Thesis Definition
A thesis is a statement in a non- fiction or a fiction work that a writer intends to support and prove. One can find examples of thesis statement at the beginning of literary pieces. These thesis statements are of utmost importance, as they provide clear indicators as to which direction the writer will follow in their work.
A thesis statement is carefully crafted by a writer, and is marked by vigilant selection of words that will never miss its target. Generally, such a statement shows up in the first paragraph, or what is called an introduction . Despite writers’ efforts to prove their thesis statements, not all of these statements can be verified for their exactness. Nevertheless, they do develop an argument .

Importance of a Thesis Statement
In writing an essay , a thesis statement determines the worth of the essay by its capacity to stay focused on its thesis statement. For instance, if a writer fails to clearly mention or define a solid thesis statement in his or her essay, it will be difficult for readers to track the issue the writer plans to discuss and explain. Suppose a writer wants to write an essay on how to make a perfect fruit salad, the quality of his or her writing will exceedingly improve if he or she lets the readers know the subject matter at the start of the essay, for example:
“In this essay, I will tell you how to make the perfect fruit salad. Not only will it be tasty, but also healthy for your body.”
Narrative Thesis
In a narrative essay, or narrative section of a piece of literature, a thesis statement is called a “narrative thesis.” A narrative thesis can be an apparent one or a hidden or implied one. In both cases, such a statement is a powerful, propelling force behind an entire work, that guides it toward its ultimate purpose and the lesson it intends to instruct.
Narrative Thesis Examples
Below is a list of a few narrative thesis examples – opening lines that determine the entire course of the narratives.
Example #1: Pride and Prejudice (By Jane Austen)
“It is a truth universally acknowledged that a single man in possession of a good fortune, must be in want of a wife.”
Example #2: One Hundred Years of Solitude (By Gabriel García Márquez)
“Many years later, as he faced the firing squad, Colonel Aureliano Buendía was to remember that distant afternoon when his father took him to discover ice.”
Example #3: Lolita (By Vladimir Nabokov)
“Lolita, light of my life, fire of my loins.”
Example #4: Anna Karenina (By Leo Tolstoy)
“Happy families are all alike; every unhappy family is unhappy in its own way.”
Example #5: 1984 (By George Orwell)
“It was a bright cold day in April, and the clocks were striking thirteen.”
Example #6: A Tale of Two Cities (By Charles Dickens)
“It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness , it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair.”
Example #7: The Catcher in the Rye (By J. D. Salinger)
“If you really want to hear about it, the first thing you’ll probably want to know is where I was born, and what my lousy childhood was like, and how my parents were occupied and all before they had me, and all that David Copperfield kind of crap, but I don’t feel like going into it, if you want to know the truth.”
Example #8: A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man (By James Joyce)
“Once upon a time and a very good time it was there was a moocow coming down along the road and this moocow that was coming down along the road met a nicens little boy named baby tuckoo.”
Function of Thesis
The above arguments clearly reveal the function of a thesis statements or a narrative thesis as a driving force behind a literary composition. It guides the narrative toward its ultimate purpose, which is the moral lesson it aims to inculcate.
Related posts:
- Thesis Statement
Post navigation

- Literary Terms
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write a Thesis
I. What is a Thesis?
The thesis (pronounced thee -seez), also known as a thesis statement, is the sentence that introduces the main argument or point of view of a composition (formal essay, nonfiction piece, or narrative). It is the main claim that the author is making about that topic and serves to summarize and introduce that writing that will be discussed throughout the entire piece. For this reason, the thesis is typically found within the first introduction paragraph.
II. Examples of Theses
Here are a few examples of theses which may be found in the introductions of a variety of essays :
In “The Mending Wall,” Robert Frost uses imagery, metaphor, and dialogue to argue against the use of fences between neighbors.
In this example, the thesis introduces the main subject (Frost’s poem “The Mending Wall”), aspects of the subject which will be examined (imagery, metaphor, and dialogue) and the writer’s argument (fences should not be used).
While Facebook connects some, overall, the social networking site is negative in that it isolates users, causes jealousy, and becomes an addiction.
This thesis introduces an argumentative essay which argues against the use of Facebook due to three of its negative effects.
During the college application process, I discovered my willingness to work hard to achieve my dreams and just what those dreams were.
In this more personal example, the thesis statement introduces a narrative essay which will focus on personal development in realizing one’s goals and how to achieve them.
III. The Importance of Using a Thesis
Theses are absolutely necessary components in essays because they introduce what an essay will be about. Without a thesis, the essay lacks clear organization and direction. Theses allow writers to organize their ideas by clearly stating them, and they allow readers to be aware from the beginning of a composition’s subject, argument, and course. Thesis statements must precisely express an argument within the introductory paragraph of the piece in order to guide the reader from the very beginning.
IV. Examples of Theses in Literature
For examples of theses in literature, consider these thesis statements from essays about topics in literature:
In William Shakespeare’s “ Sonnet 46,” both physicality and emotion together form powerful romantic love.
This thesis statement clearly states the work and its author as well as the main argument: physicality and emotion create romantic love.
In The Scarlet Letter, Nathaniel Hawthorne symbolically shows Hester Prynne’s developing identity through the use of the letter A: she moves from adulteress to able community member to angel.
In this example, the work and author are introduced as well as the main argument and supporting points: Prynne’s identity is shown through the letter A in three ways: adulteress, able community member, and angel.
John Keats’ poem “To Autumn” utilizes rhythm, rhyme, and imagery to examine autumn’s simultaneous birth and decay.
This thesis statement introduces the poem and its author along with an argument about the nature of autumn. This argument will be supported by an examination of rhythm, rhyme, and imagery.
V. Examples of Theses in Pop Culture
Sometimes, pop culture attempts to make arguments similar to those of research papers and essays. Here are a few examples of theses in pop culture:

America’s food industry is making a killing and it’s making us sick, but you have the power to turn the tables.
The documentary Food Inc. examines this thesis with evidence throughout the film including video evidence, interviews with experts, and scientific research.

Orca whales should not be kept in captivity, as it is psychologically traumatizing and has caused them to kill their own trainers.
Blackfish uses footage, interviews, and history to argue for the thesis that orca whales should not be held in captivity.
VI. Related Terms
Just as a thesis is introduced in the beginning of a composition, the hypothesis is considered a starting point as well. Whereas a thesis introduces the main point of an essay, the hypothesis introduces a proposed explanation which is being investigated through scientific or mathematical research. Thesis statements present arguments based on evidence which is presented throughout the paper, whereas hypotheses are being tested by scientists and mathematicians who may disprove or prove them through experimentation. Here is an example of a hypothesis versus a thesis:
Hypothesis:
Students skip school more often as summer vacation approaches.
This hypothesis could be tested by examining attendance records and interviewing students. It may or may not be true.
Students skip school due to sickness, boredom with classes, and the urge to rebel.
This thesis presents an argument which will be examined and supported in the paper with detailed evidence and research.
Introduction
A paper’s introduction is its first paragraph which is used to introduce the paper’s main aim and points used to support that aim throughout the paper. The thesis statement is the most important part of the introduction which states all of this information in one concise statement. Typically, introduction paragraphs require a thesis statement which ties together the entire introduction and introduces the rest of the paper.
VII. Conclusion
Theses are necessary components of well-organized and convincing essays, nonfiction pieces, narratives , and documentaries. They allow writers to organize and support arguments to be developed throughout a composition, and they allow readers to understand from the beginning what the aim of the composition is.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
When You Write
Do Short Stories Have A Thesis? The Answer May Surprise You
Did you know that short stories can have a thesis? It’s true! Many people assume that only longer works like novels and academic papers have central ideas, but short stories can pack a powerful punch with a clear message as well.
In fact, the brevity of a short story can make its thesis even more impactful. So, whether you’re a writer or a reader, it’s important to understand the potential for meaning and depth in short fiction.
As you dive into the world of short stories, you’ll discover that they come in many different forms and styles. Some are plot-driven, while others are character-driven. Some are lighthearted and humorous, while others are dark and brooding.
But no matter the genre or tone, a well-crafted short story will often have a central idea or theme that ties everything together. This might be a moral lesson, a commentary on society, or a personal reflection on the human experience.
So, get ready to explore the power of short stories and uncover the surprising world of thesis in bite-sized literature.
Key Takeaways
- Short stories have a central idea or theme that acts as a thesis for the story.
- The structure of a short story follows a simple pattern with an introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and conclusion.
- Short stories are different from longer works in their conciseness, focused themes, and reliance on reader interpretation.
- Short stories can be incredibly powerful and impactful, conveying deep meaning and leaving a lasting impression on readers.
Understanding the Structure of Short Stories
You might be wondering how short stories are structured, but don’t worry, it’s not as complicated as you may think!
Understanding the structure of a short story can help you better appreciate the narrative elements that make it a compelling read.
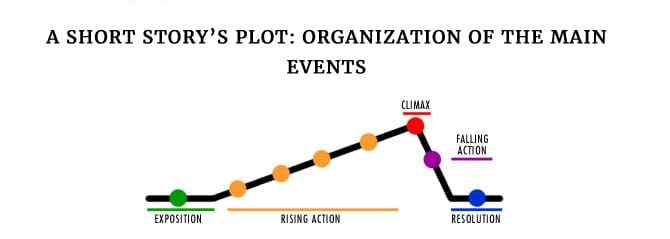
At its core, a short story typically follows a simple structure that includes an introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and conclusion.
The introduction sets the scene and introduces the characters, while the rising action builds tension and conflict.
The climax is the turning point of the story, where the conflict reaches its peak.
The falling action follows the climax and leads to the conclusion, where the conflict is resolved, and the story ends.
By understanding this structure, you can better appreciate the narrative elements of the story, such as the characters, setting, conflict, and resolution.
Examples of Short Stories with Central Ideas
So, you wanna explore some examples of short stories with central ideas? Well, let’s dive into Edgar Allan Poe’s haunting tale ‘The Tell-Tale Heart’. The narrator’s guilt over a murder drives him to confess.
Or perhaps you’re interested in Kate Chopin’s ‘The Story of an Hour’. It explores the complex emotions of a woman who learns of her husband’s death.
And let’s not forget Ernest Hemingway’s ‘Hills Like White Elephants’. It’s a powerful story about a couple’s struggle with a difficult decision.
These stories all have central ideas that drive the plot and leave a lasting impact on the reader.
Edgar Allan Poe’s “The Tell-Tale Heart”
Contrary to popular belief, Edgar Allan Poe’s short story ‘The Tell-Tale Heart’ does indeed have a clear and thought-provoking thesis statement. The story is not just a random collection of events, but a carefully crafted piece of literature that explores the psychological tension within the main character and the symbolism surrounding the old man’s eye.
To understand the thesis of ‘The Tell-Tale Heart’, it is essential to analyze the symbolism and characterization in the story. The narrator’s obsession with the old man’s vulture-like eye represents his own inner turmoil and guilt. The eye is a metaphor for the narrator’s conscience, which he ultimately destroys by murdering the old man.
Additionally, the characterization of the narrator as an unreliable and mentally unstable individual highlights the destructive power of guilt and obsession. These elements work together to convey Poe’s thesis that guilt and obsession can lead to madness and self-destruction.
Kate Chopin’s “The Story of an Hour”
If you’re looking for a compelling short story that delves into the complexities of human emotion, Kate Chopin’s ‘The Story of an Hour’ is a must-read, even if you may initially dismiss it as just another piece of feminist literature.
The story, written in 1894, follows the life of Mrs. Mallard, a woman who just received the news of her husband’s death. However, as the plot unfolds, we see that Mrs. Mallard’s reaction to her husband’s death is not what we would expect. Instead of being consumed by grief, she experiences a sense of liberation, freedom, and joy.
Chopin’s use of symbolism is evident throughout the story. For instance, the open window in Mrs. Mallard’s room represents the possibility of new beginnings and the chance to escape from the social constraints that were imposed on women during that time. Also, the heart disease that Mrs. Mallard suffers from is a metaphor for the emotional and psychological burden that society imposed on her.
The story provides a feminist perspective, as it highlights the limitations that were imposed on women in the 19th century and the possibility of freedom that they could experience when their husbands were no longer around.
Ernest Hemingway’s “Hills Like White Elephants”
You’ll feel like you’re eavesdropping on a couple’s conversation as you read Ernest Hemingway’s ‘Hills Like White Elephants’, set in a train station in Spain. The story revolves around a man and a woman who are discussing whether or not to undergo an abortion.
The author doesn’t explicitly state the topic of their conversation but rather uses symbolism to convey the message. The hills, the white elephant, and the train tracks all have a deeper meaning that adds to the complexity of the story.
A symbolism analysis reveals that the hills represent the woman’s pregnancy, the white elephant symbolizes the unwanted burden of having a child, and the train tracks symbolize the irreversible decision they are about to make.
As you read, you’ll notice that the woman’s motivation for wanting to keep the child stems from her desire to have a meaningful relationship with the man. However, the man’s motivation for wanting her to have an abortion is rooted in his fear of losing his freedom and his desire to continue living a carefree life.
The story ends abruptly, leaving the reader to draw their own conclusion about what decision the couple ultimately made. Hemingway’s use of symbolism and character motivation examination makes ‘Hills Like White Elephants’ a thought-provoking and memorable short story.
How Short Stories Differ from Longer Works
As you dive into a short story, you’ll find that it’s like a small gemstone, with all the facets of a larger work condensed and shining brilliantly in a compact space. Unlike longer works, short stories have to be concise in their storytelling techniques. They have to grab your attention quickly and keep it throughout the entire story.
Here are three ways that short stories differ from longer works:
- Short stories have a limited amount of time and space to convey their themes. This means that every sentence, every word, has to count. The author has to choose their words carefully to make sure that the story has impact.
- Short stories often have a more focused theme than longer works. While a novel may have multiple themes, a short story will usually have one central idea that it’s exploring. This means that the author can delve deep into that theme and explore it thoroughly.
- Short stories often leave more up to the reader’s interpretation than longer works. Because there isn’t as much room for exposition, the author has to rely on the reader to fill in some of the gaps. This can make the story more engaging, as the reader becomes an active participant in the story.
Overall, short stories are a unique and challenging form of storytelling. They require precision and focus, but when done well, they can be incredibly powerful. As you read more short stories, keep these differences in mind and see if you can spot them in action.
The Potential for Power and Impact in Short Stories
Short stories possess a unique potential for wielding powerful and impactful storytelling that can leave a lasting impression on readers. The power of brevity is a key aspect of short stories that allows authors to explore themes in a concise and effective manner.
Through carefully crafted characters, settings, and plotlines, short stories can pack a punch and leave readers with a sense of fulfillment that longer works may not achieve.
In addition, short stories allow for experimentation and innovation in storytelling. Authors can take risks and push boundaries, using their limited word count to their advantage. This leaves readers with a sense of excitement and anticipation as they never know what to expect from a short story.
Overall, the potential for power and impact in short stories should not be underestimated, as they have the ability to convey deep meaning and leave a lasting impression on their readers in a way that longer works may not.
Tips for Writing Short Stories with a Central Idea
If you want to craft a short story with a powerful central idea, consider using symbolism and imagery to allude to deeper meaning throughout your narrative. This can create tension and intrigue for your readers as they try to decipher the underlying message of your story.
For example, you could use a recurring object or color throughout the story that represents a certain theme or idea.
In addition to using symbolism, developing strong and dynamic characters is essential for a short story with a central idea. Your characters should be complex and multi-dimensional, with flaws and motivations that drive the plot forward.
By creating characters that readers can relate to, you can further emphasize the central idea of your story and make it more impactful. So, when crafting your short story, be intentional about the symbols and characters you use to convey your central idea.
You may have been skeptical at first, but hopefully you now understand how even the shortest of stories can pack a powerful punch with a clear message or theme.
With careful crafting and attention to detail, a writer can use the limited space of a short story to convey a complex idea or emotion. Imagine each word as a brushstroke on a canvas, creating a vivid image in the reader’s mind.
So, whether you’re a writer looking to hone your craft or a reader seeking thought-provoking stories, don’t overlook the potential of short fiction.
Within those few pages, you may just find a world of ideas waiting to be explored.
Recommended Reading...
Why short stories are important for readers and writers alike, why do authors use short stories the advantages of this genre, why are short stories so hard to write understanding the challenges, what is a novelette exploring the short story genre.
Keep in mind that we may receive commissions when you click our links and make purchases. However, this does not impact our reviews and comparisons. We try our best to keep things fair and balanced, in order to help you make the best choice for you.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
© 2024 When You Write

Literary Criticism
- Introduction
- Literary Theories
- Steps to Literary Criticism
- Find Resources
- Cite Sources
- thesis examples
SAMPLE THESIS STATEMENTS
These sample thesis statements are provided as guides, not as required forms or prescriptions.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________
The thesis may focus on an analysis of one of the elements of fiction, drama, poetry or nonfiction as expressed in the work: character, plot, structure, idea, theme, symbol, style, imagery, tone, etc.
In “A Worn Path,” Eudora Welty creates a fictional character in Phoenix Jackson whose determination, faith, and cunning illustrate the indomitable human spirit.
Note that the work, author, and character to be analyzed are identified in this thesis statement. The thesis relies on a strong verb (creates). It also identifies the element of fiction that the writer will explore (character) and the characteristics the writer will analyze and discuss (determination, faith, cunning).
Further Examples:
The character of the Nurse in Romeo and Juliet serves as a foil to young Juliet, delights us with her warmth and earthy wit, and helps realize the tragic catastrophe.
The works of ecstatic love poets Rumi, Hafiz, and Kabir use symbols such as a lover’s longing and the Tavern of Ruin to illustrate the human soul’s desire to connect with God.
The thesis may focus on illustrating how a work reflects the particular genre’s forms, the characteristics of a philosophy of literature, or the ideas of a particular school of thought.
“The Third and Final Continent” exhibits characteristics recurrent in writings by immigrants: tradition, adaptation, and identity.
Note how the thesis statement classifies the form of the work (writings by immigrants) and identifies the characteristics of that form of writing (tradition, adaptation, and identity) that the essay will discuss.
Further examples:
Samuel Beckett’s Endgame reflects characteristics of Theatre of the Absurd in its minimalist stage setting, its seemingly meaningless dialogue, and its apocalyptic or nihilist vision.
A close look at many details in “The Story of an Hour” reveals how language, institutions, and expected demeanor suppress the natural desires and aspirations of women.
The thesis may draw parallels between some element in the work and real-life situations or subject matter: historical events, the author’s life, medical diagnoses, etc.
In Willa Cather’s short story, “Paul’s Case,” Paul exhibits suicidal behavior that a caring adult might have recognized and remedied had that adult had the scientific knowledge we have today.
This thesis suggests that the essay will identify characteristics of suicide that Paul exhibits in the story. The writer will have to research medical and psychology texts to determine the typical characteristics of suicidal behavior and to illustrate how Paul’s behavior mirrors those characteristics.
Through the experience of one man, the Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, An American Slave, accurately depicts the historical record of slave life in its descriptions of the often brutal and quixotic relationship between master and slave and of the fragmentation of slave families.
In “I Stand Here Ironing,” one can draw parallels between the narrator’s situation and the author’s life experiences as a mother, writer, and feminist.
SAMPLE PATTERNS FOR THESES ON LITERARY WORKS
1. In (title of work), (author) (illustrates, shows) (aspect) (adjective).
Example: In “Barn Burning,” William Faulkner shows the characters Sardie and Abner Snopes struggling for their identity.
2. In (title of work), (author) uses (one aspect) to (define, strengthen, illustrate) the (element of work).
Example: In “Youth,” Joseph Conrad uses foreshadowing to strengthen the plot.
3. In (title of work), (author) uses (an important part of work) as a unifying device for (one element), (another element), and (another element). The number of elements can vary from one to four.
Example: In “Youth,” Joseph Conrad uses the sea as a unifying device for setting, structure and theme.
4. (Author) develops the character of (character’s name) in (literary work) through what he/she does, what he/she says, what other people say to or about him/her.
Example: Langston Hughes develops the character of Semple in “Ways and Means”…
5. In (title of work), (author) uses (literary device) to (accomplish, develop, illustrate, strengthen) (element of work).
Example: In “The Masque of the Red Death,” Poe uses the symbolism of the stranger, the clock, and the seventh room to develop the theme of death.
6. (Author) (shows, develops, illustrates) the theme of __________ in the (play, poem, story).
Example: Flannery O’Connor illustrates the theme of the effect of the selfishness of the grandmother upon the family in “A Good Man is Hard to Find.”
7. (Author) develops his character(s) in (title of work) through his/her use of language.
Example: John Updike develops his characters in “A & P” through his use of figurative language.
Perimeter College, Georgia State University, http://depts.gpc.edu/~gpcltc/handouts/communications/literarythesis.pdf
- << Previous: Cite Sources
- Next: Get Help >>
- Last Updated: May 10, 2024 3:27 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uta.edu/literarycriticism
University of Texas Arlington Libraries 702 Planetarium Place · Arlington, TX 76019 · 817-272-3000
- Internet Privacy
- Accessibility
- Problems with a guide? Contact Us.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Developing a Thesis

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Once you've read the story or novel closely, look back over your notes for patterns of questions or ideas that interest you. Have most of your questions been about the characters, how they develop or change?
For example: If you are reading Conrad's The Secret Agent , do you seem to be most interested in what the author has to say about society? Choose a pattern of ideas and express it in the form of a question and an answer such as the following: Question: What does Conrad seem to be suggesting about early twentieth-century London society in his novel The Secret Agent ? Answer: Conrad suggests that all classes of society are corrupt. Pitfalls: Choosing too many ideas. Choosing an idea without any support.
Once you have some general points to focus on, write your possible ideas and answer the questions that they suggest.
For example: Question: How does Conrad develop the idea that all classes of society are corrupt? Answer: He uses images of beasts and cannibalism whether he's describing socialites, policemen or secret agents.
To write your thesis statement, all you have to do is turn the question and answer around. You've already given the answer, now just put it in a sentence (or a couple of sentences) so that the thesis of your paper is clear.
For example: In his novel, The Secret Agent , Conrad uses beast and cannibal imagery to describe the characters and their relationships to each other. This pattern of images suggests that Conrad saw corruption in every level of early twentieth-century London society.
Now that you're familiar with the story or novel and have developed a thesis statement, you're ready to choose the evidence you'll use to support your thesis. There are a lot of good ways to do this, but all of them depend on a strong thesis for their direction.
For example: Here's a student's thesis about Joseph Conrad's The Secret Agent . In his novel, The Secret Agent , Conrad uses beast and cannibal imagery to describe the characters and their relationships to each other. This pattern of images suggests that Conrad saw corruption in every level of early twentieth-century London society. This thesis focuses on the idea of social corruption and the device of imagery. To support this thesis, you would need to find images of beasts and cannibalism within the text.

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
While Sandel argues that pursuing perfection through genetic engineering would decrease our sense of humility, he claims that the sense of solidarity we would lose is also important.
This thesis summarizes several points in Sandel’s argument, but it does not make a claim about how we should understand his argument. A reader who read Sandel’s argument would not also need to read an essay based on this descriptive thesis.
Broad thesis (arguable, but difficult to support with evidence)
Michael Sandel’s arguments about genetic engineering do not take into consideration all the relevant issues.
This is an arguable claim because it would be possible to argue against it by saying that Michael Sandel’s arguments do take all of the relevant issues into consideration. But the claim is too broad. Because the thesis does not specify which “issues” it is focused on—or why it matters if they are considered—readers won’t know what the rest of the essay will argue, and the writer won’t know what to focus on. If there is a particular issue that Sandel does not address, then a more specific version of the thesis would include that issue—hand an explanation of why it is important.
Arguable thesis with analytical claim
While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake” (54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well” (51) is less convincing.
This is an arguable analytical claim. To argue for this claim, the essay writer will need to show how evidence from the article itself points to this interpretation. It’s also a reasonable scope for a thesis because it can be supported with evidence available in the text and is neither too broad nor too narrow.
Arguable thesis with normative claim
Given Sandel’s argument against genetic enhancement, we should not allow parents to decide on using Human Growth Hormone for their children.
This thesis tells us what we should do about a particular issue discussed in Sandel’s article, but it does not tell us how we should understand Sandel’s argument.
Questions to ask about your thesis
- Is the thesis truly arguable? Does it speak to a genuine dilemma in the source, or would most readers automatically agree with it?
- Is the thesis too obvious? Again, would most or all readers agree with it without needing to see your argument?
- Is the thesis complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of argument?
- Is the thesis supportable with evidence from the text rather than with generalizations or outside research?
- Would anyone want to read a paper in which this thesis was developed? That is, can you explain what this paper is adding to our understanding of a problem, question, or topic?
- picture_as_pdf Thesis
- How It Works
- Prices & Discounts
Story Analysis: How to Analyze a Short Story Step-by-Step
Table of contents
Have there been times that you have read a short story in class and tried to analyze its meaning by deep-diving into the text to understand it better? If yes, this article is for you.
Short stories are relatively much shorter and less complex than most novels or plays. But that does not mean that they don’t require an in-depth analysis of what is written in the text and what messages the author of the book intends to convey to its readers.
In this article, you will learn how to analyze a short story step-by-step, along with the essential elements of a short story.
What are the Elements of a Short Story
In order to analyze a short story step-by-step, it is important to know the basics of story analysis. Let’s take a look at the five key elements of a short story.
Characters (both major and minor) are what bring life to a story. Writers use them to transcend important messages throughout the plotline.
Every character has a purpose, a particular personality, and a developmental arc. To analyze these characters for your short story, you must have the answer to the following questions:
- Who is the plotline’s protagonist?
- Do you have your antagonist? If yes, who is it? What antagonistic qualities do they have?
- Are the characters dynamic (changing) or static (unchanging)?
- How does the author describe the character's appearance, personality, mindset, and actions?
- What are your thoughts, feelings, or opinions about the characters?
- What is the relationship between all the characters?
People get invested in fictional characters, relate to them, and see them as real individuals with real personalities, going through real hardships in life.
That's the key motive of the author, and that's what needs to be analyzed.
Setting or Theme
The setting of a short story depicts the theme of the plot through key metaphors. It revolves around three important points:
- Circumstances
This also aids the flow of the plotline, distinguishes the characters, influences viewpoints, and creates an aura for your story.
Even if a story is placed in a historic time and place, from when and where it was originally written, it can influence the entire context of the narrative.
Many stories would seem different and altered if their original setting was changed completely and is thus very crucial in interpreting the concept of the story.
Thus, try to assess how the setting affects the story and how it motivates its characters. Analyze why the author has chosen this particular setting, how the readers respond to it, as well as if there’s any symbolic meaning behind it.
The plotline makes a story by giving it a pattern and a structure to the events that are about to happen. Identifying and analyzing these plotlines will help in giving insights into the explanation of the story.
In short stories, the plot is majorly centered around one important character and their actions, or around one key experience that impacts the story greatly.
Usually, a short story plot has one major storyline, unlike novels, which have multiple trajectories of storylines. Thus, short stories are easier to analyze.
Authors use symbolism to convey messages poetically or indirectly, through their stories, making them more interesting and complex pieces.
Symbolism is depicted using a physical object or even a person to be an abstract idea. For example, a dove represents love and peace and a storm represents hostility and turmoil.
Symbolism can also be used as a metaphor in the narrative, such as life is a roller coaster which portrays life to have its ups and downs.
Similarly, in short story novels, authors symbolize certain conflicts and important issues by using a metaphor or a simile in their story. For example, in Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar, the officials dismantled the coronations of Caesar's statues, foreshadowing their plan to topple him.
Lastly, the reason you are reading the short story is to identify what you have learned from it and what the moral of the narrative is.
Even though short story novels are crisp, interesting, and entertaining, there is always a life lesson behind each of them. This moral is implied to help the readers understand the author’s perspective, what they want to convey, and what lesson you should learn from the text.
How to Analyze a Short Story Step-by-Step
Now that we know the major elements that are involved in crafting an exceptional story analysis, let's take a look at five tips for how to analyze a short story step-by-step.
Read and summarize
As you prepare to analyze the short story assigned to you, it is recommended to read and re-read it multiple times. Since it is a short story, you’ll have plenty of time to understand all the details included within the story and the context of the plot.
To analyze the book, divide the narrative into sections. Read each of these sections and write down key points and essential details that are related to these portions of the story. As you do that, summarize your interpretation of the plot into a more understandable and easy piece.
Brainstorm and take notes
While reading the text, if you come across an interesting subplot, a challenging character arc, or even a major theme that isn't showcased through the text, make it a point of writing them down.
These notes will be your crutch as you begin analyzing your short story for your class assignment. Taking notes brings organization to your thoughts and ideas, as well as gives you proper knowledge about every detail you find in the short story.
Brainstorm multiple ideas and write down the concepts that you find fascinating while reading the book. Always pay close attention to the details to understand the purpose of the text, as well as the author’s point of view on multiple important situations or events.
Here’s an interesting video by Jesse on how to take notes while reading
Identify crucial concepts
Identifying important concepts in the short story, such as the main conflict that helps with creating the primary argument for the thesis statement, the characters’ personalities, their defining traits, the choices they make, and also the point of view of the narrator.
The point of view is an essential aspect of the storyline as it creates a lens for the reader to understand and analyze themes, details, characters, and important events in the story.
While examining these concepts, you will realize the intention of the author, how the story was significant to them, and why they made certain choices while writing the short story.
Similarly, exploring the literary devices of the short story, such as the setting, mood, tone, and style of the text, will help further in analyzing the plotline in a more notable way.
Include examples and evidence
When you state an argument in your story analysis, it is always better to back it up with credible sources and accurate evidence. For example, you can paraphrase or directly quote a sentence from your assigned story to claim your point.
However, quotations cannot become evidence unless it is explained how it proves the claims that are being made.
Having good sources for your story analysis gives you a higher level of authority over the book that you are writing about and also makes it easier for the reader to understand the author’s perspective.
Craft the thesis statement
It is important to make sure that all the points that have been made for the analysis tie together and ultimately support your thesis.
Keep in mind that the thesis for your short story should not just summarize the plot, and neither should it be a review of the book. Your thesis statement should be an interpretation of the text or an argument that is based on the storyline.
Writing a quality analysis for short stories requires a solid thought process, an organized structure , and the ability to dive deep into the literary meaning of a text.
Here, you understand and think through the author's perspective of the book and why they have chosen to write their thoughts and ideas through this narrative.
Hence, to know how to analyze a short story step-by-step for your class assignments and also score high, you need proper guidance, key steps, and other tips and tricks that put your analysis at the front of the line. This article is here just for that!
If you still find yourself to be stuck, reach out to our analytical essay writing service . Our team of professional writers are experts in analyzing stories and will help you deliver a 100% original short story analysis written from scratch.
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Crafted from Scratch for You.
Ensuring Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Main Navigation
- Skip to Search

Indiana University Bloomington Indiana University Bloomington IU Bloomington

- Mission, Vision, and Inclusive Language Statement
- Locations & Hours
- Undergraduate Employment
- Graduate Employment
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Newsletter Archive
- Support WTS
- Schedule an Appointment
- Online Tutoring
- Before your Appointment
- WTS Policies
- Group Tutoring
- Students Referred by Instructors
- Paid External Editing Services
- Writing Guides
- Scholarly Write-in
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Journal Article Writing Groups
- Early Career Graduate Student Writing Workshop
- Workshops for Graduate Students
- Teaching Resources
- Syllabus Information
- Course-specific Tutoring
- Nominate a Peer Tutor
- Tutoring Feedback
- Schedule Appointment
- Campus Writing Program

Writing Tutorial Services
How to write a thesis statement, what is a thesis statement.
Almost all of us—even if we don’t do it consciously—look early in an essay for a one- or two-sentence condensation of the argument or analysis that is to follow. We refer to that condensation as a thesis statement.
Why Should Your Essay Contain a Thesis Statement?
- to test your ideas by distilling them into a sentence or two
- to better organize and develop your argument
- to provide your reader with a “guide” to your argument
In general, your thesis statement will accomplish these goals if you think of the thesis as the answer to the question your paper explores.
How Can You Write a Good Thesis Statement?
Here are some helpful hints to get you started. You can either scroll down or select a link to a specific topic.
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is Assigned How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is not Assigned How to Tell a Strong Thesis Statement from a Weak One
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is Assigned
Almost all assignments, no matter how complicated, can be reduced to a single question. Your first step, then, is to distill the assignment into a specific question. For example, if your assignment is, “Write a report to the local school board explaining the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class,” turn the request into a question like, “What are the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class?” After you’ve chosen the question your essay will answer, compose one or two complete sentences answering that question.
Q: “What are the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class?” A: “The potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class are . . .”
A: “Using computers in a fourth-grade class promises to improve . . .”
The answer to the question is the thesis statement for the essay.
[ Back to top ]
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is not Assigned
Even if your assignment doesn’t ask a specific question, your thesis statement still needs to answer a question about the issue you’d like to explore. In this situation, your job is to figure out what question you’d like to write about.
A good thesis statement will usually include the following four attributes:
- take on a subject upon which reasonable people could disagree
- deal with a subject that can be adequately treated given the nature of the assignment
- express one main idea
- assert your conclusions about a subject
Let’s see how to generate a thesis statement for a social policy paper.
Brainstorm the topic . Let’s say that your class focuses upon the problems posed by changes in the dietary habits of Americans. You find that you are interested in the amount of sugar Americans consume.
You start out with a thesis statement like this:
Sugar consumption.
This fragment isn’t a thesis statement. Instead, it simply indicates a general subject. Furthermore, your reader doesn’t know what you want to say about sugar consumption.
Narrow the topic . Your readings about the topic, however, have led you to the conclusion that elementary school children are consuming far more sugar than is healthy.
You change your thesis to look like this:
Reducing sugar consumption by elementary school children.
This fragment not only announces your subject, but it focuses on one segment of the population: elementary school children. Furthermore, it raises a subject upon which reasonable people could disagree, because while most people might agree that children consume more sugar than they used to, not everyone would agree on what should be done or who should do it. You should note that this fragment is not a thesis statement because your reader doesn’t know your conclusions on the topic.
Take a position on the topic. After reflecting on the topic a little while longer, you decide that what you really want to say about this topic is that something should be done to reduce the amount of sugar these children consume.
You revise your thesis statement to look like this:
More attention should be paid to the food and beverage choices available to elementary school children.
This statement asserts your position, but the terms more attention and food and beverage choices are vague.
Use specific language . You decide to explain what you mean about food and beverage choices , so you write:
Experts estimate that half of elementary school children consume nine times the recommended daily allowance of sugar.
This statement is specific, but it isn’t a thesis. It merely reports a statistic instead of making an assertion.
Make an assertion based on clearly stated support. You finally revise your thesis statement one more time to look like this:
Because half of all American elementary school children consume nine times the recommended daily allowance of sugar, schools should be required to replace the beverages in soda machines with healthy alternatives.
Notice how the thesis answers the question, “What should be done to reduce sugar consumption by children, and who should do it?” When you started thinking about the paper, you may not have had a specific question in mind, but as you became more involved in the topic, your ideas became more specific. Your thesis changed to reflect your new insights.
How to Tell a Strong Thesis Statement from a Weak One
1. a strong thesis statement takes some sort of stand..
Remember that your thesis needs to show your conclusions about a subject. For example, if you are writing a paper for a class on fitness, you might be asked to choose a popular weight-loss product to evaluate. Here are two thesis statements:
There are some negative and positive aspects to the Banana Herb Tea Supplement.
This is a weak thesis statement. First, it fails to take a stand. Second, the phrase negative and positive aspects is vague.
Because Banana Herb Tea Supplement promotes rapid weight loss that results in the loss of muscle and lean body mass, it poses a potential danger to customers.
This is a strong thesis because it takes a stand, and because it's specific.
2. A strong thesis statement justifies discussion.
Your thesis should indicate the point of the discussion. If your assignment is to write a paper on kinship systems, using your own family as an example, you might come up with either of these two thesis statements:
My family is an extended family.
This is a weak thesis because it merely states an observation. Your reader won’t be able to tell the point of the statement, and will probably stop reading.
While most American families would view consanguineal marriage as a threat to the nuclear family structure, many Iranian families, like my own, believe that these marriages help reinforce kinship ties in an extended family.
This is a strong thesis because it shows how your experience contradicts a widely-accepted view. A good strategy for creating a strong thesis is to show that the topic is controversial. Readers will be interested in reading the rest of the essay to see how you support your point.
3. A strong thesis statement expresses one main idea.
Readers need to be able to see that your paper has one main point. If your thesis statement expresses more than one idea, then you might confuse your readers about the subject of your paper. For example:
Companies need to exploit the marketing potential of the Internet, and Web pages can provide both advertising and customer support.
This is a weak thesis statement because the reader can’t decide whether the paper is about marketing on the Internet or Web pages. To revise the thesis, the relationship between the two ideas needs to become more clear. One way to revise the thesis would be to write:
Because the Internet is filled with tremendous marketing potential, companies should exploit this potential by using Web pages that offer both advertising and customer support.
This is a strong thesis because it shows that the two ideas are related. Hint: a great many clear and engaging thesis statements contain words like because , since , so , although , unless , and however .
4. A strong thesis statement is specific.
A thesis statement should show exactly what your paper will be about, and will help you keep your paper to a manageable topic. For example, if you're writing a seven-to-ten page paper on hunger, you might say:
World hunger has many causes and effects.
This is a weak thesis statement for two major reasons. First, world hunger can’t be discussed thoroughly in seven to ten pages. Second, many causes and effects is vague. You should be able to identify specific causes and effects. A revised thesis might look like this:
Hunger persists in Glandelinia because jobs are scarce and farming in the infertile soil is rarely profitable.
This is a strong thesis statement because it narrows the subject to a more specific and manageable topic, and it also identifies the specific causes for the existence of hunger.
Produced by Writing Tutorial Services, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN
Writing Tutorial Services social media channels

4.4 COMPOSITION: The Three-Story Thesis
Another way to improve your academic writing is to write a better thesis statement. You already know that a strong thesis statement is more than just naming the topic. It includes some sort of claim, or what the author (in this case, you!) wants to say about the topic. If you can do that, then you are ready to take it a step further by exploring the ideas below.
What makes a good thesis in college?

- A good thesis is arguable. This means that it’s worth questioning or debating: it’s something with which a reasonable person might disagree. A thesis like “sustainability is important” isn’t at all difficult to argue for, and the reader would have little motivation to read the rest of the paper. However, an arguable thesis like “sustainability policies will fail if they do not include social justice,” brings up some interesting questions. Thus, the arguable thesis makes the reader want to keep reading.
- A good thesis is specific. Don’t just say that a particular policy is effective or fair; say what makes it so.
- A good thesis includes implications. In other words, why does it matter? What are the consequences? Why do you care? And why should the reader care?
There are one-story intellects, two-story intellects, and three-story intellects with skylights. All fact collectors who have no aim beyond their facts are one-story men. Two-story men compare, reason, generalize using the labor of fact collectors as their own. Three-story men idealize, imagine, predict—their best illumination comes from above the skylight. — Oliver Wendell Holmes, Sr. One way to strengthen your thesis statement is to write it as a three-story thesis. Here, when we talk about “story,” we mean “level” or “floor” (like a three-story building). Each “story” builds upon the previous one to make a strong structure. You can think of it this way:
- One-story theses state inarguable facts. What’s the background?
- Two-story theses bring in an arguable (interpretive or analytical) point. What’s your main idea?
- Three-story theses place that point within its larger, compelling implications. Why does it matter?
For example, imagine you have been assigned a paper about the impact of online learning in higher education. To outline this example:
- First story: Online learning is becoming more common and takes many different forms.
- Second story: While most people see it as a transformation of higher education, it is better to think of online learning as an extension of higher education because it reaches learners who do not want to participate — or cannot participate — in traditional campus-based education.
- Third story: Online learning appears to be one way to better integrate higher education with other institutions in society since online learners integrate their educational experiences with other parts of their life, promoting a better flow of ideas between college and the rest of society.
- Final thesis (all three stories combined): Online learning is becoming more common and takes many different forms. While most people see it as a transformation of higher education, it is better to think of online learning as an extension of higher education because it reaches learners who do not want to participate — or cannot participate — in traditional campus-based education. Online learning appears to be one way to better integrate higher education with other institutions in society since online learners integrate their educational experiences with other parts of their life, promoting a better flow of ideas between college and the rest of society.
Here’s another example of a three-story thesis:
- First story: Edith Wharton did not consider herself a modernist writer, and she did not write like her peers.
- Second story: However, in her work we can see her thinking about both the questions and forms that fascinated modernist writers of her time. While not a modernist herself, she did engage with modernist themes and questions.
- Third story: Thus, it is more revealing to think of modernism as a conversation rather than a category or practice.
- Final thesis (all three stories combined): Edith Wharton did not consider herself a modernist writer, and she did not write like her peers. However, in her work we can see her thinking about both the questions and forms that fascinated modernist writers of her time. While not a modernist herself, she did engage with modernist themes and questions. Thus, it is more revealing to think of modernism as a conversation rather than a category or practice.
Use the following exercise to review what you’ve learned. You can complete this exercise as many times as you want; it is not graded.
Let’s try writing a three-story thesis. Here is a list of one-story theses. Choose one to rewrite. Make it a full three-story thesis (in other words, it should have three sentences).
- Television programming includes content that some find objectionable.
- The percent of children and youth who are overweight or obese has risen in recent decades.
- First-year college students must learn how to independently manage their time.
- The things we surround ourselves with symbolize who we are.
Text adapted from: Guptill, Amy. Writing in College: From Competence to Excellence . 2022. Open SUNY Textbooks, 2016, milneopentextbooks.org/writing-in-college-from-competence-to-excellence/ . Accessed 16 Jan. 2022. CC BY-NC-SA
Image adapted from Tampa, Florida Code of Ordinances .
Synthesis Copyright © 2022 by Timothy Krause is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Short Story Analysis: How to Write It Step by Step [New]
Have you ever tried to write a story analysis but ended up being completely confused and lost? Well, the task might be challenging if you don’t know the essential rules for literary analysis creation.
But don’t get frustrated! We know how to write a short story analysis, and we are willing to share some tips with you.
Below you will find some tips that will help you:
- to analyze the story while reading;
- to put the findings in words;
- to edit and polish your work.
Our team listed the essential guide for writing an analysis of a short story. Check it out to nail your paper!
- 👣 How to Analyze a Story
- ✒️ Methods of Story Analysis
- ✍️ Analysis Format
- 📜 Proofreading Tips
- 📝 Analysis Example
👣 How to Analyze a Short Story Step by Step
Have you ever felt confused analyzing short stories for your school or college assignment? Not this time! We have prepared for you a step-by-step guide on how to analyze a short piece of writing quickly and effectively.
Step 1: Read Smart
The key to smart reading is to be critical. Criticism can be positive or negative. In your short story analysis, you need to have confidence in your own views of the work, regardless of the author’s reputation or whatever anyone else thinks.
The bottom line with literary criticism is that there are no right or wrong answers. As long as you back everything up with evidence, you can still attain a top grade if you take the opposite view to the author, your teacher, or the best student in your class.
But your reading needs to be methodical.
Step 2: Analyze & Find Examples
After you read the short story, you need to summarize it in your own words in no more than two sentences. This way, you will ensure that you’ve grasped its main idea.
Next, read the story one more time, paying attention to its literary elements, such as allusion, figurative language, plot, symbolism , etc. Analyze how they help the author convey the intended message. In addition, find relevant examples, quotes, or important passages that you can cite in your essay afterward.
Step 3: Create an Outline
Outlining is a crucial aspect of essay writing. It will help you understand how you can link all the facts to support the thesis statement and the paper’s arguments. Your short story analysis outline should look the following way:
- Introduction of the work (the author and title)
- A short summary of the story
- Thesis statement
- Topic sentence
- Example from the text
- Analysis of the example
- Restated thesis
- Summary of main points
- Concluding statement
If you need help outlining your short story analysis, try our free essay outline generator .
Step 4: Write Your Short Story Analysis
Now, it’s time to start drafting your essay. Here’s how to do it:
- At the beginning of your short story analysis, indicate the work’s title and the author’s name. Next, provide background information that may be helpful for understanding the story. End your introduction with an analytical thesis statement , clearly stating your evaluation of the text.
- Then, create body paragraphs based on your outline, including topic sentences and supporting examples.
- In the concluding paragraph , restate your thesis statement and highlight the important points you have made throughout the essay, giving the reader a feeling of closure.
Step 5: Revise and Proofread
Last but not least, proofread your short story analysis. It will help you to avoid grammatical mistakes, spelling errors, and typos.
If you have questions regarding your essay’s format or topic, it is always a good idea to ask for help from your teacher or classmate. Their experience and insights can help you adjust your analysis and improve its overall quality.
✒️ How to Analyze a Short Story: 6 Methods
When analyzing a short story, it is essential to examine all its main elements. In the following sections, we will discuss how to analyze the plot, characters, setting, themes, point of view, and style in detail.
Analyzing the Plot
For the first sitting, focus on the sequence of events that takes place throughout the story.
An analysis of a short story’s plot is easy because, unlike novels, which can contain multiple plotlines, short stories usually have only one.
To make the process even easier, here are some questions that you can ask yourself as you read:
- Does the plot hold your interest from beginning to end?
- What are the most important events, and why?
- Is plotline realistic?
- Are there any parts of the plotline that seem irrelevant to the main story?
- Does the plot deal with external conflict, internal conflict, or both?
- What is the moral of the story?
Next, you can look at the way the author portrays the characters in the story.
Short stories will not have many characters and often center around one main character, known as the protagonist.
Analyzing Characterization
Wondering how to analyze characters in a short story? The best way is to ask these questions:
- Who is the protagonist?
- How effectively does the author describe the characters’ actions, appearance, and thoughts?
- What are your feelings towards the characters?
- Does the way the characters speak give you any information about their personality?
- Do the characters change throughout the story?
- If the story contains minor characters, are they necessary and effective?
Alongside plot and characters, there is a third element that is a crucial part of any story:
Analyzing the Setting
Short stories are usually set in a single location and period, but some do have more than one.
These questions will help you master the setting :
- How does the author describe the location of the events?
- Does the story take place in the past, the present, or the future (or all three)?
- What are the broader circumstances surrounding the story’s setting?
- Does the setting play an essential role in the story?
- Do the place and time in which the author lived and worked affect the location and period in which the story is set?
- Has the author successfully given you a feeling of really being in the story’s setting?
Your next read-through might require some creative thinking and detective work as you consider the ideas, messages, or lessons behind the story.
Analyzing Themes
Analyzing a theme is your chance to stand out. While some themes are apparent and intended by the author, it is also possible to find more obscure ones. Even the author may not have been aware of them.
Answer these questions, and you’ve nailed the theme:
- What is the central theme? Are there any others?
- How is the theme conveyed?
- If the author is using the story to deliver a particular message, are you convinced by it?
- What does the theme reveal about the author?
Now you’re confident you understand the author’s message and can explore it in your short story analysis. Not so fast! You need to think about who is telling the story.
Analyzing the Point of View
Analyzing the point of view will give a more in-depth insight into all of the previous aspects you have dealt with. So ask yourself:
- Who is narrating the story?
- Does the author use a consistent point of view?
- Is the narrator telling the truth?
- Does the author have the same mindset as the narrator?
- Would the story be different if it were narrated from another point of view?

Finally, you need to look at the way the author uses language to tell the story.
Analyzing the Style
Ask the following questions when analyzing style :
- What is the author’s tone? Humorous? Serious? Sarcastic? Sentimental?
- Does the author use any unusual words or phrases? What effect do they have?
- Is there anything in the story – an object, for example – that has any special meaning?
- Does the author’s use of literary devices affect your enjoyment of the story in any way?
- What would the story be like if the author used a different style?
By now, you should be familiar with analyzing a short story and have enough great ideas to produce an A+ essay . Look again at the set question, and decide on the main direction you want your literary criticism essay to take.
Because now it’s time to wipe the dust off that keyboard:
✍️ Short Story Analysis Format
To get how to write a short story analysis step by step, you have to keep in mind the two golden rules:
- Your essay must be focused on the set question.
- Your opinions are only valid if you can support them with evidence.
Divide your work into three sections:
- Introduction (about 10% of the total word count)
- Main body (about 80% of the total word count)
- Conclusion (about 10% of the total word count)
Start with an Introduction
Your introduction should consist of one or two paragraphs that outline your statement of intent. You do not need to provide any evidence to back up your assertions at this stage – save that for the main body.
Here are the ingredients for a perfect introduction:
- An engaging opening line that captures the reader’s interest.
- The title of the short story and the name of the author.
- A brief outline of the main points and arguments that you intend to make.
Provide Arguments
Any story analysis has to list your points with proof. The main body is used to set out your case in detail and provide evidence to support it. Each paragraph should deal with a different point and follow a logical order that develops your overall argument.
Your main body is ready for the beach when it has:
- A persuasive and articulate argument.
- Evidence and quotes from the short story and external references, where appropriate, to support your case.
- Acknowledgment of any competing arguments to provide balance.
- Clear and concise language, with no repetition or irrelevant material.
- A clear focus on the set question.
Finish with a Bang
A conclusion ties everything together and briefly sums up your response to the set question. Like the introduction, it should be only one paragraph long and should not contain any new arguments, information, or evidence. If you can’t get rid of excessive fullf in your text, we’d suggest trying to use a paragraph shortener .
To finish your essay with a bang, you will need:
- A summary of the ideas that you have presented in the main body.
- Acknowledgment of any issues that need to be considered in the future.
- A powerful closing statement that encapsulates your overall position.
Once you have finished writing your literary analysis essay, the best thing you can do is take a break. When you return to review what you have done, it will be with a refreshed mind.
You’ve had fun criticizing the author. Now it’s time to look in the mirror:
📜 Short Story Analysis: Proofreading Tips
As usual, good things come in threes. Break your review down into these stages:
- Content editing
- Copy-editing
- Proofreading
For the first of these, you need to look at your essay as a whole and consider:
- Does your essay deal exclusively with the set question?
- Does your introduction accurately preview the content of the main body?
- Does each paragraph in the main body follow a logical order?
- Does your essay contain any repetition, inaccuracy, or irrelevant material?
- Does your conclusion successfully sum up your argument?
- Are your references accurate and appropriate?
- Will your reader find your essay to be enjoyable, easy to understand, and persuasive?
Once you are happy with your essay’s content, you can review it in more detail to deal with the text’s accuracy and consistency.
Reading carefully, line by line, ask yourself:
- Is your language as clear and concise as possible?
- Are your grammar and spelling correct?
- Have you presented acronyms, abbreviations, capitalization correctly and consistently?
- Are your quotations and references in the correct format?
- Are there any other formatting issues with your document?
Take another break, then review your essay one last time . Use your spellchecker, then print off a copy and read slowly and carefully, line by line. Hopefully, there won’t be too many errors by this stage but think of this process as a final polish to make your work really shine.
📝 Short Story Analysis Example
We have prepared an analysis example of the short story “The Last Leaf” by O. Henry. You can use it to find inspiration and see how everything works in practice.
In O. Henry’s “The Last Leaf,” a sick artist named Johnsy sees hope fading with each falling leaf outside her window. She is convinced that she will die when the last leaf falls. But two things stand against her despair: Behrman, an old, seemingly failed artist, and Sue, Johnsy’s loyal friend. This story shows how the actions of Johnsy’s companions become her lifelines, proving that art and friendship can blossom even in the direst circumstances.
Behrman’s sacrifice is one of the key themes in the story. O. Henry devotes much of his story to describing Behrman, a loser who drinks too much gin and lives a mostly wasted life. He appears to have no family and has not produced any notable work despite identifying himself as an artist: “Behrman was a failure in art. Forty years he had wielded the brush without getting near enough to touch the hem of his Mistress’s robe.” Despite Behrman’s never being successful in his craft, the realistic painting of a leaf he created before his death saved Johnsy’s life.
Friendship is another important motif in the story. Sue and Johnsy are more than just good friends; they are like sisters. Sue’s care and support have also played a key role in helping Johnsy recover. When Johnsy asks Sue to leave, Sue says, “I’d rather be here by you.” And she is actually there for Johnsy, caring for her in the worst moments of her life.
“The Last Leaf” reminds us that even when darkness creeps in, the power of art and friendship can bring light. Through Behrman’s final masterpiece and Sue’s unwavering support, Johnsy finds her way back from the brink. This simple story leaves readers with a powerful message: even in the darkest times, hope can be a driving force that can save a human life.
📚 Short Story Analysis Topics
- Analysis of Faulkner’s A Rose for Emily .
- Discuss the clues that suggest the unreliability of the narrator in E. A. Poe’s The Fall of the House of Usher .
- Describe the stylistic devices James Joyce uses in his short story Araby .
- Irony and double denouement in O. Henry’s The Gift of the Magi .
- Analysis of A&P by John Updike .
- Interpret Raymond Carver’s message in his story What We Talk About When We Talk About Love .
- Examine the theme of the short story The Yellow Wall-Paper by Charlotte Perkins Gilman .
- Analyze the rhetoric means used in Edith Wharton’s The Other Two .
- Literature analysis of Shirley Jackson’s short story The Lottery .
- The impact of gender and racial stereotypes in Sweat by Hurston.
- Discuss August Wilson’s presentation of conflicts in the short story Fences.
- Symbolism in Ernest Hemingway’s Hills Like White Elephants .
- Describe the rhetoric techniques Nathaniel Hawthorne uses in his short story The Birth-Mark .
- The Minister’s Black Veil by Nathaniel Hawthorne analysis.
- Analyze the social issues presented in Toni Bambara’s The Lesson .
- Explore the central theme of the story Alien by Riley Brett .
- Social problems of women and role of racial differences in Kate Chopin’s Desiree’s Baby .
- Discuss the central ethical dilemma presented by Sarah Hall in Theatre 6 .
- Analysis of A Clean, Well-Lighted Place by Ernest Hemingway.
- Examine the techniques Edwidge Danticat uses to paint a picture of life in Haiti in A Wall of Fire Rising .
- Discuss the core idea of The Things They Carried by Tim O’Brien.
- Literary devices in The Dinner Party short story by Mona Gardner .
- Analyze the author’s message in Lore Segal’s The Arbus Factor .
- Interpret the meaning of symbols in Rip Van Winkle by W. Irving .
- The meaning of setting in The Boarder by Isaac Bashevis Singer .
- Describe the different layers of meaning presented in Joyce Carol Oates’ Where Are You Going, Where Have You Been?
- Analyze the tone of the story The Masque of the Red Death by Edgar Allan Poe .
- Allegory in The Devil and Tom Walker short story by Washington Irving .
- Analyze the main female character of the short story A Good Man Is Hard to Find by Flannery O’Connor.
- Discuss the rhetoric used by Guy de Maupassant in The Necklace .
- Examine the symbols in Mr. Green by Olen Butler.
- Explore the main theme of James Joyce’s The Dead .
- Interpret the meaning of the dolls in a short story Barbie-Q by Sandra Cisneros
- Symbolism in A Jury of Her Peers by Susan Glaspell .
- Analyze the core idea of Jack London’s To Build a Fire .
- The conflict between the expectations and reality in Jamel Brinkley’s A Family .
- Examine the message E. Hemingway includes in his short story The Killer .
- Discuss the stylistic means used by Anton Chekhov in Sleepy .
- Describe the ideas O. Henry uses to present the moral lesson in The Last Leaf .
- Analysis of The Outcasts of Poker Flat by Bret Harte .
- Psychologism and mystique in W. W. Jacob’s The Monkey’s Paw .
- Analyze the symbols in the story A Worn Path by Eudora Welty .
- Describe how William Faulkner presents a theme of revenge in Barn Burning .
- Interpret creativity Kate Chopin’s The Storm .
- Discuss the techniques E. A. Poe uses to create the suspense in the short story Cask of the Amontillado .
- Cathedral by Raymond Carver analysis .
- The issues of stereotypes and isolation in Margaret Atwood’s Lusus Naturae .
- Magic realism in The Secret Miracle by Jorge Luis Borges .
- Interpret the meaning of symbols used by Flannery O’Connor in Good Country People .
- Technology development and its effect on human in Ray Bradbury’s The Veldt .
So, now you know how to analyze a short story step by step. A flawless piece of work will be a pleasure for your reader to behold! Share the page with others who may find it useful. And thanks for reading it!
Learn more on this topic:
- How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay Step by Step
- How to Write an Analysis Essay: Rules for a Good Analysis
- Case Study Analysis Example + How-to Guide
- Literary Analysis Essay Topics Ideas
- How to Write a Film Analysis Essay
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Have you ever tried to get somebody round to your way of thinking? Then you should know how daunting the task is. Still, if your persuasion is successful, the result is emotionally rewarding. A persuasive essay is a type of writing that uses facts and logic to argument and substantiate...
![thesis short story meaning Common Essay Mistakes—Writing Errors to Avoid [Updated]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/avoid-mistakes-ccw-284x153.jpg)
One of the most critical skills that students gain during their college years is assignment writing. Composing impressive essays and research papers can be quite challenging, especially for ESL students. Nonetheless, before learning the art of academic writing, you may make numerous common essay mistakes. Such involuntary errors appear in:...

You’re probably thinking: I’m no Mahatma Gandhi or Steve Jobs—what could I possibly write in my memoir? I don’t even know how to start an autobiography, let alone write the whole thing. But don’t worry: essay writing can be easy, and this autobiography example for students is here to show...
![thesis short story meaning Why I Want to Be a Teacher Essay: Writing Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/senior-male-professor-writing-blackboard-with-chalk3-284x153.jpg)
Some people know which profession to choose from childhood, while others decide much later in life. However, and whenever you come to it, you may have to elaborate on it in your personal statement or cover letter. This is widely known as “Why I Want to Be a Teacher” essay.
![thesis short story meaning Friendship Essay: Writing Guide & Topics on Friendship [New]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/smiley-female-friends-fist-bumping-284x153.jpg)
Assigned with an essay about friendship? Congrats! It’s one of the best tasks you could get. Digging through your memories and finding strong arguments for this paper can be an enjoyable experience. I bet you will cope with this task effortlessly as we can help you with the assignment. Just...

When you are assigned an autobiography to write, tens, and even hundreds of questions start buzzing in your head. How to write autobiography essay parts? What to include? How to make your autobiography writing flow? Don’t worry about all this and use the following three simple principles and 15 creative...

“Where is your thesis statement?” asks your teacher in a dramatic tone. “Where is my what?” you want to reply, but instead, you quickly point your finger at a random sentence in your paper, saying, “Here it is…” To avoid this sad situation (which is usually followed by a bad...

A life experience essay combines the elements of narration, description, and self-reflection. Such a paper has to focus on a single event that had a significant impact on a person’s worldview and values. Writing an essay about life experience prompts students to do the following: You may struggle with such...

Who has made a significant impact in your life and why? Essay on the topic might be challenging to write. One is usually asked to write such a text as a college admission essay. A topic for this paper can be of your choice or pre-established by the institution. Either...

Are you about to start writing a financial assistance essay? Most probably, you are applying for a scholarship that will provide additional funding for your education or that will help you meet some special research objectives.
![thesis short story meaning Growing Up Essay: Guide & Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/gardening-concept-with-mother-daughter-284x153.jpg)
What does it mean to grow up? Essays on this topic might be entertaining yet challenging to write. Growing up is usually associated with something new and exciting. It’s a period of everything new and unknown. Now, you’ve been assigned to write a growing up essay. You’re not a kid...
![thesis short story meaning Murder Essay: Examples, Topics, and Killer Tips [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/man-holding-gun-as-evidence-284x153.jpeg)
Probably, a murder essay is not a fascinating assignment to complete. Talking about people’s deaths or crazy murderers can be depressing. However, all assignments are different, and you are supposed to work on every task hard. So, how are you going to deal with a murder essay? You can make...
Can someone help me with what are the key tips of ” How to move from the subject of the evaluation to the working thesis?
Your source is not enough.
This is a great resource for getting help in writing various paper types. Thanks for the perfect guide to literary criticism essay writing! Once again, thanks for the awesome help!
Excellent information on literary criticism essay writing! I think it’s enough to write an essay yourself.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

16.4: The Three-Story Thesis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 175854
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
You have no doubt been drilled on the need for a thesis statement and its proper location at the end of the introduction. And you also know that all of the key points of the paper should clearly support the central driving thesis. Indeed, the whole model of the five-paragraph theme hinges on a clearly stated and consistent thesis. However, some students are surprised—and dismayed—when some of their early college papers are criticized for not having a good thesis. Their professor might even claim that the paper doesn’t have a thesis when, in the author’s view it clearly does. So, what makes a good thesis in college?
- A good thesis is non-obvious . High school teachers needed to make sure that you and all your classmates mastered the basic form of the academic essay. Thus, they were mostly concerned that you had a clear and consistent thesis, even if it was something obvious like “sustainability is important.” A thesis statement like that has a wide-enough scope to incorporate several supporting points and concurring evidence, enabling the writer to demonstrate his or her mastery of the five-paragraph form. Good enough! When they can, high school teachers nudge students to develop arguments that are less obvious and more engaging. College instructors, though, fully expect you to produce something more developed.
- A good thesis is arguable . In everyday life, “arguable” is often used as a synonym for “doubtful.” For a thesis, though, “arguable” means that it’s worth arguing: it’s something with which a reasonable person might disagree. This arguability criterion dovetails with the non-obvious one: it shows that the author has deeply explored a problem and arrived at an argument that legitimately needs 3, 5, 10, or 20 pages to explain and justify. In that way, a good thesis sets an ambitious agenda for a paper. A thesis like “sustainability is important” isn’t at all difficult to argue for, and the reader would have little intrinsic motivation to read the rest of the paper. However, an arguable thesis like “sustainability policies will inevitably fail if they do not incorporate social justice,” brings up some healthy skepticism. Thus, the arguable thesis makes the reader want to keep reading.
- A good thesis is well specified . Some student writers fear that they’re giving away the game if they specify their thesis up front; they think that a purposefully vague thesis might be more intriguing to the reader. However, consider movie trailers: they always include the most exciting and poignant moments from the film to attract an audience. In academic papers, too, a well specified thesis indicates that the author has thought rigorously about an issue and done thorough research, which makes the reader want to keep reading. Don’t just say that a particular policy is effective or fair; say what makes it is so. If you want to argue that a particular claim is dubious or incomplete, say why in your thesis.
- A good thesis includes implications . Suppose your assignment is to write a paper about some aspect of the history of linen production and trade, a topic that may seem exceedingly arcane. And suppose you have constructed a well supported and creative argument that linen was so widely traded in the ancient Mediterranean that it actually served as a kind of currency. [1] That’s a strong, insightful, arguable, well specified thesis. But which of these thesis statements do you find more engaging?
Linen served as a form of currency in the ancient Mediterranean world, connecting rival empires through circuits of trade.
Linen served as a form of currency in the ancient Mediterranean world, connecting rival empires through circuits of trade. The economic role of linen raises important questions about how shifting environmental conditions can influence economic relationships and, by extension, political conflicts.
Putting your claims in their broader context makes them more interesting to your reader and more impressive to your professors who, after all, assign topics that they think have enduring significance. Finding that significance for yourself makes the most of both your paper and your learning.
How do you produce a good, strong thesis? And how do you know when you’ve gotten there? Many instructors and writers find useful a metaphor based on this passage by Oliver Wendell Holmes, Sr. [2] :
There are one-story intellects, two-story intellects, and three-story intellects with skylights. All fact collectors who have no aim beyond their facts are one-story men. Two-story men compare, reason, generalize using the labor of fact collectors as their own. Three-story men idealize, imagine, predict—their best illumination comes from above the skylight.

The biggest benefit of the three-story metaphor is that it describes a process for building a thesis. To build the first story, you first have to get familiar with the complex, relevant facts surrounding the problem or question. You have to be able to describe the situation thoroughly and accurately. Then, with that first story built, you can layer on the second story by formulating the insightful, arguable point that animates the analysis. That’s often the most effortful part: brainstorming, elaborating and comparing alternative ideas, finalizing your point. With that specified, you can frame up the third story by articulating why the point you make matters beyond its particular topic or case.
For example, imagine you have been assigned a paper about the impact of online learning in higher education. You would first construct an account of the origins and multiple forms of online learning and assess research findings about its use and effectiveness. If you’ve done that well, you’ll probably come up with a well considered opinion that wouldn’t be obvious to readers who haven’t looked at the issue in depth. Maybe you’ll want to argue that online learning is a threat to the academic community. Or perhaps you’ll want to make the case that online learning opens up pathways to college degrees that traditional campus-based learning does not. In the course of developing your central, argumentative point, you’ll come to recognize its larger context; in this example, you may claim that online learning can serve to better integrate higher education with the rest of society, as online learners bring their educational and career experiences together.
To outline this example:
- First story : Online learning is becoming more prevalent and takes many different forms.
- Second story : While most observers see it as a transformation of higher education, online learning is better thought of an extension of higher education in that it reaches learners who aren’t disposed to participate in traditional campus-based education.
- Third story : Online learning appears to be a promising way to better integrate higher education with other institutions in society, as online learners integrate their educational experiences with the other realms of their life, promoting the freer flow of ideas between the academy and the rest of society.
Here’s another example of a three-story thesis: [4]
- First story : Edith Wharton did not consider herself a modernist writer, and she didn’t write like her modernist contemporaries.
- Second story : However, in her work we can see her grappling with both the questions and literary forms that fascinated modernist writers of her era. While not an avowed modernist, she did engage with modernist themes and questions.
- Third story : Thus, it is more revealing to think of modernism as a conversation rather than a category or practice.
Here’s one more example:
- First story : Scientists disagree about the likely impact in the U.S. of the light brown apple moth (LBAM) , an agricultural pest native to Australia.
- Second story : Research findings to date suggest that the decision to spray pheromones over the skies of several southern Californian counties to combat the LBAM was poorly thought out.
- Third story : Together, the scientific ambiguities and the controversial response strengthen the claim that industrial-style approaches to pest management are inherently unsustainable.
A thesis statement that stops at the first story isn’t usually considered a thesis. A two-story thesis is usually considered competent, though some two-story theses are more intriguing and ambitious than others. A thoughtfully crafted and well informed three-story thesis puts the author on a smooth path toward an excellent paper.
- For more see Fabio Lopez-Lazaro “Linen.” In Encyclopedia of World Trade from Ancient Times to the Present . Armonk: M.E. Sharpe, 2005. ↵
- Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr., The Poet at the Breakfast Table (New York: Houghton & Mifflin, 1892) ↵
- The metaphor is extraordinarily useful even though the passage is annoying. Beyond the sexist language of the time, it displays condescension toward “fact-collectors” which reflects a general modernist tendency to elevate the abstract and denigrate the concrete. In reality, data-collection is a creative and demanding craft, arguably more important than theorizing. ↵
- Drawn from Jennifer Haytock, Edith Wharton and the Conversations of Literary Modernism (New York: Palgrave-MacMillan, 2008). ↵
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- The three-story thesis: from the ground up. Authored by : Amy Guptill. Provided by : The College at Brockport, SUNY. Located at : http://textbooks.opensuny.org/writing-in-college-from-competence-to-excellence/ . Project : Writing in College: From Competence to Excellence. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of pagoda corner. Authored by : Takashi Hososhima. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/gGhtya . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
Chapter 5: Thesis Statements, Introductions, and Conclusions
The three-story thesis.
You have no doubt been drilled on the need for a thesis statement and its proper location at the end of the introduction. And you also know that all of the key points of the paper should clearly support the central driving thesis. Indeed, the whole model of the five-paragraph theme hinges on a clearly stated and consistent thesis. However, some students are surprised—and dismayed—when some of their early college papers are criticized for not having a good thesis. Their professor might even claim that the paper doesn’t have a thesis when, in the author’s view it clearly does. So, what makes a good thesis in college?
- A good thesis is non-obvious . High school teachers needed to make sure that you and all your classmates mastered the basic form of the academic essay. Thus, they were mostly concerned that you had a clear and consistent thesis, even if it was something obvious like “sustainability is important.” A thesis statement like that has a wide-enough scope to incorporate several supporting points and concurring evidence, enabling the writer to demonstrate his or her mastery of the five-paragraph form. Good enough! When they can, high school teachers nudge students to develop arguments that are less obvious and more engaging. College instructors, though, fully expect you to produce something more developed.
- A good thesis is arguable or relevant . In everyday life, “arguable” or is often used as a synonym for “doubtful.” For a thesis, though, “arguable” means that it’s worth arguing: it’s something with which a reasonable person might disagree. This arguability criterion dovetails with the non-obvious one: it shows that the author has deeply explored a problem and arrived at an argument that legitimately needs 3, 5, 10, or 20 pages to explain and justify. In that way, a good thesis sets an ambitious agenda for a paper. A thesis like “sustainability is important” isn’t at all difficult to argue for, and the reader would have little intrinsic motivation to read the rest of the paper. However, an arguable thesis like “sustainability policies will inevitably fail if they do not incorporate social justice,” brings up some healthy skepticism. Thus, the arguable thesis makes the reader want to keep reading. If the thesis aims to inform or analyze without taking a stance, the most important part of the thesis is actually not the thesis statement itself; it is the preview of main points of development (more on that to follow).
- A good thesis is well specified . Some student writers fear that they’re giving away the game if they specify their thesis up front; they think that a purposefully vague thesis might be more intriguing to the reader. However, consider movie trailers: they always include the most exciting and poignant moments from the film to attract an audience. In academic papers, too, a well specified thesis indicates that the author has thought rigorously about an issue and done thorough research, which makes the reader want to keep reading. Don’t just say that a particular policy is effective or fair; say what makes it is so. If you want to argue that a particular claim is dubious or incomplete, say why in your thesis.
- A good thesis includes implications . Suppose your assignment is to write a paper about some aspect of the history of linen production and trade, a topic that may seem exceedingly arcane. And suppose you have constructed a well supported and creative argument that linen was so widely traded in the ancient Mediterranean that it actually served as a kind of currency. [1] That’s a strong, insightful, potentially arguable, well specified thesis. But which of these thesis statements do you find more engaging?
Version A: Linen served as a form of currency in the ancient Mediterranean world, connecting rival empires through circuits of trade. Version B: Linen served as a form of currency in the ancient Mediterranean world, connecting rival empires through circuits of trade. The economic role of linen raises important questions about how shifting environmental conditions can influence economic relationships and, by extension, political conflicts.
Putting your claims in their broader context makes them more interesting to your reader and more impressive to your professors who, after all, assign topics that they think have enduring significance. Finding that significance for yourself makes the most of both your paper and your learning.
How do you produce a good, strong thesis? And how do you know when you’ve gotten there? Many instructors and writers find useful a metaphor based on this passage by Oliver Wendell Holmes, Sr. [2] :
There are one-story intellects, two-story intellects, and three-story intellects with skylights. All fact collectors who have no aim beyond their facts are one-story men. Two-story men compare, reason, generalize using the labor of fact collectors as their own. Three-story men idealize, imagine, predict—their best illumination comes from above the skylight.

The biggest benefit of the three-story metaphor is that it describes a process for building a thesis. To build the first story, you first have to get familiar with the complex, relevant facts surrounding the problem or question. You have to be able to describe the situation thoroughly and accurately. Then, with that first story built, you can layer on the second story by formulating the insightful, arguable point that animates the analysis. That’s often the most effortful part: brainstorming, elaborating and comparing alternative ideas, finalizing your point. With that specified, you can frame up the third story by articulating why the point you make matters beyond its particular topic or case.
For example, imagine you have been assigned a paper about the impact of online learning in higher education. You would first construct an account of the origins and multiple forms of online learning and assess research findings about its use and effectiveness. If you’ve done that well, you’ll probably come up with a well considered opinion that wouldn’t be obvious to readers who haven’t looked at the issue in depth. Maybe you’ll want to argue that online learning is a threat to the academic community. Or perhaps you’ll want to make the case that online learning opens up pathways to college degrees that traditional campus-based learning does not. In the course of developing your central, argumentative point, you’ll come to recognize its larger context; in this example, you may claim that online learning can serve to better integrate higher education with the rest of society, as online learners bring their educational and career experiences together.
To outline this example:
- First story : Online learning is becoming more prevalent and takes many different forms.
- Second story : While most observers see it as a transformation of higher education, online learning is better thought of an extension of higher education in that it reaches learners who aren’t disposed to participate in traditional campus-based education.
- Third story : Online learning appears to be a promising way to better integrate higher education with other institutions in society, as online learners integrate their educational experiences with the other realms of their life, promoting the freer flow of ideas between the academy and the rest of society.
Here’s another example of a three-story thesis: [4]
- First story : Edith Wharton did not consider herself a modernist writer, and she didn’t write like her modernist contemporaries.
- Second story : However, in her work we can see her grappling with both the questions and literary forms that fascinated modernist writers of her era. While not an avowed modernist, she did engage with modernist themes and questions.
- Third story : Thus, it is more revealing to think of modernism as a conversation rather than a category or practice.
Here’s one more example:
- First story : Scientists disagree about the likely impact in the U.S. of the light brown apple moth (LBAM) , an agricultural pest native to Australia.
- Second story : Research findings to date suggest that the decision to spray pheromones over the skies of several southern Californian counties to combat the LBAM was poorly thought out.
- Third story : Together, the scientific ambiguities and the controversial response strengthen the claim that industrial-style approaches to pest management are inherently unsustainable.
A thesis statement that stops at the first story isn’t usually considered a thesis. A two-story thesis is usually considered competent, though some two-story theses are more intriguing and ambitious than others. A thoughtfully crafted and well informed three-story thesis puts the author on a smooth path toward an excellent paper.
The three-story thesis is a beautiful thing. For one, it gives a paper authentic momentum. The first paragraph doesn’t just start with some broad, vague statement; every sentence is crucial for setting up the thesis. The body paragraphs build on one another, moving through each step of the logical chain. Each paragraph leads inevitably to the next, making the transitions from paragraph to paragraph feel wholly natural. The conclusion, instead of being a mirror-image paraphrase of the introduction, builds out the third story by explaining the broader implications of the argument. It offers new insight without departing from the flow of the analysis.
A paper with this kind of momentum often reads like it was knocked out in one inspired sitting. But in reality, just like accomplished athletes and artists, masterful writers make the difficult thing look easy. As writer Anne Lamott notes, reading a well written piece feels like its author sat down and typed it out, “bounding along like huskies across the snow.” However, she continues,
This is just the fantasy of the uninitiated. I know some very great writers, writers you love who write beautifully and have made a great deal of money, and not one of them sits down routinely feeling wildly enthusiastic and confident. Not one of them writes elegant first drafts. All right, one of them does, but we do not like her very much. [1]
Experienced writers don’t figure out what they want to say and then write it. They write in order to figure out what they want to say.
Experienced writers develop theses in dialog with the body of the essay. An initial characterization of the problem leads to a tentative thesis, and then drafting the body of the paper reveals thorny contradictions or critical areas of ambiguity, prompting the writer to revisit or expand the body of evidence and then refine the thesis based on that fresh look. The revised thesis may require that body paragraphs be reordered and reshaped to fit the emerging three-story thesis. Throughout the process, the thesis serves as an anchor point while the author wades through the morass of facts and ideas. The dialogue between thesis and body continues until the author is satisfied or the due date arrives, whatever comes first.
Another benefit of the three-story thesis framework is that it demystifies what a “strong” argument is in academic culture. In an era of political polarization, many students may think that a strong argument is based on a simple, bold, combative statement that is promoted it in the most forceful way possible. “Gun control is a travesty!” “Shakespeare is the best writer who ever lived!” When students are encouraged to consider contrasting perspectives in their papers, they fear that doing so will make their own thesis seem mushy and weak. However, in academics a “strong” argument is comprehensive and nuanced, not simple and polemical. The purpose of the argument is to explain to readers why the author—through the course of his or her in-depth study—has arrived at a somewhat surprising point. On that basis, it has to consider plausible counter-arguments and contradictory information. Academic argumentation exemplifies the popular adage about all writing: show, don’t tell. In crafting and carrying out the three-story thesis, you are showing your reader the work you have done.
- For more see Fabio Lopez-Lazaro “Linen.” In Encyclopedia of World Trade from Ancient Times to the Present . Armonk: M.E. Sharpe, 2005. ↵
- Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr., The Poet at the Breakfast Table (New York: Houghton & Mifflin, 1892) ↵
- The metaphor is extraordinarily useful even though the passage is annoying. Beyond the sexist language of the time, it displays condescension toward “fact-collectors” which reflects a general modernist tendency to elevate the abstract and denigrate the concrete. In reality, data-collection is a creative and demanding craft, arguably more important than theorizing. ↵
- Drawn from Jennifer Haytock, Edith Wharton and the Conversations of Literary Modernism (New York: Palgrave-MacMillan, 2008). ↵
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- The three-story thesis: from the ground up. Authored by : Amy Guptill. Provided by : The College at Brockport, SUNY. Located at : http://textbooks.opensuny.org/writing-in-college-from-competence-to-excellence/ . Project : Writing in College: From Competence to Excellence. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of pagoda corner. Authored by : Takashi Hososhima. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/gGhtya . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike

Privacy Policy
'Bridgerton' Season 3's Eros and Psyche Reference Has a Deeper Meaning

Your changes have been saved
Email Is sent
Please verify your email address.
You’ve reached your account maximum for followed topics.
The Big Picture
- The legendary myth of Eros and Psyche is referenced during Colin and Penelope's love story in Bridgerton Season 3.
- The elements of trust, betrayal, and divine intervention play a significant role in Penelope and Colin's relationship.
- Penelope will have to prove her love for Colin and earn his trust as she wrestles with whether to reveal her secret identity as Lady Whistledown.
Dearest gentle reader, Bridgerton Season 3 has us buzzing! The Netflix romance series has returned and turned its focus towards Colin Bridgerton ( Luke Newton ) and Penelope Featherington ( Nicola Coughlan ), taking the baton from Anthony Bridgerton ( Jonathan Bailey ) and Kate Sharma ( Simone Ashley ) in the previous season.
While Colin and Penelope’s story fully embraces the friends-to-lovers trope, there’s actually more to their story than meets the eye thanks to a comment from Penelope’s rival, Cressida Cowper ( Jessica Madsen ). As Colin and Penelope heatedly argue about Penelope’s plans to marry Lord Debling ( Sam Phillips ) in Season 3, Episode 4, “Old Friends,” Cressida remarks to Lord Debling that they’re like Eros and Psyche battling it out. While at first this might seem random, this reference to these specific Greek mythological characters does have deeper implications , adding another layer to Bridgerton Season 3's main love story.
The eight close-knit siblings of the Bridgerton family look for love and happiness in London high society.
The Story of Eros and Psyche Is the Stuff of (Greek) Legend
For those who don’t know or just need a refresher, the tale of Eros and Psyche is a beautiful Greek myth about love overcoming the odds . Psyche was a mortal woman, one of three sisters, who became famous for her beauty. According to the myth, the goddess of love and beauty, Aphrodite was jealous of Psyche’s beauty and ordered her son, Eros, to kill off man’s desire for Psyche. However, upon seeing her, Eros accidentally shoots himself in the foot with one of his arrows, and he, too, becomes enamored with Psyche.
Although Psyche expresses to her parents that she only wants to marry a man she loves, her parents seek out the counsel of an oracle. Thanks to manipulation from Eros, the oracle tells Psyche’s parents that Psyche will marry an ugly beast whose face she’d never see. Disheartened, her parents accept Psyche’s fate and arrange for their daughter to be wed. The stipulation is that Psyche can only be with her new husband at night , and she is never allowed to know who he really is; despite this, she is overwhelmed by the amount of love and tenderness her mysterious husband has for her.
Psyche is genuinely happy about her situation until her two sisters start filling her head with doubt about her husband's true identity, claiming that her new husband really was a beast and, eventually, that he would kill her. Fearing for her life, Psyche intends to kill her husband while sleeping but discovers that it is really Eros . Unfortunately, she accidentally wakes him up when the oil lamp she is holding above him drips, and he flees from her due to her betrayal. Psyche then wanders the earth looking for her beloved husband until she pleads for Aphrodite’s help. Aphrodite then forces Psyche to prove her love for Eros in a series of three tasks.
Eros has never stopped loving Psyche , so when she falls into a slumber from her final task in the underworld, Eros begs Zeus to save Psyche’s life. Not only does Zeus save Psyche’s life, but Zeus also makes Psyche immortal, so the couple will be together forever. Despite the betrayal and the odds, the love between Psyche and Eros was worth fighting for, and it became legendary.
Colin and Penelope's Romance Mirrors the Myth of Eros and Psyche
Even before Cressida utters the names “Psyche” and “Eros,” the parallels between the mythological couple and Colin and Penelope have been there since the beginning of the series. Like Psyche, Penelope is one of three sisters who, by all accounts, was going to end up unmarried. Although she insists that she needs to marry in order to escape her family, Penelope does want love, something she expresses to both Lord Debling and Portia Featherington ( Polly Walker ). On the other hand, Colin is part of one of the most prestigious families in London society, practically their own pantheon of Greek gods and goddesses. A family born out of a love match, each Bridgerton child has their own legendary love story that the rest of the ton passes around like ancient myths.
The story of Eros and Psyche is a struggle between the head and the heart, which is something we see play out during the third season of Bridgerton . As much as Penelope wants a love match, she resigns herself to making a smart, secure match. Colin tries to help her find a suitable husband; but like Eros shooting himself in the foot, Colin realizes, while helping Penelope, that he’s in love with her . If the story parallels weren’t enough, the dance at the ball during Season 3, Episode 4 is indeed a performance inspired by Eros and Psyche. Not to put too fine a point on it, but an early scene between Penelope and Madame Delacroix ( Kathryn Drysdale ) during Season 3, Episode 1, “Out of the Shadows,” transitions to Gregory Bridgerton ( Will Tilston ) marveling at a bow and arrow that Colin got him during his most recent travels; the bow and arrow are signature to the winged god of love.
If Colin and Penelope are the Bridgerton equivalent of Eros and Psyche, then we can expect the famed Greek myth to continue to play out into the next part of the third season. For Eros and Psyche, there is an emphasis on trust between lovers . Eros left Psyche because she broke his trust, while in Bridgerton , Penelope has been keeping her Lady Whistledown secret from Colin this whole time. Even though Eloise Bridgerton ( Claudia Jessie ) has known Penelope’s secret for almost a year, it’s only a matter of time before Colin learns the truth. If Eros’ reaction to Psyche’s betrayal is any indication, Colin is going to feel betrayed by his fiancée for keeping this from him. Although she intended her writing to help save her friends from making poor decisions, Penelope has caused damage as Lady Whistledown, particularly towards the Bridgerton family. This is going to cause a rift that threatens to separate the lovers forever.
At the same time, Bridgerton is a romance series where each Bridgerton sibling will get their happily ever after. For Colin, Penelope is going to have to prove her love and earn his trust again before the end of the season. She might do this by appealing to the closest woman Bridgerton has to a goddess : Queen Charlotte ( Golda Rosheuvel ). If that’s the case and Penelope has to confess her identity as Lady Whistledown to her royal adversary, she might end up in danger, which could prompt Colin out of his hurt feelings to save the woman he loves. Regardless of how the Lady Whistledown secret and the rest of the season will play out, Penelope and Colin’s love story has been a fan favorite for a while, and the fight for their love to win out will make their eventual happily ever after all the more divine.
Part 1 of Bridgerton Season 3 is now streaming on Netflix in the U.S., with Part 2 premiering on June 13.
WATCH ON NETFLIX
- TV Features
What verdict will voters render after jury finds Trump guilty in hush money case?

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
The sometimes-breathless gavel-to-gavel coverage of former President Trump’s trial was no surprise, as a singularly divisive figure sat for more than a month at the defense table, the first president to face criminal charges and the possibility of a trip to jail.
But for all the trial’s spectacle, many political observers predict that the impact of Thursday’s 34 guilty verdicts will be muted and unlikely to change the dynamic in a presidential race that appears extremely close, just over five months before the last day of voting.
The New York jury’s verdict puts Trump in an unprecedented position: trying to win the White House as a felon, guilty of falsifying business records to bury the details of his extramarital one-night stand with a porn star.
While a Trump appeal could still remove the threat of probation or jail, he still will have to explain to voters why a man convicted of a political cover-up should be entrusted with the most powerful office in the world.

World & Nation
Guilty: Trump becomes first former U.S. president convicted of felony crimes
Jurors deliberated for 9½ hours over two days before convicting former President Trump of all 34 counts he faced in a hush-money scheme surrounding the 2016 election.
May 30, 2024
Trump has provoked both admiration and despair — depending on the audience’s political leanings — with his ability to survive what some judged to be fatal missteps.
“I already gave up my membership in the He-Certainly-Can’t-Survive-This Club,” David Axelrod, the top strategist in Barack Obama’s two successful presidential campaigns, said in an interview. “Look at how many other times he has gotten away with things. He is an extraordinary escape artist.” (Axelrod and other experts spoke before the verdict.)
In 2016, candidate Trump famously told a campaign crowd that he could stand in the middle of Fifth Avenue in New York and shoot someone without losing his core supporters. Though the charges in the hush money case fell short of assault with a deadly weapon, they stand as a real-world test of Trump’s seeming invulnerability from political norms.
I already gave up my membership in the He-Certainly-Can’t-Survive-This Club
— David Axelrod
With about a month to go in the 2016 race, a previously secret video showed Trump boasting about his ability to sexually prey on women because of his fame. Many observers believed the “Access Hollywood” recording effectively killed his chances of winning the presidency. But Trump overtook front-runner Hillary Clinton in the final weeks of the race and won the presidency.
When Trump was thrown out by voters in 2020 in favor of Joe Biden, some pundits again predicted Trump’s days were numbered. But he pushed aside all his Republican primary challengers this year, despite a pair of legal setbacks: a jury verdict that found him liable for sexually abusing advice columnist E. Jean Carroll in 1996 and a judge’s order to pay a $454-million penalty for falsely inflating the value of his real estate empire.
Trump’s conviction plays out at a time when Americans are deeply divided, a fracture exacerbated by a sharply fragmented information ecosystem. Mainstream outlets parsed the detailed evidence presented by prosecutors in the trial, while right-leaning outlets bolstered Trump’s claims that the charges amounted to a political hit job by Democratic prosecutors.
After closing arguments Tuesday, one Newsmax cable television commentator suggested that the evidence in the case pointed to crimes — not by Trump but by Stormy Daniels, who testified she had sex with Trump in 2006, and by prosecution witness Michael Cohen, Trump’s former lawyer, who testified he helped facilitate the payments to keep Daniels quiet about the one-night stand.
A Marquette Law School Poll completed in mid-May suggested the verdict might have some effect on the presidential race.
When a national sample of voters was presented with the possibility that Trump would be found guilty in the New York case, 43% said they would vote for Biden, 38% would vote for Trump and 18% said they would vote for someone else or remained undecided.
Presented with the opposite outcome, Trump being acquitted, the survey tipped in his favor, with voters preferring him by 44% to 38% over Biden. Again, 18% favored another candidate or were undecided.
But both those results fall within the margin of error of more than 6%, said Charles Franklin, director of the Wisconsin-based poll. And previous experience suggests that public opinion about the hush money case might have been well settled for many voters long before the verdict, because the facts had been aired for many months, Franklin said.

Column: Trump is officially a convicted felon, but that may not stand in his way
Trump guilty: Despite the former president’s felony conviction in his hush money trial, many voters will react to the jury decision with a shrug.
Franklin compared the long run-up to the verdict with the prolonged public debate that occurred during Trump’s first impeachment, when the onetime reality TV host was accused of soliciting foreign interference in a bid to help win the 2020 election.
“As the House considered the impeachment, then voted to impeach him and then the Senate voted to acquit him, the public’s views [of Trump] and of the impeachment and then of the conviction didn’t change,” Franklin said.
He predicted that future surveys about this week’s trial verdict were likely to show only a modest shift in voter sentiments.
Charles Cook, a nonpartisan political analyst based in Washington, agreed that it was hard to imagine the verdict swaying many voters.
“Swing voters, particularly the ‘pure independents’ who don’t lean to either party, tend to be driven by other issues and have other priorities in mind when making their decisions to vote,” Cook said via email. He said that the small group of voters who do not have hardened views on the 2024 race “don’t follow current events that much, believe all politicians and political parties are corrupt and are not particularly moved by this.”
The thought that Trump might entirely escape the wrath of voters seemed unfathomable to some.
“At some point, there is going to have to be a discussion of whether we want a liar and a convict in the Oval Office,” said Ben Austin, a Los Angeles Democrat who worked in President Clinton’s White House. “I mean, what kind of country are we?”
Reed Galen, a lifelong Republican who left the party and co-founded the anti-Trump Lincoln Project, wondered if GOP voters who once favored former South Carolina Gov. Nikki Haley might be put off by the revelations from the hush money case.
“Some of them were already highly skeptical of Trump, and this might take them off Trump Island, hopefully once and for all,” Galen said.

Q&A: Yes, Trump could be elected president as a convicted felon
Donald Trump faces multiple criminal charges, but a conviction would not legally prevent him from serving as president — in theory, even from jail.
But Trump stalwarts say his detractors should have long ago recognized that he is impervious to critiques by mainstream media outlets and old-guard Republicans. Even those who have accepted that Trump is a flawed candidate said they find him preferable in a country they are convinced is going the wrong way under President Biden.
“By now, a lot of Arizonans are just numb to the trial and all of this,” said Stan Barnes, a Republican who runs a public affairs and lobbying firm in the battleground state. “They’re a lot more focused on what kind of policies they want from the president. When Trump was in the White House, mortgage rates were [as low as] 2½%, unemployment was [low]. And the southern border felt secure.”
Barnes said nothing that happened in the Manhattan courtroom would change those views, predicting that many Americans will be ready to vote again to promote Trump and his “America first” agenda.
More to Read

In a battleground congressional district north of L.A., Trump verdict may be a wildcard in the November election
May 31, 2024

Trump responds to his guilty verdict by falsely claiming a ‘rigged trial’ and attacking star witness

At Trump hotel in Las Vegas, supporters are undeterred by guilty verdict: ‘I don’t care’

Ali: The jury has spoken. What happens next will be a great test of American democracy

Opinion: The guilty verdict only makes Donald Trump stronger

Litman: Does it matter that Donald Trump just became a convicted criminal? Of course it does

Editorial: Even before guilty verdict, Trump was unfit to serve

Get the L.A. Times Politics newsletter
Deeply reported insights into legislation, politics and policy from Sacramento, Washington and beyond. In your inbox three times per week.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.

James Rainey has covered multiple presidential elections, the media and the environment, mostly at the Los Angeles Times, which he first joined in 1984. He was part of Times teams that won three Pulitzer Prizes.
More From the Los Angeles Times

Trump rages, Biden struggles to tame the war in Gaza: The contrasting days of a former and current president

Democratic Sen. Joe Manchin, citing ‘partisan extremism,’ registers as independent

Trump plans to raise money in California in the aftermath of felony conviction

Granderson: With this guilty verdict, Trump has gone full Bond villain
Trump guilty, now what? Why the verdict isn't the most shocking part of the trial

The most shocking thing about the first-ever criminal trial of a former U.S. president may not be the guilty verdict that a New York jury delivered Thursday afternoon.
It's this: It is possible, even probable, that one of the most momentous trials in American history won't end up affecting American history − at least not in time to reshape the presidential campaign in which Donald Trump is all−but-guaranteed to be the Republican nominee.
"Unprecedented" − admittedly an overworked word since Trump announced his first presidential campaign nine years ago − undeniably applies. The 45th president of the United States is now a convicted felon.
In a hushed courtroom, the jury foreperson read their unanimous conclusion.
Count 1: Guilty.
Prep for the polls: See who is running for president and compare where they stand on key issues in our Voter Guide
Count 2: Guilty.
Count 3: Guilty.
Count 4: Guilty.
Count 5: Guilty.
And so, it went through all 34 counts: Guilty. Guilty. Guilty. Convicted of falsifying business records to cover up hush money payments to a porn star, part of an effort to affect the outcome of the 2016 election. The jury of seven men and five women dismissed the protestations of innocence from a defendant who once lived in the White House and has a realistic possibility of moving back in.
Judge Juan Merchan set sentencing for July 11, four days before the Republican National Convention begins in Milwaukee. None of the other three criminal cases against Trump is likely to go to trial before the November election.
"The FIX was always in..." Trump's campaign manager, Chris LaCivita, posted instantly on the social-media platform known as X, formerly called Twitter. Florida Sen. Marco Rubio, on the list of Trump's potential running mates, declared, "The verdict in New York is a complete travesty that makes a mockery of our system of justice," calling it "a political show trial."
A seething Trump, his face flushed, used the word "rigged" five times when he briefly addressed reporters outside the courtroom.
"This is far from over," he declared looking ahead to Election Day, now less than six months away. Calling it a "rigged, disgraceful trial," Trump said "the real verdict is going to be Nov. 5 by the people who know what happened here."
He blamed, without evidence, that President Biden had orchestrated a politically motivated prosecution.
Trump announced his determination to appeal, a process that will have to unfold before he could conceivably be sent to jail or be fined.
Even so, the unanimous verdict by 12 citizens, a decision that took them less than 12 hours of deliberation to reach, surely carried a certain force. For Trump, the conviction immediately became his leading grievance. "I'm a political prisoner!" he declared on Truth Social, asking for campaign contributions.
For Biden, it just as quickly became a rallying cry.
"There's only one way to keep Donald Trump out of the Oval Office: At the ballot box," the president, who generally shied from commenting on the trial while it was going on, posted on X.
Biden coupled it with an appeal for campaign contributions, too.

COMMENTS
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why. The best thesis statements are: Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don't use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
Theme - the central and dominating idea in a literary work. Using "thesis" to describe a theme, idea, or message in a story is not entirely accurate as it positions the text as an argument ...
Thesis Definition. A thesis is a statement in a non-fiction or a fiction work that a writer intends to support and prove. One can find examples of thesis statement at the beginning of literary pieces. These thesis statements are of utmost importance, as they provide clear indicators as to which direction the writer will follow in their work.
The thesis (pronounced thee -seez), also known as a thesis statement, is the sentence that introduces the main argument or point of view of a composition (formal essay, nonfiction piece, or narrative). It is the main claim that the author is making about that topic and serves to summarize and introduce that writing that will be discussed ...
A good thesis fits the assignment length, makes a statement about your overall point and includes the specific points you will give to support that idea about the story. The thesis must relate to a specific point about the short story such as the argumentative point you want to explain or defend. Place the thesis at the end of the introductory ...
Short stories have a central idea or theme that acts as a thesis for the story. The structure of a short story follows a simple pattern with an introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and conclusion. Short stories are different from longer works in their conciseness, focused themes, and reliance on reader interpretation.
The thesis may focus on an analysis of one of the elements of fiction, drama, poetry or nonfiction as expressed in the work: character, plot, structure, idea, theme, symbol, style, imagery, tone, etc. ... In Willa Cather's short story, "Paul's Case," Paul exhibits suicidal behavior that a caring adult might have recognized and remedied ...
This thesis focuses on the idea of social corruption and the device of imagery. To support this thesis, you would need to find images of beasts and cannibalism within the text. This handout covers major topics relating to writing about fiction. This covers prewriting, close reading, thesis development, drafting, and common pitfalls to avoid.
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Analyzing Novels & Short Stories. Literary analysis looks critically at a work of fiction in order to understand how the parts contribute to the whole. When analyzing a novel or short story, you'll need to consider elements such as the context, setting, characters, plot, literary devices, and themes. Remember that a literary analysis isn't ...
The Literary Thesis Statement. Literary essays are argumentative or persuasive essays. Their purpose is primarily analysis, but analysis for the purposes of showing readers your interpretation of a literary text. So the thesis statement is a one to two sentence summary of your essay's main argument, or interpretation.
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
Read and summarize. As you prepare to analyze the short story assigned to you, it is recommended to read and re-read it multiple times. Since it is a short story, you'll have plenty of time to understand all the details included within the story and the context of the plot. To analyze the book, divide the narrative into sections.
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
How to Tell a Strong Thesis Statement from a Weak One 1. A strong thesis statement takes some sort of stand. Remember that your thesis needs to show your conclusions about a subject. For example, if you are writing a paper for a class on fitness, you might be asked to choose a popular weight-loss product to evaluate. Here are two thesis statements:
Assignment Description: For this essay, you will choose a short story and write an analysis that offers an interpretation of the text. You should identify some debatable aspect of the text and argue for your interpretation using your analysis of the story supported by textual evidence. Content: The essay should have a clear argumentative thesis ...
Third story: Online learning appears to be one way to better integrate higher education with other institutions in society since online learners integrate their educational experiences with other parts of their life, promoting a better flow of ideas between college and the rest of society. Final thesis (all three stories combined): Online ...
Analyze the main female character of the short story A Good Man Is Hard to Find by Flannery O'Connor. Discuss the rhetoric used by Guy de Maupassant in The Necklace. Examine the symbols in Mr. Green by Olen Butler. Explore the main theme of James Joyce's The Dead. Interpret the meaning of the dolls in a short story Barbie-Q by Sandra Cisneros
A thesis statement that stops at the first story isn't usually considered a thesis. A two-story thesis is usually considered competent, though some two-story theses are more intriguing and ambitious than others. A thoughtfully crafted and well informed three-story thesis puts the author on a smooth path toward an excellent paper.
A two-story thesis is usually considered competent, though some two-story theses are more intriguing and ambitious than others. A thoughtfully crafted and well informed three-story thesis puts the author on a smooth path toward an excellent paper. The three-story thesis is a beautiful thing. For one, it gives a paper authentic momentum.
short story, brief fictional prose narrative that is shorter than a novel and that usually deals with only a few characters. The short story is usually concerned with a single effect conveyed in only one or a few significant episodes or scenes. The form encourages economy of setting, concise narrative, and the omission of a complex plot ...
There is no deadline for the jury to stop deliberating, but O'Brein says three days would be considered a long time. He also said a quick decision could signal good things for the defense, as it ...
The Big Picture. The legendary myth of Eros and Psyche is referenced during Colin and Penelope's love story in Bridgerton Season 3. The elements of trust, betrayal, and divine intervention play a ...
When a national sample of voters was presented with the possibility that Trump would be found guilty in the New York case, 43% said they would vote for Biden, 38% would vote for Trump and 18% said ...
Florida Sen. Marco Rubio, on the list of Trump's potential running mates, declared, "The verdict in New York is a complete travesty that makes a mockery of our system of justice," calling it "a ...