CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free

Class 11 Business Studies Assignments
We have provided below free printable Class 11 Business Studies Assignments for Download in PDF. The Assignments have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 11 Business Studies . These Assignments for Grade 11 Business Studies cover all important topics which can come in your standard 11 tests and examinations. Free printable Assignments for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies , school and class assignments, and practice test papers have been designed by our highly experienced class 11 faculty. You can free download CBSE NCERT printable Assignments for Business Studies Class 11 with solutions and answers. All Assignments and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Business Studies Class 11. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf Assignments for Business Studies class 11 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 11 Business Studies Assignments with Answers and test papers are given below.
Business Studies Class 11 Assignments Pdf Download
We have provided below the biggest collection of free CBSE NCERT KVS Assignments for Class 11 Business Studies . Students and teachers can download and save all free Business Studies assignments in Pdf for grade 11th. Our expert faculty have covered Class 11 important questions and answers for Business Studies as per the latest syllabus for the current academic year. All test papers and question banks for Class 11 Business Studies and CBSE Assignments for Business Studies Class 11 will be really helpful for standard 11th students to prepare for the class tests and school examinations. Class 11th students can easily free download in Pdf all printable practice worksheets given below.
Topicwise Assignments for Class 11 Business Studies Download in Pdf

Advantages of Class 11 Business Studies Assignments
- As we have the best and largest collection of Business Studies assignments for Grade 11, you will be able to easily get full list of solved important questions which can come in your examinations.
- Students will be able to go through all important and critical topics given in your CBSE Business Studies textbooks for Class 11 .
- All Business Studies assignments for Class 11 have been designed with answers. Students should solve them yourself and then compare with the solutions provided by us.
- Class 11 Students studying in per CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools will be able to free download all Business Studies chapter wise worksheets and assignments for free in Pdf
- Class 11 Business Studies question bank will help to improve subject understanding which will help to get better rank in exams
Frequently Asked Questions by Class 11 Business Studies students
At https://www.cbsencertsolutions.com, we have provided the biggest database of free assignments for Business Studies Class 11 which you can download in Pdf
We provide here Standard 11 Business Studies chapter-wise assignments which can be easily downloaded in Pdf format for free.
You can click on the links above and get assignments for Business Studies in Grade 11, all topic-wise question banks with solutions have been provided here. You can click on the links to download in Pdf.
We have provided here topic-wise Business Studies Grade 11 question banks, revision notes and questions for all difficult topics, and other study material.
We have provided the best collection of question bank and practice tests for Class 11 for all subjects. You can download them all and use them offline without the internet.
Related Posts

Class 11 Commercial Arts Assignments

Class 11 Biology Assignments

Class 11 Mathematics Straight Lines Assignments
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Business Services Class 11 Notes CBSE Business Studies Chapter 4 (Free PDF Download)
Revision Notes

Revision Notes for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 - Free PDF Download
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 - Business Services are given in this study in the form of a free-to-download pdf version.
Business Studies is quite a broad topic and the Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Notes by Vedantu will help you to develop a precise understanding of what the chapter entails. In Chapter 4 Business Studies Notes in PDF format, students will find a comprehensive outline of notes of the chapter with solved exercises in the back to help them with understanding the chapter better. These Business Studies Chapter 4 revision notes and exercises which can be completely downloaded will help students develop a thorough understanding of the subject.
Download CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 11 Business Studies revision notes for All chapters:
Access Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 - Business Services Notes in 30 Minutes
Following are the benefits of the revision notes that the students of CBSE Class 11 can gain advantages from:
Students can revise from this revision material in a capsulated manner this will help them to revise the chapter in a short duration.
Revision from this study material will promote the smart study of the students.
Revision is a key study for every student, thus our ready-to-revise revision material will help the students to revise without making self-notes.
The revision material is prepared by our expert teachers thus this makes the revision notes reliable for the students of Class 11 to revise.
Revision before the exam now becomes even more convenient with the help of our revision material. You just have to download the revision pdf and save it for later use.
Business Services Class 11 Notes CBSE Business Studies Chapter 4 - Topics Covered
Take note of the following concepts which are covered in this chapter:
Service sector
Nature of sectors
Classification or Types of services
Various categories of business services
Functions of Commercial banks
Types of Insurance
Communication services
Postal services
Telecom services
Transportation
Warehousing services
Business Services Class 11 Notes CBSE Business Studies Chapter 4 - Key Takeaways
Here in this Chapter 4 Business Studies Notes PDF by Vedantu, students will learn about goods and services, types of services, and the differences between goods and services. The chapter also talks about banks and the different types of banks that are present. Also included is the modern interpretation of the banking system, which is E-Banking and its various advantages over the traditional method.
The Business Studies Chapter 4 Notes also covers the topic of Insurance and the Principles of Insurance along with Insurance and its various types. The Class 11 Chapter 4 Business Studies Notes also elaborate about the various other aspects of a business such as communication, transportation and warehousing. Towards the end of the chapter, the differences between the types of insurance are covered and then there practice questions that students can attempt.
Goods and Services
A good is a product that is tangible and involves the transfer of ownership from one person to another. A service, on the other hand, is essentially an intangible service that can provide the satisfaction of wants and usually takes place after the transaction is over. The nature of services are as follows:
This is experimental in nature and therefore, cannot be touched. The quality of service cannot be predicted before its consumption.
Inconsistency
The difference between a good and service is that a service is catered differently according to the customer's demands and expectations. So each customer experiences a different service every time.
Inseparability
The production and consumption of the service must not be different, but it should happen simultaneously. Services have to be consumed as soon as they are produced.
Unlike goods, services cannot be stored and must be consumed immediately after production.
Involvement
This is one of the best characteristics of services where customers have to be present for most of the production of the service to make sure it meets their standards and they can change it according to their will.
Banking Company and its Types
A banking company in India means it uses its company to transact money and help with the withdrawal and lending of money to people and also allows them to deposit money for investment or for its safekeeping.
The types of banks are:
Commercial Banks: These banks are governed by the Indian Regulation Act of 1949, and according to it, banking is the accepting of money from the public for lending and investment.
Cooperative Banks: These are the banks that are governed by the provisions of the State Cooperative Societies Act. In this banking system, cheap credit is provided to the members and therefore serves better for its members in the long run.
Specialised Banks: These banks are Foreign Exchange Banks that help cater to the various needs of Industrial Banks, Developmental Banks and Export-Import Banks. These banks provide financial aid to these industries, massive projects and foreign trade.
Central Bank: This bank supervises all the commercial banks in the country.
Business Services Class 11 Notes CBSE Business Studies Chapter 4 - Extra Questions to Practice (Solved)
1. Name three types of insurance.
Ans.
Three types of insurance are:
Life Insurance
Fire Insurance
Marine Insurance
2. How would you define service and goods?
Ans. Services are referred to as any intangible activity that involves interaction between the service provider and consumer. Purchasing the service does not result in ownership of any physical item.
Goods refer to objects that are tangible and have a physical appearance. The ownership of a good is transferred as soon as it is purchased.
3. What are the advantages of E-Banking?
It ensures the round-the-clock availability of most banking services which helps make life comfortable for the customers.
Banking transactions can be conducted anytime either through mobile or computer/laptop.
It reduces the load on banks by facilitating transactions online.
Tips to Study Business Studies Better
Following are the tips which will help the students to study business studies in a better way:
Students are required to understand the chapters intently.
Solve the HOTS and other exercise questions.
Check out the questions asked in the previous year's CBSE Class 11 Business Studies.
Reliable study with the best guide and resource material like CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes and NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies - Free PDF Download .
Students can revise from the revision material of Business Services Class 11 Notes CBSE Business Studies Chapter 4, this will help the students to properly understand and revise the chapter.
Take note of the tips and topics discussed in this article and download the free-to-download pdf of the revision study and save it for later revision.

FAQs on Business Services Class 11 Notes CBSE Business Studies Chapter 4 (Free PDF Download)
1. What are the functions of commercial banks?
The various functions of the Commercial Banks are as follows:
Acceptance of Deposits - These are the basis on which banks function and also cause banks to be both borrowers and lenders of money.
Cheque Facility - This one of the more developed credit facilities, that has been in practice for a couple of years.
Lending of Funds - To provide loans through advances from the deposits received
Remittance of Funds - It is the facility of transfer of money from one place to another.
Allied Services - Include bill payments, locker facilities and underwriting facilities.
2. What are the types of insurance?
The types of Insurance are:
Life Insurance - In this, the insurer in consideration of the contract agrees to pay either in a lump sum or periodical payments, an amount of money to the assurer wherein any contingency to the insurer, they will receive that amount in either full or to cover certain costs.
Fire Insurance - In this insurance, the insurer is guaranteed payment for the goods that are under the fire insurance contract.
Marine Insurance - Against any marine losses the insurer will get the money that is put up in the contract.
3. What do you mean by Business Services in Class 11?
A service is an intangible service that can satisfy wants, and usually occurs after a transaction has been completed. Business services are one of the types of services that include banking, insurance, transportation, warehousing, communication, and other services that are used by businesses to run their operations more efficiently. Today, the majority of businesses rely on such specialised business services. When it comes to providing services to the developed economies of the world, India has been gaining a significant advantage over other countries.
4. What is a Bank in Class 11?
An institution licensed to accept deposits and make loans is known as a bank. Money management, currency exchanges are a few of the financial services that banks may offer. The banking services come under the category of business services. The banking industry has a wide range of interests, needs, and methods. As a result, we need different types of banks to deal with them. Banks can be categorised into the below categories:
Commercial banks
Cooperative banks
Specialised banks
Central bank
5. What are the types of banks?
When it comes to monetary requirements, a country needs to have various kinds of banking sectors so as to cater all the monetary needs. Keeping this in mind, banks are categorised into several types which are as follows:
Commercial Banks - It deals with money.
Cooperative Banks - These banks supply low-cost loans for their customers.
Specialised Banks - These banks lend money to industries, large industrial projects, and foreign trade.
Central Bank - The central bank monitors, controls and regulates its activities in general.
6. Which is the best book for Business Studies in Class 11 Chapter 4?
While preparing any subject, the most important thing to keep in mind is what source of learning you are referring to for your learning purpose. And if you are a Class 11 student, the best material is the NCERT book. NCERT books contain all the basic concepts an 11th grader needs to ace their exam. It explains all the topics in easy and simple language and also provides a set of questions to enhance the concepts even more. You can download the NCERT Solutions or study material for free and study offline as well from Vedantu’s official website or you can download their app.
7. Why should I prefer revision notes Chapter 4 Business Studies Class 11?
If you want to seek help in making effective and reliable notes for your exams, then the revision notes provided on Vedantu is the best option for you. These notes are prepared by the professional team of tutors who explain the concepts in easy to understand language. You can refer to the revision notes of Chapter 4 Business Studies Class 11 in downloadable PDF format.
CBSE Study Materials
myCBSEguide
- Business Services class 11...
Business Services class 11 Notes Business Studies
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Business Services class 11 Notes Business Studies in PDF are available for free download in myCBSEguide mobile app. The best app for CBSE students now provides Business Services class 11 Notes Business Studies latest chapter wise notes for quick preparation of CBSE board exams and school-based annual examinations. Class 11 Business Studies notes on Chapter 4 Business Services class 11 Notes Business Studies are also available for download in CBSE Guide website.
Download CBSE class 11th revision notes for Chapter 4 Business Services class 11 Notes Business Studies in PDF format for free. Download revision notes for Business Services class 11 Notes Business Studies and score high in exams. These are the Business Services class 11 Notes Business Studies prepared by team of expert teachers. The revision notes help you revise the whole chapter in minutes. Revising notes in exam days is on of the best tips recommended by teachers during exam days.
Download Revision Notes as PDF
CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes Business Services
It has already been stated that commerce consists of trade and auxiliaries to trade. Auxiliaries or aids to trade refer to the activities related to the buying and selling of goods and services. These auxiliaries to trade are also known as business services or facilities. These services are essential and indispensable for the smooth flow of trade and industry. The examples of business services are Banking, insurance, transport, warehousing Advertisement and communication.
NATURE OF BUSINESS SERV1CES:
1. Intangibility: Cannot be seen, touched or smelled. Just can only be felt, yet their benefits can be availed of e.g. Treatment by doctor.
2. Inconsistency: Different customers have different demands & expectation.e.g. Mobile services/Beauty Parlour.
3. In Separability: Production and consumption are performed simultaneously.For e.g. ATM may replace clerk but presence of customer is must.
4. Inventory Loss: Services cannot be stored for future use or performed earlier to be consumed at a later date. e.g. underutilized capacity of hotels and airlines during slack demand cannot be stored for future when there will be a peak demand.
5. Involvement: Participation of the customer in the service delivery is a must e.g. A customer can get the service modified according to specific requirement.
Type of Services:
1. Social Services: Provided voluntarily to achieve certain goals e.g. healthcare and education services provided by NGOs.
2. Personal Services: Services which are experienced differently by different customers. e.g. tourism, restaurants etc.
3. Business Services: Services used by business enterprises to conduct their activities smoothly. e.g. Banking, Insurance, communication, Warehousing and transportation.
Banks occupy an important position in the modern business World. No country can make commercial and industrial progress without a well organized banking system. Banks encourage the habit of saving among the public. They mobilize small savings and channelize them into productive uses.
Meaning of Bank
A bank is an institution which deals in money and credit. It collects deposits from the public and supplies credit, thereby facilitating exchange. It also performs many other functions like credit creation, agency functions, general services etc Hence, a Bank is an organization which accepts deposits, lends money and perform other agency functions.
Primary Functions
1. Accepting Deposits: Accepting deposits is the main function of commercial banks. Banks offer different types of Bank accounts to suit the requirements and needs of different customers. Different types of Bank accounts areas follows:
A. Fixed Deposit Account: Money is deposited in the account for a fixed period is called as Fixed Deposit account. After expiry of specified period ,person can claim his money from the bank. Usually the rate of interest is maximum in this account. The longer the period of deposit, the higher will be the rate of interest on deposit.
B. Current Deposit Account: Current deposit Accounts are opened by businessman. The account holder can deposit and Withdraw money. Whenever desired. As the deposit is repayable on demand, it is also known as demand deposit. Withdrawals are always made by cheque. No interest is paid on current accounts. Rather charges are taken by bank for services rendered by it.
C. Saving Deposit Account: The aim of a saving account is to mobilize savings of the public. A person can open this account by depositing a small sum of money. He can withdraw money from his account and make additional deposits at will. Account holder also gets interest on his deposit. In this account though the rate of interest is lower than the rate of interest on fixed deposit account.
D. Recurring Deposit Account: The aim of recurring deposit is to encourage regular savings by the people. A depositor can deposit a fixed amount, say Rs. 100 every month for a fixed period. The amount together with interest is repaid on maturity. The interest rate on this account is higher than that on saving deposits.
E. Multiple Option Deposit Account: It is a type of saving Bank A/c in which deposit in excess of a particular limit get automatically transferred into fixed Deposit. On the other hand, in case adequate fund is not available in our saving Bank Account so, as to honour a cheque that we have issued the required amount gets automatically transferred from fixed deposit to the saving bank account. Therefore, the account holder has twin benefits from this amount (i) he can earn more interest and (ii) It lowers the risk of dishonoring a cheque.
2. Lending Money with the help of money collected through various types of deposits, commercial banks lend finance to businessman, farmers, and others. The main ways of lending money are as follows:
A. Term Loans : These loans are provided by the banks to their customers for a fixed period to purchases Machinery. Truck. Scooter. House etc. The borrowers repay the loans in Monthly/Quarterly/Half Yearly/Annual installments.
B. Bank Overdraft : The customer who maintains a current account with the bank, takes permission from the bank to withdraw more money than deposited in his account. The extra amount withdrawn is called overdraft. This facility is available to trustworthy customers for a small period. This facility is usually given against the security of some assets or on the personal security of the customer. Interest is charged on the actual amount overdrawn by the customer.
C. Cash Credit : Under this arrangement, the bank advances cash loan up to a specified limit against current assets and other securities. The bank opens an account in the name of the borrower and allows him to withdraw the borrowed money from time to time subject to the sanctioned limit. Interest is charged on the amount actually withdraw.
D. Discounting of Bill of Exchange : Under this, a bank gives money to its customers on the security of a bill of exchange before the expiry of the bill in ease of customers needs it. For this service bank charges discount for the remaining period of the bill.
Secondary Functions
The secondary functions of commercial banks are as under:
(1) Agent Functions
As an agent of its customers a commercial bank provides the following services:
(I) Collecting bills of exchange, promissory notes and cheques.
(II) Collecting dividends, interest etc.
(III) Buying and selling shares, debentures and other securities.
(IV) Payment of interest, insurance premium etc.
(V) Transferring funds from one branch to another and from one place to another.
(VI) Acting as an agent of representative while dealing with other banks and financial institutions. A Commercial banks performs the above functions on behalf of and as per the instructions of its customers.
(2) General Utility Functions:
Commercial banks also perform the following miscellaneous functions:
(I) Providing lockers for safe custody of jewellery and other valuables of customers.
(II) Giving references about the financial position of customers.
(III) Providing information to a customer about the credit worthiness of other customers.
(IV) Supplying various types of trade information useful to customer.
(V) Issuing letter of credit, pay orders, bank draft, credit cards and travelers cheques to customers.
(VI) Underwriting issues of shares and debentures.
(VII) Providing foreign exchange to importers and travellers going abroad.
Bank Draft: It is a financial instrument with the help of which money can be remitted from one place to another. Anyone can obtain a bank draft after depositing the amount in the bank. The bank issues a draft for the amount in its own branch at other places or other banks (only in case of tie up with those banks) on those places. The payee can present the draft on the drawee bank at his place and collect the money. Bank charges some commission for issuing a bank draft.
Banker’s cheque or Pay Order: It is almost like a bank draft. It refers to that bank draft which is payable within the town. In other words banks issue pay order for local purpose and issue bank draft for outstation transactions.
ELECTRONIC BANKING SERVICES/E-BANKING
Use of computers and internet in the functioning of the banks is called electronic banking. Because of these services the customers don’t need to go to the bank every time for every transaction. He can make transactions with the bank at any time and from any place. The chief electronic services are the following:
1 . Electronic. Fund Transfer: Under it, a bank transfers wages and salaries directly from the company s account to the accounts of employees of the company. The other examples of EFTs are online payment of electricity bill, water bill, insurance premium, house tax etc.
2. Automatic Teller Machines: (ATMs) ATM is an automatic machine with the help of which money can be withdrawn or deposited by inserting the card and entering personal Identity Number (PIN). This machine operates for all the 24 hours.
3. Debit Card: A Debit Card is issued to customers in lieu of his money deposited in the bank. The customers can make immediate payment of goods purchased or services obtained on the basis of his debit card provided the terminal facility is available with the seller.
4. Credit Card: A. bank issues a credit card to those of its customers who enjoy good reputation. This is a sort of overdraft facility. With the help of this card ,the holder can buy goods or obtain services up to a certain amount even without having sufficient deposit in their bank accounts.
5. TeleBanking: Under this facility, a customer can get information about the account balance or any other information about the latest transactions on the telephone.
6. Core Banking Solution Centralized Banking Solution: In this system customer by opening a bank account in one branch (which has CBS facility) can operate the same account in all CBS branches of the same bank anywhere across the country. It is immaterial with which branch of the bank the customer deals with when he/she is a CBS branch customer.
7. National Electronic Fund Transfer: NEFT refers to a nationwide system that facilitate individuals, firms and companies to electronically transfer funds from any branch to any individual, firm or company having an account with any other bank branch in the country. NEFT settles transactions in batches. The settlement takes place at a particular point of time for example, NEFT settlement takes place 6 times a day during the weekdays (9.30am, 10.30 am, 12.00 noon, 1.00 pm. 3.00 pm & 4.00pm) and 3 times during Saturday 9.30 am, 10.30 am and 12.00 noon) Any transaction initiated after a designated settlement time is settled on the next fixed settlement time.
8. Real Time Gross Settlement: RTGS refers to a funds transfer system where transfer of funds takes place from one bank to another on a Real-time and on Gross basis. Settlement in Real-time means transactions are settled as soon as they are processed and are not subject to any waiting period. Gross settlement means the transaction is settled on one to one basis without bunching or netting with any other transaction. This is the fastest possible money transfer system through the banking channel. The RTGS service for customers is available from 9.00 am to 3.00 pm on weekdays and from 9.00 am to 12.00 noon on Saturdays. The basic difference between RTGS and NEFT is that while RTGS transactions are processed continuously, NEFT settles transactions in batches.
Benefits of E-Banking to Customer:
1. E-Banking provides 24 hours a day X 365 days a year services to the customers.
2. Customers can make transactions from office or house or while traveling via mobile telephone.
3. There is greater customer satisfactions through E-banking as it offers unlimited access and great security as they can avoid travelling with cash.
Benefits of E-Banking to Banks:
1 . E-Banking lowers the transaction cost.
2. Load on branches can be reduced by establishing centralized database.
3. E-Banking provides competitive advantage to the bank, adds value to the banking relationship.
Meaning of insurance :
Insurance is a contract under which one party (Insureror Insurance Company) agrees in return of a consideration (Insurance premium) to pay an agreed sum of money to another party (Insured) to make good for a loss, damage or injury to something of value in which the insured has financial interest as a result of some uncertain event.
Principles of Insurance : These principles are :
1. Utmost Good Faith: Insurance contracts are based upon mutual trust and confidence between the insurer and the insured. It is a condition of every insurance contract that both the parties i.e.insurer and the insured must disclose every material fact and information related to insurance contract to each other.
2. Insurable Interest: It means some pecuniary interest in the subject matter of insurance contract. The insured must have insurable interest in the subject matter of insurance i.e., life or property insured the insured will have to incur loss due to this damage and insured will be benefitted if full security is being provided. A businessman has insurable interest in his house, stock, his own life and that of his wife, children etc.
3. Indemnity: Principle of indemnity applies to all contracts except the contract of life insurance because estimation regarding loss of life cannot be made. The objective of contract of insurance is to compensate to the insured for the actual loss he has incurred. These contracts ‘provide security from loss and no profit can be made out of these contracts.
4. Proximate Cause: The insurance company will compensate for the loss incurred by the insured due to reasons mentioned in insurance policy. But if losses are incurred due to reasons not mentioned in insurance policy than principle of proximate cause or the nearest cause is followed.
5. Subrogation: This principle applies to all insurance contracts which are contracts of indemnity. As per this principle, when any insurance company compensates the insured for loss of any of his property, then all rights related to that property automatically gets transferred to insurance company.
6. Contribution: According to this principle if a person has taken more than one insurance policy for the same risk then all the insurers will contribute the amount of loss in proportion to the amount assured by each of them and compensate for the actual amount of loss because he has no right to recover more than the full amount of his actual loss.
7. Mitigation: According to this principle the insured must take reasonable steps to minimize the loss or damage to the insured property otherwise the claim from the insurance company may be lost.

Concept of Life Insurance:
Under life insurance the amount of Insurance is paid on the maturity of policy or the death of policy holder whichever is earlier. If the policy holder survives till maturity he enjoys the amount of insurance. If he dies before maturity then the insurance claim helps in maintenance of his family. The insurance company insures the life of a person in exchange for a premium which may be paid in one lump sum or periodically say yearly, half yearly quarterly or monthly.
Types of Life Insurance Policies:
1. Whole Life Policy: Under this policy the sum insured is not payable earlier than death of the insured. The sum becomes payable to the heir of the deceased.
2. Endowment Life Insurance Policy: Under this policy the insures undertakes to pay the assured to his heirs or nominees a specified summon the attainment of a particular age or on his death whichever is earlier.
3. Joint Life Policy: It involves the insurance of two or more lives simultaneously. The policy money is payable on the death of any one olives assured and the assured sum will be payable to the survivor or survivors.
4. Annuity Policy: This policy is one under which amount is payable in monthly, quarterly, half yearly or annual installments after the assured attains a certain age. This is useful to those who prefer a regular income after a certain age.
5. Children’s Endowment Policy: This policy is taken for the purpose of education of children or to meet marriage expenses. The insurer agrees to pay a assured sum when the child attains a certain age.
Fire Insurance: It provides safety against loss from fire. If property of insured gets damaged due to property as compensation from insurance company. If no such event happens,then no claim shall be given.
1. Utmost Good Faith
2. Contract of Indemnity
3. Insurable Interest in Subject matter.
4. Subject to the doctrine of causa proxima.
5. It is a contract for an year. It generally comes to an end at the expiry of the year and may be renewed.
Marine Insurance: Marine Insurance provides protection against loss during sea voyage. The businessmen can get his ship insured by paying the premium fixed by the insurance company. The functional principles of marine insurance are the same as the general principles of Insurance.
OTHER INSURANCE
Health Insurance : With a lot of awareness today, Health insurance has gained a lot of popularity. General Insurance companies provide special health insurance policies such as Mediclaim for the general public. The insurance company charges a nominal premium every year and in return undertakes to provide up to stipulated amount for the treatment of certain diseases such as heart problem, cancer, etc.
Communication: In this fast moving and competitive world it is essential to have advanced technology for quick exchange of information with the help of electronic media. It is an important service that helps in establishing links between businessmen. Organization, suppliers, customers etc. It educates people, widen their knowledge and broaden their outlook. It overcomes the problem of distance between people, businessmen and institutions and thus,it helps in smooth running of business activities. The main services can be classified into postal and telecom.
Postal Services: This service is required by every business to send and receive letters, market reports, parcel, money order etc.on regular. All these services are provided by the post and telegraph offices scattered throughout the country. The postal department performs the following services.
1 . Financial Services: They provide postal banking facilities to the general public and mobilize their savings through the following saving schemes like public provident fund (PPF), KisanVikasPatra, National Saving Certificate, Recurring Deposit Scheme and Money Order facility.
2. Mail Services: The mail services offered by post offices includes transmission of messages through postcards, Inland letters, envelops etc. The various mail services all:
1. UPC (under postal certificate): When ordinary letters are posted the post office does not issue any receipt. However, if sender wants to have proof then a certificate can be obtained from the post office on payment of prescribed fee. This paper now serves as a evidence of posting the letters.
2. Registered Post: Sometimes we want to ensure that our mail is definitely delivered to the addressee otherwise it should come back to us. In such situations the post office offers registered post facility which serves as a proof that mail has been posed.
3. Parcel: Transmission of articles from one place to another in the form of parcels is known as parcel post. Postal charges vary according to the weight of the parcels.
Allied Postal Services
1 . Greetings Post: Greetings can be sent through post offices to people at different places.
2. Media Post: Cooperates can advertise their brands through post cards, envelops etc.
3 . Speed Post: It allows speedy transmission of articles (within 24 hours) to people in specified cities.
4 . e-bill post: The post offices collect payment of bills on behalf of BSNL and other organizations.
5. Courier Services: Letters, documents, parcels etc. can be sent through the courier service. It being a private service the employees work with more responsibility.
Telecom Services : Today’s global business world, the dream of doing business across the world, will remain a dream only in the absence of telecom services. The various types of telecom services are
1. Cellular mobile services: cordless mobile communication device including voice and non-voice messages, data services and PCO services.
2 . Radio Paging Services means of transmitting information to persons even when they are mobile.
3. Fixed Line Services includes voice and non-voice messages and data services to establish linkage for long distance traffic.
4 . Cable services Linkages and switched services within a licensed area of operation to operate media services which are essentially oneway entertainment related services.
5. VSAT Service (Very small Aperture Terminal) is a Satellite based communication service. It offers government and business agencies a highly flexible and reliable communication solution in both urban and rural areas.
6. DTH Services (Direct to Home) a Satellite based media services provided by cellular companies with the help of small dish antenna and a setup box.
Tranportation: Transportation comprises freight services together with supporting and auxiliary services by all the modes of transportation i.e rail, road, air and sea for the movement of goods and international carriage of passengers.
Warehousing: The warehouse was initially viewed as a static unit for keeping and storing goods in a scientific and systematic manner so as to maintain their original quality, value and usefulness.
CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes and Key Points
Business Services class 11 Notes Business Studies. CBSE quick revision note for class-11 Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry, Biology and other subject are very helpful to revise the whole syllabus during exam days. The revision notes covers all important formulas and concepts given in the chapter. Even if you wish to have an overview of a chapter, quick revision notes are here to do if for you. These notes will certainly save your time during stressful exam days.
- Mathematics
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Computer Science
- Informatics Practices
To download Business Services class 11 Notes, sample paper for class 11 Chemistry, Physics, Biology, History, Political Science, Economics, Geography, Computer Science, Home Science, Accountancy, Business Studies and Home Science; do check myCBSEguide app or website. myCBSEguide provides sample papers with solution, test papers for chapter-wise practice, NCERT solutions, NCERT Exemplar solutions, quick revision notes for ready reference, CBSE guess papers and CBSE important question papers. Sample Paper all are made available through the best app for CBSE students and myCBSEguide website.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Sources of Business Finance class 11 Notes Business Studies
- Olympic Movement class 11 Notes Physical Education
- Changing Trends and Career class 11 Notes Physical Education
- Physical Activity Environment class 11 Notes Physical Education
- Yoga class 11 Notes Physical Education
- Pollution of Air and Water class 8 Notes Science
- Stars and the Solar System Class 8 Notes Science
- Light class 8 Notes Science
2 thoughts on “Business Services class 11 Notes Business Studies”
“Invaluable insights! These class 11 Business Studies notes are a treasure trove for understanding business services. Thank you for sharing.”
Jhhjoiiiiii
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Business Services
Detailed, Step-by-Step NCERT Solutions for 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Business Services Questions and Answers were solved by Expert Teachers as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines covering each topic in chapter to ensure complete preparation.
Business Services NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4
Business services questions and answers class 11 business studies chapter 4.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. DTH services are provided by (a) Transport company (b) Bank (c) Cellular company (d) None of the above Answer: (c) Cellular company
Question 2. The benefits of public warehousing includes – (a) Control (b) Flexibility (c) Dealer relationship (d) None of the above Answer: (b) Flexibility
Question 3. Which of the following is not a function of insurance? (a) Risk sharing (b) Assist in capital formation (c) Lending of funds (d) None of the above Answer: (c) Lending of funds
Question 4. Which of the following is not applicable in life insurance contract? (a) Conditional contract (b) Unilateral contract (c) Indemnity contract (d) None of the above Answer: (c) Indemnity contract
Question 5. CWC stands for – (a) Central water commission (b) Central warehousing commission (c) Central warehousing corporation (d) Central water corporation Answer: (c) Central warehousing corporation
Short Answer Questions
Question 1. Define services and goods. Answer: Services are those separately identifiable, essentially intangible activities that provide the satisfaction of wants, and are not necessarily linked to the sale of a product or another service.
A good is a physical product capable of being delivered to a purchaser and involves the transfer of ownership from the seller to the customer. Goods are also generally used to refer to commodities or items of all types except services, involved in trade or commerce. While goods are produced, services are performed. A service is an act which cannot be taken home.
What we can take home is the effect of the services. There are five basic features of services. These features also distinguish them from goods and are known as’’ intangibility, inconsistency, inseparability, inventory and involvement (five I’s). Service facilities help ensure the supply of the right place at the right time. These facilities ensure a smooth flow of exchange of goods and services. Efficient service facilities provide the following benefits:
- Improved customer service.
- Lower distribution costs.
- Additional sales volume.
- Time and place utilities.
- Stabilization of prices.
Services required in business are transportation banking, insurance, communication, and warehousing.
Question 2. What is e-banking. What are the advantages of e-banking? Answer: Electronic Banking (E-Banking) These days banks have been providing the following new services due to the introduction of computerised equipments : (1) Electronic Funds Transfer System (EFTs) – It allows transfer of funds electronically. It is a cost-saving scheme for the convenience of customers. Under the scheme the banks transfer the wages and salaries from company’s account to employees’ accounts as per the instruction of the employer.
This system removes the risk and inconvenience of handling cash. Similarly, a company can distribute dividend to its shareholders electronically. This is very safe method of transfer money.
(2) Automated Teller Machine (ATMs) – It is a free-standing self-service terminal which renders the facility of withdraw and deposit a money. While using ATM a plastic card is inserted into the terminal. After that identification code is also inserted. The machine responds by delivering required cash, cashing cheques, taking deposits and simple banking transactions.
(3) Debit Card – The card issued to the Bank Account holders against their bank balance to facilitate and simplify the payment, withdrawal and transfer of money any time, any where through the computer is known as Debit Card. There is no overdraft facility to Debit Cardholders. There is no fee interest and charge for issuing these cards. These cards are being issued in India by ICICI, HDFC, HSBC, Citi Banks, SBI, PNB etc.
Under the scheme point-of-sale (POS) terminals are located at merchants check out counters audited electronically to a bank computer. When the customer presents a debit card, the point-of-sale terminal automatically) transfers the money for the purchase from customer’s account to store’s account. Under this system an individual can pay bills automatically by using a personal computer, which is linked by telephone to the bank computer.
Net Banking – In order to provide convenience to the customers for banking anytime, anywhere in the world, net banking is used. Customers are provided secured log in id and password through which they can access their account and make transactions like account balance enquiry, cheque book request, fund transfer etc.
(4) Credit Card – It is also called plastic money as it allow the cardholder to withdraw money without depositing. The card issued to selected customers to enable them to make payment of credit bills upto specified limit any time anywhere through computer is known as credit card. It is also used for withdrawing cash from ATMs.
The amount overdrawn is repaid upto specified date. Interest is charged if payment is not made upto specified date. The credit card system has facilitate simplified encourage credit transactions.
Credit card is a substitute for cash that can be used by selected customers. It is the key to the opening of bank account for daily payments. It provides overdraft facilities also. These are plastic cards having the photo identity and the signature embossed on the cards. It also contains issuing bank’s name and validity period of the card. The credit card holder has to deposit the amount withdrawn along with interest due to credit and company or bank.
Question 3. Write a note on various telecom services available for enhancing business. Answer: The various types of telecom services are: (i) Cellular mobile services: These are all types of mobile telecom services including voice and non-voice messages, data services, and PCO services utilizing any type of network equipment within their service area. They can also provide direct interconnectivity with any other type of telecom service provider.
(ii) Radio paging services: Radio paging service is an affordable means of transmitted information to persons even when they are mobile. It is a one-way information broadcasting solution and has spread its reach far and wide. Radio paging services are available including tone only, numeric only, and alpha / numeric paging.
(iii) Fixed line services: These are all types of fixed services including voice and non-voice messages and data services to established linkages for long-distance traffic. These utilize any type of network equipment primarily connected through fiber optic cables laid across the length and breadth of the country. They also provide interconnectivity with other types of telecom services.
(iv) Cable services: These are linkages and switched services within a licensed area of operation to operate services. The two-way communication including voice, data and information services through cable networks would emerge significantly in the future. Offering services through the cable network would be similar to providing fixed services.
(v) VSAT services: VSAT (Very Small Aperture Terminal) is a satellite-based communications service. It offers businesses and government agencies a highly flexible and reliable communication solution in both urban and rural areas. Compared to land-based services, VSAT offers the assurance of reliable and uninterrupted service that is equal to or better than based services.
It can be used to provide innovative applications such as telemedicine, newspapers, online, market, rates, and tele-education even in the most remote areas of our country.
(vi) DTH services: DTH (Direct to Home) is again a satellite-based media service provided by cellular companies. One can received media services directly through a satellite with the help of a small dish antenna and a set-top box. The service provider of DTH services provides a bouquet of multiple channels. It can be viewed on our television without being dependent on the services provided by the cable network services provider.
Question 4. Explain briefly the principles of insurance with suitable examples. Answer: Fundamental Principles Of Insurance (1) Principle of utmost good faith (uberrimate fide). This principle implies that the insurer and insured must disclose all the material facts apd information to each other. Material facts, here means all the important information, which would have affected the insurance policy as regards accepting the risk at that rate of premium.
Concealment of the material fact wi 11 make the contract voidable at the discretion of the aggrieved party. For example, the insured is a cancer patient but does not disclose this material fact in his proposal form. If the insured dies of cancer, the insurance company is not liable to pay the insurance money.
In case of fire insurance if certain flammable material like patrol is stored in the godown, it must be intimated to the insurance company. If this fact is concealed and the godown catches fire, the insurance company will not be liable to compensate for damages. Misrepresentation or failure to reveal material information gives the affected party the right to cancel the control.
(2) Principle of insurable interest – It is the basic and essential requirement of an insurance contract that the person taking the insurance policy must have personal and direct insurable interest in the insured person or property. The insured must have insurable interest.
The person is said to have an insurable interest, when he stands to gain with the safe existence of the insured person or property and would suffer personal loss due to the destruction of the insured. The objective behind this principle is that the insured should be compensated for the loss.
The loss will be suffered by the insured, if his own personal property is destroyed. He cannot be said to have suffered loss due to the destruction of the property of someone else. In case of life insurance, it must be present at the time of falling the policy. In fire insurance, both at the time of calling policy and at the time of actual loss.
(3) Principle of Indemnity – All insurance contract, except life insurance, are contract so find enmity. The objective behind this principle is to place the insured person as far as possible in the same financial position which he had enjoyed before the loss. In case of loss the insured will be paid the amount of actual loss or the amount of the policy, whichever is lesser.
The policy behind this arrangement is that nobody should treat insurance contract as the source of profit. The purpose of this principle is to put the insured in the same position after the event happened in which he was immediately before the event.
Example – The owner of the house gets his house insured for Rs. 10,00,000. Unfortunately the house catches fire and half of the house is destroyed. In this case the insurance company will pay only Rs.5,00,000 as compensation. It is the amount of actual loss. Suppose the house was worth Rs.20,00,000 but insured for Rs. 10,00,000. In this case if the entire house is fully destroyed, the insurance company will pay only Rs. 10,00,000. If half of the house is damaged the insurance company will pay Rs.5,00,000 only.
(4) Principle of Mitigation of losses – In the event of misshaping it is the duty of the insured that he must take all reasonable steps to minimise the loss in the same manner, which he would have done if the property was not insured. If the insured suffers any loss or incurs expenses in minimising the loss, he can recover the loss from the insurers.
If it is proved that the insured did not take steps to minimise the loss, which many prudent persons would have done, simply because the loss will be borne by the insurance company not by him, the insurance claim may be lost. The insured must act in the same manner as he would have gone, if the property were not insured.
(5) Principle of causa Proxima – According to this principle compensation is paid to the insured if the causes responsible for loss were insured. In case, the cause of the loss was not insured, compensation is not paid. The insured risk must be the proximate or nearest not remote. If the risk insured is the remote cause of the loss, then the insurer is not bound to pay compensation.
In case of marine insurance, shipping company is held responsible for certain risks, some risks are borne by the owner of goods and the insurance company is held liable if the loss is caused by the insured risk. If the loss is due to many complex causes, the nearest cause of the loss is ascertained.
For example, sugar sent by ship was insured against sea hazards. Rats made hole by cutting the pipe of the toilet. Sea-water entered through-hole and the sugar was destroyed. In this case, the nearest cause of the loss of sugar is the seawater, a risk, which was insured and the insurance company will be liable for risk. If the rats would have damaged the sugar directly insurance company would not have been liable for the risk.
(6) Principle of subrogation – Do6trine of subrogation states that after making compensation for the loss, the, insurer steps into the shoes of the insured. It means that the insurance company becomes entitled to exercise all the rights and remedies, which the insured had in respect of the property.
Let us take an example. Anil ensured his factory for Rs. 4,50,000. There was partial damage of the factory by fire due to the negligence of employee Anil’s claim for Rs.2,00,000 was admitted by the insurance company and paid later on. An filed a case against employee and received Rs.40,000 as compensation. The insurance company is entitled to receive Rs.40,000 from Anil which he received from employee.
(7) Principle of contribution – It implies that when property is insured for the some risk with two or more insurers, the different insurers will contribute to the total payment in proportion to the amount assured to each. In case one insurer has paid full compensation of loss, he is entitled to receive proportionate contribution from other insurers.
For example, A gets his house insured against fire for Rs. 1 lakh with insurer B and for Rs.50000 with insurer C.A loss of Rs.75000 occurs to the house due to a fire. Then, B is liable to contribute Rs.50000 and C Rs.25000. In case B pays the whole amount of loss, he can recover Rs.25000 from C. This principle is not applicable to life insurance.
Question 5. Explain warehousing and its functions. Answer: Meaning Of Warehousing A warehouse in simple language is the place used for the storage or accumulation of goods. Warehousing means holding and preservation of goods from the time of their production or purchase and until their sale or use. It involves making suitable and effective arrangements for keeping the goods in proper condition.
A warehouse is a place used for the storage of surplus goods. It helps the businessmen to keep suits during dull session. It may also be defined as an establishment that assumes responsibility for the safe custody of goods. Warehousing enables businessmen to produce goods throughout the year and sell them whenever there is adequate demand. It creates time utility by bridging the time gap between production and distribution of goods. Thus, warehousing creates time utility.
Functions of Warehouses A modern warehouse performs the following important functions: (1) Storage-The basic function of a warehouse is to store the surplus goods which are not needed immediately. Surplus goods are preserved and made available when required. A warehouse acts as a reservoir or storehouse of surplus goods and made available whenever they are demanded by the customers.
(2) Safety of Goods-A warehouse protects goods against pilferage, theft and damage. Goods are preserved safely from rain, sun, moisture, pests, fire, etc. Perishable goods such as fruits, vegetables, eggs, etc. can be preserved in cold storages. Thus, warehouses provide for the safe custody of goods.
(3) Price Stabilisation – Warehouses facilitate the smooth supply of goods and remove the fluctuations in the prices of goods. A warehouse enables businessmen to store excess goods and thereby avoid emergency sale. In the absence of storage facilities they have to dispose of the entire stock as soon as it is produced.
In warehouses available goods can be stored when they are in abundant supply and released when the demand is high. Thus, fall in prices is checked when the supply is at its peak and rise in prices is avoided during the slack season. In this way, producers can realise better prices and consumers can buy goods at reasonable prices.
(4) Risk Bearing- Warehouses safeguard the stock of goods against damage due to fire or theft. Once goods are handed to a warehouse the responsibility for ensuring the safety of goods passes to the warehouse¬keeper. The risk of loss or damage is borne by the warehouse-keeper. Moreover, goods kept in a recognised warehouse can be insured at a low premium. In case of loss or damage the value of goods can be recovered from the insurance company. Building of warehouses are specially constructed to safeguard the goods against several risks.
(5) Financing – In India, warehouse authorities advance money to owners of goods on security of goods deposited. Warehouses issue receipts to the persons who keep their goods on rent in warehouses. The receipt issued by a warehouse is a good collateral security against which money can be borrowed from banks and other financial institutions. In this way, warehouses help in financing trade.
(6) Mass Production – A warehouse removes the hindrance of time of production and consumption. Warehouses facilitate production in anticipation of demand. They create time utility by bridging the time gap between production and demand. In the absence of warehouses, the scale of production will be restricted to the level of current demand. Warehousing enables businessmen to avail of the economics of large- scale production and bulk-buying.
(7) Facilities-Warehouses provide facilities of processing, packing, blending etc. for the purpose of sale. A modern warehouse provides several facilities to businessmen. Goods can be prepared for sale by arranging them in small and suitable lots. They can be repacked, graded, blended and labelled. Prospective buyers can be taken to the warehouse for inspecting the goods. A warehouse can also deliver goods strictly according to the instructions of their owner.
(8) Employment – Warehouses provide jobs to a large number of persons. They offer direct employment and also generate employment opportunities by increasing the scale of operations.
(9) Facilitate Foreign Trade – An importer can keep the imported goods in bonded warehouses if he is unable or willing to pay customs duty immediately. He can pay duties in installments and draw goods gradually.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1. What are services? Explain their distinct characteristics? Answer: Services are essentially intangible activities which are separately identifiable and provide satisfaction wants. Their purchase does not result in the ownership of anything physical Services involve an interaction to be realized between the service provider and the consumer.
(i) Intangibility: Services are intangible, i.e., they cannot be touched. They are experiential in nature. One cannot taste a doctor’s treatment, or touch entertainment. One can only experience it. An important implication of this is that the quality of the offer can often not be determined before consumption and, therefore, purchase.
It is, therefore, important for the service providers that they consciously work on creating the desired service so that the customer undergoes a favourable experience. For example, treatment by a doctor should be a favourable experience.
(ii) Inconsistency: The second important characteristic of services is inconsistency. Since there is no standard tangible product, services have to be performed exclusively each time. Different customers have different demands and expectations. Service providers need to have an opportunity to alter their offer to closely meet the requirements of the customers. This is happening, for example, in the case of mobile services.
(iii) Inseparability: Another important characteristic of services is the simultaneous activity of production and consumption being performed. This makes the production and consumption of services seem to be inseparable. While we can manufacture a car today and sell it after, say, a month this is often not possible with services that have to be consumed as and when they are produced.
Service providers may design a substitute for the person by using appropriate technology but the interaction with the customer remains a key feature of services. Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) may replace the banking clerk for the front office activities like cash withdrawal and cheque deposit. But, at the same time, the presence of the customer, is required and his/her interaction with the process has to be managed.
(iv) Inventory (Less): Services have little or no tangible components and, therefore, cannot be stored for a future use. That is, services are perishable and providers can, at best, store some associated goods but not the service itself. This means that the demand and supply needs to be managed as the service has to be performed as and when the customer asks for it.
They cannot be performed earlier to be consumed at a later date. For example, a railway ticket can be stored but the railway journey will be experienced only when the railways provide it.
(v) Involvement: One of the most important characteristics of services is the participation of the customer in the service delivery process. A customer has the opportunity to get the services modified according to specific requirements.
Question 2. Explain the functions of commercial banks with an example of each : Answer: Commercial Banks Commercial banks are very popular in every country due to services rendered by them. A commercial bank is a financial institution; which deals in money and credit. It accepts deposits from those who have a surplus and lends to those who need them. The difference between the rate of interest on deposits and loans is the profit of the bank.
Definition of the Bank – According to Indian Banking Companies Act 1949, “A bank is an institution accepting for the purpose of lending or investment in deposit money from public repayable on demand or otherwise, withdrawal by cheque, drafts, order or otherwise’.
In the words of R.S.Mayers, “Banks are institutions whose debts are referred to as ‘bank deposits ’ and they are commonly accepted in final settlement of ‘other people s debts ’
According to Justice Holmes, “The real business of banker is to obtain deposits of money which he may use for his own profits by lending it out again ‘
Bank is German word, which means ‘to collect’. The main function of the bank is the collection of funds as deposits. Later on bank started performing other functions such as lending etc.
Bank has occupied very important place in the economic structure of the country. After independence in order to achieve social objectives of the country banks were nationalised. According to 20 point programme of the government banks have been entrusted the responsibility for developing the undeveloped regions of the country.
In the light of these recent thinking, banks may be defined as the financial institution dealing in money and credit to achieve the economic and social objectives of the business. In India, some of major commercial banks are – State Bank of India, Punjab National Bank, Bank of Baroda, Canera Bank and Syndicate Bank etc.

(1) Accepting deposits – This is one of the primary function of the bank. The main purpose of banks is to promote savings and accept deposits from customers. Banks offer facilities in different ways to suit the needs, tastes and preferences of the customers. Deposits are accepted mainly in current, savings, fixed deposit, home safe and recurring deposits accounts.
(2) Advancing loans – This is also the important function of the bank. The bank advances loans to merchants and manufacturers at higher rates of interest than what it allows on deposits. The difference between the two rate of interest is the profit of the bank. The bank advances loans through cash credit, bank overdraft, discounting of bills etc.
(a) Cash credit- In this method, the bank instead of making payment to the borrower in cash, deposits the money in the Current Account, opened in the name of the borrower. The borrower can withdraw the money by using cheques upto specified limit. The bank asks the borrower to submit a promissory note for the loan. Cash credit is like overdraft arrangement, but for this purpose it is not necessary to operate a current account. Interest is to be paid on the amounts with drums.
(b) Bank overdraft – This facility is granted by the bank to its current account holders. Under this arrangement the customer is authorised to withdraw more than the amount deposited. The amount of overdraft is settled between the bank and customer. This facility is granted without holding security’. Interest is charged by the bank on the amount actually withdrawn on monthly basis. In practice the customer pledges security of stock of goods.
(c) Discounting of the bills – Financial help can also be sought from the bank by discounting Bills of exchange before the due date. The bank charges interest in the shape of discount for the period between date of discounting and the due date of the bill. The bank pays the amount or credits the amount into the account of the drawer after deducting discount.
3. Agency functions – Commercial banks perform the following agency functions:
(a) Collection of cheques, bills and drafts- Bank collects cheques, drafts and bills on behalf of its customers. The customer deposits his cheques received from outside parties, bills accepted by other parties and bank drafts received from outside. Bank collects the amounts of these documents and credits the money into the customers’ accounts.
(b) Collection of interest and dividends etc. – The customer may – have invested in shares and debentures and received interest and dividend. The bank may be instructed to collect interest and dividend on behalf of the customer and deposit in his account.
(c) Payment of interest, instalment of loan and insurance premium etc.-The customer may instruct the bank to make the payment of his instalment of loan borrowed by him and interest thereon. He may also instruct the bank to make payment of his insurance premium, rent of the shop, factory, residence etc. The bank, after making payment of these expenses debits the amount to customers’ account.
(d) Purchase/Sale of securities – The bank can also work as an agent of the customer and assist in purchasing/selling shares, debentures, bonds, certificates and government securities.
(e) Transfer of funds through drafts/mail transfers – Bank provide facilities to transfer funds from one place to another place at nominal charges. Bank also provides the facility of purchase and sale in foreign currencies.
4. Other services – In addition to agency services banks provide other miscellaneous services also:
(a) Issuing travellers cheques – There is always risk to undertake long journey from one place to another place with large sum of money in cash. Banks issue travellers cheques for the desired amount. The cheque can be encashed for the desired amount at different places. The amount paid against cheque are entered at its back. The total amount withdrawn cannot exceed the amount of the cheque. Travellers cheque ensure safe journey without risks.
(b) Issuing letter of credit – The bank issues letter of credit on-demand to its customers. Sometimes suppliers of goods and lenders of money insist upon letter of credit issued by the bank.
(c) Locker or custodial services – There is always great risk in keeping large amount of cash, jewellery and other valuables. The bank offers an opportunity in the form of lockers in the premises of the bank itself, where valuables can be kept on payment of nominal charges. There are two or three keys of the locker, so for opening and closing it both the keys (one kept by the bank and the other kept by the customers) are used. The locker is operated by the customer as and when required.
(d) Underwriting securities – Underwriting means undertaking the risk to subscribe for shares and debentures of Companies in case applications from public fall short. Banks also underwrite shares and debentures of companies. In this way, banks help in building and strengthening capital market.
(e) Dealing in foreign exchange – Foreign currency is required for import, export, foreign travel and all sorts of foreign dealings. We can get foreign exchange through banks.
(f) Providing references – Sometimes creditors and money lenders require from the customers trade references, preferably from banks. Reference services are also provided by the government.
(g) Issuing bank drafts – Bank drafts are the economical and safest means of sending money. It is an instruction of the bank to its branch to pay the certain specified amount to the particular party. These bank drafts can be obtained against bank account and can also be obtained by cash payment.
(h) Advisory functions – Bank also functions as a friend, philosopher and guide of his customers. Bank renders advisory services on economic matters to its customers.
Question 3. Write a detailed note on various facilities offered by the Indian Postal Department. Answer: Indian post and telegraph department provides various postal services a cross India. For providing these services the whole country had been divided into 22 postal circles. These circles manage the day-to-day functioning of the various head post offices, sub-post offices and branch post offices. Through their regional and divisional level arrangements, the various facilities provided by postal department are broadly categorized into:
(i) Financial facilities: These facilities are provided through the post office’ savings scheme like Public Provident Fund (PPF), Kisan Vikas Patra and National Saving Certificates in association to normal retail banking functions of monthly income schemes, recurring deposits, savings account, time deposits and money order facility.
(ii) Mail facilities: Mail services consist of parcel facilities that is the transmission of articles from one place to another; registration facility to provide security of the transmitted articles and insurance facility to provide insurance cover for all risks in the course of transmission by post.
(iii) Financial services: (SCSS, PPF, KVP, NSC, TDJ) Senior Citizen Savings Scheme (SCSS): Any individual who has attained the age 60 years on the date of opening or who has attained the age of 55 years and who has voluntarily retired from the service can open this account. Here, the account holder gets an attractive interest. Automatic transfer of interest into savings account facility is available.
Joint account is opened with the spouse only and not with any other person. The amount of deposit is Rs. 500/- and maximum is Rs. 1.0 lakh. Subject to certain conditions loan facilities are available after 3 years. The investment by an individual will qualify for tax deduction under section 88 of IT Act. .
(iv) Kisan Vikas Patras (KVP): The certificates will be available in the denominations of Rs. 100, Rs.500, Rs. 1000, Rs.5000, Rs. 10000 and Rs.50000. certificates will be issued to individuals only. There is no limit for purchase. Certificates can be cashed at any time after expiry of 2 years and 6 months from the date of purchase. Nomination and identity slip facilities are available. .
(v) National Saving Certificate (NSC): NSC VIII Issue available in denominations of. 100,500,1000,5000 and 10,000 can be issued to individuals only. The maturity period shall be 6 years from the date of issue. There is no limit for purchase. Only local cheques are accepted. They can be pledged as security.
A nomination facility is available. No premature encashment is permitted in the normal course. Investments by individuals will qualify for tax deduction under Income Tax Act.
(vi) Time Deposit Accounts (TD): There are four types of accounts, namely 1-year, 2-year, 3-year and 5-year accounts. A single can open an account, two adults jointly, Guardian on behalf of a minor or a minor himself who has attained the age of 10 years. Any number of accounts can be opened. There shall be only one deposit in an account.
The deposit should be in multiples of Rs. 200 and there is no maximum limit. Annual interest can be automatically credited to the savings account of the depositors, Post maturity interest shall be allowed for a maximum period of 24 months SB rate premature closure of the account is permitted on some conditions.
Question 4. Describe various types of insurance and examine the nature of risks protected by each type of insurance. Answer: 1. Life Insurance Life insurance is a contract between a person and an Insurance company. According to the contract of insurance a specified sum of money is payable by insurance company on the death of the insured or after the expiry of the policy period, whichever is earlier in consideration to the payment of the premiums, whenever due. The amount of the premium is determined on the basis of the amount of the policy, the period of the policy and terms of the premium, whether monthly, quarterly, half-yearly or annually.
There is an element of investment in the life insurance, because the amount of the policy is received in both the cases i.e. on the death of the insured or at the expiry of the policy. Life insurance is not a contract of indemnity because it is impossible to compensate the deceased policyholder. The person whose life is insured is called the assured. The consideration paid to the insurance company is premium. It is based on good faith and based on insurable interest in the like assured.
2. Fire Insurance Fire insurance is an agreement between the insurance company and the owner of the property, wherein insurance company, after receiving specified premium assures actual loss or the amount of the fire policy (whichever is less) will be paid if the insured property catches fire.
Fire insurance is a contract of indemnity. It is based upon the principle of good faith. The insured must have an Insurable interest in the subject-matter of Insurance. It must exist both at the time of insurance and at the time of loss. It is a contract from year to year on a renewable basis.
3. Marine Insurance Marine insurance is an agreement in which the insurance company assures to compensate for the loss, if any, caused by insured marine perils after the receipt of the premium. Marine policies can be taken for the ship, loaded goods (cargo) for freight” and salaries of employees etc.
This contract is based on utmost good faith. Both the insured and the insurer must disclose everything which is in their knowledge and can affect the contract. Insurable interest must exist at the time of actual loss incurred and based on the approximate cause for which insurance policy is taken.
4. Miscellaneous Insurance Some important types of insurance have been discussed below:
(1) Motor Vehicle Insurance – Under this insurance vehicles on roads such as motors, trucks, cars, vans, motorcycles, scooters etc. are insured. If the insured vehicle is lost or damaged or becomes the victim of accident, the insurance company compensates for the actual loss or the amount of the policy, whichever is lower. If the insured vehicle causes damage to any other vehicle the insurance company will compensate to the owner of other vehicle. Motor vehicle insurance is classified as follows:
(a) Comprehensive Insurance — This insurance covers all types of risk causing damage to the insured vehicle.
(b) Third Party Insurance – If any vehicle causes damage to any person or vehicle the owner of the vehicle will compensate. The insurance company under Third Party Insurance will compensate to the owner of vehicle only.
(2) Burglary Insurance – Under this insurance, loss due to theft or burglary is compensated by the insurance company. While taking policy detailed information of the article to be insured is furnished. The insurance company compensates for the loss of the insured due to theft or burglary. Insured items may include gold and ornaments, other household items such as refrigerator, T.V., Air Conditioners etc.
(3) Personal Accident Insurance – This insurance policy is taken to compensate for the loss caused by accident. If the insured person dies or meets any fatal accident, the insurance company makes the payment of the insured amount to the person himself if he survives or to the nominee of the insured person, if he dies. In case of partial disability the amount is paid according to the terms and conditions of the insurance policy. The insurer, in an accident policy, is liable only if the unfair or death is caused by an accident and not due to natural causes.
(4) Fidelity Insurance-This insurance policy protects against the loss caused by embezzlement, dishonesty and fraud of employees. In order to protect itself from losses caused by these misshaping the insurance company guarantees to compensate for the loss caused by dishonesty of employees. If the business suffers any lose due to the fraud of the employee, the insurance company compensates for it. In case of this insurance policy the business cannot make any change in the service conditions of the employee without consulting insurance company.
(5) Employees Accident Insurance – Workers working in the factory may be subjected to any accident.at any time while working in the factory. In case of partial loss of limbs or disability, the owner of the factories have to compensate for the loss to the employees as per the provisions of factory act. If the factory owner desires, he can get the risk insured with the insurance company. In the case of insurance, the insurance company will have to compensate the employee.
(6) Health Insurance – Under this insurance policy medical expenses of illness and disability are covered by the Insurance. This type of Insurance can transfer the burden, of the costs of illness or accident, so that people do not have to face financial ruin, because of poor health. This insurance covers basic medical expenses, major medical expenses, disability income and long term hospitalization reimbursement of charges.
Question 5. Explain in detail the warehousing services. Answer: Functions Of Warehousing (1) Stability in prices-Warehousing maintains the stability of price by storing goods in the godown and releasing as per requirements of the market. Prices of seasonal commodities can be stabilised. Warehousing help in removing violent fluctuation in the prices of goods through smooth supply throughout the year.
(2) Surety for loan – The warehouse receipt can be deposited with the bank and the lending institution as security against loans borrowed.
(3) Storage facility—Surplus goods required to be used in future can be stored in godown and taken back, whenever required.
(4) Safety of goods – Godowns are specially made to keep goods safe. Certain godown storing specific commodities are built to suit the nature of the commodity. Goods are always safe in their proper godowns. Godown safeguards the show of merchandise from deterioration pilferage and vastage etc.
(5) Other functions-Warehouses provide facilities for grading and packaging of goods. In case of bonded warehouse, the importer gets reasonable time to arrange funds to make the payment of customs and other dock charges.
Importance Of Warehousing
Goods are stored by manufacturers, producers, farmers, wholesalers and even retailers. Storage and warehousing have the following advantages and importance:
(1) Protection of goods-A warehouse protect goods against pilferage, theft and damage. After keeping goods in the godown the businessman are carefree. Goods are preserved free from rain moisture, pests, fire etc.
(2) Useful for seasonal goods – There are certain things which are produced once in a year and used throughout the year, such as wheat, rice, sugar, potatoes etc. By keeping goods in the warehouses, goods are available throughout the year.
(3) Seasonal consumption of goods – There are certain commodities which are produced throughout the year but consumed during the season. These commodities are woolen garments, heaters, coolers etc. As such in order to maintain balance between demand and supply these commodities are required to be stored safely. A warehouse acts as a reservoir of store house of surplus goods.
(4) Production to meet future demand – These days goods are produced on a large scale in anticipation of future demand. There is time gap between the production and consumption of goods. It is, therefore, necessary that goods should be kept safe and secured during this period.
(5) Storage of raw material – Production is a continuing activity, so raw material is required throughout the year. Supply of raw material can be maintained throughout the year by proper storing of raw material.
(6) Stability of prices – In order to maintain the stability of price, it is necessary that surplus goods during the season should be stored and brought out during the offseason. This will also check the fluctuation of price.
- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes Chapter 4
Home » CBSE » CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes Chapter 4

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes Chapter 4 – Business Services
The Business Studies Class 11 Notes Chapter 4 gives a comprehensive and detailed outline of all topics entailed in the chapter following the latest CBSE Syllabus. Extramarks provides Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Notes to help students develop an in-depth understanding of the chapter. Going through the notes will help them score better marks in exams.
Quick Links
Access Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 – Business Services Notes in 30 Minutes
Introduction to class 11 business studies chapter 4 notes .
In Chapter 4 Business Studies Class 11 Notes , students will have an overview of varied topics such as goods and services, types of services and the differences between goods and services. It also covers what banks are and the different types of banks. Even the modern interpretation of the banking system, which is E-Banking and its numerous advantages over the traditional method are elaborated.
Insurance, its principles, the various types of insurance and their differences are discussed towards the end of the notes. Business Studies Class 11 Chapter 4 Notes also include pointers on the different aspects of a business like transportation, communication and warehousing.
Goods and Services
A good can be defined as a product that is tangible and involves the transfer of ownership from the seller to the buyer.
On the contrary, a service is an intangible action that meets the demands but is not related to the selling of a product or service. The nature of services is discussed below:
- Intangible – Services are experiential and hence, cannot be touched. One cannot predict the quality of service unless it is consumed.
- Inconsistency – A major difference between a good and a service is that services are catered differently depending on the customer’s demands and expectations. Every customer experiences a different service each time.
- Inseparability – Unlike goods, the production and consumption of services happen simultaneously. They are depleted as soon as they are manufactured.
- Inventory – Services cannot be stored like goods. They are consumed immediately after production.
- Involvement – This is one of the major characteristics of services. The presence of customers during the production of the service is a must. It is so as to make sure it meets their standards. Hence, a customer can get the service modified as per his/her specific requirement.
The different types of services that are provided are:
- Social Services: These are provided voluntarily to achieve some goals. For example, healthcare and education services are provided by Non-Governmental Organisations.
- Personal Services: These services are offered according to the wants and preferences of the customer. Each client has a unique experience with these services. For example, tourism.
- Business Services: These services are used by business enterprises to facilitate soother functioning. For example, banking, warehousing, insurance, communication, etc.
Banking and Types
A bank is a financial institution authorised to both, accept deposits and issue loans. It transacts money, helps with the withdrawal and lending of money to people and allows them to deposit money for investment and saving purposes. The various types of banks are:
Commercial banks: Commercial banks, which are governed by the Indian Regulation Act of 1949, assist in accepting funds from the general public for lending and investing. Commercial banks perform the following duties:
Primary Functions
- Accepting Deposits: It is the main function of commercial banks. To meet the demands and needs of customers, they provide the following types of bank accounts:
- Fixed Deposit Account: A fixed deposit account is one where money is deposited for a predetermined amount of time. In such a case, after the expiry of the specified period, the account holder can claim the money from the bank. Generally, the rate of interest is maximum in such accounts, the longer the period of deposit, the higher the rate of interest on the deposit.
- Current Deposit Account: Current deposit Accounts are used in business. The amount that the account holder may deposit and withdraw is not restricted. The deposit is referred to as a demand deposit because it is repayable immediately. For current accounts, there is no interest due. Instead, the account holder is charged by the bank for the services it provides.
- Saving Deposit Account: Saving accounts help in mobilising the savings of the public. People can open this account by depositing only a small sum of money. He/she can further withdraw money from the account and make additional deposits in his/her will. Generally, the rate of interest on a savings deposit account is lower than the rate of interest payable on a fixed deposit account.
- Recurring Deposit Account: Such accounts aim to encourage regular savings by the people. The account holder can deposit a fixed amount, say Rs. 500 each month for a fixed period, the amount being repayable along with interest on maturity. The rate of interest on such an account is usually higher than that on saving accounts.
- Multiple Option Deposit Account: This type of savings account automatically transfers deposits that exceed the predetermined limit into a fixed deposit account. On the other hand, the necessary amount is automatically transferred from the fixed deposit to the savings bank account when there is not enough money in the savings bank account to honour an issued check. As a result, the account holder gains two main advantages from having one of these accounts: they can earn more interest and there is less chance that their cheque will be returned.
2. Lending Money: Commercial banks lend money to people using the funds they have accumulated from various types of deposits. The various ways that commercial banks lend money include the following:
- Term Loans: These loans are provided for a fixed period by the banks to purchase machinery, trucks, houses, etc. Such loans are repaid in monthly/ quarterly/ half-yearly or annual instalments.
- Bank Overdraft: A bank overdraft occurs when a current account holder requests permission from the bank to withdraw more money than has been deposited into his account. This loan is typically granted in exchange for the customer’s personal security or the security of some of his or her assets. In this scenario, the customer is responsible for paying interest on the actual overdraft.
- Cash Credit: In this option, the bank makes cash advances on loans that are backed by securities up to a predetermined sum. The bank establishes an account in the borrower’s name and allows limited, intermittent withdrawals of the borrowed funds. On the amount that was actually withdrawn, interest must be paid later.
- Discounting of a Bill of Exchange: Under this arrangement, when any customer needs money before the expiry of the bill of exchange, the bank gives money to him on the security of a bill of exchange. In return, the bank charges a discount for the remaining period of the bill.
Secondary Functions
The secondary functions of commercial banks are:
(A) Agent Functions- As an agent of its customers a commercial bank provides services like:
(B) Collecting bills of exchange, promissory notes and cheques on behalf of its customers.
(C) Collecting dividends, interest, etc. on behalf of its customers.
(D) Purchase and sale of shares, debentures and other securities.
(E) Payment of interest and transferring funds from one branch to another.
(F) They act as agents of representation while dealing with other financial institutions and banks on behalf of their customers.
2) General Utility Functions- Commercial banks also perform the following general utility functions:
(A) They provide lockers for the safe custody of jewellery and other valuable items of customers.
(B) They give references about the financial position of customers.
(C) They provide customers with information regarding the creditworthiness of other customers.
(D) They provide various types of trade information useful to customers.
(E) Issuance of letter of credit, pay orders, credit and debit cards, bank draft and traveller’s cheques to customers.
(F) Providing foreign exchange to importers and people travelling abroad.
Cooperative Banks: These banks are governed by the provisions of the State Cooperative Societies Act. In this banking system, cheap credit is provided to the members which helps to serve them better in the long run.
Specialised Banks: These banks are Foreign Exchange Banks that provide financial aid to industries for massive projects and foreign trade.
Central Bank: It is the supervisor of all the commercial banks in the country. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central bank in India.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. discuss the functions of commercial banks..
Some functions of the commercial banks are as follows:
- Acceptance of Deposits – It is the basis on which commercial banks function and also causes them to be both borrowers and lenders of money.
- Cheque Facility – This is one of the most developed credit facilities in practice for a couple of years.
- Lending of Funds – Commercial banks lend funds (in the form of loans) through advances from the deposits received.
- Remittance of Funds – It is the facility of money transfer from one place to another.
- Allied Services – Include locker facilities, bill payments and underwriting facilities provided by commercial banks.
2. Discuss the various types of Insurance.
The various types of Insurance are as follows:
- Life Insurance – In this insurance, the insurer in consideration of the contract agrees to pay either a lump sum or periodical payments of the lump sum amount to the assurer. Herein, in case of any contingency to the insurer, that amount is received in full by the nominee.
- Fire Insurance – In this insurance, the insurer receives guaranteed compensation for the goods damaged (by fire) that are under the fire insurance contract.
- Marine Insurance – Against any marine losses, the insurer of such insurance receives the money that is put up in the contract.
3. Why should I prefer Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 revision notes of Extramarks?
If you want to be quick with revision and exam preparation, the revision notes provided by Extramarks are the best option for you. These notes are prepared by the subject-matter experts of the field to help you get conceptual clarity in all chapters.
4. What is a business service?
A service is an immaterial good that can satisfy desires; it typically happens after a transaction is finished. Businesses use a variety of services, such as banking, warehousing, communication, insurance and transportation to operate more successfully and efficiently. These specialised business services are now necessary for the majority of businesses to operate effectively.
5. What is a bank?
A bank is a financial establishment that has the authorisation to both, lend money and accept deposits. A couple of the financial services that banks offer are money management and currency exchange. For instance, a business service might be banking. We require various kinds of banks to meet these needs because the banking sector encompasses a wide range of interests, needs and strategies. Commercial, cooperative, central and specialised banks are the four different categories of banks.

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.
Business Studies for Class 11 Chapter 4 Business Services
Learn cbse business studies index terms for class 11, chapter 4 including definitions and meanings.
1. Business Service – Business services are the activities that assist businesses yet do not deliver a tangible commodity. For instance, Information technology is one business service that supports various other business services such as shipping, procurement, and finance. Most businesses today are inclined towards such specialised business services.
In other words, business services are services used by business enterprises in conducting the activities of the business. For example, Banking, insurance, warehousing, communication services, etc.
2. E-Banking – Electronic banking has many names like web-based banking, e-banking, virtual banking, web banking, and online banking. It is just the utilisation of telecommunications networks and electronic networks for conveying different financial services and products. Through e-banking, clients can acquire their records and manage numerous exchanges utilising their cell phones or personal computers.
3. Commercial Banks – The term commercial bank is concerned with a monetary establishment that acknowledges deposits, offers financial account services, makes various advances, and offers fundamental monetary items like savings accounts and certificates of deposit (CDs) to people and private business entities.
4. Banking – Banking is directly or indirectly connected with the trade of a country and the life of each individual. It is an industry that manages credit, cash, and other financial transactions. In banking, the commercial bank is the most influential institution for any country’s economy or for providing any credit to its customers.
In India, a banking company is responsible for transacting all business transactions, including the withdrawal of cheques, payments, investments, etc. In other words, the bank is involved in the deposit and withdrawal of money, repayable on demand, savings, and earning a decent amount of profits by lending money.
Banks also help to mobilise the savings of an individual, making funds accessible to businesses and helping them to start a new venture.
5. Insurance – Represented in the form of policy, insurance is a contract in which the individual or an entity gets financial protection; in other words, reimbursement from the insurance company for the damage (big or small) caused to their property.
The insurer and the insured enter a legal contract for the insurance called the insurance policy that provides financial security from future uncertainties.
6. Insurable Interest – The principle of insurable interest says that the individual (insured) must have an insurable interest in the subject matter. Insurable interest means that the subject matter for which the individual enters the insurance contract must provide some financial gain to the insured and also lead to a financial loss if there is any damage, destruction, or loss.
7. Indemnity – The principle of indemnity says that insurance is done only for the coverage of the loss; hence insured should not make any profit from the insurance contract. In other words, the insured should be compensated the amount equal to the actual loss and not the amount exceeding the loss. The purpose of the indemnity principle is to set back the insured in the same financial position as he was before the loss occurred. The principle of indemnity is observed strictly for property insurance and is not applicable to the life insurance contract.
8. Proximate Cause – The principle of proximate cause is also called the principle of ‘Causa Proxima’ or the nearest cause. This principle applies when the loss is the result of two or more causes. The insurance company will find the nearest cause of loss to the property. If the proximate cause is the one in which the property is insured, then the company must pay compensation. If it is not a cause the property is insured against, then no payment will be made by the insured.
9. Subrogation – Subrogation means one party stands in for another. As per this principle, after the insured, i.e. the individual has been compensated for the incurred loss to him on the subject matter that was insured, the rights of the ownership of that property go to the insurer, i.e. the company.
Subrogation gives the right to the insurance company to claim the amount of loss from the third party responsible for the same.
10. Contribution – The principle of contribution applies when the insured takes more than one insurance policy for the same subject matter. It states the same thing as in the principle of indemnity, i.e. the insured cannot make a profit by claiming the loss of one subject matter from different policies or companies.
11. Mitigation – The principle of mitigation says that as an owner, it is obligatory on the part of the insurer to take necessary steps to minimise the loss to the insured property. The principle does not allow the owner to be irresponsible or negligent just because the subject matter is insured.
12. Life Insurance – The insurance policy whereby the policyholder (insured) can ensure financial freedom for their family members after death. It offers financial compensation in case of death or disability.
While purchasing the life insurance policy, the insured either pays the lump-sum amount or makes periodic payments known as premiums to the insurer. In exchange, of which the insurer promises to pay an assured sum to the family if insured in the event of death or disability or at maturity.
13. Fire Insurance – Fire insurance is a type of general insurance policy where the insurer helps in paying off any damage that is caused to the insured by an accidental fire till the specified period of time, as mentioned in the insurance policy.
Generally, a fire insurance policy is valid for a period of one year, and it can be renewed each year by paying a premium, which can be a lump sum or in instalments.
The claim for a fire loss must satisfy the following conditions:
i. It should be an actual loss
ii. The fire must be accidental and not done intentionally.
14. Marine Insurance – Marine insurance is a contract between the insured and the insurer. In marine insurance, protection is provided against the perils of the sea. The instances of dangers in the sea can be a collision of the ship with rocks present in the sea, attacking off the ship by pirates, or fire on the ship.
Marine insurance covers three different types of insurance which are ship hull, cargo, and freight insurance.
15. Telecom Services – Telecom services are the exchange of data and information between the sender and the receiver over long distances by electronic means. This includes the transmission of voice, audio, and video information from one place to another.
16. Warehousing – Warehousing was initially viewed as a provision of static units for keeping and storing goods in a scientific and systematic manner so as to maintain their original quality, value, and usefulness, but now it is viewed as a logistical service provider of the right quantity, at the right place, in the right time, in the right physical form at the right cost.
We hope that the offered Business Studies Index Terms for Class 11 with respect to Chapter 4: Business Services, will help you.
Related Links:
- Business Studies for Class 11 Chapter 1 Nature and Purpose of Business Index Terms
- Business Studies for Class 11 Chapter 2 Forms of Business Organisation
- Business Studies for Class 11 Chapter 3 Public, Private, and Global Enterprise
- Business Studies for Class 11 Chapter 5 Emerging Modes of Business
- Business Studies for Class 11 Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics
- Business Studies for Class 11 Chapter 7 Formation of a Company
- Business Studies for Class 11 Chapter 8 Sources of Business Finance
- Business Studies for Class 11 Chapter 9 MSME and Business Entrepreneurship
- Business Studies for Class 11 Chapter 10 Internal Trade
- Business Studies for Class 11 Chapter 11 International Trade
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Business Services
Class 11 business studies chapter 4 business services.
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Business Services, (Business Studies) exam are Students are taught thru NCERT books in some of state board and CBSE Schools. As the chapter involves an end, there is an exercise provided to assist students prepare for evaluation. Students need to clear up those exercises very well because the questions withinside the very last asked from those.
Sometimes, students get stuck withinside the exercises and are not able to clear up all of the questions. To assist students solve all of the questions and maintain their studies with out a doubt, we have provided step by step NCERT Solutions for the students for all classes. These answers will similarly help students in scoring better marks with the assist of properly illustrated Solutions as a way to similarly assist the students and answering the questions right.
Short Questions Answers
1. Define services and goods?
Services are referred to as any intangible activity that involves interaction between the service provider and consumer. Purchasing the service does not result in ownership of any physical item.
Goods refer to objects that are tangible and have a physical appearance. The ownership of a good is transferred as soon as it is purchased.
2. What is e-banking? What are the advantages of e-banking?
Electronic banking or e-banking is the application of electronic medium for conducting different types of banking transactions which includes money transfer, account balance checking, applying for cheque book and applying loans. These services are provided by banks to help their customers access banking facilities anywhere, anytime.
Some advantages of e-banking are:
1. It ensures round the clock availability of most banking services which helps make life comfortable for the customers.
2. Banking transactions can be conducted anytime either through mobile or computer/laptop.
3. It reduces the load on banks by facilitating transactions online.
3. Write a note on various telecom services available for enhancing business?
Various types of telecom services are available which help in enhancing business. These are mentioned below:
1. Cellular Mobile Service: This includes all types of voice, non-voice and data transmission services.
2. Radio Paging Service: This service helps transmit information in the form of a tone, numeric or alphanumeric message.
3. Fixed-line service: It is about services that include voice, non-voice and data services that establish links for long distance traffic using network connectivity through fiber optic cables.
4. Cable Service: In cable service media information is transmitted in a defined area and for transmitting such information license needs to be acquired. Flow of information is one sided in this type of service.
5. VSAT Service: VSAT stands for Very Small Aperture Terminal, it is a type of satellite based communication system that can be used to provide information to remote areas.
6. DTH Service: DTH stands for Direct-to-home services, these are satellite based media service in which media channels can be transmitted through a satellite and received through small dish and antenna.
4. Explain briefly the principles of insurance with suitable examples?
Principle of insurance are as follows:
1. Utmost good faith: This principle states that both insurer and insured must have faith in each other and on the contract signed by them. For e.g. if a person is suffering from cancer, and does not inform the same to the insurance company, the insurance can reject the claim.
2. Insurable Interest: The owner of an insurance policy should have an ownership interest in the subject matter or object that is insured. The absence of an insurable interest makes the policy null and void.
For e.g a truck driver has an insurable interest in truck as it is source of income, if he sells the truck he cannot earn any more money from it.
3. Indemnity: The principle of indemnity ensures that the insurance contract protects and compensates the insured from any loss. For e.g if a car is insured for 2 lakhs suffers some damage amounting to Rs.1 lakh, then the insurance company will compensate only the 1 lakh to the insured. The idea is to compensate the insured, not to make him gain any profit.
4. Proximate cause: This principle is used to determine the cause of loss and if that loss is due to the object insured. For e.g. If a house is burnt down by fire, it will be checked to see how fire started, and the compensation will be based on insurance against fire.
5. Subrogation: This principle states that once the appropriate compensation is paid, the ownership of the property or object gets transferred to insurer so that the insured cannot sell the property for profit.
For e.g. If a person receives 1 lakh as damage to car from car insurance, He can repair the car, but not sell it for profit.
6. Contribution: If there are 2 insures from which insurance is taken then in case of any loss, both the insurance will contribute to fill up the loss. For e.g. a person has taken loan from 2 banks, then in case of repayment both banks should equally contribute.
7. Mitigation: The insured should be taking care of the object that is insured. Like it was taken care before getting the insurance. For e.g. if a car is purchased the owner should take proper care and maintain the car.
5. Explain warehousing and its functions?
Warehousing was initially thought of as an arrangement for storing goods in a scientific manner in order to preserve their quality, value and usefulness. In modern times, it has become more relevant as a logistical service provider with emphasis on providing goods at the right time and in a cost effective manner, while preserving the value and quality.
Functions of a Warehouse:
1. Goods that are not needed on an immediate basis can be stored in warehouses. The goods can be supplied as and when required by the customers.
2. Consolidating is necessary for goods that are produced in small quantities but sold to customers in bulk. Warehouse help in consolidation of the goods.
3. A warehouse also stocks goods in bulk and then dispatches the items in small quantities as per requirements of consumers. This is called breaking the bulk.
4. The functions of packaging, labelling and sorting of goods are some of the value added service that a warehouse provides.
5. It also helps in price stabilisation by adjusting supply of goods as per demand in market.
Long Questions Answers
1. What are services? Explain their distinct characteristics?
The distinct characteristics of services are:
1. Intangibility: The first and the foremost characteristic of service is that it is intangible in nature, i.e. it lacks a physical form. It can only be experienced.
2. Inseparability: Services are inseparable in nature unlike goods which can be produced at one time and consumed at a different time. Service have to be consumed as soon as it is presented.
3. Inconsistency: Services need to be performed each time and it should be according to the customer requirements. Hence, it is inconsistent in nature.
4. Involvement: There should be involvement between the user availing the service and provider of the service at the time of service delivery. It is essential for accurate delivery of services.
5. Inventory: Services cannot be stored for being used at a later date, it should be provided as soon as it is asked for. Services loses value if it is not consumed immediately.
2. Explain the functions of commercial banks with an example of each.
Commercial banks perform the following functions:
1. Accepting Deposits: Banks accept deposit from customers in the form savings account, recurring deposit, fixed deposit and current account deposit and pay interest to customers on a quarterly, or yearly basis.
2. Lending: Banks also act as lenders by granting loans in form of overdrafts, cash credit, trade bills etc. The bank earns profit by charging interest to customers on such loans.
3. Fund Remittance: Banks provide the facility of transferring funds of customers to different places. These transfers are facilitated by banks in form of pay orders and bank draft adding some transaction charge.
4. Check extension facility: Banks collect cheques from other banks and therefore act as clearing house for all cheques. Cheques are of two types: bearer cheques and crossed cheques.
5. Other value added service: Banks provide value added services like locker facility, bill payment, selling and buying of shares.
3. Write a detailed note on various facilities offered by Indian Postal Department.
The Indian Postal Department provides the following facilities:
Various saving schemes are offered which includes
1. Kisan Vikas Patra
2. National Savings Certificate
3. Fixed Deposit Scheme
4. Public Provident Fund
5. Recurring Deposit
6. Money order
Mail Services: Post office provides these type of facilities in mailing which includes:
1. Parcel Facility: It is the facility of providing parcel service from one destination to other.
2. Registration of parcels to provide security during the transit.
3. Insurance facility providing safety cushion.
Other Facilities:
1. Passport Service: Helps in applying for Passport
2. Direct Post: These comprises of brouchers, questionnaires, pamphlets.
3. This service involves speedy transfer of article to the intended addresses.
(iv) Speed Post:
It involves fast and speedy transfer of articles to the addressees within a specified period.
4. Describe various types of insurance and examine the nature of risks protected by each type of insurance.
Following types of insurance are there:
1. Life Insurance
2. Fire Insurance
3. Marine Insurance
Life insurance: It is a type of insurance where there is a contract between the insurer and the insured in which the insurer agrees to pay a pre-specified amount on the event of death of the insured or on the maturity of the insurance policy. The need of an insurance policy arises in current times due to the uncertainties of the life. In case of death of the insured the family members receive the assured amount, while if the insured survives the maturity period, he will be getting a specified sum of money. The insured needs to pay a premium to the insurer which may be monthly, quarterly or yearly. Life insurance policies protects the insured from the risk of dying early.
Fire Insurance: This type of insurance protects the insured from damage to property caused by fire, here the insurer accepts a premium from the insured with the assurance of compensating the insured in an event of loss, damage to the property caused due to fire. Fire insurance protects against the risk of property damage due to fire.
Marine Insurance: In a marine insurance the owner of a ship, cargo is protected against loss or damage of ship or cargo in sea. It provides protection against the risks faced at the sea in forms of high tides, pirates, storm, rock or damages caused by fire. The insured needs to pay a certain amount of premium based on the amount protected.
5. Explain in detail the warehousing services.
Benefits of NCERT Solutions
NCERT’s Class 11 solution contains extremely important points, and for each chapter, each concept has been simplified to make it easier to remember and increase your chances of achieving excellent exam results. Exam Preparation References Here are some tips on how these solutions can help you prepare for the exam.
- This helps students solve many of the problems in each chapter and encourages them to make their concepts more meaningful.
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 solutions encourage you to update your knowledge and refine your concepts so that you can get good results in the exam.
- These solutions are the best exam materials, allowing you to learn more about your week and your strengths. To get good results in the exam, it is important to overcome your weaknesses.
- Most of the questions in the exam are formulated in a similar way to NCERT textbooks. Therefore, students should review the solutions in each chapter in order to better understand the topic.
- It is free of cost.
Tips & Strategies for Class 11 Exam Preparation
- Plan your course and syllabus and make time for revision
- Please refer to the NCERT solution available on the cbsestudyguru website to clarify your concepts every time you prepare for the exam.
- Use the cbsestudyguru learning app to start learning to successfully pass the exam. Provide complete teaching materials, including resolved and unresolved tasks.
- It is important to clear all your doubts before the exam with your teachers or Alex (an Al study Bot).
- When you read or study a chapter, write down algorithm formulas, theorems, etc., and review them quickly before the exam.
- Practice an ample number of question papers to make your concepts stronger.
- Take rest and a proper meal. Don’t stress too much.
Why opt for cbsestudyguru NCERT Solutions for Class 11 ?
- cbsestudyguru provide NCERT Solutions for all subjects at your fingertips.
- These solutions are designed by subject matter experts and provide solutions to every NCERT textbook questions.
- cbsestudyguru especially focuses on making learning interactive, effective and for all classes.
- We provide free NCERT Solutions for class 11 and all other classes.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

WorkSheets Buddy
Download Math, Science, English and Many More WorkSheets
CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies
CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies: One of the best teaching strategies employed in most classrooms today is Worksheets. CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Worksheet for students has been used by teachers & students to develop logical, lingual, analytical, and problem-solving capabilities. So in order to help you with that, we at WorksheetsBuddy have come up with Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 11 Business Studies Worksheets for the students of Class 11. All our CBSE NCERT Class 11 Business Studies practice worksheets are designed for helping students to understand various topics, practice skills and improve their subject knowledge which in turn helps students to improve their academic performance. These chapter wise test papers for Class 11 Business Studies will be useful to test your conceptual understanding.
Board: Central Board of Secondary Education(www.cbse.nic.in) Subject: Class 11 Business Studies Number of Worksheets: 40
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Worksheets PDF
All the CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies provided in this page are provided for free which can be downloaded by students, teachers as well as by parents. We have covered all the Class 11 Business Studies important questions and answers in the worksheets which are included in CBSE NCERT Syllabus. Just click on the following link and download the CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Worksheet. CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies can also use like assignments for Class 11 Business Studies students.
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Business and Business Ethics Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Classification of Business Activities Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Commercial Bank Assignment 1
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Commercial Bank Assignment 2
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Communication services Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies e-banking Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Financial Market Project Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies General Insurance Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Insurance Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Internal Trade Assignment 1
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Internal Trade Assignment 2
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies term source of finance Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Nature And Purpose Of Business Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Priciples of Insurance Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Private, Public And Global Enterprises Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Social Responsibilities Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Sources of Finance Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Telecom Services Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Types of Business Services Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Types of Insurance Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Types of other insurances Assignment
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 1
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 2
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 3
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 4
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 5
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 6
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 7
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 8
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 9
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 10
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 11
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 12
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 13
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 14
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 15
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 16
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 17
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 18
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies Assignment 19
Advantages of CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Worksheets
- By practising NCERT CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Worksheet , students can improve their problem solving skills.
- Helps to develop the subject knowledge in a simple, fun and interactive way.
- No need for tuition or attend extra classes if students practise on worksheets daily.
- Working on CBSE worksheets are time-saving.
- Helps students to promote hands-on learning.
- One of the helpful resources used in classroom revision.
- CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Workbook Helps to improve subject-knowledge.
- CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Worksheets encourages classroom activities.
Worksheets of CBSE Class 11 Business Studies are devised by experts of WorksheetsBuddy experts who have great experience and expertise in teaching Maths. So practising these worksheets will promote students problem-solving skills and subject knowledge in an interactive method. Students can also download CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter wise question bank pdf and access it anytime, anywhere for free. Browse further to download free CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Worksheets PDF .
Now that you are provided all the necessary information regarding CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Worksheet and we hope this detailed article is helpful. So Students who are preparing for the exams must need to have great solving skills. And in order to have these skills, one must practice enough of Class 11 Business Studies revision worksheets . And more importantly, students should need to follow through the worksheets after completing their syllabus. Working on CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Worksheets will be a great help to secure good marks in the examination. So start working on Class 11 Business Studies Worksheets to secure good score.
CBSE Worksheets For Class 11
Share this:.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
AssignmentsBag.com
Business Services Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions
Please refer to Business Services Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 11 Business Studies based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 11 Business Studies for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 11.
Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions Business Services
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. State the five I’s of services? Answer : Nature of services are Intangibility, Inconsistency, Inseparability, Inventory and Involvement
Question. It is the prime responsibility of the insured to take reasonable steps to minimize loss/damage to the insured property. Name the principle of insurance Answer : Mitigation principle of Insurance says as the owner of an insurance policy, you have an obligation to take necessary steps to minimize the loss of your insured property. The law doesn’t allow you to be negligent or irresponsible just because you know you’re insured.
Question. Rahul’s father wants to save Rs. 100,000 so that he can gift the money to Rahul on his graduation day. Which type of deposit should he open with bank? Answer : Fixed Deposit should be opened with bank. Fixed accounts are time deposits with higher rate of interest as compared to the savings accounts.
Question. A company insures its stock against fire for Rs. 15 Lakh. A fire broke down and the total stock was lost. At the time of fire there was stock worth Rs. 25 Lakh. What is the value of compensation company would be entitled to? Answer : The contract of fire insurance is a contract of strict indemnity. The insured can, in the event of loss, recover the actual amount of loss from the insurer. This is subject to the maximum amount for which the subject matter is insured. So, maximum amount of Rs, 15 lakh is the value of compensation.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Mr. Satish gets his house insured against fire of Rs. 20 Lakh with insurer A and for Rs. 10 Lakh with insurer B. A loss of Rs. 3 Lakh occurred. (1) How much compensation can be claimed from A and B separately and Why? (2) Name the principle of Insurance in the above case. Answer : 1. According to this principle, the insured can claim the compensation only to the extent of actual loss either from all insurers or from any one insurer. If one insurer pays full compensation then that insurer can claim proportionate claim from the other insurers A=20Lakh*3Lakh/30Lakh A=2 Lakh B=10Lakh*3Lakh/30Lakh B=1Lakh 2. Principle of Contribution is followed. It applies to all contracts of indemnity, if the insured has taken out more than one policy on the same subject matter. The right of contribution arises when: (a) There are different policies which related to the same subject matters; (b) The policies cover the same period which caused the loss; (c) All the policies are in force at the time of loss; and (d) One of the insurer has paid to the insured more than his share of loss.
Question. Explain the Difference between Goods and services based on its nature Answer :
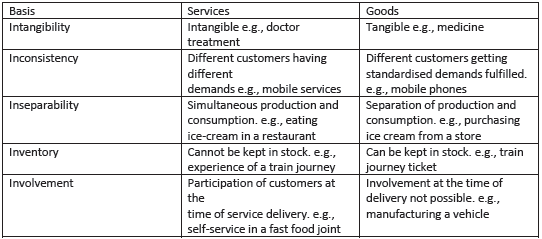
Question. Explain the types of Life Insurance Policies? Answer : Types of Life Insurance Policies: ♦ Whole Life Policy: In this kind of policy, the amount payable to the insured will not be paid before the death of the assured. The sum then becomes payable only to the beneficiaries or heir of the deceased. ♦ Endowment Life Assurance Policy: The insurer undertakes to pay a specified sum when the insured attains a particular age or on his death whichever is earlier. The sum is payable to his legal heir/s or nominee named therein in case of death of the assured. Otherwise, the sum will be paid to the assured after a fixed period ♦ Joint Life Policy: This policy is taken up by two or more persons. The premium is paid jointly or by either of them in instalments or lump sum assured sum or policy money is payable upon the death of any one person to the other survivor or survivors ♦ Annuity Policy: The assured sum or policy money is payable after the assured attains a certain age in monthly, quarterly, half yearly or annual instalments ♦ Children’s Endowment Policy: This policy is taken by a person for his/ her children to meet the expenses of their education or marriage. The agreement states that a certain sum will be paid by the insurer when the children attain a particular age
Question. Explain the Functions of Warehousing? Answer : Functions of Warehousing 1. Consolidation: The warehouse receives and consolidates, materials/goods from different production plants and dispatches the same to a particular customer on a single transportation shipment. 2. Break the bulk: The warehouse performs the function of dividing the bulk quantity of goods received from the production plants into smaller quantities. These smaller quantities are then transported according to the requirements of clients to their places of business. 3. Stock piling: The next function of warehousing is the seasonal storage of goods to select businesses. Goods or raw materials, which are not required immediately for sale or manufacturing, are stored in warehouses. They are made available to business depending on customers’ demand 4. Value added services: Certain value added services are also provided by the warehouses, such as in transit mixing, packaging and labelling. Goods sometimes need to be opened and repackaged and labelled again at the time of inspection by prospective buyers 5. Price stablisation: By adjusting the supply of goods with the demand situation, warehousing performs the function of stabilizing prices. Thus, prices are controlled when supply is increasing and demand is slack and vice versa 6. Financing: Warehouse owners advance money to the owners on security of goods and further supply goods on credit terms to customers
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Describe briefly Types of warehouses? Answer :
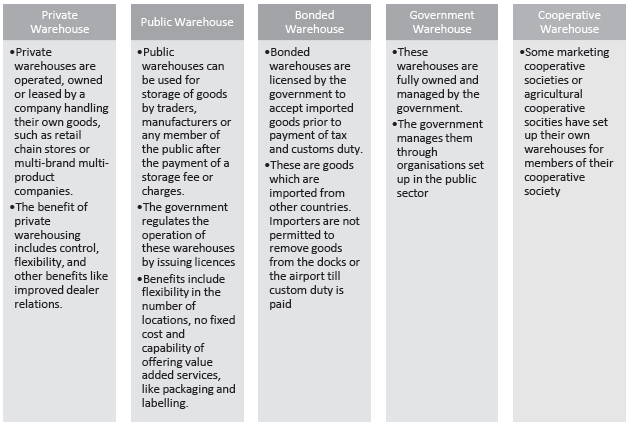
Question. Write notes on RTGS system and NEFT. Also state the difference between them. Answer : NEFT refers to National Electronic Funds Transfer. It is an online system for transferring funds from one financial institution to another within India (usually banks). The system was launched in November 2005, and was set to inherit every bank that was assigned to the SEFT clearing system. It was made mandatory by the RBI for all banks on the SEFT system to migrate to NEFT by mid December 2005. As such, SEFT was discontinued as of January 2006. The RBI welcomed banks that were full members of the RTGS to join the NEFT system. RTGS is an acronym that stands for Real Time Gross Settlement. RTGS is a funds transfer system where money is moved from one bank to another in ‘real-time’, and on gross basis. When using the banking method, RTGS is the fastest possible way to transfer money. ‘Real-time’ means that the payment transaction isn’t subject to any waiting period. The transaction will be completed as soon as the processing is done, and gross settlement means that the money transfer is completed on a one to one basis without clustering with another transaction. The transaction is treated as final and irrevocable as the money transfer occurs in the books of the RBI (Reserve Bank of India). This system is maintained by the RBI, and is available during working days for a given number of hours. Banks using RTGS need to have Core banking to be able to initiate RTGS transactions. Difference between RTGS and NEFT: 1. RTGS is Real Time Gross Settlement, while NEFT is National Electronic Funds Transfer. 2. RTGS completes transactions in real-time, and is therefore faster than NEFT, which completes transactions in cycles. 3. RTGS is gross settlement, where a transfer is completed on a one-to-one basis, while NEFT is on a Deferred Net Basis, where transfers are bundled and deferred for a specific time. 4. RTGS is a high value transfer system, handling funds worth Rs 100,000 and above, while NEFT transfers smaller amounts below Rs 100,000.
Question. Write a detailed note on various facilities offered by Indian Postal Department and different types of telecom services offered? Answer : Indian post and telegraph department provides various postal services across India. Through their regional and divisional level arrangements the various facilities provided by postal department are broadly categorised into: o Financial facilities: These facilities are provided through the post office’s savings schemes like Public Provident Fund (PPF), Kisan Vikas Patra, and National Saving Certificate o Mail facilities: Mail services consist of parcel facilities that is transmission of articles from one place to another; registration facility to provide security f the transmitted articles and insurance facility to provide insurance cover for all risks in the course of transmission by post o Allied Facilities: Greeting post, media post, International money transfer, speed post, passport facilities, e-bill Different types of Telecom services are as follows: ♦ Cellular mobile services: These are all types of mobile telecom services including voice and non-voice messages, data services and PCO services utilising any type of network equipment within their service area. ♦ Fixed line services: These are all types of fixed services including voice and non-voice messages and data services to establish linkages for long distance traffic. These utilise any type of network equipment primarily connected through fiber optic cables ♦ Cable services: These are linkages and switched services within a licensed area of operation to operate media services, which are essentially one-way entertainment related services. ♦ VSAT services: VSAT (Very Small Aperture Terminal) is a satellite-based communications service. It offers businesses and government agencies a highly flexible and reliable communication solution in both urban and rural areas. ♦ DTH services: DTH (Direct to Home) is again a satellite-based media services provided by cellular companies. One can receive media services directly through a satellite with the help of a small dish antenna and a set top box.
Question. Explain in detail the principles of Insurance? Answer :
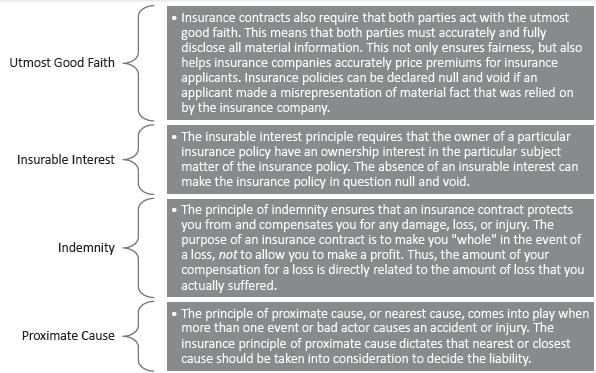
Related Posts

Animal Kingdom Class 11 Biology Important Questions

Mineral Nutrition Class 11 Biology Important Questions

The Living World Class 11 Biology Important Questions
- Saved Papers
Similar Essays
- Personality Theories Workbook Case Study 9: Karen Horney
- Practice Workbook
- Math Workbook Comparison
©2024 Brainia.com
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- CA Privacy Policy
- Advertise With Us

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
All Assignments and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Business Studies Class 11. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf Assignments for Business Studies class 11 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 11 Business Studies Assignments with Answers and test papers are given ...
Short Questions for NCERT Business Studies Solutions Class 11 Chapter 4. 1. Define services and goods. Services are referred to as any intangible activity that involves interaction between the service provider and consumer. Purchasing the service does not result in ownership of any physical item.
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 - Business Services are given in this study in the form of a free-to-download pdf version. Business Studies is quite a broad topic and the Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Notes by Vedantu will help you to develop a precise understanding of what the chapter entails.
These are the Business Services class 11 Notes Business Studies prepared by team of expert teachers. The revision notes help you revise the whole chapter in minutes. Revising notes in exam days is on of the best tips recommended by teachers during exam days. Download Revision Notes as PDF.
Business Services Questions and Answers Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4. Multiple Choice Questions. Question 1. DTH services are provided by. (a) Transport company. (b) Bank. (c) Cellular company. (d) None of the above. Answer:
In Chapter 4 Business Studies Class 11 Notes, students will have an overview of varied topics such as goods and services, types of services and the differences between goods and services. It also covers what banks are and the different types of banks. Even the modern interpretation of the banking system, which is E-Banking and its numerous ...
Learn CBSE Business Studies Index Terms for Class 11, Chapter 4 Including Definitions and Meanings. 1. Business Service - Business services are the activities that assist businesses yet do not deliver a tangible commodity. For instance, Information technology is one business service that supports various other business services such as shipping, procurement, and finance.
Here we are providing Business Studies Class 11 Important Extra Questions and Answers Chapter 4 Business Services. Business Studies Class 11 Important Questions with Answers are the best resource for students which helps in class 11 board exams. ... Assignment: A life assurance policy can be assigned without the permission of the insurance company.
Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Business Services. NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Business Services, (Business Studies) exam are Students are taught thru NCERT books in some of state board and CBSE Schools. As the chapter involves an end, there is an exercise provided to assist students prepare for evaluation.
By practising NCERT CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Worksheet, students can improve their problem solving skills. Helps to develop the subject knowledge in a simple, fun and interactive way. No need for tuition or attend extra classes if students practise on worksheets daily. Working on CBSE worksheets are time-saving.
Assignments Assignments for Class 11. Assignments for Class 11 Business Studies have been developed for Standard 11 students based on the latest syllabus and textbooks applicable in CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools. Parents and students can download the full collection of class assignments for class 11 Business Studies from our website as we have ...
Follow us: Also, you can read the NCERT book Notes Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Business Services online in these sections Solutions by Expert Teachers as per SCERTClass 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Business Services ( CBSE) Book guidelines. These solutions are part of SCERT All Subject Solutions. Here we have given Assam Board Class 11 ...
Please refer to Business Services Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been. Skip to content. AssignmentsBag.com. Class Assignments. Assignments Class 12; Assignments Class 11; Assignments Class 10; Assignments Class 9; Assignments Class 8; Assignments Class 7; Assignments ...
classify different types of business services; • explain the concept of e-banking; • ... describe different types of warehouses. Chapter 4.indd 79 31-12-2020 11:55:08. ationalised 2023-2. 80. BUSINESS STUDIES. 4.1 introduction You must all have, at some time or the other experienced the effect of business activities on your lives. Let us ...
Collection of cases with assignments Moscow 2011 Introduction This Workbook is designed to assist the student (i.e. you) in mastering the principles of case studies and analysis and making up a format in accordance with the Harvard Business School model. It supplies the framework for analyzing a case both at home and in class.
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 11 (DUE DATE: MAY 9, 2019) Problem 11.1. Let T be the standard representation of the Lie algebra su 2. Is the represen-tation S2Tirreducible ? Problem 11.2. For a Lie group Gand a representation T: G!GL(V) put VG= fv2V jT(g)v= v;8g2Gg: Find dim (V 2n 1) SL 2(C), where V 1 is the standard two-dimensional representation of the ...
Russian Assignment: Naval Attache At The Us Embrassy In Moscow, 1947-1949. [unknown author] on Amazon.com. *FREE* shipping on qualifying offers. Russian Assignment: Naval Attache At The Us Embrassy In Moscow, 1947-1949.
AirClips.com get all our FREE full-length ULTIMATE COCKPIT VIDEOS in high quality! Here's our updated full list: http://Movies.AirClips.comWant exclusive ful...