

Cash Book | Class 11 Accountancy (Notes & Exercises)
By Suraj Chaudhary
May 1, 2024

This article has all the exercises of Cash Book class 11. If you have been looking for the questions and answers to the exercises of the Cash Book class 11 and notes, you are in the right place.
Concept Of Cash Transactions
Cash transactions refer to cash receipts and payments. The receipts of cash from various sources and payments of cash on various heads are important routine transactions of a business. The main sources of cash receipts are the sale of goods and services, the sale of old assets, the contribution of capital, loans borrowed, interest, rent, commission, and other receipts from customers.
- To have a systematic and permanent record of all cash transactions in a separate book.
- To obtain reliable and detailed information on all the cash receipts and payments easily and immediately.
- To keep effective control over the misappropriation of cash transactions.
- To know the main sources and heads of payment of cash.
- To know cash balances.
The cash book is a complete record of all the receipts and payments, which are made either in cash or through the bank. It has two sides. The debit side shows cash receipts and the credit side shows cash payments. All the cash and cheques received and deposited are shown on the cash receipt side. All the payments made in cash and or by cheque are shown on the payment side. At the end of the given period, its balance is obtained to know the amount of cash and bank balances.
Single-column cash books, Double column cash book,s and triple-column cash books are the types of cash books.
Contra Entry
Contra Entry is the act of recording a transaction both on the receipt and payment sides of the cash book. It completes the double effect of the transactions entering the amount one in the cash column and the next in the bank column. Again such an entry, the alphabet ‘C’ is mentioned in the L.F column. The alphabet ‘C’ indicates that the entry is contra and the posting is not necessary. Contra entry is passed for the deposited and withdrawn for office use.
Numericals:
Single Column Cash Book ( Cash Column )
The following transactions are extracted from the books of Mr. Bhakti Sharma: Bhadra-1 Commencement of business with cash of Rs 120,000 Bhadra-5 Sold goods in cash of Rs 40,500 Bhadra-6 Paid salaries of Rs 30,500 Bhadra-10 Purchased furniture of Rs 45,000 Bhadra-15 Received from the debtor of Rs 12,500 Bhadra-25 Purchased stationery of Rs 500 Bhadra-30 Paid to the creditors of Rs 15,000
(Receipt) (Payment)
The following transactions are extracted from Mr. Jackson’s Books for the month of Shrawn: Shrawn-1 Opening cash balance of Rs 25,000 Shrawn-5 Received cash from debtors of Rs 42,000 Shrawn-10 Purchased goods of Rs 12,500 Shrawn-12 Paid wages of Rs 7,200 Shrawn-13 Withdrawn cash by the owner of Rs 5,200 Shrawn-14 Paid rent of Rs 1,550 Shrawn-25 Purchased a machine of Rs 15,000 Required: Single column cash book
Single Column Cash Book ( Bank Column ) On Jestha 1, Mr. Luca Pacioli commenced a business with depositing cash of Rs 175,000 into Nepal Bank Ltd. The following transactions are provided during the month: Jestha-4 Received a cheque from Amir of Rs 40,000 Jestha-5 Withdrew from the bank for personal use of Rs 3,700 Jestha-15 Received interest by cheque of Rs 5,000 Jestha-25 Deposited cash into the bank of Rs 12,000 Jestha-27 Paid interest on overdraft of Rs 1,000 Jestha-28 Purchased furniture and paid by cheque of Rs 35,000 Required: Single column cash book with bank column
The following transactions are extracted from the books of Mr. Basanta for the month of Marga assuming that all transactions were settled through bank: Marga-1 Opening bank balance of Rs 250,000 Marga-4 Cheque received from Sajan of Rs 40,000 Marga-6 Purchased goods for Rs 105,000 Marga-10 Paid for sundry expenses of Rs 15,000 Marga-15 Paid for school fees of the owner’s son of Rs 5,000 Marga-22 Sold goods for Rs 60,000 Marga-28 Withdrew from bank for personal use of Rs 3,000 Required: Cash Book with Bank column
Double Column Cash Book ( Cash and Discount Columns ) The following information is related to a business: Jan-1 Cash in hand Rs 10,000 Jan-3 Bought goods for Rs 500 Jan-7 Deposited cash into the bank of Rs 650 Jan-13 Paid to Hari Rs 450 in full settlement of Rs 500 Jan-20 Received Rs 750 from Subash and discount allowed Rs 150 Jan-25 Withdrew from bank for office use Rs 1,000 Jan-27 Purchased books for the proprietor Rs 750 Required: Cash book with cash and discount columns
Double Column Cash Book ( Bank and Discount Columns ) The following information is taken from the books of Mr. Sabin assuming that all transactions were settled through the bank: Baisakh-2 Mr. Sabin started a business with Rs 30,000 by opening the bank account Baisakh-7 Purchased office equipment by issuing a cheque of Rs 2,500 Baisakh-9 Purchased goods for Rs 5,000 from Subash and paid 3,000 partially Baisakh-15 Sold goods for Rs 4,000 to Mr. Shakya and received a cheque of Rs 2,000 partially Baisakh-22 Issued a cheque of Rs 1,800 to Mr. Subash in full settlement of Rs 2,000 Baisakh-25 Withdrew from the bank for personal expenses by the owner of Rs 700 Baisakh-27 Received a cheque of Rs 1,700 from Mr. Shakya in full settlement. Baisakh-29 Issued a cheque for sundry expenses of Rs 750 Baisakh-30 Mr. Sabin brought additional capital of Rs 5,000 and deposited into the bank. Required: Cash book with bank and discount columns
Double column cash book ( Cash and Bank Columns ) Mr. Khetan has started a business with cash of Rs 75,000 and bank balance of Rs 125,000 on 1st January. The other information is as follows: January-7 Deposited into the bank Rs. 40,000 January-10 Sold goods for Rs 15,000 to Ram and received a cheque. January-15 Withdrew Rs 5,000 from the bank for office use and Rs 2,000 for personal use. January-25 Received dividend of Rs 8,000 January-30 Paid for sundry expenses Rs 800 Required: Cash book with cash and bank columns
The following transactions were recorded in the books of Mr. Robinson for the month of January : January-1 Opening balances of cash and bank of Rs 30,000 and Rs 160,000 respectively. January-4 Purchased goods of Rs 30,000 and paid by cheque. January-9 Sold goods on cash Rs 21,500 January-15 Deposited into the bank Rs 25,000 January-25 Paid wages of Rs 500 January-27 Withdrew cash of Rs 2,500 from the bank for personal use. January-30 Received commission by cheque of Rs 5,000 Required: Cash book with cash and bank columns
Enter the following transactions in the cash book of Raj for the month of Asadh with cash and bank columns: Asadh-1 Opening balances of cash Rs 5,000 and bank overdraft of Rs 10,000 Asadh-3 Mr. Raj brought Rs. 12,000 as additional capital Asadh-5 Deposited cash Rs 4,000 into the bank. Asadh-11 Paid Rs 8,000 by cheque to Hari Asadh-15 Paid for stationery Rs 400 Asadh-29 Received a cheque of Rs 1,000 from Hari
Mr. B.K. started a business with cash of Rs 22,000 and bank balance of Rs 100,000 on 1st February. The other related information is given below: February-2 Purchased goods for Rs 10,000 from Anil and paid Rs 6,000 by cheque. February-5 Sold goods to Mr. Bijay for Rs 8,000 and received a cheque. February-8 Paid by cheque to Anil Rs 4,000 February-12 Deposited Binay’s cheque into the bank. February-21 Paid salary by cheque of Rs 8,000 February-23 Paid rent Rs 4,000 and wages of Rs 1,000 February-25 Deposited the remaining balance of cash except Rs 500 into the bank. Required: Cash book with cash and bank columns
Triple Columns Cash Book (Cash, Bank and Discount Columns)
The following transactions are the transactions of Karun: Baisakh-1 Commenced a business with cash of Rs 100,000 Baisakh-3 Deposited into the bank Rs 80,000 Baisakh-6 Sold goods to Mr. KK for Rs 5,000 and received cash after 5% discount. Baisakh-10 Withdrawn cash of Rs 15,000 from the bank for office use and of Rs 5,000 for private use. Baisakh-15 Purchased goods from Mr. Ganesh for Rs 12,000 and paid cash Rs 7,000 as partial payment. Baisakh-25 Issued a cheque to Mr. Ganesh after deducting 5% discount as discount in full settlement. Required: Triple Column Cash Book
The following information is extracted from the books of Mr. Karan Bhatt: January-1 Opening balance of cash and bank Rs 12,000 and Rs 51,000 respectively. January-5 Purchased goods for Rs 35,000 from Amir and paid by cheque Rs 25,000 partially. January-8 Sold goods to Mr. Sanjay for Rs 30,000 and received a cheque of Rs 25,000 partially. January-18 Paid salary of Rs 10,000 by cheque and wages of Rs 2,000 in cash. January-20 Received Rs 4,500 from Sanjay in full settlement. January-22 Issued a cheque of Rs 9,000 to Mr. Amir in full settlement. Required: Triple column cash book
Following cash related transactions of Mr. Bhandari are given below: Chaitra-1 Started a business with cash and bank balance of Rs 20,000 and Rs 100,000 respectively. Chaitra-4 Purchased goods for Rs 100,000 from Achala and paid her partially by cheque of Rs 80,000. Chaitra-5 Sold goods to Mr. Y for Rs 50,000 and received a cheque of Rs 18,000 as partial payment. Chaitra-11 Paid rent of Rs 5,000 by cheque. Chaitra-17 Paid Rs 5,000 to Gopal in full settlement of Rs 6,000 Chaitra-21 Received cash from Mr. Y Rs 31,000 in full settlement. Chaitra-24 Deposited the remaining cash balance except Rs 2,000 into the bank. Required: Triple column cash book
Other Articles:
- Accounting Terminologies
Suraj Chaudhary is a writer, developer, founder, and a constant learner. He shares lessons and resource to living a fuller life every week. On this blog, he shares helpful guides and helpful articles that help his 70,000+ monthly readers find answers, solve problems, and meet their curious needs.
14 thoughts on “Cash Book | Class 11 Accountancy (Notes & Exercises)”
Outstanding post, you have pointed out some fantastic points, I likewise think this s a very wonderful website.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Slide to prove you're not a bot/spammer *
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Recording of Transactions - II Class 11 Notes CBSE Accountancy Chapter 4 (Free PDF Download)
Revision Notes

Revision Notes for CBSE Class 11 Accountancy Chapter-4 - Free PDF Download
The accountancy class 11 chapter 4 notes are essential study materials, which will help the students to understand the chapter precisely. The class 11 accounts chapter 4 notes provide a comprehensive view of the chapter along with solved exercises, short keynotes, revision notes and practice papers to improvise the exam preparation. The chapter encompasses and briefs on all the essential topics such as the Cash Book, Purchases Return (Return Outwards), Purchases Book, Sales, Sales Return Book (Return Inwards) and Journal Proper. Students can also download the PDF files of accounts class 11, chapter 4 notes arranged by qualified and expert educators. From this article, students can enhance their revision process.
Download CBSE Class 11 Accountancy Revision Notes 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 11 Accountancy revision notes for All chapters:

Access Class- 11 Accountancy Chapter 4 - Recording Of Transactions - II Notes
Cash book .
This book is used for recording all the transactions related to cash payment and cash receipt.
All bank related transactions are also recorded in this book.
Difference Between a Cash Account and a Cash Book.
Single Column Cash Book
Let’s Practice It With a Question:-
Enter the Following Transaction in a Single Column Cash Book:-
1. Commenced business with cash Rs10000.
2. Bought goods for cash Rs 2500.
5. Sold goods for cash Rs 2000.
10. Goods purchased from Ravi on credit Rs 5000.
13. Paid to Ravi Rs 3500.
15. Cash sale Rs 4000.
18. Purchased furniture for cash Rs 3099.
20. Paid wages Rs 190.
24. Paid rent Rs 200.
26. Received commission Rs 300.
28. Withdrew for personal use Rs 500.
31. Paid salary Rs 450.
Double Column Cash Book
A double column cash book is a cash book with two columns on each side, one column for recording cash transactions and the other for recording bank transactions.
Let’s Practice it with a Question:-
Books of Original Entry-
Special Purpose Subsidiary Books:-
Purchase Book or Purchase Journal
Purchase book records all the credit purchases of goods. It records only those things in which a firm or Business organisation deals.
Format of Purchase Book:
Let's Practice with a Question:-
Enter the Following Transactions in the Purchase Book of Superior Cloth House,
New Delhi, Assuming CGST @ 2.5% and SGST @ 2.5%.
Sales Book:-
In the sales book, all credit sales of goods are recorded. Cash sales will be recorded in the cash book, not in the sales book. Credit sales of things other than the goods in which the firm deals, are not recorded in the sales book.
Format of Sales Book:-
Let’s Do It With An Example :-
Purchase Return Book:-
Purchase return book is used to record the return of such goods as were purchased on a credit basis.
This book is also known as the return outward book.
Format of Purchase Return Book:-
Sale Return Book
Sale return book is used to record the return of such goods as were sold to the customers on a credit basis.
This book is also known as a return inward book.
Format of Sale Return Book:
Journal Proper:-
In the journal proper, only those transactions are recorded which cannot be recorded in any other subsidiary book. In such a case a journal is called a proper journal.
Let's do it with an example:--
Record the following transactions in the JOURNAL PROPER of m/s Ramesh traders
1. Old machinery sold to Sailash for ₹ 5,000 on credit
2. Goods worth ₹20, 000 was destroyed by fire
3. A bill receivable for ₹20, 000 endorsed
Recording of Transactions 2 NCERT Solutions Class 11 - Introduction
Recording of transactions 2 notes is considered as a method of managing accounting transactions in different books of accounts. The recording of transactions class 11 notes executes the use of journal book, cash book and ledger accounts. The class 11 accountancy chapter 4 notes present a complete outline of the chapter. The recording of transactions 2 notes introduces the registered transactions and preparation of the source documents which have already been registered in the basic book called a journal. After completion of these steps, the entries in the journal book are reported in a private account called ledger.
1. Cash Book
The book in which all the transactions related to cash payments and cash receipts are registered is known as Cash Book. It begins with the bank balances or cash at the starting of a period. This book is commonly used every month. It is maintained by all big or small organisations, profit or not-for-profit. It serves the objective of both ledger accounts as well as the journals.
Single Column Cash Book: The cash book which records all the cash transactions of the business in the achronological system is known as the Single Column Cash Book. It is a complete account of all the cash receipts and cash payments.
Double Column Cash Book: This cash book contains two columns of amount on each side - one to record bank transactions and one to record cash transactions. In today's time, bank transactions are substantial, and therefore in most of the organisations, receipts and payments are affected by the bank. A double column cash book provides bank balance as well as cash balance information at the same time; most organisations prefer to keep a double column cash book rather than holding two separate ledger accounts for recording bank transactions and cash.
Petty Cash Book: In every organisation, a massive amount of small payments such as cartage, postage, conveyance, telegrams and other expenses are listed under various accounts. If these payments are recorded in the main cash book, the cashier may be overburdened, and the cash book may look bulky. To avoid this, many organisations designate one more cashier, also known as a petty cashier who maintains a separate cash book to record these transactions. Such a cashbook managed by the petty cashier is known as the petty cash book.
2. Purchase Book
The Purchase book is a subsidiary book. This book includes the account of all credit-purchases and does not hold the record of purchases of assets. The Journal proper holds the records of purchases of assets. The entries are listed in the Purchase book from source documents.
(image will be uploaded soon)

3. Journal Proper
The book of original record (simple journal) in which different credit transactions which do not fit in any other records are registered is known as the Journal Proper book. It is also termed as the miscellaneous journal.
Conclusion
Recording of Transactions - II," Chapter 4 of Class 11 CBSE Accountancy, delves into advanced aspects of precise financial recording. This chapter explores compound journal entries, voucher systems, and their connection to source documents. It guides students through the meticulous process of voucher preparation and subsequent ledger entry. Balancing and closing of ledger accounts, trial balance preparation, and error identification techniques are underscored. The chapter offers practical exercises for hands-on experience. These notes provide invaluable insights into accurate financial record-keeping, enhancing students' ability to navigate intricate transactions effectively. While I can't offer direct PDF downloads, this summary serves as a condensed guide for comprehensive learning.

FAQs on Recording of Transactions - II Class 11 Notes CBSE Accountancy Chapter 4 (Free PDF Download)
1. What are the Advantages of Subdividing the Journal?
The advantages of the sub-dividing of the journal are:
Accountability: As each statement is managed by individual accountants, it makes them more liable and assures that accounts are correctly maintained.
Accuracy: Each accountant will be functional in work allotted to them, and hence there are fewer possibilities of errors.
Division of Labour: As separate accountants manage accounts, it assures parallel recording and faster recording of transactions.
Economical: As a division of labour brings in specialisation, the method becomes effective and thereby becomes economical.
2. State the Requirements for Special Purpose Books.
Special purpose books benefit bookkeeping as each journal is maintained by a different auditor having particular expertise which improves accuracy and decreases errors. It increases efficiency by dividing the workload. The journal explains the idea of recording in brief descriptions. It reduces the bulk of posting as totals can be done systematically. Fraud prevention is also prevented as the record-keeping of various journals is assigned to a different individual, and as multiple accountants supervise multiple books, the recording work moves faster.
3. How does the voucher system work in recording transactions?
The voucher system involves the use of vouchers as documentary evidence for transactions. Vouchers provide details of the transaction, facilitating accurate recording in the books.
4. What are source documents, and how are they related to vouchers?
Source documents are original records that serve as evidence for a transaction. They provide information for creating vouchers, which are then used for recording in the books.
5. How do you prepare vouchers?
Vouchers are prepared by following a systematic process that includes details of the transaction, classification of accounts, and narration. They must be accurate and complete.
6. What is the process of recording voucher transactions in the books?
Voucher transactions are recorded in the respective ledger accounts using journal entries. This ensures that the impact of the transaction is correctly reflected in the accounts.
7. Why is balancing and closing of ledger accounts important?
Balancing and closing of ledger accounts ensure that the accounts are up to date and ready for the next accounting period. Balancing helps in calculating the account balance, while closing transfers balances to the appropriate accounts.
CBSE Study Materials

DK Goel Solutions
- DK Goel Solutions Class 11
DK Goel Solutions Chapter 11 Books of Original Entry – Cash Book
Read below DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 11 Books of Original Entry Cash Book . These solutions have been prepared based on the latest Class 11 DK Goel Accountancy book issued for the current year and the questions given in each chapter.
In this chapter of DK Goel Accounting Solutions Class 11 , explain various concepts relating to cash books, what they mean, and their importance. It also provides basic steps on how to prepare cash books.
The chapter also includes lot of good quality problems or questions which can be very helpful to understand the concepts for Class 11 students of Accountancy and will also help build a strong foundation.
DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 11 solutions are free and will help you to prepare for Class 11 Accountancy
Books of Original Entry – Cash Book DK Goel Class 11 Accountancy Solutions
Students can refer below for solutions for all questions given in your DK Goel Accountancy Textbook for Class 11 in Chapter 11
Short Answer Questions for DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 11
Question 1:
Solution 1: For any type of transactions, it is useful to keep a different book, one to record cash transactions, another to record credit purchases of goods, and still another to record credit sales of goods.
All these books ( DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 11 )are referred to as initial entry books or main entry books or subsidiary books – it is a special type of Journal, a Journal sub-division.
Question 2:
Solution 2: Original entries are recorded in the below books:-
- Purchases Book
- Purchases Return Book
- Sales Return Book
- Bills Receivable Book
- Bills Payable Book
- Journal Proper
Question 3:
Solution 3: (a) Only monetary transactions are reported in the Cash Book, since this book documents only cash or bank-related transactions. The cash book almost still reflects a debit balance.
Since cash transfers cannot surpass cash receipts, the cash column in the cash book cannot display a credit balance. If the overall cash receipt is equal to the total bill, it will display zero balance at most.
(b) As cash Book is a book in which all transactions relating to cash receipts and cash transfers are registered, Cash Book is both Journal and Ledger. At the start of the cycle, it begins with cash or bank accounts.
Question 4:
Solution 4: As an original book and a ledger, the Cash book plays both roles. The Cash Book serves the dual purpose of the original entry or both books and the Ledger.
If we create a cash book, there is no need to create a separate cash account. A transaction is recorded in a cash book or cash account only if there is either cash inflow or cash outflow. The cash book therefore has a dual purpose.
Question 5:
Solution 5: Some transactions are reported in a Two-Column Cash Book that refers to both cash and money, i.e. the balance of one will drop and, owing to such transactions, the other will increase.
Certain transactions are entered on all sides of the Cash Book. Against such entries, the letter ‘C’ is written in the L.F. column to indicate that these are contra transactions and are not posted into the Ledger Account.
(a) Cash deposited into the Bank 10,000
(b) Cash withdrawn from Bank for Office Use 1,000
Question 6:
Solution 6: The three advantages of Sub-Division of Journal are:-
(i) Division of work by capacity.
(ii) Ease of posting.
(iii) Save Time
Question 7:
Solution 7:
(i) Deposit of Cash into Bank:-
In the aforementioned trade, a cash account and a bank account are also influenced by the account. It is also contra-entry since all accounts are influenced concurrently by cash and bank.
Bank a/c Dr.
To Cash A/c
(ii) Withdrawal of money from bank for office use:-
Cash a/c Dr.
To Bank A/c
(iii) Deposit of cheque (received from other) into Bank:-
On the debit side “To Cheque-in-hand a/c” and on credit side “By Debtors a/c” with the same amount recorded.
Cheque-in-hand A/c
To Debtors A/c
(iv) Dishonour of cheque deposited into Bank:-
On the credit side “By Debtor a/c” and amount will be credited into the bank account.
Debtor a/c Dr
To Bank a/c
Question 8:
(i) Similarities of Cash Book with Journal:-
- The transactions in the cash book are documented from source records for the first time, much like a report.
- Transactions in the cashbook are reported date-wise, i.e. in a chronological order, when and when they are put, much like a document.
- Much as a log, cash book transfers are often posted in the ledger to the related accounts.
- A cash book also includes a ledger folio column, much like a journal.
(ii) Similarities of cash book with ledger:-
- The sort of cash book closely resembles the account of a ledger. Having similar columns, it has two evenly separated sides. The left side (receipt side) is the debit side and the credit side is the right side and the credit side is the right side (payment side).
- The cash book itself often functions as a cash account and as such, when a cash book is held, the cash account is not opened in the ledger. The cash book, however, is indeed a part of the ledger.
- In a cash book, much like a ledger account, the words ‘To’ and ‘By’ are sometimes used.
- Much like a ledger account, it is balanced.
Question 9:
Solution 9: Contra entries indicate entries on both sides of the cash book that are registered. When depositing or withdrawing money from the bank, these entries are made.
The two accounts, the cash account and the bank account, are influenced by Contra entries. In the Cash Book, these two accounts appear together only so that the result of entries is fulfilled in the Cash Book and there is no need to post them in the ledger.
Question 10:
Solution 10: Cash book is a journalised Ledger, it is a log because it first documents cash and bank transfers in it and a ledger since it often fits the function of a cash account. No distinct cash account is opened in the ledger when a cash book is prepared.
Question 11:
Solution 11:
Question 12:
Solution 12: The book used for the purpose of tracking expenses containing minor sums is the Petty Cash Book. In addition to minor expenditures, principal cash receipts are reported.
The Petty Cash Book is prepared by the Petty Cashier which is the Petty Cash Account. In addition to large payments, it is retained as in a company, it is important to make a variety of minor payments, such as conveyance, stationary, cartage, etc.
Question 13:
Solution 13:
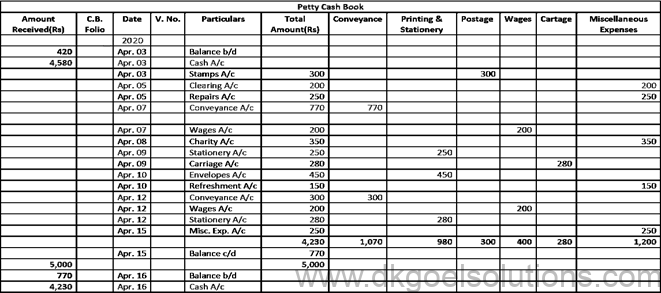
Question 14:
Solution 14: The Petty Cash imprint scheme is discussed below. Under this method, the amount needed for minor expenditures for a certain time is determined (say for a week, a fortnight or a month). At the beginning of an era, the amount so calculated is issued to the petty cashier and the amount charged by him during the period is repaid.
Numerical Question DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 11 :-
Question 1:
Solution 1:

Point in Mind:- The Cash Book Balancing is done like every other account. The debit column is often bigger than the credit column.
Question 2:
Solution 2:
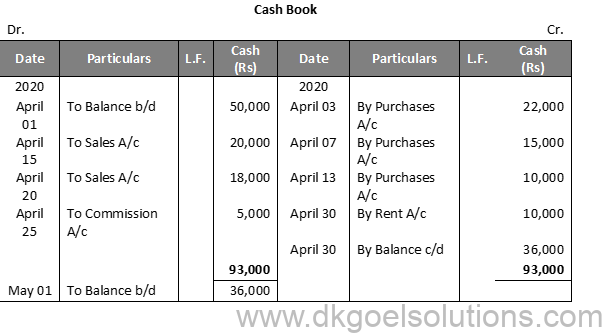
Point in mind:- Only currency transfers are reported in the cash book. There is no recording of credit transfers. The debit side is still higher than the credit, since the cash available is never surpassed by transfers.
Question 3:
Solution 3:

Solution 4:

Question 5:
Solution 5:

Question 6:
Solution 6:
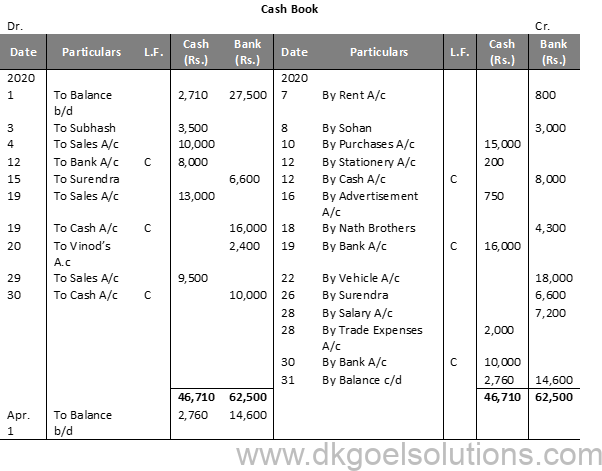
Question 7:
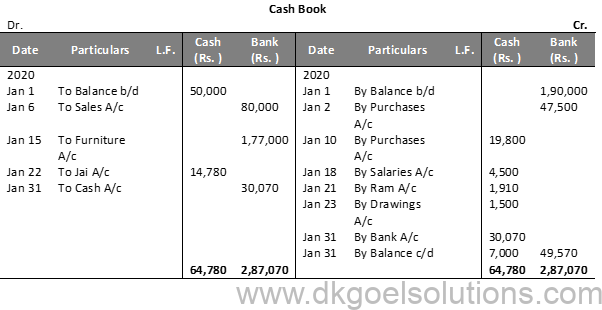
Question 8 (A):
Solution 8(A):
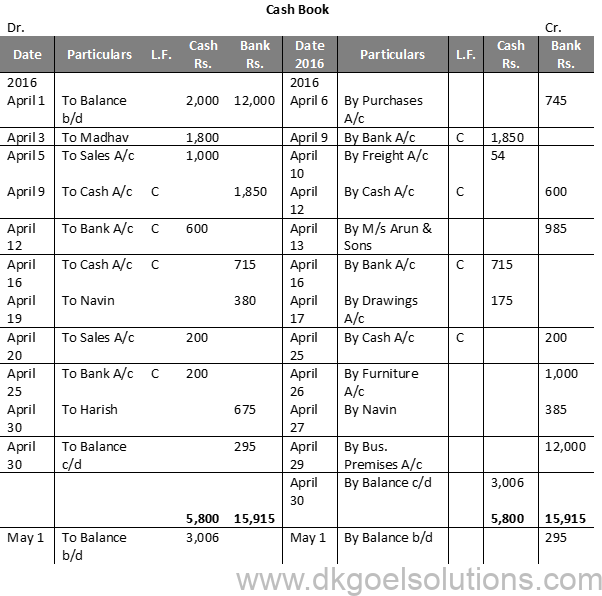
Question 8 (B):
Solution 8 (B):

Working Note:-
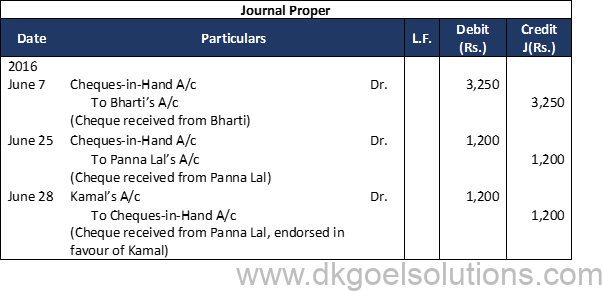
Question 9:
Solution 9:
Working Note:- On 20th April, Entry for Credit sales of Rs. 80,000 plus CGST and SGST @ 6% each will he recorded in journal.
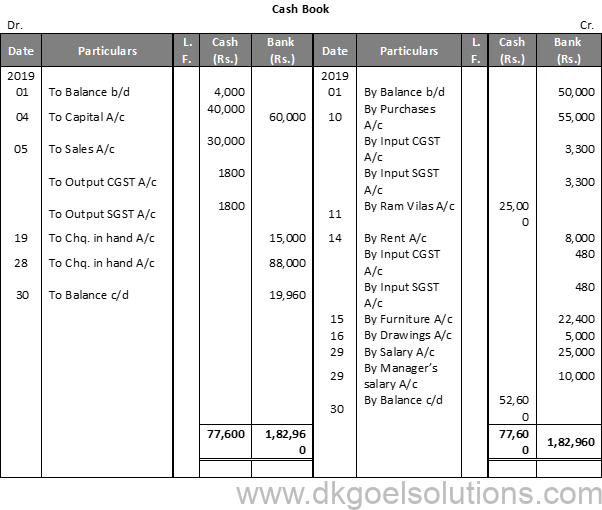
Question 10 (A):
Solution 10 (A):
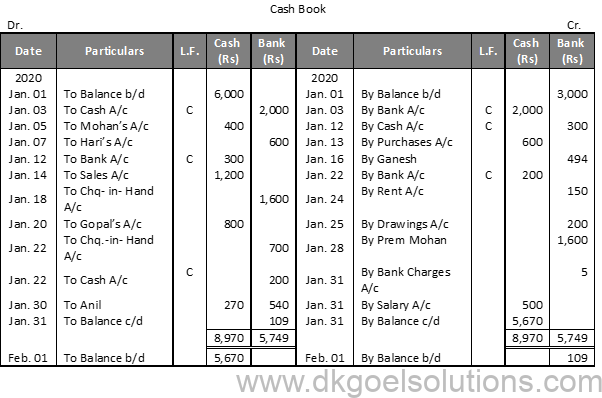
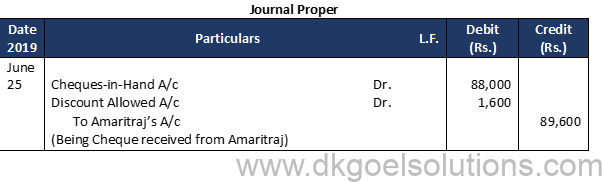
Working Note :- 1. Cheque received from Prem Mohan on 9 th and from Gopal on 20 th will be recorded through Journal. These will be recorded in the Cash Book on the dates of their deposit into the Bank.
Question 10 (B):
Solution 10 (B):

Working Note :-
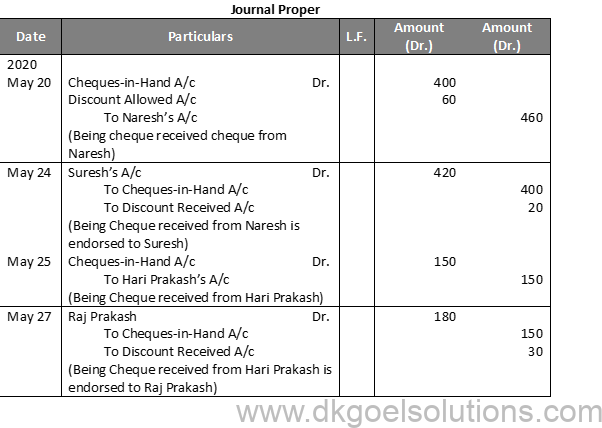
Question 11 (A):
Solution 11 (A):
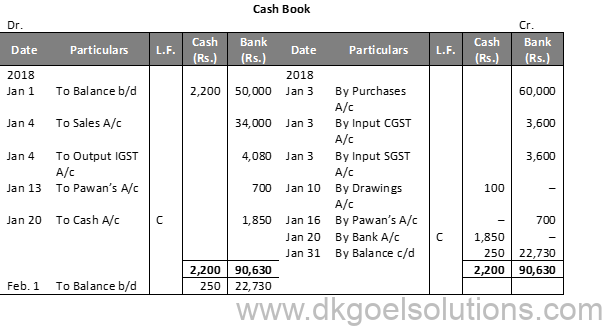
Question 11 (B):
Solution 11 (B):
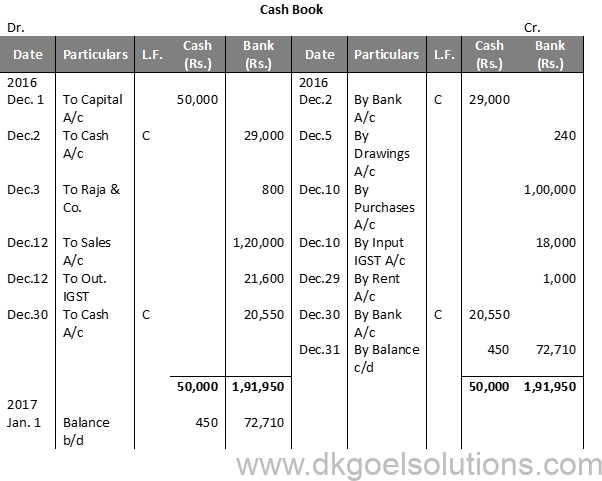
Calculation of Cash deposit into the Bank:- Cash deposit into bank = Bal. of cash column of Dr. side – Total of Cash Column of Cr. side + Cash Bal. Cash deposit into bank = 50,000 – 29,000 + 450 Cash deposit into bank = 50,000 – 29,450 Cash deposit into bank = 20,550
Question 12:
Solution 12:
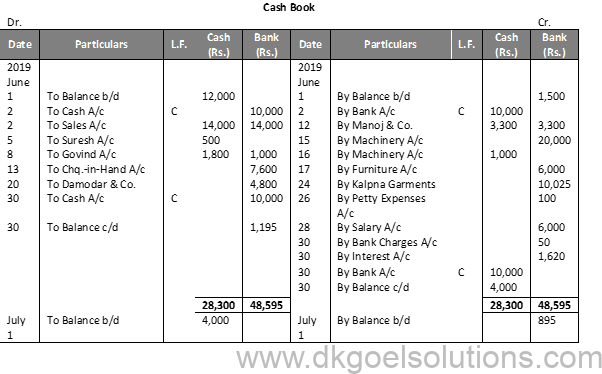
Calculation of Cash Deposit into Bank:- Cash deposit into bank = Bal. of cash column of Dr. side – Total of Cash Column of Cr. side + Cash Balance Cash deposit into bank = 28,300 – 14,300 + 4,000 Cash deposit into bank = 28,300 – 18,300 Cash deposit into bank = 10,000
Question 13 (A):
Solution 13 (A):
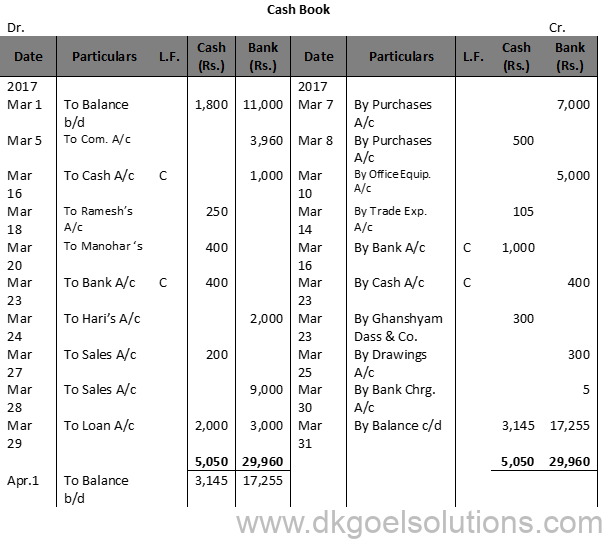
Question 13 (B):
Solution 13 (B):
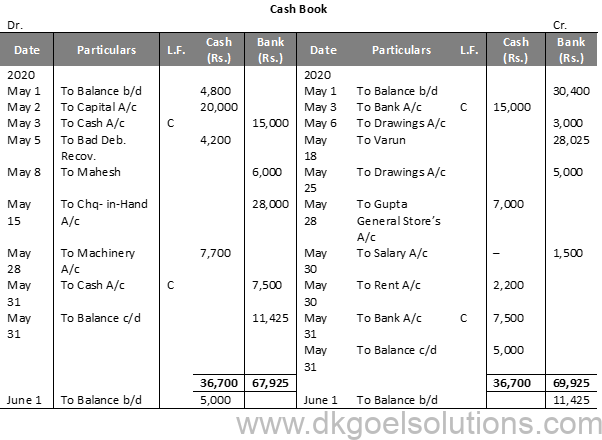
Working Note:- May 6th : Life Insurance Premium is treated as Drawings. May 12th : Entry for receipt of cheque will be recorded in Journal Proper. May 15th : To cheque in hand a/c Rs. 28,000 in bank column May 18th : by Varun Rs. 28,025 in Bank Column, Entry for discount withdrawn Rs. 2,000 will be passed through Journal Proper.

Calculation of Cash Deposit into Bank:- Cash deposit into bank = Bal. of cash column of Dr. side -Total of Cash Column of Cr. side + Cash Balance Cash deposit into bank = 36,700 – 24,200 + 5,000 Cash deposit into bank = 36,700 – 29,200 Cash deposit into bank = 7,500
Question 14:
Solution 14:
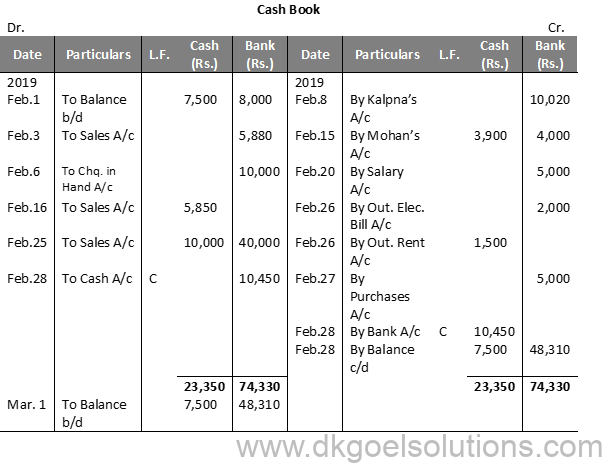
Calculation of Cash Deposit into Bank:- Cash deposit into bank = Bal. of cash column of Debit side – Total of Cash Col. of Credit side + Cash Bal. Cash deposit into bank = 23,350—5,400-+-7,500 Cash deposit into bank = 23,350 – 12,900 Cash deposit into bank = 10,450
Question 15::
Solution 15:
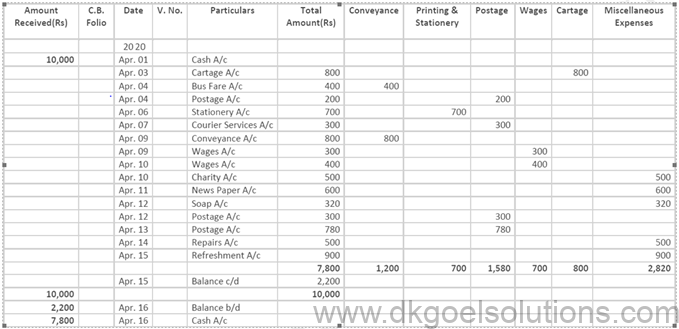
Point in mind DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 11 : – Petty Cash Book is the book that is used for the purpose of recording expenses involving petty amounts. Besides petty expenses, receipts from main cash are recorded. Petty Cash Book is prepared by Petty Cashier and acts as the Petty Cash Account.
Question 16:
Solution 16:

Working Note :- The imprest system of Petty Cash is explained below. Under this system, an estimate is made of amount required for petty expenses for a certain period (say for a week, a fortnight or a month).
Question 17:
Solution 17:

Point in mind :- Petty Cash Book is the book which is used for the purpose of recording expenses involving petty amounts. Besides petty expenses, receipts from main cash are recorded. Petty Cash Book is prepared by Petty Cashier and acts as the Petty Cash Account.
Question 18:
Solution 18:

Question 19:
Solution 19:
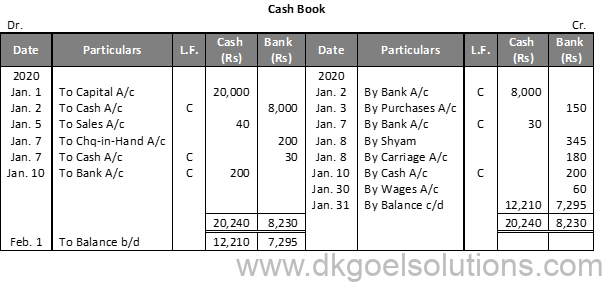
Question 20:
Solution 20:
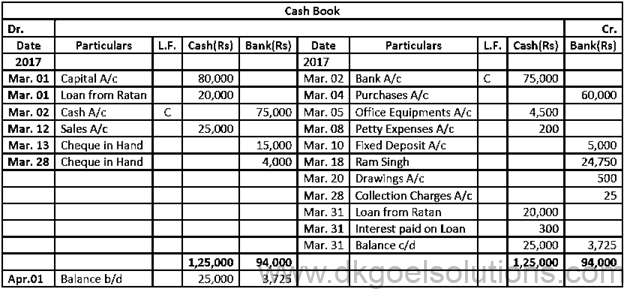
Calculation of interest on loan:- Time for loan = 1 Month Rate on Interest = 18% Interest on Loan = Rs. 20,000 × 1/12 × 18/100 Interest on Loan = Rs. 300
Question 21:
Solution 21:
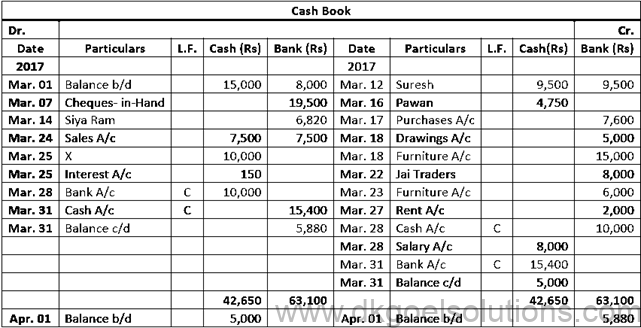
Calculation of Cash Deposit into Bank:- Cash deposit into bank = Bal. of cash column of Dr. side – Total of Cash Column of Cr. side + Cash Bal. Cash deposit into bank = 42,650 – 22,250 + 5,000 Cash deposit into bank = 42,650 – 27,250 Cash deposit into bank = 15,400
Question 22:
Solution 22:

Calculation of Cash Deposit into Bank:- Cash deposit into bank = Bal. of cash column of Dr. side – Total of Cash Column of Cr. side-+-Cash Bal. Cash deposit into bank = 42,650 – 22,250 + 5,000 Cash deposit into bank = 42,650 – 27,250 Cash deposit into bank = 15,400
Question 23:
Solution 23:

Question 24:
Solution 24:
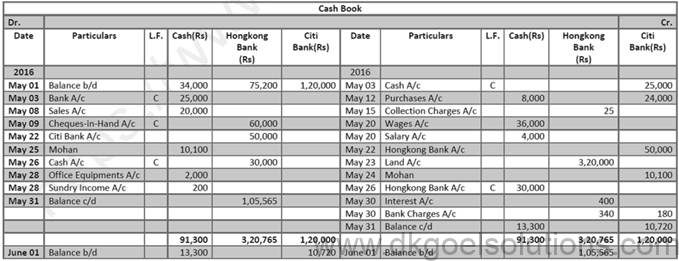
Working Note ( DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 11 ) :-

Question 25:
Solution 25:

Question 26:
Solution 26:
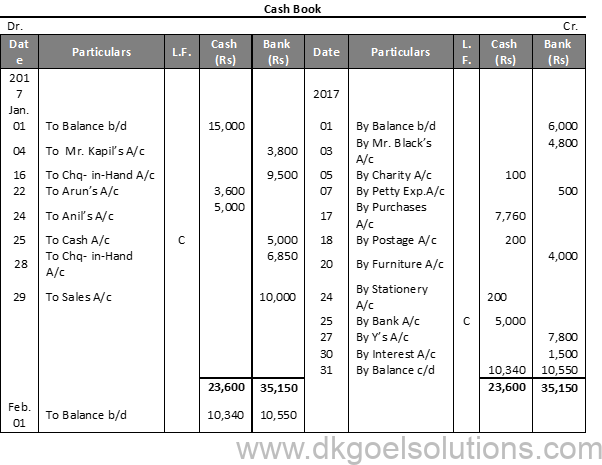
Question 27:
Solution 27:
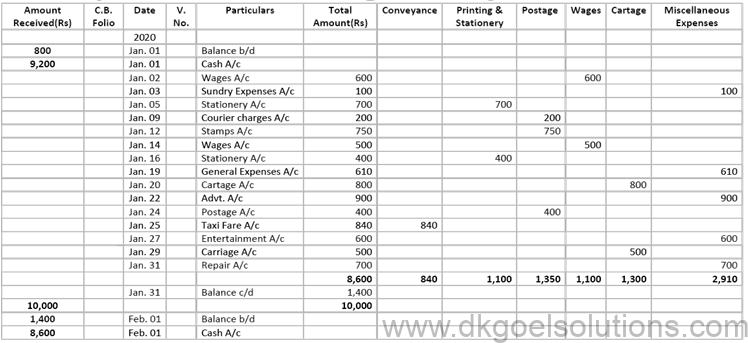
Working Note:- The imprest system of Petty Cash is explained below. Under this system, an estimate is made of amount required for petty expenses for a certain period (say for a week, a fortnight or a month).
Question 28:
Solution 28:
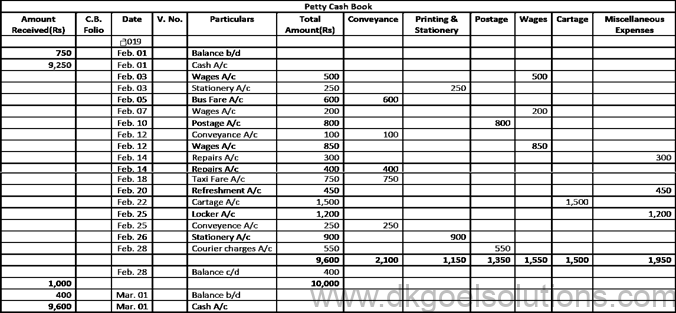
Question 29:
Solution 29;

Working Note :- The Petty Cash imprint scheme is discussed below. Under this method, the amount needed for minor expenditures for a certain time is determined (say for a week, a fortnight or a month). At the beginning of an era, the amount so calculated is issued to the petty cashier and the amount charged by him during the period is repaid.

As explained in DK Goel Solutions class 11 Chapter 11, cash book is a financial record holder which amalgamates all the cash receipts and disbursements, highlighting the financial transactions in cash. After the financial cash transactions are recorded in the cash book, they are added to the ledger. Only the bank-related and cash transactions are added to the cash book, and a cash book always highlights the debit balance.
Cash Book is considered to have dual nature being both journal and ledger, as it records all the business transactions relating to cash payments and cash receipts. It is one of the most crucial accounting books maintained by every company. A cash book is multi-functional as it acts as both ledger and books of original entry. A cashbook eliminates the need for a cash account for all organizations.
Contra Entry is a type of entry that affects both bank accounts and cash. In simple words, it defines any financial transaction involving the transfer of cash from a cash account to another bank account or from a cash account to another cash account, or from a bank account to another bank account.
A cash book is a written record of all the financial transactions relating to cash or banks arranged in a specific sequence. In contrast, a cash account is a form of a ledger account that depicts the day-to-day transactions of an organization.
Petty cash book is one of the popular accounting books utilized to record all the minor expenses. For instance, daily wages, stationery, postage and handling, and much more. These types of cash books are usually designed and handled by petty cashiers.
Here are the notable similarities between Cash Books and Journals – ● Identical to the journal, in the cash book, all the entries are arranged in chronological format according to the date and time of the transaction. ● Similar to the journals, the data from the cash books flows to the ledger. ● Cash Books also includes a ledger folio column, just like journals.

- Udaan Programs
- Udaan Webinar
- IBPS SO LAW
- Civil Judge (Pre+Mains)
- Hotel Management
- CAT & OMETs
- Jaipur [Bapu Nagar]
- Jaipur [Vaishali Nagar]
- Jaipur [JLN Marg]
- Delhi (South Extension)
- Delhi (Pitampura)
- Delhi (CP Center)
- Delhi (Dwarka)
- Gurugram (Sector 27)
- Gurugram (Sector 50)
- Mumbai (Andheri)
- Mumbai (Navi Mumbai)
- Mumbai (Thane)
- Chandigarh Sector 36D
- Chandigarh Sector 8C
- Lucknow Hazratganj
- Lucknow Aliganj
- Jaipur (Bapu Nagar)
- Jaipur (Vaishali Nagar)
- Gurugram (Sector 14)
- Chandigarh 36D Sector
- Chandigarh 8C Sector
- Jaipur[Vaishali Nagar]
- Navi Mumbai
- Lucknow [Aliganj]
- Lucknow [Hazratganj]
- CUET Law 2024
- IPMAT Indore
- IPMAT Rohtak
- Christ University
- St. Xaviers
- Judiciary Study Material
- Chhattisgarh (CGPSC)
- Haryana (HJS)
- Uttar Pradesh (UP PCSJ)
- Rajasthan (RJS)
- Madhya Pradesh [MP]
- Delhi [DJS]
- Bihar [BPSC]
- Uttarakhand [UKPSC]
- Jharkhand [JKPSC]
- Himachal Pradesh [HPPSC]
- LegalEdge AISAT
- LegalEdge IST
- Judiciary Gold AIJSAT
- Judiciary Gold IST
- SuperGrads IPM AISAT
- SuperGrads IPM IST
- Supergrads CUET AISAT
- SuperGrads CUET IST
- SuperGrads CAT
- Creative Edge
- LegalEdge AIOM
- SuperGrads AICUET
- Judiciary AIOMC
- Supergrads IPM AIOM
- CreativEdge AIOM
Free Videos
- CLAT Free Videos
- UGC NET LAW
- RBI Grade B
- Uttarakhand
- Judiciary Notes
- Judiciary Videos
- KAUN BANEGA JUDGE
- Daily Current Affairs
- Weekly Current Affairs
- Monthly Current Affairs
- LegalEdge UG
- SuperGrads Webinar
- SuperGrads CUET Webinar
- Creative Edge Webinar
- Judiciary (Beginners)
- UDAAN Webinar
- Law School Blogs
- LAW Entrances
- Management Entrances
- CUET Exam [UG & PG]
- Design & Architecture
- LAW & Judiciary
- Management Exams
- CUET Exams [UG & PG]
- Design & Architecture Exams
Bank Reconciliation Statement Accounts Class 11 Questions With Solutions
Author : Palak Khanna
Updated On : September 15, 2023
Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS) is a statement that is prepared to reconcile the difference between the bank balance shown by the cash book and bank passbook. This chapter holds a weightage of 6 marks out of 80 marks in the class 11 accountancy exam.
To help you better understand the Bank Reconciliation Statement Accounts Class 11 chapter, we have provided differences between cash book and pass book, important questions, and more in this post.
Causes for Difference Between Cash Book and Pass Book
The difference between cash book and pass book may arise due to the following reasons:
- Transactions are recorded in the cash book but not in the passbook
- Transactions are recorded in the passbook but not in the cashbook
- Differences caused by errors committed in recording transactions like transactions recorded twice in the cashbook/passbook, direct payments by the bank, bills collected by the bank on behalf of the customer, etc
Download Free Study Material and Class 11 Commerce Notes
Bank Reconciliation Questions for Class 11 2023
To help you get an idea about the type of questions that will be asked in the exam, we have provided some Class 11 Accountancy Importnat Questions for Bank Reconciliation here.
Q1. State the need for the preparation of a bank reconciliation statement.
Ans: Preparing a bank reconciliation statement is necessary for:
- Helps in identifying the difference between a cash book and a passbook.
- It helps in knowing the actual bank balance.
- Helps in the detection and prevention of frauds and errors in recording banking transactions
- Helps to create a revised Cash Book that reflects true bank balance.
- It helps in preventing the embezzlement of money from the bank account.
Q2. What is a bank overdraft?
Ans: Bank overdraft is created when there is a withdrawal, which is over the bank balance available in the account. It is an obligation to the account holder.
Q3. Briefly explain the statement ‘wrongly debited by the bank’ with the help of an example.
Ans: It means that the bank has debited the amount from the user's account for some invalid reason. The following instance can help in understanding.
Rajesh’s account is charged an overdraft of Rs.5000 even though his account has a sufficient credit balance. It can happen when the cashier has done an incorrect entry into the account.
Read Also - Class 11 Commerce Syllabus
Q4. State the causes of difference that occurred due to time lag.
Ans: The following are the causes of difference that occurred due to time lag
- The cheque issued by the firm is not yet presented for payment.
- The cheque was deposited into the bank but is yet to be realized.
- Direct debits did by the bank on behalf of the customer.
- The amount is deposited directly into the bank account.
- Interest and dividends that are not collected by the bank.
- Direct payments made by the bank on behalf of the customers
- Cheques that are deposited or bills discounted which is dishonored
Q5. Briefly explain the term favorable balance as per cash book
Ans: When the total of the debit column of the Cash Book is more than the total credit column of the Cash Book, it is known as a debit balance or favorable balance. A favorable balance is an asset to an account holder. A favorable balance can also be defined as a surplus of deposits over withdrawals.
Check Out - Class 11 Commerce Question Papers
Q6. Enumerate the steps to ascertain the correct cash book balance.
Ans: The difference between the cash book and passbook can arise due to some transactions that are recorded in the passbook not being present in the cash book. This can be rectified by recording those transactions in the cash book. The balance thus obtained is called an adjusted balance or amended balance. The following steps describe this process.
- 1. Note bank balance as per cash book.
- 2: Make corrections for errors committed in the cash book.
- 3: Transactions present only on the passbook’s credit side must be updated on the debit side of the cashbook
- 4. Transactions present only on the passbook’s debit side must be updated on the debit side of the cashbook
- 5: Calculate the new cash book balance and use it to prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement.
Q7. Explain the process of preparing a bank reconciliation statement with an amended cash balance.
Ans: The difference between the cash book and passbook can arise due to some transactions that are recorded in the passbook not being present in the cash book. This can be rectified by recording those transactions in the cash book. The balance thus obtained is called an adjusted balance or amended balance. The following steps describe this process.
- Note bank balance as per cash book.
- Make corrections for errors committed in the cash book.
- Transactions present only on the passbook’s credit side must be updated on the debit side of the cashbook
- Transactions present only on the passbook’s debit side must be updated on the debit side of the cashbook
- Calculate the new cash book balance and use it to prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement.
Q8. What is a bank reconciliation statement? Why is it prepared?
Ans: A statement that is prepared to rectify or tally the difference that exists between the user passbook and the cashbook of the firm, so that the cause of the difference can be determined and rectified is known as Bank Reconciliation Statement. Following are the reasons for its preparation:
- To determine if the balance reported by the company’s cashbook is the correct amount.
- Rectifying any errors present in the cash book so that proper statements can be generated.
- Prevents fraudulent activities like embezzlement and improves accountability.
- To discover any errors made by the bank and apply corrective measures.
- Helps check the accuracy of information recorded in both books.
Numerical Questions and Solutions for BRS Accounts Class 11 2022
Solving previous year's Class 11 Accountancy Sample Papers will help you know the difficulty level and the type of questions that were asked in the exam. The following are some of the numerical questions for the Bank Reconciliation Statement of class 11 accountancy. Go through the commonly asked BRS questions and enhance your preparation for the upcoming exam.
Q1. From the following particulars, prepare a bank reconciliation statement as of March 31, 2017.
(i) Balance as per cash book ₹ 3,200
(ii) Cheque issued but not presented for payment ₹ 1,800
(iii) Cheque deposited but not collected up to March 31, 2017, ₹ 2,000
(iv) Bank charges debited by bank ₹ 150
Ans: The reconciliation statement is shown below:
Q2. On March 31 2017 the cash book showed a balance of ₹ 3,700 as cash at the bank, but the bank passbook made up to the same date showed that cheques for ₹ 700, ₹ 300, and ₹ 180 respectively had not been presented for payment, Also, cheque amounting to ₹ 1,200 deposited into the account had not been credited. Prepare a bank reconciliation statement.

The balance as per pass book as of 31st March is ₹3, 680
Q3. The cash book shows a bank balance of ₹ 7,800. On comparing the cash book with the passbook the following discrepancies were noted:
(a)Cheque deposited in the bank but not credited ₹ 3,000
(b)Cheque issued but not yet present for payment ₹ 1,500
(c)Insurance premium paid by the bank ₹ 2,000
(d)Bank interest credit by the bank ₹ 400
(e)Bank charges ₹ 100
(d)Directly deposited by a customer ₹ 4,000
Ans: The bank reconciliation statement is shown below:
Q4. Bank balance of ₹ 40,000 showed in the cash book of Atul on December 31, 2016. It was found that three cheques of ₹ 2,000, ₹ 5,000, and ₹ 8,000 deposited during the month of December were not credited in the passbook till January 02, 2017. Two cheques of ₹ 7,000 and ₹ 8,000 issued on December 28, were not presented for payment till January 03, 2017. In addition to it, bank had credited Atul for ₹ 325 as interest and had debited him with ₹ 50 as bank charges for which there were no corresponding entries in the cash book.
Prepare a bank reconciliation statement as of December 31, 2016.
Ans: The bank reconciliation statement is shown below:

Q5. On comparing the cash book with the passbook of Naman it is found that on March 31, 2017, the bank balance of ₹ 40,960 shown by the cash book differs from the bank balance with regard to the following:
(a) Bank charges ₹ 100 on March 31, 2017, are not entered in the cash book.
(b) On March 21, 2017, a debtor paid ₹ 2,000 into the company’s bank in settlement of his account, but no entry was made in the cash book of the company in respect of this.
(c) Cheques totaling ₹ 12,980 were issued by the company and duly recorded in the cash book before March 31, 2017, but had not been presented at the bank for payment until after that date.
(d) A bill for ₹ 6,900 discounted with the bank is entered in the cash book with a recording of the discount charge of ₹ 800.
(e) ₹ 3,520 is entered in the cash book as paid into the bank on March 31st, 2017, but not credited by the bank until the following day.
(f) No entry has been made in the cash book to record the dishonor or on March 15, 2017, of a cheque for ₹ 650 received from Bhanu.
Prepare a reconciliation statement as of March 31, 2017.
Ans: The reconciliation statement is shown below:
Get CUET Study Materials
Fill your details
Recently Published
JEE Main Paper 2 Answer Key 2024
Updated On : May 15, 2024
Quadratic Equation Questions for DU JAT and IPMAT 2025
Updated On : May 14, 2024
Number Theory Questions for IPMAT 2025 Preparation
Important CrPC Questions for Rajasthan Judiciary Exam 2024
Current Affairs Preparation Tips for Bihar Judiciary Exam 2024
Frequently Asked Questions
Which are the best books to study for Class 11 accountancy?

What is the best preparation strategy for accountancy?
Will there be practical problems in the exam?
What is the most important thing for problem based questions?
How can I better prepare for Class 11th Accountancy syllabus?
How many chapters are there in Class 11 Accountancy subject?
How many units are there in Class 11 Accountancy Syllabus?
September 15, 2023
Online Coaching
Test Series
Trending Exams
- Architecture
- Career Counselling
Scholarship Tests
- Judiciary Gold
- Supergrads IPM
- SuperGrads CUET
- LegalEdge After College
Mentor Tips
- CLAT Prep Tips
- AILET Prep Tips
- IPMAT Prep Tips
- NATA Prep Tips
- NID Prep Tips
- Judiciary Prep Tips
- CAT Prep Tips
ABOUT TOP RANKERS
Toprankers, launched in 2016, is India’s most preferred digital counselling & preparation platform for careers beyond engineering & medicine. We envision to build awareness and increase the success rate for lucrative career options after 12th. We offer best learning practices and end-to-end support to every student preparing for management, humanities, law, judiciary & design entrances.
: +91-7676564400
Social Channels

Recording of Transactions – II – Simple Cash Book Solutions

myCBSEguide
- Accountancy
- CBSE Class 11 Accountancy...
CBSE Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 5 Practice Questions
Mycbseguide app.
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
CBSE Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 5 Practice Questions. myCBSEguide has just released Chapter Wise Question Answers for class 11. Accountancy is the process of communicating financial information about a business entity to users such as shareholders and managers. Accountancy describes the duties of an accountant, the person whose job is to keep, inspect and interpret financial accounts. There chapter wise Practice Questions with complete solutions are available for download in myCBSEguide website and mobile app. These Question with solution are prepared by our team of expert teachers who are teaching grade in CBSE schools for years. There are around 4-5 set of solved Accountancy Extra questions from each and every chapter. The students will not miss any concept in these Chapter wise question that are specially designed to tackle Exam. We have taken care of every single concept given in CBSE Class 11 Accountancy syllabus and questions are framed as per the latest marking scheme and blue print issued by CBSE for class 11.
Class 11 Accountancy Extra Questions
Download as PDF
Bank Reconciliation Statement Class 11 Accountancy
Ch-5 Bank Reconciliation Statement
- What does favourable balance in passbook indicate?
- What is meant by debit balance in pass book?
- What does unfavourable balance in pass book indicate?
- Briefly explain the statement ‘wrongly debited by the bank’ with the help of an example.
- Cheques were paid into the Bank in March but were credited in April. P – Rs.3,500, Q – Rs.2,500. R – Rs.2,000
- Cheques issued in March were Presented in April X – Rs.4,000, Q – Rs.4,500
- Cheque for Rs.1,000 received from a customer entered in the cash book but was not banked
- Passbook shows a debt of Rs.1,000 for bank charges and credit of Rs.2,000 as interest
- Interest on investment Rs.2,500 collected by the bank appeared in the passbook. Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement the balance as per cash book on 31 March 2018.
- R’s overdraft as per the Pass Book Rs.12,000 as on 31st March
- On 30th March, Cheques had been issued for Rs.70,000 of which cheques worth Rs.3,000 only had been encashed up to 31st March.
- Cheques amounting to Rs.3,500 had been paid into the bank for collection but of this only Rs.500 had been credited in the Pass Book.
- Bank has charged Rs.500 as interest on overdraft and the intimation of which has been received on 2nd April 2018.
- Bank Pass Book shows credit for Rs.1,000 representing Rs.400 Paid by debtor of R direct into the Bank and Rs.600 collected directly by Bank in respect of interest on R’s investment. R had no knowledge of these items.
- A cheque for Rs.200 has been debited in bank column of Cash Book by R, but it was not sent to Bank at all.
Additional Information
- The debit side of the cash book (bank column) has been undercast by Rs 500.
- A cheque of Rs 200 paid to a creditor has been entered by mistake in the cash column.
- Bank charges Rs 80 have not been entered in the cash book.
- Rs 64 as premium on the life policy according to standing instructions.
- Rs 400 against a pro-note, as per instructions.
- The bank Balance as per Cash Book on 31st March 2018 Rs.40,000
- Cheques issued but not encashed up to 31st March 2018 amounted to Rs.10,000
- Cheques paid into the bank but not cleared up to 31st March 2018 amounted to Rs.15,000
- Interest on Investments collected by the bank but not entered in the Cash Book Rs.500
- Cheques deposited in the bank but not entered in Cash Book Rs.12,500
- Bank charges debited in Pass book but not entered in Cash Book Rs.100
- Favourable balance in the passbook indicates the actual amount customer has in its account i.e. the Credit balance.
- Debit balance in pass book indicates the overdraft i.e. the amount customer has withdrawn over the excess of amount deposited.
- Unfavourable balance as per pass book means the Debit balance as per passbook.
- Wrongly debited by the bank is an error done by the bank which means that bank has deducted wrong amount from the account which can be better understood withg the following example:-When a firm issued a cheque of Rs 1,500 to any of its creditor and it is presented for payment and paid by the bank but in place of Rs 1,500 bank debited it wrongly by Rs 15,000. The above error may be opposite too but in every situation, the balance of cash book and pass book will not tally. The term will be used for it will be wrongly debited by the bank, it generally happens at the time of posting the transaction.
BANK RECONCILIATION STATEMENT as on March 31, 2018
BANK RECONCILIATION STATEMENT as on 31st March, 2018
Bank Reconciliation Statement as on 30th Sep., 2016
BANK RECONCILIATION STATEMENT
Bank Reconciliation Statement as on 30th June, 2013
(a) BANK RECONCILIATION STATEMENT as on March 31, 2018 WITHOUT ADJUSTING CASH BOOK
(b) BANK RECONCILIATION STATEMENT ADJUSTING CASH BOOK as on March 31, 2018
AMENDED CASH BOOK (BANK COLUMN ONLY)
Class 11 Accountancy Chapter Wise Important Questions
- Introduction to accounting
- Theory Base of Accounting
- Recording of Transactions -I Vouchers, Journals & Ledgers
- Recording of Transactions -II Cash Books & other Books
- Bank Reconciliation Statement
- Depreciation Provisions and Reserves
- Bill of Exchange
- Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors
- Financial Statements -I Sole Proprietorship
- Financial Statements -II Adjustments
- Accounts from Incomplete Records
- Computers in Accounting
- Computerised Accounting System
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Class 11 Accountancy Computers in Accounting Important Questions
- CBSE Class 11 Chapter 11 Accountancy Extra Questions
- Chapter 10 Accountancy Class 11 Important Questions
- CBSE Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 9 Important Questions
- Class 11 Accountancy Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors Extra Questions
- Bill of Exchange Extra Questions of Class 11 Accountancy
- Important Questions of Class 11 Depreciation Provisions and Reserves Accountancy
- Recording of Transactions – II Extra Questions of Class 11 Accountancy
1 thought on “CBSE Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 5 Practice Questions”
very thank you for your qustion and answer.
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Example 11. Triple Columns Cash Book (Cash, Bank and Discount Columns) The following transactions are the transactions of Karun: Baisakh-1 Commenced a business with cash of Rs 100,000. Baisakh-3 Deposited into the bank Rs 80,000. Baisakh-6 Sold goods to Mr. KK for Rs 5,000 and received cash after 5% discount.
Step 3: Enter the name of the account as 'Machinery Account' (which is debited in the entry) in the 'Particulars' column in the credit side of the 'Machinery Account'. Step 4: Enter the page number of the journal where the entry is recorded in the 'J.F.' (journal folio) column.
Petty Cash Book - Numerical Problems. 11. Prepare petty cash book from the following transactions. The imprest amount is ₹ 2,000. Watch Video🎥. 12. Record the following transactions during the week ending Dec.30, 2014 2017 with a weekly imprest ₹ 500. Watch Video🎥. You might also want to refer the following pages.
Short Answers for NCERT Accountancy Solutions Class 11 Chapter 4. 1. Briefly state how the cash book is both journal and a ledger. A cash book functions as a journal because it is the original book of entries where all transactions are first recorded, just like a journal, and it functions as a ledger, as it records the credit and debit cash ...
Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 7 - Special Purpose Books 1 Cash Book. TS Grewal Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 7 - Special Purpose Books 1 Cash Book is a concept that students should consider while preparing for their Accountancy exam. Here, are few solutions rendered in a simple and a stepwise method.
Recording of transactions 2 notes is considered as a method of managing accounting transactions in different books of accounts. The recording of transactions class 11 notes executes the use of journal book, cash book and ledger accounts. The class 11 accountancy chapter 4 notes present a complete outline of the chapter.
DK Goel Accountancy Class 11 Solutions Chapter 11 Books of Original Entry - Cash Book which is outlined by expert Accountancy teachers from the latest version of DK Goel Class 11 Accountancy books. We at BYJU'S provide DK Goel Solutions to assist students to comprehend all the theories in particular. There are numerous concepts in ...
Solution 15: Point in mind DK Goel Solutions Class 11 Chapter 11:-. Petty Cash Book is the book that is used for the purpose of recording expenses involving petty amounts. Besides petty expenses, receipts from main cash are recorded. Petty Cash Book is prepared by Petty Cashier and acts as the Petty Cash Account.
CBSE Class 11 Accountancy - Cash Book - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Account cbse class 11th assignment
Class XI/ Accountancy/ 1 CONTENTS S.No Contents Page Number A. Design of the Question Paper 2 B. Learning Objectives, Methodology And Syllabus 3 C. Flashback Assignments: 1 Meaning And Objectives Of Accounting 7 2 Basic Accounting Terms 8 3 Accounting Principles 9 4 Accounting Equation 11 5 Journals 13 6 Cash Book 14
Class 11 Accountancy Bank Reconciliation Statement Solutions with questions. Check important topics & syllabus. ... On March 31 2017 the cash book showed a balance of ₹ 3,700 as cash at the bank, but the bank passbook made up to the same date showed that cheques for ₹ 700, ₹ 300, and ₹ 180 respectively had not been presented for payment ...
1. Enter the following transactions in a simple cash book for December 2016: Watch Video🎥. Cr. 2. Record the following transaction in simple cash book for November 2016: Watch Video🎥. Note: As November has only 30 days, in the solution, the date for the last transaction i.e. Paid Salary, is considered as 30 November instead of the 31 ...
Install Now. CBSE Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 5 Practice Questions. myCBSEguide has just released Chapter Wise Question Answers for class 11. Accountancy is the process of communicating financial information about a business entity to users such as shareholders and managers. Accountancy describes the duties of an accountant, the person whose ...
TS Grewal Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 7 - Special Purpose Books 1 Cash Book is a concept that students should consider while preparing for their Accountancy exam. Here are a few solutions rendered in a simple and stepwise method. Class 11 TS Grewal Solutions Accountancy Chapter 7:- Download PDF Here.
Short Answers to NCERT Accountancy Solutions Class 11 Chapter 5. 1. State the need for the preparation of a bank reconciliation statement. Preparing a bank reconciliation statement is necessary for the following reasons: It helps in identifying the difference between cash books and pass books. It helps in knowing the actual bank balance.
Assignment of PUC 11, Accountancy Double Column ,petty Cash Book - Study Material. Assignment of PUC 11, Accountancy Double Column ,petty Cash Book - Study Material ... class-11th. Accountancy. 0 Likes. 1051 Views. Copied to clipboard N. Naveen Ritti. Feb 20, 2022. Homework. Recording Transactions II
Advantages of Cash Book. Cash book offers the following advantages: 1.It offers easy verification of cash by matching the balance in the cash book with actual cash in hand and is therefore helpful in identifying mistakes in the entry. 2.It helps in creating a regular record of transactions date wise for the convenience of accounting personnel.