- Locations and Hours
- UCLA Library
- Research Guides
- Biomedical Library Guides

Systematic Reviews
- Types of Literature Reviews
What Makes a Systematic Review Different from Other Types of Reviews?
- Planning Your Systematic Review
- Database Searching
- Creating the Search
- Search Filters and Hedges
- Grey Literature
- Managing and Appraising Results
- Further Resources
Reproduced from Grant, M. J. and Booth, A. (2009), A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal, 26: 91–108. doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Planning Your Systematic Review >>
- Last Updated: Apr 17, 2024 2:02 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucla.edu/systematicreviews
- University of Wisconsin–Madison
- University of Wisconsin-Madison
- Research Guides
- Evidence Synthesis, Systematic Review Services
- Literature Review Types, Taxonomies
Evidence Synthesis, Systematic Review Services : Literature Review Types, Taxonomies
- Develop a Protocol
- Develop Your Research Question
- Select Databases
- Select Gray Literature Sources
- Write a Search Strategy
- Manage Your Search Process
- Register Your Protocol
- Citation Management
- Article Screening
- Risk of Bias Assessment
- Synthesize, Map, or Describe the Results
- Find Guidance by Discipline
- Manage Your Research Data
- Browse Evidence Portals by Discipline
- Automate the Process, Tools & Technologies
- Additional Resources
Choosing a Literature Review Methodology
Growing interest in evidence-based practice has driven an increase in review methodologies. Your choice of review methodology (or literature review type) will be informed by the intent (purpose, function) of your research project and the time and resources of your team.
- Decision Tree (What Type of Review is Right for You?) Developed by Cornell University Library staff, this "decision-tree" guides the user to a handful of review guides given time and intent.
Types of Evidence Synthesis*
Critical Review - Aims to demonstrate writer has extensively researched literature and critically evaluated its quality. Goes beyond mere description to include degree of analysis and conceptual innovation. Typically results in hypothesis or model.
Mapping Review (Systematic Map) - Map out and categorize existing literature from which to commission further reviews and/or primary research by identifying gaps in research literature.
Meta-Analysis - Technique that statistically combines the results of quantitative studies to provide a more precise effect of the results.
Mixed Studies Review (Mixed Methods Review) - Refers to any combination of methods where one significant component is a literature review (usually systematic). Within a review context it refers to a combination of review approaches for example combining quantitative with qualitative research or outcome with process studies.
Narrative (Literature) Review - Generic term: published materials that provide examination of recent or current literature. Can cover wide range of subjects at various levels of completeness and comprehensiveness.
Overview - Generic term: summary of the [medical] literature that attempts to survey the literature and describe its characteristics.
Qualitative Systematic Review or Qualitative Evidence Synthesis - Method for integrating or comparing the findings from qualitative studies. It looks for ‘themes’ or ‘constructs’ that lie in or across individual qualitative studies.
Rapid Review - Assessment of what is already known about a policy or practice issue, by using systematic review methods to search and critically appraise existing research.
Scoping Review or Evidence Map - Preliminary assessment of potential size and scope of available research literature. Aims to identify nature and extent of research.
State-of-the-art Review - Tend to address more current matters in contrast to other combined retrospective and current approaches. May offer new perspectives on issue or point out area for further research.
Systematic Review - Seeks to systematically search for, appraise and synthesis research evidence, often adhering to guidelines on the conduct of a review. (An emerging subset includes Living Reviews or Living Systematic Reviews - A [review or] systematic review which is continually updated, incorporating relevant new evidence as it becomes available.)
Systematic Search and Review - Combines strengths of critical review with a comprehensive search process. Typically addresses broad questions to produce ‘best evidence synthesis.’
Umbrella Review - Specifically refers to review compiling evidence from multiple reviews into one accessible and usable document. Focuses on broad condition or problem for which there are competing interventions and highlights reviews that address these interventions and their results.
*These definitions are in Grant & Booth's "A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies."
Literature Review Types/Typologies, Taxonomies
Grant, M. J., and A. Booth. "A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies." Health Information and Libraries Journal 26.2 (2009): 91-108. DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x Link
Munn, Zachary, et al. “Systematic Review or Scoping Review? Guidance for Authors When Choosing between a Systematic or Scoping Review Approach.” BMC Medical Research Methodology , vol. 18, no. 1, Nov. 2018, p. 143. DOI: 10.1186/s12874-018-0611-x. Link
Sutton, A., et al. "Meeting the Review Family: Exploring Review Types and Associated Information Retrieval Requirements." Health Information and Libraries Journal 36.3 (2019): 202-22. DOI: 10.1111/hir.12276 Link
- << Previous: Home
- Next: The Systematic Review Process >>
- Last Updated: May 22, 2024 4:45 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.library.wisc.edu/literature_review

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

- Chester Fritz Library
- Library of the Health Sciences
- Thormodsgard Law Library
Literature Reviews
- Get started
Literature Reviews within a Scholarly Work
Literature reviews as a scholarly work.
- Finding Literature Reviews
- Your Literature Search
- Library Books
- How to Videos
- Communicating & Citing Research
- Bibliography
Literature reviews summarize and analyze what has been written on a particular topic and identify gaps or disagreements in the scholarly work on that topic.
Within a scholarly work, the literature review situates the current work within the larger scholarly conversation and emphasizes how that particular scholarly work contributes to the conversation on the topic. The literature review portion may be as brief as a few paragraphs focusing on a narrow topic area.
When writing this type of literature review, it's helpful to start by identifying sources most relevant to your research question. A citation tracking database such as Web of Science can also help you locate seminal articles on a topic and find out who has more recently cited them. See "Your Literature Search" for more details.
A literature review may itself be a scholarly publication and provide an analysis of what has been written on a particular topic without contributing original research. These types of literature reviews can serve to help keep people updated on a field as well as helping scholars choose a research topic to fill gaps in the knowledge on that topic. Common types include:
Systematic Review
Systematic literature reviews follow specific procedures in some ways similar to setting up an experiment to ensure that future scholars can replicate the same steps. They are also helpful for evaluating data published over multiple studies. Thus, these are common in the medical field and may be used by healthcare providers to help guide diagnosis and treatment decisions. Cochrane Reviews are one example of this type of literature review.
Semi-Systematic Review
When a systematic review is not feasible, a semi-systematic review can help synthesize research on a topic or how a topic has been studied in different fields (Snyder 2019). Rather than focusing on quantitative data, this review type identifies themes, theoretical perspectives, and other qualitative information related to the topic. These types of reviews can be particularly helpful for a historical topic overview, for developing a theoretical model, and for creating a research agenda for a field (Snyder 2019). As with systematic reviews, a search strategy must be developed before conducting the review.
Integrative Review
An integrative review is less systematic and can be helpful for developing a theoretical model or to reconceptualize a topic. As Synder (2019) notes, " This type of review often re quires a more creative collection of data, as the purpose is usually not to cover all articles ever published on the topic but rather to combine perspectives and insights from di ff erent fi elds or research traditions" (p. 336).
Source: Snyder, H. (2019). Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research. 104. 333-339. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.07.039
- << Previous: Get started
- Next: Finding Literature Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Dec 5, 2023 8:31 PM
- URL: https://libguides.und.edu/literature-reviews
Systematic Reviews: Types of literature review, methods, & resources
- Types of literature review, methods, & resources
- Protocol and registration
- Search strategy
- Medical Literature Databases to search
- Study selection and appraisal
- Data Extraction/Coding/Study characteristics/Results
- Reporting the quality/risk of bias
- Manage citations using RefWorks This link opens in a new window
- GW Box file storage for PDF's This link opens in a new window
Analytical reviews
GUIDELINES FOR HOW TO CARRY OUT AN ANALYTICAL REVIEW OF QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
Enhancing the QUAlity and Transparency Of health Research (EQUATOR) network. (Tracking and listing over 550 reporting guidelines for various different study types including Randomised trials, Systematic reviews, Study protocols, Diagnostic/prognostic studies, Case reports, Clinical practice guidelines, Animal pre-clinical studies, etc). http://www.equator-network.org/resource-centre/library-of-health-research-reporting/
When comparing therapies :
PRISMA (Guideline on how to perform and write-up a systematic review and/or meta-analysis of the outcomes reported in multiple clinical trials of therapeutic interventions. PRISMA replaces the previous QUORUM statement guidelines ): Liberati, A,, Altman, D,, Moher, D, et al. (2009). The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. Plos Medicine, 6 (7):e1000100. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100
When comparing diagnostic methods :
Checklist for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging (CLAIM). CLAIM is modeled after the STARD guideline and has been extended to address applications of AI in medical imaging that include classification, image reconstruction, text analysis, and workflow optimization. The elements described here should be viewed as a “best practice” to guide authors in presenting their research. Reported in Mongan, J., Moy, L., & Kahn, C. E., Jr (2020). Checklist for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging (CLAIM): A Guide for Authors and Reviewers. Radiology. Artificial intelligence , 2 (2), e200029. https://doi.org/10.1148/ryai.2020200029
STAndards for the Reporting of Diagnostic accuracy studies (STARD) Statement. (Reporting guidelines for writing up a study comparing the accuracy of competing diagnostic methods) http://www.stard-statement.org/
When evaluating clinical practice guidelines :
AGREE Research Trust (ART) (2013). Appraisal of Guidelines for Research & Evaluation (AGREE-II) . (A 23-item instrument for as sessing th e quality of Clinical Practice Guidelines. Used internationally for evaluating or deciding which guidelines could be recommended for use in practice or to inform health policy decisions.)
National Guideline Clearinghouse Extent of Adherence to Trustworthy Standards (NEATS) Instrument (2019). (A 15-item instrument using scales of 1-5 to evaluate a guideline's adherence to the Institute of Medicine's standard for trustworthy guidelines. It has good external validity among guideline developers and good interrater reliability across trained reviewers.)
When reviewing genetics studies
Human genetics review reporting guidelines. Little J, Higgins JPT (eds.). The HuGENet™ HuGE Review Handbook, version 1.0 .
When you need to re-analyze individual participant data
If you wish to collect, check, and re-analyze individual participant data (IPD) from clinical trials addressing a particular research question, you should follow the PRISMA-IPD guidelines as reported in Stewart, L.A., Clarke, M., Rovers, M., et al. (2015). Preferred Reporting Items for a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Individual Participant Data: The PRISMA-IPD Statement. JAMA, 313(16):1657-1665. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.3656 .
When comparing Randomized studies involving animals, livestock, or food:
O’Connor AM, et al. (2010). The REFLECT statement: methods and processes of creating reporting guidelines for randomized controlled trials for livestock and food safety by modifying the CONSORT statement. Zoonoses Public Health. 57(2):95-104. Epub 2010/01/15. doi: 10.1111/j.1863-2378.2009.01311.x. PubMed PMID: 20070653.
Sargeant JM, et al. (2010). The REFLECT Statement: Reporting Guidelines for Randomized Controlled Trials in Livestock and Food Safety: Explanation and Elaboration. Zoonoses Public Health. 57(2):105-36. Epub 2010/01/15. doi: JVB1312 [pii] 10.1111/j.1863-2378.2009.01312.x. PubMed PMID: 20070652.
GUIDELINES FOR HOW TO WRITE UP FOR PUBLICATION THE RESULTS OF ONE QUANTITATIVE CLINICAL TRIAL
When reporting the results of a Randomized Controlled Trial :
Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) Statement. (2010 reporting guideline for writing up a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial). http://www.consort-statement.org . Since updated in 2022, see Butcher, M. A., et al. (2022). Guidelines for Reporting Outcomes in Trial Reports: The CONSORT-Outcomes 2022 Extension . JAMA : the Journal of the American Medical Association, 328(22), 2252–2264. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2022.21022
Kilkenny, C., Browne, W. J., Cuthill, I. C., Emerson, M., & Altman, D. G. (2010). Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biology, 8(6), e1000412–e1000412. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1000412 (A 20-item checklist, following the CONSORT approach, listing the information that published articles reporting research using animals should include, such as the number and specific characteristics of animals used; details of housing and husbandry; and the experimental, statistical, and analytical methods used to reduce bias.)
Narrative reviews
GUIDELINES FOR HOW TO CARRY OUT A NARRATIVE REVIEW / QUALITATIVE RESEARCH / OBSERVATIONAL STUDIES
Campbell, M. (2020). Synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) in systematic reviews: reporting guideline. BMJ, 368. doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l6890 (guideline on how to analyse evidence for a narrative review, to provide a recommendation based on heterogenous study types).
Community Preventive Services Task Force (2021). The Methods Manual for Community Guide Systematic Reviews . (Public Health Prevention systematic review guidelines)
Enhancing the QUAlity and Transparency Of health Research (EQUATOR) network. (Tracking and listing over 550 reporting guidelines for various different study types including Observational studies, Qualitative research, Quality improvement studies, and Economic evaluations). http://www.equator-network.org/resource-centre/library-of-health-research-reporting/
Cochrane Qualitative & Implementation Methods Group. (2019). Training resources. Retrieved from https://methods.cochrane.org/qi/training-resources . (Training materials for how to do a meta-synthesis, or qualitative evidence synthesis).
Cornell University Library (2019). Planning worksheet for structured literature reviews. Retrieved 4/8/22 from https://osf.io/tnfm7/ (offers a framework for a narrative literature review).
Green, B. N., Johnson, C. D., & Adams, A. (2006). Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade . Journal of Chiropractic Medicine, 5(3): 101-117. DOI: 10.1016/ S0899-3467 (07)60142-6. This is a very good article about what to take into consideration when writing any type of narrative review.
When reviewing observational studies/qualitative research :
STrengthening the Reporting of OBservational studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement. (Reporting guidelines for various types of health sciences observational studies). http://www.strobe-statement.org
Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) http://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=192614
RATS Qualitative research systematic review guidelines. https://www.equator-network.org/reporting-guidelines/qualitative-research-review-guidelines-rats/
Methods/Guidance
Right Review , this decision support website provides an algorithm to help reviewers choose a review methodology from among 41 knowledge synthesis methods.
The Systematic Review Toolbox , an online catalogue of tools that support various tasks within the systematic review and wider evidence synthesis process. Maintained by the UK University of York Health Economics Consortium, Newcastle University NIHR Innovation Observatory, and University of Sheffield School of Health and Related Research.
Institute of Medicine. (2011). Finding What Works in Health Care: Standards for Systematic Reviews . Washington, DC: National Academies (Systematic review guidelines from the Health and Medicine Division (HMD) of the U.S. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (formerly called the Institute of Medicine)).
International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (2022). Recommendations for the Conduct, Reporting, Editing, and Publication of Scholarly work in Medical Journals . Guidance on how to prepare a manuscript for submission to a Medical journal.
Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions (International Cochrane Collaboration systematic review guidelines). The various Cochrane review groups comporise around 30,000 physicians around the world working in the disciplines on reviews of interventions with very detailed methods for verifying the validity of the research methods and analysis performed in screened-in Randmized Controlled Clinical Trials. Typically published Cochrane Reviews are the most exhaustive review of the evidence of effectiveness of a particular drug or intervention, and include a statistical meta-analysis. Similar to practice guidelines, Cochrane reviews are periodically revised and updated.
Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Manual of Evidence Synthesis . (International systematic review guidelines). Based at the University of Adelaide, South Australia, and collaborating with around 80 academic and medical entities around the world. Unlike Cochrane Reviews that strictly focus on efficacy of interventions, JBI offers a broader, inclusive approach to evidence, to accommodate a range of diverse questions and study designs. The JBI manual provides guidance on how to analyse and include both quantitative and qualitative research.
Cochrane Methods Support Unit, webinar recordings on methodological support questions
Cochrane Qualitative & Implementation Methods Group. (2019). Training resources. Retrieved from https://methods.cochrane.org/qi/training-resources . (How to do a meta-synthesis, or qualitative evidence synthesis).
Center for Reviews and Dissemination (University of York, England) (2009). Systematic Reviews: CRD's guidance for undertaking systematic reviews in health care . (British systematic review guidelines).
Agency for Health Research & Quality (AHRQ) (2013). Methods guide for effectiveness and comparative effectiveness reviews . (U.S. comparative effectiveness review guidelines)
Hunter, K. E., et al. (2022). Searching clinical trials registers: guide for systematic reviewers. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) , 377 , e068791. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj-2021-068791
Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI). The PCORI Methodology Report . (A 47-item methodology checklist for U.S. patient-centered outcomes research. Established under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, PCORI funds the development of guidance on the comparative effectivess of clinical healthcare, similar to the UK National Institute for Clinical Evidence but without reporting cost-effectiveness QALY metrics).
Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health (CADTH) (2019). Grey Matters: a practical tool for searching health-related grey literature. Retrieved from https://www.cadth.ca/resources/finding-evidence/grey-matters . A checklist of N American & international online databases and websites you can use to search for unpublished reports, posters, and policy briefs, on topics including general medicine and nursing, public and mental health, health technology assessment, drug and device regulatory, approvals, warnings, and advisories.
Hempel, S., Xenakis, L., & Danz, M. (2016). Systematic Reviews for Occupational Safety and Health Questions: Resources for Evidence Synthesis. Retrieved 8/15/16 from http://www.rand.org/pubs/research_reports/RR1463.html . NIOSH guidelines for how to carry out a systematic review in the occupational safety and health domain.
A good source for reporting guidelines is the NLM's Research Reporting Guidelines and Initiatives .
Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE). (An international group of academics/clinicians working to promote a common approach to grading the quality of evidence and strength of recommendations.)
Phillips, B., Ball, C., Sackett, D., et al. (2009). Oxford Centre for Evidence Based Medicine: Levels of Evidence. Retrieved 3/20/17 from https://www.cebm.net/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/CEBM-Levels-of-Evidence-2.1.pdf . (Another commonly used criteria for grading the quality of evidence and strength of recommendations, developed in part by EBM guru David Sackett.)
Systematic Reviews for Animals & Food (guidelines including the REFLECT statement for carrying out a systematic review on animal health, animal welfare, food safety, livestock, and agriculture)
Grant, M. J., & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies . Health Information & Libraries Journal, 26(2), 91-108. doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x. (Describes 14 different types of literature and systematic review, useful for thinking at the outset about what sort of literature review you want to do.)
Sutton, A., Clowes, M., Preston, L., & Booth, A. (2019). Meeting the review family: exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements . Health information and libraries journal, 36(3), 202–222. doi:10.1111/hir.12276 (An updated look at different types of literature review, expands on the Grant & Booth 2009 article listed above).
Garrard, J. (2007). Health Sciences Literature Review Made Easy: The Matrix Method (2nd Ed.). Sudbury, MA: Jones & Bartlett Publishers. (Textbook of health sciences literature search methods).
Zilberberg, M. (2012). Between the lines: Finding the truth in medical literature . Goshen, MA: Evimed Research Press. (Concise book on foundational concepts of evidence-based medicine).
Lang, T. (2009). The Value of Systematic Reviews as Research Activities in Medical Education . In: Lang, T. How to write, publish, & present in the health sciences : a guide for clinicians & laboratory researchers. Philadelphia : American College of Physicians. (This book chapter has a helpful bibliography on systematic review and meta-analysis methods)
Brown, S., Martin, E., Garcia, T., Winter, M., García, A., Brown, A., Cuevas H., & Sumlin, L. (2013). Managing complex research datasets using electronic tools: a meta-analysis exemplar . Computers, Informatics, Nursing: CIN, 31(6), 257-265. doi:10.1097/NXN.0b013e318295e69c. (This article advocates for the programming of electronic fillable forms in Adobe Acrobat Pro to feed data into Excel or SPSS for analysis, and to use cloud based file sharing systems such as Blackboard, RefWorks, or EverNote to facilitate sharing knowledge about the decision-making process and keep data secure. Of particular note are the flowchart describing this process, and their example screening form used for the initial screening of abstracts).
Brown, S., Upchurch, S., & Acton, G. (2003). A framework for developing a coding scheme for meta-analysis . Western Journal Of Nursing Research, 25(2), 205-222. (This article describes the process of how to design a coded data extraction form and codebook, Table 1 is an example of a coded data extraction form that can then be used to program a fillable form in Adobe Acrobat or Microsoft Access).
Elamin, M. B., Flynn, D. N., Bassler, D., Briel, M., Alonso-Coello, P., Karanicolas, P., & ... Montori, V. M. (2009). Choice of data extraction tools for systematic reviews depends on resources and review complexity . Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology , 62 (5), 506-510. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2008.10.016 (This article offers advice on how to decide what tools to use to extract data for analytical systematic reviews).
Riegelman R. Studying a Study and Testing a Test: Reading Evidence-based Health Research , 6th Edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2012. (Textbook of quantitative statistical methods used in health sciences research).
Rathbone, J., Hoffmann, T., & Glasziou, P. (2015). Faster title and abstract screening? Evaluating Abstrackr, a semi-automated online screening program for systematic reviewers. Systematic Reviews, 480. doi:10.1186/s13643-015-0067-6
Guyatt, G., Rennie, D., Meade, M., & Cook, D. (2015). Users' guides to the medical literature (3rd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Education Medical. (This is a foundational textbook on evidence-based medicine and of particular use to the reviewer who wants to learn about the different types of published research article e.g. "what is a case report?" and to understand what types of study design best answer what types of clinical question).
Glanville, J., Duffy, S., Mccool, R., & Varley, D. (2014). Searching ClinicalTrials.gov and the International Clinical Trials Registry Platform to inform systematic reviews: what are the optimal search approaches? Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA, 102(3), 177–183. https://doi.org/10.3163/1536-5050.102.3.007
Ouzzani, M., Hammady, H., Fedorowicz, Z., & Elmagarmid, A. (2016). Rayyan a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Systematic Reviews, 5 : 210, DOI: 10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4. http://rdcu.be/nzDM
Kwon Y, Lemieux M, McTavish J, Wathen N. (2015). Identifying and removing duplicate records from systematic review searches. J Med Libr Assoc. 103 (4): 184-8. doi: 10.3163/1536-5050.103.4.004. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26512216
Bramer WM, Giustini D, de Jonge GB, Holland L, Bekhuis T. (2016). De-duplication of database search results for systematic reviews in EndNote. J Med Libr Assoc. 104 (3):240-3. doi: 10.3163/1536-5050.104.3.014. Erratum in: J Med Libr Assoc. 2017 Jan;105(1):111. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27366130
McGowan J, Sampson M, Salzwedel DM, Cogo E, Foerster V, Lefebvre C. PRESS Peer Review of Electronic Search Strategies: 2015 Guideline Statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;75:40–46. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2016.01.021 . PRESS is a guideline with a checklist for librarians to critically appraise the search strategy for a systematic review literature search.
Clark, JM, Sanders, S, Carter, M, Honeyman, D, Cleo, G, Auld, Y, Booth, D, Condron, P, Dalais, C, Bateup, S, Linthwaite, B, May, N, Munn, J, Ramsay, L, Rickett, K, Rutter, C, Smith, A, Sondergeld, P, Wallin, M, Jones, M & Beller, E 2020, 'Improving the translation of search strategies using the Polyglot Search Translator: a randomized controlled trial', Journal of the Medical Library Association , vol. 108, no. 2, pp. 195-207.
Journal articles describing systematic review methods can be searched for in PubMed using this search string in the PubMed search box: sysrev_methods [sb] .
Software tools for systematic reviews
- Covidence GW in 2019 has bought a subscription to this Cloud based tool for facilitating screening decisions, used by the Cochrane Collaboration. Register for an account.
- NVIVO for analysis of qualitative research NVIVO is used for coding interview data to identify common themes emerging from interviews with several participants. GW faculty, staff, and students may download NVIVO software.
- RedCAP RedCAP is software that can be used to create survey forms for research or data collection or data extraction. It has very detailed functionality to enable data exchange with Electronic Health Record Systems, and to integrate with study workflow such as scheduling follow up reminders for study participants.
- SRDR tool from AHRQ Free, web-based and has a training environment, tutorials, and example templates of systematic review data extraction forms
- RevMan 5 RevMan 5 is the desktop version of the software used by Cochrane systematic review teams. RevMan 5 is free for academic use and can be downloaded and configured to run as stand alone software that does not connect with the Cochrane server if you follow the instructions at https://training.cochrane.org/online-learning/core-software-cochrane-reviews/revman/revman-5-download/non-cochrane-reviews
- Rayyan Free, web-based tool for collecting and screening citations. It has options to screen with multiple people, masking each other.
- GradePro Free, web application to create, manage and share summaries of research evidence (called Evidence Profiles and Summary of Findings Tables) for reviews or guidelines, uses the GRADE criteria to evaluate each paper under review.
- DistillerSR Needs subscription. Create coded data extraction forms from templates.
- EPPI Reviewer Needs subscription. Like DistillerSR, tool for text mining, data clustering, classification and term extraction
- SUMARI Needs subscription. Qualitative data analysis.
- Dedoose Needs subscription. Qualitative data analysis, similar to NVIVO in that it can be used to code interview transcripts, identify word co-occurence, cloud based.
- Meta-analysis software for statistical analysis of data for quantitative reviews SPSS, SAS, and STATA are popular analytical statistical software that include macros for carrying out meta-analysis. Himmelfarb has SPSS on some 3rd floor computers, and GW affiliates may download SAS to your own laptop from the Division of IT website. To perform mathematical analysis of big data sets there are statistical analysis software libraries in the R programming language available through GitHub and RStudio, but this requires advanced knowledge of the R and Python computer languages and data wrangling/cleaning.
- PRISMA 2020 flow diagram generator The PRISMA Statement website has a page listing example flow diagram templates and a link to software for creating PRISMA 2020 flow diagrams using R software.
GW researchers may want to consider using Refworks to manage citations, and GW Box to store the full text PDF's of review articles. You can also use online survey forms such as Qualtrics, RedCAP, or Survey Monkey, to design and create your own coded fillable forms, and export the data to Excel or one of the qualitative analytical software tools listed above.
Forest Plot Generators
- RevMan 5 the desktop version of the software used by Cochrane systematic review teams. RevMan 5 is free for academic use and can be downloaded and configured to run as stand alone software that does not connect with the Cochrane server if you follow the instructions at https://training.cochrane.org/online-learning/core-software-cochrane-reviews/revman/revman-5-download/non-cochrane-reviews.
- Meta-Essentials a free set of workbooks designed for Microsoft Excel that, based on your input, automatically produce meta-analyses including Forest Plots. Produced for Erasmus University Rotterdam joint research institute.
- Neyeloff, Fuchs & Moreira Another set of Excel worksheets and instructions to generate a Forest Plot. Published as Neyeloff, J.L., Fuchs, S.C. & Moreira, L.B. Meta-analyses and Forest plots using a microsoft excel spreadsheet: step-by-step guide focusing on descriptive data analysis. BMC Res Notes 5, 52 (2012). https://doi-org.proxygw.wrlc.org/10.1186/1756-0500-5-52
- For R programmers instructions are at https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/forestplot/vignettes/forestplot.html and you can download the R code package from https://github.com/gforge/forestplot
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Protocol and registration >>

- Last Updated: May 8, 2024 11:07 AM
- URL: https://guides.himmelfarb.gwu.edu/systematic_review

- Himmelfarb Intranet
- Privacy Notice
- Terms of Use
- GW is committed to digital accessibility. If you experience a barrier that affects your ability to access content on this page, let us know via the Accessibility Feedback Form .
- Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library
- 2300 Eye St., NW, Washington, DC 20037
- Phone: (202) 994-2850
- [email protected]
- https://himmelfarb.gwu.edu
University Libraries University of Nevada, Reno
- Skill Guides
- Subject Guides
Systematic, Scoping, and Other Literature Reviews: Overview
- Project Planning
What Is a Systematic Review?
Regular literature reviews are simply summaries of the literature on a particular topic. A systematic review, however, is a comprehensive literature review conducted to answer a specific research question. Authors of a systematic review aim to find, code, appraise, and synthesize all of the previous research on their question in an unbiased and well-documented manner. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) outline the minimum amount of information that needs to be reported at the conclusion of a systematic review project.
Other types of what are known as "evidence syntheses," such as scoping, rapid, and integrative reviews, have varying methodologies. While systematic reviews originated with and continue to be a popular publication type in medicine and other health sciences fields, more and more researchers in other disciplines are choosing to conduct evidence syntheses.
This guide will walk you through the major steps of a systematic review and point you to key resources including Covidence, a systematic review project management tool. For help with systematic reviews and other major literature review projects, please send us an email at [email protected] .
Getting Help with Reviews
Organization such as the Institute of Medicine recommend that you consult a librarian when conducting a systematic review. Librarians at the University of Nevada, Reno can help you:
- Understand best practices for conducting systematic reviews and other evidence syntheses in your discipline
- Choose and formulate a research question
- Decide which review type (e.g., systematic, scoping, rapid, etc.) is the best fit for your project
- Determine what to include and where to register a systematic review protocol
- Select search terms and develop a search strategy
- Identify databases and platforms to search
- Find the full text of articles and other sources
- Become familiar with free citation management (e.g., EndNote, Zotero)
- Get access to you and help using Covidence, a systematic review project management tool
Doing a Systematic Review
- Plan - This is the project planning stage. You and your team will need to develop a good research question, determine the type of review you will conduct (systematic, scoping, rapid, etc.), and establish the inclusion and exclusion criteria (e.g., you're only going to look at studies that use a certain methodology). All of this information needs to be included in your protocol. You'll also need to ensure that the project is viable - has someone already done a systematic review on this topic? Do some searches and check the various protocol registries to find out.
- Identify - Next, a comprehensive search of the literature is undertaken to ensure all studies that meet the predetermined criteria are identified. Each research question is different, so the number and types of databases you'll search - as well as other online publication venues - will vary. Some standards and guidelines specify that certain databases (e.g., MEDLINE, EMBASE) should be searched regardless. Your subject librarian can help you select appropriate databases to search and develop search strings for each of those databases.
- Evaluate - In this step, retrieved articles are screened and sorted using the predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria. The risk of bias for each included study is also assessed around this time. It's best if you import search results into a citation management tool (see below) to clean up the citations and remove any duplicates. You can then use a tool like Rayyan (see below) to screen the results. You should begin by screening titles and abstracts only, and then you'll examine the full text of any remaining articles. Each study should be reviewed by a minimum of two people on the project team.
- Collect - Each included study is coded and the quantitative or qualitative data contained in these studies is then synthesized. You'll have to either find or develop a coding strategy or form that meets your needs.
- Explain - The synthesized results are articulated and contextualized. What do the results mean? How have they answered your research question?
- Summarize - The final report provides a complete description of the methods and results in a clear, transparent fashion.
Adapted from
Types of reviews, systematic review.
These types of studies employ a systematic method to analyze and synthesize the results of numerous studies. "Systematic" in this case means following a strict set of steps - as outlined by entities like PRISMA and the Institute of Medicine - so as to make the review more reproducible and less biased. Consistent, thorough documentation is also key. Reviews of this type are not meant to be conducted by an individual but rather a (small) team of researchers. Systematic reviews are widely used in the health sciences, often to find a generalized conclusion from multiple evidence-based studies.
Meta-Analysis
A systematic method that uses statistics to analyze the data from numerous studies. The researchers combine the data from studies with similar data types and analyze them as a single, expanded dataset. Meta-analyses are a type of systematic review.
Scoping Review
A scoping review employs the systematic review methodology to explore a broader topic or question rather than a specific and answerable one, as is generally the case with a systematic review. Authors of these types of reviews seek to collect and categorize the existing literature so as to identify any gaps.
Rapid Review
Rapid reviews are systematic reviews conducted under a time constraint. Researchers make use of workarounds to complete the review quickly (e.g., only looking at English-language publications), which can lead to a less thorough and more biased review.
Narrative Review
A traditional literature review that summarizes and synthesizes the findings of numerous original research articles. The purpose and scope of narrative literature reviews vary widely and do not follow a set protocol. Most literature reviews are narrative reviews.
Umbrella Review
Umbrella reviews are, essentially, systematic reviews of systematic reviews. These compile evidence from multiple review studies into one usable document.
Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal , vol. 26, no. 2, 2009, pp. 91-108. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x .
- Next: Project Planning >>

Literature Reviews
- Types of reviews
- Getting started
Types of reviews and examples
Choosing a review type.
- 1. Define your research question
- 2. Plan your search
- 3. Search the literature
- 4. Organize your results
- 5. Synthesize your findings
- 6. Write the review
- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools
- Thompson Writing Studio This link opens in a new window
- Need to write a systematic review? This link opens in a new window

Contact a Librarian
Ask a Librarian
- Meta-analysis
- Systematized
Definition:
"A term used to describe a conventional overview of the literature, particularly when contrasted with a systematic review (Booth et al., 2012, p. 265).
Characteristics:
- Provides examination of recent or current literature on a wide range of subjects
- Varying levels of completeness / comprehensiveness, non-standardized methodology
- May or may not include comprehensive searching, quality assessment or critical appraisal
Mitchell, L. E., & Zajchowski, C. A. (2022). The history of air quality in Utah: A narrative review. Sustainability , 14 (15), 9653. doi.org/10.3390/su14159653
Booth, A., Papaioannou, D., & Sutton, A. (2012). Systematic approaches to a successful literature review. London: SAGE Publications Ltd.
"An assessment of what is already known about a policy or practice issue...using systematic review methods to search and critically appraise existing research" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 100).
- Assessment of what is already known about an issue
- Similar to a systematic review but within a time-constrained setting
- Typically employs methodological shortcuts, increasing risk of introducing bias, includes basic level of quality assessment
- Best suited for issues needing quick decisions and solutions (i.e., policy recommendations)
Learn more about the method:
Khangura, S., Konnyu, K., Cushman, R., Grimshaw, J., & Moher, D. (2012). Evidence summaries: the evolution of a rapid review approach. Systematic reviews, 1 (1), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-1-10
Virginia Commonwealth University Libraries. (2021). Rapid Review Protocol .
Quarmby, S., Santos, G., & Mathias, M. (2019). Air quality strategies and technologies: A rapid review of the international evidence. Sustainability, 11 (10), 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102757
Grant, M.J. & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of the 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal , 26(2), 91-108. https://www.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
Developed and refined by the Evidence for Policy and Practice Information and Co-ordinating Centre (EPPI-Centre), this review "map[s] out and categorize[s] existing literature on a particular topic, identifying gaps in research literature from which to commission further reviews and/or primary research" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 97).
Although mapping reviews are sometimes called scoping reviews, the key difference is that mapping reviews focus on a review question, rather than a topic
Mapping reviews are "best used where a clear target for a more focused evidence product has not yet been identified" (Booth, 2016, p. 14)
Mapping review searches are often quick and are intended to provide a broad overview
Mapping reviews can take different approaches in what types of literature is focused on in the search
Cooper I. D. (2016). What is a "mapping study?". Journal of the Medical Library Association: JMLA , 104 (1), 76–78. https://doi.org/10.3163/1536-5050.104.1.013
Miake-Lye, I. M., Hempel, S., Shanman, R., & Shekelle, P. G. (2016). What is an evidence map? A systematic review of published evidence maps and their definitions, methods, and products. Systematic reviews, 5 (1), 1-21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0204-x
Tainio, M., Andersen, Z. J., Nieuwenhuijsen, M. J., Hu, L., De Nazelle, A., An, R., ... & de Sá, T. H. (2021). Air pollution, physical activity and health: A mapping review of the evidence. Environment international , 147 , 105954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105954
Booth, A. (2016). EVIDENT Guidance for Reviewing the Evidence: a compendium of methodological literature and websites . ResearchGate. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.1562.9842 .
Grant, M.J. & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of the 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal , 26(2), 91-108. https://www.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
"A type of review that has as its primary objective the identification of the size and quality of research in a topic area in order to inform subsequent review" (Booth et al., 2012, p. 269).
- Main purpose is to map out and categorize existing literature, identify gaps in literature—great for informing policy-making
- Search comprehensiveness determined by time/scope constraints, could take longer than a systematic review
- No formal quality assessment or critical appraisal
Learn more about the methods :
Arksey, H., & O'Malley, L. (2005) Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology , 8 (1), 19-32. https://doi.org/10.1080/1364557032000119616
Levac, D., Colquhoun, H., & O’Brien, K. K. (2010). Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implementation Science: IS, 5, 69. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-5-69
Example :
Rahman, A., Sarkar, A., Yadav, O. P., Achari, G., & Slobodnik, J. (2021). Potential human health risks due to environmental exposure to nano-and microplastics and knowledge gaps: A scoping review. Science of the Total Environment, 757 , 143872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143872
A review that "[compiles] evidence from multiple...reviews into one accessible and usable document" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 103). While originally intended to be a compilation of Cochrane reviews, it now generally refers to any kind of evidence synthesis.
- Compiles evidence from multiple reviews into one document
- Often defines a broader question than is typical of a traditional systematic review
Choi, G. J., & Kang, H. (2022). The umbrella review: a useful strategy in the rain of evidence. The Korean Journal of Pain , 35 (2), 127–128. https://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2022.35.2.127
Aromataris, E., Fernandez, R., Godfrey, C. M., Holly, C., Khalil, H., & Tungpunkom, P. (2015). Summarizing systematic reviews: Methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach. International Journal of Evidence-Based Healthcare , 13(3), 132–140. https://doi.org/10.1097/XEB.0000000000000055
Rojas-Rueda, D., Morales-Zamora, E., Alsufyani, W. A., Herbst, C. H., Al Balawi, S. M., Alsukait, R., & Alomran, M. (2021). Environmental risk factors and health: An umbrella review of meta-analyses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Dealth , 18 (2), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020704
A meta-analysis is a "technique that statistically combines the results of quantitative studies to provide a more precise effect of the result" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 98).
- Statistical technique for combining results of quantitative studies to provide more precise effect of results
- Aims for exhaustive, comprehensive searching
- Quality assessment may determine inclusion/exclusion criteria
- May be conducted independently or as part of a systematic review
Berman, N. G., & Parker, R. A. (2002). Meta-analysis: Neither quick nor easy. BMC Medical Research Methodology , 2(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-2-10
Hites R. A. (2004). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the environment and in people: a meta-analysis of concentrations. Environmental Science & Technology , 38 (4), 945–956. https://doi.org/10.1021/es035082g
A systematic review "seeks to systematically search for, appraise, and [synthesize] research evidence, often adhering to the guidelines on the conduct of a review" provided by discipline-specific organizations, such as the Cochrane Collaboration (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 102).
- Aims to compile and synthesize all known knowledge on a given topic
- Adheres to strict guidelines, protocols, and frameworks
- Time-intensive and often takes months to a year or more to complete
- The most commonly referred to type of evidence synthesis. Sometimes confused as a blanket term for other types of reviews
Gascon, M., Triguero-Mas, M., Martínez, D., Dadvand, P., Forns, J., Plasència, A., & Nieuwenhuijsen, M. J. (2015). Mental health benefits of long-term exposure to residential green and blue spaces: a systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 12 (4), 4354–4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120404354
"Systematized reviews attempt to include one or more elements of the systematic review process while stopping short of claiming that the resultant output is a systematic review" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 102). When a systematic review approach is adapted to produce a more manageable scope, while still retaining the rigor of a systematic review such as risk of bias assessment and the use of a protocol, this is often referred to as a structured review (Huelin et al., 2015).
- Typically conducted by postgraduate or graduate students
- Often assigned by instructors to students who don't have the resources to conduct a full systematic review
Salvo, G., Lashewicz, B. M., Doyle-Baker, P. K., & McCormack, G. R. (2018). Neighbourhood built environment influences on physical activity among adults: A systematized review of qualitative evidence. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 15 (5), 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15050897
Huelin, R., Iheanacho, I., Payne, K., & Sandman, K. (2015). What’s in a name? Systematic and non-systematic literature reviews, and why the distinction matters. https://www.evidera.com/resource/whats-in-a-name-systematic-and-non-systematic-literature-reviews-and-why-the-distinction-matters/

- Review Decision Tree - Cornell University For more information, check out Cornell's review methodology decision tree.
- LitR-Ex.com - Eight literature review methodologies Learn more about 8 different review types (incl. Systematic Reviews and Scoping Reviews) with practical tips about strengths and weaknesses of different methods.
- << Previous: Getting started
- Next: 1. Define your research question >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 8:42 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.duke.edu/litreviews

Services for...
- Faculty & Instructors
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- International Students
- Patrons with Disabilities
- Harmful Language Statement
- Re-use & Attribution / Privacy
- Support the Libraries

Research Methods
- Getting Started
- Literature Review Research
- Research Design
- Research Design By Discipline
- SAGE Research Methods
- Teaching with SAGE Research Methods
Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- What is NOT a Literature Review?
- Purposes of a Literature Review
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Literature Reviews vs. Systematic Reviews
- Systematic vs. Meta-Analysis
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.
Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
- Summarizes and analyzes previous research relevant to a topic
- Includes scholarly books and articles published in academic journals
- Can be an specific scholarly paper or a section in a research paper
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic
- Help gather ideas or information
- Keep up to date in current trends and findings
- Help develop new questions
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Helps focus your own research questions or problems
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Suggests unexplored ideas or populations
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
- Identifies critical gaps, points of disagreement, or potentially flawed methodology or theoretical approaches.
- Indicates potential directions for future research.
All content in this section is from Literature Review Research from Old Dominion University
Keep in mind the following, a literature review is NOT:
Not an essay
Not an annotated bibliography in which you summarize each article that you have reviewed. A literature review goes beyond basic summarizing to focus on the critical analysis of the reviewed works and their relationship to your research question.
Not a research paper where you select resources to support one side of an issue versus another. A lit review should explain and consider all sides of an argument in order to avoid bias, and areas of agreement and disagreement should be highlighted.
A literature review serves several purposes. For example, it
- provides thorough knowledge of previous studies; introduces seminal works.
- helps focus one’s own research topic.
- identifies a conceptual framework for one’s own research questions or problems; indicates potential directions for future research.
- suggests previously unused or underused methodologies, designs, quantitative and qualitative strategies.
- identifies gaps in previous studies; identifies flawed methodologies and/or theoretical approaches; avoids replication of mistakes.
- helps the researcher avoid repetition of earlier research.
- suggests unexplored populations.
- determines whether past studies agree or disagree; identifies controversy in the literature.
- tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
As Kennedy (2007) notes*, it is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the original studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally that become part of the lore of field. In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews.
Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are several approaches to how they can be done, depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study. Listed below are definitions of types of literature reviews:
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply imbedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews.
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical reviews are focused on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [content], but how they said it [method of analysis]. This approach provides a framework of understanding at different levels (i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches and data collection and analysis techniques), enables researchers to draw on a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection and data analysis, and helps highlight many ethical issues which we should be aware of and consider as we go through our study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyse data from the studies that are included in the review. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?"
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to concretely examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review help establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
* Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147.
All content in this section is from The Literature Review created by Dr. Robert Larabee USC
Robinson, P. and Lowe, J. (2015), Literature reviews vs systematic reviews. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health, 39: 103-103. doi: 10.1111/1753-6405.12393

What's in the name? The difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review, and why it matters . By Lynn Kysh from University of Southern California

Systematic review or meta-analysis?
A systematic review answers a defined research question by collecting and summarizing all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria.
A meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of these studies.
Systematic reviews, just like other research articles, can be of varying quality. They are a significant piece of work (the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination at York estimates that a team will take 9-24 months), and to be useful to other researchers and practitioners they should have:
- clearly stated objectives with pre-defined eligibility criteria for studies
- explicit, reproducible methodology
- a systematic search that attempts to identify all studies
- assessment of the validity of the findings of the included studies (e.g. risk of bias)
- systematic presentation, and synthesis, of the characteristics and findings of the included studies
Not all systematic reviews contain meta-analysis.
Meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects of health care than those derived from the individual studies included within a review. More information on meta-analyses can be found in Cochrane Handbook, Chapter 9 .
A meta-analysis goes beyond critique and integration and conducts secondary statistical analysis on the outcomes of similar studies. It is a systematic review that uses quantitative methods to synthesize and summarize the results.
An advantage of a meta-analysis is the ability to be completely objective in evaluating research findings. Not all topics, however, have sufficient research evidence to allow a meta-analysis to be conducted. In that case, an integrative review is an appropriate strategy.
Some of the content in this section is from Systematic reviews and meta-analyses: step by step guide created by Kate McAllister.
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Research Design >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 4:07 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/researchmethods

Types of Literature Review
There are many types of literature review. The choice of a specific type depends on your research approach and design. The following types of literature review are the most popular in business studies:
Narrative literature review , also referred to as traditional literature review, critiques literature and summarizes the body of a literature. Narrative review also draws conclusions about the topic and identifies gaps or inconsistencies in a body of knowledge. You need to have a sufficiently focused research question to conduct a narrative literature review
Systematic literature review requires more rigorous and well-defined approach compared to most other types of literature review. Systematic literature review is comprehensive and details the timeframe within which the literature was selected. Systematic literature review can be divided into two categories: meta-analysis and meta-synthesis.
When you conduct meta-analysis you take findings from several studies on the same subject and analyze these using standardized statistical procedures. In meta-analysis patterns and relationships are detected and conclusions are drawn. Meta-analysis is associated with deductive research approach.
Meta-synthesis, on the other hand, is based on non-statistical techniques. This technique integrates, evaluates and interprets findings of multiple qualitative research studies. Meta-synthesis literature review is conducted usually when following inductive research approach.
Scoping literature review , as implied by its name is used to identify the scope or coverage of a body of literature on a given topic. It has been noted that “scoping reviews are useful for examining emerging evidence when it is still unclear what other, more specific questions can be posed and valuably addressed by a more precise systematic review.” [1] The main difference between systematic and scoping types of literature review is that, systematic literature review is conducted to find answer to more specific research questions, whereas scoping literature review is conducted to explore more general research question.
Argumentative literature review , as the name implies, examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply imbedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. It should be noted that a potential for bias is a major shortcoming associated with argumentative literature review.
Integrative literature review reviews , critiques, and synthesizes secondary data about research topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. If your research does not involve primary data collection and data analysis, then using integrative literature review will be your only option.
Theoretical literature review focuses on a pool of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. Theoretical literature reviews play an instrumental role in establishing what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested.
At the earlier parts of the literature review chapter, you need to specify the type of your literature review your chose and justify your choice. Your choice of a specific type of literature review should be based upon your research area, research problem and research methods. Also, you can briefly discuss other most popular types of literature review mentioned above, to illustrate your awareness of them.
[1] Munn, A. et. al. (2018) “Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach” BMC Medical Research Methodology

John Dudovskiy
Libraries | Research Guides
Literature reviews, what is a literature review, learning more about how to do a literature review.
- Planning the Review
- The Research Question
- Choosing Where to Search
- Organizing the Review
- Writing the Review
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the literature you have read.
- Sage Research Methods Core Collection This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. – Publisher
- Next: Planning the Review >>
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 10:39 AM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/literaturereviews

Literature Reviews, Critiquing, & Synthesizing Literature
- Literature Review
Types of Literature Reviews
Literature review types -- comparing, learning about study designs, critically appraised topics -- writing, integrative lit review.
- Literature Review Steps Videos
- Critiquing Literature / Critical Review
- Synthesizing Literature
- Summarizing Articles
- Other Lit Review LibGuides
Types of Literature Reviews:
Critically Appraised Topic (CATs) : A critically appraised topic (or CAT) is a short summary of evidence on a topic of interest, usually focused around a clinical question. A CAT is like a shorter and less rigorous version of a systematic review, summarizing the best available research evidence on a topic.
Integrative Review: A review via a systematic approach that uses a detailed search strategy to find relevant evidence to answer a targeted clinical question. Evidence can come from RCTs, observational studies, qualitative research, clinical experts, and other types of evidence. Does not use summary statistics.
Meta-analysis: a quantitative statistical analysis of several separate but similar experiments or studies in order to test the pooled data for statistical significance.
Narrative or Traditional Review: Critical research summary on a topic of interest, often to put a research problem into context. Captures a “snapshot” of the clinical problem or issue.
Rapid Review : A rapid literature review (RLR) is an alternative to systematic literature review (SLR) that can speed up the analysis of newly published data.
Scoping Review A s coping review is a descriptive approach, designed to chart the literature around a particular topic. It involves an extensive literature search and often uses structured mapping or charting of the literature.
Systematic Review : Comprehensive search strategies and rigorous research appraisal methods surrounding a clinical issue or question. Evidence is primarily based upon RCTs . Used to summarize, appraise, & communicate contradictory results or unmanageable amounts of research.
Umbrella Review : An umbrella review is a systematic collection and assessment of multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses on a specific research topic
- Lit Review vs Systematic Rev vs Meta Analysis
- A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Grant, M. J., & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health information and libraries journal, 26(2), 91–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
- Chart comparing Systematic Review Vs Literature Review Chart explaining differences. Chart by L. Kysh, MLIS from U. Ca
- Conducting umbrella reviews Belbasis, L., Bellou, V., & Ioannidis, J. P. (2022). Conducting umbrella reviews. BMJ medicine, 1(1).
- Meeting the review family: exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements. Sutton, A., Clowes, M., Preston, L., & Booth, A. (2019). Meeting the review family: exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements. Health Information & Libraries Journal, 36(3), 202-222.
- Part 1: Difference between systematic reviews and rapid reviews (4:43) Cochrane Training video.
- Rapid literature review: definition and methodology Smela, B., Toumi, M., Świerk, K., Francois, C., Biernikiewicz, M., Clay, E., & Boyer, L. (2023). Rapid literature review: definition and methodology. Journal of market access & health policy, 11(1), 2241234. https://doi.org/10.1080/20016689.2023.2241234
- Reviewing Research: Literature Reviews, Scoping Reviews, Systematic Reviews: Differentiating the Three Review Types University of Buffalo LibGuide
- Scoping reviews, systematic reviews, and meta-analysis: Applications in veterinary medicine Sargeant, J. M., & O'Connor, A. M. (2020). Scoping reviews, systematic reviews, and meta-analysis: Applications in veterinary medicine. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 7, 11-11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2020.00011
- Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach Munn, Z., Peters, M.D.J., Stern, C. et al. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med Res Methodol 18, 143 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-018-0611-x
- Systematic Review Service: What Type of Review is Right for You? University of Maryland Health Sciences and Human Services Library Decide with type of review. Decision Tree included.
- Systematic vs. Scoping vs. Integrative References Getting Help Systematic vs. Scoping vs. Integrative Review Duquesne University
- What Type of Review is Right for You? Cornell University Library Flowchart to decide about which review to use.
- Study Design 101 Tutorial by George Washington University. Describes different study designs.
Critically Appraised Topics (CATs)
- CEBMa Guideline for Critically Appraised Topics in Management and Organizations Barends, E., Rousseau, D. M., & Briner, R. B. (2017). CEBMa guideline for critically appraised topics in management and organizations. Center for Evidence-Based Management. https://cebma. org/wp-content/uploads/CEBMa-CAT-Guidelines. pdf.
- Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) The Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) was developed in Oxford in 1993 and has since helped to develop an evidence based approach in health and social care, working with local, national and international partner organisations.
- Evidence Based Medicine IV: how to find an evidence-based answer to a clinical question? Make a critically appraised topic! Beckers, G. M. A., Herbst, K., Kaefer, M., Harper, L., Castagnetti, M., Bagli, D., Kalfa, N., Fossum, M., & ESPU Research Committee. (2019). Evidence based medicine IV: How to find an evidence-based answer to a clinical question? make a critically appraised topic. Journal of Pediatric Urology, 15(4), 409-411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpurol.2019.05.009
- EXAMPLE: The Use of Orthotic Insoles to Prevent Lower Limb Overuse Injuries: A Critically Appraised Topic Kelly JL, Valier AR. The Use of Orthotic Insoles to Prevent Lower Limb Overuse Injuries: A Critically Appraised Topic. J Sport Rehabil. 2018 Nov 1;27(6):591-595. doi: 10.1123/jsr.2016-0142. Epub 2018 Oct 13. PMID: 28952905.
- How to Perform a Critically Appraised Topic: Part 1, Ask, Search, and Apply Aine Marie Kelly and Paul Cronin American Journal of Roentgenology November 2011, Volume 197, Number 5
- How to Perform a Critically Appraised Topic: Part 2, Appraise, Evaluate, Generate, and Recommend Aine Marie Kelly and Paul Cronin American Journal of Roentgenology November 2011, Volume 197, Number 5
- How to write a critically appraised topic (CAT) Sadigh, G., Parker, R., Kelly, A. M., & Cronin, P. (2012). How to write a critically appraised topic (CAT). Academic radiology, 19(7), 872–888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2012.02.005
- How to write a Critically Appraised Topic: evidence to underpin routine clinical practice Callander J, Anstey AV, Ingram JR, Limpens J, Flohr C, Spuls PI. How to write a Critically Appraised Topic: evidence to underpin routine clinical practice. Br J Dermatol. 2017 Oct;177(4):1007-1013. doi: 10.1111/bjd.15873. Epub 2017 Oct 1. PMID: 28967117.
- What is a Critically Appraised Topic (CAT) Physiopedia
Integrative Review: A review via a systematic approach that uses a detailed search strategy to find relevant evidence to answer a targeted clinical question. Evidence can come from RCTs, observational studies, qualitative research, clinical experts, and other types of evidence. Does not use summary statistics.
- Conducting integrative reviews: a guide for novice nursing researchers Dhollande S, Taylor A, Meyer S, Scott M. Conducting integrative reviews: a guide for novice nursing researchers. J Res Nurs. 2021 Aug;26(5):427-438. doi: 10.1177/1744987121997907. Epub 2021 Aug 5. PMID: 35251272; PMCID: PMC8894639.
- The integrative review: Updated methodology. Whittemore, R., & Knafl, K. (2005). The integrative review: Updated methodology. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 52(5), 546-553. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2005.03621.x
- Strategies for completing a successful integrative review Oermann, M. H., & Knafl, K. A. (2021). Strategies for completing a successful integrative review. Nurse Author & Editor, 31(3-4), 65-68.
- << Previous: Literature Review
- Next: Literature Review Steps Videos >>
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 8:44 PM
- URL: https://libguides.ahu.edu/LitReviewSum
Resources listed on these guides are compiled by librarians at the R.A. Williams Library. We accept content recommendations, and after review, may include suggested resources on a guide. Our time is limited, so we generally do not reply to unsolicited recommendations from individuals not affiliated with AdventHealth University or notify them regarding whether or not we have linked to suggested content.
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
Literature Reviews
- Getting Started
Selecting a Review Type
Defining the scope of your review, four common types of reviews.
- Developing a Research Question
- Searching the Literature
- Searching Tips
- ChatGPT [beta]
- Documenting your Search
- Using Citation Managers
- Concept Mapping
- Writing the Review
- Further Resources
More Review Types

This article by Sutton & Booth (2019) explores 48 distinct types of Literature Reviews:
Which Review is Right for You?

The Right Review tool has questions about your lit review process and plans. It offers a qualitative and quantitative option. At completion, you are given a lit review type recommendation.

You'll want to think about the kind of review you are doing. Is it a selective or comprehensive review? Is the review part of a larger work or a stand-alone work ?
For example, if you're writing the Literature Review section of a journal article, that's a selective review which is part of a larger work. Alternatively, if you're writing a review article, that's a comprehensive review which is a stand-alone work. Thinking about this will help you develop the scope of the review.
This exercise will help define the scope of your Literature Review, setting the boundaries for which literature to include and which to exclude.
A FEW GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS WHEN DEFINING SCOPE
- Which populations to investigate — this can include gender, age, socio-economic status, race, geographic location, etc., if the research area includes humans.
- What years to include — if researching the legalization of medicinal cannabis, you might only look at the previous 20 years; but if researching dolphin mating practices, you might extend many more decades.
- Which subject areas — if researching artificial intelligence, subject areas could be computer science, robotics, or health sciences
- How many sources — a selective review for a class assignment might only need ten, while a comprehensive review for a dissertation might include hundreds. There is no one right answer.
- There will be many other considerations that are more specific to your topic.
Most databases will allow you to limit years and subject areas, so look for those tools while searching. See the Searching Tips tab for information on how use these tools.
LITERATURE REVIEW
- Often used as a generic term to describe any type of review
- More precise definition: Published materials that provide an examination of published literature . Can cover wide range of subjects at various levels of comprehensiveness.
- Identifies gaps in research, explains importance of topic, hypothesizes future work, etc.
- Usually written as part of a larger work like a journal article or dissertation
SCOPING REVIEW
- Conducted to address broad research questions with the goal of understanding the extent of research that has been conducted.
- Provides a preliminary assessment of the potential size and scope of available research literature. It aims to identify the nature and extent of research evidence (usually including ongoing research)
- Doesn't assess the quality of the literature gathered (i.e. presence of literature on a topic shouldn’t be conflated w/ the quality of that literature)
- " Preparing scoping reviews for publication using methodological guides and reporting standards " is a great article to read on Scoping Reviews
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
- Common in the health sciences ( Taubman Health Sciences Library guide to Systematic Reviews )
- Goal: collect all literature that meets specific criteria (methodology, population, treatment, etc.) and then appraise its quality and synthesize it
- Follows strict protocol for literature collection, appraisal and synthesis
- Typically performed by research teams
- Takes 12-18 months to complete
- Often written as a stand alone work
META-ANALYSIS
- Goes one step further than a systematic review by statistically combining the results of quantitative studies to provide a more precise effect of the results.
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Developing a Research Question >>
- Last Updated: May 9, 2024 11:44 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.umich.edu/litreview

- Duke NetID Login
- 919.660.1100
- Duke Health Badge: 24-hour access
- Accounts & Access
- Databases, Journals & Books
- Request & Reserve
- Training & Consulting
- Request Articles & Books
- Renew Online
- Reserve Spaces
- Reserve a Locker
- Study & Meeting Rooms
- Course Reserves
- Pay Fines/Fees
- Recommend a Purchase
- Access From Off Campus
- Building Access
- Computers & Equipment
- Wifi Access
- My Accounts
- Mobile Apps
- Known Access Issues
- Report an Access Issue
- All Databases
- Article Databases
- Basic Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Dissertations & Theses
- Drugs, Chemicals & Toxicology
- Grants & Funding
- Interprofessional Education
- Non-Medical Databases
- Search for E-Journals
- Search for Print & E-Journals
- Search for E-Books
- Search for Print & E-Books
- E-Book Collections
- Biostatistics
- Global Health
- MBS Program
- Medical Students
- MMCi Program
- Occupational Therapy
- Path Asst Program
- Physical Therapy
- Researchers
- Community Partners
Conducting Research
- Archival & Historical Research
- Black History at Duke Health
- Data Analytics & Viz Software
- Data: Find and Share
- Evidence-Based Practice
- NIH Public Access Policy Compliance
- Publication Metrics
- Qualitative Research
- Searching Animal Alternatives
Systematic Reviews
- Test Instruments
Using Databases
- JCR Impact Factors
- Web of Science
Finding & Accessing
- COVID-19: Core Clinical Resources
- Health Literacy
- Health Statistics & Data
- Library Orientation
Writing & Citing
- Creating Links
- Getting Published
- Reference Mgmt
- Scientific Writing
Meet a Librarian
- Request a Consultation
- Find Your Liaisons
- Register for a Class
- Request a Class
- Self-Paced Learning
Search Services
- Literature Search
- Systematic Review
- Animal Alternatives (IACUC)
- Research Impact
Citation Mgmt
- Other Software
Scholarly Communications
- About Scholarly Communications
- Publish Your Work
- Measure Your Research Impact
- Engage in Open Science
- Libraries and Publishers
- Directions & Maps
- Floor Plans
Library Updates
- Annual Snapshot
- Conference Presentations
- Contact Information
- Gifts & Donations
- What is a Systematic Review?
Types of Reviews
- Manuals and Reporting Guidelines
- Our Service
- 1. Assemble Your Team
- 2. Develop a Research Question
- 3. Write and Register a Protocol
- 4. Search the Evidence
- 5. Screen Results
- 6. Assess for Quality and Bias
- 7. Extract the Data
- 8. Write the Review
- Additional Resources
- Finding Full-Text Articles

Review Typologies
There are many types of evidence synthesis projects, including systematic reviews as well as others. The selection of review type is wholly dependent on the research question. Not all research questions are well-suited for systematic reviews.
- Review Typologies (from LITR-EX) This site explores different review methodologies such as, systematic, scoping, realist, narrative, state of the art, meta-ethnography, critical, and integrative reviews. The LITR-EX site has a health professions education focus, but the advice and information is widely applicable.
Review the table to peruse review types and associated methodologies. Librarians can also help your team determine which review type might be appropriate for your project.
Reproduced from Grant, M. J. and Booth, A. (2009), A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal, 26: 91-108. doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
- << Previous: What is a Systematic Review?
- Next: Manuals and Reporting Guidelines >>
- Last Updated: May 22, 2024 8:22 PM
- URL: https://guides.mclibrary.duke.edu/sysreview
- Duke Health
- Duke University
- Duke Libraries
- Medical Center Archives
- Duke Directory
- Seeley G. Mudd Building
- 10 Searle Drive
- [email protected]

Literature Review: Types of Literature Reviews
- Literature Review
- Purpose of a Literature Review
- Work in Progress
- Compiling & Writing
- Books, Articles, & Web Pages
Types of Literature Reviews
- Departmental Differences
- Citation Styles & Plagiarism
- Know the Difference! Systematic Review vs. Literature Review
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers.
- First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish.
- Second, are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the original studies.
- Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinions, and interpretations that are shared informally that become part of the lore of the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews.
Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are several approaches to how they can be done, depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study. Listed below are definitions of types of literature reviews:
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews.
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical reviews are focused on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomenon emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [content], but how they said it [method of analysis]. This approach provides a framework of understanding at different levels (i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques), enables researchers to draw on a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection and data analysis, and helps highlight many ethical issues which we should be aware of and consider as we go through our study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?"
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to concretely examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomenon. The theoretical literature review help establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
* Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147.
All content is from The Literature Review created by Dr. Robert Larabee USC
- << Previous: Books, Articles, & Web Pages
- Next: Departmental Differences >>
- Last Updated: Oct 19, 2023 12:07 PM
- URL: https://uscupstate.libguides.com/Literature_Review
- Privacy Policy

Home » Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and Examples
Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Literature Review
Definition:
A literature review is a comprehensive and critical analysis of the existing literature on a particular topic or research question. It involves identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing relevant literature, including scholarly articles, books, and other sources, to provide a summary and critical assessment of what is known about the topic.
Types of Literature Review
Types of Literature Review are as follows:
- Narrative literature review : This type of review involves a comprehensive summary and critical analysis of the available literature on a particular topic or research question. It is often used as an introductory section of a research paper.
- Systematic literature review: This is a rigorous and structured review that follows a pre-defined protocol to identify, evaluate, and synthesize all relevant studies on a specific research question. It is often used in evidence-based practice and systematic reviews.
- Meta-analysis: This is a quantitative review that uses statistical methods to combine data from multiple studies to derive a summary effect size. It provides a more precise estimate of the overall effect than any individual study.
- Scoping review: This is a preliminary review that aims to map the existing literature on a broad topic area to identify research gaps and areas for further investigation.
- Critical literature review : This type of review evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of the existing literature on a particular topic or research question. It aims to provide a critical analysis of the literature and identify areas where further research is needed.
- Conceptual literature review: This review synthesizes and integrates theories and concepts from multiple sources to provide a new perspective on a particular topic. It aims to provide a theoretical framework for understanding a particular research question.
- Rapid literature review: This is a quick review that provides a snapshot of the current state of knowledge on a specific research question or topic. It is often used when time and resources are limited.
- Thematic literature review : This review identifies and analyzes common themes and patterns across a body of literature on a particular topic. It aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the literature and identify key themes and concepts.
- Realist literature review: This review is often used in social science research and aims to identify how and why certain interventions work in certain contexts. It takes into account the context and complexities of real-world situations.
- State-of-the-art literature review : This type of review provides an overview of the current state of knowledge in a particular field, highlighting the most recent and relevant research. It is often used in fields where knowledge is rapidly evolving, such as technology or medicine.
- Integrative literature review: This type of review synthesizes and integrates findings from multiple studies on a particular topic to identify patterns, themes, and gaps in the literature. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge on a particular topic.
- Umbrella literature review : This review is used to provide a broad overview of a large and diverse body of literature on a particular topic. It aims to identify common themes and patterns across different areas of research.
- Historical literature review: This type of review examines the historical development of research on a particular topic or research question. It aims to provide a historical context for understanding the current state of knowledge on a particular topic.
- Problem-oriented literature review : This review focuses on a specific problem or issue and examines the literature to identify potential solutions or interventions. It aims to provide practical recommendations for addressing a particular problem or issue.
- Mixed-methods literature review : This type of review combines quantitative and qualitative methods to synthesize and analyze the available literature on a particular topic. It aims to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research question by combining different types of evidence.
Parts of Literature Review
Parts of a literature review are as follows:
Introduction
The introduction of a literature review typically provides background information on the research topic and why it is important. It outlines the objectives of the review, the research question or hypothesis, and the scope of the review.
Literature Search
This section outlines the search strategy and databases used to identify relevant literature. The search terms used, inclusion and exclusion criteria, and any limitations of the search are described.
Literature Analysis
The literature analysis is the main body of the literature review. This section summarizes and synthesizes the literature that is relevant to the research question or hypothesis. The review should be organized thematically, chronologically, or by methodology, depending on the research objectives.
Critical Evaluation
Critical evaluation involves assessing the quality and validity of the literature. This includes evaluating the reliability and validity of the studies reviewed, the methodology used, and the strength of the evidence.
The conclusion of the literature review should summarize the main findings, identify any gaps in the literature, and suggest areas for future research. It should also reiterate the importance of the research question or hypothesis and the contribution of the literature review to the overall research project.
The references list includes all the sources cited in the literature review, and follows a specific referencing style (e.g., APA, MLA, Harvard).
How to write Literature Review
Here are some steps to follow when writing a literature review:
- Define your research question or topic : Before starting your literature review, it is essential to define your research question or topic. This will help you identify relevant literature and determine the scope of your review.
- Conduct a comprehensive search: Use databases and search engines to find relevant literature. Look for peer-reviewed articles, books, and other academic sources that are relevant to your research question or topic.
- Evaluate the sources: Once you have found potential sources, evaluate them critically to determine their relevance, credibility, and quality. Look for recent publications, reputable authors, and reliable sources of data and evidence.
- Organize your sources: Group the sources by theme, method, or research question. This will help you identify similarities and differences among the literature, and provide a structure for your literature review.
- Analyze and synthesize the literature : Analyze each source in depth, identifying the key findings, methodologies, and conclusions. Then, synthesize the information from the sources, identifying patterns and themes in the literature.
- Write the literature review : Start with an introduction that provides an overview of the topic and the purpose of the literature review. Then, organize the literature according to your chosen structure, and analyze and synthesize the sources. Finally, provide a conclusion that summarizes the key findings of the literature review, identifies gaps in knowledge, and suggests areas for future research.
- Edit and proofread: Once you have written your literature review, edit and proofread it carefully to ensure that it is well-organized, clear, and concise.
Examples of Literature Review
Here’s an example of how a literature review can be conducted for a thesis on the topic of “ The Impact of Social Media on Teenagers’ Mental Health”:
- Start by identifying the key terms related to your research topic. In this case, the key terms are “social media,” “teenagers,” and “mental health.”
- Use academic databases like Google Scholar, JSTOR, or PubMed to search for relevant articles, books, and other publications. Use these keywords in your search to narrow down your results.
- Evaluate the sources you find to determine if they are relevant to your research question. You may want to consider the publication date, author’s credentials, and the journal or book publisher.
- Begin reading and taking notes on each source, paying attention to key findings, methodologies used, and any gaps in the research.
- Organize your findings into themes or categories. For example, you might categorize your sources into those that examine the impact of social media on self-esteem, those that explore the effects of cyberbullying, and those that investigate the relationship between social media use and depression.
- Synthesize your findings by summarizing the key themes and highlighting any gaps or inconsistencies in the research. Identify areas where further research is needed.
- Use your literature review to inform your research questions and hypotheses for your thesis.
For example, after conducting a literature review on the impact of social media on teenagers’ mental health, a thesis might look like this:
“Using a mixed-methods approach, this study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes in teenagers. Specifically, the study will examine the effects of cyberbullying, social comparison, and excessive social media use on self-esteem, anxiety, and depression. Through an analysis of survey data and qualitative interviews with teenagers, the study will provide insight into the complex relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes, and identify strategies for promoting positive mental health outcomes in young people.”
Reference: Smith, J., Jones, M., & Lee, S. (2019). The effects of social media use on adolescent mental health: A systematic review. Journal of Adolescent Health, 65(2), 154-165. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2019.03.024
Reference Example: Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (Year). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number(issue number), page range. doi:0000000/000000000000 or URL
Applications of Literature Review
some applications of literature review in different fields:
- Social Sciences: In social sciences, literature reviews are used to identify gaps in existing research, to develop research questions, and to provide a theoretical framework for research. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as sociology, psychology, anthropology, and political science.
- Natural Sciences: In natural sciences, literature reviews are used to summarize and evaluate the current state of knowledge in a particular field or subfield. Literature reviews can help researchers identify areas where more research is needed and provide insights into the latest developments in a particular field. Fields such as biology, chemistry, and physics commonly use literature reviews.
- Health Sciences: In health sciences, literature reviews are used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments, identify best practices, and determine areas where more research is needed. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as medicine, nursing, and public health.
- Humanities: In humanities, literature reviews are used to identify gaps in existing knowledge, develop new interpretations of texts or cultural artifacts, and provide a theoretical framework for research. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as history, literary studies, and philosophy.
Role of Literature Review in Research
Here are some applications of literature review in research:
- Identifying Research Gaps : Literature review helps researchers identify gaps in existing research and literature related to their research question. This allows them to develop new research questions and hypotheses to fill those gaps.
- Developing Theoretical Framework: Literature review helps researchers develop a theoretical framework for their research. By analyzing and synthesizing existing literature, researchers can identify the key concepts, theories, and models that are relevant to their research.
- Selecting Research Methods : Literature review helps researchers select appropriate research methods and techniques based on previous research. It also helps researchers to identify potential biases or limitations of certain methods and techniques.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Literature review helps researchers in data collection and analysis by providing a foundation for the development of data collection instruments and methods. It also helps researchers to identify relevant data sources and identify potential data analysis techniques.
- Communicating Results: Literature review helps researchers to communicate their results effectively by providing a context for their research. It also helps to justify the significance of their findings in relation to existing research and literature.
Purpose of Literature Review
Some of the specific purposes of a literature review are as follows:
- To provide context: A literature review helps to provide context for your research by situating it within the broader body of literature on the topic.
- To identify gaps and inconsistencies: A literature review helps to identify areas where further research is needed or where there are inconsistencies in the existing literature.
- To synthesize information: A literature review helps to synthesize the information from multiple sources and present a coherent and comprehensive picture of the current state of knowledge on the topic.
- To identify key concepts and theories : A literature review helps to identify key concepts and theories that are relevant to your research question and provide a theoretical framework for your study.
- To inform research design: A literature review can inform the design of your research study by identifying appropriate research methods, data sources, and research questions.
Characteristics of Literature Review
Some Characteristics of Literature Review are as follows:
- Identifying gaps in knowledge: A literature review helps to identify gaps in the existing knowledge and research on a specific topic or research question. By analyzing and synthesizing the literature, you can identify areas where further research is needed and where new insights can be gained.
- Establishing the significance of your research: A literature review helps to establish the significance of your own research by placing it in the context of existing research. By demonstrating the relevance of your research to the existing literature, you can establish its importance and value.
- Informing research design and methodology : A literature review helps to inform research design and methodology by identifying the most appropriate research methods, techniques, and instruments. By reviewing the literature, you can identify the strengths and limitations of different research methods and techniques, and select the most appropriate ones for your own research.
- Supporting arguments and claims: A literature review provides evidence to support arguments and claims made in academic writing. By citing and analyzing the literature, you can provide a solid foundation for your own arguments and claims.
- I dentifying potential collaborators and mentors: A literature review can help identify potential collaborators and mentors by identifying researchers and practitioners who are working on related topics or using similar methods. By building relationships with these individuals, you can gain valuable insights and support for your own research and practice.
- Keeping up-to-date with the latest research : A literature review helps to keep you up-to-date with the latest research on a specific topic or research question. By regularly reviewing the literature, you can stay informed about the latest findings and developments in your field.
Advantages of Literature Review
There are several advantages to conducting a literature review as part of a research project, including:
- Establishing the significance of the research : A literature review helps to establish the significance of the research by demonstrating the gap or problem in the existing literature that the study aims to address.
- Identifying key concepts and theories: A literature review can help to identify key concepts and theories that are relevant to the research question, and provide a theoretical framework for the study.
- Supporting the research methodology : A literature review can inform the research methodology by identifying appropriate research methods, data sources, and research questions.
- Providing a comprehensive overview of the literature : A literature review provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge on a topic, allowing the researcher to identify key themes, debates, and areas of agreement or disagreement.
- Identifying potential research questions: A literature review can help to identify potential research questions and areas for further investigation.
- Avoiding duplication of research: A literature review can help to avoid duplication of research by identifying what has already been done on a topic, and what remains to be done.
- Enhancing the credibility of the research : A literature review helps to enhance the credibility of the research by demonstrating the researcher’s knowledge of the existing literature and their ability to situate their research within a broader context.
Limitations of Literature Review
Limitations of Literature Review are as follows:
- Limited scope : Literature reviews can only cover the existing literature on a particular topic, which may be limited in scope or depth.
- Publication bias : Literature reviews may be influenced by publication bias, which occurs when researchers are more likely to publish positive results than negative ones. This can lead to an incomplete or biased picture of the literature.
- Quality of sources : The quality of the literature reviewed can vary widely, and not all sources may be reliable or valid.
- Time-limited: Literature reviews can become quickly outdated as new research is published, making it difficult to keep up with the latest developments in a field.
- Subjective interpretation : Literature reviews can be subjective, and the interpretation of the findings can vary depending on the researcher’s perspective or bias.
- Lack of original data : Literature reviews do not generate new data, but rather rely on the analysis of existing studies.
- Risk of plagiarism: It is important to ensure that literature reviews do not inadvertently contain plagiarism, which can occur when researchers use the work of others without proper attribution.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
A Guide to Literature Reviews
- Importance of a Good Literature Review
- Conducting the Literature Review
- Structure and Writing Style
Types of Literature Reviews
- Citation Management Software This link opens in a new window
- Acknowledgements
- Argumentative
- Integrative
- Methodological
- Theoretical
- Scoping & Systematic
This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see the Systematic Review tab].
Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but on how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues that you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
- Covidence: The difference between a systematic review & scoping review
- PRISMA Guidelines for Scoping Reviews The PRISMA extension for scoping reviews was published in 2018. The checklist contains 20 essential reporting items and 2 optional items to include when completing a scoping review. Scoping reviews serve to synthesize evidence and assess the scope of literature on a topic. Among other objectives, scoping reviews help determine whether a systematic review of the literature is warranted.
- PROSPERO: international registry of systematic reviews
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analysis (Online Course) Online course from the Campbell Collaboration and the Open Learning Initiative.
- University of Waterloo: Public Health & Kinesiology Research Guide - Systematic Reviews Comprehensive list of resources for systematic and scoping reviews.
Resource Books from the Library
- << Previous: Structure and Writing Style
- Next: How do I Cite? >>
- Last Updated: May 10, 2024 11:34 AM
- URL: https://libguides.mcmaster.ca/litreview
ON YOUR 1ST ORDER
Different Types of Literature Review: Which One Fits Your Research?
By Laura Brown on 13th October 2023
You might not have heard that there are multiple kinds of literature review. However, with the progress in your academic career you will learn these classifications and may need to use different types of them. However, there is nothing to worry if you aren’t aware of them now, as here we are going to discuss this topic in detail.
There are approximately 14 types of literature review on the basis of their specific objectives, methodologies, and the way they approach and analyse existing literature in academic research. Of those 14, there are 4 major types. But before we delve into the details of each one of them and how they are useful in academics, let’s first understand the basics of literature review.
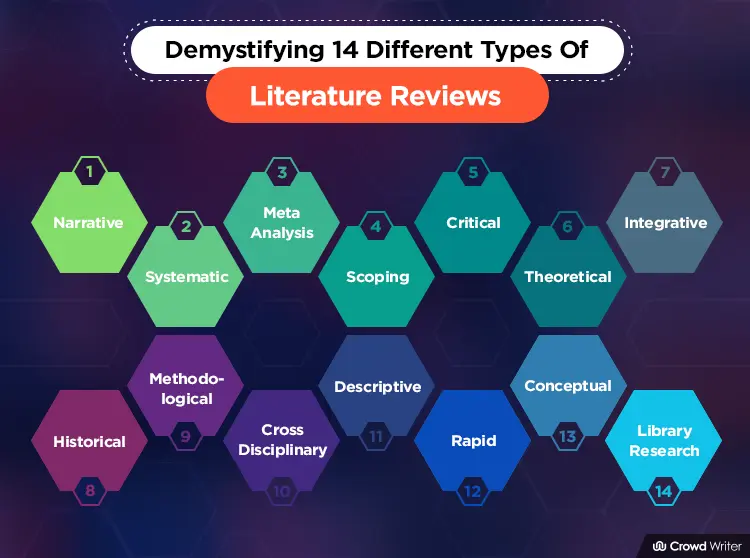
What is Literature Review?
A literature review is a critical and systematic summary and evaluation of existing research. It is an essential component of academic and research work, providing an overview of the current state of knowledge in a particular field.
In easy words, a literature review is like making a big, organised summary of all the important research and smart books or articles about a particular topic or question. It’s something scholars and researchers do, and it helps everyone see what we already know about that topic. It’s kind of like taking a snapshot of what we understand right now in a certain field.
It serves with some specific purpose in the research.
- Provides a comprehensive understanding of existing research on a topic.
- Identifies gaps, trends, and inconsistencies in the literature.
- Contextualise your own research within the broader academic discourse.
- Supports the development of theoretical frameworks or research hypotheses.
4 Major Types Of Literature Review
The four major types include, Narrative Review, Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Scoping Review. These are known as the major ones because they’re like the “go-to” methods for researchers in academic and research circles. Think of them as the classic tools in the researcher’s toolbox. They’ve earned their reputation because they have a unique style for literature review introduction , clear steps and specific qualities that make them super handy for different research needs.
1. Narrative Review
Narrative reviews present a well-structured narrative that reads like a cohesive story, providing a comprehensive overview of a specific topic. These reviews often incorporate historical context and offer a broad understanding of the subject matter, making them valuable for researchers looking to establish a foundational understanding of their area of interest. They are particularly useful when a historical perspective or a broad context is necessary to comprehend the current state of knowledge in a field.
2. Systematic Review
Systematic reviews are renowned for their methodological rigour. They involve a meticulously structured process that includes the systematic selection of relevant studies, comprehensive data extraction, and a critical synthesis of their findings. This systematic approach is designed to minimise bias and subjectivity, making systematic reviews highly reliable and objective. They are considered the gold standard for evidence-based research as they provide a clear and rigorous assessment of the available evidence on a specific research question.
3. Meta Analysis
Meta analysis is a powerful method for researchers who prefer a quantitative and statistical perspective. It involves the statistical synthesis of data from various studies, allowing researchers to draw more precise and generalisable conclusions by combining data from multiple sources. Meta analyses are especially valuable when the aim is to quantitatively measure the effect size or impact of a particular intervention, treatment, or phenomenon.
4. Scoping Review
Scoping reviews are invaluable tools, especially for researchers in the early stages of exploring a topic. These reviews aim to map the existing literature, identifying gaps and helping clarify research questions. Scoping reviews provide a panoramic view of the available research, which is particularly useful when researchers are embarking on exploratory studies or trying to understand the breadth and depth of a subject before conducting more focused research.
Different Types Of Literature review In Research
There are some more approaches to conduct literature review. Let’s explore these classifications quickly.
5. Critical Review
Critical reviews provide an in-depth evaluation of existing literature, scrutinising sources for their strengths, weaknesses, and relevance. They offer a critical perspective, often highlighting gaps in the research and areas for further investigation.
6. Theoretical Review
Theoretical reviews are centred around exploring and analysing the theoretical frameworks, concepts, and models present in the literature. They aim to contribute to the development and refinement of theoretical perspectives within a specific field.
7. Integrative Review
Integrative reviews synthesise a diverse range of studies, drawing connections between various research findings to create a comprehensive understanding of a topic. These reviews often bridge gaps between different perspectives and provide a holistic overview.
8. Historical Review
Historical reviews focus on the evolution of a topic over time, tracing its development through past research, events, and scholarly contributions. They offer valuable context for understanding the current state of research.
9. Methodological Review
Among the different kinds of literature reviews, methodological reviews delve into the research methods and methodologies employed in existing studies. Researchers assess these approaches for their effectiveness, validity, and relevance to the research question at hand.
10. Cross-Disciplinary Review
Cross-disciplinary reviews explore a topic from multiple academic disciplines, emphasising the diversity of perspectives and insights that each discipline brings. They are particularly useful for interdisciplinary research projects and uncovering connections between seemingly unrelated fields.
11. Descriptive Review
Descriptive reviews provide an organised summary of existing literature without extensive analysis. They offer a straightforward overview of key findings, research methods, and themes present in the reviewed studies.
12. Rapid Review
Rapid reviews expedite the literature review process, focusing on summarising relevant studies quickly. They are often used for time-sensitive projects where efficiency is a priority, without sacrificing quality.
13. Conceptual Review
Conceptual reviews concentrate on clarifying and developing theoretical concepts within a specific field. They address ambiguities or inconsistencies in existing theories, aiming to refine and expand conceptual frameworks.
14. Library Research
Library research reviews rely primarily on library and archival resources to gather and synthesise information. They are often employed in historical or archive-based research projects, utilising library collections and historical documents for in-depth analysis.
Each type of literature review serves distinct purposes and comes with its own set of strengths and weaknesses, allowing researchers to choose the one that best suits their research objectives and questions.
Choosing the Ideal Literature Review Approach in Academics
In order to conduct your research in the right manner, it is important that you choose the correct type of review for your literature. Here are 8 amazing tips we have sorted for you in regard to literature review help so that you can select the best-suited type for your research.
- Clarify Your Research Goals: Begin by defining your research objectives and what you aim to achieve with the literature review. Are you looking to summarise existing knowledge, identify gaps, or analyse specific data?
- Understand Different Review Types: Familiarise yourself with different kinds of literature reviews, including systematic reviews, narrative reviews, meta-analyses, scoping reviews, and integrative reviews. Each serves a different purpose.
- Consider Available Resources: Assess the resources at your disposal, including time, access to databases, and the volume of literature on your topic. Some review types may be more resource-intensive than others.
- Alignment with Research Question: Ensure that the chosen review type aligns with your research question or hypothesis. Some types are better suited for answering specific research questions than others.
- Scope and Depth: Determine the scope and depth of your review. For a broad overview, a narrative review might be suitable, while a systematic review is ideal for an in-depth analysis.
- Consult with Advisors: Seek guidance from your academic advisors or mentors. They can provide valuable insights into which review type best fits your research goals and resources.
- Consider Research Field Standards: Different academic fields have established standards and preferences for different forms of literature review. Familiarise yourself with what is common and accepted in your field.
- Pilot Review: Consider conducting a small-scale pilot review of the literature to test the feasibility and suitability of your chosen review type before committing to a larger project.
Bonus Tip: Crafting an Effective Literature Review
Now, since you have learned all the literature review types and have understood which one to prefer, here are some bonus tips for you to structure a literature review of a dissertation .
- Clearly Define Your Research Question: Start with a well-defined and focused research question to guide your literature review.
- Thorough Search Strategy: Develop a comprehensive search strategy to ensure you capture all relevant literature.
- Critical Evaluation: Assess the quality and credibility of the sources you include in your review.
- Synthesise and Organise: Summarise the key findings and organise the literature into themes or categories.
- Maintain a Systematic Approach: If conducting a systematic review, adhere to a predefined methodology and reporting guidelines.
- Engage in Continuous Review: Regularly update your literature review to incorporate new research and maintain relevance.
Some Useful Tools And Resources For You
Effective literature reviews demand a range of tools and resources to streamline the process.
- Reference management software like EndNote, Zotero, and Mendeley helps organise, store, and cite sources, saving time and ensuring accuracy.
- Academic databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and Web of Science provide access to a vast array of scholarly articles, with advanced search and citation tracking features.
- Research guides from universities and libraries offer tips and templates for structuring reviews.
- Research networks like ResearchGate and Academia.edu facilitate collaboration and access to publications. Literature review templates and research workshops provide additional support.
Some Common Mistakes To Avoid
Avoid these common mistakes when crafting literature reviews.
- Unclear research objectives result in unfocused reviews, so start with well-defined questions.
- Biased source selection can compromise objectivity, so include diverse perspectives.
- Never miss on referencing; proper citation and referencing are essential for academic integrity.
- Don’t overlook older literature, which provides foundational insights.
- Be mindful of scope creep, where the review drifts from the research question; stay disciplined to maintain focus and relevance.
While Summing Up On Various Types Of Literature Review
As we conclude this classification of fourteen distinct approaches to conduct literature reviews, it’s clear that the world of research offers a multitude of avenues for understanding, analysing, and contributing to existing knowledge.
Whether you’re a seasoned scholar or a student beginning your academic journey, the choice of review type should align with your research objectives and the nature of your topic. The versatility of these approaches empowers you to tailor your review to the demands of your project.
Remember, your research endeavours have the potential to shape the future of knowledge, so choose wisely and dive into the world of literature reviews with confidence and purpose. Happy reviewing!

Laura Brown, a senior content writer who writes actionable blogs at Crowd Writer.

- About Covidence and systematic reviews
What are the different types of review?
Systematic literature reviews (slrs).
SLR’s attempt to collate all empirical evidence that fit pre-specified eligibility criteria in order to answer a specific clearly-formulated research question. A SLR uses explicit and reproducible systematic methods that are selected with a view to minimizing bias, thus providing more reliable findings from which conclusions can be drawn and decisions made.
The process starts with a research question and a protocol or research plan. A review team searches for studies to answer the question using a highly sensitive search strategy. The retrieved studies are then screened for eligibility using pre-specified inclusion and exclusion criteria (this is done by at least two people working independently). Next, the reviewers extract the relevant data and assess the quality of the included studies. Finally, the review team synthesizes the extracted study data and presents the results.
A SLR may contain meta-analyses (statistical analysis). A SLR which is continually updated, incorporating relevant new evidence as it becomes available is often known as a living SLR.
Rapid reviews
Rapid reviews aim to produce a rigorous synthesis quickly (due to time constraints/urgency), based on a pre-defined research question. The review process for rapid reviews is the same as for a more traditional systematic review: the emphasis is on a replicable pre-specified search, and screening methods that minimize the risk of bias, although potentially isn’t as stringent as a formal systematic review.
The process operates within pre-specified limits (for example, by restricting searches to articles published during a specific timeframe) and is usually run by a multidisciplinary team with expertise in systematic review methods.
Umbrella reviews or Overview of reviews
An umbrella review is a review of multiple systematic reviews. The process uses explicit and systematic methods to search for, and identify, systematic reviews on related research questions in the same topic area. The purpose of an umbrella review is to synthesize the results of the systematic reviews across important outcomes.
Scoping reviews
Scoping reviews are exploratory and they typically address a broad question, compared to a systematic review that typically has a more targeted question.
Researchers conduct scoping reviews to assess the extent of the available evidence, to organize it into groups and to highlight gaps. If a scoping review finds no studies, this might help researchers to decide that a systematic review is likely to be of limited value and that resources could be better directed elsewhere.
Literature reviews or narrative reviews
Literature, or narrative, reviews provide an overview of what is known about a particular topic. They evaluate the material, rather than simply restating it, but the methods used to do this are not usually prespecified and they are not described in detail in the review. The search might be comprehensive but it does not aim to be exhaustive. Literature reviews are often topic based and can take the form of a discussion. Literature reviews lack precision and replicability and can present their findings in the context of what has come before. Often, this sort of synthesis does not attempt to control for the author’s own bias. The results or conclusion of a literature review is likely to be presented in a narrative format rather than statistical methods.
Take a look at the articles about the different types of review on the Covidence blog:
- Systematic review types: meet the family
- The difference between a systematic review and a literature review
- The difference between a systematic review and a meta-analysis
A Bibliometric Analysis of the Scientific Research on Erectile Dysfunction
- Original Paper
- Published: 29 May 2024
Cite this article

- Abdulaziz Ali Y. Alzharani 1 , 2 ,
- Ali M. Alshami 1 ,
- Muhammad Ajmal Khan 3 ,
- Nadeem Siddique 4 &
- Turki Abualait ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8534-6171 1
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a prevalent condition affecting over 150 million men worldwide. While there is a wealth of publications and research in the field of ED, there is a noticeable scarcity of bibliometric analyses of the literature on this topic. This study aims to analyze the scientific activity and research trends related to ED. We conducted a comprehensive search of the Scopus database to identify potentially relevant studies on ED published from 1841 to November 12, 2022. We used the primary keywords “erectile dysfunction” or “impotence” for the search. Several software tools were employed for data calculation and visualization. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) and linear correlation statistical test were used. The main outcomes of interest included the number of publications, year of publication, document type, country of origin, affiliated organizations, and journals of publication. Our search revealed a total of 30,634 publications with a cumulative 657,894 citations in the field of ED literature over the past 18 decades. “Original Article” emerged as the most common document type, accounting for 22,292 records. The United States stood out as the most prolific country, contributing 8809 publications (25% of the total). The University of California in the United States led in research output with 581 publications. Notably, the ‘Journal of Sexual Medicine’ was the leading publication source, with 1715 publications associated with it. Clinicians and experts in sexual medicine should take authorship trends into account when they review ED articles to improve patient care. A primary strength of our study is that it presents a comprehensive bibliometric review of ED reports spanning 18 decades. Results are limited to ED literature published in the sexual medicine journals and the urology analyzed. The publication volume on ED literature witnessed a substantial increase from 1975 to 2022. The findings from this bibliometric analysis provide valuable insights into research hotspots and emerging trends in the field of ED, which can aid researchers in gaining a better understanding of this topic.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

Data Availability
Data is available upon reasonable request.
Abbasi, A., Altmann, J., Hossain, L.: Identifying the effects of co-authorship networks on the performance of scholars: a correlation and regression analysis of performance measures and social network analysis measures. J. Informet. 5 (4), 594–607 (2011)
Article Google Scholar
AlRyalat, S.A.S., Malkawi, L.W., Momani, S.M.: Comparing bibliometric analysis using PubMed, scopus, and web of science databases. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. 152 , e58494 (2019)
Google Scholar
Aydin, C., Senel, E.: Impotence literature: scientometric analysis of erectile dysfunction articles between 1975 and 2018. Andrologia 52 (3), e13520 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1111/and.13520
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Ellegaard, O., Wallin, J.A.: The bibliometric analysis of scholarly production: how great is the impact? Scientometrics 105 (3), 1809–1831 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-015-1645-z
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Fabbri, A., Caprio, M., Aversa, A.: Pathology of erection. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 26 (3 Suppl), 87–90 (2003)
PubMed Google Scholar
Gee, W.F., Holtgrewe, H.L., Albertsen, P.C., Cooper, T.P., Fenninger, R.B., Litwin, M.S., Manyak, M.J., Meyer, J.J., Miles, B.J., O’Leary, M.P., Painter, M.R., Rohner, T.J., Thomas, R., Blizzard, R.T., Emmons, L.: Subspecialization, recruitment and retirement trends of American urologists. J. Urol. 159 (2), 509–511 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(01)63967-3
Giuliano, F., Droupy, S.: Erectile dysfunction. Prog. Urol. 23 (9), 629–637 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.purol.2013.01.010
Glänzel, W., De Lange, C.: A distributional approach to multinationality measures of international scientific collaboration. Scientometrics 54 (1), 75–89 (2002)
Glänzel, W., Schubert, A.: Double effort= double impact? A critical view at international co-authorship in chemistry. Scientometrics 50 (2), 199–214 (2001)
Goldstein, I.: Growth of the field of sexual medicine, vol. 10, pp. 1899–1902. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2013)
Hsieh, T.C., Edwards, N.C., Bhattacharyya, S.K., Nitschelm, K.D., Burnett, A.L.: The epidemic of COVID-19-related erectile dysfunction: a scoping review and health care perspective. Sex. Med. Rev. 10 (2), 286–310 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sxmr.2021.09.002
Hui, J., He, S., Liu, R., Zeng, Q., Zhang, H., Wei, A.: Trends in erectile dysfunction research from 2008 to 2018: a bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Impot. Res. 32 (4), 409–419 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-019-0161-8
Li, H., Gao, T., Wang, R.: The role of the sexual partner in managing erectile dysfunction. Nat. Rev. Urol. 13 (3), 168–177 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2015.315
Ma, C., Su, H., Li, H.: Global research trends on prostate diseases and erectile dysfunction: a bibliometric and visualized study. Front. Oncol. 10 , 627891–627891 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.627891
Mann, J.: Impotence not always productive of mental depression or insanity. Lancet 36 (943), 923–924 (1841)
Minto, T., Bullock, N., Brown, G.: Top 100 most influential manuscripts in erectile dysfunction. Urologia 88 (3), 175–184 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/0391560321993559
Muneer, A., Kalsi, J., Nazareth, I., Arya, M.: Erectile dysfunction. BMJ 348 , g129 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g129
Park, K.: Sexual medicine: new challenges, vol. 4, pp. e1–e1. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2016)
Rabie, A.M.: COVID-19 and sexual dysfunction in men: SARS-CoV-2 in the testes. Sexologies 30 (4), e141–e148 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sexol.2021.07.004
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Rezaee, M.E., Johnson, H.A., Munarriz, R.M., Gross, M.S.: Bibliometric analysis of erectile dysfunction publications in urology and sexual medicine journals. J. Sex. Med. 15 (10), 1426–1433 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsxm.2018.08.004
Rosen, R.C., Riley, A., Wagner, G., Osterloh, I.H., Kirkpatrick, J., Mishra, A.: The international index of erectile function (IIEF): a multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile dysfunction. Urology 49 (6), 822–830 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-4295(97)00238-0
Smyth, J.: Miscellaneous contributions to pathology and therapeutics impotence and sterility. Lancet 36 (939), 779–785 (1841)
Tian, G., Liu, X., Zeng, X., Su, X., Wei, W., Wang, X.: Bibliometric analysis on relations between cardiovascular disease and erectile dysfunction. Zhong guo di fang bing xue za ji 38 (6), 810–813 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.06.024
Walker, D.T., Mills, J.N.: Erectile Dysfunction and Neurological Comorbidities: a Contemporary Review. Curr. Sex. Health Rep. 12 , 113–119 (2020)
Xiong, K., Wang, L., Chen, X., Cao, Y., Xiang, C., Xue, L., Yan, Z.: Analysis of projects received and funded in fields of emergency and intensive care medicine/trauma/burns/plastic surgery from National natural science foundation of China during 2010–2013. Zhonghua wei Zhong Bing ji jiu yi xue 26 (1), 11–16 (2014)
Zhu, J., Liu, W.: A tale of two databases: the use of Web of Science and Scopus in academic papers. Scientometrics 123 (1), 321–335 (2020)
Download references
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Applied Medical Sciences, Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University, P. O. Box 2435, 31451, Dammam, Saudi Arabia
Abdulaziz Ali Y. Alzharani, Ali M. Alshami & Turki Abualait
Department of Physical Therapy, Armed Forces Center for Health Rehabilitation, Taif, Saudi Arabia
Abdulaziz Ali Y. Alzharani
Deanship of Library Affairs, Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University, Dammam, Saudi Arabia
Muhammad Ajmal Khan
Library Department, Lahore University of Management Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan
Nadeem Siddique
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors took part in drafting, execution, collection of data and its analysis, and critically revising this article. They agreed on the submission of the manuscript to the journal and approved this article to be published.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Turki Abualait .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
No conflict of interest related to this work were declared by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Alzharani, A.A.Y., Alshami, A.M., Khan, M.A. et al. A Bibliometric Analysis of the Scientific Research on Erectile Dysfunction. Sex Disabil (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11195-024-09849-8
Download citation
Accepted : 17 May 2024
Published : 29 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11195-024-09849-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publications
- Sexual dysfunction
- Saudi Arabia
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

COMMENTS
Learn about different types of literature reviews and their methodologies, purposes, and pros and cons. Compare narrative, systematic, scoping, and integrative reviews with examples and tips.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Rapid review. Assessment of what is already known about a policy or practice issue, by using systematic review methods to search and critically appraise existing research. Completeness of searching determined by time constraints. Time-limited formal quality assessment. Typically narrative and tabular.
The type of literature review you write will depend on your discipline and whether you are a researcher writing your PhD, publishing a study in a journal or completing an assessment task in your undergraduate study. ... Assesses what is known about an issue by using a systematic review method to search and appraise research and determine best ...
This is why the literature review as a research method is more relevant than ever. Traditional literature reviews often lack thoroughness and rigor and are conducted ad hoc, rather than following a specific methodology. Therefore, questions can be raised about the quality and trustworthiness of these types of reviews.
Mapping Review (Systematic Map) - Map out and categorize existing literature from which to commission further reviews and/or primary research by identifying gaps in research literature. Meta-Analysis - Technique that statistically combines the results of quantitative studies to provide a more precise effect of the results.
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
A literature review may itself be a scholarly publication and provide an analysis of what has been written on a particular topic without contributing original research. These types of literature reviews can serve to help keep people updated on a field as well as helping scholars choose a research topic to fill gaps in the knowledge on that topic.
Meeting the review family: exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements. Health information and libraries journal, 36(3), 202-222. doi:10.1111/hir.12276 (An updated look at different types of literature review, expands on the Grant & Booth 2009 article listed above). Garrard, J. (2007).
Choose and formulate a research question; Decide which review type (e.g., systematic, scoping, rapid, etc.) is the best fit for your project; ... A traditional literature review that summarizes and synthesizes the findings of numerous original research articles. The purpose and scope of narrative literature reviews vary widely and do not follow ...
Types of reviews and examples. Definition: "A term used to describe a conventional overview of the literature, particularly when contrasted with a systematic review (Booth et al., 2012, p. 265). Characteristics: Example: Mitchell, L. E., & Zajchowski, C. A. (2022). The history of air quality in Utah: A narrative review.
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.. Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
The choice of a specific type depends on your research approach and design. The following types of literature review are the most popular in business studies: Narrative literature review, also referred to as traditional literature review, critiques literature and summarizes the body of a literature. Narrative review also draws conclusions about ...
A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the ...
Types of Literature Reviews: Critically Appraised Topic (CATs) : A critically appraised topic (or CAT) is a short summary of evidence on a topic of interest, usually focused around a clinical question. A CAT is like a shorter and less rigorous version of a systematic review, summarizing the best available research evidence on a topic.
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
LITERATURE REVIEW. Often used as a generic term to describe any type of review. More precise definition: Published materials that provide an examination of published literature. Can cover wide range of subjects at various levels of comprehensiveness. Identifies gaps in research, explains importance of topic, hypothesizes future work, etc.
This site explores different review methodologies such as, systematic, scoping, realist, narrative, state of the art, meta-ethnography, critical, and integrative reviews. The LITR-EX site has a health professions education focus, but the advice and information is widely applicable. Types of Reviews. Review the table to peruse review types and ...
Listed below are definitions of types of literature reviews: Argumentative Review. This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint.
Learn what a literature review is and how to write one for your research. Explore different types of literature review, such as narrative, systematic, meta-analysis, scoping, and more, with definitions and examples.
A student may do a review for an assignment, while a researcher could include a literature review as support in their grant proposal. Rigor: Some reviews may want to achieve a higher scholarly or objective standard, so they include pre-established or inclusion criteria for what publications can be included. Discipline norms: a literature review ...
The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
4 Major Types Of Literature Review. The four major types include, Narrative Review, Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Scoping Review. These are known as the major ones because they're like the "go-to" methods for researchers in academic and research circles. Think of them as the classic tools in the researcher's toolbox.
An umbrella review is a review of multiple systematic reviews. The process uses explicit and systematic methods to search for, and identify, systematic reviews on related research questions in the same topic area. The purpose of an umbrella review is to synthesize the results of the systematic reviews across important outcomes.
This systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis illuminate a dynamic research landscape surrounding last-mile e-commerce delivery in urban settings. A notable geographic bias is evident, with a concentration of studies in developed economies, particularly the United States.
The World Health Organization (WHO) 2022 kidney tumor classification has introduced a novel and uncommon type of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) known as eosinophilic solid and cystic renal cell carcinoma (ESC-RCC) [].Due to its recent introduction and the limited description of around 70 cases in the literature, this entity remains a complex challenge and is probably frequently misdiagnosed or ...
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a prevalent condition affecting over 150 million men worldwide. While there is a wealth of publications and research in the field of ED, there is a noticeable scarcity of bibliometric analyses of the literature on this topic. This study aims to analyze the scientific activity and research trends related to ED. We conducted a comprehensive search of the Scopus ...