need to know, or unfamiliar words that appear several times.
Scanning is basically skimming with a more tightly focused purpose: skimming to locate a particular fact or figure, or to see whether this text mentions a subject you’re researching. Scanning is essential in the writing of research papers, when you may need to look through many articles and books in order to find the material you need. Keep a specific set of goals in mind as you scan the text, and avoid becoming distracted by other material. You can note what you’d like to return to later when you do have time to read further, and use scanning to move ahead in your research project.
Copyright © L. Freedman 2012, University of Toronto
Reprinted with permission of L. Freedman, MFA
Help for Reading Philosophy
The philosophical papers assigned for some of your reading may be more abstract and perhaps do not lend themselves to skimming for understanding or the structured abstract.
Here is an excellent guide for writing a philosophy paper from Harvard College Writing Program. Reading the guide will also help with reading a philosophy paper, since it explains how to organize it :
http://www.fas.harvard.edu/~phildept/files/ShortGuidetoPhilosophicalWriting.pdf
In summary, look for the Big Questions, then the explanation of the thesis, or the argument supporting the thesis, or the objection to the thesis, or the consequences of the thesis, or whether acceptance of another argument supports the thesis, or the acceptanceof other viewpoint(s) if I accept the thesis.
The Harvard guide suggests reading your philosophy papers slowly and carefully, several times.
Look for "signposts ," that reveal the author's intent. Examples, "this, I think, is clearly false," "I will argue that...," "I shall consider...," my strategy will be to...".
It might help to draw out the paper in "thought bubbles", giving you a visual representation, or map.
Guidelines on Reading Philosophy by author Jim Pryor suggests:
- Skim the Article to Find its Conclusion and Get a Sense of its Structure
- Go Back and Read the Article Carefully
- Evaluate the Author's Arguments
- << Previous: Tips and Tools to Aid Reading Comprehension
- Next: Tools to Aid Reading Comprehension >>
- Last Updated: Jan 18, 2023 5:27 PM
- URL: https://libguides.library.cofc.edu/critical_reading_LIBR105
College Quick Links
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
4 – Critical Writing

Critical writing depends on critical thinking. Your writing will involve reflection on written texts: that is, critical reading.
[Source: Lane, 2021, Critical Thinking for Critical Writing ]
Critical writing entails the skills of critical thinking and reading. At college, the three skills are interdependent, reflected in the kinds of assignments you have to do.
Now let’s look at some real university-level assignments across different majors. Pay attention to the highlighted words used in the assignment descriptions.
As you can tell, all the assignments have both critical reading and writing components. You have to read a lot (e.g., “Use at least 5 current Economics research articles,” “refer to 2 other documents,” and “Select 4-5 secondary sources”) and critically before you form your own opinions and then start to write. Sometimes reading is for ideas and evidence (i.e., reasons, examples, and information from sources), and other times reading is to provide an evaluation of information accuracy (e.g., research designs, statistics). Without critical thinking and reading, critical writing will have no ground. Critical thinking and reading are the prerequisites for critical writing. A clear definition of critical writing is provided below.
What is Critical Writing?
Critical writing is writing which analyses and evaluates information, usually from multiple sources, in order to develop an argument. A mistake many beginning writers make is to assume that everything they read is true and that they should agree with it, since it has been published in an academic text or journal. Being part of the academic community, however, means that you should be critical of (i.e. question) what you read, looking for reasons why it should be accepted or rejected, for example by comparing it with what other writers say about the topic, or evaluating the research methods to see if they are adequate or whether they could be improved.
[Source: Critical Writing ]
If you are used to accepting the ideas and opinions stated in a text, you have to relearn how to be critical in evaluating the reliability of the sources, particularly in the online space as a large amount of online information is not screened. In addition, critical writing is different from the types of writing (e.g., descriptive writing) you might have practiced in primary and secondary education.
The following table gives some examples to show the difference between descriptive and critical writing (adapted from the website ). Pay attention to the different verbs used in the Table for the comparisons.
You might feel familiar with the verbs used in the column describing critical writing. If you still remember, those words are also used to depict the characteristics of critical thinking and reading.
ACTIVITY #1:
Read the two writing samples, identify which one is descriptive writing and which one is critical writing, and explain your judgment.
Sample 1: Recently, President Jacob Zuma made the decision to reshuffle the parliamentary cabinet, including the firing of finance minister, Pravin Gordhan. This decision was not well received by many South Africans.
Sample 2: President Zuma’s firing of popular finance minister, Gordhan drastically impacted investor confidence. This led to a sharp decrease in the value of the Rand. Such devaluation means that all USD-based imports (including petrol) will rise in cost, thereby raising the cost of living for South Africans, and reducing disposable income. This puts both cost and price pressure on Organisation X as an importer of USD-based goods Y, requiring it to consider doing Z. Furthermore, political instability has the added impact of encouraging immigration, particularly amongst skilled workers whose expertise is valued abroad (brain drain).
[Source: Jansen, 2017, Analytical Writing vs Descriptive Writing ]
Further, to write critically, you also have to pay attention to the rhetorical and logical aspects of writing:
Writing critically involves:
- Providing appropriate and sufficient arguments and examples
- Choosing terms that are precise, appropriate, and persuasive
- Making clear the transitions from one thought to another to ensure the overall logic of the presentation
- Editing for content, structure, and language
An increased awareness of the impact of choices of content, language, and structure can help you as a writer to develop habits of rewriting and revision.
Regarding the content, when writing critically, you cannot just rely on your own ideas, experiences, and/or one source. You have to read a wide range of sources on the specific topic you are exploring to get a holistic picture of what others have discussed on the topic, from which you further make your own judgment. Through reading other sources, you not only form your own judgment and opinions but also collect evidence to support your arguments. Evidence is so important in critical writing. In addition to the collection of evidence, you also need to use different ways (e.g., quoting, paraphrasing, and synthesizing) to integrate the evidence into your writing to increase your critical analysis.
Using quotes is always an issue. Some students like to quote a lot and/or too long throughout their papers, and others do not know why they quote. Remember that when you use direct quotations, you are using others’ ideas, not yours. You should limit the use of quotes to the minimum because readers are always interested in your opinions. In other words, you need to use quotes critically.
When you quote directly from a source, use the quotation critically. This means that you should not substitute the quotation for your own articulation of a point. Rather, introduce the quotation by laying out the judgments you are making about it, and the reasons why you are using it. Often a quotation is followed by some further analysis.
[Source: Knott , n.d., Critical Reading Towards Critical Writing ]
Barna (2017) stated that “A good rule of thumb is that the evidence should only be about 5-10% of the piece.” Further, according to the EAP Foundation.org , you need to avoid doing a laundry list in critical writing:
You cannot just string quotes together (A says this, B says that, C says something else), without looking more deeply at the information and building on it to support your own argument.
This means you need to break down the information from other sources to determine how the parts relate to one another or to an overall structure or purpose [analysing], and then make judgements about it, identifying its strengths and weaknesses, and possibly ‘grey areas’ in between, which are neither strengths nor weaknesses [evaluating]. Critical reading skills will help you with this, as you consider whether the source is reliable, relevant, up-to-date, and accurate.
When and Why do you quote?
When should you use quotes?
Using quotations is the easiest way to include source material, but quotations should be used carefully and sparingly. While paraphrasing and summarizing provide the opportunity to show your understanding of the source material, quoting may only show your ability to type it.
Having said that, there are a few very good reasons that you might want to use a quote rather than a paraphrase or summary:
- Accuracy: You are unable to paraphrase or summarize the source material without changing the author’s intent.
- Authority: You may want to use a quote to lend expert authority for your assertion or to provide source material for analysis.
- Conciseness: Your attempts to paraphrase or summarize are awkward or much longer than the source material.
- Unforgettable language: You believe that the words of the author are memorable or remarkable because of their effectiveness or historical flavor. Additionally, the author may have used a unique phrase or sentence, and you want to comment on words or phrases themselves.
When you decide to quote, be careful of relying too much upon one source or quoting too much of a source and make sure that your use of the quote demonstrates an understanding of the source material. Essentially, you want to avoid having a paper that is a string of quotes with occasional input from you.
[Source: Decide when to Quote, Paraphrase and Summarize ]
How do you quote?
- With a complete sentence
- With “according to”
- With a reporting verb
- With a “that” clause
- As part of your sentence
Citing the islands of Fiji as a case in point, Bordo notes that “until television was introduced in 1995, the islands had no reported cases of eating disorders. In 1998, three years after programs from the United States and Britain began broadcasting there, 62 percent of the girls surveyed reported dieting” (149-50). Bordo’s point is that the Western cult of dieting is spreading even to remote places across the globe.
[Source: Lane, 2020, Quoting: When and How to Use Quotations ]
The firm belief which has been widely advertised is that “international students should be given equal rights and respect while studying abroad” (Lane, 2020, p. 19).
Smith, an agent working at an international company, put forward the seriousness of economic recession brought by the COVID-19 pandemic: “our economy will soon collapse, followed by business failures, elevated unemployment, and social turbulence ” (2021, p. 87).
Dominguez (2002) suggested, “teachers should reflect on their teaching constantly and proactively” to avoid teacher burnout and attrition (pp. 76-79).
According to the IEP student manual, “To study in the IEP you must be 18 years old and your English level must be ‘high beginner’ or higher” (p. 6).
[Source: Five Ways to Introduce Quotations ]
Now move on to the language aspect of critical writing, you should pay attention to the analytical verbs used in critical writing.
Analytical verbs are verbs that indicate critical thinking. They’re used in essays to dissect a text and make interpretive points, helping you to form a strong argument and remain analytical. If you don’t use analytical verbs, you may find yourself simply repeating plot points, and describing a text, rather than evaluating and exploring core themes and ideas.
[Source: What are Analytical Verbs? ]
The use of analytical verbs is also important to show your precision and appropriateness in language use. For example, instead of using says and talks, replace those verbs with states, discusses, or claims. Not only does it enhance the formality of the language, but also it helps to create the tone of writing. This further means that you have to understand the specific meaning, purpose, and function of each verb in a specific context as shown in the table below.
[Source: Impressive Verbs to use in your Research Paper ]
The verbs listed under each category are NOT synonyms and are different based on context. Please ensure that the selected verb conveys your intended meaning.
It is recommended that you check out Academic Phrasebank for more advanced and critical language use.
The accuracy of language use that is important for critical writing is also reflected in the use of hedges .
Hedging is the use of linguistic devices to express hesitation or uncertainty as well as to demonstrate politeness and indirectness.
People use hedged language for several different purposes but perhaps the most fundamental are the following:
- to minimize the possibility of another academic opposing the claims that are being made
- to conform to the currently accepted style of academic writing
- to enable the author to devise a politeness strategy where they are able to acknowledge that there may be flaws in their claims
[Source: What Is Hedging in Academic Writing?]
There are different types of hedges used in writing to make your claim less certain but more convincing. For example, what is the difference between the two sentences as shown below?
No hedging: We already know all the animals in the world.
With hedging: It’s possible that we may already know most animals in the world.
[Source: Hedges and Boosters ]
Check this table for different types of hedges.
[Source: Features of academic writing]
Practice how to tone down the arguments.
ACTIVITY #2
Add hedges to the following arguments.
Except for the content and language aspects of critical writing, the last aspect is the organization, including both the overall structure and the paragraph level.
Here is one example of a critical writing outline.
One easy-to-follow outline format is alphanumeric, which means it uses letters of the alphabet and numbers to organize text.
For example:
- Hook: _____________________
- Transition to thesis: _____________________
- Thesis statement with three supporting points:_____________________
- Topic sentence: _____________________
- Evidence (data, facts, examples, logical reasoning): _____________________
- Connect evidence to thesis: _____________________
- Restate thesis: _____________________
- Summarize points: _____________________
- Closure (prediction, comment, call to action): _____________________
[Source: Academic Writing Tip: Making an Outline ]
1. Introduction
- Thesis statement
2. Topic one
- First piece of evidence
- Second piece of evidence
3. Topic two
4. Topic three
5. Conclusion
- Summary/synthesis
- Importance of topic
- Strong closing statement
[Source: Caulfield, 2021, How to Write an Essay Outline]
ACTIVITY #3:
The following essay was adapted from a student’s writing. Please identify the components of each paragraph.
Artificial Intelligence: An Irreplaceable Assistant in Policy-making
Do you understand artificial intelligence (AI)? Are you excited that humans can create these machines that think like us? Do you ever worry that they develop too advanced to replace humans? If you have thought about these questions, you are already in the debate of the century. AI is a term used to describe machine artifacts with digital algorithms that have the ability to perceive contexts for action and the capacity to associate contexts to actions (Bryson & Winfield, 2017). The 21st century has witnessed a great number of changes in AI. As AI shows its great abilities in decision-making, humans are relying more on AI to make policies. Despite some concerns about the overuse of AI, AI is no longer to be replaced in policy-making because it has the capabilities that humans cannot achieve, such as transparent decision-making and powerful data processing.
AI has the capacity to use algorithms or systems to make the decision-making process more transparent (Walport & Sedwill, 2016). Many decisions made by humans are based upon their intuition rather than the direct result of the deliberate collection and processing of information (Dane et al., 2012). Intuition is useful in business when considering the outcome of an investment or a new product. However, in politics, the public would often question whether the policy is biased, so a transparent decision-making process should be used instead of intuition. AI can make political decisions more transparent by visualizing digital records (Calo, 2017). AI can make decisions without any discrimination and can have the public better understand of the policies.
In addition, AI can process a large amount of information at a speed faster than the cognitive ability of the most intelligent human policymakers (Jarrahi, 2018). A qualified policy must be based on facts reflected by data, so researching data is an essential part of policy-making. There are two main challenges for the human decision-makers in this area: (1) The amount of data is too large and (2) the relationship between data is too complex. Handling these two problems is where AI is superior. The high computing power of AI makes it an effective tool for retrieving and analyzing large amounts of data, thus reducing the complexity of the logic between problems (Jarrahi, 2018). Without AI, the policymakers would be overwhelmed by tons of data in this modern information age. It is almost impossible for them to convert those data into useful information. For example, data provided to the politician who is responsible for health care is mostly from the electronic health record (HER). HER is just the digital record transported from paper-based forms (Bennett et al., 2012). AI can analyze the data to generate clinical assessments, symptoms, and patient behavior and then link that information with social factors such as education level and economic status. According to the information from AI, the policy maker can make policies for healthcare improvement (Bennett et al., 2012). With the assistance of AI, the government can not only collect data easier but also utilize those data as operable Information.
However, while AI shows its great abilities in policy-making, it also brings considerable risks to contemporary society, and the most significant one is privacy. The only source for AI systems to learn human behavior is data, so AI needs to collect enormous quantities of information about users in order to perform better. Some scholars claim that the main problem with AI data collection is the use of data for unintended purposes. The data is likely to be processed, used, or even sold without the users’ permission (Bartneck et al, 2021). The 2018 Cambridge Analytica scandal showed how private data collected through Facebook can be used to manipulate elections (Bartneck et al, 2021). While privacy is a crucial problem, this is a handleable problem and we cannot deny the benefits brought by using AI. The most appropriate way to solve this problem is to establish a complete regulatory system. In fact, many policies have been made to protect user privacy in AI data collection. One of safeguard in this area is to restrict the centralized processing of data. Researchers are also conducting a lot of research in this area and have achieved some technological breakthroughs. For example, open-source code and open data formats will allow a more transparent distinction between private and transferable information, blockchain-based technologies will allow data to be reviewed and tracked, and “smart contracts” will provide transparent control over how data is used without the need for centralized authority (Yuste & Goering, 2017).
In conclusion, although there may be some privacy-related issues with AI policies, the powerful data collection capabilities and transparent decision-making process of AI will bring many benefits to humans. In the future, AI is more likely to continue to serve as an assistant to humans when making policies under a complete and strict regulatory system.
Bartneck, Christoph. Lütge, Christoph. Wagner, Alan. Welsh, Sean. (2021). Privacy Issues of AI, pp.61-70. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-51110-4_8.
Bennett C, Doub T, Selove R (2012) EHRs Connect Research and Practice: Where Predictive Modeling, Artificial Intelligence, and Clinical Decision Support Intersect https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1204/1204.4927.pdf. Accessed 1 April 2021.
Bryson J and Winfield A (2017) Standardizing Ethical Design Considerations for Artificial Intelligence and Autonomous Systems. http://www.cs.bath.ac.uk/~jjb/ftp/BrysonWinfield17-oa.pdf. Accessed 1 April 2021.
Calo, R (1993) Artificial Intelligence Policy: A Primer and Roadmap. https://lawreview.law.ucdavis.edu/issues/51/2/Symposium/51-2_Calo.pdf , Accessed 1 April 2021.
Dane, Erik., Rockmann, Kevin. W., & Pratt, Michael G. (2012). When should I trust my gut? Linking domain expertise to intuitive decision-making effectiveness. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 119(2), 187—194.
Jarrahi, M. (2018). Artificial intelligence and the future of work: Human-AI symbiosis in organizational decision making, Business Horizons, Volume 61, Issue 4, Pages 577-586, ISSN 0007-6813, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2018.03.007.
Walport M, & Sedwill M. (2016). Artificial intelligence: opportunities and implications for the future of decision making. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attach ment_data/file/566075/gs-16-19-artificial-intelligence-ai-report.pdf, Accessed 1 April 2021.
Rafael, Y., & Sara, G. (2017). Four ethical priorities for neurotechnologies an AI https://www.nature.com/news/four-ethical-priorities-for-neurotechnologies-and-ai 1.22960. Accessed 1 April 2022.
Apart from the overall structure of critical writing, it is also important to pay attention to the paragraph-level structure. There are different paragraph models for critical writing.
Model 1: TED model for writing critical paragraphs
Paragraph model for critical writing
Often in assignments, you are expected to critically evaluate – this means to assess the relevance and significance of concepts relating to a specific topic or assignment question. Introduce your point. Give examples from reading. Is there support for your argument or can you identify weaknesses? Are there different perspectives to compare and contrast? Build your explanation and create your objective, reasoned argument (case or thesis) based on the evaluation from different perspectives. You will include your conclusion and point of view, communicating your stance, having made a judgment on research you have found and its significance in contributing to answering your assignment question.
Use the TED model to integrate critical thinking into your writing:
Each example of evidence in your writing should have a clear purpose or function. Be explicit and tell the reader what it contributes to your reasoning.
Professional practice is more complex than simply applying theory to practice, since it involves a professional juggling of situational demands, intuition, experiences and knowledge (Schön, 1991). Practitioners do not apply research findings in a simple deductive process; they need time to think, translate and relate the research findings to their particular setting. The extent to which a given piece of evidence is utilised by an individual in practice depends on their sense of the situation and this inevitably involves professional judgement.
Topic (in red); Evidence (in orange); Further explanation (in blue); Discussion (in green)
Model 2: WEED model for writing critical paragraphs
This is a model for writing critical paragraphs. It’s taken from Godwin’s book called ‘Planning your Essay’. Each paragraph should be on a single topic, making a single point. A paragraph is usually around a third of a page.
W is for What
You should begin your paragraph with the topic or point that you’re making so that it’s clear to your lecturer. Everything in the paragraph should fit in with this opening sentence.
E is for Evidence
The middle of your paragraph should be full of evidence – this is where all your references should be incorporated. Make sure that your evidence fits in with your topic.
E is for Examples
Sometimes it’s useful to expand on your evidence. If you’re talking about a case study, the example might be how your point relates to the particular scenario being discussed.
D is for Do
You should conclude your paragraph with the implications of your discussion. This gives you the opportunity to add your commentary, which is very important in assignments that require you to use critical analysis. So, in effect, each paragraph is like a mini-essay, with an introduction, main body, and conclusion.
Example: a good critical paragraph
Exposure to nature and green spaces has been found to increase health, happiness, and wellbeing. Whilst trees and greenery improve air quality by reducing air pollutants, green spaces facilitate physical activity, reduce stress, and provide opportunities for social interaction (Kaplan, 1995; Lachowycz,and Jones, 2011; Ward Thompson et al., 2012; Hartig et al., 2014; Anderson et al., 2016). Older adults have described increased feelings of wellbeing while spending time in green spaces and walking past street greenery (Finaly et al., 2015; Orr et al., 2016). They are more likely to walk on streets which are aesthetically pleasing (Lockett, Willis and Edwards, 2005) while greenery such as flowers and trees play an important role in improving the aesthetics of the environment (Day, 2008). Therefore, greater integration of urban green spaces and street greenery in cities may have the potential to increase physical activity and wellbeing in older adults.
What (in red), Evidence (in orange), Do (in blue).
[Source: Learning Hub, 2021 ]
Please identify the paragraph-level components in the following paragraphs. You can use different colors to indicate different components.
Social Media plays a key role in slowing the spread of vaccine misinformation. According to Nikos-Rose (2021) from the University of California, individuals’ attitudes towards vaccination can negatively be influenced by social media. They can simply post a piece of misleading information to the public, and the deceived ones will share it with their families and friends. The role of media can also help boost the public’s confidence in the vaccination. The media can provide valuable information for the public to know that the vaccine is safe. Almost everyone in the modern era lives with a cell phone now. People on social media can also share their experiences after getting vaccinated. Influences can help boost the public’s confidence. Just as voters would receive “I voted” after casting their ballots, vaccination distribution sites can provide “I got vaccinated” stickers. This can encourage individuals to post on the media that they have received the vaccine (Milkman, 2020). Furthermore, those who spread misleading information should be fined by the authorities. This punishment would be sufficient for them to learn their lesson. People who oversee data and information in social media should be concerned about the spread of misleading information on social media. After deleting the false information, they should put up a notice stating that is fake. This will help the public to understand which information should be trusted or not. Moreover, people who find misleading information online should report it to the administration. This could help prevent false info from circulating on the internet.
Recent studies showed that the contamination of land and water can also negatively affect the production of crops and the food systems as the safety of products can be compromised by the chemicals used by fracking. In addition, the amount of freshwater required for the mixture of the fracking fluids can generate a lack of water supply to the local agricultural industries. The fresh water is the 90-97 % of the fracking fluids, and the water deployed is not possible to recycle efficiently. In fact, the wastewater became a further challenge to the agricultural sector as it can make the soil dry and unusable for crops (Pothukuchi et al. 2018). The challenges faced by the agricultural sector are reflected in the farmlands and livestocks as well. For example, in Pennsylvania, the Dairy farming is one of the major agricultural sectors. This particular sector requires unpolluted water and pasturelands to enable the cows to produce milk. Since 1996 this sector began to fail, but the largest decrease in cows that produce milk took place between 2007 and 2011. It was the exact same period when the fracking industries reached their peak in this area (Pothukuchi et al. 2018). Another piece of evidence is related to the air pollution caused by fracking, specifically, the pollution of agricultural pollinators such as bees. The population of air caused by fracking has led to a huge degradation of that volatiles endangering the local and global food production. Those outcomes are closely related to the low level of planning abilities in rural areas, where fracking usually takes place. Particularly, the gap between fracking industry actors and local officials didn’t allow the development of a proper level of policies and regulations.
References:
Academic writing tip: Making an outline. (2020, December 8). The International Language Institute of Massachusetts. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://ili.edu/2020/12/08/academic-writing-tip-making-an-outline/
Caulfield, J. (2021, December 6). How to Write an Essay Outline | Guidelines & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-outline/
Choudhary, A. (n.d.). Impressive Verbs to use in your Research Paper. Editage. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://www.editage.com/all-about-publication/research/impressive-Verbs-to-use-in-your-Research-Paper.html
Critical reading towards critical writing. (n.d.). University of Toronto. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://advice.writing.utoronto.ca/researching/critical-reading/
Critical writing. (n.d.). Teesside University. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://libguides.tees.ac.uk/ld.php?content_id=33286287
Critical writing. (n.d.-b). EAP FOUNDATION.COM. Https://www.eapfoundation.com/writing/critical/
Decide when to quote, paraphrase and summarize. (n.d.). University of Houston-Victoria. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://www.uhv.edu/curriculum-and-student-achievement/student-success/tutoring/student-resources/a-d/decide-when-to-quote-paraphrase-and-summarize/
Features of academic writing. (n.d.). UEFAP. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from http://www.uefap.com/writing/feature/hedge.htm
Five ways to introduce quotations. (n.d.). University of Georgia. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://dae.uga.edu/iep/handouts/Five-Ways-to-Introduce-Quotations.pdf
Jansen, D. (2017, April). Analytical writing vs descriptive writing. GRADCOACH. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://gradcoach.com/analytical-vs-descriptive-writing/
Hedges and Boosters. (n.d.). The Nature of Writing. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://natureofwriting.com/courses/introduction-to-rhetoric/lessons/hedges-and-boosters/topic/hedges-and-boosters
How to write critically. (n.d.). Teesside University. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://libguides.tees.ac.uk/ld.php?content_id=31275168
Lane, J. (2021, July 9). Critical thinking for critical writing. Simon Fraser University. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://www.lib.sfu.ca/about/branches-depts/slc/writing/argumentation/critical-thinking-writing
LibGuides: Critical Writing: Online study guide. (n.d.). Sheffield Hallam University. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://libguides.shu.ac.uk/criticalwriting
What are analytical verbs? (n.d.). Twinkl. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://www.twinkl.com/teaching-wiki/analytical-verbs
What is hedging in academic writing? (2022, May 3). Enago Academy. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://www.enago.com/academy/hedging-in-academic-writing/
Critical Reading, Writing, and Thinking Copyright © 2022 by Zhenjie Weng, Josh Burlile, Karen Macbeth is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Critical Reading Importance in Education Research Paper
Introduction.
Academic research is a rigorous process that involves formulation of a research topic, collection, analysis and presentation of data (Booth, 2011). This paper discusses the process of critical reading of literature and how to avoid plagiarism.
Critical Reading
Most scholarly research activities involve critical review of secondary data such as books, articles, periodicals and journals (Jupp, 2006). Although there are various ways of reading text, critical reading is important in academics activities at college and university levels (Leedy & Osmond, 2012, p. 180). The process of critical reading involves comprehension and in-depth analysis of literature (Lesley, 2001, p. 182). Critical reading is not synonymous with reading and critiquing literature because it includes text evaluation (Christensen, Johnson, & Turner, 2011). Text evaluation as an aspect of critical reading involves close examination of what is written (John, 2009, p. 99).
Elements of Critical Reading
As already mentioned, critical reading transcends mere text comprehension. Nonetheless, understanding text is the starting point in critical reading because analysis and evaluation of literature is not possible without proper text comprehension (John, 2009, pp. 98-99). Therefore, after recognizing what a text discusses, the next step is to interpret it (Leedy & Osmond, 2012). Text interpretation involves pondering what a text is trying to achieve. For instance, it is important to determine whether a book is explaining, discussing or arguing out a certain issue (Kuhn, 2012). Lastly, a critical reader should deduce what an entire literature is discussing.
Importance of Critical Reading
Critical reading is important because of the following reasons. First, it gives the reader a good understanding of arguments and ideas discussed in literature (Neuman, 2011). Secondly, critical reading of several texts enables a reader to understand a given subject from various perspectives, which is important in academics (John, 2009, pp. 99-100). Thirdly, it enables a person to interpret literature and make a logical conclusion from a personal point of view (Becky, 2011, pp. 90-92). Lastly, critical reading helps in identification of gaps and biases in literature, which creates the basis for further research in a given subject (Willis, 2007).
Research on Education Topic
When searching for research materials, it is advisable for researchers to use commonly used words in research topics. On the other hand, long phrases and sentences should be avoided because they hinder access to research materials. Some of the key words that can be used to search literature on education research topic include cause, impact, learning, challenges and effect. These words are often used in formulation of many research topics (Stribling, 2008, pp. 36-37). For instance, what are the effects of technology on education pedagogy in American universities? In this research topic, the word effect has been used in formulating the independent variable (Lesley, 2001, p. 182).
How to Avoid Plagiarism in Literature Reviews
Plagiarism is one of the challenges often experienced during presentation of academic research findings (Stribling, 2008, p. 35). Plagiarism is an aspect of piracy and can occur in various forms. In academic context, it refers to using an individual’s work without proper reference to it (John, 2009, pp. 108-109). Nonetheless, plagiarism can be avoided through proper paraphrasing. Proper internal citations and bibliography also help in avoiding plagiarism (Mannion, 2009, p. 332). Students should not cut and paste other people’s works without paraphrasing, quoting and making proper citations (Giroux, 2008, pp. 102-103).
Unintentional Plagiarism and its Consequences
Unintentional plagiarism often occurs unconsciously in the process of writing due to lack of citation and quoting skills (John, 2009, pp. 98-110). For instance, failure to quote an entire sentence can lead to plagiarism. In addition, careless paraphrasing of text by altering a few synonyms without reworking the entire sentence leads to plagiarism (Giroux, 2008, pp. 84-90).
Plagiarism has serious ramifications in academics and can lead to expulsion or suspension of a student depending on the degree of the offense (Jesson & Matheson, 2011). In extreme cases, it can lead to incarceration of an individual if he or she is found guilty of passing off another person’s intellectual work as his or hers.
Experiences with Plagiarism
Experiences with plagiarism are often disgusting because one has to face serious penalties if found guilty of committing it. In some cases, a student may have to rewrite an entire work due to plagiarism (Mannion, 2009, pp. 323-339). Rewriting an assignment is a long painful process because it requires a lot of time and resources. If a student is found guilty of plagiarism, he or she loses academic credibility, which can be really devastating (Becky, 2011, pp. 87-105). Sometimes it is not easy for students to detect plagiarism in an essay and this can lead to wastage of time. Therefore, plagiarism is a serious challenge to students.
From this discussion it is evident that critical reading is an intensive process that requires the reader to understand, analyze and interpret a text with an aim of finding out what the entire manuscript is intending to achieve. Students should therefore practice good critical reading skills.
Becky, R. (2011). From Apprehension to Critical Literacy. Journal of Education Thought , 45(1), 87-105.
Booth, A. (2011). Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review. London: Sage.
Christensen, L., Johnson, R., & Turner, L. (2011). Research Methods, Design, and Analysis. Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Giroux, H. (2008). Reading texts, literacy, and textual authority. Journal of Education , 172(1), 84-103.
Jesson, J., & Matheson, L. (2011). Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic. London: Sage.
John, W. (2009). Critical language awareness: Key principles for a course in critical reading. Language Awareness , 2(3), 98-110.
Jupp, V. (2006). The Sage Dictionary of Social Research Methods. London: Sage.
Kuhn, T. (2012). The Structure of Scientific Revolutions. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press.
Leedy, P., & Osmond, J. (2012). Practical Research: Planning and Design. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Lesley, M. (2001). Exploring the links between critical and developmental reading. Journal of Adolescent and Adult Literacy , 45(3), 180-189.
Mannion, G. (2009). Reading, writing, resonating: Striking chords across the contexts of students’ everyday and college lives. Pedagogy, Culture &Society , 17(3), 323- 339.
Neuman, W. (2011). Social Research Methods: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches. Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Stribling, S. (2008). Using Critical Literacy Practices in the Classroom. New England Reading Association , 44(1),34-38.
Willis, J. (2007). Foundations of Qualitative Research: Interpretive and Critical Approaches. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 31). Critical Reading Importance in Education. https://ivypanda.com/essays/critical-reading-importance-in-education/
"Critical Reading Importance in Education." IvyPanda , 31 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/critical-reading-importance-in-education/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Critical Reading Importance in Education'. 31 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Critical Reading Importance in Education." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/critical-reading-importance-in-education/.
1. IvyPanda . "Critical Reading Importance in Education." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/critical-reading-importance-in-education/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Critical Reading Importance in Education." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/critical-reading-importance-in-education/.
- Paraphrasing and Quoting Special Education Articles
- Avoiding Plagiarism With Paraphrasing
- Plagiarism and Paraphrasing
- Paraphrasing and Plagiarism
- Plagiarism Elimination in Academic Writing
- Maintaining Academic Integrity by Avoiding Plagiarism
- Plagiarism: For and Against
- Tips on Avoiding Plagiarism
- Academic Honesty and Plagiarism
- Importance of Plagiarism Strategies in Writing
- Academic Integrity Definition
- Cooperative Learning Models
- Place Value Misconceptions and Techniques to Correct Them
- Learning Styles in Asian International Students
- Online Classes Vs. Traditional Classes Essay

What is Critical Reading and Why is it Important?
What is critical reading, what not to do....
Some students enjoy reading academic texts like a novel: from the beginning to the end and think they can remember everything they've read, but that is inefficient and unrealistic. Critical reading places an emphasis on determining which texts can be trusted as pertinent and credible, as some are more compelling or valid than others. It is critical that you keep your topic or research question in mind when selecting relevant passages.
What to do...
- Who wrote this resource, and on what authority
- Why has this resource been written?
- When was this resource written?
- What does this resource reveal that is useful to me?
In summary...
- Have a basic understanding of the topic: This can be gained from the lectures, tutorials, textbooks, or other general resources.
- Read the text with a dictionary in hand and watch for words you don't know. Ask yourself why the author wrote the passage and how it will be useful to you in your research.
- Read slowly: When you slow down your reading, you are more likely to make more connections within the text.
Get access today for 20% off by using the code: ABYDBLOG .

- Business Solutions
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Affiliate Program Terms and Conditions
Connect with us
- ABY D Blog
Huge offer is waiting for you!
Do not miss, great offer today.

Sign in/up with Google
Sign in/up with Facebook
Sign in/up with Linkedin
Sign in/up with Apple
Sign in/up with Twitter

- Roadmap to Oxbridge
- Roadmap to Ivy Leagues
- Pathway Discovery
- Course Discovery
- Pre-University
- Our Partners
- Testimonials
- Book Free Consultation

Why Students Should Practice Critical Reading
How often do people read these days? According to Cartridge People , 41% of people in the UK spend less than an hour a week reading or listening to books. The pandemic has increased the amount of people reading, and with it, the need to read critically.
What is critical reading and why should people, especially students, practice it? Read on to find out.
What is critical reading?
Critical reading is an act of active reading . While many students may consume a lot of storybooks or online text, they often do so without questioning the text or analysing it. Critical reading creates a deeper understanding of the text, as you would analyse, interpret and evaluate it. For example, one may look into a news report about a traditional festival from a cultural perspective and think about how the text represented the event to their audience.
Of course, critical reading is not something that should be practiced all the time, as it requires a lot of mental exercise, but can be a good habit to establish when encountering text. Reading is still a good source of mental stimulation and entertainment. However, asking questions like ‘Why is this text written?’ or ‘Why is this text written in this way?’ not only helps students understand how a text works, it can also improve their writing.
Why should students practice critical reading?
Without putting critical reading or thinking into practice, some students simply do not question what they read . This can lead them to miss out important information or implications of the text, leaving them susceptible to being manipulated. Take a look at advertisements for example, most advertisements use persuasive language to sell their product or service to the audience. Questioning the claims or promises in the ad is an example of critical reading.
Students who read critically will be able to separate opinion from fact . This skill is particularly important not only in reading but for discussions as well. Students who are able to distinguish them can extract key information quickly and avoid being tricked by misrepresented opinions. They will be able to sort out valid and relevant information depending on the topic, avoiding fallacies and protecting them from fake news .
Reflecting on their own biases and opinions is also part of critical reading. Students get to think about what assumptions they are making when reading something. This helps them challenge their own thoughts and opens their mind to newer ideas and perspectives. This aspect of critical reading comes hand-in-hand with critical thinking, an important, sought-after skill. Read about how to think critically here .
Like critical thinking, critical reading should be put into practice from upper primary level onwards. StarWorks is our comprehensive enrichment programme which focuses on critical reading, critical thinking, writing and speaking. Sign up today to be eligible for an early bird discount! The offer will end on 1 April 2021.
Read what our students have to say about StarWorks:
“PrepWorks has features such as friendly staff and amazing education techniques. The teachers there are very experienced and they are also very caring for our needs. I can see why PrepWorks is a popular choice for most parents and it is only through PrepWorks that I managed to come this far in writing. Before I went to PrepWorks I did not know how to write a good persuasive argument, input my feelings and describe my surroundings using my five senses. Now that I have experienced PrepWorks, I am very confident in my writing skills. I am astonished by the amount of hard work and generosity the teachers have put into my education. I would like to thank teacher Nazya in particular as she was the one who guided me through the concepts of writing.”
Chong Yong Ho, Student

Related Posts

You're one step closer to reaching your education goals.
Great! Just enter the student name, email address and phone number to register.
Okay. Let's begin with the student introduction.
- Select Country
- Åland Islands
- Afghanistan
- American Samoa (US)
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bermuda (UK)
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Burkina Faso
- Burma (Myanmar)
- Central African Republic
- Congo, Democratic Republic of the
- Congo, Republic of the
- Cook Islands (NZ)
- Czech Republic
- Dominican Republic
- East Timor (Timor-Leste)
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Falkland Islands (UK)
- Faroe Islands (Denmark)
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia (France)
- Gibraltar (UK)
- Greenland (Denmark)
- Guernsey (UK)
- Guinea-Bissau
- Hong Kong (China)
- Isle of Man (UK)
- Ivory Coast
- Jersey (UK)
- Korea, North
- Korea, South
- Liechtenstein
- Macau (China)
- Marshall Islands
- Mayotte (France)
- Micronesia, Federated States of
- Netherlands
- New Caledonia (France)
- New Zealand
- Norfolk Island (Australia)
- Northern Mariana Islands (US)
- Palestinian territories
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Pitcairn Islands (UK)
- Réunion (France)
- Russian Federation
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha (UK)
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon (France)
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Saudi Arabia
- Sierra Leone
- Solomon Islands
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Svalbard and Jan Mayen (Norway)
- Switzerland
- Tokelau (NZ)
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turkmenistan
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Vatican City
- Wallis and Futuna (France)
- Western Sahara
Guardian Information
Terms & Conditions
By enrolling into programs offered through PrepWorks Sdn. Bhd. and any of its related companies or subsidiaries (collectively referred to as "PrepWorks"), the applicant and parent acknowledge and agree to our Terms and Conditions as specified below:
Enrollment:
- PrepWorks reserves the right to discontinue a student's enrollment at any time due to non-payment of tuition in part or in full, disruptive behavior in the tutorial.
- Enrollment will be on a first come first served basis. PrepWorks reserves the right to release students’ tutoring weekly slot if payment is not received in full by the indicated due date.
- PrepWorks reserves the right to change the class instructor for courses or individual private lessons as deemed appropriate or necessary. PrepWorks is not required to provide prior notice for such arrangements.
- Students must settle all tutoring fees before indicated due date on invoice for the month. PrepWorks reserves the right to discontinue tutoring services if student has not settled the course fee.
- All tutoring payments are non-refundable once the student’s tutoring slot has been confirmed.
- Late payments received after the indicated due date will be subject to a penalty fee. This applies to all tutoring, academic and enrichment programs.
- 5% penalty charge will apply on outstanding fees after one month of due date
- 10% penalty charge will apply on outstanding fees after three months of due date
- 15% penalty charge will apply on outstanding fees after six months of due date
Make-up Classes:
- PrepWorks offers make-up tutoring sessions for tutoring sessions missed at a date agreed with the tutor within the following month. If a date cannot be agreed upon, a refund in the form of credit in the following invoice can be done. In the event of tutor absence, PrepWorks will notify the student of any tutor substitution or tuition rescheduling.
- It is the parent’s/student’s responsibility to inform PrepWorks (by phone or e-mail) before the start of the lesson in the event of absence due to illness. Other than sick leave with a doctor’s note, we require at least 48 hours advance notice for absence and will not accommodate rescheduling or make- up lesson request for notification given less than 48 hours prior to the lesson or after lesson.
- Missed lesson(s) by the student are non-refundable and non-transferable if notification is later than the 48 hours advance notice period. It is the parent’s/student’s responsibility to contact PrepWorks and/or the respective tutor to schedule lessons and notify PrepWorks and/or the respective tutor of any rescheduling.
- In the event of tutor absence, the tutor will notify parent/student of lesson rescheduling or PrepWorks will notify parent/student as soon as PrepWorks is notified by the tutor. Other than rescheduling lesson due to illness, the tutor will provide 48 hours’ notice or will reschedule lesson. If lesson cannot be rescheduled, the missed lesson will not be charged or refunded as credit in the following month's invoice.
Tutoring Withdrawal:
- To withdraw from any course or private lesson, it is the parent/student’s responsibility to provide PrepWorks with at least one month’s prior notice in writing (e-mail, fax or letter). For withdrawals without proper notification, parents/students are liable for the following month’s tutoring fees.
Refund Policy:
- In case of school closure prior to the commencement of a course, we will refund in full the outstanding tutoring fee collected to the parent/student immediately.
- There is no refund for tutoring confirmed by PrepWorks. However, in the event that a confirmed tutoring session needs to be cancelled by PrepWorks and the student declines the revised arrangements offered by PrepWorks, we will refund in full or on a pro-rata basis the tutoring fees collected as soon as possible and in any event no later than one month after the notification date of the tutoring cancellation.
Refund Procedures:
- We will inform the parent/student of refund arrangements either by phone or in writing (e-mail,fax or letter).
- We will refund tutoring fee payments to the student in accordance to the above policies.
- Parents/students agree not to reproduce, distribute or show to any other person, in whole or in part, any of the class materials, lesson notes, assessments and tests distributed by PrepWorks without the prior written consent of PrepWorks.
- Parents/students are not permitted to solicit or make private arrangements for tuition with instructors/tutors employed by PrepWorks. In such cases, all services from PrepWorks can be withdrawn from the student with immediate effect with no refund of any outstanding, and the tutor will be at risk of losing their contract with PrepWorks.
- Photographs and videos may be taken occasionally during the tutoring time. Students and participants agree to be photographed or taped. PrepWorks reserves all rights to images and footages.
- PrepWorks reserves the right to use the applicant/student’s work for promotional or educational purposes.
- Parents are responsible to arrange appropriate transportation or pick-up for students to and from PrepWorks premises. PrepWorks does not require students to sign-out or notify us when they are leaving the premises.
- PrepWorks will not be held responsible for personal injuries, accidents, losses and damages incurred by the student while at home or PrepWorks' premises.

- Importance Of Reading Essay
Importance of Reading Essay
500+ words essay on reading.
Reading is a key to learning. It’s a skill that everyone should develop in their life. The ability to read enables us to discover new facts and opens the door to a new world of ideas, stories and opportunities. We can gather ample information and use it in the right direction to perform various tasks in our life. The habit of reading also increases our knowledge and makes us more intellectual and sensible. With the help of this essay on the Importance of Reading, we will help you know the benefits of reading and its various advantages in our life. Students must go through this essay in detail, as it will help them to create their own essay based on this topic.
Importance of Reading
Reading is one of the best hobbies that one can have. It’s fun to read different types of books. By reading the books, we get to know the people of different areas around the world, different cultures, traditions and much more. There is so much to explore by reading different books. They are the abundance of knowledge and are best friends of human beings. We get to know about every field and area by reading books related to it. There are various types of books available in the market, such as science and technology books, fictitious books, cultural books, historical events and wars related books etc. Also, there are many magazines and novels which people can read anytime and anywhere while travelling to utilise their time effectively.
Benefits of Reading for Students
Reading plays an important role in academics and has an impactful influence on learning. Researchers have highlighted the value of developing reading skills and the benefits of reading to children at an early age. Children who cannot read well at the end of primary school are less likely to succeed in secondary school and, in adulthood, are likely to earn less than their peers. Therefore, the focus is given to encouraging students to develop reading habits.
Reading is an indispensable skill. It is fundamentally interrelated to the process of education and to students achieving educational success. Reading helps students to learn how to use language to make sense of words. It improves their vocabulary, information-processing skills and comprehension. Discussions generated by reading in the classroom can be used to encourage students to construct meanings and connect ideas and experiences across texts. They can use their knowledge to clear their doubts and understand the topic in a better way. The development of good reading habits and skills improves students’ ability to write.
In today’s world of the modern age and digital era, people can easily access resources online for reading. The online books and availability of ebooks in the form of pdf have made reading much easier. So, everyone should build this habit of reading and devote at least 30 minutes daily. If someone is a beginner, then they can start reading the books based on the area of their interest. By doing so, they will gradually build up a habit of reading and start enjoying it.
Frequently Asked Questions on the Importance of Reading Essay
What is the importance of reading.
1. Improves general knowledge 2. Expands attention span/vocabulary 3. Helps in focusing better 4. Enhances language proficiency
What is the power of reading?
1. Develop inference 2. Improves comprehension skills 3. Cohesive learning 4. Broadens knowledge of various topics
How can reading change a student’s life?
1. Empathy towards others 2. Acquisition of qualities like kindness, courtesy
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Your task as an enlightened critical reader is to read what is on the page, giving the writer a fair chance to develop ideas and allowing yourself to reflect thoughtfully, objectively, on the text. 3. Consider the title. This may seem obvious, but the title may provide clues to the writer's attitude, goals, personal viewpoint, or approach.
Critical reading is the process of reading texts with the purpose to understand them fully. It involves asking questions about the author's intention, the text's structure and purpose, and the meanings of individual words and phrases. Critical readers also consider the context in which a text was written and how it might be interpreted by ...
Critical reading involves making observations and insights—track them! My process involves underlining, especially as I see recurring terms, images, or themes. ... which helps me complicate my own conclusions—a great start to a potential essay! Critical reading is an important prerequisite for the academic writing that Princeton professors ...
Critical Thinking is an Extension of Critical Reading. Thinking critically, in the academic sense, involves being open-minded - using judgement and discipline to process what you are learning about without letting your personal bias or opinion detract from the arguments. Critical thinking involves being rational and aware of your own feelings ...
Being critical is indeed a key skill you will need for your assessments, whether this be an essay, exam or oral presentation. But thinking critically is only the second step in a three-step process. This 'critical process' normally begins with critical reading and ends with critical writing (in the case of an essay); critical thinking comes ...
While the best way to develop your skills as a writer is to actually practice by writing, practicing critical reading skills is crucial to becoming a better writer. Careful and skilled readers develop a stronger understanding of topics, learn to better anticipate the needs of the audience, and pick up writing "maneuvers" and strategies from ...
To read critically is to make judgements about how a text is argued. This is a highly reflective skill requiring you to "stand back" and gain some distance from the text you are reading. (You might have to read a text through once to get a basic grasp of content before you launch into an intensive critical reading.) THE KEY IS THIS:
Critical reading is a vital part of the writing process. In fact, reading and writing processes are alike. In both, you make meaning by actively engaging a text. As a reader, you are not a passive participant, but an active constructor of meaning. Exhibiting an inquisitive, "critical" attitude towards what you read will make anything you read ...
www.communicate.gse.harvard.edu | 5 • A piece uses racial terminology that would be unacceptable for a modern author, but was standard at the time of writing. • An article about the role of standardized testing may rest on different assumptions depending on the author's home country. • A specialized journal of economics likely selects and publishes articles with a
Reading critically does not simply mean being moved, affected, informed, influenced, and persuaded by a piece of writing. It refers to analyzing and understanding the overall composition of the writing as well as how the writing has achieved its effect on the audience. This level of understanding begins with thinking critically about the texts ...
Writers make claims for personal reasons that critical readers need to learn to understand and evaluate. Feelings can be a source of shareable good reason for belief. Readers and writers need to use, judiciously, ethical and pathetic proofs in interpreting texts and in creating their own. Research is recursive.
The process of reading is learned through instruction and recruits brain mechanisms that evolved for other purposes. In other words, you weren't born to read. Reading is a learned skill that relies on interaction nature, nurture, and culture. It is a cognitive tool that is developed through learning and practice.
To read critically is to make judgments about how a text is argued. This is a highly reflective skill requiring you to "stand back" and gain some distance from the text you are reading. (You might have to read a text through once to get a basic grasp of content before you launch into an intensive critical reading.) THE KEY IS THIS: When you ...
Being critical: Critical reading. The way we read depends on what we're reading and why we're reading it. The way we read a novel is different to the way we read a menu. Perhaps we are reading to understand a subject, to increase our knowledge, to analyse data, to retrieve information, or maybe even to have fun!
Why is it important to have critical reading skills? As a student, you can raise questions from the content and then be able to evaluate and solve any problems. You will also be able to base all judgments on evidence. These skills will also help readers identify various arguments and ask thought-provoking questions.
To read critically is to make judgments about how a text is argued. This is a highly reflective. skill requiring you to "stand back" and gain some distance from the text you are reading. (You. might have to read a text through once to get a basic grasp of content before you launch into an. intensive critical reading.)
Critical reading does not have to be all negative. The aim of critical reading is not to find fault but to assess the strength of the evidence and the argument. It is just as useful to conclude that a study, or an article, presents very strong evidence and a well-reasoned argument, as it is to identify the studies or articles that are weak.
Critical writing depends on critical thinking. Your writing will involve reflection on written texts: that is, critical reading. [Source: Lane, 2021, Critical Thinking for Critical Writing] Critical writing entails the skills of critical thinking and reading. At college, the three skills are interdependent, reflected in the kinds of assignments ...
Importance of Critical Reading. Critical reading is important because of the following reasons. First, it gives the reader a good understanding of arguments and ideas discussed in literature (Neuman, 2011). Secondly, critical reading of several texts enables a reader to understand a given subject from various perspectives, which is important in ...
Critical reading is a skill that is used to analyse, question, and interpret written works. It allows for the understanding and assessment of an author's argument, and the ability to form an independent judgement. Critical reading is important because it allows for a greater understanding of the world around us and helps us to develop our own ...
Students get to think about what assumptions they are making when reading something. This helps them challenge their own thoughts and opens their mind to newer ideas and perspectives. This aspect of critical reading comes hand-in-hand with critical thinking, an important, sought-after skill. Read about how to think critically here .
Remember, reading empowers! If parents are not encouraging their children to read independently, then this encouragement has to take place in the classroom. Oscar Wilde said: "It is what you read when you don't have to that determines what you will be when you can't help it.". The importance of reading for students is no secret.
1. Empathy towards others 2. Acquisition of qualities like kindness, courtesy. 500+ Words Essay on Importance of Reading is provided here to help students learn how to write an effective essay on this topic. They must go through this essay in-depth and then try to write their own essay.