How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree?
Earning a Ph.D. from a U.S. grad school typically requires nearly six years, federal statistics show.
How Long It Takes to Get a Ph.D. Degree

Caiaimage | Tom Merton | Getty Images
A Ph.D. is most appropriate for someone who is a "lifelong learner."
Students who have excelled within a specific academic discipline and who have a strong interest in that field may choose to pursue a Ph.D. degree. However, Ph.D. degree-holders urge prospective students to think carefully about whether they truly want or need a doctoral degree, since Ph.D. programs last for multiple years.
According to the Survey of Earned Doctorates, a census of recent research doctorate recipients who earned their degree from U.S. institutions, the median amount of time it took individuals who received their doctorates in 2017 to complete their program was 5.8 years. However, there are many types of programs that typically take longer than six years to complete, such as humanities and arts doctorates, where the median time for individuals to earn their degree was 7.1 years, according to the survey.
Some Ph.D. candidates begin doctoral programs after they have already obtained master's degrees, which means the time spent in grad school is a combination of the time spent pursuing a master's and the years invested in a doctorate. In order to receive a Ph.D. degree, a student must produce and successfully defend an original academic dissertation, which must be approved by a dissertation committtee. Writing and defending a dissertation is so difficult that many Ph.D. students drop out of their Ph.D. programs having done most of the work necessary for degree without completing the dissertation component. These Ph.D. program dropouts often use the phrase " all but dissertation " or the abbreviation "ABD" on their resumes.
According to a comprehensive study of Ph.D. completion rates published by The Council of Graduate Schools in 2008, only 56.6% of people who begin Ph.D. programs earn Ph.D. degrees.
Ian Curtis, a founding partner with H&C Education, an educational and admissions consulting firm, who is pursuing a Ph.D. degree in French at Yale University , says there are several steps involved in the process of obtaining a Ph.D. Students typically need to fulfill course requirements and pass comprehensive exams, Curtis warns. "Once these obligations have been completed, how long it takes you to write your dissertation depends on who you are, how you work, what field you're in and what other responsibilities you have in life," he wrote in an email. Though some Ph.D. students can write a dissertation in a single year, that is rare, and the dissertation writing process may last for several years, Curtis says.
Curtis adds that the level of support a Ph.D. student receives from an academic advisor or faculty mentor can be a key factor in determining the length of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. program. "Before you decide to enroll at a specific program, you’ll want to meet your future advisor," Curtis advises. "Also, reach out to his or her current and former students to get a sense of what he or she is like to work with."
Curtis also notes that if there is a gap between the amount of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. and the amount of time a student's funding lasts, this can slow down the Ph.D. completion process. "Keep in mind that if you run out of funding at some point during your doctorate, you will need to find paid work, and this will leave you even less time to focus on writing your dissertation," he says. "If one of the programs you’re looking at has a record of significantly longer – or shorter – times to competition, this is good information to take into consideration."
He adds that prospective Ph.D. students who already have master's degrees in the field they intend to focus their Ph.D. on should investigate whether the courses they took in their master's program would count toward the requirements of a Ph.D. program. "You’ll want to discuss your particular situation with your program to see whether this will be possible, and how many credits you are likely to receive as the result of your master’s work," he says.

How to Write M.D.-Ph.D. Application Essays
Ilana Kowarski May 15, 2018

Emmanuel C. Nwaodua, who has a Ph.D. degree in geology, says some Ph.D. programs require candidates to publish a paper in a first-rate, peer-reviewed academic journal. "This could extend your stay by a couple of years," he warns.
Pierre Huguet, the CEO and co-founder of H&C Education, says prospective Ph.D. students should be aware that a Ph.D. is designed to prepare a person for a career as a scholar. "Most of the jobs available to Ph.D. students upon graduation are academic in nature and directly related to their fields of study: professor, researcher, etc.," Huguet wrote in an email. "The truth is that more specialization can mean fewer job opportunities. Before starting a Ph.D., students should be sure that they want to pursue a career in academia, or in research. If not, they should make time during the Ph.D. to show recruiters that they’ve traveled beyond their labs and libraries to gain some professional hands-on experience."
Jack Appleman, a business writing instructor, published author and Ph.D. candidate focusing on organizational communication with the University at Albany—SUNY , says Ph.D. programs require a level of commitment and focus that goes beyond what is necessary for a typical corporate job. A program with flexible course requirements that allow a student to customize his or her curriculum based on academic interests and personal obligations is ideal, he says.
Joan Kee, a professor at the University of Michigan with the university's history of art department, says that the length of time required for a Ph.D. varies widely depending on what subject the Ph.D. focuses on. "Ph.D. program length is very discipline and even field-specific; for example, you can and are expected to finish a Ph.D, in economics in under five years, but that would be impossible in art history (or most of the humanities)," she wrote in an email.
Kee adds that humanities Ph.D. programs often require someone to learn a foreign language, and "fields like anthropology and art history require extensive field research." Kee says funding for a humanities Ph.D. program typically only lasts five years, even though it is uncommon for someone to obtain a Ph.D. degree in a humanities field within that time frame. "Because of this, many if not most Ph.D. students must work to make ends meet, thus further prolonging the time of completion," she says.
Jean Marie Carey, who earned her Ph.D. degree in art history and German from the University of Otago in New Zealand, encourages prospective Ph.D. students to check whether their potential Ph.D. program has published a timeline of how long it takes a Ph.D. student to complete their program. She says it is also prudent to speak with Ph.D. graduates of the school and ask about their experience.
Online Doctoral Programs: What to Expect
Ronald Wellman March 23, 2018

Kristin Redington Bennett, the founder of the Illumii educational consulting firm in North Carolina, encourages Ph.D. hopefuls to think carefully about whether they want to become a scholar. Bennett, who has a Ph.D. in curriculum and assessment and who previously worked as an assistant professor at Wake Forest University , says a Ph.D. is most appropriate for someone who is a "lifelong learner." She says someone contemplating a Ph.D. should ask themselves the following questions "Are you a very curious person... and are you persistent?"
Bennett urges prospective Ph.D. students to visit the campuses of their target graduate programs since a Ph.D. program takes so much time that it is important to find a school that feels comfortable. She adds that aspiring Ph.D. students who prefer a collaborative learning environment should be wary of graduate programs that have a cut-throat and competitive atmosphere, since such students may not thrive in that type of setting.
Alumni of Ph.D. programs note that the process of obtaining a Ph.D. is arduous, regardless of the type of Ph.D. program. "A Ph.D. is a long commitment of your time, energy and financial resources, so it'll be easier on you if you are passionate about research," says Grace Lee, who has a Ph.D. in neuroscience and is the founder and CEO of Mastery Insights, an education and career coaching company, and the host of the Career Revisionist podcast.
"A Ph.D. isn't about rehashing years of knowledge that is already out there, but rather it is about your ability to generate new knowledge. Your intellectual masterpiece (which is your dissertation) takes a lot of time, intellectual creativity and innovation to put together, so you have to be truly passionate about that," Lee says.
Curtis says a prospective Ph.D. student's enthusiasm for academic work, teaching and research are the key criteria they should use to decide whether to obtain a Ph.D. degree. "While the time it takes to complete a doctorate is an understandable concern for many, my personal belief is that time is not the most important factor to consider," he says. "Good Ph.D. programs provide their students with generous stipends, health care and sometimes even subsidized housing."
Erin Skelly, a graduate admissions counselor at the IvyWise admissions consulting firm, says when a Ph.D. students struggles to complete his or her Ph.D. degree, it may have more to do with the student's academic interests or personal circumstances than his or her program.
"The time to complete a Ph.D. can depend on a number of variables, but the specific discipline or school would only account for a year or two's difference," she wrote in an email. "When a student takes significantly longer to complete a Ph.D. (degree), it's usually related to the student's coursework and research – they need to take additional coursework to complete their comprehensive exams; they change the focus of their program or dissertation, requiring extra coursework or research; or their research doesn't yield the results they hoped for, and they need to generate a new theory and conduct more research."
Skelly warns that the average completion time of a Ph.D. program may be misleading in some cases, if the average is skewed based on one or two outliers. She suggests that instead of focusing on the duration of a particular Ph.D. program, prospective students should investigate the program's attritition and graduation rates.
"It is worthwhile to look at the program requirements and the school's proposed timeline for completion, and meet current students to get their input on how realistic these expectations for completion are," Skelly says. "That can give you an honest idea of how long it will really take to complete the program."
Searching for a grad school? Access our complete rankings of Best Graduate Schools.
Tags: graduate schools , education , students
You May Also Like
What to ask law students and alumni.
Gabriel Kuris April 22, 2024

Find a Strong Human Rights Law Program
Anayat Durrani April 18, 2024

Environmental Health in Medical School
Zach Grimmett April 16, 2024

How to Choose a Law Career Path
Gabriel Kuris April 15, 2024

Questions Women MBA Hopefuls Should Ask
Haley Bartel April 12, 2024

Law Schools With the Highest LSATs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 11, 2024

MBA Programs That Lead to Good Jobs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 10, 2024

B-Schools With Racial Diversity
Sarah Wood April 10, 2024

Law Schools That Are Hardest to Get Into
Sarah Wood April 9, 2024

Grad School Housing Options
Anayat Durrani April 9, 2024


Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation
How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD?
Earning a Ph.D. is a remarkable academic achievement, often seen as the pinnacle of one’s educational journey. It’s a pursuit that demands unwavering dedication, intellectual prowess, and an unshakable commitment to research. Yet, when setting out on this academic odyssey, prospective doctoral students often find themselves grappling with a common question: How long will it take to reach the coveted destination of a PhD?
In the world of academia, where timeframes can be as diverse as the subjects studied, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. The duration of a PhD program can be influenced by a multitude of factors, ranging from the chosen field of study to the country in which one embarks on this intellectual voyage.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the intricate web of considerations that determine the timeline of a Ph.D. We’ll delve into the typical duration, international variations, the stages of the Ph.D. journey, and even the strategies that can expedite or prolong this academic quest.
Through real-life experiences and insights, we aim to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the fascinating, challenging, and often unpredictable timeline associated with pursuing a PhD.
So, if you’ve ever wondered about the time commitment required for a PhD, join us on this educational voyage as we uncover the secrets of this academic adventure and navigate the complex terrain of doctoral studies.
Introduction
Factors influencing phd duration, typical duration of phd, phd duration: variations by country, stages of a phd program, shortening the phd timeline, lengthening the timeline of phd.
A PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy, is the highest academic degree one can attain. It represents expertise in a specific field and often involves original research contributing to the world’s knowledge. However, this academic feat isn’t for the faint of heart. To embark on this journey, you should be aware of the formidable challenges it presents, and one of the most fundamental questions is, “How long will it take?” In the introduction, you can touch upon the idea of academic ambition, the pursuit of knowledge, and the unique challenges that come with obtaining a Ph.D.
It’s essential to emphasize why understanding the time commitment is crucial. Pursuing a Ph.D. isn’t just an intellectual endeavor; it’s also a significant personal and professional commitment. It can impact one’s life, career, and even mental and emotional well-being. You can mention that by knowing what you’re getting into time-wise, you can make informed decisions about your academic and career goals. For instance, if you’re aware that a Ph.D. typically takes several years, you can plan your life accordingly, set expectations, and ensure you have the necessary resources and support in place.
Imagine standing at the crossroads of ambition and dedication. You’re passionate about a particular field, and the thought of making a meaningful contribution to it excites you. You dream of becoming a respected expert, perhaps even shaping the future of your discipline. This ambition has led you to consider pursuing a PhD, a journey that represents the highest echelon of academic achievement.
But before you dive into the world of research, scholarly papers, and intellectual debates, there’s a critical question that looms large—how long will it take to earn that coveted Doctor of Philosophy degree? The answer isn’t as straightforward as one might hope. It’s a complex equation, influenced by various factors, and it’s a puzzle that many aspiring doctoral students grapple with.
Understanding the time commitment of a PhD is not merely a matter of academic curiosity. It’s a pivotal factor that can shape your life’s trajectory in significant ways. This introduction explores the intricacies of a PhD journey, from the initial spark of academic passion to the profound understanding of what it takes, in terms of time, to turn that passion into a doctoral reality.
Earning a PhD is a highly individualized journey, and its duration can vary significantly from person to person. This section will delve into the myriad factors that play a role in determining the length of a PhD program. It’s important to understand that the timeline is not a fixed number of years but is influenced by various variables. Here are some key factors:
- Field of Study: The nature of your research area has a significant impact. Some fields, such as the natural sciences or engineering, might require extensive laboratory work and data collection, which can lengthen the Ph.D. process. In contrast, fields like humanities or social sciences might involve less time-intensive data collection but demand extensive writing and analysis.
- Country: The country in which you pursue your PhD can greatly affect the duration. Different countries have different academic systems and expectations. For example, in the United States, it’s common for PhD programs to last longer compared to some European countries where they tend to be shorter and more structured.
- Research Focus: The specific focus of your research project can influence the time required. If your research involves cutting-edge, complex topics, it might take longer to gather and analyze data or develop new methodologies. On the other hand, a well-defined and less ambitious research question could lead to a quicker completion.
Let’s take a closer look at the intricate web of factors that influence the duration of a PhD program. Imagine two students, both embarking on their journeys to earn a PhD, but in different fields.
Student A is pursuing a PhD in physics. This field often involves conducting elaborate experiments, gathering extensive data, and fine-tuning intricate instruments. The pursuit of new discoveries in the realm of physics can be time-consuming, and the PhD program might extend to several years to complete all the necessary research.
Student B, on the other hand, is studying literature and cultural studies. Their research involves in-depth analysis of existing texts, interpretations, and critical theories. While the reading and writing process is extensive, it may not require as many years as Student A’s experimental work.
Now, consider these students in the context of the country in which they are pursuing their PhD Student A is in the United States, where doctoral programs typically span several years. Meanwhile, Student B is in a European country known for its structured and shorter Ph.D. programs.
Lastly, let’s factor in research focus. Student A’s project is ambitious, attempting to uncover the mysteries of the universe, which can be a time-intensive endeavor. In contrast, Student B’s research question is more narrowly defined, making the path to completion relatively shorter.
These examples illustrate how the combination of field of study, country, and research focus can significantly influence the duration of a PhD program.
Understanding the average duration of a PhD program can help prospective students set realistic expectations. This section will provide an overview of the typical timeframes for completing a PhD.
- Average Duration: On a global scale, a PhD program often spans between 5 to 7 years. This period includes coursework, research, and the writing and defense of a dissertation. However, it’s important to note that this duration can vary significantly. In the United States , for instance, it’s common for PhD programs to take longer, often 5 to 7 years or even more, due to the inclusion of coursework and comprehensive exams. In contrast, in some European countries, PhD programs are designed to be shorter, typically around 3 to 4 years, as they are research-focused with less emphasis on coursework.
- Variations by Field: The average duration can also differ based on the field of study. Fields requiring extensive data collection, such as the natural sciences or engineering, might take longer, while fields like humanities or social sciences with more writing and analysis may have shorter timeframes.
When it comes to the average duration of a PhD program, the common adage ‘it’s a marathon, not a sprint’ certainly applies. The typical journey to a PhD is a long and demanding one, taking aspiring scholars through a series of rigorous academic challenges.
Globally, a PhD program often spans between 5 to 7 years. This period includes the initial coursework phase, where students delve deep into the theoretical foundations of their field. This is followed by a substantial research phase, during which they gather data, conduct experiments, or engage in extensive fieldwork. Finally, the culmination of this journey is the completion and defense of a dissertation, a written document that contributes new knowledge to their field.
However, it’s crucial to remember that these timeframes are general averages and can vary significantly based on various factors. In the United States, for example, it’s quite common for PhD programs to extend to the longer end of the spectrum, taking 5 to 7 years or even more to complete. This is because American PhD programs often include a significant coursework component and comprehensive exams before the dissertation phase begins.
On the other hand, in some European countries, PhD programs are designed to be more streamlined and research-focused. They typically take around 3 to 4 years to complete, reflecting a shorter timeframe. This structure is influenced by the belief that students entering PhD programs are already well-prepared in their chosen field, and the primary focus is on conducting independent research.
Additionally, the duration can also vary based on the specific field of study. Fields that require extensive data collection or experimental work, such as the natural sciences or engineering, tend to have longer PhD programs. In contrast, fields like humanities or social sciences, where research involves more reading, writing, and analysis, may have shorter timeframes.
Keep in mind that these are general guidelines, and individual PhD experiences can deviate from the average.
Ph.D. program durations can vary significantly between countries due to differences in educational systems and academic traditions. This section will explore how and why PhD programs’ lengths differ by country.
- United States: In the United States, PhD programs are known for their comprehensive structure. They often include a combination of coursework, comprehensive exams, and dissertation research. This makes them typically longer, often spanning 5 to 7 years or more.
- European Countries: In many European countries, PhD programs are more streamlined and research-focused. They tend to be shorter, typically around 3 to 4 years. European programs often assume that students have a strong foundation in their field when they enter the Ph.D. phase.
- Other Countries: The duration of PhD programs can also vary in other parts of the world. For instance, in some Asian countries, the length of a PhD program can be influenced by the nature of the research and the institution’s specific requirements.
When contemplating the pursuit of a Ph.D., it’s important to recognize that the path you tread can be markedly different depending on the country in which you choose to study. The world’s countries have diverse academic systems and traditions, and these intricacies play a significant role in shaping the duration of PhD programs.
Consider the United States, a country renowned for its rigorous academic programs. Here, PhD programs are known for their comprehensive nature. Students often undergo a period of intensive coursework, followed by comprehensive exams to assess their knowledge. This is in addition to the research phase, which involves conducting experiments, gathering data, or delving deep into the chosen area of study. As a result, PhD programs in the United States are often among the longer ones, frequently taking 5 to 7 years or even more to complete.
In contrast, many European countries have adopted a more streamlined approach to PhD programs. These programs tend to be research-focused from the outset, with the assumption that students entering PhD programs already possess a strong foundation in their chosen field. The result is a shorter program, typically spanning around 3 to 4 years. In countries like the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and Denmark, students can transition directly into their research, which contributes to the shorter duration.
Outside of the United States and Europe, PhD program lengths can vary significantly depending on the country’s educational system and specific institutional requirements. For instance, in certain Asian countries, PhD programs might also be research-intensive and shorter in duration, or they might extend to accommodate the complexity of the research involved.
It’s important to understand these country-specific variations when considering a PhD program, as they can have a profound impact on the length of your academic journey.
A Ph.D. program is not a single, continuous journey but is typically divided into distinct stages. This section will provide an overview of the common stages of a PhD program, which include coursework, research, and dissertation writing.
- Coursework: The journey usually starts with a coursework phase, where students dive deep into the theoretical foundations of their field. During this stage, students take classes and seminars to build a strong academic foundation. The duration of this stage varies by country and field but generally lasts from 1 to 2 years.
- Comprehensive Exams: In some countries, notably the United States, students are required to pass comprehensive exams to demonstrate their mastery of their field. This stage can add a few months to a couple of years to the timeline.
- Research Phase: After coursework and exams, students transition into the research phase, which is the heart of a Ph.D. program. This phase involves conducting original research, experiments, fieldwork, or in-depth analysis, depending on the field of study. It can last several years, usually 3 to 5 years or more, depending on the complexity of the research and the progress made.
- Dissertation Writing: The final stage involves writing the PhD dissertation, a comprehensive document that presents the research findings and contributes to the academic field. The duration of this stage varies but often takes at least a year.
A PhD program is akin to an academic epic, with distinct stages that collectively make up the hero’s journey. As an aspiring doctoral candidate, it’s essential to understand the key stages you’ll encounter along the way.
The odyssey begins with coursework. During this initial stage, students embark on a voyage into the theoretical underpinnings of their chosen field. They attend classes, seminars, and lectures to deepen their understanding. This coursework phase, which can last anywhere from 1 to 2 years, serves as the foundation upon which the rest of the journey is built.
In some countries, particularly the United States, there’s another formidable challenge—comprehensive exams. These exams test the student’s mastery of the field’s core concepts and are often required before moving on to the next stage. Comprehensive exams can extend the journey by several months to a couple of years.
The heart of the PhD journey lies in the research phase. This is where students immerse themselves in original research, which could entail conducting experiments, gathering data, or engaging in extensive fieldwork, depending on their field of study. The duration of this stage is the most variable, spanning approximately 3 to 5 years or even longer, depending on the complexity of the research and the progress made.
Lastly, the culmination of the PhD adventure is the dissertation writing stage. Here, students craft a comprehensive document that presents their research findings, methodology, and contributions to the academic field. This final stage can vary in length but often takes at least a year to complete.
These stages collectively shape the journey towards a PhD, and understanding them is vital for anyone embarking on this academic odyssey.
While earning a Ph.D. is a significant commitment, there are strategies to expedite the process. This section will discuss strategies and approaches that can help shorten the timeline of your PhD journey .
- Efficient Time Management: Effective time management is essential for expediting a PhD program. Planning and prioritizing tasks, setting clear goals, and maintaining a structured schedule can help students make the most of their research and coursework, reducing the time spent on unnecessary or unproductive activities.
- Choosing the Right Advisor: The relationship between a Ph.D. student and their advisor can significantly impact the program’s duration. A supportive and experienced advisor can guide the student effectively, provide valuable insights, and help them navigate research challenges more efficiently. A strong advisor-student relationship can lead to better research progress and a quicker completion.
- Prior Research Experience: Entering a PhD program with prior research experience can be a significant advantage. If you’ve already conducted research related to your PhD topic during a master’s program or as an undergraduate, you may be able to accelerate your research and data collection, potentially shortening the overall timeline.
When it comes to earning a PhD, the duration can be an intimidating factor. However, it’s important to remember that there are strategies that can help expedite the journey. Let’s explore some of these approaches:
One of the most fundamental strategies is efficient time management. Effective planning, prioritization, and maintaining a structured schedule can make a world of difference. By setting clear goals and staying organized, students can optimize their time and reduce the risk of distractions or time wasted on non-essential activities. This approach ensures that every moment spent on research or coursework is meaningful and productive.
Another pivotal factor is the choice of an advisor. The advisor-student relationship plays a crucial role in a Ph.D. program. A supportive, experienced, and engaged advisor can guide a student through the research process more effectively. They can offer valuable insights, help troubleshoot research challenges, and provide a sense of direction. With the right advisor, students often find themselves making more efficient progress and thus shortening the overall timeline of their PhD journey.
For those entering a PhD program with prior research experience, there’s an advantage. If you’ve already dabbled in research during your master’s program or as an undergraduate, you’re poised for a quicker start. The knowledge, skills, and methodologies you’ve acquired can significantly expedite your research and data collection, potentially helping you complete your PhD in less time.
These strategies, when applied thoughtfully, can make the road to a PhD a bit smoother and shorter, ultimately allowing students to achieve their academic goals more efficiently.
While shortening the Ph.D. journey is a common goal, there are situations that can unexpectedly lengthen the timeline. This section will discuss various reasons a Ph.D. might take longer than expected, including research challenges and personal circumstances.
- Complex Research Challenges: Research is at the core of a Ph.D., and sometimes, research challenges can extend the timeline. For instance, unexpected technical issues, data collection difficulties, or unanticipated roadblocks in the research process can delay progress. Dealing with these complexities often requires additional time and problem-solving efforts.
- Scope of the Project: Sometimes, students may underestimate the scope of their research project. If the research topic turns out to be more extensive or multifaceted than initially anticipated, it can lead to a longer journey. Expanding the research scope can also be driven by a desire to make a more substantial contribution to the field.
- Personal Circumstances: Personal circumstances can also play a significant role in lengthening the timeline. Life events, such as family responsibilities, health issues, or other personal challenges, can disrupt the academic trajectory and extend the Ph.D. program.
While aspiring doctoral candidates often set out with the goal of completing their PhD as efficiently as possible, it’s important to acknowledge that unexpected factors can sometimes extend the journey. Let’s delve into some of the reasons a PhD might take longer than initially expected:
One of the most common factors is research challenges. Research is the backbone of a Ph.D., and it’s not uncommon to encounter unanticipated complexities along the way. For instance, imagine a Ph.D. student in the field of environmental science who encounters technical issues with specialized equipment required for data collection. These unexpected hurdles can require additional time and effort to resolve, extending the research phase.
Another factor that can elongate the timeline is the scope of the project. Sometimes, students may begin their research with a particular understanding of the project’s scale, only to discover that the topic is more extensive or multifaceted than initially thought. This realization can lead to an expansion of the research scope, often driven by the desire to make a more significant and impactful contribution to the field. While noble in its intent, this expansion can result in a longer and more extensive research phase.
Personal circumstances can also have a profound impact. Life doesn’t always adhere to the academic calendar, and various personal challenges can disrupt the PhD journey. These challenges can include family responsibilities, health issues, or other unforeseen life events. Balancing these personal circumstances with academic commitments can sometimes lead to a longer timeline for completing a PhD.
It’s crucial to recognize that while we often have our sights set on a timely completion, the PhD journey can be influenced by a myriad of unforeseen factors. Overcoming these challenges is a testament to resilience and dedication in the pursuit of knowledge.
I have written several articles related to PhD. You can visit them Here. These articles will guide you in the smooth completion of your PhD.
An unconventional PhD demands quality publications and presentations. I have written articles related to Research Journals and Research Conferences. Please visit them
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
To sum it up, figuring out how long a Ph.D. takes is like solving a puzzle. In the U.S., it’s a bit like a long journey, taking about 5 to 7 years, while in Europe, it’s more like a focused sprint, finishing in about 3 to 4 years.
We also learned about the different stages of a Ph.D., from classes to big research and a huge paper called a dissertation. Some folks speed up their Ph.D. by managing time well, picking a good advisor, or using past research experience. But unexpected stuff, like tough research problems or personal things, can make the Ph.D. journey longer.
In Ph.D. land, time is like money you spend to learn and get smart. Whether someone is thinking about starting a Ph.D. or already on the journey, it’s their special story. Enjoy the good parts, handle the tough bits, and feel proud of becoming a real expert, adding to what everyone knows together.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- How to End Your Academic/Research Internship?
- PhD or Industry Job? A Comprehensive Career Guide
- Post Doc Positions in India
- 04 Reasons for Outsourcing Academic Conference Management
- How to Put Research Grants on Your CV ?
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com


- How Long Does A PhD Take?
- Doing a PhD
Sometimes, just knowing how long a PhD takes can be enough to sway your decision on whether a research degree is for you. So with that in mind, exactly how long does a PhD take?
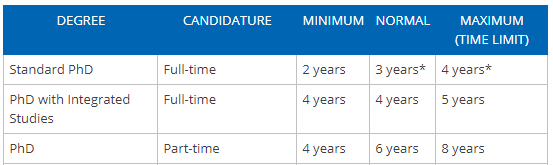
In the UK, a full-time PhD takes 3 to 4 years to finish whilst a part-time PhD takes twice as long at 6 to 7 years. Alongside these average durations, there are time limits on how long you can be enrolled on to a PhD programme. To discover these limits, the factors which most influence doctoral degree durations and how the UK durations compare to international PhDs, continue reading on.
How Long Does It Take to Get a Full-time PhD?
In the UK, a full-time PhD will typically take you 3 to 4 years. You will usually spend the first three years on the technical aspects of your doctorate. This includes undertaking independent research, designing your research methodology and collecting and analysing data. You will then spend an additional academic year on writing up your PhD thesis and sitting your viva.
How Long Does It Take to Get a Part-time PhD?
In the UK, a part-time PhD will typically take you 6 to 7 years; twice as long as doing a full-time PhD. The reason for this is that as a part-time PhD student, you would dedicate around 20 hours per week to your PhD as opposed to the typical 40 hours full-time students would put into their subject.
How Long Does a Distance Learning PhD Take?
Similarly, distance learning PhD’s take an average of 6 to 7 years to complete. This is because the vast majority of students who undertake a distance learning PhD do so because they can’t relocate closer to the university. Although these commitments will differ, they often mean the student isn’t able to dedicate 40 hours per week to their studies.
Students in STEM disciplines will often take longer to finish a distance learning doctorate degree than those in non-STEM disciplines. This because the progress of a STEM PhD student will be limited by how often they can access a laboratory for experiment work.
How Does Funding Impact a PhD’s Duration?
In reality, the actual time it will take you to complete your PhD degree will depend on your funding situation.
If you’re receiving funding , it will usually only cover you for 3.5 years if you’re studying full-time or for 7 years at half the stipend if you’re studying part-time. Although this could vary slightly, most PhD funding providers, e.g. Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC), follow this timescale as indicated on their ‘ length of PhD studentships’ page. Because of this, most students who obtain scholarships try to complete their PhD within the timeframe of their funding so they don’t incur additional fees which they need to cover themselves.
It’s also worth noting that some funded PhD positions have additional conditions attached to them as part of their eligibility requirements. For example, they may require teaching undergraduate students, hosting laboratory sessions or attend presentations and conferences. This will be especially true if you’re on a Graduate Teaching Assistantship (GTA). Although these shouldn’t add considerable time to the length of a PhD programme, they have the potential to do so if they aren’t managed properly.
As self-funded students cover their own annual tuition fees and other associated costs, how long they’ll spend to complete their PhD project will largely depend on their own personal financial situation. Because of this, most self-funded PhD students find it best to complete their PhD study in the shortest time-frame they can manage.
Are There Deadlines?
Yes – unfortunately, all good things must come to an end! Within the UK, the deadline for your PhD is defined as the last date which you must submit your final thesis by. This date is set by your university’s overall regulations and varies depending on the arrangements of your PhD, e.g. whether it’s full or part time. In the vast majority of cases, the adopted deadlines are four years for full-time PhDs and seven years for part-time PhDs from the date you were officially registered onto your programme, as shown below from the University of Leicester’s registration guidance page .

This time-frame may vary from university to university. For example, the University of Sheffield adopts an additional year for part-time PhDs as shown below.
Can I Complete It Faster?
Although it’s possible to complete a full-time PhD in under 3 years, it’s a significant feat that’s rarely heard of. When these feats occur, they’re usually where the doctoral student already has extensive knowledge and experience in their field before undertaking their PhD.
Whilst it’s possible to complete a part-time PhD in under 6 years, it largely depends on your commitments outside your studies. For example, if you have a part-time career alongside your PhD, it’s unlikely that you’ll be able to commit the additional hours required to complete your doctorate a year faster.
However, if instead of a steady part-time job you take on occasional work as a freelancer, you’ll be able to set aside many more hours towards your doctoral degree.
Will Having only A Bachelor’s Degree or Being an International Student Limit My Rate of Progression?
Not at all. While there are benefits to having a Master’s degree such as an additional year of learning and greater research experience due to your fourth-year dissertation project, this doesn’t mean not having one would limit you. A PhD is very different to both Bachelor and Master degrees due to being heavily research-based, therefore, both types of students will have just as much to learn on their way to completing their doctorate.
Similarly, whether you’re an international student will bear no influence on the duration of your PhD.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
How Does This Compare to the Duration of EU and US PhDs?
PhD hosted by universities within the EU, such as those in France, Norway and Spain, have the same programme structure as those within the UK. As a result, there are no noticeable differences in the time to complete a doctorate between UK and EU institutions.
However, this is not the case in the US. Compared to PhDs conducted within the UK or EU, PhDs conducted within the US take considerably longer to obtain. According to a 2017 study conducted by the National Science Foundation, a US government agency which supports research and higher education, the average time to get a PhD within the US is 5.8 years. Besides this, the average completion time can further increase depending on the disciplines. For example, they found doctorates within the humanities and arts to take an average of 7.1 years to achieve.
The primary reason for this difference is the way PhD degrees are structured within the United States. As mentioned previously, PhDs conducted within UK and EU universities are essentially broken into two sections – one covering the analytical aspects and the other covering the writing up aspects. However, within the US, doctorate programmes comprise additional sections. PhD students are first required to undertake 2 to 3 years of courses, which cover a broad range of topics related to their schools’ discipline. This is then followed by coursework and several examinations, which only once passed can the PhD candidate then start working on their research project and dissertation.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
- Utility Menu
Apply | Contact Us | Carol Davis Fund Anonymous Feedback to the Physics Chair
Graduate studies, commencement 2019.
The Harvard Department of Physics offers students innovative educational and research opportunities with renowned faculty in state-of-the-art facilities, exploring fundamental problems involving physics at all scales. Our primary areas of experimental and theoretical research are atomic and molecular physics, astrophysics and cosmology, biophysics, chemical physics, computational physics, condensed-matter physics, materials science, mathematical physics, particle physics, quantum optics, quantum field theory, quantum information, string theory, and relativity.
Our talented and hardworking students participate in exciting discoveries and cutting-edge inventions such as the ATLAS experiment, which discovered the Higgs boson; building the first 51-cubit quantum computer; measuring entanglement entropy; discovering new phases of matter; and peering into the ‘soft hair’ of black holes.
Our students come from all over the world and from varied educational backgrounds. We are committed to fostering an inclusive environment and attracting the widest possible range of talents.
We have a flexible and highly responsive advising structure for our PhD students that shepherds them through every stage of their education, providing assistance and counseling along the way, helping resolve problems and academic impasses, and making sure that everyone has the most enriching experience possible.The graduate advising team also sponsors alumni talks, panels, and advice sessions to help students along their academic and career paths in physics and beyond, such as “Getting Started in Research,” “Applying to Fellowships,” “Preparing for Qualifying Exams,” “Securing a Post-Doc Position,” and other career events (both academic and industry-related).
We offer many resources, services, and on-site facilities to the physics community, including our electronic instrument design lab and our fabrication machine shop. Our historic Jefferson Laboratory, the first physics laboratory of its kind in the nation and the heart of the physics department, has been redesigned and renovated to facilitate study and collaboration among our students.
Members of the Harvard Physics community participate in initiatives that bring together scientists from institutions across the world and from different fields of inquiry. For example, the Harvard-MIT Center for Ultracold Atoms unites a community of scientists from both institutions to pursue research in the new fields opened up by the creation of ultracold atoms and quantum gases. The Center for Integrated Quantum Materials , a collaboration between Harvard University, Howard University, MIT, and the Museum of Science, Boston, is dedicated to the study of extraordinary new quantum materials that hold promise for transforming signal processing and computation. The Harvard Materials Science and Engineering Center is home to an interdisciplinary group of physicists, chemists, and researchers from the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences working on fundamental questions in materials science and applications such as soft robotics and 3D printing. The Black Hole Initiative , the first center worldwide to focus on the study of black holes, is an interdisciplinary collaboration between principal investigators from the fields of astronomy, physics, mathematics, and philosophy. The quantitative biology initiative https://quantbio.harvard.edu/ aims to bring together physicists, biologists, engineers, and applied mathematicians to understand life itself. And, most recently, the new program in Quantum Science and Engineering (QSE) , which lies at the interface of physics, chemistry, and engineering, will admit its first cohort of PhD students in Fall 2022.
We support and encourage interdisciplinary research and simultaneous applications to two departments is permissible. Prospective students may thus wish to apply to the following departments and programs in addition to Physics:
- Department of Astronomy
- Department of Chemistry
- Department of Mathematics
- John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS)
- Biophysics Program
- Molecules, Cells and Organisms Program (MCO)
If you are a prospective graduate student and have questions for us, or if you’re interested in visiting our department, please contact [email protected] .
- GRADUATE STUDIES
- Admissions & Financial Aid
- Admissions FAQs
- Advising Team
- Advising Portal (Graduate)
- Course Requirements
- Other PhD Tracks
- Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
- GSAS Student Council
- PhD Thesis Help
- Tax Information
- Search All Scholarships
- Exclusive Scholarships
- Easy Scholarships to Apply For
- No Essay Scholarships
- Scholarships for HS Juniors
- Scholarships for HS Seniors
- Scholarships for College Students
- Scholarships for Grad Students
- Scholarships for Women
- Scholarships for Black Students
- Scholarships
- Student Loans
- College Admissions
- Financial Aid
- Scholarship Winners
- Scholarship Providers
Student-centric advice and objective recommendations
Higher education has never been more confusing or expensive. Our goal is to help you navigate the very big decisions related to higher ed with objective information and expert advice. Each piece of content on the site is original, based on extensive research, and reviewed by multiple editors, including a subject matter expert. This ensures that all of our content is up-to-date, useful, accurate, and thorough.
Our reviews and recommendations are based on extensive research, testing, and feedback. We may receive commission from links on our website, but that doesn’t affect our editors’ opinions. Our marketing partners don’t review, approve or endorse our editorial content. It’s accurate to the best of our knowledge when posted. You can find a complete list of our partners here .
How Long Does It Take to Earn a PhD?

Cece Gilmore is a Content Writer at Scholarships360. Cece earned her undergraduate degree in Journalism and Mass Communications from Arizona State University. While at ASU, she was the education editor as well as a published staff reporter at Downtown Devil. Cece was also the co-host of her own radio show on Blaze Radio ASU.
Learn about our editorial policies

Cari Schultz is an Educational Review Board Advisor at Scholarships360, where she reviews content featured on the site. For over 20 years, Cari has worked in college admissions (Baldwin Wallace University, The Ohio State University, University of Kentucky) and as a college counselor (Columbus School for Girls).

Maria Geiger is Director of Content at Scholarships360. She is a former online educational technology instructor and adjunct writing instructor. In addition to education reform, Maria’s interests include viewpoint diversity, blended/flipped learning, digital communication, and integrating media/web tools into the curriculum to better facilitate student engagement. Maria earned both a B.A. and an M.A. in English Literature from Monmouth University, an M. Ed. in Education from Monmouth University, and a Virtual Online Teaching Certificate (VOLT) from the University of Pennsylvania.

How long is a PhD program? That might be one of the first questions you ask yourself If you are thinking of earning a PhD. You have probably heard a range of years, and that is because how long it takes to earn a PhD depends on a number of factors. Keep reading to learn more!!
What is a PhD?
PhD stands for a “Doctorate of Philosophy.” This is an academic degree that qualifies the degree holder to teach their chosen subject at university level or to work in a specialized position in their chosen field. In general, the PhD is the highest level of degree a student can achieve.
Also see: Top fully funded PhD programs
Why get a PhD?
A PhD is a serious commitment with a serious return on investment. Here is a list of professional and personal benefits for earning a PhD.
How long does it take to earn a PhD?
Earning a PhD usually takes between four and seven years to complete, depending on the type of PhD as well as the schools requirements, the students educational background, and personal progress. Students who take full-time classes can typically finish in four years. A typical PhD program requires anywhere from 60 to 120 semester credit hours .
Why earning a PhD takes years to earn
Assistantship obligations.
Teaching and research assistantships can be very beneficial for the experience they provide and the potential funding, but they can also be time consuming obligations for PhD students. Therefore, assistantships may affect the amount of time it takes to complete a PhD program.
Comprehensive examinations
Universities often require students to demonstrate their readiness in a PhD program through comprehensive exams. These comprehensive exams may be known as:
- Preliminary examinations
- Major field examinations
- Comprehensive exams or “Comps”
- General examinations
Dissertation
A dissertation is an in-depth research document that serves as the culmination of a doctoral program. It is an important document that demonstrates a student’s original research and contribution to their field of study.
The dissertation involves conducting extensive research, reviewing previous literature, analyzing data, and presenting your findings in a structured manner. Once the dissertation is completed, it is typically defended orally in front of a committee of faculty members who assess the quality and validity of the research.
Average PhD timeline
The specific of a PhD timeline carried by college and university. However, the following is a good overview of the average PhD program.
- Year 1: Take advanced courses
- Year 2: Take advanced courses and begin preparing for exams
- Year 3: Study, take and defend your comprehensive exams and begin researching your dissertation proposal
- Year 4: Begin working on your dissertation
- Year 5: Finish and defend your dissertation
Average PhD completion by focus
According to data from the National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics the average time in years from graduate school entry to doctorate it took students to receive their degree in 2020 in certain fields is listed below.
- Life sciences = 6.9 years
- Physical sciences and earth sciences = 6.3 years
- Mathematics and computer sciences = 7.0 years
- Psychology and social sciences = 7.9 years
- Engineering = 6.8 years
- Education = 12.0 years
- Humanities and arts = 9.6 years
- Other non-S&E fields = 9.3 years
Related : Top 10 PhD in Education programs
How to finish your PhD is less time
Look for accelerated classes.
Accelerated courses are an easy way to reduce the amount of time it takes to finish a PhD. Therefore, look into if your program offers any shorter courses.
Work on your dissertation throughout the program
Working on your dissertation little by little throughout the program will allow you to speed up your doctoral timeline. In addition, it may reduce the likelihood that you’ll drop out before finishing your final project.
Maintain regular communication with your advisor
Establish regular communication with your advisor or supervisor. Regular meetings can help you receive guidance, address any issues, and ensure you are heading in the right direction.
Seek feedback early and often
Share your work and progress with your advisor, peers, or other trusted individuals often. Then, you should incorporate suggestions and revisions as you go along. This will help you refine your work and avoid major revisions later.
Maintain a healthy school-life balance
While it is important to be dedicated to your PhD, it’s just as important to maintain a healthy work-life balance. Therefore, be sure to prioritize yourself! While finishing your PhD in less time is a great feat, it is important that you are not sacrificing your well-being while doing so.
Key Takeaways
- PhD stands for “doctorate of philosophy” and is generally the highest level of degree a student can earn
- There are many professional and personal benefits to earning a PhD which can lead to a serious return on investment
- A PhD program typically takes 4-7 years to complete. However, it can take longer or shorter depending on personal circumstances and field of study
- With planning and guidance from advisors, students can sometimes complete PhDs in less time
Start your scholarship search
- Vetted scholarships custom-matched to your profile
- Access exclusive scholarships only available to Scholarships360 members
Frequently asked questions about how long it takes to earn a PhD
Do i need to have a master’s degree to get a phd, what is the easiest phd to earn, can i finish my phd earlier than the estimated time frame, what happens if i don’t complete my phd within the expected timeframe, can i work while pursuing a phd, can i accelerate the process of earning a phd, scholarships360 recommended.

10 Tips for Successful College Applications

Coalition vs. Common App: What is the difference?

College Application Deadlines 2023-2024: What You Need to Know
Trending now.

How to Convert Your GPA to a 4.0 Scale

PSAT to SAT Score Conversion: Predict Your Score

What Are Public Ivy League Schools?
3 reasons to join scholarships360.
- Automatic entry to our $10,000 No-Essay Scholarship
- Personalized matching to thousands of vetted scholarships
- Quick apply for scholarships exclusive to our platform
By the way...Scholarships360 is 100% free!

PhD in Population Health Sciences
Prepare for a high-impact career tackling public health problems from air pollution to obesity to global health equity to the social determinants of health.
The PhD in population health sciences is a multidisciplinary research degree that will prepare you for a career focused on challenges and solutions that affect the lives of millions around the globe. Collaborating with colleagues from diverse personal and professional backgrounds and conducting field and/or laboratory research projects of your own design, you will gain the deep expertise and powerful analytical and quantitative tools needed to tackle a wide range of complex, large-scale public health problems.
Focusing on one of five complementary fields of study at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and drawing on courses, resources, and faculty from the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, you will become well-versed in a wide variety of disciplines while gaining specialized knowledge in your chosen area of study.
As a population health sciences graduate, you will be prepared for a career in research, academics, or practice, tackling complex diseases and health problems that affect entire populations. Those interested in pursuing research may go on to work at a government agency or international organization, or in the private sector at a consulting, biotech, or pharmaceutical firm. Others may choose to pursue practice or on-the-ground interventions. Those interested in academics may become a faculty member in a college, university, medical school, research institute, or school of public health.
The PhD in population health sciences is a four-year program based at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in the world-renowned Longwood Medical Area of Boston, Massachusetts. The degree will prepare you to apply diverse approaches to solving difficult public health research issues in your choice of one of five primary fields of study:
- Environmental health
- Epidemiology
- Social and behavioral sciences
- Global health and population
In your first semester, you and your faculty adviser will design a degree plan to guide you through the program’s interdisciplinary requirements and core courses, as well as those in your chosen field of study. After successfully completing the preliminary qualifying examination, usually at the end of your second year, you will finalize your general research topics and identify a dissertation adviser who will mentor you through the dissertation process and help you nominate a dissertation advisory committee.
All population health sciences students are trained in pedagogy and teaching and are required to work as a teaching fellow and/or research assistant to ensure they gain meaningful teaching and research experience before graduation. Students also attend a special weekly evening seminar that features prominent lecturers, grant-writing modules, feedback dinners, and training opportunities.
All students, including international students, who maintain satisfactory progress (B+ or above) receive a multiyear funding package, which includes tuition, fees , and a competitive stipend.
WHO SHOULD APPLY?
Anyone with a distinguished undergraduate record and a demonstrated enthusiasm for the rigorous pursuit of scientific public health knowledge is encouraged to apply. Although a previous graduate degree is not required, applicants should have successfully completed coursework in introductory statistics or quantitative methods. Preference will be given to applicants who have either some relevant work experience or graduate-level work in their desired primary field of study.
APPLICATION PROCESS
Like all PhD (doctor of philosophy) programs at the School, the PhD in population health sciences is offered under the aegis of the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences (Harvard Griffin GSAS). Applications are processed through the Harvard Griffin GSAS online application system located at gsas.harvard.edu/admissions/apply.
OUR COMMUNITY: COMMITTED, ACCOMPLISHED, COLLABORATIVE
As a PhD in population health sciences candidate, you will be part of a diverse and accomplished group of students with a broad range of research and other interests. The opportunity to learn from each other and to share ideas both inside and outside the classroom will be one of the most rewarding and productive parts of the program for any successful candidate. The program in population health sciences provides these opportunities by sponsoring an informal curriculum of seminars, a dedicated student gathering and study area, and events that will enhance your knowledge, foster interaction with your peers, and encourage you to cooperatively evaluate scientific literature, while providing a supportive, collaborative community within which to pursue your degree.
As members of both the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences communities, students have access to the Cambridge and Longwood Medical Area campuses. Students also qualify for affordable transportation options, access to numerous lectures and academic seminars, and a wealth of services to support their academic and personal needs on both sides of the Charles River.
LEARN MORE Population Health Sciences Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health www.hsph.harvard.edu/phdphs
Email forwarding for @cs.stanford.edu is changing. Updates and details here . CS Commencement Ceremony June 16, 2024. Learn More .
PhD Admissions
Main navigation.
The Computer Science Department PhD program is a top-ranked research-oriented program, typically completed in 5-6 years. There are very few course requirements and the emphasis is on preparation for a career in Computer Science research.
Eligibility
To be eligible for admission in a Stanford graduate program, applicants must meet:
- Applicants from institutions outside of the United States must hold the equivalent of a United States Bachelor's degree from a college or University of recognized good standing. See detailed information by region on Stanford Graduate Admissions website.
- Area of undergraduate study . While we do not require a specific undergraduate coursework, it is important that applicants have strong quantitative and analytical skills; a Bachelor's degree in Computer Science is not required.
Any questions about the admissions eligibility should be directed to [email protected] .
Application Checklist
An completed online application must be submitted by the CS Department application deadline and can be found here .
Application Deadlines
The online application can be found here and we will only one admissions cycle for the PhD program per respective academic term.
- Search This Site All UCSD Sites Faculty/Staff Search Term
- School Factsheet
- Faculty Honors
- Dean's Leadership Council
- Research Topics
- Academic Departments
- Initiatives and Units
- Facilities and Resources
- Undergraduate
- Student Success
- Contiguous BS/MS Program
- Concurrent Enrollment
- Co-Op Program
- Message from the Director
- Who are we?
- Faculty Expectations
- Get Involved
- Accountability
- Postdoctoral
- Instructional
- Professional Researcher
- Instructional Assistants
- Summer Session
- Alumni Spotlights
- Ways to Give
- Eureka! Scholars Program
- Units & Resources
- Directories
Ph.D. Program

The philosophy of the PhD program, along with the Affiliated Ph.D. Program with the Salk Institute for Biological Studies, is to provide world-class research training in the basic biological sciences to equip a diverse group of trainees for a variety of scientific careers ranging from academia and industry to education, communication, or policy. Core principles of the program are to be student centered and attuned to the goals of the trainee.
The core curriculum focuses on development of core competencies and transferable skills in critical thinking, communication, and leadership. The first year prepares students for the core of the PhD program, the development of intellectual independence and creativity through original thesis research, guided by a thesis advisor and committee. Students have a high degree of flexibility in choice of thesis advisor through the rotation program. Throughout the program, there is strong emphasis on engaged mentoring through regular committee meetings, annual reports and Individual Development Plans.
As a central hub of the thriving San Diego biosciences community, the program maintains strong partnerships with other campus units and programs through joint faculty appointments, organized research units, and research collaborations, enabling a wide range of interdisciplinary opportunities . The mission is to conduct leading edge research in the basic biological sciences. Major areas of emphasis currently include structural biology, cell biology, developmental biology, neurobiology, immunology, microbiology, virology, plant biology, ecology, and evolutionary biology. Research in the School has emphasized studies using model organisms or in vitro mechanistic approaches, with human studies and clinical research concentrated in other departments or in the Health Sciences. Current and future areas of growth include quantitative biology, data science, and the biological consequences of climate change.
- Rigor, reproducibility, and responsibility as hallmarks of high-quality science
- Commitment to quality mentorships, student mental health, and well-being
- Equity, Diversity and Inclusion as integral to program admissions and retention
- Open science practices valuing multiple research outputs and holistic assessment of scholarly excellence
- Communication and outreach as key aspects of scientific training
As a doctoral program embedded in a large undergraduate instructional unit, our approach incorporates substantial training in teaching methodology and best practices. Our philosophy remains that teaching and research are interdependent facets of engaged scholarship.
- Curricular Requirements
- Training Programs
- Course Offerings
- Academic Advising
- Financial Support
- Professional Development
- Graduate Student Awards
- Graduate Student Representatives
- Student Directory
- Joint Doctoral Program (SDSU)
Quick Links
- Salk Institute
- Graduate Student Handbook
CS PhD Course Guidelines
The following program guidelines (a.k.a model pogram) serve as a starting point for a discussion with the faculty about areas of interest. This description of the Computer Science PhD course guidelines augments the school-wide PhD course requirements . Students should make themselves familiar with both.
Course Guidelines for Ph.D. Students in Computer Science
We expect students to obtain broad knowledge of computer science by taking graduate level courses in a variety of sub-areas in computer science, such as systems, networking, databases, algorithms, complexity, hardware, human-computer interaction, graphics, or programming languages.
Within our school, CS courses are roughly organized according to sub-area by their middle digit, so we expect students to take courses in a minimum of three distinct sub-areas, one of which should be theory (denoted by the middle digit of 2, or CS 231). Theory is specifically required as we expect all students to obtain some background in the mathematical foundations that underlie computer science. The intention is not only to give breadth to students, but to ensure cross-fertilization across different sub-disciplines in Computer Science.
Just as we expect all students obtaining a Ph.D. to have experience with the theoretical foundations of computer science, we expect all students to have some knowledge of how to build large software or hardware systems , on the order of thousands of lines of code, or the equivalent complexity in hardware. That experience may be evidenced by coursework or by a project submitted to the CHD for examination. In almost all cases a course numbered CS 26x or CS 24x will satisfy the requirement (exceptions will be noted in the course description on my.harvard). Students may also petition to use CS 161 for this requirement. For projects in other courses, research projects, or projects done in internships the student is expected to write a note explaining the project, include a link to any relevant artifacts or outcomes, describe the student's individual contribution, and where appropriate obtain a note from their advisor, their class instructor, or their supervisors confirming their contributions. The project must include learning about systems concepts, and not just writing many lines of code. Students hoping to invoke the non-CS24x/26x/161 option must consult with Prof. Mickens , Prof, Kung, or Prof. Idreos well in advance of submitting their Program Plan to the CHD.
Computer science is an applied science, with connections to many fields. Learning about and connecting computer science to other fields is a key part of an advanced education in computer science. These connections may introduce relevant background, or they may provide an outlet for developing new applications.
For example, mathematics courses may be appropriate for someone working in theory, linguistics courses may be appropriate for someone working in computational linguistics, economics courses may be appropriate for those working in algorithmic economics, electrical engineering courses may be appropriate for those working in circuit design, and design courses may be appropriate for someone working in user interfaces.
Requirements
The Graduate School of Arts & Sciences (GSAS) requires all Ph.D. students to complete 16 half-courses (“courses”, i.e., for 4 units of credit) to complete their degree. Of those 16 courses, a Ph.D. in Computer Science requires 10 letter-graded courses. (The remaining 6 courses are often 300-level research courses or other undergraduate or graduate coursework beyond the 10 required courses.)
The requirements for the 10 letter-graded courses are as follows:
- Of the 7 technical courses, at least 3 must be 200-level Computer Science courses, with 3 different middle digits (from the set 2,3,4,5,6,7,8), and with one of these three courses either having a middle digit of 2 or being CS 231 (i.e., a “theory” course). Note that CS courses with a middle digit of 0 are valid technical courses, but do not contribute to the breadth requirement.
- At least 5 of the 8 disciplinary courses must be SEAS or SEAS-equivalent 200-level courses. A “SEAS equivalent” course is a course taught by a SEAS faculty member in another FAS department.
- For any MIT course taken, the student must provide justification why the MIT course is necessary (i.e. SEAS does not offer the topic, the SEAS course has not been offered in recent years, etc.). MIT courses do not count as part of the 5 200-level SEAS/SEAS-equivalent courses.
- 2 of the 10 courses must constitute an external minor (referred to as "breadth" courses in the SEAS “ Policies of the Committee on Higher Degrees [CHD] ”) in an area outside of computer science. These courses should be clearly related; generally, this will mean the two courses are in the same discipline, although this is not mandatory. These courses must be distinct from the 8 disciplinary courses referenced above.
- Students must demonstrate practical competence by building a large software or hardware system during the course of their graduate studies. This requirement will generally be met through a class project, but it can also be met through work done in the course of a summer internship, or in the course of research.
- In particular, for Computer Science graduate degrees, Applied Computation courses may be counted as 100-level courses, not 200-level courses.
- Up to 2 of the 10 courses can be 299r courses, but only 1 of the up to 2 allowed 299r courses can count toward the 8 disciplinary courses. 299r courses do not count toward the 5 200-level SEAS/SEAS-equivalent courses. If two 299r’s are taken, they can be with the same faculty but the topics must be sufficiently different.
- A maximum of 3 graduate-level transfer classes are allowed to count towards the 10 course requirement.
- All CS Ph.D. program plans must adhere to the SEAS-wide Ph.D. requirements, which are stated in the SEAS Policies of the Committee on Higher Degrees (CHD) . These SEAS-wide requirements are included in the items listed above, though students are encouraged to read the CHD document if there are questions, as the CHD document provides further explanation/detail on several of the items above.
- All program plans must be approved by the CHD. Exceptions to any of these requirements require a detailed written explanation of the reasoning for the exception from the student and the student’s research advisor. Exceptions can only be approved by the CHD, and generally exceptions will only be given for unusual circumstances specific to the student’s research program.
Requirement Notes
- Courses below the 100-level are not suitable for graduate credit.
- For students who were required to take it, CS 2091/2092 (formerly CS 290a/b or 290hfa/hfb may be included as one of the 10 courses but it does not count toward the 200-level CS or SEAS/SEAS-equivalent course requirements nor toward the SM en route to the PhD.
Your program plan must always comply with both our school's General Requirements, in addition to complying with the specific requirements for Computer Science. All program plans must be approved by the Committee on Higher Degrees [CHD]. Exceptions to the requirements can only be approved by the CHD, and generally will only be given for unusual circumstances specific to the student’s research program
In Computer Science
- First-Year Exploration
- Concentration Information
- Secondary Field
- Senior Thesis
- AB/SM Information
- Student Organizations
- How to Apply
- PhD Timeline
- PhD Course Requirements
- Qualifying Exam
- Committee Meetings (Review Days)
- Committee on Higher Degrees
- Research Interest Comparison
- Collaborations
- Cross-Harvard Engagement
- Lecture Series
- Clubs & Organizations
- Centers & Initiatives
- Alumni Stories
Smart. Open. Grounded. Inventive. Read our Ideas Made to Matter.
Which program is right for you?

Through intellectual rigor and experiential learning, this full-time, two-year MBA program develops leaders who make a difference in the world.
A rigorous, hands-on program that prepares adaptive problem solvers for premier finance careers.
A 12-month program focused on applying the tools of modern data science, optimization and machine learning to solve real-world business problems.
Earn your MBA and SM in engineering with this transformative two-year program.
Combine an international MBA with a deep dive into management science. A special opportunity for partner and affiliate schools only.
A doctoral program that produces outstanding scholars who are leading in their fields of research.
Bring a business perspective to your technical and quantitative expertise with a bachelor’s degree in management, business analytics, or finance.
A joint program for mid-career professionals that integrates engineering and systems thinking. Earn your master’s degree in engineering and management.
An interdisciplinary program that combines engineering, management, and design, leading to a master’s degree in engineering and management.
Executive Programs
A full-time MBA program for mid-career leaders eager to dedicate one year of discovery for a lifetime of impact.
This 20-month MBA program equips experienced executives to enhance their impact on their organizations and the world.
Non-degree programs for senior executives and high-potential managers.
A non-degree, customizable program for mid-career professionals.
PhD Program
Program overview.
Now Reading 1 of 4
Rigorous, discipline-based research is the hallmark of the MIT Sloan PhD Program. The program is committed to educating scholars who will lead in their fields of research—those with outstanding intellectual skills who will carry forward productive research on the complex organizational, financial, and technological issues that characterize an increasingly competitive and challenging business world.
Start here.
Learn more about the program, how to apply, and find answers to common questions.
Admissions Events
Check out our event schedule, and learn when you can chat with us in person or online.
Start Your Application
Visit this section to find important admissions deadlines, along with a link to our application.
Click here for answers to many of the most frequently asked questions.
PhD studies at MIT Sloan are intense and individual in nature, demanding a great deal of time, initiative, and discipline from every candidate. But the rewards of such rigor are tremendous: MIT Sloan PhD graduates go on to teach and conduct research at the world's most prestigious universities.
PhD Program curriculum at MIT Sloan is organized under the following three academic areas: Behavior & Policy Sciences; Economics, Finance & Accounting; and Management Science. Our nine research groups correspond with one of the academic areas, as noted below.
MIT Sloan PhD Research Groups
Behavioral & policy sciences.
Economic Sociology
Institute for Work & Employment Research
Organization Studies
Technological Innovation, Entrepreneurship & Strategic Management
Economics, Finance & Accounting
Accounting
Management Science
Information Technology
System Dynamics
Those interested in a PhD in Operations Research should visit the Operations Research Center .

PhD Program Structure
Additional information including coursework and thesis requirements.

MIT Sloan Predoctoral Opportunities
MIT Sloan is eager to provide a diverse group of talented students with early-career exposure to research techniques as well as support in considering research career paths.
Rising Scholars Conference
The fourth annual Rising Scholars Conference on October 25 and 26 gathers diverse PhD students from across the country to present their research.
Now Reading 2 of 4
The goal of the MIT Sloan PhD Program's admissions process is to select a small number of people who are most likely to successfully complete our rigorous and demanding program and then thrive in academic research careers. The admission selection process is highly competitive; we aim for a class size of nineteen students, admitted from a pool of hundreds of applicants.
What We Seek
- Outstanding intellectual ability
- Excellent academic records
- Previous work in disciplines related to the intended area of concentration
- Strong commitment to a career in research
MIT Sloan PhD Program Admissions Requirements Common Questions
Dates and Deadlines
Admissions for 2024 is closed. The next opportunity to apply will be for 2025 admission. The 2025 application will open in September 2024.
More information on program requirements and application components
Students in good academic standing in our program receive a funding package that includes tuition, medical insurance, and a fellowship stipend and/or TA/RA salary. We also provide a new laptop computer and a conference travel/research budget.
Funding Information
Throughout the year, we organize events that give you a chance to learn more about the program and determine if a PhD in Management is right for you.
PhD Program Events
May phd program overview.
During this webinar, you will hear from the PhD Program team and have the chance to ask questions about the application and admissions process.
June PhD Program Overview
July phd program overview, august phd program overview.
Complete PhD Admissions Event Calendar
Unlike formulaic approaches to training scholars, the PhD Program at MIT Sloan allows students to choose their own adventure and develop a unique scholarly identity. This can be daunting, but students are given a wide range of support along the way - most notably having access to world class faculty and coursework both at MIT and in the broader academic community around Boston.
Now Reading 3 of 4

Profiles of our current students
MIT Sloan produces top-notch PhDs in management. Immersed in MIT Sloan's distinctive culture, upcoming graduates are poised to innovate in management research and education.
Academic Job Market
Doctoral candidates on the current academic market
Academic Placements
Graduates of the MIT Sloan PhD Program are researching and teaching at top schools around the world.
view recent placements
MIT Sloan Experience
Now Reading 4 of 4
The PhD Program is integral to the research of MIT Sloan's world-class faculty. With a reputation as risk-takers who are unafraid to embrace the unconventional, they are engaged in exciting disciplinary and interdisciplinary research that often includes PhD students as key team members.
Research centers across MIT Sloan and MIT provide a rich setting for collaboration and exploration. In addition to exposure to the faculty, PhD students also learn from one another in a creative, supportive research community.
Throughout MIT Sloan's history, our professors have devised theories and fields of study that have had a profound impact on management theory and practice.
From Douglas McGregor's Theory X/Theory Y distinction to Nobel-recognized breakthroughs in finance by Franco Modigliani and in option pricing by Robert Merton and Myron Scholes, MIT Sloan's faculty have been unmatched innovators.
This legacy of innovative thinking and dedication to research impacts every faculty member and filters down to the students who work beside them.
Faculty Links
- Accounting Faculty
- Economic Sociology Faculty
- Finance Faculty
- Information Technology Faculty
- Institute for Work and Employment Research (IWER) Faculty
- Marketing Faculty
- Organization Studies Faculty
- System Dynamics Faculty
- Technological Innovation, Entrepreneurship, and Strategic Management (TIES) Faculty
Student Research
“MIT Sloan PhD training is a transformative experience. The heart of the process is the student’s transition from being a consumer of knowledge to being a producer of knowledge. This involves learning to ask precise, tractable questions and addressing them with creativity and rigor. Hard work is required, but the reward is the incomparable exhilaration one feels from having solved a puzzle that had bedeviled the sharpest minds in the world!” -Ezra Zuckerman Sivan Alvin J. Siteman (1948) Professor of Entrepreneurship
Sample Dissertation Abstracts - These sample Dissertation Abstracts provide examples of the work that our students have chosen to study while in the MIT Sloan PhD Program.
We believe that our doctoral program is the heart of MIT Sloan's research community and that it develops some of the best management researchers in the world. At our annual Doctoral Research Forum, we celebrate the great research that our doctoral students do, and the research community that supports that development process.
The videos of their presentations below showcase the work of our students and will give you insight into the topics they choose to research in the program.
How Should We Measure the Digital Economy?
2020 PhD Doctoral Research Forum Winner - Avinash Collis
Watch more MIT Sloan PhD Program Doctoral Forum Videos

Keep Exploring
Ask a question or register your interest
Faculty Directory
Meet our faculty.
Main navigation
The PhD program requires three years of full-time graduate study, at least two years of which must be at Stanford. Typically, however, students take four to five years after entering the program to complete all PhD requirements. The University requires a minimum of 135 units for a PhD, up to 45 units of which may be transferred from another graduate program, or used toward a master's degree at Stanford.
Areas of research
Breadth requirement, qualification procedure requirements, degree progress and student responsibility.
Oral examination
Doctoral students are required to take a number of courses, both to pass a qualifying exam in one of these areas, and to complete a dissertation based on research which must make an original contribution to knowledge. The PhD is generally organized around the expectation that the student acquires a certain breadth across all areas of the department, and depth in one area.
The current areas are: Computational Social Science Decision and Risk Analysis Operations Research Organizations, Technology and Entrepreneurship Policy and Strategy Quantitative Finance
Each student admitted to the PhD program must satisfy a breadth requirement.
All first year students are required to attend and participate in MS&E 302 Fundamental Concepts in Management Science and Engineering, which will meet in the Autumn Quarter.
Each course session will be devoted to a specific MS&E PhD research area. At a given session, several advanced PhD students in that area will make carefully prepared presentations designed for first-year doctoral students regardless of area. The presentations will be devoted to: (a) illuminating how people in the area being explored that day think about and approach problems, and (b) illustrating what can and cannot be done when addressing problems by deploying the knowledge, perspectives, and skills acquired by those who specialize in the area in question.
Faculty in the focal area of the week will comment on the student presentations. The rest of the session will be devoted to questions posed and comments made by the first-year PhD students.
During the last two weeks of the quarter groups of first year students will make presentations on how they would approach a problem drawing on two or more of the perspectives to which they have been exposed earlier in the class.
Attendance is mandatory and performance will be assessed on the basis of the quality of the students’ presentations and class participation.
Each student admitted to the PhD program must pass an area qualification procedure. The purpose of the qualification procedure is to assess the student’s command of the field and to evaluate his or her potential to complete a high-quality dissertation in a timely manner. The student must complete specified course work in one of the areas of the department. The qualification decision is based on the student’s coursework and grade point average (GPA), on the one or two preliminary papers prepared by the student with close guidance from two faculty members, at least one of whom must be an MS&E faculty member, the student’s performance in an area examination or defense of the written paper(s), and an overall assessment by the faculty of the student's ability to conduct high-quality PhD research. Considering this evidence, the department faculty will vote on advancing the student to candidacy in the department at large.
The qualification procedure is based on depth in an area of the student’s choice and preparation for dissertation research. The qualification process must be completed by the end of the month of May in the student’s second year of graduate study in the department. The performance of all doctoral students will be reviewed every year at a department faculty meeting at the end of May or beginning of June. PhD qualification decisions will be made at that time and individual feedback will be provided.
The PhD qualification requirements comprise the following elements:
Courses and GPA: Students must complete the depth requirements of one of the areas of the MS&E department. All courses used to satisfy depth requirements must be taken for a letter grade, if the letter-graded option is available. Course substitutions may be approved by the doctoral program advisor or the MS&E dissertation advisor on the candidacy form or on a request for graduate course substitution form. A student must maintain a GPA of at least 3.4 in the set of all courses taken by the student within the department. The GPA will be computed on the basis of the nominal number of units for which each course is offered.
Paper(s): A student may choose between two options. The first option involves one paper supervised by a primary faculty advisor and a second faculty reader. This paper should be written in two quarters. The second option involves two shorter sequential tutorials, with two different faculty advisors. Each tutorial should be completed in one quarter. In both options, the student chooses the faculty advisor(s)/reader with the faculty members’ consent. There must be two faculty members, at least one of whom must be an MS&E faculty member, supervising and evaluating this requirement for advancement to candidacy. The paper/tutorials must be completed before the Spring Quarter of a student’s second year of graduate study in the department if the student’s qualifying exam is during the Spring Quarter, and before the end of May of that year otherwise.
Area qualification: In addition, during the second year, a student must pass an examination in one of the areas of the MS&E department, or defense of the written paper(s). The student chooses the area/program in which to take the examination. This area examination will be written, oral, or both at the discretion of the area faculty administering the exam. Most areas offer the qualifying exam only once per year, which may be early in the second year.
Each doctoral student’s progress is reviewed annually by the MS&E faculty. Typically, this occurs at a faculty meeting at the end of Spring Quarter, and appropriate email notifications are sent over the summer to the students and their advisors. It shall be the responsibility of the student to initiate each required step in completing the PhD program. To maintain good standing in the PhD program,
First year students must: 1. Complete 30 units, including MS&E 302 and doctoral courses taught by faculty in their research area; 2. Develop relationships with faculty members who can potentially serve as dissertation advisor or reading committee member. A faculty member is more likely to accept the responsibility of supervising the research of a student whom he or she knows fairly well than a student whose abilities, initiative, and originality the faculty member knows less. It is recommended that students participate in research rotations with MS&E and related faculty to facilitate the development of these relationships.
Second year students must: 1. Complete at least two one-quarter research rotations or tutorials, or one two-quarter research rotation, tutorial, or research paper, continuing to develop relationships with faculty members who might serve as dissertation advisor or reading committee member; 2. Pass an area qualifying exam or defense of the written paper(s); 3. Submit a candidacy form signed by at least one MS&E faculty member with whom they have or will complete research rotations, tutorials, or papers, and listing the course requirements agreed upon by both the student and the program advisor; 4. Complete 30 units, including most, if not all, of the required courses listed on the candidacy form; 5. Be advanced to candidacy by the faculty.
Third year students must: 1. Submit a progress form listing the dissertation topic and signed by the dissertation advisor (if the dissertation advisor is not an MS&E faculty member, the form must also be signed by an MS&E faculty member who agrees to be on the student's reading committee, as well as the student's point of contact within the department); 2. Complete 30 units, including any remaining depth courses.
Fourth year students must: 1. Select a reading committee (a dissertation advisor and two readers) with at least one member from the student's major department, and submit the reading committee form signed by each member on the reading committee; 2. Make satisfactory progress on their dissertation as determined by their dissertation advisor; 3. If the student has not transferred any previous graduate units to Stanford, complete 30 dissertation units.
Students beyond their fourth year must make satisfactory progress on their dissertation as determined by their dissertation advisor and approved by the faculty. Indeed, the dissertation advisor will have to present the case to (and seek approval for good standing of the student from) the faculty in the annual faculty meeting for student review. It should be noted that each student inherently has to pass the oral examination (see below) and submit their dissertation before their candidacy expires.
Oral Examination
As administered in this department, the University oral examination is a defense of the dissertation; however, the candidate should be prepared to answer any question raised by any members of the Academic Council who choose to be present. The examining committee consists of the three members of the reading committee as well as a fourth faculty member and an orals chair. The chair must be an Academic Council member and may not be affiliated with either the Department of Management Science and Engineering nor any department in which the student's adviser has a regular appointment; emeriti professors are eligible to serve as an orals chair. It is the responsibility of the student's adviser to find an appropriate orals chair. The University oral examination may be scheduled after the dissertation reading committee has given tentative approval to the dissertation.
The student must be enrolled in the quarter of their oral examination. Students should schedule three hours for the oral examination, which usually consists of a 45-minute public presentation, followed by closed-session questioning of the examinee by the committee, and committee deliberation. The student needs to reserve a room, and meet with the student services manager to complete the oral examination schedule and pick up other paper work. This paperwork, along with an abstract, needs to be delivered to the orals chair at least one week prior to the oral examination.
Personalise your experience
Graduate Research
Doctor of Philosophy - Science
- Course code: DR-PHILSCI
Course overview
Join one of our world-renowned research groups, work with state-of-the-art equipment, and soak up all the professional development opportunities and international connections that come with studying at Australia's leading university.
With many research disciplines to choose from (Ecosystem Sciences, BioSciences, Chemistry, Geography, Earth and Atmospheric Sciences, Mathematics and Statistics and Physics), and more than 500 academic researchers to work with, you’re sure to find a team and a PhD project that will suit you.
Global opportunities
In addition to our own leading PhD program, we also offer several joint PhD opportunities, where you can conduct your research at both the University of Melbourne and a top research institution overseas .
Industry connections
To prepare you for your post-PhD career, you can take advantage of the time between submitting your thesis and it being conferred by completing a 3–6 month industry placement through our Specialist Certificate in Research Practice for Scientists .

Not just a researcher
The Melbourne experience enables our graduates to become specialists within their field, leaders in communities, attuned to cultural diversity, and active global citizens.
Related study areas
- Agricultural and veterinary sciences
- Agricultural sciences
- Bioinformatics
- Biological sciences
- Biomedical sciences
- Computer science
- Conservation
- Data and analytics
- Data science
- Earth and environmental sciences
- Engineering
- Environment
- Environmental engineering
- Environmental law, policy and sustainability
- Food science
- Health sciences
- Information systems
- Information technology and computer science
- Mathematics and statistics
- Veterinary science
- Crimson Careers
- For Employers
- Harvard College
- Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts & Sciences
- Harvard Extension School
- Premed / Pre-Health
- Families & Supporters
- Faculty & Staff
- Prospective Students
- First Generation / Low Income
- International Students
- Students of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Undocumented Students
- Explore Interests & Make Career Decisions
- Create a Resume/CV or Cover Letter
- Expand Your Network
- Engage with Employers
- Search for a Job
- Find an Internship
- January Experiences (College)
- Find & Apply for Summer Opportunities Funding
- Prepare for an Interview
- Negotiate an Offer
- Apply to Graduate or Professional School
- Access Resources
- AI for Professional Development and Exploration
- Arts & Entertainment
- Business & Entrepreneurship
- Climate, Sustainability, Environment, Energy
- Government, Int’l Relations, Education, Law, Nonprofits
- Life Sciences & Health
- Technology & Engineering
- Still Exploring
- Talk to an Advisor
How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree?
- Share This: Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on Facebook Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on LinkedIn Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on X
Earning a Ph.D. from a U.S. grad school typically requires nearly six years, federal statistics show.

(CAIAIMAGE/TOM MERTON/GETTY IMAGES)
A Ph.D. is most appropriate for someone who is a “lifelong learner.”
Students who have excelled within a specific academic discipline and who have a strong interest in that field may choose to pursue a Ph.D. degree. However, Ph.D. degree-holders urge prospective students to think carefully about whether they truly want or need a doctoral degree, since Ph.D. programs last for multiple years.
According to the Survey of Earned Doctorates, a census of recent research doctorate recipients who earned their degree from U.S. institutions, the median amount of time it took individuals who received their doctorates in 2017 to complete their program was 5.8 years. However, there are many types of programs that typically take longer than six years to complete, such as humanities and arts doctorates, where the median time for individuals to earn their degree was 7.1 years, according to the survey.
Some Ph.D. candidates begin doctoral programs after they have already obtained master’s degrees, which means the time spent in grad school is a combination of the time spent pursuing a master’s and the years invested in a doctorate. In order to receive a Ph.D. degree, a student must produce and successfully defend an original academic dissertation, which must be approved by a dissertation committtee. Writing and defending a dissertation is so difficult that many Ph.D. students drop out of their Ph.D. programs having done most of the work necessary for degree without completing the dissertation component. These Ph.D. program dropouts often use the phrase “ all but dissertation ” or the abbreviation “ABD” on their resumes.
According to a comprehensive study of Ph.D. completion rates published by The Council of Graduate Schools in 2008, only 56.6% of people who begin Ph.D. programs earn Ph.D. degrees.
Ian Curtis, a founding partner with H&C Education, an educational and admissions consulting firm, who is pursuing a Ph.D. degree in French at Yale University , says there are several steps involved in the process of obtaining a Ph.D. Students typically need to fulfill course requirements and pass comprehensive exams, Curtis warns. “Once these obligations have been completed, how long it takes you to write your dissertation depends on who you are, how you work, what field you’re in and what other responsibilities you have in life,” he wrote in an email. Though some Ph.D. students can write a dissertation in a single year, that is rare, and the dissertation writing process may last for several years, Curtis says.
[ READ: What Is a Doctorate or a Doctoral Degree? ]
Curtis adds that the level of support a Ph.D. student receives from an academic advisor or faculty mentor can be a key factor in determining the length of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. program. “Before you decide to enroll at a specific program, you’ll want to meet your future advisor,” Curtis advises. “Also, reach out to his or her current and former students to get a sense of what he or she is like to work with.”
Curtis also notes that if there is a gap between the amount of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. and the amount of time a student’s funding lasts, this can slow down the Ph.D. completion process. “Keep in mind that if you run out of funding at some point during your doctorate, you will need to find paid work, and this will leave you even less time to focus on writing your dissertation,” he says. “If one of the programs you’re looking at has a record of significantly longer – or shorter – times to competition, this is good information to take into consideration.”
Pierre Huguet, the CEO and co-founder of H&C Education, says prospective Ph.D. students should be aware that a Ph.D. is designed to prepare a person for a career as a scholar. “Most of the jobs available to Ph.D. students upon graduation are academic in nature and directly related to their fields of study: professor, researcher, etc.,” Huguet wrote in an email. “The truth is that more specialization can mean fewer job opportunities. Before starting a Ph.D., students should be sure that they want to pursue a career in academia, or in research. If not, they should make time during the Ph.D. to show recruiters that they’ve traveled beyond their labs and libraries to gain some professional hands-on experience.”
Jack Appleman, a business writing instructor, published author and Ph.D. candidate focusing on organizational communication with the University at Albany—SUNY , says Ph.D. programs require a level of commitment and focus that goes beyond what is necessary for a typical corporate job. A program with flexible course requirements that allow a student to customize his or her curriculum based on academic interests and personal obligations is ideal, he says.
[ READ: Ph.D. Programs Get a Lot More Practical. ]
Joan Kee, a professor at the University of Michigan with the university’s history of art department, says that the length of time required for a Ph.D. varies widely depending on what subject the Ph.D. focuses on. “Ph.D. program length is very discipline and even field-specific; for example, you can and are expected to finish a Ph.D, in economics in under five years, but that would be impossible in art history (or most of the humanities),” she wrote in an email.
Jean Marie Carey, who earned her Ph.D. degree in art history and German from the University of Otago in New Zealand, encourages prospective Ph.D. students to check whether their potential Ph.D. program has published a timeline of how long it takes a Ph.D. student to complete their program. She says it is also prudent to speak with Ph.D. graduates of the school and ask about their experience.
Bennett urges prospective Ph.D. students to visit the campuses of their target graduate programs since a Ph.D. program takes so much time that it is important to find a school that feels comfortable. She adds that aspiring Ph.D. students who prefer a collaborative learning environment should be wary of graduate programs that have a cut-throat and competitive atmosphere, since such students may not thrive in that type of setting.
[ READ: 4 Fields Where Doctorates Lead to Jobs. ]
Alumni of Ph.D. programs note that the process of obtaining a Ph.D. is arduous, regardless of the type of Ph.D. program. “A Ph.D. is a long commitment of your time, energy and financial resources, so it’ll be easier on you if you are passionate about research,” says Grace Lee, who has a Ph.D. in neuroscience and is the founder and CEO of Mastery Insights, an education and career coaching company, and the host of the Career Revisionist podcast.
“A Ph.D. isn’t about rehashing years of knowledge that is already out there, but rather it is about your ability to generate new knowledge. Your intellectual masterpiece (which is your dissertation) takes a lot of time, intellectual creativity and innovation to put together, so you have to be truly passionate about that,” Lee says.
Erin Skelly, a graduate admissions counselor at the IvyWise admissions consulting firm, says when a Ph.D. students struggles to complete his or her Ph.D. degree, it may have more to do with the student’s academic interests or personal circumstances than his or her program.
“The time to complete a Ph.D. can depend on a number of variables, but the specific discipline or school would only account for a year or two’s difference,” she wrote in an email. “When a student takes significantly longer to complete a Ph.D. (degree), it’s usually related to the student’s coursework and research – they need to take additional coursework to complete their comprehensive exams; they change the focus of their program or dissertation, requiring extra coursework or research; or their research doesn’t yield the results they hoped for, and they need to generate a new theory and conduct more research.”
Skelly warns that the average completion time of a Ph.D. program may be misleading in some cases, if the average is skewed based on one or two outliers. She suggests that instead of focusing on the duration of a particular Ph.D. program, prospective students should investigate the program’s attritition and graduation rates.
“It is worthwhile to look at the program requirements and the school’s proposed timeline for completion, and meet current students to get their input on how realistic these expectations for completion are,” Skelly says. “That can give you an honest idea of how long it will really take to complete the program.”
Searching for a grad school? Access our complete rankings of Best Graduate Schools.
PhD Time Limits & Milestones
Graduate college time requirements for degree.
- Bachelors to PhD Program Time Limits - 7 years from first term enrolled in doctoral program. Please see Illinois CS PhD Milestones below for the Department's Time Requirement for Ph.D.
- PhD Program Time Limits with a MS at Illinois - 5 years (2 yrs. for MS and 5 yrs. for PhD)
- PhD Program Time Limits with a Non-Illinois MS - 6 years from first term enrolled in doctoral program
Illinois CS PhD Milestone Timeline
The department's timeline is an average of 6 years to complete the Ph.D. degree. The timeline below is based on a 5-year program of study.
Graduate Advising
The Graduate Academic Office, a guiding hand for CS graduate students, assistance is available every weekday.
- MSE Strategic Plan 2023
- Undergraduate Programs
- Graduate Programs
- Research Topics
- Research Groups
- Research Videos
- Research Professionals
- Graduate Students
- MSE Advisory Council
- Awards and Honors
- Position Openings in MSE
- Collaborative Facilities Across Campus
- Alumni Spotlights
- Distinguished Alumni Award
- Class Photos
- Giving Opportunities
- Recruit Students
- MSE Newsletters
- Experience and Employment
- Graduate Services and Activities
- Forms & Checklists
- Identity, Health, Wellness
- Graduate TAs for Current Semester
Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.)
The fall 2024 mse ph.d. application will open september 15, 2023. if you have admissions questions, please contact [email protected] ..
Students in the Cornell Materials Science and Engineering (MSE) Ph.D. program come from a variety of engineering and physical science backgrounds. Some are MS&E undergraduates while many have degrees in areas such as mechanical engineering, chemical engineering, chemistry, and other fields. At Cornell, we embrace this breadth of experience and offer students a unique opportunity to explore the broad and inherently interdisciplinary nature of MSE.
Our Ph.D. students have established a legacy of outstanding professional achievement, rising to the top of their respective fields. They pursue distinguished careers in the U.S. and abroad with employers in the corporate, government, and academic sectors.
Distinguishing Factors
- Our graduate students are part of a relatively small, close-knit department with exposure and access to faculty in a wide range of specializations across campus. They may choose to work with one or more of them on their research, if their interests align.
- Cornell NanoScale Facility
- Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source
- Cornell Center for Materials Research
- MSK-Cornell Center for Translation of Cancer Nanomedicine
- Our graduate students form a vibrant community within this, extending their relationships beyond the laboratories to a range of social and extracurricular activities. One of the reasons for our success in collaboration is that Cornell has a longstanding history as “the friendly school” where faculty and students genuinely support and champion one another. It’s a way of life that extends long past graduation and makes the network of Cornell alumni warm and powerful.
Questions? Contact the graduate field representative at [email protected]
Planning your PhD research: A 3-year PhD timeline example
Planning out a PhD trajectory can be overwhelming. Example PhD timelines can make the task easier and inspire. The following PhD timeline example describes the process and milestones of completing a PhD within 3 years.
Elements to include in a 3-year PhD timeline
The example scenario: completing a phd in 3 years, example: planning year 1 of a 3-year phd, example: planning year 2 of a 3-year phd, example: planning year 3 of a 3-year phd, example of a 3 year phd gantt chart timeline, final reflection.
Every successful PhD project begins with a proper plan. Even if there is a high chance that not everything will work out as planned. Having a well-established timeline will keep your work on track.
What to include in a 3-year PhD timeline depends on the unique characteristics of a PhD project, specific university requirements, agreements with the supervisor/s and the PhD student’s career ambitions.
For instance, some PhD students write a monograph while others complete a PhD based on several journal publications. Both monographs and cumulative dissertations have advantages and disadvantages , and not all universities allow both formats. The thesis type influences the PhD timeline.
Furthermore, PhD students ideally engage in several different activities throughout a PhD trajectory, which link to their career objectives. Regardless of whether they want to pursue a career within or outside of academia. PhD students should create an all-round profile to increase their future chances in the labour market. Think, for example, of activities such as organising a seminar, engaging in public outreach or showcasing leadership in a small grant application.
The most common elements included in a 3-year PhD timeline are the following:
- Data collection (fieldwork, experiments, etc.)
- Data analysis
- Writing of different chapters, or a plan for journal publication
- Conferences
- Additional activities
The whole process is described in more detail in my post on how to develop an awesome PhD timeline step-by-step .
Many (starting) PhD students look for examples of how to plan a PhD in 3 years. Therefore, let’s look at an example scenario of a fictional PhD student. Let’s call her Maria.
Maria is doing a PhD in Social Sciences at a university where it is customary to write a cumulative dissertation, meaning a PhD thesis based on journal publications. Maria’s university regulations require her to write four articles as part of her PhD. In order to graduate, one article has to be published in an international peer-reviewed journal. The other three have to be submitted.
Furthermore, Maria’s cumulative dissertation needs an introduction and conclusion chapter which frame the four individual journal articles, which form the thesis chapters.
In order to complete her PhD programme, Maria also needs to complete coursework and earn 15 credits, or ECTS in her case.
Maria likes the idea of doing a postdoc after her graduation. However, she is aware that the academic job market is tough and therefore wants to keep her options open. She could, for instance, imagine to work for a community or non-profit organisation. Therefore, she wants to place emphasis on collaborating with a community organisation during her PhD.
You may also like: Creating awesome Gantt charts for your PhD timeline
Most PhD students start their first year with a rough idea, but not a well-worked out plan and timeline. Therefore, they usually begin with working on a more elaborate research proposal in the first months of their PhD. This is also the case for our example PhD student Maria.
- Months 1-4: Maria works on a detailed research proposal, defines her research methodology and breaks down her thesis into concrete tasks.
- Month 5 : Maria follows a short intensive course in academic writing to improve her writing skills.
- Months 5-10: Maria works on her first journal paper, which is based on an extensive literature review of her research topic. At the end of Month 10, she submits the manuscript. At the same time, she follows a course connected to her research topic.
- Months 11-12: Maria does her data collection.
Maria completed her first round of data collection according to plan, and starts the second year of her PhD with a lot of material. In her second year, she will focus on turning this data into two journal articles.
- Months 1-2: Maria works on her data analysis.
- Months 3-7: Maria works on her second journal paper.
- Month 7: Maria attends her first conference, and presents the results of her literature-review paper.
- Month 8: Maria received ‘major revisions’ on her first manuscript submission, and implements the changes in Month 8 before resubmitting her first journal paper for publication.
- Month 9: Maria follows a course on research valorisation to learn strategies to increase the societal impact of her thesis.
- Months 9-12: Maria works on her third journal paper. She uses the same data that she collected for the previous paper, which is why she is able to complete the third manuscript a bit faster than the previous one.
Time flies, and Maria finds herself in the last year of her PhD. There is still a lot of work to be done, but she sticks to the plan and does her best to complete her PhD.
- Month 1: Maria starts a second round of data collection, this time in collaboration with a community organisation. Together, they develop and host several focus groups with Maria’s target audience.
- Month 2: Maria starts to analyse the material of the focus group and develops the argumentation for her fourth journal paper.
- Month 3: Maria presents the results of her second journal paper at an international conference. Furthermore, she helps out her supervisor with a grant application. They apply for funding to run a small project that is thematically connected to her PhD.
- Months 4-9: Maria writes her fourth and final journal article that is required for her PhD.
- Month 10: Maria writes her thesis introduction .
- Month 11: Maria works on her thesis conclusion.
- Month 12 : Maria works on the final edits and proof-reading of her thesis before submitting it.
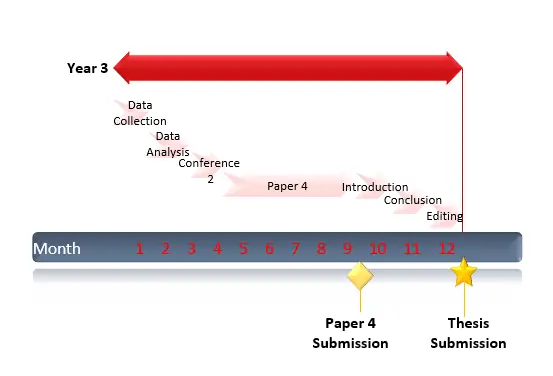
Combining the 3-year planning for our example PhD student Maria, it results in the following PhD timeline:
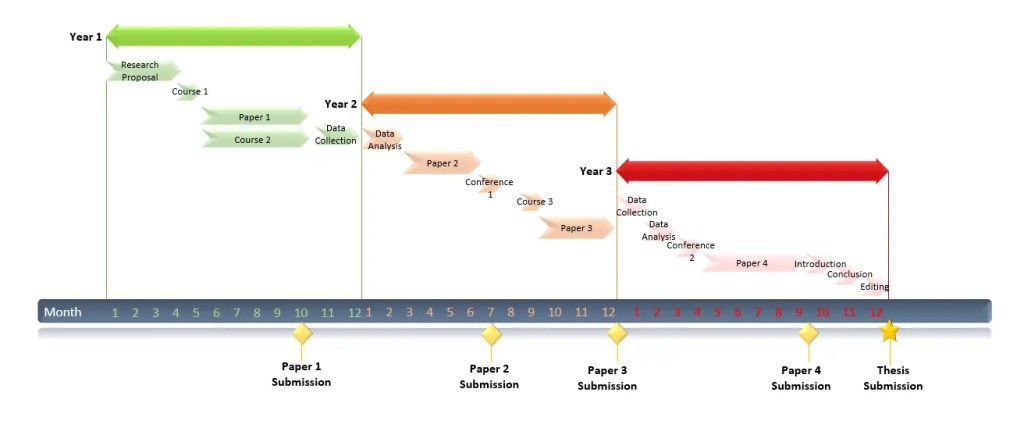
Creating these PhD timelines, also called Gantt charts, is easy. You can find instructions and templates here.
Completing a PhD in 3 years is not an easy task. The example of our fictional PhD student Maria shows how packed her timeline is, and how little time there is for things to go wrong.
In fact, in real life, many PhD students spend four years full-time to complete a PhD based on four papers, instead of three. Some extend their studies even longer.
Furthermore, plan in some time for thesis editing, which is a legitimate practice and can bring your writing to the next level. Finding a reputable thesis editor can be challenging, so make sure you make an informed choice.
Finishing a PhD in 3 years is not impossible, but it surely is not easy. So be kind to yourself if things don’t work out entirely as planned, and make use of all the help you can get.
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox!
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
10 amazing benefits of getting a PhD later in life
How to prepare your viva opening speech, related articles.

Character traits of ‘bad’ PhD students

Are summer schools for master’s students worth it?

Deciding between a one- or a two-year master’s degree

Pursuing A Part-Time Phd In Computer Science: What You Need To Know
Earning a PhD is the pinnacle of academic achievement in computer science, opening doors to research, teaching, and leadership roles. But taking 4+ years off work for a full-time program isn’t feasible for everyone.
Part-time PhD options allow professionals to attain this goal while continuing their careers.
If you’re short on time, here’s the key takeaway: Part-time CS PhD programs typically take 5-7 years to complete . They provide flexibility for working students but require diligence to balance school, research, and professional demands.
The Benefits of a Part-Time CS PhD
Progress academically without leaving your job.
A part-time PhD in Computer Science offers the unique opportunity to advance your academic career while still maintaining your professional commitments. This flexibility allows you to continue working in your current job, providing financial stability and practical application of your studies.
Balancing work and study can be challenging, but the rewards are worth it. By pursuing a part-time PhD, you can deepen your knowledge in your chosen field and make significant contributions to the advancement of computer science.
Network with faculty and peers in your field
One of the key advantages of pursuing a part-time PhD in Computer Science is the opportunity to network with esteemed faculty members and like-minded peers who share your passion for the subject. Interacting with experts in the field can provide valuable insights, guidance, and collaboration opportunities.
Attending conferences, workshops, and seminars can further expand your network and expose you to the latest developments in computer science. Building these connections can open doors to new opportunities and enhance your career prospects.
Strengthen research skills and resume
A part-time PhD program allows you to develop and refine your research skills, which are highly valued in the field of computer science. Through conducting in-depth research, analyzing data, and writing scholarly papers, you can enhance your ability to critically think, problem solve, and contribute to the body of knowledge in your area of expertise.
Moreover, having a PhD in Computer Science on your resume demonstrates your dedication, perseverance, and expertise, making you a highly sought-after candidate for both academic and industry positions.
Program Structure and Requirements
Reduced course load each semester.
Pursuing a part-time PhD in Computer Science offers flexibility in terms of course load. Unlike full-time students, part-time students typically take a reduced number of courses each semester. This allows them to balance their academic commitments with other personal and professional responsibilities.
By taking fewer courses at a time, part-time students can focus on their coursework more effectively and ensure a better understanding of the material.
Original dissertation research
The cornerstone of a part-time PhD program in Computer Science is the dissertation research. Students are required to embark on an original research project under the guidance of a faculty advisor. This research should contribute to the existing body of knowledge in the field and demonstrate a deep understanding of a specific area of computer science.
The research can involve developing new algorithms, designing innovative software systems, or exploring cutting-edge technologies.
Qualifying exams and proposal defense
Part-time PhD students in Computer Science are typically required to pass qualifying exams to demonstrate their readiness for conducting research. These exams assess the student’s knowledge and understanding of the core concepts in the field.
Once the exams are passed, students need to prepare a research proposal outlining the objectives, methodology, and expected contributions of their dissertation. The proposal is then defended in front of a committee of faculty members who evaluate its feasibility and significance.
It’s important to note that the specific structure and requirements of a part-time PhD program in Computer Science may vary depending on the institution. It is advisable to consult the program’s official website or contact the program coordinator for more detailed information.
Finding the Right Program
When pursuing a part-time PhD in Computer Science, finding the right program is crucial for success. Here are some key factors to consider:
On-campus and online options
One of the first decisions to make is whether to pursue your PhD on-campus or online. On-campus programs offer the benefit of face-to-face interactions with professors and fellow students, while online programs provide flexibility for those who are working or have other commitments.
It’s important to weigh the pros and cons of each option and choose the one that aligns best with your lifestyle and goals.
Focus on faculty research expertise
Another important factor to consider when choosing a program is the faculty’s research expertise. Look for programs where the faculty members have research interests and expertise that align with your own.
This will ensure that you receive guidance and mentorship from experts in your field of interest. Additionally, professors with strong research backgrounds can provide valuable networking opportunities and connections in the industry.
Funding availability
Funding is a significant consideration for many part-time PhD students. Look for programs that offer funding options such as scholarships, grants, or assistantships. These can help alleviate the financial burden and allow you to focus on your studies.
It’s also worth exploring external funding opportunities from organizations or government agencies that support research in your field.
Managing Your Time Effectively
Stay organized with schedules and goals.
When pursuing a part-time PhD in computer science, time management becomes crucial. It is important to create a schedule that includes dedicated study hours, research time, and coursework completion. By setting goals for each week or month, you can track your progress and ensure that you are staying on track.
One effective strategy is to use a planner or a digital calendar to keep track of deadlines, meetings, and other important events. By having a visual representation of your commitments, you can prioritize your tasks and allocate time accordingly.
Additionally, breaking down larger tasks into smaller, manageable chunks can help you stay organized and prevent overwhelm. By setting realistic goals for each study session, you can make progress towards your PhD while still managing other responsibilities.
Communicate needs clearly at work
When pursuing a part-time PhD, it is essential to communicate your needs with your employer or colleagues. Letting them know about your academic commitments and the time required for your studies can help them understand your availability and make necessary adjustments.
Consider having a conversation with your supervisor or manager to discuss your situation and explore potential flexible working arrangements. This could include adjusting your work schedule, reducing your workload, or even exploring opportunities for research collaboration between your job and your PhD.
Open and honest communication can go a long way in ensuring that both your work and academic responsibilities are managed effectively.
Leverage support systems
Pursuing a part-time PhD can be challenging, but you don’t have to do it alone. It is crucial to leverage the support systems available to you.
Reach out to your academic advisor or supervisor for guidance and support. They can provide valuable insights on managing your time, selecting courses, and balancing your academic and work commitments.
Additionally, consider joining or forming study groups with fellow part-time PhD students. Collaborating with others who are facing similar challenges can provide a sense of camaraderie and support. You can share study materials, discuss research ideas, and offer each other encouragement along the way.
Lastly, don’t forget about the support of your family and friends. Let them know about your academic journey and the challenges you may face. Their understanding and encouragement can help you stay motivated and focused on your goals.
Remember, pursuing a part-time PhD in computer science requires dedication, discipline, and effective time management. By staying organized, communicating your needs, and leveraging support systems, you can successfully navigate this exciting academic journey while maintaining a balance with your work and personal life.
Completion, Careers and Next Steps
Job prospects post-phd.
Completing a part-time PhD in computer science opens up a world of exciting job prospects. With a doctoral degree in this field, you are well-equipped to pursue highly specialized positions in both industry and academia.
The demand for computer science professionals continues to grow, and obtaining a PhD can give you a competitive edge in the job market. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the employment of computer and information research scientists is projected to grow 15 percent from 2019 to 2029, much faster than the average for all occupations.
This means that there will be ample opportunities for individuals with advanced degrees in computer science.
Potential teaching and research roles
One of the key benefits of earning a PhD in computer science is the opportunity to pursue teaching and research roles. Many universities and research institutions are constantly seeking experts in the field to join their faculty and contribute to cutting-edge research.
As a PhD holder, you can become a professor, teaching and mentoring the next generation of computer scientists. Additionally, you can engage in research projects, pushing the boundaries of knowledge in the field and making significant contributions to the advancement of technology.
The opportunity to share your expertise and make a lasting impact in the academic community is truly rewarding.
Higher salaries and senior positions
Earning a PhD in computer science can also lead to higher salaries and senior positions. With the advanced knowledge and skills gained during your doctoral studies, you become a valuable asset to companies and organizations.
Employers often recognize the expertise and dedication required to complete a PhD, and are willing to offer higher salaries to attract and retain top talent. In addition, holding a doctoral degree can open doors to senior management and leadership positions, where you can have a greater influence on strategic decisions and shape the direction of the company.
According to a survey conducted by the National Association of Colleges and Employers, computer science PhD graduates earned an average starting salary of $123,000 in 2020, significantly higher than those with a bachelor’s or master’s degree.
While requiring diligence and time management skills, part-time computer science PhD programs make this high-level credential attainable for busy professionals. From strengthening your research abilities to opening new career doors, the long-term benefits of earning a PhD on a flexible schedule are immense.
If you’re willing to balance work, research, and coursework, a part-time CS PhD can help you achieve your pinnacle academic and career aspirations.
Similar Posts

The Critical Importance Of Publishing Results In Science
Publishing research results is a fundamental part of the scientific process. Without the dissemination of findings through peer-reviewed journals, conferences, and other outlets, science would fail to progress and build on itself. In this comprehensive article, we’ll examine why sharing results publicly is so vital to the enterprise of science. If you’re short on time,…

Computational Science Vs Computer Science: Understanding The Key Differences
In today’s digital world, both computational science and computer science are appealing fields of study for students interested in technology and programming. But what exactly is the difference between the two disciplines? If you’re short on time, here’s a quick answer to your question: While computational science focuses on using computers to analyze and solve…

Why Do Vets Recommend Science Diet Pet Foods?
Science Diet is one of the most commonly recommended pet food brands by veterinarians. If you’re short on time, here’s a quick answer to your question: Veterinarians often recommend Science Diet because it is backed by extensive research, designed by nutritionists, made with quality ingredients, and shown to provide health benefits for pets. In this…

What Does Mantle Mean In Science? An In-Depth Explanation
The mantle is one of the major layers making up the interior of the Earth. If you’re short on time, here’s a quick answer: In science, the mantle refers to the very hot, viscous layer found between the Earth’s crust and core. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the scientific meaning of the mantle in…

Is Exercise Science A Hard Major?
If you’re considering a major in exercise science, you may be wondering how challenging the coursework is and whether it’s the right choice for you. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the various aspects of an exercise science degree and look at just how difficult this popular major really is. If you’re short on…

The Top 10 Schools For Exercise Science In 2023
Exercise science is an exciting and growing field that allows you to blend an interest in fitness, health, and science. If you’re considering a career in exercise science, choosing the right college or university program is crucial. If you’re short on time, here’s a quick answer to your question: Some of the best schools for…

NYU Center for Data Science
Harnessing Data’s Potential for the World
PhD in Data Science
An NRT-sponsored program in Data Science
- Areas & Faculty
- Admission Requirements
- Medical School Track
- NRT FUTURE Program
Advances in computational speed and data availability, and the development of novel data analysis methods, have birthed a new field: data science. This new field requires a new type of researcher and actor: the rigorously trained, cross-disciplinary, and ethically responsible data scientist. Launched in Fall 2017, the pioneering CDS PhD Data Science program seeks to produce such researchers who are fluent in the emerging field of data science, and to develop a native environment for their education and training. The CDS PhD Data Science program has rapidly received widespread recognition and is considered among the top and most selective data science doctoral programs in the world. It has recently been recognized by the NSF through an NRT training grant.
The CDS PhD program model rigorously trains data scientists of the future who (1) develop methodology and harness statistical tools to find answers to questions that transcend the boundaries of traditional academic disciplines; (2) clearly communicate to extract crisp questions from big, heterogeneous, uncertain data; (3) effectively translate fundamental research insights into data science practice in the sciences, medicine, industry, and government; and (4) are aware of the ethical implications of their work.
Our programmatic mission is to nurture this new generation of data scientists, by designing and building a data science environment where methodological innovations are developed and translated successfully to domain applications, both scientific and social. Our vision is that combining fundamental research on the principles of data science with translational projects involving domain experts creates a virtuous cycle: Advances in data science methodology transform the process of discovery in the sciences, and enable effective data-driven governance in the public sector. At the same time, the demands of real-world translational projects will catalyze the creation of new data science methodologies. An essential ingredient of such methodologies is that they embed ethics and responsibility by design.
These objectives will be achieved by a combination of an innovative core curriculum, a novel data assistantship mechanism that provides training of skills transfer through rotations and internships, and communication and entrepreneurship modules. Students will be exposed to a wider range of fields than in more standard PhD programs while working with our interdisciplinary faculty. In particular, we are proud to offer a medical track for students eager to explore data science as applied to healthcare or to develop novel theoretical models stemming from medical questions.
In short, the CDS PhD Data Science program prepares students to become leaders in data science research and prepares them for outstanding careers in academia or industry. Successful candidates are guaranteed financial support in the form of tuition and a competitive stipend in the fall and spring semesters for up to five years.* We invite you to learn more through our webpage or by contacting [email protected] .
*The Ph.D. program also offers students the opportunity to pursue their study and research with Data Science faculty based at NYU Shanghai. With this opportunity, students generally complete their coursework in New York City before moving full-time to Shanghai for their research. For more information, please visit the NYU Shanghai Ph.D. page .
- Data Science
- Digital Marketing
- DBA Courses
- Machine Learning & AI
- Product Management

Table of Contents
PhD is the highest degree available from an institution of higher learning. Finding out which doctoral program fits your needs and goals is crucial, whether you wish to pursue academic and research endeavors full-time or become eligible for top leadership roles in your industry.
Read on if you’re not familiar with the specifics of a PhD degree. You will discover the definition of a doctorate, how long is a PhD program , the specializations it encompasses, and the advantages of seeking one in this post. So, let’s get going.
How Long Is a PhD Program: Duration
Mostly, people ask how long a PhD take before they enroll in any PhD program. The doctoral degree (PhD) can last up to seven years. However, it usually lasts five to seven. The goal of a PhD is to produce original, freshly brewed research.
However, it can occasionally become laborious and take longer than anticipated to finish. They concentrate on extending the limits of the field’s understanding through several research and case studies that cause delays.
Top PhD Specializations
You can classify the various types of doctorate degrees based on specialization. So, here are some of the top PhD specializations to choose from:
PhD Commerce
A Ph.D. in commerce is a doctorate program that takes at least two years to complete. Many universities say a thesis or research paper must be completed within five years after the application date. Some universities offer part-time PhD programs in commerce.
PhD Humanities
Analyzing human cognition and culture critically is the focus of a doctorate in humanities. The course explores how philosophy, music, art, and the arts impact our daily lives. The growth of ideas and concepts, the operation of a society, behavioral patterns and the difficulties encountered, human interactions and relationships, etc., would all be thoroughly taught to the students.
PhD Science
Students with an MSc or MTech background can pursue a 3- to 5-year doctorate/doctoral degree in science called PhD Science. Candidates must do research in any of the science disciplines, including biology, chemistry, physics, and so on.
PhD Engineering and Technology
Research-based instruction is frequently the focus of an engineering or technology PhD. It might entail the advancement of degree programs or the creation of new technologies. A program tailored to the individual student’s interests, such as mastering a highly specialized technology or engineering field, may also be included.
PhD after MBA
A business management education at the doctorate level is called a PhD in Business Management. With online doctor in business administration programs , like the ones from UpGrads, you learn to handle the different operations of a corporation, including organizing, planning, monitoring, managing, and leading. The PhD program in business management lasts for three years.
Advantages of Having a Doctoral Degree
Now that you know how long is a PhD program and the types of PhD specializations, let’s explore some of its advantages:
Career Advancement
Opportunities for career progression are one advantage of obtaining a PhD. For example, after receiving your PhD, you might get promoted or decide to change careers. This could help you reach your professional objectives and improve your level of job happiness.
Boosts Earning Potential
Getting a degree could help you make more money. This may occur due to your increased knowledge and abilities to support an organization’s growth or enhance its operations.
Increases Recognition & Networking
The status and distinction that come with earning a PhD are further advantages. You can get requests to offer your knowledge at conferences or events in your industry. Getting a PhD can also help you build a stronger professional network by putting you in contact with leading authorities in your field and improving your standing in the business.
If you decide to pursue one, you’ll probably be shocked at the variety of PhD programs available. Furthermore, although several programs within a given area may share the same general academic requirements and study topics, there are also less obvious distinctions.
When you’re prepared to pursue a PhD, after giving your interests and professional objectives considerable thought, be sure to look into a wide range of options offered by several colleges — to the extent your circumstances allow.
1. Can I finish my PhD in India in two years?
In India, earning a PhD can take three to seven years to complete. A PhD must be completed within three years of being admitted through PhD Entrance Exams.
2. What variety of PhD programs are there?
The academic degree (PhD) and the applied degree (doctoral), as we have already discussed, are the two categories of doctoral degrees. Here’s a general guideline to follow: Pursue your doctorate.
3. Is finding employment following a PhD easy?
Finding a job opportunity with a PhD is easier than it is without one because many organizations want candidates with this degree.
Online PhD in Accounting Degrees – Top Programs Offering Flexible Doctorates
Executive mba jobs: how an online business master’s degree can prepare you for top management roles, business administration salary in the us – which certification matters, title image box.
Add an Introductory Description to make your audience curious by simply setting an Excerpt on this section
Get Free Consultation
Most popular, master business and entrepreneurship with a management degree for startup leaders, career guide to account management – qualifications, day-to-day tasks, and growth prospects, what does an accountant do a close look at the roles and responsibilities of accounting professionals, editor picks, popular posts, popular category.
- Doctorate of Business Administration 36
- Data Science & Analytics 31
- Machine Learning & AI 26
- Digital Marketing 26
- Product and Project Management 24
- Management 9
Get Free career counselling from upGrad experts!
Book a session with an industry professional today!
© 2015-2021 upGrad Education Private Limited. All rights reserved
- Data Science & Analytics
- Doctorate of Business Administration
- Product and Project Management
Materials Scientist Awarded Schmidt Science Fellowship
- Katherine Connor - [email protected]
Published Date
Share this:, article content.
Wonjun Yim, who earned a PhD in materials science at the University of California San Diego, is one of 32 researchers selected from the world’s leading science and engineering institutions to receive a 2024 Schmidt Science Fellowship . The prestigious postdoctoral scholar program, launched in 2018, harnesses an interdisciplinary approach as a way to break down silos among scientific fields in order to solve the world’s biggest challenges and support future leaders in STEM.
{/exp:typographee}
As a Schmidt Science Fellow, Yim will apply materials science to cancer diagnostics, integrating nanotechnology with medical devices to develop a new biomedical chemical imaging tool with the goal of improving the early detection of cancer.
The fellowship is supported by Schmidt Sciences , a philanthropic initiative co-founded by former Google CEO Eric Schmidt and his wife Wendy, in partnership with Rhodes Trust . The fellowship aims to equip the next generation of scientists and engineers to collaborate across disciplines by funding training for the scientists and their research.
As a Ph.D. student at UC San Diego, Yim studied in the lab of Jesse Jokerst, a professor in the Department of NanoEngineering at the Jacobs School of Engineering, focused on developing nanomaterials made out of a class of chemicals called phenols, for biomedical applications. Now a postdoctoral scholar at MIT, Yim plans to develop novel nanosensors for early-stage cancer diagnostics in a clinical setting.
“Specifically, I work with single-walled carbon nanotubes, functionalizing them with polymer libraries to detect cancer biomarkers,” said Yim. “My primary objective is to integrate nanotechnology into medical platforms for cancer diagnosis. By incorporating nanosensors into medical devices, I aim to create a powerful imaging platform to significantly advance the current state of cancer diagnosis.”
While at UC San Diego, Yim learned that context and understanding the broader impacts of research is key.
“UC San Diego holds a special place in my heart,” he said. “I met my amazing advisor, wonderful colleagues, and friends. I vividly remember the moment when I published my first research paper on disinfection methods for respirators , a project that made a positive impact during the COVID-19 pandemic. This memory ignited my passion for biomedical research to improve global human health. In the final year of my Ph.D. I was honored to receive the Gareth Thomas Materials Excellence Award. During the ceremony, I made a promise to myself and the committee members to continually ask myself 'why' questions in pursuit of scientific breakthroughs. I remain committed to this promise, striving to push the boundaries of knowledge and make meaningful contributions to science.”
You May Also Like
Computer scientists unveil novel attacks on cybersecurity, scientists discover a new signaling pathway and design a novel drug for liver fibrosis, foreign-born doctors help serve rural and low-income communities, higher resolution brain mapping tech wins big at research expo, stay in the know.
Keep up with all the latest from UC San Diego. Subscribe to the newsletter today.
You have been successfully subscribed to the UC San Diego Today Newsletter.
Campus & Community
Arts & culture, visual storytelling.
- Media Resources & Contacts
Signup to get the latest UC San Diego newsletters delivered to your inbox.
Award-winning publication highlighting the distinction, prestige and global impact of UC San Diego.
Popular Searches: Covid-19 Ukraine Campus & Community Arts & Culture Voices
- MyU : For Students, Faculty, and Staff
Onrí Jay Benally receives 2024 NSF Graduate Research Fellowship

Doctoral student Onrí Jay Benally is a 2024 recipient of the prestigious National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship. Benally is currently pursuing his doctoral research under the guidance of Distinguished McKnight Professor and Robert F. Hartmann chair Jian-Ping Wang exploring the world of quantum computing and spintronic devices.
A Navaho (Diné) tribesman and carpenter, Benally comes to us from the mountains of Red Valley and Oak Springs, Arizona. After graduating from tribal high school, he found himself building off-road electric vehicles at a Utah State University lab led by Professors Curtiz Frazier and Jared Barrett. Two years later, in 2017, he transferred to the University of Minnesota and accepted a Research Experiences for Undergraduates (REU) through the NSF-funded Materials Research Science and Engineering Center (MRSEC) at the University. During this time, he worked with Professor Vlad Pribiag (School of Physics and Astronomy) building nanoelectronic devices in the cleanroom for Majorana fermion research. The REU was Benally’s first brush with quantum technology exploration. He returned to the MRSEC REU in summer 2018 and this time he worked with Wang on micro and nanoscale magnetic tunnel junctions for classical computer memory and logic applications. He earned his bachelor’s degree in multidisciplinary studies from the University in 2021.
While Benally was working on his undergraduate degree, he earned an IBM certificate in quantum computation using Qiskit, and began hypothesizing how metallic-based spintronics and new architectures could be used to support the expansion of quantum supercomputing worldwide. The initial hypothesis motivated him to enter ECE’s doctoral program in fall 2022.
Reflecting on his interest in quantum technology and his skills as a carpenter, Benally says, "Carpentry was my livelihood on the tribe before completing my undergraduate degree. It is a big part of who I am and has indirectly led to my success as a nanofabricator of spintronics and quantum chips." Benally shares that one of his first toys as a kid was a toy hammer.
Benally’s research interests revolve around the engineering of quantum computing hardware and spintronic devices. An interdisciplinary area, his research involves the nanofabrication of ultrafast nanoscale magnetic tunnel junctions, cryogenic magnetic random-access memory (cryo-MRAM), and hybrid spintronic quantum processing units (QPUs), systems that can form scalable, sustainable quantum hardware architectures. Under the guidance of Wang, Benally designs and fabricates these systems at the Minnesota Nano Center at the University. Benally addressed these new developments in his keynote speech at the Arizona State University-led Quantum Collaborative Summit this past fall in San Antonio, Texas. Over the upcoming summer, Benally will be a graduate intern with IBM Research in Yorktown Heights, New York. As a quantum hardware engineer, he will be working on cutting edge cryogenic electronics for large-scale superconducting quantum computers.
Benally has accepted the NSF Graduate Research Fellowship and feels honored to start delivering on his proposed ideas on supporting quantum supercomputing through spintronics and new architectures.
The NSF Graduate Research Fellowship Program helps “ensure the quality, vitality, and diversity of the scientific and engineering workforce of the United States.” Learn about the program and eligibility requirements.
Related feature stories
- In Conversation with alumna Pushpavati Paladugu
- Wen Zhou receives doctoral dissertation fellowship and Early Innovation Fund award
- Burhaneddin Yaman recognized with best dissertation award
- Renata Saha's team wins third place at MMM 2022 Magnetic Sensor Challenge
- Alumnus Thomas Coughlin is 2023 IEEE President-Elect
- Future undergraduate students
- Future transfer students
- Future graduate students
- Future international students
- Diversity and Inclusion Opportunities
- Learn abroad
- Living Learning Communities
- Mentor programs
- Programs for women
- Student groups
- Visit, Apply & Next Steps
- Information for current students
- Departments and majors overview
- Departments
- Undergraduate majors
- Graduate programs
- Integrated Degree Programs
- Additional degree-granting programs
- Online learning
- Academic Advising overview
- Academic Advising FAQ
- Academic Advising Blog
- Appointments and drop-ins
- Academic support
- Commencement
- Four-year plans
- Honors advising
- Policies, procedures, and forms
- Career Services overview
- Resumes and cover letters
- Jobs and internships
- Interviews and job offers
- CSE Career Fair
- Major and career exploration
- Graduate school
- Collegiate Life overview
- Scholarships
- Diversity & Inclusivity Alliance
- Anderson Student Innovation Labs
- Information for alumni
- Get engaged with CSE
- Upcoming events
- CSE Alumni Society Board
- Alumni volunteer interest form
- Golden Medallion Society Reunion
- 50-Year Reunion
- Alumni honors and awards
- Outstanding Achievement
- Alumni Service
- Distinguished Leadership
- Honorary Doctorate Degrees
- Nobel Laureates
- Alumni resources
- Alumni career resources
- Alumni news outlets
- CSE branded clothing
- International alumni resources
- Inventing Tomorrow magazine
- Update your info
- CSE giving overview
- Why give to CSE?
- College priorities
- Give online now
- External relations
- Giving priorities
- Donor stories
- Impact of giving
- Ways to give to CSE
- Matching gifts
- CSE directories
- Invest in your company and the future
- Recruit our students
- Connect with researchers
- K-12 initiatives
- Diversity initiatives
- Research news
- Give to CSE
- CSE priorities
- Corporate relations
- Information for faculty and staff
- Administrative offices overview
- Office of the Dean
- Academic affairs
- Finance and Operations
- Communications
- Human resources
- Undergraduate programs and student services
- CSE Committees
- CSE policies overview
- Academic policies
- Faculty hiring and tenure policies
- Finance policies and information
- Graduate education policies
- Human resources policies
- Research policies
- Research overview
- Research centers and facilities
- Research proposal submission process
- Research safety
- Award-winning CSE faculty
- National academies
- University awards
- Honorary professorships
- Collegiate awards
- Other CSE honors and awards
- Staff awards
- Performance Management Process
- Work. With Flexibility in CSE
- K-12 outreach overview
- Summer camps
- Outreach events
- Enrichment programs
- Field trips and tours
- CSE K-12 Virtual Classroom Resources
- Educator development
- Sponsor an event
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Latest science news, discoveries and analysis

Could a rare mutation that causes dwarfism also slow ageing?

Bird flu in US cows: is the milk supply safe?

Future of Humanity Institute shuts: what's next for ‘deep future’ research?

Judge dismisses superconductivity physicist’s lawsuit against university
Nih pay raise for postdocs and phd students could have us ripple effect, hello puffins, goodbye belugas: changing arctic fjord hints at our climate future, china's moon atlas is the most detailed ever made, ‘shut up and calculate’: how einstein lost the battle to explain quantum reality, ecologists: don’t lose touch with the joy of fieldwork chris mantegna.

Should the Maldives be creating new land?

Lethal AI weapons are here: how can we control them?

Algorithm ranks peer reviewers by reputation — but critics warn of bias

How gliding marsupials got their ‘wings’
Audio long read: why loneliness is bad for your health, nato is boosting ai and climate research as scientific diplomacy remains on ice, rat neurons repair mouse brains — and restore sense of smell, plastic pollution: three numbers that support a crackdown.
Retractions are part of science, but misconduct isn’t — lessons from a superconductivity lab

Any plan to make smoking obsolete is the right step

Citizenship privilege harms science
European ruling linking climate change to human rights could be a game changer — here’s how charlotte e. blattner, will ai accelerate or delay the race to net-zero emissions, current issue.

The Maldives is racing to create new land. Why are so many people concerned?
Surprise hybrid origins of a butterfly species, stripped-envelope supernova light curves argue for central engine activity, optical clocks at sea, research analysis.

Ancient DNA traces family lines and political shifts in the Avar empire
A chemical method for selective labelling of the key amino acid tryptophan
Robust optical clocks promise stable timing in a portable package
Targeting RNA opens therapeutic avenues for Timothy syndrome
Bioengineered ‘mini-colons’ shed light on cancer progression, galaxy found napping in the primordial universe, tumours form without genetic mutations, marsupial genomes reveal how a skin membrane for gliding evolved.

Scientists urged to collect royalties from the ‘magic money tree’

Breaking ice, and helicopter drops: winning photos of working scientists

Shrouded in secrecy: how science is harmed by the bullying and harassment rumour mill
Want to make a difference try working at an environmental non-profit organization, how ground glass might save crops from drought on a caribbean island, books & culture.

How volcanoes shaped our planet — and why we need to be ready for the next big eruption

Dogwhistles, drilling and the roots of Western civilization: Books in brief

Cosmic rentals
Las borinqueñas remembers the forgotten puerto rican women who tested the first pill, dad always mows on summer saturday mornings, nature podcast.

Latest videos
Nature briefing.
An essential round-up of science news, opinion and analysis, delivered to your inbox every weekday.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Popular Searches
- EagleExpress
- Master plan
Graduate & Professional Studies
Apply for Graduate Women in Science Milwaukee Scientific Advancement Award

- April 25, 2024
- < 1 min. read
A total of three, $500 scientific advancement awards will be given to full-time female-identifying graduate students and post-doctorates in a STEM field. Awards may be applied as needed to advance research and professional development in the sciences.
Applications are due Saturday, June 15.
Full application instructions are available online .
If you have any questions, contact [email protected] .
Related Articles

Campus Life, Uncategorized
Save the date: Marquette Fun Run, Sept. 28

Campus Life, University Initiatives
Community meal program temporarily moving to Church of the Gesu starting April 28

Campus Life
Harry Baker | The Difference Makers at Marquette University
- Health Care
Doctors Need to Get Better at Recognizing Munchausen Syndrome by Proxy

W hether fictional or fact-based, Munchausen syndrome by proxy grips the public. Media depictions in The Sixth Sense and Sharp Objects and real-life news coverage of Gypsy Rose Blanchard’s December 2023 release from jail are hard to look away from. The most well-known cases—real or dramatized—are often the starkest ones, but Munchausen by proxy comes in subtler, harder-to-detect forms too.
“The media are fascinated, but they tend to depict the most extreme cases,” says Dr. Marc D. Feldman, distinguished life fellow of the American Psychiatric Association and author of Dying to Be Ill: True Stories of Medical Deception .
So how do more health care providers develop the skills to recognize this form of medical child abuse and report it to the appropriate authorities?
What Is Munchausen by proxy?
Munchausen by proxy “is a form of abuse in which a caregiver feigns, exaggerates, or induces illness in another person. Typically, the caregiver is the mother, and the victim is her child,” Feldman says.
While this deception may result in tangible benefits—like disability funds or opioid medications the caregiver then abuses—the perpetrator’s primary motivation is typically attention, says Mary Sanders, a clinical psychology professor at Stanford University School of Medicine.
You may hear this type of abuse referred to by many names. While it was once primarily called Munchausen syndrome by proxy, many experts now leave out the word “syndrome” because it implied there was a neat-and-tidy checklist for diagnosing a perpetrator. There are some commonalities among the caregivers who inflict this type of abuse, but not everyone matches the same criteria, Sanders says.
Increasingly, the phenomenon is called Munchausen by proxy (MBP) abuse to emphasize the negative effects on the victim or a type of medical child abuse, Feldman says.
Medical child abuse doesn’t specify why a caregiver is overmedicalizing a child, Sanders explains. But if the caregiver is being intentionally deceptive about an illness in a child, they are also said to have factitious disorder imposed on another (FDIA), according to changes made in the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , a glossary of mental health diagnoses. Whatever the behavior is called, it’s pernicious—and often hard to spot.
“In the past, making a diagnosis of Munchausen by proxy was challenging because understanding the motivations of the caregiver was part of the definition,” says child abuse pediatrician Dr. Amy Gavril, a past member of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Council on Child Abuse and Neglect and an associate professor at West Virginia University School of Medicine. “The motivation of an adult is an incredibly challenging thing to figure out, and, as a pediatrician, when it’s not your patient, it makes it even harder.”
Experts believe this form of abuse is largely underreported because it’s so difficult to recognize. The official incidence is about 0.5 to 2.0 cases in every 100,000 children under the age of 16, according to a 2013 Pediatrics report, but things might be much more serious than that.
“My sense is it’s vastly underrecognized by doctors because many haven’t even heard the term Munchausen abuse or medical child abuse, or they don’t really know what it is,” Feldman says. “You can’t diagnose something you don’t understand or have never heard of.”
Read More: 6 Things to Do if Your Doctor Isn’t Listening to You
Deception is central to Munchausen by proxy
It makes sense that MBP abuse is hard to recognize, considering the perpetrator has set out to fool everyone. “If the parent is really trying to be deceptive, they’re going to get away with it for a while,” Sanders says.
To skate by for as long as possible, caregivers frequently change medical practices before a health care provider has time to grow suspicious, Feldman says. But even qualified experts can have difficulty spotting MBP abuse. “The foundation of it is fabrication, and it’s very difficult to identify when a caregiver is not telling you the truth because we’re trained to listen to and take very seriously what a child’s caregiver has to say,” Gavril says.
Sometimes, seemingly harmless instances of deception may be an early tipoff. “I had a mother who said her child was born premature at 4 pounds, 3 ounces. But when I get the birth records, it says 8 pounds, so that’s clear falsification,” Sanders says.
A host of red flags
MBP abuse remains confusing to health care providers, legal professionals, and the public, per a 2020 review article in Annals of Pediatrics & Child Health authored by Brenda Bursch, a professor of clinical psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences and pediatrics at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. But this isn’t the fault of any physician or specialty; it’s a problem with the medical education and child welfare systems. “Most clinicians lack the training and guidance needed to professionally, ethically, and skillfully protect victims of MBP,” she wrote.
Even without intensive training, however, it’s possible to become more alert to the red flags, the most common of which is inconsistency. “You’re looking for this mismatch between what you’re being told is going on with the child and what you’re objectively seeing,” Gavril says. “It’s those ongoing inconsistencies rather than a particular symptom” that raise suspicions, she adds, because the caregiver might claim any number of medical issues afflict the child.
Munchausen by proxy perpetrators are often very involved in the child’s medical care. They might be active in advocacy organizations for the rare condition they say the child has, or they might try to act like they are friends with you as the child’s doctor, Sanders says.
Another telltale sign is if symptoms ease when the child is separated from the abusive caregiver. “I often hear from fathers who say, ‘My former wife is presenting the child as autistic, but when he’s with me on vacation, he’s perfectly fine,’ or ‘His dietary limitations are severe and imposed by his mother. When he’s with me, he eats whatever he wants.’ That kind of information is invaluable,” Feldman says.
A 2007 Pediatrics article from the AAP’s Council on Child Abuse and Neglect suggests clinicians ask themselves the following three questions to help determine if a child may be a victim of MBP abuse:
- Are the history, signs, and symptoms of disease credible?
- Is the child receiving unnecessary and harmful or potentially harmful medical care?
- If so, who is instigating the evaluations and treatment?
Any suspicion is enough to report
Physicians are mandated to report suspicions of child abuse . But that doesn’t mean doctors have to be sure of what they're seeing. “You don't have to know for certain that this abuse is going on. If you have a reasonable suspicion, it’s not a choice; you are a mandated reporter,” Sanders says.
Still, it’s not uncommon, Feldman says, for him to “come across cases where 20 pediatricians were consulted in a very obvious case, and no one documented any suspicions of abuse.”
That’s a problem because “the longer it goes undiagnosed, the more likely it is that permanent or severe harm is going to occur to the child,” Gavril says.
Pediatricians and mental health care providers may be most likely to notice something out of the ordinary. But every practitioner should at least be aware of the possibility of MBP abuse because victims often toggle among many different specialists, such as gastroenterologists, pediatric neurologists, and infectious disease physicians, Gavril says. These experts likely have even less training in recognizing medical child abuse than pediatricians.
Too often, health care workers are “a little frightened of documenting their concern because they’re lawsuit-averse, and they fear it’s going to be provocative if the caregiver finds out,” Feldman says. For example, in the high-profile Munchausen case of Olivia Gant, who died at age 7 in 2017, many care providers had suspicions, but none voiced concerns because “they were afraid of the bossy, domineering mom and what she might do if they made a report to child protective services,” he says. Gant’s mother is now serving 16 years in prison.
“Most doctors say ‘I didn’t report because I couldn’t prove it.’ That’s the job of child protective services or the police. We have to recognize our professional duties to the patient, and that patient is the child,” Feldman says.
Read More: Why It Takes Forever to Get a Doctor’s Appointment
Systematic issues prohibit further advancements
Child protection services don’t currently have a specific code or label for MBP abuse, so it typically gets lumped into medical neglect, Feldman says. This makes it hard to track prevalence, Bursch says.
But if advances can be made in that coding system, it could open the door for better training and education. “If we are successful in advocating for a specific category for child/adult protective services to use to correctly label and track MBP, then mandatory training will be required to educate caseworkers about proper investigation approaches and management of suspected cases," Bursch says. "This support would help clinicians who have a duty to report suspected abuse even when they do not feel certain it has occurred."
A more universal approach to electronic medical records could help, too. “We all should advocate for electronic health records to be standardized such that we can easily look at records from other facilities,” Feldman says, making it easier to recognize patterns of deception.
As Sanders emphasizes, it's essential for doctors to trust their intuition when a situation feels off. “If something is just not making sense, look further,” she says. “And not in the sense of doing more invasive investigations, but recognizing that you may not be getting accurate information.”
More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- Coco Gauff Is Playing for Herself Now
- Scenes From Pro-Palestinian Encampments Across U.S. Universities
- 6 Compliments That Land Every Time
- If You're Dating Right Now , You're Brave: Column
- The AI That Could Heal a Divided Internet
- Fallout Is a Brilliant Model for the Future of Video Game Adaptations
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Kee says funding for a humanities Ph.D. program typically only lasts five years, even though it is uncommon for someone to obtain a Ph.D. degree in a humanities field within that time frame ...
Graduate students pursuing a PhD in science or engineering were an average of 31.6 years old by the time they earned their degree in 2016, according to the National Science Foundation . In effect, some PhD students may have competing obligations, such as family.
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD, Ph.D., or DPhil; Latin: philosophiae doctor or doctor philosophiae) is the most common degree at the highest academic level, awarded following a course of study and research. The degree is abbreviated PhD and sometimes, especially in the U.S., as Ph.D. It is derived from the Latin Philosophiae Doctor, pronounced as three separate letters (/ p iː eɪ tʃ ˈ d iː ...
Understanding the average duration of a PhD program can help prospective students set realistic expectations. This section will provide an overview of the typical timeframes for completing a PhD. Average Duration: On a global scale, a PhD program often spans between 5 to 7 years. This period includes coursework, research, and the writing and ...
In the UK, a full-time PhD takes 3-4 years and a part-time PhD takes 6-7 years. Read our post to find out why! Search for PhDs; PhD Experiences; Blog; PhD Advice. Types of Doctorates ... According to a 2017 study conducted by the National Science Foundation, a US government agency which supports research and higher education, the average time ...
Graduate Studies. Commencement 2019. The Harvard Department of Physics offers students innovative educational and research opportunities with renowned faculty in state-of-the-art facilities, exploring fundamental problems involving physics at all scales. Our primary areas of experimental and theoretical research are atomic and molecular physics ...
Average PhD completion by focus. According to data from the National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics the average time in years from graduate school entry to doctorate it took students to receive their degree in 2020 in certain fields is listed below. Life sciences = 6.9 years; Physical sciences and earth sciences = 6.3 years
The PhD in population health sciences is a four-year program based at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in the world-renowned Longwood Medical Area of Boston, Massachusetts. The degree will prepare you to apply diverse approaches to solving difficult public health research issues in your choice of one of five primary fields of study ...
The Computer Science Department PhD program is a top-ranked research-oriented program, typically completed in 5-6 years. There are very few course requirements and the emphasis is on preparation for a career in Computer Science research. Eligibility. To be eligible for admission in a Stanford graduate program, applicants must meet: Degree level ...
3 to 4 years. In the USA, a PhD takes four to six years. There are several reasons for this. While in the UK, you tend to apply for a specific project, in the US, your application is aimed at a certain department and your actual proposal takes shape in the first couple of years of PhD study. The US model involves a two-phase programme, wherein ...
The philosophy of the PhD program, along with the Affiliated Ph.D. Program with the Salk Institute for Biological Studies, is to provide world-class research training in the basic biological sciences to equip a diverse group of trainees for a variety of scientific careers ranging from academia and industry to education, communication, or policy.
The degree of Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in the Faculty of Science will allow you to pursue research from the many fields in whic... more information. Course details. Faculty/University School: Faculty of Science. Credit points required: Course abbreviation: PhD. USyd code: RPPHDSCI6000. UAC code: N/A. Study mode: Research.
8 of the 10 courses must be disciplinary, and at least 7 of those must be technical courses drawn from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, FAS or MIT. Of the 7 technical courses, at least 3 must be 200-level Computer Science courses, with 3 different middle digits (from the set 2,3,4,5,6,7,8), and with one of ...
A 12-month program focused on applying the tools of modern data science, optimization and machine learning to solve real-world business problems. ... PhD studies at MIT Sloan are intense and individual in nature, demanding a great deal of time, initiative, and discipline from every candidate. ...
PhD Degree. The PhD program requires three years of full-time graduate study, at least two years of which must be at Stanford. Typically, however, students take four to five years after entering the program to complete all PhD requirements. The University requires a minimum of 135 units for a PhD, up to 45 units of which may be transferred from ...
Complete your PhD in Science with an independent research project to produce an original thesis and contribution to knowledge. ... you can take advantage of the time between submitting your thesis and it being conferred by completing a 3-6 month industry placement through our Specialist Certificate in Research Practice for Scientists.
However, there are many types of programs that typically take longer than six years to complete, such as humanities and arts doctorates, where the median time for individuals to earn their degree was 7.1 years, according to the survey. Some Ph.D. candidates begin doctoral programs after they have already obtained master's degrees, which means ...
PhD Program Time Limits with a MS at Illinois - 5 years (2 yrs. for MS and 5 yrs. for PhD) PhD Program Time Limits with a Non-Illinois MS - 6 years from first term enrolled in doctoral program. Illinois CS PhD Milestone Timeline. The department's timeline is an average of 6 years to complete the Ph.D. degree.
The Fall 2024 MSE Ph.D. application will open September 15, 2023. If you have admissions questions, please contact [email protected]. Students in the Cornell Materials Science and Engineering (MSE) Ph.D. program come from a variety of engineering and physical science backgrounds. Some are MS&E undergraduates while many have degrees in ...
Example: Planning year 2 of a 3-year PhD. Maria completed her first round of data collection according to plan, and starts the second year of her PhD with a lot of material. In her second year, she will focus on turning this data into two journal articles. Months 1-2: Maria works on her data analysis.
By Jamie Foster November 5, 2023. Earning a PhD is the pinnacle of academic achievement in computer science, opening doors to research, teaching, and leadership roles. But taking 4+ years off work for a full-time program isn't feasible for everyone. Part-time PhD options allow professionals to attain this goal while continuing their careers.
Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center designed its hybrid Doctor of Science in physical therapy to help practicing physical therapists advance their careers. The post-professional 36-credit ...
RSH500 Graduate Level Courses. RSH611 Independent Study 1. RSH612 Independent Study 2. 10 to 20 cu. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ELECTIVES. COU505 Research and Evaluation in Counselling. GER510 Applied Research in Gerontology. HDS501 Qualitative Research Methods and Analysis. RES511 Research Methods in Science and Engineering.
An NRT-sponsored program in Data Science Overview Overview Advances in computational speed and data availability, and the development of novel data analysis methods, have birthed a new field: data science. This new field requires a new type of researcher and actor: the rigorously trained, cross-disciplinary, and ethically responsible data scientist. Launched in Fall 2017, the …
How Long Is a PhD Program: Duration. Mostly, ... PhD Science. Students with an MSc or MTech background can pursue a 3- to 5-year doctorate/doctoral degree in science called PhD Science. Candidates must do research in any of the science disciplines, including biology, chemistry, physics, and so on. ...
Article Content. Wonjun Yim, who earned a PhD in materials science at the University of California San Diego, is one of 32 researchers selected from the world's leading science and engineering institutions to receive a 2024 Schmidt Science Fellowship.The prestigious postdoctoral scholar program, launched in 2018, harnesses an interdisciplinary approach as a way to break down silos among ...
Doctoral student Onrí Jay Benally is a 2024 recipient of the prestigious National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship. Benally is currently pursuing his doctoral research under the guidance of Distinguished McKnight Professor and Robert F. Hartmann chair Jian-Ping Wang exploring the world of quantum computing and spintronic devices.
Find breaking science news and analysis from the world's leading research journal.
A total of three, $500 scientific advancement awards will be given to full-time female-identifying graduate students and post-doctorates in a STEM field. Awards may be applied as needed to advance research and professional development in the sciences. Applications are due Saturday, June 15. Full application instructions are available online.
W hether fictional or fact-based, Munchausen syndrome by proxy grips the public. Media depictions in The Sixth Sense and Sharp Objects and real-life news coverage of Gypsy Rose Blanchard's ...