- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Business consultants
Entrepreneurs and Small Business
Accelerators and Incubators
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai pitch deck generator
Stratrgic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
Small Business Tools
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Strategic Planning

Table of Contents in Business Plan – Example, Template

Free Problem Statement Templates
Ayush Jalan
- December 12, 2023
A business plan is a document that describes what your company is, does, and plans to do in the future. It helps you map out all the objectives, goals, strategies, resources, and every other detail of your business. But arranging all this can get messy.
To Solve This, We Need a Business Plan Table of Contents
Think of it like this: If your business plan aims to define your prospects and incur funding, a table of contents helps investors study your business in-depth and build confidence in your business idea.
Furthermore, it also helps focus on and prioritize tasks, quickly revise strategies according to the ever-changing business environment, make operations more fluid, and manage finances systematically.
A business plan table of contents provides a bird’s-eye view of your business landscape to help better navigate KPIs .
Every company needs a business plan to sustain itself in the market. Ultimately, it’s the content inside the business plan and its quality that directs a business to achieve goals using actionable steps.
As much as the elements of a business plan matter, the way they’re presented also plays a pivotal role in grabbing the reader’s attention.
The first few things that pique the reader’s interest are the cover page and the table of contents. In this article, we’ll see why and how you should write a professional business plan table of contents.
Why Include a Business Plan Table of Contents?
A table of contents serves as the outline of a business plan . It assists the reader to navigate through the document and is placed at the beginning of a business plan. This helps the reader effortlessly find and browse through the topics that interest them.
It includes all the major sections and subcategories of a business plan. The sections are arranged logically with page numbers. And it usually precedes the executive summary.
Pros of Adding a Business Plan Table of Contents
A table of contents is an extremely important part of any formal document, let alone a business plan. It is the most commonly found aspect in every large format document, from books to magazines to business plans.
Let’s see the benefits of a business plan table of contents:
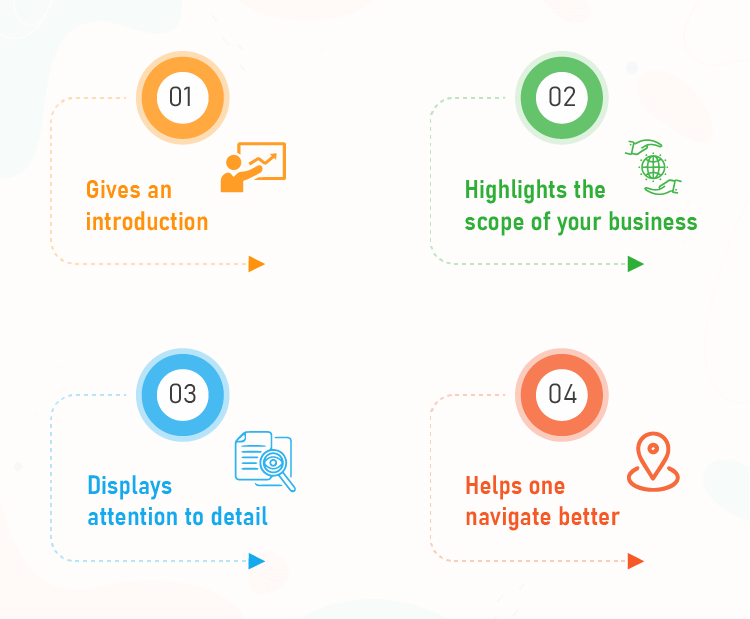
1. Acts as an introduction
The table of contents is placed before all the sections of a business plan. This will help the reader get a good look at the contents before diving into the details. Primarily, it introduces the reader to your business plan. In other words, a table of contents acts as an executive summary of the entire document.
2. Gives an overview of the scope
A table of contents further enables the reader to judge the scope of your business. To mirror the exact essence of your business plan, the table of contents should be crafted carefully.
Whether it’s an investor or another company you wish to work in partnership with, any formal entity interested in your business skims through your table of contents. Hence, it is wise to convey exactly what you intend to.
3. Displays attention to detail
While creating a table of contents, you include not only the major sections of your business plan but also the subsections. These subsections will convey that you have paid attention to the smallest of things while drafting your business. This indirectly sends a message that you are serious about your business ventures.
4. Provides easier navigation
This is an obvious but very significant advantage of a table of contents. Incorporating it into your business plan will add a navigational aspect to your document. Regardless if it’s a physical document or an e-document, a table of contents will help the reader go to any specific section they want.
These are the advantages of including a table of contents. You can now go ahead and create one for your business plan. To help you get started, we have also created a sample table of contents for you.
Feel free to use the following template and revamp it according to your unique business.
Sample for Table of Contents
- EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- Mission Statement
- Vision Statement
- Purpose and Values
- Problem Identification
- Problem Statement
- Industry Analysis
- Product & Service Overview
- Product & Service Specifications
- Product & Service Benefits and USPs
- Available Substitutes
- Competitive Overview
- Direct and Indirect Competitors
- SWOT Analysis
- Competitive Position
- Market Share Analysis
- Barriers to Entry
- Market Overview
- Market Size
- Market Segmentation
- Ideal Customer Profile
- Sales & Marketing Objectives
- Pricing Strategies
- Promotion Strategies
- Site Location
- Staffing and Training
- Resource Allocation
- Purchasing Process
- Production Process
- Quality Control Metrics
- Customer Service
- Key Management
- Board of Directors
- Board of Advisors
- Financial Overview
- Business Model
- Financial Projections
- Marketing and Personnel Expenses
- Funding Requirements
- Terms of Investment
- Exit Strategy
Build Trust in Your Business with a Table of Contents
Writing a table of contents for your business plan is a subtle yet powerful way to captivate your potential investors or business partners . It is essentially a summary of the document that acts as a roadmap for your business activities.
A smart entrepreneur is one who uses every opportunity available to grow closer to success. Creating a striking business plan table of contents to engage your investors is a detail you shouldn’t miss.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.

About the Author

Ayush is a writer with an academic background in business and marketing. Being a tech-enthusiast, he likes to keep a sharp eye on the latest tech gadgets and innovations. When he's not working, you can find him writing poetry, gaming, playing the ukulele, catching up with friends, and indulging in creative philosophies.
Related Articles
Write a Mission Statement For Your Business Plan: Explained with Examples

How to Write a Vision Statement for Your Business

Business Problem Statement Explained with Examples
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Contents of a Business Plan: Everything You Need to Know
The contents of a business plan consist of a detailed description of what, when, why, where, and how the business's operations will be accomplished. 3 min read updated on January 01, 2024
Overview of a Business Plan
A business plan includes the cost of organizing the business, the anticipated sources of revenue, how the products and services are customer oriented, and anticipated profit margins. Business plans serve two main purposes. First, they are a guide business owners use to streamline management and planning/organization of the business. Second, they show potential venture capitalists, bankers, and other lenders a comprehensive plan to encourage them to invest in the business.
Sublevels of a business plan include:
- Marketing plan
- Financial plan
- Human resource plan
- Production plan
Elements of a Business Plan
A well-written business plan will include the following:
- Cover letter
Table of Contents
Executive Summary
- Mission statement
- Company background
- Products and services
- Competitive analysis
Marketing/Realization
- Location/Production/Administrative
- Management and international organization
- Risk analysis
- Financial planning
Summary/Conclusion
Cover Letter
The business plan's cover letter has the same purpose as a cover letter for a resume. The point is to engage prospective investors using the cover letter so they'll look at the entire plan. The cover letter should include the recipient's address, the date, and your address. Begin the cover letter with "Dear" followed by the person's name.
In the body of the cover letter, let the recipient know you're submitting a business plan with a short one-sentence description of the business and what the recipient can expect when reading the plan. In the next paragraph, indicate that you look forward to hearing from them and provide a phone number they can call at their convenience.
Thank them for their time. Sign off. Include your name in typewritten form along with your signature.
Keep this page short and to the point. Include your business logo, business name, if there is a founder, and the name. Add "Business Plan," an image (optional), and the date.
The table of contents is a roadmap to help the recipient peruse the list and easily find each section. Some people may choose to read sections one after the other while others may choose to skip around. Include every section and subsection that may be of interest to a potential investor.
This is an important section. Because you're targeting executives, the overview of your business should be top-quality information to entice them to read the complete plan. The focus should be a summary of the main facets of your business plan.
Mission Statement
This section is a short statement about your business's goal and what you plan to create through the enterprise.
Company Background
This is a short statement including the date the business was developed, its founders, stages of development, the date it was incorporated, and, for existing businesses, the level of success.
Also, include the key figures in the business and the ownership and legal structure.
Products and Services
Under this section, provide a detailed description of your customer needs, benefits to customers, marketing services, and advantages and disadvantages of any competitor services or products.
Marketing Plan
This will include an overview of the market in general with an emphasis on purchase incentives, market analysis, and customer structure. It will also include the position your business holds in the market using information from target customer groups, canvassed market segments, and sale channels.
Competitive Analysis
Provide information about your main competitors' names, locations, market positions, weaknesses, strengths, and target markets.
This section covers details about product range, services, and pricing strategies. Sales targets for the next five years should also be included.
Location/Production/Administration
Include the location of the business and the advantages and disadvantages of its location. The production should discuss in-house and/or outsourced production and material costs. The administration portion will discuss the office infrastructure, such as accounting and technical support.
Management and International Organization
This section could work written as an organizational chart outlining member functions and responsibilities, special skills, and salaries.
Risk Analysis
Provide information on anticipated internal risks such as marketing, production, management, and financing. External risks would include information on ecological, economic, social, and legal areas.
Financial Planning
Lay out your plan for short- and long-term financial planning.
This is a final wrap up of the business plan that binds the everything together.
If you need help with outlining the contents of a business plan, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Creating a Business Plan
- Business Plan Contents Page
- How to Make a Business Plan Format
- Business Description Outline
- Service Business Plan
- LLC Business Plan Template
- Business Plan for Existing Company
- Parts of Business Plan and Definition
- IT Company Business Plan
- Business Plan Format: Everything you Need to Know
How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)
- 3 years ago

Have you ever wondered how to write a business plan step by step? Mike Andes, told us:
This guide will help you write a business plan to impress investors.
Throughout this process, we’ll get information from Mike Andes, who started Augusta Lawn Care Services when he was 12 and turned it into a franchise with over 90 locations. He has gone on to help others learn how to write business plans and start businesses. He knows a thing or two about writing business plans!
We’ll start by discussing the definition of a business plan. Then we’ll discuss how to come up with the idea, how to do the market research, and then the important elements in the business plan format. Keep reading to start your journey!

What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is simply a road map of what you are trying to achieve with your business and how you will go about achieving it. It should cover all elements of your business including:
- Finding customers
- Plans for developing a team
- Competition
- Legal structures
- Key milestones you are pursuing
If you aren’t quite ready to create a business plan, consider starting by reading our business startup guide .
Get a Business Idea
Before you can write a business plan, you have to have a business idea. You may see a problem that needs to be solved and have an idea how to solve it, or you might start by evaluating your interests and skills.
Mike told us, “The three things I suggest asking yourself when thinking about starting a business are:
- What am I good at?
- What would I enjoy doing?
- What can I get paid for?”
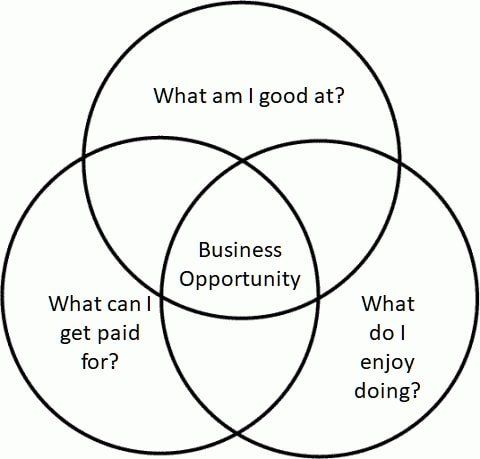
If all three of these questions don’t lead to at least one common answer, it will probably be a much harder road to success. Either there is not much market for it, you won’t be good at it, or you won’t enjoy doing it.
As Mike told us, “There’s enough stress starting and running a business that if you don’t like it or aren’t good at it, it’s hard to succeed.”
If you’d like to hear more about Mike’s approach to starting a business, check out our YouTube video
Conduct Market Analysis
Market analysis is focused on establishing if there is a target market for your products and services, how large the target market is, and identifying the demographics of people or businesses that would be interested in the product or service. The goal here is to establish how much money your business concept can make.
Product and Service Demand
A search engine is your best friend when trying to figure out if there is demand for your products and services. Personally, I love using presearch.org because it lets you directly search on a ton of different platforms including Google, Youtube, Twitter, and more. Check out the screenshot for the full list of search options.
With quick web searches, you can find out how many competitors you have, look through their reviews, and see if there are common complaints about the competitors. Bad reviews are a great place to find opportunities to offer better products or services.
If there are no similar products or services, you may have stumbled upon something new, or there may just be no demand for it. To find out, go talk to your most honest friend about the idea and see what they think. If they tell you it’s dumb or stare at you vacantly, there’s probably no market for it.
You can also conduct a survey through social media to get public opinion on your idea. Using Facebook Business Manager , you could get a feel for who would be interested in your product or service.
I ran a quick test of how many people between 18-65 you could reach in the U.S. during a week. It returned an estimated 700-2,000 for the total number of leads, which is enough to do a fairly accurate statistical analysis.
Identify Demographics of Target Market
Depending on what type of business you want to run, your target market will be different. The narrower the demographic, the fewer potential customers you’ll have. If you did a survey, you’ll be able to use that data to help define your target audience. Some considerations you’ll want to consider are:
- Other Interests
- Marital Status
- Do they have kids?
Once you have this information, it can help you narrow down your options for location and help define your marketing further. One resource that Mike recommended using is the Census Bureau’s Quick Facts Map . He told us,
“It helps you quickly evaluate what the best areas are for your business to be located.”
How to Write a Business Plan

Now that you’ve developed your idea a little and established there is a market for it, you can begin writing a business plan. Getting started is easier with the business plan template we created for you to download. I strongly recommend using it as it is updated to make it easier to create an action plan.
Each of the following should be a section of your business plan:
- Business Plan Cover Page
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Description of Products and Services
SWOT Analysis
- Competitor Data
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Expenses Strategy
Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Channel Assessment
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organizational Strategy
- Financial Statements and/or Financial Projections
We’ll look into each of these. Don’t forget to download our free business plan template (mentioned just above) so you can follow along as we go.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page
The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions.
A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
- Professionally designed logo
- Company name
- Mission or Vision Statement
- Contact Info
Basically, think of a cover page for your business plan like a giant business card. It is meant to capture people’s attention but be quickly processed.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 2. Create a Table of Contents
Most people are busy enough that they don’t have a lot of time. Providing a table of contents makes it easy for them to find the pages of your plan that are meaningful to them.
A table of contents will be immediately after the cover page, but you can include it after the executive summary. Including the table of contents immediately after the executive summary will help investors know what section of your business plan they want to review more thoroughly.
Check out Canva’s article about creating a table of contents . It has a ton of great information about creating easy access to each section of your business plan. Just remember that you’ll want to use different strategies for digital and hard copy business plans.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 3. Write an Executive Summary

An executive summary is where your business plan should catch the readers interest. It doesn’t need to be long, but should be quick and easy to read.
Mike told us,
How long should an executive summary bein an informal business plan?
For casual use, an executive summary should be similar to an elevator pitch, no more than 150-160 words, just enough to get them interested and wanting more. Indeed has a great article on elevator pitches . This can also be used for the content of emails to get readers’ attention.
It consists of three basic parts:
- An introduction to you and your business.
- What your business is about.
- A call to action
Example of an informal executive summary
One of the best elevator pitches I’ve used is:
So far that pitch has achieved a 100% success rate in getting partnerships for the business.
What should I include in an executive summary for investors?
Investors are going to need a more detailed executive summary if you want to secure financing or sell equity. The executive summary should be a brief overview of your entire business plan and include:
- Introduction of yourself and company.
- An origin story (Recognition of a problem and how you came to solution)
- An introduction to your products or services.
- Your unique value proposition. Make sure to include intellectual property.
- Where you are in the business life cycle
- Request and why you need it.
Successful business plan examples
The owner of Urbanity told us he spent 2 months writing a 75-page business plan and received a $250,000 loan from the bank when he was 23. Make your business plan as detailed as possible when looking for financing. We’ve provided a template to help you prepare the portions of a business plan that banks expect.
Here’s the interview with the owner of Urbanity:

When to write an executive summary?
Even though the summary is near the beginning of a business plan, you should write it after you complete the rest of a business plan. You can’t talk about revenue, profits, and expected expenditures if you haven’t done the market research and created a financial plan.
What mistakes do people make when writing an executive summary?
Business owners commonly go into too much detail about the following items in an executive summary:
- Marketing and sales processes
- Financial statements
- Organizational structure
- Market analysis
These are things that people will want to know later, but they don’t hook the reader. They won’t spark interest in your small business, but they’ll close the deal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 4. Company Description
Every business plan should include a company description. A great business plan will include the following elements while describing the company:
- Mission statement
- Philosophy and vision
- Company goals
Target market
- Legal structure
Let’s take a look at what each section includes in a good business plan.
Mission Statement
A mission statement is a brief explanation of why you started the company and what the company’s main focus is. It should be no more than one or two sentences. Check out HubSpot’s article 27 Inspiring Mission Statement for a great read on informative and inspiring mission and vision statements.
Company Philosophy and Vision

The company philosophy is what drives your company. You’ll normally hear them called core values. These are the building blocks that make your company different. You want to communicate your values to customers, business owners, and investors as often as possible to build a company culture, but make sure to back them up.
What makes your company different?
Each company is different. Your new business should rise above the standard company lines of honesty, integrity, fun, innovation, and community when communicating your business values. The standard answers are corporate jargon and lack authenticity.
Examples of core values
One of my clients decided to add a core values page to their website. As a tech company they emphasized the values:
- Prioritize communication.
- Never stop learning.
- Be transparent.
- Start small and grow incrementally.
These values communicate how the owner and the rest of the company operate. They also show a value proposition and competitive advantage because they specifically focus on delivering business value from the start. These values also genuinely show what the company is about and customers recognize the sincerity. Indeed has a great blog about how to identify your core values .
What is a vision statement?
A vision statement communicate the long lasting change a business pursues. The vision helps investors and customers understand what your company is trying to accomplish. The vision statement goes beyond a mission statement to provide something meaningful to the community, customer’s lives, or even the world.
Example vision statements
The Alzheimer’s Association is a great example of a vision statement:
A world without Alzheimer’s Disease and other dementia.
It clearly tells how they want to change the world. A world without Alzheimers might be unachievable, but that means they always have room for improvement.
Business Goals
You have to measure success against goals for a business plan to be meaningful. A business plan helps guide a company similar to how your GPS provides a road map to your favorite travel destination. A goal to make as much money as possible is not inspirational and sounds greedy.
Sure, business owners want to increase their profits and improve customer service, but they need to present an overview of what they consider success. The goals should help everyone prioritize their work.
How far in advance should a business plan?
Business planning should be done at least one year in advance, but many banks and investors prefer three to five year business plans. Longer plans show investors that the management team understands the market and knows the business is operating in a constantly shifting market. In addition, a plan helps businesses to adjust to changes because they have already considered how to handle them.
Example of great business goals
My all time-favorite long-term company goals are included in Tesla’s Master Plan, Part Deux . These goals were written in 2016 and drive the company’s decisions through 2026. They are the reason that investors are so forgiving when Elon Musk continually fails to meet his quarterly and annual goals.
If the progress aligns with the business plan investors are likely to continue to believe in the company. Just make sure the goals are reasonable or you’ll be discredited (unless you’re Elon Musk).

You did target market research before creating a business plan. Now it’s time to add it to the plan so others understand what your ideal customer looks like. As a new business owner, you may not be considered an expert in your field yet, so document everything. Make sure the references you use are from respectable sources.
Use information from the specific lender when you are applying for lending. Most lenders provide industry research reports and using their data can strengthen the position of your business plan.
A small business plan should include a section on the external environment. Understanding the industry is crucial because we don’t plan a business in a vacuum. Make sure to research the industry trends, competitors, and forecasts. I personally prefer IBIS World for my business research. Make sure to answer questions like:
- What is the industry outlook long-term and short-term?
- How will your business take advantage of projected industry changes and trends?
- What might happen to your competitors and how will your business successfully compete?
Industry resources
Some helpful resources to help you establish more about your industry are:
- Trade Associations
- Federal Reserve
- Bureau of Labor Statistics
Legal Structure
There are five basic types of legal structures that most people will utilize:
- Sole proprietorships
- Limited Liability Companies (LLC)
Partnerships
Corporations.
- Franchises.
Each business structure has their pros and cons. An LLC is the most common legal structure due to its protection of personal assets and ease of setting up. Make sure to specify how ownership is divided and what roles each owner plays when you have more than one business owner.
You’ll have to decide which structure is best for you, but we’ve gathered information on each to make it easier.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the easiest legal structure to set up but doesn’t protect the owner’s personal assets from legal issues. That means if something goes wrong, you could lose both your company and your home.
To start a sole proprietorship, fill out a special tax form called a Schedule C . Sole proprietors can also join the American Independent Business Alliance .
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is the most common business structure used in the United States because an LLC protects the owner’s personal assets. It’s similar to partnerships and corporations, but can be a single-member LLC in most states. An LLC requires a document called an operating agreement.
Each state has different requirements. Here’s a link to find your state’s requirements . Delaware and Nevada are common states to file an LLC because they are really business-friendly. Here’s a blog on the top 10 states to get an LLC.
Partnerships are typically for legal firms. If you choose to use a partnership choose a Limited Liability Partnership. Alternatively, you can just use an LLC.
Corporations are typically for massive organizations. Corporations have taxes on both corporate and income tax so unless you plan on selling stock, you are better off considering an LLC with S-Corp status . Investopedia has good information corporations here .

There are several opportunities to purchase successful franchises. TopFranchise.com has a list of companies in a variety of industries that offer franchise opportunities. This makes it where an entrepreneur can benefit from the reputation of an established business that has already worked out many of the kinks of starting from scratch.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 5. Products and Services
This section of the business plan should focus on what you sell, how you source it, and how you sell it. You should include:
- Unique features that differentiate your business products from competitors
- Intellectual property
- Your supply chain
- Cost and pricing structure
Questions to answer about your products and services
Mike gave us a list of the most important questions to answer about your product and services:
- How will you be selling the product? (in person, ecommerce, wholesale, direct to consumer)?
- How do you let them know they need a product?
- How do you communicate the message?
- How will you do transactions?
- How much will you be selling it for?
- How many do you think you’ll sell and why?
Make sure to use the worksheet on our business plan template .
How to Write a Business Plan Step 6. Sales and Marketing Plan
The marketing and sales plan is focused on the strategy to bring awareness to your company and guides how you will get the product to the consumer. It should contain the following sections:
SWOT Analysis stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Not only do you want to identify them, but you also want to document how the business plans to deal with them.
Business owners need to do a thorough job documenting how their service or product stacks up against the competition.
If proper research isn’t done, investors will be able to tell that the owner hasn’t researched the competition and is less likely to believe that the team can protect its service from threats by the more well-established competition. This is one of the most common parts of a presentation that trips up business owners presenting on Shark Tank .
SWOT Examples
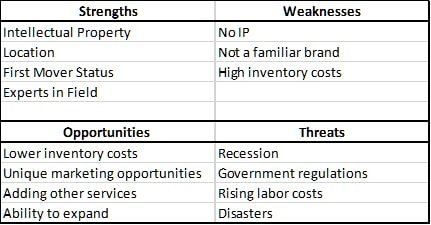
Examples of strengths and weaknesses could be things like the lack of cash flow, intellectual property ownership, high costs of suppliers, and customers’ expectations on shipping times.
Opportunities could be ways to capitalize on your strengths or improve your weaknesses, but may also be gaps in the industry. This includes:
- Adding offerings that fit with your current small business
- Increase sales to current customers
- Reducing costs through bulk ordering
- Finding ways to reduce inventory
- And other areas you can improve
Threats will normally come from outside of the company but could also be things like losing a key member of the team. Threats normally come from competition, regulations, taxes, and unforeseen events.
The management team should use the SWOT analysis to guide other areas of business planning, but it absolutely has to be done before a business owner starts marketing.
Include Competitor Data in Your Business Plan
When you plan a business, taking into consideration the strengths and weaknesses of the competition is key to navigating the field. Providing an overview of your competition and where they are headed shows that you are invested in understanding the industry.
For smaller businesses, you’ll want to search both the company and the owners names to see what they are working on. For publicly held corporations, you can find their quarterly and annual reports on the SEC website .
What another business plans to do can impact your business. Make sure to include things that might make it attractive for bigger companies to outsource to a small business.
Marketing Strategy
The marketing and sales part of business plans should be focused on how you are going to make potential customers aware of your business and then sell to them.
If you haven’t already included it, Mike recommends:
“They’ll want to know about Demographics, ages, and wealth of your target market.”
Make sure to include the Total addressable market . The term refers to the value if you captured 100% of the market.
Advertising Strategy
You’ll explain what formats of advertising you’ll be using. Some possibilities are:
- Online: Facebook and Google are the big names to work with here.
- Print : Print can be used to reach broad groups or targeted markets. Check out this for tips .
- Radio : iHeartMedia is one of the best ways to advertise on the radio
- Cable television : High priced, hard to measure ROI, but here’s an explanation of the process
- Billboards: Attracting customers with billboards can be beneficial in high traffic areas.
You’ll want to define how you’ll be using each including frequency, duration, and cost. If you have the materials already created, including pictures or links to the marketing to show creative assets.
Mike told us “Most businesses are marketing digitally now due to Covid, but that’s not always the right answer.”
Make sure the marketing strategy will help team members or external marketing agencies stay within the brand guidelines .

This section of a business plan should be focused on pricing. There are a ton of pricing strategies that may work for different business plans. Which one will work for you depends on what kind of a business you run.
Some common pricing strategies are:
- Value-based pricing – Commonly used with home buying and selling or other products that are status symbols.
- Skimming pricing – Commonly seen in video game consoles, price starts off high to recoup expenses quickly, then reduces over time.
- Competition-based pricing – Pricing based on competitors’ pricing is commonly seen at gas stations.
- Freemium services – Commonly used for software, where there is a free plan, then purchase options for more functionality.
HubSpot has a great calculator and blog on pricing strategies.
Beyond explaining what strategy your business plans to use, you should include references for how you came to this pricing strategy and how it will impact your cash flow.
Distribution Plan
This part of a business plan is focused on how the product or service is going to go through the supply chain. These may include multiple divisions or multiple companies. Make sure to include any parts of the workflow that are automated so investors can see where cost savings are expected and when.
Supply Chain Examples
For instance, lawn care companies would need to cover aspects such as:
- Suppliers for lawn care equipment and tools
- Any chemicals or treatments needed
- Repair parts for sprinkler systems
- Vehicles to transport equipment and employees
- Insurance to protect the company vehicles and people.
Examples of Supply Chains
These are fairly flat supply chains compared to something like a clothing designer where the clothes would go through multiple vendors. A clothing company might have the following supply chain:
- Raw materials
- Shipping of raw materials
- Converting of raw materials to thread
- Shipping thread to produce garments
- Garment producer
- Shipping to company
- Company storage
- Shipping to retail stores
There have been advances such as print on demand that eliminate many of these steps. If you are designing completely custom clothing, all of this would need to be planned to keep from having business disruptions.
The main thing to include in the business plan is the list of suppliers, the path the supply chain follows, the time from order to the customer’s home, and the costs associated with each step of the process.
According to BizPlanReview , a business plan without this information is likely to get rejected because they have failed to research the key elements necessary to make sales to the customer.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 7. Company Organization and Operational Plan
This part of the business plan is focused on how the business model will function while serving customers. The business plan should provide an overview of how the team will manage the following aspects:
Quality Control
- Legal environment
Let’s look at each for some insight.
Production has already been discussed in previous sections so I won’t go into it much. When writing a business plan for investors, try to avoid repetition as it creates a more simple business plan.
If the organizational plan will be used by the team as an overview of how to perform the best services for the customer, then redundancy makes more sense as it communicates what is important to the business.

Quality control policies help to keep the team focused on how to verify that the company adheres to the business plan and meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Quality control can be anything from a standard that says “all labels on shirts can be no more than 1/16″ off center” to a defined checklist of steps that should be performed and filled out for every customer.
There are a variety of organizations that help define quality control including:
- International Organization for Standardization – Quality standards for energy, technology, food, production environments, and cybersecurity
- AICPA – Standard defined for accounting.
- The Joint Commission – Healthcare
- ASHRAE – HVAC best practices
You can find lists of the organizations that contribute most to the government regulation of industries on Open Secrets . Research what the leaders in your field are doing. Follow their example and implement it in your quality control plan.
For location, you should use information from the market research to establish where the location will be. Make sure to include the following in the location documentation.
- The size of your location
- The type of building (retail, industrial, commercial, etc.)
- Zoning restrictions – Urban Wire has a good map on how zoning works in each state
- Accessibility – Does it meet ADA requirements?
- Costs including rent, maintenance, utilities, insurance and any buildout or remodeling costs
- Utilities – b.e.f. has a good energy calculator .
Legal Environment
The legal requirement section is focused on defining how to meet the legal requirements for your industry. A good business plan should include all of the following:
- Any licenses and/or permits that are needed and whether you’ve obtained them
- Any trademarks, copyrights, or patents that you have or are in the process of applying for
- The insurance coverage your business requires and how much it costs
- Any environmental, health, or workplace regulations affecting your business
- Any special regulations affecting your industry
- Bonding requirements, if applicable
Your local SBA office can help you establish requirements in your area. I strongly recommend using them. They are a great resource.
Your business plan should include a plan for company organization and hiring. While you may be the only person with the company right now, down the road you’ll need more people. Make sure to consider and document the answers to the following questions:
- What is the current leadership structure and what will it look like in the future?
- What types of employees will you have? Are there any licensing or educational requirements?
- How many employees will you need?
- Will you ever hire freelancers or independent contractors?
- What is each position’s job description?
- What is the pay structure (hourly, salaried, base plus commission, etc.)?
- How do you plan to find qualified employees and contractors?
One of the most crucial parts of a business plan is the organizational chart. This simply shows the positions the company will need, who is in charge of them and the relationship of each of them. It will look similar to this:
Our small business plan template has a much more in-depth organizational chart you can edit to include when you include the organizational chart in your business plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 8. Financial Statements
No business plan is complete without financial statements or financial projections. The business plan format will be different based on whether you are writing a business plan to expand a business or a startup business plan. Let’s dig deeper into each.
Provide All Financial Income from an Existing Business
An existing business should use their past financial documents including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to find trends to estimate the next 3-5 years.
You can create easy trendlines in excel to predict future revenue, profit and loss, cash flow, and other changes in year-over-year performance. This will show your expected performance assuming business continues as normal.
If you are seeking an investment, then the business is probably not going to continue as normal. Depending on the financial plan and the purpose of getting financing, adjustments may be needed to the following:
- Higher Revenue if expanding business
- Lower Cost of Goods Sold if purchasing inventory with bulk discounts
- Adding interest if utilizing financing (not equity deal)
- Changes in expenses
- Addition of financing information to the cash flow statement
- Changes in Earnings per Share on the balance sheet
Financial modeling is a challenging subject, but there are plenty of low-cost courses on the subject. If you need help planning your business financial documentation take some time to watch some of them.
Make it a point to document how you calculated all the changes to the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in your business plan so that key team members or investors can verify your research.
Financial Projections For A Startup Business Plan
Unlike an existing business, a startup doesn’t have previous success to model its future performance. In this scenario, you need to focus on how to make a business plan realistic through the use of industry research and averages.
Mike gave the following advice in his interview:
Financial Forecasting Mistakes
One of the things a lot of inexperienced people use is the argument, “If I get one percent of the market, it is worth $100 million.” If you use this, investors are likely to file the document under bad business plan examples.
Let’s use custom t-shirts as an example.
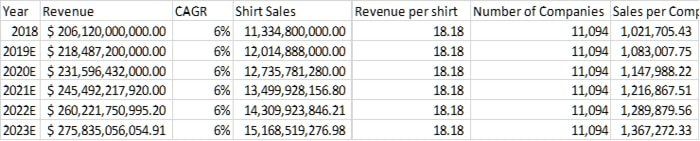
Credence Research estimated in 2018 there were 11,334,800,000 custom t-shirts sold for a total of $206.12 Billion, with a 6% compound annual growth rate.
With that data, you can calculate that the industry will grow to $270 Billion in 2023 and that the average shirt sold creates $18.18 in revenue.
Combine that with an IBIS World estimate of 11,094 custom screen printers and that means even if you become an average seller, you’ll get .009% of the market.
Here’s a table for easier viewing of that information.
The point here is to make sure your business proposal examples make sense.
You’ll need to know industry averages such as cost of customer acquisition, revenue per customer, the average cost of goods sold, and admin costs to be able to create accurate estimates.
Our simple business plan templates walk you through most of these processes. If you follow them you’ll have a good idea of how to write a business proposal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 9. Business Plan Example of Funding Requests
What is a business plan without a plan on how to obtain funding?
The Small Business Administration has an example for a pizza restaurant that theoretically needed nearly $20k to make it through their first month.
In our video, How to Start a $500K/Year T-Shirt Business (Pt. 1 ), Sanford Booth told us he needed about $200,000 to start his franchise and broke even after 4 months.
Freshbooks estimates it takes on average 2-3 years for a business to be profitable, which means the fictitious pizza company from the SBA could need up to $330k to make it through that time and still pay their bills for their home and pizza shop.
Not every business needs that much to start, but realistically it’s a good idea to assume that you need a fairly large cushion.
Ways to get funding for a small business
There are a variety of ways to cover this. the most common are:
- Bootstrapping – Using your savings without external funding.
- Taking out debt – loans, credit cards
- Equity, Seed Funding – Ownership of a percentage of the company in exchange for current funds
- Crowdsourcing – Promising a good for funding to create the product
Keep reading for more tips on how to write a business plan.
How funding will be used
When asking for business financing make sure to include:
- How much to get started?
- What is the minimum viable product and how soon can you make money?
- How will the money be spent?
Mike emphasized two aspects that should be included in every plan,
How to Write a Business Plan Resources
Here are some links to a business plan sample and business plan outline.
- Sample plan
It’s also helpful to follow some of the leading influencers in the business plan writing community. Here’s a list:
- Wise Plans – Shares a lot of information on starting businesses and is a business plan writing company.
- Optimus Business Plans – Another business plan writing company.
- Venture Capital – A venture capital thread that can help give you ideas.
How to Write a Business Plan: What’s Next?
We hope this guide about how to write a simple business plan step by step has been helpful. We’ve covered:
- The definition of a business plan
- Coming up with a business idea
- Performing market research
- The critical components of a business plan
- An example business plan
In addition, we provided you with a simple business plan template to assist you in the process of writing your startup business plan. The startup business plan template also includes a business model template that will be the key to your success.
Don’t forget to check out the rest of our business hub .
Have you written a business plan before? How did it impact your ability to achieve your goals?

Brandon Boushy
Brandon Boushy lives to improve people’s lives by helping them become successful entrepreneurs. His journey started nearly 30 years ago. He consistently excelled at everything he did, but preferred to make the rules rather than follow him. His exploration of self and knowledge has helped him to get an engineering degree, MBA, and countless certifications. When freelancing and rideshare came onto the scene, he recognized the opportunity to play by his own rules. Since 2017, he has helped businesses across all industries achieve more with his research, writing, and marketing strategies. Since 2021, he has been the Lead Writer for UpFlip where he has published over 170 articles on small business success.
Related posts

- September 27, 2023
How to Start a Business: The Ultimate Guide (2024)

- August 3, 2022
Free Business Plan Template (With Examples)

- May 3, 2022
How to Get a Business License (In 3 Steps)
Join the discussion cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
2 thoughts on “How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)”
My Name is PRETTY NGOMANE. A south African female. Aspiring to do farming. And finding a home away from home for the differently abled persons in their daily needs.
nice work https://binarychemist.com/
Compare listings
Reset Password
Please enter your username or email address. You will receive a link to create a new password via email.
Home > Business > Business Startup
How To Write a Business Plan

We are committed to sharing unbiased reviews. Some of the links on our site are from our partners who compensate us. Read our editorial guidelines and advertising disclosure .

Starting a business is a wild ride, and a solid business plan can be the key to keeping you on track. A business plan is essentially a roadmap for your business — outlining your goals, strategies, market analysis and financial projections. Not only will it guide your decision-making, a business plan can help you secure funding with a loan or from investors .
Writing a business plan can seem like a huge task, but taking it one step at a time can break the plan down into manageable milestones. Here is our step-by-step guide on how to write a business plan.
Table of contents
- Write your executive summary
- Do your market research homework
- Set your business goals and objectives
- Plan your business strategy
- Describe your product or service
- Crunch the numbers
- Finalize your business plan

By signing up I agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Step 1: Write your executive summary
Though this will be the first page of your business plan , we recommend you actually write the executive summary last. That’s because an executive summary highlights what’s to come in the business plan but in a more condensed fashion.
An executive summary gives stakeholders who are reading your business plan the key points quickly without having to comb through pages and pages. Be sure to cover each successive point in a concise manner, and include as much data as necessary to support your claims.
You’ll cover other things too, but answer these basic questions in your executive summary:
- Idea: What’s your business concept? What problem does your business solve? What are your business goals?
- Product: What’s your product/service and how is it different?
- Market: Who’s your audience? How will you reach customers?
- Finance: How much will your idea cost? And if you’re seeking funding, how much money do you need? How much do you expect to earn? If you’ve already started, where is your revenue at now?
Step 2: Do your market research homework
The next step in writing a business plan is to conduct market research . This involves gathering information about your target market (or customer persona), your competition, and the industry as a whole. You can use a variety of research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and online research to gather this information. Your method may be formal or more casual, just make sure that you’re getting good data back.
This research will help you to understand the needs of your target market and the potential demand for your product or service—essential aspects of starting and growing a successful business.
Step 3: Set your business goals and objectives
Once you’ve completed your market research, you can begin to define your business goals and objectives. What is the problem you want to solve? What’s your vision for the future? Where do you want to be in a year from now?
Use this step to decide what you want to achieve with your business, both in the short and long term. Try to set SMART goals—specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound benchmarks—that will help you to stay focused and motivated as you build your business.
Step 4: Plan your business strategy
Your business strategy is how you plan to reach your goals and objectives. This includes details on positioning your product or service, marketing and sales strategies, operational plans, and the organizational structure of your small business.
Make sure to include key roles and responsibilities for each team member if you’re in a business entity with multiple people.
Step 5: Describe your product or service
In this section, get into the nitty-gritty of your product or service. Go into depth regarding the features, benefits, target market, and any patents or proprietary tech you have. Make sure to paint a clear picture of what sets your product apart from the competition—and don’t forget to highlight any customer benefits.
Step 6: Crunch the numbers
Financial analysis is an essential part of your business plan. If you’re already in business that includes your profit and loss statement , cash flow statement and balance sheet .
These financial projections will give investors and lenders an understanding of the financial health of your business and the potential return on investment.
You may want to work with a financial professional to ensure your financial projections are realistic and accurate.
Step 7: Finalize your business plan
Once you’ve completed everything, it's time to finalize your business plan. This involves reviewing and editing your plan to ensure that it is clear, concise, and easy to understand.
You should also have someone else review your plan to get a fresh perspective and identify any areas that may need improvement. You could even work with a free SCORE mentor on your business plan or use a SCORE business plan template for more detailed guidance.
Compare the Top Small-Business Banks
Data effective 1/10/23. At publishing time, rates, fees, and requirements are current but are subject to change. Offers may not be available in all areas.
The takeaway
Writing a business plan is an essential process for any forward-thinking entrepreneur or business owner. A business plan requires a lot of up-front research, planning, and attention to detail, but it’s worthwhile. Creating a comprehensive business plan can help you achieve your business goals and secure the funding you need.
Related content
- 5 Best Business Plan Software and Tools in 2023 for Your Small Business
- How to Get a Business License: What You Need to Know
- What Is a Cash Flow Statement?
Best Small Business Loans

5202 W Douglas Corrigan Way Salt Lake City, UT 84116
Accounting & Payroll
Point of Sale
Payment Processing
Inventory Management
Human Resources
Other Services
Best Inventory Management Software
Best Small Business Accounting Software
Best Payroll Software
Best Mobile Credit Card Readers
Best POS Systems
Best Tax Software
Stay updated on the latest products and services anytime anywhere.
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Disclaimer: The information featured in this article is based on our best estimates of pricing, package details, contract stipulations, and service available at the time of writing. All information is subject to change. Pricing will vary based on various factors, including, but not limited to, the customer’s location, package chosen, added features and equipment, the purchaser’s credit score, etc. For the most accurate information, please ask your customer service representative. Clarify all fees and contract details before signing a contract or finalizing your purchase.
Our mission is to help consumers make informed purchase decisions. While we strive to keep our reviews as unbiased as possible, we do receive affiliate compensation through some of our links. This can affect which services appear on our site and where we rank them. Our affiliate compensation allows us to maintain an ad-free website and provide a free service to our readers. For more information, please see our Privacy Policy Page . |
© Business.org 2023 All Rights Reserved.
550+ Business Plan Examples to Launch Your Business

Need help writing your business plan? Explore over 550 industry-specific business plan examples for inspiration.
Find your business plan example

Accounting, Insurance & Compliance Business Plans
- View All 25

Children & Pets Business Plans
- Children's Education & Recreation
- View All 33

Cleaning, Repairs & Maintenance Business Plans
- Auto Detail & Repair
- Cleaning Products
- View All 39

Clothing & Fashion Brand Business Plans
- Clothing & Fashion Design
- View All 26

Construction, Architecture & Engineering Business Plans
- Architecture
- Construction
- View All 46

Consulting, Advertising & Marketing Business Plans
- Advertising
- View All 54

Education Business Plans
- Education Consulting
- Education Products
Business plan template: There's an easier way to get your business plan done.

Entertainment & Recreation Business Plans
- Entertainment
- Film & Television
- View All 60

Events Business Plans
- Event Planning
- View All 17

Farm & Agriculture Business Plans
- Agri-tourism
- Agriculture Consulting
- View All 16

Finance & Investing Business Plans
- Financial Planning
- View All 10

Fine Art & Crafts Business Plans

Fitness & Beauty Business Plans
- Salon & Spa
- View All 36

Food and Beverage Business Plans
- Bar & Brewery
- View All 77

Hotel & Lodging Business Plans
- Bed and Breakfast

IT, Staffing & Customer Service Business Plans
- Administrative Services
- Customer Service
- View All 22

Manufacturing & Wholesale Business Plans
- Cleaning & Cosmetics Manufacturing
- View All 68

Medical & Health Business Plans
- Dental Practice
- Health Administration
- View All 41

Nonprofit Business Plans
- Co-op Nonprofit
- Food & Housing Nonprofit
- View All 13

Real Estate & Rentals Business Plans
- Equipment Rental

Retail & Ecommerce Business Plans
- Car Dealership
- View All 116

Technology Business Plans
- Apps & Software
- Communication Technology

Transportation, Travel & Logistics Business Plans
- Airline, Taxi & Shuttle
- View All 62
View all sample business plans
Example business plan format
Before you start exploring our library of business plan examples, it's worth taking the time to understand the traditional business plan format . You'll find that the plans in this library and most investor-approved business plans will include the following sections:
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally only one to two pages. You should also plan to write this section last after you've written your full business plan.
Your executive summary should include a summary of the problem you are solving, a description of your product or service, an overview of your target market, a brief description of your team, a summary of your financials, and your funding requirements (if you are raising money).
Products & services
The products & services chapter of your business plan is where the real meat of your plan lives. It includes information about the problem that you're solving, your solution, and any traction that proves that it truly meets the need you identified.
This is your chance to explain why you're in business and that people care about what you offer. It needs to go beyond a simple product or service description and get to the heart of why your business works and benefits your customers.
Market analysis
Conducting a market analysis ensures that you fully understand the market that you're entering and who you'll be selling to. This section is where you will showcase all of the information about your potential customers. You'll cover your target market as well as information about the growth of your market and your industry. Focus on outlining why the market you're entering is viable and creating a realistic persona for your ideal customer base.
Competition
Part of defining your opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage may be. To do this effectively you need to get to know your competitors just as well as your target customers. Every business will have competition, if you don't then you're either in a very young industry or there's a good reason no one is pursuing this specific venture.
To succeed, you want to be sure you know who your competitors are, how they operate, necessary financial benchmarks, and how you're business will be positioned. Start by identifying who your competitors are or will be during your market research. Then leverage competitive analysis tools like the competitive matrix and positioning map to solidify where your business stands in relation to the competition.
Marketing & sales
The marketing and sales plan section of your business plan details how you plan to reach your target market segments. You'll address how you plan on selling to those target markets, what your pricing plan is, and what types of activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success.
The operations section covers the day-to-day workflows for your business to deliver your product or service. What's included here fully depends on the type of business. Typically you can expect to add details on your business location, sourcing and fulfillment, use of technology, and any partnerships or agreements that are in place.
Milestones & metrics
The milestones section is where you lay out strategic milestones to reach your business goals.
A good milestone clearly lays out the parameters of the task at hand and sets expectations for its execution. You'll want to include a description of the task, a proposed due date, who is responsible, and eventually a budget that's attached. You don't need extensive project planning in this section, just key milestones that you want to hit and when you plan to hit them.
You should also discuss key metrics, which are the numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common data points worth tracking include conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, profit, etc.
Company & team
Use this section to describe your current team and who you need to hire. If you intend to pursue funding, you'll need to highlight the relevant experience of your team members. Basically, this is where you prove that this is the right team to successfully start and grow the business. You will also need to provide a quick overview of your legal structure and history if you're already up and running.
Financial projections
Your financial plan should include a sales and revenue forecast, profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, and a balance sheet. You may not have established financials of any kind at this stage. Not to worry, rather than getting all of the details ironed out, focus on making projections and strategic forecasts for your business. You can always update your financial statements as you begin operations and start bringing in actual accounting data.
Now, if you intend to pitch to investors or submit a loan application, you'll also need a "use of funds" report in this section. This outlines how you intend to leverage any funding for your business and how much you're looking to acquire. Like the rest of your financials, this can always be updated later on.
The appendix isn't a required element of your business plan. However, it is a useful place to add any charts, tables, definitions, legal notes, or other critical information that supports your plan. These are often lengthier or out-of-place information that simply didn't work naturally into the structure of your plan. You'll notice that in these business plan examples, the appendix mainly includes extended financial statements.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. To get the most out of your plan, it's best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you'll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or in any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It's faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan . This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business.
By starting with a one-page plan , you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You'll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan.
Growth planning
Growth planning is more than a specific type of business plan. It's a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, forecast, review, and refine based on your performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27 minutes . However, it's even easier to convert into a more detailed plan thanks to how heavily it's tied to your financials. The overall goal of growth planning isn't to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the growth planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and remain stable through times of crisis.
It's faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Download a free sample business plan template
Ready to start writing your own plan but aren't sure where to start? Download our free business plan template that's been updated for 2024.
This simple, modern, investor-approved business plan template is designed to make planning easy. It's a proven format that has helped over 1 million businesses write business plans for bank loans, funding pitches, business expansion, and even business sales. It includes additional instructions for how to write each section and is formatted to be SBA-lender approved. All you need to do is fill in the blanks.
How to use an example business plan to help you write your own

How do you know what elements need to be included in your business plan, especially if you've never written one before? Looking at examples can help you visualize what a full, traditional plan looks like, so you know what you're aiming for before you get started. Here's how to get the most out of a sample business plan.
Choose a business plan example from a similar type of company
You don't need to find an example business plan that's an exact fit for your business. Your business location, target market, and even your particular product or service may not match up exactly with the plans in our gallery. But, you don't need an exact match for it to be helpful. Instead, look for a plan that's related to the type of business you're starting.
For example, if you want to start a vegetarian restaurant, a plan for a steakhouse can be a great match. While the specifics of your actual startup will differ, the elements you'd want to include in your restaurant's business plan are likely to be very similar.
Use a business plan example as a guide
Every startup and small business is unique, so you'll want to avoid copying an example business plan word for word. It just won't be as helpful, since each business is unique. You want your plan to be a useful tool for starting a business —and getting funding if you need it.
One of the key benefits of writing a business plan is simply going through the process. When you sit down to write, you'll naturally think through important pieces, like your startup costs, your target market , and any market analysis or research you'll need to do to be successful.
You'll also look at where you stand among your competition (and everyone has competition), and lay out your goals and the milestones you'll need to meet. Looking at an example business plan's financials section can be helpful because you can see what should be included, but take them with a grain of salt. Don't assume that financial projections for a sample company will fit your own small business.
If you're looking for more resources to help you get started, our business planning guide is a good place to start. You can also download our free business plan template .
Think of business planning as a process, instead of a document
Think about business planning as something you do often , rather than a document you create once and never look at again. If you take the time to write a plan that really fits your own company, it will be a better, more useful tool to grow your business. It should also make it easier to share your vision and strategy so everyone on your team is on the same page.
Adjust your plan regularly to use it as a business management tool
Keep in mind that businesses that use their plan as a management tool to help run their business grow 30 percent faster than those businesses that don't. For that to be true for your company, you'll think of a part of your business planning process as tracking your actual results against your financial forecast on a regular basis.
If things are going well, your plan will help you think about how you can re-invest in your business. If you find that you're not meeting goals, you might need to adjust your budgets or your sales forecast. Either way, tracking your progress compared to your plan can help you adjust quickly when you identify challenges and opportunities—it's one of the most powerful things you can do to grow your business.
Prepare to pitch your business
If you're planning to pitch your business to investors or seek out any funding, you'll need a pitch deck to accompany your business plan. A pitch deck is designed to inform people about your business. You want your pitch deck to be short and easy to follow, so it's best to keep your presentation under 20 slides.
Your pitch deck and pitch presentation are likely some of the first things that an investor will see to learn more about your company. So, you need to be informative and pique their interest. Luckily, just like you can leverage an example business plan template to write your plan, we also have a gallery of over 50 pitch decks for you to reference.
With this gallery, you have the option to view specific industry pitches or get inspired by real-world pitch deck examples.
Ready to get started?
Now that you know how to use an example business plan to help you write a plan for your business, it's time to find the right one.
Use the search bar below to get started and find the right match for your business idea.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Plan Smarter, Grow Faster:
25% Off Annual Plans! Save Now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained
Posted february 21, 2022 by kody wirth.

What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.
Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential. By regularly returning to your plan you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface for why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those that are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those that have an idea and want to determine if it’s actually possible or not. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
The market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea. Is the marketplace too crowded? Is the solution you have in mind not really needed? Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability and you can paint a pretty clear picture of the potential of your business.
Document your strategy and goals
For those starting or managing a business understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there are vital. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you are considering all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll have an idea of where you want your business to go as well as how you’ve performed in the past. This alone better prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors. So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can instead keep your plan up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.
What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover the problem you’re solving, a description of your product or service, your target market, organizational structure, a financial summary, and any necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table. Lastly, be sure to outline the steps or milestones that you’ll need to hit to successfully launch your business. If you’ve already hit some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include it here to further prove the validity of your business.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the overall state and potential of the industry, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business. This helps you better explore the long-term trends of the market, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to initially introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps .
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add it.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history. Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing the viability of your business. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex on the surface, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- Sales and revenue projections
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first and only add documentation that you think will be beneficial for anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you’ll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations. This is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan. This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan. This plan type is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is the Lean Plan . This is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes . However, it’s even easier to convert into a full plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of Lean Planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the Lean Planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Try the LivePlan Method for Lean Business Planning
Now that you know the basics of business planning, it’s time to get started. Again we recommend leveraging a Lean Plan for a faster, easier, and far more useful planning process.
To get familiar with the Lean Plan format, you can download our free Lean Plan template . However, if you want to elevate your ability to create and use your lean plan even further, you may want to explore LivePlan.
It features step-by-step guidance that ensures you cover everything necessary while reducing the time spent on formatting and presenting. You’ll also gain access to financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process. Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results.
Check out how LivePlan streamlines Lean Planning by downloading our Kickstart Your Business ebook .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Posted in Business Plan Writing
Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
How to Develop a Content Strategy in 7 Steps: A Start-to-Finish Guide
Published: April 10, 2024
Whether you‘re just starting out with content marketing or you’ve been using the same approach for a while, it never hurts to revisit your content strategy plan and make sure it's innovative and engaging for your prospects and customers.

If you're having trouble planning for the upcoming year or need some fresh ideas to include in your plan, read on.

In this post, we'll dive into what content strategy is, why your business needs a content marketing plan, and what steps you need to take to create your strategy.
Plus, we'll explore some examples of effective content marketing strategies for inspiration.
Table of Contents
What is content strategy?
Why marketers need to create a content marketing strategy, elements of a content strategy plan, how to create a content strategy framework.
- Content Marketing Strategy Statistics
Questions to Ask When Creating a Content Strategy
Content strategy template, content marketing strategy example, content strategy tactics.
A content strategy is the planning, creation, publication, management, and governance of content. A great content strategy will attract and engage a target audience, meeting their needs while driving business goals.
Say your business goals include increasing brand awareness.
To achieve this, you might implement a content strategy that focuses on SEO to increase your website's visibility on the search engine results pages (SERPs) and drive traffic to your products or services.
New business owners might assume a content strategy is a nice-to-have, but not necessary early on. However, producing high-quality content can be invaluable in building trust with new audiences and succeeding in the long haul.
In essence, a good content strategy is the foundation of your Attract and Delight stages in a buyer's journey that follows the inbound marketing framework.
Along with attracting prospects to your brand, you can leverage a content strategy for sales enablement and customer satisfaction.
Plus, with 70% of marketers actively investing in content marketing , it's critical to develop a good content strategy to compete in your industry.

Content Marketing Planning Templates
Plan your content strategically with these handy templates.
- Editorial Calendar Template
- Buyer Persona Templates
- SWOT Analysis Templates
- SMART Goal Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A couple of years ago, I worked as a content writer for a literary company that just launched.
Despite all the meetings the team had before the launch, the founder and CEO of the company didn’t understand why it was important to create a content marketing strategy we’d adhere to when the website went live.
Three months after the launch, the CEO called another meeting and expressed their dissatisfaction with the poor performance so far.
Both the website and the company’s social media profiles were receiving crickets by way of organic traffic, and the paid ads were not converting at all.
I suggested that we create a content strategy plan for the next quarter and see what happens.
We did that, and sure enough, by the end of Q2, we recorded an increase in traffic and conversions from both the website and social media profiles.
No matter the kind of company or industry you work in, a content marketing strategy is integral for the success of your digital marketing efforts.
Here are some reasons why.

1. It aligns the team on goals and objectives.
A content marketing strategy ensures that everyone on the marketing team understands the overarching goals and specific objectives of the business.
When content creators, social media managers, writers, and other team members are aligned on goals such as brand awareness, lead generation, or customer engagement, they can produce content that consistently supports these aims.
This increases the chances of getting tangible results.
Carl Broadbent , a digital marketing expert, values content marketing strategies for the alignment they bring.
“After years of publishing blogs, ebooks, and videos, I‘ve learned that a strong content strategy acts like a guiding compass. It points you towards topics and formats aligned with business goals, so you’re not just cranking out content for content's sake,” Broadbent says.
Broadbent also notes that teams will make mistakes along the way.
He recalls, “‘I've made that mistake! Last year, we invested heavily in podcasts, thinking it would attract our target buyers. Turns out our audience preferred snappy infographics. Our podcast push fizzled out fast without the right strategy in place.”
2. It guides content creation and distribution.
Ayomide Joseph , a freelance content marketer for SaaS companies like Aura, Nextiva, and Trengo, explains the purpose of a content marketing strategy:
“The concept of ‘strategy’ in content marketing is simply to give you a roadmap that’ll guide you from where you are to where you want to be,” Joseph says.
For example, Joseph notes that if you’re looking to drive more inbound leads via content, ideally, creating bottom-of-the-funnel content is the way to go.
“A content marketing strategy answers the questions, ‘How do you go about it? What’s the keyword you’re going to target, search volume, difficulty — and what distribution approach will you utilize?’” Joseph says. “If you don’t have a content marketing strategy, you’ll be working blind.”
A content marketing strategy requires you to plan the type of content to create, such as blog posts, infographics, videos, and podcasts.
You’ll also determine the most effective channels for distribution, whether that be social media platforms, email marketing, or the company’s website.
This planning ensures that content is consistent, timely, and relevant to the audience’s interests and needs, fostering brand loyalty and advocacy.
3. It optimizes resources.
When you map out a fully-fledged content marketing strategy, you’ll be able to allocate resources more efficiently, whether those resources are time, budget, or manpower, to bring the strategy to life.
By knowing the type of content you need to produce and the platforms through which you’ll distribute it, you can direct your efforts and budget toward activities that offer the best return on investment (ROI).
4. It improves online visibility.
A well-executed content marketing strategy can alleviate this problem by improving a brand’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs).
High-quality, optimized content is favored by search engines and ranks higher in search results, which leads to increased organic traffic.
By targeting specific keywords and topics relevant to your target audience, you can attract more qualified leads to your website.
5. It builds brand authority and trust.
By consistently producing high-quality, relevant, and valuable content, you can establish your business as a thought leader in its industry.
This authority builds trust with your audience, which is crucial for long-term relationships and customer loyalty.
A content marketing strategy ensures that your content not only attracts attention but also provides value and encourages your audience to return and interact with the brand further.
Since a content strategy plan is a roadmap designed to guide the creation, publication, and governance of useful content, here are some key elements you should include when creating yours.
1. Goals and Objectives
What do you want to achieve with your content?
Do you want to increase brand awareness? Generate leads? Or maybe, improve customer engagement? Is it all three — or something else?
When you define the goals and objectives you want your content to help you achieve, you’re establishing your North Star.
So, if you’re not sure whether to include a certain type of content in your strategy, you can look to your North Star and determine if that content type will lead you in the direction you want to go.
2. Audience Persona
An audience persona (or buyer persona) is a semi-fictional representation of your ideal customer based on data and research.
It helps you understand who you’re creating content for.
To create an accurate audience persona, you’ll need to conduct research through surveys and interviews and analyze your social media engagement to gather insights.
These insights include your audience’s demographic information, interests, pain points, and content preferences, to mention a few.
Knowing this information will help you understand the content types, topics, and marketing channels that will help you reach your goals.
3. Content Audit and Analysis
Once you’ve gotten your audience persona down, review your existing content to determine what’s working and what’s not.
This way, you’ll be able to identify gaps and opportunities for content.
In the Content Audit section of your content strategy plan, explain:
- The kinds of content and topics that are already working well for you (e.g., blogs that discuss web development, micro-videos that explain coding tips and tricks, etc.)
- The kinds of content and topics that are not gaining traction (e.g., white papers about the evolution of programming)
- The content gaps and opportunities you’ve discovered
Pro tip: Use tools like Google Analytics and social media analytics to evaluate the performance of your content. Look for patterns in what types of content perform best and use this to inform future content creation.
4. Content Types and Channels
The Feedly RSS feed is a wonderful way to track trendy topics in your industry and find content ideas at the same time.
You start by telling the software what topics you're most interested in, and its AI tool will do the rest.
You won't need to scour the internet to find new content ideas anymore. Instead, you can go through your curated list, compiled from news sites, newsletters, and social media.
2. BuzzSumo
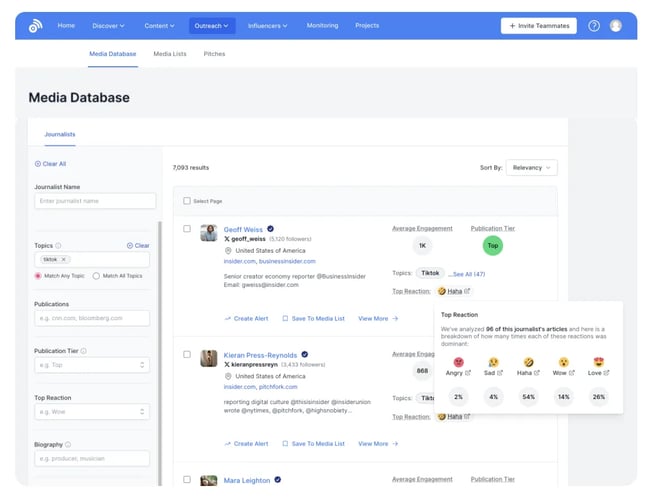
Want to discover popular content and content ideas?
This company offers several market research tools, one of which uses social media shares to figure out if a piece of content is popular and well-liked.
This information helps you see which content ideas would do well if you were to create content about them.
3. BlogAbout
Get your mind gears going with IMPACT's blog title generator.
This tool works a bit like Mad Libs, but instead of joke sentences, it shows you common headline formats with blanks where you can fill in the subject you have in mind.
This brainstorming technique helps you put general ideas in contexts that would be appealing to your target audience. Once you have a headline you like, BlogAbout lets you add it to your “Notebook” so you can save your best ideas.
4. CoSchedule Headline Analyzer
You can get blog post ideas for an entire year with HubSpot's Blog Ideas Generator .
All you need to do is enter general topics or terms you'd like to write about, and this content idea generator does all the work for you.
This tool analyzes headlines and titles and gives feedback on length, word choice, grammar, and keyword search volume.
If you have an idea in mind, run a few title options through the Headline Analyzer to see how you could make it stronger.
5. HubSpot's Website Grader
This is a great tool to use when you want to see where you're at with your website and SEO efforts.
The Website Grader grades you on vital areas of your website performance and sends you a detailed report to help you optimize.
With this tool, you can figure out how to make your website more SEO-friendly and discover areas of improvement.

Refine and rank your ideas.
The brainstorming process should be loose and unstructured.
It can be tempting to jump on an idea and start creating content right away. But instead, try to throw out your wildest ideas and see where they lead.
Then, take that list of content ideas and refine them.
To start, break ideas into groups and organize them around your goals, topics, or personas. Then, review each idea in detail and add specifics.
For example, say your topic is AI . One of your content ideas might be image generation. You can break this idea down further with content for image-generation tools, text-to-image prompts, or how to edit existing images.
Another way to refine content ideas is to conduct keyword research .
You can also define your process for refining ideas in your content workflow .
7. Publish and manage your content.
Your marketing plan should go beyond the types of content you‘ll create — it should also cover how you’ll organize your content.
Develop a content calendar.
With the help of an editorial calendar, you'll be on the right track to publishing a well-balanced and diverse content library on your website.
Then, create a social media content calendar to promote and manage your content on other sites.
Featured Tool: Free Editorial Calendar Templates

An ebook here might dive deeper into a particular problem and solution options and include templates or calculators.
[Lastly,] ebooks further down the funnel should become more personalized and offer more sales content. Comparison guides or an ebook of case studies are beneficial for prospects at this stage."
Ebooks are the next step in the inbound marketing process . After reading a blog post, visitors might want more information.
This is where calls-to-action (CTAs) come into play, directing people to a landing page where they can submit their contact information and download an ebook to learn more valuable information for their business.
In turn, the business producing the ebook has a new lead for the sales team to contact.
Featured Tool: 18 Free Ebook Templates

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

8 Steps to Launching an Online Learning Academy Your Customers Will Love

What is Content Governance? 4 Easy Steps to Create a Model in 2022

Top B2B Content Marketing Trends to Watch This Year, According to Experts

The Ultimate Round-Up of Content Marketing Tips

The Future of Content Strategy

What Is a Micro Niche ... and Do You Need One?

Rethinking Your Premium Content: How to Build a Guided Learning Course

What Are Website Traffic Exchange Sites? (And Why You Shouldn't Use Them)

What You Need to Know About Commercial Use

Why A Digital PR Specialist Should Always Be Involved in Content Creation
A Beginner's Guide to Applying Content Marketing to your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
Business Plan Template for Content Creators
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

As a content creator, you know that success in the digital landscape requires more than just creating great content. It takes careful planning, strategic thinking, and a solid business plan. Luckily, ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Content Creators has got you covered!
With this template, you can:
- Strategically outline your goals, target audience, and content strategy to stay focused and on track
- Develop a monetization plan that aligns with your brand and audience, maximizing your earning potential
- Track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure your progress and make data-driven decisions
Whether you're a blogger, YouTuber, or social media influencer, ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Content Creators will help you create a structured roadmap for success in the competitive digital landscape. Start planning and achieving your content creation goals today!
Business Plan Template for Content Creators Benefits
A business plan template for content creators can provide numerous benefits, including:
- Streamlining your content creation process and ensuring consistency across platforms
- Helping you identify your target audience and create content that resonates with them
- Setting clear goals and objectives to measure your success and track your progress
- Outlining your monetization strategies and identifying new revenue streams
- Providing a structured roadmap for growth and expansion in the digital landscape
- Helping you stay organized and focused on your content strategy
- Guiding your decision-making process and facilitating effective resource allocation
- Enabling you to pitch your ideas and secure partnerships or sponsorships with brands
- Allowing you to adapt to changes in the industry and pivot your content strategy as needed
- Increasing your credibility and professionalism as a content creator.
Main Elements of Content Creators Business Plan Template
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Content Creators is the perfect tool to help you strategically outline your goals and create a structured roadmap for success in the competitive digital landscape. This template includes:
- Custom Statuses: Keep track of the progress of your business plan with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do, ensuring that you stay organized and on top of your tasks.
- Custom Fields: Use custom fields such as Reference, Approved, and Section to track important information and annotations within your business plan, making it easy to access and reference critical details.
- Custom Views: Access five different views, including Topics, Status, Timeline, Business Plan, and Getting Started Guide, allowing you to visualize and manage your content strategy, track progress, and stay on top of your goals.
With ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Content Creators, you'll have all the tools you need to create a comprehensive and effective business plan that sets you up for success in the digital world.
How To Use Business Plan Template for Content Creators
If you're a content creator looking to take your business to the next level, using the Business Plan Template in ClickUp can help you organize your strategy and goals. Follow these five steps to make the most of this template:
1. Define your target audience
Start by clearly identifying your target audience. Who are you creating content for? What are their demographics, interests, and pain points? Understanding your audience will help you tailor your content and marketing efforts to effectively reach and engage them.
Use custom fields in ClickUp to categorize and track information about your target audience.
2. Set your goals
Determine what you want to achieve with your content creation business. Are you aiming to increase your subscriber count, generate more leads, or monetize your content through partnerships and sponsorships? Set specific, measurable goals that align with your overall business objectives.
Use Goals in ClickUp to set and track your content creation goals.
3. Plan your content calendar
Creating a content calendar is essential for staying organized and consistent with your content creation efforts. Map out your content ideas, topics, and publishing schedule for the coming weeks or months. This will help you stay on track and ensure that you're consistently delivering valuable content to your audience.
Use the Calendar view in ClickUp to visually plan and schedule your content.
4. Identify revenue streams
Explore different ways to monetize your content creation business. This could include sponsored content, affiliate marketing, selling digital products, or offering coaching or consulting services. Identify the revenue streams that align with your niche and target audience.
Use custom fields in ClickUp to track and analyze your revenue streams.
5. Track and analyze your performance
Regularly track and analyze your content performance to understand what's working and what needs improvement. Monitor metrics such as engagement, traffic, conversion rates, and revenue generated. This data will help you make informed decisions and optimize your content strategy for better results.
Use Dashboards in ClickUp to create visual reports and track your content performance metrics.
By following these steps and using the Business Plan Template in ClickUp, you'll have a clear roadmap for growing your content creation business and achieving your goals.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Content Creators
Content creators can use the Business Plan Template for Content Creators to strategically outline their goals, target audience, content strategy, monetization plans, and key performance indicators (KPIs), helping them create a structured roadmap for success in the competitive digital landscape.
First, hit "Add Template" to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you'd like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a comprehensive business plan:
- Use the Topics View to organize your business plan by different sections, such as goals, target audience, content strategy, monetization plans, and KPIs
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do
- The Timeline View will give you a visual representation of your content creation milestones and deadlines
- The Business Plan View will provide a comprehensive overview of your entire business plan, allowing you to easily navigate and make updates
- The Getting Started Guide View will serve as a step-by-step guide to help you implement your business plan effectively
- Utilize custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to add additional information and categorize your content
- Update statuses as you progress through each section to keep track of your progress
- Monitor and analyze your business plan to ensure you're on track to achieve your goals.
- Business Plan Template for Cleaning Technicians
- Business Plan Template for Landscaping Company
- Business Plan Template for Chauffeurs
- Business Plan Template for Claim Adjusters
- Business Plan Template for Payroll Staff
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide
Content Planning for Social Media: 8-Step Guide for Marketers
Content planning is more than scheduling. Run your accounts like a well-oiled machine with a strategic social media content plan.

How to create a winning content plan
Content planning is the most important factor in the success of your social media strategy. (There, I said it.) It’s much more than choosing a photo, writing a caption, and scheduling it to post.
You can have the world’s best social media marketing strategy, but it won’t be successful without proper content planning.
Here’s why that is, and the 8 steps anyone can do to plan effective, goal-crushing social media content.

OwlyWriter AI instantly generates captions and content ideas for every social media network. It’s seriously easy.
What does “content planning” mean for social media managers?
Scheduling your social posts ahead of time is great, but it’s only a small part of what makes up a content plan. Truly effective content planning focuses on the big picture: Your marketing goals.
Well-planned content is:
- Created in batches to optimize efficiency.
- Part of a cross-platform campaign and repurposed across all your channels for maximum impact.
- Connected to one or more marketing goals.
- Balanced between your own original content and curated content .
Why is content planning so important?
Which strategy is more likely to succeed?
- Chaotic social media content written and posted whenever inspiration strikes.
- Identifying your social media marketing goals and creating content in advance that aligns with and furthers those goals.
Your social media marketing strategy is what you want to achieve and how you will get there. Content planning is the process of designing content for those goals to actually get you there.
It keeps you organized
Batching your content is way more efficient than trying to come up with a post on the fly every day, or for a specific campaign. Batching means you’re taking the time to specifically write a bunch of social media content at once.
Besides being a more efficient way to write content, you’ll get more out of it. As you write each piece of content, extract pieces of it to repurpose. One post can quickly become five or more without much extra time. For example:
- Write an Instagram Reels script.
- Create a text caption from that script to use on text-based platforms like Twitter.
- Create an image or infographic from the Reel content to use as an alternative way to communicate the information.
- And, of course, the most basic: Make a note to save your completed Reel video in different sizes to use on other platforms, such as YouTube, Facebook Pages, TikTok, and more. Check the current recommended post sizes for each platform before saving.
- Plus many more options, including writing an article about the topic to a series of short Tweets of the key takeaways and everything in between.
Content planning saves time and gets you the most mileage out of your work.
It helps you avoid last-minute pressure (and writers’ block)
Oh, crap, it’s 10am on National Do A Grouch a Favor Day and you haven’t got anything scheduled to go out. (It’s February 16th in case you were wondering when you need to do me a favor.)
What will your customers think of you? Whether you post for every made-up holiday or only the real ones, content planning means you and your team will never stress out trying to create something last-minute because you forgot why this weekend is a long weekend.
More than the expected holiday observances, content planning ensures you do your best work. Planning ahead allows space for creative thinking, collaboration, and avoids burnout. All are important for creating a positive workplace culture where employees become brand advocates .
It connects your social media activity to marketing goals
Content planning keeps your eyes on the prize. You’ve got a formal marketing strategy, and hopefully a content strategy, too. (No? We’ve got a free social media strategy template for ya.) Your content planning process is what connects those big picture documents to the day-to-day marketing work your team does.
Each social media post = not that important on its own.
All your posts together = what determines if your social media strategy will sink or swim. Fail or fly. Crash out or cash in. You get it.
How to create a winning content plan in 8 steps
Content planning is the most important part of a social marketer’s job, but don’t sweat it: It’s easy once you’ve got the right process.
Your content plan brings together 3 key elements:
- Your social media strategy
- Your social media content calendar
- How often you’ll post
Let’s create your personalized content plan right now.
Step 1: Plan themes for your content
Before you can create content, you need to choose the categories you’ll post about. How many topics you have and what they are depends on your unique business, but as an example, Hootsuite posts about:
- Social media marketing tips
- Social network updates and best practices
- Marketing research and statistics, like the free Social Trends 2022 report
- Social media marketing experiments
- Product updates and features
- Company news
- Product education (tutorials, tips)
This is your content creation roadmap. If a post isn’t about one of the things on your list, you don’t post it. (Or, you rethink your marketing strategy and add a new category for it if it’s merited.)
Step 2: Brainstorm campaign and post ideas
With your topic list in front of you, create! Just… think! Write! Do it!
Write down all the ideas you can think of that meet the following criteria:
- It’s about one of the topics on your list.
- It’s connected to your marketing goals.
It’s not that simple to “think of ideas,” even for those of us who smash keyboards all day for a living. How you brainstorm is up to you, but here are a few ways I get inspired:
- Scope out your competition: What are they posting? Can you put your own spin on those ideas?
- Review the past: What campaigns have been most successful for you before? What elements of those campaigns were most effective? How can you replicate that for your new goal or campaign?
To know what’s worked before, you need top-notch analytics reports , right? Yes, you can piece together the information manually from each social platform, Google Analytics, and other sources… but why would you?
Hootsuite Analytics measures the real data you need to determine success, not just basic engagement metrics. It gives you a full 360 degree view of your performance across all networks with the ability to customize and run reports however you like, in real-time.
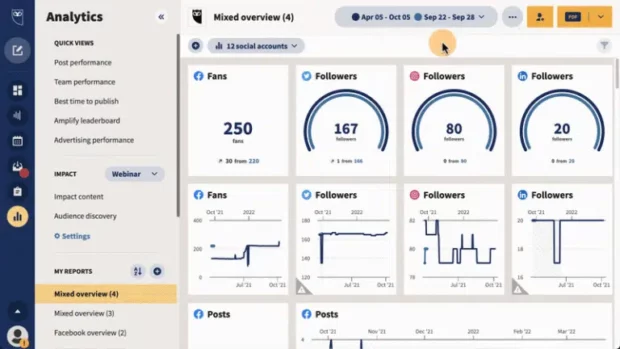
Start free 30-day trial
Step 3: Decide when you will post
We’ve got our why and what , now we need the when .
- Why: Why are you posting this? (What business goal is this content serving?)
- What: What will you post? (The actual content you brainstormed.)
- When: When is the best time to post it?
Sometimes, the when is obvious: Holiday content, a product launch, etc. But there’s a lot more to the when than the day you’re scheduling it for. You also need to consider your overall posting frequency .
You’ll need to experiment with how often you’re posting every week, how many posts per day, and the times of day. And, platforms change their algorithms all the time so what’s working now might not in six months.
Thankfully, you can back up your experiments with personalized intelligence, thanks to Hootsuite’s Best Time to Publish feature. It analyzes your unique audience engagement patterns to determine the best times to post across all your accounts.
Going a step further, it also recommends different times for different goals. For example, when to post awareness or brand-building content, and when to push hard for sales.
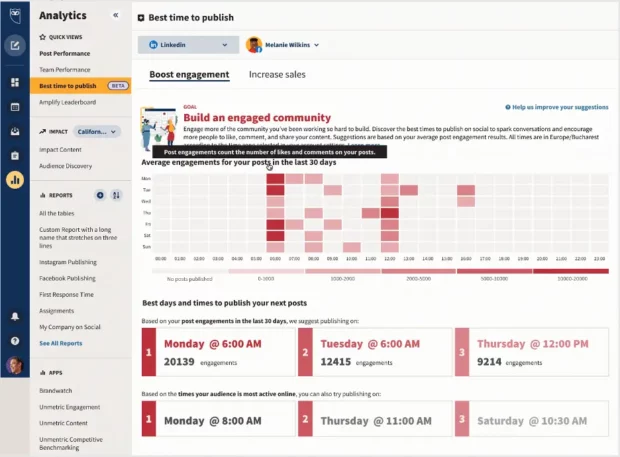
Need to get your social marketing started quickly and hit the ground running? Add your posts, either individually or via bulk upload, hit AutoSchedule , and Hootsuite does the rest. Boom—your social media for the month done in under five minutes.
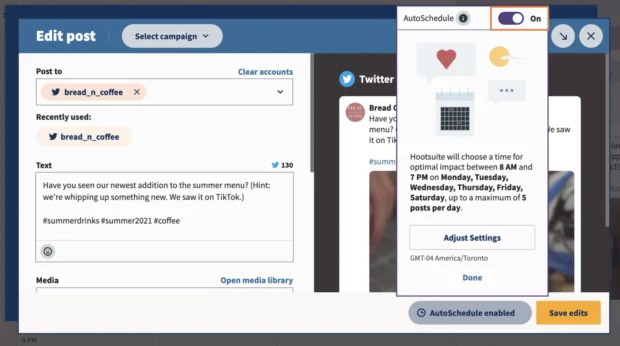
Of course, AutoSchedule is great for those pressed for time, but you should still experiment with different numbers of posts per week and times of day to find what works best for your target audience.
You can customize AutoSchedule to only post during set times or days of the week. Once you decide how often and when to post, either with Hootsuite Analytics or other tools, modify your AutoSchedule settings and now you have effortless social media post scheduling. Nice.

Only want to post once a day at a specific time? No problem.
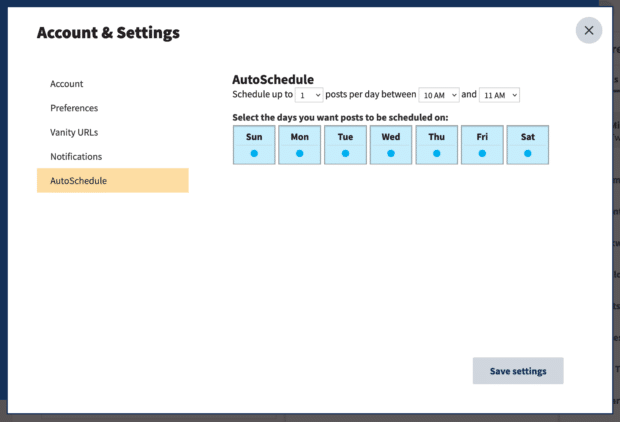
Step 4: Decide on your content mix
There’s no need to reinvent the wheel daily. A successful social media and content marketing plan contains a mix of original and curated content . But what should you curate? Where from? How often?
Great curated content is:
- Relevant to your audience.
- Related to one of your content themes (from Step 1).
- Connected to a business goal.
How each piece and type of content fits in with your other social media content is more important than how much of it you share, but a standard content mix is 40% original and 60% curated . Of course, adjust that up or down depending on your preferences and production capacity for your own content.
Some weeks you may share more curated content than others, but on average, stick to your plan. A surefire method for ensuring you don’t overdo it? Share one post, create one post—repeat!
With Hootsuite, you can easily add content from around the web to build a library of quality content to share later. When you find something to share, create a new post with the link and save it to your Drafts section.
And, you can use Streams to easily capture content from social media accounts you follow to re-share later.
When it’s time to schedule out your content—more on that later—you can just drag and drop from Drafts straight into your editorial calendar in Hootsuite Planner.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Hootsuite 🦉 (@hootsuite)
Step 5: Assign responsibilities
It can be easy to lose track of planning content ahead of time and end up in that familiar “Oh, crap, we need posts for tomorrow!” space, right? It’s the planner’s job to ensure the work that needs to get done flows down through to everyone else.
Clear expectations around who’s doing what are essential for content planning (and, so I hear, life). If you’re a lone content manager and don’t have a dedicated social marketing team with writers, designers, customer support peeps, and so on, now’s the time to build one.
If you’re on a tight budget, find freelancers to outsource tasks to as you need them so you can control expenses. For in-house and larger teams, you need to plan your planning. It’s redundant, and truly true.
So spell it out: Literally put it on your calendar. Assign a planner/strategist to manage the overall content planning process and assign each week or month’s work. Then, assign a designer, writer, project manager, etc to each client and/or campaign you’re managing.
Everything you need to make engaging content. AI support for captions, an AI hashtag generator, and access to Canva in Hootsuite.
Step 6: Write post captions
Whenever possible, it’s best to write your social media post content before the campaign goes off to the design team (the next step).
This has a few key benefits:
- It gives context to the designer so they can work efficiently.
- They will have a better understanding of the entire campaign’s structure and goals.
- While writing the posts, you may think of more ideas to add to the campaign to fill gaps.
- It saves time by allowing copyediting and approvals to happen simultaneously with design, so you can publish it sooner.
Did you know that Hootsuite comes with OwlyWriter AI, a built-in creative AI tool that saves social media pros hours of work?
You can use OwlyWriter to:
- Write a new social media caption in a specific tone, based on a prompt
- Write a post based on a link (e.g. a blog post or a product page)
- Generate post ideas based on a keyword or topic (and then write posts expanding on the idea you like best)
- Identify and repurpose your top-performing posts
- Create relevant captions for upcoming holidays
To get started with OwlyWriter, sign in to your Hootsuite account and head to the Inspiration section of the dashboard. Then, pick the type of AI magic you want to see in action.

For example, if you’re not sure what to post, click on Get inspired . Then, type in the general, high-level topic you want to address and click Get ideas .
Start your free 30-day trial
OwlyWriter will generate a list of post ideas related to the topic:
Click on the one you like best to move to the next step — captions and hashtags.
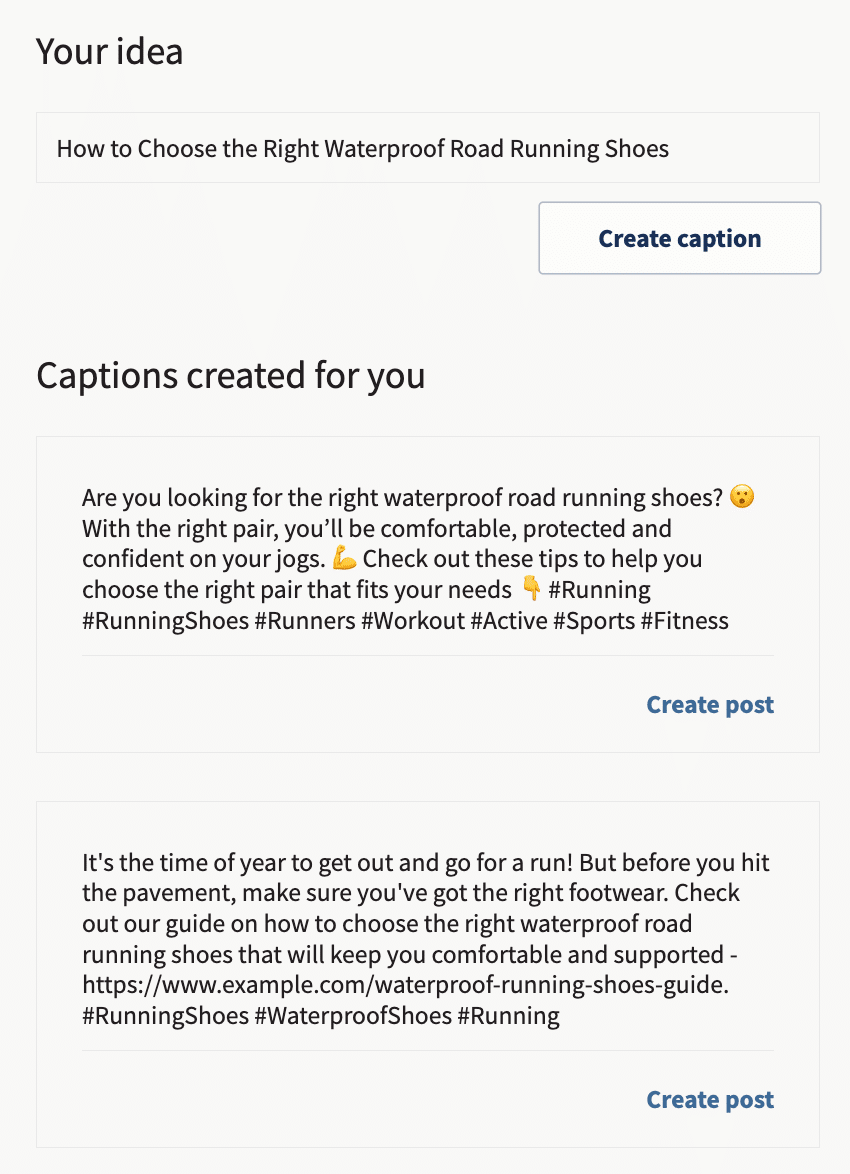
Pick the caption you like and click Create post . The caption will open in Hootsuite Composer, where you can make edits, add media files and links, check the copy against your compliance guidelines — and schedule your post to go live later.
And that’s it! OwlyWriter never runs out of ideas, so you can repeat this process until your social media calendar is full — and sit back to watch your engagement grow.
Step 7: Create (or source) design assets
This is often where content plans get bottlenecked. You can think up all these amazing campaigns, but without the creative assets that get it noticed, like graphics and videos, you can be stuck in your drafts forever.
But this is exactly why assigning responsibilities is important. Having a dedicated person for each part of the content planning process keeps things moving along and everyone’s on the same page.
With Hootsuite Planner , you can collaborate with other team members on specific campaigns, view the overall calendar, and map out your content to identify opportunities and gaps to fill. Plus, approvals are a snap with a built-in review process so the only content that gets posted is the content that should be.
Here’s how everyone can work together inside Hootsuite to bring a campaign from idea to finished:
Step 8: Schedule content in advance
Last but very un-least, scheduling. I don’t need to tell you scheduling your content ahead of time is important for basic efficiency. But it’s also the one thing that can make or break your entire social media marketing strategy . No pressure.
But really, what’s the point of content planning and following all the steps here if you’re not going to schedule out that content ahead of time in an organized, efficient, strategic way? Exactly.
There’s always room for improvement, though. If you’re not already using Hootsuite, try it out and see how much time you’ll save scheduling posts. Plus: team collaboration, detailed analytics, ads management, social listening, and more—all in one convenient place.
You can create single posts in Composer or dial up your efficiency to 11 with the much-loved bulk upload tool, where you and 350 of your best posts can be scheduled in under 2 minutes flat.
Bonus: Download our free, customizable social media calendar template to easily plan and schedule all your content in advance.
Hootsuite is your content planning partner in success with robust scheduling, collaboration, analytics, and smart insights like the Best Time to Publish feature to make your job easier. Sign up for free today.
Get Started
Save time and grow faster with OwlyWriter AI, the tool that instantly generates social media captions and content ideas .
Become a better social marketer.
Get expert social media advice delivered straight to your inbox.
As an ex-agency strategist turned freelance WFH fashion icon, Michelle is passionate about putting the sass in SaaS content. She's known for quickly understanding and distilling complicated technical topics into conversational copy that gets results. She has written for Fortune 500 companies and startups, and her clients have earned features in Forbes, Strategy Magazine and Entrepreneur.
Related Articles

How to Create a Social Media Marketing Strategy in 9 Easy Steps [Free Template]
Creating your social media marketing strategy doesn’t need to be painful. Create an effective plan for your business in 9 simple steps.

How to Create a Social Media Calendar and Stay Organized
Social media content calendars are the best way to plan and organize your content. Build one in 4 easy steps or use our free templates.
5 Ways to Nail Your Social Media Promotion Strategy
The data is in — people use social media to shop. We’ll help you make sure your social media promotion strategy is on point.

17 Fresh Social Media Post Ideas for 2024
This list of engaging social media post ideas will help you out the next time you need to beat that dreaded writer’s block.

13 Content Creation Tools That Make Your Job Way Easier
These content creation tools cover every stage of the digital marketing process, from inspiration to execution.

How to write a business plan for a content marketing agency?

Putting together a business plan for a content marketing agency can be daunting - especially if you're creating a business for the first time - but with this comprehensive guide, you'll have the necessary tools to do it confidently.
We will explore why writing one is so important in both starting up and growing an existing content marketing agency, as well as what should go into making an effective plan - from its structure to content - and what tools can be used to streamline the process and avoid errors.
Without further ado, let us begin!
In this guide:
Why write a business plan for a content marketing agency?
What information is needed to create a business plan for a content marketing agency.
- How do I build a financial forecast for a content marketing agency?
The written part of a content marketing agency business plan
- What tool should I use to write my content marketing agency business plan?
Understanding the document's scope and goals will help you easily grasp its structure and content. Before diving into the specifics of the plan, let's take a moment to explore the key reasons why having a content marketing agency business plan is so crucial.
To have a clear roadmap to grow the business
Small businesses rarely experience a constant and predictable environment. Economic cycles go up and down, while the business landscape is mutating constantly with new regulations, technologies, competitors, and consumer behaviours emerging when we least expect it.
In this dynamic context, it's essential to have a clear roadmap for your content marketing agency. Otherwise, you are navigating in the dark which is dangerous given that - as a business owner - your capital is at risk.
That's why crafting a well-thought-out business plan is crucial to ensure the long-term success and sustainability of your venture.
To create an effective business plan, you'll need to take a step-by-step approach. First, you'll have to assess your current position (if you're already in business), and then identify where you'd like your content marketing agency to be in the next three to five years.
Once you have a clear destination for your content marketing agency, you'll focus on three key areas:
- Resources: you'll determine the human, equipment, and capital resources needed to reach your goals successfully.
- Speed: you'll establish the optimal pace at which your business needs to grow if it is to meet its objectives within the desired timeframe.
- Risks: you'll identify and address potential risks you might encounter along the way.
By going through this process regularly, you'll be able to make informed decisions about resource allocation, paving the way for the long-term success of your business.
To get visibility on future cash flows
If your small content marketing agency runs out of cash: it's game over. That's why we often say "cash is king", and it's crucial to have a clear view of your content marketing agency's future cash flows.
So, how can you achieve this? It's simple - you need to have an up-to-date financial forecast.
The good news is that your content marketing agency business plan already includes a financial forecast (which we'll discuss further in this guide). Your task is to ensure it stays current.
To accomplish this, it's essential to regularly compare your actual financial performance with what was planned in your financial forecast. Based on your business's current trajectory, you can make adjustments to the forecast.
By diligently monitoring your content marketing agency's financial health, you'll be able to spot potential financial issues, like unexpected cash shortfalls, early on and take corrective actions. Moreover, this practice will enable you to recognize and capitalize on growth opportunities, such as excess cash flow enabling you to expand to new locations.
To secure financing
Whether you are a startup or an existing business, writing a detailed content marketing agency business plan is essential when seeking financing from banks or investors.
This makes sense given what we've just seen: financiers want to ensure you have a clear roadmap and visibility on your future cash flows.
Banks will use the information included in the plan to assess your borrowing capacity (how much debt your business can support) and your ability to repay the loan before deciding whether they will extend credit to your business and on what terms.
Similarly, investors will review your plan carefully to assess if their investment can generate an attractive return on investment.
To do so, they will be looking for evidence that your content marketing agency has the potential for healthy growth, profitability, and cash flow generation over time.
Now that you understand why it is important to create a business plan for a content marketing agency, let's take a look at what information is needed to create one.
Writing a content marketing agency business plan requires research so that you can project sales, investments and cost accurately in your financial forecast.
In this section, we cover three key pieces of information you should gather before drafting your business plan!
Carrying out market research for a content marketing agency
As you consider writing your business plan for a content marketing agency, conducting market research becomes a vital step to ensure accurate and realistic financial projections.
Market research provides valuable insights into your target customer base, competitors, pricing strategies, and other key factors that can significantly impact the commercial success of your business.
Through this research, you may uncover trends that could influence your content marketing agency.
You may find that companies are increasingly looking for content marketing agencies that specialize in developing content for their specific industry. Additionally, it is possible that businesses could be seeking out content marketing strategies that have a greater focus on digital marketing, such as social media campaigns.
Such market trends play a significant role in forecasting revenue, as they offer valuable data about potential customers' spending habits and preferences.
By incorporating these findings into your financial projections, you can present investors with more accurate information, helping them make informed decisions about investing in your content marketing agency.
Developing the sales and marketing plan for a content marketing agency
As you embark on creating your content marketing agency business plan, it is crucial to budget sales and marketing expenses beforehand.
A well-defined sales and marketing plan should include precise projections of the actions required to acquire and retain customers. It will also outline the necessary workforce to execute these initiatives and the budget required for promotions, advertising, and other marketing efforts.
This approach ensures that the appropriate amount of resources is allocated to these activities, aligning with the sales and growth objectives outlined in your business plan.
The staffing and equipment needs of a content marketing agency
Whether you are at the beginning stages of your content marketing agency or expanding its horizons, having a clear plan for recruitment and capital expenditures (investment in equipment and real estate) is vital to ensure your business's success.
To achieve this, both the recruitment and investment plans must align coherently with the projected timing and level of growth in your forecast. It is essential to secure appropriate funding for these plans.
Staffing costs may include salaries for a content marketing manager, a content writer, a graphic designer, and a social media manager. Equipment costs may include computers, software, and other necessary technology for the team to work effectively.
To create a financial forecast that accurately represents your business's outlook, remember to factor in other day-to-day operating expenses.
Now that you have all the necessary information, it's time to dive in and start creating your business plan and developing the financial forecast for your content marketing agency.
What goes into your content marketing agency's financial forecast?
The financial forecast of your content marketing agency's business plan will enable you to assess the growth, profitability, funding requirements, and cash generation potential of your business in the coming years.
The four key outputs of a financial forecast for a content marketing agency are:
- The profit and loss (P&L) statement ,
- The projected balance sheet ,
- The cash flow forecast ,
- And the sources and uses table .
Let's look at each of these in a bit more detail.
The projected P&L statement
The projected P&L statement for a content marketing agency shows how much revenue and profits your business is expected to generate in the future.
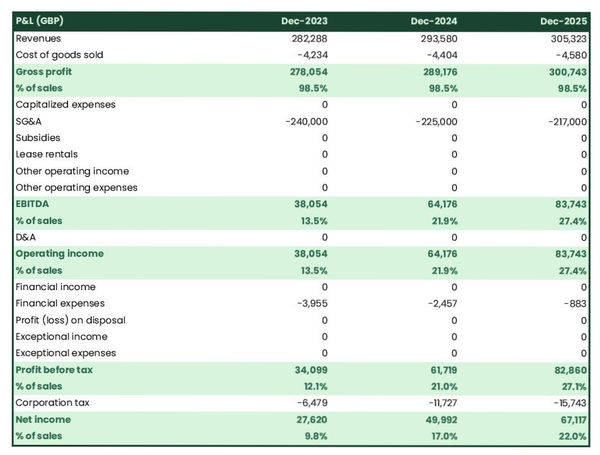
Ideally, your content marketing agency's P&L statement should show:
- Healthy growth - above inflation level
- Improving or stable profit margins
- Positive net profit
Expectations will vary based on the stage of your business. A startup will be expected to grow faster than an established content marketing agency. And similarly, an established company should showcase a higher level of profitability than a new venture.
The forecasted balance sheet of your content marketing agency
The projected balance sheet of your content marketing agency will enable the reader of your business plan to assess the overall financial health of your business.
It shows three elements: assets, liabilities and equity:
- Assets: are productive resources owned by the business, such as equipment, cash, and accounts receivable (money owed by clients).
- Liabilities: are debts owed to creditors, lenders, and other entities, such as accounts payable (money owed to suppliers).
- Equity: includes the sums invested by the shareholders or business owners and the profits and losses accumulated by the business to date (which are called retained earnings). It is a proxy for the value of the owner's stake in the business.
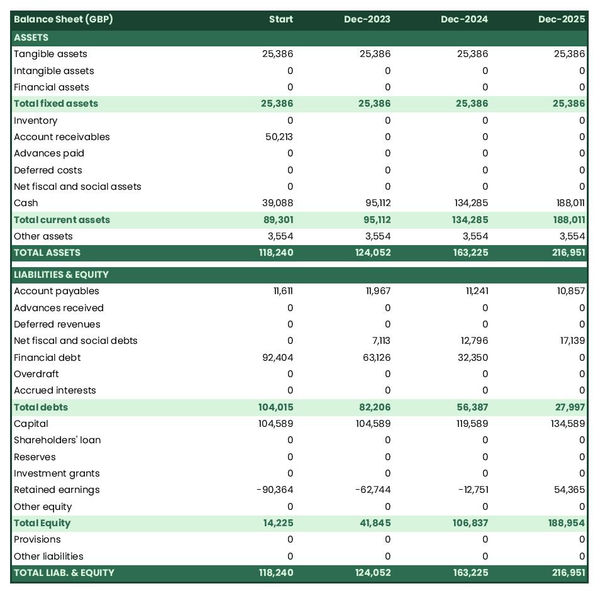
Analysing your content marketing agency projected balance sheet provides an understanding of your content marketing agency's working capital structure, investment and financing policies.
In particular, the readers of your plan can compare the level of financial debt on the balance sheet to the equity value to measure the level of financial risk (equity doesn't need to be reimbursed, while financial debt must be repaid, making it riskier).
They can also use your balance sheet to assess your content marketing agency's liquidity and solvency:
- A liquidity analysis: focuses on whether or not your business has sufficient cash and short-term assets to cover its liabilities due in the next 12 months.
- A solvency analysis: takes and longer view to assess whether or not your business has the capacity to repay its debts over the medium-term.
The projected cash flow statement
A cash flow forecast for a content marketing agency shows how much cash the business is projected to generate or consume.
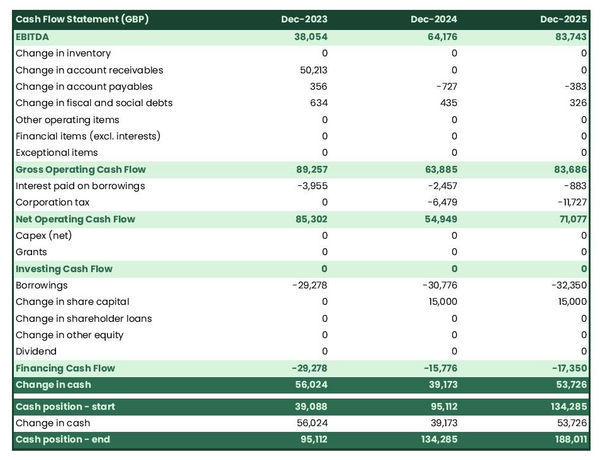
The cash flow statement is divided into 3 main areas:
- The operating cash flow shows how much cash is generated or consumed by the operations (running the business)
- The investing cash flow shows how much cash is being invested in capital expenditure (equipment, real estate, etc.)
- The financing cash flow shows how much cash is raised or distributed to investors and lenders
Looking at the cash flow forecast helps you to ensure that your business has enough cash to keep running, and can help you anticipate potential cash shortfalls.
It is also a best practice to include a monthly cash flow statement in the appendices of your content marketing agency business plan so that the readers can view the impact of seasonality on your business cash position and generation.
The initial financing plan
The initial financing plan - also called a sources and uses table - is an important tool when starting a content marketing agency.
It shows where the money needed to set up the business will come from (sources) and how it will be allocated (uses).
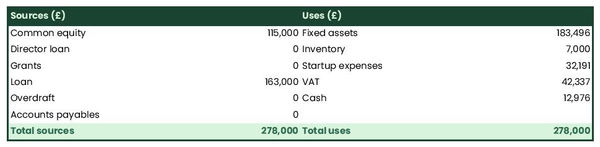
Having this table helps understand what costs are involved in setting up the content marketing agency, how the risks are distributed between the shareholders and the lenders, and what will be the starting cash position (which needs to be sufficient to sustain operations until the business breaks even).
Now that the financial forecast of a content marketing agency business plan is understood, let's focus on what goes into the written part of the plan.
The written part of the business plan is where you will explain what your business does and how it operates, what your target market is, whom you compete against, and what strategy you will put in place to seize the commercial opportunity you've identified.
Having this context is key for the reader to form a view on whether or not they believe that your plan is achievable and the numbers in your forecast realistic.
The written part of a content marketing agency business plan is composed of 7 main sections:
- The executive summary
- The presentation of the company
- The products and services
- The market analysis
- The strategy
- The operations
- The financial plan
Let's go through the content of each section in more detail!
1. The executive summary
In your content marketing agency's business plan, the first section is the executive summary — a captivating overview of your plan that aims to pique the reader's interest and leave them eager to learn more about your business.
When crafting the executive summary, start with an introduction to your business, including its name, concept, location, how long it has been running, and what sets it apart. Briefly mention the products and services you plan to offer and your target customer profile.
Following that, provide an overview of the addressable market for your content marketing agency, current trends, and potential growth opportunities.
Next, include a summary of key financial figures like projected revenues, profits, and cash flows.
Finally, in the "ask" section, detail any funding requirements you may have.
2. The presentation of the company
The second section in your content marketing agency's business plan should focus on the structure and ownership, location, and management team of the company.
The structure and ownership part provides an overview of the legal structure of the business, who the owners are and how much each has invested and owns. If you are seeking financing it is important that the reader gets a clear picture of which legal entity is receiving the funds, and who controls the business.
The location part should give an overview of the premises from which the company is operating, and why that location is of particular interest (catchment area, accessibility, amenities nearby, etc.).
When describing the location of your content marketing agency, you could emphasize its potential to reach a wide variety of markets. You may mention that it is in a relatively urban area, with a diverse population and access to a large consumer base. You might also highlight how it is close to major transportation routes, providing convenience for potential partners and clients. Finally, you could emphasize how the area is a hub for the creative and digital industries, and may offer a unique opportunity to collaborate with like-minded individuals.
Finally, you should introduce the management team. Explain each member's role, background, and experience.
It is also important to emphasize any past successes that the members of the management team have achieved, and how long they've been working together, as this will help potential lenders or investors understand why they should trust in their leadership.
3. The products and services section
The products and services section of your business plan should include a detailed description of the offerings that your company provides to its customers.
For example, your content marketing agency might offer blog writing and social media management services to help customers reach their target audience and increase brand visibility. Additionally, the agency could provide SEO and keyword research services to help customers optimize their content and ensure that their target keywords are reaching their desired audience. Finally, the agency might offer copywriting services to help customers craft compelling copy that drives conversions.
When drafting this section, you should be precise about the categories of products or services you sell, the types of customers you are targeting and how customers can buy them.
4. The market analysis
When you present your market analysis in your content marketing agency business plan, it's crucial to include detailed information about customers' demographics and segmentation, target market, competition, barriers to entry, and any relevant regulations.
The main objective of this section is to help the reader understand the size and attractiveness of the market while demonstrating your solid understanding of the industry.
Begin with the demographics and segmentation subsection, providing an overview of the addressable market for your content marketing agency, the key trends in the marketplace, and introducing different customer segments along with their preferences in terms of purchasing habits and budgets.
Next, focus on your target market, zooming in on the specific customer segments your content marketing agency aims to serve and explaining how your products and services fulfil their distinct needs.
For example, your target market might include small businesses who need help creating a content marketing strategy. These businesses may have limited resources to create content and need help to create an effective strategy. They may require help creating content, optimizing it for various platforms, and distributing it.
Then proceed to the competition subsection, where you introduce your main competitors and highlight what sets you apart from them.
Finally, conclude your market analysis with an overview of the key regulations applicable to your content marketing agency.
5. The strategy section
When writing the strategy section of a business plan for your content marketing agency, it is essential to include information about your competitive edge, pricing strategy, sales & marketing plan, milestones, and risks and mitigants.
The competitive edge subsection should explain what sets your company apart from its competitors. This part is especially key if you are writing the business plan of a startup, as you have to make a name for yourself in the marketplace against established players.
The pricing strategy subsection should demonstrate how you intend to remain profitable while still offering competitive prices to your customers.
The sales & marketing plan should outline how you intend to reach out and acquire new customers, as well as retain existing ones with loyalty programs or special offers.
The milestones subsection should outline what your company has achieved to date, and its main objectives for the years to come - along with dates so that everyone involved has clear expectations of when progress can be expected.
The risks and mitigants subsection should list the main risks that jeopardize the execution of your plan and explain what measures you have taken to minimize these. This is essential in order for investors or lenders to feel secure in investing in your venture.
1. Your content marketing agency could face competition from other agencies. As the industry grows, other companies may emerge with similar services and expertise, which could lead to a decreased demand for your services. 2. Your agency could face potential legal issues. Depending on the type of content and campaigns you create, there might be potential copyright violations or other legal issues that could arise and require expensive legal representation.
6. The operations section
The operations of your content marketing agency must be presented in detail in your business plan.
The first thing you should cover in this section is your staffing team, the main roles, and the overall recruitment plan to support the growth expected in your business plan. You should also outline the qualifications and experience necessary to fulfil each role, and how you intend to recruit (using job boards, referrals, or headhunters).
You should then state the operating hours of your content marketing agency - so that the reader can check the adequacy of your staffing levels - and any plans for varying opening times during peak season. Additionally, the plan should include details on how you will handle customer queries outside of normal operating hours.
The next part of this section should focus on the key assets and IP required to operate your business. If you depend on any licenses or trademarks, physical structures (equipment or property) or lease agreements, these should all go in there.
You could have key assets such as your team's expertise and experience in content marketing, as well as your content library of information and resources. Your intellectual property (IP) might include your knowledge base for content creation and optimization, as well as any unique tools and strategies you have developed for content marketing.
Finally, you should include a list of suppliers that you plan to work with and a breakdown of their services and main commercial terms (price, payment terms, contract duration, etc.). Investors are always keen to know if there is a particular reason why you have chosen to work with a specific supplier (higher-quality products or past relationships for example).
7. The presentation of the financial plan
The financial plan section is where we will present the financial forecast we talked about earlier in this guide.
Now that you have a clear idea of what goes in your content marketing agency business plan, let's look at the solutions you can use to draft yours.
What tool should I use to write my content marketing agency's business plan?
There are two main ways of creating your content marketing agency business plan:
- Using specialized business planning software,
- Hiring a business plan writer.
Using an online business plan software for your content marketing agency's business plan
The modern and most efficient way to write a content marketing agency business plan is to use business plan software .
There are several advantages to using specialized software:
- You can easily create your financial forecast by letting the software take care of the financial calculations for you without errors
- You are guided through the writing process by detailed instructions and examples for each part of the plan
- You can access a library of dozens of complete business plan samples and templates for inspiration
- You get a professional business plan, formatted and ready to be sent to your bank or investors
- You can easily track your actual financial performance against your financial forecast
- You can create scenarios to stress test your forecast's main assumptions
- You can easily update your forecast as time goes by to maintain visibility on future cash flows
- You have a friendly support team on standby to assist you when you are stuck
If you're interested in using this type of solution, you can try The Business Plan Shop for free by signing up here .
Hiring a business plan writer to write your content marketing agency's business plan
Outsourcing your content marketing agency business plan to a business plan writer can also be a viable option.
Business plan writers are experienced in writing business plans and adept at creating financial forecasts without errors. Furthermore, hiring a consultant can save you time and allow you to focus on the day-to-day operations of your business.
However, hiring business plan writers is expensive as you are paying for the software used by the consultant, plus their time, and their profit margin of course.
From experience, you need to budget at least £1.5k ($2.0k) excluding tax for a complete business plan, more if you need to make changes after the initial version (which happens frequently after the initial meetings with lenders or investors).
You also need to be careful when seeking investment. Investors want their money to be used to grow the business, not spent on consulting fees. Therefore, the amount you spend on business plan writing services (and other consulting services such as legal services) needs to be negligible relative to the amount raised.
The other drawback is that you usually don't own the business plan itself: you just get the output, while the actual document is saved in the consultant's business plan software - which makes it difficult to maintain the document up to date without hiring the consultant on a retainer.
For these reasons, outsourcing the content marketing agency business plan to a business plan writer should be considered carefully, weighing both the advantages and disadvantages of hiring outside help.
Ultimately, it may be the right decision for some businesses, while others may find it beneficial to write their business plan using online software.
Why not create your content marketing agency's business plan using Word or Excel?
Using Microsoft Excel and Word (or their Google, Apple, or open-source equivalents) to write a content marketing agency business plan is a terrible idea.
For starters, creating an accurate and error-free financial forecast on Excel (or any spreadsheet) is very technical and requires both a strong grasp of accounting principles and solid skills in financial modelling.
As a result, it is unlikely anyone will trust your numbers unless - like us at The Business Plan Shop - you hold a degree in finance and accounting and have significant financial modelling experience in your past.
The second reason is that it is inefficient. Building forecasts on spreadsheets was the only option in the 1990s and early 2000s, nowadays technology has advanced and software can do it much faster and much more accurately.
And with the rise of AI, software is also becoming smarter at helping us detect mistakes in our forecasts and helping us analyse the numbers to make better decisions.
Also, using software makes it easy to compare actuals vs. forecasts and maintain our forecasts up to date to maintain visibility on future cash flows - as we discussed earlier in this guide - whereas this is a pain to do with a spreadsheet.
That's for the forecast, but what about the written part of my content marketing agency business plan?
This part is less error-prone, but here also software brings tremendous gains in productivity:
- Word processors don't include instructions and examples for each part of your business plan
- Word processors don't update your numbers automatically when they change in your forecast
- Word processors don't handle the formatting for you
Overall, while Word or Excel may be viable options for creating a content marketing agency business plan for some entrepreneurs, it is by far not the best or most efficient solution.
- Having an up-to-date business plan is key to maintaining visibility on your future cash flows.
- A business plan has 2 parts: a financial forecast highlighting the expected growth, profitability and cash generation of the business; and a written part which provides the context needed to interpret and assess the quality of the forecast.
- Using business plan software is the modern way of writing and maintaining business plans.
We hope that this guide helped you to better understand how to write the business plan for a content marketing agency. If you still have questions, do not hesitate to contact us.
Also on The Business Plan Shop
- How to write a 5 years business plan
- Business plan myths
Know someone who owns or wants to start a content marketing agency? Share this article with them!

Founder & CEO at The Business Plan Shop Ltd
Guillaume Le Brouster is a seasoned entrepreneur and financier.
Guillaume has been an entrepreneur for more than a decade and has first-hand experience of starting, running, and growing a successful business.
Prior to being a business owner, Guillaume worked in investment banking and private equity, where he spent most of his time creating complex financial forecasts, writing business plans, and analysing financial statements to make financing and investment decisions.
Guillaume holds a Master's Degree in Finance from ESCP Business School and a Bachelor of Science in Business & Management from Paris Dauphine University.
Create a convincing business plan
Assess the profitability of your business idea and create a persuasive business plan to pitch to investors
500,000+ entrepreneurs have already tried our solution - why not join them?
Not ready to try our on-line tool ? Learn more about our solution here
Need some inspiration for your business plan?
Subscribe to The Business Plan Shop and gain access to our business plan template library.

Need a professional business plan? Discover our solution
Write your business plan with ease!

It's easy to create a professional business plan with The Business Plan Shop
Want to find out more before you try? Learn more about our solution here

- Search Search Search …
How to Create a Content Plan (Step-by-Step Guide + Examples)
Content marketing got you feeling like this?
I don’t blame you. If you care about the quality and efficacy of your content, there’s a lot to consider.
But a content plan will simplify the process. It’ll help you figure out the who, what, when, where, why and how before you dive in (and help you stay in charge of it all when you do).
Here’s everything you need to know about content planning so that you can create quality content at scale and with ease:
What Is a Content Plan?
Why you need a content plan, how to create a content plan, content plan examples and templates, top tips for creating a content plan.
A content plan is where you map out and organize all of the tasks related to content creation and promotion. It should include content assets and/or campaigns along with deadlines or key dates.
If you’re in charge of a team, you’ll assign ownership of tasks or entire projects. You may also allocate resources and budget in your content plan.
The best content plans contain defined processes and workflows for content creation/promotion. For example, you might outline the finer details of each activity and include templates or briefs.
You may be wondering about the difference between a content plan and a content strategy. Well, your content strategy is a bit like your content marketing manual and your content plan comprises a significant chapter of that manual.
A documented content strategy contains your goals, research and analysis, the overarching methods you’ll use to achieve your goals, as well as your content plan. You’ll need to refer to the other elements, i.e. the research and so on, to put together your content plan.
Some don’t bother with a content plan because it seems like a lot of unnecessary, hard work. Others are like hummingbirds, flitting around, eager to just get started on content creation.
But, trust me, having a content plan will pay off. Here’s why:
1. Scale and Speed
You might feel like you’d need a time-freezing device to be able to scale content production. There’s a demand for quality content (and rightly so). Thus, it takes a long time to create a good infographic, email newsletter, blog post etc.
For instance, we now spend 63% more time creating a blog post than six years ago.
Yet, the defined, repeatable processes within your content plan mean you can create more content within a given time period. And the automation features of many content planning tools save even more time.
2. Manage Content Easily
Create a lot of content? Manage a content team or group of freelancers? A content plan will help you allocate your time accordingly and/or delegate tasks to others easily, all while staying on top of everything.
Four out of five of the most successful content marketers use an editorial calendar. So, there’s a lot to be said about being super organized in your approach.
3. Create Better Content
54% of marketers think their organization’s level of content marketing success is mediocre.
We need to do better.
A content plan forces you to think carefully about each content asset or content marketing activity – how it’ll help your audience, how it fits in with your wider goals, how you can get the most from it and so on. This makes it almost impossible not to create better content.
Speedier production, easier management and better quality content – aren’t these three things what all content creators and marketers want at the end of the day?
Here’s how to put your content plan together:
1. Choose Your Weapon
The very first step is figuring out the best way to document your content plan. Here are the main options:
- Regular Documents
You might want to put all or some elements of your content plan, e.g. templates, in regular doc format. However, this is not the clearest nor most collaborative route.
- Spreadsheets
Spreadsheets work well for content management. You can keep all of the information you and/or your colleagues need well-organized.
- A Project Management Tool
Project management tools, such as Trello or Asana make collaboration and content management super easy.
- A Content Management Tool
There are some fantastic tools geared specifically towards content management and organization, such as CoSchedule and Contently .
2. Weigh Your Content Strategies
What are your most important goals?
You’ll create content assets or use content marketing tactics that’ll help you achieve every one of your goals, but you must give more weight to what’s most important.
If it’s not immediately clear, you might want to use a scoring system e.g. rate how well an asset aligns with your goals or what kind of ROI it will produce.
To complicate things, *sigh*, you also have to keep best practices in mind. For example, you might only need to blog twice a month but tweet daily to get the kind of impact you hope to achieve.
3. Include the 5 Ws and 1H
Now we’re getting onto the good stuff… The actual contents of your content strategy. However you choose to document your plan, here’s what it should include:
You’ll need to assign tasks and responsibilities to the right members of your team (unless you’re a superstar that’s doing it all yourself). Make sure each person knows every step of content creation or promotion that they’re in charge of.
Add your content assets, campaigns and/or projects to your content plan. Include the types of content you’ll create e.g. infographic, blog post, video etc, as well as the topic, headline and any other information you think is relevant, such as calls to action.
Set realistic and achievable deadlines for your content projects. You may also wish to set deadlines for individual tasks, i.e. each step of creation and promotion.
Add the channels you’ll use to publish and promote content. Also, note when and where you’ll be able to repurpose content on other channels.
Outline the purpose of each content asset. Who are you targeting and why? What action would you like them to take?
It’s a good idea to include content templates, style guides and/or briefs to guide content creation. You may also wish to create workflows or checklists for content creation and promotion. These are examples of the kind of repeatable processes that’ll help you speed up your content marketing efforts.
Now you know what a content plan should include. But, what will it look like?
Here are some fantastic examples and templates you can use to create your own content plan:
Content Planning Spreadsheet
This example from Smartsheet covers most of the bases:
As you can see the content is split into categories in the first column according to format. The next columns establish the topic, ownership, important dates, the status of the piece and more. As you move across, there are also columns with metrics for measuring content performance.
This would be a great general overview to share with your team. Use Smartsheet’s content planning template or create your own custom version on Excel or Google Sheets.
Content Plan for Social Media
If you create a lot of native social media content or social media content takes up the lion’s share of your strategy, you may want to create a content plan that’s purely for social media.
Here’s an example from Content Marketing Institute:
For each social media channel, it covers goals, topics, a posting schedule, ownership, a mini style guide, calls to action and more. In other words, it covers the 5Ws and 1H pretty darn well.
You can use CMI’s social media plan template or create something similar for you and your team.
Editorial Calendar Examples
Some of my clients like to use Trello to manage content projects and it works really well in my experience. Here’s an example of a blog editorial calendar on Trello :
Each block contains a piece of content, which you can move through the various stages of completion from “Writing” to “Ready to Upload”. This is a simple way to organize content and monitor progress.
Within each block, you can label the type of content, set a deadline, add custom fields e.g. the focus keyword and add a description. In the description field, you might want to outline the goals of the piece, the target audience etc.
You can also add any attachments that the content creator might need, e.g. templates, outlines, guides, or resources.
And finally, you can place a checklist that acts as a workflow for content creation.
If you decide to use Trello to plan content, you could create more boards for the other types of content you create, e.g. video, podcasts etc.
I, personally, like to use Asana to manage my blog and other content projects. If you want to get started quickly, the tool has ready-made content and editorial calendar templates .
The big selling-point of Asana for me is the different view formats. You can use a calendar format for an overview of all your projects:
( Image Source )
You can move each individual piece of content through a kanban board as you’re working on it:
And there are more views you can use such as a simple list format or timeline for project milestones.
Similar to Trello, there’s lots you can do within each individual task block. Assign a task, set a due date, add a description, create sub-tasks and so on:
As an added bonus, a little rainbow unicorn sometimes flashes across the screen when you complete a task. *eek*
In my humble opinion, tools like these make content planning much easier. You (and your team) have all of the information you need set out clearly in one place. Plus, you can easily tweak your content plan as you go along.
Now you should have a good grasp of the practical side of creating a content plan. Here’s some further advice that’ll help you create the most useful and effective content plan possible:
1. Make Good Use of Your Research
There are some steps that come before creating a content plan. As part of creating your content strategy, hopefully, you’ve already carried out a content audit, audience research, goal-setting and so on.
As mentioned above, you really need to refer to this research and analysis when creating your content plan. It’ll not only make content planning easier but also more effective.
MavSocial’s Kieran Driver told me:
“My number one tip for creating a content plan would be to understand who your audience is. The better picture you have of your audience, the more you will be able to plan, create, and publish content that they will be able to relate with and enjoy. Only then will you be able to effectively meet your audience’s expectations, have them come back for more and get them to remain engaged with your business.” Kieran Driver, Digital Marketing Associate, MavSocial
2. Come up With Ideas for High-Performing Content
The ideation stage or the “what” is one of the most important and time-consuming aspects of creating a content plan. But, you can use your research and analysis to come up with the content ideas that are most likely to perform well.
CoSchedule’s Ben Sailer shared his formula for generating first-rate content ideas with me:
“Put your customer’s needs first. Prioritize content that fits at the intersection of 1) the primary functions of your product or service and 2) your customer’s most pressing pain points. If you can align those topics with solid keyword research, then so much the better (common problems often have high search volume and high difficulty, but don’t let that scare you away — just focus on providing the best content you can that meets those needs). Uncovering these topics may be more complex than it seems on the surface, and they may change over time as your product evolves or your target market changes, but this is where everything should start at the most basic level. Not exactly a groundbreaking tip, but it’s imperative to get good at the fundamentals so you can build your content strategy on a strong foundation.” Ben Sailer, Inbound Marketing Director, CoSchedule
3. Make Sure Everybody Is on the Same Page
When you run a business or head up a content marketing department, you need to make sure your content plan is aligned with wider business goals and the activities of other departments. Not only that, it’s a good idea to make sure those departments or colleagues have a solid understanding of what you’re doing and why.
G2’s Lauren Pope explains:
“You must create content with intention. A lot of companies have a blog or they’ll do a periodic webinar, but they aren’t leveraging content marketing to the fullest extent. You need to know who your audience is and what action you’re trying to get them to take before the pen ever hits paper. This doesn’t mean you need to waste months crafting a meticulous content calendar. You just need a North Star for the goal of each piece before you begin. All of the content I create needs to fit into one of these buckets: – Content that drives traffic (80%) – This is your long-form SEO content designed to rank for organic search. This content is perfect for reaching people who have a problem your product fixes, they just might not know it yet. – Content that drives opinions (10%) – These are your podcasts, career profiles, video series, and thought-leader hot takes designed to get people talking. This is the stuff that gets shared across social media. – Content that drives leads (10%) – This is the stuff your sales team wants. Why such a small percent? These are comprehensive guides where quality beats quantity. You don’t need a ton of these resources to do it right. If someone asks me to create something that falls outside these existing buckets, I can sit down with them and figure out why. A lot of times we have existing content types for other teams’ needs, they just don’t know it. Internal education about our content strategy is just as important as the content we create for our readers. Taking the time to ensure our sales team knows what is available to them, how we can partner with them, and most importantly how content marketing can aid in winning deals totally changes the game.” Lauren Pope, Content Marketing Manager, G2
4. Be Flexible
Things happen that may mean you need to alter your content plan. To give you a totally random example off the top of my head, say a global pandemic occurred…
In all seriousness, there needs to be flexibility within your content plan for many reasons. Firstly, to account for trending topics. Also, you’ll need to measure content performance and tweak your content plan accordingly.
Jordan Teicher at Contently suggests organizing content around larger themes and leaving a decent amount of wiggle room for whatever comes up:
“My number one tip is to think in terms of content series and bigger projects. When you’re developing a new content plan, there’s a tendency to try to predict every single story you’re going to create over the next 12 months. That sounds good in theory, but it winds up boxing you in. A better approach would be to map out some major themes and then schedule a series of e-books, webinars, and videos around them. For example, when Contently’s marketing team met at the beginning of the year, we decided to organize our content based on our key industries. So in the first quarter, we’d focus on finance. In the second quarter, healthcare. Third quarter, B2B tech, and so on. For each quarter, I knew we’d need an industry report and an accompanying webinar. Those two big content series gave us major releases spread out during the year. They also gave us the freedom to explore relevant topics for one-off blog posts, videos, etc. that fit under those themes. This approach gives you good structure but still provides enough flexibility for new ideas that are timely.” Jordan Teicher, Director of Content, Contently
It’s tempting to dive right in and just start creating content. But, if you’ve got higher goals for your content then you need to use your brain and have some form of plan in place.
Set your intentions like a yogi and start putting together your content plan.
Bonus Material: Content Marketing Strategy Checklist
From goal-setting to research to content planning, make sure you cover every step of creating your content marketing manual:
You may also like

The 5 Best Content Marketing Strategies for Growth
Content marketing drives growth in many areas. Here are just a few of the things marketers plan to achieve through content marketing […]

47+ Content Marketing ROI Statistics for 2020
Content marketing – is it worth it? Let me work it. I put my thang down, flip it and reverse it… To […]

Build a Winning Lead Magnet Strategy (in 8 Steps)
Finding new customers (and keeping existing ones) is difficult, especially in a crowded industry. With the rise in social media, paid advertising, […]
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
2 thoughts on “ How to Create a Content Plan (Step-by-Step Guide + Examples) ”
- 2 comments
Thanks for the great tips! I love how simple you make it. It’s not rocket science, but it does require an investment of time and a lot of marketers are intimidated just because they don’t know where to start.
Very true! I hope marketers will be able to use this post to make a strong start. Thanks for your comment, Alison.
Free Content Plan Templates and Samples
By Joe Weller | July 27, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve compiled the most useful expert-tested and expert-approved content plan templates available to download in Word, PDF, and Excel formats.
Included on this page, you’ll find a content plan sample , a content planning calendar template , a digital content plan , and more. We’ve also included content planning tips to boost your content creation efforts.
Content Plan Sample Template
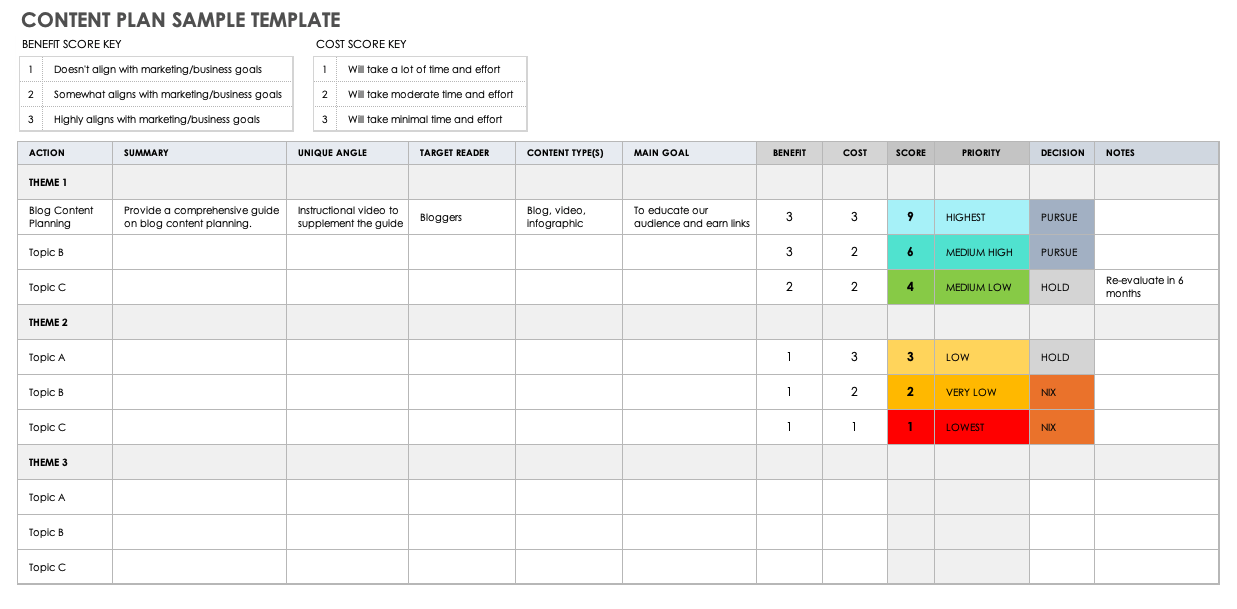
Use this content plan template to organize and prioritize potential topics by theme or by any category that suits your needs. Provide a brief summary of a topic, identify the content’s unique angle, pinpoint your target reader, decide which types of content you’ll need, and describe your main goal. Next, add a benefit and cost score value using the provided keys. Once you enter those values, the built-in formula auto-calculates a topic score to help you decide if a topic is worth pursuing.
Download Content Plan Sample Template - Excel
Content Planning Calendar Template
Use this content planning calendar template to map out and organize your content plan by content type or any category that suits your needs. Add the content title, description, and theme, then assign ownership and key dates. You can track the status of each content piece, along with monthly performance metrics to determine which pieces are high performers and which need updates.
Download Content Planning Calendar Template
Excel | Smartsheet
Content Planning and Documentation Template
This customizable template is ideal for establishing and tracking documentation for all aspects of the content planning process in one location. Add the name and description of guidelines and processes, assign ownership, input the key dates and status for documents that you need to create or modify, then add the location or link where users can access the documents. Use this template to manage your team’s resources and to ensure all policies and procedures are up to date.
Download Content Planning and Documentation Template
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Monthly Content Plan Template
Use this template to plan and track content topics and ideas monthly. Provide a summary of the topic, identify opportunities that exist with current search trends and seasonal patterns, then outline the content types, keywords, distribution channels, and more. You also have room to assign the topic, establish the start and publish date, and designate a status using the provided key.
Download Monthly Content Plan Template
Excel | Word | PDF
Annual Content Planning Template Set
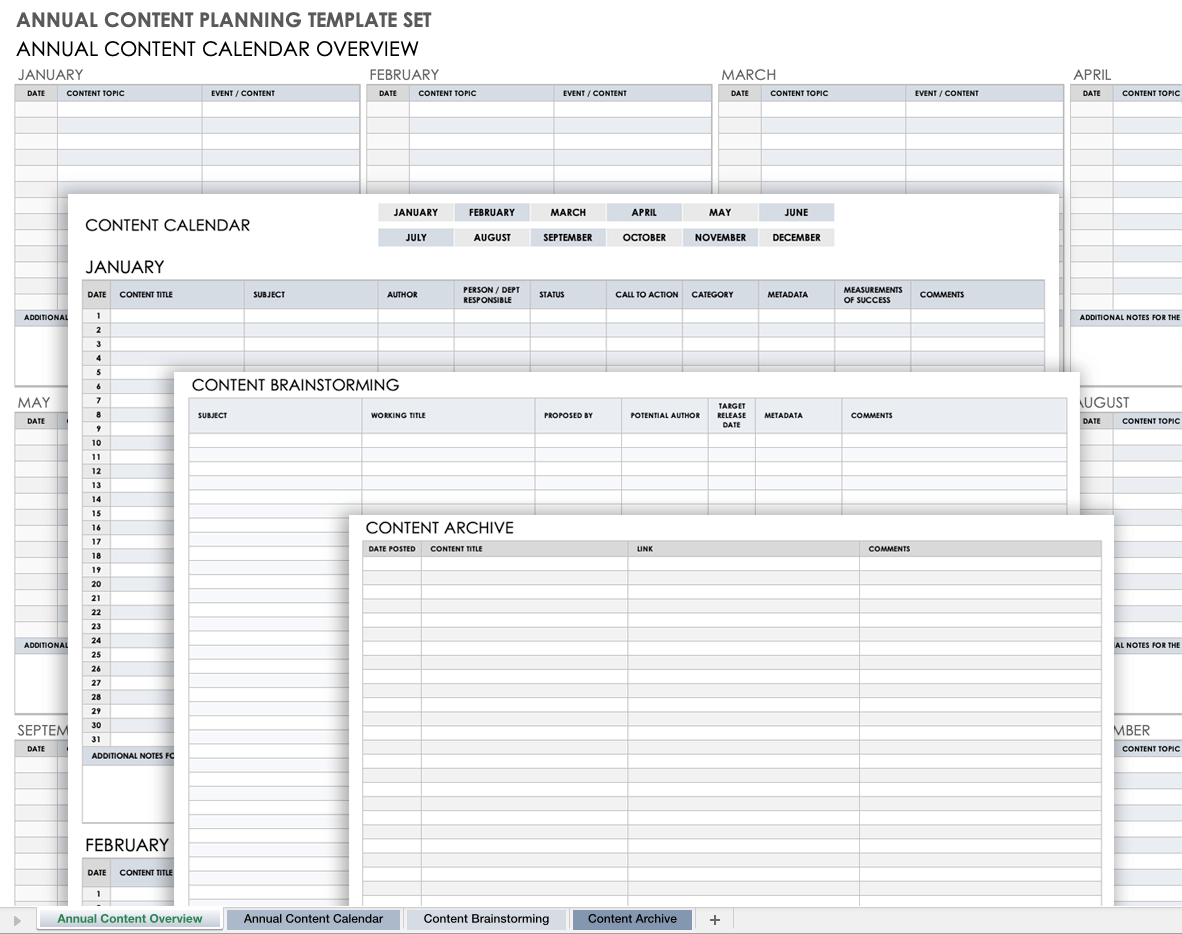
This customizable template set serves as a tool to brainstorm, plan, and track content ideas for each month of the year. This set includes a content calendar to execute on topics approved in the brainstorming phase, and it provides space to assign and schedule topics, determine measurements of success, and much more. The template also has a tab you can use to track previous posts and archived content in a central location.
Download Annual Content Planning Template Set - Excel
Digital Content Plan Template
Use this customizable digital content plan template to plan, assign, and track digital content ideas on a monthly basis for the entire year. In the space provided, you can add the content topic, type, category, goal, and unique angle that sets the piece apart from the competition. Then assign an owner, due date, and status to ensure your plan stays on track.
Download Digital Content Plan Template - Excel
Social Media Content Plan Template
This customizable social media template can help you plan and categorize your content across social platforms for each month of the year. Add the content idea or theme, choose the content category, detail the stage of the buyer journey for your targeted leads, then add the date posted. There is also space to include post details for multiple platforms, including the post title, author, link, key performance metrics, and other pertinent information.
Download Social Media Content Plan Template - Excel
For additional resources, visit “ Free Social Media Templates for Excel .”
Marketing Content Plan Template
This template is useful for planning and tracking marketing content monthly and annually according to the stage of the buyer’s journey your content is targeting. This template helps you plan for each topic by outlining its theme, category, and target audience, along with the content type, owner, due date, and status. There is also space for you to add details associated with marketing distribution channels for each piece of content, including the channel type, publish date, and key performance metrics.
Download Marketing Marketing Content Plan Template - Excel
For additional resources, visit “ The 61 Best Free Content Marketing Templates to Drive Performance .”
Blog Content Plan Template
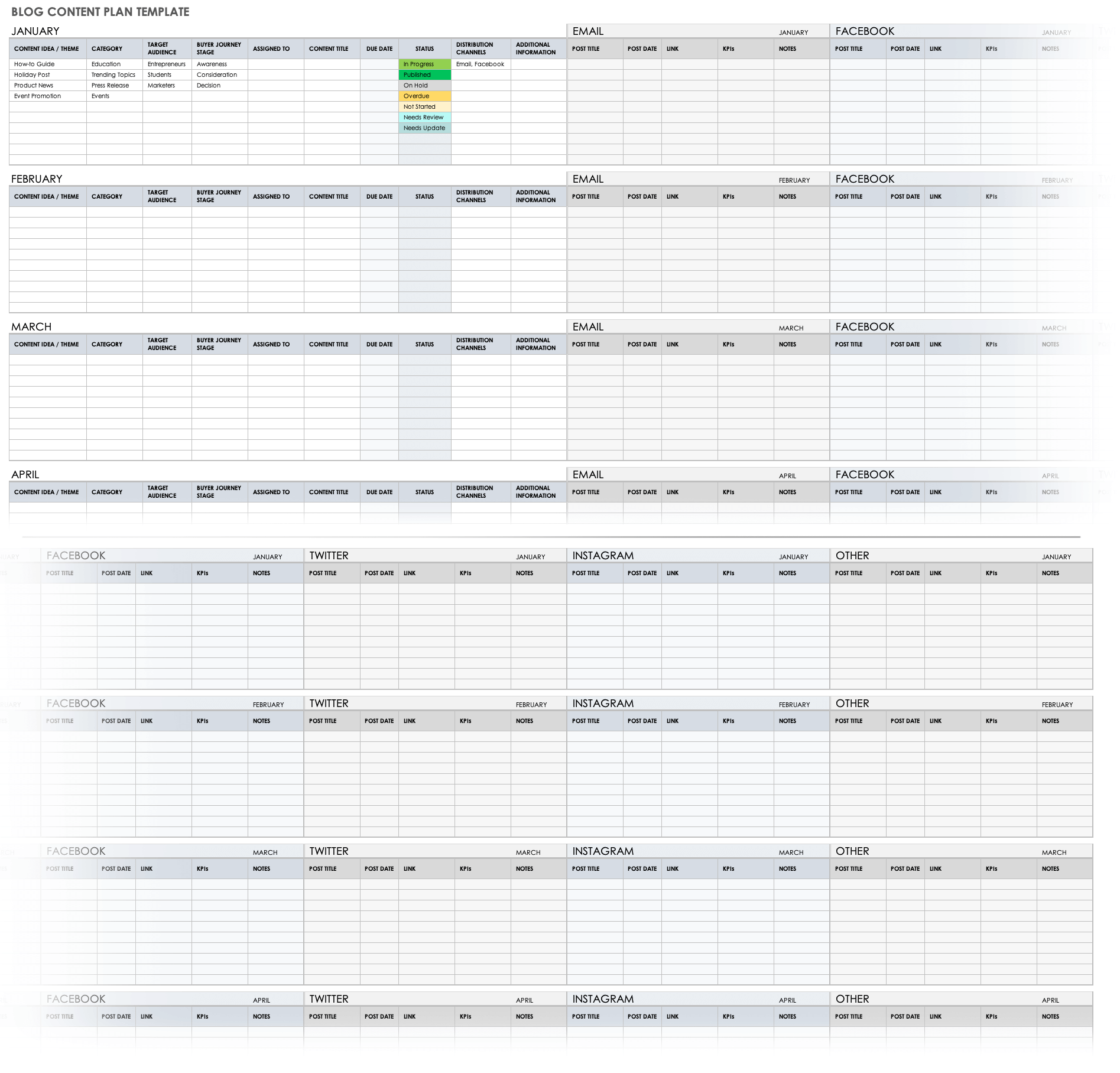
Use this blog content plan template to develop a strategy for blog posts on a weekly, monthly, or yearly basis. Add content details by theme, determine a category, pinpoint the target audience, assign and schedule content, track the status of each piece, and more. This template also provides space to include details for each marketing distribution channel, such as the post title, date, link, performance metrics, and important notes.
Download Blog Content Plan Template - Excel
For additional resources, including expert tips and checklists, take a look at the tools and advice for creating an effective blog strategy and plan .
Video Content Plan Template
Use this customizable video content plan template to identify and classify ideas that align with your business and marketing goals during each stage of the buyer’s journey. There’s space to add the video category, content topic, key audience takeaways, topic owner, estimated release date, and marketing platforms used to reach your target audience.
Download Video Content Plan Template
Excel | Word
Website Content Plan Template
Use this template to plan and organize your website content into groups. In the space provided, modify the main categories according to sitemap and business needs, then determine the pages that fall under each category to establish a hierarchy. Add a description and purpose for each entry, and detail the audience takeaway to ensure you’ve structured your content in a way that is useful for visitors. There is also room to include the content goal, call to action, ownership, status, and key dates to keep the plan on track.
Download Website Content Plan Template - Excel
Content Curation Plan Template
Use this content curation plan template to create standards on the process of compiling and selecting topics that align with business and marketing goals. In the space included, you can establish process guidelines, assign role ownership, and set deadlines to identify key opportunities for adding value to existing content.
Download Content Curation Plan Template
Content Inventory Audit Worksheet
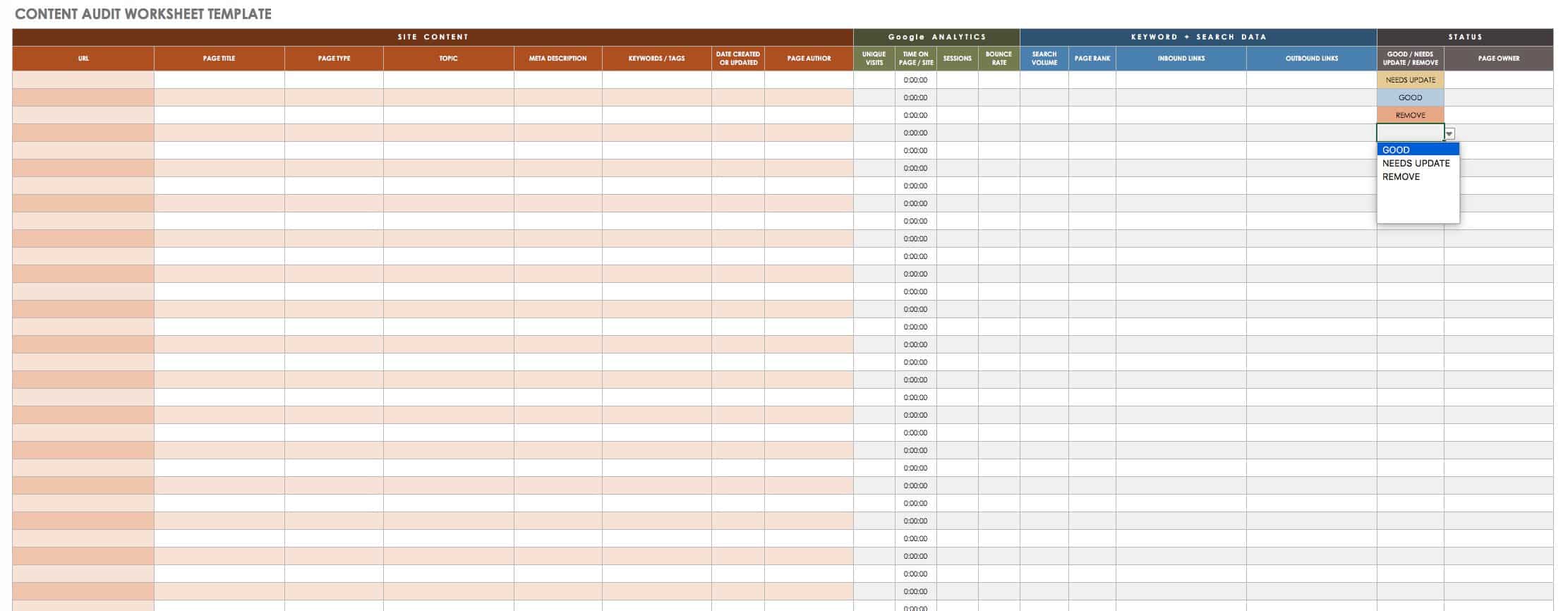
Use this content inventory audit worksheet to track content inventory and to use in conjunction with your content curation plan. This worksheet helps you organize all of your content and provides space to add the page title, page type, topic, meta description, keywords, page author, and more. You can also track search data and performance metrics to identify existing content that you can update and improve.
Download Content Inventory Audit Worksheet Template
Excel | Smartsheet
Content Decision-Making Matrix Template
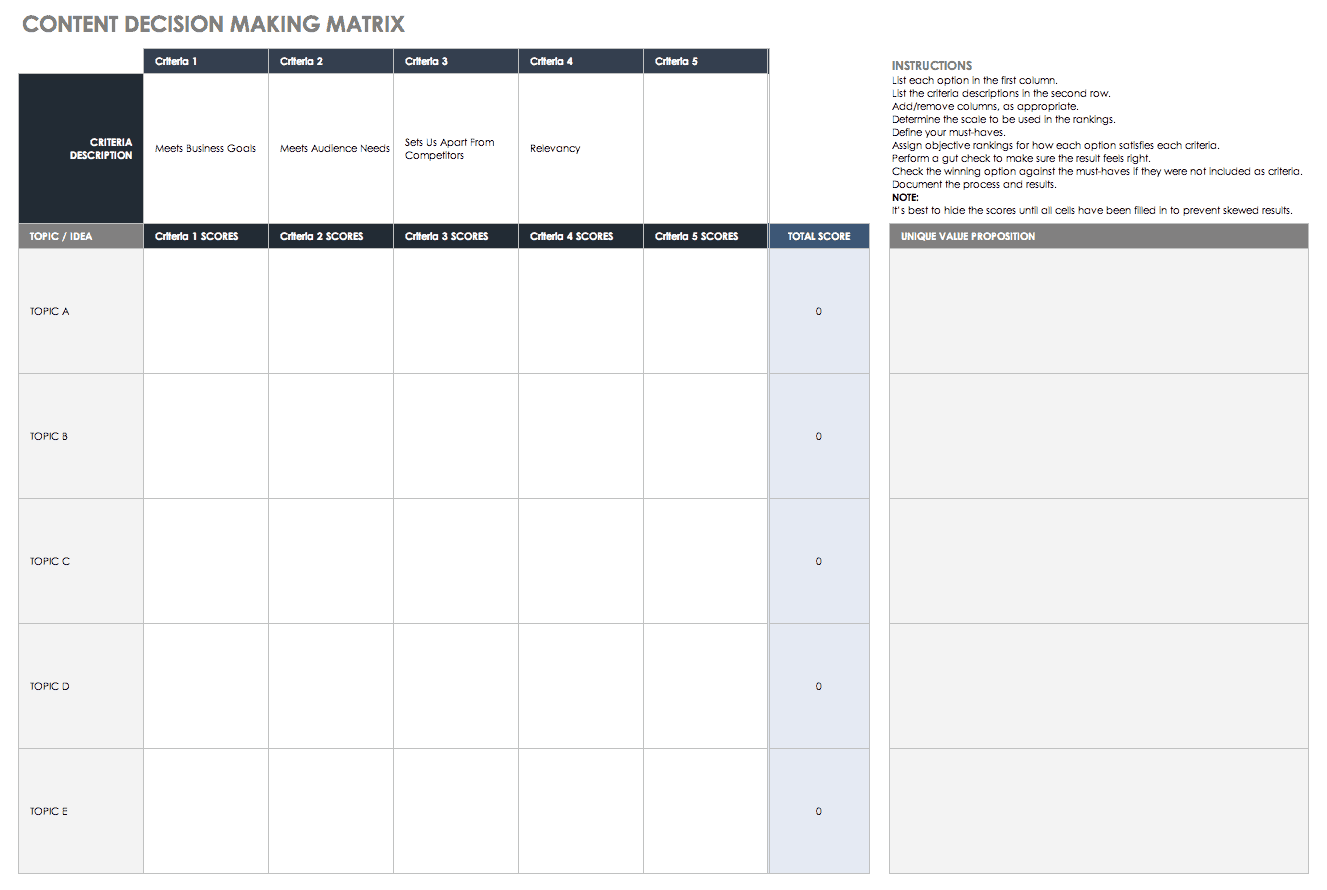
This content decision-making matrix template is useful for evaluating potential content topics ideas that align closely with criteria you establish. Add criteria descriptions at the top of the matrix, then list topic ideas to analyze. Determine the rating scale you’ll use for rankings and assign a score to each topic. Once you input values, the built-in formulas calculate the total scores. Use this information to determine which topics have the potential to bring the most value.
Download Content Decision-Making Matrix Template - Excel
Content Planning Tips
The content you produce connects your business to your audience. It also requires careful planning in order to effectively attract customers and reach business goals.
The following tips can help you create a streamlined process to develop a successful content plan .
- Research, Research, Research: Conduct research on the themes and topics outlined in your content strategy to identify opportunities. Take a look at what competitors are offering for inspiration, and be sure to account for industry trends and seasonal patterns.
- Prioritize Content Ideas: Tackle the low-hanging fruit first. List, evaluate, and score topic ideas (see the content decision-making matrix template above), then identify your high-value, low-cost topics for quick wins.
- Focus on Your Audience: Plan your content around your intended reader. Consider the problem you are solving or the question that you are answering for the viewer. Determine who is seeking out and consuming your content, and create your content accordingly.
- Know Your Goal: Determine what you are trying to achieve before you execute to avoid losing time and wasting resources on efforts that don’t align with goals. Are you trying to raise awareness about your brand? Are you educating a group of people on a particular topic? By understanding what you’re trying to achieve, you can decide on a direction and determine the type of content to produce (e.g. video, infographic, blog content).
- Hold Brainstorming Sessions: Create an environment to get creative juices flowing and to encourage others to share fresh ideas. Learn effective ways to brainstorm to find ways to produce better, more valuable content than what’s currently available. This includes looking at your content inventory to find ways to repurpose and improve upon existing assets, which leads to the next tip.
- Check Your Content Inventory: Don’t waste time reinventing the wheel when you have current pieces available that you can modify to satisfy current search trends and business goals. Use the content inventory audit worksheet above to organize and list published assets in one place. Then pinpoint which pieces are high performers and which ones you can update to better align with present-day marketing and business objectives.
- Prepare for Plan Execution: Decide if you will create content in-house or outsource it. Prepare a creative brief to provide a clear action plan to writers and designers. The brief also helps ensure the content “voice” and style are consistent with the brand.
Seamlessly Execute Your Content Plan with Smartsheet for Marketing
The best marketing teams know the importance of effective campaign management, consistent creative operations, and powerful event logistics -- and Smartsheet helps you deliver on all three so you can be more effective and achieve more.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Improve your marketing efforts and deliver best-in-class campaigns.
General Motors to move Detroit HQ to new downtown building, plans to redevelop Renaissance Center

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
General Motors will move its Detroit headquarters to a new downtown office building next year and work to redevelop its iconic home along the Detroit River, company and city officials confirmed Monday.
The announcement was made at the site of the old Hudson’s department store, which is being developed into a tower and 12-story office building that will house GM and is being built by the Bedrock real estate firm.
Bedrock will join GM, the city, and Wayne County in coming up with ideas to remake the seven-building Renaissance Center, the company’s current world headquarters and a showpiece on the city’s skyline that’s often shown on televised sports broadcasts.
GM CEO Mary Barra said the move to a brand new state-of-the-art office building in the heart of the city will help GM recruit talent in the future. The new site is about a mile (1.6 kilometers) north of the Renaissance Center. The move also keeps GM’s headquarters in the city for the foreseeable future, she said.
“We’re going to be in the heart of the city,” Barra said. “Our people are already excited to be in Detroit and live here. I think having this workspace that’s modern and new that really fits the way people work today, I think it’s definitely going to be an attraction.”
Bedrock Chairman Dan Gilbert said office building on the Hudson’s site on Woodward Avenue was designed and built to house a major corporation. The building and the adjacent tower will have meeting space, retail, a luxury hotel and living space, along what was America’s first paved road, he said.
The move will help Detroit continue to thrive, he said.
Mayor Mike Duggan said GM and Detroit have risen and fallen together for the past century, and he’s pleased to say that “GM and Detroit are rising together again.”
The future of Renaissance Center, home to GM through its brush with death and bankruptcy in 2009 as well as multiple years of huge profits, remains unclear. But the move next year will mark the end of an era for the automotive giant.
The main tower, the tallest building in Detroit, is 73 stories.
Through the years and especially after the pandemic, the number of GM employees at the building has dwindled, and multiple businesses located there have closed.
Barra said GM is open to ideas about the Renaissance Center complex, which the company bought nearly three decades ago. The company invested more than $1 billion there, she said. It’s not selling the building at present, but that is possible.
Bedrock owns multiple office buildings throughout the city’s downtown and has renovated many of them.
Barra said GM, Bedrock and governments will explore residential, commercial and mixed uses for the iconic tower complex, known locally as the RenCen.
“I am confident that together we can create a right future for that site,” Barra said Monday.
Duggan said Gilbert will know what to do with the complex in the future.
GM bought the tower complex in 1996 and later moved its headquarters there from a site north of downtown. It has housed the company ever since.
Bedrock has been buying up properties downtown for many years and has led its rebirth. Gilbert also runs loan company Rocket Mortgage.
In a 2022 interview, Barra told The Associated Press that GM will keep its main office in the RenCen complex just across the Detroit River from Canada.
But she qualified her statements, saying she couldn’t predict what might happen in five, 10 or 15 years. Since then, about 5,000 white-collar workers at GM took early retirement buyouts, and may workers are still on a hybrid office-home work schedule, so GM needs less office space.
The company takes up about 1 1/2 of the RenCen’s towers, which have seen little pedestrian traffic for years. Much of GM’s work force, including product development and engineering, is north of the city at an updated 1950s technical center in suburban Warren. After GM’s 2009 bankruptcy, the company considered moving the headquarters there.
The Renaissance Center was built by Henry Ford II, who formed a coalition in the 1970s in an effort to reinvigorate Detroit’s downtown.
Bedrock announced last week that the final structural steel beam had been put in place on the Hudson’s tower, which is expected to have 1.5 million square feet of retail, office, dining, hospitality and residential space.
Get U-T Business in your inbox on Mondays
Get ready for your week with the week’s top business stories from San Diego and California, in your inbox Monday mornings.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the San Diego Union-Tribune.
More in this section

National Business
Weedkiller manufacturer seeks lawmakers’ help to squelch claims it failed to warn about cancer
The maker of a popular weedkiller is turning to lawmakers in key states to try to squelch legal claims that it failed to warn about cancer risks

Trump trial: Why can’t Americans see or hear what is going on inside the courtroom?
It’s a moment in history

Characters enter the public domain. Winnie the Pooh becomes a killer. Where is remix culture going?
Winnie the Pooh and Mickey Mouse have recently entered the public domain, making it possible for artists to use them freely

China’s economy grew 5.3% in first quarter, beating expectations
China’s economy beat expectations in the first quarter of the year with help from policies and stronger demand
China’s economy grew at 5.3% in the first quarter, beating estimates with help from policies and better demand
April 15, 2024
Grains mixed, Livestock higher
Wheat for May was off 4.25 cents at $5.5175 a bushel; May corn fell 4 cents at $4.3150 a bushel, May oats was up 6.25 cents at $3.5775 a bushel; while May soybeans lost 15.75 cents at $11.5825 a bushel.
Our use of cookies
We use necessary cookies to make our site work (for example, to manage your session). We’d also like to use some non-essential cookies (including third-party cookies) to help us improve the site. By clicking ‘Accept recommended settings’ on this banner, you accept our use of optional cookies.
Necessary cookies
Necessary cookies enable core functionality on our website such as security, network management, and accessibility. You may disable these by changing your browser settings, but this may affect how the website functions.
Analytics cookies
We use analytics cookies so we can keep track of the number of visitors to various parts of the site and understand how our website is used. For more information on how these cookies work please see our Cookie policy .
Prudential Regulation Authority Business Plan 2024/25
Related links related links.
- PRA annual reports and business plans
- CP4/24 – Regulated fees and levies: Rates proposals 2024/25
Maintain and build on the safety and soundness of the banking and insurance sectors, and ensure continuing resilience
Be at the forefront of identifying new and emerging risks, and developing international policy
Support competitive and dynamic markets, alongside facilitating international competitiveness and growth, in the sectors that we regulate, run an inclusive, efficient, and modern regulator within the central bank, the pra’s strategy.
Our strategy for 2024/25 will be delivered through our strategic goals, extracts of which are below. For the full detail of our workplan against each strategic priorities, see pages 10 to 41 of this Business Plan .
Foreword by Chief Executive Sam Woods
Sam Woods Deputy Governor, Prudential Regulation Chief Executive of the PRA
First, this will be our first full year operating under the Financial Services and Markets Act (FSMA 2023), which established a new, post-Brexit regulatory framework for the UK. FSMA 2023 expanded our rulemaking responsibilities and gave us a new secondary objective to support the competitiveness and growth of the United Kingdom.
Competitiveness and growth have always been important considerations for the PRA. Nonetheless, this new objective represents a significant change, and embedding it into our approach has been a major priority for the organisation as a whole, and for me personally as CEO. That effort will continue this year.
Our business plan includes a range of initiatives aimed squarely at promoting the UK’s competitiveness and growth. Some of the most significant are:
- Our ‘Strong and Simple’ project, which aims to simplify regulatory requirements for smaller banks, thus reducing compliance burdens without compromising on strong standards.
- The ‘Solvency UK’ reforms of insurance capital standards, which will reduce bureaucracy in the regulatory regime, while also allowing insurers to invest in a wider range of productive assets.
- The Banking Data Review, which aims to reduce burdens on firms by focusing our data collection on the most useful and relevant information.
- Improvements to our authorisation processes – we have made significant progress in improving the speed and efficiency of authorisations without sacrificing the robustness of our controls; maintaining this progress will be a key focus for next year.
- Reforms to ring-fencing, following the independent review led by Sir Keith Skeoch.
The second point I want to highlight is our ongoing programme of work to maintain the resilience of the UK’s banking and insurance sectors, which is at the heart of our role. The events of 2023 (including the high-profile failures of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) and Credit Suisse (CS)) demonstrate the importance of a focus on resilience – and while I am encouraged by how the UK banking and insurance sectors have remained stable through a stressful period, we cannot take this for granted.
A major priority this year will be the implementation of the Basel 3.1 standards, which will complete the long process of post-financial crisis regulatory reform. While I expect the capital impact of these reforms to be limited for UK banks, they will nonetheless play a vital role in maintaining sufficient consistency in risk measurement across firms and jurisdictions – which is the cornerstone of the bank capital regime.
Another major priority this year will be ensuring firms have adequate standards of operational and cyber resilience. Following FSMA 2023, we have new powers to oversee the services provided to regulated firms by so-called ‘critical third parties’, and we will be implementing that regime over the coming year. And in March 2025 we will reach an important milestone with the full implementation of our wider operational resilience policy.
The day-to-day work of supervision will continue alongside these reforms. As always, our supervisory teams continue to work with PRA-regulated firms to ensure high standards of financial and operational resilience, governance, risk management, and controls. Stress testing remains a key element of our approach to resilience, and alongside colleagues from the wider Bank of England we will deliver a desk-based stress test of banks, and a system-wide exploratory scenario, in 2024. We will also work towards the next round of insurance stress tests in 2025.
I have really only scratched the surface of the work we are doing this year, as you can see from a glance at this document’s contents page. In order to deliver this work, we will need to run an efficient and effective regulator, and I am particularly excited by the potential of our data and analytics agenda to create new opportunities to improve how we work. And if past years are anything to go by, we will continue to engage with innovation in many forms across the industry, whether in the form of new entrants or new approaches to doing business in areas like digital money.
I am very much looking forward to the challenges that the next year will bring, and to working together with a team of very committed colleagues at the PRA to deliver on this business plan.
11 April 2024
Overview of responsibilities and approach
The PRA has two primary objectives: a general objective to promote the safety and soundness of PRA-authorised persons, and an objective specific to insurance firms for the protection of policyholders.
The PRA has two secondary objectives:
- the competition objective, which is focused on facilitating effective competition in the markets for services provided by PRA-authorised persons in carrying on regulated activities; and
- the competitiveness and growth objective, which is focused on facilitating, subject to alignment with relevant international standards, (a) the international competitiveness of the economy of the UK (including, in particular, the financial services sector through the contribution of PRA-authorised persons), and (b) its growth in the medium to long term.
In its December 2022 recommendations letter to the Prudential Regulation Committee (PRC), HM Treasury (HMT) set out aspects of the Government’s economic policy to which the PRA must have regard, while building on the important themes of openness, competitiveness, competition, and innovation, as well as delivering energy security and net zero.
In December 2023, the PRA published a consultation paper (CP)27/23 – The Prudential Regulation Authority’s approach to policy , which sets out the PRA’s approach to policymaking as it takes on expanded rule-making powers introduced through FSMA 2023. These expanded powers will enable the PRA to replace relevant assimilated law (previously known as retained EU law) with PRA rules and other policy material, and move towards a more British system of regulation, with most of the technical rules made by independent UK regulators within a framework set by Parliament. In addition, FSMA 2023 introduces new accountability measures that require the PRA to keep its rules under review , and to establish a Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) Panel composed of external members, which will scrutinise and provide input into the PRA’s CBA framework. These measures should enable the PRA to deliver policies that are well suited to the UK’s financial sector. In addition:
- In December 2023, the PRA took a significant step towards implementing the remaining Basel III standards in the UK by publishing the first of two near-final sets of rules with policy statement (PS)17/23 – Implementation of the Basel 3.1 standards near-final part 1 , which takes account of responses received to CP16/22 . The near-final rules aim to promote the safety and soundness of PRA-regulated firms and support their international competitiveness by making capital ratios more consistent, comparable, and aligned with international standards. The PRA will publish its second near-final policy statement in 2024 Q2 on the remaining aspects of the Basel 3.1 package, which include credit risk, the output floor, reporting, and disclosure requirements. The PRA plans to implement the Basel 3.1 standards over a 4.5-year transitional period beginning on 1 July 2025 and ending on 1 January 2030. Among other things, the PRA will also continue to support international efforts to monitor and promote the implementation of Basel 3.1.
- In December 2023, the PRA published PS15/23 – The Strong and Simple Framework: Scope Criteria, Liquidity and Disclosure Requirements , taking account of feedback to CP4/23 . The policy addresses liquidity and disclosure requirements for Simpler-regime Firms and Pillar 3 remuneration disclosure. The PRA will move further towards finalising and implementing the Strong and Simple prudential framework for Small Domestic Deposit Takers (SDDTs) during 2024. footnote [1]
- Following the publication of discussion paper (DP)3/22 – Operational resilience: Critical third parties to the UK financial sector , in December 2023, the PRA published CP26/23 , jointly with the Bank of England (‘the Bank’) and FCA (‘the supervisory authorities’). CP26/23 sets out the supervisory authorities’ proposed requirements for critical third parties (CTPs), footnote [2] including the mechanism for identifying potential CTPs, recommending them for designation by HMT, incident notification triggers and requirements, and proposed CTP Fundamental Rules. In 2024, the PRA will continue to work with the supervisory and other authorities to develop the final policy and oversight approach.
- In September 2023, the PRA published CP19/23 – Review of Solvency II: Reform of the Matching Adjustment , which marks a significant milestone in the PRA's reforms to the Solvency II regime for the UK insurance market. Following the publication of PS2/24 – Review of Solvency II: Adapting to the UK insurance market and PS3/24 – Review of Solvency II: Reporting and disclosure phase 2 near-final , the PRA will publish its final rules, subject to alignment with anticipated legislation, in 2024.
The PRA’s objectives and priorities are delivered through regulation and supervision, and by developing standards and policies that set out expectations of firms. The PRA’s approach to supervision is forward-looking, judgement-based, and focused on the issues and firms that pose the greatest risk to the stability of the UK financial system and policyholders. This approach is set out in the PRA’s approach to supervision of the banking and insurance sectors .
The PRA’s regulatory focus is primarily at the individual firm and sector level, with the most important decisions taken by the PRC, which works with the Bank’s other areas of remit, including its role as supervisor of Financial Market Infrastructures (FMIs), the UK’s Resolution Authority, and its committees, including the Financial Policy Committee (FPC), which has responsibility for the stability of the entire UK financial system. The PRA also works closely with the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), including through the Chief Executive of the PRA being a member of the FCA Board and the Chief Executive of the FCA being a member of the PRC.
The PRA regulates 1,330 firms and groups. footnote [3] These consist of 730 deposit-takers (banks, building societies, credit unions, and designated investment firms footnote [4] (DIFs)), and 600 insurers of all types (general insurers, life insurers, friendly societies, mutuals, the London market, and insurance special purpose vehicles (ISPVs)).
Chart 1: PRA supervised deposit-takers, as at January 2024
Chart 2: pra supervised insurers, as at january 2024, the pra’s strategy, shaping the pra’s strategy.
Each year, the PRA is required by law footnote [5] to review and, if necessary, revise its strategy in line with its statutory objectives:
- the general primary objective to promote the safety and soundness of PRA-authorised firms;
- specifically for insurance firms, a primary objective to contribute to the securing of an appropriate degree of protection for those who are or may become policyholders;
- a secondary objective to act, so far as is reasonably possible, in a way that facilitates effective competition in the markets for services provided by PRA-authorised firms; and
- a new secondary objective to act, so far as reasonably possible, in a way that facilitates the UK economy’s international competitiveness and its growth over the medium to long term, subject to alignment with international standards.
In addition to the statutory objectives, the PRA’s strategy is shaped by other responsibilities, such as the requirement to implement legislation and other changes necessary to meet international standards, and to continue to adapt to market changes in areas such as financial technology (FinTech), climate change, and digitalisation.
When considering how to advance its objectives, there are a set of regulatory principles to which the PRA must also have regard. This includes regulatory principles from FSMA 2000, and considerations from HMT’s December 2022 letter to the PRC on the Government’s economic policy, the Equality Act 2010, the Legislative and Regulatory Reform Act 2006, and the Natural Environment and Rural Communities Act 2006. In its pursuit of its objectives, the PRA will review all the regulatory principles, identify which are significant to the proposed policy, and judge the extent to which they should influence the outcome being sought.
Furthermore, as part of the Bank, the PRA contributes to the delivery of the Bank’s wider financial stability and monetary policy objectives, for example by:
- maintaining and, where appropriate, strengthening or updating prudential standards;
- being at the forefront of identifying new and emerging risks, and developing international policy; and
- ensuring that banks and other financial institutions can continue to provide essential services.
Strategic priorities for 2024/25
This year’s business plan continues to be structured around the PRA’s four strategic priorities, as set out in its 2023/24 Business Plan . The PRA’s strategic priorities for 2024/25 will remain unchanged because the PRA updated its priorities in 2023 to take account of its new powers, new secondary objective, and expanded role brought about by FSMA 2023. The strategic priorities for 2024/25 are to:
- maintain and build on the safety and soundness of the banking and insurance sectors, and ensure continuing resilience;
- be at the forefront of identifying new and emerging risks, and developing international policy;
- support competitive and dynamic markets, alongside facilitating international competitiveness and growth, in the sectors that we regulate; and
- run an inclusive, efficient, and modern regulator within the central bank.
PRA Business Plan 2024/25
Maintain and build on the safety and soundness of the banking and insurance sectors and ensure continuing resilience.
During the decade following the financial crisis of 2007-09, the PRA designed and implemented extensive reforms that materially improved the safety and soundness of firms, insurance policyholder protection, and financial stability. Since then, the robust regulatory standards that the PRA has implemented and its strong international collaboration have played a key role in maintaining the resilience of the banking and insurance sectors, consistent with its objectives and those of the FPC. The PRA will continue to ensure that the firms it regulates remain adequately capitalised and have sufficient liquidity and stable funding profiles, with appropriately defined impact tolerances for disruption to their business services. The PRA’s regulatory framework encourages PRA-regulated firms to take a holistic approach to managing risks by identifying, monitoring, and taking action to remove or reduce systemic risks.
The PRA’s role as a rulemaker was further expanded following the introduction of FSMA 2023. Under the new regulatory framework , the PRA will continue to be a strong, accountable, responsive, and accessible policymaker, and make rules to meet its regulatory obligations, while adopting a risk-based approach, as set out in CP27/23 , in a way that is tailored to the specific features of financial services in the UK. Among other things, the PRA will continue to faithfully implement agreed international standards and reforms in a way that best serves the UK. For example, in 2024 the PRA will publish its final rules on the implementation of the Basel 3.1 standards and on replacing relevant and/or remaining firm-facing Solvency II requirements from assimilated law with the PRA’s own rules, which will become part of the PRA’s Rulebook and other policy materials. In addition, the PRA will move further towards finalising and implementing the Strong and Simple prudential framework , which provides a simpler but robust set of prudential rules for non-systemic, domestic-focused banks and building societies in the UK.
The PRA will also continue to pay particular attention to the business opportunities and threats that are posed by changes in the economic environment, both in the UK and other jurisdictions, that could pose risks to the UK.
The PRA will continue to promote a strong risk culture among regulated firms, including a conscious and controlled approach to risk taking activities, and ensure that this is supported by adequate financial and non-financial resources. At the same time, the PRA will maintain a robust regulatory regime that is able to respond to the external factors that pose the greatest risk to firms’ safety and soundness.
Risk factors also include global geopolitical risks, which have intensified over the past year. The PRA will continue to ensure that PRA-regulated firms are resilient to such risks by liaising with both domestic and international regulatory counterparts and continuing to monitor and engage with affected firms. Effective international collaboration remains central to addressing global risks and maintaining UK financial stability as well as the safety and soundness of internationally active firms.
The PRA will monitor and assess firms’ ability to manage cyber threats through the ongoing use of threat-led penetration testing ( CBEST and STAR-FS ) and the cyber questionnaire ( CQUEST ). In collaboration with the FCA, including in response to known technology, cyber and third-party incidents, the PRA will continue to monitor and engage with firms on their execution of large and complex IT change programmes. Furthermore, the FPC’s cyber stress testing has broadened the PRA’s understanding of how operational disruptions such as cyberattacks may affect financial stability.
The PRA will continue to engage in collective action to develop a view on sector-wide risks, support the building of firm- and sector-level resilience, and enhance the sector’s ability to respond to system-wide disruption. This will include ongoing sector engagement through the Cross-Market Operational Resilience Group (CMORG), which delivers industry guidance, response capabilities, and technical solutions, and through cross-jurisdictional coordination via the G7 Cyber Experts Group (CEG). Through CMORG, the PRA will deliver a sector-wide simulation exercise (SIMEX24) to assess the sector’s resilience to major operational disruption. The PRA will continue to develop its ability to respond to operational incidents in the sector through its authorities ( Authorities Response Framework ) and sector ( Cross Market Business Continuity Group ) response mechanisms.
Financial resilience – banking
Implementation of the basel 3.1 standards.
In March 2023, the PRA concluded its consultation on proposals published in November 2022 about the parts of the Basel III standards that remain to be implemented in the UK (‘Basel 3.1’). In September 2023, the PRA announced that it would split the publication of the near-final Basel 3.1 rules in two, moving implementation back by six months to 1 July 2025 to reduce the transitional period to 4.5 years and ensure full implementation by 1 January 2030, in line with the proposals set out in CP16/22. The first near-final PS17/23 – Implementation of the Basel 3.1 standards near-final part 1 , covering market risk, credit valuation adjustment risk, counterparty credit risk, and operational risk, was published in December 2023. The PRA will publish the second near-final PS, covering the remaining elements of credit risk, the output floor, as well as Pillar 3 disclosure and reporting requirements, in due course.
The near-final rules from the two PSs will be made final once Parliament has revoked the relevant parts of the Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR). The PRA expects this to happen later in 2024. In addition to finalising Basel 3.1 rules, the PRA will continue to increase its supervisory focus on firms’ implementation plans.
Bank stress testing
The concurrent stress testing of firms is one of the key tools used by the PRA and the Bank to support their microprudential and macroprudential objectives. Banking stress tests examine the potential impact of a hypothetical scenario on the major UK banks and building societies that make up the banking system, and on the system as a whole. The PRA normally runs two types of banking stress test – the annual cyclical scenario and other exploratory scenarios.
In 2024, the PRA will support the Bank in taking stock of and updating its framework for concurrent bank stress testing. The stocktake will draw on lessons from the first decade of concurrent stress testing, and so ensure that the framework continues to support the FPC and PRC in meeting its objectives. The PRA will also contribute to supporting the Bank’s desk-based stress test in 2024, which is being conducted in place of an ACS. The desk-based exercise will make use of the PRA’s risk expertise along with models developed in the PRA and elsewhere in the Bank to test the financial resilience of the UK banking system under more than one adverse macroeconomic scenario. Stress testing exercises involving firm submissions of stressed projections are currently expected to resume in 2025.
In addition, the Bank is conducting a system-wide exploratory scenario (SWES), working closely with and with the full support of the PRA, FCA, and TPR (The Pensions Regulator). The exercise was launched in June 2023 and aims to improve the understanding of the behaviours of banks and non-bank financial institutions (NBFI) in stressed financial market conditions. The participating firms in this exercise are representative of markets that are core to UK financial stability.
Private equity and credit
The evolving macro environment is expected to challenge firms’ approach to risk management, increasing the need for robust governance, risk management, and controls. One area of focus for the PRA will be exposures to NBFI, particularly any challenges that may manifest around the trend toward illiquid private equity financing and private credit. The PRA will continue to closely monitor private asset financing and the way that firms consider the risks they could face from these activities. In particular, the PRA will look for further improvements in firms’ ability to identify and assess correlations across financing activities with multiple clients.
Replacing assimilated law
HMT has prioritised the CRR as one of the initial areas of focus in the process of transferring assimilated law into the supervisory authorities’ rules and legislation following the enactment of FSMA 2023. The latter granted the PRA expanded rulemaking powers to replace assimilated law with PRA rules, thereby moving towards a more British system of regulation. In 2024/25, the PRA will consult on proposed rules to replace, with modifications where appropriate, the relevant firm-facing provisions in Part Two of the CRR.
Model risk management (MRM) and internal ratings-based approach/hybrid models
Banks’ use of and reliance on models and scenario analysis to assess future risks has increased significantly over the past decade. The introduction of new, sophisticated modelling techniques – including the potential use of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML) – has highlighted the need for sound model governance and effective model risk management practices.
In 2023, the PRA published a supervisory statement (SS)1/23 – Model risk management principles for banks , which applies to firms with internal model (IM) approval to calculate regulatory capital requirements. It is structured around five high-level principles that set out the core disciplines necessary for a robust model risk management framework to manage model risk effectively across all model and risk types. The adoption of these principles will help banks to develop good practices of model risk management, raising prudential standards at banks operating in the UK. The new policy comes into effect on 17 May 2024. Banks within the scope of the policy are expected to conduct an initial self-assessment against these principles, and, where relevant, prepare remediation plans to address any identified shortcomings.
During 2024, the PRA will focus on how banks are embedding and implementing the expectations set out in SS1/23. In particular, the PRA will seek to understand the extent to which banks’ management teams are adopting the principles and promoting the management of model risk as a risk discipline in its own right across their firms.
The PRA has published a range of policy statements on changes to the internal ratings-based (IRB) approach to credit risk over recent years. footnote [6] The PRA will continue to work with firms as they progress their model approval and review submissions in line with these requirements and expectations. The PRA will focus on the ‘hybrid’ approach to mortgage modelling, and the IRB repair programme, both carried forward from previous years.
Where appropriate, firms are holding post-model adjustments (PMAs) in the form of risk-weighted asset (RWA) add-ons, helping to mitigate potential capital underestimation while they develop their new models. During 2024, the PRA will continue to assess the adequacy of the PMAs to ensure any potential capital underestimation is addressed.
Liquidity risk management
The events of 2023 brought a further focus on the liquidity and funding risks faced by deposit takers, in particular the deposit outflows experienced by CS and SVB leading up to their acquisition and resolution, respectively.
The PRA will continue its close supervision of firms’ liquidity and funding risks in light of recent stresses. Through its ongoing supervision of banks and building societies, the PRA will follow up on how firms are taking account of the lessons they learnt from the events at CS and SVB. The PRA will continue to use its regular programme of Liquidity Supervisory Review and Evaluation Processes (L-SREPs) across PRA-authorised firms to assess their liquidity and funding risks, in quantitative and qualitative terms, and to ensure appropriate financial and non-financial resources are in place to manage and mitigate these risks.
The PRA will also continue to engage with firms and within the wider Bank on PRA-authorised firms’ access to the Bank’s Sterling Monetary Framework .
The PRA will also monitor closely how firms consider changes in depositor behaviour in the current funding environment and proactively take into consideration forthcoming changes in bank funding and liquidity conditions. footnote [7]
Credit risk management
The PRA is closely monitoring firms’ credit risk management practices given the uncertain credit risk outlook across key markets. The PRA’s assessment will include a focus on how credit risk management practices have evolved – in particular, how they can remain robust and adaptable to changing conditions, whether there is appropriate consideration of downside and contagion risks, as well as firms’ monitoring and planning for the impacts of customer refinancing. The PRA will undertake a thematic review of smaller firms’ credit risk management frameworks during 2024/25.
The PRA will monitor changes to firms’ business mix and credit exposures, and continue to monitor vulnerable segments, including cyclical sectors and key international portfolios, as well as traditionally higher-risk portfolios such as buy-to-let, credit cards, unsecured personal loans, small to medium-sized enterprises, leveraged lending, and commercial real estate. In addition, counterparty credit risk will remain a key area of supervisory focus through 2024, especially exposures to NBFI across certain business lines.
Separately, in 2024, the PRA will continue to progress its review of regulatory policies to assess whether the policy framework for trading book risk management, controls, and culture is adequate, robust, and accessible.
The UK banking system is well capitalised. However, the overall operating and risk environment remains challenging, and firms must manage their financial resilience to ensure that the financial sector can continue to support businesses and households. The PRA will continue to assess firms’ capital positions and planning, including firms’ use of forward-looking capital indicators, stress testing, and contingency plans.
The PRA intends to review its Pillar 2A methodologies (see section ‘Review of the Pillar 2 framework’ of PS17/23 ) for banks after the rules on Basel 3.1 are finalised, with a view to consulting on any proposed changes in 2025.
Securitisation regulation
HMT has prioritised the Securitisation Regulation as one of the initial areas of focus in the process of transferring assimilated law into regulatory rules and legislation following the enactment of FSMA 2023. The PRA will publish its final policy (simultaneously with the FCA) on final rules to replace or modify the relevant firm-facing provisions in the Securitisation Regulation and related Technical Standards in 2024-25.
The PRA also intends to consult on draft PRA rules to replace firm-facing requirements, subject to HMT making the necessary legislation. The PRA has gathered views and evidence from firms through DP3/23 – Securitisation: capital requirements , which will inform its approach to capital requirements for securitisation.
Financial resilience – insurers
Solvency uk implementation.
In June 2024, the PRA will publish its final policy on the matching adjustment (MA) reforms set out in CP19/23 – Review of Solvency II: Reform of the Matching Adjustment . The majority of these reforms will take effect from end-June to allow PRA-authorised firms to take immediate advantage of new investment opportunities. The remaining Solvency II reforms consulted upon in CP12/23 – Review of Solvency II: Adapting to the UK insurance market will take effect on 31 December 2024.
To facilitate implementation of the reforms consulted on in CP12/23 and CP19/23, the PRA will streamline the application processes for new internal model permissions and variations of existing permissions. There will be similar proposals for MA permissions, if the final policy is the same as set out in the CP. The PRA remains committed to assessing and providing decisions on applications for permissions as quickly as possible and aims to do this within the timescales published in the associated statements of policy. This will be supported by the establishment of dedicated, specialised teams for reviewing applications.
In practice, delivering timely decisions will in part depend on good engagement between firms and the PRA during the application process, and on the preparation of high-quality and complete applications by firms. To facilitate this, the PRA will publish templates for use by firms , including templates for reporting the updated Matching Adjustment Asset and Liability Information Return (MALIR) and the Analysis of Change (AoC) and Quarterly Model Change (QMC) for internal models. These measures are intended to assist with a smooth transition to the Solvency UK regime.
A variety of proposals were made in responses to CP19/23 to further reform the MA in the form of so-called ‘sandboxes’, which would allow an element of self-certification of eligibility, or a route to further expand eligibility in response to innovations in primary financing markets. In 2024, the PRA will explore these proposals with industry with the goal of determining whether they can be developed into schemes that further advance the objectives of the Solvency II review.
Solvency II reporting reforms
To deliver the regulatory reporting and disclosure reforms consulted on in CP14/22 and CP12/23 , the PRA published PS3/24 – Review of Solvency II: Reporting and disclosure phase 2 near-final , including finalised templates and instruction files. The PRA will also publish a finalised single taxonomy package in 2024 Q2, which encompasses proposals in CP14/22 and CP12/23 , and deletions published in PS29/21 . The PRA will engage with firms, including through industry roundtables, to prepare them in meeting the new reporting requirements coming into force from 31 December 2024.
Solvency II transfer
The PRA will publish a CP in 2024 H1 that will set out how it will transfer the remaining Solvency II requirements from assimilated law into the PRA Rulebook and other policy material such as supervisory statements or statements of policy (‘the UK framework’).
This will provide a more comprehensive Rulebook and will make it easier for firms to access and navigate the rules that apply to them.
Insurance stress testing
Stress testing forms an important part of the PRA’s supervisory approach and risk assessment of insurance firms, helping to assess and identify the vulnerabilities of life and general insurance sectors to a range of risks in different scenarios.
Major life insurers participate in regular and concurrent stress testing prescribed by the PRA, and the next test will take place in 2025. For the first time, the PRA will publish the individual results of the largest annuity-writing firms to help inform stakeholders about the level of firms’ resilience in the scenarios set out, and thereby strengthen market discipline.
The PRA will continue to engage with the industry on the technical, operational, and communication aspects of the stress test, and will publish an approach document for the life insurance stress test 2025. The 2025 test will for the first time include an exploratory scenario to assess exposure to the recapture of funded reinsurance contracts.
For general insurers, the PRA has previously conducted four general insurance stress test exercises between 2015 and 2022. In 2025, the PRA will run its first dynamic stress test . The objectives of the exercise will be to:
- assess the industry’s solvency and liquidity resilience to a specific adverse scenario;
- assess the effectiveness of insurers’ risk management and management actions following an adverse scenario; and
- inform the PRA’s supervisory response following a market-wide adverse scenario.
The dynamic nature of the 2025 exercise represents a significant change from previous exercises and will involve simulating a sequential set of adverse events over a short period of time. The PRA has begun engaging with industry trade bodies and will provide more details of this exercise (including participation, design, and timelines) during 2024. Results of this exercise will be disclosed at an aggregate industry level.
Cyber underwriting risk
As the scope of technology continues to expand globally, cyber underwriting risk has become increasingly relevant, as reflected in the actual and planned growth of cyber insurance within the UK sector. As well as being inherently volatile and systemic in nature, cyber underwriting risk is diverse in how it can manifest in different lines of business.
Given the uncertainty of this risk, robust risk management, risk appetite-setting, and stress testing will be important factors in ensuring that capital and exposure management capabilities reflect firms’ actual exposures.
Monitoring and assessing cyber underwriting risk will be at the core of the PRA’s supervisory focus, particularly for firms with material exposures. The PRA will share the aggregate findings of its recent thematic project focused on cyber underwriting risk with industry, and continue to monitor the risk landscape and market dynamics to identify and assess potential risk drivers, including areas such as contract (un)certainty risk.
Model drift
The PRA will continue its scrutiny of internal models used by insurers to calculate capital requirements and aid risk management, to identify potential trends in the strength of firms’ calibrations, and as an indicator of the effectiveness of firms’ risk management.
In its 2023 model drift analysis , the PRA identified a number of findings across firms using internal models within the non-life sector. These are related to levels of allowances for inflation uncertainty, potential optimism in expected underwriting profits, potential optimism in the cost and benefit of reinsurance, and the limited allowance for economic and geopolitical uncertainties.
In 2024, the PRA will address perceived systemic trends that may weaken the robustness of models used across the market as a whole. The PRA will also focus on specific model drift within individual firms, with an emphasis on improving the effectiveness of internal model validation, so that firms can develop the capability to self-identify and address potential challenges.
Funded reinsurance
In 2024, the PRA will continue to pay close attention to the rapidly increasing use of funded reinsurance transactions in the UK life insurance market, and the risks that the growth in their use may pose to policyholder protection and UK financial stability. The PRA is particularly focused on the risk of an erosion in standards for assets used as collateral in these transactions, and individual and sectoral concentrated exposures to correlated, credit-focused counterparties.
As well as preparing to examine exposures to the recapture of funded reinsurance in the 2025 life insurance stress test, in 2024. The PRA will also, subject to responses to CP24/23 – Funded reinsurance , finalise and implement its policy expectations for UK life insurers that use funded reinsurance arrangements. As stated in the PRA’s letter on ‘ Insurance supervision: 2024 priorities ’, these policy expectations will cover how firms should manage risks associated with funded reinsurance at both individual transaction and at aggregate level. This will include the expectation that firms place limits on their activities to ensure sound risk management.
Impact on general and claims inflation
Claims inflation continues to be a significant risk for general insurers. Following a thematic review, the PRA published a Dear Chief Actuary letter in June 2023 setting out its findings that, while reserves have increased, there remains material uncertainty and the potential for excessive optimism with respect to reserving, pricing, and capital and reinsurance planning.
The PRA expects a continued lag in the emergence of claims inflation in the data, which insurers should be alert to. The PRA will continue to monitor the ongoing impact through the regulatory data collected and supervisory activities throughout 2024. Should the PRA’s assessment of this risk change, further focused work may be considered.
Market-wide stresses in March 2020 and September 2022 highlighted gaps in insurers’ liquidity risk management frameworks and, consequently, the importance of having comparable, accurate, and timely information on insurers’ liquidity. The PRA will build on the existing liquidity framework, currently based on risk management expectations set out in SS5/19 – Liquidity risk management for insurers , and develop liquidity reporting requirements for insurance firms most exposed to liquidity risk. The information collected will be used to supervise firms’ liquidity positions more effectively and produce meaningful peer comparisons. The PRA will work closely with firms to inform them about its development of these requirements and explore the necessity of a minimum liquidity requirement as part of a future policy consultation.
In addition, the Bank has signalled its intention to develop a new lending tool for eligible NBFIs to help tackle future episodes of severe dysfunction in core markets that threaten UK financial stability. The development of the PRA’s approach to supervising liquidity will therefore inform the design of the lending tool as it relates to insurers.
The reforms to Solvency II offer life insurers opportunities to expand the range of credit risk assets that are used to back their annuity liabilities, and enable them to meet their commitment to invest in assets that contribute to the productivity of the economy and the transition to net zero. These opportunities require sophisticated credit risk management, and insurers’ capabilities will remain a key focus. Increased activity in the bulk purchase annuity (BPA) market is expected to lead to further growth in firms’ exposure to credit risk, and potentially to concentrations in exposure to internally valued and rated assets.
The PRA will continue to focus on the effectiveness of firms’ credit risk management capabilities and seek further assurance that firms’ internal credit assessments appropriately reflect the risk profile of their asset holdings. The PRA will assess how firms’ credit risk management frameworks are evolving in line with its supervisory expectations, and also review the suitability of firms’ current and forward-looking internal credit assessment validation plans and approaches. In both cases, the PRA will seek to provide feedback on a firm-specific or thematic basis as appropriate.
Regulatory reforms
Operational risk and resilience (including the implementation of the critical third-party regime).
Operational disruption can impact financial stability, threaten the safety and soundness of individual firms and financial market infrastructures, or cause harm to consumers, policyholders, and other parts of the financial system. The PRA defines operational resilience as the ability of firms and the financial sector to prevent, respond to, recover, and learn from operational disruptions, including cyber threats.
The FCA, Bank, and PRA’s operational resilience policies came into force in March 2022 . Firms have now identified their most important business services, set impact tolerances, and commenced a programme of scenario testing. The PRA will continue to work closely with the FCA to assess firms’ progress, with a particular focus on the ability of firms to deliver important business services within defined impact tolerances during severe but plausible scenarios over a reasonable time frame, and no later than March 2025.
The PRA will also continue to monitor threats to firms’ resilience, including their growing dependency on third parties, while respecting the principle of proportionality.
Critical third parties to the UK financial sector
Section 312L of FSMA 2023 gave HMT the power to designate certain third-party service providers as ‘critical’ if they provide services to the financial sector, which, if disrupted or subject to failure, could cause financial stability concerns or risks to the confidence in the UK’s financial system. Prior to designating these parties, HMT must consult with the Bank, PRA, and FCA (the authorities the Act appoints as Regulators of the new regime). FSMA 2023 also gives the Regulators new powers to oversee the services provided by critical third parties (CTPs) to regulated firms. In December 2023, the PRA, Bank, and FCA jointly published CP26/23 – Operational resilience: Critical third parties to the UK financial sector , proposing how these powers could be used to assess and strengthen the resilience of services provided by CTPs to firms and FMIs, thereby reducing the risk of systemic disruption. The PRA will continue to work with other authorities to develop the final policy and oversight approach in 2024.
Additionally, the PRA is developing regulatory expectations on incident reporting, aligned with its operational resilience expectations.
Review of enforcement policies
Enforcement supports and supplements the PRA’s regulatory and supervisory tools by ensuring that it has credible mechanisms for holding regulated firms to account when they do not meet requirements and expectations. Enforcement policies also provide a wider deterrent effect. The PRA is therefore committed to holding individuals to account and, when appropriate, taking regulatory and/or enforcement action against those individuals that breach its standards. The PRA clearly sets out, for the benefit of the whole regulated community, the actions and standards of behaviour that are considered unacceptable ( The Bank of England’s approach to enforcement ).
In January 2024, following a review of its policies and public consultation, the PRA published PS1/24 – The Bank of England's approach to enforcement , which sets out the revised approach to enforcement across the Bank’s full remit (including when acting as the PRA).
The PRA is committed to conducting any enforcement investigations as promptly and efficiently as possible. In line with that aim, PS1/24 introduced a new Early Account Scheme (EAS or ‘the Scheme’), which provides for a new path for early cooperation and greater incentives for early admissions with the aim of reaching outcomes more quickly in specific cases.
Diversity and inclusion in PRA-regulated firms
Enhancing diversity and inclusion (D&I) can support better governance, decision-making, and risk management in firms by reducing groupthink and promoting a culture that allows employees to feel able to speak up and challenge the status quo.
In September 2023, the PRA published CP18/23 – Diversity and inclusion in PRA-regulated firms . Under the proposals, all in-scope firms would need to understand their D&I position, develop appropriate strategies to make meaningful progress, and monitor and report on progress. The proposals are flexible and carefully tailored to recognise that firms are at different stages of their work on D&I, and, most importantly, are best placed to develop their own D&I solutions.
The PRA also outlined that the proposals in CP18/23 contribute towards its secondary objectives of ensuring effective competition and facilitating competitiveness and growth, because enhanced D&I can help support greater innovation and make firms more attractive in the labour market.
In 2024, the PRA will continue its industry engagement, assess responses to CP18/23, and provide a further update in due course.
The PRA maintains flexibility to adapt and respond to changes in the external environment, economic and market developments, and any other risks that may affect its statutory objectives or priorities. The PRA has continued to use its horizon-scanning programme to achieve the following aims:
- identify emerging external risks, regulatory arbitrage, and potentially dangerous practices;
- highlight features of the regulatory regime that are not yet delivering the desired results; and
- allocate supervisory and policy resources to tackling the highest-priority risks in a timely manner.
Consistent with its mission, the PRA will continue to contribute to lessons learned internationally, policy/standards evaluation, and, in particular, internationally agreed standards with the aim of promoting the safety and soundness of the firms it regulates. For example, in 2024/25, the PRA will continue to focus on identifying and addressing emerging risks internationally, working closely with the BCBS on its response to consultations launched in 2023 (including on cryptoassets; disclosure for climate-related financial risks; and the Basel Core Principles and other outstanding work in support of its 2023/24 work programme and strategic priorities ). The PRA will also continue to work closely with the International Association of Insurance Supervisors (IAIS) on its finalisation of the Insurance Capital Standard (ICS), Insurance Core Principles on valuation (ICP 14) and capital adequacy (ICP17) .
In addition, the PRA will continue to monitor the potential for capital and profit erosion in firms that are slower to adopt new technologies, as well as firms’ involvement in new technologies, and changes in the profile of cyber-risks they face.
International engagement and influencing regulatory standards
The PRA plays a leading role in influencing international regulatory standards and will continue to participate actively in global standard-setting bodies, such as the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) , the IAIS, and the Financial Stability Board (FSB) .
Building on the BCBS’s report on the 2023 banking turmoil , the PRA will work with international stakeholders and the BCBS to strengthen supervisory effectiveness and identify issues that could merit additional guidance at a global level. The PRA will work with BCBS to pursue additional follow-up analytical work based on empirical evidence to assess whether specific features of the Basel Framework have performed as intended, such as liquidity risk and interest rate risk in the banking book, and assess the need to explore policy options over the medium term, alongside supporting the BCBS in pursuing its medium-term programme on evaluating the impact and efficacy of Basel III, and in light of lessons drawn from the Covid-19 pandemic.
In addition, the PRA pursues international collaboration through less formal mechanisms, for example through regular bilateral and trilateral engagements, ensuring close collaboration on a number of supervision, risk, and policy topics of joint interest. The PRA also collaborates internationally on joint global thematic reviews with other regulatory authorities, for example, to address a joint interest in banks’ exposures to NBFIs and the use of critical third parties.
The PRA will also continue to support international efforts to monitor and promote consistent implementation of Basel 3.1, as well as the implementation and monitoring of the ICS.
Supervisory co-operation
Effective international collaboration remains crucial to addressing global risks, and is central to maintaining UK financial stability, the safety and soundness of internationally active firms, and reducing regulatory arbitrage.
The PRA will continue to promote international collaboration through supervisory colleges and set out clear expectations for firms wanting to branch into the UK. The PRA will also maintain its existing memoranda of understanding (MoUs) and, if needed, expand the number of jurisdictions with which it has an MoU to facilitate the supervision of international groups and therefore enhance the safety and openness of the UK for financial services activities.
The PRA will continue to support HMT via its international collaboration activities (eg The Berne Financial Services Agreement ) and with assessments of other jurisdictions to facilitate safe access to overseas markets for UK firms, among other benefits.
Overseas bank branches
The PRA will consult on targeted refinements to its approach to banks branching into the UK, reflecting lessons from the failure of SVB to ensure the PRA’s framework for assessing branches captures activities of potential concern. The PRA is committed to the UK remaining a responsibly open jurisdiction for branches, and expects the vast majority of branch business to be unaffected by any changes. The PRA also intends to consult on clarifying expectations for group entity senior manager functions (SMFs) footnote [8] and expectations of booking arrangements.
Operational and cyber resilience
The PRA engages internationally on operational and cyber resilience, in support of its supervision objectives and to raise international standards. The PRA co-chairs the G7 Cyber Expert Group (CEG), which works to coordinate cyber resilience strategy and management across G7 jurisdictions. The PRA also co-chairs the European Systemic Cyber Group (ESCG), which helps European authorities develop systemic capabilities to prevent and mitigate risks to the financial system that might emanate from cyber incidents. The PRA has also led work at the Financial Stability Board (FSB) on cyber incident reporting. In 2024, the PRA will continue to engage with standard-setting bodies and bilaterally with other jurisdictions on third-party risk management and CTPs.
Managing the financial risks arising from climate change
Climate change presents a source of material and increasing financial risk to firms and the financial system. Managing the risks to firms’ safety and soundness from climate change requires action and remains a key priority for the PRA. The Bank first set out expectations around enhancing banks’ and insurers’ approaches to managing the financial risks emanating from climate change in April 2019 via SS3/19 – Enhancing banks’ and insurers’ approaches to managing the financial risks from climate change . The PRA has since provided further guidance via two Dear CEO letters, footnote [9] incorporating observations from supervisory processes and the 2022 Climate Biennial Exploratory Scenario exercise , as well as by providing thematic feedback via Dear CFO letters footnote [10] to promote high-quality and consistent accounting for climate change .
As noted in its 2024 priorities letter to firms, the PRA expects firms to make further progress and demonstrate how they are responding to the PRA’s expectations, and to set out the steps they are taking to address barriers to progress. The PRA will continue to assess firms’ progress in managing climate-related financial risks. In 2024, the PRA will commence work to update SS3/19 and publish thematic findings on banks’ processes to quantify the impact of climate risks on expected credit losses.
The PRA, alongside the FCA, will continue to work with industry through the Climate Financial Risk Forum to produce practical guides and tools that help financial firms embed the financial risks from climate change into their operations. The PRA will also continue to engage with domestic and international partners, including international standard-setters, to contribute to the development of international frameworks in support of managing climate-related risks.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Following the publication of a feedback statement (FS)2/23 – Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning , the PRA and FCA intends to conduct the third edition of the joint survey on machine learning in UK financial services , in 2024 Q2. Responses to the survey will allow the PRA and FCA to further explore how best to address the issues/risks posed by AI/ML in a way that is aligned with the PRA’s and FCA’s statutory objectives. The PRA will also continue to monitor firms’ compliance of its expectations, as set out in SS1/23 , and will seek to explore further updates where necessary.
International policy on digitalisation and managing associated risks
The PRA aims to be at the forefront of identifying and responding to opportunities and risks faced by PRA-authorised firms as they seek to use technology in innovative ways to attract and retain customers, reduce costs, and increase efficiencies.
External context and business risk are important facets of the PRA’s approach to supervision. Developments are monitored, with specialist input from the Bank’s Fintech Hub , to identify risks such as fragmentation of the value chain, novel outsourcing arrangements, and concentration risks across and within firms.
In order to take a responsive and responsibly open approach, the PRA will continue to consider policy proposals to respond to digitalisation and adapt its supervisory approach accordingly. Through the New Bank Start-up and Insurer Start-Up Units, the PRA will continue to engage with applicant firms that have novel uses of technology. The PRA will continue to work closely with domestic and international partners, and through engagement with industry and stakeholders, to take a pro-active approach to digital innovations within the financial sector.
The PRA is a significant contributor to discussions on digitalisation in international standard-setting fora, and will continue to support the BCBS’s work on the developments in the digitalisation of finance and the implications for banks and supervisors . The PRA will also continue be an active part of the IAIS Fintech Forum.
Digital money and innovation
In February 2023, HMT published a consultation and Call for Evidence on the future financial services regulatory regime for cryptoassets , focused on enhancing market integrity, custody requirements, and transparency. The consultation closed in October 2023 with the publication of an update on the government’s plans for its legislative approach to the regulation of stablecoins. HMT confirmed that tokenised deposits would continue to be regulated as deposits. The PRA will continue to work with HMT and the FCA to ensure that the regulatory perimeter and the boundaries between different activities are clearly and robustly delineated.
In November 2023, the Bank, PRA, and FCA published a cross-authority package on innovations in money and payments . As part of this, the PRA published a Dear CEO letter to provide clarity on the PRA’s expectation on how deposit-takers should address risks arising from the emergence of multiple forms of digital money and money-like instruments. footnote [11] It published the letter alongside the Bank’s proposed regime for systemic payment systems using stablecoins and related service providers , and the FCA’s proposed regime for stablecoin issuers, custodians, and the use of stablecoins as a means of payment. A roadmap paper was also published to explain how these regimes fit together.
The PRA will continue to contribute to the Bank’s broader work on innovation in money and payments, which in 2024 will include work on wholesale payments and settlements – and their interaction with retail payments.
In 2024, the PRA will continue to work within the global regulatory community to finalise a set of amendments made to the international standard on the treatment of banks’ cryptoassets exposures. These amendments were published for consultation by the Basel Committee in December 2023, following the finalisation of the standard in 2022.
Once the amendments are finalised, the PRA will implement the standard within the UK, following the PRA’s policymaking process. Alongside this, the PRA will continue to engage with international partners, including the BCBS, to assess bank-related developments in cryptoassets markets, the role of banks as issuers of stablecoins and tokenised deposits, custodians of cryptoassets, and potential channels of interconnections with the cryptoassets ecosystem.
The PRA advances its primary and secondary objectives by making rules that support competitive and dynamic markets in the sectors that it regulates. The PRA will go further in developing proportionate and efficient prudential requirements, thereby reducing the burden on firms where appropriate, and pursuing its secondary objectives. The PRA also remains committed to playing an active role in international standard-setting, given the important role of global rules in safeguarding the UK’s open economy through ensuring safe financial markets.
Regulatory change – embedding the PRA’s approach to rule-making
FSMA 2023 has significantly changed the powers and responsibilities of the PRA, allowing it to ensure the UK financial services framework is fit for the future, reflecting the UK’s position outside of the EU. FSMA 2023 also introduces enhanced objectives and accountability requirements that support the PRA’s transparency and accountability to Parliament.
FSMA 2023 provides a framework to repeal and replace assimilated law relating to financial services. Most technical rules will now be made by operationally independent regulators within a framework set by Parliament, enabling the PRA to deliver policies better suited to the UK financial sector. The PRA’s responsibility, in cooperation with HMT and FCA, is to ensure that the new rules are made in accordance with the PRA’s remit and statutory objectives, including the new secondary competitiveness and growth objective.
The PRA has worked closely with HMT and FCA on the sequencing of the repeal and the replacement of the files of assimilated law. Once the replacement material is in PRA rules, the PRA will have the power to evaluate these rules, amend them if needed, and/or create new rules when required.
The PRA has already made good progress with respect to the files that HMT has prioritised into the first two ‘tranches’, including key files such as Solvency II, Securitisation, CRR, among others. The PRA has consulted on significant parts of tranches 1 and 2 in 2023 and will continue this work throughout 2024 and 2025. The completion of the repeal and replacement of Solvency II and Securities Regulation files is expected by the end of 2024, and the last of the PRA's tranche 1 and 2 files is planned for implementation in 2026. Work on the remaining files that were not included in tranches 1 and 2 will begin in 2024.
The PRA is consulting its stakeholders as it develops its approach to policymaking in light of the new requirements. In December 2023, the PRA published CP27/23 , setting out the proposed approach to policy under the regulatory framework as amended by FSMA 2023, and building on the previously published DP4/22 – The Prudential Regulation Authority’s future approach to policy . CP27/23 outlines the PRA's planned approach to maintain robust prudential standards, which are the cornerstone of UK financial stability and long-term economic growth, while addressing risks and opportunities in a responsive manner, appropriately adapted to the circumstances of the UK. Responses to CP27/23 will inform the PRA’s finalised approach document to be published in 2024 H2.
Secondary competitiveness and growth objective (SCGO)
FSMA 2023 gave the PRA a new secondary objective which requires the PRA to act, so far as reasonably possible, to facilitate the UK economy’s international competitiveness (including in particular the financial services sector through the contribution of PRA-authorised persons) and its growth over the medium to long term, subject to alignment with international standards. FSMA 2023 maintained the PRA’s other objectives without change.
In addition to specific policy measures, the PRA has taken practical steps to embed the SCGO in its operations, including through internal changes, and the launch of a research programme to deepen its understanding of the ways prudential requirements can affect the international competitiveness and growth of the UK economy.
The PRA will continue to look for ways in which it can facilitate the UK’s competitiveness and growth when discharging its general functions. The approach focuses on strengthening the three regulatory foundations that were set out in CP27/23, specifically:
- Maintaining trust among domestic and foreign firms in the PRA and UK prudential framework via a range of policies, including those that promote strong prudential standards appropriately calibrated for the UK, and the alignment of said policies with international standards.
- Adopting effective regulatory processes and engagement, including providing for the efficient handling of regulatory processes, such as authorisations and data collections, as well as facilitating the accessibility of the PRA Rulebook to reduce the operating costs of firms.
- Taking a responsive and responsibly open approach to UK risks and opportunities, including making rules that account more effectively for the needs of the UK. This approach means responding faster to emerging risks and opportunities in the UK financial sector, for example, by using regulatory tools to support innovation safely. To this end, in 2024, the PRA will hold a pilot roundtable to gather stakeholders’ views on how the PRA can help to reduce the barriers to innovation that the industry faces.
The policy initiatives discussed in the rest of this section provide examples of how the PRA will advance its secondary objectives in 2024/25.
Furthermore, the Bank’s Independent Evaluation Office (IEO) is evaluating the PRA’s approach to its new secondary objective. Both the outcome of the IEO’s evaluation and the PRA’s response to it will be included in the PRA’s – ‘Secondary Objectives Report’ to be published alongside the PRA’s Annual Report 2023/24. The Secondary Objectives Report will also give an overview of all the PRA’s policy initiatives that have advanced the SCO and the SCGO .
Strong and Simple framework
In 2021, the PRA published FS1/21 – A strong and simple prudential framework for non-systemic banks and building societies , that set out a vision to simplify prudential requirements for smaller, domestic-focused banks and building societies, while maintaining those firms’ resilience.
As outlined in the PRA 2023/24 Business Plan , the PRA will continue its planned programme of work on creating a simpler but equally resilient prudential framework for smaller, domestically focused banks and building societies, known as the Strong and Simple framework. This framework is designed to maintain the financial resilience of banks and building societies operating in the UK, while reducing costs associated with prudential requirements for non-systemic banks and building societies. In 2023/24, the PRA published its final policy on scope criteria and simplified liquidity and disclosure requirements for SDDTs in PS15/23.
In December 2023, the PRA published PS16/23 – The Strong and Simple Framework: Scope criteria, liquidity and disclosure requirements , which finalises the scope of the framework. The PS builds on the first layer of the Strong and Simple framework, which focused on the smallest firms and is known as the SDDT regime. The overall aim of the framework is to maintain the financial resilience of banks and building societies operating in the UK, while addressing the ‘complexity problem,’ under which the same prudential requirements are applied to all firms, regardless of size, even though the costs of interpreting and operationalising those requirements are higher for small firms, relative to the associated public policy benefits.
In 2024/25, the PRA will move further towards finalising and implementing the Strong and Simple prudential framework for SDDTs. A key step will be to implement the simplifications to liquidity requirements that were introduced in Phase 1. The PRA will also finalise the rules for the Interim Capital Regime, which will allow firms eligible to be SDDTs to stay under capital rules equivalent to those currently in place until the simplified capital regime for SDDTs is implemented. The PRA plans to consult on a simplified capital regime for SDDTs in 2024 Q2.
Insurance Special Purpose Vehicles regime
In 2017, the PRA introduced a framework for the authorisation and supervision of ISPVs to provide guidance for parties wishing to obtain authorisation as an ISPV, or for insurers and reinsurers seeking to use UK ISPVs as risk mitigation in accordance with Solvency II.
The UK ISPV regime has not seen as much activity as originally envisaged. While new issuances of insurance-linked securitisations (ILS) transactions in the UK over the last two years have exceeded USD400 million, there are steps to be taken which can improve the regime and increase its usage.
The PRA has been in discussion with industry on this matter with the aim of understanding the key areas of the regime in which market participants would recommend changes.
The PRA expects to consult on a package of reforms to the UK ISPV regime. These reforms are intended to:
- allow a wider range of transaction structures in the UK regime;
- improve the speed of the application process, and thereby also reduce costs for applicants; and
- clarify the PRA’s expectations of UK insurers who cede risks to ISPVs, wherever they are established.
Remuneration reforms
The PRA’s remuneration rules ensure that key decision-makers and material risk-takers at PRA-regulated firms have the right incentives and can be held accountable. In 2023, following consultation, the PRA removed the bonus cap and made changes to its rules to enhance proportionality for small firms .
In advancing its primary and secondary objectives, the PRA is considering further changes to the remuneration regime that is better suited to the UK’s financial sector, while maintaining the remuneration regime’s overall structure and objectives, which are based on internationally agreed FSB principles and standards . The PRA intends to consult on any changes in 2024 H2.
Implementing changes to the Senior Managers & Certification Regime (SM&CR)
In March 2023, the PRA and FCA jointly published DP1/23 – Review of the Senior Managers and Certification Regime (SM&CR) , with a particular focus on gathering views about the regime’s effectiveness, scope, and proportionality. HMT in parallel launched a Call for Evidence covering the legislative aspects of the SM&CR. The period for sending responses to the discussion paper ended on 1 June 2023.
The PRA received over 90 responses relevant to its work as a prudential regulator, reflecting the significant level of stakeholder interest in the regime. The PRA, working closely with the FCA and HMT, is considering potential policy options for reform in response to the comments received and intends to consult on proposed changes to the regime in 2024 H1.
Complete the establishment of the Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) Panel
The PRA is continuing to make progress under the new framework provided by FSMA 2023, setting out CBA as an integral part of developing the best possible policy approach, and the results will help shape the PRA’s policymaking. CBAs inform and refine the policy approach to identified issues, helping to design approaches that offer the greatest benefits.
One of the key elements of enhancing the PRA’s scrutiny and accountability mechanisms relates to its approach to CBA and the establishment of a new CBA panel. The role of the CBA Panel is to support increased transparency and scrutiny of the PRA’s policymaking by providing regular, independent input into the PRA’s CBAs relating to PRA rules and the PRA’s statement of policy in relation to CBAs . The Panel will review how the PRA is performing more generally in carrying out its duties with regard to CBA and may provide recommendations to the PRA.
The PRA has completed an open, competitive, and rigorous recruitment process for identifying and appointing a diverse range of expert individuals to constitute the CBA Panel. The PRA will finalise the set-up of the Panel and then start consulting it on the PRA’s statement of policy in relation to CBAs and on the preparation of CBAs. The appointments, including that of the Chair, will be announced in due course.
In 2024, the PRA will consult on its CBA framework, which will set out how the PRA intends to continue to conduct a robust CBA and how it engages with the CBA panel.
PRA Rulebook
The new regulatory framework set out in FSMA 2023 enables the PRA to develop a more coherent and easily accessible Rulebook. The aim is to improve the efficiency and accessibility of the PRA Rulebook by reducing the number of policy document formats currently in use to three: rules, supervisory statements, and statements of policy. In order to achieve this, the PRA’s specialist teams will begin the process of reviewing the EU Guidelines, European Supervisory Authorities (ESA) Q&As, and UK technical standards (UKTS) that are relevant to PRA rules, to determine what should be incorporated into those rules or related supervisory statements and statements of policy. Once the review of these documents is completed, references to the EU Guidelines, ESA Q&As, and UKTSs will be removed.
The PRA is also looking at grouping the elements in the Rulebook to make it easier for users to access relevant information. To support usability and clarity, the PRA will take a consistent approach to the structure of, and language in its policies.
The speed at which the PRA will achieve many of its ambitions for the Rulebook will partly depend on the Government’s approach to the repeal of relevant assimilated law and its replacement in PRA rules and other policy materials. However, the PRA will move ahead with the proposed reforms as quickly as possible to help users more easily navigate the new regulatory landscape.
Banking Data Review
The Banking Data Review BDR, launched in 2023-24, will be delivered as an integral part of the Transforming Data Collection TDC programme. The work will enable the PRA’s banking regulatory data collections to be better aligned with the day-to-day needs of supervisors, ensure the PRA has good-quality data to carry out its new policymaking responsibilities in line with the post-Brexit regulatory framework, and reduce burdens on firms by better integrating and streamlining data collections.
The PRA will consult on the first of three phases of reforms under the BDR in 2024 H2. The consultation will focus on streamlining of the existing regulatory reporting estate, removing reporting templates that may no longer be needed or which contain information that can be gathered at lower cost elsewhere, reviewing collections of counterparty credit information, and incorporating lessons from recent market events.
In parallel, the PRA will continue to work on plans for future phases of reform, focused on credit risk in the second phase, and with all remaining areas covered in a third phase. Engagement with industry participants will be done under the newly appointed TDC Advisory Board, which will be responsible for setting industry working groups on key topics relating to TDC. The TDC’s main industry forum in this area is the Data Standards Committee (DSC), which led the work on the recommendations underpinning the jointly published response by the Bank and the FCA, entitled Transforming data collection – Data Standards Review with recommendations and Bank of England and FCA response . A further working group is the BDR Industry Consultative Forum that is open to all PRA-regulated banks.
Supporting and authorising new market entrants via new ‘mobilisation’ regime
The PRA will continue to support potential market entrants in navigating the authorisation process. This includes providing clear online guidance and industry engagement to build awareness of expectations and seek feedback on firms’ experience of the process. The PRA offers potential applicants the opportunity to meet with staff through a structured pre-application stage, allowing firms to iterate and develop their proposition to support a better-quality application.
The PRA will continue to make use of the mobilisation stage for newly authorised banks, where appropriate, to allow them to operate with restrictions while they complete their set-up before starting to trade fully.
In line with PS2/24 – Review of Solvency II: Adapting to the UK insurance market , the PRA will introduce a new ‘mobilisation’ regime to facilitate entry and expansion for new insurers from 31 December 2024, similar to the mobilisation stage for new banks. Mobilisation will help to facilitate competition, and the international competitiveness and growth of the UK insurance sector, with the aim of benefiting firms who are contemplating applying for authorisation as an insurer in the UK now or in the future.
Newly authorised insurers in mobilisation could be offered the option of using a set period of extra time to build up systems and resources while operating with business restrictions, proportionate regulatory requirements, and lower minimum capital requirements. New insurers could be suitable for mobilisation when they have a shortlist of activities to complete before they can meet full regulatory requirements.
Ease of exit
Improving how firms can leave regulated markets in an orderly way is a vital corollary to greater ease of entry into those markets. It enables a dynamic and competitive market which entrants can join and leave with minimal impact on the wider market and the PRA’s statutory objectives. The PRA has published the first of two planned policy in this topic, (eg, PS5/24 – Solvent exit planning for non-systemic banks and building societies ). A further PS on solvent exit planning for insurers is expected in 2024 H2, following the completion of the market consultation initiated by CP2/24 – Solvent exit planning for insurers . Both of these form part of the PRA’s strategic focus on increasing the ease of exit.
Ring-fencing regime
The Bank and PRA continue to work closely with HMT on implementing the recommendations made in March 2022 by the Independent Review of Ring-fencing and Proprietary Trading , led by Sir Keith Skeoch. On 28 September 2023, both HMT and the PRA published consultations with the aim of giving effect to recommendations of that review.
HMT consulted on removing the blanket restriction which prevents ring-fenced bodies (RFBs) operating in countries outside the EEA. The PRA consulted on introducing a new rule and updating SS8/16 – Ring-fenced bodies (RFBs) , to align with HMT’s proposed legislative changes. These changes aim to implement certain safeguards to ensure that RFBs are not exposed to material risks through the business of their overseas subsidiaries or branches. The PRA will publish its policy and a rule Instrument once the legislative changes are brought into force. Simultaneously, the PRA will update SS8/16 to reflect the changes.
FSMA requires the PRA to conduct a review of its ring-fencing rules and provide a report to HMT every five years. The first such review was completed on 12 December 2023 and the resulting report was laid before Parliament on 25 January 2024 and published on the Bank’s website.
The PRA intends to consult on potential changes to the ring-fencing regime identified by the Rule Review once a fuller exploration of costs and benefits has been undertaken. The Bank and PRA will continue to support HMT with technical advice to enable HMT to finalise its legislative changes, and to consider responses to its Call for Evidence on longer-term reforms.
Effective authorisation processes
The PRA handles over 1,800 regulatory transactions a year, ranging from new firm authorisations to variations of permission for existing firms and cancellations of permission for firms leaving the market. Over the coming year, the PRA will continue to handle these transactions in more streamlined, efficient, transparent, and accessible way while maintaining strong risk controls to ensure the UK’s success as a global financial centre.
In parallel to consulting on reforms to the SM&CR, the PRA will continue to enhance and streamline internal processes on SM&CR applications and other transactions to drive further improvements in operational effectiveness, as measured through the quarterly publication of metrics on timeliness of decisions. This will include close collaboration with the FCA to ensure an efficient and coordinated review of cases, as well as improvements to case handling and recording technology platforms. The PRA will extend existing industry engagement on New Bank Start-ups to also cover new insurers and SM&CR applications in order to promote transparency and spread best practice in support of efficient case handling. In addition, the Wholesale Insurance Accelerated Authorisation Pathway, developed jointly by the PRA and FCA, will continue to provide an accelerated route for the authorisation of a sub-set of London market wholesale applicants.
The PRA’s operation within the Bank plays a critical role in maintaining the stability and integrity of the UK’s financial system. In pursuit of its objectives and work programme, the PRA ensures that its regulatory framework is inclusive, considering the diverse landscape of financial institutions. It aims to create a level playing field, while recognising and planning for the potential impact of the changes in the environment in which we are operating.
In line with its mission, the PRA continually adapts regulations to address emerging risks and opportunities, fostering inclusivity to enhance trust, transparency, and accountability in the financial sector. As a prudential regulator, the PRA maintains and strives for operational efficiency in its regulatory processes, technology, and its workforce. This involves streamlining procedures, driving inclusive recruitment, and leveraging technology to enhance effectiveness – noting that efficient regulation benefits both regulated entities and the broader economy by reducing unnecessary burdens and facilitating smoother interactions between financial institutions and the regulator.
Data and technology
The PRA will continue its programme of work to strengthen and transform its data-related capabilities. The PRA will also continue to play a leading role in international collaboration on the regulatory use of data and technology, liaising closely with other regulators, central banks, academic institutions, and industry. The PRA intends to run a multi-day innovation-focused event for PRA colleagues to support learning and increase awareness about the impact of technological advances and initiatives across the financial sector.
Transforming Data Collection by building on digital regulatory reporting
The PRA will continue to work towards achieving the objectives of the TDC programme for 2026:
- Goal 1: the PRA has the data and tools it needs to rapidly identify and probe emerging issues, risk, and policy questions, including integration into a single customisable supervisory dashboard; and
- Goal 2: the PRA only collects data that it needs from firms, thereby reducing unnecessary burdens on firms.
Regarding Goal 1, the PRA will continue to improve existing and deliver new priority data visualisation and analysis tools to support supervision, covering financial and operational data for PRA-regulated firms. The PRA will also make use of speech-to-text technology to support day-to-day work for staff, and to contribute to the Bank’s wider work on the appropriate use of artificial intelligence to support its objectives, including large third-party language models. This will be underpinned by ongoing support for PRA staff undertaking renewed digital skills training alongside individual and group coaching for some staff cohorts, and planning for those programmes in future years.
Regarding Goal 2, the PRA will continue to work with the FCA and the wider Bank on the TDC programme , which envisions that ‘regulators are able to get the data they need to fulfil their mission at the lowest possible cost to industry’ through improvements to the integration of reporting, reporting instructions, and data standards. Over the coming years, TDC therefore aims to deliver a new target operating model for all of the Bank’s regulatory, statistical, and stress-testing data collections.
Diversity, equity and inclusion at the PRA
The PRA continues to take action to strengthen its culture and working environment. The Bank’s Court review into ethnic diversity and inclusion reported its findings in July 2021. The PRA, alongside the rest of the Bank, is implementing the recommendations of this review and has made considerable progress in terms of embedding inclusive recruitment, investing in talent development, and advancing a psychologically safe culture to promote employees’ ability to voice their opinions via the ‘speak my mind’ initiative. There is also increased accountability for senior leaders to advance a diverse and inclusive Bank.
The PRA recognises the importance of all staff feeling valued and being able to thrive. Key focus areas for 2024/25 include progressing initiatives to improve psychological safety, ethnic and gender representation, and disability disclosure. The PRA continues to benefit from the Bank’s excellent employee networks that cater to diverse groups such as disability, LGBTQ+, social mobility, gender, age, carers, different ethnicities, and many more.
PRA Agenda for Research
The PRA plans to build on its research efforts in 2024/25, including through improving central coordination and capacity-building projects.
Research priorities are captured in the PRA Research agenda 2023+ below (Table 1). The PRA will continue to deliver on those, while making sure that a timely delivery of high-quality research, expertise, and critical evaluation is given to PRC, FPC, and other senior decision-making activities. These deliverables are captured in the research metrics and the PRA Research Annual. The metrics track the quantity, quality, and impact of the PRA’s research, while the PRA Research Annual provides further details on how timely and effective the research advisory (inside and outside the institution) has been. New for this business year is that the PRA will additionally produce impact cases, with the purpose of tracking the lifespan of key research projects and evaluating their total policy/social impact.
To ensure that the organisation has the right capacity and skills, the PRA will initiate new capacity-building projects on models, tools, and data, while reinforcing external collaborations on those. It will also continue efforts to disseminate this work and foster strategic cooperations with research departments at other central banks, regulatory authorities, research institutes, or universities.
Table 1: PRA Research agenda 2023+
Risks to delivery of business plan.
Operating in a complex and fast-moving environment gives rise to risks to the delivery of this business plan. The PRA monitors, manages, actively mitigates (where possible), and reports these risks to the PRC and relevant Bank fora on a regular basis.
Over the course of 2023/24, attrition levels reduced and there was an improvement in recruitment into key roles. Looking ahead to 2024/25, headcount required to deliver this Business Plan is forecast to remain broadly flat.
The PRA will continue to impose discipline on how it deploys its budget to ensure resources are allocated appropriately. The PRA will also need to reprioritise during the year in response to changes in the external environment, as it routinely does. The PRA will continue to focus on managing operational risks and strengthening horizon-scanning capabilities so that it can respond quickly to changes in risk and drive decisions on prioritisation, business planning, and resourcing.
Having access to the right technology and data remains a key area of focus in 2024/25 as part of a multi-year investment across the PRA and the Bank to ensure that the PRA’s technology capabilities support its strategic priorities. This focus will take account of developments in regulatory technology, reduce inefficiencies, and leverage the benefits of being a regulator within the UK’s central bank. There is a risk that the PRA may be unable to deliver its intended technology ambition given the congested change agenda across the Bank. This challenge is being managed through careful prioritisation and scoping of key projects, including delaying some lower-priority activities.
Dependencies
Given the interconnected nature of the global financial system, dependencies on external parties, such as the FCA, HMT, and overseas regulators, could present a risk for the PRA. Policy development, authorisation processes, and supervision activities are contingent on maintaining relationships and co-operation with these parties. The PRA fosters its domestic relationships to ensure effective regulation and supervision across the UK financial sector. The PRA also works closely with international regulators to address cross-border risks for firms operating internationally. The PRA continues to foster these important relationships at all levels of the organisation through several channels, including international committees, supervisory colleges, joint reviews, information-sharing, and joint publications.
PRA Budget 2024/25
The PRA’s provisional budget for 2024/25, which is subject to finalisation of pension costs and year-end adjustments, is estimated at £353.0 million. This is an increase of £34.0 million (11%) on the 2023/24 budget. To reduce the impact to firms in 2024/25, the PRA has taken two measures, as set out in CP4/24 , to limit the increase in fees paid by firms to 7%. This increase follows a 1% reduction to fees in 2023/24 compared with 2022/23.
The PRA is constraining the increase in its own direct costs to 2%, which means a real-terms cut to the budget that will be managed by increasing efficiency in the PRA’s supervisory approach, end-to-end policymaking process, and operations. Alongside this, the PRA needs to fund inflation-driven increases in support services provided to the PRA by the Bank and the PRA’s share of tackling obsolescence in the Bank’s technology estate on which the PRA relies.
Budgeted headcount is forecast to remain broadly flat for 2024/25 ending the year at 1,541 (this compares closely to the actual year-end headcount position for 2023/24 of 1,537). The budgeted headcount reflects the PRA’s need to invest in key areas, including increasing the capacity to approve the efficiency of the IRB model review process, the implementation and supervision of CTPs, investment in the BDR, and implementing lessons learned from the failure of SVB and CS.
Details on how the PRA proposes to fund its budget can be found in CP4/24 – Regulated fees and levies: Rates proposals 2024/25 . It includes proposals for allocating costs of the PRA’s 2024/25 ongoing regulatory activities across PRA fee payers.
Abbreviations
ACS – Annual Cyclical Scenario
AI/ML – Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning
AoC – Analysis of Change
Bank – Bank of England
BCBS – Basel Committee on Banking Supervision
BDR – Banking Data Review
CBA – Cost Benefit Analysis
CEG – Cyber Expert Group
CEO – Chief Executive Officer
CMORG – Cross Market Operational Resilience Group
CP – Consultation Paper
CRR – Capital Requirements Regulation
CTP – Critical Third Party
DEI – Diversity, equity, and inclusion
DP – Discussion paper
DSC – Data Standards Committee
D&I – Diversity and inclusion
EAS – Early Account Scheme
EU – European Union
ESA – European Securities and Markets Authority
ESCG – European Systemic Cyber group
FCA – Financial Conduct Authority
FinTech – Financial Technology
FMI – Financial Market Intermediary
FMIs – Financial Market Infrastructures
FPC – Financial Policy Committee
FRF – Future Regulatory Framework
FSB – Financial Stability Board
FSMA – Financial Services and Markets Act 2000 (as amended)
HMT – His Majesty's Treasury
IAIS – International Association of Insurance Supervisors
ICS – Insurance Capital Standard
ILS – insurance-linked securitisations
IRB – internal ratings-based
IRRBB – interest rate risk in the banking book
ISPV – Insurance special purpose vehicle
L-SREPs – Liquidity Supervisory Review and Evaluation Processes
MA – Matching adjustment
MALIR – Matching Adjustment Asset and Liability Information Return
MDA - Maximum distributable amount
MoU – Memorandum of Understanding
MRM – Model Risk Management
NBFI – Non-Bank Financial Institution
PMA – Post Model Adjustment
PRA – Prudential Regulation Authority
PRC – Prudential Regulation Committee
PS – Policy statement
QMC – Quarterly Model Change
RFB – Ring-fenced bodies
RWA – Risk-weighted asset
SCGO – Secondary Competitiveness and Growth Objective
SCO – Secondary Competition Objective
SDDT – Small domestic deposit takers
SMCR – Senior Managers and Certification Regime
SME – Small and medium-sized enterprise
SMF – Senior management function
SS – Supervisory statement
SVB – Silicon Valley Bank
SWES – System-wide exploratory scenario
TDC – Transforming Data Collection
TFSME – Term Funding Scheme with additional incentives for SMEs
TPR – The Pension Regulator
UKTS – UK Technical Standards
Contacting the Bank of England and the PRA
Please send any enquiries related to this publication to [email protected] .
In PS15/23, the PRA set out its rationale to rename Simpler-regime firms to Small Domestic Deposit Takers (SDDTs), and Simpler-regime consolidation entities to SDDT consolidation entities. To avoid confusion, throughout the rest of this document, the PRA will refer to SDDTs, SDDT consolidation entities, the Small Domestic Deposit Takers regime or SDDT regime, and SDDT criteria, rather than Simpler-regime firm, Simpler-regime consolidation entities, simpler regime, and Simpler-regime criteria, even when referring to past consultations.
A CTP is an entity that will be designated by HMT by a regulation made in exercise of the power in section 312L(1) of 2000, as amended by the FSMA 2023.
As at 1 January 2024.
Strictly speaking, DIFs do not accept deposits and are included under the category of deposit-takers for presentational purposes only.
Section 2E of FSMA.
SS11/13 – Internal Ratings Based (IRB) approaches .
As set out in the 2024 priorities letter on UK deposit takers .
SMFs are a type of controlled function carried out by ‘approved persons’, ie individuals who have to be approved. SMFs are the most senior people in a firm with the greatest potential to cause harm or impact upon market integrity.
Managing climate-related financial risk – thematic feedback from the PRA’s review of firms’ SS3/19 plans and clarifications of expectations and Thematic feedback on the PRA’s supervision of climate-related financial risk and the Bank of England’s Climate Biennial Exploratory Scenario exercise .
Thematic feedback from the 2021/2022 round of written auditor reporting and Thematic feedback from the 2022/2023 round of written auditor reporting.
‘Digital money’ refers to claims on deposit-takers or other financial institutions, which exist only in electronic form and whose value is preserved through a combination of strict regulation and issuers’ access to central bank deposits. ‘Digital money-like instruments’ refers to other assets that exist only in electronic form and are used for payments. Some of these are regulated to support a stable value, but their issuers do not have access to central bank deposits and are subject to lighter regulation.
Back to top
- How can I sign up for Max?
How much is Max?
Does max offer a free trial, where can i watch max.
- Is HBO Max merging with Discovery Plus?
- Can I watch movies in 4K?
What movies and shows are on Max?
Hbo max has relaunched as 'max' — here's what that means for new and existing subscribers.
When you buy through our links, Business Insider may earn an affiliate commission. Learn more
HBO Max is now called Max . The relaunched streaming service merges HBO's library of original series with content from Discovery Plus , along with a huge catalog of blockbuster movies and TV shows.
The service costs $20/month for the Ultimate plan with ad-free 4K support, $16/month for ad-free HD streaming, or $10/month for ad-supported HD streaming. Most people who already have HBO through cable automatically get Max without having to pay extra.
In its previous form, HBO Max was already one of the best streaming services , and the "Max" rebranding and expansion should add a bit more value. Its large selection of hit movies, prestige series, and unscripted content makes it a strong competitor in the increasingly crowded digital entertainment market.
Below, we've detailed all the basics to help you decide if Max is right for your needs, including pricing, content selection, and what the Discovery Plus merger means for existing HBO Max members.
How can I sign up for Max (formerly HBO Max)?
You can sign up for Max through Max.com. You can also subscribe directly through select partner services, including Amazon Prime Video , AT&T , DirecTV , Spectrum , Hulu , and YouTube TV . If you were an existing HBO Max member, your subscription automatically transitioned to Max on May 23, 2023.
Max costs $16/month for ad-free streaming or $10/month for ad-supported streaming, the same as HBO Max did. In addition, Max now has a new Ultimate ad-free plan for $20/month.
Subscribers can save up to 20% by signing up for an annual subscription to any plan. An annual Ultimate plan is $200 a year, an ad-free plan is $150 a year, and an ad-supported plan is $100 a year.
Max's ad-supported plan offers HD streaming on up to two screens at a time with commercials. The ad-free plan offers commercial-free streaming in HD on up to two screens, along with support for 30 downloads. The Ultimate ad-free plan adds 4K support with Dolby Atmos audio, 100 downloads, and lets you stream on up to four screens at a time.
Though HBO Max initially offered a free trial after launch, Max does not give new members a trial. However, there is one workaround. Amazon Prime Video members can get a one-week free trial of Max if they sign up for the service as a Prime Video channel . The trial is only available to new members.
Max can be streamed via its official website and the Max app, which was formerly the HBO Max app. Existing members might need to manually download the new Max app.
You can find the app on Apple, Android, Roku, PlayStation, Xbox, Amazon Fire TV, and Chromecast devices, as well as smart TVs from LG and Samsung.
Those who sign up for Max directly through a partnered service, like Hulu, will be able to access regular HBO content through the partner service's app. To watch Max exclusives, however, you still need the separate Max app.
When is HBO Max merging with Discovery Plus?
HBO Max and Discovery Plus merged into one streaming service called Max on May 23, 2023. The new service replaced HBO Max, but Discovery Plus continues to remain as a separate platform.
Ad-supported and ad-free Max plans remain the same price as those on HBO Max. A new Ultimate tier with 4K streaming support is now available for $20 a month. Existing HBO Max accounts will automatically migrate to Max.
On its own, Discovery Plus still costs $5/month with ads or $7/month without ads. The service offers shows from Discovery, TLC, Animal Planet, Food Network, and HGTV, along with several original series .
During its Q2 2022 earnings call, Warner Bros. Discovery outlined how HBO Max and Discovery Plus complement each other by appealing to different demographics . Now that they're combined, the new service has the potential to attract a wider range of subscribers by offering all of HBO Max's scripted content and Discovery Plus' unscripted titles .
Can I watch movies in 4K on Max?
HBO Max previously offered a limited selection of 4K titles through its ad-free plan ($16/month), but new Max subscribers now need the Ultimate plan to get 4K support ($20/month). If you signed up for HBO Max's ad-free plan before May 23, 2023, you still received 4K streaming for six months but now need to switch to continue.
Though 4K support is now more expensive, Warner Bros. Discovery has expanded Max's library of 4K content as part of the rebranding. At launch, Max had more than 1,000 movies and TV episodes in 4K, which is almost eight times the amount of 4K content that was on HBO Max. Many 4K titles also support HDR (high dynamic range) using the HDR10 and Dolby Vision formats.
Some notable titles in 4K on Max include " The Last of Us ," " Game of Thrones ," the " Harry Potter " films, and classics like "The Wizard of Oz" and "Goodfellas." You can find a full list of 4K titles and supported 4K streaming devices on Max's website.
Like HBO Max, Max includes access to new and classic HBO shows, from " The Last of Us " and "The Sopranos" to " Succession " and " House of the Dragon ." On top of that, Max offers content from Discovery Plus, additional movies and shows from the Warner Bros. Discovery catalog, and brand-new originals .
Warner Bros. will also bring all of its new theatrical releases to Max after they play on the big screen. Some notable movies on Max right now include "Barbie," "Shazam: Fury of the Gods," "Blue Beetle," " The Menu ," " The Batman ," " Black Adam ," " Don't Worry Darling ," and " Elvis ."
Meanwhile, some popular Max original series you can stream right now include hit shows like:
- The White Lotus
- " Peacemaker "
- " Our Flag Means Death "
- " Doom Patrol "
- " Tokyo Vice "
Beyond original programs, the catalog offers a wide range of TV series from Discovery, HGTV, TLC, DC, Cartoon Network, CNN, and Adult Swim. The Max movie catalog also incorporates critically acclaimed films from TCM, Criterion Collection, and Studio Ghibli, alongside hundreds of blockbuster Warner Bros. movies.
The Max catalog is not permanent, however, and the service is known for removing content with little warning. For example, recent cost-cutting measures led to the removal of shows like " Westworld " and shorts from the "Looney Tunes" franchise.
You can purchase logo and accolade licensing to this story here . Disclosure: Written and researched by the Insider Reviews team. We highlight products and services you might find interesting. If you buy them, we may get a small share of the revenue from the sale from our partners. We may receive products free of charge from manufacturers to test. This does not drive our decision as to whether or not a product is featured or recommended. We operate independently from our advertising team. We welcome your feedback. Email us at [email protected] .

- Main content
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing. A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all ...
Write the Executive Summary. This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what's in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company. Add a Company Overview. Document the larger company mission and vision.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
1. Acts as an introduction. The table of contents is placed before all the sections of a business plan. This will help the reader get a good look at the contents before diving into the details. Primarily, it introduces the reader to your business plan. In other words, a table of contents acts as an executive summary of the entire document.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
A business plan includes the cost of organizing the business, the anticipated sources of revenue, how the products and services are customer oriented, and anticipated profit margins. Business plans serve two main purposes. First, they are a guide business owners use to streamline management and planning/organization of the business.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page. The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions. A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
Step 2: Do your market research homework. The next step in writing a business plan is to conduct market research. This involves gathering information about your target market (or customer persona), your competition, and the industry as a whole. You can use a variety of research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and online research to ...
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea. The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template.
If you want to gain the financial autonomy to run a business or become an entrepreneur, a financial advisor can help align your finances. 1. Executive Summary. Your executive summary should appear first in your business plan. It should summarize what you expect your business to accomplish.
It's the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you'll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance. A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and ...
Download Simple Business Plan Outline Template. Word | PDF. Use this simple business plan outline as a basis to create your own business plan. This template contains 11 sections, including a title page and a table of contents, which details what each section should cover in a traditional business plan.
This section of your content strategy plan outlines the steps for producing content, from idea generation to publication. This process includes assigning roles and responsibilities to other team members or freelancers. Pro tip: Develop a content calendar to plan and schedule content in advance. Use collaboration tools to streamline the content ...
Effective business plans contain several key components that cover various aspects of a company's goals. The most important parts of a business plan include: 1. Executive summary. The executive summary is the first and one of the most critical parts of a business plan. This summary provides an overview of the business plan as a whole and ...
It takes careful planning, strategic thinking, and a solid business plan. Luckily, ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Content Creators has got you covered! With this template, you can: Strategically outline your goals, target audience, and content strategy to stay focused and on track. Develop a monetization plan that aligns with your brand ...
1. Executive summary. This short section introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, development goals, and why it will succeed. If you are seeking funding, summarise the basics of the financial plan. 2.
How to create a winning content plan. Step 1: Plan themes for your content. Step 2: Brainstorm campaign and post ideas. Step 3: Decide when you will post. Step 4: Decide on your content mix. Step 5: Assign responsibilities. Step 6: Write post captions. Step 7: Create (or source) design assets.
Let's go through the content of each section in more detail! 1. The executive summary. In your content marketing agency's business plan, the first section is the executive summary — a captivating overview of your plan that aims to pique the reader's interest and leave them eager to learn more about your business.
Let's dive into our selection of table of content examples. Category #1: Table of Contents for Business Plans. Business Plans are documents that showcase a specific plan for a business. It can be an overarching plan or a particular project plan. These include pages like goals, projections and timelines.
2. Come up With Ideas for High-Performing Content. The ideation stage or the "what" is one of the most important and time-consuming aspects of creating a content plan. But, you can use your research and analysis to come up with the content ideas that are most likely to perform well.
Content Plan Sample Template. Use this content plan template to organize and prioritize potential topics by theme or by any category that suits your needs. Provide a brief summary of a topic, identify the content's unique angle, pinpoint your target reader, decide which types of content you'll need, and describe your main goal.
DETROIT — General Motors and real estate firm Bedrock will jointly study how to redevelop the automaker's huge headquarters tower complex in downtown Detroit, a person briefed on the plans said.
Apr 15, 2024. A new dual-branded hotel is slated to break ground in May at the USAA campus and master-planned Norterra community in Phoenix. A partnership with Texas-based Jackson-Shaw Co. and ...
This year's business plan continues to be structured around the PRA's four strategic priorities, as set out in its 2023/24 Business Plan. The PRA's strategic priorities for 2024/25 will remain unchanged because the PRA updated its priorities in 2023 to take account of its new powers, new secondary objective, and expanded role brought ...
CCBC Center for Business Innovation's 11th Annual Business Plan Competition awards $62,500 in prize money to aspiring entrepreneurs. Community College of Baltimore County's Center for Business Innovation hosted its 11th Annual Business Plan Competition Virtual Awards Ceremony on Monday, Feb. 5, 2024. The event featured the top nine pitches ...
HBO Max previously offered a limited selection of 4K titles through its ad-free plan ($16/month), but new Max subscribers now need the Ultimate plan to get 4K support ($20/month). If you signed up ...
April 10, 2024 at 9:17 AM PDT. Listen. 2:09. Barings laid out a plan to rebuild its direct-lending team after one of the largest asset management raids in years, according to people with knowledge ...