Literature Searching


Literature Searching vs. Literature Review
You may hear about conducting a literature search and literature review inter-changeably. In general, a literature search is the process of seeking out and identifying the existing literature related to a topic or question of interest, while a literature review is the organized synthesis of the information found in the existing literature.
In research, a literature search is typically the first step of a literature review. The search identifies relevant existing studies and articles, and the review is the end result of analyzing, synthesizing, and organizing the information found in the search.
When writing a research paper, the literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Show how your research addresses a knowledge gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
References/Additional Resources
Baker, J. D. (2016). T he Purpose, Process, and Methods of Writing a Literature Review . AORN Journal, 103(3), 265–269.
Patrick, L. J., & Munro, S. (2004). The Literature Review: Demystifying the Literature Search. The Diabetes Educator, 30(1), 30–38.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Major Steps in a Literature Search >>
Literature Review vs Systematic Review
- Literature Review vs. Systematic Review
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources
- Databases and Articles
- Specific Journal or Article
Subject Guide

Definitions
It’s common to confuse systematic and literature reviews because both are used to provide a summary of the existent literature or research on a specific topic. Regardless of this commonality, both types of review vary significantly. The following table provides a detailed explanation as well as the differences between systematic and literature reviews.
Kysh, Lynn (2013): Difference between a systematic review and a literature review. [figshare]. Available at: http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.766364
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Primary vs. Secondary Sources >>
- Last Updated: Dec 15, 2023 10:19 AM
- URL: https://libguides.sjsu.edu/LitRevVSSysRev
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
Research Methods
- Getting Started
- Literature Review Research
- Research Design
- Research Design By Discipline
- SAGE Research Methods
- Teaching with SAGE Research Methods
Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- What is NOT a Literature Review?
- Purposes of a Literature Review
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Literature Reviews vs. Systematic Reviews
- Systematic vs. Meta-Analysis
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.
Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
- Summarizes and analyzes previous research relevant to a topic
- Includes scholarly books and articles published in academic journals
- Can be an specific scholarly paper or a section in a research paper
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic
- Help gather ideas or information
- Keep up to date in current trends and findings
- Help develop new questions
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Helps focus your own research questions or problems
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Suggests unexplored ideas or populations
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
- Identifies critical gaps, points of disagreement, or potentially flawed methodology or theoretical approaches.
- Indicates potential directions for future research.
All content in this section is from Literature Review Research from Old Dominion University
Keep in mind the following, a literature review is NOT:
Not an essay
Not an annotated bibliography in which you summarize each article that you have reviewed. A literature review goes beyond basic summarizing to focus on the critical analysis of the reviewed works and their relationship to your research question.
Not a research paper where you select resources to support one side of an issue versus another. A lit review should explain and consider all sides of an argument in order to avoid bias, and areas of agreement and disagreement should be highlighted.
A literature review serves several purposes. For example, it
- provides thorough knowledge of previous studies; introduces seminal works.
- helps focus one’s own research topic.
- identifies a conceptual framework for one’s own research questions or problems; indicates potential directions for future research.
- suggests previously unused or underused methodologies, designs, quantitative and qualitative strategies.
- identifies gaps in previous studies; identifies flawed methodologies and/or theoretical approaches; avoids replication of mistakes.
- helps the researcher avoid repetition of earlier research.
- suggests unexplored populations.
- determines whether past studies agree or disagree; identifies controversy in the literature.
- tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
As Kennedy (2007) notes*, it is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the original studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally that become part of the lore of field. In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews.
Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are several approaches to how they can be done, depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study. Listed below are definitions of types of literature reviews:
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply imbedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews.
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical reviews are focused on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [content], but how they said it [method of analysis]. This approach provides a framework of understanding at different levels (i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches and data collection and analysis techniques), enables researchers to draw on a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection and data analysis, and helps highlight many ethical issues which we should be aware of and consider as we go through our study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyse data from the studies that are included in the review. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?"
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to concretely examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review help establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
* Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147.
All content in this section is from The Literature Review created by Dr. Robert Larabee USC
Robinson, P. and Lowe, J. (2015), Literature reviews vs systematic reviews. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health, 39: 103-103. doi: 10.1111/1753-6405.12393

What's in the name? The difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review, and why it matters . By Lynn Kysh from University of Southern California

Systematic review or meta-analysis?
A systematic review answers a defined research question by collecting and summarizing all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria.
A meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of these studies.
Systematic reviews, just like other research articles, can be of varying quality. They are a significant piece of work (the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination at York estimates that a team will take 9-24 months), and to be useful to other researchers and practitioners they should have:
- clearly stated objectives with pre-defined eligibility criteria for studies
- explicit, reproducible methodology
- a systematic search that attempts to identify all studies
- assessment of the validity of the findings of the included studies (e.g. risk of bias)
- systematic presentation, and synthesis, of the characteristics and findings of the included studies
Not all systematic reviews contain meta-analysis.
Meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects of health care than those derived from the individual studies included within a review. More information on meta-analyses can be found in Cochrane Handbook, Chapter 9 .
A meta-analysis goes beyond critique and integration and conducts secondary statistical analysis on the outcomes of similar studies. It is a systematic review that uses quantitative methods to synthesize and summarize the results.
An advantage of a meta-analysis is the ability to be completely objective in evaluating research findings. Not all topics, however, have sufficient research evidence to allow a meta-analysis to be conducted. In that case, an integrative review is an appropriate strategy.
Some of the content in this section is from Systematic reviews and meta-analyses: step by step guide created by Kate McAllister.
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Research Design >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 4:07 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/researchmethods
- Open access
- Published: 14 August 2018
Defining the process to literature searching in systematic reviews: a literature review of guidance and supporting studies
- Chris Cooper ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0864-5607 1 ,
- Andrew Booth 2 ,
- Jo Varley-Campbell 1 ,
- Nicky Britten 3 &
- Ruth Garside 4
BMC Medical Research Methodology volume 18 , Article number: 85 ( 2018 ) Cite this article
203k Accesses
207 Citations
118 Altmetric
Metrics details
Systematic literature searching is recognised as a critical component of the systematic review process. It involves a systematic search for studies and aims for a transparent report of study identification, leaving readers clear about what was done to identify studies, and how the findings of the review are situated in the relevant evidence.
Information specialists and review teams appear to work from a shared and tacit model of the literature search process. How this tacit model has developed and evolved is unclear, and it has not been explicitly examined before.
The purpose of this review is to determine if a shared model of the literature searching process can be detected across systematic review guidance documents and, if so, how this process is reported in the guidance and supported by published studies.
A literature review.
Two types of literature were reviewed: guidance and published studies. Nine guidance documents were identified, including: The Cochrane and Campbell Handbooks. Published studies were identified through ‘pearl growing’, citation chasing, a search of PubMed using the systematic review methods filter, and the authors’ topic knowledge.
The relevant sections within each guidance document were then read and re-read, with the aim of determining key methodological stages. Methodological stages were identified and defined. This data was reviewed to identify agreements and areas of unique guidance between guidance documents. Consensus across multiple guidance documents was used to inform selection of ‘key stages’ in the process of literature searching.
Eight key stages were determined relating specifically to literature searching in systematic reviews. They were: who should literature search, aims and purpose of literature searching, preparation, the search strategy, searching databases, supplementary searching, managing references and reporting the search process.
Conclusions
Eight key stages to the process of literature searching in systematic reviews were identified. These key stages are consistently reported in the nine guidance documents, suggesting consensus on the key stages of literature searching, and therefore the process of literature searching as a whole, in systematic reviews. Further research to determine the suitability of using the same process of literature searching for all types of systematic review is indicated.
Peer Review reports
Systematic literature searching is recognised as a critical component of the systematic review process. It involves a systematic search for studies and aims for a transparent report of study identification, leaving review stakeholders clear about what was done to identify studies, and how the findings of the review are situated in the relevant evidence.
Information specialists and review teams appear to work from a shared and tacit model of the literature search process. How this tacit model has developed and evolved is unclear, and it has not been explicitly examined before. This is in contrast to the information science literature, which has developed information processing models as an explicit basis for dialogue and empirical testing. Without an explicit model, research in the process of systematic literature searching will remain immature and potentially uneven, and the development of shared information models will be assumed but never articulated.
One way of developing such a conceptual model is by formally examining the implicit “programme theory” as embodied in key methodological texts. The aim of this review is therefore to determine if a shared model of the literature searching process in systematic reviews can be detected across guidance documents and, if so, how this process is reported and supported.
Identifying guidance
Key texts (henceforth referred to as “guidance”) were identified based upon their accessibility to, and prominence within, United Kingdom systematic reviewing practice. The United Kingdom occupies a prominent position in the science of health information retrieval, as quantified by such objective measures as the authorship of papers, the number of Cochrane groups based in the UK, membership and leadership of groups such as the Cochrane Information Retrieval Methods Group, the HTA-I Information Specialists’ Group and historic association with such centres as the UK Cochrane Centre, the NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, the Centre for Evidence Based Medicine and the National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE). Coupled with the linguistic dominance of English within medical and health science and the science of systematic reviews more generally, this offers a justification for a purposive sample that favours UK, European and Australian guidance documents.
Nine guidance documents were identified. These documents provide guidance for different types of reviews, namely: reviews of interventions, reviews of health technologies, reviews of qualitative research studies, reviews of social science topics, and reviews to inform guidance.
Whilst these guidance documents occasionally offer additional guidance on other types of systematic reviews, we have focused on the core and stated aims of these documents as they relate to literature searching. Table 1 sets out: the guidance document, the version audited, their core stated focus, and a bibliographical pointer to the main guidance relating to literature searching.
Once a list of key guidance documents was determined, it was checked by six senior information professionals based in the UK for relevance to current literature searching in systematic reviews.
Identifying supporting studies
In addition to identifying guidance, the authors sought to populate an evidence base of supporting studies (henceforth referred to as “studies”) that contribute to existing search practice. Studies were first identified by the authors from their knowledge on this topic area and, subsequently, through systematic citation chasing key studies (‘pearls’ [ 1 ]) located within each key stage of the search process. These studies are identified in Additional file 1 : Appendix Table 1. Citation chasing was conducted by analysing the bibliography of references for each study (backwards citation chasing) and through Google Scholar (forward citation chasing). A search of PubMed using the systematic review methods filter was undertaken in August 2017 (see Additional file 1 ). The search terms used were: (literature search*[Title/Abstract]) AND sysrev_methods[sb] and 586 results were returned. These results were sifted for relevance to the key stages in Fig. 1 by CC.
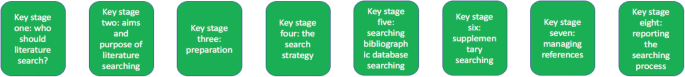
The key stages of literature search guidance as identified from nine key texts
Extracting the data
To reveal the implicit process of literature searching within each guidance document, the relevant sections (chapters) on literature searching were read and re-read, with the aim of determining key methodological stages. We defined a key methodological stage as a distinct step in the overall process for which specific guidance is reported, and action is taken, that collectively would result in a completed literature search.
The chapter or section sub-heading for each methodological stage was extracted into a table using the exact language as reported in each guidance document. The lead author (CC) then read and re-read these data, and the paragraphs of the document to which the headings referred, summarising section details. This table was then reviewed, using comparison and contrast to identify agreements and areas of unique guidance. Consensus across multiple guidelines was used to inform selection of ‘key stages’ in the process of literature searching.
Having determined the key stages to literature searching, we then read and re-read the sections relating to literature searching again, extracting specific detail relating to the methodological process of literature searching within each key stage. Again, the guidance was then read and re-read, first on a document-by-document-basis and, secondly, across all the documents above, to identify both commonalities and areas of unique guidance.
Results and discussion
Our findings.
We were able to identify consensus across the guidance on literature searching for systematic reviews suggesting a shared implicit model within the information retrieval community. Whilst the structure of the guidance varies between documents, the same key stages are reported, even where the core focus of each document is different. We were able to identify specific areas of unique guidance, where a document reported guidance not summarised in other documents, together with areas of consensus across guidance.
Unique guidance
Only one document provided guidance on the topic of when to stop searching [ 2 ]. This guidance from 2005 anticipates a topic of increasing importance with the current interest in time-limited (i.e. “rapid”) reviews. Quality assurance (or peer review) of literature searches was only covered in two guidance documents [ 3 , 4 ]. This topic has emerged as increasingly important as indicated by the development of the PRESS instrument [ 5 ]. Text mining was discussed in four guidance documents [ 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 ] where the automation of some manual review work may offer efficiencies in literature searching [ 8 ].
Agreement between guidance: Defining the key stages of literature searching
Where there was agreement on the process, we determined that this constituted a key stage in the process of literature searching to inform systematic reviews.
From the guidance, we determined eight key stages that relate specifically to literature searching in systematic reviews. These are summarised at Fig. 1 . The data extraction table to inform Fig. 1 is reported in Table 2 . Table 2 reports the areas of common agreement and it demonstrates that the language used to describe key stages and processes varies significantly between guidance documents.
For each key stage, we set out the specific guidance, followed by discussion on how this guidance is situated within the wider literature.
Key stage one: Deciding who should undertake the literature search
The guidance.
Eight documents provided guidance on who should undertake literature searching in systematic reviews [ 2 , 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ]. The guidance affirms that people with relevant expertise of literature searching should ‘ideally’ be included within the review team [ 6 ]. Information specialists (or information scientists), librarians or trial search co-ordinators (TSCs) are indicated as appropriate researchers in six guidance documents [ 2 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ].
How the guidance corresponds to the published studies
The guidance is consistent with studies that call for the involvement of information specialists and librarians in systematic reviews [ 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 ] and which demonstrate how their training as ‘expert searchers’ and ‘analysers and organisers of data’ can be put to good use [ 13 ] in a variety of roles [ 12 , 16 , 20 , 21 , 24 , 25 , 26 ]. These arguments make sense in the context of the aims and purposes of literature searching in systematic reviews, explored below. The need for ‘thorough’ and ‘replicable’ literature searches was fundamental to the guidance and recurs in key stage two. Studies have found poor reporting, and a lack of replicable literature searches, to be a weakness in systematic reviews [ 17 , 18 , 27 , 28 ] and they argue that involvement of information specialists/ librarians would be associated with better reporting and better quality literature searching. Indeed, Meert et al. [ 29 ] demonstrated that involving a librarian as a co-author to a systematic review correlated with a higher score in the literature searching component of a systematic review [ 29 ]. As ‘new styles’ of rapid and scoping reviews emerge, where decisions on how to search are more iterative and creative, a clear role is made here too [ 30 ].
Knowing where to search for studies was noted as important in the guidance, with no agreement as to the appropriate number of databases to be searched [ 2 , 6 ]. Database (and resource selection more broadly) is acknowledged as a relevant key skill of information specialists and librarians [ 12 , 15 , 16 , 31 ].
Whilst arguments for including information specialists and librarians in the process of systematic review might be considered self-evident, Koffel and Rethlefsen [ 31 ] have questioned if the necessary involvement is actually happening [ 31 ].
Key stage two: Determining the aim and purpose of a literature search
The aim: Five of the nine guidance documents use adjectives such as ‘thorough’, ‘comprehensive’, ‘transparent’ and ‘reproducible’ to define the aim of literature searching [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ]. Analogous phrases were present in a further three guidance documents, namely: ‘to identify the best available evidence’ [ 4 ] or ‘the aim of the literature search is not to retrieve everything. It is to retrieve everything of relevance’ [ 2 ] or ‘A systematic literature search aims to identify all publications relevant to the particular research question’ [ 3 ]. The Joanna Briggs Institute reviewers’ manual was the only guidance document where a clear statement on the aim of literature searching could not be identified. The purpose of literature searching was defined in three guidance documents, namely to minimise bias in the resultant review [ 6 , 8 , 10 ]. Accordingly, eight of nine documents clearly asserted that thorough and comprehensive literature searches are required as a potential mechanism for minimising bias.
The need for thorough and comprehensive literature searches appears as uniform within the eight guidance documents that describe approaches to literature searching in systematic reviews of effectiveness. Reviews of effectiveness (of intervention or cost), accuracy and prognosis, require thorough and comprehensive literature searches to transparently produce a reliable estimate of intervention effect. The belief that all relevant studies have been ‘comprehensively’ identified, and that this process has been ‘transparently’ reported, increases confidence in the estimate of effect and the conclusions that can be drawn [ 32 ]. The supporting literature exploring the need for comprehensive literature searches focuses almost exclusively on reviews of intervention effectiveness and meta-analysis. Different ‘styles’ of review may have different standards however; the alternative, offered by purposive sampling, has been suggested in the specific context of qualitative evidence syntheses [ 33 ].
What is a comprehensive literature search?
Whilst the guidance calls for thorough and comprehensive literature searches, it lacks clarity on what constitutes a thorough and comprehensive literature search, beyond the implication that all of the literature search methods in Table 2 should be used to identify studies. Egger et al. [ 34 ], in an empirical study evaluating the importance of comprehensive literature searches for trials in systematic reviews, defined a comprehensive search for trials as:
a search not restricted to English language;
where Cochrane CENTRAL or at least two other electronic databases had been searched (such as MEDLINE or EMBASE); and
at least one of the following search methods has been used to identify unpublished trials: searches for (I) conference abstracts, (ii) theses, (iii) trials registers; and (iv) contacts with experts in the field [ 34 ].
Tricco et al. (2008) used a similar threshold of bibliographic database searching AND a supplementary search method in a review when examining the risk of bias in systematic reviews. Their criteria were: one database (limited using the Cochrane Highly Sensitive Search Strategy (HSSS)) and handsearching [ 35 ].
Together with the guidance, this would suggest that comprehensive literature searching requires the use of BOTH bibliographic database searching AND supplementary search methods.
Comprehensiveness in literature searching, in the sense of how much searching should be undertaken, remains unclear. Egger et al. recommend that ‘investigators should consider the type of literature search and degree of comprehension that is appropriate for the review in question, taking into account budget and time constraints’ [ 34 ]. This view tallies with the Cochrane Handbook, which stipulates clearly, that study identification should be undertaken ‘within resource limits’ [ 9 ]. This would suggest that the limitations to comprehension are recognised but it raises questions on how this is decided and reported [ 36 ].
What is the point of comprehensive literature searching?
The purpose of thorough and comprehensive literature searches is to avoid missing key studies and to minimize bias [ 6 , 8 , 10 , 34 , 37 , 38 , 39 ] since a systematic review based only on published (or easily accessible) studies may have an exaggerated effect size [ 35 ]. Felson (1992) sets out potential biases that could affect the estimate of effect in a meta-analysis [ 40 ] and Tricco et al. summarize the evidence concerning bias and confounding in systematic reviews [ 35 ]. Egger et al. point to non-publication of studies, publication bias, language bias and MEDLINE bias, as key biases [ 34 , 35 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 ]. Comprehensive searches are not the sole factor to mitigate these biases but their contribution is thought to be significant [ 2 , 32 , 34 ]. Fehrmann (2011) suggests that ‘the search process being described in detail’ and that, where standard comprehensive search techniques have been applied, increases confidence in the search results [ 32 ].
Does comprehensive literature searching work?
Egger et al., and other study authors, have demonstrated a change in the estimate of intervention effectiveness where relevant studies were excluded from meta-analysis [ 34 , 47 ]. This would suggest that missing studies in literature searching alters the reliability of effectiveness estimates. This is an argument for comprehensive literature searching. Conversely, Egger et al. found that ‘comprehensive’ searches still missed studies and that comprehensive searches could, in fact, introduce bias into a review rather than preventing it, through the identification of low quality studies then being included in the meta-analysis [ 34 ]. Studies query if identifying and including low quality or grey literature studies changes the estimate of effect [ 43 , 48 ] and question if time is better invested updating systematic reviews rather than searching for unpublished studies [ 49 ], or mapping studies for review as opposed to aiming for high sensitivity in literature searching [ 50 ].
Aim and purpose beyond reviews of effectiveness
The need for comprehensive literature searches is less certain in reviews of qualitative studies, and for reviews where a comprehensive identification of studies is difficult to achieve (for example, in Public health) [ 33 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 ]. Literature searching for qualitative studies, and in public health topics, typically generates a greater number of studies to sift than in reviews of effectiveness [ 39 ] and demonstrating the ‘value’ of studies identified or missed is harder [ 56 ], since the study data do not typically support meta-analysis. Nussbaumer-Streit et al. (2016) have registered a review protocol to assess whether abbreviated literature searches (as opposed to comprehensive literature searches) has an impact on conclusions across multiple bodies of evidence, not only on effect estimates [ 57 ] which may develop this understanding. It may be that decision makers and users of systematic reviews are willing to trade the certainty from a comprehensive literature search and systematic review in exchange for different approaches to evidence synthesis [ 58 ], and that comprehensive literature searches are not necessarily a marker of literature search quality, as previously thought [ 36 ]. Different approaches to literature searching [ 37 , 38 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 ] and developing the concept of when to stop searching are important areas for further study [ 36 , 59 ].
The study by Nussbaumer-Streit et al. has been published since the submission of this literature review [ 63 ]. Nussbaumer-Streit et al. (2018) conclude that abbreviated literature searches are viable options for rapid evidence syntheses, if decision-makers are willing to trade the certainty from a comprehensive literature search and systematic review, but that decision-making which demands detailed scrutiny should still be based on comprehensive literature searches [ 63 ].
Key stage three: Preparing for the literature search
Six documents provided guidance on preparing for a literature search [ 2 , 3 , 6 , 7 , 9 , 10 ]. The Cochrane Handbook clearly stated that Cochrane authors (i.e. researchers) should seek advice from a trial search co-ordinator (i.e. a person with specific skills in literature searching) ‘before’ starting a literature search [ 9 ].
Two key tasks were perceptible in preparing for a literature searching [ 2 , 6 , 7 , 10 , 11 ]. First, to determine if there are any existing or on-going reviews, or if a new review is justified [ 6 , 11 ]; and, secondly, to develop an initial literature search strategy to estimate the volume of relevant literature (and quality of a small sample of relevant studies [ 10 ]) and indicate the resources required for literature searching and the review of the studies that follows [ 7 , 10 ].
Three documents summarised guidance on where to search to determine if a new review was justified [ 2 , 6 , 11 ]. These focused on searching databases of systematic reviews (The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR) and the Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE)), institutional registries (including PROSPERO), and MEDLINE [ 6 , 11 ]. It is worth noting, however, that as of 2015, DARE (and NHS EEDs) are no longer being updated and so the relevance of this (these) resource(s) will diminish over-time [ 64 ]. One guidance document, ‘Systematic reviews in the Social Sciences’, noted, however, that databases are not the only source of information and unpublished reports, conference proceeding and grey literature may also be required, depending on the nature of the review question [ 2 ].
Two documents reported clearly that this preparation (or ‘scoping’) exercise should be undertaken before the actual search strategy is developed [ 7 , 10 ]).
The guidance offers the best available source on preparing the literature search with the published studies not typically reporting how their scoping informed the development of their search strategies nor how their search approaches were developed. Text mining has been proposed as a technique to develop search strategies in the scoping stages of a review although this work is still exploratory [ 65 ]. ‘Clustering documents’ and word frequency analysis have also been tested to identify search terms and studies for review [ 66 , 67 ]. Preparing for literature searches and scoping constitutes an area for future research.
Key stage four: Designing the search strategy
The Population, Intervention, Comparator, Outcome (PICO) structure was the commonly reported structure promoted to design a literature search strategy. Five documents suggested that the eligibility criteria or review question will determine which concepts of PICO will be populated to develop the search strategy [ 1 , 4 , 7 , 8 , 9 ]. The NICE handbook promoted multiple structures, namely PICO, SPICE (Setting, Perspective, Intervention, Comparison, Evaluation) and multi-stranded approaches [ 4 ].
With the exclusion of The Joanna Briggs Institute reviewers’ manual, the guidance offered detail on selecting key search terms, synonyms, Boolean language, selecting database indexing terms and combining search terms. The CEE handbook suggested that ‘search terms may be compiled with the help of the commissioning organisation and stakeholders’ [ 10 ].
The use of limits, such as language or date limits, were discussed in all documents [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ].
Search strategy structure
The guidance typically relates to reviews of intervention effectiveness so PICO – with its focus on intervention and comparator - is the dominant model used to structure literature search strategies [ 68 ]. PICOs – where the S denotes study design - is also commonly used in effectiveness reviews [ 6 , 68 ]. As the NICE handbook notes, alternative models to structure literature search strategies have been developed and tested. Booth provides an overview on formulating questions for evidence based practice [ 69 ] and has developed a number of alternatives to the PICO structure, namely: BeHEMoTh (Behaviour of interest; Health context; Exclusions; Models or Theories) for use when systematically identifying theory [ 55 ]; SPICE (Setting, Perspective, Intervention, Comparison, Evaluation) for identification of social science and evaluation studies [ 69 ] and, working with Cooke and colleagues, SPIDER (Sample, Phenomenon of Interest, Design, Evaluation, Research type) [ 70 ]. SPIDER has been compared to PICO and PICOs in a study by Methley et al. [ 68 ].
The NICE handbook also suggests the use of multi-stranded approaches to developing literature search strategies [ 4 ]. Glanville developed this idea in a study by Whitting et al. [ 71 ] and a worked example of this approach is included in the development of a search filter by Cooper et al. [ 72 ].
Writing search strategies: Conceptual and objective approaches
Hausner et al. [ 73 ] provide guidance on writing literature search strategies, delineating between conceptually and objectively derived approaches. The conceptual approach, advocated by and explained in the guidance documents, relies on the expertise of the literature searcher to identify key search terms and then develop key terms to include synonyms and controlled syntax. Hausner and colleagues set out the objective approach [ 73 ] and describe what may be done to validate it [ 74 ].
The use of limits
The guidance documents offer direction on the use of limits within a literature search. Limits can be used to focus literature searching to specific study designs or by other markers (such as by date) which limits the number of studies returned by a literature search. The use of limits should be described and the implications explored [ 34 ] since limiting literature searching can introduce bias (explored above). Craven et al. have suggested the use of a supporting narrative to explain decisions made in the process of developing literature searches and this advice would usefully capture decisions on the use of search limits [ 75 ].
Key stage five: Determining the process of literature searching and deciding where to search (bibliographic database searching)
Table 2 summarises the process of literature searching as reported in each guidance document. Searching bibliographic databases was consistently reported as the ‘first step’ to literature searching in all nine guidance documents.
Three documents reported specific guidance on where to search, in each case specific to the type of review their guidance informed, and as a minimum requirement [ 4 , 9 , 11 ]. Seven of the key guidance documents suggest that the selection of bibliographic databases depends on the topic of review [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 10 ], with two documents noting the absence of an agreed standard on what constitutes an acceptable number of databases searched [ 2 , 6 ].
The guidance documents summarise ‘how to’ search bibliographic databases in detail and this guidance is further contextualised above in terms of developing the search strategy. The documents provide guidance of selecting bibliographic databases, in some cases stating acceptable minima (i.e. The Cochrane Handbook states Cochrane CENTRAL, MEDLINE and EMBASE), and in other cases simply listing bibliographic database available to search. Studies have explored the value in searching specific bibliographic databases, with Wright et al. (2015) noting the contribution of CINAHL in identifying qualitative studies [ 76 ], Beckles et al. (2013) questioning the contribution of CINAHL to identifying clinical studies for guideline development [ 77 ], and Cooper et al. (2015) exploring the role of UK-focused bibliographic databases to identify UK-relevant studies [ 78 ]. The host of the database (e.g. OVID or ProQuest) has been shown to alter the search returns offered. Younger and Boddy [ 79 ] report differing search returns from the same database (AMED) but where the ‘host’ was different [ 79 ].
The average number of bibliographic database searched in systematic reviews has risen in the period 1994–2014 (from 1 to 4) [ 80 ] but there remains (as attested to by the guidance) no consensus on what constitutes an acceptable number of databases searched [ 48 ]. This is perhaps because thinking about the number of databases searched is the wrong question, researchers should be focused on which databases were searched and why, and which databases were not searched and why. The discussion should re-orientate to the differential value of sources but researchers need to think about how to report this in studies to allow findings to be generalised. Bethel (2017) has proposed ‘search summaries’, completed by the literature searcher, to record where included studies were identified, whether from database (and which databases specifically) or supplementary search methods [ 81 ]. Search summaries document both yield and accuracy of searches, which could prospectively inform resource use and decisions to search or not to search specific databases in topic areas. The prospective use of such data presupposes, however, that past searches are a potential predictor of future search performance (i.e. that each topic is to be considered representative and not unique). In offering a body of practice, this data would be of greater practicable use than current studies which are considered as little more than individual case studies [ 82 , 83 , 84 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 88 , 89 , 90 ].
When to database search is another question posed in the literature. Beyer et al. [ 91 ] report that databases can be prioritised for literature searching which, whilst not addressing the question of which databases to search, may at least bring clarity as to which databases to search first [ 91 ]. Paradoxically, this links to studies that suggest PubMed should be searched in addition to MEDLINE (OVID interface) since this improves the currency of systematic reviews [ 92 , 93 ]. Cooper et al. (2017) have tested the idea of database searching not as a primary search method (as suggested in the guidance) but as a supplementary search method in order to manage the volume of studies identified for an environmental effectiveness systematic review. Their case study compared the effectiveness of database searching versus a protocol using supplementary search methods and found that the latter identified more relevant studies for review than searching bibliographic databases [ 94 ].
Key stage six: Determining the process of literature searching and deciding where to search (supplementary search methods)
Table 2 also summaries the process of literature searching which follows bibliographic database searching. As Table 2 sets out, guidance that supplementary literature search methods should be used in systematic reviews recurs across documents, but the order in which these methods are used, and the extent to which they are used, varies. We noted inconsistency in the labelling of supplementary search methods between guidance documents.
Rather than focus on the guidance on how to use the methods (which has been summarised in a recent review [ 95 ]), we focus on the aim or purpose of supplementary search methods.
The Cochrane Handbook reported that ‘efforts’ to identify unpublished studies should be made [ 9 ]. Four guidance documents [ 2 , 3 , 6 , 9 ] acknowledged that searching beyond bibliographic databases was necessary since ‘databases are not the only source of literature’ [ 2 ]. Only one document reported any guidance on determining when to use supplementary methods. The IQWiG handbook reported that the use of handsearching (in their example) could be determined on a ‘case-by-case basis’ which implies that the use of these methods is optional rather than mandatory. This is in contrast to the guidance (above) on bibliographic database searching.
The issue for supplementary search methods is similar in many ways to the issue of searching bibliographic databases: demonstrating value. The purpose and contribution of supplementary search methods in systematic reviews is increasingly acknowledged [ 37 , 61 , 62 , 96 , 97 , 98 , 99 , 100 , 101 ] but understanding the value of the search methods to identify studies and data is unclear. In a recently published review, Cooper et al. (2017) reviewed the literature on supplementary search methods looking to determine the advantages, disadvantages and resource implications of using supplementary search methods [ 95 ]. This review also summarises the key guidance and empirical studies and seeks to address the question on when to use these search methods and when not to [ 95 ]. The guidance is limited in this regard and, as Table 2 demonstrates, offers conflicting advice on the order of searching, and the extent to which these search methods should be used in systematic reviews.
Key stage seven: Managing the references
Five of the documents provided guidance on managing references, for example downloading, de-duplicating and managing the output of literature searches [ 2 , 4 , 6 , 8 , 10 ]. This guidance typically itemised available bibliographic management tools rather than offering guidance on how to use them specifically [ 2 , 4 , 6 , 8 ]. The CEE handbook provided guidance on importing data where no direct export option is available (e.g. web-searching) [ 10 ].
The literature on using bibliographic management tools is not large relative to the number of ‘how to’ videos on platforms such as YouTube (see for example [ 102 ]). These YouTube videos confirm the overall lack of ‘how to’ guidance identified in this study and offer useful instruction on managing references. Bramer et al. set out methods for de-duplicating data and reviewing references in Endnote [ 103 , 104 ] and Gall tests the direct search function within Endnote to access databases such as PubMed, finding a number of limitations [ 105 ]. Coar et al. and Ahmed et al. consider the role of the free-source tool, Zotero [ 106 , 107 ]. Managing references is a key administrative function in the process of review particularly for documenting searches in PRISMA guidance.
Key stage eight: Documenting the search
The Cochrane Handbook was the only guidance document to recommend a specific reporting guideline: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [ 9 ]. Six documents provided guidance on reporting the process of literature searching with specific criteria to report [ 3 , 4 , 6 , 8 , 9 , 10 ]. There was consensus on reporting: the databases searched (and the host searched by), the search strategies used, and any use of limits (e.g. date, language, search filters (The CRD handbook called for these limits to be justified [ 6 ])). Three guidance documents reported that the number of studies identified should be recorded [ 3 , 6 , 10 ]. The number of duplicates identified [ 10 ], the screening decisions [ 3 ], a comprehensive list of grey literature sources searched (and full detail for other supplementary search methods) [ 8 ], and an annotation of search terms tested but not used [ 4 ] were identified as unique items in four documents.
The Cochrane Handbook was the only guidance document to note that the full search strategies for each database should be included in the Additional file 1 of the review [ 9 ].
All guidance documents should ultimately deliver completed systematic reviews that fulfil the requirements of the PRISMA reporting guidelines [ 108 ]. The guidance broadly requires the reporting of data that corresponds with the requirements of the PRISMA statement although documents typically ask for diverse and additional items [ 108 ]. In 2008, Sampson et al. observed a lack of consensus on reporting search methods in systematic reviews [ 109 ] and this remains the case as of 2017, as evidenced in the guidance documents, and in spite of the publication of the PRISMA guidelines in 2009 [ 110 ]. It is unclear why the collective guidance does not more explicitly endorse adherence to the PRISMA guidance.
Reporting of literature searching is a key area in systematic reviews since it sets out clearly what was done and how the conclusions of the review can be believed [ 52 , 109 ]. Despite strong endorsement in the guidance documents, specifically supported in PRISMA guidance, and other related reporting standards too (such as ENTREQ for qualitative evidence synthesis, STROBE for reviews of observational studies), authors still highlight the prevalence of poor standards of literature search reporting [ 31 , 110 , 111 , 112 , 113 , 114 , 115 , 116 , 117 , 118 , 119 ]. To explore issues experienced by authors in reporting literature searches, and look at uptake of PRISMA, Radar et al. [ 120 ] surveyed over 260 review authors to determine common problems and their work summaries the practical aspects of reporting literature searching [ 120 ]. Atkinson et al. [ 121 ] have also analysed reporting standards for literature searching, summarising recommendations and gaps for reporting search strategies [ 121 ].
One area that is less well covered by the guidance, but nevertheless appears in this literature, is the quality appraisal or peer review of literature search strategies. The PRESS checklist is the most prominent and it aims to develop evidence-based guidelines to peer review of electronic search strategies [ 5 , 122 , 123 ]. A corresponding guideline for documentation of supplementary search methods does not yet exist although this idea is currently being explored.
How the reporting of the literature searching process corresponds to critical appraisal tools is an area for further research. In the survey undertaken by Radar et al. (2014), 86% of survey respondents (153/178) identified a need for further guidance on what aspects of the literature search process to report [ 120 ]. The PRISMA statement offers a brief summary of what to report but little practical guidance on how to report it [ 108 ]. Critical appraisal tools for systematic reviews, such as AMSTAR 2 (Shea et al. [ 124 ]) and ROBIS (Whiting et al. [ 125 ]), can usefully be read alongside PRISMA guidance, since they offer greater detail on how the reporting of the literature search will be appraised and, therefore, they offer a proxy on what to report [ 124 , 125 ]. Further research in the form of a study which undertakes a comparison between PRISMA and quality appraisal checklists for systematic reviews would seem to begin addressing the call, identified by Radar et al., for further guidance on what to report [ 120 ].
Limitations
Other handbooks exist.
A potential limitation of this literature review is the focus on guidance produced in Europe (the UK specifically) and Australia. We justify the decision for our selection of the nine guidance documents reviewed in this literature review in section “ Identifying guidance ”. In brief, these nine guidance documents were selected as the most relevant health care guidance that inform UK systematic reviewing practice, given that the UK occupies a prominent position in the science of health information retrieval. We acknowledge the existence of other guidance documents, such as those from North America (e.g. the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) [ 126 ], The Institute of Medicine [ 127 ] and the guidance and resources produced by the Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health (CADTH) [ 128 ]). We comment further on this directly below.
The handbooks are potentially linked to one another
What is not clear is the extent to which the guidance documents inter-relate or provide guidance uniquely. The Cochrane Handbook, first published in 1994, is notably a key source of reference in guidance and systematic reviews beyond Cochrane reviews. It is not clear to what extent broadening the sample of guidance handbooks to include North American handbooks, and guidance handbooks from other relevant countries too, would alter the findings of this literature review or develop further support for the process model. Since we cannot be clear, we raise this as a potential limitation of this literature review. On our initial review of a sample of North American, and other, guidance documents (before selecting the guidance documents considered in this review), however, we do not consider that the inclusion of these further handbooks would alter significantly the findings of this literature review.
This is a literature review
A further limitation of this review was that the review of published studies is not a systematic review of the evidence for each key stage. It is possible that other relevant studies could help contribute to the exploration and development of the key stages identified in this review.
This literature review would appear to demonstrate the existence of a shared model of the literature searching process in systematic reviews. We call this model ‘the conventional approach’, since it appears to be common convention in nine different guidance documents.
The findings reported above reveal eight key stages in the process of literature searching for systematic reviews. These key stages are consistently reported in the nine guidance documents which suggests consensus on the key stages of literature searching, and therefore the process of literature searching as a whole, in systematic reviews.
In Table 2 , we demonstrate consensus regarding the application of literature search methods. All guidance documents distinguish between primary and supplementary search methods. Bibliographic database searching is consistently the first method of literature searching referenced in each guidance document. Whilst the guidance uniformly supports the use of supplementary search methods, there is little evidence for a consistent process with diverse guidance across documents. This may reflect differences in the core focus across each document, linked to differences in identifying effectiveness studies or qualitative studies, for instance.
Eight of the nine guidance documents reported on the aims of literature searching. The shared understanding was that literature searching should be thorough and comprehensive in its aim and that this process should be reported transparently so that that it could be reproduced. Whilst only three documents explicitly link this understanding to minimising bias, it is clear that comprehensive literature searching is implicitly linked to ‘not missing relevant studies’ which is approximately the same point.
Defining the key stages in this review helps categorise the scholarship available, and it prioritises areas for development or further study. The supporting studies on preparing for literature searching (key stage three, ‘preparation’) were, for example, comparatively few, and yet this key stage represents a decisive moment in literature searching for systematic reviews. It is where search strategy structure is determined, search terms are chosen or discarded, and the resources to be searched are selected. Information specialists, librarians and researchers, are well placed to develop these and other areas within the key stages we identify.
This review calls for further research to determine the suitability of using the conventional approach. The publication dates of the guidance documents which underpin the conventional approach may raise questions as to whether the process which they each report remains valid for current systematic literature searching. In addition, it may be useful to test whether it is desirable to use the same process model of literature searching for qualitative evidence synthesis as that for reviews of intervention effectiveness, which this literature review demonstrates is presently recommended best practice.
Abbreviations
Behaviour of interest; Health context; Exclusions; Models or Theories
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects
Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research
Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Healthcare
National Institute for Clinical Excellence
Population, Intervention, Comparator, Outcome
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Setting, Perspective, Intervention, Comparison, Evaluation
Sample, Phenomenon of Interest, Design, Evaluation, Research type
STrengthening the Reporting of OBservational studies in Epidemiology
Trial Search Co-ordinators
Booth A. Unpacking your literature search toolbox: on search styles and tactics. Health Information & Libraries Journal. 2008;25(4):313–7.
Article Google Scholar
Petticrew M, Roberts H. Systematic reviews in the social sciences: a practical guide. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing Ltd; 2006.
Book Google Scholar
Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG). IQWiG Methods Resources. 7 Information retrieval 2014 [Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK385787/ .
NICE: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Developing NICE guidelines: the manual 2014. Available from: https://www.nice.org.uk/media/default/about/what-we-do/our-programmes/developing-nice-guidelines-the-manual.pdf .
Sampson M. MJ, Lefebvre C, Moher D, Grimshaw J. Peer Review of Electronic Search Strategies: PRESS; 2008.
Google Scholar
Centre for Reviews & Dissemination. Systematic reviews – CRD’s guidance for undertaking reviews in healthcare. York: Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York; 2009.
eunetha: European Network for Health Technology Assesment Process of information retrieval for systematic reviews and health technology assessments on clinical effectiveness 2016. Available from: http://www.eunethta.eu/sites/default/files/Guideline_Information_Retrieval_V1-1.pdf .
Kugley SWA, Thomas J, Mahood Q, Jørgensen AMK, Hammerstrøm K, Sathe N. Searching for studies: a guide to information retrieval for Campbell systematic reviews. Oslo: Campbell Collaboration. 2017; Available from: https://www.campbellcollaboration.org/library/searching-for-studies-information-retrieval-guide-campbell-reviews.html
Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: searching for studies. In: JPT H, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; 2011.
Collaboration for Environmental Evidence. Guidelines for Systematic Review and Evidence Synthesis in Environmental Management.: Environmental Evidence:; 2013. Available from: http://www.environmentalevidence.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Review-guidelines-version-4.2-final-update.pdf .
The Joanna Briggs Institute. Joanna Briggs institute reviewers’ manual. 2014th ed: the Joanna Briggs institute; 2014. Available from: https://joannabriggs.org/assets/docs/sumari/ReviewersManual-2014.pdf
Beverley CA, Booth A, Bath PA. The role of the information specialist in the systematic review process: a health information case study. Health Inf Libr J. 2003;20(2):65–74.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Harris MR. The librarian's roles in the systematic review process: a case study. Journal of the Medical Library Association. 2005;93(1):81–7.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Egger JB. Use of recommended search strategies in systematic reviews and the impact of librarian involvement: a cross-sectional survey of recent authors. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0125931.
Li L, Tian J, Tian H, Moher D, Liang F, Jiang T, et al. Network meta-analyses could be improved by searching more sources and by involving a librarian. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014;67(9):1001–7.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
McGowan J, Sampson M. Systematic reviews need systematic searchers. J Med Libr Assoc. 2005;93(1):74–80.
Rethlefsen ML, Farrell AM, Osterhaus Trzasko LC, Brigham TJ. Librarian co-authors correlated with higher quality reported search strategies in general internal medicine systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015;68(6):617–26.
Weller AC. Mounting evidence that librarians are essential for comprehensive literature searches for meta-analyses and Cochrane reports. J Med Libr Assoc. 2004;92(2):163–4.
Swinkels A, Briddon J, Hall J. Two physiotherapists, one librarian and a systematic literature review: collaboration in action. Health Info Libr J. 2006;23(4):248–56.
Foster M. An overview of the role of librarians in systematic reviews: from expert search to project manager. EAHIL. 2015;11(3):3–7.
Lawson L. OPERATING OUTSIDE LIBRARY WALLS 2004.
Vassar M, Yerokhin V, Sinnett PM, Weiher M, Muckelrath H, Carr B, et al. Database selection in systematic reviews: an insight through clinical neurology. Health Inf Libr J. 2017;34(2):156–64.
Townsend WA, Anderson PF, Ginier EC, MacEachern MP, Saylor KM, Shipman BL, et al. A competency framework for librarians involved in systematic reviews. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2017;105(3):268–75.
Cooper ID, Crum JA. New activities and changing roles of health sciences librarians: a systematic review, 1990-2012. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2013;101(4):268–77.
Crum JA, Cooper ID. Emerging roles for biomedical librarians: a survey of current practice, challenges, and changes. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2013;101(4):278–86.
Dudden RF, Protzko SL. The systematic review team: contributions of the health sciences librarian. Med Ref Serv Q. 2011;30(3):301–15.
Golder S, Loke Y, McIntosh HM. Poor reporting and inadequate searches were apparent in systematic reviews of adverse effects. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61(5):440–8.
Maggio LA, Tannery NH, Kanter SL. Reproducibility of literature search reporting in medical education reviews. Academic medicine : journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges. 2011;86(8):1049–54.
Meert D, Torabi N, Costella J. Impact of librarians on reporting of the literature searching component of pediatric systematic reviews. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2016;104(4):267–77.
Morris M, Boruff JT, Gore GC. Scoping reviews: establishing the role of the librarian. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2016;104(4):346–54.
Koffel JB, Rethlefsen ML. Reproducibility of search strategies is poor in systematic reviews published in high-impact pediatrics, cardiology and surgery journals: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2016;11(9):e0163309.
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Fehrmann P, Thomas J. Comprehensive computer searches and reporting in systematic reviews. Research Synthesis Methods. 2011;2(1):15–32.
Booth A. Searching for qualitative research for inclusion in systematic reviews: a structured methodological review. Systematic Reviews. 2016;5(1):74.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Egger M, Juni P, Bartlett C, Holenstein F, Sterne J. How important are comprehensive literature searches and the assessment of trial quality in systematic reviews? Empirical study. Health technology assessment (Winchester, England). 2003;7(1):1–76.
Tricco AC, Tetzlaff J, Sampson M, Fergusson D, Cogo E, Horsley T, et al. Few systematic reviews exist documenting the extent of bias: a systematic review. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61(5):422–34.
Booth A. How much searching is enough? Comprehensive versus optimal retrieval for technology assessments. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2010;26(4):431–5.
Papaioannou D, Sutton A, Carroll C, Booth A, Wong R. Literature searching for social science systematic reviews: consideration of a range of search techniques. Health Inf Libr J. 2010;27(2):114–22.
Petticrew M. Time to rethink the systematic review catechism? Moving from ‘what works’ to ‘what happens’. Systematic Reviews. 2015;4(1):36.
Betrán AP, Say L, Gülmezoglu AM, Allen T, Hampson L. Effectiveness of different databases in identifying studies for systematic reviews: experience from the WHO systematic review of maternal morbidity and mortality. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2005;5
Felson DT. Bias in meta-analytic research. J Clin Epidemiol. 1992;45(8):885–92.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Franco A, Malhotra N, Simonovits G. Publication bias in the social sciences: unlocking the file drawer. Science. 2014;345(6203):1502–5.
Hartling L, Featherstone R, Nuspl M, Shave K, Dryden DM, Vandermeer B. Grey literature in systematic reviews: a cross-sectional study of the contribution of non-English reports, unpublished studies and dissertations to the results of meta-analyses in child-relevant reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2017;17(1):64.
Schmucker CM, Blümle A, Schell LK, Schwarzer G, Oeller P, Cabrera L, et al. Systematic review finds that study data not published in full text articles have unclear impact on meta-analyses results in medical research. PLoS One. 2017;12(4):e0176210.
Egger M, Zellweger-Zahner T, Schneider M, Junker C, Lengeler C, Antes G. Language bias in randomised controlled trials published in English and German. Lancet (London, England). 1997;350(9074):326–9.
Moher D, Pham B, Lawson ML, Klassen TP. The inclusion of reports of randomised trials published in languages other than English in systematic reviews. Health technology assessment (Winchester, England). 2003;7(41):1–90.
Pham B, Klassen TP, Lawson ML, Moher D. Language of publication restrictions in systematic reviews gave different results depending on whether the intervention was conventional or complementary. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005;58(8):769–76.
Mills EJ, Kanters S, Thorlund K, Chaimani A, Veroniki A-A, Ioannidis JPA. The effects of excluding treatments from network meta-analyses: survey. BMJ : British Medical Journal. 2013;347
Hartling L, Featherstone R, Nuspl M, Shave K, Dryden DM, Vandermeer B. The contribution of databases to the results of systematic reviews: a cross-sectional study. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2016;16(1):127.
van Driel ML, De Sutter A, De Maeseneer J, Christiaens T. Searching for unpublished trials in Cochrane reviews may not be worth the effort. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62(8):838–44.e3.
Buchberger B, Krabbe L, Lux B, Mattivi JT. Evidence mapping for decision making: feasibility versus accuracy - when to abandon high sensitivity in electronic searches. German medical science : GMS e-journal. 2016;14:Doc09.
Lorenc T, Pearson M, Jamal F, Cooper C, Garside R. The role of systematic reviews of qualitative evidence in evaluating interventions: a case study. Research Synthesis Methods. 2012;3(1):1–10.
Gough D. Weight of evidence: a framework for the appraisal of the quality and relevance of evidence. Res Pap Educ. 2007;22(2):213–28.
Barroso J, Gollop CJ, Sandelowski M, Meynell J, Pearce PF, Collins LJ. The challenges of searching for and retrieving qualitative studies. West J Nurs Res. 2003;25(2):153–78.
Britten N, Garside R, Pope C, Frost J, Cooper C. Asking more of qualitative synthesis: a response to Sally Thorne. Qual Health Res. 2017;27(9):1370–6.
Booth A, Carroll C. Systematic searching for theory to inform systematic reviews: is it feasible? Is it desirable? Health Info Libr J. 2015;32(3):220–35.
Kwon Y, Powelson SE, Wong H, Ghali WA, Conly JM. An assessment of the efficacy of searching in biomedical databases beyond MEDLINE in identifying studies for a systematic review on ward closures as an infection control intervention to control outbreaks. Syst Rev. 2014;3:135.
Nussbaumer-Streit B, Klerings I, Wagner G, Titscher V, Gartlehner G. Assessing the validity of abbreviated literature searches for rapid reviews: protocol of a non-inferiority and meta-epidemiologic study. Systematic Reviews. 2016;5:197.
Wagner G, Nussbaumer-Streit B, Greimel J, Ciapponi A, Gartlehner G. Trading certainty for speed - how much uncertainty are decisionmakers and guideline developers willing to accept when using rapid reviews: an international survey. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2017;17(1):121.
Ogilvie D, Hamilton V, Egan M, Petticrew M. Systematic reviews of health effects of social interventions: 1. Finding the evidence: how far should you go? J Epidemiol Community Health. 2005;59(9):804–8.
Royle P, Milne R. Literature searching for randomized controlled trials used in Cochrane reviews: rapid versus exhaustive searches. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2003;19(4):591–603.
Pearson M, Moxham T, Ashton K. Effectiveness of search strategies for qualitative research about barriers and facilitators of program delivery. Eval Health Prof. 2011;34(3):297–308.
Levay P, Raynor M, Tuvey D. The Contributions of MEDLINE, Other Bibliographic Databases and Various Search Techniques to NICE Public Health Guidance. 2015. 2015;10(1):19.
Nussbaumer-Streit B, Klerings I, Wagner G, Heise TL, Dobrescu AI, Armijo-Olivo S, et al. Abbreviated literature searches were viable alternatives to comprehensive searches: a meta-epidemiological study. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;102:1–11.
Briscoe S, Cooper C, Glanville J, Lefebvre C. The loss of the NHS EED and DARE databases and the effect on evidence synthesis and evaluation. Res Synth Methods. 2017;8(3):256–7.
Stansfield C, O'Mara-Eves A, Thomas J. Text mining for search term development in systematic reviewing: A discussion of some methods and challenges. Research Synthesis Methods.n/a-n/a.
Petrova M, Sutcliffe P, Fulford KW, Dale J. Search terms and a validated brief search filter to retrieve publications on health-related values in Medline: a word frequency analysis study. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association : JAMIA. 2012;19(3):479–88.
Stansfield C, Thomas J, Kavanagh J. 'Clustering' documents automatically to support scoping reviews of research: a case study. Res Synth Methods. 2013;4(3):230–41.
PubMed Google Scholar
Methley AM, Campbell S, Chew-Graham C, McNally R, Cheraghi-Sohi S. PICO, PICOS and SPIDER: a comparison study of specificity and sensitivity in three search tools for qualitative systematic reviews. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014;14:579.
Andrew B. Clear and present questions: formulating questions for evidence based practice. Library Hi Tech. 2006;24(3):355–68.
Cooke A, Smith D, Booth A. Beyond PICO: the SPIDER tool for qualitative evidence synthesis. Qual Health Res. 2012;22(10):1435–43.
Whiting P, Westwood M, Bojke L, Palmer S, Richardson G, Cooper J, et al. Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of tests for the diagnosis and investigation of urinary tract infection in children: a systematic review and economic model. Health technology assessment (Winchester, England). 2006;10(36):iii-iv, xi-xiii, 1–154.
Cooper C, Levay P, Lorenc T, Craig GM. A population search filter for hard-to-reach populations increased search efficiency for a systematic review. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014;67(5):554–9.
Hausner E, Waffenschmidt S, Kaiser T, Simon M. Routine development of objectively derived search strategies. Systematic Reviews. 2012;1(1):19.
Hausner E, Guddat C, Hermanns T, Lampert U, Waffenschmidt S. Prospective comparison of search strategies for systematic reviews: an objective approach yielded higher sensitivity than a conceptual one. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;77:118–24.
Craven J, Levay P. Recording database searches for systematic reviews - what is the value of adding a narrative to peer-review checklists? A case study of nice interventional procedures guidance. Evid Based Libr Inf Pract. 2011;6(4):72–87.
Wright K, Golder S, Lewis-Light K. What value is the CINAHL database when searching for systematic reviews of qualitative studies? Syst Rev. 2015;4:104.
Beckles Z, Glover S, Ashe J, Stockton S, Boynton J, Lai R, et al. Searching CINAHL did not add value to clinical questions posed in NICE guidelines. J Clin Epidemiol. 2013;66(9):1051–7.
Cooper C, Rogers M, Bethel A, Briscoe S, Lowe J. A mapping review of the literature on UK-focused health and social care databases. Health Inf Libr J. 2015;32(1):5–22.
Younger P, Boddy K. When is a search not a search? A comparison of searching the AMED complementary health database via EBSCOhost, OVID and DIALOG. Health Inf Libr J. 2009;26(2):126–35.
Lam MT, McDiarmid M. Increasing number of databases searched in systematic reviews and meta-analyses between 1994 and 2014. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2016;104(4):284–9.
Bethel A, editor Search summary tables for systematic reviews: results and findings. HLC Conference 2017a.
Aagaard T, Lund H, Juhl C. Optimizing literature search in systematic reviews - are MEDLINE, EMBASE and CENTRAL enough for identifying effect studies within the area of musculoskeletal disorders? BMC Med Res Methodol. 2016;16(1):161.
Adams CE, Frederick K. An investigation of the adequacy of MEDLINE searches for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of the effects of mental health care. Psychol Med. 1994;24(3):741–8.
Kelly L, St Pierre-Hansen N. So many databases, such little clarity: searching the literature for the topic aboriginal. Canadian family physician Medecin de famille canadien. 2008;54(11):1572–3.
Lawrence DW. What is lost when searching only one literature database for articles relevant to injury prevention and safety promotion? Injury Prevention. 2008;14(6):401–4.
Lemeshow AR, Blum RE, Berlin JA, Stoto MA, Colditz GA. Searching one or two databases was insufficient for meta-analysis of observational studies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005;58(9):867–73.
Sampson M, Barrowman NJ, Moher D, Klassen TP, Pham B, Platt R, et al. Should meta-analysts search Embase in addition to Medline? J Clin Epidemiol. 2003;56(10):943–55.
Stevinson C, Lawlor DA. Searching multiple databases for systematic reviews: added value or diminishing returns? Complementary Therapies in Medicine. 2004;12(4):228–32.
Suarez-Almazor ME, Belseck E, Homik J, Dorgan M, Ramos-Remus C. Identifying clinical trials in the medical literature with electronic databases: MEDLINE alone is not enough. Control Clin Trials. 2000;21(5):476–87.
Taylor B, Wylie E, Dempster M, Donnelly M. Systematically retrieving research: a case study evaluating seven databases. Res Soc Work Pract. 2007;17(6):697–706.
Beyer FR, Wright K. Can we prioritise which databases to search? A case study using a systematic review of frozen shoulder management. Health Info Libr J. 2013;30(1):49–58.
Duffy S, de Kock S, Misso K, Noake C, Ross J, Stirk L. Supplementary searches of PubMed to improve currency of MEDLINE and MEDLINE in-process searches via Ovid. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2016;104(4):309–12.
Katchamart W, Faulkner A, Feldman B, Tomlinson G, Bombardier C. PubMed had a higher sensitivity than Ovid-MEDLINE in the search for systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(7):805–7.
Cooper C, Lovell R, Husk K, Booth A, Garside R. Supplementary search methods were more effective and offered better value than bibliographic database searching: a case study from public health and environmental enhancement (in Press). Research Synthesis Methods. 2017;
Cooper C, Booth, A., Britten, N., Garside, R. A comparison of results of empirical studies of supplementary search techniques and recommendations in review methodology handbooks: A methodological review. (In Press). BMC Systematic Reviews. 2017.
Greenhalgh T, Peacock R. Effectiveness and efficiency of search methods in systematic reviews of complex evidence: audit of primary sources. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2005;331(7524):1064–5.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hinde S, Spackman E. Bidirectional citation searching to completion: an exploration of literature searching methods. PharmacoEconomics. 2015;33(1):5–11.
Levay P, Ainsworth N, Kettle R, Morgan A. Identifying evidence for public health guidance: a comparison of citation searching with web of science and Google scholar. Res Synth Methods. 2016;7(1):34–45.
McManus RJ, Wilson S, Delaney BC, Fitzmaurice DA, Hyde CJ, Tobias RS, et al. Review of the usefulness of contacting other experts when conducting a literature search for systematic reviews. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 1998;317(7172):1562–3.
Westphal A, Kriston L, Holzel LP, Harter M, von Wolff A. Efficiency and contribution of strategies for finding randomized controlled trials: a case study from a systematic review on therapeutic interventions of chronic depression. Journal of public health research. 2014;3(2):177.
Matthews EJ, Edwards AG, Barker J, Bloor M, Covey J, Hood K, et al. Efficient literature searching in diffuse topics: lessons from a systematic review of research on communicating risk to patients in primary care. Health Libr Rev. 1999;16(2):112–20.
Bethel A. Endnote Training (YouTube Videos) 2017b [Available from: http://medicine.exeter.ac.uk/esmi/workstreams/informationscience/is_resources,_guidance_&_advice/ .
Bramer WM, Giustini D, de Jonge GB, Holland L, Bekhuis T. De-duplication of database search results for systematic reviews in EndNote. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2016;104(3):240–3.
Bramer WM, Milic J, Mast F. Reviewing retrieved references for inclusion in systematic reviews using EndNote. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2017;105(1):84–7.
Gall C, Brahmi FA. Retrieval comparison of EndNote to search MEDLINE (Ovid and PubMed) versus searching them directly. Medical reference services quarterly. 2004;23(3):25–32.
Ahmed KK, Al Dhubaib BE. Zotero: a bibliographic assistant to researcher. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2011;2(4):303–5.
Coar JT, Sewell JP. Zotero: harnessing the power of a personal bibliographic manager. Nurse Educ. 2010;35(5):205–7.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097.
Sampson M, McGowan J, Tetzlaff J, Cogo E, Moher D. No consensus exists on search reporting methods for systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61(8):748–54.
Toews LC. Compliance of systematic reviews in veterinary journals with preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis (PRISMA) literature search reporting guidelines. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2017;105(3):233–9.
Booth A. "brimful of STARLITE": toward standards for reporting literature searches. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2006;94(4):421–9. e205
Faggion CM Jr, Wu YC, Tu YK, Wasiak J. Quality of search strategies reported in systematic reviews published in stereotactic radiosurgery. Br J Radiol. 2016;89(1062):20150878.
Mullins MM, DeLuca JB, Crepaz N, Lyles CM. Reporting quality of search methods in systematic reviews of HIV behavioral interventions (2000–2010): are the searches clearly explained, systematic and reproducible? Research Synthesis Methods. 2014;5(2):116–30.
Yoshii A, Plaut DA, McGraw KA, Anderson MJ, Wellik KE. Analysis of the reporting of search strategies in Cochrane systematic reviews. Journal of the Medical Library Association : JMLA. 2009;97(1):21–9.
Bigna JJ, Um LN, Nansseu JR. A comparison of quality of abstracts of systematic reviews including meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials in high-impact general medicine journals before and after the publication of PRISMA extension for abstracts: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev. 2016;5(1):174.
Akhigbe T, Zolnourian A, Bulters D. Compliance of systematic reviews articles in brain arteriovenous malformation with PRISMA statement guidelines: review of literature. Journal of clinical neuroscience : official journal of the Neurosurgical Society of Australasia. 2017;39:45–8.
Tao KM, Li XQ, Zhou QH, Moher D, Ling CQ, Yu WF. From QUOROM to PRISMA: a survey of high-impact medical journals' instructions to authors and a review of systematic reviews in anesthesia literature. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27611.
Wasiak J, Tyack Z, Ware R. Goodwin N. Jr. Poor methodological quality and reporting standards of systematic reviews in burn care management. International wound journal: Faggion CM; 2016.
Tam WW, Lo KK, Khalechelvam P. Endorsement of PRISMA statement and quality of systematic reviews and meta-analyses published in nursing journals: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2017;7(2):e013905.
Rader T, Mann M, Stansfield C, Cooper C, Sampson M. Methods for documenting systematic review searches: a discussion of common issues. Res Synth Methods. 2014;5(2):98–115.
Atkinson KM, Koenka AC, Sanchez CE, Moshontz H, Cooper H. Reporting standards for literature searches and report inclusion criteria: making research syntheses more transparent and easy to replicate. Res Synth Methods. 2015;6(1):87–95.
McGowan J, Sampson M, Salzwedel DM, Cogo E, Foerster V, Lefebvre C. PRESS peer review of electronic search strategies: 2015 guideline statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;75:40–6.
Sampson M, McGowan J, Cogo E, Grimshaw J, Moher D, Lefebvre C. An evidence-based practice guideline for the peer review of electronic search strategies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62(9):944–52.
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2017;358.
Whiting P, Savović J, Higgins JPT, Caldwell DM, Reeves BC, Shea B, et al. ROBIS: a new tool to assess risk of bias in systematic reviews was developed. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;69:225–34.
Relevo R, Balshem H. Finding evidence for comparing medical interventions: AHRQ and the effective health care program. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(11):1168–77.
Medicine Io. Standards for Systematic Reviews 2011 [Available from: http://www.nationalacademies.org/hmd/Reports/2011/Finding-What-Works-in-Health-Care-Standards-for-Systematic-Reviews/Standards.aspx .
CADTH: Resources 2018.
Download references
Acknowledgements
CC acknowledges the supervision offered by Professor Chris Hyde.
This publication forms a part of CC’s PhD. CC’s PhD was funded through the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Health Technology Assessment (HTA) Programme (Project Number 16/54/11). The open access fee for this publication was paid for by Exeter Medical School.
RG and NB were partially supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Collaboration for Leadership in Applied Health Research and Care South West Peninsula.
The views expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Health Research, University of Exeter Medical School, Exeter, UK
Chris Cooper & Jo Varley-Campbell
HEDS, School of Health and Related Research (ScHARR), University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK
Andrew Booth
Nicky Britten
European Centre for Environment and Human Health, University of Exeter Medical School, Truro, UK
Ruth Garside
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
CC conceived the idea for this study and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. CC discussed this publication in PhD supervision with AB and separately with JVC. CC revised the publication with input and comments from AB, JVC, RG and NB. All authors revised the manuscript prior to submission. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Chris Cooper .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional file
Additional file 1:.
Appendix tables and PubMed search strategy. Key studies used for pearl growing per key stage, working data extraction tables and the PubMed search strategy. (DOCX 30 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Cooper, C., Booth, A., Varley-Campbell, J. et al. Defining the process to literature searching in systematic reviews: a literature review of guidance and supporting studies. BMC Med Res Methodol 18 , 85 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-018-0545-3
Download citation
Received : 20 September 2017
Accepted : 06 August 2018
Published : 14 August 2018
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-018-0545-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Literature Search Process
- Citation Chasing
- Tacit Models
- Unique Guidance
- Information Specialists
BMC Medical Research Methodology
ISSN: 1471-2288
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Literature reviews
What this guide covers, what is a literature review, literature review resources, types of literature reviews, what is the difference between a literature review and a systematic review, related information and guides, further help.
- Conducting your search
- Store and organise the literature
- Evaluate and critique the literature
- Different subject areas
- Find literature reviews
Reusing content from this guide

Attribute our work under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.

The literature review process involves a number of steps.
This guide focuses on:
- evaluating.
A literature review is a survey and critical analysis of what has been written on a particular topic, theory, question or method.
"In writing the literature review, the purpose is to explore what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, what approaches and viewpoints have been adopted, and what are their strengths and weaknesses."
Source: "Focus and frame". (2008). In Eriksson, P. & Kovalainen, A. Introducing Qualitative Methods: Qualitative methods in business research (pp. 44) . London: SAGE Publications Ltd. doi: 10.4135/9780857028044.
Get an overview on doing a literature review:
- Sage research methods online - Literature review methods map Information on the literature review methodology with links to further resources - the Project Planner, books, articles, videos and more.
- Ten simple rules for writing a literature review Gives 10 tips on how to approach and carry out a literature review. By Pautasso M (2013) Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review. PLoS Comput Biol9(7): e1003149.
- The literature review. In: Doing your undergraduate program This chapter looks at the purpose of literature reviews, how it is done, setting the boundaries of your search and more.
- More books on literature reviews A selection of literature review books available via UQ Library Search.
The type of literature review you do will depend on a variety of factors:
- Your discipline
- The purpose - undergraduate assessment, PHD thesis, journal article?
- Your lecturer or supervisor's requirements
Always follow the guidelines outlined by your lecturer or supervisor or consult the instructions for authors (for journal articles), when conducting your literature review.
- is an overview of the significant literature on a topic
- typically includes a critical analysis of each work included
- demonstrates the reviewers knowledge of the topic
- is a list of citations of research sources (books, journal articles, websites etc) on a topic
- includes a brief summary and analysis or evaluation of each citation = the annotation
- a critical assessment of all research studies on a particular research question
- has specific criteria for collecting and evaluating the literature
- includes a synthesis of the findings of the included studies
- This method developed by Griffith University's School of Environment bridges the gap between traditional narrative review methods and meta-analyses to enable students to produce results that are reliable, quantifiable and reproducible.
The requirements of narrative literature reviews are usually quite different than systematic reviews . However, you may be required to adopt some of the characteristics of a systematic approach when doing your literature review. Check the guidelines or criteria that have been set by your supervisor so you know what is expected of you.
Characteristics of reviews
- Meeting the review family: Exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements This article defines different review types and discusses appropriate search methods for each type.
- Writing literature reviews - Student Support Student Support provides information on how to write effective literature reviews.
- Writing skills Learn strategies for good writing from the Graduate School.
- Systematic reviews An overview of systematic reviews and resources to support producing one.
- Subject guides See recommended resources in different subject areas.
- Grey literature Find literature that is not available in traditional channels of publishing and distribution.
- How to find guides Techniques and resources to find specific information formats.
Contact the Librarian team .
Phone: + 617 334 64312 during opening hours
Email: [email protected]
- Next: Conducting your search >>
- Last Updated: Dec 15, 2023 12:09 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.uq.edu.au/research-techniques/literature-reviews

Literature Reviews
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain what literature reviews are and offer insights into the form and construction of literature reviews in the humanities, social sciences, and sciences.
Introduction
OK. You’ve got to write a literature review. You dust off a novel and a book of poetry, settle down in your chair, and get ready to issue a “thumbs up” or “thumbs down” as you leaf through the pages. “Literature review” done. Right?
Wrong! The “literature” of a literature review refers to any collection of materials on a topic, not necessarily the great literary texts of the world. “Literature” could be anything from a set of government pamphlets on British colonial methods in Africa to scholarly articles on the treatment of a torn ACL. And a review does not necessarily mean that your reader wants you to give your personal opinion on whether or not you liked these sources.
What is a literature review, then?
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period.
A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information. It might give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations. Or it might trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates. And depending on the situation, the literature review may evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant.
But how is a literature review different from an academic research paper?
The main focus of an academic research paper is to develop a new argument, and a research paper is likely to contain a literature review as one of its parts. In a research paper, you use the literature as a foundation and as support for a new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.
Why do we write literature reviews?
Literature reviews provide you with a handy guide to a particular topic. If you have limited time to conduct research, literature reviews can give you an overview or act as a stepping stone. For professionals, they are useful reports that keep them up to date with what is current in the field. For scholars, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the writer in his or her field. Literature reviews also provide a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. Comprehensive knowledge of the literature of the field is essential to most research papers.
Who writes these things, anyway?
Literature reviews are written occasionally in the humanities, but mostly in the sciences and social sciences; in experiment and lab reports, they constitute a section of the paper. Sometimes a literature review is written as a paper in itself.
Let’s get to it! What should I do before writing the literature review?
If your assignment is not very specific, seek clarification from your instructor:
- Roughly how many sources should you include?
- What types of sources (books, journal articles, websites)?
- Should you summarize, synthesize, or critique your sources by discussing a common theme or issue?
- Should you evaluate your sources?
- Should you provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history?
Find models
Look for other literature reviews in your area of interest or in the discipline and read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or ways to organize your final review. You can simply put the word “review” in your search engine along with your other topic terms to find articles of this type on the Internet or in an electronic database. The bibliography or reference section of sources you’ve already read are also excellent entry points into your own research.
Narrow your topic
There are hundreds or even thousands of articles and books on most areas of study. The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to get a good survey of the material. Your instructor will probably not expect you to read everything that’s out there on the topic, but you’ll make your job easier if you first limit your scope.
Keep in mind that UNC Libraries have research guides and to databases relevant to many fields of study. You can reach out to the subject librarian for a consultation: https://library.unc.edu/support/consultations/ .
And don’t forget to tap into your professor’s (or other professors’) knowledge in the field. Ask your professor questions such as: “If you had to read only one book from the 90’s on topic X, what would it be?” Questions such as this help you to find and determine quickly the most seminal pieces in the field.
Consider whether your sources are current
Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. In the sciences, for instance, treatments for medical problems are constantly changing according to the latest studies. Information even two years old could be obsolete. However, if you are writing a review in the humanities, history, or social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be what is needed, because what is important is how perspectives have changed through the years or within a certain time period. Try sorting through some other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to consider what is currently of interest to scholars in this field and what is not.
Strategies for writing the literature review
Find a focus.
A literature review, like a term paper, is usually organized around ideas, not the sources themselves as an annotated bibliography would be organized. This means that you will not just simply list your sources and go into detail about each one of them, one at a time. No. As you read widely but selectively in your topic area, consider instead what themes or issues connect your sources together. Do they present one or different solutions? Is there an aspect of the field that is missing? How well do they present the material and do they portray it according to an appropriate theory? Do they reveal a trend in the field? A raging debate? Pick one of these themes to focus the organization of your review.
Convey it to your reader
A literature review may not have a traditional thesis statement (one that makes an argument), but you do need to tell readers what to expect. Try writing a simple statement that lets the reader know what is your main organizing principle. Here are a couple of examples:
The current trend in treatment for congestive heart failure combines surgery and medicine. More and more cultural studies scholars are accepting popular media as a subject worthy of academic consideration.
Consider organization
You’ve got a focus, and you’ve stated it clearly and directly. Now what is the most effective way of presenting the information? What are the most important topics, subtopics, etc., that your review needs to include? And in what order should you present them? Develop an organization for your review at both a global and local level:
First, cover the basic categories
Just like most academic papers, literature reviews also must contain at least three basic elements: an introduction or background information section; the body of the review containing the discussion of sources; and, finally, a conclusion and/or recommendations section to end the paper. The following provides a brief description of the content of each:
- Introduction: Gives a quick idea of the topic of the literature review, such as the central theme or organizational pattern.
- Body: Contains your discussion of sources and is organized either chronologically, thematically, or methodologically (see below for more information on each).
- Conclusions/Recommendations: Discuss what you have drawn from reviewing literature so far. Where might the discussion proceed?
Organizing the body
Once you have the basic categories in place, then you must consider how you will present the sources themselves within the body of your paper. Create an organizational method to focus this section even further.
To help you come up with an overall organizational framework for your review, consider the following scenario:
You’ve decided to focus your literature review on materials dealing with sperm whales. This is because you’ve just finished reading Moby Dick, and you wonder if that whale’s portrayal is really real. You start with some articles about the physiology of sperm whales in biology journals written in the 1980’s. But these articles refer to some British biological studies performed on whales in the early 18th century. So you check those out. Then you look up a book written in 1968 with information on how sperm whales have been portrayed in other forms of art, such as in Alaskan poetry, in French painting, or on whale bone, as the whale hunters in the late 19th century used to do. This makes you wonder about American whaling methods during the time portrayed in Moby Dick, so you find some academic articles published in the last five years on how accurately Herman Melville portrayed the whaling scene in his novel.
Now consider some typical ways of organizing the sources into a review:
- Chronological: If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials above according to when they were published. For instance, first you would talk about the British biological studies of the 18th century, then about Moby Dick, published in 1851, then the book on sperm whales in other art (1968), and finally the biology articles (1980s) and the recent articles on American whaling of the 19th century. But there is relatively no continuity among subjects here. And notice that even though the sources on sperm whales in other art and on American whaling are written recently, they are about other subjects/objects that were created much earlier. Thus, the review loses its chronological focus.
- By publication: Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on biological studies of sperm whales if the progression revealed a change in dissection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies.
- By trend: A better way to organize the above sources chronologically is to examine the sources under another trend, such as the history of whaling. Then your review would have subsections according to eras within this period. For instance, the review might examine whaling from pre-1600-1699, 1700-1799, and 1800-1899. Under this method, you would combine the recent studies on American whaling in the 19th century with Moby Dick itself in the 1800-1899 category, even though the authors wrote a century apart.
- Thematic: Thematic reviews of literature are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time. However, progression of time may still be an important factor in a thematic review. For instance, the sperm whale review could focus on the development of the harpoon for whale hunting. While the study focuses on one topic, harpoon technology, it will still be organized chronologically. The only difference here between a “chronological” and a “thematic” approach is what is emphasized the most: the development of the harpoon or the harpoon technology.But more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. For instance, a thematic review of material on sperm whales might examine how they are portrayed as “evil” in cultural documents. The subsections might include how they are personified, how their proportions are exaggerated, and their behaviors misunderstood. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point made.
- Methodological: A methodological approach differs from the two above in that the focusing factor usually does not have to do with the content of the material. Instead, it focuses on the “methods” of the researcher or writer. For the sperm whale project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of whales in American, British, and French art work. Or the review might focus on the economic impact of whaling on a community. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed. Once you’ve decided on the organizational method for the body of the review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out. They should arise out of your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period. A thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue.
Sometimes, though, you might need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. Put in only what is necessary. Here are a few other sections you might want to consider:
- Current Situation: Information necessary to understand the topic or focus of the literature review.
- History: The chronological progression of the field, the literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Methods and/or Standards: The criteria you used to select the sources in your literature review or the way in which you present your information. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed articles and journals.
Questions for Further Research: What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
Begin composing
Once you’ve settled on a general pattern of organization, you’re ready to write each section. There are a few guidelines you should follow during the writing stage as well. Here is a sample paragraph from a literature review about sexism and language to illuminate the following discussion:
However, other studies have shown that even gender-neutral antecedents are more likely to produce masculine images than feminine ones (Gastil, 1990). Hamilton (1988) asked students to complete sentences that required them to fill in pronouns that agreed with gender-neutral antecedents such as “writer,” “pedestrian,” and “persons.” The students were asked to describe any image they had when writing the sentence. Hamilton found that people imagined 3.3 men to each woman in the masculine “generic” condition and 1.5 men per woman in the unbiased condition. Thus, while ambient sexism accounted for some of the masculine bias, sexist language amplified the effect. (Source: Erika Falk and Jordan Mills, “Why Sexist Language Affects Persuasion: The Role of Homophily, Intended Audience, and Offense,” Women and Language19:2).
Use evidence
In the example above, the writers refer to several other sources when making their point. A literature review in this sense is just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence to show that what you are saying is valid.
Be selective
Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the review’s focus, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological.
Use quotes sparingly
Falk and Mills do not use any direct quotes. That is because the survey nature of the literature review does not allow for in-depth discussion or detailed quotes from the text. Some short quotes here and there are okay, though, if you want to emphasize a point, or if what the author said just cannot be rewritten in your own words. Notice that Falk and Mills do quote certain terms that were coined by the author, not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. But if you find yourself wanting to put in more quotes, check with your instructor.
Summarize and synthesize
Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each paragraph as well as throughout the review. The authors here recapitulate important features of Hamilton’s study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study’s significance and relating it to their own work.
Keep your own voice
While the literature review presents others’ ideas, your voice (the writer’s) should remain front and center. Notice that Falk and Mills weave references to other sources into their own text, but they still maintain their own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with their own ideas and their own words. The sources support what Falk and Mills are saying.
Use caution when paraphrasing
When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author’s information or opinions accurately and in your own words. In the preceding example, Falk and Mills either directly refer in the text to the author of their source, such as Hamilton, or they provide ample notation in the text when the ideas they are mentioning are not their own, for example, Gastil’s. For more information, please see our handout on plagiarism .
Revise, revise, revise
Draft in hand? Now you’re ready to revise. Spending a lot of time revising is a wise idea, because your main objective is to present the material, not the argument. So check over your review again to make sure it follows the assignment and/or your outline. Then, just as you would for most other academic forms of writing, rewrite or rework the language of your review so that you’ve presented your information in the most concise manner possible. Be sure to use terminology familiar to your audience; get rid of unnecessary jargon or slang. Finally, double check that you’ve documented your sources and formatted the review appropriately for your discipline. For tips on the revising and editing process, see our handout on revising drafts .
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Jones, Robert, Patrick Bizzaro, and Cynthia Selfe. 1997. The Harcourt Brace Guide to Writing in the Disciplines . New York: Harcourt Brace.
Lamb, Sandra E. 1998. How to Write It: A Complete Guide to Everything You’ll Ever Write . Berkeley: Ten Speed Press.
Rosen, Leonard J., and Laurence Behrens. 2003. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook , 5th ed. New York: Longman.
Troyka, Lynn Quittman, and Doug Hesse. 2016. Simon and Schuster Handbook for Writers , 11th ed. London: Pearson.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

- University Libraries
- Research Guides
- Reviewing Research: Literature Reviews, Scoping Reviews, Systematic Reviews
- Differentiating the Three Review Types
Reviewing Research: Literature Reviews, Scoping Reviews, Systematic Reviews: Differentiating the Three Review Types
- Framework, Protocol, and Writing Steps
- Working with Keywords/Subject Headings
- Citing Research
The Differences in the Review Types
Grant, M.J. and Booth, A. (2009), A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. H ealth Information & Libraries Journal , 26: 91-108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x The objective of this study is to provide descriptive insight into the most common types of reviews, with illustrative examples from health and health information domains.
- What Type of Review is Right for you (Cornell University)
Literature Reviews
Literature Review: it is a product and a process.
As a product , it is a carefully written examination, interpretation, evaluation, and synthesis of the published literature related to your topic. It focuses on what is known about your topic and what methodologies, models, theories, and concepts have been applied to it by others.
The process is what is involved in conducting a review of the literature.
- It is ongoing
- It is iterative (repetitive)
- It involves searching for and finding relevant literature.
- It includes keeping track of your references and preparing and formatting them for the bibliography of your thesis
- Literature Reviews (University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill) This handout will explain what literature reviews are and offer insights into the form and construction of literature reviews in the humanities, social sciences, and sciences.
Scoping Reviews
Scoping reviews are a " preliminary assessment of potential size and scope of available research literature . Aims to identify nature and extent of research evidence (usually including ongoing research)." Grant and Booth (2009).
Scoping reviews are not mapping reviews: Scoping reviews are more topic based and mapping reviews are more question based.
- examining emerging evidence when specific questions are unclear - clarify definitions and conceptual boundaries
- identify and map the available evidence
- a scoping review is done prior to a systematic review
- to summarize and disseminate research findings in the research literature
- identify gaps with the intention of resolution by future publications
- Scoping review timeframe and limitations (Touro College of Pharmacy
Systematic Reviews
Many evidence-based disciplines use ‘systematic reviews," this type of review is a specific methodology that aims to comprehensively identify all relevant studies on a specific topic, and to select appropriate studies based on explicit criteria . ( https://cebma.org/faq/what-is-a-systematic-review/ )
- clearly defined search criteria
- an explicit reproducible methodology
- a systematic search of the literature with the defined criteria met
- assesses validity of the findings - no risk of bias
- a comprehensive report on the findings, apparent transparency in the results
- Better evidence for a better world Browsable collection of systematic reviews
- Systematic Reviews in the Health Sciences by Molly Maloney Last Updated May 7, 2024 532 views this year
- Next: Framework, Protocol, and Writing Steps >>

- Research Process
Systematic Literature Review or Literature Review?
- 3 minute read
- 45.5K views
Table of Contents
As a researcher, you may be required to conduct a literature review. But what kind of review do you need to complete? Is it a systematic literature review or a standard literature review? In this article, we’ll outline the purpose of a systematic literature review, the difference between literature review and systematic review, and other important aspects of systematic literature reviews.
What is a Systematic Literature Review?
The purpose of systematic literature reviews is simple. Essentially, it is to provide a high-level of a particular research question. This question, in and of itself, is highly focused to match the review of the literature related to the topic at hand. For example, a focused question related to medical or clinical outcomes.
The components of a systematic literature review are quite different from the standard literature review research theses that most of us are used to (more on this below). And because of the specificity of the research question, typically a systematic literature review involves more than one primary author. There’s more work related to a systematic literature review, so it makes sense to divide the work among two or three (or even more) researchers.
Your systematic literature review will follow very clear and defined protocols that are decided on prior to any review. This involves extensive planning, and a deliberately designed search strategy that is in tune with the specific research question. Every aspect of a systematic literature review, including the research protocols, which databases are used, and dates of each search, must be transparent so that other researchers can be assured that the systematic literature review is comprehensive and focused.
Most systematic literature reviews originated in the world of medicine science. Now, they also include any evidence-based research questions. In addition to the focus and transparency of these types of reviews, additional aspects of a quality systematic literature review includes:
- Clear and concise review and summary
- Comprehensive coverage of the topic
- Accessibility and equality of the research reviewed
Systematic Review vs Literature Review
The difference between literature review and systematic review comes back to the initial research question. Whereas the systematic review is very specific and focused, the standard literature review is much more general. The components of a literature review, for example, are similar to any other research paper. That is, it includes an introduction, description of the methods used, a discussion and conclusion, as well as a reference list or bibliography.
A systematic review, however, includes entirely different components that reflect the specificity of its research question, and the requirement for transparency and inclusion. For instance, the systematic review will include:
- Eligibility criteria for included research
- A description of the systematic research search strategy
- An assessment of the validity of reviewed research
- Interpretations of the results of research included in the review
As you can see, contrary to the general overview or summary of a topic, the systematic literature review includes much more detail and work to compile than a standard literature review. Indeed, it can take years to conduct and write a systematic literature review. But the information that practitioners and other researchers can glean from a systematic literature review is, by its very nature, exceptionally valuable.
This is not to diminish the value of the standard literature review. The importance of literature reviews in research writing is discussed in this article . It’s just that the two types of research reviews answer different questions, and, therefore, have different purposes and roles in the world of research and evidence-based writing.
Systematic Literature Review vs Meta Analysis
It would be understandable to think that a systematic literature review is similar to a meta analysis. But, whereas a systematic review can include several research studies to answer a specific question, typically a meta analysis includes a comparison of different studies to suss out any inconsistencies or discrepancies. For more about this topic, check out Systematic Review VS Meta-Analysis article.
Language Editing Plus
With Elsevier’s Language Editing Plus services , you can relax with our complete language review of your systematic literature review or literature review, or any other type of manuscript or scientific presentation. Our editors are PhD or PhD candidates, who are native-English speakers. Language Editing Plus includes checking the logic and flow of your manuscript, reference checks, formatting in accordance to your chosen journal and even a custom cover letter. Our most comprehensive editing package, Language Editing Plus also includes any English-editing needs for up to 180 days.

- Publication Recognition
How to Make a PowerPoint Presentation of Your Research Paper

- Manuscript Preparation
What is and How to Write a Good Hypothesis in Research?
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper


Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
University Libraries University of Nevada, Reno
- Skill Guides
- Subject Guides
Systematic, Scoping, and Other Literature Reviews: Overview
- Project Planning
What Is a Systematic Review?
Regular literature reviews are simply summaries of the literature on a particular topic. A systematic review, however, is a comprehensive literature review conducted to answer a specific research question. Authors of a systematic review aim to find, code, appraise, and synthesize all of the previous research on their question in an unbiased and well-documented manner. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) outline the minimum amount of information that needs to be reported at the conclusion of a systematic review project.
Other types of what are known as "evidence syntheses," such as scoping, rapid, and integrative reviews, have varying methodologies. While systematic reviews originated with and continue to be a popular publication type in medicine and other health sciences fields, more and more researchers in other disciplines are choosing to conduct evidence syntheses.
This guide will walk you through the major steps of a systematic review and point you to key resources including Covidence, a systematic review project management tool. For help with systematic reviews and other major literature review projects, please send us an email at [email protected] .
Getting Help with Reviews
Organization such as the Institute of Medicine recommend that you consult a librarian when conducting a systematic review. Librarians at the University of Nevada, Reno can help you:
- Understand best practices for conducting systematic reviews and other evidence syntheses in your discipline
- Choose and formulate a research question
- Decide which review type (e.g., systematic, scoping, rapid, etc.) is the best fit for your project
- Determine what to include and where to register a systematic review protocol
- Select search terms and develop a search strategy
- Identify databases and platforms to search
- Find the full text of articles and other sources
- Become familiar with free citation management (e.g., EndNote, Zotero)
- Get access to you and help using Covidence, a systematic review project management tool
Doing a Systematic Review
- Plan - This is the project planning stage. You and your team will need to develop a good research question, determine the type of review you will conduct (systematic, scoping, rapid, etc.), and establish the inclusion and exclusion criteria (e.g., you're only going to look at studies that use a certain methodology). All of this information needs to be included in your protocol. You'll also need to ensure that the project is viable - has someone already done a systematic review on this topic? Do some searches and check the various protocol registries to find out.
- Identify - Next, a comprehensive search of the literature is undertaken to ensure all studies that meet the predetermined criteria are identified. Each research question is different, so the number and types of databases you'll search - as well as other online publication venues - will vary. Some standards and guidelines specify that certain databases (e.g., MEDLINE, EMBASE) should be searched regardless. Your subject librarian can help you select appropriate databases to search and develop search strings for each of those databases.
- Evaluate - In this step, retrieved articles are screened and sorted using the predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria. The risk of bias for each included study is also assessed around this time. It's best if you import search results into a citation management tool (see below) to clean up the citations and remove any duplicates. You can then use a tool like Rayyan (see below) to screen the results. You should begin by screening titles and abstracts only, and then you'll examine the full text of any remaining articles. Each study should be reviewed by a minimum of two people on the project team.
- Collect - Each included study is coded and the quantitative or qualitative data contained in these studies is then synthesized. You'll have to either find or develop a coding strategy or form that meets your needs.
- Explain - The synthesized results are articulated and contextualized. What do the results mean? How have they answered your research question?
- Summarize - The final report provides a complete description of the methods and results in a clear, transparent fashion.
Adapted from
Types of reviews, systematic review.
These types of studies employ a systematic method to analyze and synthesize the results of numerous studies. "Systematic" in this case means following a strict set of steps - as outlined by entities like PRISMA and the Institute of Medicine - so as to make the review more reproducible and less biased. Consistent, thorough documentation is also key. Reviews of this type are not meant to be conducted by an individual but rather a (small) team of researchers. Systematic reviews are widely used in the health sciences, often to find a generalized conclusion from multiple evidence-based studies.
Meta-Analysis
A systematic method that uses statistics to analyze the data from numerous studies. The researchers combine the data from studies with similar data types and analyze them as a single, expanded dataset. Meta-analyses are a type of systematic review.
Scoping Review
A scoping review employs the systematic review methodology to explore a broader topic or question rather than a specific and answerable one, as is generally the case with a systematic review. Authors of these types of reviews seek to collect and categorize the existing literature so as to identify any gaps.
Rapid Review
Rapid reviews are systematic reviews conducted under a time constraint. Researchers make use of workarounds to complete the review quickly (e.g., only looking at English-language publications), which can lead to a less thorough and more biased review.
Narrative Review
A traditional literature review that summarizes and synthesizes the findings of numerous original research articles. The purpose and scope of narrative literature reviews vary widely and do not follow a set protocol. Most literature reviews are narrative reviews.
Umbrella Review
Umbrella reviews are, essentially, systematic reviews of systematic reviews. These compile evidence from multiple review studies into one usable document.
Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal , vol. 26, no. 2, 2009, pp. 91-108. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x .
- Next: Project Planning >>

How to Write a Literature Review
- What is a literature review
How is a literature review different from a research paper?
- What should I do before starting my literature review?
- What type of literature review should I write and how should I organize it?
- What should I be aware of while writing the literature review?
- For more information on Literature Reviews
- More Research Help
The purpose of an academic research paper is to develop a new argument. The literature review is one part of a research paper. In a research paper, you use the literature review as a foundation and as support for the new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and analyze the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.
- << Previous: What is a literature review
- Next: What should I do before starting my literature review? >>
- Last Updated: Feb 26, 2021 11:35 AM
- URL: https://midway.libguides.com/LiteratureReview
RESEARCH HELP
- Research Guides
- Databases A-Z
- Journal Search
- Citation Help
LIBRARY SERVICES
- Accessibility
- Interlibrary Loan
- Study Rooms
INSTRUCTION SUPPORT
- Course Reserves
- Library Instruction
- Little Memorial Library
- 512 East Stephens Street
- 859.846.5316
- [email protected]

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Med Libr Assoc
- v.106(4); 2018 Oct
A systematic approach to searching: an efficient and complete method to develop literature searches
Associated data.
Creating search strategies for systematic reviews, finding the best balance between sensitivity and specificity, and translating search strategies between databases is challenging. Several methods describe standards for systematic search strategies, but a consistent approach for creating an exhaustive search strategy has not yet been fully described in enough detail to be fully replicable. The authors have established a method that describes step by step the process of developing a systematic search strategy as needed in the systematic review. This method describes how single-line search strategies can be prepared in a text document by typing search syntax (such as field codes, parentheses, and Boolean operators) before copying and pasting search terms (keywords and free-text synonyms) that are found in the thesaurus. To help ensure term completeness, we developed a novel optimization technique that is mainly based on comparing the results retrieved by thesaurus terms with those retrieved by the free-text search words to identify potentially relevant candidate search terms. Macros in Microsoft Word have been developed to convert syntaxes between databases and interfaces almost automatically. This method helps information specialists in developing librarian-mediated searches for systematic reviews as well as medical and health care practitioners who are searching for evidence to answer clinical questions. The described method can be used to create complex and comprehensive search strategies for different databases and interfaces, such as those that are needed when searching for relevant references for systematic reviews, and will assist both information specialists and practitioners when they are searching the biomedical literature.
INTRODUCTION
Librarians and information specialists are often involved in the process of preparing and completing systematic reviews (SRs), where one of their main tasks is to identify relevant references to include in the review [ 1 ]. Although several recommendations for the process of searching have been published [ 2 – 6 ], none describe the development of a systematic search strategy from start to finish.
Traditional methods of SR search strategy development and execution are highly time consuming, reportedly requiring up to 100 hours or more [ 7 , 8 ]. The authors wanted to develop systematic and exhaustive search strategies more efficiently, while preserving the high sensitivity that SR search strategies necessitate. In this article, we describe the method developed at Erasmus University Medical Center (MC) and demonstrate its use through an example search. The efficiency of the search method and outcome of 73 searches that have resulted in published reviews are described in a separate article [ 9 ].
As we aimed to describe the creation of systematic searches in full detail, the method starts at a basic level with the analysis of the research question and the creation of search terms. Readers who are new to SR searching are advised to follow all steps described. More experienced searchers can consider the basic steps to be existing knowledge that will already be part of their normal workflow, although step 4 probably differs from general practice. Experienced searchers will gain the most from reading about the novelties in the method as described in steps 10–13 and comparing the examples given in the supplementary appendix to their own practice.
CREATING A SYSTEMATIC SEARCH STRATEGY
Our methodology for planning and creating a multi-database search strategy consists of the following steps:
- Determine a clear and focused question
- Describe the articles that can answer the question
- Decide which key concepts address the different elements of the question
- Decide which elements should be used for the best results
- Choose an appropriate database and interface to start with
- Document the search process in a text document
- Identify appropriate index terms in the thesaurus of the first database
- Identify synonyms in the thesaurus
- Add variations in search terms
- Use database-appropriate syntax, with parentheses, Boolean operators, and field codes
- Optimize the search
- Evaluate the initial results
- Check for errors
- Translate to other databases
- Test and reiterate
Each step in the process is reflected by an example search described in the supplementary appendix .
1. Determine a clear and focused question
A systematic search can best be applied to a well-defined and precise research or clinical question. Questions that are too broad or too vague cannot be answered easily in a systematic way and will generally result in an overwhelming number of search results. On the other hand, a question that is too specific will result into too few or even zero search results. Various papers describe this process in more detail [ 10 – 12 ].
2. Describe the articles that can answer the question
Although not all clinical or research questions can be answered in the literature, the next step is to presume that the answer can indeed be found in published studies. A good starting point for a search is hypothesizing what the research that can answer the question would look like. These hypothetical (when possible, combined with known) articles can be used as guidance for constructing the search strategy.
3. Decide which key concepts address the different elements of the question
Key concepts are the topics or components that the desired articles should address, such as diseases or conditions, actions, substances, settings, domains (e.g., therapy, diagnosis, etiology), or study types. Key concepts from the research question can be grouped to create elements in the search strategy.
Elements in a search strategy do not necessarily follow the patient, intervention, comparison, outcome (PICO) structure or any other related structure. Using the PICO or another similar framework as guidance can be helpful to consider, especially in the inclusion and exclusion review stage of the SR, but this is not necessary for good search strategy development [ 13 – 15 ]. Sometimes concepts from different parts of the PICO structure can be grouped together into one search element, such as when the desired outcome is frequently described in a certain study type.
4. Decide which elements should be used for the best results
Not all elements of a research question should necessarily be used in the search strategy. Some elements are less important than others or may unnecessarily complicate or restrict a search strategy. Adding an element to a search strategy increases the chance of missing relevant references. Therefore, the number of elements in a search strategy should remain as low as possible to optimize recall.
Using the schema in Figure 1 , elements can be ordered by their specificity and importance to determine the best search approach. Whether an element is more specific or more general can be measured objectively by the number of hits retrieved in a database when searching for a key term representing that element. Depending on the research question, certain elements are more important than others. If articles (hypothetically or known) exist that can answer the question but lack a certain element in their titles, abstracts, or keywords, that element is unimportant to the question. An element can also be unimportant because of expected bias or an overlap with another element.

Schema for determining the optimal order of elements
Bias in elements
The choice of elements in a search strategy can introduce bias through use of overly specific terminology or terms often associated with positive outcomes. For the question “does prolonged breastfeeding improve intelligence outcomes in children?,” searching specifically for the element of duration will introduce bias, as articles that find a positive effect of prolonged breastfeeding will be much more likely to mention time factors in their titles or abstracts.
Overlapping elements
Elements in a question sometimes overlap in their meaning. Sometimes certain therapies are interventions for one specific disease. The Lichtenstein technique, for example, is a repair method for inguinal hernias. There is no need to include an element of “inguinal hernias” to a search for the effectiveness of the Lichtenstein therapy. Likewise, sometimes certain diseases are only found in certain populations. Adding such an overlapping element could lead to missing relevant references.
The elements to use in a search strategy can be found in the plot of elements in Figure 1 , by following the top row from left to right. For this method, we recommend starting with the most important and specific elements. Then, continue with more general and important elements until the number of results is acceptable for screening. Determining how many results are acceptable for screening is often a matter of negotiation with the SR team.
5. Choose an appropriate database and interface to start with
Important factors for choosing databases to use are the coverage and the presence of a thesaurus. For medically oriented searches, the coverage and recall of Embase, which includes the MEDLINE database, are superior to those of MEDLINE [ 16 ]. Each of these two databases has its own thesaurus with its own unique definitions and structure. Because of the complexity of the Embase thesaurus, Emtree, which contains much more specific thesaurus terms than the MEDLINE Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) thesaurus, translation from Emtree to MeSH is easier than the other way around. Therefore, we recommend starting in Embase.
MEDLINE and Embase are available through many different vendors and interfaces. The choice of an interface and primary database is often determined by the searcher’s accessibility. For our method, an interface that allows searching with proximity operators is desirable, and full functionality of the thesaurus, including explosion of narrower terms, is crucial. We recommend developing a personal workflow that always starts with one specific database and interface.
6. Document the search process in a text document
We advise designing and creating the complete search strategies in a log document, instead of directly in the database itself, to register the steps taken and to make searches accountable and reproducible. The developed search strategies can be copied and pasted into the desired databases from the log document. This way, the searcher is in control of the whole process. Any change to the search strategy should be done in the log document, assuring that the search strategy in the log is always the most recent.
7. Identify appropriate index terms in the thesaurus of the first database
Searches should start by identifying appropriate thesaurus terms for the desired elements. The thesaurus of the database is searched for matching index terms for each key concept. We advise restricting the initial terms to the most important and most relevant terms. Later in the process, more general terms can be added in the optimization process, in which the effect on the number of hits, and thus the desirability of adding these terms, can be evaluated more easily.
Several factors can complicate the identification of thesaurus terms. Sometimes, one thesaurus term is found that exactly describes a specific element. In contrast, especially in more general elements, multiple thesaurus terms can be found to describe one element. If no relevant thesaurus terms have been found for an element, free-text terms can be used, and possible thesaurus terms found in the resulting references can be added later (step 11).
Sometimes, no distinct thesaurus term is available for a specific key concept that describes the concept in enough detail. In Emtree, one thesaurus term often combines two or more elements. The easiest solution for combining these terms for a sensitive search is to use such a thesaurus term in all elements where it is relevant. Examples are given in the supplementary appendix .
8. Identify synonyms in the thesaurus
Most thesauri offer a list of synonyms on their term details page (named Synonyms in Emtree and Entry Terms in MeSH). To create a sensitive search strategy for SRs, these terms need to be searched as free-text keywords in the title and abstract fields, in addition to searching their associated thesaurus terms.
The Emtree thesaurus contains more synonyms (300,000) than MeSH does (220,000) [ 17 ]. The difference in number of terms is even higher considering that many synonyms in MeSH are permuted terms (i.e., inversions of phrases using commas).
Thesaurus terms are ordered in a tree structure. When searching for a more general thesaurus term, the more specific (narrower) terms in the branches below that term will also be searched (this is frequently referred to as “exploding” a thesaurus term). However, to perform a sensitive search, all relevant variations of the narrower terms must be searched as free-text keywords in the title or abstract, in addition to relying on the exploded thesaurus term. Thus, all articles that describe a certain narrower topic in their titles and abstracts will already be retrieved before MeSH terms are added.
9. Add variations in search terms (e.g., truncation, spelling differences, abbreviations, opposites)
Truncation allows a searcher to search for words beginning with the same word stem. A search for therap* will, thus, retrieve therapy, therapies, therapeutic, and all other words starting with “therap.” Do not truncate a word stem that is too short. Also, limitations of interfaces should be taken into account, especially in PubMed, where the number of search term variations that can be found by truncation is limited to 600.
Databases contain references to articles using both standard British and American English spellings. Both need to be searched as free-text terms in the title and abstract. Alternatively, many interfaces offer a certain code to replace zero or one characters, allowing a search for “pediatric” or “paediatric” as “p?ediatric.” Table 1 provides a detailed description of the syntax for different interfaces.
Field codes in five most used interfaces for biomedical literature searching
Searching for abbreviations can identify extra, relevant references and retrieve more irrelevant ones. The search can be more focused by combining the abbreviation with an important word that is relevant to its meaning or by using the Boolean “NOT” to exclude frequently observed, clearly irrelevant results. We advise that searchers do not exclude all possible irrelevant meanings, as it is very time consuming to identify all the variations, it will result in unnecessarily complicated search strategies, and it may lead to erroneously narrowing the search and, thereby, reduce recall.
Searching partial abbreviations can be useful for retrieving relevant references. For example, it is very likely that an article would mention osteoarthritis (OA) early in the abstract, replacing all further occurrences of osteoarthritis with OA . Therefore, it may not contain the phrase “hip osteoarthritis” but only “hip oa.”
It is also important to search for the opposites of search terms to avoid bias. When searching for “disease recurrence,” articles about “disease free” may be relevant as well. When the desired outcome is survival , articles about mortality may be relevant.
10. Use database-appropriate syntax, with parentheses, Boolean operators, and field codes
Different interfaces require different syntaxes, the special set of rules and symbols unique to each database that define how a correctly constructed search operates. Common syntax components include the use of parentheses and Boolean operators such as “AND,” “OR,” and “NOT,” which are available in all major interfaces. An overview of different syntaxes for four major interfaces for bibliographic medical databases (PubMed, Ovid, EBSCOhost, Embase.com, and ProQuest) is shown in Table 1 .
Creating the appropriate syntax for each database, in combination with the selected terms as described in steps 7–9, can be challenging. Following the method outlined below simplifies the process:
- Create single-line queries in a text document (not combining multiple record sets), which allows immediate checking of the relevance of retrieved references and efficient optimization.
- Type the syntax (Boolean operators, parentheses, and field codes) before adding terms, which reduces the chance that errors are made in the syntax, especially in the number of parentheses.
- Use predefined proximity structures including parentheses, such as (() ADJ3 ()) in Ovid, that can be reused in the query when necessary.
- Use thesaurus terms separately from free-text terms of each element. Start an element with all thesaurus terms (using “OR”) and follow with the free-text terms. This allows the unique optimization methods as described in step 11.
- When adding terms to an existing search strategy, pay close attention to the position of the cursor. Make sure to place it appropriately either in the thesaurus terms section, in the title/abstract section, or as an addition (broadening) to an existing proximity search.
The supplementary appendix explains the method of building a query in more detail, step by step for different interfaces: PubMed, Ovid, EBSCOhost, Embase.com, and ProQuest. This method results in a basic search strategy designed to retrieve some relevant references upon which a more thorough search strategy can be built with optimization such as described in step 11.
11. Optimize the search
The most important question when performing a systematic search is whether all (or most) potentially relevant articles have been retrieved by the search strategy. This is also the most difficult question to answer, since it is unknown which and how many articles are relevant. It is, therefore, wise first to broaden the initial search strategy, making the search more sensitive, and then check if new relevant articles are found by comparing the set results (i.e., search for Strategy #2 NOT Strategy #1 to see the unique results).
A search strategy should be tested for completeness. Therefore, it is necessary to identify extra, possibly relevant search terms and add them to the test search in an OR relationship with the already used search terms. A good place to start, and a well-known strategy, is scanning the top retrieved articles when sorted by relevance, looking for additional relevant synonyms that could be added to the search strategy.
We have developed a unique optimization method that has not been described before in the literature. This method often adds valuable extra terms to our search strategy and, therefore, extra, relevant references to our search results. Extra synonyms can be found in articles that have been assigned a certain set of thesaurus terms but that lack synonyms in the title and/or abstract that are already present in the current search strategy. Searching for thesaurus terms NOT free-text terms will help identify missed free-text terms in the title or abstract. Searching for free-text terms NOT thesaurus terms will help identify missed thesaurus terms. If this is done repeatedly for each element, leaving the rest of the query unchanged, this method will help add numerous relevant terms to the query. These steps are explained in detail for five different search platforms in the supplementary appendix .
12. Evaluate the initial results
The results should now contain relevant references. If the interface allows relevance ranking, use that in the evaluation. If you know some relevant references that should be included in the research, search for those references specifically; for example, combine a specific (first) author name with a page number and the publication year. Check whether those references are retrieved by the search. If the known relevant references are not retrieved by the search, adapt the search so that they are. If it is unclear which element should be adapted to retrieve a certain article, combine that article with each element separately.
Different outcomes are desired for different types of research questions. For instance, in the case of clinical question answering, the researcher will not be satisfied with many references that contain a lot of irrelevant references. A clinical search should be rather specific and is allowed to miss a relevant reference. In the case of an SR, the researchers do not want to miss any relevant reference and are willing to handle many irrelevant references to do so. The search for references to include in an SR should be very sensitive: no included reference should be missed. A search that is too specific or too sensitive for the intended goal can be adapted to become more sensitive or specific. Steps to increase sensitivity or specificity of a search strategy can be found in the supplementary appendix .
13. Check for errors
Errors might not be easily detected. Sometimes clues can be found in the number of results, either when the number of results is much higher or lower than expected or when many retrieved references are not relevant. However, the number expected is often unknown, and very sensitive search strategies will always retrieve many irrelevant articles. Each query should, therefore, be checked for errors.
One of the most frequently occurring errors is missing the Boolean operator “OR.” When no “OR” is added between two search terms, many interfaces automatically add an “AND,” which unintentionally reduces the number of results and likely misses relevant references. One good strategy to identify missing “OR”s is to go to the web page containing the full search strategy, as translated by the database, and using Ctrl-F search for “AND.” Check whether the occurrences of the “AND” operator are deliberate.
Ideally, search strategies should be checked by other information specialists [ 18 ]. The Peer Review of Electronic Search Strategies (PRESS) checklist offers good guidance for this process [ 4 ]. Apart from the syntax (especially Boolean operators and field codes) of the search strategy, it is wise to have the search terms checked by the clinician or researcher familiar with the topic. At Erasmus MC, researchers and clinicians are involved during the complete process of structuring and optimizing the search strategy. Each word is added after the combined decision of the searcher and the researcher, with the possibility of directly comparing results with and without the new term.
14. Translate to other databases
To retrieve as many relevant references as possible, one has to search multiple databases. Translation of complex and exhaustive queries between different databases can be very time consuming and cumbersome. The single-line search strategy approach detailed above allows quick translations using the find and replace method in Microsoft Word (<Ctrl-H>).
At Erasmus MC, macros based on the find-and-replace method in Microsoft Word have been developed for easy and fast translation between the most used databases for biomedical and health sciences questions. The schema that is followed for the translation between databases is shown in Figure 2 . Most databases simply follow the structure set by the Embase.com search strategy. The translation from Emtree terms to MeSH terms for MEDLINE in Ovid often identifies new terms that need to be added to the Embase.com search strategy before the translation to other databases.

Schematic representation of translation between databases used at Erasmus University Medical Center
Dotted lines represent databases that are used in less than 80% of the searches.
Using five different macros, a thoroughly optimized query in Embase.com can be relatively quickly translated into eight major databases. Basic search strategies will be created to use in many, mostly smaller, databases, because such niche databases often do not have extensive thesauri or advanced syntax options. Also, there is not much need to use extensive syntax because the number of hits and, therefore, the amount of noise in these databases is generally low. In MEDLINE (Ovid), PsycINFO (Ovid), and CINAHL (EBSCOhost), the thesaurus terms must be adapted manually, as each database has its own custom thesaurus. These macros and instructions for their installation, use, and adaptation are available at bit.ly/databasemacros.
15. Test and reiterate
Ideally, exhaustive search strategies should retrieve all references that are covered in a specific database. For SR search strategies, checking searches for their recall is advised. This can be done after included references have been determined by the authors of the systematic review. If additional papers have been identified through other non-database methods (i.e., checking references in included studies), results that were not identified by the database searches should be examined. If these results were available in the databases but not located by the search strategy, the search strategy should be adapted to try to retrieve these results, as they may contain terms that were omitted in the original search strategies. This may enable the identification of additional relevant results.
A methodology for creating exhaustive search strategies has been created that describes all steps of the search process, starting with a question and resulting in thorough search strategies in multiple databases. Many of the steps described are not new, but together, they form a strong method creating high-quality, robust searches in a relatively short time frame.
Our methodology is intended to create thoroughness for literature searches. The optimization method, as described in step 11, will identify missed synonyms or thesaurus terms, unlike any other method that largely depends on predetermined keywords and synonyms. Using this method results in a much quicker search process, compared to traditional methods, especially because of the easier translation between databases and interfaces (step 13). The method is not a guarantee for speed, since speed depends on many factors, including experience. However, by following the steps and using the tools as described above, searchers can gain confidence first and increase speed through practice.
What is new?
This method encourages searchers to start their search development process using empty syntax first and later adding the thesaurus terms and free-text synonyms. We feel this helps the searcher to focus on the search terms, instead of on the structure of the search query. The optimization method in which new terms are found in the already retrieved articles is used in some other institutes as well but has to our knowledge not been described in the literature. The macros to translate search strategies between interfaces are unique in this method.
What is different compared to common practice?
Traditionally, librarians and information specialists have focused on creating complex, multi-line (also called line-by-line) search strategies, consisting of multiple record sets, and this method is frequently advised in the literature and handbooks [ 2 , 19 – 21 ]. Our method, instead, uses single-line searches, which is critical to its success. Single-line search strategies can be easily adapted by adding or dropping a term without having to recode numbers of record sets, which would be necessary in multi-line searches. They can easily be saved in a text document and repeated by copying and pasting for search updates. Single-line search strategies also allow easy translation to other syntaxes using find-and-replace technology to update field codes and other syntax elements or using macros (step 13).
When constructing a search strategy, the searcher might experience that certain parentheses in the syntax are unnecessary, such as parentheses around all search terms in the title/abstract portion, if there is only one such term, there are double parentheses in the proximity statement, or one of the word groups exists for only one word. One might be tempted to omit those parentheses for ease of reading and management. However, during the optimization process, the searcher is likely to find extra synonyms that might consist of one word. To add those terms to the first query (with reduced parentheses) requires adding extra parentheses (meticulously placing and counting them), whereas, in the latter search, it only requires proper placement of those terms.
Many search methods highly depend on the PICO framework. Research states that often PICO or PICOS is not suitable for every question [ 22 , 23 ]. There are other acronyms than PICO—such as sample, phenomenon of interest, design, evaluation, research type (SPIDER) [ 24 ]—but each is just a variant. In our method, the most important and specific elements of a question are being analyzed for building the best search strategy.
Though it is generally recommended that searchers search both MEDLINE and Embase, most use MEDLINE as the starting point. It is considered the gold standard for biomedical searching, partially due to historical reasons, since it was the first of its kind, and more so now that it is freely available via the PubMed interface. Our method can be used with any database as a starting point, but we use Embase instead of MEDLINE or another database for a number of reasons. First, Embase provides both unique content and the complete content of MEDLINE. Therefore, searching Embase will be, by definition, more complete than searching MEDLINE only. Second, the number of terms in Emtree (the Embase thesaurus) is three times as high as that of MeSH (the MEDLINE thesaurus). It is easier to find MeSH terms after all relevant Emtree terms have been identified than to start with MeSH and translate to Emtree.
At Erasmus MC, the researchers sit next to the information specialist during most of the search strategy design process. This way, the researchers can deliver immediate feedback on the relevance of proposed search terms and retrieved references. The search team then combines knowledge about databases with knowledge about the research topic, which is an important condition to create the highest quality searches.
Limitations of the method
One disadvantage of single-line searches compared to multi-line search strategies is that errors are harder to recognize. However, with the methods for optimization as described (step 11), errors are recognized easily because missed synonyms and spelling errors will be identified during the process. Also problematic is that more parentheses are needed, making it more difficult for the searcher and others to assess the logic of the search strategy. However, as parentheses and field codes are typed before the search terms are added (step 10), errors in parentheses can be prevented.
Our methodology works best if used in an interface that allows proximity searching. It is recommended that searchers with access to an interface with proximity searching capabilities select one of those as the initial database to develop and optimize the search strategy. Because the PubMed interface does not allow proximity searches, phrases or Boolean “AND” combinations are required. Phrase searching complicates the process and is more specific, with the higher risk of missing relevant articles, and using Boolean “AND” combinations increases sensitivity but at an often high loss of specificity. Due to some searchers’ lack of access to expensive databases or interfaces, the freely available PubMed interface may be necessary to use, though it should never be the sole database used for an SR [ 2 , 16 , 25 ]. A limitation of our method is that it works best with subscription-based and licensed resources.
Another limitation is the customization of the macros to a specific institution’s resources. The macros for the translation between different database interfaces only work between the interfaces as described. To mitigate this, we recommend using the find-and-replace functionality of text editors like Microsoft Word to ease the translation of syntaxes between other databases. Depending on one’s institutional resources, custom macros can be developed using similar methods.
Results of the method
Whether this method results in exhaustive searches where no important article is missed is difficult to determine, because the number of relevant articles is unknown for any topic. A comparison of several parameters of 73 published reviews that were based on a search developed with this method to 258 reviews that acknowledged information specialists from other Dutch academic hospitals shows that the performance of the searches following our method is comparable to those performed in other institutes but that the time needed to develop the search strategies was much shorter than the time reported for the other reviews [ 9 ].
CONCLUSIONS
With the described method, searchers can gain confidence in their search strategies by finding many relevant words and creating exhaustive search strategies quickly. The approach can be used when performing SR searches or for other purposes such as answering clinical questions, with different expectations of the search’s precision and recall. This method, with practice, provides a stepwise approach that facilitates the search strategy development process from question clarification to final iteration and beyond.
SUPPLEMENTAL FILE
Acknowledgments.
We highly appreciate the work that was done by our former colleague Louis Volkers, who in his twenty years as an information specialist in Erasmus MC laid the basis for our method. We thank Professor Oscar Franco for reviewing earlier drafts of this article.
What are the differences between a literature search, a literature review, a systematic review and a meta-analysis? And why is a systematic review considered to be so good?
Affiliation.
- 1 Graduate Entry Medical School, University of Limerick. [email protected]
- PMID: 24273836
- Evidence-Based Medicine
- Knowledge Discovery*
- Meta-Analysis as Topic*
- Review Literature as Topic*
- Systematic Reviews as Topic*
Penn State University Libraries
- Home-Articles and Databases
- Asking the clinical question
- PICO & Finding Evidence
- Evaluating the Evidence
- Systematic Review vs. Literature Review
- Ethical & Legal Issues for Nurses
- Nursing Library Instruction Course
- Data Management Toolkit This link opens in a new window
- Useful Nursing Resources
- Writing Resources
- LionSearch and Finding Articles
- The Catalog and Finding Books
Know the Difference! Systematic Review vs. Literature Review
It is common to confuse systematic and literature reviews as both are used to provide a summary of the existent literature or research on a specific topic. Even with this common ground, both types vary significantly. Please review the following chart (and its corresponding poster linked below) for the detailed explanation of each as well as the differences between each type of review.
- What's in a name? The difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review, and why it matters by Lynn Kysh, MLIS, University of Southern California - Norris Medical Library
- << Previous: Evaluating the Evidence
- Next: Ethical & Legal Issues for Nurses >>
- Last Updated: Mar 1, 2024 11:54 AM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/nursing

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
Literature Review vs Research Paper: What’s the Difference?
by Antony W
January 8, 2023

This is a complete student’s guide to understanding literature review vs research paper.
We’ll teach you what they’re, explain why they’re important, state the difference between the two, and link you to our comprehensive guide on how to write them.
Literature Review Writing Help
Writing a literature review for a thesis, a research paper, or as a standalone assignment takes time. Much of your time will go into research, not to mention you have other assignments to complete.
If you find writing in college or university overwhelming, get in touch with our literature review writers for hire at 25% discounts and enjoy the flexibility and convenience that comes with professional writing help. We’ll help you do everything, from research and outlining to custom writing and proofreading.
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a secondary source of information that provides an overview of existing knowledge, which you can use to identify gaps or flaws in existing research. In literature review writing, students have to find and read existing publications such as journal articles, analyze the information, and then state their findings.
Credit: Pubrica
You’ll write a literature review to demonstrate your understanding on the topic, show gaps in existing research, and develop an effective methodology and a theoretical framework for your research project.
Your instructor may ask you to write a literature review as a standalone assignment. Even if that’s the case, the rules for writing a review paper don’t change.
In other words, you’ll still focus on evaluating the current research and find gaps around the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
There are three types of review papers and they’re a follows:
1. Meta-analysis
In meta-analysis review paper, you combine and compare answers from already published studies on a given subject.
2. Narrative Review
A narrative review paper looks into existing information or research already conducted on a given topic.
3. Systematic Review
You need to do three things if asked to write a systematic review paper.
First, read and understand the question asked. Second, look into research already conducted on the topic. Third, search for the answer to the question from the established research you just read.
What’s a Research Paper?
A research paper is an assignment in which you present your own argument, evaluation, or interpretation of an issue based on independent research.

In a research paper project, you’ll draw some conclusions from what experts have already done, find gaps in their studies, and then draw your own conclusions.
While a research paper is like an academic essay, it tends to be longer and more detailed.
Since they require extended research and attention to details, research papers can take a lot of time to write.
If well researched, your research paper can demonstrate your knowledge about a topic, your ability to engage with multiple sources, and your willingness to contribute original thoughts to an ongoing debate.
Types of Research Papers
There are two types of research papers and they’re as follows:
1. Analytical Research Papers
Similar to analytical essay , and usually in the form of a question, an analytical research paper looks at an issue from a neutral point and gives a clear analysis of the issue.
Your goal is to make the reader understand both sides of the issue in question and leave it to them to decide what side of the analysis to accept.
Unlike an argumentative research paper, an analytical research paper doesn’t include counterarguments. And you can only draw your conclusion based on the information stretched out all through the analysis.
2. Argumentative Research Papers
In an argumentative research paper, you state the subject under study, look into both sides of an issue, pick a stance, and then use solid evidence and objective reasons to defend your position.
In argumentative writing, your goal isn’t to persuade your audience to take an action.
Rather, it’s to convince them that your position on the research question is more accurate than the opposing point of views.
Regardless of the type of research paper that you write, you’ll have to follow the standard outline for the assignment to be acceptable for review and marking.
Also, all research paper, regardless of the research question under investigation must include a literature review.
Literature Review vs Research Paper
The table below shows the differences between a literature review (review paper) and a research paper.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. is there a literature review in a research paper.
A research paper assignment must include a literature review immediately after the introduction chapter.
The chapter is significant because your research work would otherwise be incomplete without knowledge of existing literature.
2. How Many Literature Review Should Be in Research Paper?
Your research paper should have only one literature review. Make sure you write the review based on the instructions from your teacher.
Before you start, check the required length, number of sources to summarize, and the format to use. Doing so will help you score top grades for the assignment.
3. What is the Difference Between Research and Literature?
Whereas literature focuses on gathering, reading, and summarizing information on already established studies, original research involves coming up with new concepts, theories, and ideas that might fill existing gaps in the available literature.
4. How Long is a Literature Review?
How long a literature review should be will depend on several factors, including the level of education, the length of the assignment, the target audience, and the purpose of the review.
For example, a 150-page dissertation can have a literature review of 40 pages on average.
Make sure you talk to your instructor to determine the required length of the assignment.
5. How Does a Literature Review Look Like?
Your literature review shouldn’t be a focus on original research or new information. Rather, it should give a clear overview of the already existing work on the selected topic.
The information to review can come from various sources, including scholarly journal articles , government reports, credible websites, and academic-based books.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.

About Systematic Reviews
Understanding the Differences Between a Systematic Review vs Literature Review

Automate every stage of your literature review to produce evidence-based research faster and more accurately.
Let’s look at these differences in further detail.
Goal of the Review
The objective of a literature review is to provide context or background information about a topic of interest. Hence the methodology is less comprehensive and not exhaustive. The aim is to provide an overview of a subject as an introduction to a paper or report. This overview is obtained firstly through evaluation of existing research, theories, and evidence, and secondly through individual critical evaluation and discussion of this content.
A systematic review attempts to answer specific clinical questions (for example, the effectiveness of a drug in treating an illness). Answering such questions comes with a responsibility to be comprehensive and accurate. Failure to do so could have life-threatening consequences. The need to be precise then calls for a systematic approach. The aim of a systematic review is to establish authoritative findings from an account of existing evidence using objective, thorough, reliable, and reproducible research approaches, and frameworks.
Level of Planning Required
The methodology involved in a literature review is less complicated and requires a lower degree of planning. For a systematic review, the planning is extensive and requires defining robust pre-specified protocols. It first starts with formulating the research question and scope of the research. The PICO’s approach (population, intervention, comparison, and outcomes) is used in designing the research question. Planning also involves establishing strict eligibility criteria for inclusion and exclusion of the primary resources to be included in the study. Every stage of the systematic review methodology is pre-specified to the last detail, even before starting the review process. It is recommended to register the protocol of your systematic review to avoid duplication. Journal publishers now look for registration in order to ensure the reviews meet predefined criteria for conducting a systematic review [1].
Search Strategy for Sourcing Primary Resources
Learn more about distillersr.
(Article continues below)
Quality Assessment of the Collected Resources
A rigorous appraisal of collected resources for the quality and relevance of the data they provide is a crucial part of the systematic review methodology. A systematic review usually employs a dual independent review process, which involves two reviewers evaluating the collected resources based on pre-defined inclusion and exclusion criteria. The idea is to limit bias in selecting the primary studies. Such a strict review system is generally not a part of a literature review.
Presentation of Results
Most literature reviews present their findings in narrative or discussion form. These are textual summaries of the results used to critique or analyze a body of literature about a topic serving as an introduction. Due to this reason, literature reviews are sometimes also called narrative reviews. To know more about the differences between narrative reviews and systematic reviews , click here.
A systematic review requires a higher level of rigor, transparency, and often peer-review. The results of a systematic review can be interpreted as numeric effect estimates using statistical methods or as a textual summary of all the evidence collected. Meta-analysis is employed to provide the necessary statistical support to evidence outcomes. They are usually conducted to examine the evidence present on a condition and treatment. The aims of a meta-analysis are to determine whether an effect exists, whether the effect is positive or negative, and establish a conclusive estimate of the effect [2].
Using statistical methods in generating the review results increases confidence in the review. Results of a systematic review are then used by clinicians to prescribe treatment or for pharmacovigilance purposes. The results of the review can also be presented as a qualitative assessment when the end goal is issuing recommendations or guidelines.
Risk of Bias
Literature reviews are mostly used by authors to provide background information with the intended purpose of introducing their own research later. Since the search for included primary resources is also less exhaustive, it is more prone to bias.
One of the main objectives for conducting a systematic review is to reduce bias in the evidence outcome. Extensive planning, strict eligibility criteria for inclusion and exclusion, and a statistical approach for computing the result reduce the risk of bias.
Intervention studies consider risk of bias as the “likelihood of inaccuracy in the estimate of causal effect in that study.” In systematic reviews, assessing the risk of bias is critical in providing accurate assessments of overall intervention effect [3].
With numerous review methods available for analyzing, synthesizing, and presenting existing scientific evidence, it is important for researchers to understand the differences between the review methods. Choosing the right method for a review is crucial in achieving the objectives of the research.
[1] “Systematic Review Protocols and Protocol Registries | NIH Library,” www.nihlibrary.nih.gov . https://www.nihlibrary.nih.gov/services/systematic-review-service/systematic-review-protocols-and-protocol-registries
[2] A. B. Haidich, “Meta-analysis in medical research,” Hippokratia , vol. 14, no. Suppl 1, pp. 29–37, Dec. 2010, [Online]. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3049418/#:~:text=Meta%2Danalyses%20are%20conducted%20to
3 Reasons to Connect

Differences in quality of anticoagulation care delivery according to ethnoracial group in the United States: A scoping review
- Open access
- Published: 11 May 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Sara R. Vazquez ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9267-8980 1 ,
- Naomi Y. Yates 2 ,
- Craig J. Beavers 3 , 4 ,
- Darren M. Triller 3 &
- Mary M. McFarland 5
316 Accesses
6 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Anticoagulation therapy is standard for conditions like atrial fibrillation, venous thromboembolism, and valvular heart disease, yet it is unclear if there are ethnoracial disparities in its quality and delivery in the United States. For this scoping review, electronic databases were searched for publications between January 1, 2011 – March 30, 2022. Eligible studies included all study designs, any setting within the United States, patients prescribed anticoagulation for any indication, outcomes reported for ≥ 2 distinct ethnoracial groups. The following four research questions were explored: Do ethnoracial differences exist in 1) access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy, 2) quality of anticoagulation therapy management, 3) clinical outcomes related to anticoagulation care, 4) humanistic/educational outcomes related to anticoagulation therapy. A total of 5374 studies were screened, 570 studies received full-text review, and 96 studies were analyzed. The largest mapped focus was patients’ access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy (88/96 articles, 91.7%). Seventy-eight articles made statistical outcomes comparisons among ethnoracial groups. Across all four research questions, 79 articles demonstrated favorable outcomes for White patients compared to non-White patients, 38 articles showed no difference between White and non-White groups, and 8 favored non-White groups (the total exceeds the 78 articles with statistical outcomes as many articles reported multiple outcomes). Disparities disadvantaging non-White patients were most pronounced in access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy (43/66 articles analyzed) and quality of anticoagulation management (19/21 articles analyzed). Although treatment guidelines do not differentiate anticoagulant therapy by ethnoracial group, this scoping review found consistently favorable outcomes for White patients over non-White patients in the domains of access to anticoagulation therapy for guideline-based indications and quality of anticoagulation therapy management. No differences among groups were noted in clinical outcomes, and very few studies assessed humanistic or educational outcomes.
Graphical Abstract
Scoping Review: Differences in quality of United States anticoagulation care delivery by ethnoracial group. AF = atrial fibrillation; AMS = anticoagulation management service; DOACs = direct oral anticoagulants; INR = international normalized ratio; PSM = patient self-management; PST = patient self-testing
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
It is well-established that in the United States (US) ethnoracial disparities exist in various aspects of health care. Specifically, persons identifying with an ethnoracial minority group may have more challenging access to health care, worse clinical outcomes, and higher dissatisfaction with care compared to White persons [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]. There are differences by ethnoracial group in the prevalence of the three most common indications for which anticoagulants are prescribed, stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation (AF), treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE), and valvular heart disease [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ]. Specifically, VTE is most prevalent in Black patients compared to White and Asian patients, whereas AF is most prevalent in White patients compared to Black, Asian, and Hispanic patients [ 9 , 10 , 15 ]. Calcific heart valve disease has the most relevance to the US population, and epidemiologic data has shown that aortic stenosis is more prevalent in White patients compared to Black, Asian, and Hispanic patients [ 17 ]. Despite these epidemiologic differences, there is no evidence to suggest there should be any difference in treatment strategies across ethnoracial patient groups.
While studies have demonstrated genotypic differences that may result in different warfarin dose requirements[ 18 ], and early studies may indicate genotypic differences in direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) response [ 19 ], no US-based labeling or guidelines recommend a difference in prescription or delivery of anticoagulation care based on race or ethnicity. However, it is unclear if there are in fact differences in the type and quality of anticoagulation therapy, which is standard of care for each of these conditions [ 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 ]. Anticoagulants remain in the top three classes of drugs causing adverse drug events (primarily bleeding) in the United States, according to the 2014 National Action Plan for Adverse Drug Event Prevention. One of the goals of the National Action Plan was to identify patient populations at higher risk for these adverse drug events to inform the development of targeted harm reduction strategies [ 25 ]. If ethnoracial minority patients are receiving sub-optimal anticoagulation therapy in certain measurable areas of anticoagulation quality, it is vital to highlight the areas of disparity so that these can be explored and care optimized. Anticoagulation providers often have high frequency contact with their patients and can be a reliable connection between disproportionately affected patients and a system in need of change. Systematic reviews of ethnoracial disparities in AF and VTE have been conducted. The AF review assessed AF prevalence among racial groups as well as differences in symptoms and management, including stroke prevention with warfarin or DOACs [ 9 ]. The VTE review specifically assessed VTE prevalence and racial differences in COVID-19 and did report the use of any prophylactic anticoagulation, but this was not part of the analysis [ 26 ]. No review of racial disparities in quality of anticoagulation therapy was found in search results conducted prior to protocol.
In this study we aimed to identify any potential ethnoracial disparities in anticoagulation care quality in the US. The decision to limit the study to a US population was based on our observation that the US has a unique history of interactions between racial and ethnic groups that may not necessarily be reflected by studies conducted in other countries. Additionally, health care delivery systems vary widely across the world, and we wanted to include the data most relevant to the potential racial disparities existing in the US health care system. The term “race” was used to identify a group of people with shared physical characteristics believed to be of common ancestry whereas the term “ethnicity” refers to a group of people with shared cultural traditions [ 27 ]. We recognize these terms may be far more complex. In order to encompass both the physical and cultural aspects of a patient’s identity we have chosen to use the term “ethnoracial” for this study [ 27 ]. Highlighting existing differences will serve as a stimulus for institutions and clinicians to assess current services, implement quality improvement measures, and inform future research efforts to deliver optimal anticoagulation care for all patients. The scoping review protocol was registered December 22, 2021 to Open Science Framework, https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/9SE7H [ 28 ].
We conducted this scoping review with guidance from the 2020 version of the JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis and organized to Arksey's five stages: 1) identifying the research question, 2) identifying relevant studies, 3) study selection, 4) charting the data and 5) collating, summarizing and reporting the results [ 29 , 30 ]. For transparency and reproducibility, we followed the PRISMA-ScR and PRISMA-S reporting guidelines in reporting our results [ 31 ]. We used Covidence (Veritas Health Innovation,) an online systematic reviewing platform to screen and select studies. Citation management and duplicate detection and removal was accomplished with EndNote, version 19 (Clarivate Analytics.) Data was charted from our selected studies using REDCap, an electronic data capture tool hosted at the University of Utah [ 32 ].
Literature searching
An information specialist developed and translated search strategies for the online databases using a combination of keywords and controlled subject headings unique to each database along with team feedback. Peer review of the strategies was conducted by library colleagues using the PRESS guidelines. [ 33 ] Electronic databases searched included Medline (Ovid) 2011–2022, Embase (embase.com) 2011–2022, CINAHL Complete (Ebscohost) 2011–2022, Sociological Abstracts (ProQuest) 2011–2022, International Pharmaceutical Abstracts (Ovid) 2011–2022, Scopus (scopus.org) 2011–2022 and Web of Science Core Collection (Clarivate Analytics) 2011–2022. Limits included a date range from January 1, 2011 to March 30—April 19, 2022, as not all database results were exported on the same day. See Supplemental File 1 for detailed search strategies. A search of grey literature was not conducted due to time and resource constraints.
Study Selection
For inclusion, each study required two votes by independent reviewers for screening of titles and abstracts followed by full-text review. A third reviewer provided the deciding vote. Data extraction was performed by two independent reviewers, and consensus on any discrepancies was reached via discussion between the reviewers. The data form was piloted by two team members using sentinel articles prior to data extraction.
Eligible studies included all types of study designs in any setting with a population of patients of any age or gender located within the US who were prescribed anticoagulant therapy for any indication, published between January 1, 2011 – March 30, 2022 in order to capture contemporary and clinically relevant practices.
We defined the following research questions for this scoping review as described in Table 1 .
Studies must have reported any of these anticoagulation care delivery outcomes for at least 2 distinct racial or ethnic groups. We excluded genotyping studies and non-English language articles at full text review, as we had no funding for translation services. In checking references of included studies, no additional studies met inclusion criteria. In accordance with scoping review methodology, no quality assessment of included studies was conducted as our goal was to rapidly map the literature. As this is a scoping review of the literature, no aggregate or pooled analysis was performed; however, for ease of interpretation, when assessing for the directionality of the outcomes in the various studies, we categorized studies into Favoring White Group, Favoring Non-White Group, and No Differences Among Ethnoracial Groups. If studies had mixed outcomes of favoring one group for one outcome and no difference for another, then the study was categorized with the favoring group.
A PRISMA flow diagram in Fig. 1 depicts search results, exclusions, and inclusions. The search strategies retrieved 6900 results with 1526 duplicates removed. Following title and abstract screening of 5374 references, 570 articles received full-text review. The most common reason for the exclusion of 474 studies was that outcomes were not reported for two distinct ethnoracial groups (171 studies). Ninety-six studies underwent data extraction.
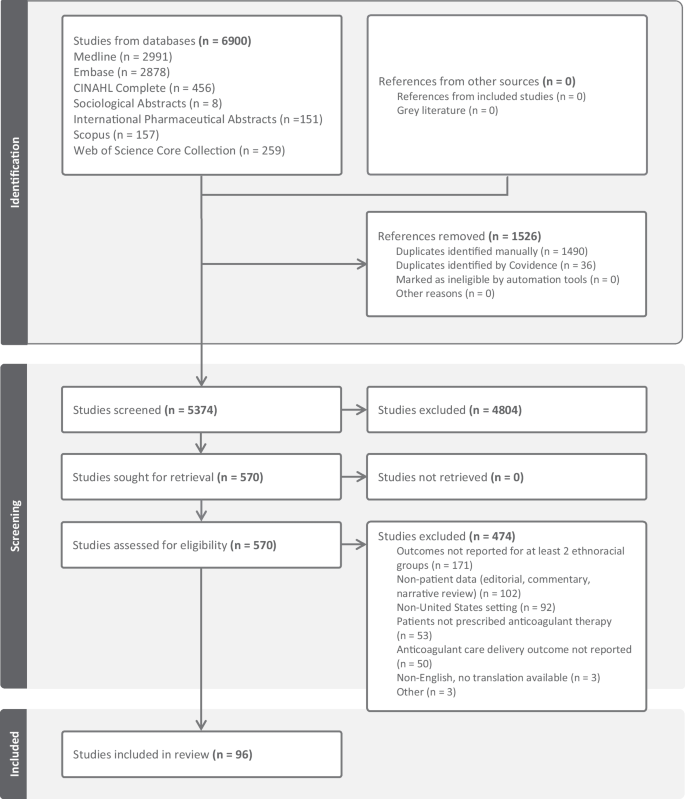
PRISMA Flow Diagram
Study characteristics-overall
Fifty of the 96 studies were published between 2011 and 2018 (an average of 6.25 articles per year that compared outcomes between two ethnoracial groups) and 43 of 96 studies were published in the years 2019–2021 (average 14.3 articles per year; 2022 excluded here because only 4 months of data was captured) (Fig. 2 ). Most studies analyzed an outpatient population (65.6%) for an indication of stroke prevention in AF (67.7%) in patients taking warfarin (71.9%) or DOACs (49.0%). Study population size was heterogenous, ranging from a study size of 24 patients to over 1.3 million patients (median 5,238 patients) in the 69 studies that reported population size by racial group. When stratified by size, 60.9% of the articles in the scoping review (42 articles) represented < 10,000 patients (Table 2 ).
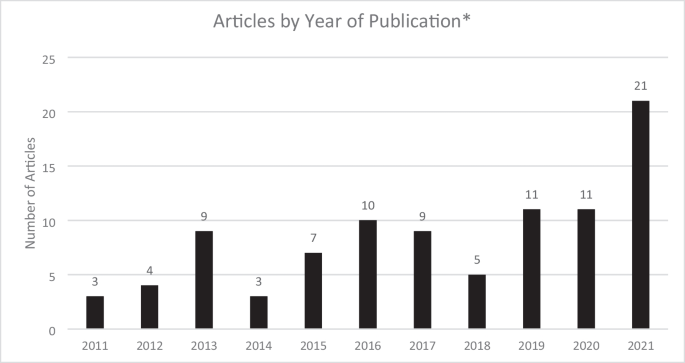
Number of Articles by Publication Year. *2022 excluded from this figure since the search period did not capture the entire year
Study characteristics-by ethnoracial group
There were 50 studies (52.1%) where race or ethnicity was either mentioned in the title or objective of the article, with 24 of these published over the 7-year period 2011–2018 and 26 published over the 3-year period 2019 to first quarter 2022. The method for reporting race or ethnicity was unclear or unspecified in most studies (77.1%) and 16 articles (16.7%) utilized self-reporting of race or ethnicity. Most studies analyzed White or Caucasian racial groups (94.8%), followed by Black or African-American (80.2%), and many studies grouped all other racial groups into an “Other” category (41.7%) (Fig. 3 ).
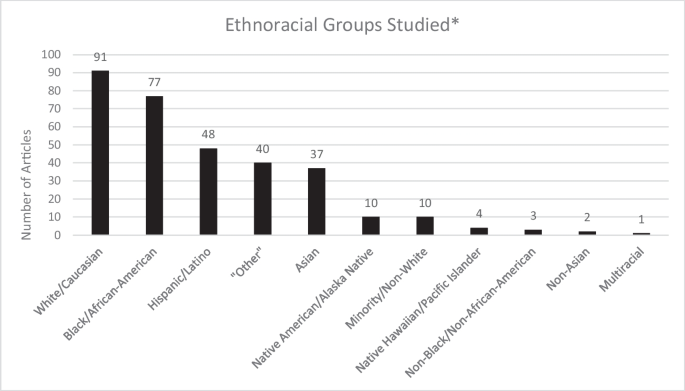
Number of Articles by Ethnoracial Groups. *For study inclusion, a study had to compare outcomes for least two distinct ethnoracial groups
White patients accounted for a median 77% of study populations, Black patients 9.5%, Hispanic/Latino patients 6.2%, “Other” racial groups 5.3%, and Asian patients 2.5%.
Study outcomes-overall
Of the 4 research questions, most studies included in this review analyzed patients’ access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy (88/96 articles, 91.7%), clinical outcomes (42/96 articles, 43.8%), or quality of anticoagulation management (24/96 articles, 25.0%), while very few addressed humanistic or educational outcomes (5/96 articles, 5.2%) (Fig. 4 ). Many studies addressed multiple outcomes within the single study.
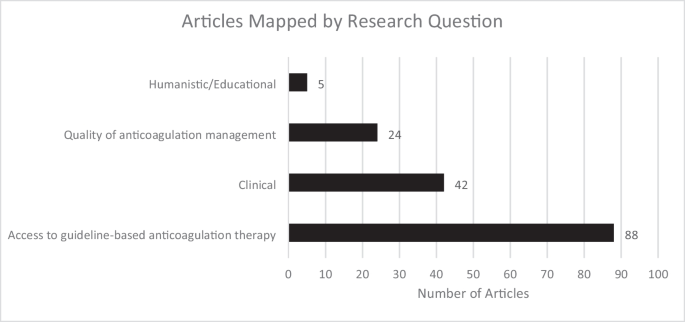
Number of Articles Mapped by Research Question
Seventy-eight of the 96 included studies provided statistical comparisons between ethnoracial groups, and these data are presented below.
Outcomes for research question 1: Do ethnoracial differences exist in access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy?
Anticoagulation for a guideline-based indication.
This question focused on patients who had an indication for anticoagulation actually receiving an anticoagulant, specifically AF and VTE prophylaxis (based on risk stratification) and acute VTE. The majority of the AF studies (25/34 studies) demonstrated White patients receiving anticoagulation at significantly higher rates compared to non-White patients [ 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 ], while the six VTE studies largely demonstrated no difference among ethnoracial groups [ 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 ].
DOACs as first-line therapy for AF or VTE
Eighteen individual studies statistically assessed the outcome of DOAC as first-line therapy (compared to warfarin) for AF (15 studies), VTE treatment (2 studies), or both indications (1 study). Twelve of the 15 AF studies showed a significantly higher proportion of White patients received DOACs as first-line therapy compared to non-White patients [ 36 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 54 , 55 , 67 , 68 ]. Of those 12, 9 specifically compared White patients to Black patients. Both VTE treatment studies and the study that assessed both AF and VTE indications showed significantly higher DOAC prescribing rates for White patients compared to Black patients [ 69 , 70 , 71 ].
Anticoagulant therapy adherence/persistence
The eight studies that addressed anticoagulation therapy adherence/persistence showed variability in outcome directionality by ethnoracial group: 5 no difference [ 41 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 ], 2 showed better treatment adherence/persistence for White patients compared to Black patients[ 76 ] or non-White patients [ 77 ], and one showed better treatment adherence/persistence for White patients compared to Hispanic patients, but no difference in White versus Black patients [ 78 ].
Figure 5 summarizes the outcome directionality for Research Question 1 regarding access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy. Overall, the areas of disparity identified included anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation and preferential use of DOAC therapy for AF and VTE treatment.
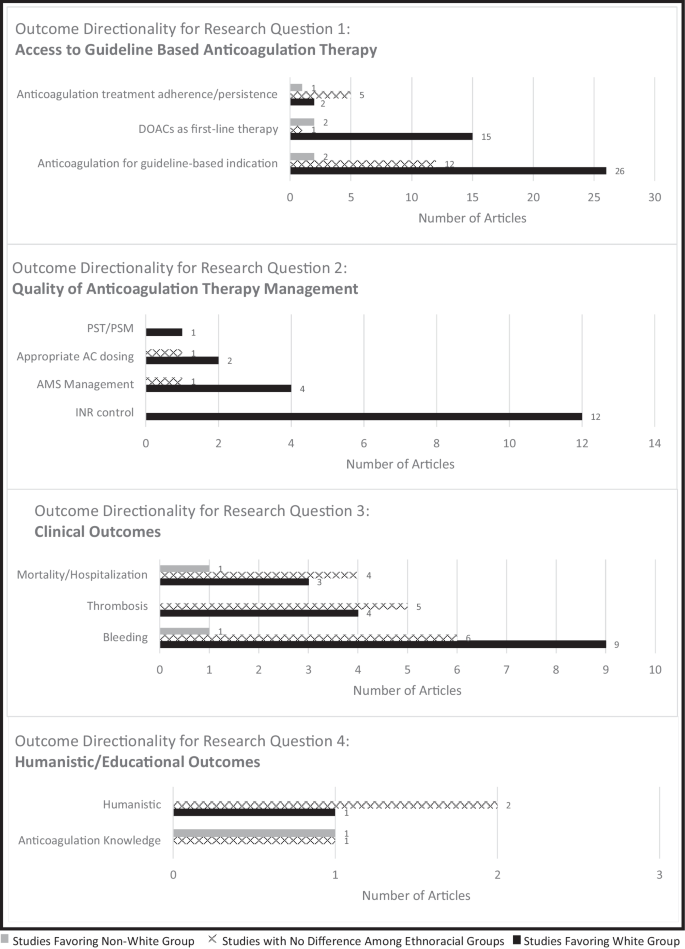
Outcome Directionality for the 4 Research Questions and their Subcategories. AC = anticoagulant; AMS = anticoagulation management service; INR = international normalized ratio; PST = patient self-testing; PSM = patient self-management
Research question 2: Do ethnoracial differences exist in the quality of anticoagulation therapy management?
A total of 21 studies assessed quality of anticoagulation therapy management: Warfarin time in therapeutic range (TTR)/INR (International Normalized Ratio) control 12 studies, appropriate anticoagulant dosing 3 studies, enrollment in an anticoagulation management service 5 studies, and PST/PSM one study.
In statistical comparisons of INR control in warfarin patients, all 12 studies (7 assessed mean or median TTR, 5 assessed other measures of INR control such as days spent above/below range, gaps in INR monitoring) showed White patients had favorable INR control compared to non-White patients (most comparisons included Black patients) [ 41 , 75 , 79 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 , 84 , 85 , 86 , 87 ]. Enrollment in an anticoagulation management service was statistically compared among ethnoracial groups in 5 studies, and this opportunity favored White patients compared to other racial groups in four of the five [ 41 , 82 , 86 , 88 ]. Two of the three studies that statistically analyzed appropriate anticoagulant dosing showed a higher rate of appropriate DOAC dosing in White patients compared to non-White patients [ 41 , 89 ], and the third showed no difference among ethnoracial groups for enoxaparin dosing in the emergency department [ 90 ]. The one study assessing access to PST/PSM showed that more White patients used PST compared to Black or Hispanic patients[ 91 ] (Fig. 5 ).
Research question 3: Do ethnoracial differences exist in the clinical outcomes related to anticoagulation care?
Articles assessing clinical outcomes among ethnoracial groups primarily assessed bleeding (15 articles) or thrombosis (9 articles) outcomes, and 8 articles assessing anticoagulation related hospitalization or mortality. One article addressed a net clinical outcome including major bleeding, stroke or systemic embolism, and death from any cause. This was included in the bleeding outcomes category so that it was not double-counted in the other two outcome categories. Additional details about the 24 unique studies that statistically assessed clinical outcomes including the study design, population size, ethnoracial groups studied, anticoagulants used, and statistical outcomes measured can be found in Supplementary Tables 1 and 2 .
Sixteen studies statistically assessed bleeding outcomes of varying definitions (major bleeding 13 studies, clinically relevant non-major bleeding 3 studies, any bleeding 3 studies, bleeding otherwise defined 3 studies). Six studies demonstrated no difference in bleeding outcomes by ethnoracial group [ 55 , 92 , 93 , 94 , 95 , 96 ]9 reported that White patients had lower rates of bleeding compared to Black or Asian patients,[ 53 , 80 , 83 , 85 , 97 , 98 , 99 , 100 , 101 ]. In the remaining study, Asian patients had a more favorable net clinical outcome compared to non-Asian patients [ 102 ].
Nine studies statistically assessed thrombosis outcomes among ethnoracial groups, including stroke/systemic embolism (5 studies), recurrent VTE (3 studies), or any thrombosis (1 study). The stroke outcomes by racial group were heterogeneous, with 3 studies showing better outcomes for White patients compared to Black patients[ 103 , 104 , 105 ] and two studies showing no difference in outcomes when White patients were compared to Non-White patients [ 55 , 95 ]. In three of the four VTE studies there were no differences in outcomes by ethnoracial group [ 61 , 93 , 96 ], and in one study White patients had more favorable outcomes compared to Black patients [ 106 ].
Nine studies assessed anticoagulation-related hospitalizations or mortality by ethnoracial group. Outcomes were mixed, as four studies showed no difference in hospitalizations or mortality among ethnoracial groups,[ 89 , 95 , 96 , 107 ], three studies showed White patients had a lower rate of hospitalizations[ 85 , 105 ] or mortality[ 104 , 105 ] Another study showed lower rate of mortality or hospice after intracranial hemorrhage in Black and Other race patients [ 108 ].(Fig. 5 ).
Research question 4: Do ethnoracial differences exist in the humanistic/educational outcomes related to anticoagulation therapy?
The five studies reporting this category of outcomes were heterogeneous. Of the two studies assessing anticoagulation knowledge, one showed no difference by ethnoracial group [ 109 ], and the other favored the non-White group in appropriately estimating bleeding risk [ 110 ]. One study assessed an atrial fibrillation quality of life score at 2-year follow-up after AF diagnosis and found the outcomes favored White patients [ 79 ]. Another study assessed satisfaction with VTE care and found no difference among ethnoracial groups [ 111 ]. A third study found no difference in the percentage of racial groups having a cost conversation when initiating DOAC therapy (78% Whites, 72.2% non-Whites)[ 112 ] (Fig. 5 ).
Overall outcome directionality for all four research questions is shown in Fig. 6 . A total of 79 articles demonstrated favorable outcomes for White patients compared to non-White patients, 38 articles showed no difference between White and non-White groups, and 8 articles had outcomes favoring non-White groups (the total exceeds the 78 articles with statistical outcomes as many articles reported multiple outcomes). The biggest areas of disparity between White and non-White groups are access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy and quality of anticoagulation therapy management. Clinical outcomes relating to anticoagulation care had the least difference among ethnoracial groups. Relatively few studies assessed potential ethnoracial disparities in humanistic and educational outcomes.
Outcome Directionality for All 4 Research Questions
This scoping review assessing ethnoracial differences in the quality of anticoagulation care and its delivery to patients in the United States encompassed eleven full years of literature and resulted in the inclusion of 96 studies, 78 of which contained statistical outcomes comparisons among ethnoracial groups. The most common reason for study exclusion was that outcomes were not reported for at least two distinct ethnoracial groups. We observed that beginning in 2019 and following the racial unrest of 2020, the density of articles addressing ethnoracial disparities in anticoagulation care more than doubled. During the entire study period, half of studies had race or ethnicity as the focus or objective of the paper, but this was largely driven by articles published after 2019.
Only 16% of included articles documented self-reporting of racial identity, with most of the remainder using an unspecified method for documenting racial identity. It is likely that many studies utilize demographic information extracted from an electronic medical record (EMR), but it is often unclear if that is truly self-reported race. A second element this scoping review identified was that many studies analyzed two or three ethnoracial groups and then categorized all others into a heterogenous “Other” category. For example, frequently studies would categorize patients as White, Black, and “Other.” It is unclear whether those in a racial category labeled as “Other” had an unknown or missing racial identity in the EMR, or intentionally chose not to disclose. It is also likely that study investigators decided to classify ethnoracial groups with lower population sizes into a miscellaneous category. There were few studies (15%) that specifically assessed patients identifying as Native American/Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, and multiracial. While Hispanic/Latino is an ethnicity, most studies categorized it as a separate “race” category. Of the 37 studies that analyzed “Asian” patient populations, none specifically defined “Asian” beyond that. The US Census Bureau defines “Asian” race as a person having origins of the Far East, Southeast Asia, or the Indian subcontinent [ 113 ]. This broad definition encompasses many different ethnicities which could represent variability in health outcomes if better defined and more frequently analyzed. These may be opportunities for EMR systems to improve transparency for how race, ethnicity, and language preference are captured and for those designing research studies to be thoughtful and intentional about analyzing the ethnoracial identities of the study population, perhaps in alignment with the minimum 5 racial categories utilized by the US Census Bureau, the National Institutes of Health, and the Office of Management and Budget (White, Black, American Indian/Alaska Native, Asian, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, with permission for a “some other race” category and the option to select multiple races) [ 113 ]. Since 2017 Clinicaltrials.gov has required the reporting of race/ethnicity if collected, and there is good compliance with this requirement, but less so in publication of the work [ 114 ].
We examined the proportion of ethnoracial groups represented for each of the disease states in the studies included in this scoping review, relative to disease state prevalence and found a discrepancy. For AF, prevalence in White patients was 11.3%, in Black patients 6.6%, and in Hispanic patients 7.8% [ 15 ]. However, the representation in AF studies in this review were 74% White, 13% Black, and 8% Hispanic. Assessing VTE incidence by race is more difficult, as studies have shown regional and time variation, with Black patients typically having a higher incidence compared to other ethnoracial groups [ 16 ]. In this review, however, of the studies assessing VTE treatment or prophylaxis, only 16% of the patient population identified as Black, whereas 70% identified as White. There were only 3 studies that assessed a valvular heart disease population, making ethnoracial group representation difficult to assess.
The majority of studies captured in this review analyzed patients in the outpatient setting, for the anticoagulation indication of stroke prevention in AF, taking either warfarin or DOAC. Few studies involved the acute care setting or injectable anticoagulants, representing an area for future study of potential ethnoracial disparities.
Overall, the majority of studies in this scoping review addressed ethnoracial disparities in patients’ access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy, clinical outcomes related to anticoagulation care, and quality of anticoagulation management. A research gap identified was more study is needed to assess gaps in educational outcomes such as anticoagulation and disease state knowledge, shared decision-making willingness and capability, and humanistic outcomes such as quality of life or satisfaction with anticoagulation therapy.
In analyzing the first research question regarding ethnoracial differences in access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy, the majority of studies addressed use of any anticoagulation for stroke prevention in AF in patients above a threshold risk score and the preferential use of DOACs as first-line therapy instead of warfarin for AF. In both categories, patients in a non-White ethnoracial group (particularly Black patients) received recommended therapy less often than patients identified as White. It is unclear why this is the case. It could be on the patient, provider, and/or system level. It is possible that some studies more successfully adjusted for covariates than others. Sites or settings with systematic processes like order sets or clinical decision support systems in place for standard prescribing may be more successful in equitably prescribing indicated therapies. In one large study in the Veterans Affairs population of AF patients, even after adjusting for numerous variables that included clinical, demographic, socioeconomic, prescriber, and geographic site factors, DOAC prescribing remained lower in Asian and Black patients when compared with White patients. The authors in that study postulate that non-White populations may be less receptive to novel therapies due to historical mistrust of the health care system or have reduced access to education about the latest treatments, and they give the example of direct-to-consumer advertising [ 42 ]. It has also previously been demonstrated that prescribing of oral anticoagulation and particularly DOACs is lower in non-White patients [ 41 ]. These are difficult to capture as standard covariates, which is why further study is needed. We examined the publication dates for both access categories to see if perhaps there was a lack of contemporary data skewing the outcomes. However, for both anticoagulation for a guideline-based indication and DOACs as first-line therapy, the majority of articles came from the time period 2019–2021 (24 of 40 articles, and 15 of 18 articles, respectively), well after guideline updates preferentially recommended DOACs [ 34 , 35 ]. Also, there were relatively few studies addressing guideline-based therapy for VTE treatment and prophylaxis, making assessment of disparities difficult. Regarding access, it is well established that race and ethnicity often determine a patient’s socioeconomic status and that low socioeconomic status and its correlates (e.g., reduced education, income, and healthcare access) are associated with poorer health outcomes [ 115 ]. However, at each level of income or education, Black patients experience worse health outcomes than Whites [ 116 ]. So, low socioeconomic status does not fully explain poorer health outcomes for non-White individuals.
After examining access to appropriate and preferred anticoagulation therapy, the second research question of this scoping review examined potential ethnoracial disparities in the quality of anticoagulation therapy management. INR control measures such as time in therapeutic INR range are a surrogate measure of both thrombotic and bleeding outcomes and frequently used as a way to assess quality of warfarin therapy. The studies identified in this review showed clear disparity between White and non-White patient groups (especially Black patients), however all twelve studies comparing TTR among ethnoracial groups were published prior to 2019. This could be due to the decline in warfarin prescribing relative to increases in DOAC prescribing [ 117 , 118 , 119 ], but there remain patient populations that require or choose warfarin, so this marker of anticoagulation control remains relevant and requires continued reassessment. There were relatively few studies assessing other markers of anticoagulation management quality such as anticoagulation management service enrollment, appropriate DOAC dosing, and access to quality improvement strategies like PST or PSM. Few studies assessed educational outcomes, yet this may have relevance to the above anticoagulation care quality question. For those patients who remain on warfarin, dietary Vitamin K consistency is an example of a key educational point that links directly to INR control. It is unclear if there are disparities in this type of education among ethnoracial groups that may have more far-reaching effects.
Of note, clinical outcomes related to anticoagulant therapy seemed to have the fewest areas of disparity, although the number of articles was small. This suggests that if patients have access to high quality anticoagulation therapy, there is a promising sign that optimal clinical outcomes can be achieved for all ethnoracial groups.
There are some limitations of this scoping review that warrant consideration. First, we chose fairly broad inclusion criteria (all anticoagulants, all study types) because a review of this type had never been performed before. This resulted in a relatively large number of included articles for a scoping review. Second, there is likely a high degree of heterogeneity among patient populations and outcomes definitions. However, as this is a scoping review with the goal to present an overview of the literature and not report on composite outcomes, a risk of bias assessment was not performed. Third is our decision to group patients into White and non-White groups for assessment of outcome directionality. In doing so, we may have missed subtle differences in outcomes between various non-White ethnoracial groups. Fourth, in our main search we included all studies that reported outcomes, but due to scope, we only reported outcome directionality for studies that statistically compared outcomes between ethnoracial groups. Finally, due to the large number of studies that required review and analysis, this was a lengthy undertaking and we are certain that additional studies have been published since the closure of our search period.
In line with the 2014 National Action Plan for Adverse Drug Event Prevention’s goal of identifying patient populations at higher risk of adverse drug events, this scoping review highlights several areas where quality of anticoagulation care can be optimized for all patients. Future research opportunities in ethnoracial differences in the quality of anticoagulation care are summarized in Table 3 . While the scoping review focused exclusively on the evaluation of peer-reviewed manuscripts, the heterogeneity of terminology and methodologies identified in the published papers may have implications for national health policy relating to the quality and safety of care (e.g.the Medicare Quality Payment Program) [ 120 ]. To accurately and reliably quantify important disparities in AC-related care and support effective improvement initiatives, attention and effort will need to be invested across the full continuum of quality measure development [ 121 ], measure endorsement [ 122 ], measure selection, and status assignment within value-based payment programs (e.g., required/optional, measure weighting) [ 123 ]. The findings of the scoping review may be of utility to such efforts, and the development and implementation of suitable quality measures will likely be of value to future research efforts in this important therapeutic area.
Conclusions
Treatment guidelines do not recommend differentiating anticoagulant therapy by ethnoracial group, yet this scoping review of the literature demonstrates consistent directionality in favor of White patients over non-White patients in the domains of access to anticoagulation therapy for guideline-based indications, prescription of preferred anticoagulation therapies, and quality of anticoagulation therapy management. These data should serve as a stimulus for an assessment of current services, implementation of quality improvement measures, and inform future research to make anticoagulation care quality more equitable.
Data Availability
Data are available on request from the corresponding author.
Wheeler SM, Bryant AS (2017) Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health and Health Care. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 44(1):1–11
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Manuel JI (2018) Racial/Ethnic and Gender Disparities in Health Care Use and Access. Health Serv Res 53(3):1407–1429
Nadeem MF, Kaiser LR (2022) Disparities in Health Care Delivery Systems. Thorac Surg Clin 32(1):13–21
Wallace J et al (2021) Changes in Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Access to Care and Health Among US Adults at Age 65 Years. JAMA Intern Med 181(9):1207–1215
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Churchwell K et al (2020) Call to Action: Structural Racism as a Fundamental Driver of Health Disparities: A Presidential Advisory From the American Heart Association. Circulation 142(24):e454–e468
Gomez SE et al (2023) Racial, ethnic, and sex disparities in atrial fibrillation management: rate and rhythm control. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 66(5):1279–1290
Tamirisa KP et al (2021) Racial and Ethnic Differences in the Management of Atrial Fibrillation. CJC Open 3(12 Suppl):S137–S148
Eberly LA et al (2021) Racial/Ethnic and Socioeconomic Disparities in Management of Incident Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA Netw Open 4(2):e210247
Ugowe FE, Jackson LR, Thomas KL (2018) Racial and ethnic differences in the prevalence, management, and outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation: A systematic review. Heart Rhythm 15(9):1337–1345
Xu Y, Siegal DM, Anand SS (2021) Ethnoracial variations in venous thrombosis: Implications for management, and a call to action. J Thromb Haemost 19(1):30–40
Erinne I et al (2021) Racial disparities in the treatment of aortic stenosis: Has transcatheter aortic valve replacement bridged the gap? Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 98(1):148–156
Ali A et al (2022) Racial and Ethnic Disparities in the Use of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in the State of Connecticut. Cardiovasc Revasc Med 37:7–12
Pienta MJ et al (2023) Racial disparities in mitral valve surgery: A statewide analysis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 165(5):1815-1823.e8
Alkhouli M et al (2019) Racial Disparities in the Utilization and Outcomes of Structural Heart Disease Interventions in the United States. J Am Heart Assoc 8(15):e012125
Heckbert SR et al (2020) Differences by Race/Ethnicity in the Prevalence of Clinically Detected and Monitor-Detected Atrial Fibrillation: MESA. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 13(1):e007698
Zakai NA et al (2014) Racial and regional differences in venous thromboembolism in the United States in 3 cohorts. Circulation 129(14):1502–1509
Lamprea-Montealegre JA et al (2021) Valvular Heart Disease in Relation to Race and Ethnicity: JACC Focus Seminar 4/9. J Am Coll Cardiol 78(24):2493–2504
Tamargo J et al (2022) Racial and ethnic differences in pharmacotherapy to prevent coronary artery disease and thrombotic events. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother 8(7):738–751
Kanuri SH, Kreutz RP (2019) Pharmacogenomics of Novel Direct Oral Anticoagulants: Newly Identified Genes and Genetic Variants. J Pers Med 9(1):7
Craig TJ, Wann LS, Calkins H, Chen LY, Cigarroa JE, Cleveland CJ Jr, Ellinor PT, Ezekowitz MD, Field ME, Furie LK, Heidenreich PA, Murray KT, Shea JB, Tracy CM, Yancy CW (2019) Circulation 140 (2):e125–e151. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.000000000000066
Ortel TL et al (2020) American Society of Hematology 2020 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Blood Adv 4(19):4693–4738
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Stevens SM et al (2021) Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease: Second Update of the CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest 160(6):e545–e608
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Schünemann HJ et al (2018) American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: prophylaxis for hospitalized and nonhospitalized medical patients. Blood Adv 2(22):3198–3225
Otto CM et al (2021) 2020 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Management of Patients With Valvular Heart Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 143(5):e72–e227
PubMed Google Scholar
National Action Plan for Adverse Drug Event Prevention (2014) Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. US Department of Health and Human Services, Washington, DC
Google Scholar
Bhakta S et al (2022) A systematic review and meta-analysis of racial disparities in deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism events in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord 10(4):939-944.e3
Corbie-Smith G et al (2008) Conceptualizing race in research. J Natl Med Assoc 100(10):1235–1243
Vazquez SR, Yates NYY, McFarland MM (2022). Differences in anticoagulant care delivery according to ethnoracial group in the United States: a scoping review protocol. Open Sci Fram osf.io/eydsa. https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/9SE7H
Peters MDJ, Godfrey C, McInerney P, Munn Z, Tricco AC, Khalil H (2020) Joanna briggs institute reviewer's manual. Aromataris E, Munn Z (eds). Publisher: Joanna briggs institute. Chapter: chapter 11: scoping reviews
Arksey H, O’Malley L (2005) Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol 8(1):19–32
Article Google Scholar
Rethlefsen ML et al (2021) PRISMA-S: an extension to the PRISMA Statement for Reporting Literature Searches in Systematic Reviews. Syst Rev 10(1):39
Harris PA et al (2009) Research electronic data capture (REDCap)–a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform 42(2):377–381
McGowan J et al (2016) PRESS Peer Review of Electronic Search Strategies: 2015 Guideline Statement. J Clin Epidemiol 75:40–46
Kearon C et al (2016) Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest 149(2):315–352
Lip GYH et al (2018) Antithrombotic Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest 154(5):1121–1201
al Taii, H. and S. Al-Kindi, Racial disparities in prescriptions of oral anticoagulants among patients with atrial fibrillation., in 24th International Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (2019) Boston. MA, USA
Bhave PD et al (2015) Race- and sex-related differences in care for patients newly diagnosed with atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 12(7):1406–1412
Chapman SA et al (2017) Adherence to treatment guidelines: the association between stroke risk stratified comparing CHADS. BMC Health Serv Res 17(1):127
Chen Q et al (2021) Prevalence and the factors associated with oral anticoagulant use among nursing home residents. J Clin Pharm Ther 46(6):1714–1728
Deitelzweig S et al (2020) Utilization of anticoagulants and predictors of treatment among hospitalized patients with atrial fibrillation in the USA. J Med Econ 23(12):1389–1400
Essien UR et al (2018) Association of Race/Ethnicity With Oral Anticoagulant Use in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Findings From the Outcomes Registry for Better Informed Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation II. JAMA Cardiol 3(12):1174–1182
Essien UR et al (2021) Disparities in Anticoagulant Therapy Initiation for Incident Atrial Fibrillation by Race/Ethnicity Among Patients in the Veterans Health Administration System. JAMA Netw Open 4(7):e2114234
Essien UR, Kim N, Hausmann LR, Mor MK, Good C, Gellad WF, Fine MJ (2020) Abstract: racial and ethnic disparities in anticoagulant choice for atrial fibrillation in the veterans health administration: results from the reach-af study. J Gen Int Med J 35(1):S250–251
Essien UR et al (2022) Association of Race and Ethnicity and Anticoagulation in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Dually Enrolled in Veterans Health Administration and Medicare: Effects of Medicare Part D on Prescribing Disparities. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 15(2):e008389
Essien UR et al (2020) Race/Ethnicity and Sex-Related Differences in Direct Oral Anticoagulant Initiation in Newly Diagnosed Atrial Fibrillation: A Retrospective Study of Medicare Data. J Natl Med Assoc 112(1):103–108
Fohtung RB, Novak E, Rich MW (2017) Effect of New Oral Anticoagulants on Prescribing Practices for Atrial Fibrillation in Older Adults. J Am Geriatr Soc 65(11):2405–2412
Lewis WR et al (2011) Improvement in use of anticoagulation therapy in patients with ischemic stroke: results from Get With The Guidelines-Stroke. Am Heart J 162(4):692-699.e2
Martin Diaz C et al (2021) Anticoagulation After Ischemic Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) in the Time of Direct Oral Anticoagulation (DOAC) and Thrombectomy. Cureus 13(8):e17392
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mentias A et al (2021) Racial and Sex Disparities in Anticoagulation After Electrical Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation and Flutter. J Am Heart Assoc 10(17):e021674
Obi CA et al (2022) Examination of anticoagulation prescription among elderly patients with atrial fibrillation after in-hospital fall. J Thromb Thrombolysis 53(3):683–689
Piccini JP et al (2019) Adherence to Guideline-Directed Stroke Prevention Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation Is Achievable. Circulation 139(12):1497–1506
Raji MA et al (2013) National utilization patterns of warfarin use in older patients with atrial fibrillation: a population-based study of Medicare Part D beneficiaries. Ann Pharmacother 47(1):35–42
Schwartz SM et al (2019) Discriminative Ability of CHA. Am J Cardiol 123(12):1949–1954
Shahid I et al (2021) Meta-Analysis of Racial Disparity in Utilization of Oral Anticoagulation for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 153:147–149
Tedla YG et al (2020) Racial Disparity in the Prescription of Anticoagulants and Risk of Stroke and Bleeding in Atrial Fibrillation Patients. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 29(5):104718
Thomas KL et al (2013) Racial differences in the prevalence and outcomes of atrial fibrillation among patients hospitalized with heart failure. J Am Heart Assoc 2(5):e000200
Waddy SP et al (2020) Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Atrial Fibrillation Treatment and Outcomes among Dialysis Patients in the United States. J Am Soc Nephrol 31(3):637–649
Wetmore JB et al (2019) Relation of Race, Apparent Disability, and Stroke Risk With Warfarin Prescribing for Atrial Fibrillation in Patients Receiving Maintenance Hemodialysis. Am J Cardiol 123(4):598–604
Winkelmayer WC et al (2012) Prevalence of atrial fibrillation and warfarin use in older patients receiving hemodialysis. J Nephrol 25(3):341–353
Zahuranec DB et al (2017) Stroke Quality Measures in Mexican Americans and Non-Hispanic Whites. J Health Dispar Res Pract 10(1):111–123
Addo-Tabiri NO et al (2020) Black Patients Experience Highest Rates of Cancer-associated Venous Thromboembolism. Am J Clin Oncol 43(2):94–100
Freeman AH et al (2016) Venous thromboembolism following minimally invasive surgery among women with endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol 142(2):267–272
Friedman AM et al (2013) Underuse of postcesarean thromboembolism prophylaxis. Obstet Gynecol 122(6):1197–1204
Lau BD et al (2015) Eliminating Health Care Disparities With Mandatory Clinical Decision Support: The Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Example. Med Care 53(1):18–24
Owodunni OP et al (2020) Using electronic health record system triggers to target delivery of a patient-centered intervention to improve venous thromboembolism prevention for hospitalized patients: Is there a differential effect by race? PLoS ONE 15(1):e0227339
Shah S et al (2021) Implementation of an Anticoagulation Practice Guideline for COVID-19 via a Clinical Decision Support System in a Large Academic Health System and Its Evaluation: Observational Study. JMIR Med Inform 9(11):e30743
Steinberg BA et al (2013) Early adoption of dabigatran and its dosing in US patients with atrial fibrillation: results from the outcomes registry for better informed treatment of atrial fibrillation. J Am Heart Assoc 2(6):e000535
Vaughan Sarrazin MS et al (2014) Bleeding rates in Veterans Affairs patients with atrial fibrillation who switch from warfarin to dabigatran. Am J Med 127(12):1179–1185
Nathan AS et al (2019) Racial, Ethnic, and Socioeconomic Inequities in the Prescription of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients With Venous Thromboembolism in the United States. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 12(4):e005600
Singh BP, Sitlinger A, Saber I, Thames E, Beckman M, Reyes N, Schulteis RD, Ortel T (2016) Direct oral anticoagulant usage in the treatment of venous thromboembolism across racial groups in Durham County, NC. J Gen Int Med 31:S191–S192
Schaefer JK et al (2017) Sociodemographic factors in patients continuing warfarin vs those transitioning to direct oral anticoagulants. Blood Adv 1(26):2536–2540
Lank RJ et al (2019) Ethnic Differences in 90-Day Poststroke Medication Adherence. Stroke 50(6):1519–1524
O'Brien EC, Holmes ND, Thomas L, Fonarow GC, Kowey PR, Ansell JE, Mahaffey KW, Gersh BJ, Peterson ED, Piccini JP, Hylek EM (2018) J Am Heart Assoc 7(12):e006391
Singh RR et al (2016) Adherence to Anticoagulant Therapy in Pediatric Patients Hospitalized With Pulmonary Embolism or Deep Vein Thrombosis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 22(3):260–264
Yong C, Xu XY, Than C, Ullal A, Schmitt S, Azarbal F, Heidenreich P, Turakhia M (2013) Abstract 14134: racial disparities in warfarin time in INR therapeutic range in patients with atrial fibrillation: Findings from the TREAT-AF Study. Circul 128(22). https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/circ.128.suppl_22.A14134
Chen N, Brooks MM, Hernandez I (2020) Latent Classes of Adherence to Oral Anticoagulation Therapy Among Patients With a New Diagnosis of Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA Netw Open 3(2):e1921357
Pham Nguyen TP et al (2003) Does hospitalization for thromboembolism improve oral anticoagulant adherence in patients with atrial fibrillation? J Am Pharm Assoc 60(6):986-992.e2
Patel AA et al (2013) Persistence of warfarin therapy for residents in long-term care who have atrial fibrillation. Clin Ther 35(11):1794–1804
Golwala H et al (2016) Racial/ethnic differences in atrial fibrillation symptoms, treatment patterns, and outcomes: Insights from Outcomes Registry for Better Informed Treatment for Atrial Fibrillation Registry. Am Heart J 174:29–36
Limdi NA et al (2017) Quality of anticoagulation control and hemorrhage risk among African American and European American warfarin users. Pharmacogenet Genomics 27(10):347–355
Lip GY et al (2016) Determinants of Time in Therapeutic Range in Patients Receiving Oral Anticoagulants (A Substudy of IMPACT). Am J Cardiol 118(11):1680–1684
Rao SR et al (2015) Explaining racial disparities in anticoagulation control: results from a study of patients at the Veterans Administration. Am J Med Qual 30(3):214–222
Thigpen JL, Yah Q, Beasley M, Limdi NA (2012) Abstract: racial differences in anticoagulation control and risk of hemorrhage among warfarin users. Pharmacoth 32(10):E189
Yong C et al (2016) Racial Differences in Quality of Anticoagulation Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation (from the TREAT-AF Study). Am J Cardiol 117(1):61–68
Moffett BS, Kim S, Bomgaars LR (2013) Readmissions for warfarin-related bleeding in pediatric patients after hospital discharge. Pediatr Blood Cancer 60(9):1503–1506
Rose AJ et al (2013) Gaps in monitoring during oral anticoagulation: insights into care transitions, monitoring barriers, and medication nonadherence. Chest 143(3):751–757
Mahle WT et al (2011) Management of warfarin in children with heart disease. Pediatr Cardiol 32(8):1115–1119
Meade M et al (2011) Impact of health disparities on staff workload in pharmacist-managed anticoagulation clinics. Am J Health Syst Pharm 68(15):1430–1435
Aguilar F et al (2021) Off-label direct oral anticoagulants dosing in atrial fibrillation and venous thromboembolism is associated with higher mortality. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 19(12):1119–1126
Jellinek-Cohen SP, Li M, Husk G (2018) Enoxaparin dosing errors in the emergency department. World J Emerg Med 9(3):195–202
Triller DM et al (2015) Trends in Warfarin Monitoring Practices Among New York Medicare Beneficiaries, 2006–2011. J Community Health 40(5):845–854
Akhtar T et al (2020) Factors associated with bleeding events in patients on rivaroxaban for non-valvular atrial fibrillation: A real-world experience. Int J Cardiol 320:78–82
Cires-Drouet RS et al (2022) Prevalence and clinical outcomes of hospitalized patients with upper extremity deep vein thrombosis. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord 10(1):102–110
Doucette K et al (2020) Efficacy and Safety of Direct-Acting Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs) in the Overweight and Obese. Adv Hematol 2020:3890706
Gu K et al (2021) Racial disparities among Asian Americans with atrial fibrillation: An analysis from the NCDR® PINNACLE Registry. Int J Cardiol 329:209–216
Yamashita Y et al (2018) Asian patients versus non-Asian patients in the efficacy and safety of direct oral anticoagulants relative to vitamin K antagonist for venous thromboembolism: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Thromb Res 166:37–42
Di Nisio M et al (2016) Risk of major bleeding in patients with venous thromboembolism treated with rivaroxaban or with heparin and vitamin K antagonists. Thromb Haemost 115(2):424–432
Hernandez I et al (2015) Risk of bleeding with dabigatran in atrial fibrillation. JAMA Intern Med 175(1):18–24
Majeed A et al (2016) Bleeding events with dabigatran or warfarin in patients with venous thromboembolism. Thromb Haemost 115(2):291–298
Hankey GJ et al (2014) Intracranial hemorrhage among patients with atrial fibrillation anticoagulated with warfarin or rivaroxaban: the rivaroxaban once daily, oral, direct factor Xa inhibition compared with vitamin K antagonism for prevention of stroke and embolism trial in atrial fibrillation. Stroke 45(5):1304–1312
Kobayashi L et al (2017) Novel oral anticoagulants and trauma: The results of a prospective American Association for the Surgery of Trauma Multi-Institutional Trial. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 82(5):827–835
Gencer B et al (2022) Edoxaban versus Warfarin in high-risk patients with atrial fibrillation: A comprehensive analysis of high-risk subgroups. Am Heart J 247:24–32
Chen N et al (2021) Joint Latent Class Analysis of Oral Anticoagulation Use and Risk of Stroke or Systemic Thromboembolism in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs 21(5):573–580
Kabra R et al (2015) Effect of race on outcomes (stroke and death) in patients >65 years with atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 116(2):230–235
Kim MH, Xu L, Puckrein G (2018) Patient Diversity and Population Health-Related Cardiovascular Outcomes Associated with Warfarin Use in Atrial Fibrillation: An Analysis Using Administrative Claims Data. Adv Ther 35(11):2069–2080
Abu-Zeinah G, Oromendia C, DeSancho MT (2019) Thrombotic risk factors in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome: a single center experience. J Thromb Thrombolysis 48(2):233–239
Banala SR et al (2017) Discharge or admit? Emergency department management of incidental pulmonary embolism in patients with cancer: a retrospective study. Int J Emerg Med 10(1):19
LaDuke ZJ et al (2019) Association of mortality among trauma patients taking preinjury direct oral anticoagulants versus vitamin K antagonists. Surgery 166(4):564–571
Moreland CJ et al (2013) Anticoagulation education: do patients understand potential medication-related emergencies? Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf 39(1):22–31
Bamgbade BA et al (2021) Differences in Perceived and Predicted Bleeding Risk in Older Adults With Atrial Fibrillation: The SAGE-AF Study. J Am Heart Assoc 10(17):e019979
Webb D et al (2019) Patient Satisfaction With Venous Thromboembolism Treatment. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 25:1076029619864663
Kamath CC et al (2021) Cost Conversations About Anticoagulation Between Patients With Atrial Fibrillation and Their Clinicians: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open 4(7):e2116009
U.S. Census Bureau . [cited 2023 10/20/23]; Available from: https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/note/US/RHI625222#:~:text=Asian.,Japan%2C%20Korea%2C%20or%20Vietnam .
Fain KM et al (2021) Race and ethnicity reporting for clinical trials in ClinicalTrials.gov and publications. Contemp Clin Trials 101:106237
American Psychological Association Ethnic and racial minorities & socioeconomic status. 3/22/24]; Available from: https://www.apa.org/pi/ses/resources/publications/minorities#:~:text=The%20relationship%20between%20SES%2C%20race,SES%2C%20race%2C%20and%20ethnicity . Accessed 22 Mar 2024
Braveman PA et al (2010) Socioeconomic disparities in health in the United States: what the patterns tell us. Am J Public Health 100 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):186–96
Wheelock KM et al (2021) Clinician Trends in Prescribing Direct Oral Anticoagulants for US Medicare Beneficiaries. JAMA Netw Open 4(12):e2137288
Barnes GD et al (2015) National Trends in Ambulatory Oral Anticoagulant Use. Am J Med 128(12):1300–5.e2
Iyer GS et al (2023) Trends in the Use of Oral Anticoagulants for Adults With Venous Thromboembolism in the US, 2010–2020. JAMA Netw Open 6(3):e234059
MACRA Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (MACRA). 03/19/24]; Available from: https://www.cms.gov/medicare/quality/value-based-programs/chip-reauthorization-act . Accessed 19 Mar 2024
Blueprint Measure Lifecycle Overview. 03/19/2024]; Available from: https://mmshub.cms.gov/blueprint-measure-lifecycle-overview . Accessed 19 Mar 2024
Endorsement and Maintenance (E&M) Guidebook. 3/19/24]; Available from: https://p4qm.org/sites/default/files/2023-12/Del-3-6-Endorsement-and-Maintenance-Guidebook-Final_0_0.pdf . Accessed 19 Mar 2024
Measure Implementation. 3/19/24]; Available from: https://mmshub.cms.gov/measure-lifecycle/measure-implementation/selection . Accessed 19 Mar 2024
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the following individuals for their work in screening articles for this scoping review: April Allen, PharmD, CACP; Allison Burnett, PharmD, PhC, CACP; Stacy Ellsworth, RN, MSN, CCRC; Danielle Jenkins, MBA, RN, BSN, CRNI; Amanda Katz, MBA; Lea Kistenmacher, Julia Mulheman, PharmD; Surhabi Palkimas, PharmD, MBA; Terri Schnurr, RN, CCRC; Deborah Siegal, MD, MSc, FRCPC; Kimberly Terry, PharmD, BCPS, BCCCP; and Terri Wiggins, MS.
The authors wish to acknowledge the support of the Anticoagulation Forum in the development of this manuscript. The Anticoagulation Forum is a non-profit organization dedicated to improving the quality of care for patients taking antithrombotic medications.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Utah Health Thrombosis Service, 6056 Fashion Square Drive, Suite 1200, Murray, UT, 84107, USA
Sara R. Vazquez
Kaiser Permanente Clinical Pharmacy Services, 200 Crescent Center Pkwy, Tucker, GA, 30084, USA
Naomi Y. Yates
Anticoagulation Forum, Inc, 17 Lincoln Street, Suite 2B, Newton, MA, 02461, USA
Craig J. Beavers & Darren M. Triller
University of Kentucky College of Pharmacy, 789 S Limestone, Lexington, KY, 40508, USA
Craig J. Beavers
University of Utah Spencer S. Eccles Health Sciences Library, 10 N 1900 E, Salt Lake City, UT, 84112, USA
Mary M. McFarland
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation was performed by Sara Vazquez, Naomi Yates, and Mary McFarland. Data collection and analysis were performed by Sara Vazquez, Naomi Yates, Craig Beavers, and Darren Triller. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Sara Vazquez and all authors edited subsequent drafts. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sara R. Vazquez .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
Dr. Vazquez discloses that she is a member of the Anticoagulation Forum Advisory Council and an editorial consultant for UptoDate, Inc.
Dr. Yates has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Dr. Beavers has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Dr. Triller has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ms. McFarland has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 22 KB)
Supplementary file2 (docx 14 kb), rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Vazquez, S.R., Yates, N.Y., Beavers, C.J. et al. Differences in quality of anticoagulation care delivery according to ethnoracial group in the United States: A scoping review. J Thromb Thrombolysis (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-024-02991-2
Download citation
Accepted : 27 April 2024
Published : 11 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-024-02991-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Ethnoracial
- Disparities
- Anticoagulation
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

COMMENTS
In general, a literature search is the process of seeking out and identifying the existing literature related to a topic or question of interest, while a literature review is the organized synthesis of the information found in the existing literature. In research, a literature search is typically the first step of a literature review. The ...
Regardless of this commonality, both types of review vary significantly. The following table provides a detailed explanation as well as the differences between systematic and literature reviews. Kysh, Lynn (2013): Difference between a systematic review and a literature review.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A literature search is distinguished from, but integral to, a literature review. Literature reviews are conducted for the purpose of (a) locating information on a topic or identifying gaps in the literature for areas of future study, (b) synthesising conclusions in an area of ambiguity and (c) helping clinicians and researchers inform decision-making and practice guidelines.
In general, a literature search is the process of seeking out and identifying the existing literature related to a topic or question of interest, while a literature review is the organized synthesis of the information found in the existing literature. In research applications, a literature search is typically the first step of a literature review.
relevance and the differences between the literature review and other forms of academic writing. The fundamental steps involved in undertaking a literature ... broad literature search and then review, you will eventually be at the stage of fine-tuning and narrowing down your research idea or question in the context of other literature. A ...
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
1. Narrative Literature Review. A narrative literature review, also known as a traditional literature review, involves analyzing and summarizing existing literature without adhering to a structured methodology. It typically provides a descriptive overview of key concepts, theories, and relevant findings of the research topic.
Example: Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398 ; Systematic review: "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139).
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic. A literature review is important because it: Explains the background of research on a topic. Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area. Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
Background Systematic literature searching is recognised as a critical component of the systematic review process. It involves a systematic search for studies and aims for a transparent report of study identification, leaving readers clear about what was done to identify studies, and how the findings of the review are situated in the relevant evidence. Information specialists and review teams ...
Conducting your literature review by Susanne Hempel. Publication Date: 2020. This book is a step-by-step guide to writing a literature review, and includes tips for modifying the process as needed depending on your audience, purpose, and goals. 7 steps to a comprehensive literature review by Anthony J. Onwuegbuzie; Rebecca K. Frels.
As mentioned previously, there are a number of existing guidelines for literature reviews. Depending on the methodology needed to achieve the purpose of the review, all types can be helpful and appropriate to reach a specific goal (for examples, please see Table 1).These approaches can be qualitative, quantitative, or have a mixed design depending on the phase of the review.
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period. A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis.
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
Literature Review: it is a product and a process. As a product, it is a carefully written examination, interpretation, evaluation, and synthesis of the published literature related to your topic.It focuses on what is known about your topic and what methodologies, models, theories, and concepts have been applied to it by others.. The process is what is involved in conducting a review of the ...
The difference between literature review and systematic review comes back to the initial research question. Whereas the systematic review is very specific and focused, the standard literature review is much more general. The components of a literature review, for example, are similar to any other research paper.
A scoping review employs the systematic review methodology to explore a broader topic or question rather than a specific and answerable one, as is generally the case with a systematic review. Authors of these types of reviews seek to collect and categorize the existing literature so as to identify any gaps.
Acommon type of submission at any Journal is a review of the published information related to a topic.These are often returned to their authors without review, usually because they are literature reviews rather than systematic reviews. There is a big difference between the two (Table 1).Here, we summarise the differences, how they are used in academic work, and why a general literature review ...
The literature review is one part of a research paper. In a research paper, you use the literature review as a foundation and as support for the new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and analyze the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.
Literature reviews establish the foundation of academic inquires. However, in the planning field, we lack rigorous systematic reviews. In this article, through a systematic search on the methodology of literature review, we categorize a typology of literature reviews, discuss steps in conducting a systematic literature review, and provide suggestions on how to enhance rigor in literature ...
INTRODUCTION. Librarians and information specialists are often involved in the process of preparing and completing systematic reviews (SRs), where one of their main tasks is to identify relevant references to include in the review [].Although several recommendations for the process of searching have been published [2-6], none describe the development of a systematic search strategy from ...
What are the differences between a literature search, a literature review, a systematic review and a meta-analysis? ... What are the differences between a literature search, a literature review, a systematic review and a meta-analysis? And why is a systematic review considered to be so good? Ir Med J. 2013 Feb;106(2 Suppl):8-10. Authors
What are the differences between a literature search, a literature review, a systematic review and a meta-analysis? And why is a systematic review considered to be so good? February 2013
Systematic Review vs. Literature Review. It is common to confuse systematic and literature reviews as both are used to provide a summary of the existent literature or research on a specific topic. Even with this common ground, both types vary significantly. Please review the following chart (and its corresponding poster linked below) for the ...
The information you use to write a research paper comes from different sources and is often considered raw. Function. The purpose of a literature review is to help readers find what's already published on the subject in. The purpose of a research paper is to present your own unique research on a subject. Writing.
The methodology involved in a literature review is less complicated and requires a lower degree of planning. For a systematic review, the planning is extensive and requires defining robust pre-specified protocols. It first starts with formulating the research question and scope of the research. The PICO's approach (population, intervention ...
Purpose This systematic review aims to explore the conceptualization of health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in China. With HRQoL influenced by both modern medicine (MM) and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), the study seeks to identify differences and common ground between the frameworks of MM and TCM as defined in the literature. Method A systematic literature search was conducted across ...
An extensive literature review was conducted to systematically analyze NBS, listing the type, the location, the status of the implementation, and the possible recommendations proposed to optimize future NBS applications. Finally, a comparison is made between small- and large-scale applications of NBS.
Anticoagulation therapy is standard for conditions like atrial fibrillation, venous thromboembolism, and valvular heart disease, yet it is unclear if there are ethnoracial disparities in its quality and delivery in the United States. For this scoping review, electronic databases were searched for publications between January 1, 2011 - March 30, 2022. Eligible studies included all study ...