

Class 9 Science Case Study Questions Chapter 1 Matter in our Surroundings
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case study Questions in Class 9 Science Chapter 1 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving Class 9 Science Case Study Questions Chapter 1 Matter in our Surroundings
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Matter in our Surroundings Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in our Surroundings
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1: There are three states of matter – solid, liquid, and gas.
Solids have a definite shape, distinct boundaries, and fixed volumes, that is, have negligible compressibility. Solids have a tendency to maintain their shape when subjected to outside force. Solids may break under force but it is difficult to change their shape, so they are rigid.
Liquids have no fixed shape but have a fixed volume. They take up the shape of the container in which they are kept. Liquids flow and change shape, so they are not rigid but can be called fluid.
Gas has an indefinite shape and no fixed volume. Gas gets the shape and volume of the container.Gas has a very low density and hence is light. Gas can flow easily and hence is called fluid.
i.) Which of the following state of matter takes the shape of the container in which it is filled?
d.) Both b and c
Answer: d.) Both b and c
ii.) Distance between particles of matter least in
d.) None of these
Answer: a.) Solid
iii.) Compressibility is least in case of
Case Study 2: Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. It exists in various forms, such as solid, liquid, and gas. The physical properties of matter, such as shape, size, and state, can be observed and measured. The particles that makeup matter are constantly in motion, and their motion determines the state of matter. In a solid, the particles are tightly packed and have a fixed shape and volume. In a liquid, the particles are close together but can move past each other, giving the substance a fixed volume but no fixed shape. In a gas, the particles are far apart and move freely, allowing the substance to occupy any volume and shape. Matter can undergo changes in its state through the processes of evaporation, condensation, melting, and freezing. Understanding the properties and behavior of matter is essential for studying various scientific phenomena and practical applications in our daily lives.
What is matter? a) Anything that occupies space and has mass b) Anything that is visible to the naked eye c) Anything that is in a solid state d) Anything that is in a gaseous state Answer: a) Anything that occupies space and has mass
What determines the state of matter? a) Physical properties b) Chemical properties c) The motion of particles d) The color of the substance Answer: c) The motion of particles
How are particles arranged in a solid? a) Far apart and move freely b) Close together but can move past each other c) Tightly packed and have a fixed shape d) Tightly packed but have no fixed shape Answer: c) Tightly packed and have a fixed shape
What is the behavior of particles in a gas? a) They are far apart and move freely b) They are close together but can move past each other c) They are tightly packed and have a fixed shape d) They are tightly packed but have no fixed shape Answer: a) They are far apart and move freely
What processes can matter undergo to change its state? a) Evaporation, condensation, melting, and freezing b) Dissolution, combustion, sublimation, and oxidation c) Fermentation, photosynthesis, respiration, and digestion d) Oxidation, reduction, precipitation, and ionization Answer: a) Evaporation, condensation, melting, and freezing
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in our Surroundings with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 9 Science Matter in our Surroundings Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like

1569+ Class 9 Science MCQ Questions with Answers PDF Download
Class 9 mcq questions for chapter 11 work and energy with answers, mcq questions of class 9 social science history chapter 5 pastoralists in the modern world with answers, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 9 Science Matter in our Surroundings
Case study questions class 9 science chapter 1 matter in our surroundings.
CBSE Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Matter in our Surroundings. Important Case Study Questions for Class 9 Exam. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Matter in our Surroundings.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks or 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science – Matter in our Surroundings
Case study 1:.
1.) A matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Pen, paper, clips, sand, air, ice, etc. are different forms of matter. Every matter is made up of small particles. These particles are so tiny that they can’t be seen with naked eyes. Let’s see about the different characteristics of particles of matter.
- All matter is made up of very small particles.
- .Particles of matter has spaces between them.
- Particles of matter are continuously moving.
- Particles of matter attract each other.
Answer the following questions by referring above paragraph.
i.) Which of following is not matter?
c.) smell of perfume
d.) None of these
ii.) Thoughts coming in our mind are example of matter. True or false
c.) None of these
iii.) Which of the following is true about particles of matter?
a.) Particles of matter has spaces between them
b.) Particles of matter are continuously moving
c.) Particles of matter attract each other
d.) All of these
iv.) Give 5 examples of matter in our surroundings
v.) Enlist all properties of particles of matter
Answer key-1
iv.) pen, pencil, notebook, ice and water
v.) Different characteristics of particles of matter are
Case Study 2:
2.) There are three states of matter – solid, liquid and gas.
Solids have a definite shape, distinct boundaries and fixed volumes, that is, have negligible compressibility. Solids have a tendency to maintain their shape when subjected to outside force. Solids may break under force but it is difficult to change their shape, so they are rigid.
Liquids have no fixed shape but have a fixed volume. They take up the shape of the container in which they are kept. Liquids flow and change shape, so they are not rigid but can be called fluid.
Gas as has indefinite shape, no fixed volume. Gas gets the shape and volume of container.
Gas has very low density hence are light. Gas can flow easily and hence are called fluid.
i.) Which of the following state of matter takes shape of container in which it is filled?
d.) Both b and c
ii.) Distance between particles of matter least in
iii.) Compressibility is least in case of
iv.) Give properties of solids.
v.) Give properties of Gases.
Answer key-2
iv.) properties of solid are given below
- Solid has fixed volume.
- Solid has fixed shape.
- Solid has high density.
- Solids are heavy.
- Solid does not flow.
v.) Properties of gases are
- Gas has indefinite shape
- Gas has no fixed volume.
- Gas gets the shape and volume of container.
- Gas fills the container completely.
- Gas has very low density.
- Because of low density gas are light.
- Gas can flow easily and hence are called fluid.
Case Study 3:
3.) What happens inside the matter during change of state? On increasing the temperature of solids, the kinetic energy of the particles increases. Due to the increase in kinetic energy, the
Particles start vibrating with greater speed. The energy supplied by heat overcomes the forces of attraction between the particles. The particles leave their fixed positions and start moving more freely. A stage is reached when the solid melts and is converted to a liquid. The minimum temperature at which a solid melts to become a liquid at the atmospheric pressure is called its melting point.
The temperature of the system does not change after the melting point is reached, till all the ice melts. This happens even though we continue to heat the beaker, that is, we continue to supply heat. This heat gets used up in changing the state by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles. The amount of heat energy that is required to change 1 kg of a solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure at its melting point is known as the latent heat of fusion. So, particles in water at 0 0 C (273 K) have more energy as compared to particles in ice at the same temperature.
The temperature at which a liquid starts boiling at the atmospheric pressure is known as its boiling point. Boiling is a bulk phenomenon. Particles from the bulk of the liquid gain enough energy to change into the vapour state. A change of state directly from solid to gas without changing into liquid state is called sublimation and the direct change of gas to solid without changing into liquid is called deposition.
i.) A change of state directly from solid to gas without changing into liquid state is called
a.) Sublimation
b.) Deposition
c.) Boiling point
ii.) The direct change of gas to solid without changing into liquid is called
iii.) The energy supplied by heat to solid is used to overcome the forces of attraction between the particles. True or false
iv.) Define melting point and boiling point
v.) Define latent heat of fusion
Answer key-3
iv.) The minimum temperature at which a solid melts to become a liquid at the atmospheric pressure is called its melting point.
The temperature at which a liquid starts boiling at the atmospheric pressure is known as its boiling point.
v.) The amount of heat energy that is required to change 1 kg of a solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure at its melting point is known as the latent heat of fusion.
Case Study 4:
4 .) Do we always need to heat or change pressure for changing the state of matter? Can you quote some examples from everyday life where change of state from liquid to vapour takes place without the liquid reaching the boiling point? In the case of liquids, a small fraction of particles at the surface, having higher kinetic energy, is able to break away from the forces of attraction of other particles and gets converted into vapour. This phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapors at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation.
i.) Evaporation of liquid takes place at
a.) Boiling point
b.) Above boiling point
c.) Below boiling point
ii.) Evaporation takes place at surface of liquid because
a.) They are heavy as compare to other particles
b.) They have sufficient kinetic energy to break the force
c.) They are light weight as compare to other particles
iii.) During evaporation particles of liquid change into vapour
a.) From the surface
b.) From the bottom
c.) From all over the liquid
iv.) Define evaporation.
v.) Explain process of evaporation
Answer key-4
iv.) The phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapors at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation.
v.) In the case of liquids, a small fraction of particles at the surface, having higher kinetic energy, is able to break away from the forces of attraction of other particles and gets converted into vapour. This phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapors at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation.
Case Study 5:
5.) You must have observed that the rate of evaporation increases with–
- an increase of surface area:
- We know that evaporation is a surface phenomenon. If the surface area is increased, the rate of evaporation increases. For example, while putting clothes for drying up we spread them out.
- an increase of temperature:
With the increase of temperature, more number of particles get enough kinetic energy to go into the vapour state.
In an open vessel, the liquid keeps on evaporating. The particles of liquid absorb energy from the surrounding to regain the energy lost during evaporation. This absorption of energy from the surroundings makes the surroundings cold. What happens when you pour some acetone (nail polish remover) on your palm? The particles gain energy from your palm or surroundings and evaporate causing the palm to feel cool. After a hot sunny day, people sprinkle water on the roof or open ground because the large latent heat of vaporization of water helps to cool the hot surface.
i.) Evaporation is surface phenomenon. True or false
ii.) As temperature increases the rate of evaporation is
a.) increases
b.) decreases
c.) remains constant
iii.) The rate of evaporation increases with
a.) Increase in wind speed
b.) Decrease in wind speed
c.) Does not have any effect from wind speed
iv.) What happens when you pour some acetone (nail polish remover) on your palm?
v.) We are able to sip hot tea from saucer than from cup. Why?
Answer key-5
iv.) The particles gain energy from your palm or surroundings and evaporate causing the palm to feel cool.
v.) We are able to sip hot tea from saucer than from cup. This is because saucer has large surface area, due to large surface area as compare to cut area tea evaporates at faster rate.
Thank you It helped me a lot
Why smell of Perfume is not a matter?
Because there is no particle
Because their are perfume particles suspended in air
These all case study questions are really helpful . Thanks
This is my first I was so nervous but these questions help me alot thank you
Smell of perfume is a matter because it have gas particles means perfume particles
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Amader poribesh class 4 solutions chapter 8 manusher poribar o somaj, dav class 6 sst india – the land of monsoon climate extra questions, amader poribesh class 4 solutions chapter 3 sorir, sikkim scert class 5 english chapter 6e sushma gets picture postcards solution.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
myCBSEguide
- Class 9 Science Case...
Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you are wondering how to solve class 9 science case study questions, then myCBSEguide is the best platform to choose. With the help of our well-trained and experienced faculty, we provide solved examples and detailed explanations for the recently added Class 9 Science case study questions.
You can find a wide range of solved case studies on myCBSEguide, covering various topics and concepts. Class 9 Science case studies are designed to help you understand the application of various concepts in real-life situations.
The rationale behind Science
Science is crucial for Class 9 students’ cognitive, emotional, and psychomotor development. It encourages curiosity, inventiveness, objectivity, and aesthetic sense.
In the upper primary stage, students should be given a variety of opportunities to engage with scientific processes such as observing, recording observations, drawing, tabulating, plotting graphs, and so on, whereas in the secondary stage, abstraction and quantitative reasoning should take a more prominent role in science teaching and learning. As a result, the concept of atoms and molecules as matter’s building units, as well as Newton’s law of gravitation, emerges.
Science is important because it allows Class 9 Science students to understand the world around us. It helps to find out how things work and to find solutions to problems at the Class 9 Science level. Science is also a source of enjoyment for many people. It can be a hobby, a career, or a source of intellectual stimulation.
Case study questions in Class 9 Science
The inclusion of case study questions in Class 9 science CBSE is a great way to engage students in critical thinking and problem-solving. By working through real-world scenarios, Class 9 Science students will be better prepared to tackle challenges they may face in their future studies and careers. Class 9 Science Case study questions also promote higher-order thinking skills, such as analysis and synthesis. In addition, case study questions can help to foster creativity and innovation in students. As per the recent pattern of the Class 9 Science examination, a few questions based on case studies/passages will be included in the CBSE Class 9 Science Paper. There will be a paragraph presented, followed by questions based on it.
Examples of Class 9 science class case study questions
Class 9 science case study questions have been prepared by myCBSEguide’s qualified teachers. Class 9 case study questions are meant to evaluate students’ knowledge and comprehension of the material. They are not intended to be difficult, but they will require you to think critically about the material. We hope you find Class 9 science case study questions beneficial and that they assist you in your exam preparation.
The following are a few examples of Class 9 science case study questions.
Class 9 science case study question 1
- due to its high compressibility
- large volumes of a gas can be compressed into a small cylinder
- transported easily
- all of these
- shape, volume
- volume, shape
- shape, size
- size, shape
- the presence of dissolved carbon dioxide in water
- the presence of dissolved oxygen in the water
- the presence of dissolved Nitrogen in the water
- liquid particles move freely
- liquid have greater space between each other
- both (a) and (b)
- none of these
- Only gases behave like fluids
- Gases and solids behave like fluids
- Gases and liquids behave like fluids
- Only liquids are fluids
Answer Key:
- (d) all of these
- (a) shape, volume
- (b) the presence of dissolved oxygen in the water
- (c) both (a) and (b)
- (c) Gases and liquids behave like fluids
Class 9 science case study question 2
- 12/32 times
- 18 g of O 2
- 18 g of CO 2
- 18 g of CH 4
- 1 g of CO 2
- 1 g of CH 4 CH 4
- 2 moles of H2O
- 20 moles of water
- 6.022 × 1023 molecules of water
- 1.2044 × 1025 molecules of water
- (I) and (IV)
- (II) and (III)
- (II) and (IV)
- Sulphate molecule
- Ozone molecule
- Phosphorus molecule
- Methane molecule
- (c) 8/3 times
- (d) 18g of CH 4
- (c) 1g of H 2
- (d) (II) and (IV)
- (c) phosphorus molecule
Class 9 science case study question 3
- collenchyma
- chlorenchyma
- It performs photosynthesis
- It helps the aquatic plant to float
- It provides mechanical support
- Sclerenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Epithelial tissue
- Parenchyma tissues have intercellular spaces.
- Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at corners.
- Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues.
- Meristematic tissues, in its early stage, lack vacuoles, muscles
- (I) and (II)
- (III) and (I)
- Transpiration
- Provides mechanical support
- Provides strength to the plant parts
- None of these
- (a) Collenchyma
- (b) help aquatic plant to float
- (b) Sclerenchyma
- (d) Only (III)
- (c) provide strength to plant parts
Cracking Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
There is no one definitive answer to Class 9 Science case study questions. Every case study is unique and will necessitate a unique strategy. There are, nevertheless, certain general guidelines to follow while answering case study questions.
- To begin, double-check that you understand the Class 9 science case study questions. Make sure you understand what is being asked by reading it carefully. If you’re unclear, seek clarification from your teacher or tutor.
- It’s critical to read the Class 9 Science case study material thoroughly once you’ve grasped the question. This will provide you with a thorough understanding of the problem as well as the various potential solutions.
- Brainstorming potential solutions with classmates or other students might also be beneficial. This might provide you with multiple viewpoints on the situation and assist you in determining the best solution.
- Finally, make sure your answer is presented simply and concisely. Make sure you clarify your rationale and back up your claim with evidence.
A look at the Class 9 Science Syllabus
The CBSE class 9 science syllabus provides a strong foundation for students who want to pursue a career in science. The topics are chosen in such a way that they build on the concepts learned in the previous classes and provide a strong foundation for further studies in science. The table below lists the topics covered in the Class 9 Science syllabus of the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). As can be seen, the Class 9 science syllabus is divided into three sections: Physics, Chemistry and Biology. Each section contains a number of topics that Class 9 science students must study during the course.
CBSE Class 9 Science (Code No. 086)
Theme: Materials Unit I: Matter-Nature and Behaviour Definition of matter; solid, liquid and gas; characteristics – shape, volume, density; change of state-melting (absorption of heat), freezing, evaporation (cooling by evaporation), condensation, sublimation. Nature of matter: Elements, compounds and mixtures. Heterogeneous and homogenous mixtures, colloids and suspensions. Particle nature and their basic units: Atoms and molecules, Law of constant proportions, Atomic and molecular masses. Mole concept: Relationship of mole to mass of the particles and numbers. Structure of atoms: Electrons, protons and neutrons, valency, the chemical formula of common compounds. Isotopes and Isobars.
Theme: The World of the Living Unit II: Organization in the Living World Cell – Basic Unit of life: Cell as a basic unit of life; prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, multicellular organisms; cell membrane and cell wall, cell organelles and cell inclusions; chloroplast, mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus; nucleus, chromosomes – basic structure, number. Tissues, Organs, Organ System, Organism: Structure and functions of animal and plant tissues (only four types of tissues in animals; Meristematic and Permanent tissues in plants).
Theme: Moving Things, People and Ideas Unit III: Motion, Force and Work Motion: Distance and displacement, velocity; uniform and non-uniform motion along a straight line; acceleration, distance-time and velocity-time graphs for uniform motion and uniformly accelerated motion, derivation of equations of motion by graphical method; elementary idea of uniform circular motion. Force and Newton’s laws: Force and Motion, Newton’s Laws of Motion, Action and Reaction forces, Inertia of a body, Inertia and mass, Momentum, Force and Acceleration. Elementary idea of conservation of Momentum. Gravitation: Gravitation; Universal Law of Gravitation, Force of Gravitation of the earth (gravity), Acceleration due to Gravity; Mass and Weight; Free fall. Floatation: Thrust and Pressure. Archimedes’ Principle; Buoyancy. Work, energy and power: Work done by a Force, Energy, power; Kinetic and Potential energy; Law of conservation of energy. Sound: Nature of sound and its propagation in various media, speed of sound, range of hearing in humans; ultrasound; reflection of sound; echo.
Theme: Food Unit IV: Food Production Plant and animal breeding and selection for quality improvement and management; Use of fertilizers and manures; Protection from pests and diseases; Organic farming.
PRESCRIBED BOOKS:
- Science-Textbook for class IX-NCERT Publication
- Assessment of Practical Skills in Science-Class IX – CBSE Publication
- Laboratory Manual-Science-Class IX, NCERT Publication
- Exemplar Problems Class IX – NCERT Publication
myCBSEguide: A true helper
There are numerous advantages to using myCBSEguide to achieve the highest results in Class 9 Science.
- myCBSEguide offers high-quality study materials that cover all of the topics in the Class 9 Science curriculum.
- myCBSEguide provides practice questions and mock examinations to assist students in the best possible preparation for their exams.
- On our myCBSEguide app, you’ll find a variety of solved Class 9 Science case study questions covering a variety of topics and concepts. These case studies are intended to help you understand how certain principles are applied in real-world settings
- myCBSEguide is that the study material and practice problems are developed by a team of specialists who are always accessible to assist students with any questions they may have. As a result, students may be confident that they will receive the finest possible assistance and support when studying for their exams.
So, if you’re seeking the most effective strategy to study for your Class 9 Science examinations, myCBSEguide is the place to go!
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE Expert
Case Study Questions of Chapter 1 Matter in our Surroundings PDF Download
Case study Questions on Class 9 Science Chapter 1 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in our Surroundings

In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Matter in our Surroundings Case Study Questions With answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in our Surroundings
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
There are three states of matter – solid, liquid, and gas.
Solids have a definite shape, distinct boundaries, and fixed volumes, that is, have negligible compressibility. Solids have a tendency to maintain their shape when subjected to outside force. Solids may break under force but it is difficult to change their shape, so they are rigid.
Liquids have no fixed shape but have a fixed volume. They take up the shape of the container in which they are kept. Liquids flow and change shape, so they are not rigid but can be called fluid.
Gas has an indefinite shape and no fixed volume. Gas gets the shape and volume of the container.
Gas has very low density hence is light. Gas can flow easily and hence is called fluid.
i.) Which of the following state of matter takes shape of the container in which it is filled?
d.) Both b and c
Answer: d.) Both b and c
ii.) Distance between particles of matter least in
d.) None of these
Answer: a.) Solid
iii.) Compressibility is least in case of
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in our Surroundings with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 9 Science Matter in our Surroundings Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (chemistry) Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings are given below. In these solutions, we have answered all the intext and exercise questions provided in NCERT class 9 science textbook. Class 9 NCERT Solutions Science Chapter 1 provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum. Students can easily download these solutions in PDF format for free from our app.
Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Textbook Questions and Answers
Intext Questions
Question 1: Which of the following are matter?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cold drink, smell of perfume.
Answer: Chair, air, almonds, and cold-drink are matters.
Explanation: Things that occupy space and have some mass are called matter. Since chair, air, almonds and cold-drink occupy some space and have some mass, so these are matter.
Question 2: Give reasons for the following observation:
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several metres away, but to get the smell from cold food you have to go close.
Answer: The smell of hot sizzling food reaches severed meters away, as the particles of hot food have more kinetic energy and hence the rate of diffusion is more than the particles of cold food.
Smell of anything comes because of gases emanating from the given thing. The smell reaches to us because of diffusion of gas. The rate of diffusion increases with increase in temperature. This happens because of higher kinetic energy due to higher temperature. That is why smell of hot sizzling food reaches to us from several feet. On the other hand, the kinetic energy of gases emanating from cold food is low because of lower temperature. Due to this, we need to move closer to a cold food to take its smell.
Question 3: A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. Which property of matter does this observation show?
Answer: A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. This shows that the particles of water have intermolecular space and has less force of attraction.
Question 4: What are the characteristics of particles of matter?
Answer: The characteristics of particles of matter are:
- Particles of matter have spaces between them.
- Particles of matter are continuously moving.
- Particles of mater attract each other.
Question 1: The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density (density = mass/volume). Arrange the following in order of increasing density − air, exhaust from chimney, honey, water, chalk, cotton, and iron.
Answer: The given substances in the increasing order of their densities can be represented as:
Air < Exhaust from chimney < Cotton < Water < Honey < Chalk < Iron
Explanation: Air is the mixture of gases. Chimney exhaust is also a mixture of gases; along with some heavier particles, such as ash. This makes the density of chimney exhaust more than air. Cotton is a porous solid and which has lot of air trapped within pores. This makes its volume more than water. Therefore, it is less dense than water.
Question 2: (a) Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of states of matter. (b) Comment upon the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy and density.
Answer: (a) The differences in the characteristics of states of matter are given in the following table.
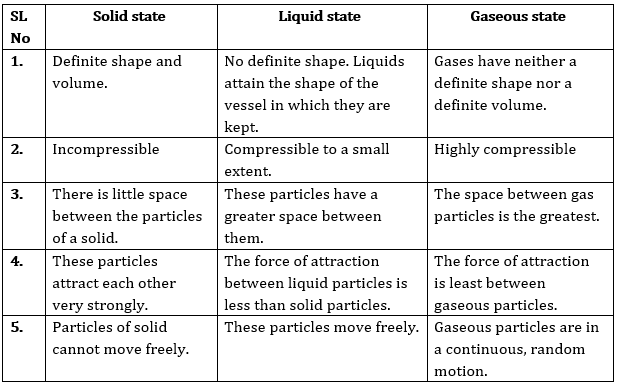
The difference in the characteristics of the three states of matter.
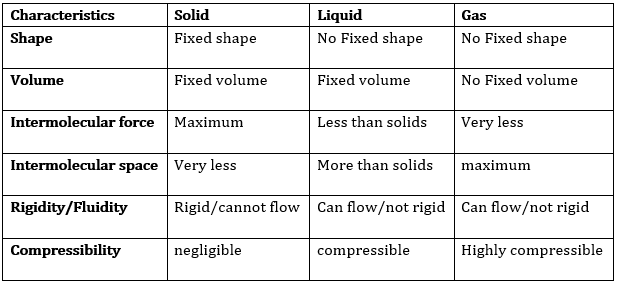
(b) Rigidity: The greatest force of attraction between particles and close packing of particles make solids rigid. Rigidity is one of the unique properties of solids. Because of rigidity, a solid can resist from getting distorted. Because of rigidity a solid has definite shape and volume. Rigidity is negligible in fluid and gas.
Compressibility: Compressibility is one of the most important characteristics of gas. Because of lot of space between particles, a gas can be compressed to a great extent.
Liquid and solid cannot be compressed because of the least space between their particles.
Fluidity: The ability to flow is called fluidity. The less force of attraction and more space between particles make liquid and gas to flow. That’s why liquid and gas are called fluid.
Filling of a gas container: Liquids do not fill a gas container completely, while gases fill the gas container completely in which it is kept. This is because the particles of gas can move in all the directions.
Shape: Solids have fixed shape. Liquid and gas take the shape of the container in which they are kept. This happens because of less force of attraction and more kinetic energy between particles of liquids and negligible force of attraction and highest kinetic energy between particles of gas.
Kinetic energy: The kinetic energy of particles of solid is the minimum. They only vibrate at their fixed position. The kinetic energy of particles of liquid is more than that of solid. But they can slide above one another. The kinetic energy of particles of gas is the maximum.
Density: The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density. The density of solid is highest, of liquid is less than solid and of gas is minimum.
Question 3: Give reasons: (a) A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept. (b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container. (c) A wooden table should be called a solid. (d) We can easily move our hand in air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
Answer: (a) There is little attraction between particles of gas. Thus, gas particles move freely in all directions. Therefore, gas completely fills the vessel in which it is kept.
(b) Because of negligible force of attraction between particles of gas, the particles of gas have the highest kinetic energy. These properties enable the particles of gas to move in all directions and hit the walls of container from all sides. Because of this a gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container in which it is kept.
(c) A wooden table has a definite shape and volume. It is very rigid and cannot be compressed i.e., it has the characteristics of a solid. Hence, a wooden table should be called a solid.
(d) Particles of air have large spaces between them. On the other hand, wood has little space between its particles. Also, it is rigid. For this reason, we can easily move our hands in air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
Since, air is gas, so its particles are loosely packed and there is negligible force of attraction between its particles. Because of that we can easily move our hand in air. But wood is a solid, so the force of attraction between its particles is greatest. The particles of wooden block are closely packed. That’s why we cannot move our hand through a solid block of wood. However, a karate expert can exert required pressure to break the great force of attraction of the particles of a solid wooden block.
Question 4: Liquids generally have lower density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why.
Answer: During freezing of water, some space between the particles of water is left vacant with some air trapped between them. These empty spaces having air in them makes the density of ice; lower than that of water. That’s why ice floats on water.
Question 1: Convert the following temperatures into the Celsius scale. (a) 300 K (b) 573 K
Answer: (a) 300 K = (300 − 273)°C = 27°C (b) 573 K = (573 − 273)°C = 300°C
Question 2: What is the physical state of water at (a) 250°C (b) 100°C
Answer: (a) Water at 250°C exists in gaseous state.
(b) At 100°C, water can exist in both liquid and gaseous form. At this temperature, after getting the heat equal to the latent heat of vaporization, water starts changing from liquid state to gaseous state.
Question 3: For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
Answer: During a change of state, the temperature remains constant. This is because all the heat supplied to increase the temperature is utilized (as latent heat) in changing the state by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles. Therefore, this heat does not contribute in increasing the temperature of the substance.
Question 4: Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases.
Answer: Atmospheric gas is liquefied by increasing pressure and decreasing temperature.
PAGE NO. 10
Question 1: Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
Answer: Desert cooler works on the basis of evaporation. In hot and dry days the moisture level is very low in atmosphere which increases the rate of evaporation. Because of faster evaporation, cooler works well. That’s why desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day.
When a liquid evaporates, the particles of the liquid absorb energy from the surroundings to compensate the loss of energy during evaporation. This makes the surroundings cool.
In a desert cooler, the water inside it is made to evaporate. This leads to absorption of energy from the surroundings, thereby cooling the surroundings. Again, we know that evaporation depends on the amount of water vapour present in air (humidity). If the amount of water vapour present in air is less, then evaporation is more. On a hot dry day, the amount of water vapour present in air is less. Thus, water present inside the desert cooler evaporates more, thereby cooling the surroundings more. That is why a desert cooler cools better on a hot dry day.
Question 2: How does water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cool during summers?
Answer: Water from porous wall of earthen pot evaporates continuously, which lowers the temperature of water kept in the earthen pot. In summer moisture level is very low in the atmosphere, which increases the rate of evaporation as evaporation is inversely proportional to the moisture level in atmosphere. That is why in summer water kept in earthen pot becomes cool.
Question 3: Why does our palm feel cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it?
Answer: When we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on our palm, it evaporates. During evaporation, particles of the liquid absorb energy from the surrounding or the surface of the palm to compensate for the loss of energy, making the surroundings cool. Hence, our palm feels cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it.
Question 4: Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer than a cup?
Answer: When hot tea or milk is kept in a saucer, the liquid is exposed over a larger surface area as compared to in case of the liquid being kept in a cup. The larger surface area enables the faster cooling. That’s why we are able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer rather than from a cup.
Question 5: What type of clothes should we wear in summers?
Answer: In summer, it is preferred to wear light-coloured cotton clothes because light colour reflects heat and cotton materials have pores that absorb sweat, facilitating their evaporation hence causing a cooling effect in the skin.
Question 1: Convert the following temperatures into the Celsius scale. (a) 293 K (b) 470 K
Answer: Temperature in Celsius scale = Temperature in Kelvin scale – 273
(a) 293K= (293 – 273)°C = 20°C
(b) 470K= (470 – 273)°C = 197°C
Question 2: Convert the following temperatures into the Kelvin scale. (a) 25°C (b) 373°C
Answer: Temperature in Kelvin scale = Temperature in Celsius scale + 273
(a) 25°C = (25+273)K = 298K
(b) 373°C = (373+273)K = 646K
Question 3: Give reasons for the following observations. (a) Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid. (b) We can get the smell of perfume while sitting several metres away.
Answer: (a) At room temperature, naphthalene balls undergo sublimation wherein they directly get converted from a solid to a gaseous state without having to undergo the intermediate state, i.e., the liquid state.
(b) Perfumes vaporize very fast and its vapours diffuse into air easily. That is why we can smell perfume sitting several meters away.
Question 4: Arrange the following in increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles – water, sugar, oxygen.
Answer: Oxygen < Water < Sugar.
Explanation: Oxygen is a gas, thus force of attraction is negligible between particles. Water is a liquid, thus force of attraction between particles is more than liquid and less than solid. Sugar is a solid, thus force of attraction between particles is greatest.
Question 5: What is the physical state of water at — (a) 25°C (b) 0°C (c) 100°C?
Answer: (a) At 25°C – water is in liquid state. (b) At 0°C – water is in solid state. (c) At 100°C – water is in transition state, i.e. in liquid and gas both.
Question 6: Give two reasons to justify: (a) water at room temperature is a liquid. (b) an iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
Answer: (a) At room temperature (25 °C), water is a liquid because it has the following characteristic of liquid:
(i) Water has definite volume, but not definite shape as it takes the shape of the container in which it is kept. (ii) Water flows at room temperature.
(b) An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature because: (i) It has definite shape. (ii) It has definite volume.
Question 7: Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
Answer: At 273K ice requires more latent heat to melt into water, while water at 273K requires less latent heat; to come to the room temperature. So, ice at 273 K is more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature.
Question 8: What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
Answer: Steam produces more severe burns than boiling water. This is because steam has more energy than boiling water, present in it in the form of latent heat of vaporization.
Question 9: Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing change in its state:
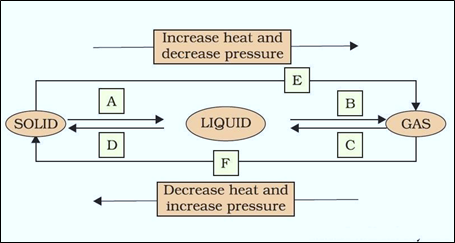
Answer: A: Melting (or) fusion (or) liquefaction B: Evaporation (or) vaporization C: Condensation D: Solidification E: Sublimation F: Sublimation
Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
CBSE Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 helps students to clear their doubts and to score good marks in the board exam. All the questions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments & homework. Having a good grasp over CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science will further help the students in their preparation for board exams and other competitive exams such as NTSE, Olympiad, etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 PDF
Below we have listed the topics discussed in NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1. The list gives you a quick look at the different topics and subtopics of this chapter.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Intext and Exercises question answers based on rationalised NCERT books published for session 2024-25. Get here the solutions of Page 3, Page 6, page 9, page 10 and Exercises question answers in English Medium and Hindi Medium.
Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Answers in English Medium
- Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Exercises
- Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Intext Questions
- Class 9 Science Chapter 1 MCQ
- Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Extra Questions
- Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Hindi Medium
- Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Notes in English
- Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Notes in Hindi
- Class 9 Science Chapter 1 NCERT Book
- Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 all Subjects NCERT Solutions
NCERT Class 9 Science textbook, Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings covers the most of the important topics. Definition of Matter Characteristics of Matter, three states of matter – Solid, Liquid, and Gas Comparison of the characteristics of these states Interconversion of States of Matter.
The main topics of class 9 science chapter 1 Change of state melting, freezing, evaporation, and condensation Effect of change of temperature on the states of matter. Evaporation : Factors affecting the rate of evaporation Applications of evaporation. Sublimation : Definition of sublimation Examples of substances that sublime. Diffusion : Definition of diffusion Examples of diffusion in daily life Characteristics of Particles of Matter.
Download App for Class 9 all Subjects free. UP Board Solutions, NCERT Solutions, NCERT Solutions Offline Apps 2024-25 are free to download for all students using latest NCERT Books 2024-25. Here you can use NCERT Solutions of chapter 1 of Class 9 Science online or download in PDF file format for offline use. Download Class 9 Science Solutions Apps in Hindi & English version for offline use.
Particles in solids, liquids, and gases. Kinetic Theory of Matter : Explanation of the kinetic theory Explanation of the behavior of particles in matter according to the kinetic theory. Measurement of Matter : Mass and weight measuring the mass of an object Units of measurement. Density and Relative Density : Definition of density Calculation of density Relative density and its applications.

These are the main topics covered in Chapter 1 of the NCERT Class 9 Science textbook. This chapter provides an introduction to the fundamental concepts related to matter and its various properties. It serves as the foundation for further exploration of chemistry and physics topics in the curriculum.
Preparing for NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings, or any chapter, requires a systematic approach to understanding the concepts and practicing them effectively. Here are some tips on how students can prepare for this chapter in a better way. Start by reading the chapter carefully from the NCERT textbook. Pay attention to the text, diagrams, and examples provided. While reading, make concise notes of important concepts, definitions, and key points. This will help you with quick revision.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings all the in-text questions as well as chapter end exercises question’s answers are given below. Solutions are available in Hindi and English Medium to study online or download in PDF form free.
Ensure that you have a clear understanding of fundamental concepts such as matter, states of matter, and the kinetic theory of matter. Use diagrams and illustrations provided in the book to visualize how particles are arranged in different states of matter and during phase changes. Work through the examples and exercises provided at the end of the chapter. Practice solving numerical problems related to density, and other concepts to reinforce your understanding.
If you find any topics challenging, consult additional resources like reference books, online tutorials, or videos to clarify your doubts. If you have questions or face difficulties in understanding certain concepts, don’t hesitate to seek help from your teacher or discuss them with your classmates. Where possible, perform simple experiments related to states of matter, diffusion, or density to gain practical insights into the concepts. Create Flashcards: Create flashcards for important terms, definitions, and formulas. This can help you with quick revision.
Consistent practice is key to mastering any subject. Allocate regular study time to science and review the chapter periodically. Take self-assessment quizzes or practice tests to gauge your understanding of the chapter. A few days before your exams, revise the chapter thoroughly. Focus on your notes and important points. Keep your notes, textbooks, and other study materials well-organized so that you can easily access them for review.
Science is about exploring and asking questions. Stay curious and be open to learning new concepts and ideas. Remember that understanding the fundamental concepts in Chapter 1 of Class 9 Science is crucial as it forms the basis for more advanced topics in chemistry and physics in the later chapters. Building a strong foundation in this chapter will benefit you throughout your science studies.
Tiwari Academy is an online educational platform that provides resources and materials to help students prepare for their CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education) Class 9 Science exams, including Chapter 1. Tiwari Academy offers free access to a wide range of study materials, including NCERT solutions, textbooks, revision notes, and practice papers. These materials are designed to help students understand and revise the content effectively.
Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Extra Practice Questions
Why do substance undergo change in physical state.
Substance undergo change in physical state because both inter-particle spaces and inter-particle forces can be changed by changing the condition of temperature and pressure.
When sugar is dissolved in water, there is hardly an increase in volume. Which characteristic of matter is illustrated by this observation?
This is because of the presence of inter particle space or empty spaces. Particles or molecules of water can fill the empty space in the particles or molecules of sugar and vice versa. That is why there is hardly any change in the volume as a result of dissolution of sugar in water.
Define gaseous state of a substance.
A substance is said to be in the gaseous state if under normal pressure, its boiling point is below the room temperature.
How does pressure help in the liquefication of a gas?
Increase in pressure helps in the liquefication of a gas. The particles or molecules of a gas come closer and closer as the pressure is being increased gradually. They ultimately condense and as a result, the gas liquefies or changes into the liquid state.
Solids are generally very heavy while gases are light. Explain.
In the solids, the particle are very closely packed. As a result, the number of particles per unit volume is quite large. Therefore, the solids are normally quite heavy. In the gases, the particles are loosely packed. The number of particle per unit volume is completely small. Therefore, gases are light.
Tiwari Academy offers comprehensive NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1, guiding students step-by-step through exercises in the NCERT textbook. These solutions are invaluable for students, helping them decipher the best ways to tackle diverse problems. The platform might also feature video tutorials that break down intricate concepts of the chapter. By using visual tools and explanations, students can more easily understand challenging subjects.
By working through additional exercises and questions, students solidify their comprehension and enhance their problem-solving capabilities. Tiwari Academy typically provides succinct and organized revision notes, which are instrumental for quick recaps of the chapter’s main ideas and crucial details. Some digital platforms, including Tiwari Academy, even have online exams that emulate the actual test atmosphere, which can be instrumental for student evaluation and exam readiness.

Question 1: Solids are normally not compressible. Why can a sponge be readily pressed? Answer 1: A sponge made up of rubber has a large number of fine pores in which air remains filled. When the sponge is pressed, the air from the pores escapes and vacant space are left. Therefore, the sponge can be readily pressed on applying pressure.
Accessible around the clock, Tiwari Academy’s digital tools let students learn at a rhythm that suits them. This constant availability is especially beneficial for those who wish to revisit the chapter several times. Doubt Resolution: Certain online educational platforms grant students the opportunity to post their chapter-related queries. These queries might be addressed by seasoned educators or tutors, offering students needed explanations. Additionally, Tiwari Academy might have archives of past exam papers with their solutions. Working on these papers can assist students in acclimating to the exam structure and honing their time-management skills.
Question 2: Why do we sweat on a humid day? Answer 2: In humid day, the air around us has already high percentage of water vapours. Therefore, the water coming from the skin gets less opportunity to charge into vapours and remains sticking to our body. We therefore, swear more on a humidity day.
Tiwari Academy online platforms have discussion forum where students can interact, share their experiences, and seek advice from peers. It’s important to note that the availability of specific resources and features may vary on Tiwari Academy or any other educational platform. Students should explore the platform to determine which resources are most helpful for their individual learning needs and preferences. Additionally, using a combination of resources, including the official NCERT textbook, school notes, and online materials like Tiwari Academy, can provide a comprehensive approach to exam preparation.
From an examination point of view, NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings, holds significant importance for several reasons. Chapter 1 introduces fundamental concepts related to matter, states of matter, and the kinetic theory of matter. These concepts serve as the foundation for understanding more advanced topics in chemistry and physics in higher classes. A strong grasp of these basics is crucial for building a solid scientific knowledge base.
Question 3: Kelvin scale of temperature is regarded as better than the Celsius scale. Give reason. Answer 3: In the Celsius scale of temperature we often come across a negative sign for the temperature (e.g., -8.5⁰C). Since the sign is always positive in the Kelvin scale, it is regarded as better.
Questions from 9th science chapter 1 are often included in Class 9 Science examinations. This chapter is considered an essential part of the curriculum, and students can expect to see questions related to states of matter, properties of matter, and related calculations in their exams. Chapter 1 helps students develop a deeper understanding of how matter behaves, how particles are arranged in different states, and how temperature affects matter. This conceptual understanding is not only essential for exams but also for a broader understanding of science.
The chapter 1 of 9th science includes numerical problems related to density and the states of matter. These problems require students to apply mathematical concepts to scientific scenarios, which is a valuable skill for both exams and real-world applications. The concepts discussed in Chapter 1 are applicable to various everyday situations, such as cooking, weather changes, and material properties. Understanding these applications can help students relate science to their daily lives and answer practical questions in exams.
Important Questions on 9th Science Chapter 1
Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid. why.
Naphthalene shows the property of sublimation. Evaporation of naphthalene takes place easily and so it disappears during course of time without leaving a solid.
We can get the smell of perfume sitting several meters away. Why?
Perfumes vaporize very fast and its vapours diffuse into air easily. That is why we can smell perfume sitting several meters away.
Water at room temperature is a liquid. Give reason.
Water at room temperature is a liquid because it has fluidity and has definite volume but no definite shape.
An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature. Give reason.
An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature because it is rigid and has a definite shape.
Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
Ice at 273 K is less energetic than water. It is because of the difference in the latent heat of fusion which is present in water at the same temperature in the form of extra energy.
What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
Steam produces more severe burns than boiling water. This is because steam has more energy than boiling water, present in it in the form of latent heat of vaporization.
Successfully mastering the first chapter of the textbook can boost a student’s confidence in their ability to handle the rest of the science curriculum. It sets a positive tone for the subject and encourages students to explore further. The knowledge gained from Chapter 1 will be built upon in higher classes. Topics like states of matter, kinetic theory, and properties of matter are revisited and expanded upon in later chapters and classes.
A strong foundation in Chapter 1 is, therefore, essential for future success. In summary, NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 1 is not only important for scoring well in exams but also for laying the groundwork for a deeper understanding of science in the later stages of education. Students should dedicate time and effort to comprehensively learn the concepts presented in this chapter to ensure a strong foundation in science.

NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 2 »
Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 1 (Free PDF Download)
- Revision Notes

CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings Revision Notes - Free PDF Download
Matter can be defined as something that has mass and occupies space. For instance, air, water, oxygen, fruits, etc. All these are considered as matter in our surroundings and are classified as solids, liquids and gases. They are made up of microscopic particles called molecules which are tightly, loosely and very loosely packed, respectively. Being the elementary lesson of Class 9 Science , you must be thorough on the same. In this regard, Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes by Vedantu can be of immense help. Along with textbooks, make sure to refer to this material for revision purposes and also achieve desired scores in exams. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions, they can download Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
The revision notes of Chapter 1, Class 9 Science subject are present here. The students can simply study these notes before the exam to get a comprehensive overview of teh whole chapter.
We also have provided the free pdf to download which will help the students to revise the chapter anytime, with or without the internet.
Download CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 9 Science revision notes for All chapters:

Access Class 9 Science Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surrounding Notes
Introduction
Everything around us is formed of the matter: a pencil, a pen, a table, the food we consume, the clothes we wear, the walls of our homes. But what is the matter?
Anything that occupies space has mass, and can be sensed by our senses is considered the matter. In other words, the term "matter" refers to all of the substances and materials that make up the cosmos.
Composition of Matter
According to ancient Indian philosophers, the matter is made up of five constituents or tattvas, according to studies found in our sacred books and scriptures.
Illustration 1. How many different ways did ancient Indian philosophers classify matter?
a. $2$
b. $6$
c. $7$
d. $5$
Ans: $\left( D \right)$
Matter is made up of Particles
Now that we have defined matter let us ask ourselves the question – What is a matter made up of?
All matter comprises very small particles.
All matter can be broken up in a similar manner to get very small particles.
Hence we now conclude that all matter is made up of small particles.
(Image will be uploaded soon)
Illustration 2. Which of the following are matters?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cold-drink, the smell of perfume.
Ans: chair, air, almond, cool drink
Properties of Matter
Small particles of matter make up all matter. Some features are shared by all of these particles. A theory called Kinetic Theory of Matter explains forth these features.
Simply said, The Kinetic Theory of Matter States is a theory that describes how matter changes throughout time.
a. All matter is made up of tiny particles.
b. There is space between these particles.
c. The particles are in constant motion.
d. The particles are attracted to one another.
Particles of Matter have space between them
Small particles make up matter, and these particles have small spaces between them.
These areas are not visible to the naked eye, yet particles of other matter can pass through them without changing their volume.
Particles of Matter are continuously moving
Particles in the matter are constantly moving. Three types of motion were seen in the matter particles.
a. Translatory Motion - It occurs when particles move in straight lines and change direction without losing energy after interacting with another particle or the container's wall. When compared to liquids, translational motion is greatest in gases and least in solids.
b. Rotational motion: When particles travel about their own axis, this is known as rotational motion . This motion is comparable to the earth's rotation around its axis. In gases and liquids, the rotational motion will be quite high.
c. Vibrational Motion - When particles move back and forth around a central point. Solids have the greatest amount of motion because the particles are held in a hard framework.
Particles of Matter attract each other
1. The force with which they attract one another differs depending on the matter.
2. The force is modest in some types of materials (waste paper, matchsticks) (as we can tear or break them easily).
3. The force is large in other types of material (iron nail) (as we cannot break the nail easily).
Illustration 3. When sugar dissolves in water, what happens to it? What happens to the sugar? What does the dissolution of sugar in water tell you about the nature of matter?
a. When sugar dissolves in water, the solid sugar crystals are broken up into microscopic particles.
b. The sugar particles interact with the water particles in the gaps between them (to form a sugar solution).
c. Sugar dissolving in water indicates that the stuff (in this case, sugar and water) is made up of minute particles. There are voids between the particles of stuff (in this case, water).
Diffusion
“The mixing and spreading out of a substance with another substance due to the movement or motion of its particles is called diffusion.”
The process of one substance diffusing into another continues until a homogenous mixture is achieved. Let's have a look at an example.
Put a crystal of potassium permanganate (purple colour) in one of the beakers that is full of water. Gradually, you'll notice that the purple-colored crystal begins to diffuse or dissolve into water, and after a while, it turns purple.
Diffusion in Gases
Gases have a very fast diffusion rate. Because gas particles move very swiftly in all directions, this is the case.
Examples \[1:\]
Even from a long distance, the smell of food being prepared in the kitchen reaches us.
The smell of hot, sizzling food reaches us even when we are a long way away, but we must approach close to get the smell of cold food.
This is because the rate of diffusion of hot gases is substantially faster than the rate of diffusion of cold gases released by cold food.
Example \[2:\]
When someone opens a bottle of perfume in one corner of a room, the scent soon travels throughout the space.
When a perfume bottle is opened, the liquid perfume soon turns into vapour (or gas).
The scent vapours flow quickly in all directions in the air, mixing with the air particles and spreading across the room.
Example
The diffusion of a strong-smelling chemical (ethyl mercaptan) found in the cooking gas into the air detects the leaking of cooking gas (LPG) in our houses.
Diffusion in Liquids
Liquid diffusion is slower than gas diffusion. This is due to the fact that particles in liquids move slower than particles in gases.
Solid in Liquid
When a crystal of potassium permanganate is placed in the bottom of a beaker of water, the purple colour of the potassium permanganate progressively spreads throughout the water.
The liquid in Liquid:
When a drop of ink is dropped into a beaker of water, the colour of the ink spreads across the entire water in the beaker; this is due to the diffusion of ink particles into water.
Gases like carbon dioxide and oxygen are necessary for aquatic plants and animals to survive. The carbon dioxide and oxygen gases in the air (or atmosphere) diffuse into and dissolve in water (ponds, lakes, and rivers). Aquatic plants use dissolved carbon dioxide to prepare food through photosynthesis, whereas aquatic animals breathe using dissolved oxygen in the water.
Diffusion in Solids
Solid-state diffusion is an extremely slow process.
Example :
If we write something on a blackboard and then leave it filthy for a long time (say, 10 to 15 days), cleaning the blackboard becomes quite tough. This is owing to the fact that certain chalk particles have dispersed into the backboard's surface.
When two metal blocks are closely linked together and left undisturbed for several years, the particles of one metal permeate into the other metal. Gases dissipate quickly. A gas's rate of diffusion is proportional to the square root of its density.
Force of Attraction (or Cohesion)
Between the particles of matter, there is an attractive force that binds them together. The force of attraction is the attraction between particles of the same substance (or cohesion).
In general, the force of attraction is greatest in solid matter particles and least in gaseous matter particles.
Illustration 4. Analyse the effects of diffusion in different states of matter, such as solid, gas, and liquid.
Ans: $\text{Solid}<\text{Liquid}<\text{Gases}$
Slow Fast Very Fast
States of Matter
Solids have a definite volume and shape. They are more difficult to break than liquids and gases.
Liquids have a specific volume but not a specific shape. They take on the shape of the container they're housed in.
Gases do not have a defined shape or volume. They take up all of the available space and take on the shape of the container in which they are kept.
Plasma - At extremely high temperatures, the plasma state is a fused and ionic condition of matter (like the core of the sun, stars). Because it is made up of positive ions and a pool of electrons, the fused ionic mass is neutral. Around 99 per cent of the universe is made up of fused ionic matter.
Illustration 5.
a. Give two reasons why wood is a solid material.
b. ‘A material has a known volume but no known shape.' Indicate if the substance is solid, liquid, or gaseous.
c. Describe the physical state of matter that can be squeezed readily.
d. ‘A substance has both a definite shape and a defined volume.' Which physical state does this statement represent? A substance has neither a fixed shape nor a fixed volume. State whether it is a solid, a liquid or a gas.
e. Give two reasons to justify that:
i. Water is a liquid at room temp.
ii. An iron almirah is solid.
a. Wood has
i. fixed shape, and
ii. fixed volume
b. Liquid
c. Gas
d. Solid
e. Gas
i. Fixed volume but no fixed shape
ii. Fixed shape and fixed volume.
Rigid and Fluid
Rigid is a word that denotes "unbending" or "inflexible." Because it is unbending or inflexible, a stone is stiff. Fluid is defined as "a material that flows easily" and requires the use of a vessel (container) to keep it contained.
A solid is a kind of stuff that is unyielding. Solids have a tendency to keep their shape when subjected to external force due to their rigidity. As a result, rigidity is the primary distinguishing feature of solids. As a result, rigidity is the primary distinguishing feature of solids. Solids don't need to be kept in a container. Two common solids are a brick and a log of wood.
A liquid is a fluid type of stuff that fills the container's lower half. Liquids must be kept in a container because they are fluids. Because liquids have a well-defined surface, they can be stored in an open container. The liquid will not spontaneously escape from the open container. Water and milk are two prevalent liquids found in our environment.
Gas is a form of stuff that fills the entire container in which it is contained. Gases, like liquids, require a container to keep them contained. Because gas has no open surface, it must be stored in a closed container. If gas is kept in an open container, it will escape. Gases are frequently stored in airtight gas cylinders because of this. Cooking gas (LPG), for example, is stored in airtight metal cylinders. We can conclude from this discussion that fluids include both liquids and gases. Fluidity is a property of liquids and gases that allows them to flow smoothly. When exposed to external stress, liquids and gases change shape quickly due to their fluidity.
Illustration 6. Which of the following is a rigid form of matter
Ans: Ether and alcohol
Interconversion of the state of matter
Changing the temperature, pressure, or both can cause matter to change its physical condition.
a. Melting is the transformation of a solid into a liquid.
b. Solidification is the process of turning a liquid into a solid.
c. The process of converting a liquid to a gas is known as vaporisation.
d. Condensation is the process of turning a gas into a liquid.
e. Sublimation is the process of converting a solid to a gas.
Note: While increasing pressure in gas will not change the physical condition of the gas, it will bring the particles closer together, causing the gas to liquefy.
Vaporization is promoted by lowering pressure over a liquid's surface.
Illustration 7. When solid carbon dioxide is exposed to air, which of the following factors is responsible for the change in state?
a. Increase in pressure
b. Decrease in pressure
c. Increase in temperature
d. Decrease in temperature
Ans: $(a)$ Decrease in pressure; Increase in temperature
Effect of change of Temperature and Pressure
We can change the physical condition of matter in two ways:
a. by changing the temperature; and
b. by changing the pressure
A solid can be changed to a liquid state by raising the temperature, and a liquid may be converted to a gaseous state by lowering the temperature.
Melting (Fusion)
Melting is the transformation of a solid substance into a liquid when it is heated (or fusion).
Melting of the substance refers to the temperature at which a solid melts and transforms into a liquid at atmospheric pressure.
The heat energy in a solid substance causes its particles to vibrate more vigorously. At the melting point, a solid's particles have enough kinetic energy to overcome the strong forces of attraction that keep them in fixed places, and they break apart into small groups. And the solid transforms into a liquid.
The greater the force of attraction between the particles of a solid substance, the higher its melting point. The melting point of iron metal, for example, is extremely high (1535 degrees celsius), indicating that the force of attraction between the particles of iron is extremely strong.
Boiling (Vaporisation)
Boiling is the transformation of a liquid substance into a gas when heated rapidly.
The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which it boils and transforms rapidly into a gas at atmospheric pressure.
Condensation
When a gas (or vapour) is cooled sufficiently, the process of turning it into a liquid is termed condensation.
Condensation of steam occurs when steam (or water vapour) cools and converts to water (or condensation of water vapour).
It's the polar opposite of vaporisation. (Boiling)
Freezing
Freezing is the process of turning a liquid (solidification) into a solid by chilling it, the reverse of melting.
When a liquid cools, its particles lose energy, slowing its movement.
If the liquid is sufficiently chilled (to the point of freezing), each particle ceases to move and vibrates in a fixed location. The liquid freezes and solidifies at this point.
As a result of the preceding discussion, we can conclude that changing the temperature can change the state of matter.
Effect of the change in Pressure on the state of matter
Short particles separated by small distances make up matter.
Interparticle distances are exceedingly short in the solid-state.
The inter-particle distances in liquids are slightly greater than in solids.
When compared to liquids or solids, interparticle distances are greatest in the gaseous state.
As a result, it can be shown that when pressure is applied to matter, the effect on solids is insignificant because the particles are so close together.
In liquids, the effect of pressure will be minimal.
Because the interparticle distances are vast, the effect of pressure on gases will be the greatest.
As a result, when pressure is applied to gases, the particles begin to move closer together. The attractive forces between the particles increase as the particles get closer together.
This rise in attracting forces aids the gas's transition of state. When enough pressure is applied, the attraction forces build to the point where the physical state transforms from gaseous to liquid.
The reverse can be expected to happen if the pressure on a gas is decreased.
Illustration 8. Define melting process
Ans: Melting is the transformation of a solid substance into a liquid when it is heated.
Latent Heat
The heat that a substance needs to change its condition without increasing its temperature. It's called latent heat (hidden heat) because it's buried in the substance undergoing a state transition and doesn't show up as a rise in temperature.
“During a transition of state, the latent heat is used up in overcoming the force of attraction between the particles of the substance. It has no effect on the kinetic energy of the substance's particles. And since the substance's temperature does not rise.”
Illustration 9. What is the latent heat of fusion of ice?
Ans: $3.34\times {{10}^{5}}j/kg$
Latent heat of Vaporization and Fusion
There are two types of latent heat:
i. Latent heat of fusion
ii. Latent heat of vaporization
Latent heat of Vaporization
The latent heat of vaporisation is the amount of heat in Joules necessary to turn a unit quantity of 1 kg liquid into vapours without a temperature change.
Experiments have shown that it takes \[22.5\text{ }\times \text{ }{{10}^{5}}\] joules of heat to convert 1 kilogramme of water (at its boiling point, \[\text{100 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ C}\]) to steam at the same temperature. As a result, water's latent heat of vaporisation is \[22.5\text{ }\times \text{ }{{10}^{5}}\] joules per kilogramme (or \[22.5\text{ }\times \text{ }{{10}^{5}}\]J/kg).
“If the liquid freezes to create a solid and steam condenses to form water, the substance will emit an equal amount of latent heat of fusion and vaporisation.”
The Latent Heat of Vaporization varies depending on the substance.
Latent heat of Fusion (Solid to Liquid)
It is the amount of heat in Joules required to transform one kilogramme of solid into liquid form without causing a temperature increase.
Experiments have shown that to turn 1 kilogramme of ice into water at the same temperature (\[\text{0 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ C}\]), \[3.34\times {{10}^{5}}\] J of heat is required.
So, latent heat of fusion of ice is \[3.34\times {{10}^{5}}\] J/ Kg.
Different substances have different Latent Heat of Fusion.
Illustration 10. Why the temperature of melting ice does not rise even though heat is being supplied continuously.
Ans: Because ice is solid, its particles are attracted to one another by strong forces. These attraction forces keep the particles tightly packed in solid ice. The heat we give ice during melting is completely consumed by overcoming the forces of attraction between ice particles, causing them to loosen up and become liquid water. As a result of this heat not increasing the kinetic energy of particles, no temperature rise occurs during the melting of ice. However, once all of the ice has melted to create water, additional heating increases the kinetic energy of water particles, causing the temperature of the water to rapidly rise.
Sublimation
Sublimation is defined as the transformation of a solid into vapours on heating and back to a solid on cooling.
$\text{Solid}\rightleftarrows \text{Vapour (or Gas)}$
Ammonium chloride, iodine, camphor, naphthalene, and anthracene are some of the common substances that sublimate.
Solid carbon dioxide is yet another example of sublimation (which is commonly known as dry ice).
Carbon dioxide gas is formed when solid carbon dioxide (or dry ice) sublimates.
Illustration 11.
a. When heated, which of the following substances sublimates:
iv. Camphor
v. Sodium Chloride
b. What happens to the heat energy that has been delivered once a solid has melted?
c. A substance's melting point is lower than room temperature. Predict the state of its physical state.
d. Is it permissible to refer to ammonia in its gaseous state as vapours?
e. What is the name of the chemical reaction that converts a solid into a gas?
f. During a substance's change of state, which of the following energy is absorbed?
i. Specific Heat
ii. Latent heat
iii. Heat of solution
g. Identify one common chemical that can change state when heated or cooled.
a. Camphor and iodine
b. It is converted into latent heat of fusion
c. It is a liquid.
d. No, it is not
e. It is called sublimation
e. Latent heat
Evaporation
The phenomenon of evaporation occurs when a liquid transforms to a gaseous state below its boiling point.
Water molecules are attracted to other water molecules in all directions, but the water molecules near the surface of the water are only dragged inward, which is below the water's surface.
Note: Evaporation is a phenomenon that occurs in all liquids in theory. But, in general, when we talk about evaporation, we're talking about water evaporation.
Vapour is a substance that can remain in a gaseous state at a temperature where it would ordinarily be a solid or liquid.
Examples of solids that can exist as a vapour: camphor, naphthalene
Factors Affecting Evaporation
Evaporation depends on temperature, surface area and weather conditions
a. As the quantity of water molecules at the surface grows, evaporation increases if the surface area of the water is big. As a result, more water molecules are likely to break out once they have enough kinetic energy.
b. As the temperature approaches the boiling point of water, evaporation increases. The kinetic energy of the molecules increases as the temperature rises. The extra kinetic energy required by surface molecules to break loose or evaporate is reduced as a result. As a result, evaporation increases.
c. Evaporation decreases in excessively humid weather because the air is saturated with water molecules.
d. As water evaporates, the air just above the water surface becomes saturated with water molecules.
Illustration 12. What effect does temperature and surface area have on evaporation?
Ans: Evaporation increases as the temperature and surface area increase.
Cooling Effect
How Does Evaporation Cause Cooling?
When a liquid evaporates, the energy is extracted from the liquid. As a result, it continues to cool. The liquid absorbs the energy lost by the surroundings, causing them to cool. During the summer, for example, air coolers are used to provide forced cooling.
Illustration 13. Make a note of the cooling mechanism.
Ans: As a gas particle's energy drops due to cooling, the particle's moment slows down. The particles also become significantly closer to one another, resulting in the intermolecular attraction force. The gas contracts as a result of this.
Matter in our Surroundings Notes Free PDF Download
Class 9 Science Notes Chapter 1 PDF material is entirely free and can be easily availed from Vedantu’s website or application. So download the same and make it a revision guide for both unit test and final examinations. By downloading the Chapter 1 Science Class 9 Notes, you no longer need to prepare a list of essential topics and explanations by yourself. Besides the usage of simple and lucid language, this material is also drafted as per the latest CBSE curriculum, which makes it a perfect revision guide.
Class 9 Chapter 1 Science Notes – Summary
The notes of Ch 1 Science Class 9 begins with the introduction about the matter in our surroundings, its composition, what are they made up of, etc. Although you have learnt this in your previous classes, you must study it again to have a proper grasp over this concept. The next part of Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Notes explain the properties of matter. As you all know that matter is made up of tiny particles, and have unique characteristics. Additionally, these characteristics of matter are provided by a theory termed as Kinetic Theory of Matter which states the following:
Particles of matter have space between them.
Particles of matter are continuously moving – rotational and vibrational motion.
Particles of matter attract each other.
In the next section of Science Class 9 Chapter 1 Notes, students will get to know about diffusion; especially the provided diagram makes it easy to comprehend. You will also learn that diffusion occurs at a fast rate in gases. The reason for this is elaborated with suitable examples in the PDF material of Matter in our Surroundings Class 9 Notes. Besides, diffusion in liquids and solids are also discussed precisely that will help you to understand this concept clearly.
Information about the three states of matter – solid, liquid and gas are correctly laid out in this Class 9 Matter in our Surroundings Notes PDF alongside their various properties. Plus a tabular representation of differences between solid, liquid and gases is also given.
Inter Conversion of the States of Matter
With a change in pressure and temperature, matter can change from one form to another form. This section of Class 9 Science Ch 1 Notes deal regarding the same. You will get to know about all the various changes of states like melting, solidification, vaporisation, condensation, sublimation, etc in the Matter in our Surroundings Class 9 Notes.

Latent Heat and Latent Heat of Vaporisation and Fusion
This section of Class 9 th Science Chapter 1 Notes discuss latent heat and different types of the same – latent heat of fusion and latent heat of vaporisation. The different values of latent heat are also given which you can learn in the Matter in our Surroundings Class 9 Notes to write accurate answers.
Sublimation, Evaporation and Cooling Effect
In the last section of Science Chapter 1 Class 9 Notes, you will get an insight about sublimation, evaporation and cooling effect. All these state change processes are supported with appropriate examples.
Make sure to download notes of Science Class 9 Chapter 1 PDF file today from Vedantu’s official website or the app. Along with topic wise explanation, few questions and solutions are also provided in Class 9 Ch 1 Science Notes that will assist you during quick recapitulation before the exams.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 1 provides a comprehensive understanding of the fundamental concepts related to matter. This chapter introduces students to the basic properties of matter, including its physical nature, states, and characteristics. The notes offer a concise and organised overview of the chapter, aiding students in grasping the key concepts effectively.
By studying these notes, students can gain knowledge about the different states of matter, such as solids, liquids, and gases, and the changes they undergo under various conditions. They also learn about the concept of the particle nature of matter and the behaviour of particles at the microscopic level.

FAQs on Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 1 (Free PDF Download)
1. Is matter in our surroundings pure Class 9 notes?
Not all matter surrounding us exists in its pure form. The chapter discusses the difference between a substance and a mixture. A substance is present in its pure form, whereas, a mixture is a combination of two or more pure substances that can be separated into other types of matter through physical processes. For instance, seawater is a mixture of water and salt. Salt can be separated from it by the process of evaporation.
2. What are the basics of Class 9 Science, Chapter 1 - ‘Matter in Our Surroundings?’
Class 9 Science, Chapter 1 - "Matter in Our Surroundings," covers the fundamentals of Physical Chemistry. It starts with an introduction to matter and the three states of matter: solids, liquids, and gases. The chapter then dives into the process through which matter may change states. Some key ideas taught include the boiling and melting points. As the chapter progresses, the distinction between the latent heat of fusion and the latent heat of vapourization becomes obvious. The chapter concludes with a discussion of evaporation and the elements that influence it.
3. Will Revision Notes help ace Class 9 Science, Chapter 1 - ‘Matter in Our Surroundings?’
Yes, Revision Notes of Class 9 Chapter 1 are the ultimate and end saviour for before the exams. The students are required to go through other study material as well.
The first step is to properly read NCERT Class 9 Science, Chapter 1 - "Matter in Our Surroundings." Study the chapter attentively and attempt to grasp the fundamental principles. Clarify your doubts and reason through everything you encounter in the chapter to ensure a thorough comprehension of all the principles. Finally, using Vedantu's Revision notes, answer the back exercise questions. All issues should be reviewed on a regular basis. Answer a large number of previous year problems to learn this chapter and do well on the Science exam.
4. What are the best Revision Notes for Class 9 Science, Chapter 1 - ‘Matter in Our Surroundings?’
The best Revision Notes for Class 9 Science, Chapter 1 - ‘Matter in Our Surroundings,' can be accessed by visiting the page CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter 1 on the Vedantu website. Vedantu's Revision Notes are the most credible and productive study material from an examination viewpoint. If you study from these notes, you don't have to look for other study materials. These notes have zero errors and have been prepared by the best faculty of Chemistry teachers in India. All the important topics of this chapter are covered in simple language. These PDFs are available at free of cost on the Vedantu website and the Vedantu app.
5. Can I use these revision notes even in offline mode?
Yes, by pre-downloading the pdf of revision notes the students can easily study the notes late on even when they are offline.
STUDY MATERIALS FOR CLASS 9
- RS Aggarwal
- ML Aggarwal
- Merchant of Venice
- NCERT Books
- Questions and Answers
- NCERT Notes
- Important Questions
- Matter in Our Surroundings
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Science
Which of the following are matter ?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cold drink, smell of perfume.
The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density (density = mass/volume).
Air, Exhaust from chimneys, cotton, water, honey, chalk, and iron.
→ Rigidity: It is the property of matter to resist the change of its shape. → Compressibility: It is the property of matter in which its volume is decreased by applying force. → Fluidity: It is the ability of matter to flow. → Filling a gas container: On filling a gas takes the shape of the container. → Shape: Having definite boundaries. → Kinetic Energy: It is the energy possessed by the particles of matter due to its motion. → Density: It is the ratio of mass with per unit volume.
(a) The force of attraction between particles of gas is negligible. Because of this, particles of gas move in all directions. Thus, a gas fills the vessel completely in which it is kept.
(b) Particles of gas move randomly in all directions at high speed. As a result, the particles hit each other and also hit the walls of the container with a force. Therefore, gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
(c) A wooden table has fixed shape and fixed volume, which are the main characteristics of solid. Thus a wooden table should be called a solid. (d) Particles of the air have large spaces between them. On the other hand, wood has little space between its particles. Also, it is rigid. For this reason, we can easily move our hands in the air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
► 300 K = (300 - 273)°C
► 573 K = (573 - 273)°C
What is the physical state of water at:
(b) Since water boils at this temperature thus it can exist in both liquid and gaseous form. At this temperature, after getting the heat equal to the latent heat of vaporisation, water starts changing from liquid state to gaseous state.
For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state ?
(For Conversion Process we must know, Kelvin is an SI unit of temperature, where 0°C = 273 K approx.)
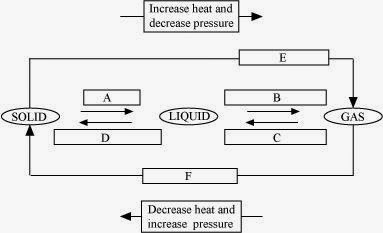
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialisation Class 10 History
Related chapters.
- Is Matter Around Us Pure
- Atoms and Molecules
- Structure of the Atom
- The Fundamental Unit of Life
Related Questions
- NCERT Revision Notes for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Science
- VSAQ for Ch 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Science NCERT
Report a problem
- Question is incorrect
- Answer is Incorrect
- Spelling Mistakes
- Not explained in detail

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ Test (Online Available)
Free mcq test, table of content, matter in our surrounding test - 33.
Duration: 10 Mins
Maximum Marks: 10
Read the following instructions carefully.
1. The test contains 10 total questions.
2. Each question has 4 options out of which only one is correct .
3. You have to finish the test in 10 minutes.
4. You will be awarded 1 mark for each correct answer.
5. You can view your Score & Rank after submitting the test.
6. Check detailed Solution with explanation after submitting the test.
7. Rank is calculated on the basis of Marks Scored & Time
Matter in Our Surrounding Test - 32
Matter in our surrounding test - 31, matter in our surrounding test - 30, matter in our surrounding test - 29, matter in our surrounding test - 28, matter in our surrounding test - 27, matter in our surrounding test - 26, matter in our surrounding test - 25, matter in our surrounding test - 24, matter in our surrounding test - 23, matter in our surrounding test - 22, matter in our surrounding test - 21, matter in our surrounding test - 20, matter in our surrounding test - 19, matter in our surrounding test - 18, matter in our surrounding test - 17, matter in our surrounding test - 16, matter in our surrounding test - 15, matter in our surrounding test - 14, matter in our surrounding test - 13, matter in our surrounding test - 12, matter in our surrounding test - 11, matter in our surrounding test - 10, matter in our surrounding test - 9, matter in our surrounding test - 8, matter in our surrounding test - 7, matter in our surrounding test - 6, matter in our surrounding test - 5, matter in our surrounding test - 4, matter in our surrounding test - 3, matter in our surrounding test - 2, matter in our surrounding test - 1.
In the Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ, students need to make an accurate decision between alternatives. As this process is never considered to be an easy one as the options need to be analysed based on the concepts and topics of the chapter Matter in Our Surrounding. To have a proper analysation process students need to complete the chapter Matter in Our Surrounding in a proper way.
The Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ can be helpful for both teachers and students for better learning as well as teaching. With the help of multiple choice questions, teachers don’t need to waste the unnecessary time in searching for questions, they can utilise their precious time in teaching the Matter in Our Surrounding concepts. Students can practise a vast amount of questions so that they can make the preparation process of the chapter Matter in Our Surrounding easier.
Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ Online
The Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ Online can be accessed quickly as the website provides the questions to practise for all students. The Online Test of the Class 9 MCQ provides prompt feedback to students, accordingly they can improve their grip on the chapter Matter in Our Surrounding so that they can score well.
How to Attempt the Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ?
Students need to follow some given steps to attempt the Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ, steps are discussed below:
- Visit the Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards CBSE which can be seen in the navigation bar/ button.
- A drop down menu will appear, select MCQ Test from the list.
- New page will appear, select Class 9th from the list of classes.
- Click Science from the list of subjects.
- A pop-up menu will appear, select the chapter Matter in Our Surrounding.
- Again a new page will appear and one can easily start the test.
Everything You Need to Know About the Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ
Here are some things that every student need to know before solving the Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ, those features are:
- Objective Assessment: The Matter in Our Surrounding MCQ is an objective assessment that students need to select the accurate option from the given four options.
- Variety of Questions: In the MCQ of Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9, it may include all sorts of questions: easy, moderate, advanced so that students upgrade their preparation in each test.
- Concept Based: The MCQ on Matter in Our Surrounding are generally concept based so that students can understand all concepts and topics without any complexity.
- Instructions are Given: Some instructions are given, these guidelines need to be followed and taken care of while solving the MCQ of Matter in Our Surrounding.
- Solutions are Given: In the MCQ Matter in Our Surrounding, solutions are given so that students can refer to whenever they need any help in solving objective questions.
- Re Attempt Option is Given: Students can solve the same set of MCQ on Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 number of times as a re-attempt option is given.
Top 6 Benefits of the Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ
One of the prominent reasons of solving the Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ is that by looking through the options, students can recollect the facts and important concepts, this is one of the important benefit, other benefits are:
- Easy to Answer: The Matter in Our Surrounding MCQ are easy to answer, that is students just need to select the accurate option within secs. For this, students need to complete the topics and concepts of the Matter in Our Surrounding in a better way.
- Quicker to Evaluate: The MCQ of Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 are quicker to evaluate as compared to essay type questions.
- Enhances Thinking Skills: To attempt the MCQ on Matter in Our Surrounding, students need to analyse and evaluate the options given, this enhances the thinking skills.
- Helps to Identify the Area of Strengths and Weaknesses: By practising MCQ on Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9, students can identify their strengths as well as weaknesses and accordingly they can improve.
- Device Friendly: This MCQ Matter in Our Surrounding is considered to be mobile friendly, that is it can be downloaded from anywhere without any complexity and can practise objective questions.
- Acts as a Revision Tool: The Class 9 Matter in Our Surrounding MCQ acts as a revision tool that is it can be used to revise all the key concepts of the chapter.
Steps to Master in the Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ
Mastering in the Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ requires systematic and focused approach, below are some steps to master in the objective questions:
- Understand the Concepts: Students need to first understand the topics and concepts of the chapter Matter in Our Surrounding, so that they can build a strong foundation and accordingly they can solve multiple choice questions in a better way.
- Practise Sample MCQs: Students are advised to practise the sample Matter in Our Surrounding MCQ so that they can get familiarised about the format of questions.
- Analyse the Mistakes: Students need to analyse the mistakes while practising MCQ of Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 so that they can analyse the weak points and accordingly they can progress.
- Recall on a Regular Basis: It is a must for students to recall the topics and concepts of the Matter in Our Surrounding so that they can master multiple choice questions and score well.
- Stay Focused: Students need to be focused while preparing for MCQ of Matter in Our Surrounding accordingly they can enhance their knowledge as well as can master in the MCQ.
- Maintain a Positive Attitude: Students need to maintain a positive attitude: feel relaxed while marking the MCQ of Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 so that they can mark the accurate answers.
When to Start Solving the Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ?
Students can start solving the Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ according to their preference and study schedule, they can follow general guidelines to practise the multiple choice questions:
- After Completing the Chapter: It is generally recommended for students to start solving the Matter in Our Surrounding MCQ as soon as they complete the chapter accordingly they can reinforce their understanding for the chapter.
- Before Final Exams: Students can start solving the MCQ of Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 before the final exams so that they can identify the gaps in the understanding of the concepts.
- During Classroom Study: Students can solve the MCQ of Matter in Our Surrounding during classroom study and can seek help from their teachers to solve confusions.
- To Solve Doubts: Students can also start solving the MCQ on Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 to solve doubts and confusions regarding the chapter.
- To Understand the Pattern: Students can solve the MCQ of Matter in Our Surrounding so that they can understand the pattern of objective questions.
How Mark Right Answers in Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ?
It is very important for students to marks the accurate answers in Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ so they can score good marks in it, tips to mark the right answer are:
- Read the Entire Question Carefully: Students are advised to read the entire question carefully so that they can develop a logical thinking to mark the accurate answers.
- Read Every Option: Prior to choosing the right answer in MCQ Matter in Our Surrounding, students need to read each and every option thoroughly otherwise they can end up selecting the wrong answer.
- Try to Answer it in Mind First: Firstly, students need to answer the MCQ on Matter in Our Surrounding in their mind so that they can prevent silly mistakes.
- Try to Use the Process of Elimination: Students need to use the process of elimination by crossing out all the wrong answers while attempting Class 9 Matter in Our Surrounding MCQ.
- Select the Best Answer: Some answers can seem right but it may not be accurate so students need to be very careful while marking the answer in the MCQ of Matter in Our Surrounding.
- Double Check the Answers: Students need to double check the all answers before submitting the Class 9 Matter in Our Surrounding MCQ so that they can have a surety of marking the right answers.
How to Analyse the Wrong Answers in the Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ?
Analysing the wrong answers in the Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ is very important for students as it helps them to identify the skills and flaws, tips to analyse the mistakes are:
- Identify the Incorrect Ones: Students are advised to ident/ify the incorrect ones and compare it with the right ones while attempting Matter in Our Surrounding MCQ.
- Understand the Reason for Incorrect Ones: Students need to understand the reason for incorrect MCQs of Matter in Our Surrounding so that they can focus on the weak concepts.
- Seek Clarification: Students need to seek clarification from the teachers so that they don’t repeat the same set of mistakes while attempting MCQ of Matter in Our Surrounding.
- Practise Different Levels of Questions: Students need to practise different levels of multiple choice questions of Matter in Our Surrounding: easy, moderate, advance so that they can understand weak parts and work accordingly.
- Note Down the Mistakes: It is a must for students to note down the mistakes made while attempting the Class 9 Matter in Our Surrounding MCQ so that they can easily rectify the mistakes.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
Ncert solutions for class 9 science chapter 1 matter in our surroundings.

Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
Contact form.
- CBSE Notes For Class 9
- Class 9 Science Notes
- Chapter 1: Matter In Our Surroundings
Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes - Chapter 1
Cbse class 9 science notes chapter 1 matter in our surroundings, states of matter.
- Matter can be classified as solid, liquid or gas on the basis of interparticle forces and the arrangement of particles.
- These three forms of matter are interconvertible by increasing or decreasing pressure and temperature. For example, ice can be converted from solid to a liquid by increasing the temperature.
For more information on Matter Around Us, watch the below video

To know more about the States of Matter, visit here .
For more information on the States of Matter, watch the below video

Atomic View of the Three States of Matter
Physical Nature of Matter
- A physical property is an aspect of matter that can be observed or measured without changing its nature or composition.
- It is independent of the amount of matter present.
- Physical properties include appearance, colour, odour, density, texture, melting point, boiling point, solubility, etc.
For more information on Physical Nature of Matter, watch the below video

To know more about the Physical Nature of Matter, visit here .
Characteristics of Particles of Matter
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space.
- Everything that we can touch, see, hear, taste and also smell is matter.
- It is made up of really tiny particles which cannot be seen through the eye.
For more information on Characteristics of Particles of Matter, watch the below video

The particles of which the matter is comprised influence its state and properties (physical and chemical).
1. Particles of matter have spaces between them
- This characteristic is one of the concepts behind the solubility of a substance in other substances. For example, on dissolving sugar in water, there is no rise in the water level because the particles of sugar get into the interparticle spaces between the water particles.
2. Particles of matter are always in motion
- Particles of matter show continuous random movements due to the kinetic energy they possess.
- A rise in temperature increases the kinetic energy of the particles, making them move more vigorously.
3. Particles of matter attract each other In every substance, there is an interparticle force of attraction acting between the particles. To break a substance, we need to overcome this force. The strength of the force differs from one substance to another.
To know more about the Characteristics of Particles of Matter, visit here .
When the particles of matter intermix on their own with each other, the phenomenon is called diffusion . For example, spreading of ink in water.
- During diffusion, the particles occupy the interparticle spaces.
- The rate of diffusion increases with an increase in temperature due to increase in the kinetic energy of the particles.
To know more about Diffusion, visit here .
Can Matter Change Its State?
Effect of change of temperature on the state of matter.
On increasing the temperature, the kinetic energy of the particles of the matter increases, and they begin to vibrate with higher energy. Therefore, the interparticle force of attraction between the particles reduces, and particles get detached from their position and begin to move freely.
- As a result, the state of matter begins to change.
- Solids undergo a phase change to form liquids.
- Similarly, liquids also undergo a phase change to form gases.
To know more about the Changing State of Matter, visit here .
Melting Point
The melting point of a solid is defined as the temperature at which solid melts to become liquid at the atmospheric pressure.
- At the melting point, these two phases, i.e., solid and liquid, are in equilibrium, i.e., at this point, both solid state and liquid state exist simultaneously.
When two atoms collide to create a heavier atom, such as when two hydrogen atoms combine to create one helium atom, this process is known as fusion. This process generates enormous amounts of energy, many times more than fission, and powers the sun. Furthermore, it doesn’t generate radioactive fission products.
The melting point at which ice, a solid, turns to water, a liquid, is 32°F (0°C).
Boiling Point
The boiling point of a liquid is defined as the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the liquid is equal to the atmospheric pressure.
The boiling point for any material is the temperature point at which the material transforms into the gas phase in the liquid phase. This happens at 100 degrees centigrade for water. The Celsius scale was in fact created on the basis of the ice/water melting point and the liquid water/vapor boiling point.
Read more: Celsius to Kelvin
Latent Heat of Fusion
It is the amount of heat energy that is required to change 1 kg of a solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure at its melting point.
Latent Heat of Vaporisation
It is the amount of heat energy that is required to change 1 kg of a liquid into gas at atmospheric pressure at its boiling point.
Sublimation
The transition of a substance directly from its solid phase to gaseous phase without changing into the liquid phase (or vice versa) is called sublimation.

Effect of Change in Pressure on the State of Matter
By applying pressure, the interparticle spaces between particles of matter decrease. Thus, by applying pressure and reducing temperature, we can convert a solid to liquid and a liquid to gas.
Flowchart for Inter-Conversion of the Three States of Matter

Evaporation
The phenomenon by which molecules in liquid state undergo a spontaneous transition to the gaseous phase at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation.
- For example, the gradual drying of damp clothes is caused by the evaporation of water to water vapour.
For more information on Evaporation, watch the below video

To know more about Evaporation, visit here .
Factors Affecting Evaporation
- Temperature: The rate of evaporation increases with an increase in temperature.
- Surface area: The rate of evaporation increases with an increase in surface area.
- Humidity: The rate of evaporation decreases with an increase in humidity.
- Wind speed: The rate of evaporation increases with an increase in wind speed.
To know more about Factors Affecting Rate of Evaporation, visit here .
Cooling Due to Evaporation
During evaporation, the particles of a liquid absorb energy from the surroundings to overcome the inter-particle forces of attraction and undergo phase change. The absorption of heat from the surrounding makes the surroundings cool.
For example, sweating cools down our body.
Applications of Evaporative Cooling
- To keep water cool, it is kept in earthenware containers. Similar to the pores in cotton fabric, the pores in the earthen pot’s surface area allow for more evaporation.
- To keep our bodies cool, we sweat a lot. Evaporation is what transpiration ultimately is. Our body’s water evaporates, using energy in the process and lowering our body temperature as a result.
- We dress in cotton during the summer. Since cotton is a powerful water absorbent, it allows more perspiration to come into touch with the air, promoting more evaporation. We have a cooling effect when wearing cotton clothing because of this.
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter In Our Surroundings
- Important Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 –Matter In Our Surroundings
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions for Chapter 1 – Matter In Our Surroundings
- Matter In Our Surroundings
- Maths Notes For Class 9
- CBSE Class 9 Social Science Notes
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 9 Biology Notes Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
What is the ‘latent heat of fusion’.
The latent heat of fusion is the enthalpy change of any amount of substance when it melts.
What does ‘sublimation critical point’ mean?
The sublimation critical point refers to the maximum or minimum temperature and pressure beyond which the state of the matter cannot be changed.
What does ‘interconversion of matter’ mean?
Interconversion of matter refers to the change from one state to another. It is a process by which matter changes from one state to another and back to its original state without any change in its chemical composition.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion
- Last modified on: 2 years ago
- Reading Time: 6 Minutes
Case Study/Passage Based Questions:
Question 1:
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below :
In the figure below the card is flicked with a push. It was observed that the card moves ahead while coin falls in glass.

(i) Give reason for the above observation. (a) The coin possesses inertia of rest, it resists the change and hence falls in the glass. (b) The coin possesses inertia of motion; it resists the change and hence falls in the glass. (c) The coin possesses inertia of rest, it accepts the change and hence falls in the glass. (d) The coin possesses inertia of rest, it accepts the change and hence falls in the glass.
(ii) Name the law involved in this case. (a) Newton’s second law of motion. (b) Newton’s first law of motion. (c) Newton’s third law of motion. (d) Law of conservation of energy
(iii) If the above coin is replaced by a heavy five-rupee coin, what will be your observation. Give reason. (a) Heavy coin will possess more inertia so it will not fall in tumbler. (b) Heavy coin will possess less inertia so it will fall in tumbler. (c) Heavy coin will possess more inertia so it will fall in tumbler. (d) Heavy coin will possess less inertia so it will not fall in tumbler.
(iv) Name the law which provides the definition of force. (a) Law of conservation of mass (b) Newton’s third law. (c) Newton’s first law (d) Newton’s second law.
(v) State Newton’s first law of motion. (a) Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed, it can be converted from one form to another, total amount of energy always remains constant. (b) A body at rest remains at rest or, if in motion, remains in motion at constant velocity unless it is acted upon by an external unbalanced force. (c) For every action in nature there is an equal and opposite reaction. (d) The acceleration in an object is directly related to the net force and inversely related to its mass.
Other Chapters:
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:5MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of Atom
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of Atom In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then questions based…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given,…
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

COMMENTS
b) Dissolution, combustion, sublimation, and oxidation. c) Fermentation, photosynthesis, respiration, and digestion. d) Oxidation, reduction, precipitation, and ionization. Answer: a) Evaporation, condensation, melting, and freezing. Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 ...
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings. Here we are providing case study questions for class 9 science chapter 12 sound. Students are suggested to go through each and every case study questions for better understanding of the chapter. Case Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1:
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks or 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science - Matter in our Surroundings Case Study 1: 1.) A matter is anything that has mass and occupies ...
Class 9 science case study question 1. Gases are highly compressible as compared to solids and liquids. The liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) cylinder that we get in our home for cooking or the oxygen supplied to hospitals in cylinders is compressed gas. Compressed natural gas (CNG) is used as fuel these days in vehicles.
Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in our Surroundings. In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. ...
NCERT Solution of class 9 Science chapter 1 has been created, keeping in mind the primary goal of helping students to secure more marks and improve grades. The academic requirements and needs of students have been addressed in the solution for class 9 Science chapter 1. The topics in chapter 1 related to Matter in Our Surrounding are discussed according to the CBSE syllabus.
Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings. CBSE Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 helps students to clear their doubts and to score good marks in the board exam. All the questions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments & homework.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science - List of Chapters. Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings. Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure. Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules. Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom. Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life. Chapter 6 Tissues. Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms. Chapter 8 Motion.
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 1 - Free PDF Download. NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (Chemistry) Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings is an important study material from the standpoint of your CBSE Class 9 Science examination. Detailed NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Chemistry provided here will help you understand the fundamental concepts taught in the chapter.
on October 16, 2023, 10:44 AM. NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Intext and Exercises question answers based on rationalised NCERT books published for session 2024-25. Get here the solutions of Page 3, Page 6, page 9, page 10 and Exercises question answers in English Medium and Hindi Medium.
Yes, Revision Notes of Class 9 Chapter 1 are the ultimate and end saviour for before the exams. The students are required to go through other study material as well. The first step is to properly read NCERT Class 9 Science, Chapter 1 - "Matter in Our Surroundings." Study the chapter attentively and attempt to grasp the fundamental principles.
Answer (a) The force of attraction between particles of gas is negligible. Because of this, particles of gas move in all directions. Thus, a gas fills the vessel completely in which it is kept. (b) Particles of gas move randomly in all directions at high speed.As a result, the particles hit each other and also hit the walls of the container with a force.
MatterThe matter is the material of which everything in this universe, in and around us is made up of in different shapes. It is anything that occupies space and has mass and offers resistance to any applied force.Physical Nature of Particles :Matter is made up of particles. The particles of matter are very-very small. Characteristics … Continue reading Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter In ...
Q4. Arrange the three states of matter in the increasing order of: (i) rate of diffusion. (ii) particle motion. Answer. (i) Rate of diffusion: solid < liquid < gas. (ii) Particle motion: solid < liquid < gas. Q5. Mention two properties of water to justify that water is liquid at room temperature.
Study Material and Notes of Ch 1 Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9th Science. Topics in the Chapter. → Since early times human beings have been trying to understand their nature. Early Indian philosopher classified matter into five basic elements. the"Panch Tatva"- air, earth, fire, sky and water. According to them, living as well as ...
The NCERT Exemplar Solution for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surrounding is provided here for the benefit of the students. Studying the NCERT Exemplar Solution will give you in-depth knowledge of the concepts discussed in the chapter. NCERT Exemplar questions are designed in such a way that students can learn all the basic and ...
Students need to follow some given steps to attempt the Matter in Our Surrounding Class 9 MCQ, steps are discussed below: Visit the Selfstudys website. Bring the arrow towards CBSE which can be seen in the navigation bar/ button. A drop down menu will appear, select MCQ Test from the list. New page will appear, select Class 9th from the list of ...
Students can cross check their answers and also whether they learned it properly or not. Chapter 1 of NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science consists of 9 exercise questions and 17 in-text questions. Topics in the Chapter. • Physical Nature of Matter. → Matter is Made Up of Particles.
April 25, 2022 April 25, 2022 Physics Gurukul Leave a Comment on Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion. ... Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Motion; Case Study Question for Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields; NUMERICALS BASED ON CONVEX AND ...
In this chapter we shall learn about matter based on its physical properties. Chemical aspects of matter will be taken up in subsequent chapters. 1.1 Physical Nature of Matter 1.1.1 MATTER IS MADE UP OF PARTICLES For a long time, two schools of thought pr evailed regar ding the nature of matter. One school believed matter to be continuous like ...
CBSE Class 9 Science Notes Chapter 1 Matter In Our Surroundings. Download PDF. Anything that has mass and takes up space is referred to as matter. hydrogen and oxygen, sugar and sand, air and water, etc. Small, minuscule particles make up matter. Due to the space between them, matter particles are attracted to one another.
2024 AP Exam Dates. The 2024 AP Exams will be administered in schools over two weeks in May: May 6-10 and May 13-17. AP coordinators are responsible for notifying students when and where to report for the exams. Early testing or testing at times other than those published by College Board is not permitted under any circumstances.
Case Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1: Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below : In the figure below the card is flicked with a push. It was observed that the card moves ahead while coin falls in glass. (i) Give reason for the above observation.(a) The coin possesses … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science ...