- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Summary – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide

Research Summary – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Summary
Definition:
A research summary is a brief and concise overview of a research project or study that highlights its key findings, main points, and conclusions. It typically includes a description of the research problem, the research methods used, the results obtained, and the implications or significance of the findings. It is often used as a tool to quickly communicate the main findings of a study to other researchers, stakeholders, or decision-makers.
Structure of Research Summary
The Structure of a Research Summary typically include:
- Introduction : This section provides a brief background of the research problem or question, explains the purpose of the study, and outlines the research objectives.
- Methodology : This section explains the research design, methods, and procedures used to conduct the study. It describes the sample size, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques.
- Results : This section presents the main findings of the study, including statistical analysis if applicable. It may include tables, charts, or graphs to visually represent the data.
- Discussion : This section interprets the results and explains their implications. It discusses the significance of the findings, compares them to previous research, and identifies any limitations or future directions for research.
- Conclusion : This section summarizes the main points of the research and provides a conclusion based on the findings. It may also suggest implications for future research or practical applications of the results.
- References : This section lists the sources cited in the research summary, following the appropriate citation style.
How to Write Research Summary
Here are the steps you can follow to write a research summary:
- Read the research article or study thoroughly: To write a summary, you must understand the research article or study you are summarizing. Therefore, read the article or study carefully to understand its purpose, research design, methodology, results, and conclusions.
- Identify the main points : Once you have read the research article or study, identify the main points, key findings, and research question. You can highlight or take notes of the essential points and findings to use as a reference when writing your summary.
- Write the introduction: Start your summary by introducing the research problem, research question, and purpose of the study. Briefly explain why the research is important and its significance.
- Summarize the methodology : In this section, summarize the research design, methods, and procedures used to conduct the study. Explain the sample size, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques.
- Present the results: Summarize the main findings of the study. Use tables, charts, or graphs to visually represent the data if necessary.
- Interpret the results: In this section, interpret the results and explain their implications. Discuss the significance of the findings, compare them to previous research, and identify any limitations or future directions for research.
- Conclude the summary : Summarize the main points of the research and provide a conclusion based on the findings. Suggest implications for future research or practical applications of the results.
- Revise and edit : Once you have written the summary, revise and edit it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors. Make sure that your summary accurately represents the research article or study.
- Add references: Include a list of references cited in the research summary, following the appropriate citation style.
Example of Research Summary
Here is an example of a research summary:
Title: The Effects of Yoga on Mental Health: A Meta-Analysis
Introduction: This meta-analysis examines the effects of yoga on mental health. The study aimed to investigate whether yoga practice can improve mental health outcomes such as anxiety, depression, stress, and quality of life.
Methodology : The study analyzed data from 14 randomized controlled trials that investigated the effects of yoga on mental health outcomes. The sample included a total of 862 participants. The yoga interventions varied in length and frequency, ranging from four to twelve weeks, with sessions lasting from 45 to 90 minutes.
Results : The meta-analysis found that yoga practice significantly improved mental health outcomes. Participants who practiced yoga showed a significant reduction in anxiety and depression symptoms, as well as stress levels. Quality of life also improved in those who practiced yoga.
Discussion : The findings of this study suggest that yoga can be an effective intervention for improving mental health outcomes. The study supports the growing body of evidence that suggests that yoga can have a positive impact on mental health. Limitations of the study include the variability of the yoga interventions, which may affect the generalizability of the findings.
Conclusion : Overall, the findings of this meta-analysis support the use of yoga as an effective intervention for improving mental health outcomes. Further research is needed to determine the optimal length and frequency of yoga interventions for different populations.
References :
- Cramer, H., Lauche, R., Langhorst, J., Dobos, G., & Berger, B. (2013). Yoga for depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Depression and anxiety, 30(11), 1068-1083.
- Khalsa, S. B. (2004). Yoga as a therapeutic intervention: a bibliometric analysis of published research studies. Indian journal of physiology and pharmacology, 48(3), 269-285.
- Ross, A., & Thomas, S. (2010). The health benefits of yoga and exercise: a review of comparison studies. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 16(1), 3-12.
Purpose of Research Summary
The purpose of a research summary is to provide a brief overview of a research project or study, including its main points, findings, and conclusions. The summary allows readers to quickly understand the essential aspects of the research without having to read the entire article or study.
Research summaries serve several purposes, including:
- Facilitating comprehension: A research summary allows readers to quickly understand the main points and findings of a research project or study without having to read the entire article or study. This makes it easier for readers to comprehend the research and its significance.
- Communicating research findings: Research summaries are often used to communicate research findings to a wider audience, such as policymakers, practitioners, or the general public. The summary presents the essential aspects of the research in a clear and concise manner, making it easier for non-experts to understand.
- Supporting decision-making: Research summaries can be used to support decision-making processes by providing a summary of the research evidence on a particular topic. This information can be used by policymakers or practitioners to make informed decisions about interventions, programs, or policies.
- Saving time: Research summaries save time for researchers, practitioners, policymakers, and other stakeholders who need to review multiple research studies. Rather than having to read the entire article or study, they can quickly review the summary to determine whether the research is relevant to their needs.
Characteristics of Research Summary
The following are some of the key characteristics of a research summary:
- Concise : A research summary should be brief and to the point, providing a clear and concise overview of the main points of the research.
- Objective : A research summary should be written in an objective tone, presenting the research findings without bias or personal opinion.
- Comprehensive : A research summary should cover all the essential aspects of the research, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions.
- Accurate : A research summary should accurately reflect the key findings and conclusions of the research.
- Clear and well-organized: A research summary should be easy to read and understand, with a clear structure and logical flow.
- Relevant : A research summary should focus on the most important and relevant aspects of the research, highlighting the key findings and their implications.
- Audience-specific: A research summary should be tailored to the intended audience, using language and terminology that is appropriate and accessible to the reader.
- Citations : A research summary should include citations to the original research articles or studies, allowing readers to access the full text of the research if desired.
When to write Research Summary
Here are some situations when it may be appropriate to write a research summary:
- Proposal stage: A research summary can be included in a research proposal to provide a brief overview of the research aims, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
- Conference presentation: A research summary can be prepared for a conference presentation to summarize the main findings of a study or research project.
- Journal submission: Many academic journals require authors to submit a research summary along with their research article or study. The summary provides a brief overview of the study’s main points, findings, and conclusions and helps readers quickly understand the research.
- Funding application: A research summary can be included in a funding application to provide a brief summary of the research aims, objectives, and expected outcomes.
- Policy brief: A research summary can be prepared as a policy brief to communicate research findings to policymakers or stakeholders in a concise and accessible manner.
Advantages of Research Summary
Research summaries offer several advantages, including:
- Time-saving: A research summary saves time for readers who need to understand the key findings and conclusions of a research project quickly. Rather than reading the entire research article or study, readers can quickly review the summary to determine whether the research is relevant to their needs.
- Clarity and accessibility: A research summary provides a clear and accessible overview of the research project’s main points, making it easier for readers to understand the research without having to be experts in the field.
- Improved comprehension: A research summary helps readers comprehend the research by providing a brief and focused overview of the key findings and conclusions, making it easier to understand the research and its significance.
- Enhanced communication: Research summaries can be used to communicate research findings to a wider audience, such as policymakers, practitioners, or the general public, in a concise and accessible manner.
- Facilitated decision-making: Research summaries can support decision-making processes by providing a summary of the research evidence on a particular topic. Policymakers or practitioners can use this information to make informed decisions about interventions, programs, or policies.
- Increased dissemination: Research summaries can be easily shared and disseminated, allowing research findings to reach a wider audience.
Limitations of Research Summary
Limitations of the Research Summary are as follows:
- Limited scope: Research summaries provide a brief overview of the research project’s main points, findings, and conclusions, which can be limiting. They may not include all the details, nuances, and complexities of the research that readers may need to fully understand the study’s implications.
- Risk of oversimplification: Research summaries can be oversimplified, reducing the complexity of the research and potentially distorting the findings or conclusions.
- Lack of context: Research summaries may not provide sufficient context to fully understand the research findings, such as the research background, methodology, or limitations. This may lead to misunderstandings or misinterpretations of the research.
- Possible bias: Research summaries may be biased if they selectively emphasize certain findings or conclusions over others, potentially distorting the overall picture of the research.
- Format limitations: Research summaries may be constrained by the format or length requirements, making it challenging to fully convey the research’s main points, findings, and conclusions.
- Accessibility: Research summaries may not be accessible to all readers, particularly those with limited literacy skills, visual impairments, or language barriers.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
The Sheridan Libraries
- Write a Literature Review
- Sheridan Libraries
- Find This link opens in a new window
- Evaluate This link opens in a new window

Not every source you found should be included in your annotated bibliography or lit review. Only include the most relevant and most important sources.
Get Organized
- Lit Review Prep Use this template to help you evaluate your sources, create article summaries for an annotated bibliography, and a synthesis matrix for your lit review outline.
Summarize your Sources
Summarize each source: Determine the most important and relevant information from each source, such as the findings, methodology, theories, etc. Consider using an article summary, or study summary to help you organize and summarize your sources.
Paraphrasing
- Use your own words, and do not copy and paste the abstract
- The library's tutorials about plagiarism are excellent, and will help you with paraphasing correctly
Annotated Bibliographies
Annotated bibliographies can help you clearly see and understand the research before diving into organizing and writing your literature review. Although typically part of the "summarize" step of the literature review, annotations should not merely be summaries of each article - instead, they should be critical evaluations of the source, and help determine a source's usefulness for your lit review.
Definition:
A list of citations on a particular topic followed by an evaluation of the source’s argument and other relevant material including its intended audience, sources of evidence, and methodology
- Explore your topic.
- Appraise issues or factors associated with your professional practice and research topic.
- Help you get started with the literature review.
- Think critically about your topic, and the literature.
Steps to Creating an Annotated Bibliography:
- Find Your Sources
- Read Your Sources
- Identify the Most Relevant Sources
- Cite your Sources
- Write Annotations
Annotated Bibliography Resources
- Purdue Owl Guide
- Cornell Annotated Bibliography Guide
- << Previous: Evaluate
- Next: Synthesize >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 10:25 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.jhu.edu/lit-review
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as you go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface with the option to save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.
- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., how to write a successful book chapter for..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, what is academic writing: tips for students.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

How religious scientists balance work and faith
Career Feature 20 MAY 24

How to set up your new lab space
Career Column 20 MAY 24

I’m worried I’ve been contacted by a predatory publisher — how do I find out?
Career Feature 15 MAY 24

US halts funding to controversial virus-hunting group: what researchers think
News 16 MAY 24
Japan can embrace open science — but flexible approaches are key
Correspondence 07 MAY 24

Illuminating ‘the ugly side of science’: fresh incentives for reporting negative results
Career Feature 08 MAY 24

Mount Etna’s spectacular smoke rings and more — April’s best science images
News 03 MAY 24
Senior Postdoctoral Research Fellow
Senior Postdoctoral Research Fellow required to lead exciting projects in Cancer Cell Cycle Biology and Cancer Epigenetics.
Melbourne University, Melbourne (AU)
University of Melbourne & Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre
Overseas Talent, Embarking on a New Journey Together at Tianjin University
We cordially invite outstanding young individuals from overseas to apply for the Excellent Young Scientists Fund Program (Overseas).
Tianjin, China
Tianjin University (TJU)
Chair Professor Positions in the School of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology
SPST seeks top Faculty scholars in Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Chair Professor Positions in the School of Precision Instruments and Optoelectronic Engineering
We are committed to accomplishing the mission of achieving a world-top-class engineering school.
Chair Professor Positions in the School of Mechanical Engineering
Aims to cultivate top talents, train a top-ranking faculty team, construct first-class disciplines and foster a favorable academic environment.
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
How to Write a Peer Review

When you write a peer review for a manuscript, what should you include in your comments? What should you leave out? And how should the review be formatted?
This guide provides quick tips for writing and organizing your reviewer report.
Review Outline
Use an outline for your reviewer report so it’s easy for the editors and author to follow. This will also help you keep your comments organized.
Think about structuring your review like an inverted pyramid. Put the most important information at the top, followed by details and examples in the center, and any additional points at the very bottom.
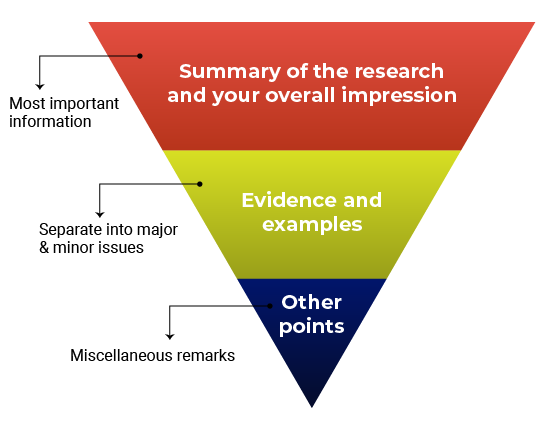
Here’s how your outline might look:
1. Summary of the research and your overall impression
In your own words, summarize what the manuscript claims to report. This shows the editor how you interpreted the manuscript and will highlight any major differences in perspective between you and the other reviewers. Give an overview of the manuscript’s strengths and weaknesses. Think about this as your “take-home” message for the editors. End this section with your recommended course of action.
2. Discussion of specific areas for improvement
It’s helpful to divide this section into two parts: one for major issues and one for minor issues. Within each section, you can talk about the biggest issues first or go systematically figure-by-figure or claim-by-claim. Number each item so that your points are easy to follow (this will also make it easier for the authors to respond to each point). Refer to specific lines, pages, sections, or figure and table numbers so the authors (and editors) know exactly what you’re talking about.
Major vs. minor issues
What’s the difference between a major and minor issue? Major issues should consist of the essential points the authors need to address before the manuscript can proceed. Make sure you focus on what is fundamental for the current study . In other words, it’s not helpful to recommend additional work that would be considered the “next step” in the study. Minor issues are still important but typically will not affect the overall conclusions of the manuscript. Here are some examples of what would might go in the “minor” category:
- Missing references (but depending on what is missing, this could also be a major issue)
- Technical clarifications (e.g., the authors should clarify how a reagent works)
- Data presentation (e.g., the authors should present p-values differently)
- Typos, spelling, grammar, and phrasing issues
3. Any other points
Confidential comments for the editors.
Some journals have a space for reviewers to enter confidential comments about the manuscript. Use this space to mention concerns about the submission that you’d want the editors to consider before sharing your feedback with the authors, such as concerns about ethical guidelines or language quality. Any serious issues should be raised directly and immediately with the journal as well.
This section is also where you will disclose any potentially competing interests, and mention whether you’re willing to look at a revised version of the manuscript.
Do not use this space to critique the manuscript, since comments entered here will not be passed along to the authors. If you’re not sure what should go in the confidential comments, read the reviewer instructions or check with the journal first before submitting your review. If you are reviewing for a journal that does not offer a space for confidential comments, consider writing to the editorial office directly with your concerns.
Get this outline in a template
Giving Feedback
Giving feedback is hard. Giving effective feedback can be even more challenging. Remember that your ultimate goal is to discuss what the authors would need to do in order to qualify for publication. The point is not to nitpick every piece of the manuscript. Your focus should be on providing constructive and critical feedback that the authors can use to improve their study.
If you’ve ever had your own work reviewed, you already know that it’s not always easy to receive feedback. Follow the golden rule: Write the type of review you’d want to receive if you were the author. Even if you decide not to identify yourself in the review, you should write comments that you would be comfortable signing your name to.
In your comments, use phrases like “ the authors’ discussion of X” instead of “ your discussion of X .” This will depersonalize the feedback and keep the focus on the manuscript instead of the authors.
General guidelines for effective feedback

- Justify your recommendation with concrete evidence and specific examples.
- Be specific so the authors know what they need to do to improve.
- Be thorough. This might be the only time you read the manuscript.
- Be professional and respectful. The authors will be reading these comments too.
- Remember to say what you liked about the manuscript!

Don’t
- Recommend additional experiments or unnecessary elements that are out of scope for the study or for the journal criteria.
- Tell the authors exactly how to revise their manuscript—you don’t need to do their work for them.
- Use the review to promote your own research or hypotheses.
- Focus on typos and grammar. If the manuscript needs significant editing for language and writing quality, just mention this in your comments.
- Submit your review without proofreading it and checking everything one more time.

Before and After: Sample Reviewer Comments
Keeping in mind the guidelines above, how do you put your thoughts into words? Here are some sample “before” and “after” reviewer comments
✗ Before
“The authors appear to have no idea what they are talking about. I don’t think they have read any of the literature on this topic.”
✓ After
“The study fails to address how the findings relate to previous research in this area. The authors should rewrite their Introduction and Discussion to reference the related literature, especially recently published work such as Darwin et al.”
“The writing is so bad, it is practically unreadable. I could barely bring myself to finish it.”
“While the study appears to be sound, the language is unclear, making it difficult to follow. I advise the authors work with a writing coach or copyeditor to improve the flow and readability of the text.”
“It’s obvious that this type of experiment should have been included. I have no idea why the authors didn’t use it. This is a big mistake.”
“The authors are off to a good start, however, this study requires additional experiments, particularly [type of experiment]. Alternatively, the authors should include more information that clarifies and justifies their choice of methods.”
Suggested Language for Tricky Situations
You might find yourself in a situation where you’re not sure how to explain the problem or provide feedback in a constructive and respectful way. Here is some suggested language for common issues you might experience.
What you think : The manuscript is fatally flawed. What you could say: “The study does not appear to be sound” or “the authors have missed something crucial”.
What you think : You don’t completely understand the manuscript. What you could say : “The authors should clarify the following sections to avoid confusion…”
What you think : The technical details don’t make sense. What you could say : “The technical details should be expanded and clarified to ensure that readers understand exactly what the researchers studied.”
What you think: The writing is terrible. What you could say : “The authors should revise the language to improve readability.”
What you think : The authors have over-interpreted the findings. What you could say : “The authors aim to demonstrate [XYZ], however, the data does not fully support this conclusion. Specifically…”
What does a good review look like?
Check out the peer review examples at F1000 Research to see how other reviewers write up their reports and give constructive feedback to authors.
Time to Submit the Review!
Be sure you turn in your report on time. Need an extension? Tell the journal so that they know what to expect. If you need a lot of extra time, the journal might need to contact other reviewers or notify the author about the delay.
Tip: Building a relationship with an editor
You’ll be more likely to be asked to review again if you provide high-quality feedback and if you turn in the review on time. Especially if it’s your first review for a journal, it’s important to show that you are reliable. Prove yourself once and you’ll get asked to review again!
- Getting started as a reviewer
- Responding to an invitation
- Reading a manuscript
- Writing a peer review
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
Libraries | Research Guides
Literature reviews, what is a literature review, learning more about how to do a literature review.
- Planning the Review
- The Research Question
- Choosing Where to Search
- Organizing the Review
- Writing the Review
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the literature you have read.
- Sage Research Methods Core Collection This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. – Publisher
- Next: Planning the Review >>
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 10:39 AM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/literaturereviews

Literature Reviews
- Getting started
What is a literature review?
Why conduct a literature review, stages of a literature review, lit reviews: an overview (video), check out these books.
- Types of reviews
- 1. Define your research question
- 2. Plan your search
- 3. Search the literature
- 4. Organize your results
- 5. Synthesize your findings
- 6. Write the review
- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools
- Thompson Writing Studio This link opens in a new window
- Need to write a systematic review? This link opens in a new window

Contact a Librarian
Ask a Librarian
Definition: A literature review is a systematic examination and synthesis of existing scholarly research on a specific topic or subject.
Purpose: It serves to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge within a particular field.
Analysis: Involves critically evaluating and summarizing key findings, methodologies, and debates found in academic literature.
Identifying Gaps: Aims to pinpoint areas where there is a lack of research or unresolved questions, highlighting opportunities for further investigation.
Contextualization: Enables researchers to understand how their work fits into the broader academic conversation and contributes to the existing body of knowledge.

tl;dr A literature review critically examines and synthesizes existing scholarly research and publications on a specific topic to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge in the field.
What is a literature review NOT?
❌ An annotated bibliography
❌ Original research
❌ A summary
❌ Something to be conducted at the end of your research
❌ An opinion piece
❌ A chronological compilation of studies
The reason for conducting a literature review is to:

Literature Reviews: An Overview for Graduate Students
While this 9-minute video from NCSU is geared toward graduate students, it is useful for anyone conducting a literature review.

Writing the literature review: A practical guide
Available 3rd floor of Perkins

Writing literature reviews: A guide for students of the social and behavioral sciences
Available online!

So, you have to write a literature review: A guided workbook for engineers

Telling a research story: Writing a literature review

The literature review: Six steps to success

Systematic approaches to a successful literature review
Request from Duke Medical Center Library

Doing a systematic review: A student's guide
- Next: Types of reviews >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 8:42 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.duke.edu/litreviews

Services for...
- Faculty & Instructors
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- International Students
- Patrons with Disabilities
- Harmful Language Statement
- Re-use & Attribution / Privacy
- Support the Libraries

- All eBooks & Audiobooks
- Academic eBook Collection
- Home Grown eBook Collection
- Off-Campus Access
- Literature Resource Center
- Opposing Viewpoints
- ProQuest Central
- Course Guides
- Citing Sources
- Library Research
- Websites by Topic
- Book-a-Librarian
- Research Tutorials
- Use the Catalog
- Use Databases
- Use Films on Demand
- Use Home Grown eBooks
- Use NC LIVE
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary vs. Secondary
- Scholarly vs. Popular
- Make an Appointment
- Writing Tools
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing Center
Service Alert

Article Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
Writing an article summary.
- Writing an article REVIEW
- Writing an article CRITIQUE
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- About RCC Library
Text: 336-308-8801
Email: [email protected]
Call: 336-633-0204
Schedule: Book-a-Librarian
Like us on Facebook
Links on this guide may go to external web sites not connected with Randolph Community College. Their inclusion is not an endorsement by Randolph Community College and the College is not responsible for the accuracy of their content or the security of their site.
When writing a summary, the goal is to compose a concise and objective overview of the original article. The summary should focus only on the article's main ideas and important details that support those ideas.
Guidelines for summarizing an article:
- State the main ideas.
- Identify the most important details that support the main ideas.
- Summarize in your own words.
- Do not copy phrases or sentences unless they are being used as direct quotations.
- Express the underlying meaning of the article, but do not critique or analyze.
- The summary should be about one third the length of the original article.
Your summary should include:
- Give an overview of the article, including the title and the name of the author.
- Provide a thesis statement that states the main idea of the article.
- Use the body paragraphs to explain the supporting ideas of your thesis statement.
- One-paragraph summary - one sentence per supporting detail, providing 1-2 examples for each.
- Multi-paragraph summary - one paragraph per supporting detail, providing 2-3 examples for each.
- Start each paragraph with a topic sentence.
- Use transitional words and phrases to connect ideas.
- Summarize your thesis statement and the underlying meaning of the article.
Adapted from "Guidelines for Using In-Text Citations in a Summary (or Research Paper)" by Christine Bauer-Ramazani, 2020
Additional Resources
All links open in a new window.
How to Write a Summary - Guide & Examples (from Scribbr.com)
Writing a Summary (from The University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center)
- Next: Writing an article REVIEW >>
- Last Updated: Mar 15, 2024 9:32 AM
- URL: https://libguides.randolph.edu/summaries
University Libraries
Literature review.
- What is a Literature Review?
- What is Its Purpose?
- 1. Select a Topic
- 2. Set the Topic in Context
- 3. Types of Information Sources
- 4. Use Information Sources
- 5. Get the Information
- 6. Organize / Manage the Information
- 7. Position the Literature Review
- 8. Write the Literature Review

A literature review is a comprehensive summary of previous research on a topic. The literature review surveys scholarly articles, books, and other sources relevant to a particular area of research. The review should enumerate, describe, summarize, objectively evaluate and clarify this previous research. It should give a theoretical base for the research and help you (the author) determine the nature of your research. The literature review acknowledges the work of previous researchers, and in so doing, assures the reader that your work has been well conceived. It is assumed that by mentioning a previous work in the field of study, that the author has read, evaluated, and assimiliated that work into the work at hand.
A literature review creates a "landscape" for the reader, giving her or him a full understanding of the developments in the field. This landscape informs the reader that the author has indeed assimilated all (or the vast majority of) previous, significant works in the field into her or his research.
"In writing the literature review, the purpose is to convey to the reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. The literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (eg. your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries.( http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/specific-types-of-writing/literature-review )
Recommended Reading
- Next: What is Its Purpose? >>
- Last Updated: Oct 2, 2023 12:34 PM
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: May 20, 2024 9:47 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 24, Issue 2
- Five tips for developing useful literature summary tables for writing review articles
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0157-5319 Ahtisham Younas 1 , 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7839-8130 Parveen Ali 3 , 4
- 1 Memorial University of Newfoundland , St John's , Newfoundland , Canada
- 2 Swat College of Nursing , Pakistan
- 3 School of Nursing and Midwifery , University of Sheffield , Sheffield , South Yorkshire , UK
- 4 Sheffield University Interpersonal Violence Research Group , Sheffield University , Sheffield , UK
- Correspondence to Ahtisham Younas, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St John's, NL A1C 5C4, Canada; ay6133{at}mun.ca
https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2021-103417
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research. 1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis in reviews, the use of literature summary tables is of utmost importance. A literature summary table provides a synopsis of an included article. It succinctly presents its purpose, methods, findings and other relevant information pertinent to the review. The aim of developing these literature summary tables is to provide the reader with the information at one glance. Since there are multiple types of reviews (eg, systematic, integrative, scoping, critical and mixed methods) with distinct purposes and techniques, 2 there could be various approaches for developing literature summary tables making it a complex task specialty for the novice researchers or reviewers. Here, we offer five tips for authors of the review articles, relevant to all types of reviews, for creating useful and relevant literature summary tables. We also provide examples from our published reviews to illustrate how useful literature summary tables can be developed and what sort of information should be provided.
Tip 1: provide detailed information about frameworks and methods
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Tabular literature summaries from a scoping review. Source: Rasheed et al . 3
The provision of information about conceptual and theoretical frameworks and methods is useful for several reasons. First, in quantitative (reviews synthesising the results of quantitative studies) and mixed reviews (reviews synthesising the results of both qualitative and quantitative studies to address a mixed review question), it allows the readers to assess the congruence of the core findings and methods with the adapted framework and tested assumptions. In qualitative reviews (reviews synthesising results of qualitative studies), this information is beneficial for readers to recognise the underlying philosophical and paradigmatic stance of the authors of the included articles. For example, imagine the authors of an article, included in a review, used phenomenological inquiry for their research. In that case, the review authors and the readers of the review need to know what kind of (transcendental or hermeneutic) philosophical stance guided the inquiry. Review authors should, therefore, include the philosophical stance in their literature summary for the particular article. Second, information about frameworks and methods enables review authors and readers to judge the quality of the research, which allows for discerning the strengths and limitations of the article. For example, if authors of an included article intended to develop a new scale and test its psychometric properties. To achieve this aim, they used a convenience sample of 150 participants and performed exploratory (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) on the same sample. Such an approach would indicate a flawed methodology because EFA and CFA should not be conducted on the same sample. The review authors must include this information in their summary table. Omitting this information from a summary could lead to the inclusion of a flawed article in the review, thereby jeopardising the review’s rigour.
Tip 2: include strengths and limitations for each article
Critical appraisal of individual articles included in a review is crucial for increasing the rigour of the review. Despite using various templates for critical appraisal, authors often do not provide detailed information about each reviewed article’s strengths and limitations. Merely noting the quality score based on standardised critical appraisal templates is not adequate because the readers should be able to identify the reasons for assigning a weak or moderate rating. Many recent critical appraisal checklists (eg, Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool) discourage review authors from assigning a quality score and recommend noting the main strengths and limitations of included studies. It is also vital that methodological and conceptual limitations and strengths of the articles included in the review are provided because not all review articles include empirical research papers. Rather some review synthesises the theoretical aspects of articles. Providing information about conceptual limitations is also important for readers to judge the quality of foundations of the research. For example, if you included a mixed-methods study in the review, reporting the methodological and conceptual limitations about ‘integration’ is critical for evaluating the study’s strength. Suppose the authors only collected qualitative and quantitative data and did not state the intent and timing of integration. In that case, the strength of the study is weak. Integration only occurred at the levels of data collection. However, integration may not have occurred at the analysis, interpretation and reporting levels.
Tip 3: write conceptual contribution of each reviewed article
While reading and evaluating review papers, we have observed that many review authors only provide core results of the article included in a review and do not explain the conceptual contribution offered by the included article. We refer to conceptual contribution as a description of how the article’s key results contribute towards the development of potential codes, themes or subthemes, or emerging patterns that are reported as the review findings. For example, the authors of a review article noted that one of the research articles included in their review demonstrated the usefulness of case studies and reflective logs as strategies for fostering compassion in nursing students. The conceptual contribution of this research article could be that experiential learning is one way to teach compassion to nursing students, as supported by case studies and reflective logs. This conceptual contribution of the article should be mentioned in the literature summary table. Delineating each reviewed article’s conceptual contribution is particularly beneficial in qualitative reviews, mixed-methods reviews, and critical reviews that often focus on developing models and describing or explaining various phenomena. Figure 2 offers an example of a literature summary table. 4
Tabular literature summaries from a critical review. Source: Younas and Maddigan. 4
Tip 4: compose potential themes from each article during summary writing
While developing literature summary tables, many authors use themes or subthemes reported in the given articles as the key results of their own review. Such an approach prevents the review authors from understanding the article’s conceptual contribution, developing rigorous synthesis and drawing reasonable interpretations of results from an individual article. Ultimately, it affects the generation of novel review findings. For example, one of the articles about women’s healthcare-seeking behaviours in developing countries reported a theme ‘social-cultural determinants of health as precursors of delays’. Instead of using this theme as one of the review findings, the reviewers should read and interpret beyond the given description in an article, compare and contrast themes, findings from one article with findings and themes from another article to find similarities and differences and to understand and explain bigger picture for their readers. Therefore, while developing literature summary tables, think twice before using the predeveloped themes. Including your themes in the summary tables (see figure 1 ) demonstrates to the readers that a robust method of data extraction and synthesis has been followed.
Tip 5: create your personalised template for literature summaries
Often templates are available for data extraction and development of literature summary tables. The available templates may be in the form of a table, chart or a structured framework that extracts some essential information about every article. The commonly used information may include authors, purpose, methods, key results and quality scores. While extracting all relevant information is important, such templates should be tailored to meet the needs of the individuals’ review. For example, for a review about the effectiveness of healthcare interventions, a literature summary table must include information about the intervention, its type, content timing, duration, setting, effectiveness, negative consequences, and receivers and implementers’ experiences of its usage. Similarly, literature summary tables for articles included in a meta-synthesis must include information about the participants’ characteristics, research context and conceptual contribution of each reviewed article so as to help the reader make an informed decision about the usefulness or lack of usefulness of the individual article in the review and the whole review.
In conclusion, narrative or systematic reviews are almost always conducted as a part of any educational project (thesis or dissertation) or academic or clinical research. Literature reviews are the foundation of research on a given topic. Robust and high-quality reviews play an instrumental role in guiding research, practice and policymaking. However, the quality of reviews is also contingent on rigorous data extraction and synthesis, which require developing literature summaries. We have outlined five tips that could enhance the quality of the data extraction and synthesis process by developing useful literature summaries.
- Aromataris E ,
- Rasheed SP ,
Twitter @Ahtisham04, @parveenazamali
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests None declared.
Patient consent for publication Not required.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
Advertisement
Low-carbon economy and policy implications: a systematic review and bibliometric analysis
- Research Article
- Published: 29 April 2022
- Volume 29 , pages 65432–65451, ( 2022 )
Cite this article

- Jingtian Wang 1 ,
- Yi Zhou 2 &
- Fang Lee Cooke 2
1643 Accesses
8 Citations
15 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
In the face of the rapid increase of carbon emissions, climate warming, and an epidemic situation, low-carbon economy is attracting growing attention. Using bibliometric analysis and machine learning methods, the paper conducts a systematic review in the low-carbon economy. Using the Web of Science Core Collection database, 1433 articles from 1990 to 2021 were selected for review. We find that the trajectories of the low-carbon economy research can be divided into four phases: exploration, fermentation, rising, and flourishing. The low-carbon economy research can be categorized into five clusters: low-carbon energy policy, carbon footprint and carbon trading, energy–economy–environment system, energy efficiency and its decomposition, and carbon emission drivers. The findings of this review study shed light on the role and effects of low-carbon economic policies on energy futures.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Mapping trends and knowledge structure of energy efficiency research: what we know and where we are going
The Effect of Energy Consumption on Economic Growth: a Scientometric Analysis

Review on carbon emissions, energy consumption and low-carbon economy in China from a perspective of global climate change
Data availability.
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Akef I, Arango JSM, Xu X (2016) Mallet vs GenSim: topic modeling for 20 news groups report. Univ Ark Little Rock Law J 2(19179):39205 (10.13140/RG)
Google Scholar
Ang BW, Zhang FQ, Choi KH (1998) Factorizing changes in energy and environmental indicators through decomposition. Energy 23(6):489–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-5442(98)00016-4
Article Google Scholar
Ang BW (2000) Decomposition analysis for policymaking in energy: which is the preferred method? Energy Policy 32(9):1131–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4215(03)00076-4
Ang BW, Zhang FQ (2004) A survey of index decomposition analysis in energy and environmental studies. Energy 25(12):1149–1176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-5442(00)00039-6
Ang BW (2005) The LMDI approach to decomposition analysis: a practical guide. Energy Policy 33(7):867–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2003.10.010
Ang JB (2007) CO2 emissions, energy consumption, and output in France. Energy Policy 35(10):4772–4778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2007.03.032
Babiker MH, Reilly JM, Mayer M, Eckaus RS, Sue Wing I, Hyman RC (2001) The MIT emissions prediction and policy analysis (EPPA) model: revisions, sensitivities, and comparisons of results.
Babiker MH, Metcalf GE, Reilly J (2003) Tax distortions and global climate policy. J Environ Econ Manag 46(2):269–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0095-0696(02)00039-6
Benavides C, Gonzales L, Diaz M, Fuentes R, Garcia G et al (2015) The Impact of a Carbon Tax on the Chilean Electricity Generation Sector. Energies 8(4):2674–2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8042674
Bhattacharya M, Paramati SR, Ozturk I, Bhattacharya S (2016) The effect of renewable energy consumption on economic growth: evidence from top 38 countries. Appl Energ 162:733–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.10.104
Braulio-Gonzalo M, Bovea MD (2020) Relationship between green public procurement criteria and sustainability assessment tools applied to office buildings. Environ Impact Asses 81:106310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2019.106310
Brookes G, McEnery T (2019) The utility of topic modelling for discourse studies: a critical evaluation. Discourse Stud 21(1):3–21. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461445618814032
Campiglio E (2016) Beyond carbon pricing: the role of banking and monetary policy in financing the transition to a low-carbon economy. Ecol Econ 121:220–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2015.03.020
Cao K, Xu X, Wu Q, Zhang Q (2017) Optimal production and carbon emission reduction level under cap-and-trade and low carbon subsidy policies. J Clean Prod 167:505–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.251
Capros P, Tasios N, De Vita A, Mantzos L, Paroussos L (2012a) Model-based analysis of decarbonising the EU economy in the time horizon to 2050. Energy Strateg Rev 1(2):76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2012.06.003
Capros P, Tasios N, De Vita A, Mantzos L, Paroussos L (2012b) Transformations of the energy system in the context of the decarbonisation of the EU economy in the time horizon to 2050. Energy Strateg Rev 1(2):85–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2012.06.001
Capros P, Paroussos L, Fragkos P, Tsani S, Boitier B et al (2014) European decarbonisation pathways under alternative technological and policy choices: A multi-model analysis. Energy Strateg Rev 2(3–4):231–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2013.12.007
Carron-Arthur B, Reynolds J, Bennett K, Bennett A, Griffiths KM (2016) What’s all the talk about? Topic modelling in a mental health Internet support group. BMC Psychiatry 16(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-016-1073-5
Charnes A, Cooper WW, Rhodes E (1978) Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur J Oper Res 2:429–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(78)90138-8
Chen C, Chen C (2003) Mapping scientific frontiers. Springer-Verlag, London, England
Chen ZM, Liu Y, Qin P, Zhang B, Lester L et al (2015) Environmental externality of coal use in China: welfare effect and tax regulation. Appl Energ 156:16–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.06.066
Chen K, Zhang Y, Fu X (2019) International research collaboration: an emerging domain of innovation studies? Res Policy 48(1):149–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2018.08.005
Choi Y, Zhang N, Zhou P (2012) Efficiency and abatement costs of energy-related CO2 emissions in China: a slacks-based efficiency measure. Appl Energ 98:198–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.03.024
Cojoianu TF, Clark GL, Hoepner AG, Veneri P, Wójcik D (2020) Entrepreneurs for a low carbon world: how environmental knowledge and policy shape the creation and financing of green start-ups. Res Policy 49(6):103988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2020.103988
Cui LB, Fan Y, Zhu L, Bi QH (2014) How will the emissions trading scheme save cost for achieving China’s 2020 carbon intensity reduction target? Appl Energy 136, 1043–1052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.05.021
Dai S, Duan X, Zhang W (2020) Knowledge map of environmental crisis management based on keywords network and co-word analysis, 2005–2018. J Clean Prod 262:121168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121168
Dantu R, Dissanayake I, Nerur S (2021) Exploratory analysis of internet of things (IoT) in healthcare: a topic modelling & co-citation approaches. Inform Syst Manage 38(1):62–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/10580530.2020.1746982
Dietz T, Rosa EA (1994) Rethinking the environmental impacts of population, affluence, and technology. Hum Ecol Rev 1(2):277–300
Dutta A (2018) Modeling and forecasting the volatility of carbon emission market: The role of outliers, time-varying jumps and oil price risk. J Clean Prod 172:2773–2781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.135
Du L, Li X, Zhao H, Ma W, Jiang P (2018) System dynamic modeling of urban carbon emissions based on the regional National Economy and Social Development Plan: A case study of Shanghai city. J Clean Prod 172:1501–1513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.128
Department of Trade and Industry, U. K (2003) Our energy future — creating a low carbon economy. The Stationery Office. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/our-energy-future-creating-a-low-carbon-economy
Ehrilich PR, Holdren JP (1971) Impact of population growth. Science 171(3977):1212–1217
Fan D, Lo CK, Ching V, Kan CW (2014) Occupational health and safety issues in operations management: a systematic and citation network analysis review. Int J Prod Econ 158:334–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2014.07.025
Fang K, Dong L, Ren J, Zhang Q, Han L, Fu H (2017) Carbon footprints of urban transition: Tracking circular economy promotions in Guiyang, China. Ecol Model 365:30–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2017.09.024
Foxon TJ (2011) A coevolutionary framework for analysing a transition to a sustainable low carbon economy. Ecol Econ 70(12):2258–2267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2011.07.014
Gabrielatos C, Baker P (2008) Fleeing, sneaking, flooding: a corpus analysis of discursive constructions of refugees and asylum seekers in the UK press, 1996–2005. J Engl Linguist 36:5–38. https://doi.org/10.1177/0075424207311247
Geels FW (2002) Technological transitions as evolutionary reconfiguration processes: a multi-level perspective and a case-study. Res Policy 31(8–9):1257–1274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-7333(02)00062-8
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic Growth and the Environment. Q J Econ 110(2):353–377. https://doi.org/10.2307/2118443
Gomi K, Shimada K, Matsuoka Y (2010) A low-carbon scenario creation method for a local-scale economy and its application in Kyoto city. Energy Policy 38(9):4783–4796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.07.026
Goulder LH (1995) Environmental taxation and the double dividend: a reader’s guide. Int Tax Public Finan 2:157–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00877495
Goulder LH, Schneider SH (1999) Induced technological change and the attractiveness of CO2 abatement policies. Resour Energy Econ 21(3–4):211–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0928-7655(99)00004-4
Hache E, Palle A (2019) Renewable energy source integration into power networks, research trends and policy implications: a bibliometric and research actors survey analysis. Energy Policy 124:23–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.09.036
Halicioglu F (2009) An econometric study of CO2 emissions, energy consumption, income and foreign trade in Turkey. Energy Policy 37:1156–1164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2008.11.012
Hu JL, Wang SC (2006) Total-Factor Energy Efficiency of Regions in China. Energy Policy 34:3206–3217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2005.06.015
Hu Z, Yuan J, Hu Z (2011) Study on China’s low carbon development in an Economy–Energy–Electricity–Environment framework. Energy Policy 39(5):2596–2605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2011.02.028
Ji CJ, Li XY, Hu YJ, Wang XY, Tang BJ (2019) Research on carbon price in emissions trading scheme: a bibliometric analysis. Nat Hazards 99(3):1381–1396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3433-6
Jiang B, Sun ZQ, Liu MQ (2010) China’s energy development strategy under the low-carbon economy. Energy 35(11):4257–4264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2009.12.040
Jiang K, Ashworth P (2021) The development of carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS) research in China: a bibliometric perspective. Renew Sust Energ Rev 138:110521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110521
Article CAS Google Scholar
Kawase R, Matsuoka Y, Fujino J (2006) Decomposition analysis of CO2 emission in long-term climate stabilization scenarios. Energy Policy 34(15):2113–2122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2005.02.005
Kaya Y (1989) Impact of carbon dioxide emission on gnp growth: interpretation of proposed scenarios; presentation to the energy and industry subgroup; Response Strategies Working Group. IPCC: Paris, France, pp 1–25
Kern F, Rogge KS, Howlett M (2019) Policy mixes for sustainability transitions: new approaches and insights through bridging innovation and policy studies. Res Policy 48(10):103832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2019.103832
Leontief W (1970) Environmental repercussions and the economic structure: an input-output approach. Rev Econ Stat 52(3):262–271. https://doi.org/10.2307/1926294
Li B, Hu K, Lysenko V, Khan KY, Wang Y, Jiang Y, Guo Y (2022) A scientometric analysis of agricultural pollution by using bibliometric software VoSViewer and Histcite™. Environ Sci Pollut R 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18491-w
Li H, Bao Q, Ren X, Xie Y, Ren J, Yang Y (2017) Reducing rebound effect through fossil subsidies reform: a comprehensive evaluation in China. J Clean Prod 141:305–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.09.108
Li W, Zhang YW, Lu C (2018) The impact on electric power industry under the implementation of national carbon trading market in China: a dynamic CGE analysis. J Clean Prod 200:511–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.325
Lin B, Xu M (2019) Good subsidies or bad subsidies? Evidence from low-carbon transition in China’s metallurgical industry. Energy Econ 83:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2019.06.015
Liu X, Ishikawa M, Wang C, Dong Y, Liu W (2010) Analyses of CO2 emissions embodied in Japan-China trade. Energy Policy 38(3):1510–1518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.11.034
Lyu XH, Shi A, Wang X (2020) Research on the impact of carbon emission trading system on low-carbon technology innovation. Carbon Manag 11(2):183–193. https://doi.org/10.1080/17583004.2020.1721977
Mathews JA (2008) How carbon credits could drive the emergence of renewable energies. Energy Policy 36(10):3633–3639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2008.05.033
Mallapaty S (2020) How China could be carbon neutral by mid-century. Nature 586(7830):482–483. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-02927-9
McFarland JR, Reilly JM, Herzog HJ (2004) Representing energy technologies in top-down economic models using bottom-up information. Energy Econ 26(4):685–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2004.04.026
Meng L, Guo JE, Chai J, Zhang Z (2011) China’s regional CO2 emissions: characteristics, inter-regional transfer and emission reduction policies. Energy Policy 39(10):6136–6144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2011.07.013
Meng S, Siriwardana M, McNeill J (2013) The environmental and economic impact of the carbon tax in Australia. Environ Resour Econ 54:313–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-012-9600-4
Meng XC, Seong YH, Lee MK (2021) Research characteristics and development trend ofgGlobal low-carbon power—based on bibliometric analysis of 1983–2021. Energies 14(16):4983. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14164983
Miles MB, Huberman AM (1994) Qualitative data analysis. Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA
Niknejad N, Nazari B, Foroutani S, Hussin ARBC (2022) A bibliometric analysis of green technologies applied to water and wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Pollut R 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18705-1
Nong D, Meng S, Siriwardana M (2017) An assessment of a proposed ETS in Australia by using the MONASH-Green model. Energy Policy 108:281–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.06.004
Nwaobi GC (2004) Emission policies and the Nigerian economy: simulations from a dynamic applied general equilibrium model. Energ Econ 26(5):921–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2004.04.003
OECD (2002) Indicators to measure decoupling of environmental pressure from economic growth. OECD, Paris
Omoregbe O, Mustapha AN, Steinberger-Wilckens R, El-Kharouf A, Onyeaka H (2020) Carbon capture technologies for climate change mitigation: a bibliometric analysis of the scientific discourse during 1998–2018. Energy Rep 6:1200–1212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2020.05.003
Paltsev SV (2001) The Kyoto Protocol: Regional and sectoral contributions to the carbon leakage. Energ J 22(4):53–79. https://doi.org/10.5547/ISSN0195-6574-EJ-Vol22-No4-3
Peng Y, Bai X (2018) Experimenting towards a low-carbon city: Policy evolution and nested structure of innovation. J Clean Prod 174:201–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.116
Pritchard A (1969) Statistical Bibliography or Bibliometrics. J Doc 25(4):348–349
Reuveny R (2007) Climate change-induced migration and violent conflict. Polit Geogr 26:656–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polgeo.2007.05.001
Roughgarden T, Schneider SH (1999) Climate change policy: quantifying uncertainties for damages and optimal carbon taxes. Energy Policy 27(7):415–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4215(99)00030-0
Sandoval R, Karplus VJ, Paltsev S, Reilly JM (2009) Modelling prospects for hydrogen-powered transportation until 2100. J Transp Econ Policy 43(3):291–316
Schandl H, Hatfield-Dodds S, Wiedmann T, Geschke A, Cai Y et al (2016) Decoupling global environmental pressure and economic growth: scenarios for energy use, materials use and carbon emissions. J Clean Prod 132:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.06.100
Schneider M, Holzer A, Hoffmann VH (2008) Understanding the CDM’s contribution to technology transfer. Energy Policy 36(8):2930–2938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2008.04.009
Schroeder PM, Chapman RB (2014) Renewable energy leapfrogging in China’s urban development? Current status and outlook. Sustain Cities Soc 11:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2013.11.007
Shang T, Yang L, Liu P, Shang K, Zhang Y (2020) Financing mode of energy performance contracting projects with carbon emissions reduction potential and carbon emissions ratings. Energy Policy 144:111632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111632
Shimada K, Tanaka Y, Gomi K, Matsuoka Y (2007) Developing a long-term local society design methodology towards a low-carbon economy: an application to Shiga Prefecture in Japan. Energy Policy 35(9):4688–4703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2007.03.025
Simoes S, Nijs W, Ruiz P, Sgobbi A, Thiel C (2017) Comparing policy routes for low-carbon power technology deployment in EU-an energy system analysis. Energy Policy 101:353–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.10.006
Small H (1973) Co-citation in the scientific literature: A new measure of the relationship between two documents. J Am Soc Inf Sci Tec 24(4):265–269. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.4630240406
Su M, Liang C, Chen B, Chen S, Yang Z (2012) Low-carbon development patterns: observations of typical Chinese cities. Energies 5(2):291–304. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5020291
Tang KY, Chang CY, Hwang GJ (2021) Trends in artificial intelligence-supported e-learning: a systematic review and co-citation network analysis (1998-2019). Interact Learn Envir 1-19. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2021.1875001
Tapio P (2005) Towards a theory of decoupling: degree of decoupling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finland between 1970 and 2001. Transp Policy 12(2):137–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2005.01.001
Timilsina GR (2009) Carbon tax under the clean development mechanism: a unique approach for reducing greenhouse gas emissions in developing countries. Clim Policy 9(2):139–154. https://doi.org/10.3763/cpol.2008.0546
Unruh GC (2000) Understanding carbon lock-in. Energy Policy 28(12):817–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4215(00)00070-7
Unruh GC (2002) Escaping carbon lock-in. Energy Policy 30(4):317–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4215(01)00098-2
Uyterlinde MA, Junginger M, de Vries HJ, Faaij AP, Turkenburg WC (2007) Implications of technological learning on the prospects for renewable energy technologies in Europe. Energy Policy 35(8):4072–4087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2007.02.004
Verbruggen A (2008) Renewable and nuclear power: A common future? Energy Policy 36(11):4036–4047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2008.06.024
Verbruggen A, Lauber V (2009) Basic concepts for designing renewable electricity support aiming at a full-scale transition by 2050. Energy Policy 37(12):5732–5743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.08.044
Viola L, Verheul J (2020) Mining ethnicity: discourse-driven topic modelling of immigrant discourses in the USA, 1898–1920. Digit Scholarsh Hum 35(4):921–943. https://doi.org/10.1093/llc/fqz068
Wang P, Wu W, Zhu B, Wei Y (2013a) Examining the impact factors of energy-related CO2 emissions using the STIRPAT model in Guangdong Province, China. Appl Energ 106:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.01.036
Wang S, Fang C, Ma H, Wang Y, Qin J (2014) Spatial differences and multi-mechanism of carbon footprint based on GWR model in provincial China. J Geogr Sci 24(4):612–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-014-1109-z
Wang T, Watson J (2010) Scenario analysis of China’s emissions pathways in the 21st century for low carbon transition. Energy Policy 38(7):3537–3546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2010.02.031
Wang X, Zhu Y, Sun H, Jia F (2018) Production decisions of new and remanufactured products: implications for low carbon emission economy. J Clean Prod 171:1225–1243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.053
Wang Y, Zhao H, Li L, Liu Z, Liang S (2013b) Carbon dioxide emission drivers for a typical metropolis using input–output structural decomposition analysis. Energy Policy 58:312–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2013.03.022
Wang L, Zhao L, Mao G, Zuo J, Du H (2017) Way to accomplish low carbon development transformation: a bibliometric analysis during 1995–2014. Renew Sust Energ Rev 68:57–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.08.021
Weber G, Cabras I (2017) The transition of Germany’s energy production, green economy, low-carbon economy, socio-environmental conflicts, and equitable society. J Clean Prod 167:1222–1231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.223
Wing IS (2006) The synthesis of bottom-up and top-down approaches to climate policy modeling: electric power technologies and the cost of limiting US CO2 emissions. Energy Policy 34(18):3847–3869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2005.08.027
Wissema W, Dellink R (2007) AGE analysis of the impact of a carbon energy tax on the Irish economy. Ecol Econ 61(4):671–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2006.07.034
Xu M, Lin B, Wang S (2021) Towards energy conservation by improving energy efficiency? Evidence from China’s Metallurgical Industry Energy 216:119255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.119255
Yan Z, Du K, Yang Z, Deng M (2017) Convergence or divergence? Understanding the global development trend of low-carbon technologies. Energy Policy 109:499–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.07.024
Yin H, Zhao J, Xi X, Zhang Y (2019) Evolution of regional low-carbon innovation systems with sustainable development: an empirical study with big-data. J Clean Prod 209:1545–1563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.001
Ying D, Chowdhury GG, Foo S (2001) Bibliometric cartography of information retrieval research by using co-word analysis. Inform Process Manag 37(6):817–842. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-4573(00)00051-0
York R, Rosa EA, Dietz T (2003) STIRPAT, IPAT and ImPACT: analytic tools for unpacking the driving forces of environmental impacts. Ecol Econ 46(3):351–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8009(03)00188-5
Yu H, Wei YM, Tang BJ, Mi Z, Pan SY (2016) Assessment on the research trend of low-carbon energy technology investment: a bibliometric analysis. Appl Energ 184:960–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.07.129
Zeng DZ, Cheng L, Shi L, Luetkenhorst W (2021) China’s green transformation through eco-industrial parks. World Dev 140:105249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2020.105249
Zhang J, Zeng W, Wang J, Yang F, Jiang H (2017) Regional low-carbon economy efficiency in China: analysis based on the Super-SBM model with CO2 emissions. J Clean Prod 163:202–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.06.111
Zhang N, Wang B, Liu Z (2016a) Carbon emissions dynamics, efficiency gains, and technological innovation in China’s industrial sectors. Energy 99:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.01.012
Zhang Y, Da Y (2015) The decomposition of energy-related carbon emission and its decoupling with economic growth in China. Renew Sust Energ Rev 41:1255–1266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.09.021
Zhang Z (2010) China in the transition to a low-carbon economy. Energy Policy 38(11):6638–6653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2010.06.034
Zhang K, Wang Q, Liang QM, Chen H (2016b) A bibliometric analysis of research on carbon tax from 1989 to 2014. Renew Sust Energ Rev 58:297–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.089
Zhen W, Qin Q, Kuang Y, Huang N (2017) Investigating low-carbon crop production in Guangdong Province, China (1993–2013): A decoupling and decomposition analysis. J Clean Prod 146:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.022
Zhou P, Ang BW, Han JY (2010) Total factor carbon emission performance: a Malmquist index analysis. Energ Econ 32:194–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2009.10.003
Zhou X, Zhang J, Li J (2013) Industrial structural transformation and carbon dioxide emissions in China. Energy Policy 57:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.07.01
Zhou X, Tao X, Rahman MM, Zhang J (2017) Coupling topic modelling in opinion mining for social media analysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Web Intelligence 533–540. https://doi.org/10.1145/3106426.3106459
Download references
This article is an outcome of a project funded by the Woodside Monash Energy Partnership- WMEP-IT-2A-001.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Applied Economics, Renmin University, Beijing, China
Jingtian Wang
Department of Management, Monash University, Monash, Australia
Yi Zhou & Fang Lee Cooke
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The inception of the paper stemmed from a project: ‘Low Carbon Economy: A Multi-Level and Multi-Disciplinary Analysis of the Role of Stakeholders’ funded by the Woodside Monash Energy Partnership and led by Fang Lee Cooke. All authors contributed to the conception and design of the paper. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Jingtian Wang under the guidance of Yi Zhou and Fang Lee Cooke. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Jingtian Wang. Yi Zhou and Fang Lee Cooke provided advice on the draft and revised sections of the manuscript. All authors participated in revisions of the manuscript and read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jingtian Wang .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Roula Inglesi-Lotz
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Explanation of the criteria and rationale.
Criterion 1: We follow previous literature reviews (e.g., Fan et al, 2014 and Li et al. 2022 ) to only include publications in ‘articles’ type in our analysis because they are peer-reviewed research papers. They had rigorous review processes to make sure the research findings are robust. We only include publications in English as integrating multiple languages is a big challenge for doing the bibliometric analysis (Li et al. 2022 and Niknejad et al. 2022 ). First, the software that we use to do the bibliometric analysis can only process one language at a time. Second, transferring the research papers from other languages to English may cause interpretation and copyrights problems. Third, the citation information may not be used as they are in different languages. Although we only include publications in English, we do not exclude scholars in a specific area as the Web of Science Core Collection platform collects the relevant research of scholars all over the world.
Criterion 2: According to our research theme, we identify the research categories that are highly related to low-carbon economies such as economics, international relations, public environmental occupational health, business, public administration, ethics, urban studies, law, development studies, social sciences inte-discipline, political science, and social issues.
Criterion 3: We carefully reviewed each literature and captured the antecedents, strategies, aspects, and outcomes of each literature to ensure that the research topics have implications for low-carbon economy and its transformation. Discrepancies were resolved through back-and-forth discussions until we reached an agreement on which studies should be included.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Wang, J., Zhou, Y. & Cooke, F.L. Low-carbon economy and policy implications: a systematic review and bibliometric analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29 , 65432–65451 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20381-0
Download citation
Received : 25 November 2021
Accepted : 18 April 2022
Published : 29 April 2022
Issue Date : September 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20381-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Bibliometrics
- Energy policy
- Low-carbon economy
- Machine learning
- Systematic review
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
MIT Technology Review
- Newsletters
OpenAI’s new GPT-4o lets people interact using voice or video in the same model
The company’s new free flagship “omnimodel” looks like a supercharged version of assistants like Siri or Alexa.
- James O'Donnell archive page

OpenAI just debuted GPT-4o, a new kind of AI model that you can communicate with in real time via live voice conversation, video streams from your phone, and text. The model is rolling out over the next few weeks and will be free for all users through both the GPT app and the web interface, according to the company. Users who subscribe to OpenAI’s paid tiers, which start at $20 per month, will be able to make more requests.
OpenAI CTO Mira Murati led the live demonstration of the new release one day before Google is expected to unveil its own AI advancements at its flagship I/O conference on Tuesday, May 14.
GPT-4 offered similar capabilities, giving users multiple ways to interact with OpenAI’s AI offerings. But it siloed them in separate models, leading to longer response times and presumably higher computing costs. GPT-4o has now merged those capabilities into a single model, which Murati called an “omnimodel.” That means faster responses and smoother transitions between tasks, she said.
The result, the company’s demonstration suggests, is a conversational assistant much in the vein of Siri or Alexa but capable of fielding much more complex prompts.
“We’re looking at the future of interaction between ourselves and the machines,” Murati said of the demo. “We think that GPT-4o is really shifting that paradigm into the future of collaboration, where this interaction becomes much more natural.”
Barret Zoph and Mark Chen, both researchers at OpenAI, walked through a number of applications for the new model. Most impressive was its facility with live conversation. You could interrupt the model during its responses, and it would stop, listen, and adjust course.
OpenAI showed off the ability to change the model’s tone, too. Chen asked the model to read a bedtime story “about robots and love,” quickly jumping in to demand a more dramatic voice. The model got progressively more theatrical until Murati demanded that it pivot quickly to a convincing robot voice (which it excelled at). While there were predictably some short pauses during the conversation while the model reasoned through what to say next, it stood out as a remarkably naturally paced AI conversation.
The model can reason through visual problems in real time as well. Using his phone, Zoph filmed himself writing an algebra equation (3 x + 1 = 4) on a sheet of paper, having GPT-4o follow along. He instructed it not to provide answers, but instead to guide him much as a teacher would.
“The first step is to get all the terms with x on one side,” the model said in a friendly tone. “So, what do you think we should do with that plus one?”
Like previous generations of GPT, GPT-4o will store records of users’ interactions with it, meaning the model “has a sense of continuity across all your conversations,” according to Murati. Other new highlights include live translation, the ability to search through your conversations with the model, and the power to look up information in real time.
As is the nature of a live demo, there were hiccups and glitches. GPT-4o’s voice might jump in awkwardly during the conversation. It appeared to comment on one of the presenters’ outfits even though it wasn’t asked to. But it recovered well when the demonstrators told the model it had erred. It seems to be able to respond quickly and helpfully across several mediums that other models have not yet merged as effectively.
Previously, many of OpenAI’s most powerful features, like reasoning through image and video, were behind a paywall. GPT-4o marks the first time they’ll be opened up to the wider public, though it’s not yet clear how many interactions you’ll be able to have with the model before being charged. OpenAI says paying subscribers will “continue to have up to five times the capacity limits of our free users.”
Additional reporting by Will Douglas Heaven.
Artificial intelligence
Sam altman says helpful agents are poised to become ai’s killer function.
Open AI’s CEO says we won’t need new hardware or lots more training data to get there.
Is robotics about to have its own ChatGPT moment?
Researchers are using generative AI and other techniques to teach robots new skills—including tasks they could perform in homes.
- Melissa Heikkilä archive page
What’s next for generative video
OpenAI's Sora has raised the bar for AI moviemaking. Here are four things to bear in mind as we wrap our heads around what's coming.
- Will Douglas Heaven archive page
An AI startup made a hyperrealistic deepfake of me that’s so good it’s scary
Synthesia's new technology is impressive but raises big questions about a world where we increasingly can’t tell what’s real.
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from mit technology review.
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.
Thank you for submitting your email!
It looks like something went wrong.
We’re having trouble saving your preferences. Try refreshing this page and updating them one more time. If you continue to get this message, reach out to us at [email protected] with a list of newsletters you’d like to receive.
Atomic structure of the passive oxide film formed on iron
We have used x-ray scattering to measure the structure of the passive oxide film formed at high anodic potentials on Fe(110) and Fe(001). The crystalline film has a small crystallite size (≈ 50Å) and is oriented with the substrate. The film structure is based on Fe3O4, but with cation vacancies on octahedral and tetrahedral sites (80% and 66% occupancies, respectively) and with cations occupying octahedral interstitial sites (12% occupancy). These results resolve the long-standing controversy surrounding the film structure and provide a basis for understanding and modeling film properties important for corrosion resistance. © 1997 American Physical Society.
- Publication
- Michael F. Toney
- Alison J. Davenport
- Lucy J. Oblonsky
- Mary P. Ryan
- Carissima M. Vitus
X-ray scattering studies of the passive oxide film formed on iron
In situ surface x-ray scattering measurements of electrochemically deposited bi on ag(111): structure, compressibility, and comparison with ex situ low-energy electron diffraction measurements, x-ray depth profiling of iron oxide thin films.

Press Releases

COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Research Summary. Definition: A research summary is a brief and concise overview of a research project or study that highlights its key findings, main points, and conclusions. It typically includes a description of the research problem, the research methods used, the results obtained, and the implications or significance of the findings.
A research summary is a brief yet concise version of the research paper for a targeted audience. Read more to find out about structure of a research summary, tips to write a good research summary, and common mistakes to write a research summary. ... Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences. Sumalatha G, Nikhil ...
Annotated Bibliographies. Annotated bibliographies can help you clearly see and understand the research before diving into organizing and writing your literature review. Although typically part of the "summarize" step of the literature review, annotations should not merely be summaries of each article - instead, they should be critical ...
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review. As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications.
A research article usually has seven major sections: Title, Abstract, Introduction, Method, Results, Discussion, and References. The first thing you should do is to decide why you need to summarize the article. If the purpose of the summary is to take notes to later remind yourself about the article you may want to write a longer summary ...
Use these relevant models to determine: 1. What you are studying 2. The perspective you are taking 3. The field(s) that are relevant. STEP TWO: SEARCH THE LITERATURE. Define the Scope Search the Literature Analyze the Literature Synthesize the Literature Write the Review.
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
A literature review is defined as "a critical analysis of a segment of a published body of knowledge through summary, classification, and comparison of prior research studies, reviews of literature, and theoretical articles." (The Writing Center University of Winconsin-Madison 2022) A literature review is an integrated analysis, not just a summary of scholarly work on a specific topic.
Think about structuring your review like an inverted pyramid. Put the most important information at the top, followed by details and examples in the center, and any additional points at the very bottom. Here's how your outline might look: 1. Summary of the research and your overall impression. In your own words, summarize what the manuscript ...
This is why the literature review as a research method is more relevant than ever. Traditional literature reviews often lack thoroughness and rigor and are conducted ad hoc, rather than following a specific methodology. Therefore, questions can be raised about the quality and trustworthiness of these types of reviews.
A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the ...
What is a literature review? Definition: A literature review is a systematic examination and synthesis of existing scholarly research on a specific topic or subject. Purpose: It serves to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge within a particular field. Analysis: Involves critically evaluating and summarizing key findings, methodologies, and debates found in ...
A literature review is a surveys scholarly articles, books and other sources relevant to a particular. issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, providing a description, summary, and ...
When writing a summary, the goal is to compose a concise and objective overview of the original article. The summary should focus only on the article's main ideas and important details that support those ideas. Guidelines for summarizing an article: State the main ideas. Identify the most important details that support the main ideas.
A literature review is a comprehensive summary of previous research on a topic. The literature review surveys scholarly articles, books, and other sources relevant to a particular area of research. The review should enumerate, describe, summarize, objectively evaluate and clarify this previous research. It should give a theoretical base for the ...
Include this information when writing up the method for your review. 5 Look for previous reviews on the topic. Use them as a springboard for your own review, critiquing the earlier reviews, adding more recently published material, and pos-sibly exploring a different perspective. Exploit their refer-ences as another entry point into the literature.
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research.1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis ...
Many research disciplines feature high-impact journals that are dedicated outlets for review papers (or review-conceptual combinations) (e.g., Academy of Management Review, Psychology Bulletin, Medicinal Research Reviews).The rationale for such outlets is the premise that research integration and synthesis provides an important, and possibly even a required, step in the scientific process.
A literature review is a description, summary, and critical evaluation of scholarly works on a certain topic. A literature review combines both summary ... underpinning your research. Argumentative review: This type of literature review examines literature in a selective way in order to address a specific argument, assumption, or philosophical ...
In the face of the rapid increase of carbon emissions, climate warming, and an epidemic situation, low-carbon economy is attracting growing attention. Using bibliometric analysis and machine learning methods, the paper conducts a systematic review in the low-carbon economy. Using the Web of Science Core Collection database, 1433 articles from 1990 to 2021 were selected for review. We find that ...
Founded at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1899, MIT Technology Review is a world-renowned, independent media company whose insight, analysis, reviews, interviews and live events ...
Background: Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors represent a novel class of oral therapies showing efficacy in treating ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD), challenging conventional treatment paradigms. Summary: This review provides an overview of the potential novel uses of JAK inhibitors, focusing on their current approved indications and exploring possibilities beyond these indications.
We have used x-ray scattering to measure the structure of the passive oxide film formed at high anodic potentials on Fe (110) and Fe (001). The crystalline film has a small crystallite size (≈ 50Å) and is oriented with the substrate. The film structure is based on Fe3O4, but with cation vacancies on octahedral and tetrahedral sites (80% and ...
A New Look at the Free Trade Area of the Asia-Pacific (FTAAP): Review of APEC's Collective Progress. Published Date: May 2024: Type of Publication: Reports: Publication Under: APEC Secretariat, APEC Policy Support Unit: Accessed: 155: ... Research Outcomes: Summary of Research Projects 2023. Accessed: 149 Published Date: April 2024 Type ...
Washington, D.C. - The U.S. House of Representatives today approved the FAA Reauthorization Act of 2024 (H.R. 3935) a comprehensive, bipartisan bill to reauthorize the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and aviation infrastructure and safety programs for five years, with broad bipartisan support in a 387-26 vote.. H.R. 3935 was first introduced in the House last year by Transportation and ...