- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Five tips to set yourself apart.
Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or elevate your stature within your organization. But while there are plenty of good speakers in the world, you can set yourself apart out by being the person who can deliver something great over and over. Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired together are more memorable); don’t underestimate the power of your voice (raise and lower it for emphasis); give your audience something extra (unexpected moments will grab their attention); rehearse (the best speakers are the best because they practice — a lot).
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to Develop Effective Verbal Communication Skills
March 3, 2021 - Dom Barnard
Verbal communication skills are more important than ever. Countless meetings, presentations, code reviews, conferences and networking events mean that clear and assertive verbal communication are essential for current and future jobs .
Good communication skills can be the difference between getting a promotion or moving laterally, selling your product or struggling with slow growth, influencing colleagues with your idea or doing what you are told.
Article contents
Why is verbal communication important, characteristics of an effective communicator, the power of the mind, keep your audience in mind, actively listen, be empathetic, body language and posture, using the full range of your voice, watch videos from experts.
- 5 ways to practice communication skills
Communication skills are important to many aspects of your life and career, including:
- Managerial role – how do you command respect from your colleagues while building a strong culture and team spirit? How do you deal with an unexpected crisis and communicate your action plan to your team? Oral communication skills are essential for many areas of management.
- Workplace success – you’ll frequently be talking to clients, customers, talking in team meetings, requesting information, giving feedback and discussing problems. All require strong communication skills so that you are understood clearly without any misinterpretation.
- Secure a new job – in employer surveys, oral communication skills consistently rank amongst the top soft skills companies look for. They want new employees to be able to speak clearly, concisely and confidently.
- Advance your career – it’s important to be able to communicate your thoughts on how the processes, products or services can be improved. Business value these skills in management positions.
An effective communicator’s attributes include:
- Active listening
- Adaptability – adapting your communication styles to support the situation
- Confidence and assertiveness
- Constructive feedback – giving and receiving it
- Emotional intelligence – identifying and managing your emotions, as well as other people’s emotions
- Interpersonal skills – social skills which are especially useful in building strong rapports
- Interpretation of body language – this will help you understand how someone is feeling
- Open-mindedness
- Simplifying the complex
- Storytelling
Techniques for improving verbal communication
Communication is a skill which means that you can develop and improve it. Here are some techniques which can refine your skills.
Often we talk while we think but this can reduce our credibility because what we’re saying is usually meaningless and we come across as nervous. Much of presence is about stillness, listening and providing thoughtful response.
When answering questions and whilst engaging in conversation keep the following formula in mind and reply in a short, clear and concise way:
So don’t just say the first thing that comes to mind, instead be thoughtful and concentrate on the meaning of what you wish to communicate. When speaking, understand exactly what message you’re trying to get across. If you are unclear about your message then your audience won’t understand either.
Positive visualisation
This tactic is employed by athletes before a race , they visualise themselves winning and focus on this idea intensely. This gives them a mental boost which translates into a physical one.
You can use this technique before a big presentation – imagine standing on a podium in front of hundreds of people, imagine delivering your speech and the audience looking engaged, imagine finishing up your speech and the audience applause.
Repeating this several times and immersing yourself in the event and the emotions will build effective communication skills.
Exercise – Positive Visualisation
- Find a quiet place to sit down and relax
- Close your eyes
- Think back to an experience you have had that made you feel really good. It can be anything – a personal accomplishment, a youthful memory, a successful project at work
- Take yourself back there and replay the sequence of events
- Be as detailed as you can in reliving the moment for yourself
- Hear the sounds, see the sights and feel the emotions
- Replay this a few times until you are immersed in this event
- Now open your eyes
This is a great technique to do before a presentation as it will help you control your nerves and it will increase your confidence for the event.
You must understand your audience to communicate effectively. By having this understanding you can tailor your communication to suit them so your message has the most impact.
To develop this skill you must imagine yourself in the audience’s position – think of their demographic and shared characteristics. Ask: why are they attending? What do they want to find out? What level are they in terms of knowledge and experience?
Active listening is when you listen beyond the words being spoken – you understand the message being communicated. During conversations, a lot of the time the “listener” is thinking about how they’re going to respond rather than concentrating on what the speaker is saying.
- Course on Active Listening with Online Practice
By really listening you can provide a more thoughtful answer that takes the speaker’s thoughts and opinions into account. Like Richard Branson said, “Listen more than you talk.”

To develop active listening you should practice the following:
1. Pay attention
Give the speaker your complete attention:
- Look at them directly and maintain eye contact.
- Don’t think about your reply whilst they’re speaking.
- Interpret their body language.
- Try to avoid being distracted by what’s happening around you.
2. Show the speaker that you’re interested
- Use your body language to highlight your engagement, such as, nodding, smiling, maintaining an open posture etc.
- Use prompts, such as, “uh huh”, “yep” etc.
- Clarify your understanding…
3. Clarify your understanding
You need to ensure that you understand what the speaker is saying without your judgments and beliefs getting in the way:
- Reflect on what you have heard by summarising and paraphrasing, for example, “Sounds like you’re saying…”. Ensure you do this periodically in a conversation as it helps with your understanding and it’s also another way to show the speaker than you’re listening.
- Ask questions to ensure that you understand everything, such as, “What do you mean when you say…” Ensure that these questions are non-judgemental.
- Ask whether you’ve got it right and accept if you need to be corrected.
- Ask for specific examples.
- Admit if you’re unsure about what the speaker means.
- Ask the speaker to repeat something if you think it will help.
4. Don’t interrupt or redirect the conversation
Interrupting is not helpful as it’s irritating for the speaker and it reduces the time for you to understand the message:
- Before saying anything ensure that the speaker has finished a point.
5. Provide a suitable response
- Be honest when you respond but avoid attacking or making the speaker feel bad because this is unhelpful.
- Provide your opinions politely.
These are the most common obstacles to active listening:
- Losing concentration.
- Jumping to conclusions which subsequently leads to false assumptions.
- Hastily forming a response before the speaker is finished.
To be empathetic means that you are able to identify and understand others’ emotions i.e. imagining yourself in someone else’s position.
Understanding how people feel will help you communicate your thoughts and ideas in a way that makes sense to others and it helps you understand others when they communicate.
To develop empathy:
- Imagine yourself in someone else’s position. Even if you have not experienced a similar situation, remember a situation where you have felt the same emotion your colleague/employee is experiencing.
- Practice listening to your colleagues without interrupting them.
- Observe your colleagues and try to gauge how they’re feeling.
- Never ignore your colleagues’ emotions, for example, if someone looks upset don’t disregard this – address it.
- Try to understand first rather than form a judgement. For example, you may initially feel annoyed at a colleague who seems cold and disinterested. However, after discovering they suffer from social anxiety you may feel more sympathetic.
- To communicate your empathy, keep your body language open and regulate your voice to show your sincerity.
Your posture has the greatest impact on your communication. The impression you have on others is split approximately:
- Body (visuals) 55%
- Voice (sound) 38%
- Words (content) 7%
Folded arms, crossed legs, hunched shoulders, hands in pockets, looking down – these are just some of the protective measures that make us feel safer, and should be avoided when giving a presentation or speech. Appearing relaxed makes us exert dominance and authority.
If you watch politicians speak, notice how relaxed and confident they appear, talking slowly and making positive body movements. Use your arms to emphasis a point and illustrate the message.
Read our 8 Elements of Confident Body Language .
Exercise – Posture
- Place your feet the same width apart as your hips.
- Feel your weight at the heel of your foot on the floor
- Think of your shoulders expanding out from one another.
- Do not hunch forward or pull your shoulders back – allow them to rest centrally.
- Hold your head level.
- Let your arms hang relaxed by your side.
- Spend a moment getting used to this position.
- Do a mental check around your body and make any adjustments you need to get comfortable.
- Try moving to another spot, regaining this relaxed position.
When a person is centred, they are balanced and relaxed. Getting used to placing your attention in your centre of gravity will help you achieve an open, relaxed posture, and make room for deeper, freer breath.
Think about the place halfway between the front and back of your body, and just above your waist. Stand with your feet a shoulder length apart and let your arms hang loosely by your side. Try and put all your attention at this centre before an important meeting or presentation, it will increase your presence and bring you into the moment.
Visual rapport – things to consider
From top down: head, eyes, expressions, shoulders, posture, breathing, energy, arms, hands, gestures, movements, stance, legs and feet.

The human voice is capable of 24 notes on a musical scale. We use about three of these in everyday speech. Think about this next time you speak, as using a wider range will allow you to quickly develop effective communication skills. This will help enthuse, persuade and excite the person or people you are talking to.
Sound resonates in the mouth once your breath has delivered air to the vocal cords. Your tongue manipulates and shapes the sound, giving us speech, pitch and tone.
The more air in your lungs, the better the sounds resonate, giving us a wider range of audible voice. Most of us use less than a third of our vocal capacity and the reason is usually because we do not use our breath as well as we could.
To further understand how to use your voice, read the Toastmasters Speaking Voice Guide .
Breathe deeply to communicate effectively
Every time you think, you breathe. Every time you speak, you breathe. The fact that we breathe subconsciously, means we often don’t think about it when speaking. When we get nervous our breathing becomes shallow . Combine this with overlong sentences, which usually accompany speaking in public, and words begin to trail away at the end.
Maximising your breath and filling your lungs when speaking is very important for building effective communication skills. It makes you sound influential.
Remember to pause for emphasis, pause to take in a breath and pause to allow your message to sink in.
Exercise – Breathing
- Stand in the Neutral Position and put your hands on your stomach.
- Breathe deeply.
- Try to push your hands out as you breathe in by filling your ribs.
- Increase your awareness of this happening as you breathe – the movement and expansion of the ribs.
You can do this one in the comfort of your own home as there are lots of videos online from motivational speakers and communication experts. Watch how these people present themselves – where they look, their tone of voice, the speed at which they speak etc.
Make a list of things they do that you want to replicate in your own speaking and then imitate what the speakers do when you’re talking.
Start small and scale up to a larger audience as you become more comfortable and confident in your ability to deliver your message effectively.
This isn’t an overnight quick-fix (unfortunately, there isn’t one) and you’ll have to practice mastering speaking techniques and eliminate any bad linguistic habits you’ve picked up. If you persevere, you’ll improve your verbal communication skills quickly.
Here are two more videos to get you started:
- ‘ How great leaders inspire action ‘ – Simon Sinek presents a simple but powerful model for how leaders inspire action, starting with a golden circle and the question “Why?”
- ‘ Why We Do What We Do ‘ – Tony Robbins, motivational speaker. You can use this video to show you techniques such as pausing after important points, varying your pitch and using hand gestures to emphasise your message.
5 ways to practice verbal communication skills
Studies on the benefits of practice.
Many studies have taken place on the benefits of practice. We’ve summarised three key benefits for you.
Benefits of practicing oral communication skills:
- Practice greatly increases the likelihood that you’ll remember new information (Anderson, 2008).
- Practice increases your ability to apply knowledge automatically, without reflection. This is usually only achieved through extensive rehearsal and repetition , and frees up your cognitive resources to handle other tasks. (Brown & Bennett, 2002; Moors & De Houwer, 2006).
- Receive feedback on your communication skills so you know where and how to improve
You should think of practice not as rote repetition, but as deliberate, goal-directed rehearsal paired with reflection on communication skills.
- Practice for Knowledge Acquisition (Not Drill and Kill)
Learning vs. practicing
You may be accustomed to being good at what you do. Learning something new is hard, especially at the beginning when we’re likely to struggle and make mistakes. The reality is, the only way to learn something new is to practice.
In his book, Outliers , Malcolm Gladwell suggests that it takes 10,000 hours of practice to become expert at something. Perhaps more of a realist, Josh Kaufman, author of The Personal MBA , writes that to go from “knowing nothing to being pretty good” takes about 20 hours of practice. So whether you aspire to be “pretty good” or an “expert,” practice is essential.
Some people believe that intellectual understanding is enough for skill development. However, many studies have shown this is not that case – we need to practice, get feedback, refine our approach, practice again and generally apply the knowledge we learn. This is hard to do.
You can spend hours learning about communication skills, but without actually practicing what you learn, you’ll only have an intellectual understanding as opposed to skill development.
After learning how to communicate, you’ll need to practice what you’ve learnt in order to develop the skill. We’ve listed both traditional and new methods you can use to practice your communication skills.
1. Online simulator
More and more you may find yourself communicating over video conferencing platforms such as Zoom and Skype. These require a unique set of skills compared to in-person communication.
You can practice your oral communication skills in simulations which mimic video-conferencing software, as well as watch yourself back and receive automated feedback on your performance.
- How to Present over Video – Practice how to deliver successful video-based presentations on Zoom, Skype, Webex, Teams and more.
- Ace your Video Interview – Practice how to deliver successful video-based sales pitches on popular video conferencing platforms.
- Online Interview Training – Learn how to ace your video-based interview with best practices and a mock interview simulator.
Practice your communication skills with interactive online exercises .
2. Professional coaching
This can be in person or through a phone / Skype call. We’ve listed three examples of communication skills coaching.
- RADA Coaching – RADA can enable you to transform all aspects of your leadership, help you to master communication skills such as personal impact, presence and authenticity, or support you on a specific workplace challenge or presentation.
- Public Speaking and Presentation Coaching – get a tailored presentation skills coaching program to your skill level, over the phone or through Skype, so you achieve your goals as quickly as possible.
- Public Speaking and Communications Coaching – personalised sessions of communication skills, presentation skills or public speaking coaching to help you to develop your self-confidence, focus on specific issues or prepare for a particular event.
3. Virtual reality environments
Virtual reality (VR) lets you practice verbal communication techniques in realistic environments from the comfort of your own home. It’s a great middle ground between an online course and in-person coaching. For a more detailed list of VR apps, read our article on top public speaking apps .
- VirtualSpeech platform – practice communication skills, interview preparation, business networking, language learning, sales, and more with interactive exercises. Speech analysis technology provides instant feedback on your speech or conversation.
- Speech Trainer – this Steam based app provides a virtual auditorium where you can learn to overcome your fear of public speaking by addressing a virtual audience.

VR being used to practice a presentation.
4. Friends or colleagues
This is a great way to get detailed feedback on how you are performing. Set yourself a task and ask your colleague or friend to observe you and then give you feedback.
Giving and receiving feedback is a powerful process but needs to be handled sensitively and should follow these guidelines:
- Be specific on what needs to improve
- Provide evidence on where they can change
- Give feedback on any emotional impact you felt
- Be constructive, provide 3 positives and 2 areas to improve
- Listen and don’t interrupt
- Act on the feedback straight away if possible
5. Solo with a video camera or voice recorder
By using a video camera or voice recorder, you can work on your oral communication style. Work with short sections – for example if you need to make a presentation, start by working on your opening.
Perform and watch / listen back a number of times until you feel you have developed what you have done sufficiently to move on.
In this method of working, you alternate the role of subject and observer. When you are observing / listening to yourself, clarify any feedback by writing down what you are developing or changing. This will help you measure your progress as well as structuring your development.
- Free online voice recorder
Final thoughts
Communication is one of the most effective skills that you can cultivate for work so it’s worth the effort to develop it. It’s also helpful to keep in mind the following when working on your communication:
- What we hear last is remembered the easiest.
- We remember things that are presented with an impact, such as, using emotional appeals (pathos).
- We remember things that we have use for.
- We remember what we hear frequently so repetition is important.
This page has been archived and is no longer updated
Effective Oral Presentations
Verbally (and as a general rule), do not write down and memorize or read your full text, because then your presentation will sound like what it is: a recited written text. Instead, memorize the outline of your presentation — that is, a tree structure of main points and subpoints — and speak ex tempore, reinventing the words as you go along. As you do, you will occasionally need to think about what to say next and find the most appropriate words to say it. Instead of using filler words ( um , er , you know , I mean , etc.), simply pause. If you say um , you get about half a second of thinking time and the audience is likely to notice the um and be irritated by it. If you keep silent, you can get up to two or three seconds of thinking time without the audience noticing anything. Even if attendees do notice the silence, they will simply think that you are choosing your words carefully — and there is nothing wrong with that.
Despite pointing often at the screen, Marie nicely faces the audience with her body at all times, keeps her hands down between gestures, and maintains eye contact with the attendees. Transcript Vocally, vary the tone, rate, and volume of your voice as a function of the meaning, complexity, and importance of what you are saying. You need not invent a new intonation pattern: You simply need to amplify your normal pattern.
Visually, control your body. Adopt a stable, confident position; move only when you have a positive reason to do so (for example, move closer to the audience for taking questions), not when your body seems to ask for it. When you make a gesture, make it large and deliberate; between gestures, bring your hands down and do not fidget. Establish eye contact: Engage the audience by looking them straight in the eyes.
At all times, make sure you address the audience. Even if you have slides, tell the audience your story in a stand-alone way; do not just explain your slides. In particular, anticipate your slides. You should know at all times what your next slide is about so you can insert an appropriate transition.
Delivering as a non-native speaker
To keep the audience engaged , Jean-luc emphasizes his points with facial expressions, purposeful gestures, and — especially — a high dynamic range in his vocal delivery. Transcript If you are a non-native speaker of English, you may find it more challenging to speak ex tempore in English than in your native language. Still, even imperfect extemporaneous English is more likely to engage the audience than reciting a more polished, less spontaneous written text. To improve your delivery and overall presentation as a non-native speaker, practice more, pace yourself, and support your spoken discourse with appropriate slides.
While all speakers benefit from practicing their presentations multiple times, consider investing more time in such practice if you are less familiar with the language. Practicing helps you identify missing vocabulary, including key technical terms (which are difficult to circumvent), and express your ideas more fluently. As you practice, you may want to prepare a list of difficult words (to review on the day of your presentation) or write down an occasional complex yet crucial sentence. Still, do not feel bound to what you write down. These notes should be a help, not a constraint.
Practicing in front of an audience (a few colleagues, for example) can help you correct or refine your pronunciation. If you are unsure how to pronounce some words or phrases, you can ask native speakers in advance or check online dictionaries that offer phonetic spelling or audio rendering. Still, you may be unaware of certain words you mispronounce; a practice audience can point these words out to you if you invite it to do so.
During your presentation, pace yourself. As a non-native speaker, you may feel you need to search for your words more often or for a longer time than in your native language, but the mechanism is the same. Do not let this challenge pressure you. Give yourself the time you need to express your ideas clearly. Silence is not your enemy; it is your friend.
Pacing yourself also means speaking more slowly than you otherwise might, especially if you have an accent in English. Accents are common among non-native speakers — and among specific groups of native speakers, too — and they are not a problem as long as they are mild. Often, they are experienced as charming. Still, they take some getting used to. Remember to slow down, especially at the beginning of a presentation, so your audience can get used to your accent, whether native or not.
Handling stage fright and mishaps
Most speakers, even experienced ones, are nervous before or during an oral presentation. Such stage fright is normal and even reassuring: It shows that you care, and you should care if you want to deliver an effective presentation. Accordingly, accept your stage fright rather than feeling guilty about it. Instead of trying to suppress nervousness, strive to focus your nervous energy in your voice, your gestures, and your eye contact. Do not let it dissipate into entropy, such as by using filler words or engaging in nervous mannerisms.
Among the many ways to keep your nerves under control, perhaps the most effective one is to focus constructively on your purpose at all times. Before your presentation, eliminate all the unknowns: Prepare your presentation well, identify (or even meet) your audience, and know the room. During the presentation, do what it takes to get your message across, even if it means doing something differently than you had planned. Have a positive attitude about the presentation at all times: Visualize what you want to achieve, not what you want to avoid.
Even with careful preparation, mishaps can occur. For example, technology may fail, you may forget what you wanted to say, or you may accidentally say the wrong thing. As a rule, do not apologize for what happens — neither in advance nor after the fact. Although well-meant, such apologies provide no benefit to the audience: They are noise. If you can do something about the problem, such as fix the technology or insert what you forgot later in the presentation, concentrate on doing so instead of apologizing. If the problem is out of your control, then there is no need to apologize for it. As a specific example, if you feel your command of English is poor, then do what you can in advance to improve it; in particular, practice your presentation thoroughly. Then, on the day of the presentation, do your best with the command you have, but do not apologize at the beginning of the presentation for what you think is poor English. This apology will not solve anything, and it gives the attendees a negative image of you. Rather, let the attendees judge for themselves whether your command of English is sufficient (perhaps it is, despite what you might think). In other words, focus on delivering results, not excuses.
This page appears in the following eBook
Topic rooms within Scientific Communication

Within this Subject (22)
- Communicating as a Scientist (3)
- Papers (4)
- Correspondence (5)
- Presentations (4)
- Conferences (3)
- Classrooms (3)
Other Topic Rooms
- Gene Inheritance and Transmission
- Gene Expression and Regulation
- Nucleic Acid Structure and Function
- Chromosomes and Cytogenetics
- Evolutionary Genetics
- Population and Quantitative Genetics
- Genes and Disease
- Genetics and Society
- Cell Origins and Metabolism
- Proteins and Gene Expression
- Subcellular Compartments
- Cell Communication
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
© 2014 Nature Education
- Press Room |
- Terms of Use |
- Privacy Notice |

Visual Browse

Verbal Communication: Understanding the Power of Words
Categories Social Psychology
As human beings, we rely on communication to express our thoughts, feelings, and intentions. Verbal communication, in particular, involves using words to convey a message to another person. It is a fundamental aspect of human interaction and is crucial in our daily lives and relationships.
In this article, we will explore the importance of verbal communication, the different types of verbal communication, and some tips on improving your verbal communication skills.
Table of Contents
Importance of Verbal Communication
Verbal communication is essential because it is the primary means of interacting with others. It lets us express our thoughts and feelings, convey information, and build relationships. It is a powerful tool for connecting with others and forming social bonds.
By communicating meaning verbally, others are able to understand your needs, interests, and beliefs.
Effective verbal communication is essential in many contexts, including personal relationships, social interactions, and professional settings. In personal relationships, it can help build trust, foster intimacy, and resolve conflicts. Lack of communication can lead to serious problems, including conflicts and the breakdown of relationships.
Social interactions can help establish common ground, build rapport, and create a sense of community. For example, discussions can help people with different needs understand one another and find ways to ensure each person achieves their goals.
In the workplace, it can help to convey ideas, influence others, and achieve goals.
Types of Verbal Communication
There are two main forms of verbal communication: spoken and written communication.
- Spoken Communication : Spoken communication is the most common form of verbal communication. It involves using words, tone of voice, and body language to convey a message. Spoken communication can take many different forms, including conversations, speeches, and presentations.
- Written Communication : Written communication is using written words to convey a message. It includes emails, letters, memos, and reports. Written communication is often used in professional settings to document information and convey messages to others.
There are four main types of verbal communication, each with its own unique characteristics and purposes:
- Intrapersonal communication : Intrapersonal communication is the process of talking to oneself, either out loud or internally. This type of communication is often used for self-reflection, problem-solving, and decision-making. Intrapersonal communication can help us better understand our own thoughts and feelings, and can be a valuable tool for personal growth and development.
- Interpersonal communication : Interpersonal communication is the process of communication between two or more people. This type of communication is often used for social interaction, relationship-building, and collaboration. Interpersonal communication can involve a range of verbal communication modes, such as face-to-face communication, telephone communication, and video conferencing.
- Small group communication : Small group communication involves communication between three to ten people, typically in a group setting such as a meeting or a discussion. This type of communication is often used for decision-making, problem-solving, and brainstorming. Small group communication requires effective listening and speaking skills, as well as the ability to work collaboratively with others.
- Public communication : Public communication is communicating to a large audience, typically through a speech or a presentation. This type of communication is often used for persuasive purposes, such as advocating for a cause or presenting information to an audience. Public communication requires effective public speaking skills, including the ability to engage and connect with the audience, use effective visual aids, and communicate ideas clearly and persuasively.
Other Types of Communication
In addition to verbal communication, other important forms of communication can convey meaning, including:
Nonverbal communication : Nonverbal communication is the use of body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice to convey a message. It can be used to emphasize a point, show emotion, or convey meaning. Nonverbal communication can be just as powerful as spoken communication and can often convey a message more effectively than words alone.
Visual communication : Visual communication is the use of images, charts, and graphs to convey a message. It is often used in professional settings to present data and information in a way that is easy to understand.
Components of Verbal Communication
Verbal communication is a complex process that involves not only the words we use, but also how we say them. Tone of voice, inflection, and other vocal cues can greatly impact the meaning of our message. Here are some important aspects of verbal communication and how they convey meaning:
- Tone of voice : Tone of voice refers to the way we use our voice to convey meaning. It can be described as the emotional quality of our voice. For example, a sarcastic tone of voice can convey that the speaker is not being sincere, while a warm and friendly tone can convey that the speaker is approachable and trustworthy.
- Inflection : Inflection refers to the rise and fall of our voice as we speak. It can convey emphasis and emotion. For example, a rising inflection at the end of a sentence can indicate a question, while a falling inflection can indicate a statement.
- Volume : Volume refers to how loudly or softly we speak. It can convey confidence, authority, and assertiveness. For example, speaking loudly can convey confidence and authority, while speaking softly can convey intimacy and vulnerability.
- Pace : Pace refers to the speed at which we speak. It can convey excitement, urgency, and impatience. For example, speaking quickly can convey excitement and urgency, while speaking slowly can convey thoughtfulness and deliberation.
- Intensity : Intensity refers to the level of emotional energy that we put into our words. It can convey passion, enthusiasm, and conviction. For example, speaking with intensity can convey a strong belief in something, while speaking with low intensity can convey ambivalence or lack of interest.
- Pitch : Pitch refers to the highness or lowness of our voice. It can convey age, gender, and emotion. For example, a high-pitched voice can convey youthfulness or excitement, while a low-pitched voice can convey authority or seriousness.
It’s important to note that these aspects of verbal communication can vary greatly depending on context, culture, and personal preference. What may be considered a confident tone of voice in one culture may be perceived as aggressive in another.
Understanding these nuances is essential for effective verbal communication. By paying attention to these aspects of verbal communication, we can convey our message more effectively and avoid misunderstandings.
Modes of Verbal Communication
Verbal communication can occur through different modes, each with their own unique features and advantages. Here are some of the different ways verbal communication may occur:
Face-to-Face Verbal Communication
Face-to-face communication occurs when two or more people are in the same physical space and communicate verbally. This mode of communication allows for the use of nonverbal cues, such as facial expressions and body language, which can help convey meaning and emotion. It also allows for immediate feedback and clarification of misunderstandings.
Telephone Communication
Telephone communication occurs when two or more people communicate verbally over a telephone line. This mode of communication allows for immediate verbal communication over long distances but does not allow for the use of nonverbal cues, which can sometimes make it difficult to convey meaning and emotion.
Video Conferencing
Video conferencing occurs when two or more people communicate verbally over a video conferencing platform, such as Zoom or Skype. This mode of communication combines the benefits of face-to-face and telephone communication, allowing for the use of nonverbal cues and immediate verbal communication over long distances.
Public Speaking
Public speaking occurs when one person communicates verbally to a large audience. This mode of communication requires careful planning and preparation, as well as the ability to engage and connect with the audience through the use of tone of voice, inflection, and other vocal cues.
Group Discussion
Group discussion occurs when a group of people communicate verbally to exchange ideas, solve problems, or make decisions. This mode of communication requires active listening skills and the ability to work collaboratively with others to achieve a common goal.
Written Communication
Written communication occurs when ideas, thoughts, and information are conveyed through written words, such as emails, letters, or memos. This mode of communication allows for careful consideration and editing of the message, but can sometimes lack the immediacy and personal connection of verbal communication.
It’s important to note that each mode of verbal communication has its own strengths and weaknesses. Some modes may be more appropriate for certain contexts than others.
For example, face-to-face communication may be more effective for resolving conflicts, while written communication may be more appropriate for conveying complex information or instructions.
Tips for Improving Verbal Communication Skills
Effective verbal communication requires more than just speaking clearly and articulately. It involves listening actively, empathizing with others, and adapting your communication style to different situations. Here are some tips for improving your verbal communication skills:
- Listen actively : Effective communication requires active listening. This means paying attention to what the other person is saying, asking questions, and clarifying misunderstandings.
- Use appropriate body language : Your body language can convey as much meaning as your words. Use appropriate gestures and facial expressions to emphasize your message and convey your emotions.
- Speak clearly and confidently : Speak clearly and confidently to ensure that your message is understood.
- Empathize with others : Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. It is an important communication skill because it helps build trust and understanding.
- Be adaptable : Adapt your communication style to different situations and audiences. Use appropriate language for the context and audience, and be mindful of cultural differences.
- Back to All Programs /
Communication Strategies: Presenting with Impact
Gain skills and techniques to engage, inform and inspire others, improving your ability to communicate as a leader.
All Start Dates
8:30 AM – 4:30 PM ET
2 consecutive days
Registration Deadline
June 30, 2024
November 24, 2024
Communication Strategies Program Overview
Communication strategies: presenting with impact, a public speaking course.
Public speaking—whether delivering a presentation, making a pitch, or leading a group discussion—can cause even the most confident leader to break a sweat. Yet communicating your message with poise, confidence, and conviction is an essential leadership skill. Mastering your public speaking and presentation skills will enable you to inspire your audience as well as build trust and credibility.
Through oral presentations and small group activities, you will put proven public speaking techniques and tools into practice, test out new approaches, and learn to communicate clearly and confidently. Discover the powerful impact of storytelling and practical persuasion skills to authentically illustrate your message. Learn how to effectively organize materials to blend analytical and emotional content into a compelling story, and incorporate dynamic introductions and memorable endings into your presentations.
Who Should Register for this Public Speaking Course
This communication program is appropriate for business professionals at all levels of experience who would like to enhance their communication skills to succeed in delivering impactful presentations. It is ideal for anyone in a role that requires ceremonial speaking, persuasive speaking, or any other type of public speaking, regardless of industry or years of experience.
All participants will earn a Certificate of Participation from the Harvard Division of Continuing Education
Participants must be fluent in English to participate fully in fast-moving discussions and exercises.
Benefits of Communication Strategies: Presenting With Impact
This communication strategies program is designed to offer new techniques to improve your public speaking skills. Key takeaways from the program will help you improve your ability to persuade and influence your audience in large- and small-group settings.
During this public speaking training course, you will:
- Learn guiding principles of making effective presentations
- Build confidence in your presentation abilities
- Cultivate your personal leadership and communication style
- Learn strategies on handling hostile audiences
“Jill [Slye] shared invaluable tips that have helped me to reduce my anxiety and negative self-talk around my presentations while conveying a message that encourages others to affect change through empowering presentations.” — Lizbeth Sanches-Acre
The curriculum for this communication strategies program is designed to be interactive and hands-on. You will practice the skills and techniques you are learning in real-time through small group activities and oral presentations during the program.
The curriculum will cover topics such as:
- Effective delivery skills involving presence, vocal variety, body language, narratives and humor, and handling nerves
- Crafting clear and concise messages
- Understanding and connecting with your audience
- Techniques for effective handling of Q&A sessions
- Ways to gain buy-in and influence your audience
- Strategies for online communications, webinars, podcasts, Zoom platforms, etc.
This public speaking course is offered as a two-day on-campus program in our state-of-the-art classroom space in the heart of historic Harvard University. Program tuition is $2,990 plus the cost of travel.
Considering this program?
Send yourself the details.
Related Programs
- Effective Organizational Communication
- Influence and Persuasion in Leadership
- Becoming a Leader: Developing Your Style and Making Sound Decisions
July Schedule
- Communication Overview
- Honing Your Personal Communication Style
- Developing Audience Centered Content
- Presentations
- Strategies for Online Communications
- Leadership Communication Model
December Schedule
Jill abruzese slye, certificates of leadership excellence.
The Certificates of Leadership Excellence (CLE) are designed for leaders with the desire to enhance their business acumen, challenge current thinking, and expand their leadership skills.
This program is one of several CLE qualifying programs. Register today and get started earning your certificate.
How will this program help me improve my public speaking skills?
This program will help you improve your public speaking skills through hands-on practice of communication techniques and new approaches. As part of the program, you will engage in group exercises and oral presentations where you will receive feedback from the instructor and your peers to help you improve your skills in real time.
How will improving public speaking help me advance my career?
Public speaking is an important skill for any business professional, regardless of industry or role. To advance your career, you must possess the ability to convey your message with clarity and lead group discussions with confidence, regardless of the specific situation. Developing the techniques and strategies to communicate effectively will help build trust in your leadership skills more broadly.
What skills or experience is needed before enrolling in this program?
Participants do not need any specific experience or skills to enroll in this program. It is open to any business professional interested in improving their public speaking skills and their ability to communicate effectively and persuasively.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
4.2 Principles of Verbal Communication
eCampusOntario
Learning Objectives
- Identify the rules and complexities of verbal communication.
- Comprehend the concept of abstraction in language and its implications on communication.
Verbal communication is based on several basic principles. In this section, you’ll examine each principle and explore how it influences everyday communication. Whether it’s a simple conversation with a coworker or a formal sales presentation to a board of directors, these principles apply to all contexts of communication.
Language Has Rules
As mentioned earlier in this chapter, language is a system of symbols, words, and/or gestures used to communicate meaning.
The words themselves have meaning within their specific context or language community. Words only carry meaning if you know the understood meaning and have a grasp of their context to interpret them correctly.
Three types of rules govern or control your use of words.
Syntactic Rules – govern the order of words in a sentence.
Semantic Rules – govern the meaning of words and how to interpret them (Martinich, 1996).
Contextual Rules – govern meaning and word choice according to context and social custom.
Consider the example of a traffic light as follows:
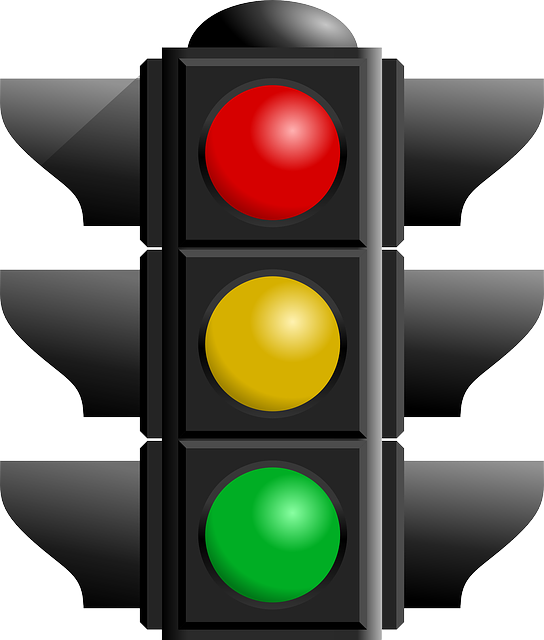
Semantics – Green means Go, and Red means Stop
Syntax – Green is on the bottom, yellow in the middle, and red on top.
Even when you follow these linguistic rules, miscommunication is possible. Your cultural context or community may hold different meanings for the words used – different from those intended by the source communicator. Words attempt to represent the ideas you want to communicate, but factors beyond your control sometimes limit them. Words often require you to negotiate meaning or to explain what you mean in more than one way in order to create a common vocabulary. You may need to state a word, define it, and provide an example in order to come to an understanding with your audience about the meaning of your message.
As discussed previously, words themselves do not have any inherent meaning. Humans give meaning to them, and their meanings change over time. The arbitrary symbols, including letters, numbers, and punctuation marks, stand for concepts in your experience. You have to negotiate the meaning of the word “home” and define it through visual images or dialogue in order to communicate with your audience.
Words have two types of meanings: denotative and connotative.

Denotative – The common meaning often found in the dictionary.
Connotative – Meaning not found in the dictionary but in the community of users itself. It can involve an emotional association with a word, positive or negative, and can be individual or collective but is not universal.
Effective communication becomes a more distinct possibility with a common vocabulary in both denotative and connotative terms. But what if you have to transfer meaning from one vocabulary to another? That is essentially what you are doing when you translate a message. For example, after bringing a U.S. campaign overseas, HSBC Bank was forced to rebrand its entire global private banking operations. In 2009, the worldwide bank spent millions of dollars to scrap its 5-year-old “Assume Nothing” campaign. Problems arose when the message was brought overseas, translated in many countries as “Do Nothing.” In the end, the bank spent $10 million to change its tagline to “The world’s private bank,” which has a much friendlier translation.

Read the following article for a few more examples of organizational messaging challenges: International Marketing Fails
Language is Abstract

Words represent aspects of our human environment and can play an important role in that environment. They may describe an important idea or concept, but labelling and invoking a word simplifies and distorts your concept of the thing itself. This ability to simplify concepts makes it easier to communicate but sometimes makes you lose track of the specific meaning you are trying to convey through abstraction.
The ladder of abstraction is a model used to illustrate how language can range from concrete to abstract. If you follow a concept up the ladder of abstraction, more and more of the “essence” of the original object is lost or left out, which leaves more room for interpretation, which can lead to misunderstanding. This process of abstracting, of leaving things out, allows you to communicate more effectively because it serves as a shorthand that keeps you from having a completely unmanageable language filled with millions of words—each referring to one specific thing (Hayakawa & Hayakawa, 1990). But it requires you to use context and often other words to generate shared meaning.
Some words are more directly related to a concept or idea than others. If you were asked to go and take a picture of a book, it might seem like a simple task. If you were asked to go and take a picture of “work,” you’d be puzzled because work is an abstract word that was developed to refer to any number of possibilities from writing a book to repairing an air conditioner to fertilizing an organic garden. You could take a picture of any of those things, but you would be challenged to take a picture of “work.”
Consider the example of a cow.

If you were in a barn with this cow, you would be experiencing stimuli coming in through your senses. You would hear the cow, likely smell the cow, and be able to touch the cow. You would perceive the actual ‘thing,’ which is the ‘cow’ in front of you. This would be considered concrete; it would be unmediated, meaning it was the moment of experience. As represented in Figure 2.2 below, the ladder of abstraction begins to move away from experience to language and description.
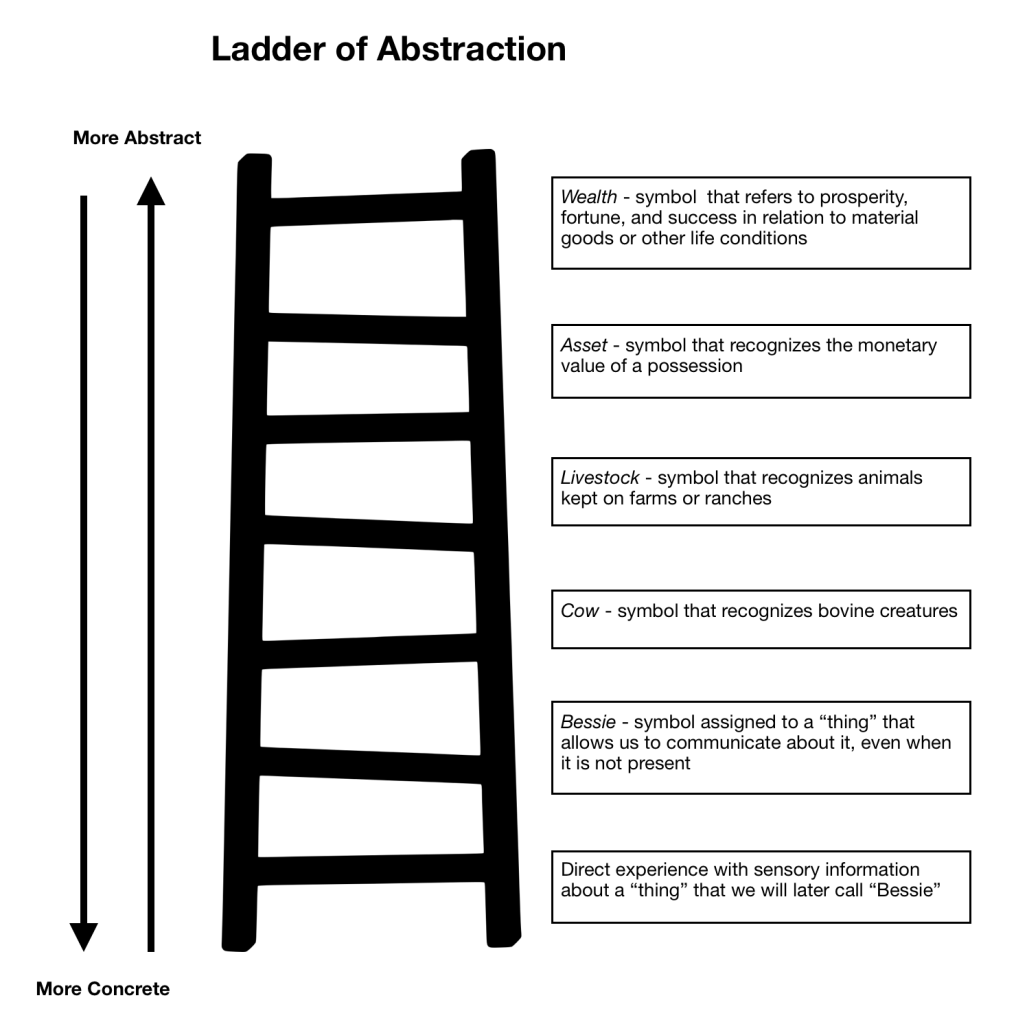
Figure 2.2 . The Ladder of Abstraction. A ladder depicting increasing abstraction of observation and language (Hayakawa & Hayakawa, 1990).
As you move up a level on the ladder of abstraction, you might give your experience a name — you are looking at ‘Bessie.’ So now, instead of the direct experience with the ‘thing’ in front of you, you have given the thing a name, which takes you one step away from the direct experience toward the use of a more abstract symbol. Now you can talk and think about Bessie even when you aren’t directly experiencing her.
At the next level, the word cow now lumps Bessie in with other bovine creatures that share similar characteristics. As you go up the ladder, the cow becomes livestock, livestock becomes an asset, and then an asset becomes wealth.
Note that it becomes increasingly difficult to define the meaning of the symbol as you go up the ladder and how with each step, you lose more of the characteristics of the original concrete experience.
Language Organizes and Classifies Reality
Humans use language to create and express a sense of order. You often group words that represent concepts by their physical proximity or their similarity to one another. For example, in biology, animals with similar traits are classified together. An ostrich may be said to be related to an emu and a nandu, but you wouldn’t group an ostrich with an elephant or a salamander. Your ability to organize is useful but artificial. The systems of organization you use are not part of the natural world but an expression of your views about the natural world.
What is a doctor? A nurse? A teacher? If a male came to mind in the case of the word ‘doctor’ and a female came to mind in reference to ‘nurse’ or ‘teacher’, then your habits of mind include a gender bias. In many cultures, there was a time when gender stereotypes were more than just stereotypes; they were the general rule, the social custom, the norm. But now, in many places, this is no longer true. More and more men are training to serve as nurses. In 2017, for example, data from the Canadian Medical Association (CMA) indicated that 41% of practising physicians in Canada were women (Canadian Medical Association, 2017).
You use systems of classification to help you navigate the world. Imagine how confusing life would be if you had no categories such as male/female, young/old, tall/short, doctor/nurse/teacher. While these categories are mentally useful, they can become problematic when you use them to uphold biases and ingrained assumptions that are no longer valid. You may assume, through your biases, that elements are related when they have no relationship at all. As a result, your thinking may become limited and your grasp of reality impaired. It is often easier to spot these biases in others, but it is important for an effective communicator to become aware of them. Holding biases unconsciously will limit your thinking, grasp of reality, and ability to communicate successfully.
Key Takeaways
- Language, while a powerful tool for communication, is governed by various rules (syntactic, semantic, and contextual) that determine the order, meaning, and contextual appropriateness of words. However, even with these rules in place, the potential for miscommunication exists due to cultural and individual differences in interpreting meanings.
- The ladder of abstraction demonstrates that language can simplify or distort our understanding of concepts, moving from concrete experiences to more generalized or abstract terms. While language helps humans organize and classify their understanding of the world, it can also perpetuate biases, stereotypes, and outdated assumptions, potentially hampering effective communication.
4.2 Principles of Verbal Communication Copyright © 2024 by eCampusOntario is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
Verbal Communication: A Complete Guide
Explore the essence of Verbal Communication. Understand the significance and benefits it brings to various aspects of life. Learn how to develop strong verbal communication skills that can enhance your personal and professional relationships. Dive into the nuances of the four different styles of verbal communication and the various types it encompasses.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Effective Communication Skills
- English Speaking Course
- Assertiveness Skills Training
- Executive Communication Training
- Interpersonal Skills Training Course

Verbal Communication is a vital skill that allows us to express ourselves clearly, connect with others, and make an impact. We can build relationships, influence others positively, and confidently navigate challenges by mastering effective Verbal Communication. Enhancing your Communication skills empowers you to excel in various areas of life, from career advancement to personal growth.
By mastering the art of Verbal Communication, we can develop understanding, influence others positively, and confidently navigate challenging situations. Learn about efficient Verbal Communication and develop your communication abilities. Discover how to master Verbal Communication by diving into our blog.
Table of Contents
1) What is Verbal Communication?
2) Benefits of Verbal Communication
3) How to develop strong Verbal Communication skills?
4) Four different styles of Verbal Communication
5) Types of Verbal Communication
6) What are the differences between Verbal and Non-verbal Communication?
7) How to overcome challenges in Verbal Communication?
8) Conclusion
What is Verbal Communication?
Verbal Communication is the process of using spoken words to express ideas, thoughts, and feelings to others. It involves using our voices to communicate with people around us, whether it's through conversations, presentations, or speeches. It allows us to convey information, share stories, ask questions, and connect with others on a deeper level.
It is essential to our everyday interactions, enabling us to express ourselves, understand others, and build relationships. By improving our Verbal Communication skills, we can become more effective Communicators and enhance our ability to convey messages clearly and confidently.
Learn all the essential techniques to excel in all aspects of Communication with our comprehensive Communication Skills Training . Join now!
Benefits of Verbal Communication
This section of the blog will expand on the various benefits of Verbal Communication.
1) Clarity and precision: Verbal Communication allows individuals to convey their thoughts and ideas with clarity and precision. They can use words, tone, and voice modulation to make sure that their message is understood accurately.
2. Immediate feedback: One of the key advantages of Verbal Communication is the ability to receive immediate feedback. This enables speakers to gauge the listener's understanding and make necessary adjustments to their message in real-time.
3) Non-verbal cues: Verbal Communication is not just about words; it also includes non-verbal cues such as body language, facial expressions, and gestures. These cues provide additional context and help convey emotions and intentions.
4) Personal connection: Speaking directly with someone allows for a personal connection that written Communication often lacks. Tone of voice and emotional expression can help build rapport and trust between individuals.
5) Effective problem-solving: Verbal Communication is essential in group discussions and collaborative problem-solving. It enables team members to share ideas, brainstorm, and reach consensus more efficiently.
6) Flexibility: Verbal Communication can be adapted to suit the audience and the situation. Whether it's a formal presentation, a casual conversation, or a negotiation, individuals can adjust their Communication style accordingly.
7) Cultural understanding: Verbal Communication allows people from different cultural backgrounds to engage in dialogue, fostering cross-cultural understanding and reducing misunderstandings that can arise from written Communication.
8) Immediate resolution of issues: Verbal Communication is ideal for addressing conflicts and resolving issues promptly. It allows individuals to discuss concerns, clarify misunderstandings, and find mutually agreeable solutions.
9) Enhanced learning: In educational settings, Verbal Communication is crucial for effective teaching and learning. Teachers can explain complex concepts, answer questions, and engage students in discussions, promoting better comprehension.
10) Emotional expression: Verbal Communication provides a platform for expressing emotions, whether it's sharing joy, offering support, or conveying empathy during difficult times. It strengthens interpersonal relationships.

How to develop strong Verbal Communication skills?
a) Practice active listening: Focus on understanding the speaker's message by paying attention, maintaining eye contact, and avoiding interruptions.
b) Enhance clarity: Speak clearly, pronounce words properly, and use appropriate tone and volume to ensure your message is easily understood.
c) Expand vocabulary: Continuously enrich your vocabulary by reading books, articles and engaging in conversations to express yourself more effectively.
d) Use body language: Pay attention to your non-verbal cues, such as maintaining good posture, using hand gestures, and displaying open and engaged body language.
e) Be concise: Express your thoughts clearly and concisely, avoiding unnecessary jargon or complex language.
f) Practice expressing ideas: Engage in conversations, debates, or presentations to practice articulating your ideas and thoughts fluently.
g) Seek feedback: Request feedback from trusted individuals on your Communication skills, allowing you to identify areas of improvement and refine your Verbal Communication abilities.
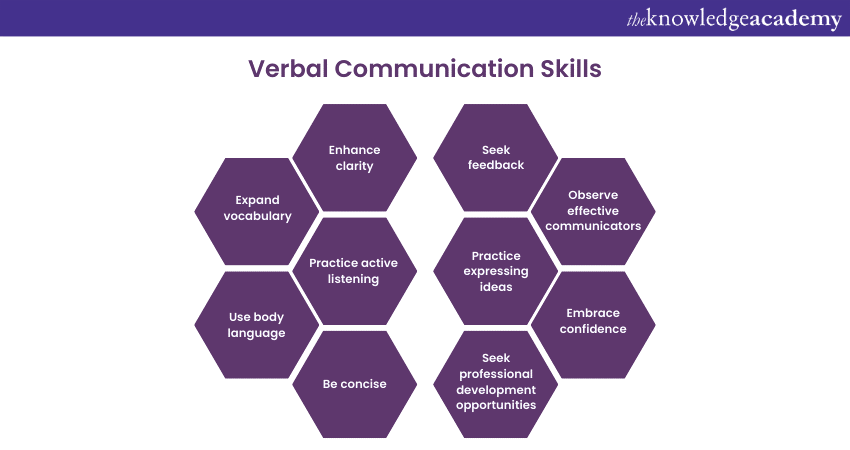
h) Observe effective communicators: Observe and learn from skilled communicators, such as Public Speakers or professionals, to gain insights into effective Verbal Communication techniques.
i) Embrace confidence: Cultivate confidence in your speaking abilities by practising and visualising successful Communication scenarios.
j) Seek professional development opportunities: Attend workshops, seminars, or courses focusing on enhancing Verbal Communication skills to gain valuable insights and techniques.
Four different styles of Verbal Communication
This section of the blog will outline four different styles of Verbal Communication and expand on them.
Style 1: Aggressive style of Verbal Communication
An aggressive style of Communication is characterised by the use of forceful and confrontational language. Individuals employing this style often dominate conversations, disregard others' opinions, and may resort to shouting or verbal attacks. This approach can lead to hostility and conflict in Communication, making it less effective for productive dialogue.
Style 2: Passive style of Verbal Communication
A passive style of Communication involves a reluctance to express one's own opinions or needs. Individuals using this style often avoid confrontation, but this can lead to poor self-advocacy and misunderstandings. While it may prevent immediate conflict, it can result in unmet personal needs and desires.
Style 3: Passive-aggressive style of Verbal Communication
The passive-aggressive style combines elements of passivity and indirect hostility. In this approach, individuals may use sarcasm, backhanded compliments, or subtle sabotage to express their displeasure or frustration. It often creates confusion and can damage relationships due to hidden resentment, as the true feelings are not openly communicated.
Style 4: Assertive style of Verbal Communication
Assertive Communication involves the clear and respectful expression of one's thoughts, feelings, and needs. It values the rights and opinions of both one’s self and others. An assertive Communicator strives to communicate honestly and directly while also actively listening to others. This style fosters healthy Communication, promotes understanding, and helps resolve conflicts constructively. It is considered one of the most effective forms of Communication for building positive relationships and achieving mutual goals.
Types of Verbal Communication
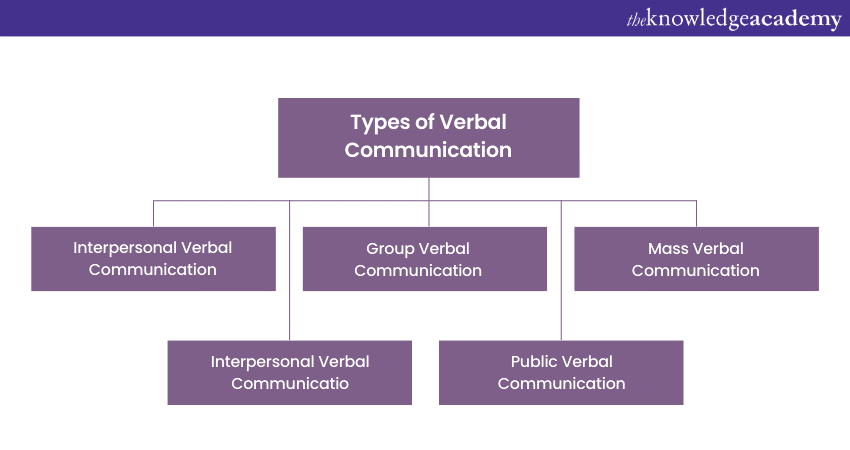
a) Intrapersonal Verbal Communication: This refers to the conversations we have with ourselves in our minds. It involves self-reflection, self-analysis, and self-expression. This internal dialogue helps us process thoughts, make decisions, and reflect on our experiences. For example, talking to yourself to prepare for a challenging situation can boost confidence and improve performance.
b) Interpersonal Verbal Communication: It occurs between two or more people and plays a crucial role in building relationships, expressing emotions, and exchanging information. It involves active listening, clear articulation, and effective response. Using verbal cues, such as words, tone of voice, and non-verbal gestures, helps convey messages accurately and establish meaningful connections.
c) Group Verbal Communication: This involves interactions within a small group of people, such as team meetings or collaborative discussions. It requires effective participation, active listening, and respectful association. Group members share ideas, exchange information, and work together to achieve common goals. Facilitating open dialogue and encouraging equal participation can enhance group dynamics and promote effective collaboration.
d) Public Verbal Communication: This involves speaking to a larger audience, such as giving a presentation, delivering a speech, or leading a public event. It requires clear articulation, engaging storytelling, and effective delivery techniques to captivate and inform the listeners. Public speaking skills can help inspire, persuade, and influence others, making it an essential skill in various professional and social settings.
e) Mass Verbal Communication: This reaches a wide audience through television, radio, or online platforms. It involves broadcasting information, news, or entertainment to the public. It relies on effective message creation, presentation, and delivery to capture and maintain the audience's attention. It influences public opinion, shapes cultural norms, and facilitates the exchange of ideas on a large scale.
What are the differences between Verbal and Non-verbal communication?
Let’s discuss some of the key differences between Verbal and Non-verbal communication:
How to overcome challenges in Verbal Communication?
Overcoming challenges in Verbal Communication leads to developing effective strategies for improved interaction and understanding. Ways to overcome challenges include:
Positive reinforcement
Positive reinforcement involves using encouraging words and non-verbal cues to develop rapport and reinforce openness in others. It encourages active participation, shows genuine interest, builds and maintains relationships, provides reassurance, and creates a warm and welcoming environment.
Effective questioning
Effective questioning is a powerful technique for gathering information and seeking support. Closed-ended questions seek brief responses, while open questions invite elaboration and encourage deeper engagement. Both types of questions serve different purposes in directing conversations and facilitating meaningful dialogue.

Reflection and clarification
Reflection involves restating the speaker's message in your own words, demonstrating understanding and active listening. It allows for clarification and confirmation, shows respect for the speaker's perspective, and fosters a deeper connection and mutual understanding.
Summarising
Summarising involves providing a concise overview of the main points or key issues discussed. It serves as a way to review and validate the shared understanding between Communicators, ensuring effective Communication and serving as a guide for further action.
Closing communication
The closing of a conversation is just as important as its opening. Verbal cues, namely expressing gratitude or signalling the need to conclude, are worth noting. Along with non-verbal cues like maintaining eye contact or engaging in appropriate parting gestures, it helps bring conversations to a natural and respectful close.
Sign up now for our Effective Communication Skills Course today and improve your ability to connect, collaborate, and succeed.
Conclusion
To sum it up, Verbal Communication can be described as a key driver of success. It enables clear expression, fosters learning, and strengthens relationships. Mastering this skill empowers us to confidently influence, collaborate, and navigate challenges. By honing your Verbal Communication skills, you can explore many opportunities for growth and achievement in your personal and professional career path.
Master the basics of Non-verbal Communication by registering for our Nonverbal Communication Training today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming business skills resources batches & dates.
Fri 28th Jun 2024
Fri 9th Aug 2024
Fri 25th Oct 2024
Fri 27th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

5 Tips to Boost Your Presentation Skills and Wow Your Audience
- The Speaker Lab
- May 24, 2024
Table of Contents
Crafting an unforgettable presentation requires more than just compelling content. The way you deliver your message is just as important. No matter your role—CEO, entrepreneur, author, professor, coach, or consultant—honing your presentation skills is key to effectively communicating your ideas and making a memorable impact on your audience. It may not always be easy, but we’re here to help. To help you nail it every time, we’ve compiled 10 essential tips for honing your presentation skills . From knowing your audience to practicing confident body language, we have the guidance you need to give a presentation that’s effective and memorable.
5 Essential Tips for Delivering a Killer Presentation
You’ve probably sat through your fair share of presentations—some good, some not so good. The difference between an effective presentation and one that falls flat often comes down to a few key factors. If you want to improve your skills and deliver a presentation that engages your audience, here are some essential tips you need to keep in mind.
1. Understand Your Audience
Before you even start putting together your presentation, you need to take some time to understand who you’ll be speaking to. What are their needs, interests, and expectations? What level of knowledge do they have about your topic?
Tailoring your content and delivery style to your specific audience is crucial for making a real connection and delivering value. For instance, if you’re giving a presentation to a group of executives who are pressed for time, you’ll probably want to give them key takeaways upfront. By adapting your approach and leading with the most important points, you would be able to better hold your audience’s attention and make a strong impact.
2. Practice Makes Perfect
If you only go away with one tip today, then know that having the discipline to practice is an essential presentation skill. Rehearsing your talk multiple times helps you build confidence, refine your delivery, and ensure a smooth flow. Make sure to practice out loud, as if you’re in front of the actual audience. You can even record yourself and watch the video back to identify areas for improvement. It might feel awkward at first, but it can make a huge difference in your final delivery.
3. Engage with Eye Contact
Making eye contact with your audience is one of the most powerful ways to connect with them and keep them engaged. When you look people in the eye, it builds trust and shows that you’re confident in what you’re saying.
During your presentation, make a point to scan the room and make brief eye contact with individuals in different sections. It creates a sense of intimacy and makes people feel like you’re speaking directly to them. Just be sure to keep it natural and avoid staring anyone down.
4. Use Compelling Visuals
Visuals can be a game-changer when it comes to delivering an effective presentation. Well-designed slides, images, and videos help reinforce your message, break up text-heavy content, and keep your audience interested.
The key is to use visuals strategically, not just for the sake of having them. Every visual element should serve a clear purpose and enhance your overall message. And don’t forget about quality—blurry images or cluttered slides can be more distracting than helpful.
5. Tell a Story
Humans are wired to respond to stories. Integrating storytelling into your presentation is a fantastic way to make your content more engaging, memorable, and relatable.
Think about how you can structure your presentation as a narrative arc, with a clear beginning, middle, and end. Use anecdotes, case studies, and examples to illustrate your points and create an emotional connection with your audience. Some of the best presentations are the ones that take the audience on a journey and leave them feeling inspired.
Find Out Exactly How Much You Could Make As a Paid Speaker
Use The Official Speaker Fee Calculator to tell you what you should charge for your first (or next) speaking gig — virtual or in-person!
Master Your Body Language for Maximum Impact
Your body language can speak volumes during a presentation, often conveying just as much as your words. Mastering non-verbal communication is key to delivering a killer presentation that commands attention and leaves a lasting impression. Below are our tips for improving this presentation skill.
Maintain Confident Posture
How you carry yourself on stage can instantly impact your perceived confidence and credibility. Stand tall, keep your shoulders back, and maintain a stable, grounded stance. Avoid slouching, fidgeting, or shifting your weight from side to side, as these habits can make you appear nervous or unsure.
In addition, make a conscious effort to take up space and own the room. It’s not about being arrogant, but about projecting self-assurance and authority. Practice power poses beforehand to get in the right headspace and boost your confidence.
Use Gestures Purposefully
Incorporating hand gestures can add emphasis, clarity, and visual interest to your presentation. However, it’s important to use them purposefully and avoid overdoing it.
What’s our tip for improving this presentation skill? Use open, expansive gestures to convey confidence and inclusivity. Pointing can be effective for directing attention or making a strong point, but use it sparingly. Avoid crossing your arms or putting your hands in your pockets, as these positions can make you seem closed off or disengaged.
Vary Your Tone and Pace
Your voice is a powerful tool for engaging your audience and keeping them interested. Vary your tone, pitch, and pacing throughout your presentation to add dynamic energy and prevent monotony.
Speak with enthusiasm and conviction, allowing your passion for the topic to shine through. Use strategic pauses for emphasis or to give the audience a moment to process a key point. Adjust your volume and speed based on the room size and acoustics.
Avoid Distracting Mannerisms
Distracting mannerisms can quickly derail an otherwise great presentation. Be aware of any nervous tics or habits you might have, such as playing with your hair, clicking a pen, or saying “um” or “like” excessively.
Practice self-awareness and work on minimizing these behaviors. It can be helpful to video record yourself and watch it back to identify any distracting mannerisms you might not realize you have. Remember, the goal is to keep the focus on your message, not your quirks.
Overcoming Stage Fright and Nerves
Even the most seasoned presenters can experience stage fright and nerves. The key is to have strategies in place to manage those feelings and deliver a confident, impactful presentation.
Prepare Thoroughly
One of the best ways to combat stage fright is to be thoroughly prepared. When you know your material inside and out, it gives you a solid foundation to fall back on, even if nerves start to creep in.
For instance, you might create a detailed outline of your presentation, including key points, transitions, and any important data or examples. Using the outline, practice delivering the content out loud multiple times until it feels natural and conversational. When it’s time to actually present, you can fall back on the outline if you feel yourself start to get nervous.
Visualize Success
Visualization is a powerful tool for boosting confidence and calming nerves. In the days leading up to your presentation, take some time to close your eyes and imagine yourself delivering your talk with ease and conviction. Picture the audience responding positively, nodding along, and applauding at the end. Envision yourself feeling calm, confident, and in control. The more vividly you can imagine a successful outcome, the more likely you are to achieve it.
Breathe Deeply
Although tips on breathing exercises might seem unrelated, they’re actually an invaluable presentation skill. Think about it. When we’re nervous, our breathing tends to become shallow and rapid. This can exacerbate feelings of anxiety and make it harder to think clearly.
Before and during your presentation, focus on taking slow, deep breaths from your diaphragm. Inhale through your nose for a count of four, hold for four, then exhale through your mouth for a count of four. This simple technique can help calm your nerves and center your mind.
Focus on Your Message
When stage fright starts to take hold, it’s easy to get caught up in worries about how you’re coming across or what the audience might be thinking. Instead, try to shift your focus to your message and the value you’re providing.
Remind yourself of why your topic matters and how it can benefit your audience. Concentrate on delivering your content with clarity, conviction, and enthusiasm. When you’re passionate about what you’re saying, it shines through and connects with your listeners.
Crafting Memorable and Engaging Content
No matter how polished your delivery is, the foundation of a killer presentation is always the content itself. Crafting a memorable and engaging message is essential for making a lasting impact on your audience.
Start Strong
The opening moments of your presentation are crucial for capturing your audience’s attention and setting the tone for what’s to come. Don’t waste this opportunity with a generic introduction or a long-winded anecdote.
Instead, start with a bang. Use a surprising statistic, a thought-provoking question, or a bold statement that immediately grabs people’s interest. Make it clear why your topic matters and what your audience stands to gain from listening to you. Practice these tips and you’ll have this presentation skill mastered in no time.
Use Examples and Anecdotes
Abstract concepts and dry data can be difficult for audiences to grasp and remember. That’s where examples and anecdotes come in. These concrete illustrations help bring your ideas to life and make them more relatable.
When crafting your presentation, always look for opportunities to weave in real-world examples, case studies, or personal stories that reinforce your key points. Not only do these elements make the content more engaging, but they also help the audience see how the information applies to their own lives and experiences.
Incorporate Humor
Injecting humor into your presentation can be a great way to break the ice, lighten the mood, and keep your audience engaged. A well-timed joke or a witty observation can make your message more memorable and help you connect with your listeners on a human level.
Of course, it’s important to use humor judiciously and appropriately. Make sure your jokes are relevant to your topic and won’t offend or alienate anyone in the audience.
End with a Call to Action
Your presentation shouldn’t just be informative—it should also be actionable. As you near the end of your talk, be sure to include a clear and compelling call to action.
What do you want your audience to do with the information you’ve shared? Is there a specific step they can take to apply your ideas or further their learning? Make it explicit and easy for them to follow through.
You can also end your presentation with a challenge or a question that encourages the audience to reflect on how they can put the content into practice. It’s a powerful way to drive home your message and ensure that your words have a lasting impact.
Handling Questions and Audience Interaction
One of the most daunting aspects of giving a presentation can be handling questions from the audience. But with the right approach, this interaction can actually be an opportunity to reinforce your message and build credibility. Below are some tips on how to improve this presentation skill and close out your speech with confidence.
Anticipate Common Questions
Before your presentation, take some time to brainstorm the questions your audience is likely to ask. Consider their background, their level of knowledge on the topic, and any potential objections or concerns they might have.
Once you have a list of anticipated questions, practice answering them out loud. This will help you feel more prepared and confident when the time comes to address them in real-time.
Listen Attentively
When an audience member asks a question, give them your full attention. Make eye contact, nod to show you’re listening, and avoid interrupting or rushing to respond. If the question is lengthy or convoluted, don’t be afraid to ask for clarification. Paraphrasing the question back to the asker can also help ensure that you’ve understood it correctly and give you a moment to gather your thoughts.
Respond Concisely
When answering questions, aim to be concise and to the point. Avoid rambling or getting sidetracked by tangential information. Stick to the key facts and insights that directly address the question at hand.
If a question requires a more in-depth response than time allows, offer to follow up with the individual after the presentation. You can also direct them to additional resources or materials that provide more detail on the topic.
Redirect Off-topic Queries
Occasionally, you may receive a question that is off-topic or not directly relevant to your presentation. In these cases, it’s important to acknowledge the question while gently redirecting the conversation back to your main points.
You might say something like, “That’s an interesting question, but it’s a bit outside the scope of what we’re focusing on today. Let’s talk more about [relevant topic] and how it relates to [your key message].”
Remember, your goal is to keep the discussion focused and productive, while still making the audience feel heard and valued.
Leveraging Technology for Impactful Presentations
In today’s digital age, technology can be a powerful tool for enhancing your presentations and engaging your audience. However, knowing how to use technology isn’t always straightforward. That’s why we’re offering you some tips on how to level up this presentation skill. Below are some insights on how to use technology strategically and not let it overshadow your message.
Keep Slides Simple
When it comes to presentation slides, less is often more. Avoid cluttering your slides with too much text, busy graphics, or distracting animations. Instead, keep them clean, concise, and visually appealing.
Use a consistent color scheme and font throughout your presentation to create a cohesive look. Stick to one main idea per slide, and use bullet points or short phrases rather than full sentences.
Remember, your slides should support and enhance your message, not compete with it. They’re meant to be a visual aid , not a crutch or a substitute for your own knowledge and expertise.
Use High-Quality Images
Incorporating relevant, high-quality images into your presentation can help illustrate your points, break up text, and keep your audience engaged. But be selective about the images you choose. Avoid generic stock photos or low-resolution graphics that can make your presentation look amateurish. Instead, opt for images that are clear, compelling, and directly related to your content.
If you’re using graphs or charts to present data, make sure they’re easy to read and interpret. Use colors and labels strategically to highlight key insights and trends.
Embed Videos Strategically
Videos can be a great way to add variety and interest to your presentation. They can help illustrate complex concepts, provide real-world examples, or evoke an emotional response from your audience.
However, it’s important to use videos judiciously and strategically. Avoid relying on them too heavily or using them as a crutch for weak content. Make sure any videos you include are high-quality, relevant, and add value to your overall message.
It’s also a good idea to test your videos beforehand to ensure they play smoothly and without technical glitches. Nothing derails a presentation faster than a video that won’t load or has poor audio quality.
Ensure Smooth Transitions
Smooth transitions between slides and sections of your presentation are key to maintaining a professional and polished look. Abrupt or jarring transitions can be distracting and disrupt the flow of your message.
Practice navigating through your slides beforehand to ensure that everything flows logically and seamlessly. Use consistent transition effects throughout your presentation, but avoid overusing flashy or gimmicky animations.
It’s also a good idea to have a backup plan in case of technical difficulties. Bring a printed copy of your slides or have them saved on a USB drive in case the technology fails. The show must go on, even if your fancy transitions don’t.
Free Download: 6 Proven Steps to Book More Paid Speaking Gigs in 2024
Download our 18-page guide and start booking more paid speaking gigs today!
Avoiding Common Presentation Mistakes
Even the most well-crafted presentation can fall flat if you make some common mistakes. Here are a few pitfalls to avoid to ensure your message lands with maximum impact.
Over-Reliance on Notes
While it’s fine to have some notes or a general outline to guide your presentation, relying too heavily on them can be a major distraction. Reading directly from your notes or slides can make you seem unprepared or disengaged from your audience.
Instead, aim to internalize your content so that you can deliver it naturally and conversationally. Use your notes as a gentle reminder of key points, but don’t let them become a crutch. If you do need to reference your notes, try to do so subtly and sparingly. Glance down briefly, then look back up and make eye contact with your audience as you speak.
Reading Slides Verbatim
One of the biggest mistakes presenters make is simply reading their slides word-for-word. Not only is this boring for your audience, but it also makes your slides redundant. If you’re just going to read them aloud, why bother having them at all?
Your slides should be a visual aid, not a script. Use them to highlight key points, provide visual examples, or reinforce your message with data or graphics. And remember that the bulk of your content should come from your own knowledge and expertise.
If you find yourself tempted to read directly from your slides, it’s a sign that you either have too much text on them or you haven’t practiced enough to feel confident delivering the content on your own.
Rushing Through Content
When you’re nervous or pressed for time, it can be tempting to rush through your presentation at breakneck speed. However, this can leave your audience feeling overwhelmed, confused, and disconnected from your message.
Remember, your audience needs time to process and absorb the information you’re sharing. Speak at a measured pace, pausing occasionally to let key points sink in or to allow for questions.
If you find yourself running short on time, resist the urge to speed up. Instead, prioritize your most important points and cut out any extraneous information.
With a few tips, anyone can improve their presentation skills. By understanding your audience, crafting compelling content, and mastering your delivery, you’ll be well on your way to giving presentations that truly resonate.
Remember, it’s not about being perfect. It’s about being authentic, engaging, and delivering value to your audience. So take these tips, make them your own, and go out there and wow your audience. You’ve got this!
- Last Updated: May 24, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Career Planning
- Skills Development
Verbal Communication Skills List and Examples
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ADHeadshot-Cropped-b80e40469d5b4852a68f94ad69d6e8bd.jpg)
What Are Verbal Communication Skills?
- Verbal Communication at Work
- Examples of Verbal Communication
- Tips to Improve Your Skills
Image by Emily Roberts © The Balance 2019
Almost every job requires workers to use verbal communication skills. That’s why verbal skills are highly ranked on the candidate evaluation checklists used by many job interviewers.
The stronger your communication skills, the better your chances of getting hired regardless of the job for which you’re applying. You’ll do better during the interview, as well as on the job.
Effective verbal communication skills include more than just talking. Verbal communication encompasses both how you deliver messages and how you receive them. Communication is a soft skill , and it’s one that is important to every employer.
Workers who can convey information clearly and effectively are highly valued by employers.
Employees who can interpret messages and act appropriately on the information that they receive have a better chance of excelling on the job.
Verbal Communication Skills in the Workplace
What constitutes effective verbal communication on the job depends on the relationships between communication partners and the work context:
- Verbal communication in a work setting takes place between many different individuals and groups such as co-workers, bosses and subordinates, employees, customers, clients, teachers and students, and speakers and their audiences.
- Verbal communication occurs in many different contexts including training sessions, presentations, group meetings, performance appraisals, one-on-one discussions, interviews, disciplinary sessions, sales pitches, and consulting engagements.
Examples of Verbal Communication Skills
Here are some examples of effective workplace verbal communication skills employed in different workplace contexts.
Verbal Communications for Supervisors: The best supervisors don’t merely tell their subordinates what to do and expect them to listen. Instead, they employ active listening skills to understand employee needs and perspectives, engage in verbal negotiation to address and defuse issues, and capitalize upon opportunities to praise individual and team achievement.
- Advising others regarding an appropriate course of action
- Assertiveness
- Conveying feedback in a constructive manner emphasizing specific, changeable behaviors
- Disciplining employees in a direct and respectful manner
- Giving credit to others
- Recognizing and countering objections
- Showing an interest in others, asking about and recognizing their feelings
- Speaking calmly even when you’re stressed
- Terminating staff
- Training others to carry out a task or role
- Using affirmative sounds and words like “uh-huh,” “got you,” “I understand,” “for sure,” “I see,” and “yes” to demonstrate understanding
- Using self-disclosure to encourage sharing
Verbal Communications for Team Members: Open and constant lines of communication are vital to team success, particularly when completing quality- and deadline-critical projects. One of the most important team-building skills, strong verbal communications help to ensure that issues will be spotted and resolved in formative stages, averting costly escalation.
- Conveying messages concisely
- Encouraging reluctant group members to share input
- Explaining a difficult situation without getting angry
- Explaining that you need assistance
- Paraphrasing to show understanding
- Posing probing questions to elicit more detail about specific issues
- Receiving criticism without defensiveness
- Refraining from speaking too often or interrupting others
- Requesting feedback
- Stating your needs, wants, or feelings without criticizing or blaming
Verbal Communications with Clients: If a large part of your work involves one-on-one communications with customers, it’s helpful to have a “gift of gab” – particularly if you are a sales professional. Keep in mind, though, that your conversations need to be focused upon identifying and addressing your clients’ needs; using your verbal talents to encourage consultative dialogues will ensure positive client relations.
- Anticipating the concerns of others
- Asking for clarification
- Asking open-ended questions to stimulate dialogue
- Calming an agitated customer by recognizing and responding to their complaints
- Emphasizing benefits of a product, service, or proposal to persuade an individual or group
- Noticing non-verbal cues and responding verbally to verify confusion, defuse anger, etc.
Verbal Communications for Presenters: Public speaking is a talent that is honed both through practice and through formal training. Speaking articulately and persuasively to a live audience involves:
- Enunciating each word you speak clearly
- Introducing the focus of a topic at the beginning of a presentation or interaction
- Planning communications prior to delivery
- Projecting your voice to fill the room
- Providing concrete examples to illustrate points
- Restating important points towards the end of a talk
- Selecting language appropriate to the audience
- Speaking at a moderate pace, not too fast or too slowly
- Speaking confidently but with modesty
- Summarizing key points made by other speakers
- Supporting statements with facts and evidence
- Tailoring messages to different audiences
- Telling stories to capture an audience
- Using humor to engage an audience
Tips to Improve Your Verbal Communications
Even if you are a shy introvert who prefers to work independently, there are ways to improve your verbal communication skills so that you can more easily cultivate rapport with others.
Practice makes perfect, and so take the time to actively practice these communications skills for workplace success: active listening, clarity and conciseness, confidence, empathy, friendliness, open-mindedness, giving and soliciting feedback, confidence, respectfulness, and non-verbal (body language, tone of voice, eye contact) communication.

- INTERPERSONAL SKILLS
- Communication Skills
What is Communication?
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Interpersonal Skills:
- A - Z List of Interpersonal Skills
- Interpersonal Skills Self-Assessment
- Interpersonal Communication Skills
- Tips for Effective Interpersonal Communication
- Principles of Communication
- Barriers to Effective Communication
- Avoiding Common Communication Mistakes
- Social Skills
- Getting Social Online
- Giving and Receiving Feedback
- Improving Communication
- Interview Skills
- Telephone Interviews
- Interviewing Skills
- Business Language Skills
- The Ladder of Inference
- Listening Skills
- Top Tips for Effective Listening
- The 10 Principles of Listening
- Effective Listening Skills
- Barriers to Effective Listening
- Types of Listening
- Active Listening
- Mindful Listening
- Empathic Listening
- Listening Misconceptions
- Non-Verbal Communication
- Personal Appearance
- Body Language
- Non-Verbal Communication: Face and Voice
- Verbal Communication
- Effective Speaking
- Conversational Skills
- How to Keep a Conversation Flowing
- Conversation Tips for Getting What You Want
- Giving a Speech
- Questioning Skills and Techniques
- Types of Question
- Clarification
- Emotional Intelligence
- Conflict Resolution and Mediation Skills
- Customer Service Skills
- Team-Working, Groups and Meetings
- Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
- Negotiation and Persuasion Skills
- Personal and Romantic Relationship Skills
The SkillsYouNeed Guide to Interpersonal Skills

Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Communication is simply the act of transferring information from one place, person or group to another.
Every communication involves (at least) one sender, a message and a recipient. This may sound simple, but communication is actually a very complex subject.
The transmission of the message from sender to recipient can be affected by a huge range of things. These include our emotions, the cultural situation, the medium used to communicate, and even our location. The complexity is why good communication skills are considered so desirable by employers around the world: accurate, effective and unambiguous communication is actually extremely hard.
This page explains more about what we mean by ‘ communication ’.
Defining Communication
communication , n . The imparting or exchanging of information by speaking, writing, or using some other medium. …The successful conveying or sharing of ideas and feelings.
Oxford English Dictionary
As this definition makes clear, communication is more than simply the transmission of information. The term requires an element of success in transmitting or imparting a message, whether information, ideas, or emotions.
A communication therefore has three parts: the sender, the message, and the recipient.
The sender ‘encodes’ the message, usually in a mixture of words and non-verbal communication. It is transmitted in some way (for example, in speech or writing), and the recipient ‘decodes’ it.
Of course, there may be more than one recipient, and the complexity of communication means that each one may receive a slightly different message. Two people may read very different things into the choice of words and/or body language. It is also possible that neither of them will have quite the same understanding as the sender.
In face-to-face communication, the roles of the sender and recipient are not distinct. The two roles will pass back and forwards between two people talking. Both parties communicate with each other, even if in very subtle ways such as through eye-contact (or lack of) and general body language. In written communication, however, the sender and recipient are more distinct.
Categories of Communication
There are a wide range of ways in which we communicate and more than one may be occurring at any given time.
The different categories of communication include:
Spoken or Verbal Communication , which includes face-to-face, telephone, radio or television and other media.
Non-Verbal Communication , covering body language, gestures, how we dress or act, where we stand, and even our scent. There are many subtle ways that we communicate (perhaps even unintentionally) with others. For example, the tone of voice can give clues to mood or emotional state, whilst hand signals or gestures can add to a spoken message.
Written Communication : which includes letters, e-mails, social media, books, magazines, the Internet and other media. Until recent times, a relatively small number of writers and publishers were very powerful when it came to communicating the written word. Today, we can all write and publish our ideas online, which has led to an explosion of information and communication possibilities.
Visualizations : graphs and charts , maps, logos and other visualizations can all communicate messages.
The desired outcome or goal of any communication process is mutual understanding.
The Communication Process
A message or communication is sent by the sender through a communication channel to a receiver, or to multiple receivers.
The sender must encode the message (the information being conveyed) into a form that is appropriate to the communication channel, and the receiver(s) then decodes the message to understand its meaning and significance.
Misunderstanding can occur at any stage of the communication process.
Effective communication involves minimising potential misunderstanding and overcoming any barriers to communication at each stage in the communication process.
See our page: Barriers to Effective Communication for more information.
An effective communicator understands their audience , chooses an appropriate communication channel, hones their message to this channel and encodes the message to reduce misunderstanding by the receiver(s).
They will also seek out feedback from the receiver(s) as to how the message is understood and attempt to correct any misunderstanding or confusion as soon as possible.
Receivers can use techniques such as Clarification and Reflection as effective ways to ensure that the message sent has been understood correctly.
Communication Channels
Communication channels is the term given to the way in which we communicate. It is therefore the method used to transmit our message to a recipient, or to receive a message from someone else.
There are multiple communication channels available to us today. These include face-to-face conversations, telephone calls, text messages, email, the Internet (including social media such as Facebook and Twitter), radio and TV, written letters, brochures and reports.
Choosing an appropriate communication channel is vital for effective communication. Each communication channel has different strengths and weaknesses.
For example, broadcasting news of an upcoming event via a written letter might convey the message clearly to one or two individuals. It will not, however, be a time- or cost-effective way to broadcast the message to a large number of people. On the other hand, conveying complex, technical information is easier via a printed document than a spoken message. The recipients are able to assimilate the information at their own pace and revisit anything that they do not fully understand.
Written communication is also useful as a way of recording what has been said, for example by taking minutes in a meeting.
See our pages: Note Taking and How to Conduct a Meeting for more.
Encoding Messages
All messages must be encoded into a form that can be conveyed by the communication channel chosen for the message.
We all do this every day when transferring abstract thoughts into spoken words or a written form. However, other communication channels require different forms of encoding, e.g. text written for a report will not work well if broadcast via a radio programme, and the short, abbreviated text used in text messages would be inappropriate in a letter or in speech.
Complex data may be best communicated using a graph, chart or other visualisation.
Effective communicators encode their messages so that they fit both the channel and the intended audience. They use appropriate language, conveying the information simply and clearly. They also anticipate and eliminate likely causes of confusion and misunderstanding. They are generally aware of the recipients’ experience in decoding similar communications.
Successful encoding of messages for the audience and channel is a vital skill in effective communication.
You may find our page The Importance of Plain English helpful.
Decoding Messages
Once received, the recipient needs to decode the message. Successful decoding is also a vital communication skill.
People will decode and understand messages in different ways.
This will depend on their experience and understanding of the context of the message, how well they know the sender, their psychological state and how they feel, and the time and place of receipt. They may also be affected by any Barriers to Communication which might be present.
There are therefore a wide range of factors that will affect decoding and understanding.
Successful communicators understand how the message will be decoded, and anticipate and remove as many as possible of the potential sources of misunderstanding.
The final part of a communication is feedback: the recipient lets the sender know that they have received and understood the message.
Recipients of messages are likely to provide feedback on how they have understood the messages through both verbal and non-verbal reactions. Effective communicators pay close attention to this feedback as it is the only way to assess whether the message has been understood as intended, and it allows any confusion to be corrected.
Bear in mind that the extent and form of feedback will vary with the communication channel. Feedback during a face-to-face or telephone conversation will be immediate and direct, whilst feedback to messages conveyed via TV or radio will be indirect and may be delayed, or even conveyed through other media such as the Internet.
Effective communicators pay close attention to this feedback as it is the only way to assess whether the message has been understood as intended, and it allows any confusion to be corrected.
You can always ask!
You may be unsure if a message has been successfully received and decoded, especially if you do not get much feedback from the recipient. If so, you can always ask!
A quick question is a good start, for example:
“ Is that OK? ” or “ Are you clear about that? ”
If you want more detailed feedback or to check that the recipient has really understood, you might say something like:
“ So, let’s just run over that one more time. I think I am going to do x, and you are going to do y. Is that your understanding too? ”
More on feedback: see our pages on Reflection , Clarification and Giving and Receiving Feedback .

Further Reading from Skills You Need
Our Communication Skills eBooks
Learn more about the key communication skills you need to be an effective communicator.
Our eBooks are ideal for anyone who wants to learn about or develop their communication skills, and are full of easy-to-follow practical information and exercises.
Being able to communicate effectively is the most important of all life skills.
Understanding is the first step to improvement
Understanding more about communication and how it works is the first step to improving your communication skills. A good understanding of the process, and how it operates, will help you to become better at encoding and decoding messages.
Continue to: Principles of Communication Interpersonal Communication Skills
See also: Intercultural Communication Skills Effective Speaking Improving Communication

What Is Verbal Communication?
“Man is by nature a social animal,” the famous Greek philosopher Aristotle wrote more than 2,000 years ago. And communication…

“Man is by nature a social animal,” the famous Greek philosopher Aristotle wrote more than 2,000 years ago.
And communication lies at the heart of all social relationships.
From the time you enter this world, you start communicating. Your first cry is your first attempt at verbal communication. And as you start growing, you find newer ways of communication. You learn to form words and sentences to communicate.
This is the beginning of verbal communication.
What Is Verbal Communication?
Characteristics of verbal communication, types of verbal communication, advantages of verbal communication.
Verbal communication means effectively presenting your thoughts in verbal format i.e., by talking. Verbal communication skills are essential in the world of business. Be it a weekly meeting or presentation to stakeholders, the importance of verbal communication is unparalleled. People always remember a person who speaks clearly, effectively, confidently, and charismatically.
For instance, Apple co-founder Steve Jobs’s speech launching the iPhone is a classic example of brilliant verbal communication that people remember even today. Similarly, many speeches made by former US President Barack Obama are also unforgettable.
A powerful speaker is also able to connect with their audience easily. Like Oprah Winfrey says, “Great communication begins with a connection.”
You too can be a great speaker with practice. Most of us possess the means of verbal communication, what’s important is to recognize how to maximize them. Read on to learn more about its distinct characteristics.
Before we explore the various defining features of verbal communication, let’s look at its primary form. Verbal communication is oral in nature. Oral communication encompasses various activities such as talking, laughing or listening. We often navigate different emotional situations through oral forms of communication.
We also have written communication that includes script, alphabets, acronyms, logos and graphics. To interpret written messages, everyone involved must understand the code (e.g., the language). This is different from verbal or spoken communication.
There are several characteristics that are specific to verbal communication, namely:
The message being communicated is directly or indirectly related to an object
We use concepts to communicate messages
The content should be understood by both the sender and receiver
Cultural factors influence the content of messages
While communicating emotions and feelings, a sender’s state of mind influences the content of messages
Even though we talk to our friends, family and coworkers on a regular basis, we may not always be aware of how we’re communicating. Mastering the art of verbal communication will help you in more ways than one. Let’s explore different types of verbal communication and how your audience factors into it.
Verbal communication goes beyond words, sounds and languages. You need to know your audience to talk to them better. Remember that you can follow the Pyramid Principle and start with your main argument and then follow up with supporting statements. You can classify verbal communication into four types based on your audience.
Intrapersonal Communication
This is your private verbal communication channel. You talk to yourself and articulate your thoughts. Communicating with yourself will give you more confidence and clarity in your thoughts. It’ll help you make up your mind, form your sentences, find suitable words and effective ways to connect with other people. This will help you gain your colleagues’ trust in the workplace.
Interpersonal Communication
You can also call this one-to-one verbal communication. This type of communication happens between two individuals. It helps you understand if you’re getting your thoughts across clearly. Reactions, responses and verbal and nonverbal cues from the other person will help you understand whether you’re being understood or not. Make sure that you listen to the other person intently. Communication doesn’t just mean to talk to someone. It’s also about listening. So, listen, think and then respond. Take time to think and make sure you don’t offend people with your response.
Small Group Communication
The number of people increases in small group communication. You move from communicating with a single participant to a few more. These small groups could be team meetings, board meetings or sales meetings. The number of participants is small enough for everyone to communicate with each other. When you attend small group meetings, be prepared with a topic to make sure you stay on track. Stay on topic and allow enough time for everyone to present their thoughts.
Public Communication
You may also know this type as ‘ public speaking ’. Here, an individual addresses a large number of people at once. Speeches, election campaigns and presentations are a few examples of public communication. Since the number of people in the audience is larger in this type of communication, be sure to use words and phrases they’ll understand easily and structure your thoughts before addressing the audience. The more prepared you are, the more confident you’ll feel like a public speaker.
Verbal communication is a broad topic. There are various elements that help us organize our thoughts around it. They are:
When you express yourself your tone determines the message to be interpreted. For example, you can be saying something nice but if your tone is a sarcastic tone, the message will be conveyed differently. Your tone makes a huge difference to your speech.
The pace at which you speak is important as it determines the reaction of your audience. You may have attended lectures or webinars where people speaking slowly and softly can get boring. Similarly, it may be difficult to understand someone speaking at a rapid pace.
Volume ranges from a whisper to a scream. The volume at which you talk can convey various meanings. For example, if you whisper into someone’s ears in the presence of multiple people, it can be misconstrued as something negative. On the other hand, screaming while someone is talking is rude. Always monitor your volume depending on the social context you’re in.
Additionally, language, grammar and vocabulary are critical aspects of verbal communication. An erroneous message to a hiring manager, for example, can make or break your career opportunity. This is why verbal communication is a critical skill for success in professional settings as well. Effective communication helps with decision-making and increases collaboration in teams. Let’s look at the benefits of different types of verbal communication.
Verbal communication is one of the most important mediums of communication. The stronger your communication skills are, the easier it is for you to establish trust and build lasting relationships with others. Here are some benefits of strong verbal communication skills:
It provides complete understanding and there’s room to clarify any messages that may have been misunderstood
It’s one of the fastest modes of communication and is time-efficient
There is space for providing feedback, which allows two or more people to engage in a conversation at the same time
It allows speakers to exercise influence and persuade listeners to agree with ideas, thoughts and opinions
It’s flexible, that is, you can change your language and tone depending on the situation you’re in or the relationship you share with an individual
In short, verbal communication is one of the most reliable methods of communication. Its benefits apply to the world of work as well. Let’s look at the various ways in which strong verbal communication skills can be beneficial for professionals:
Building Relationships
Verbal communication allows you to build strong interpersonal relationships. It’s easier when you find like-minded people who share similar interests, ideas and outlooks. This further encourages you to cooperate, collaborate and engage in teamwork.
Persuading Someone
In professional settings, you need to exert a certain amount of influence to get things going. For example, if you want your coworkers to join your project, you need to be able to convince them first. Even in brainstorming sessions, you need to be able to convince others of your ideas and perspectives.
Bringing Clarity
As verbal communication enables feedback, you can provide clarity to your message by repeating yourself. For example, in conflicts or arguments, you can repeat your message so that there’s no room for ambiguity.
Improving Productivity
With proper communication in place, you can communicate effectively with team members and people across the organization. Well-established relationships enhance the process, allowing you to cooperate and collaborate quickly. Group discussions and teamwork maximize output, therefore increasing productivity.
Increasing Motivation
Verbal communication plays a crucial role in providing feedback and recognizing individual effort. Whether it’s a congratulatory speech or email, words of support and appreciation boosts confidence levels. If you’re a manager, don’t miss the opportunity to celebrate your team’s success and efforts. Not only will they get encouraged to do better, but it also cements your relationship with them.
Therefore, effective verbal communication opens up a two-way street that allows individuals to interact, engage and collaborate with each other, improving organizational efficiency and productivity. On an individual level, it helps you become more confident and a well-rounded professional.
Harappa offers two courses to build your communication skills— Writing Proficiently and Speaking Effectively . They’ll help you break the barriers and connect with your colleagues and the people around you. With key frameworks like the Pyramid Principle and PAM (Purpose-Audience-Message), you’ll learn how to communicate with impact.
Explore blogs on topics such as effective communication , the 7 barriers of communication , types of nonverbal communication , the different types of communication , and verbal and nonverbal communication on Harappa Diaries to make your world of work better.

University of California, Santa Barbara
2024 Bren Communication Capstone Presentations
Bren Communications students present 7 capstone projects, from short films to outreach campaigns

Join us for the Class of 2024 Communication Capstone Presentations on Friday, June 7, from 12:00pm - 2:00pm Pacific Time . Students in the Strategic Environmental Media and Communication focus area of the Master of Environmental Science and Management program prepare final capstone projects in the areas of science communication, public outreach campaigns, marketing/public relations research and strategy, and video production.
Join us in Bren Hall 1414 or watch online using this link and passcode comm
This year we present seven dynamic projects for clients in the public, nonprofit, and corporate sectors:
Increasing Access & Use of Climate Models , Lindsay Edelman, Melissa Vezard
Prof. Stevenson is studying tropical Pacific climate variability and hopes to enhance the usability of climate models. This project creates a strategy to bring awareness of accessible climate model data to a broader audience through educational curriculum, tutorials, and web resources.
Native Plant Marketing & Audience Development , Samuel Desre, Olivia Somhegyi, Jenna Anderson, Chloe Swick, Jaden Husser
The mission of the Santa Barbara Botanic Garden is to conserve native plants and habitats. This team supported the Garden’s Marketing and Communications Team by exploring customer journeys and barriers to adopting native plants in landscapes across the Central Coast.
Vines to Wines: Solminer Content Strategy , Elena Perry
Regenerative viticulture is a growing industry on the California central coast, yet there is room to expand their customers. This capstone develops a strategy to expand market reach for Solminer by connecting consumers to their regenerative farming practices through content strategy & creation.
Waste Free Waves: Marine Debris Storymap , Eleri Griffiths, Tatiana Bok, Anne Youngdahl
The team created a public-facing ArcGIS StoryMap that illustrates a baseline assessment of marine debris within the proposed Chumash Heritage National Marine Sanctuary. It is based on a Bren Master’s Group Project, and is created for NOAA Sanctuaries West Coast Regional Office.
Pre-Consumer Textile Waste Outreach Strategy , Simone Berkovitz, Erin Clem, Alexis Grana
Based upon a Bren Master’s Group Project, the goal of this project is to communicate the environmental and public health impacts of pre-consumer textile waste from cut and sew factories. It will also showcase the potential for textile recycling methods to reduce these impacts.
Ocean Conservation Game: “The Swarm” , Justine Lang, Elizabeth Braun, Casey Walker
“The Swarm” is a novel by Frank Schatzing about the ocean and its creatures fighting back against humans due to the damage caused to the environment. This team created a concept for a video game to bring the story to a wider use base for UCSB’s Center for Digital Games Research.
"Sea Otter Savvy: A Mission for Stewardship & Coexistence" Short Film , Lars Nelson
Sea otters are found along central coast California, but experienced a sharp decline in the past century. Now thanks to the efforts of dedicated individuals, they are making a comeback. This film chronicles the work of dedicated groups like Sea Otter Savvy, and their successes.

- Postdoc Home
- My Postdoc Jobs
- Search Jobs

POSTDOCTORAL SCHOLAR
Requisition # 4227, position basics, position details, online application required documents, contact information.
The University of Iowa is an equal opportunity/affirmative action employer. All qualified applicants are encouraged to apply and will receive consideration for employment free from discrimination on the basis of race, creed, color, religion, national origin, age, sex, pregnancy (including childbirth and related conditions), disability, genetic information, status as a U.S. veteran, service in the U.S. military, sexual orientation, gender identity, or associational preferences. The University also affirms its commitment to providing equal opportunities and equal access to University facilities. Women and Minorities are encouraged to apply for all employment vacancies. For additional information on nondiscrimination policies, contact the Coordinator of Title IX and Section 504, and the ADA in The Office of Institutional Equity , 319/335-0705 (voice) or 319/335-0697 (text), The University of Iowa, 202 Jessup Hall, Iowa City, Iowa, 52242-1316.
Persons with disabilities may contact University Human Resources/Faculty and Staff Disability Services, (319) 335-2660 or [email protected] , to inquire or discuss accommodation needs.
Prospective employees may review the University Campus Security Policy and the latest annual crime statistics by contacting the Department of Public Safety at 319/335-5022.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This verbal communication course will give you all the tools you need to interact with customers, clients, colleagues, and bosses in the modern workplace. The course is designed with hyper-efficient methods so that you can learn all communication skills basics in 90min. 19 videos 3 readings 5 quizzes 1 assignment.
Read more on Business communication or related topics Power and influence, Presentation skills and Public speaking Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of ...
Proofread and eliminate anything that strays from your message. One of the best ways to improve communication is to work on creating concise and clear conversations, emails, and presentations that are error-free. Verbal communication tips. Remember that verbal communication goes beyond just what you say to someone else.
Enriched written and verbal communication skills. Enhanced confidence and self-image. Boosted critical thinking and problem-solving capabilities. Better motivational techniques. Increased leadership skills. Expanded time management, negotiation, and creativity. The better your presenting techniques, the more engaging your presentations will be.
Here are some tips for improving your verbal communication skills, both spoken and written: 1. Consider your message. Decide what you want to convey during your next conversation, presentation or written communication. This might involve brainstorming or outlining a list of key points you'd like to make. By reviewing the information you want ...
You can use the following 10 steps to help improve your verbal communication at work: 1. Think before speaking. People often feel uncomfortable with silence, but pausing before answering a question can improve your response. Taking time to reflect allows you to organize your thoughts into a concise, clear statement.
Verbal communication skills are more important than ever. Countless meetings, presentations, code reviews, conferences and networking events mean that clear and assertive verbal communication are essential for current and future jobs.. Good communication skills can be the difference between getting a promotion or moving laterally, selling your product or struggling with slow growth ...
A presentation is a means of communication that can be adapted to various speaking situations, such as talking to a group, addressing a meeting or briefing a team. ... eye contact (non-verbal communication), and visual aids. The message will also be affected by the audience's expectations. For example, if you have been billed as speaking on ...
Delivering effective oral presentations involves three components: what you say ( verbal ), how you say it with your voice ( vocal ), and everything the audience can see about you ( visual ). For ...
Verbal communication involves conveying messages through written or spoken signals. Learn more about the types of verbal communication and how to use it effectively. ... Spoken communication can take many different forms, including conversations, speeches, and presentations. Written Communication: Written communication is using written words to ...
Verbal communication is an important element, but only part of the overall message conveyed. Some research suggests that the verbal element is, in fact, a very small part of the overall message: just 20 to 30%. This is still, however, significant, and it is worth spending time to improve your verbal communication skills.
Cultivate your personal leadership and communication style; Learn strategies on handling hostile audiences "Jill [Slye] shared invaluable tips that have helped me to reduce my anxiety and negative self-talk around my presentations while conveying a message that encourages others to affect change through empowering presentations."
Verbal communication is based on several basic principles. In this section, you'll examine each principle and explore how it influences everyday communication. Whether it's a simple conversation with a coworker or a formal sales presentation to a board of directors, these principles apply to all contexts of communication. Language Has Rules
Learn about efficient Verbal Communication and develop your communication abilities. Discover how to master verbal communication by diving into our blog. 01344203999 - Available 24 ... whether it's through conversations, presentations, or speeches. It allows us to convey information, share stories, ask questions, and connect with others on a ...
Boost your presentation skills with these 10 essential tips. Engage your audience, overcome nerves, and deliver a memorable, impactful presentation. ... Mastering non-verbal communication is key to delivering a killer presentation that commands attention and leaves a lasting impression. Below are our tips for improving this presentation skill.
Communication is 55 percent non-verbal, 38 percent vocal (tone and inflection), and 7 percent words, according to Albert Mehrabian, a researcher who pioneered studies on body language . Up to 93 percent of communication, then, does not involve what you are actually saying. ... Design, and Presentation from the University of Colorado Boulder. ...
What is verbal communication, why employers value it, and examples of verbal communication skills to use in resumes, cover letters, and job interviews. ... Verbal communication occurs in many different contexts including training sessions, presentations, group meetings, performance appraisals, one-on-one discussions, interviews, disciplinary ...
The term requires an element of success in transmitting or imparting a message, whether information, ideas, or emotions. A communication therefore has three parts: the sender, the message, and the recipient. The sender 'encodes' the message, usually in a mixture of words and non-verbal communication. It is transmitted in some way (for ...
To master verbal communication, individuals should focus on speaking clearly, using appropriate language and tone, and organizing their thoughts coherently. Effective verbal communication enables individuals to convey their messages persuasively, engage their audience, and contribute effectively to meetings and presentations.
See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. There are many ways to facilitate effective communication. How you use your words, body language, tone of voice, and visual cues determine how you are understood. Verbal and nonverbal communication skills work in tandem to deliver an understandable message.
Verbal communication means effectively presenting your thoughts in verbal format i.e., by talking. Verbal communication skills are essential in the world of business. Be it a weekly meeting or presentation to stakeholders, the importance of verbal communication is unparalleled.
Nonverbal communication is made up primarily of movements and gestures. Identify the right combination of the two to amplify your message: Face your audience whenever possible. Maintain open body language. Move with purpose and for effect, not just for the sake of moving. Move into the group—do not "hug the wall.".
Nov 6, 2012 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 77 likes • 86,610 views. Rahul's Ventures. Presentation By Rahul Paneliya. Education. 1 of 12. Download now. Verbal Communication - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
NON-VERBAL COMMUNICATION In this type of communication, messages are relayed without the transmission of words in other word it is a method of using anything other than words for conveying information. The messages here are wordless messages. This form of communication mainly aides the verbal communication.
Take a moment alone at your desk or a break outside when possible. 12. Prioritise workplace skills. Workplace skills like problem-solving, collaboration, and time management can also enhance communication. These skills require listening, patience, and organisation, which all play a role in sound communication. 13.
By the end of this presentation, you will: 1. Consider the role of communication in science 2. See examples with ... •Align verbal and written narrative. ... presentations 3. Leverage SETO communication support resources. Title: PowerPoint Presentation Author: Ward, Allan (CONTR)
Being mindful of our non-verbal communication can prevent the wrong or unintended message from inadvertently being passed on. Face-to-face communication allows for the most richness in non-verbal communication; this richness recedes from our interactions as we move from telephone conversations to e-mail, memos, bulletins and post-it notes.
Join us for the Class of 2024 Communication Capstone Presentations on Friday, June 7, from 12:00pm - 2:00pm Pacific Time.Students in the Strategic Environmental Media and Communication focus area of the Master of Environmental Science and Management program prepare final capstone projects in the areas of science communication, public outreach campaigns, marketing/public relations research and ...
Disseminate research findings through scientific publications, presentations, and participation in grant-writing activities. ... Excellent written and verbal communication skills. Proven track record of scholarly achievements demonstrated by peer-reviewed publications. Online Application Required Documents : Curriculum Vita