- Privacy Policy

Home » How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]

How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]
Table of Contents

How To Write a Research Proposal
Writing a Research proposal involves several steps to ensure a well-structured and comprehensive document. Here is an explanation of each step:
1. Title and Abstract
- Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research.
- Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal.
2. Introduction:
- Provide an introduction to your research topic, highlighting its significance and relevance.
- Clearly state the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Discuss the background and context of the study, including previous research in the field.
3. Research Objectives
- Outline the specific objectives or aims of your research. These objectives should be clear, achievable, and aligned with the research problem.
4. Literature Review:
- Conduct a comprehensive review of relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings, identify gaps, and highlight how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge.
5. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to employ to address your research objectives.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques you will use.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate and suitable for your research.
6. Timeline:
- Create a timeline or schedule that outlines the major milestones and activities of your research project.
- Break down the research process into smaller tasks and estimate the time required for each task.
7. Resources:
- Identify the resources needed for your research, such as access to specific databases, equipment, or funding.
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources to carry out your research effectively.
8. Ethical Considerations:
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise during your research and explain how you plan to address them.
- If your research involves human subjects, explain how you will ensure their informed consent and privacy.
9. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
- Clearly state the expected outcomes or results of your research.
- Highlight the potential impact and significance of your research in advancing knowledge or addressing practical issues.
10. References:
- Provide a list of all the references cited in your proposal, following a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
11. Appendices:
- Include any additional supporting materials, such as survey questionnaires, interview guides, or data analysis plans.
Research Proposal Format
The format of a research proposal may vary depending on the specific requirements of the institution or funding agency. However, the following is a commonly used format for a research proposal:
1. Title Page:
- Include the title of your research proposal, your name, your affiliation or institution, and the date.
2. Abstract:
- Provide a brief summary of your research proposal, highlighting the research problem, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
3. Introduction:
- Introduce the research topic and provide background information.
- State the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Explain the significance and relevance of the research.
- Review relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings and identify gaps in the existing knowledge.
- Explain how your research will contribute to filling those gaps.
5. Research Objectives:
- Clearly state the specific objectives or aims of your research.
- Ensure that the objectives are clear, focused, and aligned with the research problem.
6. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to use.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate for your research.
7. Timeline:
8. Resources:
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources effectively.
9. Ethical Considerations:
- If applicable, explain how you will ensure informed consent and protect the privacy of research participants.
10. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
11. References:
12. Appendices:
Research Proposal Template
Here’s a template for a research proposal:
1. Introduction:
2. Literature Review:
3. Research Objectives:
4. Methodology:
5. Timeline:
6. Resources:
7. Ethical Considerations:
8. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
9. References:
10. Appendices:
Research Proposal Sample
Title: The Impact of Online Education on Student Learning Outcomes: A Comparative Study
1. Introduction
Online education has gained significant prominence in recent years, especially due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes by comparing them with traditional face-to-face instruction. The study will explore various aspects of online education, such as instructional methods, student engagement, and academic performance, to provide insights into the effectiveness of online learning.
2. Objectives
The main objectives of this research are as follows:
- To compare student learning outcomes between online and traditional face-to-face education.
- To examine the factors influencing student engagement in online learning environments.
- To assess the effectiveness of different instructional methods employed in online education.
- To identify challenges and opportunities associated with online education and suggest recommendations for improvement.
3. Methodology
3.1 Study Design
This research will utilize a mixed-methods approach to gather both quantitative and qualitative data. The study will include the following components:
3.2 Participants
The research will involve undergraduate students from two universities, one offering online education and the other providing face-to-face instruction. A total of 500 students (250 from each university) will be selected randomly to participate in the study.
3.3 Data Collection
The research will employ the following data collection methods:
- Quantitative: Pre- and post-assessments will be conducted to measure students’ learning outcomes. Data on student demographics and academic performance will also be collected from university records.
- Qualitative: Focus group discussions and individual interviews will be conducted with students to gather their perceptions and experiences regarding online education.
3.4 Data Analysis
Quantitative data will be analyzed using statistical software, employing descriptive statistics, t-tests, and regression analysis. Qualitative data will be transcribed, coded, and analyzed thematically to identify recurring patterns and themes.
4. Ethical Considerations
The study will adhere to ethical guidelines, ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of participants. Informed consent will be obtained, and participants will have the right to withdraw from the study at any time.
5. Significance and Expected Outcomes
This research will contribute to the existing literature by providing empirical evidence on the impact of online education on student learning outcomes. The findings will help educational institutions and policymakers make informed decisions about incorporating online learning methods and improving the quality of online education. Moreover, the study will identify potential challenges and opportunities related to online education and offer recommendations for enhancing student engagement and overall learning outcomes.
6. Timeline
The proposed research will be conducted over a period of 12 months, including data collection, analysis, and report writing.
The estimated budget for this research includes expenses related to data collection, software licenses, participant compensation, and research assistance. A detailed budget breakdown will be provided in the final research plan.
8. Conclusion
This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes through a comparative study with traditional face-to-face instruction. By exploring various dimensions of online education, this research will provide valuable insights into the effectiveness and challenges associated with online learning. The findings will contribute to the ongoing discourse on educational practices and help shape future strategies for maximizing student learning outcomes in online education settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide...

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

How to choose an Appropriate Method for Research?
How To Write A Research Proposal
A Straightforward How-To Guide (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | August 2019 (Updated April 2023)
Writing up a strong research proposal for a dissertation or thesis is much like a marriage proposal. It’s a task that calls on you to win somebody over and persuade them that what you’re planning is a great idea. An idea they’re happy to say ‘yes’ to. This means that your dissertation proposal needs to be persuasive , attractive and well-planned. In this post, I’ll show you how to write a winning dissertation proposal, from scratch.
Before you start:
– Understand exactly what a research proposal is – Ask yourself these 4 questions
The 5 essential ingredients:
- The title/topic
- The introduction chapter
- The scope/delimitations
- Preliminary literature review
- Design/ methodology
- Practical considerations and risks
What Is A Research Proposal?
The research proposal is literally that: a written document that communicates what you propose to research, in a concise format. It’s where you put all that stuff that’s spinning around in your head down on to paper, in a logical, convincing fashion.
Convincing is the keyword here, as your research proposal needs to convince the assessor that your research is clearly articulated (i.e., a clear research question) , worth doing (i.e., is unique and valuable enough to justify the effort), and doable within the restrictions you’ll face (time limits, budget, skill limits, etc.). If your proposal does not address these three criteria, your research won’t be approved, no matter how “exciting” the research idea might be.
PS – if you’re completely new to proposal writing, we’ve got a detailed walkthrough video covering two successful research proposals here .

How do I know I’m ready?
Before starting the writing process, you need to ask yourself 4 important questions . If you can’t answer them succinctly and confidently, you’re not ready – you need to go back and think more deeply about your dissertation topic .
You should be able to answer the following 4 questions before starting your dissertation or thesis research proposal:
- WHAT is my main research question? (the topic)
- WHO cares and why is this important? (the justification)
- WHAT data would I need to answer this question, and how will I analyse it? (the research design)
- HOW will I manage the completion of this research, within the given timelines? (project and risk management)
If you can’t answer these questions clearly and concisely, you’re not yet ready to write your research proposal – revisit our post on choosing a topic .
If you can, that’s great – it’s time to start writing up your dissertation proposal. Next, I’ll discuss what needs to go into your research proposal, and how to structure it all into an intuitive, convincing document with a linear narrative.
The 5 Essential Ingredients
Research proposals can vary in style between institutions and disciplines, but here I’ll share with you a handy 5-section structure you can use. These 5 sections directly address the core questions we spoke about earlier, ensuring that you present a convincing proposal. If your institution already provides a proposal template, there will likely be substantial overlap with this, so you’ll still get value from reading on.
For each section discussed below, make sure you use headers and sub-headers (ideally, numbered headers) to help the reader navigate through your document, and to support them when they need to revisit a previous section. Don’t just present an endless wall of text, paragraph after paragraph after paragraph…
Top Tip: Use MS Word Styles to format headings. This will allow you to be clear about whether a sub-heading is level 2, 3, or 4. Additionally, you can view your document in ‘outline view’ which will show you only your headings. This makes it much easier to check your structure, shift things around and make decisions about where a section needs to sit. You can also generate a 100% accurate table of contents using Word’s automatic functionality.

Ingredient #1 – Topic/Title Header
Your research proposal’s title should be your main research question in its simplest form, possibly with a sub-heading providing basic details on the specifics of the study. For example:
“Compliance with equality legislation in the charity sector: a study of the ‘reasonable adjustments’ made in three London care homes”
As you can see, this title provides a clear indication of what the research is about, in broad terms. It paints a high-level picture for the first-time reader, which gives them a taste of what to expect. Always aim for a clear, concise title . Don’t feel the need to capture every detail of your research in your title – your proposal will fill in the gaps.
Need a helping hand?
Ingredient #2 – Introduction
In this section of your research proposal, you’ll expand on what you’ve communicated in the title, by providing a few paragraphs which offer more detail about your research topic. Importantly, the focus here is the topic – what will you research and why is that worth researching? This is not the place to discuss methodology, practicalities, etc. – you’ll do that later.
You should cover the following:
- An overview of the broad area you’ll be researching – introduce the reader to key concepts and language
- An explanation of the specific (narrower) area you’ll be focusing, and why you’ll be focusing there
- Your research aims and objectives
- Your research question (s) and sub-questions (if applicable)
Importantly, you should aim to use short sentences and plain language – don’t babble on with extensive jargon, acronyms and complex language. Assume that the reader is an intelligent layman – not a subject area specialist (even if they are). Remember that the best writing is writing that can be easily understood and digested. Keep it simple.

Note that some universities may want some extra bits and pieces in your introduction section. For example, personal development objectives, a structural outline, etc. Check your brief to see if there are any other details they expect in your proposal, and make sure you find a place for these.
Ingredient #3 – Scope
Next, you’ll need to specify what the scope of your research will be – this is also known as the delimitations . In other words, you need to make it clear what you will be covering and, more importantly, what you won’t be covering in your research. Simply put, this is about ring fencing your research topic so that you have a laser-sharp focus.
All too often, students feel the need to go broad and try to address as many issues as possible, in the interest of producing comprehensive research. Whilst this is admirable, it’s a mistake. By tightly refining your scope, you’ll enable yourself to go deep with your research, which is what you need to earn good marks. If your scope is too broad, you’re likely going to land up with superficial research (which won’t earn marks), so don’t be afraid to narrow things down.
Ingredient #4 – Literature Review
In this section of your research proposal, you need to provide a (relatively) brief discussion of the existing literature. Naturally, this will not be as comprehensive as the literature review in your actual dissertation, but it will lay the foundation for that. In fact, if you put in the effort at this stage, you’ll make your life a lot easier when it’s time to write your actual literature review chapter.
There are a few things you need to achieve in this section:
- Demonstrate that you’ve done your reading and are familiar with the current state of the research in your topic area.
- Show that there’s a clear gap for your specific research – i.e., show that your topic is sufficiently unique and will add value to the existing research.
- Show how the existing research has shaped your thinking regarding research design . For example, you might use scales or questionnaires from previous studies.
When you write up your literature review, keep these three objectives front of mind, especially number two (revealing the gap in the literature), so that your literature review has a clear purpose and direction . Everything you write should be contributing towards one (or more) of these objectives in some way. If it doesn’t, you need to ask yourself whether it’s truly needed.
Top Tip: Don’t fall into the trap of just describing the main pieces of literature, for example, “A says this, B says that, C also says that…” and so on. Merely describing the literature provides no value. Instead, you need to synthesise it, and use it to address the three objectives above.

Ingredient #5 – Research Methodology
Now that you’ve clearly explained both your intended research topic (in the introduction) and the existing research it will draw on (in the literature review section), it’s time to get practical and explain exactly how you’ll be carrying out your own research. In other words, your research methodology.
In this section, you’ll need to answer two critical questions :
- How will you design your research? I.e., what research methodology will you adopt, what will your sample be, how will you collect data, etc.
- Why have you chosen this design? I.e., why does this approach suit your specific research aims, objectives and questions?
In other words, this is not just about explaining WHAT you’ll be doing, it’s also about explaining WHY. In fact, the justification is the most important part , because that justification is how you demonstrate a good understanding of research design (which is what assessors want to see).
Some essential design choices you need to cover in your research proposal include:
- Your intended research philosophy (e.g., positivism, interpretivism or pragmatism )
- What methodological approach you’ll be taking (e.g., qualitative , quantitative or mixed )
- The details of your sample (e.g., sample size, who they are, who they represent, etc.)
- What data you plan to collect (i.e. data about what, in what form?)
- How you plan to collect it (e.g., surveys , interviews , focus groups, etc.)
- How you plan to analyse it (e.g., regression analysis, thematic analysis , etc.)
- Ethical adherence (i.e., does this research satisfy all ethical requirements of your institution, or does it need further approval?)
This list is not exhaustive – these are just some core attributes of research design. Check with your institution what level of detail they expect. The “ research onion ” by Saunders et al (2009) provides a good summary of the various design choices you ultimately need to make – you can read more about that here .
Don’t forget the practicalities…
In addition to the technical aspects, you will need to address the practical side of the project. In other words, you need to explain what resources you’ll need (e.g., time, money, access to equipment or software, etc.) and how you intend to secure these resources. You need to show that your project is feasible, so any “make or break” type resources need to already be secured. The success or failure of your project cannot depend on some resource which you’re not yet sure you have access to.
Another part of the practicalities discussion is project and risk management . In other words, you need to show that you have a clear project plan to tackle your research with. Some key questions to address:
- What are the timelines for each phase of your project?
- Are the time allocations reasonable?
- What happens if something takes longer than anticipated (risk management)?
- What happens if you don’t get the response rate you expect?
A good way to demonstrate that you’ve thought this through is to include a Gantt chart and a risk register (in the appendix if word count is a problem). With these two tools, you can show that you’ve got a clear, feasible plan, and you’ve thought about and accounted for the potential risks.
Tip – Be honest about the potential difficulties – but show that you are anticipating solutions and workarounds. This is much more impressive to an assessor than an unrealistically optimistic proposal which does not anticipate any challenges whatsoever.
Final Touches: Read And Simplify
The final step is to edit and proofread your proposal – very carefully. It sounds obvious, but all too often poor editing and proofreading ruin a good proposal. Nothing is more off-putting for an assessor than a poorly edited, typo-strewn document. It sends the message that you either do not pay attention to detail, or just don’t care. Neither of these are good messages. Put the effort into editing and proofreading your proposal (or pay someone to do it for you) – it will pay dividends.
When you’re editing, watch out for ‘academese’. Many students can speak simply, passionately and clearly about their dissertation topic – but become incomprehensible the moment they turn the laptop on. You are not required to write in any kind of special, formal, complex language when you write academic work. Sure, there may be technical terms, jargon specific to your discipline, shorthand terms and so on. But, apart from those, keep your written language very close to natural spoken language – just as you would speak in the classroom. Imagine that you are explaining your project plans to your classmates or a family member. Remember, write for the intelligent layman, not the subject matter experts. Plain-language, concise writing is what wins hearts and minds – and marks!
Let’s Recap: Research Proposal 101
And there you have it – how to write your dissertation or thesis research proposal, from the title page to the final proof. Here’s a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- The purpose of the research proposal is to convince – therefore, you need to make a clear, concise argument of why your research is both worth doing and doable.
- Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper.
- Title – provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms
- Introduction – explains what you’ll be researching in more detail
- Scope – explains the boundaries of your research
- Literature review – explains how your research fits into the existing research and why it’s unique and valuable
- Research methodology – explains and justifies how you will carry out your own research
Hopefully, this post has helped you better understand how to write up a winning research proposal. If you enjoyed it, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog . If your university doesn’t provide any template for your proposal, you might want to try out our free research proposal template .

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

30 Comments
Thank you so much for the valuable insight that you have given, especially on the research proposal. That is what I have managed to cover. I still need to go back to the other parts as I got disturbed while still listening to Derek’s audio on you-tube. I am inspired. I will definitely continue with Grad-coach guidance on You-tube.
Thanks for the kind words :). All the best with your proposal.
First of all, thanks a lot for making such a wonderful presentation. The video was really useful and gave me a very clear insight of how a research proposal has to be written. I shall try implementing these ideas in my RP.
Once again, I thank you for this content.
I found reading your outline on writing research proposal very beneficial. I wish there was a way of submitting my draft proposal to you guys for critiquing before I submit to the institution.
Hi Bonginkosi
Thank you for the kind words. Yes, we do provide a review service. The best starting point is to have a chat with one of our coaches here: https://gradcoach.com/book/new/ .
Hello team GRADCOACH, may God bless you so much. I was totally green in research. Am so happy for your free superb tutorials and resources. Once again thank you so much Derek and his team.
You’re welcome, Erick. Good luck with your research proposal 🙂
thank you for the information. its precise and on point.
Really a remarkable piece of writing and great source of guidance for the researchers. GOD BLESS YOU for your guidance. Regards
Thanks so much for your guidance. It is easy and comprehensive the way you explain the steps for a winning research proposal.
Thank you guys so much for the rich post. I enjoyed and learn from every word in it. My problem now is how to get into your platform wherein I can always seek help on things related to my research work ? Secondly, I wish to find out if there is a way I can send my tentative proposal to you guys for examination before I take to my supervisor Once again thanks very much for the insights
Thanks for your kind words, Desire.
If you are based in a country where Grad Coach’s paid services are available, you can book a consultation by clicking the “Book” button in the top right.
Best of luck with your studies.
May God bless you team for the wonderful work you are doing,
If I have a topic, Can I submit it to you so that you can draft a proposal for me?? As I am expecting to go for masters degree in the near future.
Thanks for your comment. We definitely cannot draft a proposal for you, as that would constitute academic misconduct. The proposal needs to be your own work. We can coach you through the process, but it needs to be your own work and your own writing.
Best of luck with your research!
I found a lot of many essential concepts from your material. it is real a road map to write a research proposal. so thanks a lot. If there is any update material on your hand on MBA please forward to me.
GradCoach is a professional website that presents support and helps for MBA student like me through the useful online information on the page and with my 1-on-1 online coaching with the amazing and professional PhD Kerryen.
Thank you Kerryen so much for the support and help 🙂
I really recommend dealing with such a reliable services provider like Gradcoah and a coach like Kerryen.
Hi, Am happy for your service and effort to help students and researchers, Please, i have been given an assignment on research for strategic development, the task one is to formulate a research proposal to support the strategic development of a business area, my issue here is how to go about it, especially the topic or title and introduction. Please, i would like to know if you could help me and how much is the charge.
This content is practical, valuable, and just great!
Thank you very much!
Hi Derek, Thank you for the valuable presentation. It is very helpful especially for beginners like me. I am just starting my PhD.
This is quite instructive and research proposal made simple. Can I have a research proposal template?
Great! Thanks for rescuing me, because I had no former knowledge in this topic. But with this piece of information, I am now secured. Thank you once more.
I enjoyed listening to your video on how to write a proposal. I think I will be able to write a winning proposal with your advice. I wish you were to be my supervisor.
Dear Derek Jansen,
Thank you for your great content. I couldn’t learn these topics in MBA, but now I learned from GradCoach. Really appreciate your efforts….
From Afghanistan!
I have got very essential inputs for startup of my dissertation proposal. Well organized properly communicated with video presentation. Thank you for the presentation.
Wow, this is absolutely amazing guys. Thank you so much for the fruitful presentation, you’ve made my research much easier.
this helps me a lot. thank you all so much for impacting in us. may god richly bless you all
How I wish I’d learn about Grad Coach earlier. I’ve been stumbling around writing and rewriting! Now I have concise clear directions on how to put this thing together. Thank you!
Fantastic!! Thank You for this very concise yet comprehensive guidance.
Even if I am poor in English I would like to thank you very much.
Thank you very much, this is very insightful.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- 301 Academic Skills Centre
- Study skills online
How to write a research proposal
Advice and guidance on writing a proposal for a student research project.

Purpose of a Research Proposal
A research proposal should describe what you will investigate, why it is important to the discipline and how you will conduct your research.
Simply put, it is your plan for the research you intend to conduct. All research proposals are designed to persuade someone about how and why your intended project is worthwhile.
In your proposal you will need to explain and defend your choices. Always think about the exact reasons why you are making specific choices and why they are the best options available to you and your project.
Your research proposal aims should be centred on:
- Relevance - You want to convince the reader how and why your research is relevant and significant to your field and how it is original. This is typically done in parts of the introduction and the literature review.
- Context - You should demonstrate that you are familiar with the field, you understand the current state of research on the topic and your ideas have a strong academic basis (i.e., not simply based on your instincts or personal views). This will be the focus of your introduction and literature review.
- Approach - You need to make a case for your methodology, showing that you have carefully thought about the data, tools and procedures you will need to conduct the research. You need to explicitly defend all of your choices. This will be presented in the research design section.
- Feasibility - You need to demonstrate clearly that your project is both reasonable and feasible within the practical constraints of the course, timescales, institution or funding. You need to make sure you have the time and access to resources to complete the project in a reasonable period.
301 Recommends:
Our Research Writing workshop will look at some of the main writing challenges associated with writing a large-scale research project and look at strategies to manage your writing on a day-to-day basis. It will identify ways to plan, organise and map out the structure of your writing to allow you to develop an effective writing schedule and make continuous progress on your dissertation project.
Proposal format
The format of a research proposal varies between fields and levels of study but most proposals should contain at least these elements: introduction, literature review, research design and reference list.
Generally, research proposals can range from 500-1500 words or one to a few pages long. Typically, proposals for larger projects such as a PhD dissertation or funding requests, are longer and much more detailed.
Remember, the goal of your research proposal is to outline clearly and concisely exactly what your research will entail and accomplish, how it will do so and why it is important. If you are writing to a strictly enforced word count, a research proposal can be a great test of your ability to express yourself concisely!
Introduction
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project, so make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why. In other words, this is where you answer the reader’s “so what?” It should typically include: introducing the topic , outlining your problem statement and research question(s) and giving background and context. Some important questions to shape your introduction include:
- Who has an interest in the topic (e.g. scientists, practitioners, policymakers, particular members of society)?
- How much is already known about the problem and why is it important?
- What is missing from current knowledge and why?
- What new insights will your research contribute?
- Why is this research worth doing?
If your proposal is very long, you might include separate sections with more detailed information on the background and context, problem statement, aims and objectives, and importance of the research.
Literature Review
It’s important to show that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review convinces the reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory (i.e. how it relates to established research in the field).
Your literature review will also show that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said. This is also where you explain why your research is necessary. You might want to consider some of the following prompts:
- Comparing and contrasting: what are the main theories, methods, debates and controversies?
- Being critical: what are the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches?
- Showing how your research fits in: how will you build on, challenge or synthesise the work of others?
- Filling a gap in the existing body of research: why is your idea innovative?
Research design and methods
Following the literature review, it is a good idea to restate your main objectives, bringing the focus back to your own project. The research design/ methodology section should describe the overall approach and practical steps you will take to answer your research questions. You also need to demonstrate the feasibility of the project keeping in mind time and other constraints.
You should definitely include:
- Qualitative vs quantitative research? Combination?
- Will you collect original data or work with primary/secondary sources?
- Is your research design descriptive, correlational or experimental? Something completely different?
- If you are undertaking your own study, when and where will you collect the data? How will you select subjects or sources? Ethics review? Exactly what or who will you study?
- What tools and procedures will you use (e.g. systematic reviews, surveys, interviews, observation, experiments, bibliographic data) to collect your data?
- What tools/methods will you use to analyse your data?
- Why are these the best methods to answer your research question(s)? This is where you should justify your choices.
- How much time will you need to collect the data?
- How will you gain access to participants and sources?
- Do you foresee any potential obstacles and if so, how will you address them?
Make sure you are not simply compiling a list of methods. Instead, aim to make an argument for why this is the most appropriate, valid and reliable way to approach answering your question. Remember you should always be defending your choices!
Implications and Contributions to Knowledge
To ensure you finish your proposal on a strong note, it is a good idea to explore and/or emphasise the potential implications of the research. This means: what do you intend to contribute to existing knowledge on the topic?
Although you cannot know the results of your research until you have actually done the work, you should be going into the project with a clear idea of how your work will contribute to your field. This section might even be considered the most critical to your research proposal’s argument because it expresses exactly why your research is necessary.
You should consider covering at least some of the following topics:
- Ways in which your work can challenge existing theories and assumptions in your field.
- How your work will create the foundation for future research and theory.
- The practical value your findings will provide to practitioners, educators and other academics in your field.
- The problems or issues your work can potentially help to resolve.
- Policies that could be impacted by your findings.
- How your findings can be implemented in academia or other settings and how this will improve or otherwise transform these settings.
This part is not about stating the specific results that you expect to obtain but rather, this is the section where you explicitly state how your findings will be valuable.
This section is where you want to wrap it all up in a nice pretty bow. It is just like the concluding paragraph that you would structure and craft for a typical essay. You should briefly summarise your research proposal and reinforce your research purpose.
Reference List or Bibliography
Your research proposal MUST include proper citations for every source you have used and full references. Please consult your departmental referencing styles to ensure you are citing and referencing in an appropriate way.
Common mistakes to avoid
Try and avoid these common pitfalls when you are writing your research proposal:
- Being too wordy: Remember formal does not mean flowery or pretentious. In fact, you should really aim to keep your writing as concise and accessible as possible. The more economically you can express your goals and ideas, the better.
- Failing to cite relevant information/sources: You are adding to the existing body of knowledge on the subject you are covering. Therefore, your research proposal should reference the main research pieces in your field (while referencing them correctly!) and connect your proposal to these works in some way. This does not mean just communicating the relevance of your work, it should explicitly demonstrate your familiarity with the field.
- Focusing too much on minor issues: Your research is most likely important for so many great reasons. However, they do not all need to be listed in your research proposal. Generally, including too many questions and issues in your research proposal can serve as a red flag and detract from your main purpose(s). This will in turn weaken your proposal. Only involve the main/key issues you plan to address.
- Failing to make a strong argument for your research: This is the simplest way to undermine your proposal. Your proposal is a piece of persuasive and critical writing . This means that, although you are presenting your proposal in an academic and hopefully objective manner, the goal is to get the reader to say ‘yes’ to your work.
- Not polishing your writing : If your proposal has spelling or grammatical errors, an inconsistent or inappropriate tone or even just awkward phrasing it can undermine your credibility. Check out some of these resources to help guide you in the right direction: Manchester Academic Phrasebank , Proofreading Guide , Essay Checklist and Grammar Guide . Remember to double and triple check your work.
Links and Resources
You might also need to include a schedule and/or a budget depending on your requirements. Some tools to help include:
- Manchester University Academic Phrasebank
- Leeds Beckett Assignment Calculator
- Calendarpedia
Related information
Dissertation planning
Writing a literature review
Research methods

Be the first to hear about our new and upcoming workshops!
The 301 Academic Skills Centre newsletter is a fortnightly email for study skills, mathematics and statistics.
Be the first to find out about our:
- new and upcoming workshops,
- special events and programmes, and
- new and relevant online materials and resources.
How to write a good research proposal (in 9 steps)
A good research proposal is one of the keys to academic success. For bachelor’s and master’s students, the quality of a research proposal often determines whether the master’s program= can be completed or not. For PhD students, a research proposal is often the first step to securing a university position. This step-by-step manual guides you through the main stages of proposal writing.
Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may earn a small commission if you make a purchase using the links below at no additional cost to you . I only recommend products or services that I truly believe can benefit my audience. As always, my opinions are my own.
1. Find a topic for your research proposal
2. develop your research idea, 3. conduct a literature review for your research proposal, 4. define a research gap and research question, 5. establish a theoretical framework for your research proposal, 6. specify an empirical focus for your research proposal, 7. emphasise the scientific and societal relevance of your research proposal, 8. develop a methodology in your research proposal, 9. illustrate your research timeline in your research proposal.
Finding a topic for your research is a crucial first step. This decision should not be treated lightly.
Writing a master’s thesis takes a minimum of several weeks. In the case of PhD dissertations, it takes years. That is a long time! You don’t want to be stuck with a topic that you don’t care about.
How to find a research topic? Start broadly: Which courses did you enjoy? What issues discussed during seminars or lectures did you like? What inspired you during your education? And which readings did you appreciate?
Take a blank piece of paper. Write down everything that comes to your mind. It will help you to reflect on your interests.
Then, think more strategically. Maybe you have a rough idea of where you would like to work after graduation. Maybe a specific sector. Or even a particular company. If so, you could strategically alight your thesis topic with an issue that matters to your dream employer. Or even ask for a thesis internship.
Once you pinpoint your general topic of interest, you need to develop your idea.
Your idea should be simultaneously original, make a scientific contribution, prepare you for the (academic) job market, and be academically sound.
Freaking out yet?! Take a deep breath.
First, keep in mind that your idea should be very focused. Master and PhD students are often too ambitious. Your time is limited. So you need to be pragmatic. It is better to make a valuable contribution to a very specific question than to aim high and fail to meet your objectives.
Second, writing a research proposal is not a linear process. Start slowly by reading literature about your topic of interest. You have an interest. You read. You rethink your idea. You look for a theoretical framework. You go back to your idea and refine it. It is a process.
Remember that a good research proposal is not written in a day.
And third, don’t forget: a good proposal aims to establish a convincing framework that will guide your future research. Not to provide all the answers already. You need to show that you have a feasible idea.

If you are looking to elevate your writing and editing skills, I highly recommend enrolling in the course “ Good with Words: Writing and Editing Specialization “, which is a 4 course series offered by the University of Michigan. This comprehensive program is conveniently available as an online course on Coursera, allowing you to learn at your own pace. Plus, upon successful completion, you’ll have the opportunity to earn a valuable certificate to showcase your newfound expertise!
Academic publications (journal articles and books) are the foundation of any research. Thus, academic literature is a good place to start. Especially when you still feel kind of lost regarding a focused research topic.
Type keywords reflecting your interests, or your preliminary research idea, into an academic search engine. It can be your university’s library, Google Scholar , Web of Science , or Scopus . etcetera.
Look at what has been published in the last 5 years, not before. You don’t want to be outdated.
Download interesting-sounding articles and read them. Repeat but be cautious: You will never be able to read EVERYTHING. So set yourself a limit, in hours, days or number of articles (20 articles, for instance).
Now, write down your findings. What is known about your topic of interest? What do scholars focus on? Start early by writing down your findings and impressions.
Once you read academic publications on your topic of interest, ask yourself questions such as:
- Is there one specific aspect of your topic of interest that is neglected in the existing literature?
- What do scholars write about the existing gaps on the topic? What are their suggestions for future research?
- Is there anything that YOU believe warrants more attention?
- Do scholars maybe analyze a phenomenon only in a specific type of setting?
Asking yourself these questions helps you to formulate your research question. In your research question, be as specific as possible.
And keep in mind that you need to research something that already exists. You cannot research how something develops 20 years into the future.

A theoretical framework is different from a literature review. You need to establish a framework of theories as a lens to look at your research topic, and answer your research question.
A theory is a general principle to explain certain phenomena. No need to reinvent the wheel here.
It is not only accepted but often encouraged to make use of existing theories. Or maybe you can combine two different theories to establish your framework.
It also helps to go back to the literature. Which theories did the authors of your favourite publications use?
There are only very few master’s and PhD theses that are entirely theoretical. Most theses, similar to most academic journal publications, have an empirical section.
You need to think about your empirical focus. Where can you find answers to your research question in real life? This could be, for instance, an experiment, a case study, or repeated observations of certain interactions.
Maybe your empirical investigation will have geographic boundaries (like focusing on one city, or one country). Or maybe it focuses on one group of people (such as the elderly, CEOs, doctors, you name it).
It is also possible to start the whole research proposal idea with empirical observation. Maybe you’ve come across something in your environment that you would like to investigate further.
Pinpoint what fascinates you about your observation. Write down keywords reflecting your interest. And then conduct a literature review to understand how others have approached this topic academically.
Both master’s and PhD students are expected to make a scientific contribution. A concrete gap or shortcoming in the existing literature on your topic is the easiest way to justify the scientific relevance of your proposed research.
Societal relevance is increasingly important in academia, too.
Do the grandparent test: Explain what you want to do to your grandparents (or any other person for that matter). Explain why it matters. Do your grandparents understand what you say? If so, well done. If not, try again.
Always remember. There is no need for fancy jargon. The best proposals are the ones that use clear, straightforward language.
The methodology is a system of methods that you will use to implement your research. A methodology explains how you plan to answer your research question.
A methodology involves for example methods of data collection. For example, interviews and questionnaires to gather ‘raw’ data.
Methods of data analysis are used to make sense of this data. This can be done, for instance, by coding, discourse analysis, mapping or statistical analysis.
Don’t underestimate the value of a good timeline. Inevitably throughout your thesis process, you will feel lost at some point. A good timeline will bring you back on track.
Make sure to include a timeline in your research proposal. If possible, not only describe your timeline but add a visual illustration, for instance in the form of a Gantt chart.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox.
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
PhD thesis types: Monograph and collection of articles
Ten reasons not to pursue an academic career, related articles.

How to address data privacy and confidentiality concerns of AI in research

How to properly use AI in academic research

The best online courses for PhD researchers in 2024

Why and how to conduct a systematic literature review
17 Research Proposal Examples

A research proposal systematically and transparently outlines a proposed research project.
The purpose of a research proposal is to demonstrate a project’s viability and the researcher’s preparedness to conduct an academic study. It serves as a roadmap for the researcher.
The process holds value both externally (for accountability purposes and often as a requirement for a grant application) and intrinsic value (for helping the researcher to clarify the mechanics, purpose, and potential signficance of the study).
Key sections of a research proposal include: the title, abstract, introduction, literature review, research design and methods, timeline, budget, outcomes and implications, references, and appendix. Each is briefly explained below.
Watch my Guide: How to Write a Research Proposal
Get your Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
Research Proposal Sample Structure
Title: The title should present a concise and descriptive statement that clearly conveys the core idea of the research projects. Make it as specific as possible. The reader should immediately be able to grasp the core idea of the intended research project. Often, the title is left too vague and does not help give an understanding of what exactly the study looks at.
Abstract: Abstracts are usually around 250-300 words and provide an overview of what is to follow – including the research problem , objectives, methods, expected outcomes, and significance of the study. Use it as a roadmap and ensure that, if the abstract is the only thing someone reads, they’ll get a good fly-by of what will be discussed in the peice.
Introduction: Introductions are all about contextualization. They often set the background information with a statement of the problem. At the end of the introduction, the reader should understand what the rationale for the study truly is. I like to see the research questions or hypotheses included in the introduction and I like to get a good understanding of what the significance of the research will be. It’s often easiest to write the introduction last
Literature Review: The literature review dives deep into the existing literature on the topic, demosntrating your thorough understanding of the existing literature including themes, strengths, weaknesses, and gaps in the literature. It serves both to demonstrate your knowledge of the field and, to demonstrate how the proposed study will fit alongside the literature on the topic. A good literature review concludes by clearly demonstrating how your research will contribute something new and innovative to the conversation in the literature.
Research Design and Methods: This section needs to clearly demonstrate how the data will be gathered and analyzed in a systematic and academically sound manner. Here, you need to demonstrate that the conclusions of your research will be both valid and reliable. Common points discussed in the research design and methods section include highlighting the research paradigm, methodologies, intended population or sample to be studied, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures . Toward the end of this section, you are encouraged to also address ethical considerations and limitations of the research process , but also to explain why you chose your research design and how you are mitigating the identified risks and limitations.
Timeline: Provide an outline of the anticipated timeline for the study. Break it down into its various stages (including data collection, data analysis, and report writing). The goal of this section is firstly to establish a reasonable breakdown of steps for you to follow and secondly to demonstrate to the assessors that your project is practicable and feasible.
Budget: Estimate the costs associated with the research project and include evidence for your estimations. Typical costs include staffing costs, equipment, travel, and data collection tools. When applying for a scholarship, the budget should demonstrate that you are being responsible with your expensive and that your funding application is reasonable.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: A discussion of the anticipated findings or results of the research, as well as the potential contributions to the existing knowledge, theory, or practice in the field. This section should also address the potential impact of the research on relevant stakeholders and any broader implications for policy or practice.
References: A complete list of all the sources cited in the research proposal, formatted according to the required citation style. This demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the relevant literature and ensures proper attribution of ideas and information.
Appendices (if applicable): Any additional materials, such as questionnaires, interview guides, or consent forms, that provide further information or support for the research proposal. These materials should be included as appendices at the end of the document.
Research Proposal Examples
Research proposals often extend anywhere between 2,000 and 15,000 words in length. The following snippets are samples designed to briefly demonstrate what might be discussed in each section.
1. Education Studies Research Proposals
See some real sample pieces:
- Assessment of the perceptions of teachers towards a new grading system
- Does ICT use in secondary classrooms help or hinder student learning?
- Digital technologies in focus project
- Urban Middle School Teachers’ Experiences of the Implementation of
- Restorative Justice Practices
- Experiences of students of color in service learning
Consider this hypothetical education research proposal:
The Impact of Game-Based Learning on Student Engagement and Academic Performance in Middle School Mathematics
Abstract: The proposed study will explore multiplayer game-based learning techniques in middle school mathematics curricula and their effects on student engagement. The study aims to contribute to the current literature on game-based learning by examining the effects of multiplayer gaming in learning.
Introduction: Digital game-based learning has long been shunned within mathematics education for fears that it may distract students or lower the academic integrity of the classrooms. However, there is emerging evidence that digital games in math have emerging benefits not only for engagement but also academic skill development. Contributing to this discourse, this study seeks to explore the potential benefits of multiplayer digital game-based learning by examining its impact on middle school students’ engagement and academic performance in a mathematics class.
Literature Review: The literature review has identified gaps in the current knowledge, namely, while game-based learning has been extensively explored, the role of multiplayer games in supporting learning has not been studied.
Research Design and Methods: This study will employ a mixed-methods research design based upon action research in the classroom. A quasi-experimental pre-test/post-test control group design will first be used to compare the academic performance and engagement of middle school students exposed to game-based learning techniques with those in a control group receiving instruction without the aid of technology. Students will also be observed and interviewed in regard to the effect of communication and collaboration during gameplay on their learning.
Timeline: The study will take place across the second term of the school year with a pre-test taking place on the first day of the term and the post-test taking place on Wednesday in Week 10.
Budget: The key budgetary requirements will be the technologies required, including the subscription cost for the identified games and computers.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: It is expected that the findings will contribute to the current literature on game-based learning and inform educational practices, providing educators and policymakers with insights into how to better support student achievement in mathematics.
2. Psychology Research Proposals
See some real examples:
- A situational analysis of shared leadership in a self-managing team
- The effect of musical preference on running performance
- Relationship between self-esteem and disordered eating amongst adolescent females
Consider this hypothetical psychology research proposal:
The Effects of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Stress Reduction in College Students
Abstract: This research proposal examines the impact of mindfulness-based interventions on stress reduction among college students, using a pre-test/post-test experimental design with both quantitative and qualitative data collection methods .
Introduction: College students face heightened stress levels during exam weeks. This can affect both mental health and test performance. This study explores the potential benefits of mindfulness-based interventions such as meditation as a way to mediate stress levels in the weeks leading up to exam time.
Literature Review: Existing research on mindfulness-based meditation has shown the ability for mindfulness to increase metacognition, decrease anxiety levels, and decrease stress. Existing literature has looked at workplace, high school and general college-level applications. This study will contribute to the corpus of literature by exploring the effects of mindfulness directly in the context of exam weeks.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n= 234 ) will be randomly assigned to either an experimental group, receiving 5 days per week of 10-minute mindfulness-based interventions, or a control group, receiving no intervention. Data will be collected through self-report questionnaires, measuring stress levels, semi-structured interviews exploring participants’ experiences, and students’ test scores.
Timeline: The study will begin three weeks before the students’ exam week and conclude after each student’s final exam. Data collection will occur at the beginning (pre-test of self-reported stress levels) and end (post-test) of the three weeks.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: The study aims to provide evidence supporting the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing stress among college students in the lead up to exams, with potential implications for mental health support and stress management programs on college campuses.
3. Sociology Research Proposals
- Understanding emerging social movements: A case study of ‘Jersey in Transition’
- The interaction of health, education and employment in Western China
- Can we preserve lower-income affordable neighbourhoods in the face of rising costs?
Consider this hypothetical sociology research proposal:
The Impact of Social Media Usage on Interpersonal Relationships among Young Adults
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effects of social media usage on interpersonal relationships among young adults, using a longitudinal mixed-methods approach with ongoing semi-structured interviews to collect qualitative data.
Introduction: Social media platforms have become a key medium for the development of interpersonal relationships, particularly for young adults. This study examines the potential positive and negative effects of social media usage on young adults’ relationships and development over time.
Literature Review: A preliminary review of relevant literature has demonstrated that social media usage is central to development of a personal identity and relationships with others with similar subcultural interests. However, it has also been accompanied by data on mental health deline and deteriorating off-screen relationships. The literature is to-date lacking important longitudinal data on these topics.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n = 454 ) will be young adults aged 18-24. Ongoing self-report surveys will assess participants’ social media usage, relationship satisfaction, and communication patterns. A subset of participants will be selected for longitudinal in-depth interviews starting at age 18 and continuing for 5 years.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of five years, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide insights into the complex relationship between social media usage and interpersonal relationships among young adults, potentially informing social policies and mental health support related to social media use.
4. Nursing Research Proposals
- Does Orthopaedic Pre-assessment clinic prepare the patient for admission to hospital?
- Nurses’ perceptions and experiences of providing psychological care to burns patients
- Registered psychiatric nurse’s practice with mentally ill parents and their children
Consider this hypothetical nursing research proposal:
The Influence of Nurse-Patient Communication on Patient Satisfaction and Health Outcomes following Emergency Cesarians
Abstract: This research will examines the impact of effective nurse-patient communication on patient satisfaction and health outcomes for women following c-sections, utilizing a mixed-methods approach with patient surveys and semi-structured interviews.
Introduction: It has long been known that effective communication between nurses and patients is crucial for quality care. However, additional complications arise following emergency c-sections due to the interaction between new mother’s changing roles and recovery from surgery.
Literature Review: A review of the literature demonstrates the importance of nurse-patient communication, its impact on patient satisfaction, and potential links to health outcomes. However, communication between nurses and new mothers is less examined, and the specific experiences of those who have given birth via emergency c-section are to date unexamined.
Research Design and Methods: Participants will be patients in a hospital setting who have recently had an emergency c-section. A self-report survey will assess their satisfaction with nurse-patient communication and perceived health outcomes. A subset of participants will be selected for in-depth interviews to explore their experiences and perceptions of the communication with their nurses.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including rolling recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing within the hospital.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the significance of nurse-patient communication in supporting new mothers who have had an emergency c-section. Recommendations will be presented for supporting nurses and midwives in improving outcomes for new mothers who had complications during birth.
5. Social Work Research Proposals
- Experiences of negotiating employment and caring responsibilities of fathers post-divorce
- Exploring kinship care in the north region of British Columbia
Consider this hypothetical social work research proposal:
The Role of a Family-Centered Intervention in Preventing Homelessness Among At-Risk Youthin a working-class town in Northern England
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effectiveness of a family-centered intervention provided by a local council area in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth. This case study will use a mixed-methods approach with program evaluation data and semi-structured interviews to collect quantitative and qualitative data .
Introduction: Homelessness among youth remains a significant social issue. This study aims to assess the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in addressing this problem and identify factors that contribute to successful prevention strategies.
Literature Review: A review of the literature has demonstrated several key factors contributing to youth homelessness including lack of parental support, lack of social support, and low levels of family involvement. It also demonstrates the important role of family-centered interventions in addressing this issue. Drawing on current evidence, this study explores the effectiveness of one such intervention in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth in a working-class town in Northern England.
Research Design and Methods: The study will evaluate a new family-centered intervention program targeting at-risk youth and their families. Quantitative data on program outcomes, including housing stability and family functioning, will be collected through program records and evaluation reports. Semi-structured interviews with program staff, participants, and relevant stakeholders will provide qualitative insights into the factors contributing to program success or failure.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Budget: Expenses include access to program evaluation data, interview materials, data analysis software, and any related travel costs for in-person interviews.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in preventing youth homelessness, potentially informing the expansion of or necessary changes to social work practices in Northern England.
Research Proposal Template
Get your Detailed Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
This is a template for a 2500-word research proposal. You may find it difficult to squeeze everything into this wordcount, but it’s a common wordcount for Honors and MA-level dissertations.
Your research proposal is where you really get going with your study. I’d strongly recommend working closely with your teacher in developing a research proposal that’s consistent with the requirements and culture of your institution, as in my experience it varies considerably. The above template is from my own courses that walk students through research proposals in a British School of Education.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 25 Humanistic Psychology Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 17 Behaviorism Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 25 Positive Psychology Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Animism Examples
8 thoughts on “17 Research Proposal Examples”
Very excellent research proposals
very helpful
Very helpful
Dear Sir, I need some help to write an educational research proposal. Thank you.

Hi Levi, use the site search bar to ask a question and I’ll likely have a guide already written for your specific question. Thanks for reading!
very good research proposal
Thank you so much sir! ❤️
Very helpful 👌
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Student Research Proposal Examples with Templates and Samples

Are you struggling with crafting an appealing student research proposal ? Research shows that an estimated 6 of 10 students face difficulties in writing proposals at least initially - often leading to stress (Edu Survey Insights 2022).
Innovation and research are at the core of progress; therefore, a thoughtful research proposal cannot be understated. A research proposal's quality and impact could make or break your academic journey in a highly competitive environment.
Don't fret; SlideTeam Student Research Proposal Templates, renowned for their innovation and versatility can help you outshine all your competitors. Our templates are well-crafted not only to simplify proposal-writing processes but to also increase the chances of approval.
Check out our blog on University Proposal Templates for result-driven outcomes!
Join us on our journey to transform the way research proposal presentation templates work!
Let's dive right in!
Template 1: Cover Letter for Academic Student Research Proposal
This PPT Slide includes essential details, including its title, student identification number, crucial university, degree program information, primary supervisor contact details, and proposal submission date. It can benefit students preparing to present their research proposal to academic committees, advisors or potential collaborators. This premium PPT Slide provides a professional yet structured introduction to the proposal, with all critical details displayed prominently.

DOWNLOAD NOW
Template 2: Abstract for Academic Student Research Proposal
Here is a professional PowerPoint Template that includes critical elements such as the subject of study, objectives of the research project, potential contributions of the thesis to society/profession/technology, anticipated outcomes/expectations, and research methods employed during the project. This Slide allows students to present an accurate and brief overview of their proposed study. Students and researchers can use this PPT Slide to convey the significance and essence of their research proposals effectively.

Template 3: Research Questions for Academic Student Research Proposal
This PPT Slide encompasses key components like sample size requirements, required methodological steps to reach objectives, additional research inquiries needed to fulfil goals, primary hypothesis statement, and expected impacts of proposed research. It serves as a crucial part of research proposal presentations, enabling students to outline their research project's fundamental inquiries and goals. Students and researchers can use this slide to outline their research questions, objectives, and expected outcomes.

Template 4: Research Method Overview for Academic Student Research Proposal
This PPT Slide covers elements such as the logical steps that guide research area processes, strategies to address research problems, specific actions to take in response to them, methods and techniques being used, target areas of study to be studied through, execution plans as well as types of research being done. This PPT Layout is an integral component of research proposal presentations, outlining the methodology employed during research projects and explicitly designed for academic students who wish to convey the systematic approach when seeking approval or feedback from advisors or committees.

Template 5: Research Constraints for Academic Student Research Proposal
This ready to use PPT Slide includes issues like lacking prior studies in an area, restricting scope or difficulties establishing significant relationships due to small sample sizes. It is a top-notch PowerPoint Template that provides you with clarity regarding potential challenges and pitfalls related to the project. Academic students can use this slide as part of their presentation to convey challenges related to their proposed research on the target population . Download now to mitigate those constraints.
Get an insight on our Research Paper Proposal Templates blog for better growth!

Template 6: Project Context and Objectives for Academic Student Research Proposal
This PPT Slide gives a comprehensive overview of your proposed research's context and objectives such as, goals it intends to meet. This Template serves as the core element in research proposal presentations by providing clarity about its purpose and what goals will be accomplished through your proposed work. Designed specifically for use by academic students to present rationale and objectives of their proposed studies to their peers. Academic students can deploy this PowerPoint Layout to provide their audience with a concise summary of their research proposal and its goals and context.

Template 7: Plan of Action for Academic Student Research Proposal
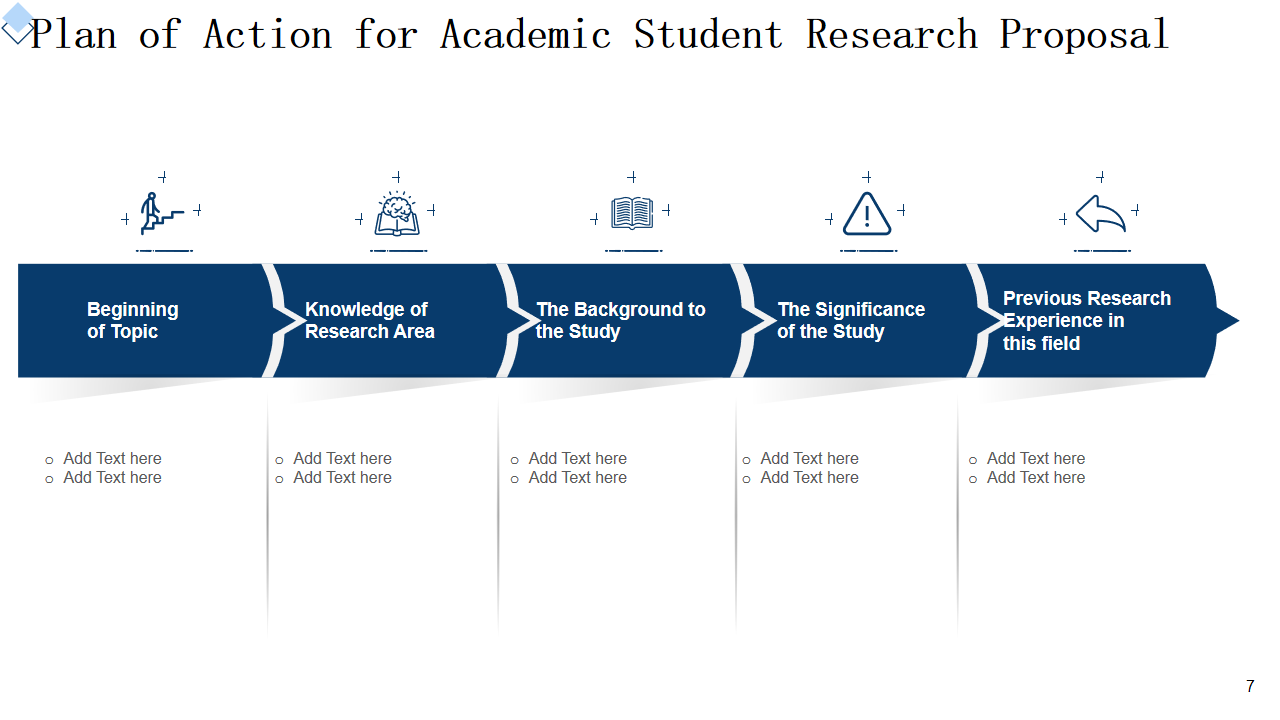
This PPT Slide outlines key components of research proposals by academic students such as, selecting their topic, outlining their knowledge, background of study, significance of study, etc. It serves as an integral element for presentation purposes by academic students presenting their proposal to demonstrate readiness and comprehension of the research process. Academic students should use this Slide to clearly communicate their research plan and preparation.
Template 8: Literature Review for Academic Student Research Proposal
This is a premium PowerPoint Template comprising key elements including a concise summation, about referenced materials, an account of previous work in the field, books or study materials consulted, and an overview of research study approach and analysis. It serves as an essential element in research proposal presentations designed for use by academic students so as to demonstrate their familiarity with existing literature as well as contextual knowledge relevant to their proposed research proposal presentation - perfect for research proposal presentations designed by academic students themselves!

Template 9: Data Analysis Strategies for Academic Student Research Proposal
This ready to use PPT Slide outlines the planned approaches for analyzing data in the proposed research. It encompasses qualitative data analysis methods such as, content analysis, narrative analysis, regression analysis and situational analysis. This PPT Diagram is a crucial component of the research proposal presentation, designed for use by academic students to convey their well-thought-out strategies for deriving meaningful insights from their data. Academic students can incorporate this PPT Template to showcase their proficiency in data analysis strategies.

Template 10: Research Project Time-frame for Academic Student Research Proposal
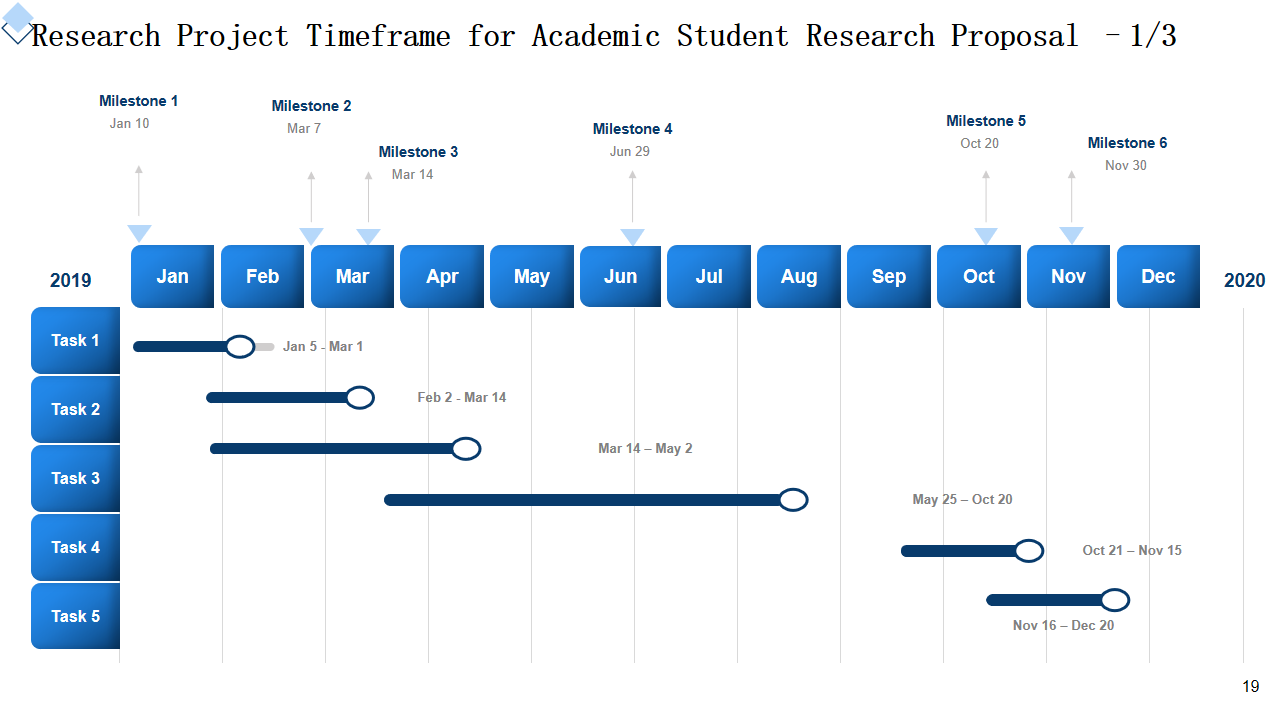
This is an actionable PPT Template that provides you with an in-depth timeline for any proposed research project. It contains milestones to mark key events during its course, weekly activities that illustrate various phases, and a map outlining all phases. It serves as an essential element in research proposal presentations by providing a clear roadmap of its timeline as well as showing its feasibility; intended to aid academic students conveying structured timelines of projects to advisors, peers or evaluators. Academic students should make use of this slide to emphasize their meticulous planning and time management abilities.
Reign Supreme with Us
Student research proposals are essential tools in academic and research pursuits. SlideTeam Templates can be invaluable, whether you are a student seeking guidance or a researcher looking to enhance their proposal by accessing their templates and samples to streamline research proposal creation and increase chances of academic success. Explore and get ahead.
Read on our blog on Proposal Cover Page Templates to make research more effective!
FAQs on Student Research Proposal
What is a student research proposal.
Student research proposals are formal documents outlining a research project or study proposed by students, which serve as blueprints for their research project or study. A good proposal includes sections such as research question/hypothesis, literature review, design methods for data collection, timeline, timeline projection and timeline plan. A well-crafted student research proposal clarifies research objectives while showing knowledge and providing guidance for conducting the study. It may serve as the basis for seeking approval, funding or academic supervision of the study.
What is a sample research proposal?
Sample research proposals serve as models or templates of research proposal documents to demonstrate how to effectively structure and present research projects. They also act as guides, providing researchers with information regarding expected formats and content requirements of proposals for research projects. Sample proposals are invaluable tools that provide a clear framework for outlining research objectives, methodologies, literature reviews and timelines. Researchers can use these sample proposals as guides when crafting their proposals to ensure they adhere to established standards and best practices. Although sample research proposals must always be customized specifically for a research project's requirements, these sample research proposals serve as applicable starting points.
What are the 7 parts of the research proposal?
An effective research proposal typically comprises seven components.
- Title: When writing the title for any research topic, its focus must be clearly communicated and capture the reader's interest quickly and succinctly.
- Introduction: This section introduces the research problem, its context, and the significance of the study. It sets the stage for your proposal.
- Literature Review: Existing research on the topic under consideration is reviewed and analyzed to demonstrate any gaps or knowledge deficits needed by this proposed research project.
- Research Objectives or Questions: Your objectives or questions for the study must be clear. Outline what you want to accomplish or investigate through your investigation.
- Methodology: Provide an in-depth and organized account of the research methods, data collection techniques, and analytic procedures you plan to employ in this section.
- Significance and Contributions: Detail your research's potential repercussions and contributions regarding relevance and importance to its field.
- Referencing: Please alphabetically list all sources and references used within your proposal using an established style (APA or MLA).
Why choose student research proposal templates?
Student Research Proposal Templates provide numerous advantages for academic and research pursuits. First, they provide a structured framework that makes creating proposals faster and more straightforward - saving time and energy. Industry experts and academic requirements have developed these templates to make your proposal comply with standards and academic regulations. Furthermore, these educational resources serve as guides on best practices for writing research proposals. Customizable and versatile templates adapt well to various research domains, making them suitable for various projects. Opting for such templates provides students a valuable resource that enhances proposal quality, fosters learning experiences, and streamlines research endeavors.
Related posts:
- Top 10 Quantitative Research Proposal Examples with Templates and Samples
- Must-have Research Proposal for Ph.D. Interview PPT Templates with Samples and Examples
- Top 10 Action Plan Proposal Templates with Examples and Samples
- Research Project Proposal Templates That Ace Your Funding Quest!
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Must-Have Team Contract Templates with Samples and Examples

Top 5 Technical Proposal Templates with Samples and Examples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage


Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.2 Steps in Developing a Research Proposal
Learning objectives.
- Identify the steps in developing a research proposal.
- Choose a topic and formulate a research question and working thesis.
- Develop a research proposal.
Writing a good research paper takes time, thought, and effort. Although this assignment is challenging, it is manageable. Focusing on one step at a time will help you develop a thoughtful, informative, well-supported research paper.
Your first step is to choose a topic and then to develop research questions, a working thesis, and a written research proposal. Set aside adequate time for this part of the process. Fully exploring ideas will help you build a solid foundation for your paper.
Choosing a Topic
When you choose a topic for a research paper, you are making a major commitment. Your choice will help determine whether you enjoy the lengthy process of research and writing—and whether your final paper fulfills the assignment requirements. If you choose your topic hastily, you may later find it difficult to work with your topic. By taking your time and choosing carefully, you can ensure that this assignment is not only challenging but also rewarding.
Writers understand the importance of choosing a topic that fulfills the assignment requirements and fits the assignment’s purpose and audience. (For more information about purpose and audience, see Chapter 6 “Writing Paragraphs: Separating Ideas and Shaping Content” .) Choosing a topic that interests you is also crucial. You instructor may provide a list of suggested topics or ask that you develop a topic on your own. In either case, try to identify topics that genuinely interest you.
After identifying potential topic ideas, you will need to evaluate your ideas and choose one topic to pursue. Will you be able to find enough information about the topic? Can you develop a paper about this topic that presents and supports your original ideas? Is the topic too broad or too narrow for the scope of the assignment? If so, can you modify it so it is more manageable? You will ask these questions during this preliminary phase of the research process.
Identifying Potential Topics
Sometimes, your instructor may provide a list of suggested topics. If so, you may benefit from identifying several possibilities before committing to one idea. It is important to know how to narrow down your ideas into a concise, manageable thesis. You may also use the list as a starting point to help you identify additional, related topics. Discussing your ideas with your instructor will help ensure that you choose a manageable topic that fits the requirements of the assignment.
In this chapter, you will follow a writer named Jorge, who is studying health care administration, as he prepares a research paper. You will also plan, research, and draft your own research paper.
Jorge was assigned to write a research paper on health and the media for an introductory course in health care. Although a general topic was selected for the students, Jorge had to decide which specific issues interested him. He brainstormed a list of possibilities.
If you are writing a research paper for a specialized course, look back through your notes and course activities. Identify reading assignments and class discussions that especially engaged you. Doing so can help you identify topics to pursue.
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) in the news
- Sexual education programs
- Hollywood and eating disorders
- Americans’ access to public health information
- Media portrayal of health care reform bill
- Depictions of drugs on television
- The effect of the Internet on mental health
- Popularized diets (such as low-carbohydrate diets)
- Fear of pandemics (bird flu, HINI, SARS)
- Electronic entertainment and obesity
- Advertisements for prescription drugs
- Public education and disease prevention
Set a timer for five minutes. Use brainstorming or idea mapping to create a list of topics you would be interested in researching for a paper about the influence of the Internet on social networking. Do you closely follow the media coverage of a particular website, such as Twitter? Would you like to learn more about a certain industry, such as online dating? Which social networking sites do you and your friends use? List as many ideas related to this topic as you can.
Narrowing Your Topic
Once you have a list of potential topics, you will need to choose one as the focus of your essay. You will also need to narrow your topic. Most writers find that the topics they listed during brainstorming or idea mapping are broad—too broad for the scope of the assignment. Working with an overly broad topic, such as sexual education programs or popularized diets, can be frustrating and overwhelming. Each topic has so many facets that it would be impossible to cover them all in a college research paper. However, more specific choices, such as the pros and cons of sexual education in kids’ television programs or the physical effects of the South Beach diet, are specific enough to write about without being too narrow to sustain an entire research paper.
A good research paper provides focused, in-depth information and analysis. If your topic is too broad, you will find it difficult to do more than skim the surface when you research it and write about it. Narrowing your focus is essential to making your topic manageable. To narrow your focus, explore your topic in writing, conduct preliminary research, and discuss both the topic and the research with others.
Exploring Your Topic in Writing
“How am I supposed to narrow my topic when I haven’t even begun researching yet?” In fact, you may already know more than you realize. Review your list and identify your top two or three topics. Set aside some time to explore each one through freewriting. (For more information about freewriting, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .) Simply taking the time to focus on your topic may yield fresh angles.
Jorge knew that he was especially interested in the topic of diet fads, but he also knew that it was much too broad for his assignment. He used freewriting to explore his thoughts so he could narrow his topic. Read Jorge’s ideas.
Conducting Preliminary Research
Another way writers may focus a topic is to conduct preliminary research . Like freewriting, exploratory reading can help you identify interesting angles. Surfing the web and browsing through newspaper and magazine articles are good ways to start. Find out what people are saying about your topic on blogs and online discussion groups. Discussing your topic with others can also inspire you. Talk about your ideas with your classmates, your friends, or your instructor.
Jorge’s freewriting exercise helped him realize that the assigned topic of health and the media intersected with a few of his interests—diet, nutrition, and obesity. Preliminary online research and discussions with his classmates strengthened his impression that many people are confused or misled by media coverage of these subjects.
Jorge decided to focus his paper on a topic that had garnered a great deal of media attention—low-carbohydrate diets. He wanted to find out whether low-carbohydrate diets were as effective as their proponents claimed.
Writing at Work
At work, you may need to research a topic quickly to find general information. This information can be useful in understanding trends in a given industry or generating competition. For example, a company may research a competitor’s prices and use the information when pricing their own product. You may find it useful to skim a variety of reliable sources and take notes on your findings.
The reliability of online sources varies greatly. In this exploratory phase of your research, you do not need to evaluate sources as closely as you will later. However, use common sense as you refine your paper topic. If you read a fascinating blog comment that gives you a new idea for your paper, be sure to check out other, more reliable sources as well to make sure the idea is worth pursuing.
Review the list of topics you created in Note 11.18 “Exercise 1” and identify two or three topics you would like to explore further. For each of these topics, spend five to ten minutes writing about the topic without stopping. Then review your writing to identify possible areas of focus.
Set aside time to conduct preliminary research about your potential topics. Then choose a topic to pursue for your research paper.
Collaboration
Please share your topic list with a classmate. Select one or two topics on his or her list that you would like to learn more about and return it to him or her. Discuss why you found the topics interesting, and learn which of your topics your classmate selected and why.
A Plan for Research
Your freewriting and preliminary research have helped you choose a focused, manageable topic for your research paper. To work with your topic successfully, you will need to determine what exactly you want to learn about it—and later, what you want to say about it. Before you begin conducting in-depth research, you will further define your focus by developing a research question , a working thesis, and a research proposal.
Formulating a Research Question
In forming a research question, you are setting a goal for your research. Your main research question should be substantial enough to form the guiding principle of your paper—but focused enough to guide your research. A strong research question requires you not only to find information but also to put together different pieces of information, interpret and analyze them, and figure out what you think. As you consider potential research questions, ask yourself whether they would be too hard or too easy to answer.
To determine your research question, review the freewriting you completed earlier. Skim through books, articles, and websites and list the questions you have. (You may wish to use the 5WH strategy to help you formulate questions. See Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” for more information about 5WH questions.) Include simple, factual questions and more complex questions that would require analysis and interpretation. Determine your main question—the primary focus of your paper—and several subquestions that you will need to research to answer your main question.
Here are the research questions Jorge will use to focus his research. Notice that his main research question has no obvious, straightforward answer. Jorge will need to research his subquestions, which address narrower topics, to answer his main question.
Using the topic you selected in Note 11.24 “Exercise 2” , write your main research question and at least four to five subquestions. Check that your main research question is appropriately complex for your assignment.
Constructing a Working ThesIs
A working thesis concisely states a writer’s initial answer to the main research question. It does not merely state a fact or present a subjective opinion. Instead, it expresses a debatable idea or claim that you hope to prove through additional research. Your working thesis is called a working thesis for a reason—it is subject to change. As you learn more about your topic, you may change your thinking in light of your research findings. Let your working thesis serve as a guide to your research, but do not be afraid to modify it based on what you learn.
Jorge began his research with a strong point of view based on his preliminary writing and research. Read his working thesis statement, which presents the point he will argue. Notice how it states Jorge’s tentative answer to his research question.
One way to determine your working thesis is to consider how you would complete sentences such as I believe or My opinion is . However, keep in mind that academic writing generally does not use first-person pronouns. These statements are useful starting points, but formal research papers use an objective voice.
Write a working thesis statement that presents your preliminary answer to the research question you wrote in Note 11.27 “Exercise 3” . Check that your working thesis statement presents an idea or claim that could be supported or refuted by evidence from research.
Creating a Research Proposal
A research proposal is a brief document—no more than one typed page—that summarizes the preliminary work you have completed. Your purpose in writing it is to formalize your plan for research and present it to your instructor for feedback. In your research proposal, you will present your main research question, related subquestions, and working thesis. You will also briefly discuss the value of researching this topic and indicate how you plan to gather information.
When Jorge began drafting his research proposal, he realized that he had already created most of the pieces he needed. However, he knew he also had to explain how his research would be relevant to other future health care professionals. In addition, he wanted to form a general plan for doing the research and identifying potentially useful sources. Read Jorge’s research proposal.

Before you begin a new project at work, you may have to develop a project summary document that states the purpose of the project, explains why it would be a wise use of company resources, and briefly outlines the steps involved in completing the project. This type of document is similar to a research proposal. Both documents define and limit a project, explain its value, discuss how to proceed, and identify what resources you will use.
Writing Your Own Research Proposal
Now you may write your own research proposal, if you have not done so already. Follow the guidelines provided in this lesson.
Key Takeaways
- Developing a research proposal involves the following preliminary steps: identifying potential ideas, choosing ideas to explore further, choosing and narrowing a topic, formulating a research question, and developing a working thesis.
- A good topic for a research paper interests the writer and fulfills the requirements of the assignment.
- Defining and narrowing a topic helps writers conduct focused, in-depth research.
- Writers conduct preliminary research to identify possible topics and research questions and to develop a working thesis.
- A good research question interests readers, is neither too broad nor too narrow, and has no obvious answer.
- A good working thesis expresses a debatable idea or claim that can be supported with evidence from research.
- Writers create a research proposal to present their topic, main research question, subquestions, and working thesis to an instructor for approval or feedback.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research
How to Write a Research Proposal as an Undergrad
As I just passed the deadline for my junior independent work (JIW), I wanted to explore strategies that could be helpful in composing a research proposal. In the chemistry department, JIW usually involves lab work and collecting raw data. However, this year, because of the pandemic, there is limited benchwork involved and most of the emphasis has shifted to designing a research proposal that would segue into one’s senior thesis. So far, I have only had one prior experience composing a research proposal, and it was from a virtual summer research program in my department. For this program, I was able to write a proposal on modifying a certain chemical inhibitor that could be used in reducing cancer cell proliferation. Using that experience as a guide, I will outline the steps I followed when I wrote my proposal. (Most of these steps are oriented towards research in the natural sciences, but there are many aspects common to research in other fields).
The first step is usually choosing a topic . This can be assigned to you by the principal investigator for the lab or a research mentor if you have one. For me, it was my research mentor, a graduate student in our lab, who helped me in selecting a field of query for my proposal. When I chose the lab I wanted to be part of for my summer project (with my JIW and senior thesis in mind) , I knew the general area of research I wanted to be involved in. But, usually within a lab, there are many projects that graduate students and post-docs work on within that specific area. Hence, it is important to identify a mentor with specific projects you want to be involved in for your own research. Once you choose a mentor, you can talk to them about formulating a research proposal based on the direction they plan to take their research in and how you can be involved in a similar project. Usually, mentors assign you one to three papers related to your research topic – a review paper that summarizes many research articles and one to two research articles with similar findings and methodology. In my case, the papers involved a review article on the role of the chemical inhibitor I was investigating along with articles on inhibitor design and mechanism of action.
The next step is to perform a literature review to broadly assess previous work in your research topic, using the articles assigned by your mentor. At this stage, for my proposal, I was trying to know as much about my research area from these papers as well as the articles cited in them. Here, it is helpful to use a reference management software such as Zotero and Mendeley to organize your notes along with all the articles you look into for a bibliography.
After going through your literature review, you can start thinking about identifying questions that remain to be answered in that field. For my JIW, I found some good ideas in the discussion section of the papers I had read where authors discussed what could be done in future research projects. One discussion section, for example, suggested ways to complement in-vitro experiments (outside of a living organism) with in-vivo ones (inside a living organism) . Reviewing the discussion section is a relatively straightforward way to formulate your own hypothesis. Alternatively, you could look at the papers’ raw data and find that the authors’ conclusions need to be revisited (this might require a critical review of the paper and the supplementary materials) or you could work on improving the paper’s methodology and optimizing its experiments. Furthermore, you might think about combining ideas from different papers or trying to reconcile differing conclusions reached by them.
The next step is developing a general outline ; deciding on what you want to cover in your proposal and how it is going to be structured. Here, you should try hard to limit the scope of your proposal to what you can realistically do for your senior thesis. As a junior or a senior, you will only be working with your mentor for a limited amount of time. Hence, it is not possible to plan long term experiments that would be appropriate for graduate students or post-docs in the lab. (For my summer project, there was not a follow up experiment involved, so I was able to think about possible experiments without the time or equipment constraints that would need to be considered for a JIW). Thus, your proposal should mostly focus on what you think is feasible given your timeline.
Below are two final considerations. It is important that your research proposal outlines how you plan to collect your own data , analyze it and compare it with other papers in your field. For a research project based on a proposal, you need only establish if your premises/hypotheses are true or false. To do that, you need to formulate questions you can answer by collecting your own data, and this is where experiments come in. My summer project had three specific aims and each one was in the form of a question.
It is important to keep in mind in your proposal the experiments you can perform efficiently on your own – the experimental skills you want to master as an undergraduate. In my view, it is better to learn one to two skills very well than having surface-level knowledge of many. This is because the nature of research has been very specialized in each field that there is limited room for broad investigations. This does not mean your proposal should be solely based on things you can test by yourself (although it might be preferable to put more emphasis there). If your proposal involves experiments beyond what you can learn to do in a year or two, you can think of asking for help from an expert in your lab.
A research proposal at the undergraduate level is an engaging exercise on coming up with your own questions on your chosen field. There is much leeway as an undergraduate to experiment within your field and think out of the box. In many ways, you will learn how to learn and how to formulate questions for any task you encounter in the future. Whether or not you want to be involved in research, it is an experience common to all Princeton students that you take with you after graduation.
In this post, I have described the basic elements of a natural science research proposal and my approach to writing one. Although the steps above are not comprehensive, I am hopeful they offer guidance you can adapt when you write your own proposal in the future.
— Yodahe Gebreegziabher, Natural Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
The goal of a research proposal is twofold: to present and justify the need to study a research problem and to present the practical ways in which the proposed study should be conducted. The design elements and procedures for conducting research are governed by standards of the predominant discipline in which the problem resides, therefore, the guidelines for research proposals are more exacting and less formal than a general project proposal. Research proposals contain extensive literature reviews. They must provide persuasive evidence that a need exists for the proposed study. In addition to providing a rationale, a proposal describes detailed methodology for conducting the research consistent with requirements of the professional or academic field and a statement on anticipated outcomes and benefits derived from the study's completion.
Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005.
How to Approach Writing a Research Proposal
Your professor may assign the task of writing a research proposal for the following reasons:
- Develop your skills in thinking about and designing a comprehensive research study;
- Learn how to conduct a comprehensive review of the literature to determine that the research problem has not been adequately addressed or has been answered ineffectively and, in so doing, become better at locating pertinent scholarship related to your topic;
- Improve your general research and writing skills;
- Practice identifying the logical steps that must be taken to accomplish one's research goals;
- Critically review, examine, and consider the use of different methods for gathering and analyzing data related to the research problem; and,
- Nurture a sense of inquisitiveness within yourself and to help see yourself as an active participant in the process of conducting scholarly research.
A proposal should contain all the key elements involved in designing a completed research study, with sufficient information that allows readers to assess the validity and usefulness of your proposed study. The only elements missing from a research proposal are the findings of the study and your analysis of those findings. Finally, an effective proposal is judged on the quality of your writing and, therefore, it is important that your proposal is coherent, clear, and compelling.
Regardless of the research problem you are investigating and the methodology you choose, all research proposals must address the following questions:
- What do you plan to accomplish? Be clear and succinct in defining the research problem and what it is you are proposing to investigate.
- Why do you want to do the research? In addition to detailing your research design, you also must conduct a thorough review of the literature and provide convincing evidence that it is a topic worthy of in-depth study. A successful research proposal must answer the "So What?" question.
- How are you going to conduct the research? Be sure that what you propose is doable. If you're having difficulty formulating a research problem to propose investigating, go here for strategies in developing a problem to study.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Failure to be concise . A research proposal must be focused and not be "all over the map" or diverge into unrelated tangents without a clear sense of purpose.
- Failure to cite landmark works in your literature review . Proposals should be grounded in foundational research that lays a foundation for understanding the development and scope of the the topic and its relevance.
- Failure to delimit the contextual scope of your research [e.g., time, place, people, etc.]. As with any research paper, your proposed study must inform the reader how and in what ways the study will frame the problem.
- Failure to develop a coherent and persuasive argument for the proposed research . This is critical. In many workplace settings, the research proposal is a formal document intended to argue for why a study should be funded.
- Sloppy or imprecise writing, or poor grammar . Although a research proposal does not represent a completed research study, there is still an expectation that it is well-written and follows the style and rules of good academic writing.
- Too much detail on minor issues, but not enough detail on major issues . Your proposal should focus on only a few key research questions in order to support the argument that the research needs to be conducted. Minor issues, even if valid, can be mentioned but they should not dominate the overall narrative.
Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Sanford, Keith. Information for Students: Writing a Research Proposal. Baylor University; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences, Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Structure and Writing Style
Beginning the Proposal Process
As with writing most college-level academic papers, research proposals are generally organized the same way throughout most social science disciplines. The text of proposals generally vary in length between ten and thirty-five pages, followed by the list of references. However, before you begin, read the assignment carefully and, if anything seems unclear, ask your professor whether there are any specific requirements for organizing and writing the proposal.
A good place to begin is to ask yourself a series of questions:
- What do I want to study?
- Why is the topic important?
- How is it significant within the subject areas covered in my class?
- What problems will it help solve?
- How does it build upon [and hopefully go beyond] research already conducted on the topic?
- What exactly should I plan to do, and can I get it done in the time available?
In general, a compelling research proposal should document your knowledge of the topic and demonstrate your enthusiasm for conducting the study. Approach it with the intention of leaving your readers feeling like, "Wow, that's an exciting idea and I can’t wait to see how it turns out!"
Most proposals should include the following sections:
I. Introduction
In the real world of higher education, a research proposal is most often written by scholars seeking grant funding for a research project or it's the first step in getting approval to write a doctoral dissertation. Even if this is just a course assignment, treat your introduction as the initial pitch of an idea based on a thorough examination of the significance of a research problem. After reading the introduction, your readers should not only have an understanding of what you want to do, but they should also be able to gain a sense of your passion for the topic and to be excited about the study's possible outcomes. Note that most proposals do not include an abstract [summary] before the introduction.
Think about your introduction as a narrative written in two to four paragraphs that succinctly answers the following four questions :
- What is the central research problem?
- What is the topic of study related to that research problem?
- What methods should be used to analyze the research problem?
- Answer the "So What?" question by explaining why this is important research, what is its significance, and why should someone reading the proposal care about the outcomes of the proposed study?
II. Background and Significance
This is where you explain the scope and context of your proposal and describe in detail why it's important. It can be melded into your introduction or you can create a separate section to help with the organization and narrative flow of your proposal. Approach writing this section with the thought that you can’t assume your readers will know as much about the research problem as you do. Note that this section is not an essay going over everything you have learned about the topic; instead, you must choose what is most relevant in explaining the aims of your research.
To that end, while there are no prescribed rules for establishing the significance of your proposed study, you should attempt to address some or all of the following:
- State the research problem and give a more detailed explanation about the purpose of the study than what you stated in the introduction. This is particularly important if the problem is complex or multifaceted .
- Present the rationale of your proposed study and clearly indicate why it is worth doing; be sure to answer the "So What? question [i.e., why should anyone care?].
- Describe the major issues or problems examined by your research. This can be in the form of questions to be addressed. Be sure to note how your proposed study builds on previous assumptions about the research problem.
- Explain the methods you plan to use for conducting your research. Clearly identify the key sources you intend to use and explain how they will contribute to your analysis of the topic.
- Describe the boundaries of your proposed research in order to provide a clear focus. Where appropriate, state not only what you plan to study, but what aspects of the research problem will be excluded from the study.
- If necessary, provide definitions of key concepts, theories, or terms.
III. Literature Review
Connected to the background and significance of your study is a section of your proposal devoted to a more deliberate review and synthesis of prior studies related to the research problem under investigation . The purpose here is to place your project within the larger whole of what is currently being explored, while at the same time, demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. Think about what questions other researchers have asked, what methodological approaches they have used, and what is your understanding of their findings and, when stated, their recommendations. Also pay attention to any suggestions for further research.
Since a literature review is information dense, it is crucial that this section is intelligently structured to enable a reader to grasp the key arguments underpinning your proposed study in relation to the arguments put forth by other researchers. A good strategy is to break the literature into "conceptual categories" [themes] rather than systematically or chronologically describing groups of materials one at a time. Note that conceptual categories generally reveal themselves after you have read most of the pertinent literature on your topic so adding new categories is an on-going process of discovery as you review more studies. How do you know you've covered the key conceptual categories underlying the research literature? Generally, you can have confidence that all of the significant conceptual categories have been identified if you start to see repetition in the conclusions or recommendations that are being made.
NOTE: Do not shy away from challenging the conclusions made in prior research as a basis for supporting the need for your proposal. Assess what you believe is missing and state how previous research has failed to adequately examine the issue that your study addresses. Highlighting the problematic conclusions strengthens your proposal. For more information on writing literature reviews, GO HERE .
To help frame your proposal's review of prior research, consider the "five C’s" of writing a literature review:
- Cite , so as to keep the primary focus on the literature pertinent to your research problem.
- Compare the various arguments, theories, methodologies, and findings expressed in the literature: what do the authors agree on? Who applies similar approaches to analyzing the research problem?
- Contrast the various arguments, themes, methodologies, approaches, and controversies expressed in the literature: describe what are the major areas of disagreement, controversy, or debate among scholars?
- Critique the literature: Which arguments are more persuasive, and why? Which approaches, findings, and methodologies seem most reliable, valid, or appropriate, and why? Pay attention to the verbs you use to describe what an author says/does [e.g., asserts, demonstrates, argues, etc.].
- Connect the literature to your own area of research and investigation: how does your own work draw upon, depart from, synthesize, or add a new perspective to what has been said in the literature?
IV. Research Design and Methods
This section must be well-written and logically organized because you are not actually doing the research, yet, your reader must have confidence that you have a plan worth pursuing . The reader will never have a study outcome from which to evaluate whether your methodological choices were the correct ones. Thus, the objective here is to convince the reader that your overall research design and proposed methods of analysis will correctly address the problem and that the methods will provide the means to effectively interpret the potential results. Your design and methods should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
Describe the overall research design by building upon and drawing examples from your review of the literature. Consider not only methods that other researchers have used, but methods of data gathering that have not been used but perhaps could be. Be specific about the methodological approaches you plan to undertake to obtain information, the techniques you would use to analyze the data, and the tests of external validity to which you commit yourself [i.e., the trustworthiness by which you can generalize from your study to other people, places, events, and/or periods of time].
When describing the methods you will use, be sure to cover the following:
- Specify the research process you will undertake and the way you will interpret the results obtained in relation to the research problem. Don't just describe what you intend to achieve from applying the methods you choose, but state how you will spend your time while applying these methods [e.g., coding text from interviews to find statements about the need to change school curriculum; running a regression to determine if there is a relationship between campaign advertising on social media sites and election outcomes in Europe ].
- Keep in mind that the methodology is not just a list of tasks; it is a deliberate argument as to why techniques for gathering information add up to the best way to investigate the research problem. This is an important point because the mere listing of tasks to be performed does not demonstrate that, collectively, they effectively address the research problem. Be sure you clearly explain this.
- Anticipate and acknowledge any potential barriers and pitfalls in carrying out your research design and explain how you plan to address them. No method applied to research in the social and behavioral sciences is perfect, so you need to describe where you believe challenges may exist in obtaining data or accessing information. It's always better to acknowledge this than to have it brought up by your professor!
V. Preliminary Suppositions and Implications
Just because you don't have to actually conduct the study and analyze the results, doesn't mean you can skip talking about the analytical process and potential implications . The purpose of this section is to argue how and in what ways you believe your research will refine, revise, or extend existing knowledge in the subject area under investigation. Depending on the aims and objectives of your study, describe how the anticipated results will impact future scholarly research, theory, practice, forms of interventions, or policy making. Note that such discussions may have either substantive [a potential new policy], theoretical [a potential new understanding], or methodological [a potential new way of analyzing] significance. When thinking about the potential implications of your study, ask the following questions:
- What might the results mean in regards to challenging the theoretical framework and underlying assumptions that support the study?
- What suggestions for subsequent research could arise from the potential outcomes of the study?
- What will the results mean to practitioners in the natural settings of their workplace, organization, or community?
- Will the results influence programs, methods, and/or forms of intervention?
- How might the results contribute to the solution of social, economic, or other types of problems?
- Will the results influence policy decisions?
- In what way do individuals or groups benefit should your study be pursued?
- What will be improved or changed as a result of the proposed research?
- How will the results of the study be implemented and what innovations or transformative insights could emerge from the process of implementation?
NOTE: This section should not delve into idle speculation, opinion, or be formulated on the basis of unclear evidence . The purpose is to reflect upon gaps or understudied areas of the current literature and describe how your proposed research contributes to a new understanding of the research problem should the study be implemented as designed.
ANOTHER NOTE : This section is also where you describe any potential limitations to your proposed study. While it is impossible to highlight all potential limitations because the study has yet to be conducted, you still must tell the reader where and in what form impediments may arise and how you plan to address them.
VI. Conclusion
The conclusion reiterates the importance or significance of your proposal and provides a brief summary of the entire study . This section should be only one or two paragraphs long, emphasizing why the research problem is worth investigating, why your research study is unique, and how it should advance existing knowledge.
Someone reading this section should come away with an understanding of:
- Why the study should be done;
- The specific purpose of the study and the research questions it attempts to answer;
- The decision for why the research design and methods used where chosen over other options;
- The potential implications emerging from your proposed study of the research problem; and
- A sense of how your study fits within the broader scholarship about the research problem.
VII. Citations
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used . In a standard research proposal, this section can take two forms, so consult with your professor about which one is preferred.
- References -- a list of only the sources you actually used in creating your proposal.
- Bibliography -- a list of everything you used in creating your proposal, along with additional citations to any key sources relevant to understanding the research problem.
In either case, this section should testify to the fact that you did enough preparatory work to ensure the project will complement and not just duplicate the efforts of other researchers. It demonstrates to the reader that you have a thorough understanding of prior research on the topic.
Most proposal formats have you start a new page and use the heading "References" or "Bibliography" centered at the top of the page. Cited works should always use a standard format that follows the writing style advised by the discipline of your course [e.g., education=APA; history=Chicago] or that is preferred by your professor. This section normally does not count towards the total page length of your research proposal.
Develop a Research Proposal: Writing the Proposal. Office of Library Information Services. Baltimore County Public Schools; Heath, M. Teresa Pereira and Caroline Tynan. “Crafting a Research Proposal.” The Marketing Review 10 (Summer 2010): 147-168; Jones, Mark. “Writing a Research Proposal.” In MasterClass in Geography Education: Transforming Teaching and Learning . Graham Butt, editor. (New York: Bloomsbury Academic, 2015), pp. 113-127; Juni, Muhamad Hanafiah. “Writing a Research Proposal.” International Journal of Public Health and Clinical Sciences 1 (September/October 2014): 229-240; Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005; Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Punch, Keith and Wayne McGowan. "Developing and Writing a Research Proposal." In From Postgraduate to Social Scientist: A Guide to Key Skills . Nigel Gilbert, ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2006), 59-81; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences , Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
- << Previous: Writing a Reflective Paper
- Next: Generative AI and Writing >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 9:45 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

- Request new password
- Create a new account
Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches
Student resources, research proposal tools and sample student proposals.
Sample research proposals written by doctoral students in each of the key areas covered in Research Design --quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods—are provided as a useful reference. A Research Proposal checklist also serves to help guide your own proposal-writing.
› Morales Proposal_Qualitative Study
› Kottich Proposal_Quantitative Study
› Guetterman Proposal_Mixed Methods Study
› Research Proposal Checklist
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
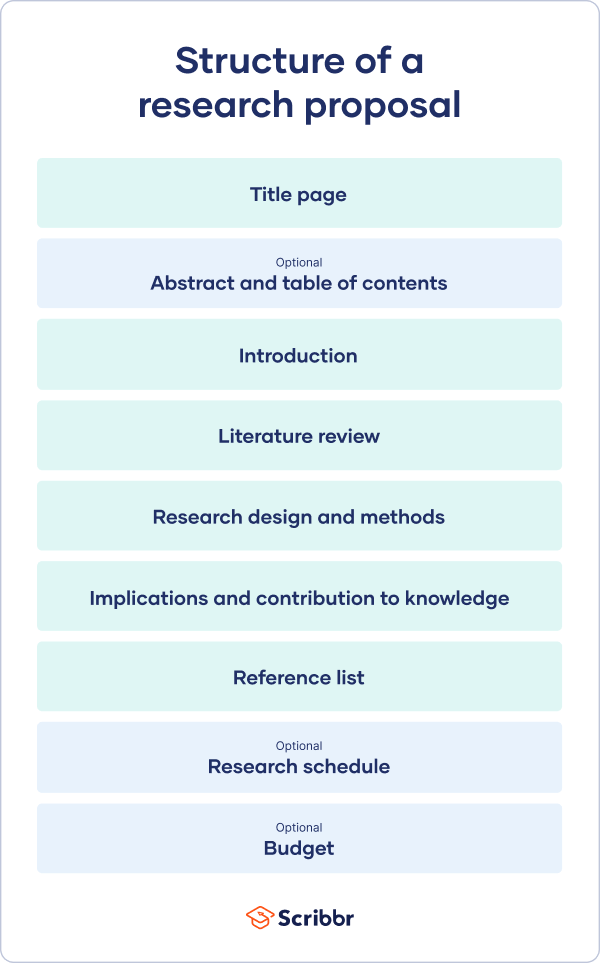
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 26 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
Sample Project Proposals
Main navigation.
Check out a few sample grant proposals below. Read ones annotated with reviewer notes (even if the topic is outside your area of interest) to learn what reviewers look for. You can also see also how resubmitted proposals respond to reviewer comments.
Please note that these proposals serve as exemplars for students applying for VPUE Student Grants. They may not be copied, retained, or distributed, and their use is subject to the Stanford Honor Code.
**To view the following samples, Stanford affiliates will be required to login with their SUNET ID. Individuals external to Stanford will not be granted access to these proposals and any requests for access will be automatically declined/deleted. **
- Arts, Creative Project, Visual Arts, Major Grant ( S. Bedford )
- Arts, Creative Writing, Chappell Lougee Scholarship ( J. Kim )
- Arts, Creative Writing, Chappell Lougee Scholarship, annotated (w/ remote plan) ( L. Laniyan )
- Arts, Music, Theater, Small Grant, annotated ( T. Pauly )
- Humanities, English, Major Grant ( J. Schaffer )
- Humanities, History, Chappell Lougee Scholarship, annotated (w/ remote plan) ( A. Kassam )
- Humanities, History, Major Grant, annotated ( J. Sonnenberg )
- Humanities, Religious Studies, Small Grant, annotated ( L. Funk )
- Humanities, Classics, Chappell Lougee Scholarship ( S. Beller )
- STEM, Biology, Major Grant, annotated ( J. Bui )
- STEM, Biology, Major Grant, annotated (w/ remote plan) ( S. Kong )
- STEM, Biology, Small Grant ( J. McGregor )
- STEM, Chemical Engineering, Major Grant ( J. O'Leary )
- STEM, Geological and Environmental Sciences, Major Grant, annotated ( V. Rosen )
- STEM, Geological and Environmental Sciences, Small Grant, annotated ( C. Kremer )
- STEM, Mathematics, Major Grant, annotated (w/ remote plan) ( M. Stevens )
- STEM, Physics, Major Grant ( J. Chaves )
- Senior Synthesis Project, Small Grant, annotated ( J. O'Leary )
- Social Science, Anthropology, Chappell Lougee Scholarship ( N. Follmann )
- Social Science, CDDRL, Small Grant ( A. Schickele )
- Social Science, Psychology, Major Grant, annotated ( C. Eggleston )
- Social Science, Sociology, Chappell Lougee Scholarship, annotated (w/ remote plan) ( A. Gomez )
- Social Science, Urban Studies, Major Grant, annotated ( K. Parish )
- Postgraduate
Research degrees
- Examples of Research proposals
- Apply for 2024
- Find a course
- Accessibility
Examples of research proposals
How to write your research proposal, with examples of good proposals.
Research proposals
Your research proposal is a key part of your application. It tells us about the question you want to answer through your research. It is a chance for you to show your knowledge of the subject area and tell us about the methods you want to use.
We use your research proposal to match you with a supervisor or team of supervisors.
In your proposal, please tell us if you have an interest in the work of a specific academic at York St John. You can get in touch with this academic to discuss your proposal. You can also speak to one of our Research Leads. There is a list of our Research Leads on the Apply page.
When you write your proposal you need to:
- Highlight how it is original or significant
- Explain how it will develop or challenge current knowledge of your subject
- Identify the importance of your research
- Show why you are the right person to do this research
- Research Proposal Example 1 (DOC, 49kB)
- Research Proposal Example 2 (DOC, 0.9MB)
- Research Proposal Example 3 (DOC, 55.5kB)
- Research Proposal Example 4 (DOC, 49.5kB)
Subject specific guidance
- Writing a Humanities PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- Writing a Creative Writing PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- About the University
- Our culture and values
- Academic schools
- Academic dates
- Press office
Our wider work
- Business support
- Work in the community
- Donate or support
Connect with us
York St John University
Lord Mayor’s Walk
01904 624 624
York St John London Campus
6th Floor Export Building
1 Clove Crescent
01904 876 944
- Policies and documents
- Module documents
- Programme specifications
- Quality gateway
- Admissions documents
- Access and Participation Plan
- Freedom of information
- Accessibility statement
- Modern slavery and human trafficking statement
© York St John University 2024
Colour Picker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Dui id ornare arcu odio.
Felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis ipsum. Et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Faucibus pulvinar elementum integer enim neque volutpat ac. Hac habitasse platea dictumst vestibulum rhoncus.
Nec ullamcorper sit amet risus nullam eget felis eget. Eget felis eget nunc lobortis mattis aliquam faucibus purus.
Research Proposal Activities
Main navigation, presentation genre game.
In this game, students practice presenting key aspects of their presentation, using different public speaking genres.
Research Proposal Planning Table
This asynchronous activity helps students thoroughly examine their research proposals with a rhetorical approach. Students not only look at different components of the research question itself, but also critically reflect on their audience and the purpose of their research to prepare for an excellent oral delivery of their research proposals.
Online Proposal Rehearsals
This activity gives students an opportunity to rehearse their oral research proposals outside of class time in small groups before receiving holistic feedback from a larger group. It is designed to be completed synchronously, in real time, in small groups.
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.
The largest-ever study of alleged racial profiling during traffic stops has found that blacks, who are pulled over more frequently than whites by day, are much less likely to be stopped after sunset, when “a veil of darkness” masks their race.
As further evidence of bias in traffic stops, Stanford researchers find that while blacks tend to get pulled over more frequently than whites, the disparity lessens at night, when a “veil of darkness” hides their face. (Image credit: Simba Munemo, Upsplash)
That is one of several examples of systematic bias that emerged from a five-year study that analyzed 95 million traffic stop records, filed by officers with 21 state patrol agencies and 35 municipal police forces from 2011 to 2018.
The Stanford-led study also found that when drivers were pulled over, officers searched the cars of blacks and Hispanics more often than whites. The researchers also examined a subset of data from Washington and Colorado, two states that legalized marijuana, and found that while this change resulted in fewer searches overall, and thus fewer searches of blacks and Hispanics, minorities were still more likely than whites to have their cars searched after a pull-over.
“Our results indicate that police stops and search decisions suffer from persistent racial bias, and point to the value of policy interventions to mitigate these disparities,” the researchers write in the May 4th issue of Nature Human Behaviour .
The paper culminates a five-year collaboration between Stanford’s Cheryl Phillips , a journalism lecturer whose graduate students obtained the raw data through public records requests, and Sharad Goel , a professor of management science and engineering whose computer science team organized and analyzed the data.
Goel and his collaborators, which included Ravi Shroff, a professor of applied statistics at New York University, spent years culling through the data, eliminating records that were incomplete or from the wrong time periods, to create the 95 million-record database that was the basis for their analysis. “There is no way to overstate the difficulty of that task,” Goel said.
Creating that database enabled the team to find the statistical evidence that a “veil of darkness” partially immunized blacks against traffic stops. That term and idea has been around since 2006 when it was used in a study that compared the race of 8,000 drivers in Oakland, California, who were stopped at any time of day or night over a six month period. But the findings from that study were inconclusive because the sample was too small to prove a link between the darkness of the sky and the race of the stopped drivers.
The Stanford team decided to repeat the analysis using the much larger dataset that they had gathered. First, they narrowed the range of variables they had to analyze by choosing a specific time of day – around 7 p.m. – when the probable causes for a stop were more or less constant. Next, they took advantage of the fact that, in the months before and after daylight saving time each year, the sky gets a little darker or lighter, day by day. Because they had such a massive database, the researchers were able to find 113,000 traffic stops, from all of the locations in their database, that occurred on those days, before or after clocks sprang forward or fell back, when the sky was growing darker or lighter at around 7 p.m. local time.
This dataset provided a statistically valid sample with two important variables – the race of the driver being stopped, and the darkness of the sky at around 7 p.m. The analysis left no doubt that the darker it got, the less likely it became that a black driver would be stopped. The reverse was true when the sky was lighter.
More than any single finding, the collaboration’s most lasting impact may be from the Stanford Open Policing Project , which the researchers started to make their data available to investigative and data-savvy reporters, and to hold workshops to help reporters learn how to use the data to do local stories. For example, the researchers helped reporters at the Seattle-based non-profit news organization, Investigate West, understand the patterns in the data for stories showing bias in police searches of Native Americans. That reporting prompted the Washington State Patrol to review its practices and boost officer training. Similarly, the researchers helped reporters at the Los Angeles Times analyze data that showed how police searched minority drivers far more often than whites. It resulted in a story that was part of a larger investigative series that prompted changes in Los Angeles Police Department practices.
“All told we’ve trained about 200 journalists, which is one of the unique things about this project,” Phillips said.
Goel and Phillips plan to continue collaborating through a project called Big Local News that will explore how data science can shed light on public issues, such as civil asset forfeitures – instances in which law enforcement is authorized to seize and sell property associated with a crime. Gathering and analyzing records of when and where such seizures occur, to whom, and how such property is disposed will help shed light on how this practice is being used. Big Local News is also working on collaborative efforts to standardize information from police disciplinary cases.
“These projects demonstrate the power of combining data science with journalism to tell important stories,” Goel said.
Other authors include current or former Stanford graduate students or research assistants Emma Pierson, Camelia Simoiu, Jan Overgoor, Sam Corbett-Davies, Daniel Jenson, Amy Shoemaker, Vignesh Ramachandran, and Phoebe Barghouty.
This work was supported in part by the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation and by the Hellman Foundation.
To read all stories about Stanford science, subscribe to the biweekly Stanford Science Digest .
Media Contacts
Tom Abate, Stanford Engineering, (650) 815-160; [email protected]
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.

- CENTERS & INSTITUTES
First-year doctoral student Ally Waters receives research grant for proposal
Posted on May 23, 2024
by Chris Hilburn-Trenkle
Ally Waters was not expecting that her graduate student research proposal would be chosen.
When she received the news in early April, while driving to meet a friend for a weekend hiking trip in Virginia, she was excited as well as surprised, she admitted.
The first-year doctoral student at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Social Work was recently awarded the Graduate Certificate in Participatory Research 2024 Seed Grant Award. Her proposal was titled, “Using Participatory Research Methods to Identify Assets and Opportunities for Diversion and Reentry Services in Rural North Carolina.”
The award is given annually to proposals that strengthen research activity for building an action-oriented learning community that supplies training and resources for carrying out research in collaboration with communities.
“I’m extremely appreciative,” Waters said. “I feel a lot of gratitude for someone seeing what I am hoping to do and encouraging it. I have also had such a warm reception from the Graduate Certificate in Participatory Research (community members) … I feel grateful for the funding, but also for the community around it.”
The idea for Waters’ proposal came to fruition thanks to a conversation she had with Woodrena Baker-Harrell, the public defender for the Orange & Chatham County Public Defender’s Office.
Waters, ‘23 (MSW), had worked with Baker-Harrell through her internship in the public defender’s office. The two still keep in touch, even though Waters now works as a clinical specialist for the Orange County Criminal Justice Resource Department, discussing ways to collaborate on research and community-engaged projects.
It was during one of those conversations when Baker-Harrell mentioned the recently established Chatham County Local Reentry Council, a group of individuals who come together to work on issues and processes and advocate for those who recently left incarceration or faced barriers due to a prior incarceration.
As Baker-Harrell shared more about the council, Waters began thinking about strategies for the organization, including the research that could be helpful to the community, goals of the council and ways that she could help support it, leading to her eventually submitting her proposal.
Waters will first meet with members of the reentry council to gain their perspectives on needs, learn what questions they want answered and get their recommendations for people to work with. From there her plan is to begin conducting interviews this summer as a data collection tool.
Although Waters plans to interview administrators of both reentry and diversion programs, she noted that the most important aspect of the project is speaking with formerly incarcerated people who can tell her which services available to them during reentry were beneficial, as well as what they would like to see changed moving forward. Some of the important needs she believes will be highlighted in interviews include housing, transportation and behavioral health treatment.
In addition to those groups, Waters plans to speak with judges in Chatham County and members of the offices of the district attorney and public defender to help form the fullest picture.
Once the interviews are complete, Waters aims to meet with reentry council members, interviewees, and other invested parties in the fall to discuss how to implement the information they received, hear the perspectives of members of the community and figure out the best ways to make the findings useful.
While Waters hopes her project helps improve reentry services for the Chatham County community, she sees her main role as doing whatever she can to help add her research perspective to the efforts underway.
“I think the big goal is to be helpful to the community in some way,” Waters said. “I have some ideas about what that might look like, but if that thing I have in mind is not actually that useful to them, pivoting so that whatever I can offer is helpful, is valuable. The goal is to support the community’s efforts at putting this local reentry council in place.”
Related Stories

Tar Heel Talents: Isabelle Borduas
UNC School of Social Work GSDI Program Manager Isabelle Borduas is working to help children across the globe while preparing for her career.

Q&A: Doctoral student Dee Williams focuses on growth of Mental Health First Aid training at UNC
We spoke with Denise “Dee” Yookong Williams, ‘25 (Ph.D.), to learn about their MHFA student doctoral grant, the growth of mental health first aid training at UNC and more.

- Enroll & Pay
- Prospective International Students
- Current International Students
- English Language Learners
- Study Abroad Students
- International Employees and Scholars
- International Partners
2024 international travel grants open for faculty and graduate students

LAWRENCE — KU International Affairs is accepting proposals and applications for travel grants that support faculty and graduate student research and collaboration abroad.
The deadline for submitting proposals and applications is March 6. Grant recipients will be notified by the end of April.
Faculty travel grants will support international travel expenses for interdisciplinary, humanistic research projects, as well as academic collaborations in Asia and Latin America. Travel grants for graduate students support internationally focused academic or training opportunities and preliminary dissertation field activities in Latin America and Africa.
The most compelling proposals will align with Jayhawks Rising’s strategic priorities of expanding KU research and its influence, furthering student success, and promoting healthy and vibrant communities.
Given out annually by KUIA, the international travel awards help foster the international orientation, expertise and outreach of KU while also enriching students’ studies.
2024 Faculty Travel Grants
The International Travel Fund for Humanistic Research supports KU faculty pursuing international interdisciplinary humanistic research abroad. Eligible faculty may receive up to $2,000 to cover airfare and related travel expenses.
The Latin America Fund , formerly the KU-UCR Exchange Support Fund, provides up to $2,000 for faculty research projects requiring travel to Latin America. Additionally, it provides up to $4,000 in travel funding for the development or maintenance of institutional exchanges, partnerships and academic collaborations between KU and counterparts at selected postsecondary institutions. The fund prioritizes helping departments and schools initiate or build relationships with peer institutions of higher learning in Latin America.
The South, Southeast, and East Asia Fund , formerly the CIK Fund, provides up to $2,000 for faculty research projects requiring travel to countries within Asia. Additionally, it provides up to $4,000 for the development or maintenance of institutional exchanges, partnerships and academic collaborations between KU and counterparts at selected postsecondary institutions. The fund prioritizes helping departments and schools initiate or build relationships with peer institutions of higher learning in South, Southeast and East Asia.
2024 Graduate Student Grants
The International Enhancement Grant provides up to $1,000 in travel expenses for graduate students to pursue relevant semester or summerlong internationally focused academic or training opportunities in Africa or Latin America that enhance their degree programs at KU. This grant supports directed, off-campus international activities in areas that do not duplicate opportunities or coursework available at KU.
The Pre-Dissertation Travel Grant provides up to $1,000 in travel expenses to graduate students to support six- to eight-week trips for preliminary dissertation field activities, such as exploring potential research sites, archives and other research resources; establishing institutional affiliations; and identifying and meeting with local scholars and contacts, as appropriate, that take place in Latin America or Africa .
Visit the KUIA travel grant website for more information.

Mumbai: Proposal seeks to make English optional for Std XI, XII students
I f the new draft proposal of the State Curriculum Framework (SCF) gets a thumbs up from stakeholders and no one objects to it, English will no longer be mandatory for Std XI and XII students in government schools and junior colleges across the state. The Maharashtra State Council for Educational Research and Training (SCERT) has invited objections and suggestions from stakeholders until June 3.
English has been a mandatory subject from Std I to XII. However, according to the draft proposal released by the SCF of SCERT on Wednesday, starting from the new academic year, students will no longer have English as a compulsory subject for Std XI and XII. Instead, they can choose two languages: one Indian and one international/foreign language, including English, the proposal suggests.
Kamaladevi Awate, in charge of SCF-SCERT , told mid-day, “This is just a draft proposal. The final draft will be prepared incorporating the feedback from the stakeholders. If the majority of stakeholders give their feedback in favour of making English an elective, we will go ahead with that. If we receive objections against the proposed change, we will not make the changes. So, it now depends on the feedback we receive.”
Multidisciplinary education
As per the draft proposal, Std XI and XII students will be able to select eight subjects in total: two languages (one has to be an Indian language and the second an international/foreign language), environmental education, physical education, and four other subjects of their choice. The SCF aims to eventually remove stream-specific (Arts, Commerce, Science) learning and promote multidisciplinary education.
“One of the languages must be of Indian origin, according to the SCF’s language chart, which lists 17 native Indian languages and nine foreign languages, with English being one of them. It will be the child`s choice, and depending on the availability at their respective school or junior college, the student can elect to study Russian, French, Spanish, German, or any other language too. The idea is to promote multilingualism in line with the NCF,” added Awate.
The list of native languages includes Marathi, Sanskrit, Hindi, Gujarati, Urdu, Kannada, Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam, Sindhi, Bengali, Punjabi, Pali, Ardhamagadhi, Maharashtri Prakrit and Avesta-Pahlavi. Tongues classified as non-native or foreign are English, German, French, Russian, Japanese, Spanish, Chinese, Persian and Arabic.
The first draft of the curriculum framework, which was largely a replica of the National Curriculum Framework for Foundation Stage (NCF-FS), was released in October last year for public feedback. The state received over 2,000 responses, following which some tweaks were made to the document. The latest draft was released on Wednesday.
Ancient wisdom
Apart from this, the new curriculum framework, prepared by a committee of education experts, also mentions the inclusion of the Indian Knowledge System—yoga, astronomy, dancing, Kathak, Odissi, etc, as part of the formal education system. The draft proposal also mentions that henceforth, experiential learning and teaching methods should be used to develop effective communication, discussion, and writing skills in languages. It states that this should include all literary genres in prose and poetry (both ancient and modern). Lifelong enrichment should be provided through reading, speaking, conversation and writing, the framework further states.

Discover the latest MyICAEW app for ACA students and members, available to download now. Find out more
- Benefits of membership
Gain access to world-leading information resources, guidance and local networks.
- Visit Benefits of membership
Becoming a member
98% of the best global brands rely on ICAEW Chartered Accountants.
- Visit Becoming a member
- Pay fees and subscriptions
Your membership subscription enables ICAEW to provide support to members.
Fees and subscriptions
Member rewards.
Take advantage of the range of value added or discounted member benefits.
- Member rewards – More from your membership
- Technical and ethics support
- Support throughout your career
Information and resources for every stage of your career.
Member Insights Survey
Let us know about the issues affecting you, your business and your clients.
- Complete the survey
From software start-ups to high-flying airlines and high street banks, 98% of the best global brands rely on ICAEW Chartered Accountants. A career as an ICAEW Chartered Accountant means the opportunity to work in any organisation, in any sector, whatever your ambitions.
Everything you need to know about ICAEW annual membership fees, community and faculty subscriptions, eligibility for reduced rates and details of how you can pay.
Membership administration
Welcome to the ICAEW members area: your portal to members'-only content, offers, discounts, regulations and membership information.
- Continuing Professional Development (CPD)
Continuing Professional Development (CPD) is an integral part of being a successful ICAEW Chartered Accountant.
The ICAEW Chartered Accountant qualification, the ACA, is one of the most advanced learning and professional development programmes available. It is valued around the world in business, practice and the public sector.

ACA for employers
Train the next generation of chartered accountants in your business or organisation. Discover how your organisation can attract, train and retain the best accountancy talent, how to become authorised to offer ACA training and the support and guidance on offer if you are already providing training.
Digital learning materials via BibliU
All ACA, ICAEW CFAB and Level 4 apprenticeship learning materials are now digital only. Read our guide on how to access your learning materials on the ICAEW Bookshelf using the BibliU app or through your browser.
- Find out more
Take a look at ICAEW training films
Focusing on professional scepticism, ethics and everyday business challenges, our training films are used by firms and companies around the world to support their in-house training and business development teams.
Attract and retain the next generation of accounting and finance professionals with our world-leading accountancy qualifications. Become authorised to offer ACA training and help your business stay ahead.
CPD guidance and help
Continuing Professional Development (CPD) is an integral part of being a successful ICAEW Chartered Accountant. Find support on ICAEW's CPD requirements and access resources to help your professional development.
ICAEW flagship events
ICAEW boasts an extensive portfolio of industry-leading conferences. These flagship events offer the opportunity to hear from and interact with all the key players in the industry. Find out what's coming up.
Leadership Development Programmes
ICAEW Academy’s in-depth leadership development programmes take a holistic approach to combine insightful mentoring or coaching, to exclusive events, peer learning groups and workshops. Catering for those significant transitions in your career, these leadership development programmes are instrumental to achieving your ambitions or fulfilling your succession planning goals.
Specialist Finance Qualifications & Programmes
Whatever future path you choose, ICAEW will support the development and acceleration of your career at each stage to enhance your career.

Why a career in chartered accountancy?
If you think chartered accountants spend their lives confined to their desks, then think again. They are sitting on the boards of multinational companies, testifying in court and advising governments, as well as supporting charities and businesses from every industry all over the world.
- Why chartered accountancy?

Search for qualified ACA jobs
Matching highly skilled ICAEW members with attractive organisations seeking talented accountancy and finance professionals.
Volunteering roles
Helping skilled and in-demand chartered accountants give back and strengthen not-for-profit sector with currently over 2,300 organisations posting a variety of volunteering roles with ICAEW.
- Search for volunteer roles
- Get ahead by volunteering
Advertise with ICAEW
From as little as £495, access to a pool of highly qualified and ambitious ACA qualified members with searchable CVs.
Early careers and training
Start your ACA training with ICAEW. Find out why a career in chartered accountancy could be for you and how to become a chartered accountant.
Qualified ACA careers
Find Accountancy and Finance Jobs
Voluntary roles
Find Voluntary roles
While you pursue the most interesting and rewarding opportunities at every stage of your career, we’re here to offer you support whatever stage you are or wherever you are in the world and in whichever sector you have chosen to work.
ACA students
"how to guides" for aca students.
- ACA student guide
- How to book an exam
- How to apply for credit for prior learning (CPL)
Exam resources
Here are some resources you will find useful while you study for the ACA qualification.
- Certificate Level
- Professional Level
- Advanced Level
Digital learning materials
All ACA learning materials are now digital only. Read our guide on how to access your learning materials on the ICAEW Bookshelf via the BibliU app, or through your browser.
- Read the guide
My online training file
Once you are registered as an ACA student, you'll be able to access your training file to log your progress throughout ACA training.
- Access your training file
- Student Insights
Fresh insights, innovative ideas and an inside look at the lives and careers of our ICAEW students and members.
- Read the latest articles
System status checks
Getting started.
Welcome to ICAEW! We have pulled together a selection of resources to help you get started with your ACA training, including our popular 'How To' series, which offers step-by-step guidance on everything from registering as an ACA student and applying for CPL, to using your online training file.
Credit for prior learning (CPL)
Credit for prior learning or CPL is our term for exemptions. High quality learning and assessment in other relevant qualifications is appropriately recognised by the award of CPL.
Apply for exams
What you need to know in order to apply for the ACA exams.
The ACA qualification has 15 modules over three levels. They are designed to complement the practical experience you will be gaining in the workplace. They will also enable you to gain in-depth knowledge across a broad range of topics in accountancy, finance and business. Here are some useful resources while you study.
- Exam results
You will receive your results for all Certificate Level exams, the day after you take the exam and usually five weeks after a Professional and Advanced Level exam session has taken place. Access your latest and archived exam results here.
Training agreement
Putting your theory work into practice is essential to complete your ACA training.
Student support and benefits
We are here to support you throughout your ACA journey. We have a range of resources and services on offer for you to unwrap, from exam resources, to student events and discount cards. Make sure you take advantage of the wealth of exclusive benefits available to you, all year round.
- Applying for membership
The ACA will open doors to limitless opportunities in all areas of accountancy, business and finance anywhere in the world. ICAEW Chartered Accountants work at the highest levels as finance directors, CEOs and partners of some of the world’s largest organisations.
ACA training FAQs
Do you have a question about the ACA training? Then look no further. Here, you can find answers to frequently asked questions relating to the ACA qualification and training. Find out more about each of the integrated components of the ACA, as well as more information on the syllabus, your training agreement, ICAEW’s rules and regulations and much more.
- Anti-money laundering
Guidance and resources to help members comply with their legal and professional responsibilities around AML.
Technical releases
ICAEW Technical Releases are a source of good practice guidance on technical and practice issues relevant to ICAEW Chartered Accountants and other finance professionals.
- ICAEW Technical Releases
- Thought leadership
ICAEW's Thought Leadership reports provide clarity and insight on the current and future challenges to the accountancy profession. Our charitable trusts also provide funding for academic research into accountancy.
- Academic research funding
Technical Advisory Services helpsheets
Practical, technical and ethical guidance highlighting the most important issues for members, whether in practice or in business.
- ICAEW Technical Advisory Services helpsheets
Bloomsbury – free for eligible firms
In partnership with Bloomsbury Professional, ICAEW have provided eligible firms with free access to Bloomsbury’s comprehensive online library of around 80 titles from leading tax and accounting subject matter experts.
- Bloomsbury Accounting and Tax Service
Country resources
Our resources by country provide access to intelligence on over 170 countries and territories including economic forecasts, guides to doing business and information on the tax climate in each jurisdiction.
Industries and sectors
Thought leadership, technical resources and professional guidance to support the professional development of members working in specific industries and sectors.
Audit and Assurance
The audit, assurance and internal audit area has information and guidance on technical and practical matters in relation to these three areas of practice. There are links to events, publications, technical help and audit representations.
The most up-to-date thought leadership, insights, technical resources and professional guidance to support ICAEW members working in and with industry with their professional development.
- Corporate Finance
Companies, advisers and investors making decisions about creating, developing and acquiring businesses – and the wide range of advisory careers that require this specialist professional expertise.
- Corporate governance
Corporate governance is the system by which companies are directed and controlled. Find out more about corporate governance principles, codes and reports, Board subcommittees, roles and responsibilities and shareholder relations. Corporate governance involves balancing the interests of a company’s many stakeholders, such as shareholders, employees, management, customers, suppliers, financiers and the community. Getting governance right is essential to build public trust in companies.
Corporate reporting
View a range of practical resources on UK GAAP, IFRS, UK regulation for company accounts and non-financial reporting. Plus find out more about the ICAEW Corporate Reporting Faculty.
Expert analysis on the latest national and international economic issues and trends, and interviews with prominent voices across the finance industry, alongside data on the state of the economy.
- Financial Services
View articles and resources on the financial services sector.
- Practice resources
For ICAEW's members in practice, this area brings together the most up-to-date thought leadership, technical resources and professional guidance to help you in your professional life.
Public Sector
Many ICAEW members work in or with the public sector to deliver public priorities and strong public finances. ICAEW acts in the public interest to support strong financial leadership and better financial management across the public sector – featuring transparency, accountability, governance and ethics – to ensure that public money is spent wisely and that public finances are sustainable.
Sustainability and climate change
Sustainability describes a world that does not live by eating into its capital, whether natural, economic or social. Members in practice, in business and private individuals all have a role to play if sustainability goals are to be met. The work being undertaken by ICAEW in this area is to change behaviour to drive sustainable outcomes.
The Tax area has information and guidance on technical and practical tax matters. There are links to events, the latest tax news and the Tax Faculty’s publications, including helpsheets, webinars and Tax representations.
Keep up-to-date with tech issues and developments, including artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, big data, and cyber security.
Trust & Ethics
Guidance and resources on key issues, including economic crime, business law, better regulation and ethics. Read through ICAEW’s Code of Ethics and supporting information.
Communities

ICAEW Communities
Information, guidance and networking opportunities on industry sectors, professional specialisms and at various stages throughout your career. Free for ICAEW members and students.
- Discover a new community

ICAEW Faculties
The accountancy profession is facing change and uncertainty. The ICAEW Faculties can help by providing you with timely and relevant support.
- Choose to join any of the faculties
UK groups and societies
We have teams on the ground in: East of England, the Midlands, London and South East, Northern, South West, Yorkshire and Humberside, Wales and Scotland.
- Access your UK region
- Worldwide support and services
Support and services we offer our members in Africa, America, Canada, the Caribbean, Europe, Greater China, the Middle East, Oceania and South East Asia.
- Discover our services
ICAEW Faculties are 'centres of technical excellence', strongly committed to enhancing your professional development and helping you to meet your CPD requirements every year. They offer exclusive content, events and webinars, customised for your sector - which you should be able to easily record, when the time comes for the completion of your CPD declaration. Our offering isn't exclusive to Institute members. As a faculty member, the same resources are available to you to ensure you stay ahead of the competition.
Communities by industry / sector
Communities by life stage and workplace, communities by professional specialism, local groups and societies.
We aim to support you wherever in the world you work. Our regional offices and network of volunteers run events and provide access to local accounting updates in major finance centres around the globe.
- Ukraine crisis: central resource hub
Learn about the actions that ICAEW members are taking to ensure that their clients comply with sanctions imposed by different countries and jurisdictions, and read about the support available from ICAEW.
Insights pulls together the best opinion, analysis, interviews, videos and podcasts on the key issues affecting accountancy and business.
- See the latest insights
- Making COP count
This series looks at the role the accountancy profession can play in addressing the climate crisis and building a sustainable economy.
- Read more on COP28
Professional development and skills
With new requirements on ICAEW members for continuing professional development, we bring together resources to support you through the changes and look at the skills accountants need for the future.
- Visit the hub
When Chartered Accountants Save The World
Find out how chartered accountants are helping to tackle some of the most urgent social challenges within the UN Sustainable Development Goals, and explore how the profession could do even more.
- Read our major series
Insights specials
A listing of one-off Insights specials that focus on a particular subject, interviewing the key people, identifying developing trends and examining the underlying issues.
Top podcasts
Insights by topic.

ICAEW Regulation

- Regulatory News
View the latest regulatory updates and guidance and subscribe to our monthly newsletter, Regulatory & Conduct News.
- Regulatory Consultations
Strengthening trust in the profession
Our role as a world-leading improvement regulator is to strengthen trust and protect the public. We do this by enabling, evaluating and enforcing the highest standards in the profession.
Regulatory applications
Find out how you can become authorised by ICAEW as a regulated firm.
ICAEW codes and regulations
Professional conduct and complaints, statutory regulated services overseen by icaew, regulations for icaew practice members and firms, additional guidance and support, popular search results.
- Training File
- Practice Exam Software
- Ethics Cpd Course
- Routes to the ACA
- ACA students membership application
- Join as a member of another body
- How much are membership fees?
- How to pay your fees
- Receipts and invoices
- What if my circumstances have changed?
- Difficulties in making changes to your membership
- Faculty and community subscription fees
- Updating your details
- Complete annual return
- Promoting myself as an ICAEW member
- Verification of ICAEW membership
- Become a life member
- Become a fellow
- Request a new certificate
- Report the death of a member
- Membership regulations
- New members
- Career progression
- Career Breakers
- Volunteering at schools and universities
- ICAEW Member App
- Working internationally
- Self employment
- Support Members Scheme
- CPD is changing
- CPD learning resources
- Your guide to CPD
- Online CPD record
- How to become a chartered accountant
- Register as a student
- Train as a member of another body
- More about the ACA and chartered accountancy
- How ACA training works
- Become a training employer
- Access the training file
- Why choose the ACA
- Training routes
- Employer support hub
- Get in touch
- Apprenticeships with ICAEW
- A-Z of CPD courses by topic
- ICAEW Business and Finance Professional (BFP)
- ICAEW Annual Conference 2024
- Audit & Assurance Conference 2024
- Restructuring & Insolvency Conference
- Virtual CPD Conference
- Virtual Healthcare Conference 2024
- All our flagship events
- Financial Talent Executive Network (F-TEN®)
- Developing Leadership in Practice (DLiP™)
- Network of Finance Leaders (NFL)
- Women in Leadership (WiL)
- Mentoring and coaching
- Partners in Learning
- Board Director's Programme e-learning
- Corporate Finance Qualification
- Diploma in Charity Accounting
- ICAEW Certificate in Insolvency
- ICAEW Data Analytics Certificate
- Financial Modeling Institute’s Advanced Financial Modeler Accreditation
- ICAEW Sustainability Certificate for Finance Professionals
- ICAEW Finance in a Digital World Programme
- All specialist qualifications
- Team training
- Start your training
- Improve your employability
- Search employers
- Find a role
- Role alerts
- Organisations
- Practice support – 11 ways ICAEW and CABA can help you
- News and advice
- ICAEW Volunteering Hub
- Support in becoming a chartered accountant
- Vacancies at ICAEW
- ICAEW boards and committees
- Exam system status
- ICAEW systems: status update
- Changes to our qualifications
- How-to guides for ACA students
- Apply for credits - Academic qualification
- Apply for credits - Professional qualification
- Credit for prior learning (CPL)/exemptions FAQs
- Applications for Professional and Advanced Level exams
- Applications for Certificate Level exams
- Tuition providers
- Latest exam results
- Archived exam results
- Getting your results
- Marks feedback service
- Exam admin check
- Training agreement: overview
- Professional development
- Ethics and professional scepticism
- Practical work experience
- Access your online training file
- How training works in your country
- Student rewards
- TOTUM PRO Card
- Student events and volunteering
- Xero cloud accounting certifications
- Student support
- Join a community
- Wellbeing support from caba
- Student mentoring programme
- Student conduct and behaviour
- Code of ethics
- Fit and proper
- Level 4 Accounting Technician Apprenticeship
- Level 7 Accountancy Professional Apprenticeship
- AAT-ACA Fast Track FAQs
- ACA rules and regulations FAQs
- ACA syllabus FAQs
- ACA training agreement FAQs
- Audit experience and the Audit Qualification FAQs
- Independent student FAQs
- Practical work experience FAQs
- Professional development FAQs
- Six-monthly reviews FAQs
- Ethics and professional scepticism FAQs
- Greater China
- Latin America
- Middle East
- North America
- Australasia
- Russia and Eurasia
- South East Asia
- Charity Community
- Construction & Real Estate
- Energy & Natural Resources Community
- Farming & Rural Business Community
- Forensic & Expert Witness
- Global Trade Community
- Healthcare Community
- Internal Audit Community
- Manufacturing Community
- Media & Leisure
- Portfolio Careers Community
- Small and Micro Business Community
- Small Practitioners Community
- Travel, Tourism & Hospitality Community
- Valuation Community
- Audit and corporate governance reform
- Audit & Assurance Faculty
- Professional judgement
- Regulation and working in audit
- Internal audit resource centre
- ICAEW acting on audit quality
- Everything business
- Latest Business news from Insights
- Strategy, risk and innovation
- Business performance management
- Financial management
- Finance transformation
- Economy and business environment
- Leadership, personal development and HR
- Webinars and publications
- Business restructuring
- The Business Finance Guide
- Capital markets and investment
- Corporate finance careers
- Corporate Finance Faculty
- Debt advisory and growth finance
- Mergers and acquisitions
- Private equity
- Start-ups, scale-ups and venture capital
- Transaction services
- Board committees and board effectiveness
- Corporate governance codes and reports
- Corporate Governance Community
- Principles of corporate governance
- Roles, duties and responsibilities of Board members
- Stewardship and stakeholder relations
- Corporate Governance thought leadership
- Corporate reporting resources
- Small and micro entity reporting
- UK Regulation for Company Accounts
- Non-financial reporting
- Improving Corporate Reporting
- Economy home
- ICAEW Business Confidence Monitor
- ICAEW Manifesto 2024
- Energy crisis
- Levelling up: rebalancing the UK’s economy
- Resilience and Renewal: Building an economy fit for the future
- Social mobility and inclusion
- Autumn Statement 2023
- Investment management
- Inspiring confidence
- Setting up in practice
- Running your practice
- Supporting your clients
- Practice technology
- TAS helpsheets
- Support for business advisers
- Join ICAEW BAS
- Public Sector hub
- Public Sector Audit and Assurance
- Public Sector Finances
- Public Sector Financial Management
- Public Sector Financial Reporting
- Public Sector Learning & Development
- Public Sector Community
- Latest public sector articles from Insights
- Climate hub
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Accountability
- Modern slavery
- Resources collection
- Sustainability Committee
- Sustainability & Climate Change community
- Sustainability and climate change home
- Tax Faculty
- Budgets and legislation
- Business tax
- Devolved taxes
- Employment taxes
- International taxes
- Making Tax Digital
- Personal tax
- Property tax
- Stamp duty land tax
- Tax administration
- Tax compliance and investigation
- UK tax rates, allowances and reliefs
- Artificial intelligence
- Blockchain and cryptoassets
- Cyber security
- Data Analytics Community
- Digital skills
- Excel community
- Finance in a Digital World
- IT management
- Technology and the profession
- Trust & Ethics home
- Better regulation
- Business Law
- UK company law
- Data protection and privacy
- Economic crime
- Help with ethical problems
- ICAEW Code of Ethics
- ICAEW Trust and Ethics team.....
- Solicitors Community
- Forensic & Expert Witness Community
- Latest articles on business law, trust and ethics
- Audit and Assurance Faculty
- Corporate Reporting Faculty
- Financial Services Faculty
- Academia & Education Community
- Construction & Real Estate Community
- Entertainment, Sport & Media Community
- Retail Community
- Career Breakers Community
- Black Members Community
- Diversity & Inclusion Community
- Women in Finance Community
- Personal Financial Planning Community
- Restructuring & Insolvency Community
- Sustainability and Climate Change Community
- London and East
- South Wales
- Yorkshire and Humberside
- European public policy activities
- ICAEW Middle East
- Latest news
- The World’s Fastest Accountant
- Access to finance special
- Attractiveness of the profession
- Audit and Fraud
- Audit and technology
- Adopting non-financial reporting standards
- Cost of doing business
- Mental health and wellbeing
- Pensions and Personal Finance
- More specials ...
- The economics of biodiversity
- How chartered accountants can help to safeguard trust in society
- Video: The financial controller who stole £20,000 from her company
- It’s time for chartered accountants to save the world
- Video: The CFO who tried to trick the market
- Video: Could invoice fraud affect your business?
- Company size thresholds and CGT on residences
- Lessons in leadership from ICAEW's CEO
- So you want to be a leader?
- A busy new tax year, plus progress on the Economic Crime Act
- Does Britain have a farming problem?
- Budget 2024: does it change anything?
- Will accountants save the world? With ICAEW CEO Michael Izza
- Crunch time: VAT (or not) on poppadoms
- Where next for audit and governance reform?
- A taxing year ahead?
- What can we expect from 2024?
- More podcasts...
- Top charts of the week
- EU and international trade
- CEO and President's insights
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Sponsored content
- Insights index
- Charter and Bye-laws
- Archive of complaints, disciplinary and fitness processes, statutory regulations and ICAEW regulations
- Qualifications regulations
- Training and education regulations
- How to make a complaint
- Guidance on your duty to report misconduct
- Public hearings
- What to do if you receive a complaint against you
- Anti-money laundering supervision
- Working in the regulated area of audit
- Local public audit in England
- Probate services
- Designated Professional Body (Investment Business) licence
- Consumer credit
- Quality Assurance monitoring: view from the firms
- The ICAEW Practice Assurance scheme
- Licensed Practice scheme
- Professional Indemnity Insurance (PII)
- Clients' Money Regulations
- Taxation (PCRT) Regulations
- ICAEW training films
- Helpsheets and guidance by topic
- ICAEW's regulatory expertise and history
- About ICAEW
- 2024 News Releases
ICAEW invites research proposals into UK VAT reform, with £5,000 prize for winning entry
Author: ICAEW
Published: 17 May 2024
SHARE THIS ARTICLE
The winning entrant will receive a £5,000 prize and the opportunity to present their research at a VAT Conference to be held at Chartered Accountants’ Hall in London in 2025.
ICAEW is seeking innovative and practical ideas, in no more than 2,000 words, on how to reform the UK’s VAT system to meet the challenges of the coming decade. The successful proposal should identify current challenges within the system and might explore the potential impact of a modernised VAT system on consumer behaviour, economic growth, or fiscal stability.
A survey of members of the OECD’s Forum on Tax Administration found that the UK’s VAT system is more burdensome on business than those of countries with a modern VAT system, such as Singapore, New Zealand and Australia. [1]
The complexity of UK VAT hinders effective policymaking, reduces the efficiency of tax collection and administration, and presents a barrier to HMRC’s digitalisation efforts, ICAEW said.
Authors are encouraged to look at international examples of successful VAT reforms and consider how these lessons can be applied to the UK, in the context of the evolving global landscape and the UK’s post-Brexit autonomy.
Ed Saltmarsh, ICAEW Technical Manager, VAT and Customs, said:
“The UK has one of the most complex systems of VAT in the developed world, hindering businesses and HMRC, and ultimately impacting taxpayers and consumers. The VAT registration threshold stifles small business growth, while the numerous exemptions and zero rates create uncertainty and can lead to absurd disputes, such as whether poppadoms are crisps or Jaffa cakes are biscuits.
“We’re looking forward to seeing the VAT reform ideas that entrants come up with to tackle the challenges of the next decade and wish all entrants the best of luck.”
Notes to editors:
CONTACT: ICAEW media office media.office@icaew or [email protected] or 07889 894431
- An assessment of the VAT compliance burden across 47 member countries of the Forum on Tax Administration found that the UK’s VAT compliance burden is higher than that in countries with a modern VAT system, such as Singapore, New Zealand and Australia. The study was co-authored by Richard Highfield, Christopher Charles Evans, Binh Tran-Nam, and Michael Walpole.
- Find out more about ICAEW's invitation for research proposals into the simplification of the UK’s VAT system.
Read out this code to the operator.

COMMENTS
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of ...
Research Proposal Example/Sample. Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level ...
The research will involve undergraduate students from two universities, one offering online education and the other providing face-to-face instruction. A total of 500 students (250 from each university) will be selected randomly to participate in the study. ... This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student ...
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face). The most important word here is "convince" - in other words, your ...
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components : Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
A research proposal is a short piece of academic writing that outlines the research a graduate student intends to carry out. It starts by explaining why the research will be helpful or necessary, then describes the steps of the potential research and how the research project would add further knowledge to the field of study.
Experience has shown that students tend to encounter difficulties in writing research proposals for their supervisors because they do not fully comprehend what constitutes a research proposal. The purpose of this article is to take students through a step-by-step process of writing good research proposals by discussing the essential ingredients ...
The format of a research proposal varies between fields and levels of study but most proposals should contain at least these elements: introduction, literature review, research design and reference list. Generally, research proposals can range from 500-1500 words or one to a few pages long. Typically, proposals for larger projects such as a PhD ...
A good research proposal is one of the keys to academic success. For bachelor's and master's students, the quality of a research proposal often determines whether the master's program= can be completed or not. For PhD students, a research proposal is often the first step to securing a university position. This step-by-step manual guides you
The Effects of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Stress Reduction in College Students. Abstract: This research proposal examines the impact of mindfulness-based interventions on stress reduction among college students, using a pre-test/post-test experimental design with both quantitative and qualitative data collection methods. Introduction: College students face heightened stress levels ...
Template 10: Research Project Time-frame for Academic Student Research Proposal. This is an actionable PPT Template that provides you with an in-depth timeline for any proposed research project. It contains milestones to mark key events during its course, weekly activities that illustrate various phases, and a map outlining all phases.
Key Takeaways. Developing a research proposal involves the following preliminary steps: identifying potential ideas, choosing ideas to explore further, choosing and narrowing a topic, formulating a research question, and developing a working thesis. A good topic for a research paper interests the writer and fulfills the requirements of the ...
For me, it was my research mentor, a graduate student in our lab, who helped me in selecting a field of query for my proposal. When I chose the lab I wanted to be part of for my summer project (with my JIW and senior thesis in mind) , I knew the general area of research I wanted to be involved in.
If you are looking for a research proposal example for students, here are some made for various disciplines and levels of study that you can emulate or derive valuable ideas from: Postgraduate Research. Sample proposal for a Clinical Health Project; Sample proposal for Social Policy and Criminology; Sample research proposal for Ph.D. Politics 1
"Crafting a Research Proposal." The Marketing Review 10 (Summer 2010): 147-168; Jones, Mark. "Writing a Research Proposal." In MasterClass in Geography Education: Transforming Teaching and Learning. Graham Butt, editor. (New York: Bloomsbury Academic, 2015), pp. 113-127; Juni, Muhamad Hanafiah. "Writing a Research Proposal."
Sample research proposals written by doctoral students in each of the key areas covered in Research Design--quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods—are provided as a useful reference. A Research Proposal checklist also serves to help guide your own proposal-writing.› Morales Proposal_Qualitative Study› Kottich Proposal_Quantitative Study
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management' Example research proposal #2: 'Medical Students as Mediators of ...
Sample Project Proposals. Check out a few sample grant proposals below. Read ones annotated with reviewer notes (even if the topic is outside your area of interest) to learn what reviewers look for. You can also see also how resubmitted proposals respond to reviewer comments. Please note that these proposals serve as exemplars for students ...
1 of 5. Research Proposals. Writing a research proposal is the first step for a research project. Before you can work on your research, it must be approved, whether that is by a professor, thesis advisor, or supervisor. It is essential to make your proposal as strong as possible; if your proposal is denied, you may not get the funding you need ...
external funder, the rules about writing a good research proposal are the same. You want to stand out from the crowd and have the best chance of being selected. This guide highlights the "Golden Rules" and provides tips on how to write a good research application. Prospective research students may find it useful when asked to provide
Research proposals. Your research proposal is a key part of your application. It tells us about the question you want to answer through your research. It is a chance for you to show your knowledge of the subject area and tell us about the methods you want to use. We use your research proposal to match you with a supervisor or team of supervisors.
Online Proposal Rehearsals. This activity gives students an opportunity to rehearse their oral research proposals outside of class time in small groups before receiving holistic feedback from a larger group. It is designed to be completed synchronously, in real time, in small groups. Explore this activity.
The Research Technology Office (RTO) can provide technological planning for proposals. Many RTO staff have worked on proposals in collaboration with other PIs. Some staff have been PIs on proposals as well. We understand the process, requirements, effort, and deadlines that go into proposals. There are a number of things that RTO can provide to help you write a stronger proposal.
Other authors include current or former Stanford graduate students or research assistants Emma Pierson, Camelia Simoiu, Jan Overgoor, Sam Corbett-Davies, Daniel Jenson, Amy Shoemaker, Vignesh ...
The first-year doctoral student at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Social Work was recently awarded the Graduate Certificate in Participatory Research 2024 Seed Grant Award. Her proposal was titled, "Using Participatory Research Methods to Identify Assets and Opportunities for Diversion and Reentry Services in Rural ...
research projects that will be supported by these funds. Eligibility Criteria: Proposals with a graduate student who received an award from the 2021-2022 Graduate Student Research Restart Program, or the 2022 or 2023 Faculty-Graduate Student Research Collaboration Programs are ineligible for this program.
KU International Affairs is accepting proposals and applications for travel grants that support faculty and graduate student research and collaboration abroad. The deadline for submitting proposals and applications is March 6. Grant recipients will be notified by the end of April.
As per the draft proposal, Std XI and XII students will be able to select eight subjects in total: two languages (one has to be an Indian language and the second an international/foreign language ...
ICAEW has invited research proposals into the simplification of the UK's VAT system to be submitted by 30 June 2024. The winning entrant will receive a £5,000 prize and the opportunity to present their research at a VAT Conference to be held at Chartered Accountants' Hall in London in 2025.