
18 Descriptive Research Examples
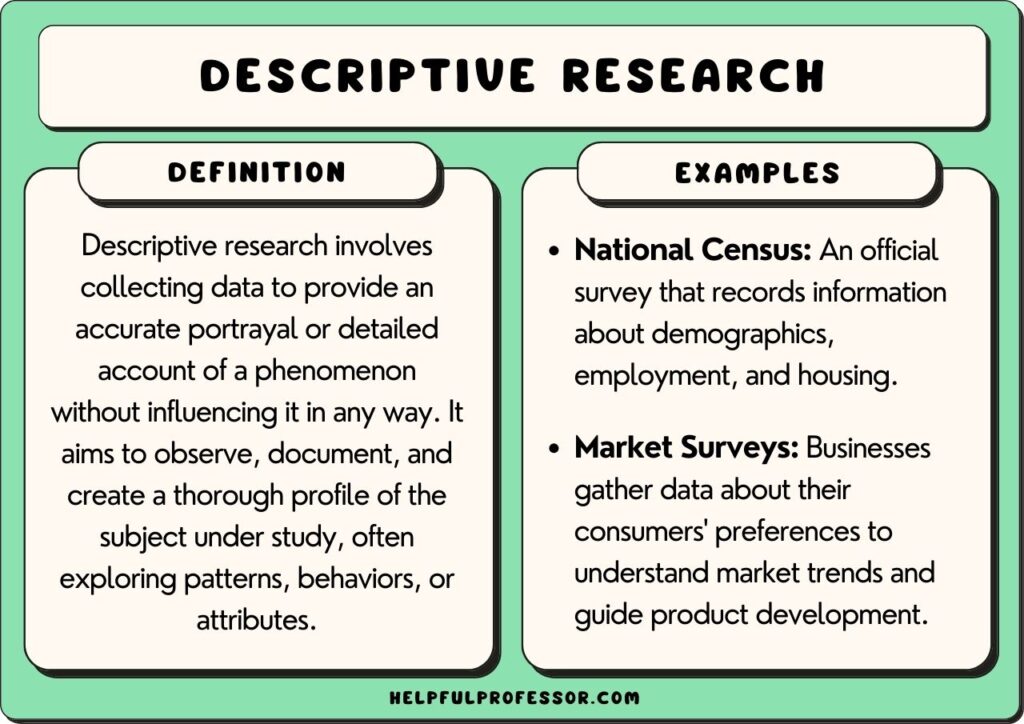
Descriptive research involves gathering data to provide a detailed account or depiction of a phenomenon without manipulating variables or conducting experiments.
A scholarly definition is:
“Descriptive research is defined as a research approach that describes the characteristics of the population, sample or phenomenon studied. This method focuses more on the “what” rather than the “why” of the research subject.” (Matanda, 2022, p. 63)
The key feature of descriptive research is that it merely describes phenomena and does not attempt to manipulate variables nor determine cause and effect .
To determine cause and effect , a researcher would need to use an alternate methodology, such as experimental research design .
Common approaches to descriptive research include:
- Cross-sectional research : A cross-sectional study gathers data on a population at a specific time to get descriptive data that could include categories (e.g. age or income brackets) to get a better understanding of the makeup of a population.
- Longitudinal research : Longitudinal studies return to a population to collect data at several different points in time, allowing for description of changes in categories over time. However, as it’s descriptive, it cannot infer cause and effect (Erickson, 2017).
Methods that could be used include:
- Surveys: For example, sending out a census survey to be completed at the exact same date and time by everyone in a population.
- Case Study : For example, an in-depth description of a specific person or group of people to gain in-depth qualitative information that can describe a phenomenon but cannot be generalized to other cases.
- Observational Method : For example, a researcher taking field notes in an ethnographic study. (Siedlecki, 2020)
Descriptive Research Examples
1. Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (Psychology): Researchers analyze various behavior patterns, cognitive skills, and social interaction abilities specific to children with Autism Spectrum Disorder to comprehensively describe the disorder’s symptom spectrum. This detailed description classifies it as descriptive research, rather than analytical or experimental, as it merely records what is observed without altering any variables or trying to establish causality.
2. Consumer Purchase Decision Process in E-commerce Marketplaces (Marketing): By documenting and describing all the factors that influence consumer decisions on online marketplaces, researchers don’t attempt to predict future behavior or establish causes—just describe observed behavior—making it descriptive research.
3. Impacts of Climate Change on Agricultural Practices (Environmental Studies): Descriptive research is seen as scientists outline how climate changes influence various agricultural practices by observing and then meticulously categorizing the impacts on crop variability, farming seasons, and pest infestations without manipulating any variables in real-time.
4. Work Environment and Employee Performance (Human Resources Management): A study of this nature, describing the correlation between various workplace elements and employee performance, falls under descriptive research as it merely narrates the observed patterns without altering any conditions or testing hypotheses.
5. Factors Influencing Student Performance (Education): Researchers describe various factors affecting students’ academic performance, such as studying techniques, parental involvement, and peer influence. The study is categorized as descriptive research because its principal aim is to depict facts as they stand without trying to infer causal relationships.
6. Technological Advances in Healthcare (Healthcare): This research describes and categorizes different technological advances (such as telemedicine, AI-enabled tools, digital collaboration) in healthcare without testing or modifying any parameters, making it an example of descriptive research.
7. Urbanization and Biodiversity Loss (Ecology): By describing the impact of rapid urban expansion on biodiversity loss, this study serves as a descriptive research example. It observes the ongoing situation without manipulating it, offering a comprehensive depiction of the existing scenario rather than investigating the cause-effect relationship.
8. Architectural Styles across Centuries (Art History): A study documenting and describing various architectural styles throughout centuries essentially represents descriptive research. It aims to narrate and categorize facts without exploring the underlying reasons or predicting future trends.
9. Media Usage Patterns among Teenagers (Sociology): When researchers document and describe the media consumption habits among teenagers, they are performing a descriptive research study. Their main intention is to observe and report the prevailing trends rather than establish causes or predict future behaviors.
10. Dietary Habits and Lifestyle Diseases (Nutrition Science): By describing the dietary patterns of different population groups and correlating them with the prevalence of lifestyle diseases, researchers perform descriptive research. They merely describe observed connections without altering any diet plans or lifestyles.
11. Shifts in Global Energy Consumption (Environmental Economics): When researchers describe the global patterns of energy consumption and how they’ve shifted over the years, they conduct descriptive research. The focus is on recording and portraying the current state without attempting to infer causes or predict the future.
12. Literacy and Employment Rates in Rural Areas (Sociology): A study aims at describing the literacy rates in rural areas and correlating it with employment levels. It falls under descriptive research because it maps the scenario without manipulating parameters or proving a hypothesis.
13. Women Representation in Tech Industry (Gender Studies): A detailed description of the presence and roles of women across various sectors of the tech industry is a typical case of descriptive research. It merely observes and records the status quo without establishing causality or making predictions.
14. Impact of Urban Green Spaces on Mental Health (Environmental Psychology): When researchers document and describe the influence of green urban spaces on residents’ mental health, they are undertaking descriptive research. They seek purely to understand the current state rather than exploring cause-effect relationships.
15. Trends in Smartphone usage among Elderly (Gerontology): Research describing how the elderly population utilizes smartphones, including popular features and challenges encountered, serves as descriptive research. Researcher’s aim is merely to capture what is happening without manipulating variables or posing predictions.
16. Shifts in Voter Preferences (Political Science): A study describing the shift in voter preferences during a particular electoral cycle is descriptive research. It simply records the preferences revealed without drawing causal inferences or suggesting future voting patterns.
17. Understanding Trust in Autonomous Vehicles (Transportation Psychology): This comprises research describing public attitudes and trust levels when it comes to autonomous vehicles. By merely depicting observed sentiments, without engineering any situations or offering predictions, it’s considered descriptive research.
18. The Impact of Social Media on Body Image (Psychology): Descriptive research to outline the experiences and perceptions of individuals relating to body image in the era of social media. Observing these elements without altering any variables qualifies it as descriptive research.
Descriptive vs Experimental Research
Descriptive research merely observes, records, and presents the actual state of affairs without manipulating any variables, while experimental research involves deliberately changing one or more variables to determine their effect on a particular outcome.
De Vaus (2001) succinctly explains that descriptive studies find out what is going on , but experimental research finds out why it’s going on /
Simple definitions are below:
- Descriptive research is primarily about describing the characteristics or behaviors in a population, often through surveys or observational methods. It provides rich detail about a specific phenomenon but does not allow for conclusive causal statements; however, it can offer essential leads or ideas for further experimental research (Ivey, 2016).
- Experimental research , often conducted in controlled environments, aims to establish causal relationships by manipulating one or more independent variables and observing the effects on dependent variables (Devi, 2017; Mukherjee, 2019).
Experimental designs often involve a control group and random assignment . While it can provide compelling evidence for cause and effect, its artificial setting might not perfectly mirror real-worldly conditions, potentially affecting the generalizability of its findings.
These two types of research are complementary, with descriptive studies often leading to hypotheses that are then tested experimentally (Devi, 2017; Zhao et al., 2021).
Benefits and Limitations of Descriptive Research
Descriptive research offers several benefits: it allows researchers to gather a vast amount of data and present a complete picture of the situation or phenomenon under study, even within large groups or over long time periods.
It’s also flexible in terms of the variety of methods used, such as surveys, observations, and case studies, and it can be instrumental in identifying patterns or trends and generating hypotheses (Erickson, 2017).
However, it also has its limitations.
The primary drawback is that it can’t establish cause-effect relationships, as no variables are manipulated. This lack of control over variables also opens up possibilities for bias, as researchers might inadvertently influence responses during data collection (De Vaus, 2001).
Additionally, the findings of descriptive research are often not generalizable since they are heavily reliant on the chosen sample’s characteristics.
See More Types of Research Design Here
De Vaus, D. A. (2001). Research Design in Social Research . SAGE Publications.
Devi, P. S. (2017). Research Methodology: A Handbook for Beginners . Notion Press.
Erickson, G. S. (2017). Descriptive research design. In New Methods of Market Research and Analysis (pp. 51-77). Edward Elgar Publishing.
Gresham, B. B. (2016). Concepts of Evidence-based Practice for the Physical Therapist Assistant . F.A. Davis Company.
Ivey, J. (2016). Is descriptive research worth doing?. Pediatric nursing , 42 (4), 189. ( Source )
Krishnaswamy, K. N., Sivakumar, A. I., & Mathirajan, M. (2009). Management Research Methodology: Integration of Principles, Methods and Techniques . Pearson Education.
Matanda, E. (2022). Research Methods and Statistics for Cross-Cutting Research: Handbook for Multidisciplinary Research . Langaa RPCIG.
Monsen, E. R., & Van Horn, L. (2007). Research: Successful Approaches . American Dietetic Association.
Mukherjee, S. P. (2019). A Guide to Research Methodology: An Overview of Research Problems, Tasks and Methods . CRC Press.
Siedlecki, S. L. (2020). Understanding descriptive research designs and methods. Clinical Nurse Specialist , 34 (1), 8-12. ( Source )
Zhao, P., Ross, K., Li, P., & Dennis, B. (2021). Making Sense of Social Research Methodology: A Student and Practitioner Centered Approach . SAGE Publications.

Dave Cornell (PhD)
Dr. Cornell has worked in education for more than 20 years. His work has involved designing teacher certification for Trinity College in London and in-service training for state governments in the United States. He has trained kindergarten teachers in 8 countries and helped businessmen and women open baby centers and kindergartens in 3 countries.
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 25 Positive Punishment Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 25 Dissociation Examples (Psychology)
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 15 Zone of Proximal Development Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ Perception Checking: 15 Examples and Definition

Chris Drew (PhD)
This article was peer-reviewed and edited by Chris Drew (PhD). The review process on Helpful Professor involves having a PhD level expert fact check, edit, and contribute to articles. Reviewers ensure all content reflects expert academic consensus and is backed up with reference to academic studies. Dr. Drew has published over 20 academic articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education and holds a PhD in Education from ACU.
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 25 Positive Punishment Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 25 Dissociation Examples (Psychology)
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Zone of Proximal Development Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link Perception Checking: 15 Examples and Definition
1 thought on “18 Descriptive Research Examples”
Very nice, educative article. I appreciate the efforts.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Introducing Research Designs
- First Online: 10 November 2021
Cite this chapter

- Stefan Hunziker 3 &
- Michael Blankenagel 3
3288 Accesses
We define research design as a combination of decisions within a research process. These decisions enable us to make a specific type of argument by answering the research question. It is the implementation plan for the research study that allows reaching the desired (type of) conclusion. Different research designs make it possible to draw different conclusions. These conclusions produce various kinds of intellectual contributions. As all kinds of intellectual contributions are necessary to increase the body of knowledge, no research design is inherently better than another, only more appropriate to answer a specific question.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Alvesson, M., & Skoldburg, K. (2000). Reflexive methodology . SAGE.
Google Scholar
Alvesson, M. (2004). Reflexive methodology: New vistas for qualitative research. SAGE.
Attia, M., & Edge, J. (2017). Be(com)ing a reflexive researcher: A developmental approach to research methodology. Open Review of Educational Research, 4 (1), 33–45.
Article Google Scholar
Brahler, C. (2018). Chapter 9 “Validity in Experimental Design”. University of Dayton. Retrieved May 27, 2021, from https://www.coursehero.com/file/30778216/CHAPTER-9-VALIDITY-IN-EXPERIMENTAL-DESIGN-KEYdocx/ .
Brown, J. D. (1996). Testing in language programs. Prentice Hall Regents.
Cambridge University Press. (n.d.a). Design. In Cambridge dictionary . Retrieved May 19, 2021, from https://dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/design .
Cambridge University Press. (n.d.b). Method. In Cambridge dictionary . Retrieved May 19, 2021, from https://dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/method .
Cambridge University Press. (n.d.c). Methodology. In Cambridge dictionary . Retrieved June 8, 2021, from https://dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/methodology .
Charmaz, K. (2017). The power of constructivist grounded theory for critical inquiry. Qualitative Inquiry, 23 (1), 34–45.
Cohen, D. J., & Crabtree, B. F. (2008). Evaluative criteria for qualitative research in health care: Controversies and recommendations. Annals of Family Medicine, 6 (4), 331–339.
de Vaus, D. A. (2001). Research design in social research. Reprinted . SAGE.
Hall, W. A., & Callery, P. (2001). Enhancing the rigor of grounded theory: Incorporating reflexivity and relationality. Qualitative Health Research, 11 (2), 257–272.
Haynes, K. (2012). Reflexivity in qualitative research. In Qualitative organizational research: Core methods and current challenges (pp. 72–89).
Koch, T., & Harrington, A. (1998). Reconceptualizing rigour: The case for reflexivity. Journal of Advanced Nursing., 28 (4), 882–890.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1985). Naturalistic Inquiry . Sage.
Malterud, K. (2001). Qualitative research: Standards, challenges and guidelines. The Lancet, 358 , 483–488.
Orr, K., & Bennett, M. (2009). Reflexivity in the co-production of academic-practitioner research. Qual Research in Orgs & Mgmt, 4, 85–102.
Trochim, W. (2005). Research methods: The concise knowledge base. Atomic Dog Pub.
Subramani, S. (2019). Practising reflexivity: Ethics, methodology and theory construction. Methodological Innovations , 12 (2).
Sue, V., & Ritter, L. (Eds.). (2007). Conducting online surveys . SAGE.
Yin, R. K. (1994). Discovering the future of the case study. method in evaluation research. American Journal of Evaluation, 15 (3), 283–290.
Yin, R. K. (2014). Case study research. Design and methods (5th ed.). SAGE.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Wirtschaft/IFZ – Campus Zug-Rotkreuz, Hochschule Luzern, Zug-Rotkreuz, Zug , Switzerland
Stefan Hunziker & Michael Blankenagel
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Stefan Hunziker .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Hunziker, S., Blankenagel, M. (2021). Introducing Research Designs. In: Research Design in Business and Management. Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-34357-6_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-34357-6_1
Published : 10 November 2021
Publisher Name : Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN : 978-3-658-34356-9
Online ISBN : 978-3-658-34357-6
eBook Packages : Business and Economics (German Language)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Descriptive Research Design | Definition, Methods & Examples
Descriptive Research Design | Definition, Methods & Examples
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Descriptive research aims to accurately and systematically describe a population, situation or phenomenon. It can answer what , where , when , and how questions , but not why questions.
A descriptive research design can use a wide variety of research methods to investigate one or more variables . Unlike in experimental research , the researcher does not control or manipulate any of the variables, but only observes and measures them.
Table of contents
When to use a descriptive research design, descriptive research methods.
Descriptive research is an appropriate choice when the research aim is to identify characteristics, frequencies, trends, and categories.
It is useful when not much is known yet about the topic or problem. Before you can research why something happens, you need to understand how, when, and where it happens.
- How has the London housing market changed over the past 20 years?
- Do customers of company X prefer product Y or product Z?
- What are the main genetic, behavioural, and morphological differences between European wildcats and domestic cats?
- What are the most popular online news sources among under-18s?
- How prevalent is disease A in population B?
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Descriptive research is usually defined as a type of quantitative research , though qualitative research can also be used for descriptive purposes. The research design should be carefully developed to ensure that the results are valid and reliable .
Survey research allows you to gather large volumes of data that can be analysed for frequencies, averages, and patterns. Common uses of surveys include:
- Describing the demographics of a country or region
- Gauging public opinion on political and social topics
- Evaluating satisfaction with a company’s products or an organisation’s services
Observations
Observations allow you to gather data on behaviours and phenomena without having to rely on the honesty and accuracy of respondents. This method is often used by psychological, social, and market researchers to understand how people act in real-life situations.
Observation of physical entities and phenomena is also an important part of research in the natural sciences. Before you can develop testable hypotheses , models, or theories, it’s necessary to observe and systematically describe the subject under investigation.
Case studies
A case study can be used to describe the characteristics of a specific subject (such as a person, group, event, or organisation). Instead of gathering a large volume of data to identify patterns across time or location, case studies gather detailed data to identify the characteristics of a narrowly defined subject.
Rather than aiming to describe generalisable facts, case studies often focus on unusual or interesting cases that challenge assumptions, add complexity, or reveal something new about a research problem .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). Descriptive Research Design | Definition, Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 22 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/descriptive-research-design/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, correlational research | guide, design & examples, qualitative vs quantitative research | examples & methods.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Descriptive Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Descriptive Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Table of Contents

Descriptive Research Design
Definition:
Descriptive research design is a type of research methodology that aims to describe or document the characteristics, behaviors, attitudes, opinions, or perceptions of a group or population being studied.
Descriptive research design does not attempt to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables or make predictions about future outcomes. Instead, it focuses on providing a detailed and accurate representation of the data collected, which can be useful for generating hypotheses, exploring trends, and identifying patterns in the data.
Types of Descriptive Research Design
Types of Descriptive Research Design are as follows:
Cross-sectional Study
This involves collecting data at a single point in time from a sample or population to describe their characteristics or behaviors. For example, a researcher may conduct a cross-sectional study to investigate the prevalence of certain health conditions among a population, or to describe the attitudes and beliefs of a particular group.
Longitudinal Study
This involves collecting data over an extended period of time, often through repeated observations or surveys of the same group or population. Longitudinal studies can be used to track changes in attitudes, behaviors, or outcomes over time, or to investigate the effects of interventions or treatments.
This involves an in-depth examination of a single individual, group, or situation to gain a detailed understanding of its characteristics or dynamics. Case studies are often used in psychology, sociology, and business to explore complex phenomena or to generate hypotheses for further research.
Survey Research
This involves collecting data from a sample or population through standardized questionnaires or interviews. Surveys can be used to describe attitudes, opinions, behaviors, or demographic characteristics of a group, and can be conducted in person, by phone, or online.
Observational Research
This involves observing and documenting the behavior or interactions of individuals or groups in a natural or controlled setting. Observational studies can be used to describe social, cultural, or environmental phenomena, or to investigate the effects of interventions or treatments.
Correlational Research
This involves examining the relationships between two or more variables to describe their patterns or associations. Correlational studies can be used to identify potential causal relationships or to explore the strength and direction of relationships between variables.
Data Analysis Methods
Descriptive research design data analysis methods depend on the type of data collected and the research question being addressed. Here are some common methods of data analysis for descriptive research:
Descriptive Statistics
This method involves analyzing data to summarize and describe the key features of a sample or population. Descriptive statistics can include measures of central tendency (e.g., mean, median, mode) and measures of variability (e.g., range, standard deviation).
Cross-tabulation
This method involves analyzing data by creating a table that shows the frequency of two or more variables together. Cross-tabulation can help identify patterns or relationships between variables.
Content Analysis
This method involves analyzing qualitative data (e.g., text, images, audio) to identify themes, patterns, or trends. Content analysis can be used to describe the characteristics of a sample or population, or to identify factors that influence attitudes or behaviors.
Qualitative Coding
This method involves analyzing qualitative data by assigning codes to segments of data based on their meaning or content. Qualitative coding can be used to identify common themes, patterns, or categories within the data.
Visualization
This method involves creating graphs or charts to represent data visually. Visualization can help identify patterns or relationships between variables and make it easier to communicate findings to others.
Comparative Analysis
This method involves comparing data across different groups or time periods to identify similarities and differences. Comparative analysis can help describe changes in attitudes or behaviors over time or differences between subgroups within a population.
Applications of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design has numerous applications in various fields. Some of the common applications of descriptive research design are:
- Market research: Descriptive research design is widely used in market research to understand consumer preferences, behavior, and attitudes. This helps companies to develop new products and services, improve marketing strategies, and increase customer satisfaction.
- Health research: Descriptive research design is used in health research to describe the prevalence and distribution of a disease or health condition in a population. This helps healthcare providers to develop prevention and treatment strategies.
- Educational research: Descriptive research design is used in educational research to describe the performance of students, schools, or educational programs. This helps educators to improve teaching methods and develop effective educational programs.
- Social science research: Descriptive research design is used in social science research to describe social phenomena such as cultural norms, values, and beliefs. This helps researchers to understand social behavior and develop effective policies.
- Public opinion research: Descriptive research design is used in public opinion research to understand the opinions and attitudes of the general public on various issues. This helps policymakers to develop effective policies that are aligned with public opinion.
- Environmental research: Descriptive research design is used in environmental research to describe the environmental conditions of a particular region or ecosystem. This helps policymakers and environmentalists to develop effective conservation and preservation strategies.
Descriptive Research Design Examples
Here are some real-time examples of descriptive research designs:
- A restaurant chain wants to understand the demographics and attitudes of its customers. They conduct a survey asking customers about their age, gender, income, frequency of visits, favorite menu items, and overall satisfaction. The survey data is analyzed using descriptive statistics and cross-tabulation to describe the characteristics of their customer base.
- A medical researcher wants to describe the prevalence and risk factors of a particular disease in a population. They conduct a cross-sectional study in which they collect data from a sample of individuals using a standardized questionnaire. The data is analyzed using descriptive statistics and cross-tabulation to identify patterns in the prevalence and risk factors of the disease.
- An education researcher wants to describe the learning outcomes of students in a particular school district. They collect test scores from a representative sample of students in the district and use descriptive statistics to calculate the mean, median, and standard deviation of the scores. They also create visualizations such as histograms and box plots to show the distribution of scores.
- A marketing team wants to understand the attitudes and behaviors of consumers towards a new product. They conduct a series of focus groups and use qualitative coding to identify common themes and patterns in the data. They also create visualizations such as word clouds to show the most frequently mentioned topics.
- An environmental scientist wants to describe the biodiversity of a particular ecosystem. They conduct an observational study in which they collect data on the species and abundance of plants and animals in the ecosystem. The data is analyzed using descriptive statistics to describe the diversity and richness of the ecosystem.
How to Conduct Descriptive Research Design
To conduct a descriptive research design, you can follow these general steps:
- Define your research question: Clearly define the research question or problem that you want to address. Your research question should be specific and focused to guide your data collection and analysis.
- Choose your research method: Select the most appropriate research method for your research question. As discussed earlier, common research methods for descriptive research include surveys, case studies, observational studies, cross-sectional studies, and longitudinal studies.
- Design your study: Plan the details of your study, including the sampling strategy, data collection methods, and data analysis plan. Determine the sample size and sampling method, decide on the data collection tools (such as questionnaires, interviews, or observations), and outline your data analysis plan.
- Collect data: Collect data from your sample or population using the data collection tools you have chosen. Ensure that you follow ethical guidelines for research and obtain informed consent from participants.
- Analyze data: Use appropriate statistical or qualitative analysis methods to analyze your data. As discussed earlier, common data analysis methods for descriptive research include descriptive statistics, cross-tabulation, content analysis, qualitative coding, visualization, and comparative analysis.
- I nterpret results: Interpret your findings in light of your research question and objectives. Identify patterns, trends, and relationships in the data, and describe the characteristics of your sample or population.
- Draw conclusions and report results: Draw conclusions based on your analysis and interpretation of the data. Report your results in a clear and concise manner, using appropriate tables, graphs, or figures to present your findings. Ensure that your report follows accepted research standards and guidelines.
When to Use Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design is used in situations where the researcher wants to describe a population or phenomenon in detail. It is used to gather information about the current status or condition of a group or phenomenon without making any causal inferences. Descriptive research design is useful in the following situations:
- Exploratory research: Descriptive research design is often used in exploratory research to gain an initial understanding of a phenomenon or population.
- Identifying trends: Descriptive research design can be used to identify trends or patterns in a population, such as changes in consumer behavior or attitudes over time.
- Market research: Descriptive research design is commonly used in market research to understand consumer preferences, behavior, and attitudes.
- Health research: Descriptive research design is useful in health research to describe the prevalence and distribution of a disease or health condition in a population.
- Social science research: Descriptive research design is used in social science research to describe social phenomena such as cultural norms, values, and beliefs.
- Educational research: Descriptive research design is used in educational research to describe the performance of students, schools, or educational programs.
Purpose of Descriptive Research Design
The main purpose of descriptive research design is to describe and measure the characteristics of a population or phenomenon in a systematic and objective manner. It involves collecting data that describe the current status or condition of the population or phenomenon of interest, without manipulating or altering any variables.
The purpose of descriptive research design can be summarized as follows:
- To provide an accurate description of a population or phenomenon: Descriptive research design aims to provide a comprehensive and accurate description of a population or phenomenon of interest. This can help researchers to develop a better understanding of the characteristics of the population or phenomenon.
- To identify trends and patterns: Descriptive research design can help researchers to identify trends and patterns in the data, such as changes in behavior or attitudes over time. This can be useful for making predictions and developing strategies.
- To generate hypotheses: Descriptive research design can be used to generate hypotheses or research questions that can be tested in future studies. For example, if a descriptive study finds a correlation between two variables, this could lead to the development of a hypothesis about the causal relationship between the variables.
- To establish a baseline: Descriptive research design can establish a baseline or starting point for future research. This can be useful for comparing data from different time periods or populations.
Characteristics of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design has several key characteristics that distinguish it from other research designs. Some of the main characteristics of descriptive research design are:
- Objective : Descriptive research design is objective in nature, which means that it focuses on collecting factual and accurate data without any personal bias. The researcher aims to report the data objectively without any personal interpretation.
- Non-experimental: Descriptive research design is non-experimental, which means that the researcher does not manipulate any variables. The researcher simply observes and records the behavior or characteristics of the population or phenomenon of interest.
- Quantitative : Descriptive research design is quantitative in nature, which means that it involves collecting numerical data that can be analyzed using statistical techniques. This helps to provide a more precise and accurate description of the population or phenomenon.
- Cross-sectional: Descriptive research design is often cross-sectional, which means that the data is collected at a single point in time. This can be useful for understanding the current state of the population or phenomenon, but it may not provide information about changes over time.
- Large sample size: Descriptive research design typically involves a large sample size, which helps to ensure that the data is representative of the population of interest. A large sample size also helps to increase the reliability and validity of the data.
- Systematic and structured: Descriptive research design involves a systematic and structured approach to data collection, which helps to ensure that the data is accurate and reliable. This involves using standardized procedures for data collection, such as surveys, questionnaires, or observation checklists.
Advantages of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design has several advantages that make it a popular choice for researchers. Some of the main advantages of descriptive research design are:
- Provides an accurate description: Descriptive research design is focused on accurately describing the characteristics of a population or phenomenon. This can help researchers to develop a better understanding of the subject of interest.
- Easy to conduct: Descriptive research design is relatively easy to conduct and requires minimal resources compared to other research designs. It can be conducted quickly and efficiently, and data can be collected through surveys, questionnaires, or observations.
- Useful for generating hypotheses: Descriptive research design can be used to generate hypotheses or research questions that can be tested in future studies. For example, if a descriptive study finds a correlation between two variables, this could lead to the development of a hypothesis about the causal relationship between the variables.
- Large sample size : Descriptive research design typically involves a large sample size, which helps to ensure that the data is representative of the population of interest. A large sample size also helps to increase the reliability and validity of the data.
- Can be used to monitor changes : Descriptive research design can be used to monitor changes over time in a population or phenomenon. This can be useful for identifying trends and patterns, and for making predictions about future behavior or attitudes.
- Can be used in a variety of fields : Descriptive research design can be used in a variety of fields, including social sciences, healthcare, business, and education.
Limitation of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design also has some limitations that researchers should consider before using this design. Some of the main limitations of descriptive research design are:
- Cannot establish cause and effect: Descriptive research design cannot establish cause and effect relationships between variables. It only provides a description of the characteristics of the population or phenomenon of interest.
- Limited generalizability: The results of a descriptive study may not be generalizable to other populations or situations. This is because descriptive research design often involves a specific sample or situation, which may not be representative of the broader population.
- Potential for bias: Descriptive research design can be subject to bias, particularly if the researcher is not objective in their data collection or interpretation. This can lead to inaccurate or incomplete descriptions of the population or phenomenon of interest.
- Limited depth: Descriptive research design may provide a superficial description of the population or phenomenon of interest. It does not delve into the underlying causes or mechanisms behind the observed behavior or characteristics.
- Limited utility for theory development: Descriptive research design may not be useful for developing theories about the relationship between variables. It only provides a description of the variables themselves.
- Relies on self-report data: Descriptive research design often relies on self-report data, such as surveys or questionnaires. This type of data may be subject to biases, such as social desirability bias or recall bias.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide
- Descriptive Research Designs: Types, Examples & Methods

One of the components of research is getting enough information about the research problem—the what, how, when and where answers, which is why descriptive research is an important type of research. It is very useful when conducting research whose aim is to identify characteristics, frequencies, trends, correlations, and categories.
This research method takes a problem with little to no relevant information and gives it a befitting description using qualitative and quantitative research method s. Descriptive research aims to accurately describe a research problem.
In the subsequent sections, we will be explaining what descriptive research means, its types, examples, and data collection methods.
What is Descriptive Research?
Descriptive research is a type of research that describes a population, situation, or phenomenon that is being studied. It focuses on answering the how, what, when, and where questions If a research problem, rather than the why.
This is mainly because it is important to have a proper understanding of what a research problem is about before investigating why it exists in the first place.
For example, an investor considering an investment in the ever-changing Amsterdam housing market needs to understand what the current state of the market is, how it changes (increasing or decreasing), and when it changes (time of the year) before asking for the why. This is where descriptive research comes in.
What Are The Types of Descriptive Research?
Descriptive research is classified into different types according to the kind of approach that is used in conducting descriptive research. The different types of descriptive research are highlighted below:
- Descriptive-survey
Descriptive survey research uses surveys to gather data about varying subjects. This data aims to know the extent to which different conditions can be obtained among these subjects.
For example, a researcher wants to determine the qualification of employed professionals in Maryland. He uses a survey as his research instrument , and each item on the survey related to qualifications is subjected to a Yes/No answer.
This way, the researcher can describe the qualifications possessed by the employed demographics of this community.
- Descriptive-normative survey
This is an extension of the descriptive survey, with the addition being the normative element. In the descriptive-normative survey, the results of the study should be compared with the norm.
For example, an organization that wishes to test the skills of its employees by a team may have them take a skills test. The skills tests are the evaluation tool in this case, and the result of this test is compared with the norm of each role.
If the score of the team is one standard deviation above the mean, it is very satisfactory, if within the mean, satisfactory, and one standard deviation below the mean is unsatisfactory.
- Descriptive-status
This is a quantitative description technique that seeks to answer questions about real-life situations. For example, a researcher researching the income of the employees in a company, and the relationship with their performance.
A survey will be carried out to gather enough data about the income of the employees, then their performance will be evaluated and compared to their income. This will help determine whether a higher income means better performance and low income means lower performance or vice versa.
- Descriptive-analysis
The descriptive-analysis method of research describes a subject by further analyzing it, which in this case involves dividing it into 2 parts. For example, the HR personnel of a company that wishes to analyze the job role of each employee of the company may divide the employees into the people that work at the Headquarters in the US and those that work from Oslo, Norway office.
A questionnaire is devised to analyze the job role of employees with similar salaries and who work in similar positions.
- Descriptive classification
This method is employed in biological sciences for the classification of plants and animals. A researcher who wishes to classify the sea animals into different species will collect samples from various search stations, then classify them accordingly.
- Descriptive-comparative
In descriptive-comparative research, the researcher considers 2 variables that are not manipulated, and establish a formal procedure to conclude that one is better than the other. For example, an examination body wants to determine the better method of conducting tests between paper-based and computer-based tests.
A random sample of potential participants of the test may be asked to use the 2 different methods, and factors like failure rates, time factors, and others will be evaluated to arrive at the best method.
- Correlative Survey
Correlative surveys are used to determine whether the relationship between 2 variables is positive, negative, or neutral. That is, if 2 variables say X and Y are directly proportional, inversely proportional or are not related to each other.
Examples of Descriptive Research
There are different examples of descriptive research, that may be highlighted from its types, uses, and applications. However, we will be restricting ourselves to only 3 distinct examples in this article.
- Comparing Student Performance:
An academic institution may wish 2 compare the performance of its junior high school students in English language and Mathematics. This may be used to classify students based on 2 major groups, with one group going ahead to study while courses, while the other study courses in the Arts & Humanities field.
Students who are more proficient in mathematics will be encouraged to go into STEM and vice versa. Institutions may also use this data to identify students’ weak points and work on ways to assist them.
- Scientific Classification
During the major scientific classification of plants, animals, and periodic table elements, the characteristics and components of each subject are evaluated and used to determine how they are classified.
For example, living things may be classified into kingdom Plantae or kingdom animal is depending on their nature. Further classification may group animals into mammals, pieces, vertebrae, invertebrae, etc.
All these classifications are made a result of descriptive research which describes what they are.
- Human Behavior
When studying human behaviour based on a factor or event, the researcher observes the characteristics, behaviour, and reaction, then use it to conclude. A company willing to sell to its target market needs to first study the behaviour of the market.
This may be done by observing how its target reacts to a competitor’s product, then use it to determine their behaviour.
What are the Characteristics of Descriptive Research?
The characteristics of descriptive research can be highlighted from its definition, applications, data collection methods, and examples. Some characteristics of descriptive research are:
- Quantitativeness
Descriptive research uses a quantitative research method by collecting quantifiable information to be used for statistical analysis of the population sample. This is very common when dealing with research in the physical sciences.
- Qualitativeness
It can also be carried out using the qualitative research method, to properly describe the research problem. This is because descriptive research is more explanatory than exploratory or experimental.
- Uncontrolled variables
In descriptive research, researchers cannot control the variables like they do in experimental research.
- The basis for further research
The results of descriptive research can be further analyzed and used in other research methods. It can also inform the next line of research, including the research method that should be used.
This is because it provides basic information about the research problem, which may give birth to other questions like why a particular thing is the way it is.
Why Use Descriptive Research Design?
Descriptive research can be used to investigate the background of a research problem and get the required information needed to carry out further research. It is used in multiple ways by different organizations, and especially when getting the required information about their target audience.
- Define subject characteristics :
It is used to determine the characteristics of the subjects, including their traits, behaviour, opinion, etc. This information may be gathered with the use of surveys, which are shared with the respondents who in this case, are the research subjects.
For example, a survey evaluating the number of hours millennials in a community spends on the internet weekly, will help a service provider make informed business decisions regarding the market potential of the community.
- Measure Data Trends
It helps to measure the changes in data over some time through statistical methods. Consider the case of individuals who want to invest in stock markets, so they evaluate the changes in prices of the available stocks to make a decision investment decision.
Brokerage companies are however the ones who carry out the descriptive research process, while individuals can view the data trends and make decisions.
Descriptive research is also used to compare how different demographics respond to certain variables. For example, an organization may study how people with different income levels react to the launch of a new Apple phone.
This kind of research may take a survey that will help determine which group of individuals are purchasing the new Apple phone. Do the low-income earners also purchase the phone, or only the high-income earners do?
Further research using another technique will explain why low-income earners are purchasing the phone even though they can barely afford it. This will help inform strategies that will lure other low-income earners and increase company sales.
- Validate existing conditions
When you are not sure about the validity of an existing condition, you can use descriptive research to ascertain the underlying patterns of the research object. This is because descriptive research methods make an in-depth analysis of each variable before making conclusions.
- Conducted Overtime
Descriptive research is conducted over some time to ascertain the changes observed at each point in time. The higher the number of times it is conducted, the more authentic the conclusion will be.
What are the Disadvantages of Descriptive Research?
- Response and Non-response Bias
Respondents may either decide not to respond to questions or give incorrect responses if they feel the questions are too confidential. When researchers use observational methods, respondents may also decide to behave in a particular manner because they feel they are being watched.
- The researcher may decide to influence the result of the research due to personal opinion or bias towards a particular subject. For example, a stockbroker who also has a business of his own may try to lure investors into investing in his own company by manipulating results.
- A case-study or sample taken from a large population is not representative of the whole population.
- Limited scope:The scope of descriptive research is limited to the what of research, with no information on why thereby limiting the scope of the research.
What are the Data Collection Methods in Descriptive Research?
There are 3 main data collection methods in descriptive research, namely; observational method, case study method, and survey research.
1. Observational Method
The observational method allows researchers to collect data based on their view of the behaviour and characteristics of the respondent, with the respondents themselves not directly having an input. It is often used in market research, psychology, and some other social science research to understand human behaviour.
It is also an important aspect of physical scientific research, with it being one of the most effective methods of conducting descriptive research . This process can be said to be either quantitative or qualitative.
Quantitative observation involved the objective collection of numerical data , whose results can be analyzed using numerical and statistical methods.
Qualitative observation, on the other hand, involves the monitoring of characteristics and not the measurement of numbers. The researcher makes his observation from a distance, records it, and is used to inform conclusions.
2. Case Study Method
A case study is a sample group (an individual, a group of people, organizations, events, etc.) whose characteristics are used to describe the characteristics of a larger group in which the case study is a subgroup. The information gathered from investigating a case study may be generalized to serve the larger group.
This generalization, may, however, be risky because case studies are not sufficient to make accurate predictions about larger groups. Case studies are a poor case of generalization.
3. Survey Research
This is a very popular data collection method in research designs. In survey research, researchers create a survey or questionnaire and distribute it to respondents who give answers.
Generally, it is used to obtain quick information directly from the primary source and also conducting rigorous quantitative and qualitative research. In some cases, survey research uses a blend of both qualitative and quantitative strategies.
Survey research can be carried out both online and offline using the following methods
- Online Surveys: This is a cheap method of carrying out surveys and getting enough responses. It can be carried out using Formplus, an online survey builder. Formplus has amazing tools and features that will help increase response rates.
- Offline Surveys: This includes paper forms, mobile offline forms , and SMS-based forms.
What Are The Differences Between Descriptive and Correlational Research?
Before going into the differences between descriptive and correlation research, we need to have a proper understanding of what correlation research is about. Therefore, we will be giving a summary of the correlation research below.
Correlational research is a type of descriptive research, which is used to measure the relationship between 2 variables, with the researcher having no control over them. It aims to find whether there is; positive correlation (both variables change in the same direction), negative correlation (the variables change in the opposite direction), or zero correlation (there is no relationship between the variables).
Correlational research may be used in 2 situations;
(i) when trying to find out if there is a relationship between two variables, and
(ii) when a causal relationship is suspected between two variables, but it is impractical or unethical to conduct experimental research that manipulates one of the variables.
Below are some of the differences between correlational and descriptive research:
- Definitions :
Descriptive research aims is a type of research that provides an in-depth understanding of the study population, while correlational research is the type of research that measures the relationship between 2 variables.
- Characteristics :
Descriptive research provides descriptive data explaining what the research subject is about, while correlation research explores the relationship between data and not their description.
- Predictions :
Predictions cannot be made in descriptive research while correlation research accommodates the possibility of making predictions.
Descriptive Research vs. Causal Research
Descriptive research and causal research are both research methodologies, however, one focuses on a subject’s behaviors while the latter focuses on a relationship’s cause-and-effect. To buttress the above point, descriptive research aims to describe and document the characteristics, behaviors, or phenomena of a particular or specific population or situation.
It focuses on providing an accurate and detailed account of an already existing state of affairs between variables. Descriptive research answers the questions of “what,” “where,” “when,” and “how” without attempting to establish any causal relationships or explain any underlying factors that might have caused the behavior.
Causal research, on the other hand, seeks to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. It aims to point out the factors that influence or cause a particular result or behavior. Causal research involves manipulating variables, controlling conditions or a subgroup, and observing the resulting effects. The primary objective of causal research is to establish a cause-effect relationship and provide insights into why certain phenomena happen the way they do.
Descriptive Research vs. Analytical Research
Descriptive research provides a detailed and comprehensive account of a specific situation or phenomenon. It focuses on describing and summarizing data without making inferences or attempting to explain underlying factors or the cause of the factor.
It is primarily concerned with providing an accurate and objective representation of the subject of research. While analytical research goes beyond the description of the phenomena and seeks to analyze and interpret data to discover if there are patterns, relationships, or any underlying factors.
It examines the data critically, applies statistical techniques or other analytical methods, and draws conclusions based on the discovery. Analytical research also aims to explore the relationships between variables and understand the underlying mechanisms or processes involved.
Descriptive Research vs. Exploratory Research
Descriptive research is a research method that focuses on providing a detailed and accurate account of a specific situation, group, or phenomenon. This type of research describes the characteristics, behaviors, or relationships within the given context without looking for an underlying cause.
Descriptive research typically involves collecting and analyzing quantitative or qualitative data to generate descriptive statistics or narratives. Exploratory research differs from descriptive research because it aims to explore and gain firsthand insights or knowledge into a relatively unexplored or poorly understood topic.
It focuses on generating ideas, hypotheses, or theories rather than providing definitive answers. Exploratory research is often conducted at the early stages of a research project to gather preliminary information and identify key variables or factors for further investigation. It involves open-ended interviews, observations, or small-scale surveys to gather qualitative data.
Read More – Exploratory Research: What are its Method & Examples?

Descriptive Research vs. Experimental Research
Descriptive research aims to describe and document the characteristics, behaviors, or phenomena of a particular population or situation. It focuses on providing an accurate and detailed account of the existing state of affairs.
Descriptive research typically involves collecting data through surveys, observations, or existing records and analyzing the data to generate descriptive statistics or narratives. It does not involve manipulating variables or establishing cause-and-effect relationships.
Experimental research, on the other hand, involves manipulating variables and controlling conditions to investigate cause-and-effect relationships. It aims to establish causal relationships by introducing an intervention or treatment and observing the resulting effects.
Experimental research typically involves randomly assigning participants to different groups, such as control and experimental groups, and measuring the outcomes. It allows researchers to control for confounding variables and draw causal conclusions.
Related – Experimental vs Non-Experimental Research: 15 Key Differences
Descriptive Research vs. Explanatory Research
Descriptive research focuses on providing a detailed and accurate account of a specific situation, group, or phenomenon. It aims to describe the characteristics, behaviors, or relationships within the given context.
Descriptive research is primarily concerned with providing an objective representation of the subject of study without explaining underlying causes or mechanisms. Explanatory research seeks to explain the relationships between variables and uncover the underlying causes or mechanisms.
It goes beyond description and aims to understand the reasons or factors that influence a particular outcome or behavior. Explanatory research involves analyzing data, conducting statistical analyses, and developing theories or models to explain the observed relationships.
Descriptive Research vs. Inferential Research
Descriptive research focuses on describing and summarizing data without making inferences or generalizations beyond the specific sample or population being studied. It aims to provide an accurate and objective representation of the subject of study.
Descriptive research typically involves analyzing data to generate descriptive statistics, such as means, frequencies, or percentages, to describe the characteristics or behaviors observed.
Inferential research, however, involves making inferences or generalizations about a larger population based on a smaller sample.
It aims to draw conclusions about the population characteristics or relationships by analyzing the sample data. Inferential research uses statistical techniques to estimate population parameters, test hypotheses, and determine the level of confidence or significance in the findings.
Related – Inferential Statistics: Definition, Types + Examples
Conclusion
The uniqueness of descriptive research partly lies in its ability to explore both quantitative and qualitative research methods. Therefore, when conducting descriptive research, researchers have the opportunity to use a wide variety of techniques that aids the research process.
Descriptive research explores research problems in-depth, beyond the surface level thereby giving a detailed description of the research subject. That way, it can aid further research in the field, including other research methods .
It is also very useful in solving real-life problems in various fields of social science, physical science, and education.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- descriptive research
- descriptive research method
- example of descriptive research
- types of descriptive research
- busayo.longe

You may also like:
Type I vs Type II Errors: Causes, Examples & Prevention
This article will discuss the two different types of errors in hypothesis testing and how you can prevent them from occurring in your research

Acceptance Sampling: Meaning, Examples, When to Use
In this post, we will discuss extensively what acceptance sampling is and when it is applied.
Extrapolation in Statistical Research: Definition, Examples, Types, Applications
In this article we’ll look at the different types and characteristics of extrapolation, plus how it contrasts to interpolation.
Cross-Sectional Studies: Types, Pros, Cons & Uses
In this article, we’ll look at what cross-sectional studies are, how it applies to your research and how to use Formplus to collect...
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.

Descriptive Research

The evolution of the periodic system started over 200 years ago. Chemists contributed to its development by continuously altering, disputing, and revising this promising project, which made it a great chart that we use today in scientific studies and educational purposes. However, did you know that these people used descriptive research to create this table? Scientists were able to categorize the elements in the periodic table by describing the characteristics of each element. And with the help of their knowledge in electrons, protons, and neutrons, they were able to arrange the fundamental elements according to what it is today.
What is Descriptive Research?
Descriptive research is a research methodology you can use to describe the characteristics of the variables that you are studying, such as events, organizations, individuals, etc. This type of research answers explicitly the “what” question instead of the “how,” “why,” and “when” questions. Through this type of research, you can obtain information about the current situation of a phenomenon but not the reason for its state.
Descriptive vs Analytical Research
While descriptive research aims to describe a phenomenon, analytical research intends to understand it deeply. Since the descriptive essay study only aims to describe its characteristics, it has no control over the affecting determinants of the variables, unlike analytical research, which can work on the factors that surround the variables.
11+ Descriptive Research Examples
To know more about how descriptive research works in the real world, refer to the following downloadable examples.
1. Descriptive Research Design Example

Size: 36 KB
2. Qualitative and Descriptive Research Example

Size: 52 KB
3. Descriptive Education Research Example

4. Basic Descriptive Research Example

Size: 299 KB
5. Praise of Descriptive Research Example

Size: 275 KB
6. Discriptive Survey Reerach Example

Size: 643 KB
7. Standard Discriptive Research Example

Size: 18 KB
8. Descriptive and Interpretive Approaches Research Example

Size: 92 KB
9. Comany Discriptive Research Example

Size: 489 KB
10. Printable Descriptive Research Example

11. Discriptive Research Question and Design Example]

12. Discriptive Research in DOC

How to Conduct Descriptive Research?
We understand that carrying out descriptive research for the first time can be difficult. That is why we included the following instructions. Whether you are conducting research for a psychology-related topic or exploring a certain event for your marketing strategy , this section will help you accomplish your project correctly.
1. State the Problem
When looking for a descriptive research problem, make sure that it answers the “what.” To make your research beneficial to society, choose a subject that will reveal hidden issues or provide solutions to specific problems. And if it sounds difficult, worry not! That should be the fun part of carrying out a research project.
2. Identify the Information
Gather more information about the research problem you have chosen by conducting preliminary research or reviewing the literature relating to it. In this process, check for the existing studies about your research and determine the information gap between your study and the existing ones. Use this information to strengthen the reason why you have to conduct the investigation. You can also modify your research problem based on this information difference.
3. Select Appropriate Data Gathering Tools
Data gathering tools such as questionnaires and interviews are the tools that you will use to gather the necessary information to come up with the research conclusion. Primary data collection is the most common tool that descriptive researchers use. This type of research may involve using qualitative research or quantitative research methods or both. Remember that there is no such thing as a perfect technique in data gathering. It is a skill that you have to master by experience.
4. Determine the Target Population or Samples
Target population and samples are a group, an individual, or an event you will analyze. Before you start collecting the needed information, you have to determine its sources.
5. Describe the Data Collection Procedures
Since you already reached this step, it is safe to assume that you have identified the appropriate tools to utilize in collecting the data from your target population. In this step, you need to create a detailed step-by-step instruction on how you will gather and analyze the information to reach a particular conclusion.
6. Collect, Analyze, and Evaluate the Information
In this stage, you will materialize the plan you came up with during the previous steps. Once you complete the data collection process, you have to analyze it. However, data analysis can be messy if you don’t know what you are doing. Thus, it would help if you will use graphical representation tools such as diagrams and graphs to simplify this process. These data visualization tools enable you to effectively communicate the results to those who will read your research paper.
8. State Your Conclusion
After the proper interpretation of the data you have collected, it will be easier for you to come up with a conclusion for your research. State your conclusion and share the data with your audience.
Descriptive research, despite its limitations, has its unique purposes. You should realize that these limitations ensure that your project focuses on its scope. As a result, your research project will arrive at the correct conclusion on time.
AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- Sample Research
FREE 10+ Descriptive Research Samples & Templates in PDF
One of the main characteristics of descriptive research is its focus on describing the “what”, “where”, “when”, “who”, and “how” of a particular phenomenon or situation. It aims to provide a detailed and accurate portrayal of a specific group, population, or event agenda, and it is often used as a preliminary step before more in-depth documentary research is conducted. Descriptive research is usually conducted when there is limited knowledge or information about a particular topic, and researchers seek to develop a general understanding of it.
Descriptive Research
Free 10+ research analysis samples in ms word pdf | google ..., free how to develop a research proposal [ steps, how to ..., free 13+ abstract writing samples and templates in pdf, free 10+ descriptive research samples & templates in pdf, 1. qualitative & descriptive research template.

Size: 52 KB
2. Partnership Description Research Template
3. Descriptive Research Template

4. Quantitative Descriptive Design Research

5. Descriptive Statistics Research Template
Size: 658 KB
6. Qualitative Descriptive Research Template

Size: 205 KB
7. Quantitative Descriptive Analysis Research
8. Descriptive Study Research Template
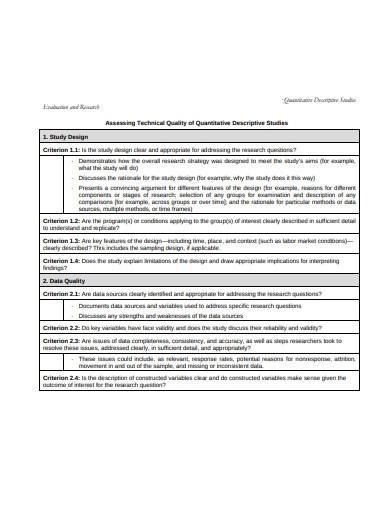
Size: 88 KB
9. Approaching Descriptive Analysis Research

10. Descriptive Research Statistics Template

Size: 364 KB
11. Descriptive Research Design Sample

Size: 36 KB
What is Descriptive Research?
Descriptive research is a fundamental type of research that seeks to describe and present a comprehensive picture of a phenomenon or situation. This type of research is often used to gain insights into the current state of a particular topic or issue, and it is a crucial tool for researchers in various fields. In this essay, we will explore the key characteristics and steps of descriptive research, as well as their significance in the research process.
How To Make Descriptive Research?
Descriptive research can be conducted using various methods such as event surveys , observation schedule , case study sample, and content analysis. The data collected through these methods are analyzed using statistical analysis , such as mean, median, mode, and frequency distributions, to provide a summary of the findings. If you are interested in conducting a descriptive research study plan , here are some steps that can guide you through the process:
Step 1- Identify Research Question
Start by identifying the specific phenomenon or situation you want to describe. Define the key variables and formulate a research question that you want to answer. Choose a research design that is suitable for your research question and the nature of the phenomenon or situation you want to describe. The most common research designs for descriptive research include surveys, observations, case studies, and content analysis.
Step 2- Develop Sampling Strategy
Determine the population you want to describe and select a sample from that population. The sampling strategy you choose will depend on the research question, the research design, and the available resources. Collect data using the research design you have chosen. For survey questionnaires , you can use online questionnaires, narrative interview report , or paper-based questionnaires. For observations, you can observe and record behaviors in natural settings. For case studies, you can collect data through interviews, observations, and document analysis. For content analysis, you can analyze documents, media, and other sources of information.
Step 3- Analyze Data
Use statistical methods such as mean, median, mode, and frequency distributions to analyze the data you have collected. You can use software such as SPSS, Excel, or R to help you analyze the data.
Step 4- Report Findings
Report your findings using tables, charts, and graphs to help visualize the data and provide a clear understanding of the phenomenon you have described. Provide a summary of your findings and discuss their implications for future research.
What are the methods of descriptive research?
Descriptive research can be conducted using various methods such as surveys, observations, case studies, and content analysis. The choice of method depends on the research question and the nature of the phenomenon being studied.
How is data analyzed in descriptive research?
Data collected through descriptive research is analyzed using statistical methods such as mean, median, mode, and frequency distributions, to provide a summary of the findings. The results of descriptive research are usually presented using tables, charts, and graphs to help visualize the data and provide a clear understanding of the phenomenon being studied.
What are the limitations of descriptive research?
One limitation of descriptive research is that it cannot establish cause and effect relationships. Descriptive research is also limited in its ability to generalize findings to other populations or situations, as it usually involves a specific sample or population. Additionally, descriptive research may be subject to bias or error if the research data collection form methods are not valid or reliable.
Overall, descriptive research is useful for providing a general understanding of a topic or issue and for identifying areas that require further investigation.
Related Posts
Free 10+ biography research report samples and templates in pdf, free 10+ system documentation samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ process document samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ action research samples & templates in pdf, free 10+ longitudinal research samples & templates in pdf | ms word, free 10+ causal research samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ client discovery samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ null hypothesis samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 9+ product knowledge samples & templates in pdf, free 10+ software documentation samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ exploratory research samples & templates in pdf | ms word, free 10+ experimental research samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ knowledge management samples & templates in pdf, free 10+ educational research ethics samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 11+ business research report samples & templates in ms word | ms excel | pdf, free 9+ research log samples & templates in pdf ms word, free 32+ research paper examples in pdf ms word, free 7+ expository writing samples and templates in pdf, free 10+ sample research proposal templates in ms word pages.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A descriptive research design is a type of research design that aims to obtain information to systematically describe a phenomenon, situation, or population. More specifically, it helps answer the ...
Box 1. Descriptive Analysis Is a Critical Component of Research Box 2. Examples of Using Descriptive Analyses to Diagnose Need and Target Intervention on the Topic of "Summer Melt" Box 3. An Example of Using Descriptive Analysis to Evaluate Plausible Causes and Generate Hypotheses Box 4.
Benefits of Descriptive Research: Limitations of Descriptive Research: Rich Data: Provides a comprehensive and detailed profile of the subject or issue through rich data, offering a thorough understanding (Gresham, 2016). Lack of Control: Cannot control variables or external factors, potentially influencing the accuracy and reliability of the data. Basis for Further Research: Helps to identify ...
Descriptive research aims to accurately and systematically describe a population, situation or phenomenon. It can answer what, where, when and how questions, but not why questions. A descriptive research design can use a wide variety of research methods to investigate one or more variables. Unlike in experimental research, the researcher does ...
Therefore, we talk about "generic" or "descriptive-interpretive" approaches to qualitative research that share in common an effort to describe, summarize, and classify what is present in the data, which always, as we explain in Chapter 4, involves a degree of interpretation. 3.
INTRODUCTION. In our previous article in this series, [ 1] we introduced the concept of "study designs"- as "the set of methods and procedures used to collect and analyze data on variables specified in a particular research question.". Study designs are primarily of two types - observational and interventional, with the former being ...
This research type is descriptive. As much as 77% of the average students in this study with a good enough category indicates that green chemistry has an important role in building chemistry ethics.
Descriptive research is often used in the Faculty of Architecture as well as outside it. It partly. concerns study linked to individual projects and direct application, with the aim of being able ...
rst step to explain the reasons for realized purchases. Descriptive research should be thought of as a means to an end rather than an end itself, as Yin (1994) suggests. As the term descriptive says, this research type aims to provide an accurate description of observations of real-world phenomena. For example, the goal of the collection of cen-
Descriptive research aims to accurately and systematically describe a population, situation or phenomenon. It can answer what, where, when, and how questions, but not why questions. A descriptive research design can use a wide variety of research methods to investigate one or more variables. Unlike in experimental research, the researcher does ...
An Introduction to Nursing Research: Research, Measurement and Computers in Nursing. Philadelphia: Lippincott Co., 1981. 486 pp. $15.75 Show details Hide details
As discussed earlier, common research methods for descriptive research include surveys, case studies, observational studies, cross-sectional studies, and longitudinal studies. Design your study: Plan the details of your study, including the sampling strategy, data collection methods, and data analysis plan.
Descriptive studies have several important roles in medical research.They are often the first foray into a new disease or area of inquiry—the first scientific "toe in the water".1 They document the health of populations and often prompt more rigorous studies. Since descriptive studies are often reported,2 clinicians need to know their
Descriptive research is about describing how reality is. In this regard descriptive research differs from prescriptive research that is primarily concerned with the question how the reality should be. Descriptive research is making inventories; prescriptive research is normative. With descriptive research in its purest form explaining and ...
Some characteristics of descriptive research are: Quantitativeness. Descriptive research uses a quantitative research method by collecting quantifiable information to be used for statistical analysis of the population sample. This is very common when dealing with research in the physical sciences. Qualitativeness.
Examples of Descriptive Research Some examples of descriptive research are: 1. A speciality food group launching a new range of barbecue rubs would like to understand what flavors of rubs are favored by different sets of people. To understand the preferred flavor palette, they conduct a descriptive research study using different methods like ...
A DESCRIPTIVE, SURVEY RESEARCH STUDY OF THE STUDENT CHARACTERISTICS INFLUENCING THE FOUR THEORETICAL SOURCES OF MATHEMATICAL SELF-EFFICACY OF COLLEGE FRESHMEN Tonja Motley Locklear University of Kentucky, [email protected] Right click to open a feedback form in a new tab to let us know how this document benefits you. Recommended Citation
These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design.1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured (descriptive research questions).1,5,14 These ...
This chapter assesses descriptive, explanatory, and interpretive approaches. 'Description', 'explanation', and 'interpretation' are distinct stages of the research process. Description ...
11+ Descriptive Research Examples. To know more about how descriptive research works in the real world, refer to the following downloadable examples. 1. Descriptive Research Design Example. pdfs.semanticscholar.org. Details. File Format. PDF. Size: 36 KB.
Descriptive research can be conducted using various methods such as event surveys, observation schedule, case study sample, and content analysis. The data collected through these methods are analyzed using statistical analysis , such as mean, median, mode, and frequency distributions, to provide a summary of the findings.
Authors abstract various longer works, including book proposals, dissertations, and online journal articles. There are two main types of abstracts: descriptive and informative. A descriptive abstract briefly describes the longer work, while an informative abstract presents all the main arguments and important results.
The purpose of the study was to describe the degree to which the involved agricultural education programs prepared their students to work with diverse populations. The study also examined attitudes and beliefs of the student teachers regarding diversity. The results of the study suggest that this group of student teachers was not adequately ...