

Fundamentals of Business - 4th Edition
(9 reviews)
Stephen J. Skripak, Virginia Tech
Ron Poff, Virginia Tech
Copyright Year: 2023
ISBN 13: 9780997920178
Publisher: Virginia Tech Libraries
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Stacy McManus, Adjunct Professor, Minnesota West Community & Technical College on 2/16/23
The book did an excellent job of covering the basics of business. Everything that I cover in my course was covered in this book. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
The book did an excellent job of covering the basics of business. Everything that I cover in my course was covered in this book.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
Book was very accurate, up-to-date and thorough.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The chapters were ordered thoughtfully and progressed in a manner which will help the students to learn the material. Content was up-to-date, and I don't feel that it will be situation where a new edition is required each year.
Clarity rating: 4
The book was clear and easy to understand.
Consistency rating: 4
The e-book is easy to navigate and follows a consistent pattern. The material is pleasing to the eye and is an easy read.
Modularity rating: 5
The chapters are set up well - not too long to lose interest but yet detailed and thorough.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The chapters and topics were arranged in a logical manner.
Interface rating: 5
I reviewed the e-book version and did not have any issues with the interface. The book was easy to navigate and the appearance was very professional.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No grammatical errors were immediately apparent.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
I did not notice anything offensive or concerning.
I was excited to find this OER book. It is well done, detailed, and thorough. I appreciated the test banks that were included. I would like to see some recommended activities for each chapter, but overall the book was excellent. I was happy to see an additional chapter on hospitality as well. I look forward to adopting this for my Foundations of Business class.
Reviewed by Marie Looby, adjunct instructor, Massasoit Community College on 6/5/21
Varied subject matters that progress logically and are covered in detail with terms well defined. Offers outside links for further enrichment. read more
Varied subject matters that progress logically and are covered in detail with terms well defined. Offers outside links for further enrichment.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
Found no errors while moving through the text including the quizzes.
The book uses modern day examples that the student can relate to and reference. Although the examples are current the skills are timeless.
Clarity rating: 5
There are embedded links for sources allowing students to access backup while reading online.
Consistency rating: 5
The text shows all the same tools throughout making it easy for students to develop study skills for this book.
The text is organized in chapters with mini quizzes built in as the subject veers in a different direction in each chapter.
The chapters build on the skills and knowledge as they go along eg: group think.
No navigation problems. While clicking on various links there were no difficulties reaching the sources.
Well done and consistent grammar.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
Illustrations showed diversity
The materials were interesting enough to encourage you to continue reading.
Reviewed by Steve Lesh, Associate Professor, Bowling Green State University on 1/8/21
I must first state that I am a Doctor of Physical Therapy educator who holds a PhD in Business which is not a common combination of degree paths. I was intrigued by the possibility of adding more business theory to my health service administration... read more
I must first state that I am a Doctor of Physical Therapy educator who holds a PhD in Business which is not a common combination of degree paths. I was intrigued by the possibility of adding more business theory to my health service administration courses, but the cost has been historically prohibitive to the students in my experience. We utilize a niche health care admin textbook which misses some of the greater foundational business skills. When this opportunity presented to review materials that I could add to my course without adding cost, I was very pleased. I find Skripak to be comprehensive with the added bonus of my favorite chapter #18 Personal Finances which for Physical Therapy students who typically leave school with great debt to be invaluable!
I found the materials to be easy to read, well organized and did not find errors. I really enjoyed the links to external videos that supported the concepts. I feel the presentation was unbiased.
As this is the second edition with a 2018 publish date it was very current, however, I noticed after I began reading the 2nds edition that a 3rd edition (2020) has been released which updates figures, graphs, and some of the recent law changes. Having the book turn over that quickly makes it even a greater value to me as the instructor and to the student. I appreciate the relevance of being able to submit suggestions or corrections to the author and that they are making a test bank available in support of this material! Doesn't get much better than that!
Well written and not overly technical. The narrative flows well from the beginning to the end of each chapter.
From what I can tell, it is very consistent. I did not observe any changes in tone or terminology, but again, I am reading this through the eyes of someone who has earned a PhD in Business, so it is all very familiar to me.
Modularity rating: 4
When you go to the website, you can easily download each chapter in bits [https://vtechworks.lib.vt.edu/handle/10919/84848]. I first started reviewing the full .pdf of the 2nd edition and found that it didn't have bookmarks for each chapter so the scrolling was a bit annoying. I would add that piece to the full .pdf if possible and it appears they did that in the 3rd ed. However, the module approach online eliminates the need for a full book .pdf download.
Starts with teamwork which is perhaps one of the most important concepts in modern business. So I really appreciate that. The 18 chapters of the 2nd (and 3rd) edition cover all of the major elements of modern business. Certainly, each chapter could be expanded into it's own book. For example, Chapter 14 is Marketing, and there are full marketing textbooks, however, that is not the function of this book. The purpose is to take you through all of the major components of business as opposed to deep dives into each topic.
Again, I loved the interface with online videos. The links appeared to all work. Adds a multimedia approach to the words on the page.
I didn't see any that were obvious during my readings.
There were no elements that were culturally insensitive or offensive that I noted.
I look forward to integrating this open textbook into my Physical Therapy health service admin course as I can now get a glimpse of business fundamentals to supplement the health care niche that my students receive! Thank you for this opportunity. I do have some ideas for writing open textbooks and would be open to doing so. Steven G. Lesh
Reviewed by Babu George, Associate Professor, Fort Hays State University on 10/26/18
This book covers the overall landscape of contemporary businesses pretty well. While nothing significant is 'lacking', I would love to have the authors provide a chapter that quickly takes students through the history of business and another... read more
This book covers the overall landscape of contemporary businesses pretty well. While nothing significant is 'lacking', I would love to have the authors provide a chapter that quickly takes students through the history of business and another chapter that discusses the futuristic dimensions of business.
The contents are accurate. The authors have provided citations to key claims. The references have hyperlinks to more scholarly resources on topics discussed in the book.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
The contents are presented in a generalized manner - meaning, the book could stand the test of time for a significant duration. The dynamism of the contemporary businesses could have been captured better, however. The digital transformation of businesses and societies has made the life cycle of knowledge shorter. More stress on e-businesses and digital models would have made the book more relevant.
The authors have used simple English. Overall, the book is very accessible.
Yes, there is a unity of purpose and a sense of unity, throughout the book.
The chapters are stand-alone, for the most part. So, professors need not teach the content sequentially.
Ideas are organized systematically. Every chapter opens with a set of learning objectives and this gives direction to the learners. The students are asked to reflect upon certain key questions, from time to time. Answers to these question are then made available in the content discussed. At the end of each chapter, certain key takeaways are listed. This facilitates a natural form of learning.
No issue noted.
Well written.
No culturally insensitive use of language or images noted. However, in the forthcoming iterations, the authors are requested to bring in more dimensions of global businesses. Examples of business practices in other countries and cultures would add value.
One chapter (Chapter 15: Hospitality and Tourism) does not make a lot of sense. One might wonder why the authors devoted a full chapter for one industry! Why not similar chapters for other industries? It almost sounds like one of the authors had a chapter written for some other purpose, which needed to be inserted in this book. There are several other examples and case studies related to tourism in this book, too. Thinking of it positively, this book thus has an added advantages for students majoring in Hospitality and Tourism.
Reviewed by Mindy Bean, Faculty, Linn-Benton Community College on 6/19/18
The OER does well on covering topics in an introductory level business course. It adds a section that is not in typical business fundamental material of hospitality which compliments our new program that we started at our college. read more
The OER does well on covering topics in an introductory level business course. It adds a section that is not in typical business fundamental material of hospitality which compliments our new program that we started at our college.
The book is consistent with most material that is available.
The examples in the book are commonly used in most topics of basic business fundamentals. It should hold relevancy for 4-5 more years.
The book is clear in the writing that can be easily read. Business terms are well represented and explained thoroughly. The material is written well for a student's first time learning business and how to apply it to what is happening around them.
The book is consistent from chapter to chapter. The sources of material are well represented. Visuals compliment the written material.
The chapters are seamless with transition from topic to topic. It could easily be broken up into sections of reading during certain points in the course. This text seems to be set up well for student team work to learn on each important topic of business basics.
Chapters are organized in a good way to learn all material and have it related to each former chapter. Personally I will be teaching the chapters in a different order to complement a business plan being created by students.
Interface rating: 3
The book could use a few more visuals for students to relate to the material. Some of the visuals could use improvement, but as for the written material, it is clear and written well for beginners understanding business.
I did not find any grammatical errors.
Globalization section addresses cultural differences in a way that is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way. It used examples of variety of countries and global management practices.
Reviewed by Jeff Bauer, Professor of Management & Dean, University of Cincinnati - Clermont on 3/27/18
The text is quite comprehensive covering: ECON, Ethics, Global Business, Forms of Ownership, Entre, MGMT, OB/OD, OM, Motivation, H/R, Unions, MKTG, Pricing, Hospitality MGMT, ACCT/FIN, and Personal FIN. Only areas "missing" = Information Systems... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
The text is quite comprehensive covering: ECON, Ethics, Global Business, Forms of Ownership, Entre, MGMT, OB/OD, OM, Motivation, H/R, Unions, MKTG, Pricing, Hospitality MGMT, ACCT/FIN, and Personal FIN. Only areas "missing" = Information Systems and Data Analytics/Analysis.
Well researched and the sources are thoroughly documented.
With a 2016 publication date, it is up-to-date and should have a shelf life of several years. The biggest challenge will be updating the stories/vignettes as new information becomes available on the firms mentioned and technology inevitably impacts the content.
The material is easily accessible to the Introduction to Business student. Well written and the material flows well. Terms/jargon are thoroughly explained in the chapter and at the end of each chapter.
Consistency format for each of the chapters and interspersed well with photos, charts, and real-world stories.
The layout presents the material well and is easy to read. Chapter lengths and the length of the entire text fit well with the organization of a class over a semester.
I might organize the material a bit differently as the Global and Ethics items are early in the text and I might bump them to later in the term after additional terminology is learned and can be applied to that material. That said, overall the text is laid out logically and "like" content is connected in successive chapters, e.g. MGMT then OB/OD, etc.
Worked fine for me reading it on-screen.
I did not edit the text, but nothing glaring related to grammar jumped out at me.
On the contrary, I think the text tackles diversity head on and provides a good review of the 21st Century workplace and marketplace.
I am VERY likely to adopt this text for the next Intro to Business class that I teach.
Reviewed by Thomas Goodwin, Part-time Instructor, Miami University on 6/20/17
This text does a good job of introducing key functions of an organization (Marketing, HR, Accounting/Finance) as well as core principles such as ethics, legal issues, and economics. The material is appropriate for an introductory course to serve... read more
This text does a good job of introducing key functions of an organization (Marketing, HR, Accounting/Finance) as well as core principles such as ethics, legal issues, and economics. The material is appropriate for an introductory course to serve as the foundation for general business or to move on to a concentration in any of these business disciplines. There are two chapters that do not quite seem to fit in with the rest of the text: chapter 12 discusses Union/Management Issues, which makes sense in the flow of the book that it follows chapter 11 on HR, but for an introductory course the chapter 12 topic gets into a lot of HR detail not generally covered in an introductory course. Chapter 15 focuses on the hospitality and tourism industry. This is a very specific chapter embedded within the book about an industry while the rest of the book is mostly general information that could be applied to any number or types of organizations. Still, out of 17 chapters there are 15 solid chapters that provide great content and overview of the subject matter.
The book is written in an easy to read format with no noticeable grammatical errors or formatting issues. It is easy to find topics within chapters based on the layout, fonts, etc. The information itself is rooted in fundamental concepts of each chapter's topic or subject matter within the business discipline and there are no overt attempts to lead the reader in a particular manner to form bias or opinions, other than to establish critical thinking of topics.
While there are some examples that may seem somewhat dated, they are explained in a manner that is easy to understand and they are relevant (or "fit") within the context of the chapters and course concepts being discussed. The book is quite lengthy but given the 17 chapters that is to be expected. The author could probably eliminate two chapters on ancillary material to make it a shorter text but the chapters are not unnecessarily bloated for the sake of adding more vocabulary or unnecessary graphics.
The book uses easy to understand language, explains course concepts and terminology, and reinforces abstract ideas with examples. Overall it does a good job of relaying topics that are being introduced to students for the first time.
The text remains consistent in present tense tone of voice, chapter structure is organized consistently throughout the text, and the use of masculine vs. feminine language is muted so that it presents information to readers in a gender-neutral manner.
One could easily pick up this course text and only read select chapters that were of interest. Gaining an understanding of the legal topics (Chapter 5 Forms of Business Ownership) was not necessary to learning about subsequent chapters such as Marketing, HR, economics, etc. An instructor could pull needed material from this course text to supplement other teaching materials as well as to expand on the introductory materials contained herein to build out a more robust, in-depth course on any of the topics contained within this textbook.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
There is a very logical structure with the early chapters discussing types of business formation, teamwork, and ethics before moving to more operational activities such as financing, marketing, management and so forth. A few chapters could be reorganized. The ethics chapter could be moved to coincide with the legal (chapters 3 & 5) and there are two chapters that do not seem to fit with the introductory material (Chapter 12 on Unions and Chapter 15 on Hospitality & Tourism) but otherwise the book had a good flow of advancing through the broad goal of introducing multiple aspects of business.
Interface rating: 4
The book could use more graphs, pictures, diagrams, etc. to emphasize course concepts; however, the author made the textbook very easy to read (especially online) so the lack of numerous photos or graphics may conversely make it easier to download and read as plain text.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
There are no noticeable grammatical, spelling, or punctuation errors. There are a few figures that are either not labeled or are not appropriately referencing the course text where they are presented, leaving "floating images" in some places that have no meaning to the topic discussed. Figure 7.3 on page 167 is an example. There is a photo of someone's arm by a laptop and notepad next to sections discussing operational plans and planning for contingencies or crises.
Gender neutral language is used throughout the course text and no offensive references are made or examples presented. The textbook examples cover a wide array of businesses, industries, and geographical reference points.
This course is an excellent resource for a first-year business student that is seeking a broad overview of several business disciplines and to lead into more in-depth study of the course topics throughout an undergraduate curriculum.
Reviewed by Ann Strunk, Adjunct Instructor, Klamath Community College on 6/20/17
The text covers all the typical topics for introductory business course. The Chapter 15: Hospitality and Tourism is relevant to the increasing industry segment. The last chapter on Personal Finances does come after Chapter 16 Accounting but seems... read more
The text covers all the typical topics for introductory business course. The Chapter 15: Hospitality and Tourism is relevant to the increasing industry segment. The last chapter on Personal Finances does come after Chapter 16 Accounting but seems out of place with no connection to the rest of the text.
There does not seem to be any errors or biases.
The textbook was recently written making issues and news items current. Social media marketing is thorough discussed. The Marketing chapter introduces the SAVE marketing model which is taking the place of the four Ps of the marketing mix. Historic ethics cases such as WorldCom and Bernie Madoff are presented.
Pages are of a simple layout with easy readability. All terms are defined and this would also be an appropriate text to use with high school dual credit courses.
Graphics are appealing and provide a distinct look for the various sections of the text. All chapters start with learning objectives and end with take-aways. The individual chapters are of various lengths. Chapter 12: Labor Unions covers just the one topic. Other chapters are much longer with up to seven sections.
There many chapters that could be assigned or presented in a different sequence. It is easy to find and refer to tables and divisions of the chapters.
I find the placement of teamwork as the preface could be very be very beneficial in setting up for class activities and useful for students as they become active in college clubs and organizations.
Effective graphics make the chapters and sections clear. There are very few photos and those are clear and useful.
I found no grammatical errors.
Cultural differences, of course, are addressed in Chapter 4: Globalization of Business. Although there are few photos only one features a person of color.
While the chapter concepts are summarized with "Key Take-Aways", there is no end of chapter "check for understanding" such as review questions, discussions, or activities. Adoption of this textbook would require significant development of assessment tools. The references section at the end of the book is organized by chapter and provides a valuable resource of website hyperlinks.
Reviewed by Ehsan Salek, Professor of Business, Virginia Wesleyan College on 2/8/17
The text has an extensive coverage and actually has several chapters one doesn't normally find in an introductory textbook on business. If this was a traditional textbook, I would not adopt it since there are superfluous chapters and sections that... read more
The text has an extensive coverage and actually has several chapters one doesn't normally find in an introductory textbook on business. If this was a traditional textbook, I would not adopt it since there are superfluous chapters and sections that I would not want in the book but since I can custom-make an electronic copy, I would cut the unnecessary section.
The content is standard and can be found in many similar textbooks. I did not find any errors or biased opinion. All assertions are backed by reputable sources.
In such a book, the only areas that need regular updating are the examples, vocabulary, and technology. 1. Examples must be current, real, and interesting for the students in order to drive home the issues. Most recent news from companies like Apple, Amazon, or Starbucks attract the attention of students. 2. Vocabulary. "Human Resources" instead of "Personnel" or "Tossed salad" instead of "Melting Pot," etc. 3. Technology. Other than specific case studies which might have a historical significance, all references to hardware, software, and telecom should show the most current examples.
It flows well if a freshman or any student new to the business major (otherwise why one would read such a book) can get past the boring look and "feel" of the book. the book looks like a long term paper! Proper use of deeper indentations and special boxes can give the book a more interesting and magazine-like feel, although I understand that part of the bland look is due to cost restrictions.
I did not find any inconsistencies.
The book, by it's electronic nature, is naturally flexible but only to the extent of being able to cut or move materials but I am not sure if an adopter can add his/her own chapters/sections.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 2
This is where I will offer the bulk of my feedback. A. Why does TEAMWORK has its own special section before the chapters start? It should be moved to chapter 7, 8, or 10. B. Chapter 12 (Union-Management Issues) is not necessary in such a basic business text. The topic can be subsumed under chapter 3 or 11. C. Another superfluous chapter is #15 (Hospitality and Tourism). It looks like one of the contributors to this text has a specialty in this area. For instance, do students also need to read a chapter about Real Estate or another one about the Airline Industry? D. As much as Personal Finance (chap. 17) is a very useful topic, especially for younger generation of students, allocating a separate chapter to it seems unnecessary to me. How about moving an itemized summary of it to an appendix at the end. E. In place of the deleted chapters, add or restructure as follows, so as to have more chapters about marketing which has the effect of making the text a lot more interesting for the commercial and consumer-driven society we all live in. Chapter 13, Marketing (Introduction to the topic plus discussion of the Product aspects) Chapter 14, Marketing (Price & Place) or (Price and Distribution) Chapter 15, Marketing (Promotion & Advertising)
The only interface issue I found is mentioned in #7.
Grammar is good.
I did not find any of words or phrases that may come across as culturally insensitive or politically incorrect.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Teamwork in Business
Chapter 2 The Foundations of Business
Chapter 3 Economics and Business
Chapter 4 Ethics and Social Responsibility
Chapter 5 Business in a Global Environment
Chapter 6 Forms of Business Ownership
Chapter 7 Entrepreneurship and Small Business Development
Chapter 8 Management and Leadership
Chapter 9 Structuring Organizations
Chapter 10 Operations Management
Chapter 11 Motivating Employees
Chapter 12 Managing Human Resources
Chapter 13 Union/Management Issues
Chapter 14 Marketing: Providing Value to Customers
Chapter 15 Pricing Strategy
Chapter 16 Hospitality and Tourism
Chapter 17 Accounting and Financial Information
Chapter 18 Personal Finances
Chapter 19 Technology in Business
Ancillary Material
About the book.
Fundamentals of Business , 4th Edition is an open education resource intended to serve as a no-cost, faculty-customizable primary text for one-semester undergraduate introductory business courses. It covers the following topics in business: Teamwork; economics; ethics; entrepreneurship; business ownership, management, and leadership; organizational structures and operations management; human resources and motivating employees; managing in labor union contexts; marketing and pricing strategy; hospitality and tourism, accounting and finance, personal finances, and technology in business. The textbook was designed for use in Virginia Tech’s Pamplin College of Business introductory level business course, MGT1104 Foundations of Business and is shared under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike 4.0 license.
If you are an instructor reviewing, adopting, or adapting this textbook, please help us understand your use by filling out this form http://bit.ly/business-interest .
A testbank is now available by request for this book: http://hdl.handle.net/10919/93404 . The testbank covers chapters 1-18 and (currently) aligns to previous editions of the textbook. It is available to any instructor who has adopted Fundamentals of Business in their course.
About the Contributors
Stephen J. Skripak is (retired) Professor of Practice in Management at Pamplin College of Business, Virginia Tech (2005 – 2021) and former Associate Dean for Graduate Programs (2006-2014). He is a senior executive with 25 years of business leadership experience, including positions as General Manager and Chief Financial Officer with divisions of Fortune 500 companies. His background includes financial services, consumer packaged goods, apparel, and industrial companies, with emphasis in turnaround situations. He was the lead contributor and subject matter expert for the 2016 and 2018 editions of Fundamentals of Business , and reviewed the 2020 and 2023 versions of the book.
Ron Poff is Assistant Professor of Management Practice in the Management Department at Pamplin College of Business, Virginia Tech, where he teaches management courses. He began his career as an enlisted member of the US Navy Reserves before entering his primary career in supply chain operations then sales and marketing, where he served in executive roles with large corporations for over 25 years. As an entrepreneur, he then founded his own marketing agency. His education includes a B.S. in Business Management, M.S. Marketing, and a Graduate Certificate in eMarketing. He is the project lead, chief contributor, and coordinator of contributors for the third (2020) and fourth editions (2023) of Fundamentals of Business.
Contribute to this Page
Brought to you by:

Writing a Business Plan: The Basics
By: HBS Press, Harvard Business School Press
Every entrepreneur is encouraged to write a business plan; those who don't quickly learn that future operations can be derailed without a cohesive printed mission and that obtaining outside funding…
- Length: 43 page(s)
- Publication Date: Oct 30, 2004
- Discipline: Entrepreneurship
- Product #: 5344BC-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Educator Copy
$4.50 per student
degree granting course
$7.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
Every entrepreneur is encouraged to write a business plan; those who don't quickly learn that future operations can be derailed without a cohesive printed mission and that obtaining outside funding is nearly impossible without one. This chapter discusses the managerial purposes of a business plan and describes the key points that potential investors look for.
This chapter is excerpted from Harvard Business Essentials: Entrepreneur's Toolkit.
Learning Objectives
To discuss the individual components of a business plan and the considerations that management must undertake in the plan's formulation and long-term success.
Oct 30, 2004
Discipline:
Entrepreneurship
Harvard Business Press Chapters
5344BC-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: Chapter 1 – Developing a Business Plan
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 21274

- Lee A. Swanson
- University of Saskatchewan
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you will be able to
- Describe the purposes for business planning
- Describe common business planning principles
- Explain common business plan development guidelines and tools
- List and explain the elements of the business plan development process
- Explain the purposes of each element of the business plan development process
- Explain how applying the business plan development process can aid in developing a business plan that will meet entrepreneurs’ goals
This chapter describes the purposes, principles, and the general concepts and tools for business planning, and the process for developing a business plan.
Purposes for Developing Business Plans
Business plans are developed for both internal and external purposes. Internally, entrepreneurs develop business plans to help put the pieces of their business together. Externally, the most common purpose is to raise capital.
Internal Purposes
As the road map for a business’s development, the business plan
- Defines the vision for the company
- Establishes the company’s strategy
- Describes how the strategy will be implemented
- Provides a framework for analysis of key issues
- Provides a plan for the development of the business
- Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical success factors
- Helps the entrepreneur to be realistic and test theories
External Purposes
The business plan provides the most complete source of information for valuation of the business. Thus, it is often the main method of describing a company to external audiences such as potential sources for financing and key personnel being recruited. It should assist outside parties to understand the current status of the company, its opportunities, and its needs for resources such as capital and personnel.
Business Plan Development Principles
Hindle and Mainprize (2006) suggested that business plan writers must strive to effectively communicate their expectations about the nature of an uncertain future and to project credibility. The liabilities of newness make communicating the expected future of new ventures much more difficult than for existing businesses. Consequently, business plan writers should adhere to five specific communication principles .
First, business plans must be written to meet the expectations of targeted readers in terms of what they need to know to support the proposed business. They should also lay out the milestones that investors or other targeted readers need to know. Finally, writers must clearly outline the opportunity , the context within the proposed venture will operate (internal and external environment), and the business model (Hindle & Mainprize, 2006).
There are also five business plan credibility principles that writers should consider. Business plan writers should build and establish their credibility by highlighting important and relevant information about the venture team . Writers need to elaborate on the plans they outline in their document so that targeted readers have the information they need to assess the plan’s credibility. To build and establish credibility, they must integrate scenarios to show that the entrepreneur has made realistic assumptions and has effectively anticipated what the future holds for their proposed venture. Writers need to provide comprehensive and realistic financial links between all relevant components of the plan. Finally, they must outline the deal , or the value that targeted readers should expect to derive from their involvement with the venture (Hindle & Mainprize, 2006).
General Guidelines for Developing Business Plans
Many businesses must have a business plan to achieve their goals. Using a standard format helps the reader understand that the you have thought everything through, and that the returns justify the risk. The following are some basic guidelines for business plan development.
As You Write Your Business Plan
1. If appropriate, include nice, catchy, professional graphics on your title page to make it appealing to targeted readers, but don’t go overboard.
2. Bind your document so readers can go through it easily without it falling apart. You might use a three-ring binder, coil binding, or a similar method. Make sure the binding method you use does not obscure the information next to where it is bound.
3. Make certain all of your pages are ordered and numbered correctly.
4. The usual business plan convention is to number all major sections and subsections within your plan using the format as follows:
1. First main heading
1.1 First subheading under the first main heading
1.1.1. First sub-subheading under the first subheading
2. Second main heading
2.1 First subheading under the second main heading
Use the styles and references features in Word to automatically number and format your section titles and to generate your table of contents. Be sure that the last thing you do before printing your document is update your automatic numbering and automatically generated tables. If you fail to do this, your numbering may be incorrect.
5. Prior to submitting your plan, be 100% certain each of the following requirements are met:
- Everything must be completely integrated. The written part must say exactly the same thing as the financial part.
- All financial statements must be completely linked and valid. Make sure all of your balance sheets balance.
- Everything must be correct. There should be NO spelling, grammar, sentence structure, referencing, or calculation errors.
- Your document must be well organized and formatted. The layout you choose should make the document easy to read and comprehend. All of your diagrams, charts, statements, and other additions should be easy to find and be located in the parts of the plan best suited to them.
- In some cases it can strengthen your business plan to show some information in both text and table or figure formats. You should avoid unnecessary repetition , however, as it is usually unnecessary—and even damaging—to state the same thing more than once.
- You should include all the information necessary for readers to understand everything in your document.
- The terms you use in your plan should be clear and consistent. For example, the following statement in a business plan would leave a reader completely confused: “There is a shortage of 100,000 units with competitors currently producing 25,000. We can help fill this huge gap in demand with our capacity to produce 5,000 units.”
Secondaria di II Grado
Francese Strumenti
Sei in possesso di una copia di
"Business Plan Plus"?
Business Plan Plus è un corso di inglese commerciale che affianca i contenuti classici della materia ai grandi temi dell'era digitale e globale. I materiali autentici e motivanti, l'apparato audio e video d'eccellenza, la presenza sistematica di attività propedeutiche all' alternanza scuola-lavoro e all'attivazione delle 21st-century skills consentono agli studenti di lavorare in modo efficace sulla microlingua .
Business Plan Plus fornisce numerose situazioni professionali realistiche ( case studies ) che invitano lo studente ad agire, a riflettere e a trovare soluzioni, attivando le Work skills . Offre un vasto repertorio di materiali autentici (articoli di giornale, video della BBC) che consentono di lavorare in maniera efficace sulla microlingua sviluppando le abilità di reading e listening in un'ottica professionale. Inoltre, il corso dedica grande attenzione alla didattica inclusiva grazie ad un vasto corredo di materiali audio visivi, essenziali per coinvolgere tutti gli studenti.
Al testo si affianca il Companion Book che offre percorsi didattici di approfondimento dedicati a: Economics and finance, Marketing, Information technology, Tourism . Ad arricchire il Companion Book, la sezione di Work related-learning con compiti di realtà , pagine dedicate alle Work skills con attività di Problem solving e Word clouds riassuntive dei concetti-chiave esposti nello Student's Book , utili per il ripasso. Questo strumento didattico complementare offre inoltre materiali che agevolano l'approccio CLIL ed attività in stile First e EUCIP core .
Corredo Digitale
Contenuti specifici correlati al corso sull' Easy eBook e sull' eBook .
Contenuti trasversali grazie al progetto Language Plus : migliaia di attività per consolidare e approfondire la lingua.

STRUMENTI DEL CORREDO DIGITALE
Estensioni offline, sito del libro, in evidenza.
eBook offline su DVD che, senza connessione e registrazione, consente di accedere a tutti i contenuti digitali del volume: audio, video, schede di approfondimento, attività interattive, dizionario bilingue .
Configurazioni

Numero Pagine
Codice ISBN
9788849421965
9788849467871
9788859505303
Email di verifica inviata
Ti abbiamo inviato un’email agli indirizzi . Segui le istruzioni e conferma l’email. Torna poi in questa pagina e aggiorna la pagina per acquistare l’ebook.
Procedi effettuando Login
Per procedere con l'acquisto dell'eBook effettua il Login con il tuo account Famiglia oppure con il tuo account Studente. L'ebook sarà associato al tuo profilo e potrai consultarlo dalla tua Area Personale.
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
- AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
- TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
See how it works →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
- BY USE CASE
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan seamlessly with your team members and clients
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow
Business Plan Examples for Students
Ajay Jagtap
- December 29, 2023
26 Min Read

Do you know what’s the most common mistake students and rookie entrepreneurs make while preparing their first business plan?
Of course, it’s the first business plan we’re talking about; there’ll definitely be a few. However, overcomplicating things and failing to consider a business plan example still remains the most common one.
That’s why we decided to come up with a solution. We’ve curated this list of top business plan examples for students to help you get going.
So whether you need a business plan for a college project, start a side hustle, or win a business competition, these examples are just what you need to create business plans that stand out.
Ready to dive in? Let’s start by understanding the key elements of a business plan example:
Key Elements of a Business Plan Example
Business planning is not as complicated of a process as people think it is; they’re just overcomplicating things. (Don’t think so?)
Let’s simplify the key elements that make up a comprehensive business plan; you’ll understand it better that way.
Executive Summary:
Company overview:, market analysis:, products and services:, sales and marketing strategies:, operations plan:, management team:, financial plan:.
That’s pretty much it about the key elements of a business plan example. Next, let’s explore the best business plan examples for students.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI assistant
Get 30% off for Students and educators

Top Business Plan Examples for Students
Now that you already know about the components of a business plan template, let’s review some of the best business plan examples for students.
1. Startup Business Plan Example
Upmetrics’ startup business plan example is the ideal solution for students planning to start up or participate in a business plan competition. This business plan template follows the SBA-approved business planning format used by thousands of successful entrepreneurs.
Whether your startup is about a new-age AI-based application, an online shopping site, or traditional IT consulting—this sample business plan is just what you need.
Unlike any traditional small business plan, this example of a startup business plan is lean and agile in approach, focuses on innovation, and emphasizes market validation.
2. Lean Business Plan Example
Since you’re transitioning from a student to an entrepreneur, you may not have enough time to spend on creating a detailed business plan. That’s where this lean business plan template can help.
It’s a condensed version of a traditional plan summarizing all its sections with a primary focus on covering only the critical aspects of the business.
This template is best for startups or businesses uncertain about business planning and student-turned-entrepreneurs with limited time and resources to prepare a business plan.
3. SBA Business Plan Example
Following an SBA-recommended business plan format is key to securing bank loans and business grants. Since it can be time-consuming to find a template that follows a similar outline as the SBA, this SBA-approved business plan example is the way to get started.
This SBA business plan template has nine primary sections, that include executive summary, company description, market analysis, organization, product description, marketing, funding request, and financial projections.
SBA business plan examples ensure you stay on track and don’t deviate from your funding needs.
4. One-Page Business Plan Example
As you may have already guessed, a one-page business plan is a one-page version of a traditional business plan. Since it’s a condensed version of a business plan, drafting it can be quite easy and quick compared to a lean or traditional plan.
Employees, partners, and vendors often use one-page business plans as a quick overview of your company and banks and investors as a summary of your operations.
While it may not be the ideal choice for entrepreneurs seeking investment or bank loans, students with side hustles and idea-stage startups can consider this option.
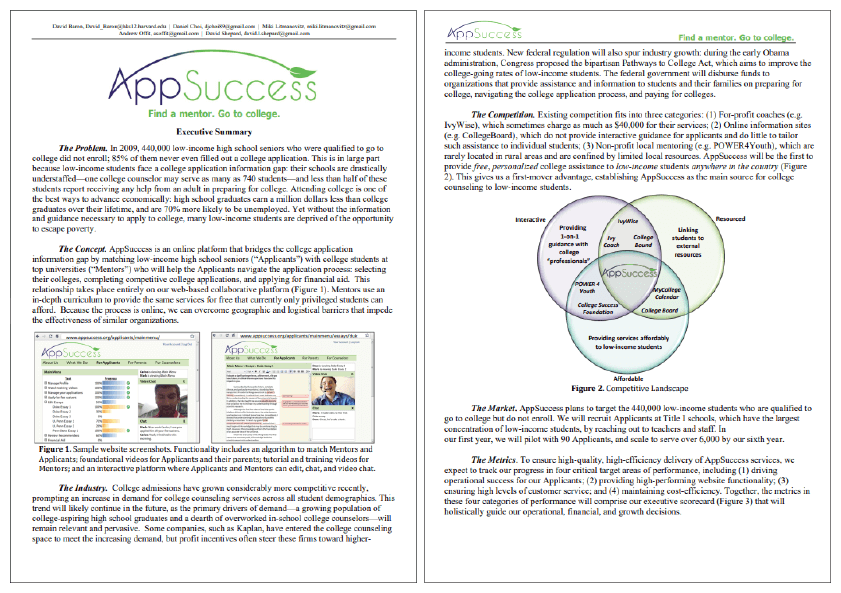
5. HBS Sample Business Plan
Harvard Business School’s new venture competition selected this sample business plan as a finalist in 2011.
This is a business plan of App Success, a collaborative web-based platform that connects low-income high school seniors with college students from top universities; this business will enable them to collaborate on college selection, college applications, and financial aid applications.
This example can be a great reference for those planning to start a mobile or web-based solution.
6. Kean University Sample Business Plan
Kean University organizes a business plan competition every year for its students where students prepare and present business plans to compete, and this is one of the sample business plans the University provides to participants to understand the format.
It’s a business plan of Blue Water Boatworks, Inc., a boat detailing and cleaning company specializing in servicing recreational fiberglass and aluminum watercraft.
This example can be a great reference for those planning to start a business related to housekeeping, cleaning, or maintenance.

7. UVM Sample Business Plan
If you are looking for a strategic business plan for a food business, the University of Vermont’s Fancy Foods Business Plan can be a guiding resource for you.
Despite the fact that it can be a good reference for detailed planning, it was written in 1998, so any statistics and numbers may not seem relevant to today’s market landscape. Make sure you keep that in mind.
You may closely follow this example as a reference if planning to start a food truck, restaurant, or any other business that serves food.
That was the list of best sample business plans for students. However, there’s more to talk about. You now have a business plan example, but what about pitching to investors? Let’s explore free pitch deck examples for students.
Free Pitch Deck Example for Students
Pitching to investors as a first-time founder can be exciting but also overwhelming at times. Worry not; we’ve got a solution—investor pitch templates. We’ve prepared a set of 8 investor pitch templates and examples for students and entrepreneurs to help create winning business pitches.
Whether you need a pitch to find an opportunity, ask for subject matter knowledge, or a problem-solving pitch, these investor pitch examples have got you covered. Download now.
How to write a winning plan for a business plan competition?
Creating a business plan is no different than creating one for a real business. Similar to how entrepreneurs prepare and present business plans to investors, Students in business plan competitions pitch to judges.
In short, the business planning process remains exactly the same. Let’s discuss how you can write a winning plan to help you win a business plan competition.
- Select a compelling business idea : everything starts with a compelling idea. Make sure you have a viable business idea to compete in the competition.
- Refer to winning business plan examples : Once you are sure about your business concept, refer to business plan examples from previous winners and how they planned the sections of their plan.
- Market Research & Industry Analysis : After referring to business plan examples, conduct industry research and market analysis to make your statistical and financial numbers accurate and realistic.
- Understand business model and revenue streams : Since you are preparing a business plan for a company that doesn’t exist, be sure about the business model and how the business will generate profit.
- Use AI business plan generator : Using an AI business plan generator like Upmetrics can be incredibly helpful in speeding up the business planning process. With industry-specific business plan templates and AI assistance to write your plan, you can write the first draft of your plan in literally no time.
- Presentation and visuals : Prepare visuals and graphs to make your business plan visually appealing and numbers digestible. You may not need to prepare these visuals if you use business plan software manually.
- Proofread and edit : Grammatical errors are the last thing judges want to see in a business plan. Make sure you proofread and edit your draft thoroughly before submitting it.
Easy as that, that’s the way to write a perfect business plan that can lead you to victory in any business plan competition on planet Earth. Let’s have a look at a real-life business and financial plan example.

Business and Financial Plan Example for Students
Having learned about business planning for students, let’s quickly discuss a coffee shop sample business plan and financial statements prepared using Upmetrics.
1. Executive Summary
The Cooper’s Cup will be a new cafe in Phoenix, Arizona. The 1,500 square foot café will be located in the newly constructed Market Square Plaza on the northeast corner of 135th Street and Mission Street. The anchor tenant, the Price Chopper grocery store, has already taken occupancy, and the excellent location brings more than 10,000 shoppers weekly.
The Cooper’s Cup, aptly named for the aromatic brown liquid that will fill the cup, fills the void of original cafes in the market and stands out from its corporate peers with its fast food concepts and prompt services. The Cooper’s Cup is the alternative to fast food/commercial/coffee shops and offers a much calmer, civilized gourmet coffee experience.
There are no televisions in the cafe, the background music is subtle, and work from local artists will hang on the walls. The restaurant is well-appointed, with overstuffed leather chairs and sofas in a library-like setting. The cafe is reminiscent of times gone by – yet is cutting edge technologically with WIFI and state-of-the-art espresso machines.
The Cooper’s Cup measures its financial success in terms of increased market share and earnings. This is a tremendous opportunity with a total local market of $54 million! The keys to success will be offering quality gourmet coffees, taking advantage of its small size, and relying on an outstanding barista staff.
To achieve these goals, the cafe will present some of the area’s finest gourmet beans from local distributors. Because of its small size, the restaurant can enjoy larger margins through lower overhead. The cafe will hand-select baristas and offer salaries comparable to the chains. The baristas will be trained to cross-sell and sell higher-margin products.
The primary objectives of the business plan for Cooper’s Cup are below:
- To increase revenues by $36,000 or 5% in Year 2 and $73,000 or 10% by Year 3
- Achieve a profit margin of 5.2% in Year 2 and 6.90% by Year 3
- Be the Cafe of Choice in the Phoenix area and the recipient of the Best Coffeehouse Award.
Guiding Principles
The Cooper’s Cup is committed to values such as excellence, passion, quality, integrity, and leadership, allowing them to navigate challenges and provide for future opportunities. These core beliefs start with their commitment to their products and their employees. Cooper’s Cup rewards excellence and cherishes loyalty. The cafe will work with its employees to build strong businesses and a secure future.
Mission statement
The Cooper’s Cup is committed to its products and employees, which they believe is the recipe for market success.
Key to success
The Cooper’s Cup stands out from the competition. Below are their Keys to Success:
- Great Products : providing exemplary products at market prices – will make customers want to return again and again.
- Hire Quality Baristas : Pay employees rates similar to the larger chains with opportunities for long-term careers and opportunities for advancement with long-term plans to open a second facility.
- Convert Customers to Connoisseurs : Only 40% of the nation’s coffee drinkers consume premium ground and whole bean coffee – this will aid in the continued growth.

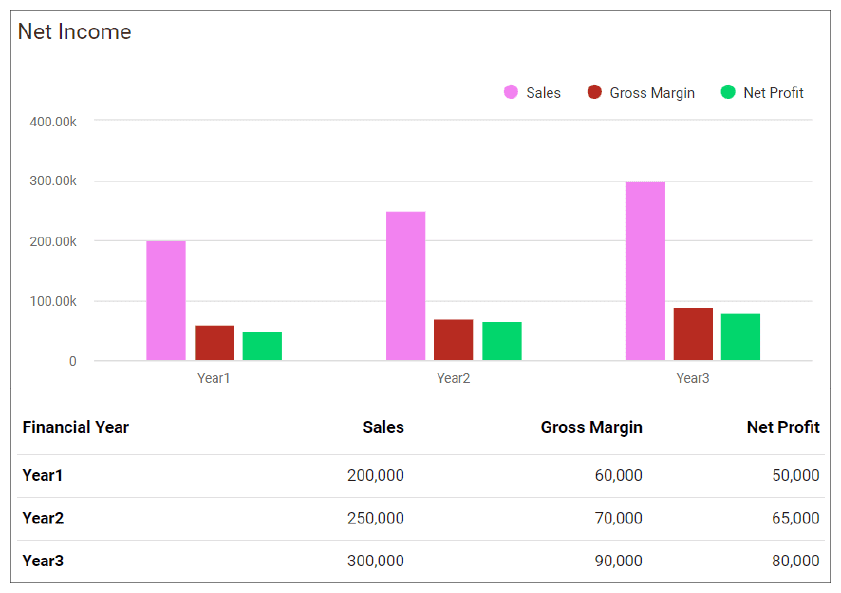
Financial Summary
2. Business Overview
The Cooper’s Cup will be a coffee house/cafe located in Phoenix, Arizona. The cozy cafe will be located in the newly completed Market Square Plaza in the Arizona City area. The cafe will serve gourmet coffee, espresso, drip coffee, lattes, and smoothies. The simple pastry offerings may vary with seasonality, but the primary line will be muffins, bread, cookies, scones, and rolls. All pastries will be supplied daily by a local bakery.
The cafe will be owned and operated by Owen Jones, a veteran restaurateur with several years of experience running and managing chain restaurants. The cafe will be open for business Monday – Thursday 7-10, Fridays and Saturdays, 7-11, and closed Sundays.
The Cooper’s Cup will be formed as an S-Corporation owned by Mr. Doe.
Start-Up Summary
The Cooper’s Cup will have seating for 40 patrons. The rent is $2,075 a month, with a three-five-year lease available. The site comprises 1500 square feet of leased space consisting of a dining room, a coffee bar, two restrooms, and a storage room in the back.
This storefront needs to be plumbed and wired appropriately to be used as a restaurant. Painting, new floors, and countertops are also needed. A custom coffee bar needs to be built. With materials bought on sale and volunteer labor, the cost to renovate will be $71,725.
The coffeehouse equipment will consist of two commercial espresso machines, air pots and urns, a commercial blender, a commercial brewer, top-loading coffee bins, barista syrups, cold drink dispenser, frothing equipment, a commercial refrigerator, microwave, and stainless steel prep bar.
The cost of the equipment is $38,275. The furniture will consist of leather couches and chairs (purchased at auction), coffee tables, bookcases, and window treatments. The artwork will come from local artists and be sold on a consignment basis. The books were secured via donations. The total cost to furnish is $14,000. Other startup expenses will be dishes, furniture, rent deposit, and marketing.
Location and Facilities

The new coffeehouse is located in the highly desirable Phoenix, Arizona, area at the northeastern intersection of 135th Street and Mission Street in the Newmarket Square Plaza. The property is situated in an excellent location, with an easy 6-minute drive time to I-435 and 69 Highway.
The property is 95% leased with Price Chopper as the Anchor Tenant. Other tenants include LifeSpring Med Spa, Jane’s Canines (Pet Store & Boarding), Pride Cleaners Kahn Dental, and Swim U.
Price Chopper brings more than 10,000 shoppers per week to the center. The location comprises a population of 9,420 within a one-mile radius, 61,102 within a 2-mile radius, and 149,550 within a 5-mile radius – with a median household income of $120,856. Sprint / Nextel’s corporate office is within 2 miles of the site.
3. Market Analysis
Phoenix, Arizona, is an award-winning place to live and work and is considered the leading business community in the Midwest. National publications and organizations recognize Phoenix for its business environment and livability. Here’s a sampling: 6th Place, America’s Best Places to Live Money, Top 50 Cities to Live and Play, National Geographic Adventure, 3rd Hottest Town in the U.S., Money, Among 20 Best Places to Live & Work Employment Review, One of only 72 Sterling Tree Cities in the U.S., National Arbor Day Foundation, Top 10 best Locations to Raise a Family, Southern Business and Development, 1st Place, Kid Friendly Report Card, Population Connection, 2nd Best City in America to Live Business Development Outlook.
Phoenix is at the core of one of the most dynamic local markets in the U.S. It offers easy access to the Arizona City region’s amenities, and, as part of the Arizona City metropolitan area, it is within the most centrally located major market in the nation. I-35, I-435, I-635, and U.S. Highway 69 all pass through Phoenix, and no point in the city is more than 3.5 miles from a freeway. The city maintains an excellent arterial street network and plans to construct additional lane-miles as the area grows. Three airports serve the region. Arizona City International Airport (MCI) is just 25 interstate highway miles north of Phoenix. Johnson County Executive Airport—the second busiest in Arizona—provides complete services for private business jets and general aviation. New Century AirCenter, just 12 miles southwest of the city, offers available aviation services and accommodates cargo or passenger jets of any size.
Phoenix supplies some of the most highly educated workers in the nation, with 97% of Phoenix adults over age 25 holding at least a high school diploma. Johnson County, where Phoenix is located, ranks first among the country’s 231 counties with populations greater than 250,000. The county ranks sixth in the percentage of adults with at least a bachelor’s degree and 16th with a graduate or professional degree.
The Phoenix area has a population of 175,265, based on the 2010 census. The median household income is $77,881, and the median age is 37.9. (2010 U.S. Census)
Industry Analysis
The U.S. coffee shop industry includes about 20,000 stores with a combined annual revenue of about $10 billion. Major companies include Caribou Coffee, International Coffee & Tea (The Coffee Bean & Tea Leaf), Peet’s Coffee, and Starbucks. The industry is concentrated: the top 50 companies generate more than 70 percent of sales. Coffee shops are part of the specialty eatery industry, including retail outlets specializing in bagels, donuts, frozen yogurt, and ice cream products. (First Research)
Competitive Landscape
Consumer taste and personal income drive demand. The profitability of individual companies depends on the ability to secure prime locations, drive store traffic, and deliver high-quality products. Large companies have advantages in purchasing, finance, and marketing. Small companies can compete effectively by offering specialized products, serving a local market, or providing superior customer service. Specialty eateries, which include coffee shops, are labor-intensive: average annual revenue per worker is about $50,000. Coffee shops compete with convenience stores, gas stations, quick service, fast food restaurants, gourmet food shops, and donut shops. (First Research)
Market Size
The U.S. coffee shop industry includes about 20,000 stores with a combined annual revenue of about $10 billion. Major companies include Caribou Coffee, International Coffee & Tea (The Coffee Bean & Tea Leaf), Pet’s Coffee, and Starbucks. The industry is concentrated: the top 50 companies generate more than 70 percent of sales. (First Research)
Target Market and Segment Strategy
Most adult coffee drinkers said their lifelong habits began during their teenage years. 54% said they began drinking coffee between 13 and 19. Another 22% reported their coffee cravings started between 20 and 24. This means that 76% of adult coffee drinkers began drinking coffee by the time they were 24. So, despite a large amount of marketing and advertising directed at the younger age groups, savvy coffee shop owners will remember to cater some of their offerings to the adult and senior market. (National Coffee Drinking Study).
The Cooper’s Cup will offer a unique experience for coffee enthusiasts by providing a quiet, cozy, yet sophisticated cafe and a sense of refinement and peace in an otherwise hectic and fast-paced world. While other coffee shops cater to convenience with drive-throughs or loud music venues late into the night, the Cooper’s Cup will stand apart from its competitors with its quiet yet soothing ambiance, capturing a truly unique (and much-needed) market niche.
- Unique products (specialized roasts, local ingredients, locally-themed or named drinks, custom drinks by the star barista, etc.)
- Games, puzzles, mind benders, and other activities that encourage customers to linger over their coffee
- Hosting or sponsoring local events (entertainment, readings, book clubs, etc.)
- Using technology to creatively compete in marketing with big chains — services like FourSquare, Yelp, and Google Places can increase visibility in the local market.
- Delivering amazing service from knowledgeable baristas — spend lots of time training staff and utilizing online services like the American Coffee & Barista School.
- Selling coffee-related items (and tracking down any co-marketing opportunities with a local community college or another student-related group in the area)
4. Products and Services
Product/services descriptions.
The Cooper’s Cup’s primary offering is gourmet roasted coffees with mocha, carmelicious, white mocha, candy bar latte, and brewed coffee. Complementing the coffee will be a smoothie line including wild berry, strawberry, peach, mango, and lemonade. Rounding out the simple menu line will be pastries obtained from an outside supplier, freshly made and delivered daily. The pastry offerings may vary with seasonality, but the primary line will be muffins, bread, cookies, scones, and rolls.

Product/Service Sourcing
The Cooper’s Cup has negotiated supplier agreements with several local food-service wholesalers and coffee wholesalers in the Phoenix area that have a reputation for quality and reliability:
- Mean Beans Coffee Roasters
- Phoenix Brewers
- Healthy Harvest Bread Co.
- Mary’s Organics
If one of the abovementioned specialty suppliers cannot meet their needs, the following national suppliers can provide all the food-service products they require. In addition, the following wholesalers will supply the cafe with general restaurant supplies:
- Lawrence Food Products Corp.
- Gerry Food Supply Inc.
Future Products/Services
Young families, which comprise Phoenix’s third largest market share, are often overlooked in the coffee market. Coffeehouses traditionally have not been considered ‘kid’ friendly. To overcome this hurdle, Cooper’s Cup has long-term plans (5 years) to open a 2nd coffee shop: A combination indoor play area/coffee bar. This concept allows parents and caregivers to meet and relax with other adults while the children can enjoy the indoor playground amenities.
Additional future services will include in-store sales for home purchases and an online store.
The website will have the option to purchase a prepaid gift card program – Prepaid gift cards provide immediate cash, reduce credit card transaction charges, and draw new customers to the business.
5. Sales and Marketing Strategies
Swot analysis.
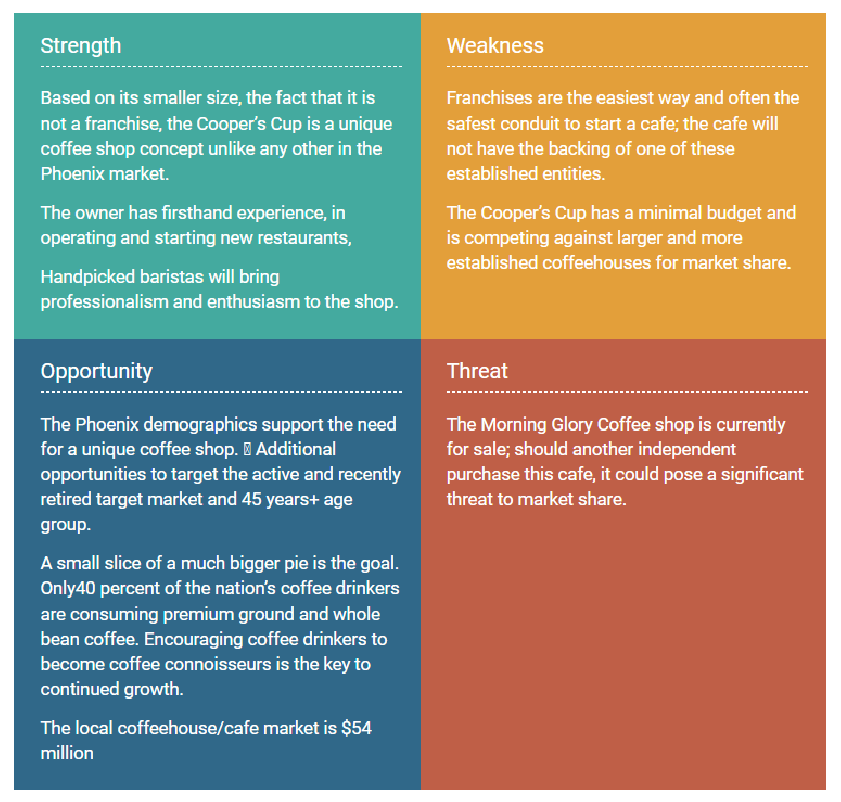
Unique Selling Proposition
The Cooper’s Cup stands out from a crowded sea of coffee chains and franchises. What sets it apart from the competition is primarily its smaller, cozier size combined with premium coffees served by knowledgeable baristas, providing so much energy and enthusiasm for its products.
Market Strategy and Positioning
The Cooper’s Cup utilizes a focus strategy on its Market. By specifically targeting three primary segments, they can cater specifically to their needs.
Senior Market (age 45+)
The Cooper’s Cup will target this Market simply by its well-selected location. Although this demographic group could readily drive downtown, they prefer a local cafe to unwind and relax and historically become some of the most loyal patrons.
Newly Hired Employees
The cafe will attract regular customers (weekly or more) – particularly the newly employed (first job) by providing free WIFI services and providing interesting games in the customer area.
Young Families
The third targeted Market, younger families, often find that coffeehouse is not ‘kid’ friendly. The company has long-term plans to create a combination coffee shop/play area so that parents and caregivers can meet with other adults while the children can enjoy the bounce houses, slides, and indoor playground equipment.
Pricing Strategy
The Cooper’s Cup primarily utilizes competition-based pricing. The cafe does not utilize coupons and discounts (other than opening promotions) because they believe that the most valuable customer demographic of daily coffee consumers is not influenced by discount programs or coupons.
Promotion and Advertising Strategy
- Online Advertising – The Cooper’s Cup will advertise regularly on popular social media sites like Facebook. Compared to traditional print advertising, this is a cost-effective tactic that will allow them to reach prospects in a highly targeted way (e.g., based on criteria such as age, gender, geography, etc.).
- Website – Cooper’s Cup will develop a simple Web site, which will provide basic information about the business, the menu, and links to their presence on the aforementioned social media channels.
- Radio Advertising – During the first six months of operation and the busy holiday shopping season, the business will advertise on local radio stations.
Sales Strategy
The Cooper’s Cup will use the following methods to increase sales revenue (as recommended by Andrew Hetzel on Better Coffee, Better Business):
- The menu will focus on the most profitable products sold. The cafe will always draw customer attention to the best products.
- As warranted, the cafe will raise prices to bolster its brand image. Prices communicate the perceived value of a product, so if set too low, the customers might assume that the beverages are inferior compared to the competition.
- Monitor flavoring inventory – Excess flavoring inventory ties up capital and valuable backroom space for storage. The cafe will utilize 4-6 varieties, including sugar-free offerings.
- Control waste and theft – audit sales and inventory reports to evaluate ingredient waste due to inefficient preparation, returned drinks, and employee consumption. Retail locations can easily waste 20% or more of their daily sales in these three key categories, which is a substantial and unnecessary loss.
- Monitor and evaluate hours of operation.
- Run employee sales contests – The baristas are the salespeople and have great influence over the customer ordering process. All baristas will have some form of sales and customer service training to make each transaction active rather than passive. Sales contests will emphasize high-margin items or cross-selling.
6. Operations Plan
Staffing and training.
An ongoing training and education program will ensure that each staff member learns and implements Cooper’s Cup’s exacting service and operational procedures standards. Staff meetings will reinforce service standards and principles. The Cafe will have detailed work descriptions and training programs for each position, from entry-level employees to the ongoing development of managers and owners. New employees will undergo an extensive training program. This ensures that each guest receives a quality experience from all employees, regardless of how long they have been employed. The Cafe embraces the concept of promoting from within. Excellence in one function typically leads to excellence in another. Regular staff evaluations and training will ensure motivation and address critical issues.
Inventory controls
The founder will be responsible for hiring and training managers who, in turn, will ensure that the day-to-day operations will comply with the standards set by Restaurant policy. Weekly management meetings will provide a forum to review and discuss financial and operational performance. Critical decisions related to purchasing, human resources, marketing, capital expenditures, and customer service will also be addressed.
Purchasing cost controls
Food preparation personnel will follow standardized recipes developed by the founders to control food costs and ensure consistency. The coffee shop will offer an innovative menu with nutritious food and beverages while achieving the most significant margin yield.
Customer Service
The hospitality business recognizes the client’s support experience is the critical driver to replicate business. The direction will Offer a superior degree of Professionalism by hiring individuals who deliver the ideal attitude to work and teaching them the skills required to accommodate guests. The restaurant will keep high levels of consumer satisfaction with talented, educated, and well-trained workers who understand and implement the fundamentals of fantastic service. Ongoing training will be provided to enable staff to perform their jobs with confidence and ability. Employees are well-spoken, well-versed, and trained to provide friendly, prompt, and professional service to each customer. This practice teaches employees who, by producing an exceptional customer experience, can optimize sales and raise their reimbursement. The team will have the knowledge and service required to create excellent daily service for every customer.
Technology & Software
While the quality of the cuisine and dining experience contributes significantly to a restaurant’s profitability, attention to business and financial details can transform small changes into significant returns. Critical sales, cost of sales, labor, inventory, marketing, and overhead metrics are monitored daily. Trends are evaluated, and constructive actions will be taken where improvement is needed. The management team will have access to the restaurant’s transactions and reports available in its real-time POS (point of sale) and accounting systems. Trends will be evaluated, and corrective action will be implemented as required.
7. Organization Structure
The Cooper’s Cup is formed as an S-Corporation wholly owned by John Doe.
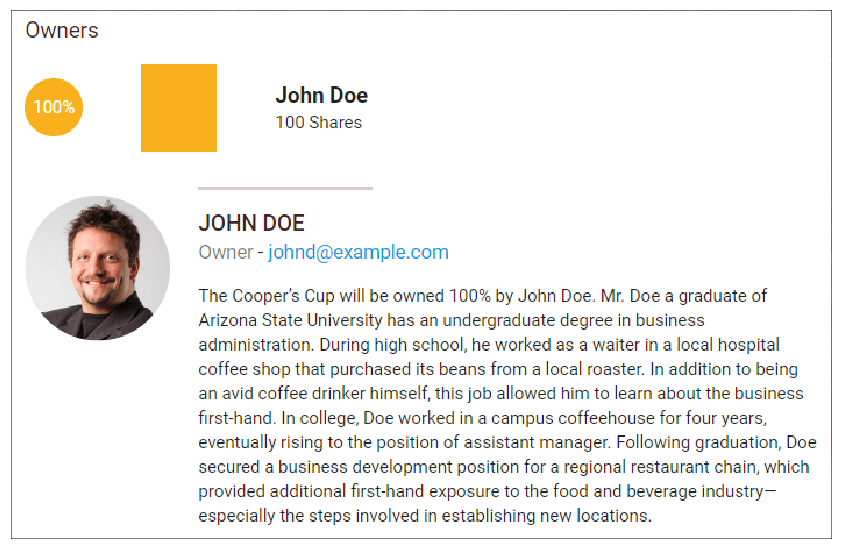
Management Team
The Cooper’s Cup will be owned 100% by John Doe. Mr. Doe, a graduate of Arizona State University, has an undergraduate degree in business administration. During high school, he worked as a waiter in a local hospital coffee shop that purchased its beans from a local roaster. In addition to being an avid coffee drinker, this job allowed him to learn about the business first-hand. In college, Doe worked in a campus coffeehouse for four years, eventually becoming an assistant manager. Following graduation, Doe secured a business development position for a regional restaurant chain, which provided additional first-hand exposure to the food and beverage industry—especially the steps involved in establishing new locations.
Management Team Gaps
The Cooper’s Cup will rely on its POS (Point of Sale) system to generate daily accounting and cost activity reports. Mr. Doe will supply these to an outside bookkeeper for the preparation of annual income taxes.
Personnel Plan
Initially, the cafe will hire 1 manager, 5 baristas, and 2 part-time servers. In Year 2, the cafe plans to hire 1 additional full-time barista.
8. Financial Plan
Important assumptions.
- The sales forecast is conservative and assumes a 5% increase in Year 2 and a 10% in Year 3.
- The analysis accounts for economic seasonality – wherein some month’s revenues peak (such as holidays ) and wane in slower months.
- The analysis assumes the owner will not withdraw any salary till the 3rd year; at any time it is assumed that the owner’s withdrawal is available at his discretion.
- Sales are cash basis – nonaccrual accounting
- Moderate ramp-up in staff over the 5 years forecast
- Barista’s salary in the forecast is $36,000 in 2023.
- In general, most cafes have an 85% gross profit margin
- In general, most cafes have a 3% net profit margin
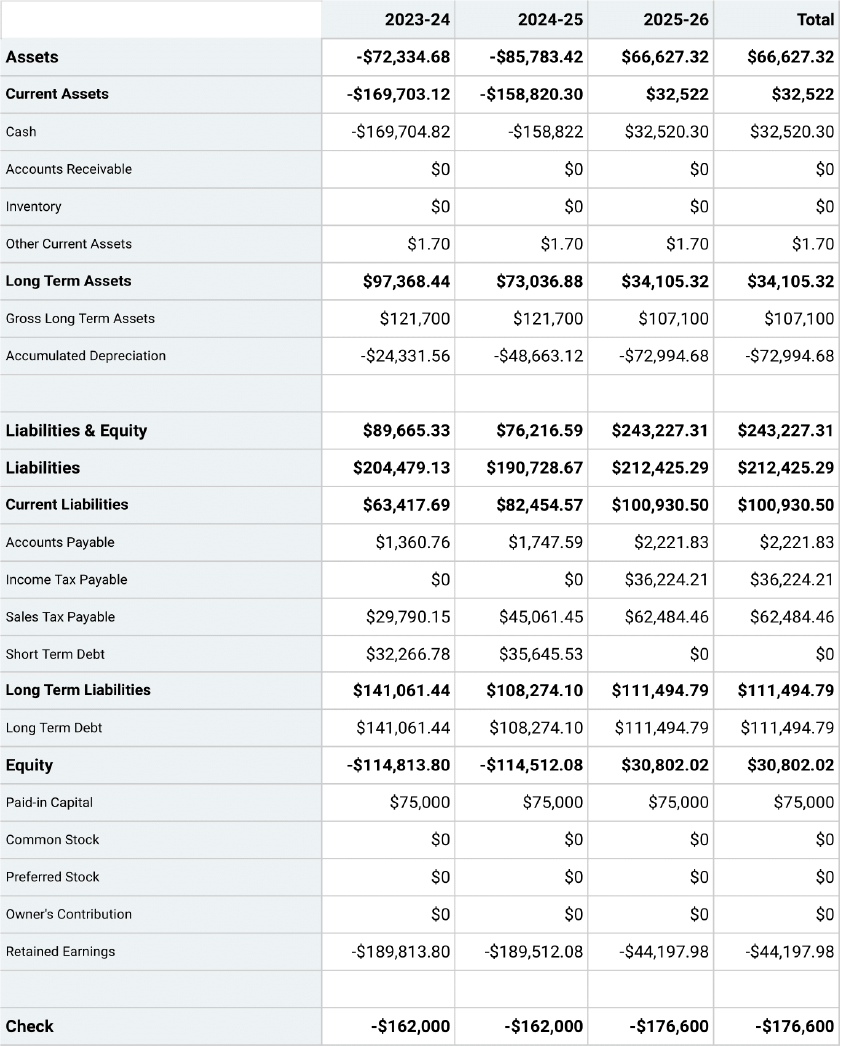
Projected Balance Sheet
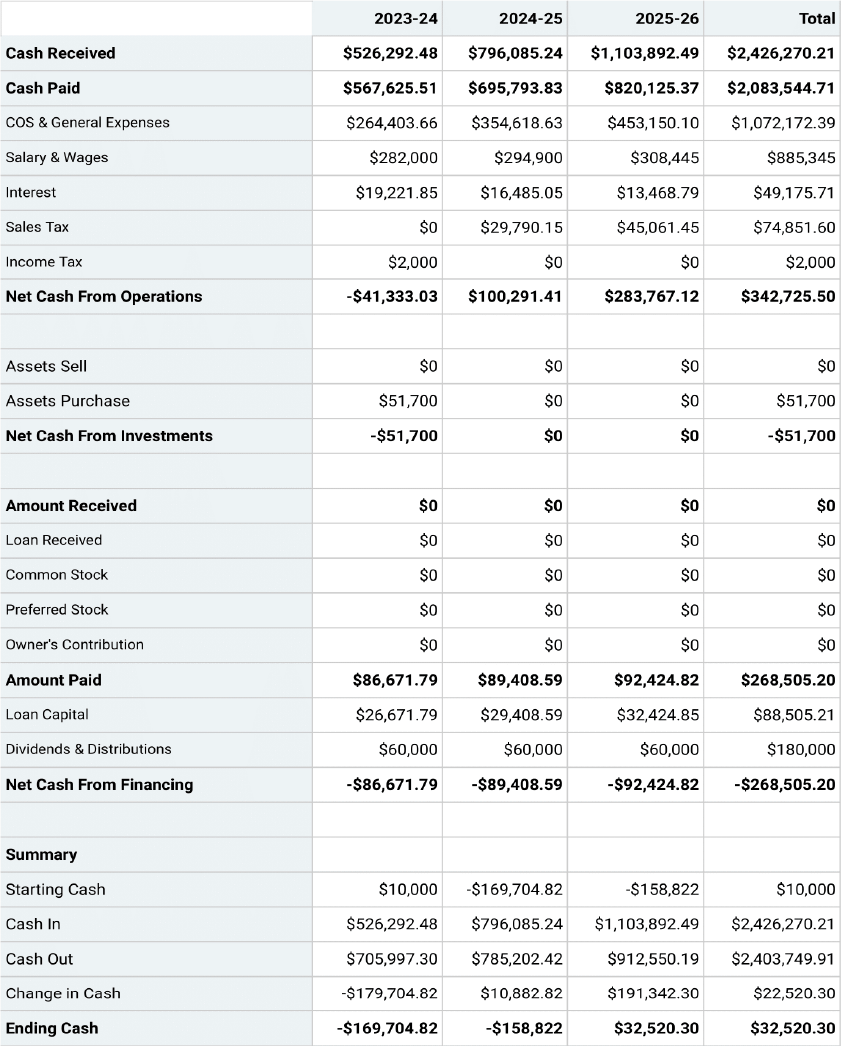
Projected Cash-Flow Statement
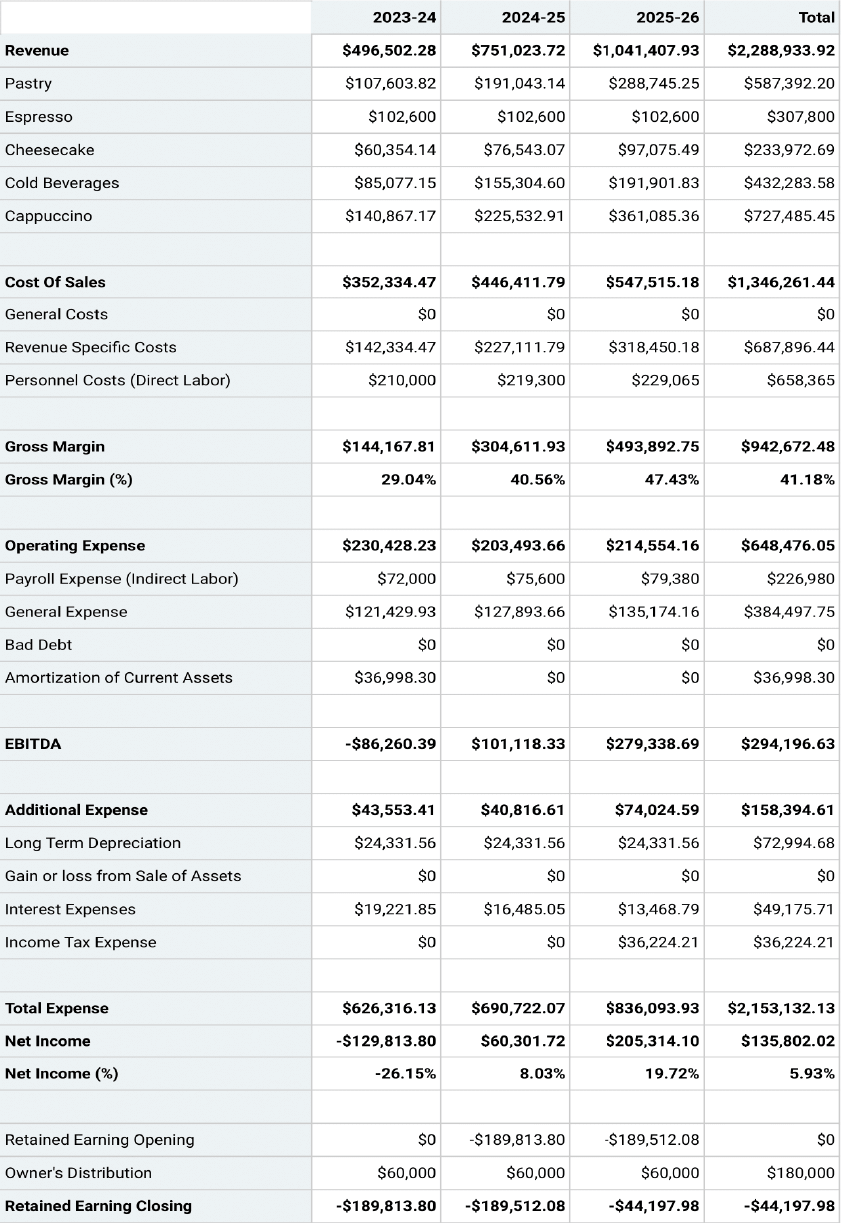
Projected Profit & Loss Statement
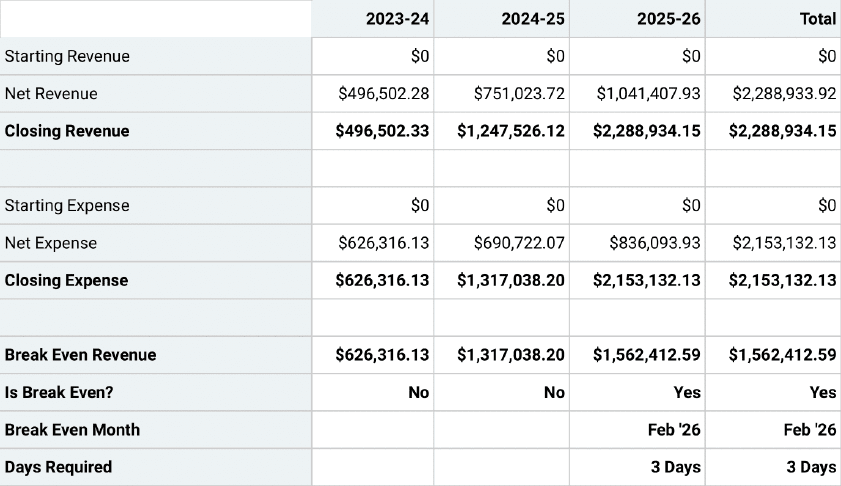
Break Even Analysis
Write Your Business Plan With Upmetrics
Whether you need a business plan to compete in a competition, win investors, or gain a competitive advantage in the market landscape, Upmetrics can help you get started.
Upmetrics is an AI business plan software that comes with AI assistance, financial forecasting features, and 400+ sample business plans so that you can prepare a business plan in no time.
So what are you waiting for? Try Upmetrics and create your business plan in a snap.
Make your plan in half the time & twice the impact with Upmetrics
Fill-in-the-blanks, AI-assistance, and automatic financials make it easy.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you write a business plan for a college project.
As mentioned earlier in the article, business planning for a college project or competition is no different than for a real business. You can write your business plan using these step-by-step instructions.
- Select a compelling business idea
- Refer to business plan examples
- Prepare a business plan outline
- Create a company description section
- Conduct market research and industry analysis
- Describe your product and services
- Outline sales and marketing strategies
- Create an operations plan
- Introduce management team
- Prepare financial projections
- Summarize your plan with an executive summary
What is a business plan for students?
A business plan is a necessary business document that highlights its purpose, business goals, product/service offerings, go-to marketing strategies, operations and financial plan, key people involved in the business operations, and other necessary details.
As a student, consider a business plan example as a document that helps you better understand business and industry dynamics and learn how a business operates inside out.
What is a business plan competition for students?
Business plan competitions are competitions mostly organized by universities for students passionate about entrepreneurship and the business world. These competitions offer students a platform to showcase their entrepreneurial skills while also providing opportunities for mentorship and networking.
How can I increase my chances of winning a business plan competition?
There cannot be a straightforward answer to this question, but there’s surely a method that can increase your chances of winning a competition—Using AI-powered business plan software.
Why? An AI tool will make you 10X more productive while writing a business plan and preparing financial forecasts. So you can spend more time researching the market and brainstorming business ideas.
Where can I find more business plan examples for students?
Upmetrics’ library of 400+ business plan examples could be an incredible source for students to find more industry-specific business plan examples. There are examples for almost every small business category, including real estate, retail, entertainment and media, food & beverages, and more.
About the Author

Ajay is a SaaS writer and personal finance blogger who has been active in the space for over three years, writing about startups, business planning, budgeting, credit cards, and other topics related to personal finance. If not writing, he’s probably having a power nap. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Chapter 1 - Developing a Business Plan. Chapter 2 - Essential Initial Research. Chapter 3 - Business Models. Chapter 4 - Initial Business Plan Draft. Chapter 5 - Making the Business Plan Realistic. Chapter 6 - Making the Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur. Chapter 7 - Finishing the Business Plan.
www.cambridge.org. Cambridge University Press 978-1-107-64068-9 - Business Plus: Preparing for the Workplace: Student's Book 1 Margaret Helliwell Excerpt More information. 2 Grammar focus The ...
978-1-107-63764-1 — Business Plus Level 2 Student's Book Margaret Helliwell Frontmatter More Information ... Plan of the book. Cambridge University Press 978-1-107-63764-1 — Business Plus Level 2 Student's Book Margaret Helliwell Frontmatter More Information
Suggest an edit to this book record. Fundamentals of Business, 4th Edition is an open education resource intended to serve as a no-cost, faculty-customizable primary text for one-semester undergraduate introductory business courses. It covers the following topics in business: Teamwork; economics; ethics; entrepreneurship; business ownership ...
BUSINESS PLAN FOR ENGLISH LANGUAGE PLUS EL+ BOUTOUATOU MOHAMED LAMINE Hay Ennasr R12, Oujda, Maroc. ... published 2014 Reprinted 2015 Printed in Singapore by C.O.S. Printers Pte Ltd 1sBN 1sBN 978-1-107-64068-9 paperback Student's Book 1 978-1-107-66880-5 paperback Teacher's Manual 1 Additional resources for this publication at www.cambridge.org ...
978-1-107-63764-1 - Business Plus Level 2 Margaret Helliwell Frontmatter ... ISBN 978-1-107-63764-1 paperback Student's Book 2 ... Plan of the book. Cambridge University Press 978-1-107-63764-1 - Business Plus Level 2 Margaret Helliwell Frontmatter More information
Start with a cogent and concise one sentence statement of the business idea. A sentence that is so clear and appealing that the reader can immediately visualise or 'see' the business. You can then go on to describe: The market at which you are aiming. The specific benefits offered by your product or service.
Readers. Secondary. Skills. Teacher Training, Development and Research. TOEFL & TOEIC. Young Learners. Business Plus Level 1 | Business Plus is a three-level, integrated-skills, business English course, from A1 (false beginner) to B1 (pre-intermediate) levels. | Margaret Helliwell.
Lesson Plan (1) Practice Test (15) Professional Development (2) ... (Business Plus Level 2 Student's Book) Audio, 59mb. Download. 3 Classroom Audio (Business Plus Level 3 Student's Book) Audio, 67mb. ... The business cycle PDF, 346kb. Download. Book With Answers And CD ROM Sample Content (Business Vocabulary in Use: Intermediate 2nd Edition ...
By: HBS Press, Harvard Business School Press. Every entrepreneur is encouraged to write a business plan; those who don't quickly learn that future operations can be derailed without a cohesive printed mission and that obtaining outside funding…. Length: 43 page (s) Publication Date: Oct 30, 2004. Discipline: Entrepreneurship.
We are again using Successful Business Plan in my business honors course this semester. Must be working, as Penn State was just named (by Kaplan and Newsweek magazine) as the 'hottest school in the U.S. for student entre-preneurs!' " — Greg Pierce, Penn State University " Successful Business Plan enables my Entrepreneurship students ...
As the road map for a business's development, the business plan. Defines the vision for the company. Establishes the company's strategy. Describes how the strategy will be implemented. Provides a framework for analysis of key issues. Provides a plan for the development of the business. Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical ...
Cambridge University Press 978-1-107-66187-5 — Business Plus Level 3 Student's Book Margaret Helliwell Excerpt More Information. E. Match the comments 1 to 5 with the responses A to E. A Yes ...
Business Plus 1 - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The book aims to help learners deal with business English and TOEIC exam
Business Plan Plus è un corso di inglese commerciale che affianca i contenuti classici della materia ai grandi temi dell'era digitale e globale. I materiali autentici e motivanti, l'apparato audio e video d'eccellenza, la presenza sistematica di attività propedeutiche all' alternanza scuola-lavoro e all'attivazione delle 21st-century skills consentono agli studenti di lavorare in modo ...
Business Plus is a three-level, integrated-skills, business English course, from A1 (false beginner) to B1 (pre-intermediate) levels. Each level of the Student's Book has 10 units. Designed to be easy and enjoyable to teach, each unit features integrated skills and language practice. Units also include cultural awareness sections that connect learners to their region and beyond.
The primary objectives of the business plan for Cooper's Cup are below: To increase revenues by $36,000 or 5% in Year 2 and $73,000 or 10% by Year 3. Achieve a profit margin of 5.2% in Year 2 and 6.90% by Year 3. Be the Cafe of Choice in the Phoenix area and the recipient of the Best Coffeehouse Award.
Your business plan should be much more specific and extensive and should present your ideals, perceptions and goals. Note: Your first attempt to put together a business plan will probably not be the last. There are over 50 examples of sample business plans at www.sba.gov. PART 1 - BUSINESS PLAN NARRATIVE THE COVER
Business Plus is a three-level, integrated-skills, business English course, from A1 (false beginner) to B1 (pre-intermediate) levels. Each level of the Student's Book has 10 units. Designed to be easy and enjoyable to teach, each unit features integrated skills and language practice. Units also include cultural awareness sections that connect learners to their region and beyond.
Digital Resources: Depending on the product offering resources could include an app, audio program, video, and additional student resources. Digital Digital products are sent to customers via email. These could be Access Codes or links to digital materials. eBook: Digital version of the book that students can access online or via a mobile device.
The Coursebook contains: Eight units with five lessons each Eight case study business workshop lessons relating to each of the eight units A review each unit revises key language and grammar Pronunciation practice for each unit Detailed grammar reference Video and audio scripts A glossary of key business vocabulary The coursebook video and audio material is available online at english.com ...
Business Plus is a three-level, integrated-skills, business English course, from A1 (false beginner) to B1 (pre-intermediate) levels. The Level 1 Teacher's Manual contains a general introduction, full unit-by-unit summaries, language notes and tips, and a complete answer key.