- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
presentation

Definition of presentation
- fairing [ British ]
- freebee
- largess
Examples of presentation in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'presentation.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
15th century, in the meaning defined at sense 1a
Phrases Containing presentation
- breech presentation
Dictionary Entries Near presentation
present arms
presentation copy
Cite this Entry
“Presentation.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/presentation. Accessed 16 May. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of presentation, medical definition, medical definition of presentation, more from merriam-webster on presentation.
Nglish: Translation of presentation for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of presentation for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about presentation
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, birds say the darndest things, a great big list of bread words, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 8 uncommon words related to love, games & quizzes.


- PRESENTATION SKILLS
What is a Presentation?
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Presentation Skills:
- A - Z List of Presentation Skills
- Top Tips for Effective Presentations
- General Presentation Skills
- Preparing for a Presentation
- Organising the Material
- Writing Your Presentation
- Deciding the Presentation Method
- Managing your Presentation Notes
- Working with Visual Aids
- Presenting Data
- Managing the Event
- Coping with Presentation Nerves
- Dealing with Questions
- How to Build Presentations Like a Consultant
- 7 Qualities of Good Speakers That Can Help You Be More Successful
- Self-Presentation in Presentations
- Specific Presentation Events
- Remote Meetings and Presentations
- Giving a Speech
- Presentations in Interviews
- Presenting to Large Groups and Conferences
- Giving Lectures and Seminars
- Managing a Press Conference
- Attending Public Consultation Meetings
- Managing a Public Consultation Meeting
- Crisis Communications
- Elsewhere on Skills You Need:
- Communication Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Teams, Groups and Meetings
- Effective Speaking
- Question Types
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
The formal presentation of information is divided into two broad categories: Presentation Skills and Personal Presentation .
These two aspects are interwoven and can be described as the preparation, presentation and practice of verbal and non-verbal communication.
This article describes what a presentation is and defines some of the key terms associated with presentation skills.
Many people feel terrified when asked to make their first public talk. Some of these initial fears can be reduced by good preparation that also lays the groundwork for making an effective presentation.
A Presentation Is...
A presentation is a means of communication that can be adapted to various speaking situations, such as talking to a group, addressing a meeting or briefing a team.
A presentation can also be used as a broad term that encompasses other ‘speaking engagements’ such as making a speech at a wedding, or getting a point across in a video conference.
To be effective, step-by-step preparation and the method and means of presenting the information should be carefully considered.
A presentation requires you to get a message across to the listeners and will often contain a ' persuasive ' element. It may, for example, be a talk about the positive work of your organisation, what you could offer an employer, or why you should receive additional funding for a project.
The Key Elements of a Presentation
Making a presentation is a way of communicating your thoughts and ideas to an audience and many of our articles on communication are also relevant here, see: What is Communication? for more.
Consider the following key components of a presentation:
Ask yourself the following questions to develop a full understanding of the context of the presentation.
When and where will you deliver your presentation?
There is a world of difference between a small room with natural light and an informal setting, and a huge lecture room, lit with stage lights. The two require quite different presentations, and different techniques.
Will it be in a setting you are familiar with, or somewhere new?
If somewhere new, it would be worth trying to visit it in advance, or at least arriving early, to familiarise yourself with the room.
Will the presentation be within a formal or less formal setting?
A work setting will, more or less by definition, be more formal, but there are also various degrees of formality within that.
Will the presentation be to a small group or a large crowd?
Are you already familiar with the audience?
With a new audience, you will have to build rapport quickly and effectively, to get them on your side.
What equipment and technology will be available to you, and what will you be expected to use?
In particular, you will need to ask about microphones and whether you will be expected to stand in one place, or move around.
What is the audience expecting to learn from you and your presentation?
Check how you will be ‘billed’ to give you clues as to what information needs to be included in your presentation.
All these aspects will change the presentation. For more on this, see our page on Deciding the Presentation Method .
The role of the presenter is to communicate with the audience and control the presentation.
Remember, though, that this may also include handing over the control to your audience, especially if you want some kind of interaction.
You may wish to have a look at our page on Facilitation Skills for more.
The audience receives the presenter’s message(s).
However, this reception will be filtered through and affected by such things as the listener’s own experience, knowledge and personal sense of values.
See our page: Barriers to Effective Communication to learn why communication can fail.
The message or messages are delivered by the presenter to the audience.
The message is delivered not just by the spoken word ( verbal communication ) but can be augmented by techniques such as voice projection, body language, gestures, eye contact ( non-verbal communication ), and visual aids.
The message will also be affected by the audience’s expectations. For example, if you have been billed as speaking on one particular topic, and you choose to speak on another, the audience is unlikely to take your message on board even if you present very well . They will judge your presentation a failure, because you have not met their expectations.
The audience’s reaction and therefore the success of the presentation will largely depend upon whether you, as presenter, effectively communicated your message, and whether it met their expectations.
As a presenter, you don’t control the audience’s expectations. What you can do is find out what they have been told about you by the conference organisers, and what they are expecting to hear. Only if you know that can you be confident of delivering something that will meet expectations.
See our page: Effective Speaking for more information.
How will the presentation be delivered?
Presentations are usually delivered direct to an audience. However, there may be occasions where they are delivered from a distance over the Internet using video conferencing systems, such as Skype.
It is also important to remember that if your talk is recorded and posted on the internet, then people may be able to access it for several years. This will mean that your contemporaneous references should be kept to a minimum.
Impediments
Many factors can influence the effectiveness of how your message is communicated to the audience.
For example background noise or other distractions, an overly warm or cool room, or the time of day and state of audience alertness can all influence your audience’s level of concentration.
As presenter, you have to be prepared to cope with any such problems and try to keep your audience focussed on your message.
Our page: Barriers to Communication explains these factors in more depth.
Continue to read through our Presentation Skills articles for an overview of how to prepare and structure a presentation, and how to manage notes and/or illustrations at any speaking event.
Continue to: Preparing for a Presentation Deciding the Presentation Method
See also: Writing Your Presentation | Working with Visual Aids Coping with Presentation Nerves | Dealing with Questions Learn Better Presentation Skills with TED Talks
- Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
- Word of the Day
- Synonym of the Day
- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
- Commonly confused
- All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
Advertisement
presentation
[ prez- uh n- tey -sh uh n , pree-zen- ]
- an act of presenting.
- the state of being presented.
- a social introduction, as of a person at court.
- an exhibition or performance, as of a play or film.
- offering, delivering, or bestowal, as of a gift.
- a demonstration, lecture, or welcoming speech.
His presentation was very poor.
- Commerce. the presentment of a bill, note, or the like.
- the position of the fetus in the uterus during labor.
a breech presentation.
- Ecclesiastical. the act or the right of presenting a member of the clergy to the bishop for institution to a benefice.
/ ˌprɛzənˈteɪʃən /
- the act of presenting or state of being presented
the presentation of the project is excellent but the content poor
his presentation of the facts was muddled
a presentation on the company results
- an offering or bestowal, as of a gift
a presentation copy of a book
- a performance or representation, as of a play
- the formal introduction of a person, as into society or at court; debut
- the act or right of nominating a clergyman to a benefice
- med the position of a baby relative to the birth canal at the time of birth
- commerce another word for presentment
- television linking material between programmes, such as announcements, trailers, or weather reports
- an archaic word for gift
- philosophy a sense datum
- often capital another name for (feast of) Candlemas
Discover More
Derived forms.
- ˌpresenˈtational , adjective
Other Words From
- nonpres·en·tation noun
- self-presen·tation noun
Word History and Origins
Origin of presentation 1
Example Sentences
Look no further than those execs who have sat through online presentations outlining a more inclusive workplace only to have to go back to working in teams where they’re made to feel different.
The day of the presentation comes, and the ecommerce team gathers around, continuously nodding along with each slide.
In the questions-and-answer presentation on Wednesday, Palantir did not address the issue of voting power.
For repurposing, you can use four different formats, which are – video series, infographics, podcasts, and presentations.
This presentation will explain the ins and outs of the process as well as the need for older children who are looking for a home as well.
We were scoring it like the Olympics: presentation, technique.
Bogucki includes the leaflet in a Powerpoint presentation he has developed.
Her biggest surprise, she said, was realizing how much presentation and technical points mattered.
That may be partially because The Big Lebowski is their most nihilistic presentation.
One of the hottest tickets at the 2014 edition of Comic-Con, the annual nerd mecca in San Diego, was the Marvel presentation.
You were obliging enough to ask me to accept a presentation copy of your verses.
Nor was ever a better presentation made of the essential program of socialism.
After the presentation of the Great Southern case our Bill was heard and all the opposition.
The presentation of the Railway case and the rebutting evidence did not begin till all the public witnesses had been heard.
Furthermore, a note is payable on demand when it is thus stated, or is payable at sight or on presentation.
Related Words
- demonstration
- introduction
Definition of 'presentation'
- presentation

presentation in British English
Presentation in american english, examples of 'presentation' in a sentence presentation, cobuild collocations presentation, trends of presentation.
View usage for: All Years Last 10 years Last 50 years Last 100 years Last 300 years
Browse alphabetically presentation
- present-day
- present-day reality
- presentable
- presentation box
- presentation ceremony
- presentation copy
- All ENGLISH words that begin with 'P'
Related terms of presentation
- award presentation
- brief presentation
- medal presentation
- oral presentation
- View more related words
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

Wordle Helper

Scrabble Tools

- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of presentation – Learner’s Dictionary
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
presentation noun ( SHOW )
Presentation noun ( talk ), presentation noun ( ceremony ).
(Definition of presentation from the Cambridge Learner's Dictionary © Cambridge University Press)
Translations of presentation
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
troubleshoot
to discover why something does not work effectively and help to improve it

Searching out and tracking down: talking about finding or discovering things

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- presentation (SHOW)
- presentation (TALK)
- presentation (CEREMONY)
- Translations
- All translations
To add presentation to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add presentation to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of presentation noun from the Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary
presentation
- presentation on/about somebody/something The sales manager will give a presentation on the new products.
- Several speakers will be making short presentations .
- The conference will begin with a keynote presentation by a leading industry figure.
- a slide/video/multimedia presentation
- presentation on
Definitions on the go
Look up any word in the dictionary offline, anytime, anywhere with the Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary app.

Business Jargons
A Business Encyclopedia
Presentation
Definition : A presentation is a form of communication in which the speaker conveys information to the audience. In an organization presentations are used in various scenarios like talking to a group, addressing a meeting, demonstrating or introducing a new product, or briefing a team. It involves presenting a particular subject or issue or new ideas/thoughts to a group of people.
It is considered as the most effective form of communication because of two main reasons:
- Use of non-verbal cues.
- Facilitates instant feedback.

Business Presentations are a tool to influence people toward an intended thought or action.
Parts of Presentation

- Introduction : It is meant to make the listeners ready to receive the message and draw their interest. For that, the speaker can narrate some story or a humorous piece of joke, an interesting fact, a question, stating a problem, and so forth. They can also use some surprising statistics.
- Body : It is the essence of the presentation. It requires the sequencing of facts in a logical order. This is the part where the speaker explains the topic and relevant information. It has to be critically arranged, as the audience must be able to grasp what the speaker presents.
- Conclusion : It needs to be short and precise. It should sum up or outline the key points that you have presented. It could also contain what the audience should have gained out of the presentation.
Purpose of Presentation
- To inform : Organizations can use presentations to inform the audience about new schemes, products or proposals. The aim is to inform the new entrant about the policies and procedures of the organization.
- To persuade : Presentations are also given to persuade the audience to take the intended action.
- To build goodwill : They can also help in building a good reputation
Factors Affecting Presentation

Audience Analysis
Communication environment, personal appearance, use of visuals, opening and closing presentation, organization of presentation, language and words, voice quality, body language, answering questions, a word from business jargons.
Presentation is a mode of conveying information to a selected group of people live. An ideal presentation is one that identifies and matches the needs, interests and understanding level of the audience. It also represents the facts, and figures in the form of tables, charts, and graphs and uses multiple colours.
Related terms:
- Verbal Communication
- Visual Communication
- Non-Verbal Communication
- Communication
- 7 C’s of Communication
Reader Interactions
Abbas khan says
October 2, 2022 at 11:33 pm
Thank you so much for providing us with brief info related to the presentation.
Farhan says
February 23, 2023 at 9:45 am
yusra shah says
July 3, 2023 at 2:04 am
it was helpful👍
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

What is a Presentation? Objectives, Elements, Important skills, Four Ps
- Post last modified: 4 June 2023
- Reading time: 19 mins read
- Post category: Business Communication

What is a Presentation?
A presentation communicates a message, an idea or information to a group. It is similar to a report, but with a key difference–the human element. A presentation conveys the speaker’s personality and enables immediate interaction among all participants.
Table of Content
- 1 What is a Presentation?
- 2.1 To Inform
- 2.2 To Train
- 2.3 To Persuade
- 2.4 To Motivate
- 2.5 To Entertain
- 3 Main Elements of Presentation
- 4.1 Analytical ability
- 4.2 Effective communication ability
- 4.3 Creative ability
- 4.4 Good interpersonal skill
- 4.5 Sound time management
- 4.6 Problem-solving ability
- 4.7 A sense of humour
- 5 Evaluation Wheel
- 6.1 Prepare
- 6.2 Practice
- 6.3 Present
- 7.1 Know Yourself
- 7.2 Know Your Material
- 7.3 Know Your Purpose
- 7.4 Know Your Audience
Objectives of Presentation
The main objectives of a presentation are:
To Persuade
To motivate, to entertain.
A presentation is created to convey some information to a group of people. For example, a presentation may display an organisation’s quarterly performance.
Most training programmes in organisations are done through the presentation mode. Such instructional presentations convey a lot of information and are created with instructional design principles to keep the audience engaged for a long period.
Some presentations are used to convince a group of people to accept a particular idea and/or make a certain choice.
The growing popularity of TED Talks indicates how a presentation can be a powerful motivation tool. These presentations trigger emotions and inspire people to act.
Presentations can also be used to celebrate an event. For example, a farewell presentation of a colleague can be used to narrate the story of his/her overall tenure, experiences and achievement in the organisation.
Main Elements of Presentation
A presentation is said to be effective if it has three main elements, which are as follows:
- Specific content : This refers to the information that a presentation will comprise. The information must be conveyed effectively so that it is absorbed by the audience in one sitting. It should be relevant and meaningful to them.
- Audience : A presentation should be targeted for a specific group of audience who share the same purpose and have a similar level of pre-knowledge.
- Presenter: The presenter should act as the advocate of the information. If his/her conviction and passion in the message are clearly articulated, the audience will also pay attention to the subject.
Important Presentation Skills
In today’s business environment, presentation skills are requisite in almost every professional arena. Employees are often required to give presentations on the targets achieved by them. A presentation can be effective if it is carefully planned and prepared.
However, delivering presentations is not always easy for every individual. Some people take presenting as a probable opportunity to showcase skills, while others find it a challenging task. To provide an effective presentation, a presenter must possess some abilities.
Some of them are explained as follows:
Analytical ability
Effective communication ability, creative ability, good interpersonal skill, sound time management, problem-solving ability, a sense of humour.
It refers to a calibre which empowers an individual to collect, organise, visualise and comprehend data. Such skills enable a person to look at related patterns, draw conclusions and find solutions to problems. In addition, sound analytical skills also enable an individual to forecast future trends using various techniques such as brainstorming, forecasting, data mining and metrics interpretation.
Communication entails much more than mere talking to the audience. To communicate effectively during a presentation, one ought to showcase information lucidly. During a presentation, a person should not just have a good set of slides together; rather he needs to engage and strike a chord with the audience to transmit the intended message.
It refers to the ability to present things in a creative way that have not been explored earlier. Creative skills in presentation enable an individual to invent or develop something path-breaking, such as a new concept, unique way out from a problem, a method, a work of art or new machinery, etc.
It encompasses how an individual portrays or presents himself to the audience and builds a rapport with the audience. During a presentation, sound interpersonal skills empower a speaker to interact, communicate and collaborate with the audience effectively.
Interpersonal skills are prevalent across all personal and professional interactions between people. Interpersonal skills entail empathy, active listening and emotional intelligence.
While delivering a presentation, a person should manage time effectively, set a presentation schedule and end a presentation within a stipulated time. If a presentation is long, there are chances the audience may lose interest and the message may not be delivered.
A speaker cannot expect audience to actively listen to the presentation for hours. At the start of presentation, a speaker should aim to grab audience’s attention and allocate time for questions and answers at the end.
Problem-solving is a requisite skill for a presentation. During a presentation, the audience may ask the speaker any kind of questions. On the other hand, it is important for the speaker to provide an appropriate answer to the audience to make the presentation successful.
A sense of humour is crucial to deliver a quality presentation to make the environment light and engaging. Appropriate usage of light jokes relieves stress and holds the attention of an audience, which makes the presentation a memorable experience for both the speaker and the audience.
Evaluation Wheel
Evaluation wheel is a creative and effective tool that accumulates information on outcomes in a simple and accessible manner. A presenter can opt for the evaluation wheel tool to show the outcomes of the research or reports. This tool is used to provide various types of information and journeys of change within the organisation.
It offers a visual representation of progression and results in the form of a spider diagram. The evaluation wheel measures the exact outcomes for a programme at the start and end. It also helps educators, designers to comprehend information systematically. Figure shows an example of evaluation wheel:
Figure states the scale questionnaire in a circle form wherein respondents will analyse the instances from their discretion and experience and give rating on a scale of 1 to 5.
For instance, service users are appropriately involved. In this case, if the respondent strongly agrees, he/she will give 5 rating and if he/she does not agree, he/she will give 1 rating. The centre of the circle is for 1 and as the respondent agrees, they reach out to edge for 5 rating.
Ps of Presentation
Even the most powerful presentation may fail if the presenter comes unprepared. A presentation is both a mental and a physical effort. There are Ps of presentation that provide a checklist to the presenter for ensuring that the presentation is well-constructed and clear so that the audience gets the message. These four Ps are explained as follows:
A thoroughly prepared presentation captivates the interests of the audience. The topic or content of the presentation must be thoroughly researched. No one would develop interest in a vague or equivocal presentation. A speaker can make use of stories or relatable examples and quote references to give more depth to the presentation and make it intriguing.
Apart from that, it should be ensured that only important points are highlighted in bullets or using other graphical elements. Providing too much of theory or full sentences can create boredom for the audience.
While preparing for a presentation, the presenter should include the following sections:
- Introduction : This section includes the name of the topic and the purpose of the presentation.
- Body : This section contains the main content of the presentation; thus, it must be prepared in a well-organised manner.
- Summary : It provides a recap of the content of the presentation. It outlines the most important points of the presentation to ensure the key message is retained by the audience.
Practice will make a man perfect is an adage that is appropriate across all spheres of life. It helps a speaker become familiar with his/her own voice, words and phrases and adjust accordingly. By practising thoroughly, a speaker can explore how to fit different pieces of information together and practise transition.
Also, a speaker should make notes wherever required as a part of presentation support. Using an index card is a common form of note-taking that provides a quick glimpse of important points.
While delivering a presentation, the speaker needs to demonstrate confidence in front of the audience. The speaker must be polite, but not apologetic in situations, such as if the session is running overtime or the microphone has stopped working.
Instead he/she should expect and ask for discipline and attention. It is important for a speaker to engage with the audience during the presentation in order to assure them that he/she is genuinely interested in talking to them. 4. Pace, pitch and pause: A presenter should deliver the presentation in an easy-to-follow pace and try changing the pace to enliven the presentation.
For example, pauses can be taken intentionally between main points to reinforce them. Along with pace, pitch is equally important. Just as pace varies in normal conversations, it should be used effectively during presentations too. For example, when asking a question, the presenter can raise the pitch and can lower it down when explaining a point.
Four Cornerstones of Making Memorable Presentations
The most crucial aspect of delivering an effective presentation is that the speaker should appear confident and the speech should look effortless. Presentations are a source of anxiety for many individuals. However, getting well-prepared before delivering a presentation can reduce this feeling considerably and ease apprehension.
There are a number of ways to overcome feelings of anxiety, stress and stage fright before the presentation in order to appear confident in front of the audience. The four cornerstones of making a memorable presentation are provided in the upcoming sections.
Know Yourself
Know your material, know your purpose, know your audience.
A presenter should acknowledge his/her strengths and weaknesses. Accordingly, he/she should decide the style of delivering a presentation. For instance, if a presenter has a great sense of humour and can use it comfortably in the speech, he/she can make the presentation more engaging and interesting.
On the other hand, if the speaker who is an introvert and prefers to talk or engage less, he/she can add visuals in the presentation. Therefore, the trick is whosoever is delivering the presentation should feel comfortable.
Knowing the topic thoroughly is the most important step in preparing and delivering a presentation. A presenter with well-versed knowledge of the topic is bound to feel more confident. One should perform extensive research of the topic using credible websites and surveys.
A presenter with minimal information about the topic will not be able to deliver a memorable presentation; rather, it would create a negative image in front of the audience. A good presentation is one that is centred around the main theme, presents relevant information and stimulates thought.
It is crucial to know the purpose of the presentation. A presenter should be aware of whether the purpose is to create awareness or to build new skills or to change attitudes. For instance, professional firms or businesses use presentations for various purposes such as to create awareness, educate, motivate and persuade internal and external audiences.
Therefore, to prepare a presentation, identify its objective/purpose, determine the method of delivery, formulate a structure, include visual aids and rehearse.
One should know the type of audience and what is their purpose of attending the presentation. For instance, whether they are there for gaining knowledge or learning new skills, etc. The age, culture and knowledge base of the audience help a presenter in designing and delivering his/her presentation effectively and in a manner in which audience can easily understand and relate to.
A well-designed presentation uses visual aids effectively to reinforce the main points and enhance the audience’s level of understanding.
Business Communication Notes
( Click on Topic to Read )
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
Communication Styles
Channels of communication.
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
Organisational Communication
- Horizontal C ommunication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
- What Is Market Segmentation?
- What Is Marketing Mix?
- Marketing Concept
- Marketing Management Process
- What Is Marketing Environment?
- What Is Consumer Behaviour?
- Business Buyer Behaviour
- Demand Forecasting
- 7 Stages Of New Product Development
- Methods Of Pricing
- What Is Public Relations?
- What Is Marketing Management?
- What Is Sales Promotion?
- Types Of Sales Promotion
- Techniques Of Sales Promotion
- What Is Personal Selling?
- What Is Advertising?
- Market Entry Strategy
- What Is Marketing Planning?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- Brand Building Process
- Kotler Five Product Level Model
- Classification Of Products
- Types Of Logistics
- What Is Consumer Research?
- What Is DAGMAR?
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- What Is Green Marketing?
- What Is Electronic Commerce?
- Agricultural Cooperative Marketing
- What Is Marketing Control?
- What Is Marketing Communication?
- What Is Pricing?
- Models Of Communication
- What is Sales Management?
- Objectives of Sales Management
- Responsibilities and Skills of Sales Manager
- Theories of Personal Selling
- What is Sales Forecasting?
- Methods of Sales Forecasting
- Purpose of Sales Budgeting
- Methods of Sales Budgeting
- Types of Sales Budgeting
- Sales Budgeting Process
- What is Sales Quotas?
- What is Selling by Objectives (SBO) ?
- What is Sales Organisation?
- Types of Sales Force Structure
- Recruiting and Selecting Sales Personnel
- Training and Development of Salesforce
- Compensating the Sales Force
- Time and Territory Management
- What Is Logistics?
- What Is Logistics System?
- Technologies in Logistics
- What Is Distribution Management?
- What Is Marketing Intermediaries?
- Conventional Distribution System
- Functions of Distribution Channels
- What is Channel Design?
- Types of Wholesalers and Retailers
- What is Vertical Marketing Systems?
- What i s Marketing?
- What i s A BCG Matrix?
- 5 M’S Of Advertising
- What i s Direct Marketing?
- Marketing Mix For Services
- What Market Intelligence System?
- What i s Trade Union?
- What Is International Marketing?
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- What i s International Marketing Research?
- What is Exporting?
- What is Licensing?
- What is Franchising?
- What is Joint Venture?
- What is Turnkey Projects?
- What is Management Contracts?
- What is Foreign Direct Investment?
- Factors That Influence Entry Mode Choice In Foreign Markets
- What is Price Escalations?
- What is Transfer Pricing?
- Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC)
- What is Promotion Mix?
- Factors Affecting Promotion Mix
- Functions & Role Of Advertising
- What is Database Marketing?
- What is Advertising Budget?
- What is Advertising Agency?
- What is Market Intelligence?
- What is Industrial Marketing?
- What is Customer Value
- What is Consumer Behaviour?
- What Is Personality?
- What Is Perception?
- What Is Learning?
- What Is Attitude?
- What Is Motivation?
- Consumer Imagery
- Consumer Attitude Formation
- What Is Culture?
- Consumer Decision Making Process
- Applications of Consumer Behaviour in Marketing
- Motivational Research
- Theoretical Approaches to Study of Consumer Behaviour
- Consumer Involvement
- Consumer Lifestyle
- Theories of Personality
- Outlet Selection
- Organizational Buying Behaviour
- Reference Groups
- Consumer Protection Act, 1986
- Diffusion of Innovation
- Opinion Leaders
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India
- What is Brand Management?
- 4 Steps of Strategic Brand Management Process
- Customer Based Brand Equity
- What is Brand Equity?
You Might Also Like
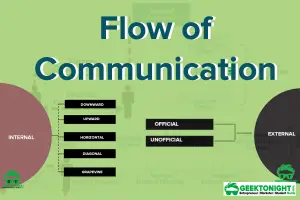
Flow of Communication: Internal and External

What is Written Communication? Advantages, Disadvantages
Difference between internal and external communication.

What are Soft Skills? Types, Importance, How to Develop
Difference between upward and downward communication.

Barriers to Communication: Types, How to Overcome
What is johari window model.

What is Report Writing? Parts, Types, Structure, Process

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
World's Best Online Courses at One Place
We’ve spent the time in finding, so you can spend your time in learning
Digital Marketing
Personal growth.

Development
Presentation
- Written By Gregg Rosenzweig
- Updated: November 8, 2023
We’re here to help you choose the most appropriate content types to fulfill your content strategy. In this series, we’re breaking down the most popular content types to their most basic fundamentals — simple definitions, clarity on formats, and plenty of examples — so you can start with a solid foundation.
What is a Presentation?
A communication device that relays a topic to an audience in the form of a slide show, demonstration, lecture, or speech, where words and pictures complement each other.
Why should you think of presentations as content?
The beauty of content creation is that almost anything can become a compelling piece of content . Just depends on the creativity used to convert it and the story that brings it to life.
The long and short of it
Although the length of a presentation in terms of time can depend on the overall approach (Are you talking a lot? Are you referring to the screen in detail or not?), consider the number of informational content slides when tallying the overall presentation length. For instance, don’t include title slides in your tally when conveying length to a content creator.
A general guide to presentation length:
- Short Form (5 content slides)
- Standard Form (10 content slides)
- Long Form (20+ content slides)
Popular use cases for presentations…
Let’s consider TED Talks for a minute: one of the best examples (bar none) of how words, pictures, and a narrative can make people care about something they otherwise might not.
These “talks” pre-date podcasts and blend a compelling use of language and imagery in presentation format to spread ideas in unique ways.
TED Talks have been viewed a billion-plus times worldwide (and counting) and are worth considering when it comes to how you might use video-presentation content to connect with your customers in creative, cool, new ways.
Business types:
Any company that has a pitch deck, executive summary , sales presentation, or any kind of internal document that can be repurposed into external-facing content pieces — without pain.
Presentation Examples – Short Form


Presentation Examples – Standard Form

Presentation Examples – Long Form

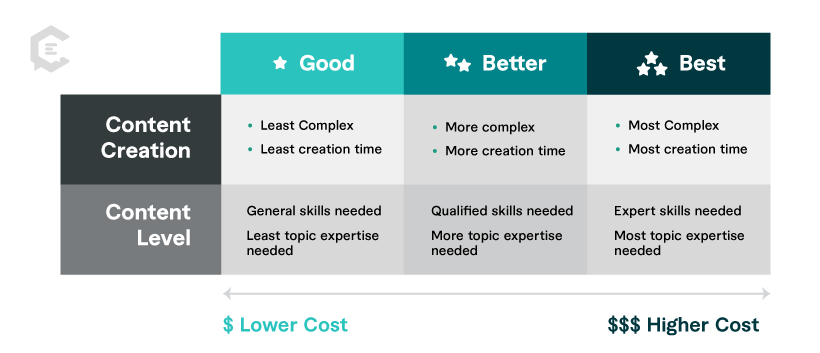
Understanding Content Quality in Examples
Our team has rated content type examples in three degrees of quality ( Good, Better, Best ) to help you better gauge resources needed for your content plan. In general, the degrees of content quality correspond to our three content levels ( General, Qualified, Expert ) based on the criteria below. Please consider there are multiple variables that could determine the cost, completion time, or content level for any content piece with a perceived degree of quality.
Impress your clients, co-workers, and leadership team with exceptional content for your next presentation, product demonstration, and more. If you need help getting your message across in a succinct, attention-grabbing, and persuasive way, talk to one of our content specialists today.
Stay in the know.
We will keep you up-to-date with all the content marketing news and resources. You will be a content expert in no time. Sign up for our free newsletter.
Elevate Your Content Game
Transform your marketing with a consistent stream of high-quality content for your brand.

You May Also Like...

The Strategic Ensemble Behind Effective Content

Everything to Know About the Power of SEO Personalization

Personalized Content Strategies: Gaining the Competitive Edge
- Content Production
- Build Your SEO
- Amplify Your Content
- For Agencies
Why ClearVoice
- Talent Network
- How It Works
- Freelance For Us
- Statement on AI
- Talk to a Specialist
Get Insights In Your Inbox
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Intellectual Property Claims
- Data Collection Preferences
- presentation
: an activity in which someone shows, describes, or explains something to a group of people
: the way in which something is arranged, designed, etc. : the way in which something is presented
: the act of giving something to someone in a formal way or in a ceremony
Full Definition of PRESENTATION
First known use of presentation, related to presentation, other business terms, rhymes with presentation, definition of presentation for kids, medical definition of presentation, learn more about presentation.
- presentation copy
- presentation piece
- presentation time
- breech presentation
- face presentation
Seen & Heard
What made you want to look up presentation ? Please tell us where you read or heard it (including the quote, if possible).
- Spanish Central
- Learner's ESL Dictionary
- WordCentral for Kids
- Visual Dictionary
- SCRABBLE ® Word Finder
- Merriam-Webster's Unabridged Dictionary
- Britannica English - Arabic Translation
- Nglish - Spanish-English Translation
- Advertising Info
- Dictionary API
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- About Our Ads
- Browser Tools
- The Open Dictionary
- Browse the Dictionary
- Browse the Thesaurus
- Browse the Spanish-English Dictionary
- Browse the Medical Dictionary

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to Structure your Presentation, with Examples
August 3, 2018 - Dom Barnard
For many people the thought of delivering a presentation is a daunting task and brings about a great deal of nerves . However, if you take some time to understand how effective presentations are structured and then apply this structure to your own presentation, you’ll appear much more confident and relaxed.
Here is our complete guide for structuring your presentation, with examples at the end of the article to demonstrate these points.
Why is structuring a presentation so important?
If you’ve ever sat through a great presentation, you’ll have left feeling either inspired or informed on a given topic. This isn’t because the speaker was the most knowledgeable or motivating person in the world. Instead, it’s because they know how to structure presentations – they have crafted their message in a logical and simple way that has allowed the audience can keep up with them and take away key messages.
Research has supported this, with studies showing that audiences retain structured information 40% more accurately than unstructured information.
In fact, not only is structuring a presentation important for the benefit of the audience’s understanding, it’s also important for you as the speaker. A good structure helps you remain calm, stay on topic, and avoid any awkward silences.
What will affect your presentation structure?
Generally speaking, there is a natural flow that any decent presentation will follow which we will go into shortly. However, you should be aware that all presentation structures will be different in their own unique way and this will be due to a number of factors, including:
- Whether you need to deliver any demonstrations
- How knowledgeable the audience already is on the given subject
- How much interaction you want from the audience
- Any time constraints there are for your talk
- What setting you are in
- Your ability to use any kinds of visual assistance
Before choosing the presentation’s structure answer these questions first:
- What is your presentation’s aim?
- Who are the audience?
- What are the main points your audience should remember afterwards?
When reading the points below, think critically about what things may cause your presentation structure to be slightly different. You can add in certain elements and add more focus to certain moments if that works better for your speech.

What is the typical presentation structure?
This is the usual flow of a presentation, which covers all the vital sections and is a good starting point for yours. It allows your audience to easily follow along and sets out a solid structure you can add your content to.
1. Greet the audience and introduce yourself
Before you start delivering your talk, introduce yourself to the audience and clarify who you are and your relevant expertise. This does not need to be long or incredibly detailed, but will help build an immediate relationship between you and the audience. It gives you the chance to briefly clarify your expertise and why you are worth listening to. This will help establish your ethos so the audience will trust you more and think you’re credible.
Read our tips on How to Start a Presentation Effectively
2. Introduction
In the introduction you need to explain the subject and purpose of your presentation whilst gaining the audience’s interest and confidence. It’s sometimes helpful to think of your introduction as funnel-shaped to help filter down your topic:
- Introduce your general topic
- Explain your topic area
- State the issues/challenges in this area you will be exploring
- State your presentation’s purpose – this is the basis of your presentation so ensure that you provide a statement explaining how the topic will be treated, for example, “I will argue that…” or maybe you will “compare”, “analyse”, “evaluate”, “describe” etc.
- Provide a statement of what you’re hoping the outcome of the presentation will be, for example, “I’m hoping this will be provide you with…”
- Show a preview of the organisation of your presentation
In this section also explain:
- The length of the talk.
- Signal whether you want audience interaction – some presenters prefer the audience to ask questions throughout whereas others allocate a specific section for this.
- If it applies, inform the audience whether to take notes or whether you will be providing handouts.
The way you structure your introduction can depend on the amount of time you have been given to present: a sales pitch may consist of a quick presentation so you may begin with your conclusion and then provide the evidence. Conversely, a speaker presenting their idea for change in the world would be better suited to start with the evidence and then conclude what this means for the audience.
Keep in mind that the main aim of the introduction is to grab the audience’s attention and connect with them.
3. The main body of your talk
The main body of your talk needs to meet the promises you made in the introduction. Depending on the nature of your presentation, clearly segment the different topics you will be discussing, and then work your way through them one at a time – it’s important for everything to be organised logically for the audience to fully understand. There are many different ways to organise your main points, such as, by priority, theme, chronologically etc.
- Main points should be addressed one by one with supporting evidence and examples.
- Before moving on to the next point you should provide a mini-summary.
- Links should be clearly stated between ideas and you must make it clear when you’re moving onto the next point.
- Allow time for people to take relevant notes and stick to the topics you have prepared beforehand rather than straying too far off topic.
When planning your presentation write a list of main points you want to make and ask yourself “What I am telling the audience? What should they understand from this?” refining your answers this way will help you produce clear messages.
4. Conclusion
In presentations the conclusion is frequently underdeveloped and lacks purpose which is a shame as it’s the best place to reinforce your messages. Typically, your presentation has a specific goal – that could be to convert a number of the audience members into customers, lead to a certain number of enquiries to make people knowledgeable on specific key points, or to motivate them towards a shared goal.
Regardless of what that goal is, be sure to summarise your main points and their implications. This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there.
Follow these steps:
- Signal that it’s nearly the end of your presentation, for example, “As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…”
- Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation – “In this speech I wanted to compare…”
- Summarise the main points, including their implications and conclusions
- Indicate what is next/a call to action/a thought-provoking takeaway
- Move on to the last section
5. Thank the audience and invite questions
Conclude your talk by thanking the audience for their time and invite them to ask any questions they may have. As mentioned earlier, personal circumstances will affect the structure of your presentation.
Many presenters prefer to make the Q&A session the key part of their talk and try to speed through the main body of the presentation. This is totally fine, but it is still best to focus on delivering some sort of initial presentation to set the tone and topics for discussion in the Q&A.

Other common presentation structures
The above was a description of a basic presentation, here are some more specific presentation layouts:
Demonstration
Use the demonstration structure when you have something useful to show. This is usually used when you want to show how a product works. Steve Jobs frequently used this technique in his presentations.
- Explain why the product is valuable.
- Describe why the product is necessary.
- Explain what problems it can solve for the audience.
- Demonstrate the product to support what you’ve been saying.
- Make suggestions of other things it can do to make the audience curious.
Problem-solution
This structure is particularly useful in persuading the audience.
- Briefly frame the issue.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it ‘s such a problem. Use logos and pathos for this – the logical and emotional appeals.
- Provide the solution and explain why this would also help the audience.
- Call to action – something you want the audience to do which is straightforward and pertinent to the solution.
Storytelling
As well as incorporating stories in your presentation , you can organise your whole presentation as a story. There are lots of different type of story structures you can use – a popular choice is the monomyth – the hero’s journey. In a monomyth, a hero goes on a difficult journey or takes on a challenge – they move from the familiar into the unknown. After facing obstacles and ultimately succeeding the hero returns home, transformed and with newfound wisdom.
Storytelling for Business Success webinar , where well-know storyteller Javier Bernad shares strategies for crafting compelling narratives.
Another popular choice for using a story to structure your presentation is in media ras (in the middle of thing). In this type of story you launch right into the action by providing a snippet/teaser of what’s happening and then you start explaining the events that led to that event. This is engaging because you’re starting your story at the most exciting part which will make the audience curious – they’ll want to know how you got there.
- Great storytelling: Examples from Alibaba Founder, Jack Ma
Remaining method
The remaining method structure is good for situations where you’re presenting your perspective on a controversial topic which has split people’s opinions.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it’s such a problem – use logos and pathos.
- Rebut your opponents’ solutions – explain why their solutions could be useful because the audience will see this as fair and will therefore think you’re trustworthy, and then explain why you think these solutions are not valid.
- After you’ve presented all the alternatives provide your solution, the remaining solution. This is very persuasive because it looks like the winning idea, especially with the audience believing that you’re fair and trustworthy.
Transitions
When delivering presentations it’s important for your words and ideas to flow so your audience can understand how everything links together and why it’s all relevant. This can be done using speech transitions which are words and phrases that allow you to smoothly move from one point to another so that your speech flows and your presentation is unified.
Transitions can be one word, a phrase or a full sentence – there are many different forms, here are some examples:
Moving from the introduction to the first point
Signify to the audience that you will now begin discussing the first main point:
- Now that you’re aware of the overview, let’s begin with…
- First, let’s begin with…
- I will first cover…
- My first point covers…
- To get started, let’s look at…
Shifting between similar points
Move from one point to a similar one:
- In the same way…
- Likewise…
- Equally…
- This is similar to…
- Similarly…
Internal summaries
Internal summarising consists of summarising before moving on to the next point. You must inform the audience:
- What part of the presentation you covered – “In the first part of this speech we’ve covered…”
- What the key points were – “Precisely how…”
- How this links in with the overall presentation – “So that’s the context…”
- What you’re moving on to – “Now I’d like to move on to the second part of presentation which looks at…”
Physical movement
You can move your body and your standing location when you transition to another point. The audience find it easier to follow your presentation and movement will increase their interest.
A common technique for incorporating movement into your presentation is to:
- Start your introduction by standing in the centre of the stage.
- For your first point you stand on the left side of the stage.
- You discuss your second point from the centre again.
- You stand on the right side of the stage for your third point.
- The conclusion occurs in the centre.
Key slides for your presentation
Slides are a useful tool for most presentations: they can greatly assist in the delivery of your message and help the audience follow along with what you are saying. Key slides include:
- An intro slide outlining your ideas
- A summary slide with core points to remember
- High quality image slides to supplement what you are saying
There are some presenters who choose not to use slides at all, though this is more of a rarity. Slides can be a powerful tool if used properly, but the problem is that many fail to do just that. Here are some golden rules to follow when using slides in a presentation:
- Don’t over fill them – your slides are there to assist your speech, rather than be the focal point. They should have as little information as possible, to avoid distracting people from your talk.
- A picture says a thousand words – instead of filling a slide with text, instead, focus on one or two images or diagrams to help support and explain the point you are discussing at that time.
- Make them readable – depending on the size of your audience, some may not be able to see small text or images, so make everything large enough to fill the space.
- Don’t rush through slides – give the audience enough time to digest each slide.
Guy Kawasaki, an entrepreneur and author, suggests that slideshows should follow a 10-20-30 rule :
- There should be a maximum of 10 slides – people rarely remember more than one concept afterwards so there’s no point overwhelming them with unnecessary information.
- The presentation should last no longer than 20 minutes as this will leave time for questions and discussion.
- The font size should be a minimum of 30pt because the audience reads faster than you talk so less information on the slides means that there is less chance of the audience being distracted.
Here are some additional resources for slide design:
- 7 design tips for effective, beautiful PowerPoint presentations
- 11 design tips for beautiful presentations
- 10 tips on how to make slides that communicate your idea
Group Presentations
Group presentations are structured in the same way as presentations with one speaker but usually require more rehearsal and practices. Clean transitioning between speakers is very important in producing a presentation that flows well. One way of doing this consists of:
- Briefly recap on what you covered in your section: “So that was a brief introduction on what health anxiety is and how it can affect somebody”
- Introduce the next speaker in the team and explain what they will discuss: “Now Elnaz will talk about the prevalence of health anxiety.”
- Then end by looking at the next speaker, gesturing towards them and saying their name: “Elnaz”.
- The next speaker should acknowledge this with a quick: “Thank you Joe.”
From this example you can see how the different sections of the presentations link which makes it easier for the audience to follow and remain engaged.
Example of great presentation structure and delivery
Having examples of great presentations will help inspire your own structures, here are a few such examples, each unique and inspiring in their own way.
How Google Works – by Eric Schmidt
This presentation by ex-Google CEO Eric Schmidt demonstrates some of the most important lessons he and his team have learnt with regards to working with some of the most talented individuals they hired. The simplistic yet cohesive style of all of the slides is something to be appreciated. They are relatively straightforward, yet add power and clarity to the narrative of the presentation.
Start with why – by Simon Sinek
Since being released in 2009, this presentation has been viewed almost four million times all around the world. The message itself is very powerful, however, it’s not an idea that hasn’t been heard before. What makes this presentation so powerful is the simple message he is getting across, and the straightforward and understandable manner in which he delivers it. Also note that he doesn’t use any slides, just a whiteboard where he creates a simple diagram of his opinion.
The Wisdom of a Third Grade Dropout – by Rick Rigsby
Here’s an example of a presentation given by a relatively unknown individual looking to inspire the next generation of graduates. Rick’s presentation is unique in many ways compared to the two above. Notably, he uses no visual prompts and includes a great deal of humour.
However, what is similar is the structure he uses. He first introduces his message that the wisest man he knew was a third-grade dropout. He then proceeds to deliver his main body of argument, and in the end, concludes with his message. This powerful speech keeps the viewer engaged throughout, through a mixture of heart-warming sentiment, powerful life advice and engaging humour.
As you can see from the examples above, and as it has been expressed throughout, a great presentation structure means analysing the core message of your presentation. Decide on a key message you want to impart the audience with, and then craft an engaging way of delivering it.
By preparing a solid structure, and practising your talk beforehand, you can walk into the presentation with confidence and deliver a meaningful message to an interested audience.
It’s important for a presentation to be well-structured so it can have the most impact on your audience. An unstructured presentation can be difficult to follow and even frustrating to listen to. The heart of your speech are your main points supported by evidence and your transitions should assist the movement between points and clarify how everything is linked.
Research suggests that the audience remember the first and last things you say so your introduction and conclusion are vital for reinforcing your points. Essentially, ensure you spend the time structuring your presentation and addressing all of the sections.
- What is PowerPoint? Video
- Create a presentation Video
- Choose the right view for the task Video
- Add and format text Video

What is PowerPoint?

Note: Microsoft 365 Copliot coming soon in PowerPoint.
With PowerPoint on your PC, Mac, or mobile device, you can:
Create presentations from scratch or a template.
Add text, images, art, and videos.
Select a professional design with PowerPoint Designer.
Add transitions, animations, and cinematic motion.
Save to OneDrive, to get to your presentations from your computer, tablet, or phone.
Share your work and work with others, wherever they are.
PowerPoint help
What's new in PowerPoint for Windows
Office Quick Start Guides
Get Microsoft presentation templates

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.

10 Tips for a Persuasive Presentation
Powerful presentation is persuasion. here's how to elevate your impact..
Posted May 11, 2024 | Reviewed by Ray Parker
- Presentations aim to effect change. It's essential to be clear about what change you want to see.
- Powerful presenters embrace and extend empathy to seek first to understand their audience.
- Substance and style both matter to create an audience-informed communication experience.
- Persuasive presentations are relevant, reasoned, real, and resonant.

How many of us realize that giving a presentation or making a speech is all about persuasion , influence, and emotional intelligence ? Impactful presenters understand the power of empathy to understand and engage their audience, the efficiency and kindness of having a clear objective and message, and the importance of substance and style—all as a way to connect in a way that engages and inspires.
Much has been written on the power and behavioral science of persuasion, not least by expert Robert Cialdini. His bestselling book Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion explains seven research-based universal principles of influence .
From my experience as a leadership coach working with thousands of people worldwide, I have compiled a list of ten essentials to elevate our presentation.
1. Maintain an "other" focus. What do you know about your audience and how can you find out more? Ask yourself what kind of a speaker will appeal to your audience, what arguments are likely to resonate with them, and what feelings you want to inspire so the audience will positively respond to your ask.
If your audience is predominantly data-driven, you may want to use more evidence-based arguments. If the audience is mixed, a combination of data, authority, and storytelling may be more appropriate. Extend Daniel Goleman’s three types of empathy to gather intelligence , understand your audience, and tailor your intervention to connect more profoundly.
2. Determine a specific objective. Presentations aim to effect change in some way. What change do you want to see in your audience?
For instance, gaining their approval for a certain investment, soliciting their buy-in for a change, or creating a sense of enthusiasm for an idea or initiative. The purpose of a presentation is to bring about change so make sure you are clear on what kind of change you want to bring about.
3. Design a grabber. Our attention spans have shrunk as we have more and more competing demands on our attention . If you want to get someone’s attention, you need to grab it at the outset and try and hold on.
You can do this in several different ways. Throw out a question that demands a response from the audience. Give a surprising fact or statistic, or quote from a well-known figure. Tell a story or an anecdote. A good grabber captures the attention of everyone there and makes them focus on what you have to say.
4. Crystalize your message and construct your arguments. Your message is the heart of your speech. Craft a brief phrase that clearly defines your proposal in 10-12 words—for example, “This post is about crafting presentations that inspire and engage others to elevate their presentations.”
Make it memorable by choosing inspiring words, symbols, catchy expressions, something that will remain in the audience's mind. As Brené Brown says: “Clear is kind,” and a clear message provides a path to develop your ideas.
When you have a clear and concise message, it helps you formulate your arguments. Think of developing your arguments using the rule of three —three compelling arguments to convince but not overwhelm your audience.
5. Prepare a call to action. Remember, we want to change our audience in some way, so we need to make our ask clearly and concretely. Consider your call to action in terms of what you want your audience to think/feel/do:
- Think: “I want you to think about how you can improve your presentations.”
- Feel: “I want you to feel enthusiastic and motivated so that you can elevate your power to persuade.”
- Do: “I want you to try out some of these tips and tools for yourself.”
6. Craft a memorable closing. Close the speech in an elegant and memorable way. We need people to remember what we've told them, so prepare it well.

This is not the time to improvise. Try to connect your closing to your opening grabber, which makes the presentation more memorable. Good preparation means preparing everything to the very end—finish well.
7. Plan your delivery. A dynamic speaker draws listeners in by using vocal variety (tone, intonation, speed, volume, pace, pauses, silence) and body language (posture, gestures, expression, and movement) to highlight important points and hold the audience’s attention. Be intentional: How will you use your voice and your body to emphasize a thought or idea? Think about it: If you increased the time you spent on style or delivery by 20 percent, what would it mean for the impact you make?
8. Think about how you will engage your audience. You want the audience to feel considered throughout. Include pauses so they can process what’s being said; connect with individuals throughout the room and make deliberate eye contact while speaking, especially when delivering key points. Read and respond to the audience by changing how you deliver as you go based on the audience’s nonverbal communication .
9. Rehearse and practice. Practice is one of the most crucial elements of presenting—and probably the most neglected one. If this is new to you, start by reading your presentation in front of a mirror to get comfortable speaking your presentation.
Next, video yourself and watch out for nervous or distracting habits to eliminate them and identify any areas where you can improve your delivery. If you are feeling brave, practice in front of an audience and ask for feedback.
10. Prepare your success rituals and mantra. Public speaking and/or stage fright can feel debilitating for some. Have your calm-down ritual prepared and ready to go before you start your presentation. This might be a certain gesture, a power pose, breathwork, or a mantra.
Try this tip: Identify three adjectives to describe how you would like to show up during this presentation. This sets an intention and helps focus our cognitive and emotional resources on success.
Powerful presenters embrace and extend empathy to seek first to understand their audience. They use this intelligence to carefully make choices about substance and style to create an audience-informed communication experience that feels relevant, reasoned, real, and resonant and creates a pathway for change.

Palena Neale, Ph.D. , is a women’s leadership coach, lecturer, and founder of unabridged, a boutique leadership development practice.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- Stream Your Favorite Sports
- Where to Watch WNBA Games
The Definition of a Slide (or Slides) in a PowerPoint Presentation
- Brock University
Presentation software such as PowerPoint generates a series of slides to accompany a human presenter or to be recorded as a stand-alone presentation. A slide is a single screen of a presentation, and every presentation is composed of several slides. Depending on the subject matter, the best presentations may consist of 10 to 12 slides to get a message across, but more may be needed for complex subjects.
Slides keep an audience's attention during a presentation and provide additional supporting information in textual or graphic format.
Selecting Slide Formats in PowerPoint
When you open a new PowerPoint presentation file, you are presented with a large selection of slide templates that you can choose from to set the tone for your presentation. Each template has a series of related slides in the same theme, color, and font choice for different purposes. You can choose a template and use only the additional slides that work for your presentation.
The first slide of a presentation is usually a title or introductory slide. It typically consists of text only, but it can include graphic elements or images as well. Subsequent slides are chosen based on the information to be transmitted. Some slides contain images, or charts and graphs.
Transitions Between Slides
Slides follow one after another during a presentation, either at a set time or when the presenter advances the slides manually. PowerPoint includes a large number of transitions you can apply to slides. A transition controls the appearance of one slide as it transitions to the next. Transitions include one slide morphing into another, a fade of one to another, and all sorts of special effects such as page curls or animated motion.
Although transitions add extra interest to a slide presentation, overdoing them by applying a different spectacular effect to each slide tends to look unprofessional and may even distract the audience from what the speaker is saying, so use transitions judiciously.
Enhancing a Slide
Slides can have sound effects attached to them. The sound effects list includes cash register, crowd laughing, drum roll, whoosh, typewriter and many more.
Adding motion to an element on a slide – a line of text or an image – is called animation. PowerPoint comes with a large selection of stock animations you can use to generate movement on a slide. For example, you can choose a headline and have it zoom in from the margin, spin around 360 degrees, flip in one letter at a time, bounce into position or one of many other stock animation effects .
As with transitions, don't use so many special effects that the audience is distracted from the content of the slide.
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
- The 8 Best Slideshow Apps of 2024
- What Is an Animation in Presentation Software?
- How to Use Google Duet in Slides
- Different Ways to View Slides in PowerPoint
- The 8 Best Google Drive Add-ons for 2024
- 10 Free PowerPoint Game Templates
- Beyond the Basics in PowerPoint
- The 10 Most Common PowerPoint Terms
- Tips for Memorial PowerPoint Presentations
- How to Hide and Unhide a Slide in PowerPoint
- Create a Wedding PowerPoint Presentation
- How to Use Google Slide Animations and Transitions
- PowerPoint Master Slide
- An Introduction to PowerPoint
- Make the Most of PowerPoint's Slide Transition Options
- Converting PowerPoint Slides to Word Documents
Arab States
Asia and the pacific, europe & central asia, latin america & the caribbean.
You’re using an outdated browser. Old browsers are unstable, unsafe and do not support the features of of this website. Please upgrade to continue.
Your browser does not support JavaScript. This site relies on JavaScript to structure its navigation and load images across all pages. Please enable JavaScript to continue.
What is climate change mitigation and why is it urgent?
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Facebook
- Share on twitter
- Share via email

- Climate change mitigation involves actions to reduce or prevent greenhouse gas emissions from human activities.
- Mitigation efforts include transitioning to renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, adopting regenerative agricultural practices and protecting and restoring forests and critical ecosystems.
- Effective mitigation requires a whole-of-society approach and structural transformations to reduce emissions and limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
- International cooperation, for example through the Paris Agreement, is crucial in guiding and achieving global and national mitigation goals.
- Mitigation efforts face challenges such as the world's deep-rooted dependency on fossil fuels, the increased demand for new mineral resources and the difficulties in revamping our food systems.
- These challenges also offer opportunities to improve resilience and contribute to sustainable development.
What is climate change mitigation?
Climate change mitigation refers to any action taken by governments, businesses or people to reduce or prevent greenhouse gases, or to enhance carbon sinks that remove them from the atmosphere. These gases trap heat from the sun in our planet’s atmosphere, keeping it warm.
Since the industrial era began, human activities have led to the release of dangerous levels of greenhouse gases, causing global warming and climate change. However, despite unequivocal research about the impact of our activities on the planet’s climate and growing awareness of the severe danger climate change poses to our societies, greenhouse gas emissions keep rising. If we can slow down the rise in greenhouse gases, we can slow down the pace of climate change and avoid its worst consequences.
Reducing greenhouse gases can be achieved by:
- Shifting away from fossil fuels : Fossil fuels are the biggest source of greenhouse gases, so transitioning to modern renewable energy sources like solar, wind and geothermal power, and advancing sustainable modes of transportation, is crucial.
- Improving energy efficiency : Using less energy overall – in buildings, industries, public and private spaces, energy generation and transmission, and transportation – helps reduce emissions. This can be achieved by using thermal comfort standards, better insulation and energy efficient appliances, and by improving building design, energy transmission systems and vehicles.
- Changing agricultural practices : Certain farming methods release high amounts of methane and nitrous oxide, which are potent greenhouse gases. Regenerative agricultural practices – including enhancing soil health, reducing livestock-related emissions, direct seeding techniques and using cover crops – support mitigation, improve resilience and decrease the cost burden on farmers.
- The sustainable management and conservation of forests : Forests act as carbon sinks , absorbing carbon dioxide and reducing the overall concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Measures to reduce deforestation and forest degradation are key for climate mitigation and generate multiple additional benefits such as biodiversity conservation and improved water cycles.
- Restoring and conserving critical ecosystems : In addition to forests, ecosystems such as wetlands, peatlands, and grasslands, as well as coastal biomes such as mangrove forests, also contribute significantly to carbon sequestration, while supporting biodiversity and enhancing climate resilience.
- Creating a supportive environment : Investments, policies and regulations that encourage emission reductions, such as incentives, carbon pricing and limits on emissions from key sectors are crucial to driving climate change mitigation.

Photo: Stephane Bellerose/UNDP Mauritius

Photo: La Incre and Lizeth Jurado/PROAmazonia
What is the 1.5°C goal and why do we need to stick to it?
In 2015, 196 Parties to the UN Climate Convention in Paris adopted the Paris Agreement , a landmark international treaty, aimed at curbing global warming and addressing the effects of climate change. Its core ambition is to cap the rise in global average temperatures to well below 2°C above levels observed prior to the industrial era, while pursuing efforts to limit the increase to 1.5°C.
The 1.5°C goal is extremely important, especially for vulnerable communities already experiencing severe climate change impacts. Limiting warming below 1.5°C will translate into less extreme weather events and sea level rise, less stress on food production and water access, less biodiversity and ecosystem loss, and a lower chance of irreversible climate consequences.
To limit global warming to the critical threshold of 1.5°C, it is imperative for the world to undertake significant mitigation action. This requires a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 45 percent before 2030 and achieving net-zero emissions by mid-century.
What are the policy instruments that countries can use to drive mitigation?
Everyone has a role to play in climate change mitigation, from individuals adopting sustainable habits and advocating for change to governments implementing regulations, providing incentives and facilitating investments. The private sector, particularly those businesses and companies responsible for causing high emissions, should take a leading role in innovating, funding and driving climate change mitigation solutions.
International collaboration and technology transfer is also crucial given the global nature and size of the challenge. As the main platform for international cooperation on climate action, the Paris Agreement has set forth a series of responsibilities and policy tools for its signatories. One of the primary instruments for achieving the goals of the treaty is Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) . These are the national climate pledges that each Party is required to develop and update every five years. NDCs articulate how each country will contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhance climate resilience. While NDCs include short- to medium-term targets, long-term low emission development strategies (LT-LEDS) are policy tools under the Paris Agreement through which countries must show how they plan to achieve carbon neutrality by mid-century. These strategies define a long-term vision that gives coherence and direction to shorter-term national climate targets.

Photo: Mucyo Serge/UNDP Rwanda

Photo: William Seal/UNDP Sudan
At the same time, the call for climate change mitigation has evolved into a call for reparative action, where high-income countries are urged to rectify past and ongoing contributions to the climate crisis. This approach reflects the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) which advocates for climate justice, recognizing the unequal historical responsibility for the climate crisis, emphasizing that wealthier countries, having profited from high-emission activities, bear a greater obligation to lead in mitigating these impacts. This includes not only reducing their own emissions, but also supporting vulnerable countries in their transition to low-emission development pathways.
Another critical aspect is ensuring a just transition for workers and communities that depend on the fossil fuel industry and its many connected industries. This process must prioritize social equity and create alternative employment opportunities as part of the shift towards renewable energy and more sustainable practices.
For emerging economies, innovation and advancements in technology have now demonstrated that robust economic growth can be achieved with clean, sustainable energy sources. By integrating renewable energy technologies such as solar, wind and geothermal power into their growth strategies, these economies can reduce their emissions, enhance energy security and create new economic opportunities and jobs. This shift not only contributes to global mitigation efforts but also sets a precedent for sustainable development.
What are some of the challenges slowing down climate change mitigation efforts?
Mitigating climate change is fraught with complexities, including the global economy's deep-rooted dependency on fossil fuels and the accompanying challenge of eliminating fossil fuel subsidies. This reliance – and the vested interests that have a stake in maintaining it – presents a significant barrier to transitioning to sustainable energy sources.
The shift towards decarbonization and renewable energy is driving increased demand for critical minerals such as copper, lithium, nickel, cobalt, and rare earth metals. Since new mining projects can take up to 15 years to yield output, mineral supply chains could become a bottleneck for decarbonization efforts. In addition, these minerals are predominantly found in a few, mostly low-income countries, which could heighten supply chain vulnerabilities and geopolitical tensions.
Furthermore, due to the significant demand for these minerals and the urgency of the energy transition, the scaled-up investment in the sector has the potential to exacerbate environmental degradation, economic and governance risks, and social inequalities, affecting the rights of Indigenous Peoples, local communities, and workers. Addressing these concerns necessitates implementing social and environmental safeguards, embracing circular economy principles, and establishing and enforcing responsible policies and regulations .
Agriculture is currently the largest driver of deforestation worldwide. A transformation in our food systems to reverse the impact that agriculture has on forests and biodiversity is undoubtedly a complex challenge. But it is also an important opportunity. The latest IPCC report highlights that adaptation and mitigation options related to land, water and food offer the greatest potential in responding to the climate crisis. Shifting to regenerative agricultural practices will not only ensure a healthy, fair and stable food supply for the world’s population, but also help to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Photo: UNDP India

Photo: Nino Zedginidze/UNDP Georgia
What are some examples of climate change mitigation?
In Mauritius , UNDP, with funding from the Green Climate Fund, has supported the government to install battery energy storage capacity that has enabled 50 MW of intermittent renewable energy to be connected to the grid, helping to avoid 81,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide annually.
In Indonesia , UNDP has been working with the government for over a decade to support sustainable palm oil production. In 2019, the country adopted a National Action Plan on Sustainable Palm Oil, which was collaboratively developed by government, industry and civil society representatives. The plan increased the adoption of practices to minimize the adverse social and environmental effects of palm oil production and to protect forests. Since 2015, 37 million tonnes of direct greenhouse gas emissions have been avoided and 824,000 hectares of land with high conservation value have been protected.
In Moldova and Paraguay , UNDP has helped set up Green City Labs that are helping build more sustainable cities. This is achieved by implementing urban land use and mobility planning, prioritizing energy efficiency in residential buildings, introducing low-carbon public transport, implementing resource-efficient waste management, and switching to renewable energy sources.
UNDP has supported the governments of Brazil, Costa Rica, Ecuador and Indonesia to implement results-based payments through the REDD+ (Reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation in developing countries) framework. These include payments for environmental services and community forest management programmes that channel international climate finance resources to local actors on the ground, specifically forest communities and Indigenous Peoples.
UNDP is also supporting small island developing states like the Comoros to invest in renewable energy and sustainable infrastructure. Through the Africa Minigrids Program , solar minigrids will be installed in two priority communities, Grand Comore and Moheli, providing energy access through distributed renewable energy solutions to those hardest to reach.
And in South Africa , a UNDP initative to boost energy efficiency awareness among the general population and improve labelling standards has taken over commercial shopping malls.

What is UNDP’s role in supporting climate change mitigation?
UNDP aims to assist countries with their climate change mitigation efforts, guiding them towards sustainable, low-carbon and climate-resilient development. This support is in line with achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those related to affordable and clean energy (SDG7), sustainable cities and communities (SDG11), and climate action (SDG13). Specifically, UNDP’s offer of support includes developing and improving legislation and policy, standards and regulations, capacity building, knowledge dissemination, and financial mobilization for countries to pilot and scale-up mitigation solutions such as renewable energy projects, energy efficiency initiatives and sustainable land-use practices.
With financial support from the Global Environment Facility and the Green Climate Fund, UNDP has an active portfolio of 94 climate change mitigation projects in 69 countries. These initiatives are not only aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, but also at contributing to sustainable and resilient development pathways.
Explore More Stories
Pacific shores, solar solutions: harnessing renewable energy in the pacific islands.

Photo: Yuichi Ishida/UNDP Timor-Leste
West Africa has great potential for solar energy. It’s time to release it.

Photo: UNDP Niger
Electric vehicles are driving a greener future in Viet Nam

Ho Tuan Anh delivers goods with his new e-motorbike. Photo by: Phan Huong Giang/UNDP Viet Nam
Why the Western Balkans are choosing decarbonization

Photo: UNDP Bosnia and Herzegovina
Six lessons on how to achieve future-smart energy efficient buildings

Solar photovoltaic systems on roofs in Lebanon. Photo: Fouad Choufany / UNDP Lebanon
Six ways to achieve sustainable energy for all

Photo: UNDP Zimbabwe
- Motorcycles
- Car of the Month
- Destinations
- Men’s Fashion
- Watch Collector
- Art & Collectibles
- Vacation Homes
- Celebrity Homes
- New Construction
- Home Design
- Electronics
- Fine Dining
- Les Marquables de Martell
- Mira Villas
- Panther National
- Reynolds Lake Oconee
- Wynn Las Vegas
- 672 Wine Club
- Sports & Leisure
- Health & Wellness
- Best of the Best
- The Ultimate Gift Guide
Kevin Hart Gave Tom Brady a $40,000 Ruby-Encrusted Ring at His Roast Last Weekend
The piece was created by celebrity jeweler jason of beverly hills., abby montanez, abby montanez's most recent stories.
- A Perfectly Preserved Victorian-Era Duplex in London Hits the Market for $5.7 Million
- No Kidding, Meta Is Building Earbuds With Cameras for Some Reason
- Natural Disasters Are Making It Harder for Wealthy Homeowners to Insure Their Properties
- Share This Article

Heavy is the hand that wears the ring.
Related Stories
- How the World’s Oldest Fabric Mill Is Helping Modern Men Suit Up
- Hublot’s New Online Experience Will Take You Inside a Flyback Chronograph
- Patek Philippe Leads Geneva’s Spring Watch Auctions to a Frothy $125 Million in Sales
“Tom, you deserve another fucking ring, but a ring fitting for a GOAT like yourself,” Hart said before handing Brady the one-of-a-kind piece for being a good sport. Per the news site, the ring, which is valued at an eye-watering $40,000, is set in yellow gold and studded with roughly 400 diamonds, rubies, and sapphires for a dramatic effect.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by JASON OF BEVERLY HILLS (@jasonofbeverlyhills)
At the top and bottom are the words “Brady G.R.O.A.T.” and in the middle is a gold football followed by sparkly fire flames. One side of the ring’s band is inscribed with his last name, his jersey number, and the acronym “LFG.” The other side has “2024” written at the top with the silhouette of a goat underneath it.
The Roast of Tom Brady , which was live-streamed from the Kia Forum in Inglewood, Calif., drew 2 million viewers when it aired over the weekend. Among the comedians tapped to take shots at the legendary QB were “roast master general” Jeff Ross, Nikki Glaser, Tony Hinchcliffe, Sam Jay, Andrew Schulz, Bert Kreischer, and Tom Segura. Brady’s former teammates Julian Edelman, Rob Gronkowski, Drew Bledsoe , and Randy Moss also took the stage along with his ex-coach Bill Belichick, and Patriots owner Robert Kraft. Overall, it was the sixth most-watched program to crack the platform’s weekly top 10.
Abigail Montanez is a staff writer at Robb Report. She has worked in both print and digital publishing for over half a decade, covering everything from real estate, entertainment, dining, travel to…
Read More On:
More jewelry.

This Massive 202-Carat Yellow Diamond Could Fetch up to $4.4 Million at Auction

Pharrell Teamed up With Tiffany & Co. on a New Jewelry Collection

Inside the Emergence of Lab-Grown Diamonds and How They Could Shape the Industry

This Insane 6.2-Carat Pink Diamond Ring Is Expected to Fetch up to $15 Million at Auction

Culinary Masters 2024
MAY 17 - 19 Join us for extraordinary meals from the nation’s brightest culinary minds.
Give the Gift of Luxury
Latest Galleries in Jewelry

Chopard’s Latest High Jewelry Collection Debuting at Cannes Is Full of Quirky Designs Inspired by Fairy Tales

Wedding Season Is Here! The 12 Best Brooches to Sport on Your Lapel
More from our brands, tranoï men show canceled for june edition, under armour plans revamp after dour earnings report, ‘grand theft auto 6’ sets fall 2025 release as take-two posts $2.9 billion quarterly loss, jenny holzer’s facile guggenheim museum show fails to meet our moment, the best yoga mats for any practice, according to instructors.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
presentation: [noun] the act of presenting. the act, power, or privilege especially of a patron of applying to the bishop or ordinary for instituting someone into a benefice.
PRESENTATION definition: 1. a talk giving information about something: 2. an occasion when prizes, qualifications, etc. are…. Learn more.
A Presentation Is... A presentation is a means of communication that can be adapted to various speaking situations, such as talking to a group, addressing a meeting or briefing a team. A presentation can also be used as a broad term that encompasses other 'speaking engagements' such as making a speech at a wedding, or getting a point across ...
Presentation definition: an act of presenting.. See examples of PRESENTATION used in a sentence.
A presentation is a communication method for delivering information to an audience. It typically involves a demonstration, illustration, or speech crafted to inform, persuade, inspire, or share a new idea. Presentations require every speaker to deliver their message with compelling elements. To ensure effectiveness, you need to know the basic ...
The definition or meaning of a formal presentation is a presentation that one has had time to prepare for. One has generally been asked in advance to give the presentation, and one has practiced ...
14 meanings: 1. the act of presenting or state of being presented 2. the manner of presenting, esp the organization of visual.... Click for more definitions.
The noun presentation means the official giving, or presenting, of something. The presentation of diplomas at a graduation ceremony is the part that makes many of the parents in the audience cry.
PRESENTATION definition: 1. the way something is arranged or shown to people: 2. a talk giving information about something…. Learn more.
[countable] a meeting at which something, especially a new product or idea, or piece of work, is shown to a group of people presentation on/about somebody/something The sales manager will give a presentation on the new products.; Several speakers will be making short presentations.; The conference will begin with a keynote presentation by a leading industry figure.
Definition: A presentation is a form of communication in which the speaker conveys information to the audience. In an organization presentations are used in various scenarios like talking to a group, addressing a meeting, demonstrating or introducing a new product, or briefing a team. It involves presenting a particular subject or issue or new ideas/thoughts to a group of people.
3. a : the act of giving something to someone in a formal way or in a ceremony. [noncount] The choir sang during the presentation of the gifts. [count] The awards were given out last night, and the mayor was on hand to make the presentations. [=to present the awards] b [count] : a ceremony in which something (such as an award) is given to ...
A presentation program is commonly used to generate the presentation content, some of which also allow presentations to be developed collaboratively, e.g. using the Internet by geographically disparate collaborators. Presentation viewers can be used to combine content from different sources into one presentation.
A presentation can be effective if it is carefully planned and prepared. However, delivering presentations is not always easy for every individual. Some people take presenting as a probable opportunity to showcase skills, while others find it a challenging task. To provide an effective presentation, a presenter must possess some abilities.
Presentation skills are the abilities and qualities necessary for creating and delivering a compelling presentation that effectively communicates information and ideas. They encompass what you say, how you structure it, and the materials you include to support what you say, such as slides, videos, or images. You'll make presentations at various ...
Presentation skills can be defined as a set of abilities that enable an individual to: interact with the audience; transmit the messages with clarity; engage the audience in the presentation; and interpret and understand the mindsets of the listeners. These skills refine the way you put forward your messages and enhance your persuasive powers. The present era places great emphasis on good ...
What is a Presentation? A communication device that relays a topic to an audience in the form of a slide show, demonstration, lecture, or speech, where words and pictures complement each other. Why should you think of presentations as content? The beauty of content creation is that almost anything can become a compelling piece of content. Just ...
presentation. : an activity in which someone shows, describes, or explains something to a group of people. : the way in which something is arranged, designed, etc. : the way in which something is presented. : the act of giving something to someone in a formal way or in a ceremony.
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
2. Persuasive presentation. If you've ever been swayed by a passionate speaker armed with compelling arguments, you've experienced a persuasive presentation . This type of presentation is like a verbal tug-of-war, aiming to convince the audience to see things from a specific perspective.
This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there. Follow these steps: Signal that it's nearly the end of your presentation, for example, "As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…". Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation - "In this speech I wanted to compare…". 5.
With PowerPoint on your PC, Mac, or mobile device, you can: Create presentations from scratch or a template. Add text, images, art, and videos. Select a professional design with PowerPoint Designer. Add transitions, animations, and cinematic motion. Save to OneDrive, to get to your presentations from your computer, tablet, or phone.
Tell a story or an anecdote. A good grabber captures the attention of everyone there, and makes them focus on what you have to say. 4. Crystalize your message and construct your arguments: Your ...
The Definition of a Slide (or Slides) in a PowerPoint Presentation. Presentation software such as PowerPoint generates a series of slides to accompany a human presenter or to be recorded as a stand-alone presentation. A slide is a single screen of a presentation, and every presentation is composed of several slides.
1. Visme. Let's start with the best app for presentations you can use to design your presentation. Visme is a cloud-based graphic design software that allows designers and non-designers alike to create beautiful and professional presentations, infographics, social media graphics and more.
GPT-4o ("o" for "omni") is a step towards much more natural human-computer interaction—it accepts as input any combination of text, audio, and image and generates any combination of text, audio, and image outputs. It can respond to audio inputs in as little as 232 milliseconds, with an average of 320 milliseconds, which is similar to ...
Climate change mitigation refers to any action taken by governments, businesses or people to reduce or prevent greenhouse gases, or to enhance carbon sinks that remove them from the atmosphere. These gases trap heat from the sun in our planet's atmosphere, keeping it warm. Since the industrial era began, human activities have led to the ...
This is the third time that Malmo, a city of 360,000 people on Sweden's southwest coast, has hosted the Eurovision Song Contest. In the last 30 years, the city has undergone a transformation to ...
Per the news site, the ring, which is valued at an eye-watering $40,000, is set in yellow gold and studded with roughly 400 diamonds, rubies, and sapphires for a dramatic effect. "Honored to ...
OpenAI, in partnership with Microsoft, announces GPT-4o, a groundbreaking multimodal model for text, vision, and audio capabilities. Learn more.