- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion

Should We Get Rid of Homework?
Some educators are pushing to get rid of homework. Would that be a good thing?

By Jeremy Engle and Michael Gonchar
Do you like doing homework? Do you think it has benefited you educationally?
Has homework ever helped you practice a difficult skill — in math, for example — until you mastered it? Has it helped you learn new concepts in history or science? Has it helped to teach you life skills, such as independence and responsibility? Or, have you had a more negative experience with homework? Does it stress you out, numb your brain from busywork or actually make you fall behind in your classes?
Should we get rid of homework?
In “ The Movement to End Homework Is Wrong, ” published in July, the Times Opinion writer Jay Caspian Kang argues that homework may be imperfect, but it still serves an important purpose in school. The essay begins:
Do students really need to do their homework? As a parent and a former teacher, I have been pondering this question for quite a long time. The teacher side of me can acknowledge that there were assignments I gave out to my students that probably had little to no academic value. But I also imagine that some of my students never would have done their basic reading if they hadn’t been trained to complete expected assignments, which would have made the task of teaching an English class nearly impossible. As a parent, I would rather my daughter not get stuck doing the sort of pointless homework I would occasionally assign, but I also think there’s a lot of value in saying, “Hey, a lot of work you’re going to end up doing in your life is pointless, so why not just get used to it?” I certainly am not the only person wondering about the value of homework. Recently, the sociologist Jessica McCrory Calarco and the mathematics education scholars Ilana Horn and Grace Chen published a paper, “ You Need to Be More Responsible: The Myth of Meritocracy and Teachers’ Accounts of Homework Inequalities .” They argued that while there’s some evidence that homework might help students learn, it also exacerbates inequalities and reinforces what they call the “meritocratic” narrative that says kids who do well in school do so because of “individual competence, effort and responsibility.” The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students. Calarco, Horn and Chen write, “Research has highlighted inequalities in students’ homework production and linked those inequalities to differences in students’ home lives and in the support students’ families can provide.”
Mr. Kang argues:
But there’s a defense of homework that doesn’t really have much to do with class mobility, equality or any sense of reinforcing the notion of meritocracy. It’s one that became quite clear to me when I was a teacher: Kids need to learn how to practice things. Homework, in many cases, is the only ritualized thing they have to do every day. Even if we could perfectly equalize opportunity in school and empower all students not to be encumbered by the weight of their socioeconomic status or ethnicity, I’m not sure what good it would do if the kids didn’t know how to do something relentlessly, over and over again, until they perfected it. Most teachers know that type of progress is very difficult to achieve inside the classroom, regardless of a student’s background, which is why, I imagine, Calarco, Horn and Chen found that most teachers weren’t thinking in a structural inequalities frame. Holistic ideas of education, in which learning is emphasized and students can explore concepts and ideas, are largely for the types of kids who don’t need to worry about class mobility. A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can’t think of one that matters more than the simple satisfaction of mastering something that you were once bad at. That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right.
Students, read the entire article, then tell us:
Should we get rid of homework? Why, or why not?
Is homework an outdated, ineffective or counterproductive tool for learning? Do you agree with the authors of the paper that homework is harmful and worsens inequalities that exist between students’ home circumstances?
Or do you agree with Mr. Kang that homework still has real educational value?
When you get home after school, how much homework will you do? Do you think the amount is appropriate, too much or too little? Is homework, including the projects and writing assignments you do at home, an important part of your learning experience? Or, in your opinion, is it not a good use of time? Explain.
In these letters to the editor , one reader makes a distinction between elementary school and high school:
Homework’s value is unclear for younger students. But by high school and college, homework is absolutely essential for any student who wishes to excel. There simply isn’t time to digest Dostoyevsky if you only ever read him in class.
What do you think? How much does grade level matter when discussing the value of homework?
Is there a way to make homework more effective?
If you were a teacher, would you assign homework? What kind of assignments would you give and why?
Want more writing prompts? You can find all of our questions in our Student Opinion column . Teachers, check out this guide to learn how you can incorporate them into your classroom.
Students 13 and older in the United States and Britain, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public.
Jeremy Engle joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2018 after spending more than 20 years as a classroom humanities and documentary-making teacher, professional developer and curriculum designer working with students and teachers across the country. More about Jeremy Engle
25 Reasons Homework Should Be Banned (Busywork Arguments)

As students across the globe plow through heaps of homework each night, one question lingers in the minds of educators, parents, and students alike: should homework be banned?
This question is not new, yet it continues to spark lively debate as research findings, anecdotal evidence, and personal experiences paint a complex picture of the pros and cons of homework.
On one hand, proponents of homework argue that it reinforces classroom learning, encourages a disciplined work ethic, and provides teachers with valuable insight into student comprehension. They see homework as an extension of classroom instruction that solidifies and enriches learning while fostering important skills like time management and self-discipline. It also offers an opportunity for parents to be involved in their children's education.
However, some people say there are a lot of downsides. They argue that excessive homework can lead to stress and burnout, reduce time for extracurricular activities and family interactions, exacerbate educational inequalities, and even negatively impact students' mental health.

This article presents 25 reasons why we might need to seriously consider this radical shift in our educational approach. But first, lets share some examples of what homework actually is.
Examples of Homework
These examples cover a wide range of subjects and complexity levels, reflecting the variety of homework assignments students might encounter throughout their educational journey.
- Spelling lists to memorize for a test
- Math worksheets for practicing basic arithmetic operations
- Reading assignments from children's books
- Simple science projects like growing a plant
- Basic geography assignments like labeling a map
- Art projects like drawing a family portrait
- Writing book reports or essays
- Advanced math problems
- Research projects on various topics
- Lab reports for science experiments
- Reading and responding to literature
- Preparing presentations on various topics
- Advanced math problems involving calculus or algebra
- Reading classic literature and writing analytical essays
- Research papers on historical events
- Lab reports for advanced science experiments
- Foreign language exercises
- Preparing for standardized tests
- College application essays
- Extensive research papers
- In-depth case studies
- Advanced problem-solving in subjects like physics, engineering, etc.
- Thesis or dissertation writing
- Extensive reading and literature reviews
- Internship or practicum experiences
Lack of proven benefits

Homework has long been a staple of traditional education, dating back centuries. However, the actual efficacy of homework in enhancing learning outcomes remains disputed. A number of studies indicate that there's no conclusive evidence supporting the notion that homework improves academic performance, especially in primary education . In fact, research suggests that for younger students, the correlation between homework and academic achievement is weak or even negative .
Too much homework can often lead to increased stress and decreased enthusiasm for learning. This issue becomes particularly pressing when considering the common 'more is better' approach to homework, where the quantity of work given to students often outweighs the quality and effectiveness of the tasks. For instance, spending countless hours memorizing facts for a history test may not necessarily translate to better understanding or long-term retention of the subject matter.
However, it's worth noting that homework isn't completely devoid of benefits. It can help foster self-discipline, time management skills, and the ability to work independently. But, these positive outcomes are usually more pronounced in older students and when homework assignments are thoughtfully designed and not excessive in volume.
When discussing the merits and drawbacks of homework, it's critical to consider the nature of the assignments. Routine, repetitive tasks often associated with 'drill-and-practice' homework, such as completing rows of arithmetic problems or copying definitions from a textbook, rarely lead to meaningful learning. On the other hand, assignments that encourage students to apply what they've learned in class, solve problems, or engage creatively with the material can be more beneficial.
Increased stress

Homework can often lead to a significant increase in stress levels among students. This is especially true when students are burdened with large volumes of homework, leaving them with little time to relax or pursue other activities. The feeling of constantly racing against the clock to meet deadlines can contribute to anxiety, frustration, and even burnout.
Contrary to popular belief, stress does not necessarily improve performance or productivity. In fact, high levels of stress can negatively impact memory, concentration, and overall cognitive function. This counteracts the very purpose of homework, which is intended to reinforce learning and improve academic outcomes.
However, one might argue that homework can teach students about time management, organization, and how to handle pressure. These are important life skills that could potentially prepare them for future responsibilities. But it's essential to strike a balance. The pressure to complete homework should not come at the cost of a student's mental wellbeing.
Limited family time
Homework often infringes upon the time students can spend with their families. After spending the entire day in school, children come home to yet more academic work, leaving little room for quality family interactions. This limited family time can hinder the development of important interpersonal skills and familial bonds.
Moreover, family time isn't just about fun and relaxation. It also plays a crucial role in the social and emotional development of children. Opportunities for unstructured play, family conversations, and shared activities can contribute to children's well-being and character building.
Nonetheless, advocates of homework might argue that it can be a platform for parental involvement in a child's education. While this may be true, the involvement should not transform into parental control or cause friction due to differing expectations and pressures.
Reduced physical activity
Homework can often lead to reduced physical activity by eating into the time students have for sports, recreation, and simply being outdoors. Physical activity is essential for children's health, well-being, and even their academic performance. Research suggests that physical activity can enhance cognitive abilities, improve concentration, and reduce symptoms of ADHD .
Homework, especially when it's boring and repetitive, can deter students from engaging in physical activities, leading to a sedentary lifestyle. This lack of balance between work and play can contribute to physical health problems such as obesity, poor posture, and related health concerns.
Homework proponents might point out that disciplined time management could allow students to balance both work and play. However, given the demanding nature of many homework assignments, achieving this balance is often easier said than done.
Negative impact on sleep

A significant concern about homework is its impact on students' sleep patterns. Numerous studies have linked excessive homework to sleep deprivation in students. Children often stay up late to complete assignments, reducing the amount of sleep they get. Lack of sleep can result in a host of issues, from poor academic performance and difficulty concentrating to physical health problems like weakened immunity.
Even the quality of sleep can be affected. The stress and anxiety from a heavy workload can lead to difficulty falling asleep or restless nights. And let's not forget that students often need to wake up early for school, compounding the negative effects of late-night homework sessions.
On the other hand, some argue that homework can teach children time management skills, suggesting that effective organization could help prevent late-night work. However, when schools assign excessive amounts of homework, even the best time management might not prevent encroachment on sleep time.
Homework can exacerbate existing educational inequalities. Not all students have access to a conducive learning environment at home, necessary resources, or support from educated family members. For these students, homework can become a source of stress and disadvantage rather than an opportunity to reinforce learning.
Children from lower socio-economic backgrounds might need to contribute to household chores or part-time work, limiting the time they have for homework. This can create a gap in academic performance and grades, reflecting not on the students' abilities but their circumstances.
While homework is meant to level the playing field by providing additional learning time outside school, it often does the opposite. It's worth noting that students from privileged backgrounds can often access additional help like tutoring, further widening the gap.
Reduced creativity and independent thinking
Homework, particularly when it involves rote learning or repetitive tasks, can stifle creativity and independent thinking. Students often focus on getting the "right" answers to please teachers rather than exploring different ideas and solutions. This can hinder their ability to think creatively and solve problems independently, skills that are increasingly in demand in the modern world.
Homework defenders might claim that it can also promote independent learning. True, when thoughtfully designed, homework can encourage this. But, voluminous or repetitive tasks tend to promote compliance over creativity.
Diminished interest in learning
Overburdening students with homework can diminish their interest in learning. After long hours in school followed by more academic tasks at home, learning can begin to feel like a chore. This can lead to a decline in intrinsic motivation and an unhealthy association of learning with stress and exhaustion.
In theory, homework can deepen interest in a subject, especially when it involves projects or research. Yet, an excess of homework, particularly routine tasks, might achieve the opposite, turning learning into a source of stress rather than enjoyment.
Inability to pursue personal interests
Homework can limit students' ability to pursue personal interests. Hobbies, personal projects, and leisure activities are crucial for personal development and well-being. With heavy homework loads, students may struggle to find time for these activities, missing out on opportunities to discover new interests and talents.
Supporters of homework might argue that it teaches students to manage their time effectively. However, even with good time management, an overload of homework can crowd out time for personal interests.
Excessive workload
The issue of excessive workload is a common complaint among students. Spending several hours on homework after a full school day can be mentally and physically draining. This workload can lead to burnout, decreased motivation, and negative attitudes toward school and learning.
While homework can help consolidate classroom learning, too much can be counterproductive. It's important to consider the overall workload of students, including school, extracurricular activities, and personal time, when assigning homework.
Limited time for reflection
Homework can limit the time students have for reflection. Reflection is a critical part of learning, allowing students to digest and integrate new information. With the constant flow of assignments, there's often little time left for this crucial process. Consequently, the learning becomes superficial, and the true understanding of subjects can be compromised.
Although homework is meant to reinforce what's taught in class, the lack of downtime for reflection might hinder deep learning. It's important to remember that learning is not just about doing, but also about thinking.
Increased pressure on young children
Young children are particularly vulnerable to the pressures of homework. At an age where play and exploration are vital for cognitive and emotional development, too much homework can create undue pressure and stress. This pressure can instigate a negative relationship with learning from an early age, potentially impacting their future attitude towards education.
Advocates of homework often argue that it prepares children for the rigors of their future academic journey. However, placing too much academic pressure on young children might overshadow the importance of learning through play and exploration.
Lack of alignment with real-world skills
Traditional homework often lacks alignment with real-world skills. Assignments typically focus on academic abilities at the expense of skills like creativity, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence. These are crucial for success in the modern workplace and are often under-emphasized in homework tasks.
Homework can be an opportunity to develop these skills when properly structured. However, tasks often focus on memorization and repetition, rather than cultivating skills relevant to the real world.
Loss of motivation
Excessive homework can lead to a loss of motivation. The constant pressure to complete assignments and meet deadlines can diminish a student's intrinsic motivation to learn. This loss of motivation might not only affect their academic performance but also their love of learning, potentially having long-term effects on their educational journey.
Some believe homework instills discipline and responsibility. But, it's important to balance these benefits against the potential for homework to undermine motivation and engagement.
Disruption of work-life balance
Maintaining a healthy work-life balance is as important for students as it is for adults. Overloading students with homework can disrupt this balance, leaving little time for relaxation, socializing, and extracurricular activities. All of these are vital for a student's overall development and well-being.
Homework supporters might argue that it prepares students for the workloads they'll face in college and beyond. But it's also crucial to ensure students have time to relax, recharge, and engage in non-academic activities for a well-rounded development.
Impact on mental health
There's a growing body of evidence showing the negative impact of excessive homework on students' mental health. The stress and anxiety from heavy homework loads can contribute to issues like depression, anxiety, and even thoughts of suicide. Student well-being should be a top priority in education, and the impact of homework on mental health cannot be ignored.
While some might argue that homework helps students develop resilience and coping skills, it's important to ensure these potential benefits don't come at the expense of students' mental health.
Limited time for self-care
With excessive homework, students often find little time for essential self-care activities. These can include physical exercise, proper rest, healthy eating, mindfulness, or even simple leisure activities. These activities are critical for maintaining physical health, emotional well-being, and cognitive function.
Some might argue that managing homework alongside self-care responsibilities teaches students valuable life skills. However, it's important that these skills don't come at the cost of students' health and well-being.
Decreased family involvement
Homework can inadvertently lead to decreased family involvement in a child's learning. Parents often feel unqualified or too busy to help with homework, leading to missed opportunities for family learning interactions. This can also create stress and conflict within the family, especially when parents have high expectations or are unable to assist.
Some believe homework can facilitate parental involvement in education. But, when it becomes a source of stress or conflict, it can discourage parents from engaging in their child's learning.
Reinforcement of inequalities
Homework can unintentionally reinforce inequalities. Students from disadvantaged backgrounds might lack access to resources like private tutors or a quiet study space, placing them at a disadvantage compared to their more privileged peers. Additionally, these students might have additional responsibilities at home, further limiting their time to complete homework.
While the purpose of homework is often to provide additional learning opportunities, it can inadvertently reinforce existing disparities. Therefore, it's essential to ensure that homework doesn't favor students who have more resources at home.
Reduced time for play and creativity
Homework can take away from time for play and creative activities. These activities are not only enjoyable but also crucial for the cognitive, social, and emotional development of children. Play allows children to explore, imagine, and create, fostering innovative thinking and problem-solving skills.
Some may argue that homework teaches discipline and responsibility. Yet, it's vital to remember that play also has significant learning benefits and should be a part of every child's daily routine.
Increased cheating and academic dishonesty
The pressure to complete homework can sometimes lead to increased cheating and academic dishonesty. When faced with a large volume of homework, students might resort to copying from friends or searching for answers online. This undermines the educational value of homework and fosters unhealthy academic practices.
While homework is intended to consolidate learning, the risk of promoting dishonest behaviors is a concern that needs to be addressed.
Strained teacher-student relationships
Excessive homework can strain teacher-student relationships. If students begin to associate teachers with stress or anxiety from homework, it can hinder the development of a positive learning relationship. Furthermore, if teachers are perceived as being unfair or insensitive with their homework demands, it can impact the overall classroom dynamic.
While homework can provide an opportunity for teachers to monitor student progress, it's important to ensure that it doesn't negatively affect the teacher-student relationship.
Negative impact on family dynamics
Homework can impact family dynamics. Parents might feel compelled to enforce homework completion, leading to potential conflict, stress, and tension within the family. These situations can disrupt the harmony in the household and strain relationships.
Homework is sometimes seen as a tool to engage parents in their child's education. However, it's crucial to ensure that this involvement doesn't turn into a source of conflict or pressure.
Cultural and individual differences
Homework might not take into account cultural and individual differences. Education is not a one-size-fits-all process, and what works for one student might not work for another. Some students might thrive on hands-on learning, while others prefer auditory or visual learning methods. By standardizing homework, we might ignore these individual learning styles and preferences.
Homework can also overlook cultural differences. For students from diverse cultural backgrounds, certain types of homework might seem irrelevant or difficult to relate to, leading to disengagement or confusion.
Encouragement of surface-level learning
Homework often encourages surface-level learning instead of deep understanding. When students are swamped with homework, they're likely to rush through assignments to get them done, rather than taking the time to understand the concepts. This can result in superficial learning where students memorize information to regurgitate it on assignments and tests, instead of truly understanding and internalizing the knowledge.
While homework is meant to reinforce classroom learning, the quality of learning is more important than the quantity. It's important to design homework in a way that encourages deep, meaningful learning instead of mere rote memorization.
Related posts:
- Diathesis-Stress Model (Definition + Examples)
- HPA Axis (Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal Axis)
- General Adaptation Syndrome Theory
- Careers in Psychology
- The Stress Response (General Adaptation Syndome)
Reference this article:
About The Author

Free Personality Test

Free Memory Test

Free IQ Test

PracticalPie.com is a participant in the Amazon Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Follow Us On:
Youtube Facebook Instagram X/Twitter
Psychology Resources
Developmental
Personality
Relationships
Psychologists
Serial Killers
Psychology Tests
Personality Quiz
Memory Test
Depression test
Type A/B Personality Test
© PracticalPsychology. All rights reserved
Privacy Policy | Terms of Use
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'
- Subscribe to BBC Science Focus Magazine
- Previous Issues
- Future tech
- Everyday science
- Planet Earth
- Newsletters
Should homework be banned?
Social media has sparked into life about whether children should be given homework - should students be freed from this daily chore? Dr Gerald Letendre, a professor of education at Pennsylvania State University, investigates.
We’ve all done it: pretended to leave an essay at home, or stayed up until 2am to finish a piece of coursework we’ve been ignoring for weeks. Homework, for some people, is seen as a chore that’s ‘wrecking kids’ or ‘killing parents’, while others think it is an essential part of a well-rounded education. The problem is far from new: public debates about homework have been raging since at least the early-1900s, and recently spilled over into a Twitter feud between Gary Lineker and Piers Morgan.
Ironically, the conversation surrounding homework often ignores the scientific ‘homework’ that researchers have carried out. Many detailed studies have been conducted, and can guide parents, teachers and administrators to make sensible decisions about how much work should be completed by students outside of the classroom.
So why does homework stir up such strong emotions? One reason is that, by its very nature, it is an intrusion of schoolwork into family life. I carried out a study in 2005, and found that the amount of time that children and adolescents spend in school, from nursery right up to the end of compulsory education, has greatly increased over the last century . This means that more of a child’s time is taken up with education, so family time is reduced. This increases pressure on the boundary between the family and the school.
Plus, the amount of homework that students receive appears to be increasing, especially in the early years when parents are keen for their children to play with friends and spend time with the family.
Finally, success in school has become increasingly important to success in life. Parents can use homework to promote, or exercise control over, their child’s academic trajectory, and hopefully ensure their future educational success. But this often leaves parents conflicted – they want their children to be successful in school, but they don’t want them to be stressed or upset because of an unmanageable workload.
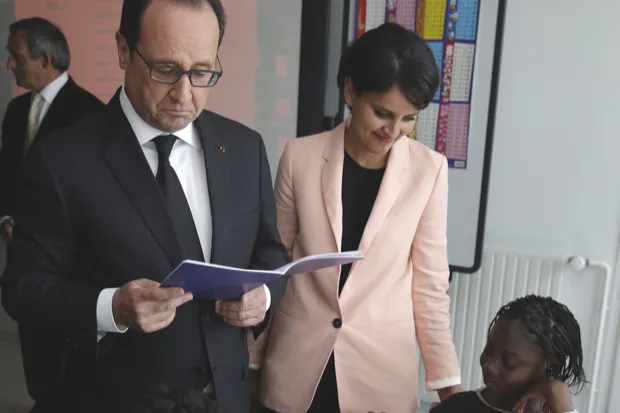

However, the issue isn’t simply down to the opinions of parents, children and their teachers – governments also like to get involved. In the autumn of 2012, French president François Hollande hit world headlines after making a comment about banning homework, ostensibly because it promoted inequality. The Chinese government has also toyed with a ban, because of concerns about excessive academic pressure being put on children.
The problem is, some politicians and national administrators regard regulatory policy in education as a solution for a wide array of social, economic and political issues, perhaps without considering the consequences for students and parents.
Does homework work?
Homework seems to generally have a positive effect for high school students, according to an extensive range of empirical literature. For example, Duke University’s Prof Harris Cooper carried out a meta-analysis using data from US schools, covering a period from 1987 to 2003. He found that homework offered a general beneficial impact on test scores and improvements in attitude, with a greater effect seen in older students. But dig deeper into the issue and a complex set of factors quickly emerges, related to how much homework students do, and exactly how they feel about it.
In 2009, Prof Ulrich Trautwein and his team at the University of Tübingen found that in order to establish whether homework is having any effect, researchers must take into account the differences both between and within classes . For example, a teacher may assign a good deal of homework to a lower-level class, producing an association between more homework and lower levels of achievement. Yet, within the same class, individual students may vary significantly in how much homework improves their baseline performance. Plus, there is the fact that some students are simply more efficient at completing their homework than others, and it becomes quite difficult to pinpoint just what type of homework, and how much of it, will affect overall academic performance.
Over the last century, the amount of time that children and adolescents spend in school has greatly increased
Gender is also a major factor. For example, a study of US high school students carried out by Prof Gary Natriello in the 1980s revealed that girls devote more time to homework than boys, while a follow-up study found that US girls tend to spend more time on mathematics homework than boys. Another study, this time of African-American students in the US, found that eighth grade (ages 13-14) girls were more likely to successfully manage both their tasks and emotions around schoolwork, and were more likely to finish homework.
So why do girls seem to respond more positively to homework? One possible answer proposed by Eunsook Hong of the University of Nevada in 2011 is that teachers tend to rate girls’ habits and attitudes towards work more favourably than boys’. This perception could potentially set up a positive feedback loop between teacher expectations and the children’s capacity for academic work based on gender, resulting in girls outperforming boys. All of this makes it particularly difficult to determine the extent to which homework is helping, though it is clear that simply increasing the time spent on assignments does not directly correspond to a universal increase in learning.
Can homework cause damage?
The lack of empirical data supporting homework in the early years of education, along with an emerging trend to assign more work to this age range, appears to be fuelling parental concerns about potential negative effects. But, aside from anecdotes of increased tension in the household, is there any evidence of this? Can doing too much homework actually damage children?
Evidence suggests extreme amounts of homework can indeed have serious effects on students’ health and well-being. A Chinese study carried out in 2010 found a link between excessive homework and sleep disruption: children who had less homework had better routines and more stable sleep schedules. A Canadian study carried out in 2015 by Isabelle Michaud found that high levels of homework were associated with a greater risk of obesity among boys, if they were already feeling stressed about school in general.
For useful revision guides and video clips to assist with learning, visit BBC Bitesize . This is a free online study resource for UK students from early years up to GCSEs and Scottish Highers.
It is also worth noting that too much homework can create negative effects that may undermine any positives. These negative consequences may not only affect the child, but also could also pile on the stress for the whole family, according to a recent study by Robert Pressman of the New England Centre for Pediatric Psychology. Parents were particularly affected when their perception of their own capacity to assist their children decreased.
What then, is the tipping point, and when does homework simply become too much for parents and children? Guidelines typically suggest that children in the first grade (six years old) should have no more that 10 minutes per night, and that this amount should increase by 10 minutes per school year. However, cultural norms may greatly affect what constitutes too much.
A study of children aged between 8 and 10 in Quebec defined high levels of homework as more than 30 minutes a night, but a study in China of children aged 5 to 11 deemed that two or more hours per night was excessive. It is therefore difficult to create a clear standard for what constitutes as too much homework, because cultural differences, school-related stress, and negative emotions within the family all appear to interact with how homework affects children.
Should we stop setting homework?
In my opinion, even though there are potential risks of negative effects, homework should not be banned. Small amounts, assigned with specific learning goals in mind and with proper parental support, can help to improve students’ performance. While some studies have generally found little evidence that homework has a positive effect on young children overall, a 2008 study by Norwegian researcher Marte Rønning found that even some very young children do receive some benefit. So simply banning homework would mean that any particularly gifted or motivated pupils would not be able to benefit from increased study. However, at the earliest ages, very little homework should be assigned. The decisions about how much and what type are best left to teachers and parents.
As a parent, it is important to clarify what goals your child’s teacher has for homework assignments. Teachers can assign work for different reasons – as an academic drill to foster better study habits, and unfortunately, as a punishment. The goals for each assignment should be made clear, and should encourage positive engagement with academic routines.

Parents should inform the teachers of how long the homework is taking, as teachers often incorrectly estimate the amount of time needed to complete an assignment, and how it is affecting household routines. For young children, positive teacher support and feedback is critical in establishing a student’s positive perception of homework and other academic routines. Teachers and parents need to be vigilant and ensure that homework routines do not start to generate patterns of negative interaction that erode students’ motivation.
Likewise, any positive effects of homework are dependent on several complex interactive factors, including the child’s personal motivation, the type of assignment, parental support and teacher goals. Creating an overarching policy to address every single situation is not realistic, and so homework policies tend to be fixated on the time the homework takes to complete. But rather than focusing on this, everyone would be better off if schools worked on fostering stronger communication between parents, teachers and students, allowing them to respond more sensitively to the child’s emotional and academic needs.
- Five brilliant science books for kids
- Will e-learning replace teachers?
Follow Science Focus on Twitter , Facebook , Instagram and Flipboard
Share this article

- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy policy
- Cookies policy
- Code of conduct
- Magazine subscriptions
- Manage preferences
Thanks for visiting! GoodRx is not available outside of the United States. If you are trying to access this site from the United States and believe you have received this message in error, please reach out to [email protected] and let us know.
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
More than two hours of homework may be counterproductive, research suggests.

A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education . The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students' views on homework. Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year. Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night. "The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students' advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being," Pope wrote. Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress : 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health : In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems. • Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits : Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were "not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills," according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy. A balancing act The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills. Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points," said Pope, who is also a co-founder of Challenge Success , a nonprofit organization affiliated with the GSE that conducts research and works with schools and parents to improve students' educational experiences.. Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. "Young people are spending more time alone," they wrote, "which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities." Student perspectives The researchers say that while their open-ended or "self-reporting" methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for "typical adolescent complaining" – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe. The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Clifton B. Parker is a writer at the Stanford News Service .
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
Should Kids Get Homework?
Homework gives elementary students a way to practice concepts, but too much can be harmful, experts say.

Getty Images
Effective homework reinforces math, reading, writing or spelling skills, but in a way that's meaningful.
How much homework students should get has long been a source of debate among parents and educators. In recent years, some districts have even implemented no-homework policies, as students juggle sports, music and other activities after school.
Parents of elementary school students, in particular, have argued that after-school hours should be spent with family or playing outside rather than completing assignments. And there is little research to show that homework improves academic achievement for elementary students.
But some experts say there's value in homework, even for younger students. When done well, it can help students practice core concepts and develop study habits and time management skills. The key to effective homework, they say, is keeping assignments related to classroom learning, and tailoring the amount by age: Many experts suggest no homework for kindergartners, and little to none in first and second grade.
Value of Homework
Homework provides a chance to solidify what is being taught in the classroom that day, week or unit. Practice matters, says Janine Bempechat, clinical professor at Boston University 's Wheelock College of Education & Human Development.
"There really is no other domain of human ability where anybody would say you don't need to practice," she adds. "We have children practicing piano and we have children going to sports practice several days a week after school. You name the domain of ability and practice is in there."
Homework is also the place where schools and families most frequently intersect.
"The children are bringing things from the school into the home," says Paula S. Fass, professor emerita of history at the University of California—Berkeley and the author of "The End of American Childhood." "Before the pandemic, (homework) was the only real sense that parents had to what was going on in schools."
Harris Cooper, professor emeritus of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University and author of "The Battle Over Homework," examined more than 60 research studies on homework between 1987 and 2003 and found that — when designed properly — homework can lead to greater student success. Too much, however, is harmful. And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary.
"Every child should be doing homework, but the amount and type that they're doing should be appropriate for their developmental level," he says. "For teachers, it's a balancing act. Doing away with homework completely is not in the best interest of children and families. But overburdening families with homework is also not in the child's or a family's best interest."
Negative Homework Assignments
Not all homework for elementary students involves completing a worksheet. Assignments can be fun, says Cooper, like having students visit educational locations, keep statistics on their favorite sports teams, read for pleasure or even help their parents grocery shop. The point is to show students that activities done outside of school can relate to subjects learned in the classroom.
But assignments that are just busy work, that force students to learn new concepts at home, or that are overly time-consuming can be counterproductive, experts say.
Homework that's just busy work.
Effective homework reinforces math, reading, writing or spelling skills, but in a way that's meaningful, experts say. Assignments that look more like busy work – projects or worksheets that don't require teacher feedback and aren't related to topics learned in the classroom – can be frustrating for students and create burdens for families.
"The mental health piece has definitely played a role here over the last couple of years during the COVID-19 pandemic, and the last thing we want to do is frustrate students with busy work or homework that makes no sense," says Dave Steckler, principal of Red Trail Elementary School in Mandan, North Dakota.
Homework on material that kids haven't learned yet.
With the pressure to cover all topics on standardized tests and limited time during the school day, some teachers assign homework that has not yet been taught in the classroom.
Not only does this create stress, but it also causes equity challenges. Some parents speak languages other than English or work several jobs, and they aren't able to help teach their children new concepts.
" It just becomes agony for both parents and the kids to get through this worksheet, and the goal becomes getting to the bottom of (the) worksheet with answers filled in without any understanding of what any of it matters for," says professor Susan R. Goldman, co-director of the Learning Sciences Research Institute at the University of Illinois—Chicago .
Homework that's overly time-consuming.
The standard homework guideline recommended by the National Parent Teacher Association and the National Education Association is the "10-minute rule" – 10 minutes of nightly homework per grade level. A fourth grader, for instance, would receive a total of 40 minutes of homework per night.
But this does not always happen, especially since not every student learns the same. A 2015 study published in the American Journal of Family Therapy found that primary school children actually received three times the recommended amount of homework — and that family stress increased along with the homework load.
Young children can only remain attentive for short periods, so large amounts of homework, especially lengthy projects, can negatively affect students' views on school. Some individual long-term projects – like having to build a replica city, for example – typically become an assignment for parents rather than students, Fass says.
"It's one thing to assign a project like that in which several kids are working on it together," she adds. "In (that) case, the kids do normally work on it. It's another to send it home to the families, where it becomes a burden and doesn't really accomplish very much."
Private vs. Public Schools
Do private schools assign more homework than public schools? There's little research on the issue, but experts say private school parents may be more accepting of homework, seeing it as a sign of academic rigor.
Of course, not all private schools are the same – some focus on college preparation and traditional academics, while others stress alternative approaches to education.
"I think in the academically oriented private schools, there's more support for homework from parents," says Gerald K. LeTendre, chair of educational administration at Pennsylvania State University—University Park . "I don't know if there's any research to show there's more homework, but it's less of a contentious issue."
How to Address Homework Overload
First, assess if the workload takes as long as it appears. Sometimes children may start working on a homework assignment, wander away and come back later, Cooper says.
"Parents don't see it, but they know that their child has started doing their homework four hours ago and still not done it," he adds. "They don't see that there are those four hours where their child was doing lots of other things. So the homework assignment itself actually is not four hours long. It's the way the child is approaching it."
But if homework is becoming stressful or workload is excessive, experts suggest parents first approach the teacher, followed by a school administrator.
"Many times, we can solve a lot of issues by having conversations," Steckler says, including by "sitting down, talking about the amount of homework, and what's appropriate and not appropriate."
Study Tips for High School Students

Tags: K-12 education , students , elementary school , children
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
Why I Think All Schools Should Abolish Homework

H ow long is your child’s workweek? Thirty hours? Forty? Would it surprise you to learn that some elementary school kids have workweeks comparable to adults’ schedules? For most children, mandatory homework assignments push their workweek far beyond the school day and deep into what any other laborers would consider overtime. Even without sports or music or other school-sponsored extracurriculars, the daily homework slog keeps many students on the clock as long as lawyers, teachers, medical residents, truck drivers and other overworked adults. Is it any wonder that,deprived of the labor protections that we provide adults, our kids are suffering an epidemic of disengagement, anxiety and depression ?
With my youngest child just months away from finishing high school, I’m remembering all the needless misery and missed opportunities all three of my kids suffered because of their endless assignments. When my daughters were in middle school, I would urge them into bed before midnight and then find them clandestinely studying under the covers with a flashlight. We cut back on their activities but still found ourselves stuck in a system on overdrive, returning home from hectic days at 6 p.m. only to face hours more of homework. Now, even as a senior with a moderate course load, my son, Zak, has spent many weekends studying, finding little time for the exercise and fresh air essential to his well-being. Week after week, and without any extracurriculars, Zak logs a lot more than the 40 hours adults traditionally work each week — and with no recognition from his “bosses” that it’s too much. I can’t count the number of shared evenings, weekend outings and dinners that our family has missed and will never get back.
How much after-school time should our schools really own?
In the midst of the madness last fall, Zak said to me, “I feel like I’m working towards my death. The constant demands on my time since 5th grade are just going to continue through graduation, into college, and then into my job. It’s like I’m on an endless treadmill with no time for living.”
My spirit crumbled along with his.
Like Zak, many people are now questioning the point of putting so much demand on children and teens that they become thinly stretched and overworked. Studies have long shown that there is no academic benefit to high school homework that consumes more than a modest number of hours each week. In a study of high schoolers conducted by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), researchers concluded that “after around four hours of homework per week, the additional time invested in homework has a negligible impact on performance.”
In elementary school, where we often assign overtime even to the youngest children, studies have shown there’s no academic benefit to any amount of homework at all.
Our unquestioned acceptance of homework also flies in the face of all we know about human health, brain function and learning. Brain scientists know that rest and exercise are essential to good health and real learning . Even top adult professionals in specialized fields take care to limit their work to concentrated periods of focus. A landmark study of how humans develop expertise found that elite musicians, scientists and athletes do their most productive work only about four hours per day .
Yet we continue to overwork our children, depriving them of the chance to cultivate health and learn deeply, burdening them with an imbalance of sedentary, academic tasks. American high school students , in fact, do more homework each week than their peers in the average country in the OECD, a 2014 report found.
It’s time for an uprising.
Already, small rebellions are starting. High schools in Ridgewood, N.J. , and Fairfax County, Va., among others, have banned homework over school breaks. The entire second grade at Taylor Elementary School in Arlington, Va., abolished homework this academic year. Burton Valley Elementary School in Lafayette, Calif., has eliminated homework in grades K through 4. Henry West Laboratory School , a public K-8 school in Coral Gables, Fla., eliminated mandatory, graded homework for optional assignments. One Lexington, Mass., elementary school is piloting a homework-free year, replacing it with reading for pleasure.
More from TIME
Across the Atlantic, students in Spain launched a national strike against excessive assignments in November. And a second-grade teacher in Texas, made headlines this fall when she quit sending home extra work , instead urging families to “spend your evenings doing things that are proven to correlate with student success. Eat dinner as a family, read together, play outside and get your child to bed early.”
It is time that we call loudly for a clear and simple change: a workweek limit for children, counting time on the clock before and after the final bell. Why should schools extend their authority far beyond the boundaries of campus, dictating activities in our homes in the hours that belong to families? An all-out ban on after-school assignments would be optimal. Short of that, we can at least sensibly agree on a cap limiting kids to a 40-hour workweek — and fewer hours for younger children.
Resistance even to this reasonable limit will be rife. Mike Miller, an English teacher at Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology in Alexandria, Va., found this out firsthand when he spearheaded a homework committee to rethink the usual approach. He had read the education research and found a forgotten policy on the county books limiting homework to two hours a night, total, including all classes. “I thought it would be a slam dunk” to put the two-hour cap firmly in place, Miller said.
But immediately, people started balking. “There was a lot of fear in the community,” Miller said. “It’s like jumping off a high dive with your kids’ future. If we reduce homework to two hours or less, is my kid really going to be okay?” In the end, the committee only agreed to a homework ban over school breaks.
Miller’s response is a great model for us all. He decided to limit assignments in his own class to 20 minutes a night (the most allowed for a student with six classes to hit the two-hour max). His students didn’t suddenly fail. Their test scores remained stable. And they started using their more breathable schedule to do more creative, thoughtful work.
That’s the way we will get to a sane work schedule for kids: by simultaneously pursuing changes big and small. Even as we collaboratively press for policy changes at the district or individual school level, all teachers can act now, as individuals, to ease the strain on overworked kids.
As parents and students, we can also organize to make homework the exception rather than the rule. We can insist that every family, teacher and student be allowed to opt out of assignments without penalty to make room for important activities, and we can seek changes that shift practice exercises and assignments into the actual school day.
We’ll know our work is done only when Zak and every other child can clock out, eat dinner, sleep well and stay healthy — the very things needed to engage and learn deeply. That’s the basic standard the law applies to working adults. Let’s do the same for our kids.
Vicki Abeles is the author of the bestseller Beyond Measure: Rescuing an Overscheduled, Overtested, Underestimated Generation, and director and producer of the documentaries “ Race to Nowhere ” and “ Beyond Measure. ”
More Must-Reads from TIME
- How Joe Biden Leads
- TIME100 Most Influential Companies 2024
- Javier Milei’s Radical Plan to Transform Argentina
- How Private Donors Shape Birth-Control Choices
- What Sealed Trump’s Fate : Column
- Are Walking Pads Worth It?
- 15 LGBTQ+ Books to Read for Pride
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.
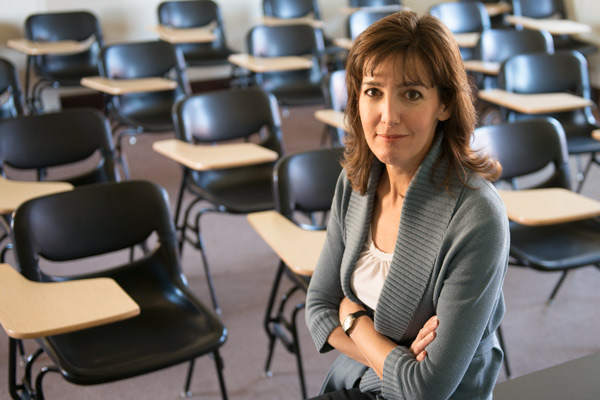

Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter.
“Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good,” wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education .
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students’ views on homework.
Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year.
Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night.
“The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students’ advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being,” Pope wrote.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with:
* Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
* Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
* Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits: Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were “not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills,” according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy.
A balancing act
The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills.
Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as “pointless” or “mindless” in order to keep their grades up.
“This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points,” Pope said.
She said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said.
“Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development,” wrote Pope.
High-performing paradox
In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. “Young people are spending more time alone,” they wrote, “which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities.”
Student perspectives
The researchers say that while their open-ended or “self-reporting” methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for “typical adolescent complaining” – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe.
The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Media Contacts
Denise Pope, Stanford Graduate School of Education: (650) 725-7412, [email protected] Clifton B. Parker, Stanford News Service: (650) 725-0224, [email protected]
15 Should Homework Be Banned Pros and Cons
Homework was a staple of the public and private schooling experience for many of us growing up. There were long nights spent on book reports, science projects, and all of those repetitive math sheets. In many ways, it felt like an inevitable part of the educational experience. Unless you could power through all of your assignments during your free time in class, then there was going to be time spent at home working on specific subjects.
More schools are looking at the idea of banning homework from the modern educational experience. Instead of sending work home with students each night, they are finding alternative ways to ensure that each student can understand the curriculum without involving the uncertainty of parental involvement.
Although banning homework might seem like an unorthodox process, there are legitimate advantages to consider with this effort. There are some disadvantages which some families may encounter as well.
These are the updated lists of the pros and cons of banning homework to review.
List of the Pros of Banning Homework
1. Giving homework to students does not always improve their academic outcomes. The reality of homework for the modern student is that we do not know if it is helpful to have extra work assigned to them outside of the classroom. Every study that has looked at the subject has had design flaws which causes the data collected to be questionable at best. Although there is some information to suggest that students in seventh grade and higher can benefit from limited homework, banning it for students younger than that seems to be beneficial for their learning experience.
2. Banning homework can reduce burnout issues with students. Teachers are seeing homework stress occur in the classroom more frequently today than ever before. Almost half of all high school teachers in North America have seen this issue with their students at some point during the year. About 25% of grade school teachers say that they have seen the same thing.
When students are dealing with the impact of homework on their lives, it can have a tremendously adverse impact. One of the most cited reasons for students dropping out of school is that they cannot complete their homework on time.
3. Banning homework would increase the amount of family time available to students. Homework creates a significant disruption to family relationships. Over half of all parents in North America say that they have had a significant argument with their children over homework in the past month. 1/3 of families say that homework is their primary source of struggle in the home. Not only does it reduce the amount of time that everyone has to spend together, it reduces the chances that parents have to teach their own skills and belief systems to their kids.
4. It reduces the negative impact of homework on the health of a student. Many students suffer academically when they cannot finish a homework assignment on time. Although assumptions are often made about the time management skills of the individual when this outcome occurs, the reasons why it happens is usually more complex. It may be too difficult, too boring, or there may not be enough time in the day to complete the work.
When students experience failure in this area, it can lead to severe mental health issues. Some perceive themselves as a scholarly failure, which translates to an inability to live life successfully. It can disrupt a desire to learn. There is even an increased risk of suicide for some youth because of this issue. Banning it would reduce these risks immediately.
5. Eliminating homework would allow for an established sleep cycle. The average high school student requires between 8-10 hours of sleep to function at their best the next day. Grade-school students may require an extra hour or two beyond that figure. When teachers assign homework, then it increases the risk for each individual that they will not receive the amount that they require each night.
When children do not get enough sleep, a significant rest deficit occurs which can impact their ability to pay attention in school. It can cause unintended weight gain. There may even be issues with emotional control. Banning homework would help to reduce these risks as well.
6. It increases the amount of socialization time that students receive. People who are only spending time in school and then going home to do more work are at a higher risk of experiencing loneliness and isolation. When these emotions are present, then a student is more likely to feel “down and out” mentally and physically. They lack meaningful connections with other people. These feelings are the health equivalent of smoking 15 cigarettes per day. If students are spending time on homework, then they are not spending time connecting with their family and friends.
7. It reduces the repetition that students face in the modern learning process. Most of the tasks that homework requires of students is repetitive and uninteresting. Kids love to resolve challenges on tasks that they are passionate about at that moment in their lives. Forcing them to complete the same problems repetitively as a way to “learn” core concepts can create issues with knowledge retention later in life. When you add in the fact that most lessons sent for homework must be done by themselves, banning homework will reduce the repetition that students face, allowing for a better overall outcome.
8. Home environments can be chaotic. Although some students can do homework in a quiet room without distractions, that is not the case for most kids. There are numerous events that happen at home which can pull a child’s attention away from the work that their teacher wants them to do. It isn’t just the Internet, video games, and television which are problematic either. Household chores, family issues, employment, and athletic requirements can make it a challenge to get the assigned work finished on time.
List of the Cons of Banning Homework
1. Homework allows parents to be involved with the educational process. Parents need to know what their children are learning in school. Even if they ask their children about what they are learning, the answers tend to be in generalities instead of specifics. By sending home work from the classroom, it allows parents to see and experience the work that their kids are doing when they are in school during the day. Then moms and dads can get involved with the learning process to reinforce the core concepts that were discovered by their children each day.
2. It can help parents and teachers identify learning disabilities. Many children develop a self-defense mechanism which allows them to appear like any other kid that is in their classroom. This process allows them to hide learning disabilities which may be hindering their educational progress. The presence of homework makes it possible for parents and teachers to identify this issue because kids can’t hide their struggles when they must work 1-on-1 with their parents on specific subjects. Banning homework would eliminate 50% of the opportunities to identify potential issues immediately.
3. Homework allows teachers to observe how their students understand the material. Teachers often use homework as a way to gauge how well a student is understanding the materials they are learning. Although some might point out that assignments and exams in the classroom can do the same thing, testing often requires preparation at home. It creates more anxiety and stress sometimes then even homework does. That is why banning it can be problematic for some students. Some students experience more pressure than they would during this assessment process when quizzes and tests are the only measurement of their success.
4. It teaches students how to manage their time wisely. As people grow older, they realize that time is a finite commodity. We must manage it wisely to maximize our productivity. Homework assignments are a way to encourage the development of this skill at an early age. The trick is to keep the amount of time required for the work down to a manageable level. As a general rule, students should spend about 10 minutes each school day doing homework, organizing their schedule around this need. If there are scheduling conflicts, then this process offers families a chance to create priorities.
5. Homework encourages students to be accountable for their role. Teachers are present in the classroom to offer access to information and skill-building opportunities that can improve the quality of life for each student. Administrators work to find a curriculum that will benefit the most people in an efficient way. Parents work hard to ensure their kids make it to school on time, follow healthy routines, and communicate with their school district to ensure the most effective learning opportunities possible. None of that matters if the student is not invested in the work in the first place. Homework assignments not only teach children how to work independently, but they also show them how to take responsibility for their part of the overall educational process.
6. It helps to teach important life lessons. Homework is an essential tool in the development of life lessons, such as communicating with others or comprehending something they have just read. It teaches kids how to think, solve problems, and even build an understanding for the issues that occur in our society right now. Many of the issues that lead to the idea to ban homework occur because someone in the life of a student communicated to them that this work was a waste of time. There are times in life when people need to do things that they don’t like or want to do. Homework helps a student begin to find the coping skills needed to be successful in that situation.
7. Homework allows for further research into class materials. Most classrooms offer less than 1 hour of instruction per subject during the day. For many students, that is not enough time to obtain a firm grasp on the materials being taught. Having homework assignments allows a student to perform more research, using their at-home tools to take a deeper look into the materials that would otherwise be impossible if homework was banned. That process can lead to a more significant understanding of the concepts involved, reducing anxiety levels because they have a complete grasp on the materials.
The pros and cons of banning homework is a decision that ultimately lies with each school district. Parents always have the option to pursue homeschooling or online learning if they disagree with the decisions that are made in this area. Whether you’re for more homework or want to see less of it, we can all agree on the fact that the absence of any reliable data about its usefulness makes it a challenge to know for certain which option is the best one to choose in this debate.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Health & Nursing
Courses and certificates.
- Bachelor's Degrees
- View all Business Bachelor's Degrees
- Business Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Healthcare Administration – B.S.
- Human Resource Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Marketing – B.S. Business Administration
- Accounting – B.S. Business Administration
- Finance – B.S.
- Supply Chain and Operations Management – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree (from the School of Technology)
- Health Information Management – B.S. (from the Leavitt School of Health)
Master's Degrees
- View all Business Master's Degrees
- Master of Business Administration (MBA)
- MBA Information Technology Management
- MBA Healthcare Management
- Management and Leadership – M.S.
- Accounting – M.S.
- Marketing – M.S.
- Human Resource Management – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration (from the Leavitt School of Health)
- Data Analytics – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Information Technology Management – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed. (from the School of Education)
Certificates
- Supply Chain
- Accounting Fundamentals
- View all Business Degrees
Bachelor's Preparing For Licensure
- View all Education Bachelor's Degrees
- Elementary Education – B.A.
- Special Education and Elementary Education (Dual Licensure) – B.A.
- Special Education (Mild-to-Moderate) – B.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary)– B.S.
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– B.S.
- View all Education Degrees
Bachelor of Arts in Education Degrees
- Educational Studies – B.A.
Master of Science in Education Degrees
- View all Education Master's Degrees
- Curriculum and Instruction – M.S.
- Educational Leadership – M.S.
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed.
Master's Preparing for Licensure
- Teaching, Elementary Education – M.A.
- Teaching, English Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Science Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Special Education (K-12) – M.A.
Licensure Information
- State Teaching Licensure Information
Master's Degrees for Teachers
- Mathematics Education (K-6) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grade) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- English Language Learning (PreK-12) – M.A.
- Endorsement Preparation Program, English Language Learning (PreK-12)
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– M.A.
- View all Technology Bachelor's Degrees
- Cloud Computing – B.S.
- Computer Science – B.S.
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – B.S.
- Data Analytics – B.S.
- Information Technology – B.S.
- Network Engineering and Security – B.S.
- Software Engineering – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration (from the School of Business)
- View all Technology Master's Degrees
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – M.S.
- Data Analytics – M.S.
- Information Technology Management – M.S.
- MBA Information Technology Management (from the School of Business)
- Full Stack Engineering
- Web Application Deployment and Support
- Front End Web Development
- Back End Web Development
3rd Party Certifications
- IT Certifications Included in WGU Degrees
- View all Technology Degrees
- View all Health & Nursing Bachelor's Degrees
- Nursing (RN-to-BSN online) – B.S.
- Nursing (Prelicensure) – B.S. (Available in select states)
- Health Information Management – B.S.
- Health and Human Services – B.S.
- Psychology – B.S.
- Health Science – B.S.
- Healthcare Administration – B.S. (from the School of Business)
- View all Nursing Post-Master's Certificates
- Nursing Education—Post-Master's Certificate
- Nursing Leadership and Management—Post-Master's Certificate
- Family Nurse Practitioner—Post-Master's Certificate
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner —Post-Master's Certificate
- View all Health & Nursing Degrees
- View all Nursing & Health Master's Degrees
- Nursing – Education (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Family Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Education (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration
- Master of Public Health
- MBA Healthcare Management (from the School of Business)
- Business Leadership (with the School of Business)
- Supply Chain (with the School of Business)
- Accounting Fundamentals (with the School of Business)
- Back End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Front End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Web Application Deployment and Support (with the School of Technology)
- Full Stack Engineering (with the School of Technology)
- Single Courses
- Course Bundles
Apply for Admission
Admission requirements.
- New Students
- WGU Returning Graduates
- WGU Readmission
- Enrollment Checklist
- Accessibility
- Accommodation Request
- School of Education Admission Requirements
- School of Business Admission Requirements
- School of Technology Admission Requirements
- Leavitt School of Health Admission Requirements
Additional Requirements
- Computer Requirements
- No Standardized Testing
- Clinical and Student Teaching Information
Transferring
- FAQs about Transferring
- Transfer to WGU
- Transferrable Certifications
- Request WGU Transcripts
- International Transfer Credit
- Tuition and Fees
- Financial Aid
- Scholarships
Other Ways to Pay for School
- Tuition—School of Business
- Tuition—School of Education
- Tuition—School of Technology
- Tuition—Leavitt School of Health
- Your Financial Obligations
- Tuition Comparison
- Applying for Financial Aid
- State Grants
- Consumer Information Guide
- Responsible Borrowing Initiative
- Higher Education Relief Fund
FAFSA Support
- Net Price Calculator
- FAFSA Simplification
- See All Scholarships
- Military Scholarships
- State Scholarships
- Scholarship FAQs
Payment Options
- Payment Plans
- Corporate Reimbursement
- Current Student Hardship Assistance
- Military Tuition Assistance
WGU Experience
- How You'll Learn
- Scheduling/Assessments
- Accreditation
- Student Support/Faculty
- Military Students
- Part-Time Options
- Virtual Military Education Resource Center
- Student Outcomes
- Return on Investment
- Students and Gradutes
- Career Growth
- Student Resources
- Communities
- Testimonials
- Career Guides
- Skills Guides
- Online Degrees
- All Degrees
- Explore Your Options
Admissions & Transfers
- Admissions Overview
Tuition & Financial Aid
Student Success
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Military and Veterans
- Commencement
- Careers at WGU
- Advancement & Giving
- Partnering with WGU
Should Students Have Homework?
- Classroom Strategies
- See More Tags

By Suzanne Capek Tingley, Veteran Educator, M.A. Degree
It used to be that students were the only ones complaining about the practice of assigning homework. For years, teachers and parents thought that homework was a necessary tool when educating children. But studies about the effectiveness of homework have been conflicting and inconclusive, leading some adults to argue that homework should become a thing of the past.
What Research Says about Homework
According to Duke professor Harris Cooper, it's important that students have homework. His meta-analysis of homework studies showed a correlation between completing homework and academic success, at least in older grades. He recommends following a "10 minute rule" : students should receive 10 minutes of homework per day in first grade, and 10 additional minutes each subsequent year, so that by twelfth grade they are completing 120 minutes of homework daily.
But his analysis didn't prove that students did better because they did homework; it simply showed a correlation . This could simply mean that kids who do homework are more committed to doing well in school. Cooper also found that some research showed that homework caused physical and emotional stress, and created negative attitudes about learning. He suggested that more research needed to be done on homework's effect on kids.
Some researchers say that the question isn't whether kids should have homework. It's more about what kind of homework students have and how much. To be effective, homework has to meet students' needs. For example, some middle school teachers have found success with online math homework that's adapted to each student's level of understanding. But when middle school students were assigned more than an hour and a half of homework, their math and science test scores went down .
Researchers at Indiana University discovered that math and science homework may improve standardized test grades, but they found no difference in course grades between students who did homework and those who didn't. These researchers theorize that homework doesn't result in more content mastery, but in greater familiarity with the kinds of questions that appear on standardized tests. According to Professor Adam Maltese, one of the study's authors, "Our results hint that maybe homework is not being used as well as it could be."
So while many teachers and parents support daily homework, it's hard to find strong evidence that the long-held practice produces positive results.
Problems with Homework
In an article in Education Week Teacher , teacher Samantha Hulsman said she's frequently heard parents complain that a 30-minute homework assignment turns into a three-hour battle with their kids. Now, she's facing the same problem with her own kids, which has her rethinking her former beliefs about homework. "I think parents expect their children to have homework nightly, and teachers assign daily homework because it's what we've always done," she explained. Today, Hulsman said, it's more important to know how to collaborate and solve problems than it is to know specific facts.
Child psychologist Kenneth Barish wrote in Psychology Today that battles over homework rarely result in a child's improvement in school . Children who don't do their homework are not lazy, he said, but they may be frustrated, discouraged, or anxious. And for kids with learning disabilities, homework is like "running with a sprained ankle. It's doable, but painful."
Barish suggests that parents and kids have a "homework plan" that limits the time spent on homework. The plan should include turning off all devices—not just the student's, but those belonging to all family members.
One of the best-known critics of homework, Alfie Kohn , says that some people wrongly believe "kids are like vending machines—put in an assignment, get out learning." Kohn points to the lack of evidence that homework is an effective learning tool; in fact, he calls it "the greatest single extinguisher of children's curiosity that we have yet invented."
Homework Bans
Last year, the public schools in Marion County, Florida, decided on a no-homework policy for all of their elementary students . Instead, kids read nightly for 20 minutes. Superintendent Heidi Maier said the decision was based on Cooper's research showing that elementary students gain little from homework, but a lot from reading.
Orchard Elementary School in South Burlington, Vermont, followed the same path, substituting reading for homework. The homework policy has four parts : read nightly, go outside and play, have dinner with your family, and get a good night's sleep. Principal Mark Trifilio says that his staff and parents support the idea.
But while many elementary schools are considering no-homework policies, middle schools and high schools have been reluctant to abandon homework. Schools say parents support homework and teachers know it can be helpful when it is specific and follows certain guidelines. For example, practicing solving word problems can be helpful, but there's no reason to assign 50 problems when 10 will do. Recognizing that not all kids have the time, space, and home support to do homework is important, so it shouldn't be counted as part of a student's grade.
So Should Students Have Homework?
Should you ban homework in your classroom? If you teach lower grades, it's possible. If you teach middle or high school, probably not. But all teachers should think carefully about their homework policies. By limiting the amount of homework and improving the quality of assignments, you can improve learning outcomes for your students.
Ready to Start Your Journey?
HEALTH & NURSING
Recommended Articles
Take a look at other articles from WGU. Our articles feature information on a wide variety of subjects, written with the help of subject matter experts and researchers who are well-versed in their industries. This allows us to provide articles with interesting, relevant, and accurate information.
{{item.date}}
{{item.preTitleTag}}
{{item.title}}
The university, for students.
- Student Portal
- Alumni Services
Most Visited Links
- Business Programs
- Student Experience
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Student Communities
share this!
August 16, 2021
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in
by Sara M Moniuszko

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework .
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace, says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework causes, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high-achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school ," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework, I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the last two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic, making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized... sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking assignments up can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
©2021 USA Today Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

How milk proteins interact with caffeine in espresso
9 minutes ago

The NYPD gave officers iPhones—here's what researchers learned about race and policing
10 minutes ago

Increasing tropical cyclone frequency may have deadly consequences for seabird populations
15 minutes ago

The rise of horse power ~4,200 years ago

Q&A: Studies reveal gut's true stem cells, challenging previous assumptions
Study links nanoparticles to altered blood vessel formation in embryos
19 minutes ago
Study suggests marine cyanobacteria communicate via membrane nanotubes
41 minutes ago

Heat-switch device boosts lunar rover longevity in harsh moon climate
46 minutes ago
Structure and function of new lysosome transporter revealed

Study of photons in quantum computing reveals that when photons collide, they create vortices
Relevant physicsforums posts, is "college algebra" really just high school "algebra ii".
May 27, 2024
UK School Physics Exam from 1967
Physics education is 60 years out of date.
May 16, 2024

Plagiarism & ChatGPT: Is Cheating with AI the New Normal?
May 13, 2024
Physics Instructor Minimum Education to Teach Community College
May 11, 2024
Studying "Useful" vs. "Useless" Stuff in School
Apr 30, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

Smartphones are lowering student's grades, study finds
Aug 18, 2020

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017

Scholar suggests ways to craft more effective homework assignments
Oct 1, 2015

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

How much math, science homework is too much?
Mar 23, 2015

Anxiety, depression, burnout rising as college students prepare to return to campus
Jul 26, 2021
Recommended for you

First-generation medical students face unique challenges and need more targeted support, say researchers

Investigation reveals varied impact of preschool programs on long-term school success
May 2, 2024

Training of brain processes makes reading more efficient
Apr 18, 2024

Researchers find lower grades given to students with surnames that come later in alphabetical order
Apr 17, 2024

Earth, the sun and a bike wheel: Why your high-school textbook was wrong about the shape of Earth's orbit
Apr 8, 2024

Touchibo, a robot that fosters inclusion in education through touch
Apr 5, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
.png)
Why homework should be banned?

Banning homework could significantly reduce stress and pressure on students while promoting a more equitable and effective educational system. Homework exacerbates educational inequalities, lacks consistent effectiveness, encourages academic dishonesty, and hinders the promotion of lifelong learning.
There are many reasons why homework should be banned. Students claim they don’t have enough time for it. Nevertheless, professors give more and more assignments for self-education. As a result, the stress of deadlines adds up, diminishing students’ motivation to learn.
Many people argue that the modern curriculum leaves too much for self-study. Students don’t get enough explanation on the topic and end up with surface-level knowledge across many fields rather than an in-depth understanding of one.
Banning or at least reducing the amount of homework could be the answer to these concerns. Yet, many educational institutions are reluctant to change their curricula or don’t see the need for it.
8 Reasons why homework should be banned
When looking for arguments to support our stance, we stopped at eight. They are as follows:
Increased stress
- Less time for family
- Lack of equality among students
Poor sleep schedules
- No time for after-school development
Questionable academic benefit
- Worsened student-teacher relationships
- Risk of burnout
All these are real implications that homework has on students. In the later sections, we will expand on each in more detail.
When it comes to the reasons why should homework be banned, stress is the first one that comes to mind. With each year, academic demands only grow. It gets harder and harder to get into educational institutions, hence, it is also hard to stay. Students are expected to perform at an extraordinary level only to secure their spot.
At the same time, they hardly ever get any financial support, so some have to combine studying with work. With such a schedule, it’s very hard to find time for homework. Learners are forced to do it at night, in between classes or at work, running the risk of making their manager or professor mad. This is why students are under insurmountable pressure from their school, family, and themselves.
No time for family
The continuing debate on homework should be banned leads us to the next point. Students who are always busy with homework, hardly have time for themselves, not to mention their family. Reduced family visits or even conversation can lead to the feelings of loneliness and isolation.
Banning homework, or at least reducing its amount, could help students reconnect with their loved ones. For many students, especially freshers, loneliness is one of the biggest concerns. Many people struggle with making friends or even striking up a casual conversation with a stranger. Even a small encounter can make one feel less lonely, yet how do you find time for it if you’re always in your room doing homework?
Lack of equality
While the demands on students are approximately the same, some peoples’ resources are more limited than others’. Students from wealthier backgrounds have access to more modern technology, and, as a result, may even have more time on their hands.
At the same time, students with less resources are stuck with outdated library computers that take 20 minutes only to turn on. This inequality can lead to unfair judgment, resentment and even more inequality among students.
At the same time, in class, everyone has the same resources - the same amount of time, pen and paper. Doing assignments in class could ensure that everyone gets the same treatments based on their knowledge.
As we’ve already mentioned, some students have to work after school. And even if they don’t work, they may have multiple assignments due on the same day. Everybody needs some time to themselves, student or not. Relaxing is also vital for comprehension and memory. If you don’t sleep well, all that cramming just goes to waste, because it doesn’t make the trip from short-term memory to long-term storage.
Luckily, there is a solution. Using a do my homework service can provide students with more time for themselves or other important assignments. Getting help with homework will not only ensure that you are well-rested before class, it can also help you see a different perspective on a topic you may be struggling with. Because when a paper is completed by a professional writer, it can be an amazing learning resource.
No time for extracurriculars
Extracurricular classes, clubs and societies play a vital role in students’ holistic development. Participating in debates, math, or drama clubs can help you learn in practice, develop leadership skills, and gain real experience that can later help you excel in your profession.
Cutting all those things out for the sake of homework will leave you with theoretical knowledge only. Which is why homework should be banned.
College should give you a well-rounded education and prepare you for the real world. If you don’t engage in after-school development, don’t socialize with other students and don’t develop leadership skills, you’re going to have to learn those skills from scratch in the workplace. That makes you a less eligible candidate compared to those with practical skills.
With all the drawbacks presented above, it’s hard to argue for homework. When a student is stressed, lonely, isolated, and hasn’t had a good night’s sleep in months, writing another essay won’t do them much good.
Some research suggests that there is little to no correlation between homework and academic success, especially for younger students. That should push educators to reassess the current teaching methods and come up with better strategies for education.
When it comes to academic success, educators should focus on what can be achieved in class rather than at home. After classes, students should have time to rest, socialize and recharge.
But who invented homework and why ? Read our article to find out all about homework and its inventor!
Poor relationships between students and teachers
When teachers ask a lot from students, it can lead to resentment. Without properly explaining the task or the benefit behind it, teachers load students with an assignment every week. But when a student doesn’t understand why it’s important, they may end up doing the task haphazardly.
On the other hand, when a student who performs well in class comes back with an assignment done carelessly, the teacher may apply even more pressure on that student.
So, why should homework be abolished? Because it leads to a lot of miscommunication between teachers and students. Teachers tend to put a lot of expectations on students without considering that they have many other commitments and classes.
Academic burnout
Burnout has become increasingly more common among students. It can be characterized by the following symptoms:
- Chronic fatigue
- Irritability
- Distraction
- Loss of motivation
- Reduced performance.
It is usually caused by high expectations placed on a student by themselves, their teachers or parents. High workload can also lead a student to burn out. Perfectionism, lack of support and poor time management are among other contributors to burning out.
The easiest way to deal with burnout would, of course, be to ban homework. But, when it’s not possible, you could also try the following:
- Self-care . Take a day off or implement small habits into every day that would remind you that you are your own priority. It can be a nice meal, sports, or meditation.
- Setting goals . Determining your priorities and writing them down can be an efficient tool for those who lack motivation.
- Seeking support . Counseling services, therapy, or just talking to a friend can make a world of difference for people struggling with burnout.
Taking a break . Sometimes, it’s hard to think straight when you’re so close to the fire. Taking a vacation, a gap year or a week off can really help you evaluate your priorities and see what’s causing you stress.
Struggling with your Homework?
Get your assignments done by real pros. Save your precious time and boost your marks with ease.
Why homework should not be required?
Homework should not be required because it can cause significant stress for children. Research indicates that extra assignments, especially for younger students, can lead to unhealthy levels of stress. When students are bombarded with numerous lessons both at school and at home, they may experience stress and anxiety if they cannot complete the assignments on time.
Many studies have confirmed that homework negatively affects students’ performance, mood, motivation and even health. Those who have access to quality homework help can consider themselves lucky. But the rest may feel isolated, struggling on their own.
What educators must understand is that homework is already a full-time job. Those teachers do not come back from work and do more work, but students do, all the while paying insane amounts of money for that education. This inevitably poses the question of whether higher education is even worth it anymore.
It can lead to burnout, cause severe mental and physical health problems while draining your family of its life’s savings.
Banning homework for students with different learning styles
It’s no secret that people have different learning styles. However, homework is not adapted to that difference, which is another r eason why homework should be banned. The four commonly defined styles are:
- Read/Write,
- Kinaesthetic.
That means that for someone who derives most benefit from Kinaesthetic-styled learning, reading a book may not be efficient. In the same way, a visual learner will hardly benefit from writing an essay.
Yet, when it comes to homework, a teacher can’t give everyone a different task. They will normally assign the same project to everyone. That means that only ¼ of the group will benefit from that task.
Socialization should be prioritized
So, why homework should be banned? Because it takes away the time that could otherwise be spent socializing. Students that don’t have a social life do worse with their studies. When you don’t have anyone to talk to, you can feel isolated, lonely, and even depressed.
On the contrary, when you have a few friends or simply are in contact with your classmates, you have someone who can share your struggles with you. College can be a great time to bond, even if over a tyrant teacher.
Extracurriculars, study groups, and clubs can give you valuable experience that you can apply in class or even in the workplace.
Having a few extra minutes to call your family can help you reduce anxiety, feelings of separation and loneliness.
Stress doesn’t have to be an integral part of the college experience
Students are under a lot of pressure. Many of them report wanting to quit because the demands are so high. People who are the first generation from their family to attend college report even higher levels of pressure due to the feeling of responsibility before their family.
Yet, at the same time, the resources to help these students are quite scarce. Counselors’ offices are always booked weeks in advance, and therapy is not affordable to an average student with zero income.
Depression is very common among college students, while those are supposed to be the happiest years of one’s life. Could homework be the reason for that? We say yes. So, why homework should be abolished is not even a question anymore.
Final thoughts
Even though in this article, we argue against homework, we also have a few arguments on why is homework important :
It can help students dive deeper into the concepts explained in class. Lectures are limited in time, but a student may need longer to grasp a concept. While studying at home, they may use different resources and gain a deeper understanding of the topic in their own time.
Homework is also vital for teachers to be able to assess students’ understanding. There’s, unfortunately, no better way for teachers to know if you’ve understood a topic other than homework.
Overall, even though it has many drawbacks, homework doesn’t yet have an alternative. And while causing stress, it also has benefits, like deeper understanding and ease of assessment.
Did you like our Homework Post?
For more help, tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert essay writing services!
Frequently Asked Questions
Why should we ban homework.
Homework doesn’t make much sense in the modern world. Most students have to work to support themselves or their families. This leaves them with little to no time for self-education. While it used to be customary for young people to live with their parents throughout college, it’s no longer the case.
Most students have to fend for themselves - pay rent, buy groceries, and pay bills, starting at about 18 years old. Doing all that while also writing endless essays and projects for school is hardly impossible. Yet, people who combine all those things often end up stressed, burnt out and unmotivated. This may lead to frustration with the educational system and even dropping out.
On top of the stress of test scores, more homework can slow down school learning for elementary students and make them lose their motivation for further studying and academic performance. So, how can they find the motivation to go through it?
Where to find motivation for doing homework?
How to motivate yourself to do homework is a big and loaded question, but we’ll try to give you an easy answer. First of all, you should try to remember what you’re here for. Did you enter college to become a highly qualified professional? Do you want to make your parents proud? Are you internally curious and want to know everything about everything? Think of other reasons that made you go to college in the first place.
Planning out your assignments will also help. Break bigger tasks into smaller ones, plan breaks in between and come up with a course of action. This way, these assignments will seem more approachable.
You can view this from the perspective of educators who are preparing students and encouraging students for more difficult academic responsibilities later on. On the other side, it's perfectly normal for your motivation to waver when met with too much homework. Too much homework, long school hours, and a lot of time spent on even more homework can explain why banning homework can be an option.
How do I find time for leisure when homework exists?
So, why should homework be banned? Because students don’t have any time for their personal lives and end up stuck doing homework for hours on end.
If you feel it influences your mental health, it’s detrimental to take a break and find some time for yourself. It may be difficult when homework has no end.
Luckily, services like Studyfy can offer a helping hand in the time of need. Outsourcing your homework to a professional writer will not only give you a few hours to spare, but also a perfect paper sample you can use to educate yourself.
Alternatively, you can:
- Ask your professor for an extension
- Combine efforts with your friends to finish the task faster
- Get smaller tasks out of the way, your schedule will clear up, and you might find time for a walk in the park.
How to improve my performance in class?
All the way from elementary school to middle school and beyond, academic achievement and academic performance have been tied to test scores and assigning homework. You may have struggled with answering can homework improve academic achievement, especially with such repetitive homework tasks. The best thing you can do for your future education is to complete assignments on time, increase your academic performance, and use the education system for essential life skills.
It’s no secret that being active and communicating with the professor can get you some cookie points. If they notice you are trying hard, and you make a good impression, they may let some of your homework mistakes slide. This is why it’s important to address other aspects of your school performance since banning homework is not an option.
To get better in your teacher’s eyes is not that hard, really. You just have to be active. Try to sit closer to them, and maybe even further away from your friends so that you don;t get distracted. Take notes, write everything down and ask questions.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Study Skills
No More Homework: 12 Reasons We Should Get Rid of It Completely
Last Updated: May 4, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Finn Kobler . Finn Kobler graduated from USC in 2022 with a BFA in Writing for Screen/Television. He is a two-time California State Champion and record holder in Original Prose/Poetry, a 2018 finalist for the Los Angeles Youth Poet Laureate, and he's written micro-budget films that have been screened in over 150 theaters nationwide. Growing up, Finn spent every summer helping his family's nonprofit arts program, Showdown Stage Company, empower people through accessible media. He hopes to continue that mission with his writing at wikiHow. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 138,558 times. Learn more...
The amount of homework students are given has increased dramatically in the 21st century, which has sparked countless debates over homework’s overall value. While some have been adamant that homework is an essential part of a good education, it’s been proven that too much homework negatively affects students’ mood, classroom performance, and overall well-being. In addition, a heavy homework load can stress families and teachers. Here are 12 reasons why homework should be banned (or at least heavily reduced).
School is already a full-time job.

- For years, teachers have followed the “10-minute rule” giving students roughly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. However, recent studies have shown students are completing 3+ hours of homework a night well before their senior years even begin. [2] X Trustworthy Source American Psychological Association Leading scientific and professional organization of licensed psychologists Go to source
Homework negatively affects students’ health.

Homework interferes with student’s opportunities to socialize.

Homework hinders students’ chances to learn new things.

Homework lowers students’ enthusiasm for school.

Homework can lower academic performance.

Homework cuts into family time.

Homework is stressful for teachers.

Homework is often irrelevant and punitive.

- There are even studies that have shown homework in primary school has no correlation with classroom performance whatsoever. [9] X Research source
Homework encourages cheating.

Homework is inequitable.

Other countries have banned homework with great results.

- There are even some U.S. schools that have adopted this approach with success. [13] X Research source
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.edutopia.org/no-proven-benefits
- ↑ https://www.apa.org/monitor/2016/03/homework
- ↑ https://healthier.stanfordchildrens.org/en/health-hazards-homework/
- ↑ https://teensneedsleep.files.wordpress.com/2011/04/galloway-nonacademic-effects-of-homework-in-privileged-high-performing-high-schools.pdf
- ↑ https://time.com/4466390/homework-debate-research/
- ↑ https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00220485.2022.2075506?role=tab&scroll=top&needAccess=true&journalCode=vece20
- ↑ https://kappanonline.org/teacher-stress-balancing-demands-resources-mccarthy/
- ↑ https://www.chicagotribune.com/lifestyles/ct-life-homework-pros-cons-20180807-story.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6294446/
- ↑ https://www.theatlantic.com/business/archive/2016/06/homework-inequality-parents-schedules-grades/485174/
- ↑ https://www.bbc.com/news/education-37716005
- ↑ https://www.wsj.com/articles/no-homework-its-the-new-thing-in-u-s-schools-11544610600
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Did this article help you?

Anonymous ..
Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

School Life Balance , Tips for Online Students
The Pros and Cons of Homework
Updated: June 5, 2024
Published: January 23, 2020

Homework is a word that most students dread hearing. After hours upon hours of sitting in class , the last thing we want is more schoolwork over our precious weekends. While it’s known to be a staple of traditional schooling, homework has also become a rather divise topic. Some feel as though homework is a necessary part of school, while others believe that the time could be better invested. Should students have homework? Have a closer look into the arguments on both sides to decide for yourself.

Photo by energepic.com from Pexels
Why should students have homework.
Homework has been a long-standing part of the education system. It helps reinforce what students learn in the classroom, encourages good study habits, and promotes a deeper understanding of subjects. Studies have shown that homework can improve students’ grades and skills. Here are some reasons why homework is important:
1. Homework Encourages Practice
Many people believe that one of the positive effects of homework is that it encourages the discipline of practice. While it may be time consuming and boring compared to other activities, repetition is needed to get better at skills. Homework helps make concepts more clear, and gives students more opportunities when starting their career .
2. Homework Gets Parents Involved
Homework can be something that gets parents involved in their children’s lives if the environment is a healthy one. A parent helping their child with homework makes them take part in their academic success, and allows for the parent to keep up with what the child is doing in school. It can also be a chance to connect together.
3. Homework Teaches Time Management
Homework is much more than just completing the assigned tasks. Homework can develop time management skills , forcing students to plan their time and make sure that all of their homework assignments are done on time. By learning to manage their time, students also practice their problem-solving skills and independent thinking. One of the positive effects of homework is that it forces decision making and compromises to be made.
4. Homework Opens A Bridge Of Communication
Homework creates a connection between the student, the teacher, the school, and the parents. It allows everyone to get to know each other better, and parents can see where their children are struggling. In the same sense, parents can also see where their children are excelling. Homework in turn can allow for a better, more targeted educational plan for the student.
5. Homework Allows For More Learning Time
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can’t see it in the moment.
6. Homework Reduces Screen Time
Many students in North America spend far too many hours watching TV. If they weren’t in school, these numbers would likely increase even more. Although homework is usually undesired, it encourages better study habits and discourages spending time in front of the TV. Homework can be seen as another extracurricular activity, and many families already invest a lot of time and money in different clubs and lessons to fill up their children’s extra time. Just like extracurricular activities, homework can be fit into one’s schedule.

The Other Side: Why Homework Is Bad
While homework has its benefits, there are also many arguments against it. Some believe that homework can cause increased stress, limit time for extracurricular activities, and reduce family time. Studies and expert opinions highlight the drawbacks of too much homework, showing how it can negatively affect students’ well-being and academic experience. Here are some reasons why homework might be bad:
1. Homework Encourages A Sedentary Lifestyle
Should students have homework? Well, that depends on where you stand. There are arguments both for the advantages and the disadvantages of homework.
While classroom time is important, playground time is just as important. If children are given too much homework, they won’t have enough playtime, which can impact their social development and learning. Studies have found that those who get more play get better grades in school , as it can help them pay closer attention in the classroom.
Children are already sitting long hours in the classroom, and homework assignments only add to these hours. Sedentary lifestyles can be dangerous and can cause health problems such as obesity. Homework takes away from time that could be spent investing in physical activity.
2. Homework Isn’t Healthy In Every Home
While many people that think homes are a beneficial environment for children to learn, not all homes provide a healthy environment, and there may be very little investment from parents. Some parents do not provide any kind of support or homework help, and even if they would like to, due to personal barriers, they sometimes cannot. Homework can create friction between children and their parents, which is one of the reasons why homework is bad .
3. Homework Adds To An Already Full-Time Job
School is already a full-time job for students, as they generally spend over 6 hours each day in class. Students also often have extracurricular activities such as sports, music, or art that are just as important as their traditional courses. Adding on extra hours to all of these demands is a lot for children to manage, and prevents students from having extra time to themselves for a variety of creative endeavors. Homework prevents self discovery and having the time to learn new skills outside of the school system. This is one of the main disadvantages of homework.
4. Homework Has Not Been Proven To Provide Results
Endless surveys have found that homework creates a negative attitude towards school, and homework has not been found to be linked to a higher level of academic success.
The positive effects of homework have not been backed up enough. While homework may help some students improve in specific subjects, if they have outside help there is no real proof that homework makes for improvements.
It can be a challenge to really enforce the completion of homework, and students can still get decent grades without doing their homework. Extra school time does not necessarily mean better grades — quality must always come before quantity.
Accurate practice when it comes to homework simply isn’t reliable. Homework could even cause opposite effects if misunderstood, especially since the reliance is placed on the student and their parents — one of the major reasons as to why homework is bad. Many students would rather cheat in class to avoid doing their homework at home, and children often just copy off of each other or from what they read on the internet.
5. Homework Assignments Are Overdone
The general agreement is that students should not be given more than 10 minutes a day per grade level. What this means is that a first grader should be given a maximum of 10 minutes of homework, while a second grader receives 20 minutes, etc. Many students are given a lot more homework than the recommended amount, however.
On average, college students spend as much as 3 hours per night on homework . By giving too much homework, it can increase stress levels and lead to burn out. This in turn provides an opposite effect when it comes to academic success.
The pros and cons of homework are both valid, and it seems as though the question of ‘‘should students have homework?’ is not a simple, straightforward one. Parents and teachers often are found to be clashing heads, while the student is left in the middle without much say.
It’s important to understand all the advantages and disadvantages of homework, taking both perspectives into conversation to find a common ground. At the end of the day, everyone’s goal is the success of the student.
FAQ Section
What are the benefits of assigning homework to students.
Homework reinforces what students learn in the classroom, helps develop good study habits, and promotes a deeper understanding of subjects. It also encourages practice, improves time management skills, and encourages parents to participate in their children’s education.
How much homework is too much for students?
Generally, it is recommended that students receive no more than 10 minutes of homework per grade level per day. For example, a first grader should have no more than 10 minutes of homework, while a fifth grader should have no more than 50 minutes.
What are the potential drawbacks of excessive homework assignments?
Excessive homework can lead to increased stress, a sedentary lifestyle, lack of free time for extracurricular activities, and diminished family time. It can also create a negative attitude towards school and learning.
How does homework impact students’ stress levels and well-being?
Too much homework can significantly increase stress levels and negatively affect students’ well-being. It can lead to anxiety, burnout, and reduced time for physical activity and relaxation.
Does homework promote independent thinking and problem-solving skills?
Yes, homework can promote independent thinking and problem-solving skills by encouraging students to tackle assignments on their own, manage their time effectively, and find solutions to problems without immediate assistance from teachers.
Are there any long-term effects of excessive homework on students?
Excessive homework over long periods can lead to chronic stress, burnout, and a negative attitude towards education. It can also hinder the development of social skills and reduce opportunities for self-discovery and creative pursuits.
How can technology enhance or supplement traditional homework practices?
Technology can provide interactive and engaging ways to complete homework, such as educational apps, online resources, and virtual collaboration tools. It can also offer personalized learning experiences and immediate feedback.
Are there any innovative approaches to homework that schools are adopting?
Some schools are adopting innovative approaches like flipped classrooms, where students watch lectures at home and do hands-on classroom activities. Project-based learning and personalized assignments tailored to individual student needs are also becoming more popular.
How do educators balance the workload with diverse student needs?
Educators can balance the workload by differentiating assignments, considering the individual needs and abilities of students, and providing flexible deadlines. Communication with students and parents helps to ensure that homework is manageable and effective for everyone.
Related Articles
- Sustainability
- Latest News
- News Reports
- Documentaries & Shows
- TV Schedule
- CNA938 Live
- Radio Schedule
- Singapore Parliament
- Mental Health
- Interactives
- Entertainment
- Style & Beauty
- Experiences
- Remarkable Living
- Send us a news tip
- Events & Partnerships
- Business Blueprint
- Health Matters
- The Asian Traveller
Trending Topics
Follow our news, recent searches, commentary: should holiday homework be banned, advertisement.
The June school holidays have started, but many students and families are experiencing a familiar mix of anticipation and dread, says Dr Eugenia Koh-Chua, a former lecturer and mother of two.
This audio is AI-generated.

Eugenia Koh-Chua
MELBOURNE: The June school holidays have started for primary and secondary schools as well as junior colleges. With school out, the fun should begin - but does it really?
While many look forward to a respite from the daily grind of school , the burden of holiday homework hangs over them.
For many parents and tutors, the mid-year break is also the perfect time for an extra academic boost. Let’s not forget June holiday boot camps and intensive revision programmes arranged by teachers and enterprising tuition centres for Primary 6 students taking their Primary School Leaving Examination (PSLE) this year.
The term “holiday homework” itself is contradictory, prompting the question: Should school breaks be a protected sanctuary from homework, or is the expectation of holiday assignments an unavoidable reality?
A BAN ON HOMEWORK?
The debate surrounding holiday homework extends beyond the borders of Singapore.
In the Philippines, legislative attempts to enforce a weekend homework ban have been ongoing since 2016. In 2021, the Chinese government enacted the Double Reduction Policy , which includes a limit on homework and a ban on private tutoring classes.
Meanwhile, in Poland, a ban on graded homework for students in lower primary took effect in April. Homework for children in upper primary levels is optional and does not count towards a grade.
These efforts share a common goal: To alleviate the burden of excessive homework and promote greater student well-being. However, the effectiveness of these measures remains questionable.
In China, the mandate has driven the industry underground and led to exorbitant rates , exacerbating educational inequity. The Chinese experience suggests the potential pitfalls of using a simplistic solution like a hard legislative ban to address a complex social issue.
Drawing lessons from these global examples, I wonder: Should the focus shift from eliminating homework to understanding why parents and schools perceive it as necessary?

Commentary: A China-like tuition ban may not work, but Singapore can still find ways to address overreliance

China launches campaign to halt school bullying, excessive homework
Is homework beneficial.
While the debate on homework rages on, educational research has acknowledged the many potential benefits it serves.
Homework helps to reinforce academic concepts at home, develops time management skills, and encourages independent learning in children.
Learning at home can offer a more adaptable environment that caters to individual student’s learning pace and needs, particularly benefiting those who thrive with additional support. Moreover, homework functions as a crucial link between school and home, allowing parents to stay informed of their children’s academic progress.
At the same time, however, an Institute of Policy Studies (IPS) survey published in 2017 showed that 66.7 per cent of parents with primary school children agreed or strongly agreed that they were stressed over assisting with homework and ferrying them to and from school, and tuition or enrichment classes.
Additionally, nearly 94 per cent of parents in the study expressed a need for the primary school curriculum to be more manageable, reflecting the struggle many parents face in grasping the modern curriculum while balancing work demands in typical dual-income Singaporean households.
In my doctoral study on Singaporean parents’ tensions within education reform, one parent candidly remarked on this struggle: “I don’t think I can impart the (knowledge) skills to them. And I don’t want my children to lose out."
Consequently, many parents delegate homework guidance to educational experts - tuition teachers.
Families spent an estimated S$1.4 billion (US$1 billion) on tuition in 2018, based on data from the last Household Expenditure Survey in 2017 and 2018, up from S$1.1 billion in 2012 and 2013.
These insights highlight parents’ challenges in supporting their children’s learning at home due to a lack of knowledge, skills, time, and energy. Consequently, schools must consider these factors when designing and assigning homework.
Daily Cuts:

Commentary: Parents, getting your preschoolers to cram for P1 can backfire

Commentary: Parents play an outsized role in academic stress children face
Perceived benefits of after-school learning.
Research consistently emphasises the importance of play in nurturing the holistic development of children. What then motivates parents to enrol their children in tuition classes during school holidays?
Many parents I’ve spoken say they feel like they have “no choice” as they mitigate the pressures of a high-stakes education system.
They question how much play alone can contribute to children’s social-emotional well-being if they fail to perform academically. One parent stated, “I don’t need (my child) to be at the top, but I don’t want him to be at the bottom either”.
Parental guilt also motivates many to enrol their children in out-of-school classes. As one parent explained: “If my kids are idle or roaming around at home, I will feel bad as a parent … because it feels like my child is wasting his life away”.
Teachers participating in my doctoral study also reluctantly acknowledge the value of tuition classes for “weaker students”. Unfortunately, in a class size of 40, teachers lack the time and staffing to cater to each child’s learning needs while covering the school curriculum.
They also cited pressure from school leaders and managing familial expectations to assign homework as an indicator of a “good teacher”.

FIND HARMONY, NOT BALANCE
Amid the ongoing discussion on finding the right balance between work and play for students, the term “balance” implies a rigid 50-50 split between “work versus play”, overlooking the unique needs and strengths of each child, family, and school.
Rather than fixating on achieving a static “balance”, might it be better to consider striving for a harmonious blend between work and play? This approach encourages families and schools to identify the optimal mix that suits their specific contexts, fostering an environment where children can thrive in both learning and well-being.
The ideal combination of work and play will naturally vary in each family, classroom, and school, based on their diverse values, cultures, and aspirations. Nonetheless, this optimal mix should be viewed as fluid and dynamic, constantly adapting to suit the evolving needs of children.
Student agency is an essential ingredient in this optimal blend. Schools should actively seek student input on their homework experiences and understand their preferences for how it is assigned and evaluated.
This not only empowers students but also ensures that homework policies are responsive to their needs and interests.
Schools could consider moving away from compulsory holiday homework towards recommended assignments. Allow parents to determine and decide the homework load that best suits their child based on their family values and aspirations.
Many teachers are already offering non-mandatory assignments in the Student Learning Space online portal during mid-year and end-of-year school holidays. However, it is crucial to complement these assignments with online explanatory videos that provide solutions.
This approach is essential to support struggling students and enhance their self-efficacy by ensuring they understand how to approach and solve the questions independently at home.
Ideally, homework tasks should prioritise inquiry-based learning, embracing a play-based approach that fosters engagement and creativity.
Given the absence of time constraints in the classroom, these tasks can encourage students to explore core learning concepts with scaffolding prompts, developing learner autonomy, and stimulating greater engagement and creativity.

Commentary: Voices of tensions behind the 'kiasu parent' label

Commentary: PSLE stress – a question of not too much, not too little
Through collaborative efforts, schools and families can create a supportive environment that fosters student success and well-being.
In an ideal scenario, if schools and families can embrace a unified approach to revamping homework practices and reimagining the objectives of holiday assignments , we may just be able to find that sweet spot between work and play during the June holidays.
Dr Eugenia Koh-Chua is a sessional lecturer and educational researcher at Swinburne University of Technology (Melbourne). She is a mother of two and a former lecturer in Singapore.
Related Topics
Also worth reading, this browser is no longer supported.
We know it's a hassle to switch browsers but we want your experience with CNA to be fast, secure and the best it can possibly be.
To continue, upgrade to a supported browser or, for the finest experience, download the mobile app.
Upgraded but still having issues? Contact us
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
When Homework Was Banned
Published: November 3, 2023
In the early 1900s, Ladies' Home Journal took up a crusade against homework, enlisting doctors and parents who say it damages children's health. In 1901 California passed a law abolishing homework!

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Poland’s kids rejoice over new rules against homework. Teachers and parents aren’t so sure
Ola Kozak, 11, sits at the table where she used to do her homework at the family home in Warsaw, Poland, Friday April 5, 2024. Ola is happy that Poland’s government has ordered strict limits on the amount of homework that teachers can impose on the lower grades, starting in April. Julian enjoyed doing his homework. (AP Photo/Czarek Sokolowski)
Arkadiusz Korporowicz teaches history to 5th grade children at Primary School number 223 in Warsaw, Poland, Wednesday April 3, 2024. Poland’s government has ordered strict limits on the amount of homework that teachers can impose on the lower grades, starting in April. in Warsaw, Poland, Wednesday April 3, 2024. (AP Photo/Czarek Sokolowski)
Pawel Kozak and his wife Magda Kozak, parents of three, stand at their home in Warsaw, Poland, Friday, April 5, 2024. They have different opinions on the decision by Poland’s government that ordered strict limits on the amount of homework that teachers can impose on the lower grades, starting in April. (AP Photo/Czarek Sokolowski)
Children enter a classroom at the Primary School number 223 in Warsaw, Poland, Wednesday April 3, 2024. Poland’s government has ordered strict limits on the amount of homework that teachers can impose on the lower grades, starting in April. (AP Photo/Czarek Sokolowski)
Julian Kozak, 9, sits at the table where he used to do his homework at the family home in Warsaw, Poland, on Friday April 5, 2024. Julian is not very happy that Poland’s government has ordered strict limits on the amount of homework that teachers can impose on the lower grades, starting in April. (AP Photo/Czarek Sokolowski)
Ola Kozak, 11, right, and her younger brother Julian Kozak, 9, sit at the table where they used to do their homework at the family home in Warsaw, Poland, Friday April 5, 2024. Ola is happy that Poland’s government has ordered strict limits on the amount of homework that teachers can impose on the lower grades, starting in April. Julian enjoyed doing his homework. (AP Photo/Czarek Sokolowski)
Poland’s Education Minister Barbara Nowacka announces restrictions on the amount of homework for primary school children, at school number 223 in Warsaw, Poland, Wednesday April 3, 2024. Opinions are divided on what results can be expected from the strict limits on the amount of homework that teachers can impose on the lower grades, starting in April. (AP Photo/Czarek Sokolowski)
Pawel Kozak, father of three, speaks at his home in Warsaw, Poland, Friday, April 5, 2024. Pawel and her wife Magda have different opinions on the decision by Poland’s government that ordered strict limits on the amount of homework that teachers can impose on the lower grades, starting in April. (AP Photo/Czarek Sokolowski)
Magda Kozak, mother of three, stands at her home in Warsaw, Poland, Friday, April 5, 2024. Magda and her husband Pawel have different opinions on the decision by Poland’s government that ordered strict limits on the amount of homework that teachers can impose on the lower grades, starting in April. (AP Photo/Czarek Sokolowski)
Julian Kozak, 9, sits at the table where he used to do his homework at the family home in Warsaw, Poland, Friday, April 5, 2024. Julian is not very happy that Poland’s government has ordered strict limits on the amount of homework that teachers can impose on the lower grades, starting in April. (AP Photo/Czarek Sokolowski)
Magda Kozak, right, spends time with her son Julian, 9, at their home in Warsaw, Poland, Friday, April 5, 2024. Neither of them is happy that starting in April, Poland’s government has ordered strict limits on the amount of homework that teachers can impose on the lower grades. (AP Photo/Czarek Sokolowski)
Children walk in the corridor of Primary School number 223 in Warsaw, Poland, Wednesday April 3, 2024. Poland’s government has ordered strict limits on the amount of homework that teachers can impose on the lower grades, starting in April. (AP Photo/Czarek Sokolowski)
Children with flowers wait for the arrival of Education Minister Barbara Nowacka at Primary School number 223 in Warsaw, Poland, Wednesday April 3, 2024. Poland’s government has ordered strict limits on the amount of homework that teachers can impose on the lower grades, starting in April. (AP Photo/Czarek Sokolowski)
Julian Kozak, 9, plays with his cat at their home in Warsaw, Poland, Friday, April 5, 2024. Starting in April, Poland’s government has ordered strict limits on the amount of homework that teachers can impose on the lower grades. (AP Photo/Czarek Sokolowski)
- Copy Link copied
WARSAW, Poland (AP) — Ola Kozak is celebrating. The 11-year-old, who loves music and drawing, expects to have more free time for her hobbies after Poland’s government ordered strict limits on the amount of homework in the lower grades.
“I am happy,” said the fifth grader, who lives in a Warsaw suburb with her parents and younger siblings. The lilac-colored walls in her bedroom are covered in her art, and on her desk she keeps a framed picture she drew of Kurt Cobain.
“Most people in my class in the morning would copy the work off someone who had done the homework or would copy it from the internet. So it didn’t make sense,” she said.
The government of Prime Minister Donald Tusk enacted the ban against required homework this month amid a broad discussion about the need to modernize Poland’s education system, which critics say puts too much emphasis on rote learning and homework, and not enough on critical thinking and creativity.
Under the decree, teachers are no longer to give required homework to kids in the first to third grades. In grades four to eight, homework is now optional and doesn’t count towards a grade.
Not everyone likes the change – and even Ola’s parents are divided.
“If there is something that will make students enjoy school more, then it will probably be good both for the students and for the school,” said her father, Pawel Kozak.
His wife, Magda Kozak, was skeptical. “I am not pleased, because (homework) is a way to consolidate what was learned,” she said. “It helps stay on top of what the child has really learned and what’s going on at school.”
(Ola’s brother Julian, a third grader, says he sees both sides.)
Debates over the proper amount of homework are common around the globe. While some studies have shown little benefit to homework for young learners, other experts say it can help them learn how to develop study habits and academic concepts.
Poland’s educational system has undergone a number of controversial overhauls. Almost every new government has tried to make changes — something many teachers and parents say has left them confused and discouraged. For example, after communism was thrown off, middle schools were introduced. Then under the last government, the previous system was brought back. More controversy came in recent years when ultra-conservative views were pushed in new textbooks.
For years, teachers have been fleeing the system due to low wages and political pressure. The current government is trying to increase teacher salaries and has promised other changes that teachers approve of.
But Sławomir Broniarz, the head of the Polish Teachers’ Union, said that while he recognized the need to ease burdens on students, the new homework rules are another case of change imposed from above without adequate consultation with educators.
“In general, the teachers think that this happened too quickly, too hastily,” he said.
He argued that removing homework could widen the educational gaps between kids who have strong support at home and those from poorer families with less support and lower expectations. Instead, he urged wider changes to the entire curriculum.
The homework rules gained impetus in the runup to parliamentary elections last year, when a 14-year-old boy, Maciek Matuszewski, stood up at a campaign rally and told Tusk before a national audience that children “had no time to rest.” The boy said their rights were being violated with so much homework on weekends and so many tests on Mondays.
Tusk has since featured Matuszewski in social media videos and made him the face of the sudden change.
Education Minister Barbara Nowacka said she was prompted by research on children’s mental health. Of the various stresses children face, she said, “the one that could be removed fastest was the burden of homework.”
Pasi Sahlberg, a prominent Finnish educator and author, said the value of homework depends on what it is and how it is linked to overall learning. The need for homework can be “very individual and contextual.”
“We need to trust our teachers to decide what is good for each child,” Sahlberg said.
In South Korea, homework limits were set for elementary schools in 2017 amid concerns that kids were under too much pressure. However, teenagers in the education-obsessed country often cram long into the night and get tutoring to meet the requirements of demanding school and university admission tests.
In the U.S., teachers and parents decide for themselves how much homework to assign. Some elementary schools have done away with homework entirely to give children more time to play, participate in activities and spend time with families.
A guideline circulated by teachers unions in the U.S. recommends about 10 minutes of homework per grade. So, 10 minutes in first grade, 20 minutes in second grade and so on.
The COVID-19 pandemic and a crisis around youth mental health have complicated debates around homework. In the U.S., extended school closures in some places were accompanied by steep losses in learning , which were often addressed with tutoring and other interventions paid for with federal pandemic relief money. At the same time, increased attention to student wellbeing led some teachers to consider alternate approaches including reduced or optional homework.
It’s important for children to learn that mastering something “usually requires practice, a lot of practice,” said Sahlberg, in Finland. If reducing homework leads kids and parents to think school expectations for excellence will be lowered, “things will go wrong.”
AP writers Jan M. Olsen in Copenhagen, Denmark, Michael Melia in Hartford, Connecticut, and Hyung-jin Kim in Seoul, South Korea, contributed.
Hochul considers smartphone ban for New York schools, citing student mental health concerns

Sign up for Chalkbeat New York’s free daily newsletter to keep up with NYC’s public schools.
Gov. Kathy Hochul is mulling how to get smartphones out of New York schools as city and state officials grapple with the potential harmful effects of social media and other online platforms on youth mental health.
This week, Hochul said smartphones should not be available to students during the school day, adding that she is exploring ways to make that happen next year. The governor and other city and state officials say social media platforms are designed to be addictive , harm young people’s mental health , and create avenues for bullying.
“They’re living in this dark place where there’s this FOMO — fear of missing out — that if they put down their device for one second, that someone might be saying something about them, or they’ve got to respond to something,” Hochul told reporters on Tuesday. “This is how addictive it is. We have to liberate them from this. We have to just draw a line now and say, ‘No. Enough is enough.’”
The governor has added she understands parent concerns over maintaining a line of communication with their children during the school day and indicated the state may consider action that solely affects the use of smartphones.
“I’m okay if you have a flip phone,” she said during a Thursday appearance on MSNBC’s “Morning Joe.” “But you don’t have to be in the world of social media throughout the day. So, let’s talk about that for New York.”
A spokesperson for Hochul confirmed she intends to engage with teachers, families, and others about potential legislative action for the next session, which begins in January 2025. But officials added there was currently no formal legislative proposal.
Julie Scelfo, founder of Mothers Against Media Addiction, said potential legislation by the governor would represent “an important step toward keeping addictive technology out of the classroom and ensuring school hours remain devoted to education and in-person social interaction.”
“Smartphones have no place in the classroom,” she said in an emailed statement. “Educators, social workers and parents understand that the presence of phones during the school day impedes students’ social, emotional and academic growth and further fuels the current youth mental health crisis.”
In New York City, Mayor Eric Adams has repeatedly blamed social media companies for the nation’s ongoing youth mental health crisis. Earlier this year, the city joined hundreds of other municipalities in filing a lawsuit against five leading social media companies .
Though the city’s schools have not adopted a system-wide policy on cellphones, schools Chancellor David Banks said officials are continuing to pay attention to the issue. While some public schools require students to turn in phones at the start of the school day, others employ more relaxed policies.
“These are all complicated issues, and we have not made any decision,” Banks said at a Thursday press briefing. “In light of what the governor just said, I think it’s incumbent upon us to absolutely start exploring these issues.
“The kids are on these phones 24 hours a day, and there’s all kinds of research that’s coming in and talking about all the negative impacts that it is having on them,” he added. “We can’t control what happens once they’re home … but maybe six to eight hours out of the day, we might have a little bit more control.”
Julian Shen-Berro is a reporter covering New York City. Contact him at [email protected] .
The state earlier removed a nondiscrimination clause that was at the heart of the lawsuit. The impact of the judge’s ruling is unclear.

John Dewey High School’s Minecraft club has inspired some students to pursue careers in computer science— and is changing the way some educators approach their lessons.

William C. Bryant School Principal Bahir Hayes wants to show young Black kids that they can achieve success like he did.

The Class of 2024 had a normal senior year with in-person classes, prom, and graduation. But this year’s seniors started high school anything but normally.
State officials writing new graduation requirements want students pursuing an advanced diploma to have work experience.

One parent, worried about potential safety issues, also said her kids missed more than 30 days of gym because of early voting.

COMMENTS
That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right. Students, read the entire article, then tell us ...
Homework can also help clue parents in to the existence of any learning disabilities their children may have, allowing them to get help and adjust learning strategies as needed. Duke University Professor Harris Cooper noted, "Two parents once told me they refused to believe their child had a learning disability until homework revealed it to ...
Excessive workload. The issue of excessive workload is a common complaint among students. Spending several hours on homework after a full school day can be mentally and physically draining. This workload can lead to burnout, decreased motivation, and negative attitudes toward school and learning.
But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether. Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for ...
Homework is a controversial topic in education, but what does the science say? Explore the pros and cons of homework and its impact on students' well-being in this article from BBC Science Focus Magazine.
Yes. Generally, the link between homework and achievement scores is stronger for math compared to subjects like English and history. For middle school students especially, math homework can strengthen school performance. There is not a lot of research into the quality of homework. Most experts agree that homework should be reinforcing what kids ...
Beyond that point, kids don't absorb much useful information, Cooper says. In fact, too much homework can do more harm than good. Researchers have cited drawbacks, including boredom and burnout toward academic material, less time for family and extracurricular activities, lack of sleep and increased stress.
Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The ...
Too much, however, is harmful. And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary. "Every child should be doing homework, but the ...
American high school students, in fact, do more homework each week than their peers in the average country in the OECD, a 2014 report found. It's time for an uprising. Already, small rebellions ...
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two ...
Should homework be banned? The big debate Homework is a polarising topic. It can cause students to feel stressed or anxious. ... Despite the positive effect that homework can have in some students, opponents argue that children and young people need time to relax and decompress after working hard all day at school.
Banning homework would help to reduce these risks as well. 6. It increases the amount of socialization time that students receive. People who are only spending time in school and then going home to do more work are at a higher risk of experiencing loneliness and isolation.
According to Duke professor Harris Cooper, it's important that students have homework. His meta-analysis of homework studies showed a correlation between completing homework and academic success, at least in older grades. He recommends following a "10 minute rule": students should receive 10 minutes of homework per day in first grade, and 10 ...
But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether. Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students ...
All in all, perhaps homework shouldn't be banned completely, but it needs to be considered in a fair and balanced way. Here are some important points to remember that take the individual needs and resources of students into account: Everyone is different: Every person is unique, and each student learns differently.
8 Reasons why homework should be banned. When looking for arguments to support our stance, we stopped at eight. They are as follows: Increased stress. Less time for family. Lack of equality among students. Poor sleep schedules. No time for after-school development. Questionable academic benefit.
Homework negatively affects students' health. Download Article. Homework takes a toll physically. Recent studies have demonstrated that too much homework can disrupt a student's sleep cycle, and cause stress headaches, stomach problems, and depression. [3] 3.
As children get older, the potential benefits of homework grow, but less than you probably think. Texas teacher's no homework policy goes viral. Courtesy Samantha Gallagher
It allows everyone to get to know each other better, and parents can see where their children are struggling. In the same sense, parents can also see where their children are excelling. Homework in turn can allow for a better, more targeted educational plan for the student. 5. Homework Allows For More Learning Time.
Well primary school children in Poland don't have to do it anymore after the government banned it. Under the new rules, teachers can't give out compulsory homework - that's homework you have to do ...
The debate surrounding holiday homework extends beyond the borders of Singapore. In the Philippines, legislative attempts to enforce a weekend homework ban have been ongoing since 2016. In 2021 ...
When Homework Was Banned. Published: November 3, 2023. copy page link Print Page. Why Homework Was Banned.
6 of 15 |. Ola Kozak, 11, right, and her younger brother Julian Kozak, 9, sit at the table where they used to do their homework at the family home in Warsaw, Poland, Friday April 5, 2024. Ola is happy that Poland's government has ordered strict limits on the amount of homework that teachers can impose on the lower grades, starting in April.
Gov. Kathy Hochul said this week that smartphones should not be available to students during the school day, adding that she is exploring ways to make that happen next year. Here, Hochul speaks ...