

Psychological Science
Prospective submitters of manuscripts are encouraged to read Editor-in-Chief Simine Vazire’s editorial , as well as the editorial by Tom Hardwicke, Senior Editor for Statistics, Transparency, & Rigor, and Simine Vazire.
Psychological Science , the flagship journal of the Association for Psychological Science, is the leading peer-reviewed journal publishing empirical research spanning the entire spectrum of the science of psychology. The journal publishes high quality research articles of general interest and on important topics spanning the entire spectrum of the science of psychology. Replication studies are welcome and evaluated on the same criteria as novel studies. Articles are published in OnlineFirst before they are assigned to an issue. This journal is a member of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) .
Quick Facts
Read the February 2022 editorial by former Editor-in-Chief Patricia Bauer, “Psychological Science Stepping Up a Level.”
Read the January 2020 editorial by former Editor Patricia Bauer on her vision for the future of Psychological Science .
Read the December 2015 editorial on replication by former Editor Steve Lindsay, as well as his April 2017 editorial on sharing data and materials during the review process.
Watch Geoff Cumming’s video workshop on the new statistics.

Current Issue

Online First Articles

List of Issues

Editorial Board

Submission Guidelines

Editorial Policies
Featured research from psychological science, teens who view their homes as more chaotic than their siblings have poorer mental health in adulthood.
Many parents ponder why one of their children seems more emotionally troubled than the others. A new study in the United Kingdom reveals a possible basis for those differences.
Rewatching Videos of People Shifts How We Judge Them, Study Indicates
Rewatching recorded behavior, whether on a Tik-Tok video or police body-camera footage, makes even the most spontaneous actions seem more rehearsed or deliberate, new research shows.
Loneliness Bookends Adulthood, Study Shows
Loneliness in adulthood follows a U-shaped pattern: It’s higher in younger and older adulthood, and lowest during middle adulthood, according to new research that examined nine longitudinal studies from around the world.
Privacy Overview
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Psychology Research Paper
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
James Lacy, MLS, is a fact-checker and researcher.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/James-Lacy-1000-73de2239670146618c03f8b77f02f84e.jpg)
Are you working on a psychology research paper this semester? Whether or not this is your first research paper, the entire process can seem a bit overwhelming at first. But, knowing where to start the research process can make things easier and less stressful.
While it can feel very intimidating, a research paper can initially be very intimidating, but it is not quite as scary if you break it down into more manageable steps. The following tips will help you break down the process into steps so it is easier to research and write your paper.
Decide What Kind of Paper You Are Going to Write
Before you begin, you should find out the type of paper your instructor expects you to write. There are a few common types of psychology papers that you might encounter.
Original Research or Lab Report
A report or empirical paper details research you conducted on your own. This is the type of paper you would write if your instructor had you perform your own psychology experiment. This type of paper follows a format similar to an APA format lab report. It includes a title page, abstract , introduction, method section, results section, discussion section, and references.
Literature Review
The second type of paper is a literature review that summarizes research conducted by other people on a particular topic. If you are writing a psychology research paper in this form, your instructor might specify the length it needs to be or the number of studies you need to cite. Student are often required to cite between 5 and 20 studies in their literature reviews and they are usually between 8 and 20 pages in length.
The format and sections of a literature review usually include an introduction, body, and discussion/implications/conclusions.
Literature reviews often begin by introducing the research question before narrowing the focus to the specific studies cited in the paper. Each cited study should be described in considerable detail. You should evaluate and compare the studies you cite and then offer your discussion of the implications of the findings.
Select an Idea for Your Research Paper
Hero Images / Getty Images
Once you have figured out the type of research paper you are going to write, it is time to choose a good topic . In many cases, your instructor may assign you a subject, or at least specify an overall theme on which to focus.
As you are selecting your topic, try to avoid general or overly broad subjects. For example, instead of writing a research paper on the general subject of attachment , you might instead focus your research on how insecure attachment styles in early childhood impact romantic attachments later in life.
Narrowing your topic will make writing your paper easier because it allows you to focus your research, develop your thesis, and fully explore pertinent findings.
Develop an Effective Research Strategy
As you find references for your psychology paper, take careful notes on the information you use and start developing a bibliography. If you stay organized and cite your sources throughout the writing process, you will not be left searching for an important bit of information you cannot seem to track back to the source.
So, as you do your research, make careful notes about each reference including the article title, authors, journal source, and what the article was about.
Write an Outline
You might be tempted to immediately dive into writing, but developing a strong framework can save a lot of time, hassle, and frustration. It can also help you spot potential problems with flow and structure.
If you outline the paper right off the bat, you will have a better idea of how one idea flows into the next and how your research supports your overall hypothesis .
You should start the outline with the three most fundamental sections: the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. Then, start creating subsections based on your literature review. The more detailed your outline, the easier it will be to write your paper.
Draft, Revise, and Edit
Once you are confident in your outline, it is time to begin writing. Remember to follow APA format as you write your paper and include in-text citations for any materials you reference. Make sure to cite any information in the body of your paper in your reference section at the end of your document.
Writing a psychology research paper can be intimidating at first, but breaking the process into a series of smaller steps makes it more manageable. Be sure to start early by deciding on a substantial topic, doing your research, and creating a good outline . Doing these supporting steps ahead of time make it much easier to actually write the paper when the time comes.
- Beins, BC & Beins, A. Effective Writing in Psychology: Papers, Posters, and Presentation. New York: Blackwell Publishing; 2011.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Search This Site All UCSD Sites Faculty/Staff Search Term
- Contact & Directions
- Climate Statement
- Cognitive Behavioral Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Adjunct Faculty
- Non-Senate Instructors
- Researchers
- Psychology Grads
- Affiliated Grads
- New and Prospective Students
- Honors Program
- Experiential Learning
- Programs & Events
- Psi Chi / Psychology Club
- Prospective PhD Students
- Current PhD Students
- Area Brown Bags
- Colloquium Series
- Anderson Distinguished Lecture Series
- Speaker Videos
- Undergraduate Program
- Academic and Writing Resources
Writing Research Papers
- Research Paper Structure
Whether you are writing a B.S. Degree Research Paper or completing a research report for a Psychology course, it is highly likely that you will need to organize your research paper in accordance with American Psychological Association (APA) guidelines. Here we discuss the structure of research papers according to APA style.
Major Sections of a Research Paper in APA Style
A complete research paper in APA style that is reporting on experimental research will typically contain a Title page, Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, and References sections. 1 Many will also contain Figures and Tables and some will have an Appendix or Appendices. These sections are detailed as follows (for a more in-depth guide, please refer to " How to Write a Research Paper in APA Style ”, a comprehensive guide developed by Prof. Emma Geller). 2
What is this paper called and who wrote it? – the first page of the paper; this includes the name of the paper, a “running head”, authors, and institutional affiliation of the authors. The institutional affiliation is usually listed in an Author Note that is placed towards the bottom of the title page. In some cases, the Author Note also contains an acknowledgment of any funding support and of any individuals that assisted with the research project.
One-paragraph summary of the entire study – typically no more than 250 words in length (and in many cases it is well shorter than that), the Abstract provides an overview of the study.
Introduction
What is the topic and why is it worth studying? – the first major section of text in the paper, the Introduction commonly describes the topic under investigation, summarizes or discusses relevant prior research (for related details, please see the Writing Literature Reviews section of this website), identifies unresolved issues that the current research will address, and provides an overview of the research that is to be described in greater detail in the sections to follow.
What did you do? – a section which details how the research was performed. It typically features a description of the participants/subjects that were involved, the study design, the materials that were used, and the study procedure. If there were multiple experiments, then each experiment may require a separate Methods section. A rule of thumb is that the Methods section should be sufficiently detailed for another researcher to duplicate your research.
What did you find? – a section which describes the data that was collected and the results of any statistical tests that were performed. It may also be prefaced by a description of the analysis procedure that was used. If there were multiple experiments, then each experiment may require a separate Results section.
What is the significance of your results? – the final major section of text in the paper. The Discussion commonly features a summary of the results that were obtained in the study, describes how those results address the topic under investigation and/or the issues that the research was designed to address, and may expand upon the implications of those findings. Limitations and directions for future research are also commonly addressed.
List of articles and any books cited – an alphabetized list of the sources that are cited in the paper (by last name of the first author of each source). Each reference should follow specific APA guidelines regarding author names, dates, article titles, journal titles, journal volume numbers, page numbers, book publishers, publisher locations, websites, and so on (for more information, please see the Citing References in APA Style page of this website).
Tables and Figures
Graphs and data (optional in some cases) – depending on the type of research being performed, there may be Tables and/or Figures (however, in some cases, there may be neither). In APA style, each Table and each Figure is placed on a separate page and all Tables and Figures are included after the References. Tables are included first, followed by Figures. However, for some journals and undergraduate research papers (such as the B.S. Research Paper or Honors Thesis), Tables and Figures may be embedded in the text (depending on the instructor’s or editor’s policies; for more details, see "Deviations from APA Style" below).
Supplementary information (optional) – in some cases, additional information that is not critical to understanding the research paper, such as a list of experiment stimuli, details of a secondary analysis, or programming code, is provided. This is often placed in an Appendix.
Variations of Research Papers in APA Style
Although the major sections described above are common to most research papers written in APA style, there are variations on that pattern. These variations include:
- Literature reviews – when a paper is reviewing prior published research and not presenting new empirical research itself (such as in a review article, and particularly a qualitative review), then the authors may forgo any Methods and Results sections. Instead, there is a different structure such as an Introduction section followed by sections for each of the different aspects of the body of research being reviewed, and then perhaps a Discussion section.
- Multi-experiment papers – when there are multiple experiments, it is common to follow the Introduction with an Experiment 1 section, itself containing Methods, Results, and Discussion subsections. Then there is an Experiment 2 section with a similar structure, an Experiment 3 section with a similar structure, and so on until all experiments are covered. Towards the end of the paper there is a General Discussion section followed by References. Additionally, in multi-experiment papers, it is common for the Results and Discussion subsections for individual experiments to be combined into single “Results and Discussion” sections.
Departures from APA Style
In some cases, official APA style might not be followed (however, be sure to check with your editor, instructor, or other sources before deviating from standards of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association). Such deviations may include:
- Placement of Tables and Figures – in some cases, to make reading through the paper easier, Tables and/or Figures are embedded in the text (for example, having a bar graph placed in the relevant Results section). The embedding of Tables and/or Figures in the text is one of the most common deviations from APA style (and is commonly allowed in B.S. Degree Research Papers and Honors Theses; however you should check with your instructor, supervisor, or editor first).
- Incomplete research – sometimes a B.S. Degree Research Paper in this department is written about research that is currently being planned or is in progress. In those circumstances, sometimes only an Introduction and Methods section, followed by References, is included (that is, in cases where the research itself has not formally begun). In other cases, preliminary results are presented and noted as such in the Results section (such as in cases where the study is underway but not complete), and the Discussion section includes caveats about the in-progress nature of the research. Again, you should check with your instructor, supervisor, or editor first.
- Class assignments – in some classes in this department, an assignment must be written in APA style but is not exactly a traditional research paper (for instance, a student asked to write about an article that they read, and to write that report in APA style). In that case, the structure of the paper might approximate the typical sections of a research paper in APA style, but not entirely. You should check with your instructor for further guidelines.
Workshops and Downloadable Resources
- For in-person discussion of the process of writing research papers, please consider attending this department’s “Writing Research Papers” workshop (for dates and times, please check the undergraduate workshops calendar).
Downloadable Resources
- How to Write APA Style Research Papers (a comprehensive guide) [ PDF ]
- Tips for Writing APA Style Research Papers (a brief summary) [ PDF ]
- Example APA Style Research Paper (for B.S. Degree – empirical research) [ PDF ]
- Example APA Style Research Paper (for B.S. Degree – literature review) [ PDF ]
Further Resources
How-To Videos
- Writing Research Paper Videos
APA Journal Article Reporting Guidelines
- Appelbaum, M., Cooper, H., Kline, R. B., Mayo-Wilson, E., Nezu, A. M., & Rao, S. M. (2018). Journal article reporting standards for quantitative research in psychology: The APA Publications and Communications Board task force report . American Psychologist , 73 (1), 3.
- Levitt, H. M., Bamberg, M., Creswell, J. W., Frost, D. M., Josselson, R., & Suárez-Orozco, C. (2018). Journal article reporting standards for qualitative primary, qualitative meta-analytic, and mixed methods research in psychology: The APA Publications and Communications Board task force report . American Psychologist , 73 (1), 26.
External Resources
- Formatting APA Style Papers in Microsoft Word
- How to Write an APA Style Research Paper from Hamilton University
- WikiHow Guide to Writing APA Research Papers
- Sample APA Formatted Paper with Comments
- Sample APA Formatted Paper
- Tips for Writing a Paper in APA Style
1 VandenBos, G. R. (Ed). (2010). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (6th ed.) (pp. 41-60). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
2 geller, e. (2018). how to write an apa-style research report . [instructional materials]. , prepared by s. c. pan for ucsd psychology.
Back to top
- Formatting Research Papers
- Using Databases and Finding References
- What Types of References Are Appropriate?
- Evaluating References and Taking Notes
- Citing References
- Writing a Literature Review
- Writing Process and Revising
- Improving Scientific Writing
- Academic Integrity and Avoiding Plagiarism
- Writing Research Papers Videos
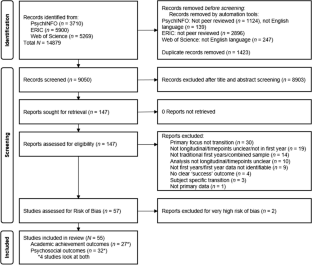
Investigating Success in the Transition to University: A Systematic Review of Personal Risk and Protective Factors Influencing Academic Achievement
- Review Article
- Published: 18 May 2024
- Volume 36 , article number 52 , ( 2024 )

Cite this article

- Isabelle Ball ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0000-6025-2021 1 ,
- Moitree Banerjee ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7031-8909 1 ,
- Andrew Holliman ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3132-6666 2 &
- Ian Tyndall ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2108-9203 1
1 Altmetric
The transition to university is a time of great change and adjustment. The challenges of university life can lead to numerous negative consequences for the students. Despite the importance of successful transition for both the student and the university, the current body of literature comprises methodological inconsistencies and disparate analytical goals that make it difficult to identify the most salient and effective factors that help predict transition success. This paper presents a systematic review of research linking personal level risk and protective factors to the outcome of academic achievement among students making the transition to university. This is part of a larger review, following Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) and Synthesis Without Meta-analysis (SWiM) guidelines, preregistered on the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO, CRD42022330515), searching PsychInfo, Web of Science, and ERIC databases. Records were included if they studied ‘traditional’ first year students transitioning to university and were longitudinal in design and excluded if they looked at specific subgroups of students (e.g. international students). The search yielded 27 articles that were eligible, highlighting a broad range of salient factors ranging from personality traits to procrastination and perfectionism. The findings are discussed in relation to moving the research forward towards an intervention to enhance the probability of successful student transition to university.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price excludes VAT (USA) Tax calculation will be finalised during checkout.
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Data Availability
Full details of data extraction can be found in the Supplementary Materials.
Studies included in the review are marked with an Asterix.
Baker, R. W., & Siryk, B. (1984). Measuring adjustment to college. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 31 (2), 179–189. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0167.31.2.179
Article Google Scholar
Ball, I., Banerjee, M., Holliman, A., & Tyndall, I. (2024a). Investigating success in the transition to university: A systematic review of operationalisations of ‘success’. Manuscript in preparation.
Ball, I., Banerjee, M., Holliman, A., & Tyndall, I. (2024b). Investigating success in the transition to university: A systematic review of personal risk and protective factors influencing psychosocial success. Manuscript in preparation.
Bero, L., Chartres, N., Diong, J., Fabbri, A., Ghersi, D., Ghersi, D., Lam, J., Lau, A., McDonald, S., Mintzes, B., Sutton, P., Turton, J. L., & Woodruff, T. J. (2018). The risk of bias in observational studies of exposures (ROBINS-E) tool: Concerns arising from application to observational studies of exposures. Systematic Reviews, 7 (1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-018-0915-2
*Berzonsky, M. D., & Kuk, L. S. (2005). Identity style, psychosocial maturity, and academic performance. Personality and Individual Differences , 39 (1), 235–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PAID.2005.01.010
Bewick, B., Koutsopoulou, G., Miles, J., Slaa, E., & Barkham, M. (2010). Changes in undergraduate students’ psychological well-being as they progress through university. Studies in Higher Education, 35 (6), 633–645. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075070903216643
Block, J. (2000). Three tasks for personality psychology. In L. R. Bergman, R. B. Cairns, L. G. Nilsson, & L. Nystedt (Eds.), Developmental science and the holistic approach (pp. 155–164). Lawrence Erlbaum.
Google Scholar
*Busseri, M. A., Rose-Krasnor, L., Mark Pancer, S., Pratt, M. W., Adams, G. R., Birnie-Lefcovitch, S., Polivy, J., & Gallander Wintre, M. (2011). A Longitudinal Study of Breadth and Intensity of Activity Involvement and theTransition to University. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 21 (2), 512–518. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1532-7795.2010.00691.X
Campbell, M., McKenzie, J. E., Sowden, A., Katikireddi, S. V., Brennan, S. E., Ellis, S., Hartmann-Boyce, J., Ryan, R., Shepperd, S., Thomas, J., Welch, V., & Thomson, H. (2020). Synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) in systematic reviews: Reporting guideline. BMJ, 368 . https://doi.org/10.1136/BMJ.L6890
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical Power for the Behavioral Sciences (2nd ed.). Erlbaum.
*Collie, R. J., Holliman, A. J., & Martin, A. J. (2016). Adaptability, engagement and academic achievement at university. Educational Psychology , 37 (5), 632–647. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410.2016.1231296
Conley, C. S., Kirsch, A. C., Dickson, D. A., & Bryant, F. B. (2014). Negotiating the transition to college: Developmental trajectories and gender differences in psychological functioning, cognitive-affective strategies, and social well-being. Emerging Adulthood, 2 (3), 195–210. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167696814521808
Cooke, R., Bewick, B. M., Barkham, M., Bradley, M., & Audin, K. (2006). Measuring, monitoring and managing the psychological well-being of first year university students. British Journal of Guidance & Counselling, 34 (4), 505–517. https://doi.org/10.1080/03069880600942624
Credé, M., & Niehorster, S. (2012). Adjustment to college as measured by the student adaptation to college questionnaire: A quantitative review of its structure and relationships with correlates and consequences. Educational Psychology Review, 24 (1), 133–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-011-9184-5
Cronbach, L. J., & Meehl, P. E. (1955). Construct validity in psychological tests. Psychological Bulletin, 52 (4), 281–302. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0040957
*De Clercq, M., Galand, B., & Frenay, M. (2017). Transition from high school to university: A person-centered approach to academic achievement. European Journal of Psychology of Education , 32 (1), 39–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-016-0298-5
*De Clercq, M., Galand, B., & Frenay, M. (2020). One goal, different pathways: Capturing diversity in processes leading to first-year students’ achievement. Learning and Individual Differences , 81 . https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LINDIF.2020.101908
De Clercq, M., Roland, N., Brunelle, M., Galand, B., & Frenay, M. (2018). The Delicate Balance to adjustment: A qualitative approach of student’s transition to the first year at university. Psychologica Belgica, 58 (1), 67. https://doi.org/10.5334/pb.409
*Del-Ben, C. M., Machado, V. F., Madisson, M. M., Resende, T. L., Valério, F. P., & Troncon, L. E. D. A. (2013). Relationship between academic performance and affective changes during the first year at medical school. Medical Teacher , 35 (5), 404–410. https://doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2013.769675
*Fokkens-Bruinsma, M., Vermue, C., Deinum, J. F., & van Rooij, E. (2021). First-year academic achievement: The role of academic self-efficacy, self-regulated learning and beyond classroom engagement. Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , 46 (7), 1115–1126. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2020.1845606
Gall, T. L., Evans, D. R., & Bellerose, S. (2000). Transition to first-year university: Patterns of change in adjustment across life domains and time. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 19 (4), 544–567.
Higher Education Statistics Agency. (2021). Non-continuation summary . UK Performance Indicators https://www.hesa.ac.uk/data-and-analysis/performance-indicators/non-continuation-summary
Hirsch, J. K., Rabon, J. K., Reynolds, E. E., Barton, A. L., & Chang, E. C. (2019). Perceived stress and suicidal behaviors in college students: Conditional indirect effects of depressive symptoms and mental health stigma. Stigma and Health, 4 (1), 98–106. https://doi.org/10.1037/sah0000125
Hobfoll, S. E. (2002). Social and psychological resources and adaptation. Review of General Psychology, 6 (4), 307–324. https://doi.org/10.1037/1089-2680.6.4.307
*Jones, E. J., & Schreier, H. M. C. (2021). Self-rated mental and physical health are prospectively associated with psychosocial and academic adjustment to college. Journal of American College Health . https://doi.org/10.1080/07448481.2021.1904956
Kahu, E. R., & Nelson, K. (2018). Student engagement in the educational interface: Understanding the mechanisms of student success. Higher Education Research & Development, 37 (1), 58–71. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2017.1344197
Kelley, T. L. (1927). Interpretation of educational measurements . World Book.
*Kljajic, K., & Gaudreau, P. (2022). Examining the association between procrastination and decreases in academic achievement during the transition from high school to university: A piecewise growth model. European Journal of Psychology of Education . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-022-00638-5
*Kolkhorst, B. B., Yazedjian, A., & Toews, M. L. (2010). A longitudinal examination of parental attachment, college adjustment, and academic achievement. Journal of the First-Year Experience & Students in Transition , 22 (1), 9–25.
*Krumrei-Mancuso, E. J., Newton, F. B., Kim, E., & Wilcox, D. (2013). Psychosocial factors predicting first-year college student success. Journal of College Student Development , 54 (3), 247–266. https://doi.org/10.1353/csd.2013.0034
*Larose, S., Robertson, D. U., Roy, R., Âed, F., & Legault, Â. (1998). Nonintellectual learning factors as determinants for success in college. In Research in higher education (Vol. 39, Issue 3).
Lawson, K. M., & Robins, R. W. (2021). Sibling constructs: What are they, why do they matter, and how should you handle them? Personality and Social Psychology Review, 25 (4), 344–366. https://doi.org/10.1177/10888683211047101
*Li, Y., & Bates, T. C. (2020). Testing the association of growth mindset and grades across a challenging transition: Is growth mindset associated with grades? Intelligence , 81 , 101471. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.INTELL.2020.101471
Liu, C. H., Stevens, C., Wong, S. H. M., Yasui, M., & Chen, J. A. (2019). The prevalence and predictors of mental health diagnoses and suicide among U.S. college students: Implications for addressing disparities in service use. Depression and Anxiety, 36 (1), 8–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.22830
*Lu, B., Deng, Y., Yao, X., & Li, Z. (2022). Learning goal orientation and academic performance: A dynamic model. Journal of Career Assessment , 30 (2), 329–344. https://doi.org/10.1177/10690727211043437
*Marley, S. C., & Wilcox, M. J. (2022). Do family and peer academic social supports predict academic motivations and achievement of first-year college students? Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education , 14 (3), 958–973. https://doi.org/10.1108/JARHE-06-2020-0158
*Martos, T., Jagodics, B., Kőrössy, J., & Szabó, É. (2021). Psychological resources, dropout risk and academic performance in university students – pattern-oriented analysis and prospective study of Hungarian freshmen. Current Psychology , 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12144-021-02073-Z
McKenzie, J. E., & Brennan, S. E. (2023). Chapter 12: Synthesizing and presenting findings using other methods. In J. P. T. Higgins, J. Thomas, J. Chandler, M. Cumpston, T. Li, M. J. Page, & V. A. Welch (Eds.), Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions (version 6.4) . Cochrane Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook
McNabb, R., Pal, S., & Sloane, P. (2002). Gender differences in educational attainment: The case of university students in England and Wales. Economica, 69 (275), 481–503. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-0335.00295
*Meng, H., Huang, P., Hou, N., & Fan, J. (2015). Social self-efficacy predicts Chinese college students’ first-year transition. Journal of Career Assessment , 23 (3), 410–426. https://doi.org/10.1177/1069072714547482
*Neuville, S., Frenay, M., Schmitz, J., Boudrenghien, G., Noël, B., & Wertz, V. (2007). Tinto’s theoretical perspective and expectancy-value paradigm: A confrontation to explain Freshmen’s academic achievement. In Psychologica Belgica (Vol. 47, Issues 1–2, pp. 31–50). Ubiquity Press Ltd. https://doi.org/10.5334/pb-47-1-31
Nicholson, N., & West, M. (1989). Transitions, work histories, and careers. In M. B. Arthur, D. T. Hall, & B. S. Lawrence (Eds.), Handbook of career theory (pp. 181–201). Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511625459.011
Chapter Google Scholar
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J. M., Akl, E. A., Brennan, S. E., Chou, R., Glanville, J., Grimshaw, J. M., Hróbjartsson, A., Lalu, M. M., Li, T., Loder, E. W., Mayo-Wilson, E., McDonald, S., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ, 372 . https://doi.org/10.1136/BMJ.N71
*Parker, J. D. A., Austin, E. J., Hogan, M. J., Wood, L. M., & Bond, B. J. (2005). Alexithymia and academic success: examining the transition from high school to university. Personality and Individual Differences , 38 (6), 1257–1267. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PAID.2004.08.008
*Parker, J. D. A., Summerfeldt, L. J., Hogan, M. J., & Majeski, S. A. (2004). Emotional intelligence and academic success: examining the transition from high school to university. Personality and Individual Differences , 36 (1), 163–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8869(03)00076-X
*Perera, H. N., Mcilveen, P., & Oliver, M. E. (2015). The mediating roles of coping and adjustment in the relationship between personality and academic achievement. British Journal of Educational Psychology , 85 (3), 440–457. https://doi.org/10.1111/BJEP.12084
*Perry, R. P., Stupnisky, R. H., Daniels, L. M., & Haynes, T. L. (2008). Attributional (explanatory) thinking about failure in new achievement settings. European Journal of Psychology of Education 2008 23:4 , 23 (4), 459–475. 10.1007/BF03172753
Patiniotis, J., & Holdsworth, C. (2005). ‘Seize that chance!’ leaving home and transitions to higher education. Journal of Youth Studies, 8 (1), 81–95. https://doi.org/10.1080/13676260500063710
Richardson, M., Abraham, C., & Bond, R. (2012). Psychological correlates of university students’ academic performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 138 (2), 353–387. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0026838
Robbins, S. B., Lauver, K., Le, H., Davis, D., Langley, R., & Carlstrom, A. (2004). Do Psychosocial and study skill factors predict college outcomes? A meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 130 (2), 261–288. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.130.2.261
ROBINS-E Development Group (2023). Risk Of Bias In Non-randomized Studies - of Exposure (ROBINS-E) . https://www.riskofbias.info/welcome/robins-e-tool
*Rodríguez, M. S., Tinajero, C., & Páramo, M. F. (2017). Pre-entry characteristics, perceived social support, adjustment and academic achievement in first-year Spanish university students: A path model. The Journal of Psychology , 151 (8), 722–738. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223980.2017.1372351
Rosenthal, R. (1979). The file drawer problem and tolerance for null results. Psychological Bulletin, 86 (3), 638–641. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.86.3.638
*Salamonson, Y., Ramjan, L. M., van den Nieuwenhuizen, S., Metcalfe, L., Chang, S., & Everett, B. (2016). Sense of coherence, self-regulated learning and academic performance in first year nursing students: A cluster analysis approach. Nurse Education in Practice , 17 , 208–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NEPR.2016.01.001
Schulenberg, J. E., Sameroff, A. J., & Cicchetti, D. (2004). The transition to adulthood as a critical juncture in the course of psychopathology and mental health. Development and Psychopathology, 16 (4), 799–806. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579404040015
Scanlon, L., Rowling, L., & Weber, Z. (2007). ‘You don’t have like an identity … you are just lost in a crowd’: Forming a Student Identity in the First-year Transition to University. Journal of Youth Studies, 10 (2), 223–241. https://doi.org/10.1080/13676260600983684
Soria, K., & Stubblefield, R. (2015). Building strengths awareness and hope in students’ transition to higher education. College Student Affairs Journal, 33 (1), 47–65. https://doi.org/10.1353/CSJ.2015.0007
Strenze, T. (2007). Intelligence and socioeconomic success: A meta-analytic review of longitudinal research. Intelligence, 35 (5), 401–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2006.09.004
Thorndike, E. L. (1904). Theory of mental and social measurements. The Science Press. https://doi.org/10.1037/13283-000
Tinto, V. (1982). Limits of theory and practice in student attrition. The Journal of Higher Education, 53 (6), 687. https://doi.org/10.2307/1981525
van der Zanden, P. J. A. C., Denessen, E., Cillessen, A. H. N., & Meijer, P. C. (2018). Domains and predictors of first-year student success: A systematic review. Educational Research Review, 23 , 57–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2018.01.001
*Veldman, J., Meeussen, L., & van Laar, C. (2019). A social identity perspective on the social-class achievement gap: Academic and social adjustment in the transition to university. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations , 22 (3), 403–418. https://doi.org/10.1177/1368430218813442
*Wilson, C. A., Babcock, S. E., & Saklofske, D. H. (2019). Sinking or swimming in an academic pool: A study of resiliency and student success in first-year undergraduates. Canadian Journal of Higher Education / Revue Canadienne d’enseignement Supérieur , 49 (1), 60–84. https://doi.org/10.7202/1060824AR
Wintre, M. G., & Yaffe, M. (2000). First-year students’ adjustment to university life as a function of relationships with parents. Journal of Adolescent Research, 15 (1), 9–37. https://doi.org/10.1177/0743558400151002
*Woosley, S. A., & Miller, A. L. (2009). Integration and institutional commitment as predictors of college student transition: Are third week indicators significant? College Student Journal , 43 (4), 1260–1272.
Zimmerman, M. A. (2013). Resiliency theory: A strengths-based approach to research and practice for adolescent health. Health Education & Behavior: The Official Publication of the Society for Public Health Education, 40 (4), 381. https://doi.org/10.1177/1090198113493782
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Psychology and Criminology, University of Chichester, College Lane, Chichester, PO19 6UZ, UK
Isabelle Ball, Moitree Banerjee & Ian Tyndall
Department of Psychology and Human Development, University College London, Gower Street, London, WC1E 6BT, UK
Andrew Holliman
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Isabelle Ball .
Ethics declarations
This work was completed as part of the first author’s PhD programme of study. No funding, grants, or other support was received. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. As per the University of Chichester’s Institutional Ethics Committee, as a systematic review with only secondary data, this paper was exempt from requiring ethical approval.
Competing of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
(DOCX 194 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Ball, I., Banerjee, M., Holliman, A. et al. Investigating Success in the Transition to University: A Systematic Review of Personal Risk and Protective Factors Influencing Academic Achievement. Educ Psychol Rev 36 , 52 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-024-09891-0
Download citation
Accepted : 03 May 2024
Published : 18 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-024-09891-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Higher education
- First year students
- Academic achievement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
Psychology articles from across Nature Portfolio
Psychology is a scientific discipline that focuses on understanding mental functions and the behaviour of individuals and groups.
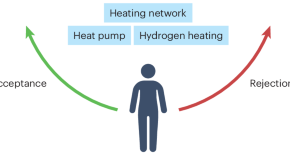
Citizens’ perceptions
The shift towards low-carbon heating technologies and associated infrastructure often disrupts citizens’ lives. Research now demonstrates how the socio-psychological context may influence the circumstances under which citizens are willing to accept heating transitions and related construction work, and those where reactance and rejection is to be expected.
- Paula Maria Bögel
Related Subjects
- Human behaviour
Latest Research and Reviews
Nostalgia increases punitiveness by intensifying moral concern.
- Jannine D. Lasaleta
- Tim Wildschut
- Constantine Sedikides
The role of breastfeeding and formula feeding regarding depressive symptoms and an impaired mother child bonding
- Clara Carvalho Hilje
- Nicola H. Bauer
- Alfred Längler
Elucidating the underlying components of metacognitive systematic bias in the human dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and inferior parietal cortex
- Peiyao Cong
- Yiting Long
- Yingjie Jiang
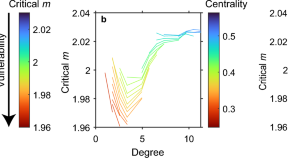
Transformation starts at the periphery of networks where pushback is less
- Ingrid A. van de Leemput
- Jordi Bascompte
- Egbert H. van Nes
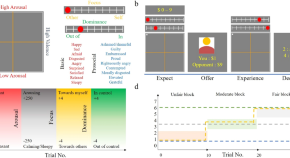
Prosocial emotions predict individual differences in economic decision-making during ultimatum game with dynamic reciprocal contexts
- Su Hyun Bong
- Bumseok Jeong
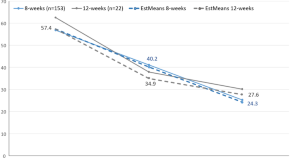
Comparison of 8-vs-12 weeks, adapted dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT) for borderline personality disorder in routine psychiatric inpatient treatment—A naturalistic study
- Milenko Kujovic
- Daniel Benz
- Eva Meisenzahl
News and Comment

From the lab to a career in behaviour change
Nature Reviews Psychology is interviewing individuals with doctoral degrees in psychology who pursued non-academic careers. We spoke with Erik Simmons about his journey from a postdoctoral research fellow to a behavioural designer.
- Teresa Schubert
Shaping vision through drawing
- Kushin Mukherjee
Does it matter if empathic AI has no empathy?
- Garriy Shteynberg
- Jodi Halpern
- Abrol Fairweather

How does ChatGPT ‘think’? Psychology and neuroscience crack open AI large language models
Researchers are striving to reverse-engineer artificial intelligence and scan the ‘brains’ of LLMs to see what they are doing, how and why.
- Matthew Hutson
Editorial: The cognitive ageing collection
Alongside rapid population ageing, we are experiencing increasing numbers of people with cognitive impairment and dementia. There is great scientific effort being committed to understanding cognitive and brain functioning, with the aim of helping to promote healthy ageing and independence, and improve quality of life. This Cognitive Ageing Collection brings together cutting-edge research using a variety of methods and from diverse disciplinary perspectives, with example topics including cognitive strategies, genetic risk factors, and emotion regulation. Articles in the Collection highlight advances in our understanding of cognitive and brain health, and outline important directions for future research.
- Louise A. Brown Nicholls
- Martina Amanzio
- Hannah Keage
Scholar activism benefits science and society
An artificial boundary is often drawn between research and activism, but scholar activism can be good for science and for society when it centres the needs of people who are multiply marginalized — especially during the current climate crisis.
- José M. Causadias
- Leoandra Onnie Rogers
- Tiffany Yip
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Recently published articles from subdisciplines of psychology covered by more than 90 APA Journals™ publications. For additional free resources (such as article summaries, podcasts, and more), please visit the Highlights in Psychological Research page. Browse and read free articles from APA Journals across the field of psychology, selected by ...
Psychological Science, the flagship journal of the Association for Psychological Science, is the highest ranked empirical journal in psychology and is truly a leader in the field. The journal publishes cutting-edge research articles and … | View full journal description. This journal is a member of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE).
Top 100 in Psychology - 2022. This collection highlights our most downloaded* psychology papers published in 2022. Featuring authors from around the world, these papers showcase valuable research ...
The most cited journal in its field, exploring psychological sciences - from clinical research to cognitive science, from imaging studies to human factors, and from animal cognition to social psych...
Psychology Top 100 of 2023. This collection highlights the most downloaded* psychology research papers published by Scientific Reports in 2023. Featuring authors from around the world, these ...
Frontiers in Psychology. doi 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1394930. Original Research. Accepted on 16 May 2024. Mental Rotation abilities of gymnasts and soccer players: A comparison of egocentric and object-based transformations. An exploratory and preliminary study. Thomas Jürgen Klotzbier.
An artificial boundary is often drawn between research and activism, but scholar activism can be good for science and for society when it centres the needs of people who are multiply marginalized ...
The British Journal of Psychology is the flagship journal of the British Psychological Society, publishing cutting-edge, multidisciplinary psychological research with major theoretical or methodological contributions across different sections of psychology. With a commitment to open science, the journal enjoys a wide international readership. It features empirical studies and critical reviews ...
Many psychology students dislike writing a research paper, their aversion driven by anxiety over various aspects of the process. This primer for undergraduates explains how to write a clear, compelling, well-organized research paper. From picking a promising topic, to finding and digesting the pertinent literature, to developing a thesis, to outlining and presenting ideas, to editing for ...
The American Journal of Psychology (AJP) was founded in 1887 by G. Stanley Hall and was edited in its early years by Titchener, Boring, and Dallenbach. The Journal has published some of the most innovative and formative papers in psychology throughout its history.AJP explores the science of the mind and behavior, publishing reports of original research in experimental psychology, theoretical ...
Psychological Science, the flagship journal of the Association for Psychological Science, is the leading peer-reviewed journal publishing empirical research spanning the entire spectrum of the science of psychology.The journal publishes high quality research articles of general interest and on important topics spanning the entire spectrum of the science of psychology.
Journal of Health Psychology is a leading international peer reviewed journal that aims to support and help shape research in health psychology from around the world. It provides a platform for traditional empirical analyses as well as more qualitative and/or critically oriented approaches. ... Call for Papers. The Journal of Health Psychology ...
Topics of Psychology Research Related to Human Cognition. Some of the possible topics you might explore in this area include thinking, language, intelligence, and decision-making. Other ideas might include: Dreams. False memories. Attention. Perception.
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on PSYCHOLOGY. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review on PSYCHOLOGY
Writing a psychology research paper can be intimidating at first, but breaking the process into a series of smaller steps makes it more manageable. Be sure to start early by deciding on a substantial topic, doing your research, and creating a good outline. Doing these supporting steps ahead of time make it much easier to actually write the ...
For more information on writing research papers in APA style, please checking out the following pages. Here you'll find details on multiple aspects of the research paper writing process, ranging from how the paper should be structured to how to write more effectively. Structure and Format - the critical components of each section of an APA ...
Component 1: The Title Page. • On the right side of the header, type the first 2-3 words of your full title followed by the page number. This header will appear on every page of you report. • At the top of the page, type flush left the words "Running head:" followed by an abbreviation of your title in all caps.
Psychological Research is dedicated to the dissemination of knowledge contributing to a basic understanding of human cognition and behavior. Focuses on human perception, attention, memory, and action. Upholds impartiality, independent of any particular approach or school of thought. Includes theoretical and historical papers alongside applied ...
Proposed papers should be empirical in scope, and may include experimental studies, as well as prevention and treatment approaches. A focus on overcoming challenges in the dissemination, implementation and uptake of sleep interventions in the context of psychological disorders are also encouraged.
In this Review, Kline and colleagues discuss effective treatments for this combination, focusing on trauma-focused treatments, and provide recommendations to improve treatment response and reduce ...
A complete research paper in APA style that is reporting on experimental research will typically contain a Title page, Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, and References sections. 1 Many will also contain Figures and Tables and some will have an Appendix or Appendices. These sections are detailed as follows (for a more in ...
The Journal of Creative Behavior is the original journal devoted specifically to creativity research, publishing papers on theory & applications of creativity. ABSTRACT This paper expands upon the invitation to rethink how psychology has constructed knowledge, theories, and research while analyzing the epistemological foundations of educational ...
This paper is written by a UK-based research team, so the natural comparison is to that of the UK context. The schooling structures differ, often in a North American college, students complete four-year degrees and select their classes each semester and declare a major often in the second year. ... European Journal of Psychology of Education ...
Psychology is a scientific discipline that focuses on understanding mental functions and the behaviour of individuals and groups. The shift towards low-carbon heating technologies and associated ...
The trend of male celebrities endorsing female products is increasing. However, research is lacking on whether this influence is due to the positive emotions generated by the male celebrity's attractiveness or the peer pressure due to mass purchases by the celebrity's fans, and how these effects differ across products with different attributes. This study aims to fill the gap in the existing ...
This paper provides a comprehensive review of the literature on recovery in mental health. It highlights various definitions and elements of recovery and synthesizes evidence from different sources, including research studies, clinical experiences, and personal narratives.
Submissions should adhere to the APA 7 th edition style guidelines and contribute original academic insights into the fields of traumatology, psychology, social work, disaster research, and resilience studies. We welcome submissions from researchers, clinicians, policymakers, and those with lived experiences. Detailed submission instructions and guidelines can be found on our website.