Part I: What is an information system?

Chapter 1: What Is an Information System?
Learning Objectives
Upon successful completion of this chapter, you will be able to:
- define what an information system is by identifying its major components;
- describe the basic history of information systems; and
- describe the basic argument behind the article “Does IT Matter?” by Nicholas Carr.
Introduction
Welcome to the world of information systems, a world that seems to change almost daily. Over the past few decades information systems have progressed to being virtually everywhere, even to the point where you may not realize its existence in many of your daily activities. Stop and consider how you interface with various components in information systems every day through different electronic devices. Smartphones, laptop, and personal computers connect us constantly to a variety of systems including messaging, banking, online retailing, and academic resources, just to name a few examples. Information systems are at the center of virtually every organization, providing users with almost unlimited resources.
Have you ever considered why businesses invest in technology? Some purchase computer hardware and software because everyone else has computers. Some even invest in the same hardware and software as their business friends even though different technology might be more appropriate for them. Finally, some businesses do sufficient research before deciding what best fits their needs. As you read through this book be sure to evaluate the contents of each chapter based on how you might someday apply what you have learned to strengthen the position of the business you work for, or maybe even your own business. Wise decisions can result in stability and growth for your future enterprise.
Information systems surround you almost every day. Wi-fi networks on your university campus, database search services in the learning resource center, and printers in computer labs are good examples. Every time you go shopping you are interacting with an information system that manages inventory and sales. Even driving to school or work results in an interaction with the transportation information system, impacting traffic lights, cameras, etc. Vending machines connect and communicate using the Internet of Things (IoT). Your car’s computer system does more than just control the engine – acceleration, shifting, and braking data is always recorded. And, of course, everyone’s smartphone is constantly connecting to available networks via Wi-fi, recording your location and other data.
Can you think of some words to describe an information system? Words such as “computers,” “networks,” or “databases” might pop into your mind. The study of information systems encompasses a broad array of devices, software, and data systems. Defining an information system provides you with a solid start to this course and the content you are about to encounter.
Defining Information Systems
Many programs in business require students to take a course in information systems . Various authors have attempted to define the term in different ways. Read the following definitions, then see if you can detect some variances.
- “An information system (IS) can be defined technically as a set of interrelated components that collect, process, store, and distribute information to support decision making and control in an organization.” [1]
- “Information systems are combinations of hardware, software, and telecommunications networks that people build and use to collect, create, and distribute useful data, typically in organizational settings.” [2]
- “Information systems are interrelated components working together to collect, process, store, and disseminate information to support decision making, coordination, control, analysis, and visualization in an organization.” [3]
The Components of Information Systems
Information systems can be viewed as having five major components: hardware, software, data, people, and processes. The first three are technology . These are probably what you thought of when defining information systems. The last two components, people and processes, separate the idea of information systems from more technical fields, such as computer science. In order to fully understand information systems, you will need to understand how all of these components work together to bring value to an organization.
Technology can be thought of as the application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes. From the invention of the wheel to the harnessing of electricity for artificial lighting, technology has become ubiquitous in daily life, to the degree that it is assumed to always be available for use regardless of location. As discussed before, the first three components of information systems – hardware, software, and data – all fall under the category of technology. Each of these will be addressed in an individual chapter. At this point a simple introduction should help you in your understanding.
Hardware is the tangible, physical portion of an information system – the part you can touch. Computers, keyboards, disk drives, and flash drives are all examples of information systems hardware. How these hardware components function and work together will be covered in Chapter 2.
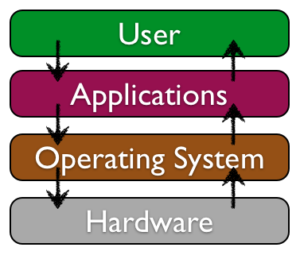
Software comprises the set of instructions that tell the hardware what to do. Software is not tangible – it cannot be touched. Programmers create software by typing a series of instructions telling the hardware what to do. Two main categories of software are: Operating Systems and Application software. Operating Systems software provides the interface between the hardware and the Application software. Examples of operating systems for a personal computer include Microsoft Windows and Ubuntu Linux. The mobile phone operating system market is dominated by Google Android and Apple iOS. Application software allows the user to perform tasks such as creating documents, recording data in a spreadsheet, or messaging a friend. Software will be explored more thoroughly in Chapter 3.
The third technology component is data. You can think of data as a collection of facts. For example, your address (street, city state, postal code), your phone number, and your social networking account are all pieces of data. Like software, data is also intangible, unable to be seen in its native state. Pieces of unrelated data are not very useful. But aggregated, indexed, and organized together into a database, data can become a powerful tool for businesses. Organizations collect all kinds of data and use it to make decisions which can then be analyzed as to their effectiveness. The analysis of data is then used to improve the organization’s performance. Chapter 4 will focus on data and databases, and how it is used in organizations.
Networking Communication
Besides the technology components (hardware, software, and data) which have long been considered the core technology of information systems, it has been suggested that one other component should be added: communication. An information system can exist without the ability to communicate – the first personal computers were stand-alone machines that did not access the Internet. However, in today’s hyper-connected world, it is an extremely rare computer that does not connect to another device or to a enetwork. Technically, the networking communication component is made up of hardware and software, but it is such a core feature of today’s information systems that it has become its own category. Networking will be covered in Chapter 5.

When thinking about information systems, it is easy to focus on the technology components and forget to look beyond these tools to fully understand their integration into an organization. A focus on the people involved in information systems is the next step. From the front-line user support staff, to systems analysts, to developers, all the way up to the chief information officer (CIO), the people involved with information systems are an essential element. The people component will be covered in Chapter 9.
The last component of information systems is process. A process is a series of steps undertaken to achieve a desired outcome or goal. Information systems are becoming more integrated with organizational processes, bringing greater productivity and better control to those processes. But simply automating activities using technology is not enough – businesses looking to utilize information systems must do more. The ultimate goal is to improve processes both internally and externally, enhancing interfaces with suppliers and customers. Technology buzzwords such as “business process re-engineering,” “business process management,” and “enterprise resource planning” all have to do with the continued improvement of these business procedures and the integration of technology with them. Businesses hoping to gain a competitive advantage over their competitors are highly focused on this component of information systems. The process element in information systems will be discussed in Chapter 8.
The Role of Information Systems
You should now understand that information systems have a number of vital components, some tangible, others intangible, and still others of a personnel nature. These components collect, store, organize, and distribute data throughout the organization. You may have even realized that one of the roles of information systems is to take data and turn it into information, and then transform that information into organizational knowledge. As technology has developed, this role has evolved into the backbone of the organization, making information systems integral to virtually every business. The integration of information systems into organizations has progressed over the decades.
The Mainframe Era
From the late 1950s through the 1960s, computers were seen as a way to more efficiently do calculations. These first business computers were room-sized monsters, with several machines linked together. The primary work was to organize and store large volumes of information that were tedious to manage by hand. Only large businesses, universities, and government agencies could afford them, and they took a crew of specialized personnel and dedicated facilities to provide information to organizations.
Time-sharing allowed dozens or even hundreds of users to simultaneously access mainframe computers from locations in the same building or miles away. Typical functions included scientific calculations and accounting, all under the broader umbrella of “data processing.”

In the late 1960s, Manufacturing Resources Planning (MRP) systems were introduced. This software, running on a mainframe computer, gave companies the ability to manage the manufacturing process, making it more efficient. From tracking inventory to creating bills of materials to scheduling production, the MRP systems gave more businesses a reason to integrate computing into their processes. IBM became the dominant mainframe company. Continued improvement in software and the availability of cheaper hardware eventually brought mainframe computers (and their little sibling, the minicomputer) into most large businesses.
Today you probably think of Silicon Valley in northern California as the center of computing and technology. But in the days of the mainframe’s dominance corporations in the cities of Minneapolis and St. Paul produced most computers. The advent of the personal computer resulted in the “center of technology” eventually moving to Silicon Valley.
The PC Revolution
In 1975, the first microcomputer was announced on the cover of Popular Mechanics : the Altair 8800. Its immediate popularity sparked the imagination of entrepreneurs everywhere, and there were soon dozens of companies manufacturing these “personal computers.” Though at first just a niche product for computer hobbyists, improvements in usability and the availability of practical software led to growing sales. The most prominent of these early personal computer makers was a little company known as Apple Computer, headed by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak, with the hugely successful “Apple II.” Not wanting to be left out of the revolution, in 1981 IBM teamed with Microsoft, then just a startup company, for their operating system software and hurriedly released their own version of the personal computer simply called the “PC.” Small businesses finally had affordable computing that could provide them with needed information systems. Popularity of the IBM PC gave legitimacy to the microcomputer and it was named Time magazine’s “Man of the Year” for 1982.

Because of the IBM PC’s open architecture, it was easy for other companies to copy, or “clone” it. During the 1980s, many new computer companies sprang up, offering less expensive versions of the PC. This drove prices down and spurred innovation. Microsoft developed the Windows operating system, with version 3.1 in 1992 becoming the first commercially successful release. Typical uses for the PC during this period included word processing, spreadsheets, and databases. These early PCs were standalone machines, not connected to a network.
Client-Server
In the mid-1980s, businesses began to see the need to connect their computers as a way to collaborate and share resources. Known as “client-server,” this networking architecture allowed users to log in to the Local Area Network (LAN) from their PC (the “client”) by connecting to a central computer called a “server.” The server would lookup permissions for each user to determine who had access to various resources such as printers and files. Software companies began developing applications that allowed multiple users to access the same data at the same time. This evolved into software applications for communicating, with the first popular use of electronic mail appearing at this time.

This networking and data sharing all stayed mainly within the confines of each business. Sharing of electronic data between companies was a very specialized function. Computers were now seen as tools to collaborate internally within an organization. These networks of computers were becoming so powerful that they were replacing many of the functions previously performed by the larger mainframe computers at a fraction of the cost. It was during this era that the first Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems were developed and run on the client-server architecture. An ERP system is an application with a centralized database that can be used to run a company’s entire business. With separate modules for accounting, finance, inventory, human resources, and many more, ERP systems, with Germany’s SAP leading the way, represented the state of the art in information systems integration. ERP systems will be discussed in Chapter 9.
The Internet, World Wide Web and E-Commerce
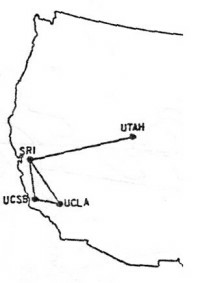
The first long distance transmission between two computers occurred on October 29, 1969 when developers under the direction of Dr. Leonard Kleinrock sent the word “login” from the campus of UCLA to Stanford Research Institute in Menlo Park, California, a distance of over 350 miles. The United States Department of Defense created and funded ARPA Net (Advanced Research Projects Administration), an experimental network which eventually became known as the Internet. ARPA Net began with just four nodes or sites, a very humble start for today’s Internet. Initially, the Internet was confined to use by universities, government agencies, and researchers. Users were required to type commands (today we refer to this as “command line”) in order to communicate and transfer files. The first e-mail messages on the Internet were sent in the early 1970s as a few very large companies expanded from local networks to the Internet. The computer was now evolving from a purely computational device into the world of digital communications.
In 1989, Tim Berners-Lee developed a simpler way for researchers to share information over the Internet, a concept he called the World Wide Web . [4] This invention became the catalyst for the growth of the Internet as a way for businesses to share information about themselves. As web browsers and Internet connections became the norm, companies rushed to grab domain names and create websites.

The digital world also became a more dangerous place as virtually all companies connected to the Internet. Computer viruses and worms, once slowly propagated through the sharing of computer disks, could now grow with tremendous speed via the Internet. Software and operating systems written for a standalone world found it very difficult to defend against these sorts of threats. A whole new industry of computer and Internet security arose. Information security will be discussed in Chapter 6.
As the world recovered from the dot-com bust, the use of technology in business continued to evolve at a frantic pace. Websites became interactive. Instead of just visiting a site to find out about a business and then purchase its products, customers wanted to be able to customize their experience and interact online with the business. This new type of interactive website, where you did not have to know how to create a web page or do any programming in order to put information online, became known as Web 2.0. This new stage of the Web was exemplified by blogging, social networking, and interactive comments being available on many websites. The new Web 2.0 world, in which online interaction became expected, had a major impact on many businesses and even whole industries. Many bookstores found themselves relegated to a niche status. Video rental chains and travel agencies simply began going out of business as they were replaced by online technologies. The newspaper industry saw a huge drop in circulation with some cities such as New Orleans no longer able to support a daily newspaper. Disintermediation is the process of technology replacing a middleman in a transaction. Web 2.0 allowed users to get information and news online, reducing dependence of physical books and newspapers.
As the world became more connected, new questions arose. Should access to the Internet be considered a right? Is it legal to copy a song that had been downloaded from the Internet? Can information entered into a website be kept private? What information is acceptable to collect from children? Technology moved so fast that policymakers did not have enough time to enact appropriate laws. Ethical issues surrounding information systems will be covered in Chapter 12.
The Post-PC World, Sort of
Ray Ozzie, a technology visionary at Microsoft, stated in 2012 that computing was moving into a phase he called the post-PC world. [5] Now six years later that prediction has not stood up very well to reality. As you will read in Chapter 13, PC sales have dropped slightly in recent years while there has been a precipitous decline in tablet sales. Smartphone sales have accelerated, due largely to their mobility and ease of operation. Just as the mainframe before it, the PC will continue to play a key role in business, but its role will be somewhat diminished as people emphasize mobility as a central feature of technology. Cloud computing provides users with mobile access to data and applications, making the PC more of a part of the communications channel rather than a repository of programs and information. Innovation in the development of technology and communications will continue to move businesses forward.
Can Information Systems Bring Competitive Advantage?
It has always been the assumption that the implementation of information systems will bring a business competitive advantage. If installing one computer to manage inventory can make a company more efficient, then it can be expected that installing several computers can improve business processes and efficiency.
In 2003, Nicholas Carr wrote an article in the Harvard Business Review that questioned this assumption. Entitled “I.T. Doesn’t Matter.” Carr was concerned that information technology had become just a commodity. Instead of viewing technology as an investment that will make a company stand out, Carr said technology would become as common as electricity – something to be managed to reduce costs, ensure that it is always running, and be as risk-free as possible.
The article was both hailed and scorned. Can I.T. bring a competitive advantage to an organization? It sure did for Walmart (see sidebar). Technology and competitive advantage will be discussed in Chapter 7.
Sidebar: Walmart Uses Information Systems to Become the World’s Leading Retailer

Walmart is the world’s largest retailer, earn 8.1 billion for the fiscal year that ended on January 31, 2018. Walmart currently serves over 260 million customers every week worldwide through its 11,700 stores in 28 countries. [6] In 2018 Fortune magazine for the sixth straight year ranked Walmart the number one company for annual revenue as they again exceeded $500 billion in annual sales. The next closest company, Exxon, had less than half of Walmart’s total revenue. [7] Walmart’s rise to prominence is due in large part to making information systems a high priority, especially in their Supply Chain Management (SCM) system known as Retail Link. ing $14.3 billion on sales of $30
This system, unique when initially implemented in the mid-1980s, allowed Walmart’s suppliers to directly access the inventory levels and sales information of their products at any of Walmart’s more than eleven thousand stores. Using Retail Link, suppliers can analyze how well their products are selling at one or more Walmart stores with a range of reporting options. Further, Walmart requires the suppliers to use Retail Link to manage their own inventory levels. If a supplier feels that their products are selling out too quickly, they can use Retail Link to petition Walmart to raise the inventory levels for their products. This has essentially allowed Walmart to “hire” thousands of product managers, all of whom have a vested interest in the products they are managing. This revolutionary approach to managing inventory has allowed Walmart to continue to drive prices down and respond to market forces quickly.
Today Walmart continues to innovate with information technology. Using its tremendous market presence, any technology that Walmart requires its suppliers to implement immediately becomes a business standard. For example, in 1983 Walmart became the first large retailer to require suppliers to the use Uniform Product Code (UPC) labels on all products. Clearly, Walmart has learned how to use I.T. to gain a competitive advantage.
In this chapter you have been introduced to the concept of information systems. Several definitions focused on the main components: technology, people, and process. You saw how the business use of information systems has evolved over the years, from the use of large mainframe computers for number crunching, through the introduction of the PC and networks, all the way to the era of mobile computing. During each of these phases, new innovations in software and technology allowed businesses to integrate technology more deeply into their organizations.
Virtually every company uses information systems which leads to the question: Does information systems bring a competitive advantage? In the final analysis the goal of this book is to help you understand the importance of information systems in making an organization more competitive. Your challenge is to understand the key components of an information system and how it can be used to bring a competitive advantage to every organization you will serve in your career.
Study Questions
- What are the five major components that make up an information system?
- List the three examples of information system hardware?
- Microsoft Windows is an example of which component of information systems?
- What is application software?
- What roles do people play in information systems?
- What is the definition of a process?
- What was invented first, the personal computer or the Internet?
- In what year were restrictions on commercial use of the Internet first lifted?
- What is Carr’s main argument about information technology?
- Suppose that you had to explain to a friend the concept of an information system. How would you define it? Write a one-paragraph description in your own words that you feel would best describe an information system to your friends or family.
- Of the five primary components of an information system (hardware, software, data, people, process), which do you think is the most important to the success of a business organization? Write a one-paragraph answer to this question that includes an example from your personal experience to support your answer.
- Everyone interacts with various information systems every day: at the grocery store, at work, at school, even in our cars. Make a list of the different information systems you interact with daily. Can you identify the technologies, people, and processes involved in making these systems work.
- Do you agree that we are in a post-PC stage in the evolution of information systems? Do some original research and cite it as you make your prediction about what business computing will look like in the next generation.
- The Walmart sidebar introduced you to how information systems was used to make them the world’s leading retailer. Walmart has continued to innovate and is still looked to as a leader in the use of technology. Do some original research and write a one-page report detailing a new technology that Walmart has recently implemented or is pioneering.
- Examine your PC. Using a four column table format identify and record the following information: 1st column: Program name, 2nd column: software manufacturer, 3rd column: software version, 4th column: software type (editor/word processor, spreadsheet, database, etc.).
- Examine your mobile phone. Create another four column table similar to the one in Lab #1. This time identify the apps, then record the requested information.
- In this chapter you read about the evolution of computing from mainframe computers to PCs and on to smartphones. Create a four column table and record the following information about your own electronic devices: 1st column – Type: PC or smartphone, 2nd column – Operating system including version, 3rd column – Storage capacity, 4th column – Storage available.
- Laudon, K.C. and Laudon, J. P. (2014) Management Information Systems , thirteenth edition. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson.
- Valacich, J. and Schneider, C. (2010). Information Systems Today – Managing in the Digital World , fourth edition. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
- Laudon, K.C. and Laudon, J. P. (2012). Management Information Systems , twelfth edition. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
- CERN . (n.d.) The Birth of the Web. Retrieved from http://public.web.cern.ch/public/en/about/web-en.html
- Marquis, J. (2012, July 16) What is the Post-PC World? Online Universities.com. Retrieved from https://www.onlineuniversities.com/blog/2012/07/what-post-pc-world/
- Walmart . (n.d.) 2017 Annual Report. Retrieved from http://s2.q4cdn.com/056532643/files/doc_financials/2017/Annual/WMT_2017_AR-(1).pdf
- McCoy, K. (2018, May 21). Big Winners in Fortune 500 List. USA Today . Retrieved from http://https://www.usatoday.com/story/money/2018/05/21/big-winners-fortune-500-list-walmart-exxon-mobil-amazon/628003002/
Information Systems for Business and Beyond (2019) by David Bourgeois is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Home — Essay Samples — Information Science and Technology — Information Systems — Management Information Systems
Management Information Systems
- Categories: Information Systems Leadership and Management Project Management
About this sample

Words: 2768 |
14 min read
Published: Sep 18, 2018
Words: 2768 | Pages: 5 | 14 min read
- Routines and business processes: Standard operating procedures have been developed that allow the organization to become productive and efficient thereby reducing costs over time.
- Organizational politics: Divergent viewpoints about how resources, rewards, and punishments should be distributed bring about political resistance to organization change.
- Organizational culture: Assumptions that define the organizational goals and products create a powerful restraint on change, especially technological change.
- Organizational environments: Reciprocal relationships exist between an organization and environments; information systems provide organizations a way to identify external changes that might require an organizational response.
- Organizational structure: Information systems reflect the type of organizational structure - entrepreneurial, machine bureaucracy, divisionalized bureaucracy, professional bureaucracy, or adhocracy.
- traditional competitors
- new market entrants
- substitute products and services
- Low-cost leadership: Lowest operational costs and the lowest prices.
- Product differentiation: Enable new products and services, or greatly change the customer convenience in using existing products and services.
- Focus on market niche: Enable a specific market focus and serve this narrow target market better than competitors.
- Strengthen customer and suppliers: Tighten linkages with suppliers and develop intimacy with customers. Describe how information systems can support each of these competitive strategies and give examples.
- Low-cost leadership: Use information systems to improve inventory management, supply management, and create efficient customer response systems. Example: Wal-Mart.
- Product differentiation: Use information systems to create products and services that are customized and personalized to fit the precise specifications of individual customers. Example: Google, eBay, Apple, Lands’ End.
- Focus on market niche: Use information systems to produce and analyze data for finely tuned sales and marketing techniques. Analyze customer buying patterns, tastes, and preferences closely in order to efficiently pitch advertising and marketing campaigns to smaller target markets. Example: Hilton Hotels, Harrah’s.
- Strengthen customer and supplier intimacies: Use information systems to facilitate direct access from suppliers to information within the company. Increase switching costs and loyalty to the company.
- What is the structure of the industry in which the firm is located? Analyze the competitive forces at work in the industry; determine the basis of competition; determine the direction and nature of change within the industry; and analyze how the industry is currently using information technology.
- What are the business, firm, and industry value chains for this particular firm? Decide how the company creates value for its customers; determine how the firm uses best practices to manage its business processes; analyze how the firm leverages its core competencies; verify how the industry supply chain and customer base are changing; establish the benefit of strategic partnerships and value webs; clarify where information systems will provide the greatest value in the firm’s value chain.
- Have we aligned IT with our business strategy and goals? Articulate the firm’s business strategy and goals; decide if IT is improving the right business processes and activities in accordance with the firm’s strategy; agree on the right metrics to measure progress toward the goals.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Information Science and Technology Business

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 766 words
2 pages / 798 words
4 pages / 1850 words
3 pages / 1370 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Information Systems
An electronic flight instrument system (EFIS) is a flight deck instrument display system located at the flight cockpit in the lower deck after the windshield. It is powered electronically and produce digital output. The [...]
The evolution of the internet has witnessed the transformation of information systems from rudimentary tools of data management to indispensable assets driving organizational competitiveness. Information systems, as a set of [...]
One of the main advantages offered is technology mobility because it allows access to the employees to the organization data, wherever they are and the service flexibility enables business development without the appeal to [...]
LIMS or the Laboratory Information Management System is an efficient method to handle large amounts of data produced in the modern laboratory. The efficiency comes from the fact that LIMS automates the process of laboratory data [...]
The wide of knowledge which deals with the creation and use of technical means and their interrelation with life, society ,and the environment and studies such as engineering ,arts, applied science and information [...]
The field information system(IS) is a combination of processes, hardware, trained personnel, software, infrastructure and standards that are designed to create, modify, store, manage and distribute information to suggest new [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

- Environment
- Information Science
- Social Issues
- Argumentative
- Cause and Effect
- Classification
- Compare and Contrast
- Descriptive
- Exemplification
- Informative
- Controversial
- Exploratory
- What Is an Essay
- Length of an Essay
- Generate Ideas
- Types of Essays
- Structuring an Essay
- Outline For Essay
- Essay Introduction
- Thesis Statement
- Body of an Essay
- Writing a Conclusion
- Essay Writing Tips
- Drafting an Essay
- Revision Process
- Fix a Broken Essay
- Format of an Essay
- Essay Examples
- Essay Checklist
- Essay Writing Service
- Pay for Research Paper
- Write My Research Paper
- Write My Essay
- Custom Essay Writing Service
- Admission Essay Writing Service
- Pay for Essay
- Academic Ghostwriting
- Write My Book Report
- Case Study Writing Service
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Coursework Writing Service
- Lab Report Writing Service
- Do My Assignment
- Buy College Papers
- Capstone Project Writing Service
- Buy Research Paper
- Custom Essays for Sale
Can’t find a perfect paper?
- Free Essay Samples
- Information Science and Technology
- Information Systems
Essays on Information Systems
Aim: The study was conducted to investigate the barriers and impact of cloud computing adoption and use on business organizations in public sector. The information would help to determine if cloud services were wholly beneficial and would always help organizations make profits. The setting of the study was London borough...
Words: 4617
Everyone dreams for that time when the elections will be of integrity, free and fair. There has been a lot of debate whether the voter ID laws are the solution or not. All Americans can freely acquire the photo IDs even though some may get it easier than others depending...
Governments and organizations have scaled up measures to increase the collection and utilization of data. In the advent of the Internet and use of gadgets, big data is one of the choices that decision-makers are embracing to leverage the broadening range of information assets for the benefit of economies. With...
Operating a successful business calls for effective management of financial and organisational data and statistics with quality information systems. Nearly every business has experienced a drastically slowed workflow due to data issues related to accuracy and reliability (Bocij, Greasley, and Hickie 2015, p. 42). This promoted the development of systems...
Words: 1826
The primary reason the figures are categorized as an enterprise is that they carry on together more than ten processes or individuals. Departmental processes could be utilized if the process was more straightforward on both figures such as handling the item and proceeding with the same. On the contrary, it...
Numerous information systems and their impact on project success Numerous information systems have been unable to perform as expected or be operational at the specified time and these have rendered them as failed projects. The fundamental problems associated with information systems include cost, design, operations, and data and they have a...
Found a perfect essay sample but want a unique one?
Request writing help from expert writer in you feed!
An appropriate information system An appropriate information system should consist of two subsystems- a social sub-system and a technical subsystem. The social subsystem entails the structure and people components while the technical subsystem entails the process and technology components (Stair, Reynolds, 2017). Ideally, a critical insight is that all...
Numerous problems associated with information systems Numerous information systems have been unable to perform as expected or be operational at the specified time and these have rendered them as failed projects. The fundamental problems associated with information systems include cost, design, operations, and data and they have a significant impact on...
Globally, information technology (IT) is now ingrained in every aspect of people's existence. Internet, web, mobile phone applications, cloud computing, digital assistants, smartphones, and personal computers are just a few examples of the different shapes that technology can take. The list is constantly expanding as new technological advancements permeate every...
Words: 2549
I work as an information security specialist for the Greenwood Company. Mr. McBride, a former engineer in the New Product division, was recently fired due to his persistent tardiness and absenteeism. In an interview with Mr. Hubert, Greenwood's human resource manager, he claimed that he was actually okay with leaving...
Words: 3206
As the internet took off, information became more easily available. According to Kensing (11), the customer Health Informatics (CHI) movement had its start at a time when emphasizing customer involvement in healthcare services was a priority. As a result, there can be a problem with misinformation. Therefore, a legitimate system...
A password is a string of alphanumeric characters that is used to verify the identity of the user of an information technology device or system. It is commonly used in computers to ensure that only authorized users have access to the device s operating operations. On the other hand, there...
Words: 1631
Related topic to Information Systems
You might also like.
- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring
Business Information Systems, Essay Example
Pages: 14
Words: 3722
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
Information Systems, because of its potential to achieve exponential synergy within organizations, are too important to be left to computer specialists. Computer Specialist can only view and interpret data extracted from activities like production, marketing, sales, quality control, accounting and customer service, and as such may lack key ingredients that are necessary to bring the company performing divisions together as one unit to provide the products and services needed by customers in a timely manner.
They might lack the technology needed to alter the composition of products to achieve higher performance ratings that will attract higher numbers of customers in diverse markets.
The BMW organization for example did not allow its computer specialists at Oracle Database 11g Management Software to dictate what happens on the $300m sail boat, but also integrated the crewmen on board to ensure their critical piloting skills are utilized in real time. The benefits from both inputs, the leader of the team as well as other support groups enable the ultimate objective to be realized at the end of the race.
Had the Computer Specialist the sole authority over the race, the other members of the team may have become demoralized less productive and cause the team to fail. Similarly leaving the information systems to computer specialist on the organizations may result in below par products and services being delivered to consumers, and a concomitant reduction in revenues and profitability.
Establishing a new website for another Major League Baseball Team will require a comprehensive, collaborative program of management, organization and prudent use of technology within the designed mission and vision statement of the business.
The primary goal of the team will be to win the World Series and to achieve this the management has to be able to recruit the most competent, skillful, versatile and efficient players they can fine, as well as support groups like trainers, nutritionist, medical experts, statistical coordinators, as well as other who will provide vital needs of the team throughout the season to facilitate decisions that will maximize the performance of the team.
The Information Systems will be vital to develop the procedures, processes, standards and strategies developed by the team manager and the Chief Executive of the company, and will affect the performance of the marketing program, stadium seating accommodation, security management, ticket sales, development of diverse revenue streams, parking facility management, food services provisions, broadcasting frequencies, advertising strategies for games and entertainment packages between innings, as well as information on the opposing teams key players and strategies deployed to achieve success.
Critical to the team will be the user friendly nature of the technology use to transmit the information needed by the team, the training levels of each member of the support group, and how the effect the information delivered will affect the team’s performance in real time, as well how the performance will impact on the fans in terms of their support attendance at the games and the revenue base of the company.
The success of UPS, which has been in operation since 1907, has not come by accident, but by the development and application of its unique intermodal transportation system using the DIAD or Delivery Information Acquisition Device technology, well executed strategic, organizational, and managerial maneuvers and use of its socially complementary assets.
Organizationally, the company has acquired 93,000 vehicles, 268 airplanes and 311 contract connection calls, so that it can access 391 airports in the USA and 219 abroad.
UPS Information Systems is extensive and specially adapted to the needs of parcel collection while connected to the intermodal transportation system which facilitate at least two modes of delivery to ensure customers globally receive their goods within 34 hours.
The company greatest assets however are its 425,000 employees and its UPSnet wireless communication system, which together ensure that the data on each parcel is transmitted through optical fibers while undergoing the management supervised consolidation, distribution and fragmentation operations over a 24 hour basis across 24, 000 distribution points into the homes and business of customers in a timely manner.
An information System can support the order fulfillment process in question by capturing every data from sales from each customer and using them to develop profiles which will forecast future orders and initiate production to meet them, thereby ensure the company is positioned to continuously to meet its customer’s needs.
The information system could also help to integrate the inventory system, customer accounts, invoice preparations, accounts payable and receivable, and all company marketing, purchasing, public relations, budgeting and planning strategies, because the information accumulated can be processed to meet the needs of the relevant department.
Computer Specialist would also be able to design real time response so that departments are able to make timely decisions in response to changing market conditions, and ensure customer’s needs are met at the most economical and efficient rates, despite the competitive pressure.
Overall then Information Systems can adequately serve the needs of the company internally and those of the customers in the external environment at the same time, so that the management and stakeholders may feel justified in the capital invested in the organization.
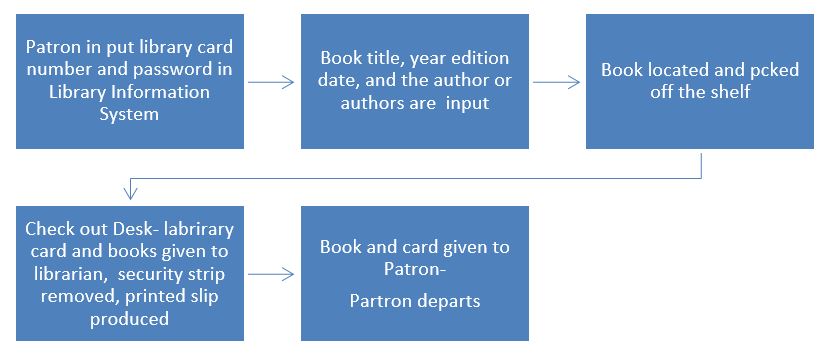
The process of selecting a book at the local library involves the patron using his or her library cards to input its title, edition, the authors or author’s last name and initials, and the year it was written, into the Library’s Information System, so that it can be sourced and located.
Once the specific book has been located it is then taken to the check out desk and given to the librarian along with the patron’s library card. The Librarian will then disable security strip and then print a slip containing the relevant information on the book, and this include the date of return, penalties for late returns, so that that the book can be taken off the premises legally.
The process ends when the card and book is given to the patron and he or she is told that the book can be renewed at least twice if there are no holds pending. Finally the patron departs with the item needed.
Present Library Book Processing System
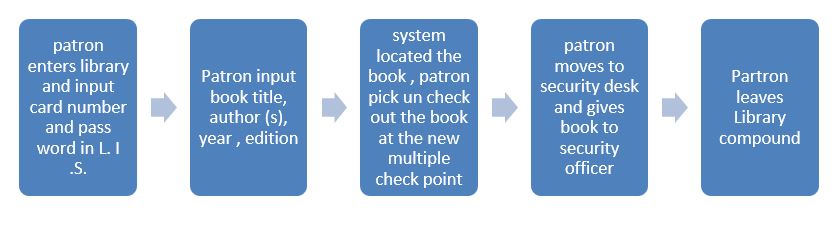
The process can be improved by personalizing the check out stage of the process, so that the patron conduct both stages with little help from the librarian except with the security stage. This new system would therefore expedite the number of check outs, reduce library traffic, and allow the institution to reallocate its human resources in other areas, where they can be fully utilize and ensure greater organizational efficiency.
New System Design
BMW Oracle team might have establish consultation with every departmental leader during training, practice runs and simulations and extract information from them as to what they deemed critical for the race to be a success.
It would then process these data into the system and used them to implement changes in the design of the boat at different stages of the journey when the weather conditions including wind speed, humidity, and other factors may reduce the speed of the unit.
This team approach would improve the morale of the entire crew and ensure greater coordination and commitment during the journey for the cup, and prevent individual team members to perceive the computer specialists are being to autocratic due to their seemingly privileged position.
There is no such thing as sustainable strategic advantage due to the fact that once a successful strategy has been used on the market, the competitors will strive to replicate even if it means doing re-engineering, so that that can use to gain the same market penetration that the creator has earned and perhaps more economically.
Companies that are keen on measure the effect of what their strategies are achieving ion the market and utilizes market intelligence, will adjust their strategies to maintain market leadership and remain sustainable.
The process will therefore continue, as change becomes the only constant especially in the global environment, as companies try to outperform each other. In some cases the customer will be the beneficiary as prices may ultimately fall due to the impact of technology and the constant desire to achieve the highest market share in the most economically efficient manner.
The advantage that retailers like Dell and Wal-Mart have over the other competitors is really the caliber of management and not the technology they possess, because the latter can be easily replicates in many instances to remove the advantages gained.
These companies has been able to recruit top class managers, pay them very well, and allowed them to have high levels of autonomy at different levels whole holding them accountable at all times.
Dell and Wal-Mart will constantly develop visions and missions statements that reflect the reality of the market place and challenge these managers to defy the odds through superior support, organizational skills, and low cost high quality product offerings that consumers always finds difficult to ignore. These companies have also established hundreds of distribution points and apply the same strategy throughout, as well as adequately capitalizing each point so that the market potentials are maximized. Other companies may not have the same chemistry, operating environment, distribution points, leveraging, influence on suppliers as well as the willingness to spend their capital to achieve the level of profitability and dominance achieved by these two companies.
Issues of concern that businesses should have, in terms of the internet providing competitive advantage are the types of software utilized, the response times to customer’s needs, the ability to identify trends and respond to them, the delivery of service, the quality of the marketing programs, the level of interactions provided to customers and the width and versatility of its products and services in comparison to its competitors.
Companies with cutting edge technologies will be able to meet these demands and achieve the desired competitive advantage to the extent that some may market their locations as one stop shop for all the goods and services in their industrial segments.
The ability of the internet to consistently and reliably provide information on the quality of services being offered is also critical for companies to gain and maintain competitive advantages, as customers who have grown accustomed to this service which they may need to forecast and plan their activities will practically remain permanent customers with such companies, in order to maintain the advantage the information has generated for them.
The producers of software based services such as ATMs should not escape being held accountable for the economic injuries customers may experience when their systems fail. They reap the financial benefits as well as consumer confidence when things are going well, and should be equally responsible when the systems fail to deliver what they no doubt advertized for several years.
These software manufacturers have cause consumers to develop considerable loyalty and trust in their design systems and should be constantly monitoring, researching, testing and updating the services provided, knowing them criminal elements are always seeking ways to sabotage their operations and inflict economic injury to customers .
Additionally the years of accumulating millions in profits should prepare them to offer the necessary insurance and other protection customers will require in the few instances when breaches may occur.
These ATM providers should under no legal consideration be allow to abdicate their responsibilities to provide all the service facilities and safety features customers will require when using their machines, because it is their creation whether the performance is excellent or poor, and they are accountable to make sure the systems provide the services they have enunciated from time to time in the advertising media.
Companies should not be held responsible for the unemployment caused by their information systems, for many reasons.
The information systems developed by these companies may be of several types with compelling features that consumers may even have difficulties making the right investment decision, but there are also risks attached to these decisions, in that the system chosen may become obsolete in a few years or months depending on the pace of technological development in their specific areas of operations.
Companies who are cognizant of these eventualities may develop the appropriate warranties to protect themselves, and as such may not be successfully sued in the courts for any harm that may result in terms of unemployment and other economic ills that may occur.
Systems should never be regarded as permanent in terms of life span or generations and manufacturers have no control on the areas of research their competitors may embark on to increase their market shares as well as revenue.
Companies that are users of information systems software should also be examining the relevance of their software to the changing markets and proactively make changes that will ensure sustainability is constantly achievable. This should include training and re-training employees as well as making new software acquisitions that will increase efficiency and productivity.
It is also worth mentioning that the very manufacturers themselves may have to terminate the services of their employees, if the information systems being offered have outlived their useful lives and are not replaced in time to meet the challenges presented by the competition.
Base on the evidence provided, there are no reasons why manufacturers of information systems should not be held responsible for the unemployment that their information systems may have caused in normal course of business operations.
Companies amassing massive data on individuals for behavioral targeting can benefit significantly them as well as create problems in terms of data security.
Collecting personal data to predict the behavior of consumers may be mutually beneficial to the marketing companies with increase in revenues and the consumers who will be supplied with products and services at the time, place and prices they can afford.
However, the possibility of hackers breaking into these systems and using the information to create havoc in the lives of individuals cannot be ignored, and marketing companies will be challenged to maintain balance and awareness as they seek to tap markets in several segments.
It will never be enough for these companies to publicly declare that there systems are well protected because things can change overnight and cause millions of data to fall in the wrong hands.
Selecting a hardware and software for an organization is an important management decision because once selected the package may have to be used in all the departments within the companies in an integrated manner to achieve high levels of productivity and efficiency.,
Each department will use the hardware and software differently from each other, and managers who are not involved in the decisions may fall behind and become obsolete in comparison to the entire process. Vital materials and services that may also be needed from one area of the company may not be supplied due to the lack of the technology required.
System Development Managers have to work with each department to ensure compatibility between what the systems require and what each operation demands to ensure that that both can co-exist and the information needed can be delivered when it is needed.
Issues like the length of time projects will take, their costs, the number of employees that will be required, the competence of suppliers, safety and security of equipment, the storage of hardcopy files, the impact on the overall company performance as well as the effect on the status of employees at the end are all issues that have to be discussed when companies are choosing the ideal hardware and software for their operations.
Cloud Computing, which came into being in 1996 via Compaq and a technologist named Sean Ossullivan, has caused a major shift in Information Technology, in that it offers more computer memory, processing power and applications in remote data centers on what is called cloud, according to Regaldo (2011).
The concept however is still not fully understood and defined in the general market, and is facing resistance by companies such as Google, Dell and IBM, because it entails selling servers to internet providers and caused rebranding and supercomputing phrases to be used to describe its effect on the internet (Regaldo, 2011)
Websites seem threatened by the advent of cloud computing due to the data services and infrastructures it provides, as well as being a cheaper source for procuring vital technology services (Regaldo, 2011).
It is absurd to think that Database Management Software is not needed in any environment where data is being processed to determine trends, behavioral patterns, comparative performance levels, inventory cost, budget constraints, and many other computations to enhance accurate decision makings within organizations.
The software becomes the vehicle to provide these answers in terms of how to increase productivity, achieve rapid problem resolution, reductions of infrastructure cost, increase database efficiency and high availability (Quest Software, 2011).
Without Database Management Software, companies are only depriving themselves of the latest analytical tools that can transform their scope in a changing global landscape where speed and accuracy with respect to information are extremely critical to achieving and maintaining competitive advantages.
Users should be involved in every state of the selection process for any Database Management Software, as they are the ones doing the hands on work that creates the data needed for processing higher up in the organization, and the famous GIGO concept is very much a threat to organizational accuracy and competence.
These users can easily identify procedures and processes that are not feasible base on their experience, and may save organizations millions of dollars and times, if they are involved in the process. This is because they can most often justify their answers with answers that many program managers may not have seen or will agree based on the logics of their arguments.
Suggestions from users may also positively impact the designs that are made within organizations and may lead to software that may be marketed in the wider industry and produce considerable profits for their employers.
Involving end users in the decision making concerning Database Management Software may provide significant and enduring benefits to organizations that sees it wise to tap into these human resources to guide their advancement in the highly competitive business environment, which often leaves many causalities on the dunghill of obsolescence.
Information Policy within a company determines what kinds of information are created, collected, stored, accessed, retained, organized as well as released internally and externally according to BCLA Information Policy Committee (1995).
Companies not having such a policy are not protective of their future viability in that they may deprive themselves of valuable intellectual properties which their competitors can used to eventually drive them out of business.
They may also cause the private information of their employees as well as key historical data to be mislaid and prevent the possible use of empirical data generated by former executives to guide critical decision making in the future.
Information policy can also help the interest of companies in lawsuit actions that involving former employees divulging information on the secrets of products that are unique to the company and has been sources of great revenues.
The statement that smart phones will become the single most important device an individual may own in the near future is indeed a correct one.
Presently the device combines the functions of a PDA and a mobile phone, while there are models that serve as portable media players and camera with high resolution touch screens and web browsers that can display standard web pages.
Smart phones also provides GPS navigation, WI-FI and broadband access and overtime will improve to due to the number of mobile operating systems that are currently on the market and will most likely be incorporated.
The device possibilities seems endless as far as innovations that companies will bring to the table but the implications can be very sobering, in that it may reduce the number of laptops and PC used in the homes and offices, photo studios, printing companies and Post Offices may go out of business, while students going to colleges and universities will significantly reduce amount of books purchased and transported.
Sadly smart phones may also be the source of many crimes and accidents on the streets as users may be too engage to keep their eyes on the road or on incoming assailants.
The devise base on these observations will provide more benefits than injuries and may really be the most significant piece of equipment an individual may own in the near future.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), which is a system that transmit the identity of objects or persons wirelessly using radio waves, should not be used by all companies but only by those in the business of marketing tangible goods and services, as well as those in key security matters that are significant to the protection of national assets and interest.
The reason behind this separation is the fact that the technology can be used to invade that private life of individuals and may result in breaches of the constitutional rights. Retailing and Manufacturing companies however could find this technology considerable useful as they could embrace it to improve the efficiency of their delivery systems, inventory status, production planning, as well as in forward planning and in financial planning. This is because they can correctly locate the stage of their product in terms of distribution, and have discussion with key individual without meeting in the same location to decide on actions to be taken.
Wi-Fi systems can potentially provide high speed multimedia content delivery to localized areas such as indoor offices, shopping malls, and airport lounges. The system provides ease of use, lowest set up and deployment costs, ubiquitous high speed computing, connections between computers the internet, wired networks as well as wireless LANS when liked with GSC and GPRS (Joseph, Manoj, Murthy, 2011)
Cellular DATA services on the other hand while providing internet connection near many large cities, are expensive, less reliable and slower than Wi-Fi connections.
This type of service provides a greater range of services than Wi-Fi and often covers large metropolis
Wi-Fi can be accessed from laptops and PC once users have the correct password, while cellular users have to be subscribers to local companies in order to access the internet.
BCLA Information Policy Committee (1995). What is Information Policy? www.vcn.bcl/bcla-ip/committee/broch95.html , 10/31/11
Joseph, D.A., Manoj, B., Murthy, C. S. A., (2011). The Interoperability of Wi-Fi Hotspots and Packet Cellular Networks and the Impact of User Behavior www.citesteerx.ist.psu.edu/view/downloads , 10/31/11
Quest Software Inc. (2011). Fog Light-Your Cross Platform Database Monitoring and Management Solution www.quest.com/landing/?ID=5733C_KWCID=TC%7C23773%7CBklyword%70%7c%Bplacement% , 10/31/11
Regaldo, A. (2011). Who Coined Cloud Computing? Technology Review www.technologyreview.com/business/38987/=chfeature , 10/32/11
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
The NIDs and HIDs, Essay Example
Legal Forensic Collection Differences and Technology, Essay Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Pages: 1
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371
Home / Essay Samples / Information Science and Technology / Information Systems / Masters Of Information System
Masters Of Information System
- Category: Information Science and Technology
- Topic: Computer Software , Information Systems
Pages: 2 (829 words)
Views: 1735
- Downloads: -->
- Professional Skills in Information Communication Technology
- Information Systems Analysis and Design
- Project Management Concepts
- Introduction to Programming
- ICT Services Management
- Database Design and Development
- E-Business Systems
- Knowledge Audits for Business Analysis
- Business Process Management
- Business Intelligence using Big Data
- Postgraduate ICT Internship
- Information Systems Project.
- Mobile Application Development
- Networks and Information Security
- Software Design and Development.
Career Goal
--> ⚠️ Remember: This essay was written and uploaded by an--> click here.
Found a great essay sample but want a unique one?
are ready to help you with your essay
You won’t be charged yet!
Negative Impact of Technology Essays
Mobile Phone Essays
Computer Essays
Open Source Software Essays
Graphic Design Essays
Related Essays
We are glad that you like it, but you cannot copy from our website. Just insert your email and this sample will be sent to you.
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Your essay sample has been sent.
In fact, there is a way to get an original essay! Turn to our writers and order a plagiarism-free paper.
samplius.com uses cookies to offer you the best service possible.By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .--> -->