- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Organisational Behaviour
- Human Resource Management
- Entrepreneurship
- CBSE Class 11 Statistics for Economics Notes

Chapter 1: Concept of Economics and Significance of Statistics in Economics
- Statistics for Economics | Functions, Importance, and Limitations
Chapter 2: Collection of Data
- Data Collection & Its Methods
- Sources of Data Collection | Primary and Secondary Sources
- Direct Personal Investigation: Meaning, Suitability, Merits, Demerits and Precautions
- Indirect Oral Investigation : Suitability, Merits, Demerits and Precautions
- Difference between Direct Personal Investigation and Indirect Oral Investigation
- Information from Local Source or Correspondents: Meaning, Suitability, Merits, and Demerits
- Questionnaires and Schedules Method of Data Collection
- Difference between Questionnaire and Schedule
- Qualities of a Good Questionnaire and types of Questions
- What are the Published Sources of Collecting Secondary Data?
- What Precautions should be taken before using Secondary Data?
- Two Important Sources of Secondary Data: Census of India and Reports & Publications of NSSO
- What is National Sample Survey Organisation (NSSO)?
- What is Census Method of Collecting Data?
- Sample Method of Collection of Data
- Methods of Sampling
- Father of Indian Census
- What makes a Sampling Data Reliable?
- Difference between Census Method and Sampling Method of Collecting Data
- What are Statistical Errors?
Chapter 3: Organisation of Data
- Organization of Data
- Objectives and Characteristics of Classification of Data
- Classification of Data in Statistics | Meaning and Basis of Classification of Data
- Concept of Variable and Raw Data
- Types of Statistical Series
- Difference between Frequency Array and Frequency Distribution
- Types of Frequency Distribution
Chapter 4: Presentation of Data: Textual and Tabular
- Textual Presentation of Data: Meaning, Suitability, and Drawbacks
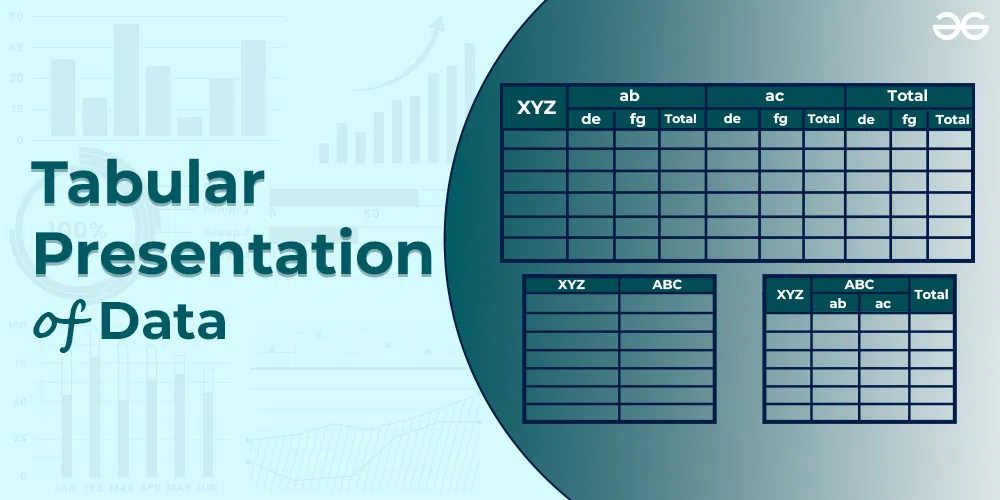
Tabular Presentation of Data: Meaning, Objectives, Features and Merits
- Different Types of Tables
- Classification and Tabulation of Data
Chapter 5: Diagrammatic Presentation of Data
- Diagrammatic Presentation of Data: Meaning , Features, Guidelines, Advantages and Disadvantages
- Types of Diagrams
- Bar Graph | Meaning, Types, and Examples
- Pie Diagrams | Meaning, Example and Steps to Construct
- Histogram | Meaning, Example, Types and Steps to Draw
- Frequency Polygon | Meaning, Steps to Draw and Examples
- Ogive (Cumulative Frequency Curve) and its Types
- What is Arithmetic Line-Graph or Time-Series Graph?
- Diagrammatic and Graphic Presentation of Data
Chapter 6: Measures of Central Tendency: Arithmetic Mean
- Measures of Central Tendency in Statistics
- Arithmetic Mean: Meaning, Example, Types, Merits, and Demerits
- What is Simple Arithmetic Mean?
- Calculation of Mean in Individual Series | Formula of Mean
- Calculation of Mean in Discrete Series | Formula of Mean
- Calculation of Mean in Continuous Series | Formula of Mean
- Calculation of Arithmetic Mean in Special Cases
- Weighted Arithmetic Mean
Chapter 7: Measures of Central Tendency: Median and Mode
- Median(Measures of Central Tendency): Meaning, Formula, Merits, Demerits, and Examples
- Calculation of Median for Different Types of Statistical Series
- Calculation of Median in Individual Series | Formula of Median
- Calculation of Median in Discrete Series | Formula of Median
- Calculation of Median in Continuous Series | Formula of Median
- Graphical determination of Median
- Mode: Meaning, Formula, Merits, Demerits, and Examples
- Calculation of Mode in Individual Series | Formula of Mode
- Calculation of Mode in Discrete Series | Formula of Mode
- Grouping Method of Calculating Mode in Discrete Series | Formula of Mode
- Calculation of Mode in Continuous Series | Formula of Mode
- Calculation of Mode in Special Cases
- Calculation of Mode by Graphical Method
- Mean, Median and Mode| Comparison, Relationship and Calculation
Chapter 8: Measures of Dispersion
- Measures of Dispersion | Meaning, Absolute and Relative Measures of Dispersion
- Range | Meaning, Coefficient of Range, Merits and Demerits, Calculation of Range
- Calculation of Range and Coefficient of Range
- Interquartile Range and Quartile Deviation
- Partition Value | Quartiles, Deciles and Percentiles
- Quartile Deviation and Coefficient of Quartile Deviation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation, and Examples
- Quartile Deviation in Discrete Series | Formula, Calculation and Examples
- Quartile Deviation in Continuous Series | Formula, Calculation and Examples
- Mean Deviation: Coefficient of Mean Deviation, Merits, and Demerits
- Calculation of Mean Deviation for different types of Statistical Series
- Mean Deviation from Mean | Individual, Discrete, and Continuous Series
- Mean Deviation from Median | Individual, Discrete, and Continuous Series
- Standard Deviation: Meaning, Coefficient of Standard Deviation, Merits, and Demerits
- Standard Deviation in Individual Series
- Methods of Calculating Standard Deviation in Discrete Series
- Methods of calculation of Standard Deviation in frequency distribution series
- Combined Standard Deviation: Meaning, Formula, and Example
- How to calculate Variance?
- Coefficient of Variation: Meaning, Formula and Examples
- Lorenz Curveb : Meaning, Construction, and Application
Chapter 9: Correlation
- Correlation: Meaning, Significance, Types and Degree of Correlation
- Methods of measurements of Correlation
- Calculation of Correlation with Scattered Diagram
- Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient
- Karl Pearson's Coefficient of Correlation
- Karl Pearson's Coefficient of Correlation | Methods and Examples
Chapter 10: Index Number
- Index Number | Meaning, Characteristics, Uses and Limitations
- Methods of Construction of Index Number
- Unweighted or Simple Index Numbers: Meaning and Methods
- Methods of calculating Weighted Index Numbers
- Fisher's Index Number as an Ideal Method
- Fisher's Method of calculating Weighted Index Number
- Paasche's Method of calculating Weighted Index Number
- Laspeyre's Method of calculating Weighted Index Number
- Laspeyre's, Paasche's, and Fisher's Methods of Calculating Index Number
- Consumer Price Index (CPI) or Cost of Living Index Number: Construction of Consumer Price Index|Difficulties and Uses of Consumer Price Index
- Methods of Constructing Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- Wholesale Price Index (WPI) | Meaning, Uses, Merits, and Demerits
- Index Number of Industrial Production : Characteristics, Construction & Example
- Inflation and Index Number
Important Formulas in Statistics for Economics
- Important Formulas in Statistics for Economics | Class 11
What is Tabulation?
The systematic presentation of numerical data in rows and columns is known as Tabulation . It is designed to make presentation simpler and analysis easier. This type of presentation facilitates comparison by putting relevant information close to one another, and it helps in further statistical analysis and interpretation. One of the most important devices for presenting the data in a condensed and readily comprehensible form is tabulation. It aims to provide as much information as possible in the minimum possible space while maintaining the quality and usefulness of the data.
“Tabulation involves the orderly and systematic presentation of numerical data in a form designed to elucidate the problem under consideration.” – L.R. Connor
Objectives of Tabulation
The aim of tabulation is to summarise a large amount of numerical information into the simplest form. The following are the main objectives of tabulation:
- To make complex data simpler: The main aim of tabulation is to present the classified data in a systematic way. The purpose is to condense the bulk of information (data) under investigation into a simple and meaningful form.
- To save space: Tabulation tries to save space by condensing data in a meaningful form while maintaining the quality and quantity of the data.
- To facilitate comparison: It also aims to facilitate quick comparison of various observations by providing the data in a tabular form.
- To facilitate statistical analysis: Tabulation aims to facilitate statistical analysis because it is the stage between data classification and data presentation. Various statistical measures, including averages, dispersion, correlation, and others, are easily calculated from data that has been systematically tabulated.
- To provide a reference: Since data may be easily identifiable and used when organised in tables with titles and table numbers, tabulation aims to provide a reference for future studies.
Features of a Good Table
Tabulation is a very specialised job. It requires a thorough knowledge of statistical methods, as well as abilities, experience, and common sense. A good table must have the following characteristics:
- Title: The top of the table must have a title and it needs to be very appealing and attractive.
- Manageable Size: The table shouldn’t be too big or too small. The size of the table should be in accordance with its objectives and the characteristics of the data. It should completely cover all significant characteristics of data.
- Attractive: A table should have an appealing appearance that appeals to both the sight and the mind so that the reader can grasp it easily without any strain.
- Special Emphasis: The data to be compared should be placed in the left-hand corner of columns, with their titles in bold letters.
- Fit with the Objective: The table should reflect the objective of the statistical investigation.
- Simplicity: To make the table easily understandable, it should be simple and compact.
- Data Comparison: The data to be compared must be placed closely in the columns.
- Numbered Columns and Rows: When there are several rows and columns in a table, they must be numbered for reference.
- Clarity: A table should be prepared so that even a layman may make conclusions from it. The table should contain all necessary information and it must be self-explanatory.
- Units: The unit designations should be written on the top of the table, below the title. For example, Height in cm, Weight in kg, Price in ₹, etc. However, if different items have different units, then they should be mentioned in the respective rows and columns.
- Suitably Approximated: If the figures are large, then they should be rounded or approximated.
- Scientifically Prepared: The preparation of the table should be done in a systematic and logical manner and should be free from any kind of ambiguity and overlapping.
Components of a Table
A table’s preparation is an art that requires skilled data handling. It’s crucial to understand the components of a good statistical table before constructing one. A table is created when all of these components are put together in a systematic order. In simple terms, a good table should include the following components:
1. Table Number:
Each table needs to have a number so it may be quickly identified and used as a reference.
- If there are many tables, they should be numbered in a logical order.
- The table number can be given at the top of the table or the beginning of the table title.
- The table is also identified by its location using subscripted numbers like 1.2, 2.1, etc. For instance, Table Number 3.1 should be seen as the first table of the third chapter.
Each table should have a suitable title. A table’s contents are briefly described in the title.
- The title should be simple, self-explanatory, and free from ambiguity.
- A title should be brief and presented clearly, usually below the table number.
- In certain cases, a long title is preferable for clarification. In these cases, a ‘Catch Title’ may be placed above the ‘Main Title’. For instance , the table’s contents might come after the firm’s name, which appears as a catch title.
- Contents of Title: The title should include the following information: (i) Nature of data, or classification criteria (ii) Subject-matter (iii) Place to which the data relates (iv) Time to which the data relates (v) Source to which the data belongs (vi) Reference to the data, if available.
3. Captions or Column Headings:
A column designation is given to explain the figures in the column at the top of each column in a table. This is referred to as a “Column heading” or “Caption”.
- Captions are used to describe the names or heads of vertical columns.
- To save space, captions are generally placed in small letters in the middle of the columns.
4. Stubs or Row Headings:
Each row of the table needs to have a heading, similar to a caption or column heading. The headers of horizontal rows are referred to as stubs. A brief description of the row headers may also be provided at the table’s left-hand top.
5. Body of Table:
The table’s most crucial component is its body, which contains data (numerical information).
- The location of any one figure or data in the table is fixed and determined by the row and column of the table.
- The columns and rows in the main body’s arrangement of numerical data are arranged from top to bottom.
- The size and shape of the main body should be planned in accordance with the nature of the figures and the purpose of the study.
- As the body of the table summarises the facts and conclusions of the statistical investigation, it must be ensured that the table does not have irrelevant information.
6. Unit of Measurement:
If the unit of measurement of the figures in the table (real data) does not change throughout the table, it should always be provided along with the title.
- However, these units must be mentioned together with stubs or captions if rows or columns have different units.
- If there are large figures, they should be rounded up and the rounding method should be stated.
7. Head Notes:
If the main title does not convey enough information, a head note is included in small brackets in prominent words right below the main title.
- A head-note is included to convey any relevant information.
- For instance, the table frequently uses the units of measurement “in million rupees,” “in tonnes,” “in kilometres,” etc. Head notes are also known as Prefatory Notes .
8. Source Note:
A source note refers to the place where information was obtained.
- In the case of secondary data, a source note is provided.
- Name of the book, page number, table number, etc., from which the data were collected should all be included in the source. If there are multiple sources, each one must be listed in the source note.
- If a reader wants to refer to the original data, the source note enables him to locate the data. Usually, the source note appears at the bottom of the table. For example, the source note may be: ‘Census of India, 2011’.
- Importance: A source note is useful for three reasons: -> It provides credit to the source (person or group), who collected the data; -> It provides a reference to source material that may be more complete; -> It offers some insight into the reliability of the information and its source.
9. Footnotes:
The footnote is the last part of the table. The unique characteristic of the data content of the table that is not self-explanatory and has not previously been explained is mentioned in the footnote.
- Footnotes are used to provide additional information that is not provided by the heading, title, stubs, caption, etc.
- When there are many footnotes, they are numbered in order.
- Footnotes are identified by the symbols *, @, £, etc.
- In general, footnotes are used for the following reasons: (i) To highlight any exceptions to the data (ii)Any special circumstances affecting the data; and (iii)To clarify any information in the data.
.webp)
Merits of Tabular Presentation of Data
The following are the merits of tabular presentation of data:
- Brief and Simple Presentation: Tabular presentation is possibly the simplest method of data presentation. As a result, information is simple to understand. A significant amount of statistical data is also presented in a very brief manner.
- Facilitates Comparison: By grouping the data into different classes, tabulation facilitates data comparison.
- Simple Analysis: Analysing data from tables is quite simple. One can determine the data’s central tendency, dispersion, and correlation by organising the data as a table.
- Highlights Characteristics of the Data: Tabulation highlights characteristics of the data. As a result of this, it is simple to remember the statistical facts.
- Cost-effective: Tabular presentation is a very cost-effective way to convey data. It saves time and space.
- Provides Reference: As the data provided in a tabular presentation can be used for other studies and research, it acts as a source of reference.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Commerce - 11th
- Statistics for Economics
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Tabular Presentation of Data

Understanding tabular representation of statistical data
The statistical data usually refers to the aggregate of the numerical data which eventually contributes to its collection, interpretation, and analysis. Quantifying this data helps with the research and statistical operations. In the tabular presentation, the data is presented in the form of rows and columns, and this data positioning makes reading and understanding the data more feasible. The logical and statistical conclusions are derived from the presentation of the data.
Objectives of Tabular Data Presentation
The objectives of tabular data presentation are as follows.
The tabular data presentation helps in simplifying the complex data.
It also helps to compare different data sets thereby bringing out the important aspects.
The tabular presentation provides the foundation for statistical analysis.
The tabular data presentation further helps in the formation of graphs, as well as diagrams for the purpose of advanced data analysis.
Parts of the Table that are Used in the Tabulation
Some of the parts that are used in the table of tabular data presentation are as follows.
Table number: This is included for the purpose of identification and it provides for easy reference.
Title: It provides the nature of information which is included in the table. This information is included adjacent to table number.
Stub: This is provided on the left-side of tabular form. The specific issues that are mentioned in the stub are presented in the horizontal rows.
Caption: The caption is put on the top of columns within the table. The columns come with the specific unit within which figures are noted down.
Body: This is the most significant of the table and it is located in the middle or centre of the table. It is made up of numerical contents.
Footnote: The footnote gives the scope or potential for further explanation that might be required for any item which is included in the table. The footnote helps with the clarification of data that is mentioned within the table.
Information source: The information source is included on the bottom of the table. It gives the source related to the specific piece of information and the authenticity of the sources that are cited here helps in contributing to the credibility of the data.
You can check out the illustration of the tabular presentation of data through the provided sample included in the Vedantu notes related to this topic. The different forms of tabular analysis are quantitative analysis, qualitative analysis, spatial analysis, and temporal analysis. When it comes to limitations related to the tabular presentation of the data, they are lack of focus on the individual items, no scope or potential for description, and requiring expert knowledge.
Illustration Of A Tabular Representation of Data
Tabular presentation of data example is shown below.
Test Your Knowledge –
1. Where Is A “Headnote” Placed In A Table?
A headnote comprises the main title
It follows the primary title within a small bracket
A headnote can be placed anywhere in the table
2. Which Of The Following is Used for Explanation of Column Figures?
Caption
Title
Forms of Tabular Analysis
Quantitative .
The quantitative tabular analysis provides a description and interpretation of items based on statistics. Such analysis is undertaken through numeric variables as well as statistical methods.
Qualitative
Qualitative analysis is done, taking into account various attributes that are non-numerical. For instance, it may include social status, nationality, and physical specifications, among others. In such classification, the attributes that are taken into consideration cannot be subjected to quantitative measurement.
Spatial
Categorisation, when done based on location such as a state, country, block, and district, etc., is called spatial analysis.
Temporal
In this analysis method, time becomes a variable for data analysis. Such consideration of time may be in the form of hours, days, weeks, and months among others.
Limitations of A Tabular Presentation
There are certain drawbacks to a table presentation of data that have been mentioned below.
Lack of Focus on Individual Items
Individual items are not presented distinctly. A tabular presentation shows data in an aggregated manner.
No Scope for Description
It is only the figures that are indicated in a tabular presentation. The attributes of those figures cannot be mentioned in tables. Moreover, the qualitative aspects of figures cannot be mentioned.
Requires Expert Knowledge
A layperson will not be able to decipher the intricacies that are mentioned in the figures within a tabular presentation. Its interpretation and analysis can only be undertaken by a person with the requisite expertise.
To know more about this topic and others, install the Vedantu app on your device and read from online study materials available over our platform.

FAQs on Tabular Presentation of Data
1. What is tabular data presentation?
The specific methods that are used for presenting statistical data in the tabular format is known as tabular presentation of data. The data is systematically and logically arranged within the rows and the columns with regards to the specific characteristics of the data. The tabular data presentation makes forthright interpretation as well as comprehensible dataset. This is the reason why tabular data presentation format is widely used in a number of applications where data needs to be organised and analysed.
2. What are the objectives related to data tabulation?
There are specific and well-defined objectives that are associated with the presentation of data tabulation. The data tabular presentation helps with the easy conversion of data into a simple and comprehensible form through tabulation. Besides data arrangement convenience, the tabular presentation of data also creates the foundation for statistical analysis. This statistical analysis might include dispersion, averages, and correlation amongst other factors. These well-laid out objectives are the primary reason behind the usage of tabular data presentation.
3. What are the primary benefits of using tabular presentation of data?
The tabular presentation of data helps with the organisation of data that is easy to understand and analyse. It also helps with the comparison of data. The data is presented in such a way that it helps reduce the time and effort of the user through the organisation as well as the simplicity of the data presentation. The easy organisation plus presentation of data in tabular form is one of the reasons why it is widely used in data analysis.
4. Can I rely on the tabular presentation of data notes from Vedantu?
Yes, you can rely on the Vedantu note for tabular presentation of data. These notes and chapters are compiled by well-qualified teachers or experts who have distinguished knowledge in the subject and who understand the comprehension skills of the students. These notes are carefully created to provide the best explanation of the topic and help students understand the concept in detail through text and illustrations wherever essential.
5. How can I access the tabular presentation of data notes provided by Vedantu?
If you want access to the Vedantu notes on tabular presentation of data then you can download it from the Vedantu app or website. These notes are available for download in the PDF file format for free. Once you are on the relevant section of the website, you will find the “Download PDF” button and when you click on that option, the file will be downloaded on your device. Now you can access the Vedantu notes even offline as per your convenience.

Statistics Made Easy
What is Tabular Data? (Definition & Example)
In statistics, tabular data refers to data that is organized in a table with rows and columns.

Within the table, the rows represent observations and the columns represent attributes for those observations.
For example, the following table represents tabular data:

This dataset has 9 rows and 5 columns.
Each row represents one basketball player and the five columns describe different attributes about the player including:
- Player name
- Minutes played
The opposite of tabular data would be visual data , which would be some type of plot or chart that helps us visualize the values in a dataset.
For example, we might have the following bar chart that helps us visualize the total minutes played by each player in the dataset:

This would be an example of visual data .
It contains the exact same information about player names and minutes played for the players in the dataset, but it’s simply displayed in a visual form instead of a tabular form.
Or we might have the following scatterplot that helps us visualize the relationship between minutes played and points scored for each player:

This is another example of visual data .
When is Tabular Data Used in Practice?
In practice, tabular data is the most common type of data that you’ll run across in the real world.
In the real world, most data that is saved in an Excel spreadsheet is considered tabular data because the rows represent observations and the columns represent attributes for those observations.
For example, here’s what our basketball dataset from earlier might look like in an Excel spreadsheet:

This format is one of the most natural ways to collect and store values in a dataset, which is why it’s used so often.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain other common terms in statistics:
Why is Statistics Important? Why is Sample Size Important in Statistics? What is an Observation in Statistics? What is Considered Raw Data in Statistics?
Featured Posts

Hey there. My name is Zach Bobbitt. I have a Masters of Science degree in Applied Statistics and I’ve worked on machine learning algorithms for professional businesses in both healthcare and retail. I’m passionate about statistics, machine learning, and data visualization and I created Statology to be a resource for both students and teachers alike. My goal with this site is to help you learn statistics through using simple terms, plenty of real-world examples, and helpful illustrations.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Join the Statology Community
Sign up to receive Statology's exclusive study resource: 100 practice problems with step-by-step solutions. Plus, get our latest insights, tutorials, and data analysis tips straight to your inbox!
By subscribing you accept Statology's Privacy Policy.
Data presentation: A comprehensive guide
Learn how to create data presentation effectively and communicate your insights in a way that is clear, concise, and engaging.
Raja Bothra
Building presentations

Hey there, fellow data enthusiast!
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on data presentation.
Whether you're an experienced presenter or just starting, this guide will help you present your data like a pro.
We'll dive deep into what data presentation is, why it's crucial, and how to master it. So, let's embark on this data-driven journey together.
What is data presentation?
Data presentation is the art of transforming raw data into a visual format that's easy to understand and interpret. It's like turning numbers and statistics into a captivating story that your audience can quickly grasp. When done right, data presentation can be a game-changer, enabling you to convey complex information effectively.
Why are data presentations important?
Imagine drowning in a sea of numbers and figures. That's how your audience might feel without proper data presentation. Here's why it's essential:
- Clarity : Data presentations make complex information clear and concise.
- Engagement : Visuals, such as charts and graphs, grab your audience's attention.
- Comprehension : Visual data is easier to understand than long, numerical reports.
- Decision-making : Well-presented data aids informed decision-making.
- Impact : It leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
Types of data presentation
Now, let's delve into the diverse array of data presentation methods, each with its own unique strengths and applications. We have three primary types of data presentation, and within these categories, numerous specific visualization techniques can be employed to effectively convey your data.
1. Textual presentation
Textual presentation harnesses the power of words and sentences to elucidate and contextualize your data. This method is commonly used to provide a narrative framework for the data, offering explanations, insights, and the broader implications of your findings. It serves as a foundation for a deeper understanding of the data's significance.
2. Tabular presentation
Tabular presentation employs tables to arrange and structure your data systematically. These tables are invaluable for comparing various data groups or illustrating how data evolves over time. They present information in a neat and organized format, facilitating straightforward comparisons and reference points.
3. Graphical presentation
Graphical presentation harnesses the visual impact of charts and graphs to breathe life into your data. Charts and graphs are powerful tools for spotlighting trends, patterns, and relationships hidden within the data. Let's explore some common graphical presentation methods:
- Bar charts: They are ideal for comparing different categories of data. In this method, each category is represented by a distinct bar, and the height of the bar corresponds to the value it represents. Bar charts provide a clear and intuitive way to discern differences between categories.
- Pie charts: It excel at illustrating the relative proportions of different data categories. Each category is depicted as a slice of the pie, with the size of each slice corresponding to the percentage of the total value it represents. Pie charts are particularly effective for showcasing the distribution of data.
- Line graphs: They are the go-to choice when showcasing how data evolves over time. Each point on the line represents a specific value at a particular time period. This method enables viewers to track trends and fluctuations effortlessly, making it perfect for visualizing data with temporal dimensions.
- Scatter plots: They are the tool of choice when exploring the relationship between two variables. In this method, each point on the plot represents a pair of values for the two variables in question. Scatter plots help identify correlations, outliers, and patterns within data pairs.
The selection of the most suitable data presentation method hinges on the specific dataset and the presentation's objectives. For instance, when comparing sales figures of different products, a bar chart shines in its simplicity and clarity. On the other hand, if your aim is to display how a product's sales have changed over time, a line graph provides the ideal visual narrative.
Additionally, it's crucial to factor in your audience's level of familiarity with data presentations. For a technical audience, more intricate visualization methods may be appropriate. However, when presenting to a general audience, opting for straightforward and easily understandable visuals is often the wisest choice.
In the world of data presentation, choosing the right method is akin to selecting the perfect brush for a masterpiece. Each tool has its place, and understanding when and how to use them is key to crafting compelling and insightful presentations. So, consider your data carefully, align your purpose, and paint a vivid picture that resonates with your audience.
What to include in data presentation
When creating your data presentation, remember these key components:
- Data points : Clearly state the data points you're presenting.
- Comparison : Highlight comparisons and trends in your data.
- Graphical methods : Choose the right chart or graph for your data.
- Infographics : Use visuals like infographics to make information more digestible.
- Numerical values : Include numerical values to support your visuals.
- Qualitative information : Explain the significance of the data.
- Source citation : Always cite your data sources.
How to structure an effective data presentation
Creating a well-structured data presentation is not just important; it's the backbone of a successful presentation. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you craft a compelling and organized presentation that captivates your audience:
1. Know your audience
Understanding your audience is paramount. Consider their needs, interests, and existing knowledge about your topic. Tailor your presentation to their level of understanding, ensuring that it resonates with them on a personal level. Relevance is the key.
2. Have a clear message
Every effective data presentation should convey a clear and concise message. Determine what you want your audience to learn or take away from your presentation, and make sure your message is the guiding light throughout your presentation. Ensure that all your data points align with and support this central message.
3. Tell a compelling story
Human beings are naturally wired to remember stories. Incorporate storytelling techniques into your presentation to make your data more relatable and memorable. Your data can be the backbone of a captivating narrative, whether it's about a trend, a problem, or a solution. Take your audience on a journey through your data.
4. Leverage visuals
Visuals are a powerful tool in data presentation. They make complex information accessible and engaging. Utilize charts, graphs, and images to illustrate your points and enhance the visual appeal of your presentation. Visuals should not just be an accessory; they should be an integral part of your storytelling.
5. Be clear and concise
Avoid jargon or technical language that your audience may not comprehend. Use plain language and explain your data points clearly. Remember, clarity is king. Each piece of information should be easy for your audience to digest.
6. Practice your delivery
Practice makes perfect. Rehearse your presentation multiple times before the actual delivery. This will help you deliver it smoothly and confidently, reducing the chances of stumbling over your words or losing track of your message.
A basic structure for an effective data presentation
Armed with a comprehensive comprehension of how to construct a compelling data presentation, you can now utilize this fundamental template for guidance:
In the introduction, initiate your presentation by introducing both yourself and the topic at hand. Clearly articulate your main message or the fundamental concept you intend to communicate.
Moving on to the body of your presentation, organize your data in a coherent and easily understandable sequence. Employ visuals generously to elucidate your points and weave a narrative that enhances the overall story. Ensure that the arrangement of your data aligns with and reinforces your central message.
As you approach the conclusion, succinctly recapitulate your key points and emphasize your core message once more. Conclude by leaving your audience with a distinct and memorable takeaway, ensuring that your presentation has a lasting impact.
Additional tips for enhancing your data presentation
To take your data presentation to the next level, consider these additional tips:
- Consistent design : Maintain a uniform design throughout your presentation. This not only enhances visual appeal but also aids in seamless comprehension.
- High-quality visuals : Ensure that your visuals are of high quality, easy to read, and directly relevant to your topic.
- Concise text : Avoid overwhelming your slides with excessive text. Focus on the most critical points, using visuals to support and elaborate.
- Anticipate questions : Think ahead about the questions your audience might pose. Be prepared with well-thought-out answers to foster productive discussions.
By following these guidelines, you can structure an effective data presentation that not only informs but also engages and inspires your audience. Remember, a well-structured presentation is the bridge that connects your data to your audience's understanding and appreciation.
Do’s and don'ts on a data presentation
- Use visuals : Incorporate charts and graphs to enhance understanding.
- Keep it simple : Avoid clutter and complexity.
- Highlight key points : Emphasize crucial data.
- Engage the audience : Encourage questions and discussions.
- Practice : Rehearse your presentation.
Don'ts:
- Overload with data : Less is often more; don't overwhelm your audience.
- Fit Unrelated data : Stay on topic; don't include irrelevant information.
- Neglect the audience : Ensure your presentation suits your audience's level of expertise.
- Read word-for-word : Avoid reading directly from slides.
- Lose focus : Stick to your presentation's purpose.
Summarizing key takeaways
- Definition : Data presentation is the art of visualizing complex data for better understanding.
- Importance : Data presentations enhance clarity, engage the audience, aid decision-making, and leave a lasting impact.
- Types : Textual, Tabular, and Graphical presentations offer various ways to present data.
- Choosing methods : Select the right method based on data, audience, and purpose.
- Components : Include data points, comparisons, visuals, infographics, numerical values, and source citations.
- Structure : Know your audience, have a clear message, tell a compelling story, use visuals, be concise, and practice.
- Do's and don'ts : Do use visuals, keep it simple, highlight key points, engage the audience, and practice. Don't overload with data, include unrelated information, neglect the audience's expertise, read word-for-word, or lose focus.
1. What is data presentation, and why is it important in 2023?
Data presentation is the process of visually representing data sets to convey information effectively to an audience. In an era where the amount of data generated is vast, visually presenting data using methods such as diagrams, graphs, and charts has become crucial. By simplifying complex data sets, presentation of the data may helps your audience quickly grasp much information without drowning in a sea of chart's, analytics, facts and figures.
2. What are some common methods of data presentation?
There are various methods of data presentation, including graphs and charts, histograms, and cumulative frequency polygons. Each method has its strengths and is often used depending on the type of data you're using and the message you want to convey. For instance, if you want to show data over time, try using a line graph. If you're presenting geographical data, consider to use a heat map.
3. How can I ensure that my data presentation is clear and readable?
To ensure that your data presentation is clear and readable, pay attention to the design and labeling of your charts. Don't forget to label the axes appropriately, as they are critical for understanding the values they represent. Don't fit all the information in one slide or in a single paragraph. Presentation software like Prezent and PowerPoint can help you simplify your vertical axis, charts and tables, making them much easier to understand.
4. What are some common mistakes presenters make when presenting data?
One common mistake is trying to fit too much data into a single chart, which can distort the information and confuse the audience. Another mistake is not considering the needs of the audience. Remember that your audience won't have the same level of familiarity with the data as you do, so it's essential to present the data effectively and respond to questions during a Q&A session.
5. How can I use data visualization to present important data effectively on platforms like LinkedIn?
When presenting data on platforms like LinkedIn, consider using eye-catching visuals like bar graphs or charts. Use concise captions and e.g., examples to highlight the single most important information in your data report. Visuals, such as graphs and tables, can help you stand out in the sea of textual content, making your data presentation more engaging and shareable among your LinkedIn connections.
Create your data presentation with prezent
Prezent can be a valuable tool for creating data presentations. Here's how Prezent can help you in this regard:
- Time savings : Prezent saves up to 70% of presentation creation time, allowing you to focus on data analysis and insights.
- On-brand consistency : Ensure 100% brand alignment with Prezent's brand-approved designs for professional-looking data presentations.
- Effortless collaboration : Real-time sharing and collaboration features make it easy for teams to work together on data presentations.
- Data storytelling : Choose from 50+ storylines to effectively communicate data insights and engage your audience.
- Personalization : Create tailored data presentations that resonate with your audience's preferences, enhancing the impact of your data.
In summary, Prezent streamlines the process of creating data presentations by offering time-saving features, ensuring brand consistency, promoting collaboration, and providing tools for effective data storytelling. Whether you need to present data to clients, stakeholders, or within your organization, Prezent can significantly enhance your presentation-making process.
So, go ahead, present your data with confidence, and watch your audience be wowed by your expertise.
Thank you for joining us on this data-driven journey. Stay tuned for more insights, and remember, data presentation is your ticket to making numbers come alive!
Sign up for our free trial or book a demo !
More zenpedia articles

How to write a problem statement slide for PowerPoint

5 Effective and powerful ways to end a presentation!

7 Simple rules to help you create effective powerpoint presentations
Get the latest from Prezent community
Join thousands of subscribers who receive our best practices on communication, storytelling, presentation design, and more. New tips weekly. (No spam, we promise!)
Reset password New user? Sign up
Existing user? Log in
Data Presentation - Tables
Already have an account? Log in here.
Tables are a useful way to organize information using rows and columns. Tables are a versatile organization tool and can be used to communicate information on their own, or they can be used to accompany another data representation type (like a graph). Tables support a variety of parameters and can be used to keep track of frequencies, variable associations, and more.
For example, given below are the weights of 20 students in grade 10: \[50, 45, 48, 39, 40, 48, 54, 50, 48, 48, \\ 50, 39, 41, 46, 44, 43, 54, 57, 60, 45.\]
To find the frequency of \(48\) in this data, count the number of times that \(48\) appears in the list. There are \(4\) students that have this weight.
The list above has information about the weight of \(20\) students, and since the data has been arranged haphazardly, it is difficult to classify the students properly.
To make the information more clear, tabulate the given data.
\[\begin{array} \\ \text{Weights in kg} & & & \text{Frequency} \\ 39 & & & 2 \\ 40 & & & 1 \\ 41 & & & 1 \\ 43 & & & 1 \\ 44 & & & 1 \\ 45 & & & 2 \\ 46 & & & 1 \\ 48 & & & 4 \\ 50 & & & 3 \\ 54 & & & 2 \\ 57 & & & 1 \\ 60 & & & 1 \end{array}\]
This table makes the data more easy to understand.
Making a Table
Making and using tables.
To make a table, first decide how many rows and columns are needed to clearly display the data. To do this, consider how many variables are included in the data set.
The following is an example of a table where there are two variables.
The following is an example of a table with three variables.
A table is good for organizing quantitative data in a way that it is easy to look things up. For example, a table would be good way to associate a person’s name, age, and favorite food. However, when trying to communicate relations, such as how a person’s favorite food changes over time, a graph would be a better choice.
Using the table below, determine the average age of the group?
Good practices for making tables Label what each row or column represents Include units in labels when data is numerical Format data consistently (use consistent units and formatting)
What is wrong with this table? Flavor of Ice Cream Number Sold (cones) Chocolate 104 Vanilla two-hundred Strawberry 143 Coconut thirty Mango 126 Show answer Answer: The data isn’t consistently formatted. The number of cones sold is written in numbers in both symbols and words. It would be easier to understand if all entries were numerical symbols.
What is wrong with this table? Jack blue Sarah yellow Billy green Ron red Christina blue Margret purple Show answer Answer: There are no labels on the columns. It is not clear what the table is displaying — does the table show what color shirt each person is wearing? Do it show what each person's favorite color is? It isn't clear because labels are missing.
Many word processing softwares include tools for making tables. You can easily make tables in Microsoft Word and Excel and in Google Docs and Sheets.
Here is an example table (left blank) with which you could record information about a person's age, weight, and height.
Tables are used to present information in all types of fields. Geologists might make a table to record data about types of rocks they find while doing field work, political researchers might create a table to record information about potential voters, and physicists might make a table to record observations about the speed of a ball rolled on various surfaces.
Problem Loading...
Note Loading...
Set Loading...
4 Introduction to Tabular Data
An email inbox is a list of messages. For each message, your inbox stores a bunch of information: its sender, the subject line, the conversation it’s part of, the body, and quite a bit more.
A music playlist. For each song, your music player maintains a bunch of information: its name, the singer, its length, its genre, and so on.

A filesystem folder or directory. For each file, your filesystem records a name, a modification date, size, and other information.

Do Now! Can you come up with more examples?
Responses to a party invitation.
A gradebook.
A calendar agenda.
They consists of rows and columns. For instance, each song or email message or file is a row. Each of their characteristics— the song title, the message subject, the filename— is a column.
Each row has the same columns as the other rows, in the same order.
A given column has the same type, but different columns can have different types. For instance, an email message has a sender’s name, which is a string; a subject line, which is a string; a sent date, which is a date; whether it’s been read, which is a Boolean; and so on.
The rows are usually in some particular order. For instance, the emails are ordered by which was most recently sent.
Exercise Find the characteristics of tabular data in the other examples described above, as well as in the ones you described.
We will now learn how to program with tables and to think about decomposing tasks involving them. You can also look up the full Pyret documentation for table operations .
4.1 Creating Tabular Data
table: name, age row: "Alice", 30 row: "Bob", 40 row: "Carol", 25 end
Exercise Change different parts of the above example— e.g., remove a necessary value from a row, add an extraneous one, remove a comma, add an extra comma, leave an extra comma at the end of a row— and see what errors you get.
check: table: name, age row: "Alice", 30 row: "Bob", 40 row: "Carol", 25 end is-not table: age, name row: 30, "Alice" row: 40, "Bob" row: 25, "Carol" end end
create the sheet on your own,
create a sheet collaboratively with friends,
find data on the Web that you can import into a sheet,
create a Google Form that you get others to fill out, and obtain a sheet out of their responses
4.2 Processing Rows
Let’s now learn how we can actually process a table. Pyret offers a variety of built-in operations that make it quite easy to perform interesting computations over tables. In addition, as we will see later [REF], if we don’t find these sufficient, we can write our own. For now, we’ll focus on the operations Pyret provides.
Which emails were sent by a particular user?
Which songs were sung by a particular artist?
Which are the most frequently played songs in a playlist?
Which are the least frequently played songs in a playlist?
4.2.1 Keeping
sieve email using sender: sender == 'Matthias Felleisen' end
sieve playlist using artist: (artist == 'Deep Purple') or (artist == 'Van Halen') end
4.2.2 Ordering
order playlist: play-count ascending end
Note that what goes between the : and end is not an expression. Therefore, we cannot write arbitrary code here. We can only name columns and indicate which way they should be ordered.
4.2.3 Combining Keeping and Ordering
Of the emails from a particular person, which is the oldest?
Of the songs by a particular artist, which have we played the least often?
Do Now! Take a moment to think about how you would write these with what you have seen so far.
mf-emails = sieve email using sender: sender == 'Matthias Felleisen' end order mf-emails: sent-date ascending end
Exercise Write the second example as a composition of keep and order operations on a playlist table.
4.2.4 Extending
extend employees using hourly-wage, hours-worked: total-wage: hourly-wage * hours-worked end
ext-email = extend email using subject: subject-length: string-length(subject) end order ext-email: subject-length descending end
4.2.5 Transforming, Cleansing, and Normalizing
There are times when a table is “almost right”, but requires a little adjusting. For instance, we might have a table of customer requests for a free sample, and want to limit each customer to at most a certain number. We might get temperature readings from different countries in different formats, and want to convert them all to one single format. Because unit errors can be dangerous ! We might have a gradebook where different graders have used different levels of precision, and want to standardize all of them to have the same level of precision.
transform orders using count: count: num-min(count, 3) end
transform gradebook using total-grade: total-grade: num-round(total-grade) end
transform weather using temp, unit: temp: if unit == "F": fahrenheit-to-celsius(temp) else: temp end unit: if unit == "F": "C" else: unit end end
Do Now! In this example, why do we also transform unit ?
4.2.6 Selecting
select name, total-grade from gradebook end
ss = select artist, song from playlist end order ss: artist ascending end
4.2.7 Summary of Row-Wise Table Operations
We’ve seen a lot in a short span. Specifically, we have seen several operations that consume a table and produce a new one according to some criterion. It’s worth summarizing the impact each of them has in terms of key table properties (where “-” means the entry is left unchanged):
The italicized entries reflect how the new table may differ from the old. Note that an entry like “reduced” or “altered” should be read as potentially reduced or altered; depending on the specific operation and the content of the table, there may be no change at all. (For instance, if a table is already sorted according to the criterion given in an order expression, the row order will not change.) However, in general one should expect the kind of change described in the above grid.
Observe that both dimensions of this grid provide interesting information. Unsurprisingly, each row has at least some kind of impact on a table (otherwise the operation would be useless and would not exist). Likewise, each column also has at least one way of impacting it. Furthermore, observe that most entries leave the table unchanged: that means each operation has limited impact on the table, careful to not overstep the bounds of its mandate.
On the one hand, the decision to limit the impact of each operation means that to achieve complex tasks, we may have to compose several operations together. We have already seen examples of this earlier this chapter. However, there is also a much more subtle consequence: it also means that to achieve complex tasks, we can compose several operations and get exactly what we want. If we had fewer operations that each did more, then composing them might have various undesired or (worse) unintended consequences, making it very difficult for us to obtain exactly the answer we want. Instead, the operations above follow the principle of orthogonality : no operation shadows what any other operation does, so they can be composed freely.
As a result of having these operations, we can think of tables also algebrically. Concretely, when given a problem, we should again begin with concrete examples of what we’re starting with and where we want to end. Then we can ask ourselves questions like, “Does the number of columns stay the same, grow, or shrink?”, “Does the number of rows stay the same or shrink?”, and so on. The grid above now provides us a toolkit by which we can start to decompose the task into individual operations. Of course, we still have to think: the order of operations matters, and sometimes we have to perform an operation mutiple times. Still, this grid is a useful guide to hint us towards the operations that might help solve our problem.
- Textual And Tabular Presentation Of Data
Think about a scenario where your report cards are printed in a textual format. Your grades and remarks about you are presented in a paragraph format instead of data tables. Would be very confusing right? This is why data must be presented correctly and clearly. Let us take a look.
Suggested Videos
Presentation of data.
Presentation of data is of utter importance nowadays. Afterall everything that’s pleasing to our eyes never fails to grab our attention. Presentation of data refers to an exhibition or putting up data in an attractive and useful manner such that it can be easily interpreted. The three main forms of presentation of data are:
- Textual presentation
- Data tables
- Diagrammatic presentation
Here we will be studying only the textual and tabular presentation, i.e. data tables in some detail.
Textual Presentation
The discussion about the presentation of data starts off with it’s most raw and vague form which is the textual presentation. In such form of presentation, data is simply mentioned as mere text, that is generally in a paragraph. This is commonly used when the data is not very large.
This kind of representation is useful when we are looking to supplement qualitative statements with some data. For this purpose, the data should not be voluminously represented in tables or diagrams. It just has to be a statement that serves as a fitting evidence to our qualitative evidence and helps the reader to get an idea of the scale of a phenomenon .
For example, “the 2002 earthquake proved to be a mass murderer of humans . As many as 10,000 citizens have been reported dead”. The textual representation of data simply requires some intensive reading. This is because the quantitative statement just serves as an evidence of the qualitative statements and one has to go through the entire text before concluding anything.
Further, if the data under consideration is large then the text matter increases substantially. As a result, the reading process becomes more intensive, time-consuming and cumbersome.
Data Tables or Tabular Presentation
A table facilitates representation of even large amounts of data in an attractive, easy to read and organized manner. The data is organized in rows and columns. This is one of the most widely used forms of presentation of data since data tables are easy to construct and read.
Components of Data Tables
- Table Number : Each table should have a specific table number for ease of access and locating. This number can be readily mentioned anywhere which serves as a reference and leads us directly to the data mentioned in that particular table.
- Title: A table must contain a title that clearly tells the readers about the data it contains, time period of study, place of study and the nature of classification of data .
- Headnotes: A headnote further aids in the purpose of a title and displays more information about the table. Generally, headnotes present the units of data in brackets at the end of a table title.
- Stubs: These are titles of the rows in a table. Thus a stub display information about the data contained in a particular row.
- Caption: A caption is the title of a column in the data table. In fact, it is a counterpart if a stub and indicates the information contained in a column.
- Body or field: The body of a table is the content of a table in its entirety. Each item in a body is known as a ‘cell’.
- Footnotes: Footnotes are rarely used. In effect, they supplement the title of a table if required.
- Source: When using data obtained from a secondary source, this source has to be mentioned below the footnote.
Construction of Data Tables
There are many ways for construction of a good table. However, some basic ideas are:
- The title should be in accordance with the objective of study: The title of a table should provide a quick insight into the table.
- Comparison: If there might arise a need to compare any two rows or columns then these might be kept close to each other.
- Alternative location of stubs: If the rows in a data table are lengthy, then the stubs can be placed on the right-hand side of the table.
- Headings: Headings should be written in a singular form. For example, ‘good’ must be used instead of ‘goods’.
- Footnote: A footnote should be given only if needed.
- Size of columns: Size of columns must be uniform and symmetrical.
- Use of abbreviations: Headings and sub-headings should be free of abbreviations.
- Units: There should be a clear specification of units above the columns.
The Advantages of Tabular Presentation
- Ease of representation: A large amount of data can be easily confined in a data table. Evidently, it is the simplest form of data presentation.
- Ease of analysis: Data tables are frequently used for statistical analysis like calculation of central tendency, dispersion etc.
- Helps in comparison: In a data table, the rows and columns which are required to be compared can be placed next to each other. To point out, this facilitates comparison as it becomes easy to compare each value.
- Economical: Construction of a data table is fairly easy and presents the data in a manner which is really easy on the eyes of a reader. Moreover, it saves time as well as space.
Classification of Data and Tabular Presentation
Qualitative classification.
In this classification, data in a table is classified on the basis of qualitative attributes. In other words, if the data contained attributes that cannot be quantified like rural-urban, boys-girls etc. it can be identified as a qualitative classification of data.
Quantitative Classification
In quantitative classification, data is classified on basis of quantitative attributes.
Temporal Classification
Here data is classified according to time. Thus when data is mentioned with respect to different time frames, we term such a classification as temporal.
Spatial Classification
When data is classified according to a location, it becomes a spatial classification.
A Solved Example for You
Q: The classification in which data in a table is classified according to time is known as:
- Qualitative
- Quantitative
Ans: The form of classification in which data is classified based on time frames is known as the temporal classification of data and tabular presentation.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Diagrammatic Presentation of Data
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Korean J Anesthesiol
- v.70(3); 2017 Jun
Statistical data presentation
1 Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
Sangseok Lee
2 Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Data are usually collected in a raw format and thus the inherent information is difficult to understand. Therefore, raw data need to be summarized, processed, and analyzed. However, no matter how well manipulated, the information derived from the raw data should be presented in an effective format, otherwise, it would be a great loss for both authors and readers. In this article, the techniques of data and information presentation in textual, tabular, and graphical forms are introduced. Text is the principal method for explaining findings, outlining trends, and providing contextual information. A table is best suited for representing individual information and represents both quantitative and qualitative information. A graph is a very effective visual tool as it displays data at a glance, facilitates comparison, and can reveal trends and relationships within the data such as changes over time, frequency distribution, and correlation or relative share of a whole. Text, tables, and graphs for data and information presentation are very powerful communication tools. They can make an article easy to understand, attract and sustain the interest of readers, and efficiently present large amounts of complex information. Moreover, as journal editors and reviewers glance at these presentations before reading the whole article, their importance cannot be ignored.
Introduction
Data are a set of facts, and provide a partial picture of reality. Whether data are being collected with a certain purpose or collected data are being utilized, questions regarding what information the data are conveying, how the data can be used, and what must be done to include more useful information must constantly be kept in mind.
Since most data are available to researchers in a raw format, they must be summarized, organized, and analyzed to usefully derive information from them. Furthermore, each data set needs to be presented in a certain way depending on what it is used for. Planning how the data will be presented is essential before appropriately processing raw data.
First, a question for which an answer is desired must be clearly defined. The more detailed the question is, the more detailed and clearer the results are. A broad question results in vague answers and results that are hard to interpret. In other words, a well-defined question is crucial for the data to be well-understood later. Once a detailed question is ready, the raw data must be prepared before processing. These days, data are often summarized, organized, and analyzed with statistical packages or graphics software. Data must be prepared in such a way they are properly recognized by the program being used. The present study does not discuss this data preparation process, which involves creating a data frame, creating/changing rows and columns, changing the level of a factor, categorical variable, coding, dummy variables, variable transformation, data transformation, missing value, outlier treatment, and noise removal.
We describe the roles and appropriate use of text, tables, and graphs (graphs, plots, or charts), all of which are commonly used in reports, articles, posters, and presentations. Furthermore, we discuss the issues that must be addressed when presenting various kinds of information, and effective methods of presenting data, which are the end products of research, and of emphasizing specific information.
Data Presentation
Data can be presented in one of the three ways:
–as text;
–in tabular form; or
–in graphical form.
Methods of presentation must be determined according to the data format, the method of analysis to be used, and the information to be emphasized. Inappropriately presented data fail to clearly convey information to readers and reviewers. Even when the same information is being conveyed, different methods of presentation must be employed depending on what specific information is going to be emphasized. A method of presentation must be chosen after carefully weighing the advantages and disadvantages of different methods of presentation. For easy comparison of different methods of presentation, let us look at a table ( Table 1 ) and a line graph ( Fig. 1 ) that present the same information [ 1 ]. If one wishes to compare or introduce two values at a certain time point, it is appropriate to use text or the written language. However, a table is the most appropriate when all information requires equal attention, and it allows readers to selectively look at information of their own interest. Graphs allow readers to understand the overall trend in data, and intuitively understand the comparison results between two groups. One thing to always bear in mind regardless of what method is used, however, is the simplicity of presentation.

Values are expressed as mean ± SD. Group C: normal saline, Group D: dexmedetomidine. SBP: systolic blood pressure, DBP: diastolic blood pressure, MBP: mean blood pressure, HR: heart rate. * P < 0.05 indicates a significant increase in each group, compared with the baseline values. † P < 0.05 indicates a significant decrease noted in Group D, compared with the baseline values. ‡ P < 0.05 indicates a significant difference between the groups.
Text presentation
Text is the main method of conveying information as it is used to explain results and trends, and provide contextual information. Data are fundamentally presented in paragraphs or sentences. Text can be used to provide interpretation or emphasize certain data. If quantitative information to be conveyed consists of one or two numbers, it is more appropriate to use written language than tables or graphs. For instance, information about the incidence rates of delirium following anesthesia in 2016–2017 can be presented with the use of a few numbers: “The incidence rate of delirium following anesthesia was 11% in 2016 and 15% in 2017; no significant difference of incidence rates was found between the two years.” If this information were to be presented in a graph or a table, it would occupy an unnecessarily large space on the page, without enhancing the readers' understanding of the data. If more data are to be presented, or other information such as that regarding data trends are to be conveyed, a table or a graph would be more appropriate. By nature, data take longer to read when presented as texts and when the main text includes a long list of information, readers and reviewers may have difficulties in understanding the information.
Table presentation
Tables, which convey information that has been converted into words or numbers in rows and columns, have been used for nearly 2,000 years. Anyone with a sufficient level of literacy can easily understand the information presented in a table. Tables are the most appropriate for presenting individual information, and can present both quantitative and qualitative information. Examples of qualitative information are the level of sedation [ 2 ], statistical methods/functions [ 3 , 4 ], and intubation conditions [ 5 ].
The strength of tables is that they can accurately present information that cannot be presented with a graph. A number such as “132.145852” can be accurately expressed in a table. Another strength is that information with different units can be presented together. For instance, blood pressure, heart rate, number of drugs administered, and anesthesia time can be presented together in one table. Finally, tables are useful for summarizing and comparing quantitative information of different variables. However, the interpretation of information takes longer in tables than in graphs, and tables are not appropriate for studying data trends. Furthermore, since all data are of equal importance in a table, it is not easy to identify and selectively choose the information required.
For a general guideline for creating tables, refer to the journal submission requirements 1) .
Heat maps for better visualization of information than tables
Heat maps help to further visualize the information presented in a table by applying colors to the background of cells. By adjusting the colors or color saturation, information is conveyed in a more visible manner, and readers can quickly identify the information of interest ( Table 2 ). Software such as Excel (in Microsoft Office, Microsoft, WA, USA) have features that enable easy creation of heat maps through the options available on the “conditional formatting” menu.
All numbers were created by the author. SBP: systolic blood pressure, DBP: diastolic blood pressure, MBP: mean blood pressure, HR: heart rate.
Graph presentation
Whereas tables can be used for presenting all the information, graphs simplify complex information by using images and emphasizing data patterns or trends, and are useful for summarizing, explaining, or exploring quantitative data. While graphs are effective for presenting large amounts of data, they can be used in place of tables to present small sets of data. A graph format that best presents information must be chosen so that readers and reviewers can easily understand the information. In the following, we describe frequently used graph formats and the types of data that are appropriately presented with each format with examples.
Scatter plot
Scatter plots present data on the x - and y -axes and are used to investigate an association between two variables. A point represents each individual or object, and an association between two variables can be studied by analyzing patterns across multiple points. A regression line is added to a graph to determine whether the association between two variables can be explained or not. Fig. 2 illustrates correlations between pain scoring systems that are currently used (PSQ, Pain Sensitivity Questionnaire; PASS, Pain Anxiety Symptoms Scale; PCS, Pain Catastrophizing Scale) and Geop-Pain Questionnaire (GPQ) with the correlation coefficient, R, and regression line indicated on the scatter plot [ 6 ]. If multiple points exist at an identical location as in this example ( Fig. 2 ), the correlation level may not be clear. In this case, a correlation coefficient or regression line can be added to further elucidate the correlation.

Bar graph and histogram
A bar graph is used to indicate and compare values in a discrete category or group, and the frequency or other measurement parameters (i.e. mean). Depending on the number of categories, and the size or complexity of each category, bars may be created vertically or horizontally. The height (or length) of a bar represents the amount of information in a category. Bar graphs are flexible, and can be used in a grouped or subdivided bar format in cases of two or more data sets in each category. Fig. 3 is a representative example of a vertical bar graph, with the x -axis representing the length of recovery room stay and drug-treated group, and the y -axis representing the visual analog scale (VAS) score. The mean and standard deviation of the VAS scores are expressed as whiskers on the bars ( Fig. 3 ) [ 7 ].

By comparing the endpoints of bars, one can identify the largest and the smallest categories, and understand gradual differences between each category. It is advised to start the x - and y -axes from 0. Illustration of comparison results in the x - and y -axes that do not start from 0 can deceive readers' eyes and lead to overrepresentation of the results.
One form of vertical bar graph is the stacked vertical bar graph. A stack vertical bar graph is used to compare the sum of each category, and analyze parts of a category. While stacked vertical bar graphs are excellent from the aspect of visualization, they do not have a reference line, making comparison of parts of various categories challenging ( Fig. 4 ) [ 8 ].

A pie chart, which is used to represent nominal data (in other words, data classified in different categories), visually represents a distribution of categories. It is generally the most appropriate format for representing information grouped into a small number of categories. It is also used for data that have no other way of being represented aside from a table (i.e. frequency table). Fig. 5 illustrates the distribution of regular waste from operation rooms by their weight [ 8 ]. A pie chart is also commonly used to illustrate the number of votes each candidate won in an election.

Line plot with whiskers
A line plot is useful for representing time-series data such as monthly precipitation and yearly unemployment rates; in other words, it is used to study variables that are observed over time. Line graphs are especially useful for studying patterns and trends across data that include climatic influence, large changes or turning points, and are also appropriate for representing not only time-series data, but also data measured over the progression of a continuous variable such as distance. As can be seen in Fig. 1 , mean and standard deviation of systolic blood pressure are indicated for each time point, which enables readers to easily understand changes of systolic pressure over time [ 1 ]. If data are collected at a regular interval, values in between the measurements can be estimated. In a line graph, the x-axis represents the continuous variable, while the y-axis represents the scale and measurement values. It is also useful to represent multiple data sets on a single line graph to compare and analyze patterns across different data sets.
Box and whisker chart
A box and whisker chart does not make any assumptions about the underlying statistical distribution, and represents variations in samples of a population; therefore, it is appropriate for representing nonparametric data. AA box and whisker chart consists of boxes that represent interquartile range (one to three), the median and the mean of the data, and whiskers presented as lines outside of the boxes. Whiskers can be used to present the largest and smallest values in a set of data or only a part of the data (i.e. 95% of all the data). Data that are excluded from the data set are presented as individual points and are called outliers. The spacing at both ends of the box indicates dispersion in the data. The relative location of the median demonstrated within the box indicates skewness ( Fig. 6 ). The box and whisker chart provided as an example represents calculated volumes of an anesthetic, desflurane, consumed over the course of the observation period ( Fig. 7 ) [ 9 ].

Three-dimensional effects
Most of the recently introduced statistical packages and graphics software have the three-dimensional (3D) effect feature. The 3D effects can add depth and perspective to a graph. However, since they may make reading and interpreting data more difficult, they must only be used after careful consideration. The application of 3D effects on a pie chart makes distinguishing the size of each slice difficult. Even if slices are of similar sizes, slices farther from the front of the pie chart may appear smaller than the slices closer to the front ( Fig. 8 ).

Drawing a graph: example
Finally, we explain how to create a graph by using a line graph as an example ( Fig. 9 ). In Fig. 9 , the mean values of arterial pressure were randomly produced and assumed to have been measured on an hourly basis. In many graphs, the x- and y-axes meet at the zero point ( Fig. 9A ). In this case, information regarding the mean and standard deviation of mean arterial pressure measurements corresponding to t = 0 cannot be conveyed as the values overlap with the y-axis. The data can be clearly exposed by separating the zero point ( Fig. 9B ). In Fig. 9B , the mean and standard deviation of different groups overlap and cannot be clearly distinguished from each other. Separating the data sets and presenting standard deviations in a single direction prevents overlapping and, therefore, reduces the visual inconvenience. Doing so also reduces the excessive number of ticks on the y-axis, increasing the legibility of the graph ( Fig. 9C ). In the last graph, different shapes were used for the lines connecting different time points to further allow the data to be distinguished, and the y-axis was shortened to get rid of the unnecessary empty space present in the previous graphs ( Fig. 9D ). A graph can be made easier to interpret by assigning each group to a different color, changing the shape of a point, or including graphs of different formats [ 10 ]. The use of random settings for the scale in a graph may lead to inappropriate presentation or presentation of data that can deceive readers' eyes ( Fig. 10 ).

Owing to the lack of space, we could not discuss all types of graphs, but have focused on describing graphs that are frequently used in scholarly articles. We have summarized the commonly used types of graphs according to the method of data analysis in Table 3 . For general guidelines on graph designs, please refer to the journal submission requirements 2) .
Conclusions
Text, tables, and graphs are effective communication media that present and convey data and information. They aid readers in understanding the content of research, sustain their interest, and effectively present large quantities of complex information. As journal editors and reviewers will scan through these presentations before reading the entire text, their importance cannot be disregarded. For this reason, authors must pay as close attention to selecting appropriate methods of data presentation as when they were collecting data of good quality and analyzing them. In addition, having a well-established understanding of different methods of data presentation and their appropriate use will enable one to develop the ability to recognize and interpret inappropriately presented data or data presented in such a way that it deceives readers' eyes [ 11 ].
<Appendix>
Output for presentation.
Discovery and communication are the two objectives of data visualization. In the discovery phase, various types of graphs must be tried to understand the rough and overall information the data are conveying. The communication phase is focused on presenting the discovered information in a summarized form. During this phase, it is necessary to polish images including graphs, pictures, and videos, and consider the fact that the images may look different when printed than how appear on a computer screen. In this appendix, we discuss important concepts that one must be familiar with to print graphs appropriately.
The KJA asks that pictures and images meet the following requirement before submission 3)
“Figures and photographs should be submitted as ‘TIFF’ files. Submit files of figures and photographs separately from the text of the paper. Width of figure should be 84 mm (one column). Contrast of photos or graphs should be at least 600 dpi. Contrast of line drawings should be at least 1,200 dpi. The Powerpoint file (ppt, pptx) is also acceptable.”
Unfortunately, without sufficient knowledge of computer graphics, it is not easy to understand the submission requirement above. Therefore, it is necessary to develop an understanding of image resolution, image format (bitmap and vector images), and the corresponding file specifications.
Resolution is often mentioned to describe the quality of images containing graphs or CT/MRI scans, and video files. The higher the resolution, the clearer and closer to reality the image is, while the opposite is true for low resolutions. The most representative unit used to describe a resolution is “dpi” (dots per inch): this literally translates to the number of dots required to constitute 1 inch. The greater the number of dots, the higher the resolution. The KJA submission requirements recommend 600 dpi for images, and 1,200 dpi 4) for graphs. In other words, resolutions in which 600 or 1,200 dots constitute one inch are required for submission.
There are requirements for the horizontal length of an image in addition to the resolution requirements. While there are no requirements for the vertical length of an image, it must not exceed the vertical length of a page. The width of a column on one side of a printed page is 84 mm, or 3.3 inches (84/25.4 mm ≒ 3.3 inches). Therefore, a graph must have a resolution in which 1,200 dots constitute 1 inch, and have a width of 3.3 inches.
Bitmap and Vector
Methods of image construction are important. Bitmap images can be considered as images drawn on section paper. Enlarging the image will enlarge the picture along with the grid, resulting in a lower resolution; in other words, aliasing occurs. On the other hand, reducing the size of the image will reduce the size of the picture, while increasing the resolution. In other words, resolution and the size of an image are inversely proportionate to one another in bitmap images, and it is a drawback of bitmap images that resolution must be considered when adjusting the size of an image. To enlarge an image while maintaining the same resolution, the size and resolution of the image must be determined before saving the image. An image that has already been created cannot avoid changes to its resolution according to changes in size. Enlarging an image while maintaining the same resolution will increase the number of horizontal and vertical dots, ultimately increasing the number of pixels 5) of the image, and the file size. In other words, the file size of a bitmap image is affected by the size and resolution of the image (file extensions include JPG [JPEG] 6) , PNG 7) , GIF 8) , and TIF [TIFF] 9) . To avoid this complexity, the width of an image can be set to 4 inches and its resolution to 900 dpi to satisfy the submission requirements of most journals [ 12 ].
Vector images overcome the shortcomings of bitmap images. Vector images are created based on mathematical operations of line segments and areas between different points, and are not affected by aliasing or pixelation. Furthermore, they result in a smaller file size that is not affected by the size of the image. They are commonly used for drawings and illustrations (file extensions include EPS 10) , CGM 11) , and SVG 12) ).
Finally, the PDF 13) is a file format developed by Adobe Systems (Adobe Systems, CA, USA) for electronic documents, and can contain general documents, text, drawings, images, and fonts. They can also contain bitmap and vector images. While vector images are used by researchers when working in Powerpoint, they are saved as 960 × 720 dots when saved in TIFF format in Powerpoint. This results in a resolution that is inappropriate for printing on a paper medium. To save high-resolution bitmap images, the image must be saved as a PDF file instead of a TIFF, and the saved PDF file must be imported into an imaging processing program such as Photoshop™(Adobe Systems, CA, USA) to be saved in TIFF format [ 12 ].
1) Instructions to authors in KJA; section 5-(9) Table; https://ekja.org/index.php?body=instruction
2) Instructions to Authors in KJA; section 6-1)-(10) Figures and illustrations in Manuscript preparation; https://ekja.org/index.php?body=instruction
3) Instructions to Authors in KJA; section 6-1)-(10) Figures and illustrations in Manuscript preparation; https://ekja.org/index.php?body=instruction
4) Resolution; in KJA, it is represented by “contrast.”
5) Pixel is a minimum unit of an image and contains information of a dot and color. It is derived by multiplying the number of vertical and horizontal dots regardless of image size. For example, Full High Definition (FHD) monitor has 1920 × 1080 dots ≒ 2.07 million pixel.
6) Joint Photographic Experts Group.
7) Portable Network Graphics.
8) Graphics Interchange Format
9) Tagged Image File Format; TIFF
10) Encapsulated PostScript.
11) Computer Graphics Metafile.
12) Scalable Vector Graphics.
13) Portable Document Format.
What is Tabular Data? (Definition & Example)
In statistics, tabular data refers to data that is organized in a table with rows and columns.

Within the table, the rows represent observations and the columns represent attributes for those observations.
For example, the following table represents tabular data:

This dataset has 9 rows and 5 columns.
Each row represents one basketball player and the five columns describe different attributes about the player including:
- Player name
- Minutes played
The opposite of tabular data would be visual data , which would be some type of plot or chart that helps us visualize the values in a dataset.
For example, we might have the following bar chart that helps us visualize the total minutes played by each player in the dataset:

This would be an example of visual data .
It contains the exact same information about player names and minutes played for the players in the dataset, but it’s simply displayed in a visual form instead of a tabular form.
Or we might have the following scatterplot that helps us visualize the relationship between minutes played and points scored for each player:

This is another example of visual data .
When is Tabular Data Used in Practice?
In practice, tabular data is the most common type of data that you’ll run across in the real world.
In the real world, most data that is saved in an Excel spreadsheet is considered tabular data because the rows represent observations and the columns represent attributes for those observations.
For example, here’s what our basketball dataset from earlier might look like in an Excel spreadsheet:

This format is one of the most natural ways to collect and store values in a dataset, which is why it’s used so often.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain other common terms in statistics:
Why is Statistics Important? Why is Sample Size Important in Statistics? What is an Observation in Statistics? What is Considered Raw Data in Statistics?
How to Write a Nested IFERROR Statement in Excel
How to use make.names function in r (with examples), related posts, how to normalize data between -1 and 1, how to interpret f-values in a two-way anova, how to create a vector of ones in..., vba: how to check if string contains another..., how to determine if a probability distribution is..., what is a symmetric histogram (definition & examples), how to find the mode of a histogram..., how to find quartiles in even and odd..., how to calculate sxy in statistics (with example), how to calculate sxx in statistics (with example).
- Privacy Policy

Home » Tables in Research Paper – Types, Creating Guide and Examples
Tables in Research Paper – Types, Creating Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Tables in Research Paper
Definition:
In Research Papers , Tables are a way of presenting data and information in a structured format. Tables can be used to summarize large amounts of data or to highlight important findings. They are often used in scientific or technical papers to display experimental results, statistical analyses, or other quantitative information.
Importance of Tables in Research Paper
Tables are an important component of a research paper as they provide a clear and concise presentation of data, statistics, and other information that support the research findings . Here are some reasons why tables are important in a research paper:
- Visual Representation : Tables provide a visual representation of data that is easy to understand and interpret. They help readers to quickly grasp the main points of the research findings and draw their own conclusions.
- Organize Data : Tables help to organize large amounts of data in a systematic and structured manner. This makes it easier for readers to identify patterns and trends in the data.
- Clarity and Accuracy : Tables allow researchers to present data in a clear and accurate manner. They can include precise numbers, percentages, and other information that may be difficult to convey in written form.
- Comparison: Tables allow for easy comparison between different data sets or groups. This makes it easier to identify similarities and differences, and to draw meaningful conclusions from the data.
- Efficiency: Tables allow for a more efficient use of space in the research paper. They can convey a large amount of information in a compact and concise format, which saves space and makes the research paper more readable.
Types of Tables in Research Paper
Most common Types of Tables in Research Paper are as follows:
- Descriptive tables : These tables provide a summary of the data collected in the study. They are usually used to present basic descriptive statistics such as means, medians, standard deviations, and frequencies.
- Comparative tables : These tables are used to compare the results of different groups or variables. They may be used to show the differences between two or more groups or to compare the results of different variables.
- Correlation tables: These tables are used to show the relationships between variables. They may show the correlation coefficients between variables, or they may show the results of regression analyses.
- Longitudinal tables : These tables are used to show changes in variables over time. They may show the results of repeated measures analyses or longitudinal regression analyses.
- Qualitative tables: These tables are used to summarize qualitative data such as interview transcripts or open-ended survey responses. They may present themes or categories that emerged from the data.
How to Create Tables in Research Paper
Here are the steps to create tables in a research paper:
- Plan your table: Determine the purpose of the table and the type of information you want to include. Consider the layout and format that will best convey your information.
- Choose a table format : Decide on the type of table you want to create. Common table formats include basic tables, summary tables, comparison tables, and correlation tables.
- Choose a software program : Use a spreadsheet program like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets to create your table. These programs allow you to easily enter and manipulate data, format the table, and export it for use in your research paper.
- Input data: Enter your data into the spreadsheet program. Make sure to label each row and column clearly.
- Format the table : Apply formatting options such as font, font size, font color, cell borders, and shading to make your table more visually appealing and easier to read.
- Insert the table into your paper: Copy and paste the table into your research paper. Make sure to place the table in the appropriate location and refer to it in the text of your paper.
- Label the table: Give the table a descriptive title that clearly and accurately summarizes the contents of the table. Also, include a number and a caption that explains the table in more detail.
- Check for accuracy: Review the table for accuracy and make any necessary changes before submitting your research paper.
Examples of Tables in Research Paper
Examples of Tables in the Research Paper are as follows:
Table 1: Demographic Characteristics of Study Participants
This table shows the demographic characteristics of 200 participants in a research study. The table includes information about age, gender, and education level. The mean age of the participants was 35.2 years with a standard deviation of 8.6 years, and the age range was between 21 and 57 years. The table also shows that 46% of the participants were male and 54% were female. In terms of education, 10% of the participants had less than a high school education, 30% were high school graduates, 35% had some college education, and 25% had a bachelor’s degree or higher.
Table 2: Summary of Key Findings
This table summarizes the key findings of a study comparing three different groups on a particular variable. The table shows the mean score, standard deviation, t-value, and p-value for each group. The asterisk next to the t-value for Group 1 indicates that the difference between Group 1 and the other groups was statistically significant at p < 0.01, while the differences between Group 2 and Group 3 were not statistically significant.

Purpose of Tables in Research Paper
The primary purposes of including tables in a research paper are:
- To present data: Tables are an effective way to present large amounts of data in a clear and organized manner. Researchers can use tables to present numerical data, survey results, or other types of data that are difficult to represent in text.
- To summarize data: Tables can be used to summarize large amounts of data into a concise and easy-to-read format. Researchers can use tables to summarize the key findings of their research, such as descriptive statistics or the results of regression analyses.
- To compare data : Tables can be used to compare data across different variables or groups. Researchers can use tables to compare the characteristics of different study populations or to compare the results of different studies on the same topic.
- To enhance the readability of the paper: Tables can help to break up long sections of text and make the paper more visually appealing. By presenting data in a table, researchers can help readers to quickly identify the most important information and understand the key findings of the study.
Advantages of Tables in Research Paper
Some of the advantages of using tables in research papers include:
- Clarity : Tables can present data in a way that is easy to read and understand. They can help readers to quickly and easily identify patterns, trends, and relationships in the data.
- Efficiency: Tables can save space and reduce the need for lengthy explanations or descriptions of the data in the main body of the paper. This can make the paper more concise and easier to read.
- Organization: Tables can help to organize large amounts of data in a logical and meaningful way. This can help to reduce confusion and make it easier for readers to navigate the data.
- Comparison : Tables can be useful for comparing data across different groups, variables, or time periods. This can help to highlight similarities, differences, and changes over time.
- Visualization : Tables can also be used to visually represent data, making it easier for readers to see patterns and trends. This can be particularly useful when the data is complex or difficult to understand.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Home Blog Design Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)
Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)
In this age of overwhelming information, the skill to effectively convey data has become extremely valuable. Initiating a discussion on data presentation types involves thoughtful consideration of the nature of your data and the message you aim to convey. Different types of visualizations serve distinct purposes. Whether you’re dealing with how to develop a report or simply trying to communicate complex information, how you present data influences how well your audience understands and engages with it. This extensive guide leads you through the different ways of data presentation.
Table of Contents
What is a Data Presentation?
What should a data presentation include, line graphs, treemap chart, scatter plot, how to choose a data presentation type, recommended data presentation templates, common mistakes done in data presentation.
A data presentation is a slide deck that aims to disclose quantitative information to an audience through the use of visual formats and narrative techniques derived from data analysis, making complex data understandable and actionable. This process requires a series of tools, such as charts, graphs, tables, infographics, dashboards, and so on, supported by concise textual explanations to improve understanding and boost retention rate.
Data presentations require us to cull data in a format that allows the presenter to highlight trends, patterns, and insights so that the audience can act upon the shared information. In a few words, the goal of data presentations is to enable viewers to grasp complicated concepts or trends quickly, facilitating informed decision-making or deeper analysis.
Data presentations go beyond the mere usage of graphical elements. Seasoned presenters encompass visuals with the art of data storytelling , so the speech skillfully connects the points through a narrative that resonates with the audience. Depending on the purpose – inspire, persuade, inform, support decision-making processes, etc. – is the data presentation format that is better suited to help us in this journey.
To nail your upcoming data presentation, ensure to count with the following elements:
- Clear Objectives: Understand the intent of your presentation before selecting the graphical layout and metaphors to make content easier to grasp.
- Engaging introduction: Use a powerful hook from the get-go. For instance, you can ask a big question or present a problem that your data will answer. Take a look at our guide on how to start a presentation for tips & insights.
- Structured Narrative: Your data presentation must tell a coherent story. This means a beginning where you present the context, a middle section in which you present the data, and an ending that uses a call-to-action. Check our guide on presentation structure for further information.
- Visual Elements: These are the charts, graphs, and other elements of visual communication we ought to use to present data. This article will cover one by one the different types of data representation methods we can use, and provide further guidance on choosing between them.
- Insights and Analysis: This is not just showcasing a graph and letting people get an idea about it. A proper data presentation includes the interpretation of that data, the reason why it’s included, and why it matters to your research.
- Conclusion & CTA: Ending your presentation with a call to action is necessary. Whether you intend to wow your audience into acquiring your services, inspire them to change the world, or whatever the purpose of your presentation, there must be a stage in which you convey all that you shared and show the path to staying in touch. Plan ahead whether you want to use a thank-you slide, a video presentation, or which method is apt and tailored to the kind of presentation you deliver.
- Q&A Session: After your speech is concluded, allocate 3-5 minutes for the audience to raise any questions about the information you disclosed. This is an extra chance to establish your authority on the topic. Check our guide on questions and answer sessions in presentations here.
Bar charts are a graphical representation of data using rectangular bars to show quantities or frequencies in an established category. They make it easy for readers to spot patterns or trends. Bar charts can be horizontal or vertical, although the vertical format is commonly known as a column chart. They display categorical, discrete, or continuous variables grouped in class intervals [1] . They include an axis and a set of labeled bars horizontally or vertically. These bars represent the frequencies of variable values or the values themselves. Numbers on the y-axis of a vertical bar chart or the x-axis of a horizontal bar chart are called the scale.
Real-Life Application of Bar Charts
Let’s say a sales manager is presenting sales to their audience. Using a bar chart, he follows these steps.
Step 1: Selecting Data
The first step is to identify the specific data you will present to your audience.
The sales manager has highlighted these products for the presentation.
- Product A: Men’s Shoes
- Product B: Women’s Apparel
- Product C: Electronics
- Product D: Home Decor
Step 2: Choosing Orientation
Opt for a vertical layout for simplicity. Vertical bar charts help compare different categories in case there are not too many categories [1] . They can also help show different trends. A vertical bar chart is used where each bar represents one of the four chosen products. After plotting the data, it is seen that the height of each bar directly represents the sales performance of the respective product.
It is visible that the tallest bar (Electronics – Product C) is showing the highest sales. However, the shorter bars (Women’s Apparel – Product B and Home Decor – Product D) need attention. It indicates areas that require further analysis or strategies for improvement.
Step 3: Colorful Insights
Different colors are used to differentiate each product. It is essential to show a color-coded chart where the audience can distinguish between products.
- Men’s Shoes (Product A): Yellow
- Women’s Apparel (Product B): Orange
- Electronics (Product C): Violet
- Home Decor (Product D): Blue
Bar charts are straightforward and easily understandable for presenting data. They are versatile when comparing products or any categorical data [2] . Bar charts adapt seamlessly to retail scenarios. Despite that, bar charts have a few shortcomings. They cannot illustrate data trends over time. Besides, overloading the chart with numerous products can lead to visual clutter, diminishing its effectiveness.
For more information, check our collection of bar chart templates for PowerPoint .
Line graphs help illustrate data trends, progressions, or fluctuations by connecting a series of data points called ‘markers’ with straight line segments. This provides a straightforward representation of how values change [5] . Their versatility makes them invaluable for scenarios requiring a visual understanding of continuous data. In addition, line graphs are also useful for comparing multiple datasets over the same timeline. Using multiple line graphs allows us to compare more than one data set. They simplify complex information so the audience can quickly grasp the ups and downs of values. From tracking stock prices to analyzing experimental results, you can use line graphs to show how data changes over a continuous timeline. They show trends with simplicity and clarity.
Real-life Application of Line Graphs
To understand line graphs thoroughly, we will use a real case. Imagine you’re a financial analyst presenting a tech company’s monthly sales for a licensed product over the past year. Investors want insights into sales behavior by month, how market trends may have influenced sales performance and reception to the new pricing strategy. To present data via a line graph, you will complete these steps.
First, you need to gather the data. In this case, your data will be the sales numbers. For example:
- January: $45,000
- February: $55,000
- March: $45,000
- April: $60,000
- May: $ 70,000
- June: $65,000
- July: $62,000
- August: $68,000
- September: $81,000
- October: $76,000
- November: $87,000
- December: $91,000
After choosing the data, the next step is to select the orientation. Like bar charts, you can use vertical or horizontal line graphs. However, we want to keep this simple, so we will keep the timeline (x-axis) horizontal while the sales numbers (y-axis) vertical.
Step 3: Connecting Trends
After adding the data to your preferred software, you will plot a line graph. In the graph, each month’s sales are represented by data points connected by a line.
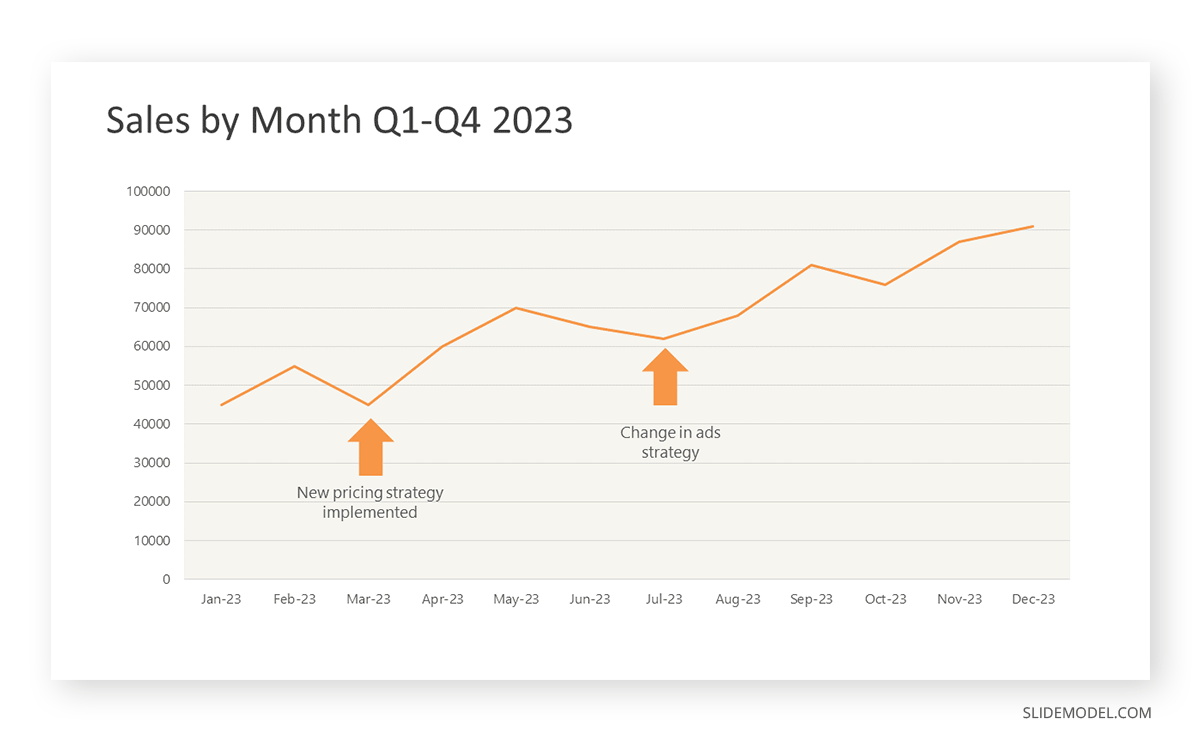
Step 4: Adding Clarity with Color
If there are multiple lines, you can also add colors to highlight each one, making it easier to follow.
Line graphs excel at visually presenting trends over time. These presentation aids identify patterns, like upward or downward trends. However, too many data points can clutter the graph, making it harder to interpret. Line graphs work best with continuous data but are not suitable for categories.
For more information, check our collection of line chart templates for PowerPoint and our article about how to make a presentation graph .
A data dashboard is a visual tool for analyzing information. Different graphs, charts, and tables are consolidated in a layout to showcase the information required to achieve one or more objectives. Dashboards help quickly see Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). You don’t make new visuals in the dashboard; instead, you use it to display visuals you’ve already made in worksheets [3] .
Keeping the number of visuals on a dashboard to three or four is recommended. Adding too many can make it hard to see the main points [4]. Dashboards can be used for business analytics to analyze sales, revenue, and marketing metrics at a time. They are also used in the manufacturing industry, as they allow users to grasp the entire production scenario at the moment while tracking the core KPIs for each line.
Real-Life Application of a Dashboard
Consider a project manager presenting a software development project’s progress to a tech company’s leadership team. He follows the following steps.
Step 1: Defining Key Metrics
To effectively communicate the project’s status, identify key metrics such as completion status, budget, and bug resolution rates. Then, choose measurable metrics aligned with project objectives.
Step 2: Choosing Visualization Widgets
After finalizing the data, presentation aids that align with each metric are selected. For this project, the project manager chooses a progress bar for the completion status and uses bar charts for budget allocation. Likewise, he implements line charts for bug resolution rates.
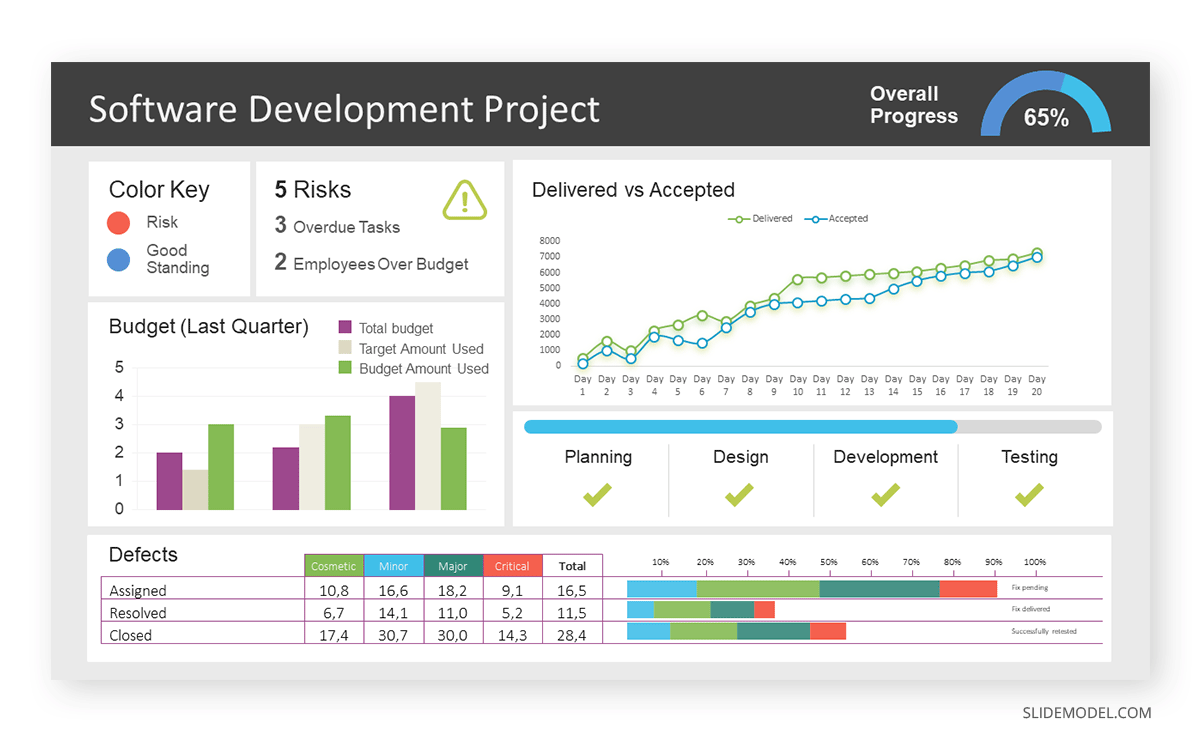
Step 3: Dashboard Layout
Key metrics are prominently placed in the dashboard for easy visibility, and the manager ensures that it appears clean and organized.
Dashboards provide a comprehensive view of key project metrics. Users can interact with data, customize views, and drill down for detailed analysis. However, creating an effective dashboard requires careful planning to avoid clutter. Besides, dashboards rely on the availability and accuracy of underlying data sources.
For more information, check our article on how to design a dashboard presentation , and discover our collection of dashboard PowerPoint templates .
Treemap charts represent hierarchical data structured in a series of nested rectangles [6] . As each branch of the ‘tree’ is given a rectangle, smaller tiles can be seen representing sub-branches, meaning elements on a lower hierarchical level than the parent rectangle. Each one of those rectangular nodes is built by representing an area proportional to the specified data dimension.
Treemaps are useful for visualizing large datasets in compact space. It is easy to identify patterns, such as which categories are dominant. Common applications of the treemap chart are seen in the IT industry, such as resource allocation, disk space management, website analytics, etc. Also, they can be used in multiple industries like healthcare data analysis, market share across different product categories, or even in finance to visualize portfolios.
Real-Life Application of a Treemap Chart
Let’s consider a financial scenario where a financial team wants to represent the budget allocation of a company. There is a hierarchy in the process, so it is helpful to use a treemap chart. In the chart, the top-level rectangle could represent the total budget, and it would be subdivided into smaller rectangles, each denoting a specific department. Further subdivisions within these smaller rectangles might represent individual projects or cost categories.
Step 1: Define Your Data Hierarchy
While presenting data on the budget allocation, start by outlining the hierarchical structure. The sequence will be like the overall budget at the top, followed by departments, projects within each department, and finally, individual cost categories for each project.
- Top-level rectangle: Total Budget
- Second-level rectangles: Departments (Engineering, Marketing, Sales)
- Third-level rectangles: Projects within each department
- Fourth-level rectangles: Cost categories for each project (Personnel, Marketing Expenses, Equipment)
Step 2: Choose a Suitable Tool
It’s time to select a data visualization tool supporting Treemaps. Popular choices include Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, PowerPoint, or even coding with libraries like D3.js. It is vital to ensure that the chosen tool provides customization options for colors, labels, and hierarchical structures.
Here, the team uses PowerPoint for this guide because of its user-friendly interface and robust Treemap capabilities.
Step 3: Make a Treemap Chart with PowerPoint
After opening the PowerPoint presentation, they chose “SmartArt” to form the chart. The SmartArt Graphic window has a “Hierarchy” category on the left. Here, you will see multiple options. You can choose any layout that resembles a Treemap. The “Table Hierarchy” or “Organization Chart” options can be adapted. The team selects the Table Hierarchy as it looks close to a Treemap.
Step 5: Input Your Data
After that, a new window will open with a basic structure. They add the data one by one by clicking on the text boxes. They start with the top-level rectangle, representing the total budget.
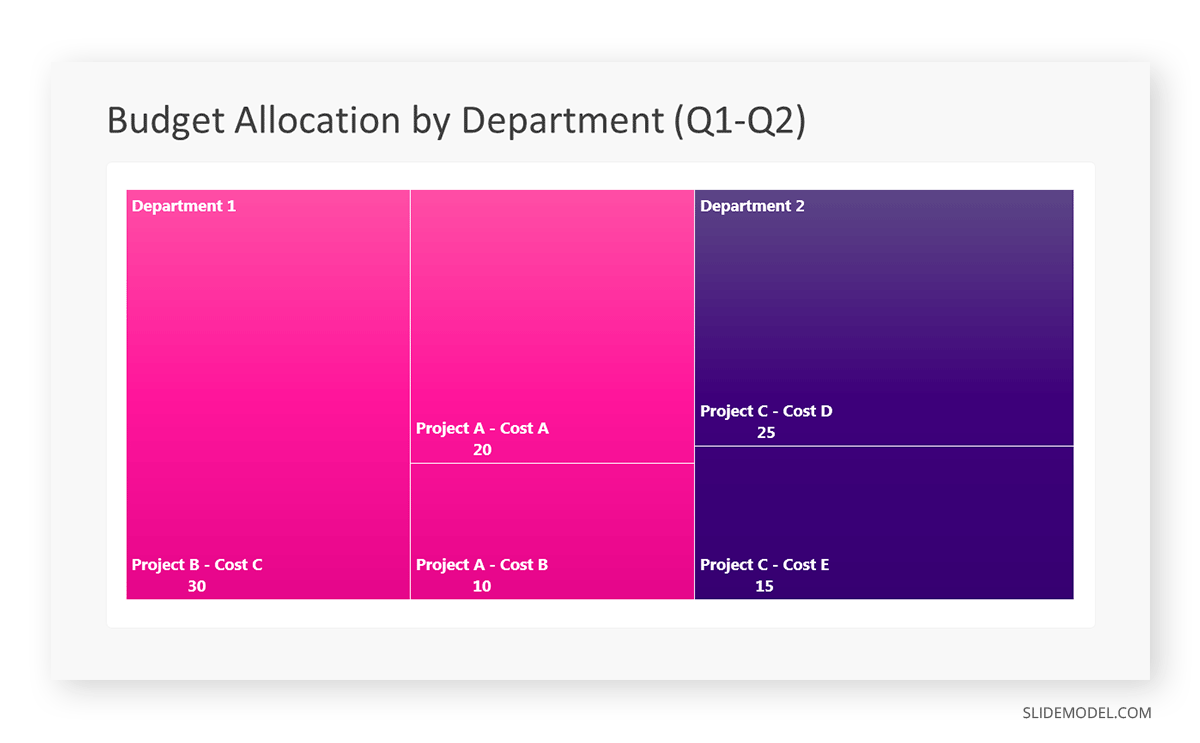
Step 6: Customize the Treemap
By clicking on each shape, they customize its color, size, and label. At the same time, they can adjust the font size, style, and color of labels by using the options in the “Format” tab in PowerPoint. Using different colors for each level enhances the visual difference.
Treemaps excel at illustrating hierarchical structures. These charts make it easy to understand relationships and dependencies. They efficiently use space, compactly displaying a large amount of data, reducing the need for excessive scrolling or navigation. Additionally, using colors enhances the understanding of data by representing different variables or categories.
In some cases, treemaps might become complex, especially with deep hierarchies. It becomes challenging for some users to interpret the chart. At the same time, displaying detailed information within each rectangle might be constrained by space. It potentially limits the amount of data that can be shown clearly. Without proper labeling and color coding, there’s a risk of misinterpretation.
A heatmap is a data visualization tool that uses color coding to represent values across a two-dimensional surface. In these, colors replace numbers to indicate the magnitude of each cell. This color-shaded matrix display is valuable for summarizing and understanding data sets with a glance [7] . The intensity of the color corresponds to the value it represents, making it easy to identify patterns, trends, and variations in the data.
As a tool, heatmaps help businesses analyze website interactions, revealing user behavior patterns and preferences to enhance overall user experience. In addition, companies use heatmaps to assess content engagement, identifying popular sections and areas of improvement for more effective communication. They excel at highlighting patterns and trends in large datasets, making it easy to identify areas of interest.
We can implement heatmaps to express multiple data types, such as numerical values, percentages, or even categorical data. Heatmaps help us easily spot areas with lots of activity, making them helpful in figuring out clusters [8] . When making these maps, it is important to pick colors carefully. The colors need to show the differences between groups or levels of something. And it is good to use colors that people with colorblindness can easily see.
Check our detailed guide on how to create a heatmap here. Also discover our collection of heatmap PowerPoint templates .
Pie charts are circular statistical graphics divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportions. Each slice represents a proportionate part of the whole, making it easy to visualize the contribution of each component to the total.
The size of the pie charts is influenced by the value of data points within each pie. The total of all data points in a pie determines its size. The pie with the highest data points appears as the largest, whereas the others are proportionally smaller. However, you can present all pies of the same size if proportional representation is not required [9] . Sometimes, pie charts are difficult to read, or additional information is required. A variation of this tool can be used instead, known as the donut chart , which has the same structure but a blank center, creating a ring shape. Presenters can add extra information, and the ring shape helps to declutter the graph.
Pie charts are used in business to show percentage distribution, compare relative sizes of categories, or present straightforward data sets where visualizing ratios is essential.
Real-Life Application of Pie Charts
Consider a scenario where you want to represent the distribution of the data. Each slice of the pie chart would represent a different category, and the size of each slice would indicate the percentage of the total portion allocated to that category.
Step 1: Define Your Data Structure
Imagine you are presenting the distribution of a project budget among different expense categories.
- Column A: Expense Categories (Personnel, Equipment, Marketing, Miscellaneous)
- Column B: Budget Amounts ($40,000, $30,000, $20,000, $10,000) Column B represents the values of your categories in Column A.
Step 2: Insert a Pie Chart
Using any of the accessible tools, you can create a pie chart. The most convenient tools for forming a pie chart in a presentation are presentation tools such as PowerPoint or Google Slides. You will notice that the pie chart assigns each expense category a percentage of the total budget by dividing it by the total budget.
For instance:
- Personnel: $40,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 40%
- Equipment: $30,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 30%
- Marketing: $20,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 20%
- Miscellaneous: $10,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 10%
You can make a chart out of this or just pull out the pie chart from the data.
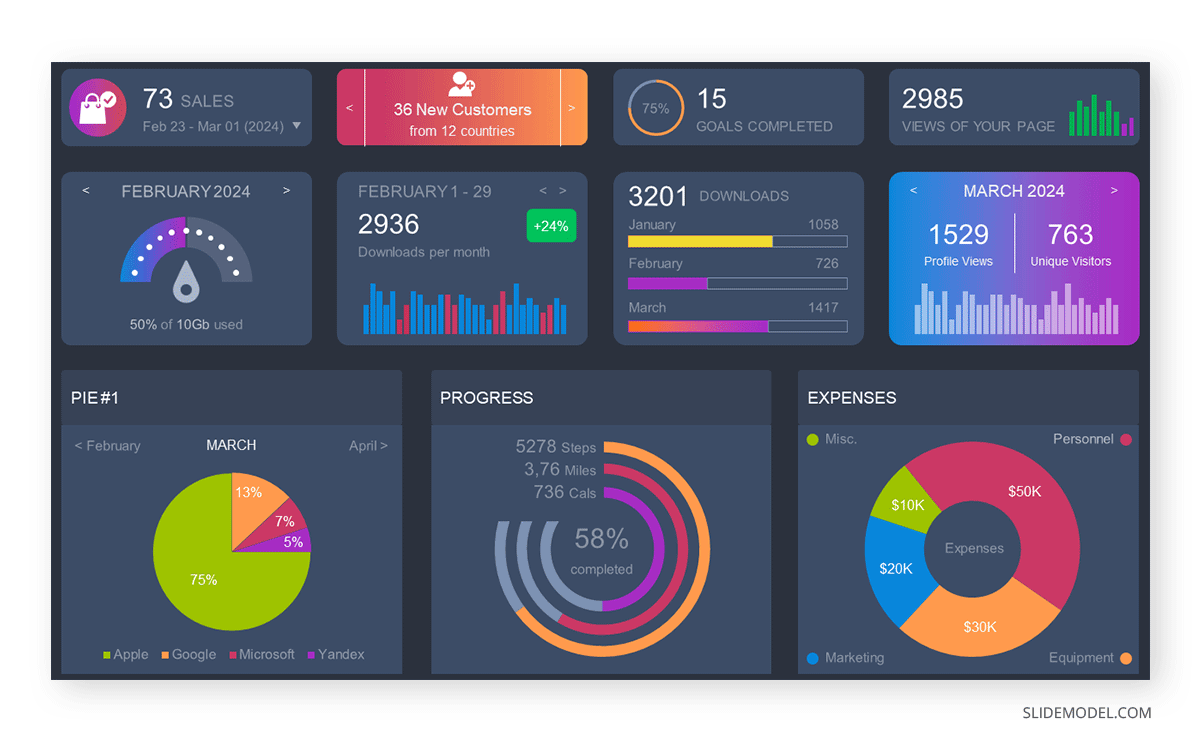
3D pie charts and 3D donut charts are quite popular among the audience. They stand out as visual elements in any presentation slide, so let’s take a look at how our pie chart example would look in 3D pie chart format.
Step 03: Results Interpretation
The pie chart visually illustrates the distribution of the project budget among different expense categories. Personnel constitutes the largest portion at 40%, followed by equipment at 30%, marketing at 20%, and miscellaneous at 10%. This breakdown provides a clear overview of where the project funds are allocated, which helps in informed decision-making and resource management. It is evident that personnel are a significant investment, emphasizing their importance in the overall project budget.
Pie charts provide a straightforward way to represent proportions and percentages. They are easy to understand, even for individuals with limited data analysis experience. These charts work well for small datasets with a limited number of categories.
However, a pie chart can become cluttered and less effective in situations with many categories. Accurate interpretation may be challenging, especially when dealing with slight differences in slice sizes. In addition, these charts are static and do not effectively convey trends over time.
For more information, check our collection of pie chart templates for PowerPoint .
Histograms present the distribution of numerical variables. Unlike a bar chart that records each unique response separately, histograms organize numeric responses into bins and show the frequency of reactions within each bin [10] . The x-axis of a histogram shows the range of values for a numeric variable. At the same time, the y-axis indicates the relative frequencies (percentage of the total counts) for that range of values.
Whenever you want to understand the distribution of your data, check which values are more common, or identify outliers, histograms are your go-to. Think of them as a spotlight on the story your data is telling. A histogram can provide a quick and insightful overview if you’re curious about exam scores, sales figures, or any numerical data distribution.
Real-Life Application of a Histogram
In the histogram data analysis presentation example, imagine an instructor analyzing a class’s grades to identify the most common score range. A histogram could effectively display the distribution. It will show whether most students scored in the average range or if there are significant outliers.
Step 1: Gather Data
He begins by gathering the data. The scores of each student in class are gathered to analyze exam scores.
After arranging the scores in ascending order, bin ranges are set.
Step 2: Define Bins
Bins are like categories that group similar values. Think of them as buckets that organize your data. The presenter decides how wide each bin should be based on the range of the values. For instance, the instructor sets the bin ranges based on score intervals: 60-69, 70-79, 80-89, and 90-100.
Step 3: Count Frequency
Now, he counts how many data points fall into each bin. This step is crucial because it tells you how often specific ranges of values occur. The result is the frequency distribution, showing the occurrences of each group.
Here, the instructor counts the number of students in each category.
- 60-69: 1 student (Kate)
- 70-79: 4 students (David, Emma, Grace, Jack)
- 80-89: 7 students (Alice, Bob, Frank, Isabel, Liam, Mia, Noah)
- 90-100: 3 students (Clara, Henry, Olivia)
Step 4: Create the Histogram
It’s time to turn the data into a visual representation. Draw a bar for each bin on a graph. The width of the bar should correspond to the range of the bin, and the height should correspond to the frequency. To make your histogram understandable, label the X and Y axes.
In this case, the X-axis should represent the bins (e.g., test score ranges), and the Y-axis represents the frequency.
The histogram of the class grades reveals insightful patterns in the distribution. Most students, with seven students, fall within the 80-89 score range. The histogram provides a clear visualization of the class’s performance. It showcases a concentration of grades in the upper-middle range with few outliers at both ends. This analysis helps in understanding the overall academic standing of the class. It also identifies the areas for potential improvement or recognition.
Thus, histograms provide a clear visual representation of data distribution. They are easy to interpret, even for those without a statistical background. They apply to various types of data, including continuous and discrete variables. One weak point is that histograms do not capture detailed patterns in students’ data, with seven compared to other visualization methods.
A scatter plot is a graphical representation of the relationship between two variables. It consists of individual data points on a two-dimensional plane. This plane plots one variable on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis. Each point represents a unique observation. It visualizes patterns, trends, or correlations between the two variables.
Scatter plots are also effective in revealing the strength and direction of relationships. They identify outliers and assess the overall distribution of data points. The points’ dispersion and clustering reflect the relationship’s nature, whether it is positive, negative, or lacks a discernible pattern. In business, scatter plots assess relationships between variables such as marketing cost and sales revenue. They help present data correlations and decision-making.
Real-Life Application of Scatter Plot
A group of scientists is conducting a study on the relationship between daily hours of screen time and sleep quality. After reviewing the data, they managed to create this table to help them build a scatter plot graph:
In the provided example, the x-axis represents Daily Hours of Screen Time, and the y-axis represents the Sleep Quality Rating.
The scientists observe a negative correlation between the amount of screen time and the quality of sleep. This is consistent with their hypothesis that blue light, especially before bedtime, has a significant impact on sleep quality and metabolic processes.
There are a few things to remember when using a scatter plot. Even when a scatter diagram indicates a relationship, it doesn’t mean one variable affects the other. A third factor can influence both variables. The more the plot resembles a straight line, the stronger the relationship is perceived [11] . If it suggests no ties, the observed pattern might be due to random fluctuations in data. When the scatter diagram depicts no correlation, whether the data might be stratified is worth considering.
Choosing the appropriate data presentation type is crucial when making a presentation . Understanding the nature of your data and the message you intend to convey will guide this selection process. For instance, when showcasing quantitative relationships, scatter plots become instrumental in revealing correlations between variables. If the focus is on emphasizing parts of a whole, pie charts offer a concise display of proportions. Histograms, on the other hand, prove valuable for illustrating distributions and frequency patterns.
Bar charts provide a clear visual comparison of different categories. Likewise, line charts excel in showcasing trends over time, while tables are ideal for detailed data examination. Starting a presentation on data presentation types involves evaluating the specific information you want to communicate and selecting the format that aligns with your message. This ensures clarity and resonance with your audience from the beginning of your presentation.
1. Fact Sheet Dashboard for Data Presentation

Convey all the data you need to present in this one-pager format, an ideal solution tailored for users looking for presentation aids. Global maps, donut chats, column graphs, and text neatly arranged in a clean layout presented in light and dark themes.
Use This Template
2. 3D Column Chart Infographic PPT Template
Represent column charts in a highly visual 3D format with this PPT template. A creative way to present data, this template is entirely editable, and we can craft either a one-page infographic or a series of slides explaining what we intend to disclose point by point.
3. Data Circles Infographic PowerPoint Template
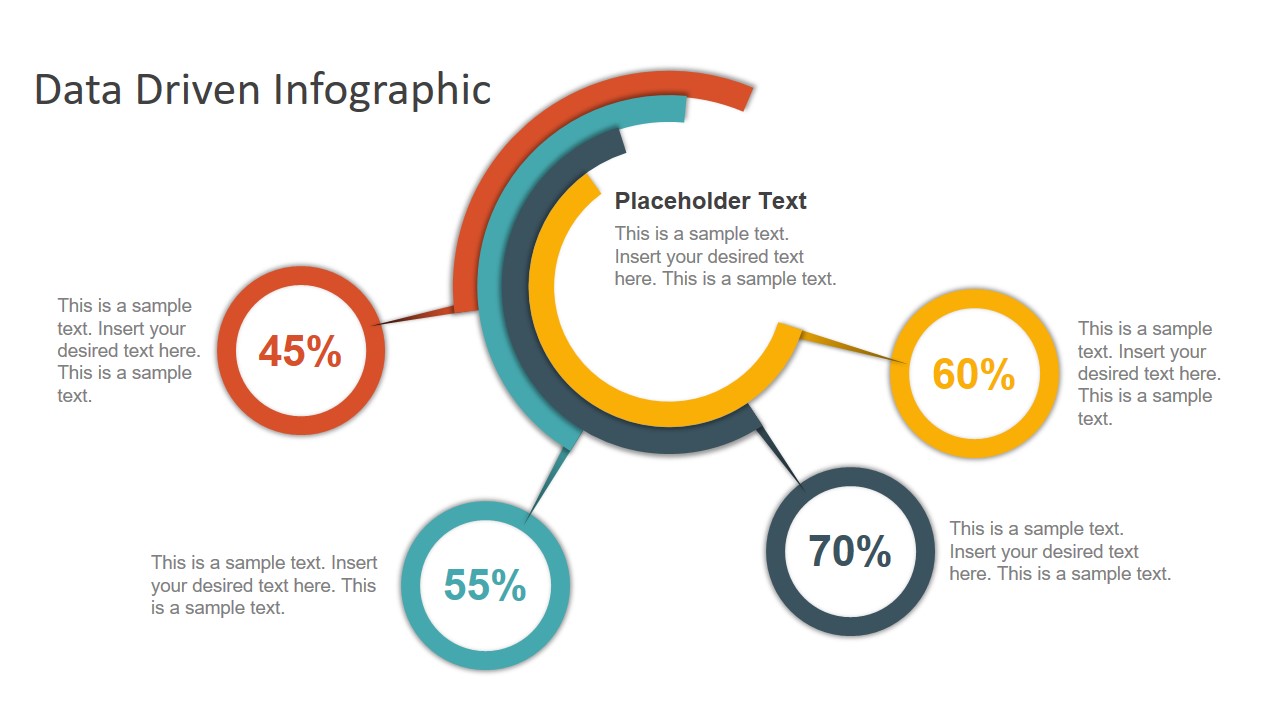
An alternative to the pie chart and donut chart diagrams, this template features a series of curved shapes with bubble callouts as ways of presenting data. Expand the information for each arch in the text placeholder areas.
4. Colorful Metrics Dashboard for Data Presentation
This versatile dashboard template helps us in the presentation of the data by offering several graphs and methods to convert numbers into graphics. Implement it for e-commerce projects, financial projections, project development, and more.
5. Animated Data Presentation Tools for PowerPoint & Google Slides
A slide deck filled with most of the tools mentioned in this article, from bar charts, column charts, treemap graphs, pie charts, histogram, etc. Animated effects make each slide look dynamic when sharing data with stakeholders.
6. Statistics Waffle Charts PPT Template for Data Presentations
This PPT template helps us how to present data beyond the typical pie chart representation. It is widely used for demographics, so it’s a great fit for marketing teams, data science professionals, HR personnel, and more.
7. Data Presentation Dashboard Template for Google Slides
A compendium of tools in dashboard format featuring line graphs, bar charts, column charts, and neatly arranged placeholder text areas.
8. Weather Dashboard for Data Presentation
Share weather data for agricultural presentation topics, environmental studies, or any kind of presentation that requires a highly visual layout for weather forecasting on a single day. Two color themes are available.
9. Social Media Marketing Dashboard Data Presentation Template
Intended for marketing professionals, this dashboard template for data presentation is a tool for presenting data analytics from social media channels. Two slide layouts featuring line graphs and column charts.
10. Project Management Summary Dashboard Template
A tool crafted for project managers to deliver highly visual reports on a project’s completion, the profits it delivered for the company, and expenses/time required to execute it. 4 different color layouts are available.
11. Profit & Loss Dashboard for PowerPoint and Google Slides
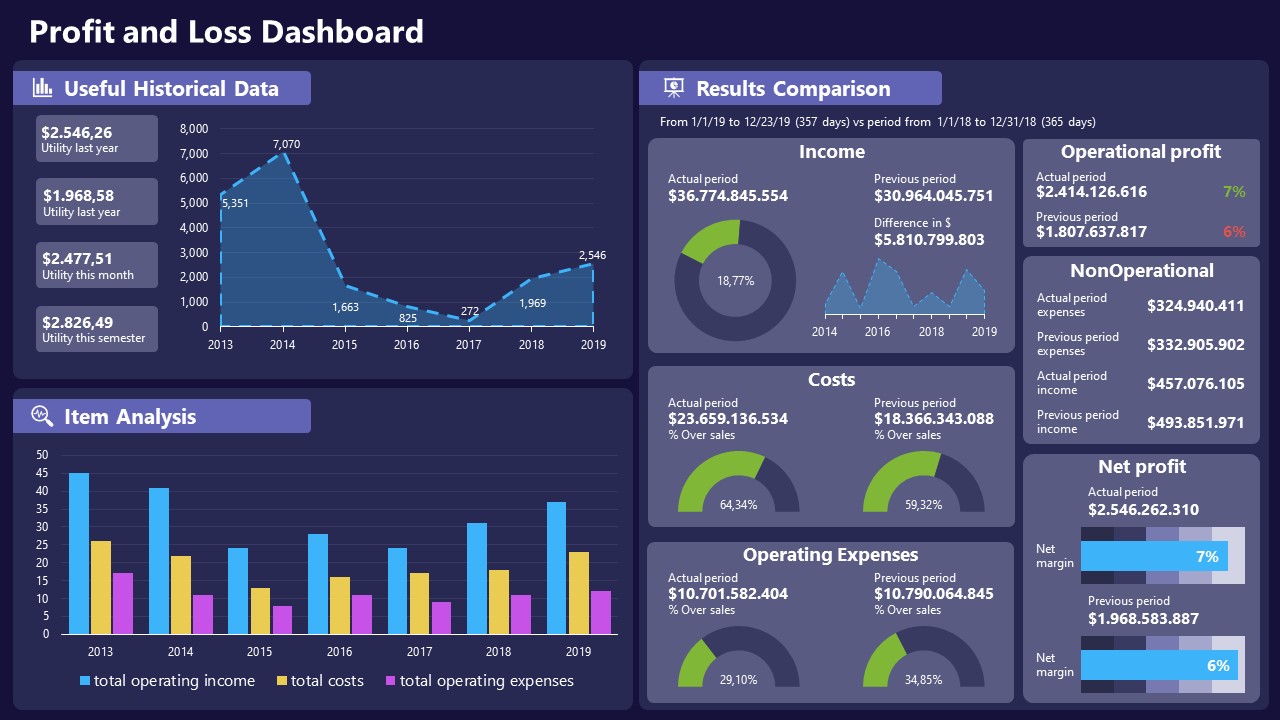
A must-have for finance professionals. This typical profit & loss dashboard includes progress bars, donut charts, column charts, line graphs, and everything that’s required to deliver a comprehensive report about a company’s financial situation.
Overwhelming visuals
One of the mistakes related to using data-presenting methods is including too much data or using overly complex visualizations. They can confuse the audience and dilute the key message.
Inappropriate chart types
Choosing the wrong type of chart for the data at hand can lead to misinterpretation. For example, using a pie chart for data that doesn’t represent parts of a whole is not right.
Lack of context
Failing to provide context or sufficient labeling can make it challenging for the audience to understand the significance of the presented data.
Inconsistency in design
Using inconsistent design elements and color schemes across different visualizations can create confusion and visual disarray.
Failure to provide details
Simply presenting raw data without offering clear insights or takeaways can leave the audience without a meaningful conclusion.
Lack of focus
Not having a clear focus on the key message or main takeaway can result in a presentation that lacks a central theme.
Visual accessibility issues
Overlooking the visual accessibility of charts and graphs can exclude certain audience members who may have difficulty interpreting visual information.
In order to avoid these mistakes in data presentation, presenters can benefit from using presentation templates . These templates provide a structured framework. They ensure consistency, clarity, and an aesthetically pleasing design, enhancing data communication’s overall impact.
Understanding and choosing data presentation types are pivotal in effective communication. Each method serves a unique purpose, so selecting the appropriate one depends on the nature of the data and the message to be conveyed. The diverse array of presentation types offers versatility in visually representing information, from bar charts showing values to pie charts illustrating proportions.
Using the proper method enhances clarity, engages the audience, and ensures that data sets are not just presented but comprehensively understood. By appreciating the strengths and limitations of different presentation types, communicators can tailor their approach to convey information accurately, developing a deeper connection between data and audience understanding.
[1] Government of Canada, S.C. (2021) 5 Data Visualization 5.2 Bar Chart , 5.2 Bar chart . https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/edu/power-pouvoir/ch9/bargraph-diagrammeabarres/5214818-eng.htm
[2] Kosslyn, S.M., 1989. Understanding charts and graphs. Applied cognitive psychology, 3(3), pp.185-225. https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/pdfs/ADA183409.pdf
[3] Creating a Dashboard . https://it.tufts.edu/book/export/html/1870
[4] https://www.goldenwestcollege.edu/research/data-and-more/data-dashboards/index.html
[5] https://www.mit.edu/course/21/21.guide/grf-line.htm
[6] Jadeja, M. and Shah, K., 2015, January. Tree-Map: A Visualization Tool for Large Data. In GSB@ SIGIR (pp. 9-13). https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1393/gsb15proceedings.pdf#page=15
[7] Heat Maps and Quilt Plots. https://www.publichealth.columbia.edu/research/population-health-methods/heat-maps-and-quilt-plots
[8] EIU QGIS WORKSHOP. https://www.eiu.edu/qgisworkshop/heatmaps.php
[9] About Pie Charts. https://www.mit.edu/~mbarker/formula1/f1help/11-ch-c8.htm
[10] Histograms. https://sites.utexas.edu/sos/guided/descriptive/numericaldd/descriptiven2/histogram/ [11] https://asq.org/quality-resources/scatter-diagram

Like this article? Please share
Data Analysis, Data Science, Data Visualization Filed under Design
Related Articles

Filed under Design • March 27th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Graph
Detailed step-by-step instructions to master the art of how to make a presentation graph in PowerPoint and Google Slides. Check it out!
Filed under Presentation Ideas • January 6th, 2024
All About Using Harvey Balls
Among the many tools in the arsenal of the modern presenter, Harvey Balls have a special place. In this article we will tell you all about using Harvey Balls.

Filed under Business • December 8th, 2023
How to Design a Dashboard Presentation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Take a step further in your professional presentation skills by learning what a dashboard presentation is and how to properly design one in PowerPoint. A detailed step-by-step guide is here!
Leave a Reply
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Data Visualization 10 Data Presentation Examples For Strategic Communication
10 Data Presentation Examples For Strategic Communication
Written by: Krystle Wong Sep 28, 2023

Knowing how to present data is like having a superpower.
Data presentation today is no longer just about numbers on a screen; it’s storytelling with a purpose. It’s about captivating your audience, making complex stuff look simple and inspiring action.
To help turn your data into stories that stick, influence decisions and make an impact, check out Venngage’s free chart maker or follow me on a tour into the world of data storytelling along with data presentation templates that work across different fields, from business boardrooms to the classroom and beyond. Keep scrolling to learn more!
Click to jump ahead:
10 Essential data presentation examples + methods you should know
What should be included in a data presentation, what are some common mistakes to avoid when presenting data, faqs on data presentation examples, transform your message with impactful data storytelling.
Data presentation is a vital skill in today’s information-driven world. Whether you’re in business, academia, or simply want to convey information effectively, knowing the different ways of presenting data is crucial. For impactful data storytelling, consider these essential data presentation methods:
1. Bar graph
Ideal for comparing data across categories or showing trends over time.
Bar graphs, also known as bar charts are workhorses of data presentation. They’re like the Swiss Army knives of visualization methods because they can be used to compare data in different categories or display data changes over time.
In a bar chart, categories are displayed on the x-axis and the corresponding values are represented by the height of the bars on the y-axis.
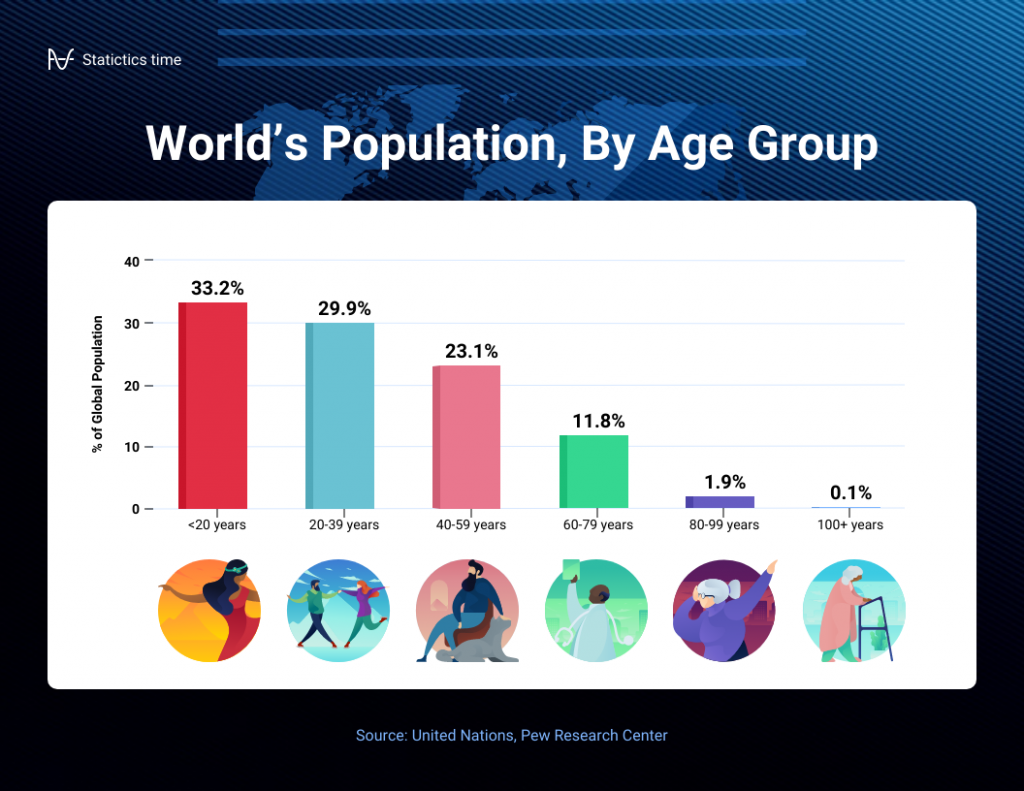
It’s a straightforward and effective way to showcase raw data, making it a staple in business reports, academic presentations and beyond.
Make sure your bar charts are concise with easy-to-read labels. Whether your bars go up or sideways, keep it simple by not overloading with too many categories.
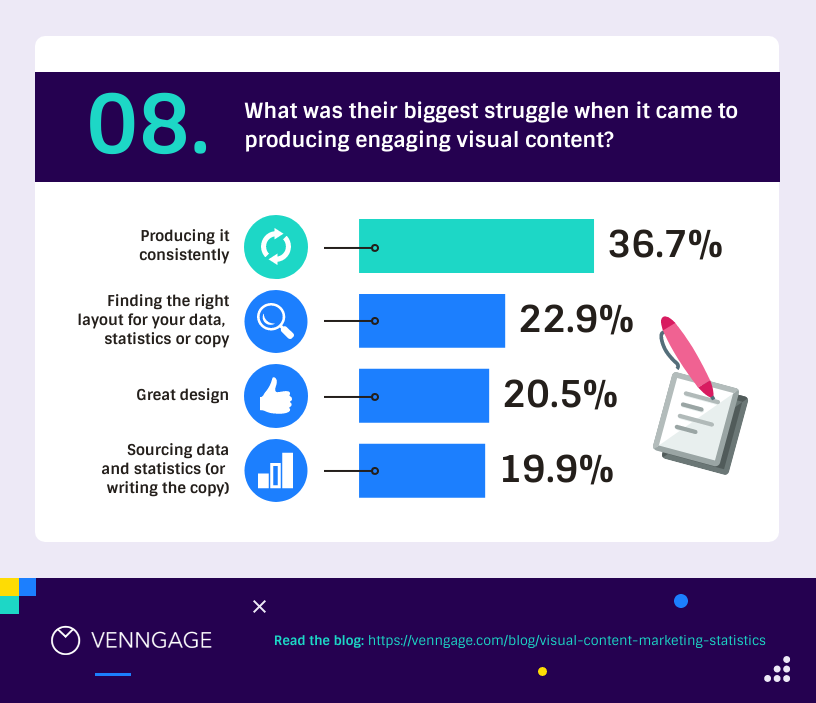
2. Line graph
Great for displaying trends and variations in data points over time or continuous variables.
Line charts or line graphs are your go-to when you want to visualize trends and variations in data sets over time.
One of the best quantitative data presentation examples, they work exceptionally well for showing continuous data, such as sales projections over the last couple of years or supply and demand fluctuations.
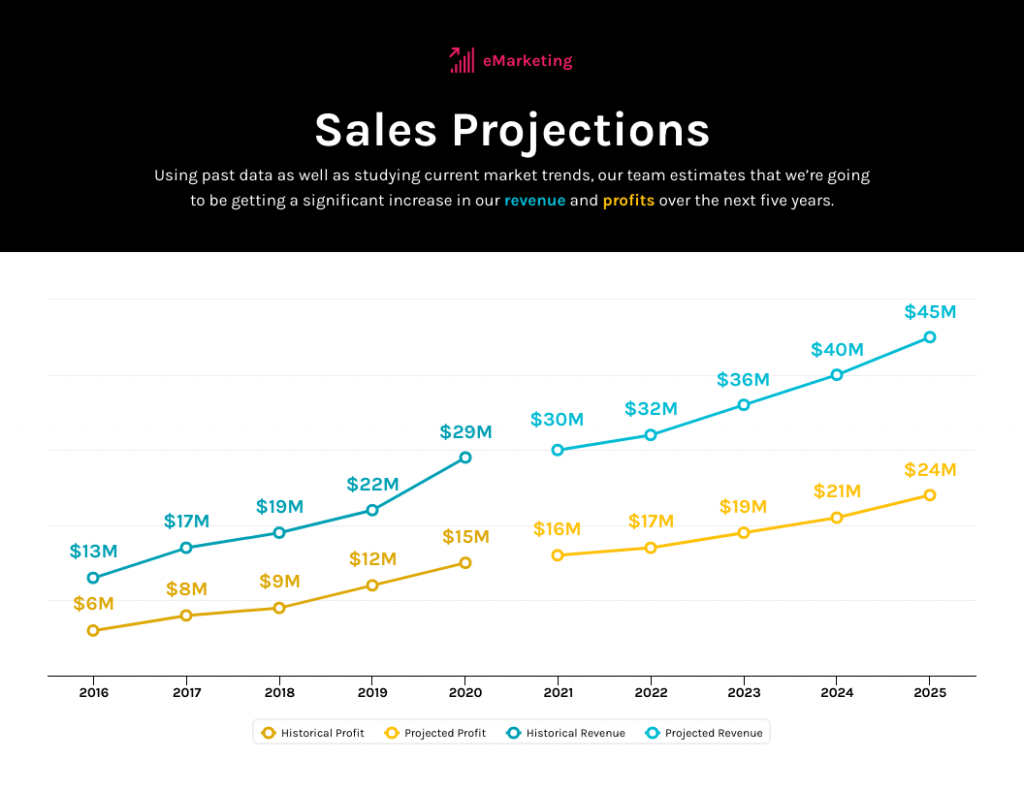
The x-axis represents time or a continuous variable and the y-axis represents the data values. By connecting the data points with lines, you can easily spot trends and fluctuations.
A tip when presenting data with line charts is to minimize the lines and not make it too crowded. Highlight the big changes, put on some labels and give it a catchy title.
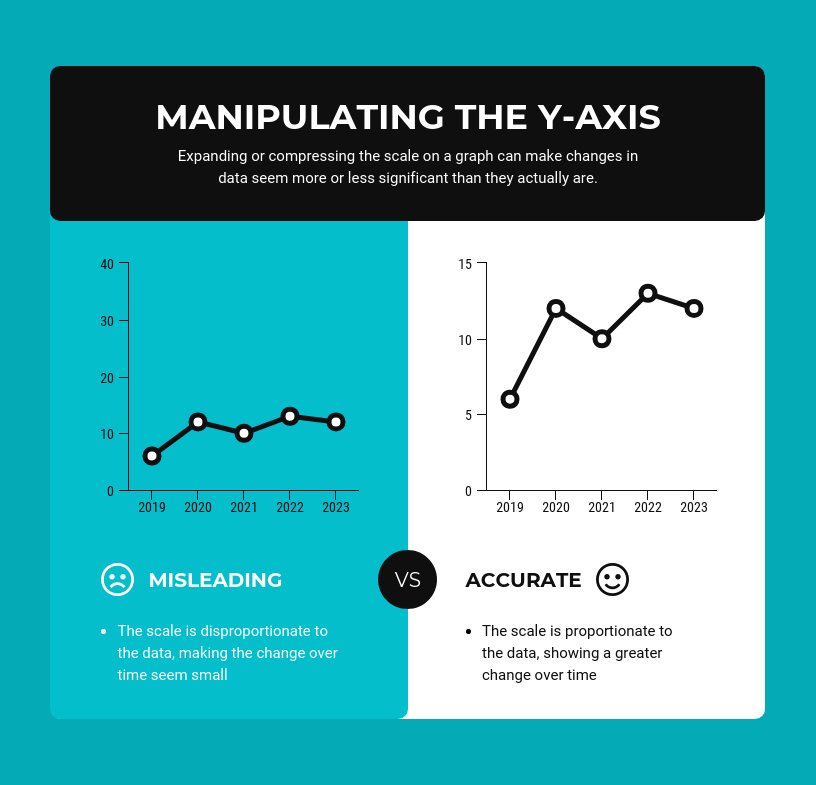
3. Pie chart
Useful for illustrating parts of a whole, such as percentages or proportions.
Pie charts are perfect for showing how a whole is divided into parts. They’re commonly used to represent percentages or proportions and are great for presenting survey results that involve demographic data.
Each “slice” of the pie represents a portion of the whole and the size of each slice corresponds to its share of the total.
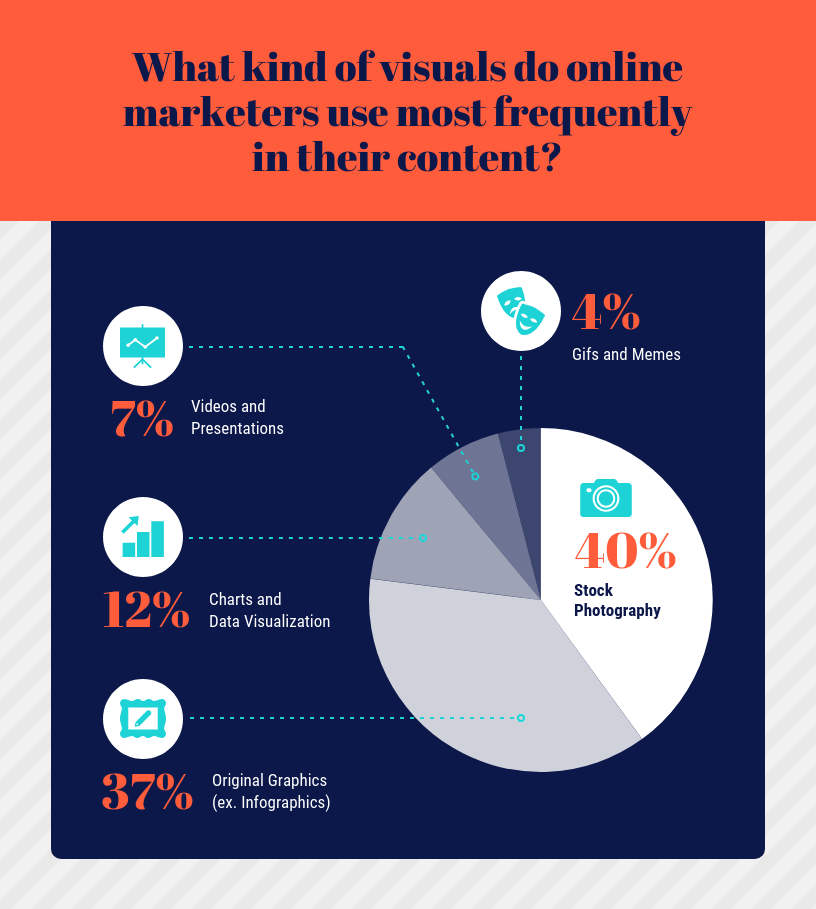
While pie charts are handy for illustrating simple distributions, they can become confusing when dealing with too many categories or when the differences in proportions are subtle.
Don’t get too carried away with slices — label those slices with percentages or values so people know what’s what and consider using a legend for more categories.
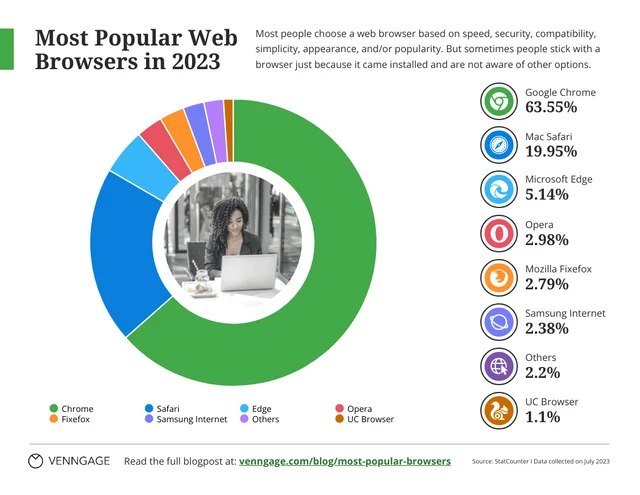
4. Scatter plot
Effective for showing the relationship between two variables and identifying correlations.
Scatter plots are all about exploring relationships between two variables. They’re great for uncovering correlations, trends or patterns in data.
In a scatter plot, every data point appears as a dot on the chart, with one variable marked on the horizontal x-axis and the other on the vertical y-axis.
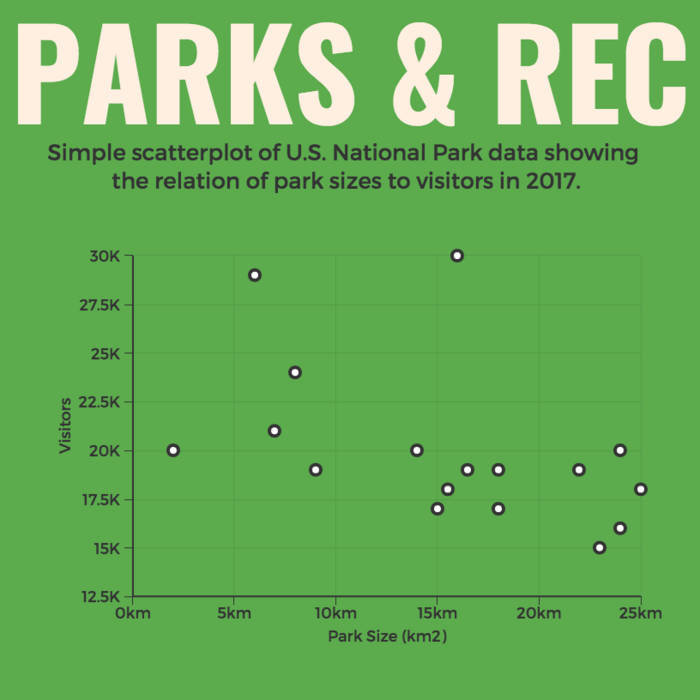
By examining the scatter of points, you can discern the nature of the relationship between the variables, whether it’s positive, negative or no correlation at all.
If you’re using scatter plots to reveal relationships between two variables, be sure to add trendlines or regression analysis when appropriate to clarify patterns. Label data points selectively or provide tooltips for detailed information.
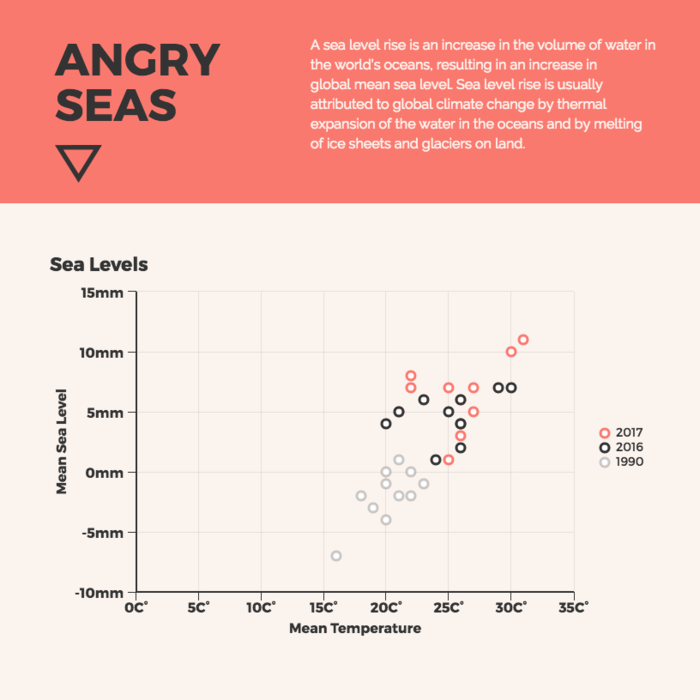
5. Histogram
Best for visualizing the distribution and frequency of a single variable.
Histograms are your choice when you want to understand the distribution and frequency of a single variable.
They divide the data into “bins” or intervals and the height of each bar represents the frequency or count of data points falling into that interval.
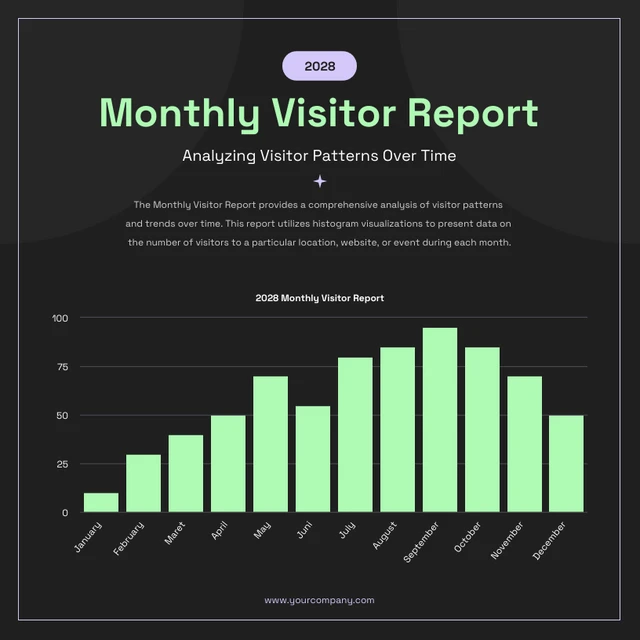
Histograms are excellent for helping to identify trends in data distributions, such as peaks, gaps or skewness.
Here’s something to take note of — ensure that your histogram bins are appropriately sized to capture meaningful data patterns. Using clear axis labels and titles can also help explain the distribution of the data effectively.
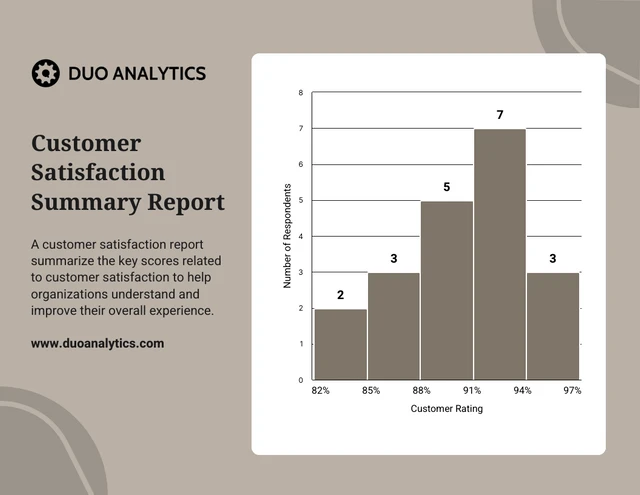
6. Stacked bar chart
Useful for showing how different components contribute to a whole over multiple categories.
Stacked bar charts are a handy choice when you want to illustrate how different components contribute to a whole across multiple categories.
Each bar represents a category and the bars are divided into segments to show the contribution of various components within each category.
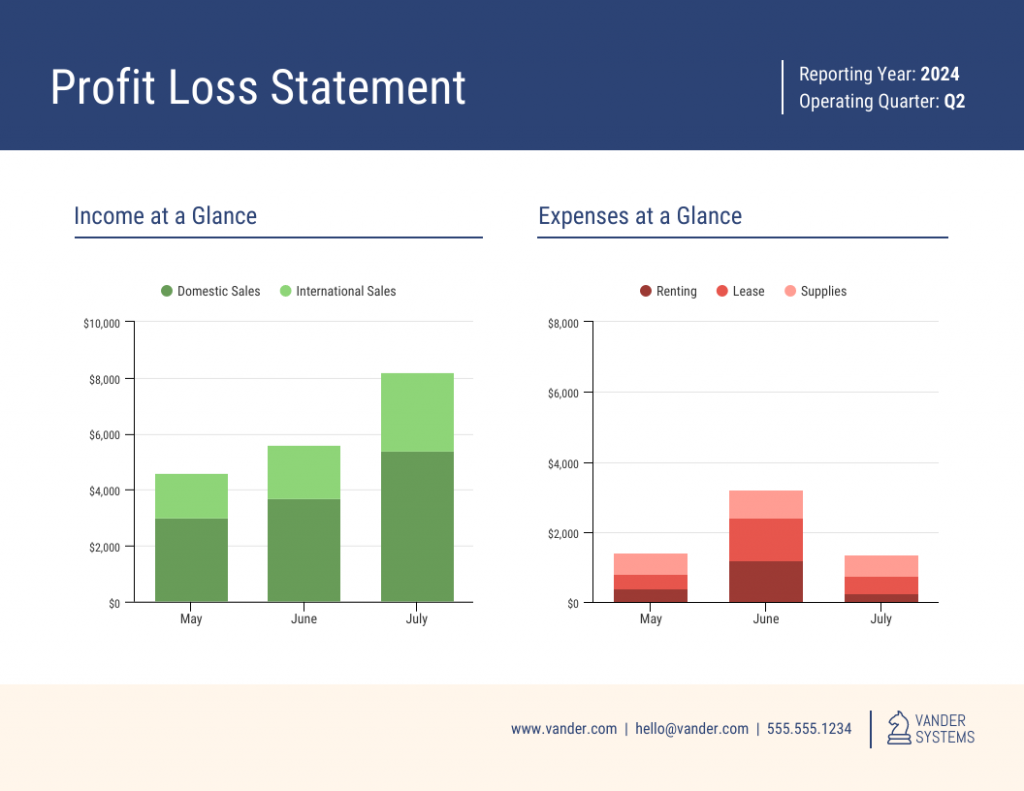
This method is ideal for highlighting both the individual and collective significance of each component, making it a valuable tool for comparative analysis.
Stacked bar charts are like data sandwiches—label each layer so people know what’s what. Keep the order logical and don’t forget the paintbrush for snazzy colors. Here’s a data analysis presentation example on writers’ productivity using stacked bar charts:
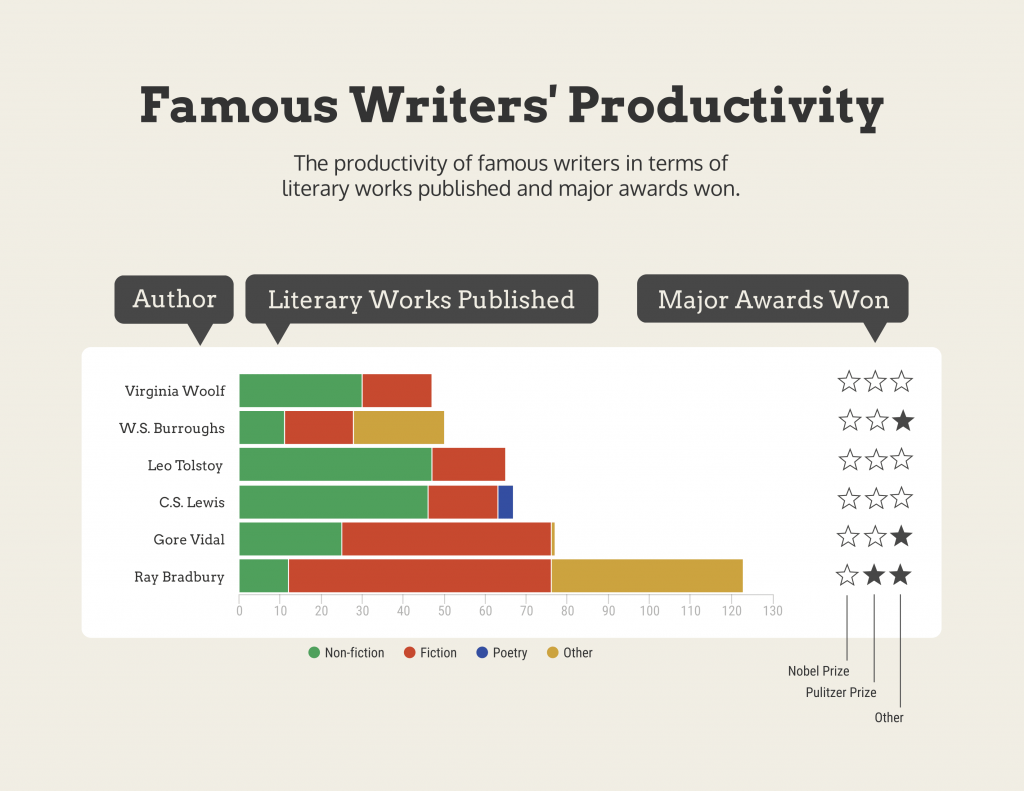
7. Area chart
Similar to line charts but with the area below the lines filled, making them suitable for showing cumulative data.
Area charts are close cousins of line charts but come with a twist.
Imagine plotting the sales of a product over several months. In an area chart, the space between the line and the x-axis is filled, providing a visual representation of the cumulative total.
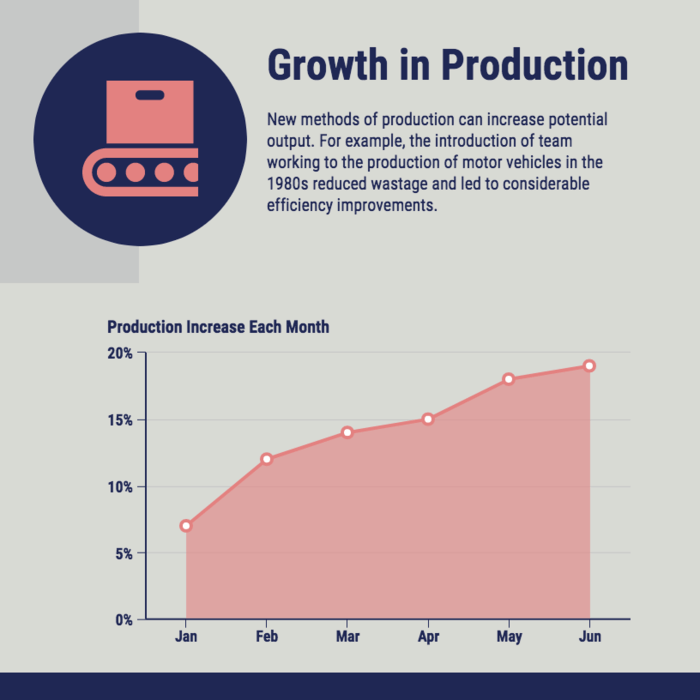
This makes it easy to see how values stack up over time, making area charts a valuable tool for tracking trends in data.
For area charts, use them to visualize cumulative data and trends, but avoid overcrowding the chart. Add labels, especially at significant points and make sure the area under the lines is filled with a visually appealing color gradient.
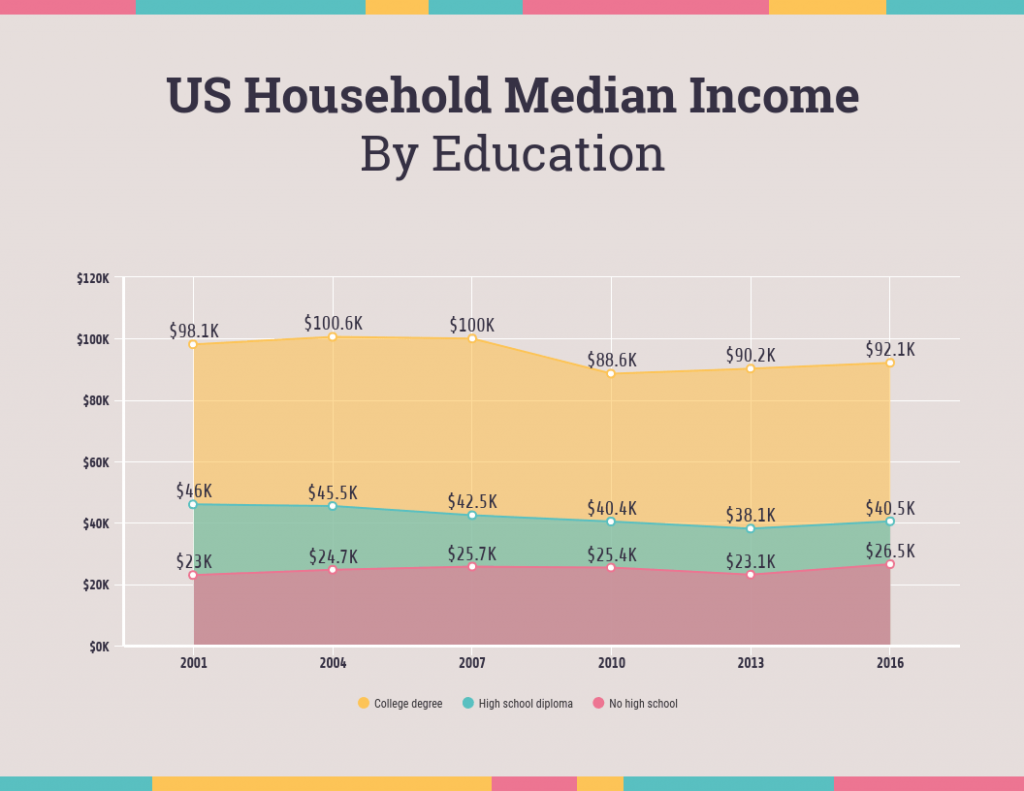
8. Tabular presentation
Presenting data in rows and columns, often used for precise data values and comparisons.
Tabular data presentation is all about clarity and precision. Think of it as presenting numerical data in a structured grid, with rows and columns clearly displaying individual data points.
A table is invaluable for showcasing detailed data, facilitating comparisons and presenting numerical information that needs to be exact. They’re commonly used in reports, spreadsheets and academic papers.
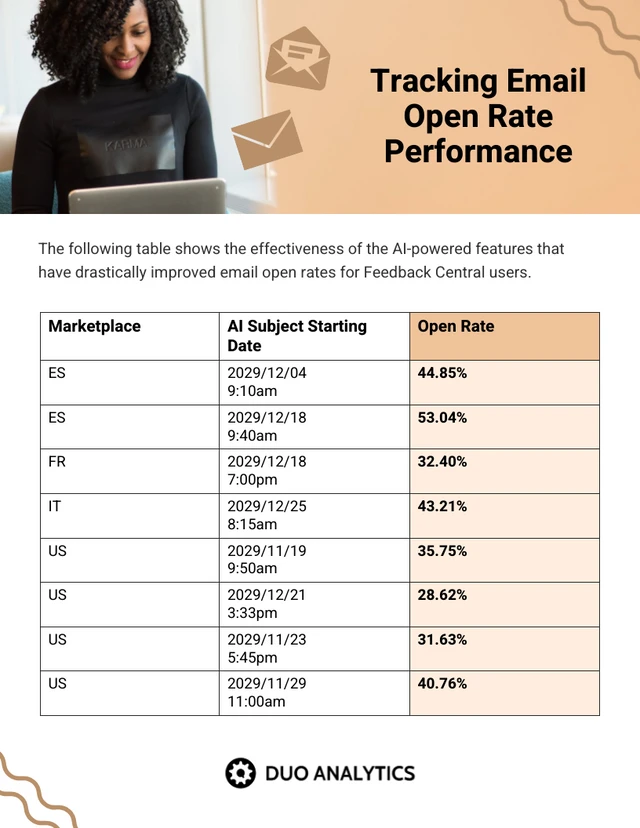
When presenting tabular data, organize it neatly with clear headers and appropriate column widths. Highlight important data points or patterns using shading or font formatting for better readability.
9. Textual data
Utilizing written or descriptive content to explain or complement data, such as annotations or explanatory text.
Textual data presentation may not involve charts or graphs, but it’s one of the most used qualitative data presentation examples.
It involves using written content to provide context, explanations or annotations alongside data visuals. Think of it as the narrative that guides your audience through the data.
Well-crafted textual data can make complex information more accessible and help your audience understand the significance of the numbers and visuals.
Textual data is your chance to tell a story. Break down complex information into bullet points or short paragraphs and use headings to guide the reader’s attention.
10. Pictogram
Using simple icons or images to represent data is especially useful for conveying information in a visually intuitive manner.
Pictograms are all about harnessing the power of images to convey data in an easy-to-understand way.
Instead of using numbers or complex graphs, you use simple icons or images to represent data points.
For instance, you could use a thumbs up emoji to illustrate customer satisfaction levels, where each face represents a different level of satisfaction.

Pictograms are great for conveying data visually, so choose symbols that are easy to interpret and relevant to the data. Use consistent scaling and a legend to explain the symbols’ meanings, ensuring clarity in your presentation.
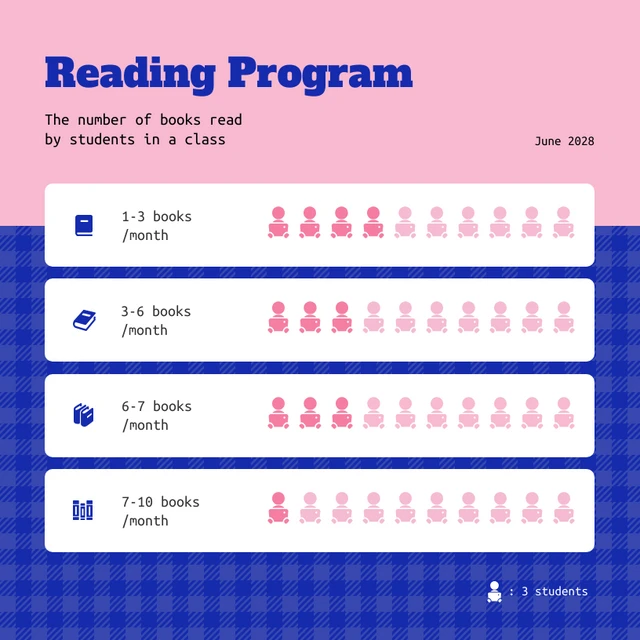
Looking for more data presentation ideas? Use the Venngage graph maker or browse through our gallery of chart templates to pick a template and get started!
A comprehensive data presentation should include several key elements to effectively convey information and insights to your audience. Here’s a list of what should be included in a data presentation:
1. Title and objective
- Begin with a clear and informative title that sets the context for your presentation.
- State the primary objective or purpose of the presentation to provide a clear focus.

2. Key data points
- Present the most essential data points or findings that align with your objective.
- Use charts, graphical presentations or visuals to illustrate these key points for better comprehension.
3. Context and significance
- Provide a brief overview of the context in which the data was collected and why it’s significant.
- Explain how the data relates to the larger picture or the problem you’re addressing.
4. Key takeaways
- Summarize the main insights or conclusions that can be drawn from the data.
- Highlight the key takeaways that the audience should remember.
5. Visuals and charts
- Use clear and appropriate visual aids to complement the data.
- Ensure that visuals are easy to understand and support your narrative.
6. Implications or actions
- Discuss the practical implications of the data or any recommended actions.
- If applicable, outline next steps or decisions that should be taken based on the data.
7. Q&A and discussion
- Allocate time for questions and open discussion to engage the audience.
- Address queries and provide additional insights or context as needed.
Presenting data is a crucial skill in various professional fields, from business to academia and beyond. To ensure your data presentations hit the mark, here are some common mistakes that you should steer clear of:
Overloading with data
Presenting too much data at once can overwhelm your audience. Focus on the key points and relevant information to keep the presentation concise and focused. Here are some free data visualization tools you can use to convey data in an engaging and impactful way.
Assuming everyone’s on the same page
It’s easy to assume that your audience understands as much about the topic as you do. But this can lead to either dumbing things down too much or diving into a bunch of jargon that leaves folks scratching their heads. Take a beat to figure out where your audience is coming from and tailor your presentation accordingly.
Misleading visuals
Using misleading visuals, such as distorted scales or inappropriate chart types can distort the data’s meaning. Pick the right data infographics and understandable charts to ensure that your visual representations accurately reflect the data.
Not providing context
Data without context is like a puzzle piece with no picture on it. Without proper context, data may be meaningless or misinterpreted. Explain the background, methodology and significance of the data.
Not citing sources properly
Neglecting to cite sources and provide citations for your data can erode its credibility. Always attribute data to its source and utilize reliable sources for your presentation.
Not telling a story
Avoid simply presenting numbers. If your presentation lacks a clear, engaging story that takes your audience on a journey from the beginning (setting the scene) through the middle (data analysis) to the end (the big insights and recommendations), you’re likely to lose their interest.
Infographics are great for storytelling because they mix cool visuals with short and sweet text to explain complicated stuff in a fun and easy way. Create one with Venngage’s free infographic maker to create a memorable story that your audience will remember.
Ignoring data quality
Presenting data without first checking its quality and accuracy can lead to misinformation. Validate and clean your data before presenting it.
Simplify your visuals
Fancy charts might look cool, but if they confuse people, what’s the point? Go for the simplest visual that gets your message across. Having a dilemma between presenting data with infographics v.s data design? This article on the difference between data design and infographics might help you out.
Missing the emotional connection
Data isn’t just about numbers; it’s about people and real-life situations. Don’t forget to sprinkle in some human touch, whether it’s through relatable stories, examples or showing how the data impacts real lives.
Skipping the actionable insights
At the end of the day, your audience wants to know what they should do with all the data. If you don’t wrap up with clear, actionable insights or recommendations, you’re leaving them hanging. Always finish up with practical takeaways and the next steps.
Can you provide some data presentation examples for business reports?
Business reports often benefit from data presentation through bar charts showing sales trends over time, pie charts displaying market share,or tables presenting financial performance metrics like revenue and profit margins.
What are some creative data presentation examples for academic presentations?
Creative data presentation ideas for academic presentations include using statistical infographics to illustrate research findings and statistical data, incorporating storytelling techniques to engage the audience or utilizing heat maps to visualize data patterns.
What are the key considerations when choosing the right data presentation format?
When choosing a chart format , consider factors like data complexity, audience expertise and the message you want to convey. Options include charts (e.g., bar, line, pie), tables, heat maps, data visualization infographics and interactive dashboards.
Knowing the type of data visualization that best serves your data is just half the battle. Here are some best practices for data visualization to make sure that the final output is optimized.
How can I choose the right data presentation method for my data?
To select the right data presentation method, start by defining your presentation’s purpose and audience. Then, match your data type (e.g., quantitative, qualitative) with suitable visualization techniques (e.g., histograms, word clouds) and choose an appropriate presentation format (e.g., slide deck, report, live demo).
For more presentation ideas , check out this guide on how to make a good presentation or use a presentation software to simplify the process.
How can I make my data presentations more engaging and informative?
To enhance data presentations, use compelling narratives, relatable examples and fun data infographics that simplify complex data. Encourage audience interaction, offer actionable insights and incorporate storytelling elements to engage and inform effectively.
The opening of your presentation holds immense power in setting the stage for your audience. To design a presentation and convey your data in an engaging and informative, try out Venngage’s free presentation maker to pick the right presentation design for your audience and topic.
What is the difference between data visualization and data presentation?
Data presentation typically involves conveying data reports and insights to an audience, often using visuals like charts and graphs. Data visualization , on the other hand, focuses on creating those visual representations of data to facilitate understanding and analysis.
Now that you’ve learned a thing or two about how to use these methods of data presentation to tell a compelling data story , it’s time to take these strategies and make them your own.
But here’s the deal: these aren’t just one-size-fits-all solutions. Remember that each example we’ve uncovered here is not a rigid template but a source of inspiration. It’s all about making your audience go, “Wow, I get it now!”
Think of your data presentations as your canvas – it’s where you paint your story, convey meaningful insights and make real change happen.
So, go forth, present your data with confidence and purpose and watch as your strategic influence grows, one compelling presentation at a time.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Graphical Representation of Data
Graphical representation of data is an attractive method of showcasing numerical data that help in analyzing and representing quantitative data visually. A graph is a kind of a chart where data are plotted as variables across the coordinate. It became easy to analyze the extent of change of one variable based on the change of other variables. Graphical representation of data is done through different mediums such as lines, plots, diagrams, etc. Let us learn more about this interesting concept of graphical representation of data, the different types, and solve a few examples.
Definition of Graphical Representation of Data
A graphical representation is a visual representation of data statistics-based results using graphs, plots, and charts. This kind of representation is more effective in understanding and comparing data than seen in a tabular form. Graphical representation helps to qualify, sort, and present data in a method that is simple to understand for a larger audience. Graphs enable in studying the cause and effect relationship between two variables through both time series and frequency distribution. The data that is obtained from different surveying is infused into a graphical representation by the use of some symbols, such as lines on a line graph, bars on a bar chart, or slices of a pie chart. This visual representation helps in clarity, comparison, and understanding of numerical data.
Representation of Data
The word data is from the Latin word Datum, which means something given. The numerical figures collected through a survey are called data and can be represented in two forms - tabular form and visual form through graphs. Once the data is collected through constant observations, it is arranged, summarized, and classified to finally represented in the form of a graph. There are two kinds of data - quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative data is more structured, continuous, and discrete with statistical data whereas qualitative is unstructured where the data cannot be analyzed.
Principles of Graphical Representation of Data
The principles of graphical representation are algebraic. In a graph, there are two lines known as Axis or Coordinate axis. These are the X-axis and Y-axis. The horizontal axis is the X-axis and the vertical axis is the Y-axis. They are perpendicular to each other and intersect at O or point of Origin. On the right side of the Origin, the Xaxis has a positive value and on the left side, it has a negative value. In the same way, the upper side of the Origin Y-axis has a positive value where the down one is with a negative value. When -axis and y-axis intersect each other at the origin it divides the plane into four parts which are called Quadrant I, Quadrant II, Quadrant III, Quadrant IV. This form of representation is seen in a frequency distribution that is represented in four methods, namely Histogram, Smoothed frequency graph, Pie diagram or Pie chart, Cumulative or ogive frequency graph, and Frequency Polygon.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Graphical Representation of Data
Listed below are some advantages and disadvantages of using a graphical representation of data:
- It improves the way of analyzing and learning as the graphical representation makes the data easy to understand.
- It can be used in almost all fields from mathematics to physics to psychology and so on.
- It is easy to understand for its visual impacts.
- It shows the whole and huge data in an instance.
- It is mainly used in statistics to determine the mean, median, and mode for different data
The main disadvantage of graphical representation of data is that it takes a lot of effort as well as resources to find the most appropriate data and then represent it graphically.
Rules of Graphical Representation of Data
While presenting data graphically, there are certain rules that need to be followed. They are listed below:
- Suitable Title: The title of the graph should be appropriate that indicate the subject of the presentation.
- Measurement Unit: The measurement unit in the graph should be mentioned.
- Proper Scale: A proper scale needs to be chosen to represent the data accurately.
- Index: For better understanding, index the appropriate colors, shades, lines, designs in the graphs.
- Data Sources: Data should be included wherever it is necessary at the bottom of the graph.
- Simple: The construction of a graph should be easily understood.
- Neat: The graph should be visually neat in terms of size and font to read the data accurately.
Uses of Graphical Representation of Data
The main use of a graphical representation of data is understanding and identifying the trends and patterns of the data. It helps in analyzing large quantities, comparing two or more data, making predictions, and building a firm decision. The visual display of data also helps in avoiding confusion and overlapping of any information. Graphs like line graphs and bar graphs, display two or more data clearly for easy comparison. This is important in communicating our findings to others and our understanding and analysis of the data.
Types of Graphical Representation of Data
Data is represented in different types of graphs such as plots, pies, diagrams, etc. They are as follows,
Related Topics
Listed below are a few interesting topics that are related to the graphical representation of data, take a look.
- x and y graph
- Frequency Polygon
- Cumulative Frequency
Examples on Graphical Representation of Data
Example 1 : A pie chart is divided into 3 parts with the angles measuring as 2x, 8x, and 10x respectively. Find the value of x in degrees.
We know, the sum of all angles in a pie chart would give 360º as result. ⇒ 2x + 8x + 10x = 360º ⇒ 20 x = 360º ⇒ x = 360º/20 ⇒ x = 18º Therefore, the value of x is 18º.
Example 2: Ben is trying to read the plot given below. His teacher has given him stem and leaf plot worksheets. Can you help him answer the questions? i) What is the mode of the plot? ii) What is the mean of the plot? iii) Find the range.
Solution: i) Mode is the number that appears often in the data. Leaf 4 occurs twice on the plot against stem 5.
Hence, mode = 54
ii) The sum of all data values is 12 + 14 + 21 + 25 + 28 + 32 + 34 + 36 + 50 + 53 + 54 + 54 + 62 + 65 + 67 + 83 + 88 + 89 + 91 = 958
To find the mean, we have to divide the sum by the total number of values.
Mean = Sum of all data values ÷ 19 = 958 ÷ 19 = 50.42
iii) Range = the highest value - the lowest value = 91 - 12 = 79
go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions on Graphical Representation of Data
Faqs on graphical representation of data, what is graphical representation.
Graphical representation is a form of visually displaying data through various methods like graphs, diagrams, charts, and plots. It helps in sorting, visualizing, and presenting data in a clear manner through different types of graphs. Statistics mainly use graphical representation to show data.
What are the Different Types of Graphical Representation?
The different types of graphical representation of data are:
- Stem and leaf plot
- Scatter diagrams
- Frequency Distribution
Is the Graphical Representation of Numerical Data?
Yes, these graphical representations are numerical data that has been accumulated through various surveys and observations. The method of presenting these numerical data is called a chart. There are different kinds of charts such as a pie chart, bar graph, line graph, etc, that help in clearly showcasing the data.
What is the Use of Graphical Representation of Data?
Graphical representation of data is useful in clarifying, interpreting, and analyzing data plotting points and drawing line segments , surfaces, and other geometric forms or symbols.
What are the Ways to Represent Data?
Tables, charts, and graphs are all ways of representing data, and they can be used for two broad purposes. The first is to support the collection, organization, and analysis of data as part of the process of a scientific study.
What is the Objective of Graphical Representation of Data?
The main objective of representing data graphically is to display information visually that helps in understanding the information efficiently, clearly, and accurately. This is important to communicate the findings as well as analyze the data.
- List of Commerce Articles
- Meaning And Objective Of Tabulation

Meaning and Objective of Tabulation
Tabulation meaning:.
Tabulation is a systematic and logical representation of numeric data in rows and columns to facilitate comparison and statistical analysis. It facilitates comparison by bringing related information close to each other and helps in statistical analysis and interpretation.
In other words, the method of placing organised data into a tabular form is known as tabulation. It may be complex, double, or simple, depending upon the nature of categorisation.
Also Check: Tabular Presentation of Data
Objectives Of Tabulation:
(1) To simplify complex data
- It reduces the bulk of information, i.e., it reduces raw data in a simplified and meaningful form so that it can be easily interpreted by a common man in less time.
(2) To bring out essential features of data
- It brings out the chief/main characteristics of data.
- It presents facts clearly and precisely without textual explanation.
(3) To facilitate comparison
- The representation of data in rows and columns is helpful in simultaneous detailed comparison on the basis of several parameters.
(4) To facilitate statistical analysis
- Tables serve as the best source of organised data for statistical analysis.
- The task of computing average, dispersion, correlation, etc., becomes easier if data is presented in the form of a table.
(5) To save space
- A table presents facts in a better way than the textual form.
- It saves space without sacrificing the quality and quantity of data.
Also Read: What are Measures Of Dispersion?
Multiple Choice Questions:
Related Read: T.R. Jain and V.K. Ohri Solutions for Presentation of Data
The above-mentioned concept is for CBSE Class 11 Statistics for Economics – Meaning and Objective of Tabulation. For solutions and study materials for Class 11 Statistics for Economics, visit BYJU’S or download the app for the best learning experience.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
This is very interesting app for us
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
As a result of this, it is simple to remember the statistical facts. Cost-effective: Tabular presentation is a very cost-effective way to convey data. It saves time and space. Provides Reference: As the data provided in a tabular presentation can be used for other studies and research, it acts as a source of reference.
The objectives of tabular data presentation are as follows. The tabular data presentation helps in simplifying the complex data. It also helps to compare different data sets thereby bringing out the important aspects. The tabular presentation provides the foundation for statistical analysis. The tabular data presentation further helps in the ...
What is Tabular Presentation of Data? It is a table that helps to represent even a large amount of data in an engaging, easy to read, and coordinated manner. The data is arranged in rows and columns. This is one of the most popularly used forms of presentation of data as data tables are simple to prepare and read.
In statistics, tabular data refers to data that is organized in a table with rows and columns. Within the table, the rows represent observations and the columns represent attributes for those observations. For example, the following table represents tabular data: This dataset has 9 rows and 5 columns. Each row represents one basketball player ...
Gary W. Oehlert. Tabular Display of Data. Or computer files. # Number of hawks responding to the "alarm" call # Variables are year (1999 or 2000), season (courtship, # nestling, fledgling), distance in meters between the # alarm call and the nest, number of hawks responding, # and number of. year season distance respond trials. 1 100 1 4.
Definition: Data presentation is the art of visualizing complex data for better understanding. Importance: Data presentations enhance clarity, engage the audience, aid decision-making, and leave a lasting impact. Types: Textual, Tabular, and Graphical presentations offer various ways to present data.
Data Presentation - Tables. Tables are a useful way to organize information using rows and columns. Tables are a versatile organization tool and can be used to communicate information on their own, or they can be used to accompany another data representation type (like a graph). Tables support a variety of parameters and can be used to keep ...
4.1 Creating Tabular Data. ... Observe that the example above uses is-not, i.e., the test passes, meaning that the tables are not equal. Of course, we can write literal tables using table. However, Pyret provides other ways to get tabular data, too! ... Finally, for presentation purposes, it is sometimes useful to see just a few of the columns ...
TL;DR: I'm going to show you some data-viz techniques for tabular data. Those techniques will help your audience focus more on the impact of your cells than the table definition itself — feel free to just to conclusions to have a quick bullet list. When to use a table. As tables are so risky you must choose carefully when to use them.
Understanding types of data and its representation is a foundational step in statistics, machine learning and data science. This article offers tips to mine information from data efficiently.
TABULAR PRESENTATION OF DATA When to Use Tables • Written documents (reports, journal articles) typically present most results in tabular form. • Research Posters for conferences. • More concise format than graphs. • In oral presentations, only VERY simple tables should be presented.
Data Tables or Tabular Presentation. A table facilitates representation of even large amounts of data in an attractive, easy to read and organized manner. The data is organized in rows and columns. This is one of the most widely used forms of presentation of data since data tables are easy to construct and read.
In this article, the techniques of data and information presentation in textual, tabular, and graphical forms are introduced. Text is the principal method for explaining findings, outlining trends, and providing contextual information. A table is best suited for representing individual information and represents both quantitative and ...
Related: 14 Data Modelling Tools For Data Analysis (With Features) Tabular Tabular presentation is using a table to share large amounts of information. When using this method, you organise data in rows and columns according to the characteristics of the data. Tabular presentation is useful in comparing data, and it helps visualise information.
In statistics, tabular data refers to data that is organized in a table with rows and columns. Within the table, the rows represent observations and the columns represent attributes for those observations. For example, the following table represents tabular data: This dataset has 9 rows and 5 columns. Each row represents one basketball player ...
Tables in Research Paper. Definition: In Research Papers, Tables are a way of presenting data and information in a structured format.Tables can be used to summarize large amounts of data or to highlight important findings. They are often used in scientific or technical papers to display experimental results, statistical analyses, or other quantitative information.
Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples) Design • March 20th, 2024. In this age of overwhelming information, the skill to effectively convey data has become extremely valuable. Initiating a discussion on data presentation types involves thoughtful consideration of the nature of your data and the message you aim to convey.
In this method, we can arrange the data in tabular form in terms of frequency. For example, 3 students scored 50 marks. Hence, the frequency of 50 marks is 3. Now, let us construct the frequency distribution table for the given data. Therefore, the presentation of data is given as below:
Steps for constructing a histogram is as follows. Step 1: Partition the data range into General guidelines are: classes. or. bins. Use between 6 and 15 bins. One suggested formula (Sturges) is: Number of Classes = 1 + 3.3 log(n) where n is the total number of observations. All bins should have the same width.
Tabular data presentation is all about clarity and precision. Think of it as presenting numerical data in a structured grid, with rows and columns clearly displaying individual data points. ... Using misleading visuals, such as distorted scales or inappropriate chart types can distort the data's meaning. Pick the right data infographics and ...
In tabular representation of data, the given data set is presented in rows and columns. When a table is used to represent a large amount of data in an arranged, organised, engaging, coordinated and easy to read form it is called the tabular representation of data. The main parts of a Table are table number, title, headnote, captions or column ...
Graphical representation is a form of visually displaying data through various methods like graphs, diagrams, charts, and plots. It helps in sorting, visualizing, and presenting data in a clear manner through different types of graphs. Statistics mainly use graphical representation to show data.
Tabulation is a systematic and logical representation of numeric data in rows and columns to facilitate comparison and statistical analysis. It facilitates comparison by bringing related information close to each other and helps in statistical analysis and interpretation. In other words, the method of placing organised data into a tabular form ...