
Visual Analysis: How to Analyze a Painting and Write an Essay

A visual analysis essay is an entry-level essay sometimes taught in high school and early university courses. Both communications and art history students use visual analysis to understand art and other visual messages. In our article, we will define the term and give an in-depth guide on how to look at a piece of art and write a visual analysis essay. Stay tuned until the end for a handy visual analysis essay example from our graduate paper writing service .
What Is Visual Analysis?
Visual analysis is the process of looking at a piece of visual art (painting, photography, film, etc.) and dissecting it for the artist’s intended meaning and means of execution. In some cases, works are also analyzed for historical significance and their impact on culture, art, politics, and the social consciousness of the time. This article will teach you how to perform a formal analysis of art.
Need Help With Your Visual Analysis?
You only need to send your paper requirements to get help from professional writers.
A visual analysis essay is a type of essay written mostly by students majoring in Art History and Communications. The process of visual analysis can be applied to painting, visual art, journalism, photo-journalism, photography, film, and writing. Works in these mediums are often meant to be consumed for entertainment or informative purposes. Visual analysis goes beyond that, focusing on form, themes, execution, and the compositional elements that make up the work.
Classical paintings are a common topic for a visual analysis essay because of their depth and historical significance. Take the famous Raphael painting Transfiguration. At first glance, it is an attractive image showing a famous scene from the Bible. But a more in-depth look reveals practical painting techniques, relationships between figures, heavy symbolism, and a remarkable choice of colors by the talented Raphael. This deeper look at a painting, a photograph, visual or written art is the process of visual analysis.
Get term paper writer from our professionals. Leave us a message ' write my paper for me ' and we'll deliver the task asap.
Formal Analysis of Art: Who Does It?
Most people who face visual analysis essays are Communication, English, and Art History students. Communications students explore mediums such as theater, print media, news, films, photos — basically anything. Comm is basically a giant, all-encompassing major where visual analysis is synonymous with Tuesday.
Art History students study the world of art to understand how it developed. They do visual analysis with every painting they look it at and discuss it in class.
English Literature students perform visual analysis too. Every writer paints an image in the head of their reader. This image, like a painting, can be clear, or purposefully unclear. It can be factual, to the point, or emotional and abstract like Ulysses, challenging you to search your emotions rather than facts and realities.
How to Conduct Visual Analysis: What to Look For
Whether you study journalism or art, writing a visual analysis essay will be a frequent challenge on your academic journey. The primary principles can be learned and applied to any medium, regardless of whether it’s photography or painting.
For the sake of clarity, we’ve chosen to talk about painting, the most common medium for the formal analysis of art.

In analyzing a painting, there are a few essential points that the writer must know.
- Who is the painter, and what era of art did they belong to? Classical painters depict scenes from the Bible, literature, or historical events (like the burning of Rome or the death of Socrates). Modernists, on the other hand, tend to subvert classical themes and offer a different approach to art. Modernism was born as a reaction to classical painting, therefore analyzing modernist art by the standards of classical art would not work.
- What was the painter’s purpose? Classical painters like Michelangelo were usually hired by the Vatican or by noble families. Michelangelo didn’t paint the Sistine Chapel just for fun; he was paid to do it.
- Who is the audience? Artists like Andy Warhol tried to appeal to the masses. Others like Marcel Duchamp made art for art people, aiming to evolve the art form.
- What is the historical context? Research your artist/painting thoroughly before you write. The points of analysis that can be applied to a Renaissance painter cannot be applied to a Surrealist painter. Surrealism is an artistic movement, and understanding its essence is the key to analyzing any surrealist painting.
Familiarizing yourself with these essential points will give you all the information and context, you need to write a good visual analysis essay.
But visual analysis can go deeper than that — especially when dealing with historic pieces of visual art. Students explore different angles of interpretation, the interplay of colors and themes, how the piece was made and various reactions, and critiques of it. Let’s dig deeper.
A Detailed Process of Analyzing Visual Art
Performing a formal analysis of art is a fundamental skill taught at entry-level art history classes. Students who study art or communications further develop this skill through the years. Not all types of analysis apply to every work of art; every art piece is unique. When performing visual analysis, it’s essential to keep in mind why this particular work of art is important in its own way.

Step 1: General Info
To begin, identify the following necessary information on the work of art and the artist.
- Subject — who or what does this work represent?
- Artist — who is the author of this piece? Refer to them by their last name.
- Date and Provenance — when and where this work of art was made. Is it typical to its historical period or geographical location?
- Past and Current Locations — where was this work was displayed initially, and where is it now?
- Medium and Creation Techniques — what medium was this piece made for and why is it important to that medium? Note which materials were used in its execution and its size.
Step 2: Describe the Painting
Next, describe what the painting depicts or represents. This section will be like an abstract, summarizing all the visible aspects of the piece, painting the image in the reader’s mind. Here are the dominant features to look for in a painting:
- Characters or Figures: who they are and what they represent.
- If this is a classical painting, identify the story or theme depicted.
- If this is an abstract painting, pay attention to shapes and colors.
- Lighting and overall mood of the painting.
- Identify the setting.
Step 3: Detailed Analysis
The largest chunk of your paper will focus on a detailed visual analysis of the work. This is where you go past the basics and look at the art elements and the principles of design of the work.
Art elements deal mostly with the artist’s intricate painting techniques and basics of composition.
- Lines — painters use a variety of lines ranging from straight and horizontal to thick, curved, even implied lines.
- Shapes — shapes can be distinct or hidden in plain sight; note all the geometrical patterns of the painting.
- Use of Light — identify the source of light, or whether the lighting is flat; see whether the painter chooses contrasting or even colors and explain the significance of their choice in relation to the painting.
- Colors — identify how the painter uses color; which colors are primary, which are secondary; what is the tone of the painting (warm or cool?)
- Patterns — are there repeating patterns in the painting? These could be figures as well as hidden textural patterns.
- Use of Space — what kind of perspective is used in the painting; how does the artist show depth (if they do).
- Passage of Time and Motion
Design principles look at the painting from a broader perspective; how the art elements are used to create a rounded experience from an artistic and a thematic perspective.
- Variety and Unity - explore how rich and varied the artists’ techniques are and whether they create a sense of unity or chaos.
- Symmetry or Asymmetry - identify points of balance in the painting, whether it’s patterns, shapes, or use of colors.
- Emphasis - identify the points of focus, both from a thematic and artistic perspective. Does the painter emphasize a particular color or element of architecture?
- Proportions - explain how objects and figures work together to provide a sense of scale, mass, and volume to the overall painting.
- Use of Rhythm - identify how the artist implies a particular rhythm through their techniques and figures.
Seeing as each work of art is unique, be thoughtful in which art elements and design principles you wish to discuss in your essay. Visual analysis does not limit itself to painting and can also be applied to mediums like photography.
Got Stuck While writing your paper?
Count on the support of the professional writers of our essay writing service .
The Structure: How to Write a Visual Analysis Paper
It’s safe to use the five-paragraph essay structure for your visual analysis essay. If you are looking at a painting, take the most important aspects of it that stand out to you and discuss them in relation to your thesis. Structure it with the simple essay structure:
Introduction: An introduction to a visual analysis essay serves to give basic information on the work of art and briefly summarize the points of discussion.
- Give a brief description of the painting: name of artist, year, artistic movement (if necessary), and the artist’s purpose in creating this work.
- Briefly describe what is in the painting.
- Add interesting facts about the artist, painting, or historical period to give your reader some context.
- As in all introductions, don’t forget to include an attention-grabber to get your audience interested in reading your work.
Thesis: In your thesis, state the points of analysis on this work of art which you will discuss in your essay.
Body: Explore the work of art and all of its aspects in detail. Refer to the section above titled “A Detailed Process of Analyzing Visual Art,” which will comprise most of your essay’s body.
Conclusion: After you’ve thoroughly analyzed the painting and the artist’s techniques, give your thoughts and opinions on the work. Your observations should be based on the points of analysis in your essay. Discuss how the art elements and design principles of the artist give the painting meaning and support your observations with facts from your essay.
Citation: Standard citation rules apply to these essays. Use in-text citations when quoting a book, website, journal, or a movie, and include a sources cited page listing your sources. And there’s no need to worry about how to cite a piece of art throughout the text. Explain thoroughly what work of art you’re analyzing in your introduction, and refer to it by name in the body of your essay like this — Transfiguration by Raphael.
If you want a more in-depth look at the classic essay structure, feel free to visit our 5 PARAGRAPH ESSAY blog
Learn From a Visual Analysis Example
Many YouTube videos are analyzing famous paintings like the Death of Socrates, which can be a great art analysis example to go by. But the best way to understand the format and presentation is by looking at a painting analysis essay example done by a scholarly writer. One of our writers has penned an outstanding piece on Leonardo Da Vinci’s La Belle Ferronnière, which you may find below. Use it as a reference point for your visual analysis essay, and you can’t go wrong!
Leonardo da Vinci was an Italian artist born in April 1452 and died in May 1519who lived in the Renaissance era. His fame and popularity were based on his painting sand contribution to the Italian artwork. Leonardo was also an active inventor, a vibrant musician, writer, and scientist as well as a talented sculptor amongst other fields. His various career fields proved that he wanted to know everything about nature. In the book “Leonardo Da Vinci: The Mind of the Renaissance” by Alessandro Vezzosi, it is argued that Leonardo was one of the most successful and versatile artists and anatomists of the Italian renaissance based on his unique artwork and paintings (Vezzosi, p1454). Some of his groundbreaking research in medicine, metal-casting, natural science, architecture, and weaponry amongst other fields have been explored in the book. He was doing all these in the renaissance period in Italy from the 1470s till his death.
Visual analysis essays will appear early in your communications and art history degrees. Learning how to formally analyze art is an essential skill, whether you intend to pursue a career in art or communications.
Before diving into analysis, get a solid historical background on the painter and their life. Analyzing a painting isn’t mere entertainment; one must pay attention to intricate details which the painter might have hidden from plain sight.
We live in an environment saturated by digital media. By gaining the skill of visual analysis, you will not only heighten your appreciation of the arts but be able to thoroughly analyze the media messages you face in your daily life.
Also, don't forget to read summary of Lord of the Flies , and the article about Beowulf characters .
Need Someone to Write Your Paper?
If you read the whole article and still have no idea how to start your visual analysis essay, let a professional writer do this job for you. Contact us, and we’ll write your work for a higher grade you deserve. All ' college essay service ' requests are processed fast.
Related Articles
.webp)
How to Look at Art and Understand What You See
There are dozens of ways of looking at visual art. None of them are wrong, but certain methods facilitate deeper connection and understanding.

In a recent Learning to Look column , we explored magazine covers and posters, trying to determine the creator’s intention. Examining the visual components of these artifacts, in conjunction with key framing information like associated text or time period, helped us uncover the deliberately crafted “meaning” of the pieces. The skills of visual analysis we learned in that context are useful even when the message of a visual object is less fixed and open to interpretation, such as with a work of fine art.

Imagine we’re walking through a museum together. Separated by time and space, we can do this together through JSTOR Shared Collections such as the Wofford College Fine Art Collection . Now that we’ve spent several months together pulling apart the components of visual communication, you may be inclined to linger longer than you might have before, searching each artwork for more information and meaning.

There are dozens of ways of looking at visual art, each shaped by the creators and the various contexts in which the pieces appear. None of them are wrong, but certain methods facilitate deeper connection and understanding.
In today’s column, we’ll explore two approaches to looking at art. First, we’ll follow closely the methodology we’ve explored in the column up to now. Then we’ll try another in which we’ll react naturally to a piece, then look again, revising our assumptions about what we see, until we come to an understanding. We can think of these as taking either a form-first approach or an intuitive approach . Neither of these strictly adheres to an analytical method you might find an art historian undertaking in an academic text. Instead, these are practical ways that you can informally but deliberately encounter works of art, thoughtfully observing and investigating your own visual experiences and eventually learning to talk about what you see with confidence.
Weekly Newsletter
Get your fix of JSTOR Daily’s best stories in your inbox each Thursday.
Privacy Policy Contact Us You may unsubscribe at any time by clicking on the provided link on any marketing message.
If you are comfortable looking at art but wish to more deeply interrogate works and your response to them, an intuitive approach might feel more grounded. If, on the other hand, you do not consider yourself someone to whom probing a work of art comes easily, a form-first approach may give you the structure and confidence to confront art head-on.
Art critics in the early twentieth century primarily concerned with formalism, including Roger Fry and Clive Bell , were largely responsible for taking foundations of compositional analysis disseminated in the seventeenth century and transforming it into the language of formal analysis that we use to describe the elements of art and principles of composition . This vocabulary helps us break down the visual components of a work and examine their effects before exploring what we think we see and what may not be immediately apparent.
- Identify: How are elements of art (line, form, color, etc.) used?
- Describe: How does the composition work as a whole?
- Connect: How does what you see relate to what is known about the artwork’s subject, creator, historical context, etc.?
- Interpret: What might the work be expressing or communicating? How do you react to it?
When exploring and appreciating art for its own sake, there is no need to parse each element . In the print you see below, two elements stand out immediately: color and line. Pale blue, yellow, and grey dominate, though bits of red punctuate the scene. Line is used heavily to define shapes as well as give expression to the star of the show: the rain.

This composition is clearly split into distinct foreground, middle ground, and background, balanced by their approximately equal size and unified by the lines of rain that slash across the entire picture. Everything looks a bit off-kilter—the distant shore tips down diagonally while the bridge arcs up—but the triangular segments the forms create largely balance one another. Movement is suggested by these diagonals as well, especially as lines intersect and shatter the composition into slices and diamonds.
Context is easy to find for this image. Try searching within JSTOR. The creator, Andō Hiroshige , produced hundreds of Ukiyo-e woodblock prints like this one. As in many of these prints , the people are dwarfed by the landscape around them, and some techniques—like the fade from saturated to pale blue towards the bottom of the image—emerge as typical, even defining, elements.

This Edo period print, while more than a hundred and fifty years old, feels modern. The graphic and concise visual elements certainly lend themselves to this, but this immediacy may also come from the subject matter: most of us can relate to the experience of the people on Shin-Ohashi Bridge. We can recall the licks of cold rain on our legs while grasping for a hat, umbrella, or jacket, anything to shelter under. Imagining this feeling, the uneasy diagonal lines and sharp edges start to make more sense.
Beginning with an identification of the formal elements of a work and description of their roles in the overall composition helps us orient ourselves within the bounds of the work of art. Having considered the parts as well as the whole, we can more confidently connect the visual components of an artwork to what lies across and beyond the page, connecting what we see with what we know but cannot observe within the frame. We then interpret the work, not necessarily pursuing an answer or conclusion but rather exploring what emerges, having stopped to gather information and consider it both in parts and as a whole.
Yet, as A Short Guide to Writing About Art declares from the bookshelf of every undergraduate, “It is now widely acknowledged that when we look, we are not looking objectively, looking with what has been called an innocent eye.” No matter how earnest the effort, no formal analysis is ever an objective observation of form alone. So, let’s set aside for a moment the methodology of formal analysis and try a different way of looking at art. This time, we’ll look not with innocent eyes, but with our own world-weary, subjective ones.
Rather than eschewing our overall judgements, let’s dive in. This works especially well with artworks like the one below, those without much information available beyond the work itself.

As I encounter this painting, I get a sense of quiet, familial closeness; maybe the central figures are headed home from a gathering as fall turns to winter in a seaside town. After my observations, I can explore what prompted those initial assumptions. I inferred that it was winter based on the warm, muted colors. I noticed how both figures are walking in step with one another and how they almost become a single entity, their dark clothes nearly merging. This made me think the people must be very close. I noticed the blue on the horizon, assuming it was the sea, and buildings in the background, close enough together to be a town or maybe even a small city.
My initial reactions may not be accurate, though, so it’s time to dig into the details and any available context. Examining and appreciating works of art requires some effort. At the very least, you have to be open to new ideas and observations as they emerge. Consider, too, that when exploring a work of art, there is no correct—or even “best”—conclusion.
As I look more closely, I see that the central figures in this painting aren’t as alone as I initially thought. Two people are only a few paces behind on the path, also arm in arm, heads bowed together. On reflection, the central figures also don’t appear to be as close as their postures might suggest. The title reveals that they are mother and son, but other than the symmetry created by their linked arms, they actually seem quite distant from one another. The son, with a heavy brow, is looking at something outside the frame and seems no more interested in his mother than in the books he carries in his other hand. Meanwhile, his mother looks distractedly down towards the path. Even my guess that the picture depicts winter is probably not accurate: wildflowers and dark green foliage explode from either side of the path. The hay to the left and right of the figures looks freshly sheaved and sits atop still green fields, suggesting it’s more likely early summer.
My initial observations weren’t necessarily wrong, or not completely: familial closeness can take many forms, and it certainly does seem that the figures are walking away from town, leaving or maybe heading to some type of gathering. But reconsidering the image, I can see more depth, both in the central figures’ interaction and the world around them.
This time, we looked broadly and observed our reactions carefully, questioning and contextualizing them before comparing our initial assumptions to new information we acquired as we spent more time with the picture. By doing so, we centered our personal experiences of and interest in the work while exploring other possibilities through careful observation of the visual information available.
- Observe: What is your overall understanding of the image? What is your initial reaction?
- Question: Consider why you reacted this way. What made you think that?
- Contextualize: Do you see new details as you look more closely?
- Compare: How is your understanding of the image different now?
Visual literacy describes one’s ability to take informed steps to explore and evaluate visual material. In the previous eight columns, we’ve discussed a foundational component of visual literacy, visual analysis, and interpretation. Next time, we’ll begin exploring another: discovery and exploration. We’ll discuss how to seek out visual material, both known and new to you. In the meantime, keep an eye out for images that you don’t immediately understand. Does closer looking, mining the visual qualities for clarity and even meaning, help you better understand an image? While you wait, you could also catch up on the Learning to Look articles you missed.
Support JSTOR Daily! Join our new membership program on Patreon today.

JSTOR is a digital library for scholars, researchers, and students. JSTOR Daily readers can access the original research behind our articles for free on JSTOR.
Get Our Newsletter
More stories.

- The Fashionable Tour : or, The First American Tourist Guidebook

- Celebrating Asian American and Pacific Islander Heritage Month

The Metaphysical Story of Chiropractic

A Bodhisattva for Japanese Women
Recent posts.
- The Development of Central American Film
- Remembering Maud Lewis
- Rice, Famine, and the Seven Wonders of the World
Support JSTOR Daily
Sign up for our weekly newsletter.
Free Visual Arts Essay Examples & Topics
Visual arts are the works of art we see with our eyes. It is a broad definition that includes a large number of disciplines and elements. From Wassily Kandinsky to Jackson Pollock, from sculptures and paintings to filmmaking and interior design – the term covers it all.
If you are writing an essay about visual arts, the chances are that you will find yourself a bit lost for words. After all, the subject matter may seem contradictory to the task at hand. However, there is no need to panic.
In this article, our experts have outlined the best way to write your very own visual arts essay step-by-step. You will see that your academic paper can be a work of art in itself. We have also included 19 outstanding visual arts essay topics from which you can choose.
Even a brief essay about visual arts can be overwhelming. It’s usually the case when you don’t know where to begin and how to organize your thoughts. That’s why creating an outline is so crucial. In this section, we have listed what can help you in writing your visual arts essay.
Try following these steps:
- Choose your topic . Of course, it’s the most critical step for your paper. The idea you pick should be narrow enough for a detailed analysis. Yet, it should not prevent you from doing extensive research. Try browsing through visual arts essay collections. For example, check Bending Concepts by Walter Benn Michaels et al. There, you can get ideas on what to write about.
- Finding relevant art. Unsurprisingly, essays on visual arts require you to interact with the artwork. To offer proper art critique, you might want to conduct a visual analysis of your subject. Besides, it is a great idea to look into art history surrounding your topic. Figure out the context of the work and incorporate it into your paper.
- Brainstorming. Jotting down all your feelings and ideas can be an excellent exercise. Everything that you think on the topic may come in handy. So, write down your thoughts about the style and technique of the artist, what message the work is trying to send, etc. When you’re done, make sure to look at your assessment criteria. Compare them to what you have thought of so far.
- Grouping information. Here is where you might want to begin thinking of a thesis statement. Begin by grouping all the information you’ve gathered so far by themes. These will later become the foundation for the outline. Sort through all your findings and decide what ideas fit well with your topic. With this in mind, write down an excellent thesis by formulating your message in one sentence. Or our thesis generator can do that for you!
- Writing the outline. Now that everything is organized, create a structure of your paper using your ideas and thesis. Begin by making an introduction to visual arts. Explain what you will be talking about in your essay. Your research and formal analysis go into the main body. Finally, your final reflection about visual arts should be left for the conclusion. This is where you get to sum up your interpretation of the work and what you see in it.
- Browse through samples. Before you begin your essay writing, you might want to spend some time looking at examples. This can give you further ideas for your outline. Besides, good samples can inspire writing your very own visual arts essay. After all, art appreciation isn’t easy!
Whether you are writing a brief response piece or an entire extended essay, following these steps will improve the quality of your work. With enough practice, you will be composing visual arts essays with your eyes closed.
Visual Art Essay Topic
Still uncertain whether to write about Pablo Picasso or The Color Theory ? Take a quick look at this list! Or allow our title generator to create an idea for you.
Here are 19 visual arts essay topics we have compiled just for you:
- From painting to filmmaking: a brief history.
- Leonardo da Vinci and the Golden Ratio.
- Baya Mahieddine – the girl that inspired Picasso.
- What do we mean by ‘contemporary art’?
- Victorian beauty standards and their depiction in art.
- How World War I gave birth to Dadaism.
- The symbolism in Frida Kahlo’s paintings.
- Cave paintings as very first artworks.
- What is the difference between art and design?
- Bollywood: how cinema evolved in India.
- How the Edo period in Japan defined its arts and culture.
- Salvador Dali’s influence on the surrealist movement.
- Perpetuation of stereotypes in modern art.
- Women in art: why are female artists often overlooked or forgotten.
- Is graffiti a legitimate form of art?
- The history and evolution of graphic novels.
- Greek and Roman sculptures: similarities and differences.
- Iconoclasm during the French revolution and its impact on art.
- The evolution of Islamic Arts.
Thank you for reading! We hope that you will find inspiration among these visual arts topic ideas. Check out our visual arts essay examples that you will find below.
383 Best Essay Examples on Visual Arts
Arguments for graffiti as art, modern, modernism, and modernization, artist’s role in society: cultures, traditions, ideas, and moral responsibilities, art and society: goals and duties of artists.
- Words: 1752
Aspects of Graffiti as Art Therapy
Impact of digital technologies on contemporary art.
- Words: 1934
Gender Roles Set in Stone: Prehistoric and Ancient Work of Arts
Sculpture and painting, modernism in art and painting, revolutionary art in america: society and artists, vincent van gogh’s “starry night”.
- Words: 1544
Kitsch – under the Title of Taste and Ethics
- Words: 3420
Visual and Performing Arts
Comparison of indian and chinese art.
- Words: 1675
Collingwood’s Distinction Between Art and Craft
Chapter 2 in “understanding comics” by scott mccloud, phenomenon of embroidery stitches, visual and performance arts in creative process.
- Words: 1031
The “Great Pyramid of Giza” and the “Terracotta Army”
“the eco artists turning trash into treasure” by webster, art styles: naturalism, idealization, stylization, formal analysis of two photos, nudity vs. pornography when used in artwork, magical realism as a literary genre.
- Words: 1098
The Islamic and Mughal Arts
- Words: 1346
Manga: “Naruto” by Masashi Kishimoto
Cabramatta’s culture and art.
- Words: 1404
The Artwork “The Virgin Mary” by Chris Ofili
Chinese art’s definition, influence and history.
- Words: 1926
Graffiti: Is a Form of Art or Vandalism?
Michelangelo’s artwork, the peculiarities of the golden griffin-headed bracelets from the oxus treasure, the symbolism of dragons in chinese art.
- Words: 1641
Western Influences on the Japanese Animation Industry
- Words: 2467
3D Animation: Main Inspirations and Personal Experience
African art and cultural heritage, the save water, save life picture analysis, the artwork “pieta” by michelangelo, visual analysis: untitled film still #21.
- Words: 1414
Asian Art and Sculpture and Their Meanings
- Words: 1667
Illuminated Manuscripts – History of Graphic Art
- Words: 1222
Damien Hirst’s Life and Works
- Words: 1418
Definition of Art
“night attack on the sanjo palace” by dr. hannah sigur.
- Words: 1157
Chapters 7-9 in “Understanding Comics” by McCloud
Chicano art as a form of identity expression, demonstrating power and authority through roman sculpture and portraiture, trend on the parody of “the mona lisa” by davinci, analisis of work “american gothic”, américa tropical mural by david alfaro siqueiros.
- Words: 1133
Drawing with/without Paper: Moving from 2D to 3D
- Words: 1243
Enigma’s “Return to Innocence” Music Video
How digital technology influences art.
- Words: 2025
Effects of World War I on the Development of Modern Art
- Words: 1192
Graffiti “Season’s Greetings” by Banksy
Is graffiti vandalism or art, visual culture understanding in modern society.
- Words: 1161
The Influence of Conceptual Image on Modern Art and Design
- Words: 1504
The Link Between Realism and Impressionism in Art
- Words: 1484
Concept of the Acceptable Range of Variations in Work
Rococo and neoclassical art.
- Words: 1267
Art in Details: Elements of Art
“the great trouble with art” by marcel duchamp: main ideas, main points in the article and video by hito steyerl.
- Words: 1395
Perception and Creativity of New Paradigms and Genres Contribute to Creativity
The shaman in transformation pose: a study of the theme of rulership in olmec art.
- Words: 1099
Picture Observations and Their Meaning
- Words: 1105
Andy Warhol’s Iconic Artwork “32 Campbell’s Soup Cans”
Principles of design in female artists’ works displayed in the louvre, art as reflection: searching for new ways of expression.
- Words: 1940
“Understanding Art” by Lois Fichner-Rathus
Visual art and photography, crafts and fine arts., art: the illness narrative of invisible disability.
- Words: 1366
Visual Analysis of Nature in Modern Art
- Words: 1701
Shaun Gladwell’s Art: Materials And Techniques
- Words: 1642
Modern Art: A Cultural-Aesthetic Movement
- Words: 1375
Art and Design Analysis
Different ways to approach the definition of art, manga: new social ideas, behaviors, and sub-cultures.
- Words: 1607
National Indian Museum
- Words: 1732
The distinction between great and mediocre art
- Words: 1082
“Why Not Sneeze, Rose Sélavy?” by Marcel Duchamp
- Words: 2097
Arts in the Community: The American Museum of Natural History
The painter van loo’s rococo revolution, the art piece “the sacred heart” by damien hirst, deaf art in the modern society, the power of color and black & white in art and design, simplified shaping in visual arts, lighting in painting, film, and photography, ambiguity of unicorn rests in a garden tapestry by jane beal.
- Words: 1702
Chauvet Cave Paintings: Unraveling the Cultural Tapestry of Paleolithic Society
The “spiral jetty” work by robert smithson.
- Words: 1212
The Early Renaissance Artworks
- Words: 1136
The Painting Styles of the Roman Domes
Baroque painting: history, commissioning, and functions, mark bradford on reimagine modernist art, interrelationships in art and humanities studies, a venn diagram: characteristics of what is art and what is not art, visual analysis of objects of islamic art, the google art project analysis, the university campus picture analysis, illustrations to “inferno” by dante alighieri, art: definition and components.
- Words: 1431
Botticelli’s and Doré’s Illustrations to Dante’s Inferno
Gazebo and “study for hotel by a railroad”: artwork connection, albert namatjira: teaching activities and methods.
- Words: 2037
Material Movements of Paper as an Artistic Material
Eduardo kobra’s graffiti as a form of art, graphic memoirs and forney’s marbles, element and principles of design: critical analysis, pectoral and necklace of sithathoryunet, “adoration of the magi” analysis, the healing wings project after covid-19, the project art heals utah analysis, sandra mayo’s “tangram” installation analysis, art analysis: daumier’s past, present, and future lithograph.
- Words: 1159
“All Seeing Eye” by Hailei Wang: Artwork Analysis
- Words: 1207
If You Were to Create a Graphic Novel
Mushrooms: the art, design, and future of fungi.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 31 October 2017
The visual essay and the place of artistic research in the humanities
- Remco Roes 1 &
- Kris Pint 1
Palgrave Communications volume 3 , Article number: 8 ( 2017 ) Cite this article
9648 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Archaeology
- Cultural and media studies
What could be the place of artistic research in current contemporary scholarship in the humanities? The following essay addresses this question while using as a case study a collaborative artistic project undertaken by two artists, Remco Roes (Belgium) and Alis Garlick (Australia). We argue that the recent integration of arts into academia requires a hybrid discourse, which has to be distinguished both from the artwork itself and from more conventional forms of academic research. This hybrid discourse explores the whole continuum of possible ways to address our existential relationship with the environment: ranging from aesthetic, multi-sensorial, associative, affective, spatial and visual modes of ‘knowledge’ to more discursive, analytical, contextualised ones. Here, we set out to defend the visual essay as a useful tool to explore the non-conceptual, yet meaningful bodily aspects of human culture, both in the still developing field of artistic research and in more established fields of research. It is a genre that enables us to articulate this knowledge, as a transformative process of meaning-making, supplementing other modes of inquiry in the humanities.
Introduction
In Being Alive: Essays on Movement, Knowledge and Description (2011), Tim Ingold defines anthropology as ‘a sustained and disciplined inquiry into the conditions and potentials of human life’ (Ingold, 2011 , p. 9). For Ingold, artistic practice plays a crucial part in this inquiry. He considers art not merely as a potential object of historical, sociological or ethnographic research, but also as a valuable form of anthropological inquiry itself, providing supplementary methods to understand what it is ‘to be human’.
In a similar vein, Mark Johnson’s The meaning of the body: aesthetics of human understanding (2007) offers a revaluation of art ‘as an essential mode of human engagement with and understanding of the world’ (Johnson, 2007 , p. 10). Johnson argues that art is a useful epistemological instrument because of its ability to intensify the ordinary experience of our environment. Images Footnote 1 are the expression of our on-going, complex relation with an inner and outer environment. In the process of making images of our environment, different bodily experiences, like affects, emotions, feelings and movements are mobilised in the creation of meaning. As Johnson argues, this happens in every process of meaning-making, which is always based on ‘deep-seated bodily sources of human meaning that go beyond the merely conceptual and propositional’ (Ibid., p. 11). The specificity of art simply resides in the fact that it actively engages with those non-conceptual, non-propositional forms of ‘making sense’ of our environment. Art is thus able to take into account (and to explore) many other different meaningful aspects of our human relationship with the environment and thus provide us with a supplementary form of knowledge. Hence Ingold’s remark in the introduction of Making: anthropology, archaeology, art and architecture (2013): ‘Could certain practices of art, for example, suggest new ways of doing anthropology? If there are similarities between the ways in which artists and anthropologists study the world, then could we not regard the artwork as a result of something like an anthropological study, rather than as an object of such study? […] could works of art not be regarded as forms of anthropology, albeit ‘written’ in non-verbal media?’ (Ingold, 2013 , p. 8, italics in original).
And yet we would hesitate to unreservedly answer yes to these rhetorical questions. For instance, it is true that one can consider the works of Francis Bacon as an anthropological study of violence and fear, or the works of John Cage as a study in indeterminacy and chance. But while they can indeed be seen as explorations of the ‘conditions and potentials of human life’, the artworks themselves do not make this knowledge explicit. What is lacking here is the logos of anthropology, logos in the sense of discourse, a line of reasoning. Therefore, while we agree with Ingold and Johnson, the problem remains how to explicate and communicate the knowledge that is contained within works of art, how to make it discursive ? How to articulate artistic practice as an alternative, yet valid form of scholarly research?
Here, we believe that a clear distinction between art and artistic research is necessary. The artistic imaginary is a reaction to the environment in which the artist finds himself: this reaction does not have to be conscious and deliberate. The artist has every right to shrug his shoulders when he is asked for the ‘meaning’ of his work, to provide a ‘discourse’. He can simply reply: ‘I don’t know’ or ‘I do not want to know’, as a refusal to engage with the step of articulating what his work might be exploring. Likewise, the beholder or the reader of a work of art does not need to learn from it to appreciate it. No doubt, he may have gained some understanding about ‘human existence’ after reading a novel or visiting an exhibition, but without the need to spell out this knowledge or to further explore it.
In contrast, artistic research as a specific, inquisitive mode of dealing with the environment requires an explicit articulation of what is at stake, the formulation of a specific problem that determines the focus of the research. ‘Problem’ is used here in the neutral, etymological sense of the word: something ‘thrown forward’, a ‘hindrance, obstacle’ (cf. probleima , Liddell-Scott’s Greek-English Lexicon). A body-in-an-environment finds something thrown before him or her, an issue that grabs the attention. A problem is something that urges us to explore a field of experiences, the ‘potentials of human life’ that are opened up by a work of art. It is often only retroactively, during a second, reflective phase of the artistic research, that a formulation of a problem becomes possible, by a selection of elements that strikes one as meaningful (again, in the sense Johnson defines meaningful, thus including bodily perceptions, movements, affects, feelings as meaningful elements of human understanding of reality). This process opens up, to borrow a term used by Aby Warburg, a ‘Denkraum’ (cf. Gombrich, 1986 , p. 224): it creates a critical distance from the environment, including the environment of the artwork itself: this ‘space for thought’ allows one to consciously explore a specific problem. Consciously here does not equal cerebral: the problem is explored not only in its intellectual, but also in its sensual and emotional, affective aspects. It is projected along different lines in this virtual Denkraum , lines that cross and influence each other: an existential line turns into a line of form and composition; a conceptual line merges into a narrative line, a technical line echoes an autobiographical line. There is no strict hierarchy in the different ‘emanations’ of a problem. These are just different lines contained within the work that interact with each other, and the problem can ‘move’ from one line to another, develop and transform itself along these lines, comparable perhaps to the way a melody develops itself when it is transposed to a different musical scale, a different musical instrument, or even to a different musical genre. But, however, abstract or technical one formulates a problem, following Johnson we argue that a problem is always a translation of a basic existential problem, emerging from a specific environment. We fully agree with Johnson when he argues that ‘philosophy becomes relevant to human life only by reconnecting with, and grounding itself in, bodily dimensions of human meaning and value. Philosophy needs a visceral connection to lived experience’ (Johnson, 2007 , p. 263). The same goes for artistic research. It too finds its relevance in the ‘visceral connection’ with a specific body, a specific situation.
Words are one way of disclosing this lived experience, but within the context of an artistic practice one can hardly ignore the potential for images to provide us with an equally valuable account. In fact, they may even prove most suited to establish the kind of space that comes close to this multi-threaded, embodied Denkraum . In order to illustrate this, we would like to present a case study, a short visual ‘essay’ (however, since the scope of four spreads offers only limited space, it is better to consider it as the image-equivalent of a short research note).
Case study: step by step reading of a visual essay
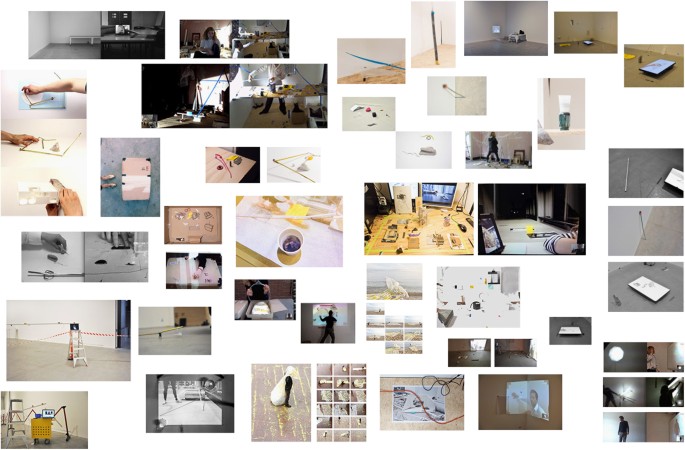
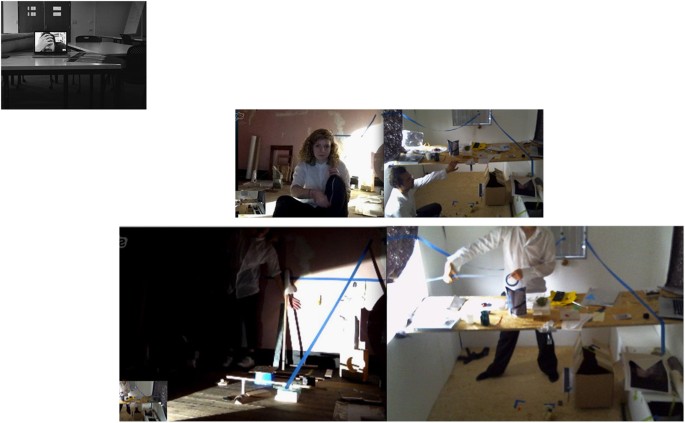
The images (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) form a short visual essay based on a collaborative artistic project 'Exercises of the man (v)' that Remco Roes and Alis Garlick realised for the Situation Symposium at Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology in Melbourne in 2014. One of the conceptual premises of the project was the communication of two physical ‘sites’ through digital media. Roes—located in Belgium—would communicate with Garlick—in Australia—about an installation that was to be realised at the physical location of the exhibition in Melbourne. Their attempts to communicate (about) the site were conducted via e-mail messages, Skype-chats and video conversations. The focus of these conversations increasingly distanced itself from the empty exhibition space of the Design Hub and instead came to include coincidental spaces (and objects) that happened to be close at hand during the 3-month working period leading up to the exhibition. The focus of the project thus shifted from attempting to communicate a particular space towards attempting to communicate the more general experience of being in(side) a space. The project led to the production of a series of small in-situ installations, a large series of video’s and images, a book with a selection of these images as well as texts from the conversations, and the final exhibition in which artefacts that were found during the collaborative process were exhibited. A step by step reading of the visual argument contained within images of this project illustrates how a visual essay can function as a tool for disclosing/articulating/communicating the kind of embodied thinking that occurs within an artistic practice or practice-based research.
Figure 1 shows (albeit in reduced form) a field of photographs and video stills that summarises the project without emphasising any particular aspect. Each of the Figs. 2 – 5 isolate different parts of this same field in an attempt to construct/disclose a form of visual argument (that was already contained within the work). In the final part of this essay we will provide an illustration of how such visual sequences can be possibly ‘read’.

First image of the visual essay. Remco Roes and Alis Garlick, as copyright holders, permit the publication of this image under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License

Second image of the visual essay. Remco Roes and Alis Garlick, as copyright holders, permit the publication of this image under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License

Third image of the visual essay. Remco Roes and Alis Garlick, as copyright holders, permit the publication of this image under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License

Fourth image of the visual essay. Remco Roes and Alis Garlick, as copyright holders, permit the publication of this image under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
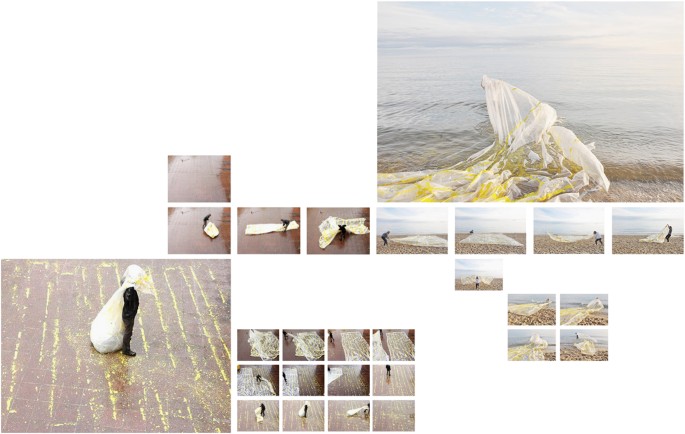

Fifth image of the visual essay. Remco Roes and Alis Garlick, as copyright holders, permit the publication of this image under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Figure 1 is a remnant of the first step that was taken in the creation of the series of images: significant, meaningful elements in the work of art are brought together. At first, we quite simply start by looking at what is represented in the pictures, and how they are presented to us. This act of looking almost inevitably turns these images into a sequence, an argument. Conditioned by the dominant linearity of writing, including images (for instance in a comic book) one ‘reads’ the images from left to right, one goes from the first spread to the last. Just like one could say that a musical theme or a plot ‘develops’, the series of images seem to ‘develop’ the problem, gradually revealing its complexity. The dominance of this viewing code is not to be ignored, but is of course supplemented by the more ‘holistic’ nature of visual perception (cf. the notion of ‘Gestalt’ in the psychology of perception). So unlike a ‘classic’ argumentation, the discursive sequence is traversed by resonance, by non-linearity, by correspondences between elements both in a single image and between the images in their specific positioning within the essay. These correspondences reveal the synaesthetic nature of every process of meaning-making: ‘The meaning of something is its relations, actual and potential, to other qualities, things, events, and experiences. In pragmatist lingo, the meaning of something is a matter of how it connects to what has gone before and what it entails for present or future experiences and actions’ (Johnson, 2007 , p. 265). The images operate in a similar way, by bringing together different actions, affects, feelings and perceptions into a complex constellation of meaningful elements that parallel each other and create a field of resonance. These connections occur between different elements that ‘disturb’ the logical linearity of the discourse, for instance by the repetition of a specific element (the blue/yellow opposition, or the repetition of a specific diagonal angle).
Confronted with these images, we are now able to delineate more precisely the problem they express. In a generic sense we could formulate it as follows: how to communicate with someone who does not share my existential space, but is nonetheless visually and acoustically present? What are the implications of the kind of technology that makes such communication possible, for the first time in human history? How does it influence our perception and experience of space, of materiality, of presence?
Artistic research into this problem explores the different ways of meaning-making that this new existential space offers, revealing the different conditions and possibilities of this new spatiality. But it has to be stressed that this exploration of the problem happens on different lines, ranging from the kinaesthetic perception to the emotional and affective response to these spaces and images. It would, thus, be wrong to reduce these experiences to a conceptual framework. In their actions, Roes and Garlick do not ‘make a statement’: they quite simply experiment with what their bodies can do in such a hybrid space, ‘wandering’ in this field of meaningful experiences, this Denkraum , that is ‘opened up’: which meaningful clusters of sensations, affects, feelings, spatial and kinaesthetic qualities emerge in such a specific existential space?
In what follows, we want to focus on some of these meaningful clusters. As such, these comments are not part of the visual essay itself. One could compare them to ‘reading remarks’, a short elaboration on what strikes one as relevant. These comments also do not try to ‘crack the code’ of the visual material, as if they were merely a visual and/or spatial rebus to be solved once and for all (‘ x stands for y’ ). They rather attempt to engage in a dialogue with the images, a dialogue that of course does not claim to be definitive or exhaustive.
The constellation itself generates a sense of ‘lacking’: we see that there are two characters intensely collaborating and interacting with each other, while never sharing the same space. They are performing, or watching the other perform: drawing a line (imaginary or physically), pulling, wrapping, unpacking, watching, framing, balancing. The small arrangements, constructions or compositions that are made as a result of these activities are all very fragile, shaky and their purpose remains unclear. Interaction with the other occurs only virtually, based on the manipulation of small objects and fragments, located in different places. One of the few materials that eventually gets physically exported to the other side, is a kind of large plastic cover. Again, one should not ‘read’ the picture of Roes with this plastic wrapped around his head as an expression, a ‘symbol’ of individual isolation, of being wrapped up in something. It is simply the experience of a head that disappears (as a head appears and disappears on a computer screen when it gets disconnected), and the experience of a head that is covered up: does it feel like choking, or does it provide a sense of shelter, protection?
A different ‘line’ operates simultaneously in the same image: that of a man standing on a double grid: the grid of the wet street tiles and an alternative, oblique grid of colourful yellow elements, a grid which is clearly temporal, as only the grid of the tiles will remain. These images are contrasted with the (obviously staged) moment when the plastic arrives at ‘the other side’: the claustrophobia is now replaced with the openness of the horizon, the presence of an open seascape: it gives a synaesthetic sense of a fresh breeze that seems lacking in the other images.
In this case, the contrast between the different spaces is very clear, but in other images we also see an effort to unite these different spaces. The problem can now be reformulated, as it moves to another line: how to demarcate a shared space that is both actual and virtual (with a ribbon, the positioning of a computer screen?), how to communicate with each other, not only with words or body language, but also with small artefacts, ‘meaningless’ junk? What is the ‘common ground’ on which to walk, to exchange things—connecting, lining up with the other? And here, the layout of the images (into a spread) adds an extra dimension to the original work of art. The relation between the different bodies does now not only take place in different spaces, but also in different fields of representation: there is the space of the spread, the photographed space and in the photographs, the other space opened up by the computer screen, and the interaction between these levels. We see this in the Fig. 3 where Garlick’s legs are projected on the floor, framed by two plastic beakers: her black legging echoing with the shadows of a chair or a tripod. This visual ‘rhyme’ within the image reveals how a virtual presence interferes with what is present.
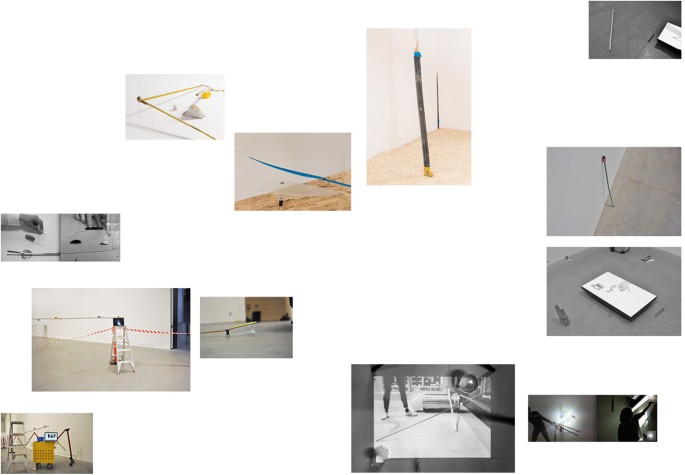
The problem, which can be expressed in this fundamental opposition between presence/absence, also resonates with other recurring oppositions that rhythmically structure these images. The images are filled with blue/yellow elements: blue lines of tape, a blue plexi form, yellow traces of paint, yellow objects that are used in the video’s, but the two tones are also conjured up by the white balance difference between daylight and artificial light. The blue/yellow opposition, in turn, connects with other meaningful oppositions, like—obviously—male/female, or the same oppositional set of clothes: black trousers/white shirt, grey scale images versus full colour, or the shadow and the bright sunlight, which finds itself in another opposition with the cold electric light of a computer screen (this of course also refers to the different time zones, another crucial aspect of digital communication: we do not only not share the same place, we also do not share the same time).
Yet the images also invite us to explore certain formal and compositional elements that keep recurring. The second image, for example, emphasises the importance placed in the project upon the connecting of lines, literally of lining up. Within this image the direction and angle of these lines is ‘explained’ by the presence of the two bodies, the makers with their roles of tape in hand. But upon re-reading the other spreads through this lens of ‘connecting lines’ we see that this compositional element starts to attain its own visual logic. Where the lines in image 2 are literally used as devices to connect two (visual) realities, they free themselves from this restricted context in the other images and show us the influence of circumstance and context in allowing for the successful establishing of such a connection.
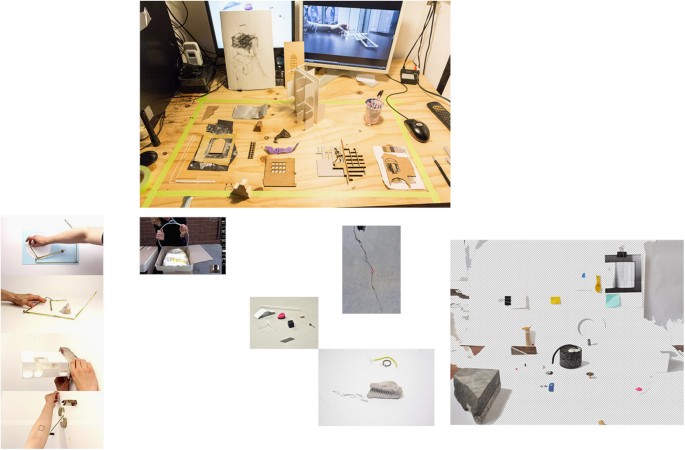
In Fig. 3 , for instance, we see a collection of lines that have been isolated from the direct context of live communication. The way two parts of a line are manually aligned (in the split-screens in image 2) mirrors the way the images find their position on the page. However, we also see how the visual grammar of these lines of tape is expanded upon: barrier tape that demarcates a working area meets the curve of a small copper fragment on the floor of an installation, a crack in the wall follows the slanted angle of an assembled object, existing marks on the floor—as well as lines in the architecture—come into play. The photographs widen the scale and angle at which the line operates: the line becomes a conceptual form that is no longer merely material tape but also an immaterial graphical element that explores its own argument.
Figure 4 provides us with a pivotal point in this respect: the cables of the mouse, computer and charger introduce a certain fluidity and uncontrolled motion. Similarly, the erratic markings on the paper show that an author is only ever partially in control. The cracked line in the floor is the first line that is created by a negative space, by an absence. This resonates with the black-stained edges of the laser-cut objects, laid out on the desktop. This fourth image thus seems to transform the manifestation of the line yet again; from a simple connecting device into an instrument that is able to cut out shapes, a path that delineates a cut, as opposed to establishing a connection. The circle held up in image 4 is a perfect circular cut. This resonates with the laser-cut objects we see just above it on the desk, but also with the virtual cuts made in the Photoshop image on the right. We can clearly see how a circular cut remains present on the characteristic grey-white chessboard that is virtual emptiness. It is evident that these elements have more than just an aesthetic function in a visual argumentation. They are an integral part of the meaning-making process. They ‘transpose’ on a different level, i.e., the formal and compositional level, the central problem of absence and presence: it is the graphic form of the ‘cut’, as well as the act of cutting itself, that turns one into the other.
Concluding remarks
As we have already argued, within the frame of this comment piece, the scope of the visual essay we present here is inevitably limited. It should be considered as a small exercise in a specific genre of thinking and communicating with images that requires further development. Nonetheless, we hope to have demonstrated the potentialities of the visual essay as a form of meaning-making that allows the articulation of a form of embodied knowledge that supplements other modes of inquiry in the humanities. In this particular case, it allows for the integration of other meaningful, embodied and existential aspects of digital communication, unlikely to be ‘detected’ as such by an (auto)ethnographic, psychological or sociological framework.
The visual essay is an invitation to other researchers in the arts to create their own kind of visual essays in order to address their own work of art or that of others: they can consider their artistic research as a valuable contribution to the exploration of human existence that lies at the core of the humanities. But perhaps it can also inspire scholars in more ‘classical’ domains to introduce artistic research methods to their toolbox, as a way of taking into account the non-conceptual, yet meaningful bodily aspects of human life and human artefacts, this ‘visceral connection to lived experience’, as Johnson puts it.
Obviously, a visual essay runs the risk of being ‘shot by both sides’: artists may scorn the loss of artistic autonomy and ‘exploitation’ of the work of art in the service of scholarship, while academic scholars may be wary of the lack of conceptual and methodological clarity inherent in these artistic forms of embodied, synaesthetic meaning. The visual essay is indeed a bastard genre, the unlawful love (or perhaps more honestly: love/hate) child of academia and the arts. But precisely this hybrid, impure nature of the visual essay allows it to explore unknown ‘conditions and potentials of human life’, precisely because it combines imagination and knowledge. And while this combination may sound like an oxymoron within a scientific, positivistic paradigm, it may in fact indicate the revival, in a new context, of a very ancient alliance. Or as Giorgio Agamben formulates it in Infancy and history: on the destruction of experience (2007 [1978]): ‘Nothing can convey the extent of the change that has taken place in the meaning of experience so much as the resulting reversal of the status of the imagination. For Antiquity, the imagination, which is now expunged from knowledge as ‘unreal’, was the supreme medium of knowledge. As the intermediary between the senses and the intellect, enabling, in phantasy, the union between the sensible form and the potential intellect, it occupies in ancient and medieval culture exactly the same role that our culture assigns to experience. Far from being something unreal, the mundus imaginabilis has its full reality between the mundus sensibilis and the mundus intellegibilis , and is, indeed, the condition of their communication—that is to say, of knowledge’ (Agamben, 2007 , p. 27, italics in original).
And it is precisely this exploration of the mundus imaginabilis that should inspire us to understand artistic research as a valuable form of scholarship in the humanities.
We consider images as a broad category consisting of artefacts of the imagination, the creation of expressive ‘forms’. Images are thus not limited to visual images. For instance, the imagery used in a poem or novel, metaphors in philosophical treatises (‘image-thoughts’), actual sculptures or the imaginary space created by a performance or installation can also be considered as images, just like soundscapes, scenography, architecture.
Agamben G (2007) Infancy and history: on the destruction of experience [trans. L. Heron]. Verso, London/New York, NY
Google Scholar
Garlick A, Roes R (2014) Exercises of the man (v): found dialogues whispered to drying paint. [installation]
Gombrich EH (1986) Aby Warburg: an intellectual biography. Phaidon, Oxford, [1970]
Ingold T (2011) Being alive: essays on movement, knowledge and description. Routledge, London/New York, NY
Ingold T (2013) Making: anthropology, archaeology, art and architecture. Routledge, London/New York, NY
Johnson M (2007) The meaning of the body: Aesthetics of human understanding. Chicago University Press, Chicago
Book Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Hasselt University, Martelarenlaan 42, 3500, Hasselt, Belgium
Remco Roes & Kris Pint
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Remco Roes .
Additional information
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Publisher’s note : Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Roes, R., Pint, K. The visual essay and the place of artistic research in the humanities. Palgrave Commun 3 , 8 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-017-0004-5
Download citation
Received : 29 June 2017
Accepted : 04 September 2017
Published : 31 October 2017
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-017-0004-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Reading Visual Art
Contributors.
- Jayson Flores
Description
Reading Visual Art deals with the study of art appreciation, interpretation, and criticism. It surveys techniques, composition, materials terminology, and the culture and social influences of art forms. Designed for the non-art major; this course provides the foundation for understanding the visual arts.

- Course Syllabus
Content Licensing
- Contributors grant the TLR a right to publish their work under the Creative Commons Licenses that allow others freely to read, download, copy and print, modify the content and disseminate. Here is the link to learn more about the CC License https://chooser-beta.creativecommons.org/
- Contributors are encouraged to put the Creative Commons Licenses in their original work.

Make a Submission
Information.
- For Readers
- For Contributors
- For Librarians
Featured Topic
ourSOUL Teaching-Learning Resources Project | Copyright 2022 | All rights Reserved | Office of Silliman Online University Learning, Silliman `University | 1 Hibbard Avenue, Dumaguete City, Negros Oriental 6200 Philippines | A project funded by the Philippine's Commission on Higher Education (CHED) through the Continuing Professional Education (CPE) Grant under the K to 12 Transition Program, in partnership with the community of teaching and learning.

IBDP Visual Arts
Website by Heather McReynolds & Shannon Brinkley
Updated 29 April 2024
Recent posts View all
- Student Access
- My favourites
- Presentation mode
- Teaching materials
- Print this page
A Good Read: the Visual Arts Extended Essay
Friday 27 March 2015
Turning the pages
A stack of extended essays is piled high on my desk..this is my reading this month. I try to pace myself, reading only a few each day so that my approach remains fresh and curious.

Although there are inevitably some essays that disappoint, there are many more delightful surprises this year. Some essays astound with their clear lucid writing, others with the sheer dedication and passion for the chosen topic. I have read engaging essays on topics as diverse as handmade artist books, cult performance art, site specific architectural decoration, Picasso's muses and many more.
The best essays have a very focused research question or topic and thus a real incentive to research; having a clear focus also helps to build up a convincing argument or thesis.
Essays driven by strong personal interest and meaningful contact with an artist, or work of art are often very successful, especially if guided in the early stages by a wise teacher who can help the student to formulate an angle or research question. Supervisors can help to point the student in the direction of appropriate resources and research methods and a good supervisor can make a big difference.
As would be expected, the weakest essays are those without a clear focused topic. Essays with topics that are too broad and general such as “the role of women in art” , or even “the role of women in abstract art” are difficult to build up a convincing argument or point of view. Much better to take a narrow approach such as “ Joan Mitchell and Agnes Martin; different approaches to abstract painting in the late 20 th century”.
I find It is always beneficial when essays refer to examples of specific artworks, which in turn allow for detailed visual analysis. An essay without these specific examples misses the opportunity for analysis and for using art terminology.
On the whole, it seems that students from schools all over the world are producing mostly high quality essays that show a genuine interest and sensitivity to the visual arts in a broader context.
The Extended Essay teaches so many important skills: not least how to research, structure, and write an essay. If students can succeed at this in high school they will be well prepared for higher education, and for any occasions in their lives when they encounter the need for formal writing skills.
Tags: EE , essay , topic , research question , supervisors

Back to blog
Literacy in Visual Art Education: Art as Text

Literacy as it relates to reading and writing has been a passion of mine since I was an elementary art teacher early in my career . In my current role as a visual art supervisor for Prince George’s County Public Schools (PGCPS) in Maryland, literacy is a focus in every content area. In visual art, we view our artwork as texts and read or analyze them using our visual art vocabulary and visual thinking/literacy strategies . U sing art in a “text-free” environment helps early readers develop decoding and comprehension skills, while also developing their reading abilities. In addition to my role at PGCPS, I teach an online, semester-long course called Developing Critical Literacies for the Maryland Institute College of Art ( MICA ), as part of their Master of Arts in Teaching program. The purpose of this course is to expose art education students to literacy-based strategies and standards which they will be required to infuse into their daily art instruction when they become art educators. On day one of the course, the expectation is set that all educators, regardless of the content they teach, are responsible for teaching literacy and that this instruction is a daily occurrence. Typically, this course, which is required for certification in Maryland, is filled with educators from various content areas and levels. At MICA, this course is unique in that all the students are visual art education majors.
Throughout the MICA course, the soon-to-be educators build a literacy toolkit of strategies they will use in the classroom. They participate in these strategies through various warmups, research and activities woven throughout the semester. I start by engaging the students in a series of Artful Thinking Strategies and Visible Thinking Strategies created by Harvard Project Zero . The following example was adapted from the Core Thinking Routine, Claim, Support, Question . Using a Google Jamboard, each student received a slide with an image by artist Michael D’Antuono to write on or annotate. In the top left corner was a digital sticky note that said, “‘ The Talk ‘ by Michael D’Antuono makes the argument that _____. This is evidenced by _____.” The students used the digital tools to mark up the work of art, highlighting any key ideas and details. Once they had thoroughly read the artwork, I asked them to complete the prompt. Next, they participated in a “gallery walk” by viewing the slides completed by other students. Finally, we synthesized our learning and key points through a whole group discussion. The image below is an example of one student’s work.

With permission from the artist Michael D’Antuono and art teacher candidate Julia Brennan.
The Maryland State Department of Education sets the expectation and emphasizes the importance that literacy instruction is woven throughout all content areas, including the arts. It is no longer solely the reading educators’ responsibility for making sure students have strong literacy capacities in reading and writing when they graduate. Through courses and programs similar to those at MICA, future educators learn skills to support students in demonstrating independence as readers, building strong content knowledge and critiquing and valuing evidence. These are some of the capacities we need our students to graduate knowing. If instruction in every content area provided a specialized version of this required course, deeper learning in literacy would be more authentic and attainable.
This post is part of AEP’s Continuing the Arts and Literacies Conversations blog post series. These posts expand on key ideas and topics from our Arts and Literacies Thinkers Meeting Series and from the resulting interactive resource . Through sharing their personal reflections and work experiences, guest authors explore a range of topics that span disciplines, age levels and education environments.
Related posts
The Arts Educator Workforce
What’s New in Arts Education Policy?
The ESSER III Deadline Explained
Title: 2280 Pasos Bajo un Cielo Nublado | Artist: Hernán Jourdan | Medium: Film
Visit Website
Title: Fluent Nature | Artist: Melli Hoppe | Medium: Film
When I was asked to create a work of art exploring literacy, I wanted to create a dance but I had no dancers or a studio, so I chose to use my own body in the space I had, my yard. Fluent Nature is video of micro-choreography that explores what cannot be expressed with words, how nature has its own language, and how placing the human body in nature changes the story.
Title: What Is Me and What Is Not Me | Artist: Alex Chadwell | Medium: Music
My thinking on arts and literacy centers around the concept of literacies and artmaking as both sense-making and meaning-making processes that organically and inevitably overlap, intersect, and reciprocate. Compositionally, What is me and what is not me is a sound collage of sorts (there is no notation for the piece, and I'd be hard pressed to recreate it accurately) that abstractly and aurally represents the relationships between literacies and artmaking.
Title: A Curious Honeybee | Artist: Gideon Young | Medium: Film
Offering welcome through traditional and digital elements of literacy, A Curious Honeybee provides an experiential learning environment by activating visual, musical, natural, and emotional literacies.
Title: Tercera Llamada | Artist: Karilú Forshee | Medium: Audio
La Carpa Theatre is a project that I am currently directing in the Detroit Latinx community. The project aims to strengthen and uplift youth voices through devised theatre, in the style of the Mexican Carpas. This audio was created in the theatrical environment envisioned for our project. The ways in which literacies are re-defined are at the heart of La Carpa Theatre's mission.

View Full Image
Title: Literaseas | Artist: MJ Robinson | Medium: Graphite and ink on paper with digital edits
Title: A Riddle | Artist: MJ Robinson | Medium: Graphite on paper with digital edits
Title: False Binaries | Artist: MJ Robinson | Medium: Graphite on paper with digital edits
17.1 “Reading” Images
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Define the key concepts and elements of visual rhetoric.
- Interpret visual information using the language of visual rhetoric.
- Interpret images differently based on cultural considerations.
- Choose digital and visual media according to the rhetorical situation and cultural context when writing for different audiences.
- Make informed decisions about intellectual property issues regarding images.
To compose an effective essay or a strong visual, a creator works with a number of elements that are remarkably similar from one medium to the other. Both stories and pictures contain information presented by a creator who has a particular point of view and arranges the work in two-dimensional space. The information is likely to be open to multiple interpret , which may or may not be justified by the text. Although the sharing of personal opinions and beliefs has value, the focus here is on interpreting or analyzing texts in combination with your personal experiences.
Interpreting Visual Information
Both words and pictures convey information, but each does so in different ways that require interpretation. Interpretation is the sense a person makes of a piece of communication—textual, oral, or visual. It includes personal experience, the context in which the communication is made, and other rhetorical elements. (See Glance at Genre: Relationship Between Image and Rhetoric for a list of key terms related to visual elements and rhetoric.) By the time readers get to college, they have internalized strategies to help them critically understand a variety of written texts.
Images present a different set of challenges for critical readers. For example, in a photograph or drawing, information is presented simultaneously, so viewers can start or stop anywhere they like. Because visual information is presented in this way, its general meaning may be apparent at a glance, while more nuanced or complicated meanings may take longer to figure out and likely will vary from one viewer to another.
Some images, however, do not really lend themselves to interpretation. Before trying to engage in rhetorical discourse about an image, be sure it contributes something of value. For example, Figure 17.2 shows a punk rock concert featuring the band Naked Raygun with several concertgoers in the foreground. Such pictures are common forms of memorabilia that serve an archival function. The features common to visual rhetoric—point of view, arrangement, color, and symbol—do not inspire much in the way of discussion in this particular image. Parts are blurry, some of the figures are obscure, and the picture’s purpose is unclear. Therefore, any analysis of the image may be guided more by personal opinion than by critical thinking. Such images are not the focus of this chapter.
Figure 17.3 , in contrast, depicts not merely a moment in time for the sake of memory, although it certainly does that. It contains a central, dominant figure. The color red is bold and centers the figure, giving the image weight. It also conveys several political messages, both obvious and nuanced. The woman in the picture is wearing a mask, as people were either asked or mandated to do during the COVID-19 pandemic. The slogan on her mask reads “I can’t breathe,” words that were made infamous after Eric Garner (1970–2014) died as the result of an illegal chokehold inflicted by a New York City police officer during arrest. These words were repeated by George Floyd (1973–2020) in an 8-minute, 46-second video showing his murder by a Minnesota police officer who knelt on Floyd’s neck. The phrase became one of several slogans of the Black Lives Matter (BLM) movement, symbolizing the struggle that people of color endure when living in an implicitly and explicitly racist culture. Breathing—like blood—is fundamental, essential. Without breath, there is no life. Thus, this slogan draws attention to the fact that people of color may be brutalized for no reason other than their existence.
Placing the slogan on a mask is a design choice likely to provoke those who have argued against mandated mask wearing as an assault on personal liberty and who have proclaimed they could not breathe while wearing masks. Juxtaposition , or placing contrasting elements close together, is a technique that image creators often use for a variety of purposes: humor, irony, sarcasm, or—as in this case—disgust or outrage. The juxtaposition of the mask with a slogan referencing literal asphyxiation emphasizes the wearer’s view that state violence against people of color is a more serious threat to her existence than a mask. Thus, the image is open to multiple interpretations.
Thinking Critically
To think critically about visual information, first identify the objects, facts, processes, or symbols portrayed in the image. Taking all the information together, ask whether there is a main or unifying idea. Is the meaning open to multiple interpretations? Is it suggested but not stated? Is it clear and unambiguous? Are there multiple levels of meaning, both stated and unstated? When you view an image, pausing to answer such questions will sharpen your critical faculties, increase your understanding of the visual information you encounter, and help you use images more meaningfully in texts you create.
Visual Rhetoric
Written texts rely on strategies such as thesis statements, topic sentences, paragraphing, tone, and sentence structure to communicate their message to their audience. Images rely on different strategies, including point of view , arrangement , color , and symbol . When writing about images or including them in your writing, think critically about the visual strategies they use and the effect they will have on your audience.
Using these techniques may or may not make you a proficient artist or creator of images. However, familiarity with the technical language of the visual arts will certainly enable you to describe what you observe as you build the evidence that allows you to interpret an image, reflect on it, analyze it, and make persuasive arguments about it.
Point of View
In written texts, point of view refers to the “person” from whose vantage point the information is delivered, either a character in the story or a narrator outside the story. However, in photographs, drawings, and paintings, point of view refers to the place from which the image creator looks at the subject—where the photographer places their camera or the artist their easel.
Photographs that haven’t been manipulated in a darkroom or digitally by a computer only reproduce the subject in front of the camera, as it exists in the moment the shutter opens and closes. They do not show anything to the left or right, above or below, or what comes before or after. A camera aimed to the east omits information from the north, west, and south. In other words, any photograph is the result of placing a camera in a certain location, at a certain height and distance, at a specific time of day and using a particular lens, film, and perhaps a filter. All of these decisions about where, when, and how to place the camera create the visual point of view.
You can find good examples of these kinds of limited truths in real-estate advertisements featuring photographs of houses for sale. The photograph might not reveal a landfill next door or a factory across the street—though you might infer such limitations from a low selling price or confirm them by driving past the house.
The creator of Figure 17.4 chooses to highlight the digital waterfall with its seductive lighting and colors. Meanwhile, the people interacting with the computer are barely visible, standing off to the side, some nearly out of the frame. The silhouetted profiles and darkened faces lack identifying details. These features are emphasized by the blurred people in the background. These figures, too, are unidentifiable and are looking out of the frame, uninterested. The effect is to imply that the waterfall and its computer interface dominate human interaction and possibly even human existence.
To think critically about point of view, answer the following questions:
- From what place or stance does the image creator view the subject?
- What effect does this particular point of view have on the way viewers may think or feel about the subject?
- What would happen if the vantage point were elsewhere—above or below, left or right?
- What would change in the image if the point of view were changed?
Arrangement
In addition to point of view, artists use arrangement to signal an image’s significance to the reader. The term arrangement in visual texts might be compared to terms such as order , organization , and structure in verbal texts, though the differences are substantial. While writers arrange , or put together, a story, essay, or poem to take place over time—that is, the time readers need to follow the text, line by line, through a number of pages—image creators arrange pictures in the two-dimensional space of their viewfinder, paper, or canvas to invite viewers to read in space rather than time. This difference is also evident in sculpture and other three-dimensional works, which require viewers to move around them to read them spatially. In visual texts, then, arrangement refers to the ways in which the various parts of a picture come together to present a single coherent experience for the viewer.
In contrast to static images, which are read spatially, videos and some types of multimodal texts—those incorporating more than one genre, discipline, or literacy (for example, GIFs that incorporate pictures or videos with language)—combine elements of both time and space. That is, they invite viewers to examine an image in motion that changes over time. Video creators often mimic linear time by telling a story, or they repeat key images to be interpreted differently after being seen in various contexts within the video.
One element to examine is the use of pattern —predictable, repeated elements within the visual field that the eye notices and seems attracted to. Just as sonnets, sestinas, and haiku follow patterns of lines, so do visual compositions. But in these, patterns are created by light and color rather than words. Documentary and commercial photographers often use visual patterns to lead viewers to an intended meaning. Patterns are especially prominent in street art, where the elements of surrounding architecture and infrastructure interact with the work, as shown in Figure 17.5 .
Many patterns are suggested by mathematics. For example, the Möbius strip is both a mathematical construct and a visual enigma. It has one side and one boundary curve. It looks like a spiral, but it does not intersect itself. Thus, it gives the impression of being infinite. In Figure 17.5 , the artist capitalizes on these features of the Möbius strip, using it to depict the seemingly endless cycle of destruction (green tanks) and reconstruction (yellow steamrollers) in one of the world’s most contested pieces of real estate: the Gaza Strip.
Ownership and control of the Gaza Strip are disputed. Approximately two million people live there, many in refugee camps. Since the mid-20th century, the region has been fought over by Israel, Egypt, and Palestinian Arabs. As you contemplate the mural, think about the way its creator uses pattern and repetition to convey various ideas and emotions. The following questions may help:
- Which elements within the mural are repeated?
- Where is its center of gravity or weight?
- Where do patterns of light/dark, large/small, and color lead the eye?
- How do pattern and balance contribute to meaning in a two-dimensional image?
- What does the arrangement suggest about the meaning of the image?
Color and Symbol
Pattern and arrangement are controlled by the image creator and intended to guide the viewer. Color and symbol allow the viewer greater latitude in interpreting the image, in part because particular colors suggest specific moods. Think about your personal reactions to different colors. What color might you select to paint your bedroom? What is your favorite color for, say, clothing or cars? While these may differ according to personal preference, traditional symbolic values are attached to different colors in literature and art. Why, for instance, does red often symbolize anger or war on the one hand and romance or passion on the other? Why does black often suggest danger or death? And why does white often stand for innocence or purity? Are the reasons for these associations arbitrary, cultural, or logical?
Particular colors also suggest or reinforce social and political ideas. What, for example, is suggested by adding a red, white, and blue American flag to a magazine advertisement for an American automobile, political poster, or bumper sticker? What is the meaning of a yellow ribbon tied to a tree in front of a house or an image of a yellow ribbon sticker attached to the tailgate of a pickup truck? By themselves, colors do not specify political positions, arguments, or ideas, but used in conjunction with specific words or forms—a flag or ribbon, for example—the emotional power of color can be influential.
Color associations globally are complicated and highly nuanced. The following overview is brief and simplified, to be considered merely as an introduction or starting point for your research and investigations into individual artistic expressions. When you interpret an artist’s use of color, one place to start is with the hues found in the natural world. Because blood is red, the color is often associated with life, heat, and passion. Yellow and green appear with the new growth of spring, so these colors often symbolize new beginnings, freshness, and hope. Both the sea and the sky are blue. Although these elements can be turbulent, many people find peace and tranquility as they reflect on them, and thus they are often associated with these emotions.
Regardless of colors’ natural associations, people from around the world understand colors differently. In China, for example, red is a celebratory color associated with holidays, feasts, and the giving of gifts, whereas in some parts of Africa the color may symbolize the sacrifice necessitated by the fight for independence. In the Western world, white can represent purity or innocence and is often worn by young women at their weddings. However, in parts of Asia, white is a color of mourning.
The colors mentioned so far are mostly primary colors: red, yellow, and blue. The secondary colors—orange, green, and purple—carry more complex meanings. Both orange and the bright shade of green called neon or chartreuse are easy to see in all light conditions. Therefore, they are often used for safety purposes, on caution signs or uniforms of emergency workers. The color orange is associated with the robes of Buddhist monks, thus representing in Buddhist cultures that which is holy, whereas in the Netherlands, orange is the color of the royal family and used for patriotic purposes.
In addition to connotations of spring, the color green is also associated with Islam. In the Christian tradition, yellow and gold are colors associated with riches and abundance. Holiness is also associated with the color blue in Egyptian, Hindu, and Christian cultures (in which blue has other associations as well). Because purple has traditionally been a difficult color to manufacture, its rarity meant that only the very wealthy, often nobility or royalty, could afford to wear it—hence its association with royals and even gods. However, some cultures, such as Thai, Brazilian, and Italian cultures, associate purple with bad luck or death. Again, this overview of colors’ different interpretations and associations is not intended as a guide for interpreting color in a visual image. Instead, consider all of the different ways in which color can be understood, some ways that the artist might intend for color to be interpreted, and the associations that colors have for you when you view a visual or digital image.
In this chapter, you have begun learning about how to interpret visual information through the lens of rhetoric. Color and its related symbolism help viewers interpret images.
Like colors, symbols are interpreted differently by individuals on the basis of their personal and cultural experiences. Here is an example of two state flags with very different symbolism: Figure 17.6 depicts the state flag of Mississippi that was adopted in 1894; Figure 17.7 depicts the one adopted in 2021. In 2021, under pressure from numerous organizations and in the wake of the Black Lives Matter movement, Mississippi replaced its state flag. The 1894 flag included the battle flag of the Confederacy , referencing Mississippi’s history of secession and violence during the Civil War (1861–1865); the single blue, white, and red bands were a reference to the stripes on the American flag. This historical allusion, coupled with the state’s history of enslavement and segregation, meant that the 1894 flag served as a stark reminder of efforts to silence Black Mississippians. In fact, Mississippi did not formally ratify the Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution—proposed in 1865 to abolish slavery—until 2013, and the state remained segregated long after the Supreme Court outlawed the practice.
Mississippi continued to use the 1894 flag throughout the Reconstruction (1865–1877) and the Jim Crow laws (ca. 1877–c. 1950) and civil rights (1950s and 1960s) eras despite multiple and sustained efforts to remove any reference to the Confederate flag. In 2020, the increasing prominence of the Black Lives Matter movement created the context in which state lawmakers were forced to consider these problems as mainstream and urgent. Further, the state came under pressure from numerous organizations, including the Southeastern Conference athletics organization (SEC), which threatened to boycott the state by no longer holding major events there if the flag were not changed.
Submitted to the legislature by Starkville-based graphic designer Rocky Vaughan (b. ca. 1977) and collaborators Sue Anna Joe , Kara Giles , and Dominique Pugh , the new flag took effect in January 2021 after voters approved it and the governor ratified it. The current flag ( Figure 17.7 ) features a central vertical band of blue, flanked by two thin gold bands and encompassed by two broader red ones. The flag’s center is dominated by a single magnolia flower, crowned by a single gold star and encircled by 20 white ones. Beneath the flower are emblazoned the words “In God We Trust.”
The gold coloring is intended to celebrate Mississippi’s contributions to the world of art, music, and literature. The white stars symbolize Mississippi’s status as the 20th state of the Union; thus, the new flag symbolizes the state’s reintegration into the Union without reference to its seditious acts in the 19th century or lingering loyalty to the beliefs that motivated them. In addition, the single gold star honors the state’s indigenous people; no reference is made to the state’s history of enslavement and racism.
Thinking critically about color and symbol, ask yourself these questions:
- Does the color enhance or distort the reality of the image?
- Imagine the image in shades of black, white, and gray. What would be lost and what would be gained if color were subtracted?
- Does the color work with or against the other compositional elements?
- What symbols are incorporated into the image? How might those symbols be interpreted in various contexts?
- What, if any, is the significance of referencing Indigenous but not Black Americans on the current flag?
Selecting and Incorporating Digital and Visual Media
In addition to analyzing visual and digital media, you may be asked to find, create, or manipulate such materials for a variety of situations and audiences. Following are some considerations to keep in mind, including copyright issues, appropriate selections, and technical manipulations .
Intellectual property laws are complicated, change frequently, and vary by country. Sharing an image is similar to quoting a text, with one exception: you must not only cite the author in a reference list or bibliography but also secure permission to use the image. To be safe, unless an image explicitly states that you are free to share it (public domain), assume it is protected by copyright.
The texts you write will have varying degrees of formality and require different levels of diction (word choice), syntax (sentence structure), content, and tone. Similarly, the images you select should reflect the tone , or attitude, that you wish to convey in your text. Ask yourself these questions to decide whether an image is appropriate for your text:
What is the image’s purpose? Include images only if they add to or supplement the text. Do not add images simply as “filler” or for audience entertainment. Such materials are more likely to confuse or distract readers than they are to enlighten or inform them.
Is the image humorous or sarcastic? Humor has value as entertainment by keeping the audience interested and engaged in your text and making it more memorable. However, determining what makes something funny is deeply personal. An image you find funny could be read with confusion or even offense by someone else. In formal communications, humor and sarcasm are better avoided because of the risk of misunderstanding. In creative contexts, you have greater latitude.
Does the image include text? Because you are already creating a text, you may wish to question the value of inserting an image with text. Consider what information the image provides in addition to the text. For example, in Figure 17.3 , the text “I can’t breathe” is enhanced by its placement on a mask and, further, by the mask’s presence on a Black woman. These details make the image with its text a valuable addition to a discussion or analysis.
Consider also the language of the text. You may be fluent in multiple languages, so an image with text in Spanish, French, or Japanese could have meaning for you. Will it have meaning for your audience? The same applies to images that include slang, jargon, or slogans with a limited shelf life. If you have to explain the image’s meaning before your readers understand it, the image is probably not worth including.
What is the image’s context? Where and when the image is placed can affect the viewer’s understanding and interpretation. A picture of poverty in one country is likely to look very different from poverty in another country. Some images can be considered universal, meaning they depict situations that have significance for all people, regardless of culture, ethnicity, or historical context. For example, an image of a mother and an infant is easily recognized by anyone anywhere and is likely to evoke similar thoughts and emotions.
What digital or technical requirements or manipulations are needed? Finally, when you think about including an image, you’ll need to consider the digital and technical requirements and manipulations necessary to do so. Aspects to consider include compatibility requirements, visibility on different devices and platforms, sizing, and placement. The technical details associated with these considerations are changing rapidly, so this chapter makes no recommendations regarding software programs or specifications. However, if an image is blurred or distorted—or invisible—the result will be confusion and frustration on the part of your reader.
Selecting an Appropriate Image
To practice selecting appropriate images, imagine you are writing an informational webpage about the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and its responsibilities in relation to the Clean Water Act . To illustrate those responsibilities, which of the following images would you use? Why? (Suggested answers follow.)
Suggested Answers
- Sample image 1 seems like an obvious choice. It depicts the name and logo of the agency you are writing about, and nothing about it is likely to be considered controversial. However, by itself, it does not convey any useful information, so its purpose is unclear.
- Sample image 2 depicts safe, clean drinking water from the tap. The glass emphasizes the clarity of the water, and its proximity to the tap shows the intimate role that water plays in daily life. It features no characters or setting, so it is not restricted by any obvious contextual clues. It is perfect for this piece.
- Sample image 3 is emotionally powerful. It depicts a woman, older and likely with a low income, holding a jar of brownish liquid. The image appears to be old, based on the coloring of the photograph, the woman’s dress, and the home in the background. Its age could help make the rhetorical point that the EPA’s enforcement of the Clean Water Act, passed in 1972, has been effective. However, its context is unclear, raising questions about its composition. When and where was the photo taken? Is it set in the United States? And what is the liquid in the jar—water? Oil? Moonshine? The image raises too many questions to be useful in this context.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/17-1-reading-images
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
Visual Arts Extended Essay: The Complete Guide for IB Students
by Antony W
May 8, 2023

An extended essay in visual arts allows you to conduct study in a particular area of visual arts that is of interest to you. The conclusion of the study should be a clear and structured piece of writing that tackles a topic or research question pertinent to the visual arts in an effective manner.
The strongest EE in arts is the one that demonstrate a thoughtful selection of socially and culturally relevant topics, which frequently have a personal significance for the candidate in respect to his or her cultural identity, a potential university program, or present creative interests, such as studio work.
It is discouraged to rely solely on textbooks and the Internet, and no long essay in visual arts should rely solely on such sources.
You should only read your textbooks to the extent that they generate unique ideas, give models of disciplined, organized, and informed methods, and foster direct and personal engagement with the essay topic.
Choice of Arts Extended Essay Topic
When it comes to choosing a visual arts extended essay, we strongly recommend that you avoid themes that rely solely on summarizing generic secondary sources and those that are likely to result in an essay that is mostly narrative or descriptive in nature.
You must address a pertinent subject or research question and reach a specific, ideally individual, conclusion.
Choosing a topic that encompasses several areas of art history or a lengthy time span is likewise unlikely to result in a great essay. Restriction of the essay’s scope will help you to establish a clear focus and create opportunities for exhibiting in-depth comprehension and critical evaluation of your extended essay.
How Should You Treat Visual Arts Extended Essay Topic?
The topic you choose must have a clear and direct connection to visual arts. If the relationship is only tenuous, you risk introducing irrelevant material, which will confuse the investigation and undermine the case.
You should construct a research issue that is of personal interest and use a range of materials to support your claims, including textual analysis, the study of actual artworks or designed artifacts, and interviews with practitioners and subject-matter experts.
Questions that do not provide a systematic examination that exhibits critical creative analysis and in-depth comprehension are unlikely to be appropriate. In certain cases, it may become apparent early in the research process that there are insufficient sources to conduct such an examination. In such situations, consider a shift in emphasis.
In visual arts extended essays, the incorporation and discussion of pertinent visual reference material is of special relevance. However, such material must directly support and be relevant to the analysis/argument. It should be cleanly presented, appropriately acknowledged, and appear as near as feasible to the first reference in the body of the essay.
To stimulate personal investment in the extended essay, your work should include local and/or original sources wherever feasible. However, you may not have access to original materials in some circumstances. In such instances, high-quality replicas, movies, films, or photographs/Internet pictures are acceptable sources.
An argument should be well supported, with remarks and conclusions supported by evidence that is relevant and well-founded, as opposed to being based only on preconceived notions.
Visual Arts Extended Essay Topics Examples
Now that you know about the kind of topic you should choose for you visual arts extended essay, let’s consider some good and bad examples.
The worst example can be something like:
- The variation within human perception
- Architecture is functional art.
- Postmodernism
- Islamic architectural design
You want avoid these types of examples because they’re broad and therefore can’t fit within the scope of extended essay requirements .
You want to consider only the best topic for the project, particularly making sure you pick a subject that’s specific enough to form a research question that you can answer within the respective scope of the assignment.
Some of the best examples include but not limited to the following:
- What role did national themes have in the creative activity of Russian avant-garde artists associated with the Knave of Diamonds society?
- How did men and women’s clothes communicate National Socialist ideals?
- How does Yinka Shonibare’s work represent the evolving importance of African art in a global society?
- What are the origins of Romanesque architecture in Arles?
- Are there pop art elements in the design of Pakistani trucks?
- Titles for Protracted Essays
- Appropriateness of Picasso’s usage of the Mbangu mask in ‘Les Demoiselles d’Avignon’ in terms of cultural borrowing
- How does Ketna Patel’s work reflect the increasing influence of media culture on Asian cultures?
- How does Yinka Shonibare’s work represent the evolving significance of African art in a global society?
- How far did Andy Warhol’s “Death and Disaster” series develop his interest in morbidity?
- How Jesse Trevino’s cultural experiences influenced his artwork
- How would one identify the crucial balance between design and function for four pedestrian bridges of the 21st century?
- In what way does Damien Hirst’s art tackle the themes of Life and Death? (2013)
- To what degree has Federation Square’s design proven successful?
- When does photojournalism become an art form?
- How does Fra Angelico’s picture of The Annunciation represent him in Renaissance Florence?
Tips for Writing a Visual Arts Extended Essay
You are supposed to assess critically the sources you consulted while writing the essay by asking yourself the following questions:
- Which sources are essential to my ideas, beliefs, and assertions?
- Which sources are irrelevant to the analysis?
For the research question, you can:
- Utilize primary and secondary sources to develop and evaluate diverse perspectives.
- Use these primary sources to explore and explain particular aspects of the visual arts, with emphasis on a particular aspect of the visual arts collecting and analyzing reproductions of artwork.
You must also exhibit an understanding of various topics associated with the studied work.
- Demonstrate a knowledge of the worth and limitations of the work you’re studying by analyzing its origin and function
- Show a continuous high level of creative comprehension by addressing the study subject comprehensively and effectively.
Relevant findings from this analysis must feature in your argument, not to mention that you should carefully support the arguments.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
Visual culture and the Moscow Metro

James Andrews first rode the Moscow Metro in the 1980s as an undergraduate student studying in the former Soviet Union.
Now after 35 years, the metro is taking him on a new journey: documenting how its iconic public spaces reveal the story of Moscow itself as the city evolved under Joseph Stalin and his Soviet and post-Soviet successors.
This May, Andrews, professor of history, gave a public lecture on his new research project at the Kennan Institute in Washington, D.C. The Kennan Institute is part of the Woodrow Wilson Center, where Andrews was a former senior resident fellow.
The talk, which has been made available on YouTube, was so well-received that Andrews immediately received an additional invitation to present at the Jordan Center for the Advanced Study of Russia at New York University.
What makes the Moscow Metro a fascinating subject for a historian? More people ride the Moscow Metro each day than the New York City Subway and London Tube combined, yet its history is relatively unknown, Andrews said.
“Everyone has a story about the metro, but there has never been a book in English about its history,” Andrews said. “Many of my generation spent an endless amount of time on the metro. Before people had cell phones, you would always say, ‘Well, we’ll meet on the platform at this station.’ Everyone spent time traveling through this cavernous system. It’s a labyrinth really, but at the same time people don’t know much about its history in detail.”
Andrews’ previous books focus on the history of Russian science, technology and the Soviet space program. His new book project on the metro is another opportunity to study iconic Soviet technology, as well as visual culture.
The original metro stations, built with deep shaft tunneling methods beginning in 1932, had airy open ceilings with gorgeous bas-relief architecture—a canvas that Stalin used to create a public art monument to socialism.
“Socialist countries had a tendency to produce technologies that they could adorn with stories,” Andrews said. “Their metro was started in the 1930s under Stalin, and they invested a lot of money in it. It was important for two reasons: there was a utilitarian nature. The crowds were incredible in Moscow. They needed better public transportation. People had been flooding in from the countryside during collectivization. The other thing was to come up with a monument to socialism. That’s why they hired all these architects to decorate, and they decorated each station thematically.”
In the years after Stalin’s death, Nikita Khrushchev issued an edict rejecting the metro’s flamboyant architectural style in favor of a pre-fabricated, practical style, Andrews said. At the same time all over the city, de-Stalinization was happening, and street signs, busts of Stalin and station names were changed or removed.
“The irony is Stalin funded it,” Andrews said. “It’s a Stalin-era display technology project, but by the Khrushchev era they were erasing Stalin’s name from it.”
Andrews has had unlimited access to Moscow’s architectural archives, including many original photographic negatives, and will return to Russia next summer to research political archives.
“The Bolsheviks liked to document everything, but I was shocked at how many photographs they had taken of all these projects, documenting every stage and how well they were preserved,” he said.
Throughout his research, he has uncovered more stories hidden within familiar metro spaces.
One Russian architectural archivist told Andrews about being born in the metro in 1942, during a time when its underground stations housed makeshift hospitals, military meetings and even cultural events such as film nights.
Public spaces bear new stories over time, and Andrews is closely following the story told by newly constructed metro stations. New stations are bringing back marble-laden aesthetics and cultural themes that highlight famous Russian figures like chemist Dmitri Mendeleev or writer Fyodor Dostoyevsky, he said.
“I think the story tells us now that during Putin’s era you see a resurgence of Russian nationalism and Russian themes,” he said. “Not every station can be imploded into this reductive narrative, but it points again to how the narrative of the metro stations changes as the politics of Russian change to some extent and the city itself.”
And it shows how the Moscow Metro has a seemingly endless amount of track for a historian to travel.
“What I love about the project is there is a political history to it, a technological history, a social history, an engineering element, and an artistic element,” Andrews said. “It’s a multi-disciplinary study, which is both fascinating to me and challenging.”
- Support Sites
Extended Essay Support Site
Visual art - klee.
Study the assessment criteria for the Extended Essay before reading the example essay and RPPF that have been provided below. How would you apply the assessment criteria ? How many marks would you award the essay for Criteria A-D and the RPPF for Criterion E? Discuss your comments and marks with a colleague or classmate, before revealing the examiner's comments and marks below.
When writing about Visual Arts
There are a few points worth considering when writing an EE in Visual Arts. Take these into consideration when reading the following essay:
- Be careful not to summarise secondary sources (i.e. history books on art).
- Focus on applying theories and ideas on art to particular artists.
- Avoid writing a biography on an artist.
- There should be evidence of critical analysis of primary sources (i.e. artwork).
- Try to come to a personal conclusion that is based on an orginial argument.
An RPPF with examiner comments is also on this site here . In fact the RPPF that is annotated is the one from this essay. In brief, it is a rather mediocre RPPF , which could have scored much better with a few key changes. Learn from this student's mistakes, so that you do not have to make them on your RPPF .
- Articles >
The Moscow Metro Museum of Art: 10 Must-See Stations
There are few times one can claim having been on the subway all afternoon and loving it, but the Moscow Metro provides just that opportunity. While many cities boast famous public transport systems—New York’s subway, London’s underground, San Salvador’s chicken buses—few warrant hours of exploration. Moscow is different: Take one ride on the Metro, and you’ll find out that this network of railways can be so much more than point A to B drudgery.
The Metro began operating in 1935 with just thirteen stations, covering less than seven miles, but it has since grown into the world’s third busiest transit system ( Tokyo is first ), spanning about 200 miles and offering over 180 stops along the way. The construction of the Metro began under Joseph Stalin’s command, and being one of the USSR’s most ambitious building projects, the iron-fisted leader instructed designers to create a place full of svet (radiance) and svetloe budushchee (a radiant future), a palace for the people and a tribute to the Mother nation.
Consequently, the Metro is among the most memorable attractions in Moscow. The stations provide a unique collection of public art, comparable to anything the city’s galleries have to offer and providing a sense of the Soviet era, which is absent from the State National History Museum. Even better, touring the Metro delivers palpable, experiential moments, which many of us don’t get standing in front of painting or a case of coins.
Though tours are available , discovering the Moscow Metro on your own provides a much more comprehensive, truer experience, something much less sterile than following a guide. What better place is there to see the “real” Moscow than on mass transit: A few hours will expose you to characters and caricatures you’ll be hard-pressed to find dining near the Bolshoi Theater. You become part of the attraction, hear it in the screech of the train, feel it as hurried commuters brush by: The Metro sucks you beneath the city and churns you into the mix.
With the recommendations of our born-and-bred Muscovite students, my wife Emma and I have just taken a self-guided tour of what some locals consider the top ten stations of the Moscow Metro. What most satisfied me about our Metro tour was the sense of adventure . I loved following our route on the maps of the wagon walls as we circled the city, plotting out the course to the subsequent stops; having the weird sensation of being underground for nearly four hours; and discovering the next cavern of treasures, playing Indiana Jones for the afternoon, piecing together fragments of Russia’s mysterious history. It’s the ultimate interactive museum.
Top Ten Stations (In order of appearance)
Kievskaya station.

Kievskaya Station went public in March of 1937, the rails between it and Park Kultury Station being the first to cross the Moscow River. Kievskaya is full of mosaics depicting aristocratic scenes of Russian life, with great cameo appearances by Lenin, Trotsky, and Stalin. Each work has a Cyrillic title/explanation etched in the marble beneath it; however, if your Russian is rusty, you can just appreciate seeing familiar revolutionary dates like 1905 ( the Russian Revolution ) and 1917 ( the October Revolution ).
Mayakovskaya Station
Mayakovskaya Station ranks in my top three most notable Metro stations. Mayakovskaya just feels right, done Art Deco but no sense of gaudiness or pretention. The arches are adorned with rounded chrome piping and create feeling of being in a jukebox, but the roof’s expansive mosaics of the sky are the real showstopper. Subjects cleverly range from looking up at a high jumper, workers atop a building, spires of Orthodox cathedrals, to nimble aircraft humming by, a fleet of prop planes spelling out CCCP in the bluest of skies.
Novoslobodskaya Station

Novoslobodskaya is the Metro’s unique stained glass station. Each column has its own distinctive panels of colorful glass, most of them with a floral theme, some of them capturing the odd sailor, musician, artist, gardener, or stenographer in action. The glass is framed in Art Deco metalwork, and there is the lovely aspect of discovering panels in the less frequented haunches of the hall (on the trackside, between the incoming staircases). Novosblod is, I’ve been told, the favorite amongst out-of-town visitors.
Komsomolskaya Station
Komsomolskaya Station is one of palatial grandeur. It seems both magnificent and obligatory, like the presidential palace of a colonial city. The yellow ceiling has leafy, white concrete garland and a series of golden military mosaics accenting the tile mosaics of glorified Russian life. Switching lines here, the hallway has an Alice-in-Wonderland feel, impossibly long with decorative tile walls, culminating in a very old station left in a remarkable state of disrepair, offering a really tangible glimpse behind the palace walls.
Dostoevskaya Station

Dostoevskaya is a tribute to the late, great hero of Russian literature . The station at first glance seems bare and unimpressive, a stark marble platform without a whiff of reassembled chips of tile. However, two columns have eerie stone inlay collages of scenes from Dostoevsky’s work, including The Idiot , The Brothers Karamazov , and Crime and Punishment. Then, standing at the center of the platform, the marble creates a kaleidoscope of reflections. At the entrance, there is a large, inlay portrait of the author.
Chkalovskaya Station
Chkalovskaya does space Art Deco style (yet again). Chrome borders all. Passageways with curvy overhangs create the illusion of walking through the belly of a chic, new-age spacecraft. There are two (kos)mosaics, one at each end, with planetary subjects. Transferring here brings you above ground, where some rather elaborate metalwork is on display. By name similarity only, I’d expected Komsolskaya Station to deliver some kosmonaut décor; instead, it was Chkalovskaya that took us up to the space station.
Elektrozavodskaya Station

Elektrozavodskaya is full of marble reliefs of workers, men and women, laboring through the different stages of industry. The superhuman figures are round with muscles, Hollywood fit, and seemingly undeterred by each Herculean task they respectively perform. The station is chocked with brass, from hammer and sickle light fixtures to beautiful, angular framework up the innards of the columns. The station’s art pieces are less clever or extravagant than others, but identifying the different stages of industry is entertaining.
Baumanskaya Statio
Baumanskaya Station is the only stop that wasn’t suggested by the students. Pulling in, the network of statues was just too enticing: Out of half-circle depressions in the platform’s columns, the USSR’s proud and powerful labor force again flaunts its success. Pilots, blacksmiths, politicians, and artists have all congregated, posing amongst more Art Deco framing. At the far end, a massive Soviet flag dons the face of Lenin and banners for ’05, ’17, and ‘45. Standing in front of the flag, you can play with the echoing roof.
Ploshchad Revolutsii Station

Novokuznetskaya Station
Novokuznetskaya Station finishes off this tour, more or less, where it started: beautiful mosaics. This station recalls the skyward-facing pieces from Mayakovskaya (Station #2), only with a little larger pictures in a more cramped, very trafficked area. Due to a line of street lamps in the center of the platform, it has the atmosphere of a bustling market. The more inventive sky scenes include a man on a ladder, women picking fruit, and a tank-dozer being craned in. The station’s also has a handsome black-and-white stone mural.
Here is a map and a brief description of our route:
Start at (1)Kievskaya on the “ring line” (look for the squares at the bottom of the platform signs to help you navigate—the ring line is #5, brown line) and go north to Belorusskaya, make a quick switch to the Dark Green/#2 line, and go south one stop to (2)Mayakovskaya. Backtrack to the ring line—Brown/#5—and continue north, getting off at (3)Novosblodskaya and (4)Komsolskaya. At Komsolskaya Station, transfer to the Red/#1 line, go south for two stops to Chistye Prudy, and get on the Light Green/#10 line going north. Take a look at (5)Dostoevskaya Station on the northern segment of Light Green/#10 line then change directions and head south to (6)Chkalovskaya, which offers a transfer to the Dark Blue/#3 line, going west, away from the city center. Have a look (7)Elektroskaya Station before backtracking into the center of Moscow, stopping off at (8)Baumskaya, getting off the Dark Blue/#3 line at (9)Ploschad Revolyutsii. Change to the Dark Green/#2 line and go south one stop to see (10)Novokuznetskaya Station.
Check out our new Moscow Indie Travel Guide , book a flight to Moscow and read 10 Bars with Views Worth Blowing the Budget For
Jonathon Engels, formerly a patron saint of misadventure, has been stumbling his way across cultural borders since 2005 and is currently volunteering in the mountains outside of Antigua, Guatemala. For more of his work, visit his website and blog .

Photo credits: SergeyRod , all others courtesy of the author and may not be used without permission

40 Facts About Elektrostal
Written by Lanette Mayes
Modified & Updated: 02 Mar 2024
Reviewed by Jessica Corbett

Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to captivate you.
This article will provide you with 40 fascinating facts about Elektrostal, giving you a better understanding of why this city is worth exploring. From its origins as an industrial hub to its modern-day charm, we will delve into the various aspects that make Elektrostal a unique and must-visit destination.
So, join us as we uncover the hidden treasures of Elektrostal and discover what makes this city a true gem in the heart of Russia.
Key Takeaways:
- Elektrostal, known as the “Motor City of Russia,” is a vibrant and growing city with a rich industrial history, offering diverse cultural experiences and a strong commitment to environmental sustainability.
- With its convenient location near Moscow, Elektrostal provides a picturesque landscape, vibrant nightlife, and a range of recreational activities, making it an ideal destination for residents and visitors alike.
Known as the “Motor City of Russia.”
Elektrostal, a city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia, earned the nickname “Motor City” due to its significant involvement in the automotive industry.
Home to the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Elektrostal is renowned for its metallurgical plant, which has been producing high-quality steel and alloys since its establishment in 1916.
Boasts a rich industrial heritage.
Elektrostal has a long history of industrial development, contributing to the growth and progress of the region.
Founded in 1916.
The city of Elektrostal was founded in 1916 as a result of the construction of the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Located approximately 50 kilometers east of Moscow.
Elektrostal is situated in close proximity to the Russian capital, making it easily accessible for both residents and visitors.
Known for its vibrant cultural scene.
Elektrostal is home to several cultural institutions, including museums, theaters, and art galleries that showcase the city’s rich artistic heritage.
A popular destination for nature lovers.
Surrounded by picturesque landscapes and forests, Elektrostal offers ample opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, and birdwatching.
Hosts the annual Elektrostal City Day celebrations.
Every year, Elektrostal organizes festive events and activities to celebrate its founding, bringing together residents and visitors in a spirit of unity and joy.
Has a population of approximately 160,000 people.
Elektrostal is home to a diverse and vibrant community of around 160,000 residents, contributing to its dynamic atmosphere.
Boasts excellent education facilities.
The city is known for its well-established educational institutions, providing quality education to students of all ages.
A center for scientific research and innovation.
Elektrostal serves as an important hub for scientific research, particularly in the fields of metallurgy, materials science, and engineering.
Surrounded by picturesque lakes.
The city is blessed with numerous beautiful lakes, offering scenic views and recreational opportunities for locals and visitors alike.
Well-connected transportation system.
Elektrostal benefits from an efficient transportation network, including highways, railways, and public transportation options, ensuring convenient travel within and beyond the city.
Famous for its traditional Russian cuisine.
Food enthusiasts can indulge in authentic Russian dishes at numerous restaurants and cafes scattered throughout Elektrostal.
Home to notable architectural landmarks.
Elektrostal boasts impressive architecture, including the Church of the Transfiguration of the Lord and the Elektrostal Palace of Culture.
Offers a wide range of recreational facilities.
Residents and visitors can enjoy various recreational activities, such as sports complexes, swimming pools, and fitness centers, enhancing the overall quality of life.
Provides a high standard of healthcare.
Elektrostal is equipped with modern medical facilities, ensuring residents have access to quality healthcare services.
Home to the Elektrostal History Museum.
The Elektrostal History Museum showcases the city’s fascinating past through exhibitions and displays.
A hub for sports enthusiasts.
Elektrostal is passionate about sports, with numerous stadiums, arenas, and sports clubs offering opportunities for athletes and spectators.
Celebrates diverse cultural festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal hosts a variety of cultural festivals, celebrating different ethnicities, traditions, and art forms.
Electric power played a significant role in its early development.
Elektrostal owes its name and initial growth to the establishment of electric power stations and the utilization of electricity in the industrial sector.
Boasts a thriving economy.
The city’s strong industrial base, coupled with its strategic location near Moscow, has contributed to Elektrostal’s prosperous economic status.
Houses the Elektrostal Drama Theater.
The Elektrostal Drama Theater is a cultural centerpiece, attracting theater enthusiasts from far and wide.
Popular destination for winter sports.
Elektrostal’s proximity to ski resorts and winter sport facilities makes it a favorite destination for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter activities.
Promotes environmental sustainability.
Elektrostal prioritizes environmental protection and sustainability, implementing initiatives to reduce pollution and preserve natural resources.
Home to renowned educational institutions.
Elektrostal is known for its prestigious schools and universities, offering a wide range of academic programs to students.
Committed to cultural preservation.
The city values its cultural heritage and takes active steps to preserve and promote traditional customs, crafts, and arts.
Hosts an annual International Film Festival.
The Elektrostal International Film Festival attracts filmmakers and cinema enthusiasts from around the world, showcasing a diverse range of films.
Encourages entrepreneurship and innovation.
Elektrostal supports aspiring entrepreneurs and fosters a culture of innovation, providing opportunities for startups and business development.
Offers a range of housing options.
Elektrostal provides diverse housing options, including apartments, houses, and residential complexes, catering to different lifestyles and budgets.
Home to notable sports teams.
Elektrostal is proud of its sports legacy, with several successful sports teams competing at regional and national levels.
Boasts a vibrant nightlife scene.
Residents and visitors can enjoy a lively nightlife in Elektrostal, with numerous bars, clubs, and entertainment venues.
Promotes cultural exchange and international relations.
Elektrostal actively engages in international partnerships, cultural exchanges, and diplomatic collaborations to foster global connections.
Surrounded by beautiful nature reserves.
Nearby nature reserves, such as the Barybino Forest and Luchinskoye Lake, offer opportunities for nature enthusiasts to explore and appreciate the region’s biodiversity.
Commemorates historical events.
The city pays tribute to significant historical events through memorials, monuments, and exhibitions, ensuring the preservation of collective memory.
Promotes sports and youth development.
Elektrostal invests in sports infrastructure and programs to encourage youth participation, health, and physical fitness.
Hosts annual cultural and artistic festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal celebrates its cultural diversity through festivals dedicated to music, dance, art, and theater.
Provides a picturesque landscape for photography enthusiasts.
The city’s scenic beauty, architectural landmarks, and natural surroundings make it a paradise for photographers.
Connects to Moscow via a direct train line.
The convenient train connection between Elektrostal and Moscow makes commuting between the two cities effortless.
A city with a bright future.
Elektrostal continues to grow and develop, aiming to become a model city in terms of infrastructure, sustainability, and quality of life for its residents.
In conclusion, Elektrostal is a fascinating city with a rich history and a vibrant present. From its origins as a center of steel production to its modern-day status as a hub for education and industry, Elektrostal has plenty to offer both residents and visitors. With its beautiful parks, cultural attractions, and proximity to Moscow, there is no shortage of things to see and do in this dynamic city. Whether you’re interested in exploring its historical landmarks, enjoying outdoor activities, or immersing yourself in the local culture, Elektrostal has something for everyone. So, next time you find yourself in the Moscow region, don’t miss the opportunity to discover the hidden gems of Elektrostal.
Q: What is the population of Elektrostal?
A: As of the latest data, the population of Elektrostal is approximately XXXX.
Q: How far is Elektrostal from Moscow?
A: Elektrostal is located approximately XX kilometers away from Moscow.
Q: Are there any famous landmarks in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to several notable landmarks, including XXXX and XXXX.
Q: What industries are prominent in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal is known for its steel production industry and is also a center for engineering and manufacturing.
Q: Are there any universities or educational institutions in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to XXXX University and several other educational institutions.
Q: What are some popular outdoor activities in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal offers several outdoor activities, such as hiking, cycling, and picnicking in its beautiful parks.
Q: Is Elektrostal well-connected in terms of transportation?
A: Yes, Elektrostal has good transportation links, including trains and buses, making it easily accessible from nearby cities.
Q: Are there any annual events or festivals in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal hosts various events and festivals throughout the year, including XXXX and XXXX.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
Share this Fact:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Visual Arts Essay 1 (100 words) A visual arts essay offers a captivating journey into the universe of art, where words translate the language of visuals. It decodes the silent dialogue between the viewer and the artwork, providing a platform for in-depth analysis and interpretation. Whether focusing on a single masterpiece or an entire artistic ...
A visual analysis essay is a type of essay written mostly by students majoring in Art History and Communications. The process of visual analysis can be applied to painting, visual art, journalism, photo-journalism, photography, film, and writing. Works in these mediums are often meant to be consumed for entertainment or informative purposes.
There are dozens of ways of looking at visual art, each shaped by the creators and the various contexts in which the pieces appear. None of them are wrong, but certain methods facilitate deeper connection and understanding. In today's column, we'll explore two approaches to looking at art. First, we'll follow closely the methodology we ...
three domain specific handbooks, one each for visual arts, music and imaginative writing, there is a companion general introductory handbook which presents a more comprehensive overview of the Arts PROPEL philosophy. A HISTORY OF ARTS PROPEL IN THE VISUAL ARTS Arts PROPEL began with a series of dialogues among researchers, teachers, and
Here are 19 visual arts essay topics we have compiled just for you: From painting to filmmaking: a brief history. Leonardo da Vinci and the Golden Ratio. ... The evolution of Islamic Arts. Thank you for reading! We hope that you will find inspiration among these visual arts topic ideas. Check out our visual arts essay examples that you will ...
Reading the Visual is an invaluable introduction to visual culture for readers across the humanities and social sciences. Eloquently written, admirably clear, passionately argued, Schirato and Webb have given us one of the best textbooks on the emergent field of visual culture. Smart, clear and relevant examples challenge readers to question ...
Evaluate your visual essay for accessibility and readability, ensuring universal comprehension and enjoyment. Creating a visual story begins an exciting campaign filled with discovery, creativity ...
The visual essay is an invitation to other researchers in the arts to create their own kind of visual essays in order to address their own work of art or that of others: they can consider their ...
Description. Reading Visual Art deals with the study of art appreciation, interpretation, and criticism. It surveys techniques, composition, materials terminology, and the culture and social influences of art forms. Designed for the non-art major; this course provides the foundation for understanding the visual arts.
On the whole, it seems that students from schools all over the world are producing mostly high quality essays that show a genuine interest and sensitivity to the visual arts in a broader context. The Extended Essay teaches so many important skills: not least how to research, structure, and write an essay. If students can succeed at this in high ...
In visual art, we view our artwork as texts and read or analyze them using our visual art vocabulary and visual thinking/literacy strategies. Using art in a "text-free" environment helps early readers develop decoding and comprehension skills, while also developing their reading abilities. In addition to my role at PGCPS, I teach an online ...
ing the effects of activities such as, drawing, visual esthetics, and. dance observation. Visual art learning is reliant on a complex system of percep-. tual, higher cognitive, and mot or ...
But in these, patterns are created by light and color rather than words. Documentary and commercial photographers often use visual patterns to lead viewers to an intended meaning. Patterns are especially prominent in street art, where the elements of surrounding architecture and infrastructure interact with the work, as shown in Figure 17.5.
An extended essay in visual arts allows you to conduct study in a particular area of visual arts that is of interest to you. The conclusion of the study should be a clear and structured piece of writing that tackles a topic or research question pertinent to the visual arts in an effective manner.. The strongest EE in arts is the one that demonstrate a thoughtful selection of socially and ...
Visual arts education cultivates skills for learning. Visual arts education helps students develop critical thinking skills, which in turn lead to a deeper understanding of educational content — both within the arts and in other core subject areas. Visual arts education also fosters creativity in students and increases student engagement in the
THE IMAGE OF A SOUND (ESSAY IN READING A VISUAL ART) Show 8 more documents Show all 17 documents... Tutorial work. Date Rating. year. Ratings. Dream catcher. 2 pages 2022/2023 None. 2022/2023 None. Save. Essays. Date Rating. year. Ratings. GE20 First Exam Canuto. Reading Visual Arts. 6 pages 2021/2022 100% (1) 2021/2022 100% (1) Save ...
James Andrews presents "Narrating the Soviet Metropolis: Visual Culture in the Moscow Metro" at the Kennan Institute in Washington, D.C., on May 17, 2016. The talk, which has been made available on YouTube, was so well-received that Andrews immediately received an additional invitation to present at the Jordan Center for the Advanced Study of ...
Duration Chapter 1: Reading the Visual = 3 hours (2 hours discussion; 1 hour assessment) Lesson Proper I am driving along in a car in the country. As I drive, I am looking out the windows—straight ahead, to the right and left, through the rear-view mirror—at the sky, hills, bush, road and the other vehicles around me.
There are a few points worth considering when writing an EE in Visual Arts. Take these into consideration when reading the following essay: Be careful not to summarise secondary sources (i.e. history books on art). Focus on applying theories and ideas on art to particular artists. Avoid writing a biography on an artist.
Arts Final Exam Answers ge 10: reading visual arts final examination test test ii true true true true true false true false false 10. 10. false test essay. Skip to document. University; High School; ... Essay. Observed elements of Art. Their contribution to the over all look of the art piece. Line I saw a horizontal, vertical, curved and zigzag ...
Have a look (7)Elektroskaya Station before backtracking into the center of Moscow, stopping off at (8)Baumskaya, getting off the Dark Blue/#3 line at (9)Ploschad Revolyutsii. Change to the Dark Green/#2 line and go south one stop to see (10)Novokuznetskaya Station. Check out our new Moscow Indie Travel Guide, book a flight to Moscow and read 10 ...
40 Facts About Elektrostal. Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to ...