Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.

Eight Instructional Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking

- Share article
(This is the first post in a three-part series.)
The new question-of-the-week is:
What is critical thinking and how can we integrate it into the classroom?
This three-part series will explore what critical thinking is, if it can be specifically taught and, if so, how can teachers do so in their classrooms.
Today’s guests are Dara Laws Savage, Patrick Brown, Meg Riordan, Ph.D., and Dr. PJ Caposey. Dara, Patrick, and Meg were also guests on my 10-minute BAM! Radio Show . You can also find a list of, and links to, previous shows here.
You might also be interested in The Best Resources On Teaching & Learning Critical Thinking In The Classroom .
Current Events
Dara Laws Savage is an English teacher at the Early College High School at Delaware State University, where she serves as a teacher and instructional coach and lead mentor. Dara has been teaching for 25 years (career preparation, English, photography, yearbook, newspaper, and graphic design) and has presented nationally on project-based learning and technology integration:
There is so much going on right now and there is an overload of information for us to process. Did you ever stop to think how our students are processing current events? They see news feeds, hear news reports, and scan photos and posts, but are they truly thinking about what they are hearing and seeing?
I tell my students that my job is not to give them answers but to teach them how to think about what they read and hear. So what is critical thinking and how can we integrate it into the classroom? There are just as many definitions of critical thinking as there are people trying to define it. However, the Critical Think Consortium focuses on the tools to create a thinking-based classroom rather than a definition: “Shape the climate to support thinking, create opportunities for thinking, build capacity to think, provide guidance to inform thinking.” Using these four criteria and pairing them with current events, teachers easily create learning spaces that thrive on thinking and keep students engaged.
One successful technique I use is the FIRE Write. Students are given a quote, a paragraph, an excerpt, or a photo from the headlines. Students are asked to F ocus and respond to the selection for three minutes. Next, students are asked to I dentify a phrase or section of the photo and write for two minutes. Third, students are asked to R eframe their response around a specific word, phrase, or section within their previous selection. Finally, students E xchange their thoughts with a classmate. Within the exchange, students also talk about how the selection connects to what we are covering in class.
There was a controversial Pepsi ad in 2017 involving Kylie Jenner and a protest with a police presence. The imagery in the photo was strikingly similar to a photo that went viral with a young lady standing opposite a police line. Using that image from a current event engaged my students and gave them the opportunity to critically think about events of the time.
Here are the two photos and a student response:
F - Focus on both photos and respond for three minutes
In the first picture, you see a strong and courageous black female, bravely standing in front of two officers in protest. She is risking her life to do so. Iesha Evans is simply proving to the world she does NOT mean less because she is black … and yet officers are there to stop her. She did not step down. In the picture below, you see Kendall Jenner handing a police officer a Pepsi. Maybe this wouldn’t be a big deal, except this was Pepsi’s weak, pathetic, and outrageous excuse of a commercial that belittles the whole movement of people fighting for their lives.
I - Identify a word or phrase, underline it, then write about it for two minutes
A white, privileged female in place of a fighting black woman was asking for trouble. A struggle we are continuously fighting every day, and they make a mockery of it. “I know what will work! Here Mr. Police Officer! Drink some Pepsi!” As if. Pepsi made a fool of themselves, and now their already dwindling fan base continues to ever shrink smaller.
R - Reframe your thoughts by choosing a different word, then write about that for one minute
You don’t know privilege until it’s gone. You don’t know privilege while it’s there—but you can and will be made accountable and aware. Don’t use it for evil. You are not stupid. Use it to do something. Kendall could’ve NOT done the commercial. Kendall could’ve released another commercial standing behind a black woman. Anything!
Exchange - Remember to discuss how this connects to our school song project and our previous discussions?
This connects two ways - 1) We want to convey a strong message. Be powerful. Show who we are. And Pepsi definitely tried. … Which leads to the second connection. 2) Not mess up and offend anyone, as had the one alma mater had been linked to black minstrels. We want to be amazing, but we have to be smart and careful and make sure we include everyone who goes to our school and everyone who may go to our school.
As a final step, students read and annotate the full article and compare it to their initial response.
Using current events and critical-thinking strategies like FIRE writing helps create a learning space where thinking is the goal rather than a score on a multiple-choice assessment. Critical-thinking skills can cross over to any of students’ other courses and into life outside the classroom. After all, we as teachers want to help the whole student be successful, and critical thinking is an important part of navigating life after they leave our classrooms.

‘Before-Explore-Explain’
Patrick Brown is the executive director of STEM and CTE for the Fort Zumwalt school district in Missouri and an experienced educator and author :
Planning for critical thinking focuses on teaching the most crucial science concepts, practices, and logical-thinking skills as well as the best use of instructional time. One way to ensure that lessons maintain a focus on critical thinking is to focus on the instructional sequence used to teach.
Explore-before-explain teaching is all about promoting critical thinking for learners to better prepare students for the reality of their world. What having an explore-before-explain mindset means is that in our planning, we prioritize giving students firsthand experiences with data, allow students to construct evidence-based claims that focus on conceptual understanding, and challenge students to discuss and think about the why behind phenomena.
Just think of the critical thinking that has to occur for students to construct a scientific claim. 1) They need the opportunity to collect data, analyze it, and determine how to make sense of what the data may mean. 2) With data in hand, students can begin thinking about the validity and reliability of their experience and information collected. 3) They can consider what differences, if any, they might have if they completed the investigation again. 4) They can scrutinize outlying data points for they may be an artifact of a true difference that merits further exploration of a misstep in the procedure, measuring device, or measurement. All of these intellectual activities help them form more robust understanding and are evidence of their critical thinking.
In explore-before-explain teaching, all of these hard critical-thinking tasks come before teacher explanations of content. Whether we use discovery experiences, problem-based learning, and or inquiry-based activities, strategies that are geared toward helping students construct understanding promote critical thinking because students learn content by doing the practices valued in the field to generate knowledge.

An Issue of Equity
Meg Riordan, Ph.D., is the chief learning officer at The Possible Project, an out-of-school program that collaborates with youth to build entrepreneurial skills and mindsets and provides pathways to careers and long-term economic prosperity. She has been in the field of education for over 25 years as a middle and high school teacher, school coach, college professor, regional director of N.Y.C. Outward Bound Schools, and director of external research with EL Education:
Although critical thinking often defies straightforward definition, most in the education field agree it consists of several components: reasoning, problem-solving, and decisionmaking, plus analysis and evaluation of information, such that multiple sides of an issue can be explored. It also includes dispositions and “the willingness to apply critical-thinking principles, rather than fall back on existing unexamined beliefs, or simply believe what you’re told by authority figures.”
Despite variation in definitions, critical thinking is nonetheless promoted as an essential outcome of students’ learning—we want to see students and adults demonstrate it across all fields, professions, and in their personal lives. Yet there is simultaneously a rationing of opportunities in schools for students of color, students from under-resourced communities, and other historically marginalized groups to deeply learn and practice critical thinking.
For example, many of our most underserved students often spend class time filling out worksheets, promoting high compliance but low engagement, inquiry, critical thinking, or creation of new ideas. At a time in our world when college and careers are critical for participation in society and the global, knowledge-based economy, far too many students struggle within classrooms and schools that reinforce low-expectations and inequity.
If educators aim to prepare all students for an ever-evolving marketplace and develop skills that will be valued no matter what tomorrow’s jobs are, then we must move critical thinking to the forefront of classroom experiences. And educators must design learning to cultivate it.
So, what does that really look like?
Unpack and define critical thinking
To understand critical thinking, educators need to first unpack and define its components. What exactly are we looking for when we speak about reasoning or exploring multiple perspectives on an issue? How does problem-solving show up in English, math, science, art, or other disciplines—and how is it assessed? At Two Rivers, an EL Education school, the faculty identified five constructs of critical thinking, defined each, and created rubrics to generate a shared picture of quality for teachers and students. The rubrics were then adapted across grade levels to indicate students’ learning progressions.
At Avenues World School, critical thinking is one of the Avenues World Elements and is an enduring outcome embedded in students’ early experiences through 12th grade. For instance, a kindergarten student may be expected to “identify cause and effect in familiar contexts,” while an 8th grader should demonstrate the ability to “seek out sufficient evidence before accepting a claim as true,” “identify bias in claims and evidence,” and “reconsider strongly held points of view in light of new evidence.”
When faculty and students embrace a common vision of what critical thinking looks and sounds like and how it is assessed, educators can then explicitly design learning experiences that call for students to employ critical-thinking skills. This kind of work must occur across all schools and programs, especially those serving large numbers of students of color. As Linda Darling-Hammond asserts , “Schools that serve large numbers of students of color are least likely to offer the kind of curriculum needed to ... help students attain the [critical-thinking] skills needed in a knowledge work economy. ”
So, what can it look like to create those kinds of learning experiences?
Designing experiences for critical thinking
After defining a shared understanding of “what” critical thinking is and “how” it shows up across multiple disciplines and grade levels, it is essential to create learning experiences that impel students to cultivate, practice, and apply these skills. There are several levers that offer pathways for teachers to promote critical thinking in lessons:
1.Choose Compelling Topics: Keep it relevant
A key Common Core State Standard asks for students to “write arguments to support claims in an analysis of substantive topics or texts using valid reasoning and relevant and sufficient evidence.” That might not sound exciting or culturally relevant. But a learning experience designed for a 12th grade humanities class engaged learners in a compelling topic— policing in America —to analyze and evaluate multiple texts (including primary sources) and share the reasoning for their perspectives through discussion and writing. Students grappled with ideas and their beliefs and employed deep critical-thinking skills to develop arguments for their claims. Embedding critical-thinking skills in curriculum that students care about and connect with can ignite powerful learning experiences.
2. Make Local Connections: Keep it real
At The Possible Project , an out-of-school-time program designed to promote entrepreneurial skills and mindsets, students in a recent summer online program (modified from in-person due to COVID-19) explored the impact of COVID-19 on their communities and local BIPOC-owned businesses. They learned interviewing skills through a partnership with Everyday Boston , conducted virtual interviews with entrepreneurs, evaluated information from their interviews and local data, and examined their previously held beliefs. They created blog posts and videos to reflect on their learning and consider how their mindsets had changed as a result of the experience. In this way, we can design powerful community-based learning and invite students into productive struggle with multiple perspectives.
3. Create Authentic Projects: Keep it rigorous
At Big Picture Learning schools, students engage in internship-based learning experiences as a central part of their schooling. Their school-based adviser and internship-based mentor support them in developing real-world projects that promote deeper learning and critical-thinking skills. Such authentic experiences teach “young people to be thinkers, to be curious, to get from curiosity to creation … and it helps students design a learning experience that answers their questions, [providing an] opportunity to communicate it to a larger audience—a major indicator of postsecondary success.” Even in a remote environment, we can design projects that ask more of students than rote memorization and that spark critical thinking.
Our call to action is this: As educators, we need to make opportunities for critical thinking available not only to the affluent or those fortunate enough to be placed in advanced courses. The tools are available, let’s use them. Let’s interrogate our current curriculum and design learning experiences that engage all students in real, relevant, and rigorous experiences that require critical thinking and prepare them for promising postsecondary pathways.

Critical Thinking & Student Engagement
Dr. PJ Caposey is an award-winning educator, keynote speaker, consultant, and author of seven books who currently serves as the superintendent of schools for the award-winning Meridian CUSD 223 in northwest Illinois. You can find PJ on most social-media platforms as MCUSDSupe:
When I start my keynote on student engagement, I invite two people up on stage and give them each five paper balls to shoot at a garbage can also conveniently placed on stage. Contestant One shoots their shot, and the audience gives approval. Four out of 5 is a heckuva score. Then just before Contestant Two shoots, I blindfold them and start moving the garbage can back and forth. I usually try to ensure that they can at least make one of their shots. Nobody is successful in this unfair environment.
I thank them and send them back to their seats and then explain that this little activity was akin to student engagement. While we all know we want student engagement, we are shooting at different targets. More importantly, for teachers, it is near impossible for them to hit a target that is moving and that they cannot see.
Within the world of education and particularly as educational leaders, we have failed to simplify what student engagement looks like, and it is impossible to define or articulate what student engagement looks like if we cannot clearly articulate what critical thinking is and looks like in a classroom. Because, simply, without critical thought, there is no engagement.
The good news here is that critical thought has been defined and placed into taxonomies for decades already. This is not something new and not something that needs to be redefined. I am a Bloom’s person, but there is nothing wrong with DOK or some of the other taxonomies, either. To be precise, I am a huge fan of Daggett’s Rigor and Relevance Framework. I have used that as a core element of my practice for years, and it has shaped who I am as an instructional leader.
So, in order to explain critical thought, a teacher or a leader must familiarize themselves with these tried and true taxonomies. Easy, right? Yes, sort of. The issue is not understanding what critical thought is; it is the ability to integrate it into the classrooms. In order to do so, there are a four key steps every educator must take.
- Integrating critical thought/rigor into a lesson does not happen by chance, it happens by design. Planning for critical thought and engagement is much different from planning for a traditional lesson. In order to plan for kids to think critically, you have to provide a base of knowledge and excellent prompts to allow them to explore their own thinking in order to analyze, evaluate, or synthesize information.
- SIDE NOTE – Bloom’s verbs are a great way to start when writing objectives, but true planning will take you deeper than this.
QUESTIONING
- If the questions and prompts given in a classroom have correct answers or if the teacher ends up answering their own questions, the lesson will lack critical thought and rigor.
- Script five questions forcing higher-order thought prior to every lesson. Experienced teachers may not feel they need this, but it helps to create an effective habit.
- If lessons are rigorous and assessments are not, students will do well on their assessments, and that may not be an accurate representation of the knowledge and skills they have mastered. If lessons are easy and assessments are rigorous, the exact opposite will happen. When deciding to increase critical thought, it must happen in all three phases of the game: planning, instruction, and assessment.
TALK TIME / CONTROL
- To increase rigor, the teacher must DO LESS. This feels counterintuitive but is accurate. Rigorous lessons involving tons of critical thought must allow for students to work on their own, collaborate with peers, and connect their ideas. This cannot happen in a silent room except for the teacher talking. In order to increase rigor, decrease talk time and become comfortable with less control. Asking questions and giving prompts that lead to no true correct answer also means less control. This is a tough ask for some teachers. Explained differently, if you assign one assignment and get 30 very similar products, you have most likely assigned a low-rigor recipe. If you assign one assignment and get multiple varied products, then the students have had a chance to think deeply, and you have successfully integrated critical thought into your classroom.

Thanks to Dara, Patrick, Meg, and PJ for their contributions!
Please feel free to leave a comment with your reactions to the topic or directly to anything that has been said in this post.
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Education Week has published a collection of posts from this blog, along with new material, in an e-book form. It’s titled Classroom Management Q&As: Expert Strategies for Teaching .
Just a reminder; you can subscribe and receive updates from this blog via email (The RSS feed for this blog, and for all Ed Week articles, has been changed by the new redesign—new ones won’t be available until February). And if you missed any of the highlights from the first nine years of this blog, you can see a categorized list below.
- This Year’s Most Popular Q&A Posts
- Race & Racism in Schools
- School Closures & the Coronavirus Crisis
- Classroom-Management Advice
- Best Ways to Begin the School Year
- Best Ways to End the School Year
- Student Motivation & Social-Emotional Learning
- Implementing the Common Core
- Facing Gender Challenges in Education
- Teaching Social Studies
- Cooperative & Collaborative Learning
- Using Tech in the Classroom
- Student Voices
- Parent Engagement in Schools
- Teaching English-Language Learners
- Reading Instruction
- Writing Instruction
- Education Policy Issues
- Differentiating Instruction
- Math Instruction
- Science Instruction
- Advice for New Teachers
- Author Interviews
- Entering the Teaching Profession
- The Inclusive Classroom
- Learning & the Brain
- Administrator Leadership
- Teacher Leadership
- Relationships in Schools
- Professional Development
- Instructional Strategies
- Best of Classroom Q&A
- Professional Collaboration
- Classroom Organization
- Mistakes in Education
- Project-Based Learning
I am also creating a Twitter list including all contributors to this column .
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In


50 Super-Fun Critical Thinking Strategies to Use in Your Classroom
by AuthorAmy
Teaching students to be critical thinkers is perhaps the most important goal in education. All teachers, regardless of subject area, contribute to the process of teaching students to think for themselves. However, it’s not always an easy skill to teach. Students need guidance and practice with critical thinking strategies at every level.
One problem with teaching critical thinking is that many different definitions of this skill exist. The Foundation for Critical Thinking offers four different definitions of the concept. Essentially, critical thinking is the ability to evaluate information and decide what we think about that information, a cumulative portfolio of skills our students need to be successful problem solvers in an ever-changing world.
Here is a list of 50 classroom strategies for teachers to use to foster critical thinking among students of all ages.
1. Don’t give them the answers
Learning is supposed to be hard, and while it may be tempting to jump in and direct students to the right answer, it’s better to let them work through a problem on their own. A good teacher is a guide, not an answer key. The goal is to help students work at their “challenge” level, as opposed to their “frustration” level.
2. Controversial issue barometer
In this activity, a line is drawn down the center of the classroom. The middle represents the neutral ground, and the ends of the line represent extremes of an issue. The teacher selects an issue and students space themselves along the line according to their opinions. Being able to articulate opinions and participate in civil discourse are important aspects of critical thinking.
3. Play devil’s advocate
During a robust classroom discussion, an effective teacher challenges students by acting as devil’s advocate, no matter their personal opinion. “I don’t care WHAT you think, I just care THAT you think” is my classroom mantra. Critical thinking strategies that ask students to analyze both sides of an issue help create understanding and empathy.
4. Gallery walk
In a gallery walk, the teacher hangs images around the classroom related to the unit at hand (photographs, political cartoons, paintings). Students peruse the artwork much like they are in a museum, writing down their thoughts about each piece.
5. Review something
A movie, TV show , a book, a restaurant, a pep assembly, today’s lesson – anything can be reviewed. Writing a review involves the complex skill of summary without spoilers and asks students to share their opinion and back it up with evidence.
6. Draw analogies
Pick two unrelated things and ask students how those things are alike (for example, how is a museum like a snowstorm). The goal here is to encourage creativity and look for similarities.
7. Think of 25 uses for an everyday thing
Pick an everyday object (I use my camera tripod) and set a timer for five minutes. Challenge students to come up with 25 things they can use the object for within that time frame. The obvious answers will be exhausted quickly, so ridiculous answers such as “coatrack” and “stool” are encouraged.
8. Incorporate riddles
Students love riddles. You could pose a question at the beginning of the week and allow students to ask questions about it all week.
9. Crosswords and sudoku puzzles
The games section of the newspaper provides great brainteasers for students who finish their work early and need some extra brain stimulation.
10. Fine tune questioning techniques
A vibrant classroom discussion is made even better by a teacher who asks excellent, provocative questions. Questions should move beyond those with concrete answers to a place where students must examine why they think the way they do.
11. Socratic seminar
The Socratic seminar is perhaps the ultimate critical thinking activity. Students are given a universal question, such as “Do you believe it is acceptable to break the law if you believe the law is wrong?” They are given time to prepare and answer, and then, seated in a circle, students are directed to discuss the topic. Whereas the goal of a debate is to win, the goal of a Socratic discussion is for the group to reach greater understanding.
12. Inquiry based learning
In inquiry-based learning, students develop questions they want answers to, which drives the curriculum toward issues they care about. An engaged learner is an essential step in critical thinking.
13. Problem-based learning
In problem-based learning, students are given a problem and asked to develop research-based solutions. The problem can be a school problem (the lunchroom is overcrowded) or a global problem (sea levels are rising).
14. Challenge all assumptions
The teacher must model this before students learn to apply this skill on their own. In this strategy, a teacher helps a student understand where his or her ingrained beliefs come from. Perhaps a student tells you they believe that stereotypes exist because they are true. An effective teacher can ask “Why do you think that?” and keep exploring the issue as students delve into the root of their beliefs. Question everything.
15. Emphasize data over beliefs
Data does not always support our beliefs, so our first priority must be to seek out data before drawing conclusions.
16. Teach confirmation bias
Confirmation bias is the human tendency to seek out information that confirms what we already believe, rather than letting the data inform our conclusions. Understanding that this phenomenon exists can help students avoid it.
17. Visualization
Help students make a plan before tackling a task.
18. Mind mapping
Mind mapping is a visual way to organize information. Students start with a central concept and create a web with subtopics that radiate outward.
19. Develop empathy
Empathy is often cited as an aspect of critical thinking. To do so, encourage students to think from a different point of view. They might write a “con” essay when they believe the “pro,” or write a letter from someone else’s perspective.
20. Summarization
Summarizing means taking all the information given and presenting it in a shortened fashion.
21. Encapsulation
Encapsulation is a skill different from summarization. To encapsulate a topic, students must learn about it and then distill it down to its most relevant points, which means students are forming judgements about what is most and least important.
22. Weigh cause and effect
The process of examining cause and effect helps students develop critical thinking skills by thinking through the natural consequences of a given choice.
23. Problems in a jar
Perfect for a bell-ringer, a teacher can stuff a mason jar with dilemmas that their students might face, such as, “Your best friend is refusing to talk to you today. What do you do?” Then, discuss possible answers. This works well for ethical dilemmas, too.
24. Transform one thing into another
Give students an object, like a pencil or a mug. Define its everyday use (to write or to drink from). Then, tell the students to transform the object into something with an entirely separate use. Now what is it used for?
25. Which one doesn’t belong?
Group items together and ask students to find the one that doesn’t belong. In first grade, this might be a grouping of vowels and a consonant; in high school, it might be heavy metals and a noble gas.
26. Compare/contrast
Compare and contrast are important critical thinking strategies. Students can create a Venn diagram to show similarities or differences, or they could write a good old-fashioned compare/contrast essay about the characters of Romeo and Juliet .
27. Pick a word, find a related word
This is another fun bell-ringer activity. The teacher starts with any word, and students go around the room and say another word related to that one. The obvious words go quickly, meaning the longer the game goes on, the more out-of-the-box the thinking gets.
28. Ranking of sources
Give students a research topic and tell them to find three sources (books, YouTube videos, websites). Then ask them, what resource is best – and why.
29. Hypothesize
The very act of hypothesizing is critical thinking in action. Students are using what they know to find an answer to something they don’t know.
30. Guess what will happen next
This works for scientific reactions, novels, current events, and more. Simply spell out what we know so far and ask students “and then what?”
31. Practice inference
Inference is the art of making an educated guess based on evidence presented and is an important component of critical thinking.
32. Connect text to self
Ask students to draw connections between what they are reading about to something happening in their world. For example, if their class is studying global warming, researching how global warming might impact their hometown will help make their studies relevant.
33. Levels of questioning
There are several levels of questions (as few as three and as many as six, depending on who you ask). These include factual questions, which have a right or wrong answer (most math problems are factual questions). There are also inferential questions, which ask students to make inferences based on both opinion and textual evidence. Additionally, there are universal questions, which are “big picture” questions where there are no right or wrong answers.
Students should practice answering all levels of questions and writing their own questions, too.
34. Demand precise language
An expansive vocabulary allows a student to express themselves more exactly, and precision is a major tool in the critical thinking toolkit.
35. Identify bias and hidden agendas
Helping students to critically examine biases in sources will help them evaluate the trustworthiness of their sources.
36. Identify unanswered questions
After a unit of study is conducted, lead students through a discussion of what questions remain unanswered. In this way, students can work to develop a lifelong learner mentality.
37. Relate a topic in one subject area to other disciplines
Have students take something they are studying in your class and relate it to other disciplines. For example, if you are studying the Civil War in social studies, perhaps they could look up historical fiction novels set during the Civil War era or research medical advancements from the time period for science.
38. Have a question conversation
Start with a general question and students must answer your question with a question of their own. Keep the conversation going.
39. Display a picture for 30 seconds, then take it down
Have students list everything they can remember. This helps students train their memories and increases their ability to notice details.
40. Brainstorm, free-write
Brainstorming and freewriting are critical thinking strategies to get ideas on paper. In brainstorming, anything goes, no matter how off-the-wall. These are great tools to get ideas flowing that can then be used to inform research.
41. Step outside your comfort zone
Direct students to learn about a topic they have no interest in or find particularly challenging. In this case, their perseverance is being developed as they do something that is difficult for them.
42. The answer is, the question might be
This is another bell-ringer game that’s great for engaging those brains. You give students the answer and they come up with what the question might be.
43. Cooperative learning
Group work is a critical thinking staple because it teaches students that there is no one right way to approach a problem and that other opinions are equally valid.
44. What? So what? Now what?
After concluding a unit of study, these three question frames can be used to help students contextualize their learning.
45. Reflection
Ask students to reflect on their work – specifically, how they can improve moving forward.
46. Classify and categorize
These are higher level Bloom’s tasks for a reason. Categorizing requires students to think about like traits and rank them in order of importance.
47. Role play
Roleplay allows students to practice creative thinking strategies. Here, students assume a role and act accordingly.
48. Set goals
Have students set concrete, measurable goals in your class so they understand why what they do matters.
No matter your subject area, encourage students to read voraciously. Through reading they will be exposed to new ideas, new perspectives, and their worlds will grow.
50. Cultivate curiosity
A curious mind is an engaged mind. Students should be encouraged to perform inquiry simply for the sake that it is a joy to learn about something we care about.

TREAT YO' INBOX!
All the trending teacher stories, resources, videos, memes, podcasts, deals, and the laughter you need in your life!
Promoting Critical Thinking in the Classroom: Strategies and Activities
ritical thinking is a valuable skill that empowers students to analyze information, think deeply, and make reasoned judgments. By promoting critical thinking in the classroom, educators can foster intellectual curiosity, enhance problem-solving abilities, and prepare students for success in an ever-evolving world. This article explores effective strategies and engaging activities to promote critical thinking among students.
1. Ask Thought-Provoking Questions
Encourage critical thinking by asking open-ended and thought-provoking questions that stimulate students' analytical thinking. For example, in a history class, instead of asking "When did World War II start?" you could ask "What were the underlying causes of World War II and how did they contribute to its outbreak?" This prompts students to go beyond simple factual recall and encourages them to analyze historical events, evaluate multiple factors, and develop a deeper understanding of the topic. Instead of seeking one correct answer, focus on guiding students to explore different perspectives, evaluate evidence, and justify their reasoning. Engage students in discussions that require them to analyze, compare, and synthesize information.
2. Provide Real-World Examples
Connect classroom learning to real-world applications by providing relevant examples and case studies. By presenting authentic scenarios, students can apply critical thinking skills to analyze and solve complex problems. Encourage students to think critically about the implications of their decisions and consider the broader impact of their choices.
3. Foster Collaboration and Debate
Promote collaborative learning environments where students can engage in respectful debates and discussions. Encourage students to express diverse opinions, support their arguments with evidence, and listen actively to others' viewpoints. Through collaborative activities, students can learn to evaluate different perspectives, challenge assumptions, and develop their critical thinking skills.
4. Encourage Reflection and Metacognition
Provide opportunities for students to reflect on their thinking processes and metacognition. Ask students to evaluate their own problem-solving strategies, analyze their decision-making processes, and assess the effectiveness of their critical thinking skills. By promoting self-awareness and reflection, students can enhance their critical thinking abilities and become more independent learners.
5. Incorporate Problem-Based Learning
Integrate problem-based learning activities that require students to apply critical thinking skills to solve complex problems. For example, in a science class, present a real-world scenario where students need to design an experiment to test the effectiveness of different fertilizers on plant growth. This activity prompts students to analyze information about fertilizers, evaluate different options, and develop a well-reasoned experimental design. By engaging in hands-on problem-solving experiences like this, students can develop their critical thinking abilities while also building their content knowledge.
Promoting critical thinking in the classroom is essential for developing students' analytical skills, problem-solving abilities, and intellectual curiosity. By incorporating strategies such as asking thought-provoking questions, providing real-world examples, fostering collaboration and debate, encouraging reflection and metacognition, and incorporating problem-based learning, educators can create an environment that nurtures critical thinking skills. By equipping students with this valuable skill set, we empower them to navigate complex challenges and become lifelong learners.
Top 10 Educational YouTube Channels for Teachers and Students
Teaching online: finding the right platform for you, top 20 online platforms for freelance tutors, assistive technologies in education: supporting students with disabilities, join our newsletter and get the latest posts to your inbox, exploring teaching opportunities in canada: provinces to consider, cultural immersion tips: making the most of your teaching experience abroad, stay in touch.

There is More Posts
Teaching with toys: using hands-on manipulatives to make learning fun, teaching english online: a guide to getting started, how to create an epic classroom playlist: using music to enhance the learning experience.

- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Don't Miss the Grand Prize: A $2,500 Office Depot/OfficeMax Card!
5 Critical Thinking Skills Every Kid Needs To Learn (And How To Teach Them)
Teach them to thoughtfully question the world around them.

Little kids love to ask questions. “Why is the sky blue?” “Where does the sun go at night?” Their innate curiosity helps them learn more about the world, and it’s key to their development. As they grow older, it’s important to encourage them to keep asking questions and to teach them the right kinds of questions to ask. We call these “critical thinking skills,” and they help kids become thoughtful adults who are able to make informed decisions as they grow older.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking allows us to examine a subject and develop an informed opinion about it. First, we need to be able to simply understand the information, then we build on that by analyzing, comparing, evaluating, reflecting, and more. Critical thinking is about asking questions, then looking closely at the answers to form conclusions that are backed by provable facts, not just “gut feelings” and opinion.
Critical thinkers tend to question everything, and that can drive teachers and parents a little crazy. The temptation to reply, “Because I said so!” is strong, but when you can, try to provide the reasons behind your answers. We want to raise children who take an active role in the world around them and who nurture curiosity throughout their entire lives.
Key Critical Thinking Skills
So, what are critical thinking skills? There’s no official list, but many people use Bloom’s Taxonomy to help lay out the skills kids should develop as they grow up.
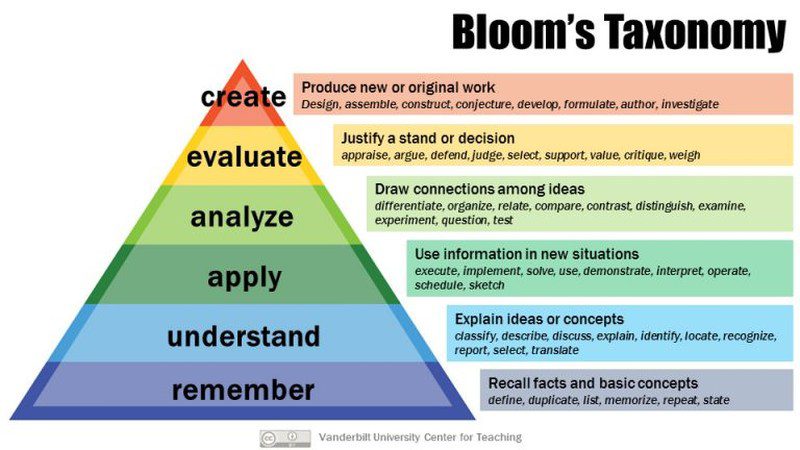
Source: Vanderbilt University
Bloom’s Taxonomy is laid out as a pyramid, with foundational skills at the bottom providing a base for more advanced skills higher up. The lowest phase, “Remember,” doesn’t require much critical thinking. These are the skills kids use when they memorize math facts or world capitals or practice their spelling words. Critical thinking doesn’t begin to creep in until the next steps.
Understanding requires more than memorization. It’s the difference between a child reciting by rote “one times four is four, two times four is eight, three times four is twelve,” versus recognizing that multiplication is the same as adding a number to itself a certain number of times. Schools focus more these days on understanding concepts than they used to; pure memorization has its place, but when a student understands the concept behind something, they can then move on to the next phase.
Application opens up whole worlds to students. Once you realize you can use a concept you’ve already mastered and apply it to other examples, you’ve expanded your learning exponentially. It’s easy to see this in math or science, but it works in all subjects. Kids may memorize sight words to speed up their reading mastery, but it’s learning to apply phonics and other reading skills that allows them to tackle any new word that comes their way.
Analysis is the real leap into advanced critical thinking for most kids. When we analyze something, we don’t take it at face value. Analysis requires us to find facts that stand up to inquiry, even if we don’t like what those facts might mean. We put aside personal feelings or beliefs and explore, examine, research, compare and contrast, draw correlations, organize, experiment, and so much more. We learn to identify primary sources for information, and check into the validity of those sources. Analysis is a skill successful adults must use every day, so it’s something we must help kids learn as early as possible.
Almost at the top of Bloom’s pyramid, evaluation skills let us synthesize all the information we’ve learned, understood, applied, and analyzed, and to use it to support our opinions and decisions. Now we can reflect on the data we’ve gathered and use it to make choices, cast votes, or offer informed opinions. We can evaluate the statements of others too, using these same skills. True evaluation requires us to put aside our own biases and accept that there may be other valid points of view, even if we don’t necessarily agree with them.
In the final phase, we use every one of those previous skills to create something new. This could be a proposal, an essay, a theory, a plan—anything a person assembles that’s unique.
Note: Bloom’s original taxonomy included “synthesis” as opposed to “create,” and it was located between “apply” and “evaluate.” When you synthesize, you put various parts of different ideas together to form a new whole. In 2001, a group of cognitive psychologists removed that term from the taxonomy , replacing it with “create,” but it’s part of the same concept.
How To Teach Critical Thinking
Using critical thinking in your own life is vital, but passing it along to the next generation is just as important. Be sure to focus on analyzing and evaluating, two multifaceted sets of skills that take lots and lots of practice. Start with these 10 Tips for Teaching Kids To Be Awesome Critical Thinkers . Then try these critical thinking activities and games. Finally, try to incorporate some of these 100+ Critical Thinking Questions for Students into your lessons. They’ll help your students develop the skills they need to navigate a world full of conflicting facts and provocative opinions.
One of These Things Is Not Like the Other
This classic Sesame Street activity is terrific for introducing the ideas of classifying, sorting, and finding relationships. All you need are several different objects (or pictures of objects). Lay them out in front of students, and ask them to decide which one doesn’t belong to the group. Let them be creative: The answer they come up with might not be the one you envisioned, and that’s OK!
The Answer Is …
Post an “answer” and ask kids to come up with the question. For instance, if you’re reading the book Charlotte’s Web , the answer might be “Templeton.” Students could say, “Who helped save Wilbur even though he didn’t really like him?” or “What’s the name of the rat that lived in the barn?” Backwards thinking encourages creativity and requires a good understanding of the subject matter.
Forced Analogies
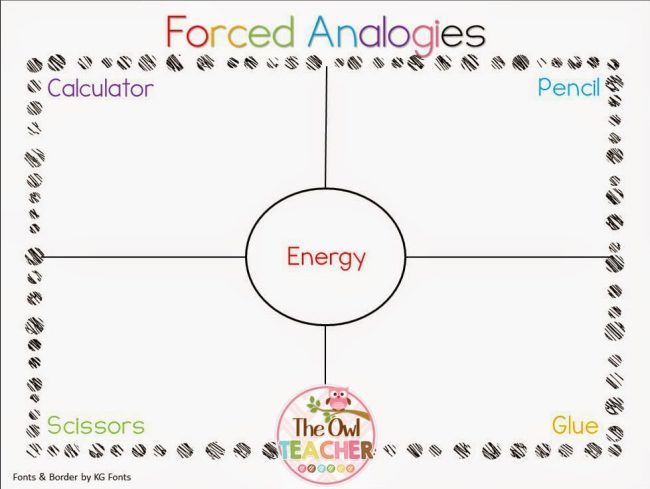
Practice making connections and seeing relationships with this fun game. Kids write four random words in the corners of a Frayer Model and one more in the middle. The challenge? To link the center word to one of the others by making an analogy. The more far out the analogies, the better!
Learn more: Forced Analogies at The Owl Teacher
Primary Sources
Tired of hearing “I found it on Wikipedia!” when you ask kids where they got their answer? It’s time to take a closer look at primary sources. Show students how to follow a fact back to its original source, whether online or in print. We’ve got 10 terrific American history–based primary source activities to try here.
Science Experiments

Hands-on science experiments and STEM challenges are a surefire way to engage students, and they involve all sorts of critical thinking skills. We’ve got hundreds of experiment ideas for all ages on our STEM pages , starting with 50 Stem Activities To Help Kids Think Outside the Box .
Not the Answer
Multiple-choice questions can be a great way to work on critical thinking. Turn the questions into discussions, asking kids to eliminate wrong answers one by one. This gives them practice analyzing and evaluating, allowing them to make considered choices.
Learn more: Teaching in the Fast Lane
Correlation Tic-Tac-Toe

Here’s a fun way to work on correlation, which is a part of analysis. Show kids a 3 x 3 grid with nine pictures, and ask them to find a way to link three in a row together to get tic-tac-toe. For instance, in the pictures above, you might link together the cracked ground, the landslide, and the tsunami as things that might happen after an earthquake. Take things a step further and discuss the fact that there are other ways those things might have happened (a landslide can be caused by heavy rain, for instance), so correlation doesn’t necessarily prove causation.
Learn more: Critical Thinking Tic-Tac-Toe at The Owl Teacher
Inventions That Changed the World
Explore the chain of cause and effect with this fun thought exercise. Start it off by asking one student to name an invention they believe changed the world. Each student then follows by explaining an effect that invention had on the world and their own lives. Challenge each student to come up with something different.
Learn more: Teaching With a Mountain View
Critical Thinking Games

There are so many board games that help kids learn to question, analyze, examine, make judgments, and more. In fact, pretty much any game that doesn’t leave things entirely up to chance (Sorry, Candy Land) requires players to use critical thinking skills. See one teacher’s favorites at the link below.
Learn more: Miss DeCarbo
This is one of those classic critical thinking activities that really prepares kids for the real world. Assign a topic (or let them choose one). Then give kids time to do some research to find good sources that support their point of view. Finally, let the debate begin! Check out 100 Middle School Debate Topics , 100 High School Debate Topics , and 60 Funny Debate Topics for Kids of All Ages .
How do you teach critical thinking skills in your classroom? Come share your ideas and ask for advice in the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, check out 38 simple ways to integrate social-emotional learning throughout the day ..

You Might Also Like

36+ Awesome Career-Readiness Activities That Teach Soft Skills
Set kids up with the skills they'll need to succeed in the workplace. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Teaching Expertise
- Classroom Ideas
- Teacher’s Life
- Deals & Shopping
- Privacy Policy
20 Critical Thinking Activities For Elementary Classrooms: Navigating Fact And Fiction (+Resources)
December 1, 2023 // by Seda Unlucay
With the barrage of mainstream news, advertising, and social media content out there, it’s vital for students to think independently and learn to differentiate between fact and fiction.
This series of critical thinking activities, STEM-based design challenges, engaging Math puzzles, and problem-solving tasks will support students in thinking rationally and understanding the logical connection between concepts.
1. Teach Students How to Obtain Verifiable News
There’s probably no 21st-century skill more important than differentiating between real and fake sources of news. This editable PowerPoint bundle covers traditional media, social networks, and various target audiences and teaches students how to find verifiable facts.
Learn More: Teachers Pay Teachers
2. Watch and Discuss a Critical Reasoning Video

This kid-friendly video teaches students to break arguments down into claims, evidence, and reasoning. Armed with this lifelong learning tool, they will be able to make more informed decisions when consuming all types of information.
Learn More: Brain Pop
3. Complete a Critical Design Challenge
This science and designed-based classroom activity challenges students to find ways to prevent a falling egg from breaking. Pairing it with the classic Humpty Dumpty nursery rhyme is sure to inspire many creative ideas.
Learn More: Education
4. Critical Community Engagement Activity
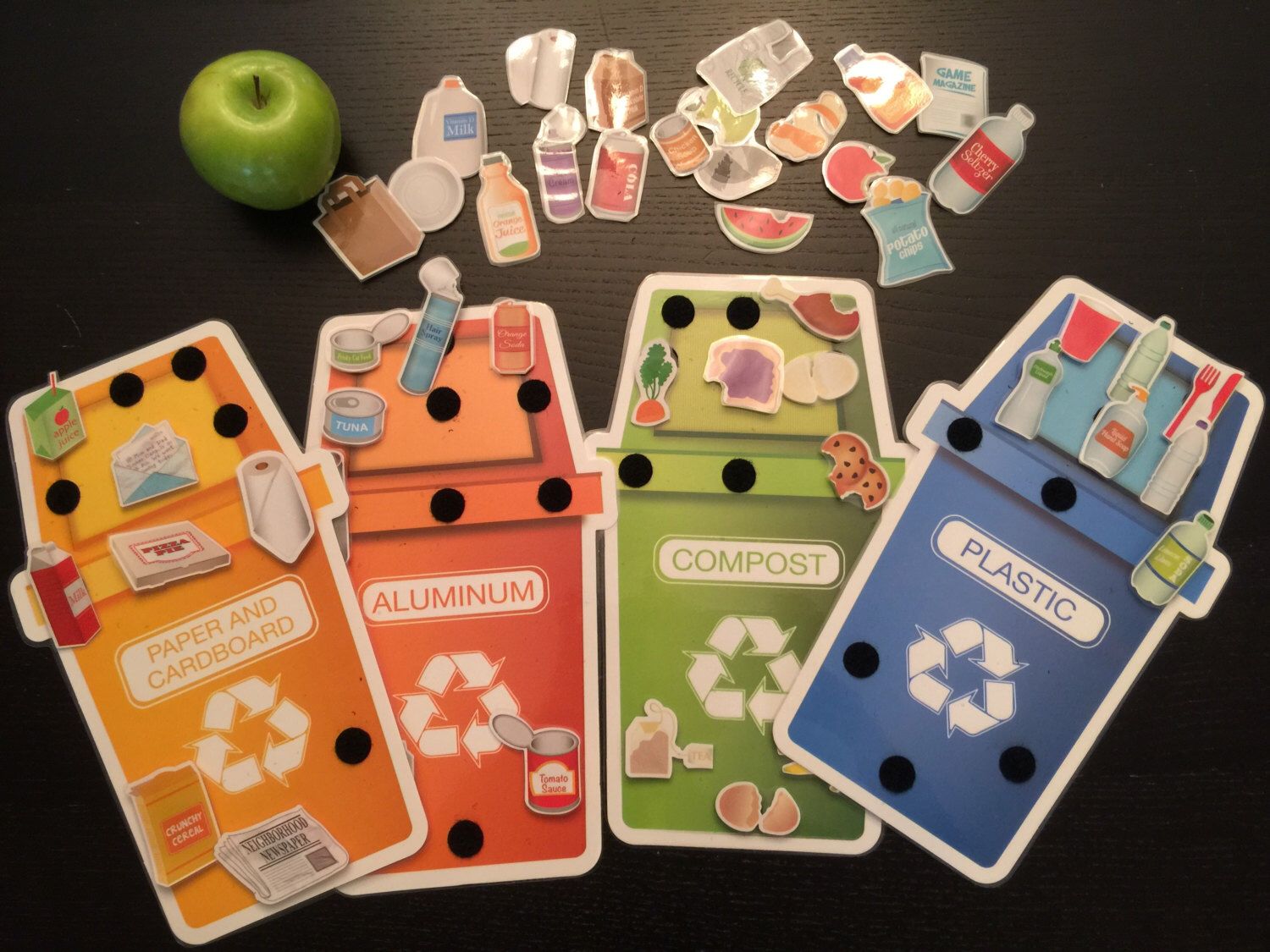

This community engagement activity requires analytical skills to determine what items can be recycled in the classroom and in their neighborhood. By creating recycling bins from reusable cardboard boxes, students have an opportunity to contribute to the environmental well-being of their community while practicing social responsibility.
Learn More: Kaboom
5. Develop Logical Skills with a Then and Now Activity
We may no longer use candles for reading or quill pens for writing, but can your students identify the objects that have replaced them? This activity engages their writing, drawing, and logical skills while giving them a chance to reflect on all the changes in our modern world.
Learn More: Education
6. Play a Critical Thinking Game
This active learning activity requires students to use their critical thinking skills to make comparisons and create meaningful analogies. The fun animal safari theme is sure to inspire many funny and creative ideas!
7. Develop Social-Emotional Problem-Solving Skills
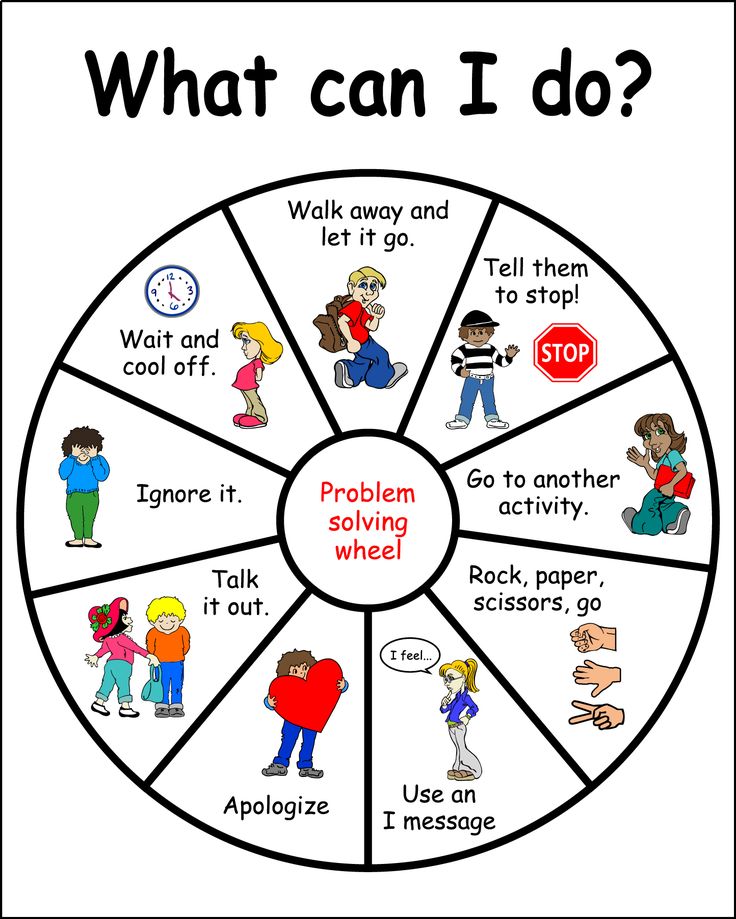
Through this lesson, students will understand that while conflicts are a normal part of life, it’s vital to have problem-solving skills to resolve them. This is also an excellent opportunity for developing their social awareness and relationship skills.
Learn More: ED Foundations
8. Desert Island Survival Game

This classic game is sure to inspire student engagement, as they use their critical thinking skills to survive being stranded on a desert island. Students have to watch out for ideological assumptions and question ideas in order to determine the appropriate items to bring.
9. Play a Problem-Solving Treasure Hunt Game
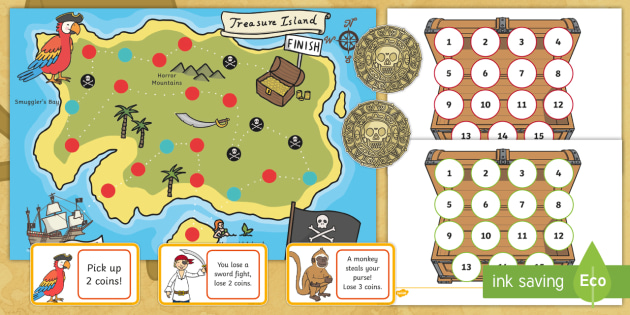
This exciting game for kids requires them to use key math skills to break a series of codes. With ample time, designated progress monitors, and sharp critical thinking skills, students are sure to find the hidden treasure.
Learn More: Twinkl
10. Use Writing to Increase Critical Empathy

This activity builds writing fluency while giving students a chance to show appreciation for each other. As they reflect emphatically on their classmates’ contributions and character, their base level of kindness and sense of ethical responsibility is bound to increase.
Learn More: Edutopia

11. Learn How to Make Logical Inferences

This activity for kids teaches the critical academic skill of making inferences from a series of texts. Students will surely enjoy playing the role of detective in order to draw their own logical conclusions.
Learn More: Study
12. Think Critically About Cultural Assumptions

This engaging activity for students challenges them to think critically about why people from a variety of cultures decorate their bodies. It helps them to break through cultural assumptions while comparing and contrasting the different forms of hand and body painting around the world.
Learn More: Harmony
13. Big Paper Silent Reflection Activity

After posing some open-ended questions, students silently write their responses with colored markers on large chart paper. After each group has circulated around the room, students can share their critical reflections and learn from the various perspectives of their classmates.
Learn More: Slideshare
14. Watch a TED Video About the Socratic Method

Socrates is one of the forefathers of critical thinking, who focused on making his students thinking visible by questioning their logic and reasoning. The accompanying quiz and discussion questions are an excellent way to reinforce student learning.
Learn More: Ted Ed
15. Brainstorm Ways to Help a Homeless Person

This lesson in civic responsibility teaches students about the causes of homelessness and guides them to find ways to help the homeless in their communities. It develops key problem-solving skills while building critical empathy.
Learn More: National Homeless.org
16. Guess the Object Game
This video features a series of twenty zoomed-in mystery objects. Students will love using their critical thinking skills to guess each one!
Learn More: Andy – The ESL Guy
17. Solve Some Challenging Math Brain Teasers
This abundant series of brain teasers is the perfect choice if you’re looking to test your children’s memory and problem-solving skills. Encourage them to use their knowledge of numbers to complete these tricky math problems that are not only designed to challenge your little brainiacs but are also compiled in an easy-to-use format.
Learn More: Mental Up
18. Complete a STEM Elevator Challenge
In this design and engineering-based lesson, students have to build a functional elevator that can carry an object to the top of a structure. It’s a terrific way to encourage cooperative learning while sharpening their problem-solving skills.
Learn More: Georgia Youth Science and Technology Centers
19. Create the Perfect Farm

There’s no better way to develop critical thinking skills than by solving real-world problems. This video encourages students to think about ways to feed a growing global population in an environmentally sustainable way.
20. Solve Logic Grid Puzzles
These logic grid puzzles will motivate students to use logical reasoning skills and the process of elimination to solve a series of clues. But be warned, they are highly addictive and difficult to put down once you get started!
Learn More: Puzzle Baron’s Logic Puzzles
- Our Mission

How to Use Gameplay to Enhance Classroom Learning
Research shows that using games in teaching can help increase student participation, foster social and emotional learning, and motivate students to take risks.
What happens when a gorilla goes into a battle with a brown hyena in an Australian rain forest?
Tanya Buxton’s high school biology students could find out as they embark on March Mammal Madness (MMM), a virtual game modeled after the annual NCAA basketball championship that aims to educate U.S. students about the importance of biodiversity and endangered species.
This is the second year in a row that Buxton has enrolled her Atherton, California, students in the tournament to deepen their understanding of global ecosystems while building community and camaraderie among peers.
Gameplay in school isn’t just about having fun though, say Buxton and other teachers, who are increasingly using games and gaming principles to enhance instruction. From Minecraft to the Game of Life and Werewolf , effective games like March Mammal Madness link content with low-stakes competition and can provide a more collaborative, engaging classroom experience—especially for students who may struggle to focus or find their niche in learning. During the pandemic, games have also provided an important outlet that keeps kids connected and motivated remotely .
These claims aren’t just anecdotal. According to research , using games in teaching can help increase student participation, foster social and emotional learning , and motivate students to take risks. One study of the popular multiple-choice quiz game Kahoot found that it improved students’ attitudes toward learning and boosted their academic scores. In addition, studies have found that virtual games can improve focus and attention for students with ADHD and help students with dyslexia improve spatial and temporal attention, which can translate into improved reading.
But games aren’t substitutes for other forms of learning. Like any educational tool, they need to be well-planned and integrated only when they’re relevant to the learning objectives.
Think of games not as Band-Aids to fix what’s broken in the classroom but as “a pedagogical approach that might help people think differently about what’s possible... limited only by a player’s imagination and by what a gaming set of rules allows,” says Antero Garcia , an assistant professor at the Stanford Graduate School of Education who studies the impact of technology and gaming on youth literacy and civic identities.
Want to integrate well-developed games or just a few gaming principles into your lessons? Here are some approaches to consider to make games a valuable teaching tool.
Test and Learn
In many games , players encounter scenarios that involve making in-the-moment decisions that let them quickly see the impact of their choices in a low-risk setting and then try (and try again) if they falter—skills that are valuable as they go through life, says Garcia.

Teachers, for example, can use role-playing games in the classroom to help students inhabit different perspectives and understand them as part of larger, holistic systems of thought, explains Matthew Farber, a former teacher and assistant professor at the University of Northern Colorado who studies the intersection of game-based learning and SEL. This system of thinking can become a good entry point for students to learn about their own agency as they weigh possibilities and consider alternate plans of action.
Because games are interactive—unlike books or movies that involve more passive consumption—they may also encourage students to explore new topics and approaches to learning that they otherwise would not consider, he says.
In the virtual game Alba: A Wildlife Adventure , for example, players launch mini-missions where they discover and protect species of endangered animals. Though students might not consider themselves adventurers or conservationists when they play the game, the low-risk setting can get them thinking about larger-scale impacts they could have in the real world, adds Farber. As a follow-up activity, students could conduct further research on animals they encountered or even take local nature walks to identify smaller ecosystems of local wildlife.
Even if teachers aren’t using a fully developed game in their class, they can use a process known as gamification , or weaving components of games such as points, leaderboards, and badges into lessons to boost students’ motivation. Because students get excited about the competition from earning badges or embarking on a quest, they tend to take more risks—and, in turn, learn from their mistakes, says Manju Banerjee, an associate professor and vice president of educational research and innovation at Landmark College in Putney, Vermont.
When students are researching a topic and conducting a literature analysis, teachers can design curricula to send them on a quest—instead of framing it as a typical assignment—or rethink assessment and “tell a student that he is at a ‘novice’ level rather than a grade of C-” to reduce academic pressure and encourage participation,” says Banerjee.
Learning in Disguise
Though it’s not the only reason to play games, the fun of gameplay is a critical part of why they are so successful with children, according to educators, who say that games can help disguise the learning of essential but challenging skills that kids might otherwise resist.

Teachers Joe Dillon and Marina Lombardo, for instance, created a poem-writing activity using Minecraft: Education Edition, in which students move through a maze and visit rooms to learn how to make their writing more descriptive. This game, inspired by Georgia Heard’s Six-Room-Poem activity , guides students through specific writing prompts, such as describing an object by focusing on the ambience of its surroundings.
Many games involve a compelling storyline that can quickly hook kids, which is what makes teaching with them so effective, explains Kendra Cameron-Jarvis, an instructional technologist for Buncombe County Schools in western North Carolina. In a game she designed called Discovering the Ancient Pyramids Adventure , sixth-grade students use Google Maps Treks—which provide a 360-degree view of the ancient structures—to go on a quest inside the Great Pyramid and solve a mystery while they explore. The game reinforces what they’re learning in class about ancient Egypt, she says.
“It’s kind of sneaky—they don’t realize they’re learning,” she says. “Kids are going to have a really good time, and they’re going to learn along the way.”
Teachers are also increasingly using apps and interactive game platforms like Kahoot and Quizizz —Kahoot says that more than 6 million teachers in 200 countries use its app to date—as fun formative assessment tools to ensure that students are on track with their learning, especially during the pandemic. Cameron-Jarvis says teachers are reporting that the platforms are so engaging, students frequently request to play them as part of their learning.
To increase the likelihood of all students participating, teachers can scaffold the difficulty levels of a game, calibrated to the current ability of the student. For students with special needs in particular, games can be beneficial because they disrupt traditional learning approaches and introduce opportunities for them to succeed where they have often struggled, says Banerjee, who has more than 29 years of experience in the field of learning disabilities.
Banerjee recommends that teachers use a myriad of low-stakes leaderboards—scoreboards that show the names and scores of participants—to highlight often-overlooked activities or skills in a way that recognizes contributions from students who typically do not perform well on traditional assignments. Teachers can give credit to the student with “the most creative calculation error” in a math class, for example, which not only makes learning more entertaining but acknowledges that all students can contribute meaningfully within a classroom.
Bringing Students Together
Though students can play games alone, most education games encourage players to collaborate effectively in teams—a building block for creating strong relationships and skills like cooperation that will be valuable as they progress through school and life, studies show.

These social interactions have been crucial during distance learning, according to Douglas Kiang, a high school computer science teacher at the Menlo School. Since schools went virtual last spring, Kiang has used Minecraft to give students a chance to interact with each other while learning social skills such as teamwork, negotiation, and respect for others. He also plays Among Us with his advisory group of about 10 students.
“I think games are useful in that respect for bonding and for allowing kids to socialize and communicate with each other,” says Kiang, who is a nationally recognized expert on game-based learning and technology integration.
Integrating more community-building elements into your classroom doesn’t always require playing a multiplayer video game, though, says Cameron-Jarvis. She suggests posting questions in the stream of popular tools like Google Classroom, Flipgrid, and Nearpod, and letting students respond, interact, and debate ideas. Other teachers have used Google tools to make their own versions of traditional games like Connect Four or Tic Tac Toe so that students get a brain break from academic learning.
The important part of using games in the classroom is trying not to gamify everything and to start small, using games with rules that students understand, says Cameron-Jarvis. The mix of games also matters, adds Farber, who says teachers should aim for variety. If you do let kids play games in class, he says, “think about the emotions those games evoke besides strategy and procedure.”
Join my list and get a FREE phonics game! GRAB THE GAME
No products in the cart.

7 Games for Critical Thinking that Add Play to Your Day

Let’s talk about the importance of PLAY and games in our classrooms today. Do you agree with the following?
Learning should be fun.
Learning should be engaging.
Learning should be JOYFUL!
I thought so! For children (and adults) play is a key the way the brain learns. When our students complete puzzles, they are working on problem-solving skills. When they play a game with rules to follow, they are learning how to cooperate and interact with others. When they play against an opponent, they are learning how to develop strategies, predict outcomes, and use logical thinking skills. What a better way to squeeze in play than with critical thinking games in the classroom? In this post, I’ll share seven of my favorite critical thinking games for primary students.
For your convenience, I’ve added links to the materials I talk about within the blog post. These are Amazon Affiliate links. This just means Amazon tosses a few cents my way if you make a purchase with the links – at absolutely, positively, no extra cost to you! These little links help me to continue sharing ideas, freebies, and giveaways with you on the site.
Finding Time for Games in the Classroom
Time. It’s a four-letter word that teachers across the world have a love-hate relationship with. “There’s not enough time!” is a phrase one will frequently hear from a kindergarten teacher as much as a middle school teacher. We know that our students need time to play and have fun in school. We know that games promote SO MANY wonderful skills and brain-friendly challenges for our students. In addition to Pinterest, teaching blogs, IG, and educational websites, I like to turn to the shelves of stores such as Target, Walmart, and Toys R Us for critical thinking games that my students will love to play! There are TONS of educational and high-quality games that you can find pre-assembled and ready to go- for a great price! So, when can we squeeze games into the classroom? Below are some of my favorite times to add board games and mind-challenging games into our schedule:
- Morning Work
- Small Groups
- Indoor Recess
- Friday Game Days (Use small group time or morning work time for games!)
- Math Centers
- Literacy Centers
- Word Work Centers
Teaching Students How to Play
It’s important to model how to play each game with your students. The critical thinking games I am going to share in this post take a lot of brain energy! They are designed to be fun- but challenging- for your students. As a result, don’t expect students to pick up how to play instantly and be able to independently play the games right away. I like to model and play the games with my students at the small group table. For example, every time I introduce a new Brainamin short or long vowel game as a word work center for my students, we play it at the small group table. I do this for math and literacy centers, too. In this way, I can correctly show students the materials, the rules, and I can even play with them to model my thinking and let them hear what I am thinking as I strategize my next moves and make decisions throughout the game. When students have had ample time to play and see how the game works WITH you, they will be more confident and have more fun when they play with their friends and classmates.
Organizing Your Games
Whenever possible, I like to get rid of the boxes the games come in and put them into plastic tubs. The boxes just seem to deteriorate over time, and the lids on the plastic bins help us keep everything tidy and organized. I use many of my critical thinking games during morning work time on Mondays and Fridays and during math and literacy centers. (On Tuesday, Wednesday, and Thursdays we use my See, Think, Wonder, Write routine for morning work .) I will be sharing more about my morning tub time (or what I like to call, Brain Bins) in future blog posts. For now, you can find the bins I use to store my critical thinking games in the links below. You’ll find two sizes of bins. For games that have a board game to them, I like to use the larger, flatter bins. For card games or other critical thinking materials such as the toys and activities I mentioned in this post , I use the medium bins because they take up less space and are really deep!
Medium Bins:
Now, let’s get started learning about seven really fun games that you can use for centers in your classroom. These games will challenge your students’ minds, while encouraging them to use problem-solving, critical thinking, logical thinking, deductive reasoning skills, and most importantly, have fun learning!
Hoot Owl Hoot
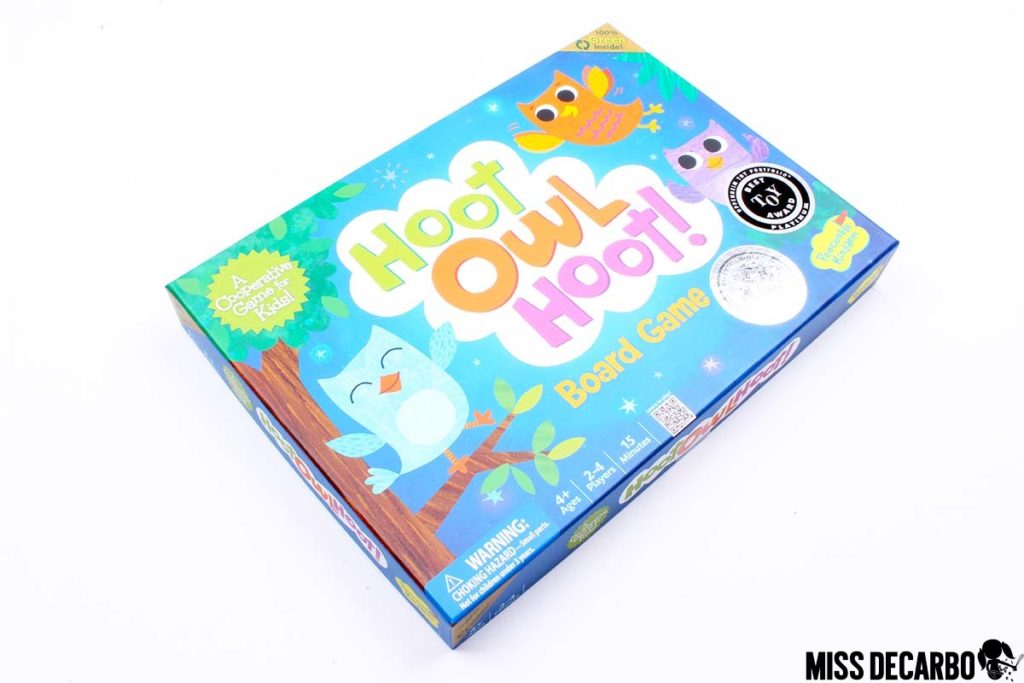

If you teach little ones, Hoot Owl Hoot is a MUST. Hoot Owl Hoot is designed by a company called Peaceable Kingdom. This is an award-winning game that focuses on cooperative play. (The game won the Oppenheim Toy Portfolio Platinum Award.) The object of the game is to help the owls fly back to their nest before the sun comes up. Students use color cards to move the owls closer to the nest. If they draw a sun card, they are one step closer to daylight. The BEST part of this game? EVERYONE wins! That’s right. The students must work together to get all of the owls to their nest. Whether you have a preschooler at home or teach kindergarten or first grade, this is a great game for kids! On top of the cooperative play, students have to use problem-solving skills and shared decision-making skills to be successful. It’s truly a wonderful game that challenges little ones’ thinking skills while having fun with friends!
SEQUENCE LETTERS

Sequence Letters is a game designed for ages 4-7, making it the perfect literacy and word work center for the kindergarten and first-grade classroom. To play, students name the letter on their card, say the sound for that letter, and then match it to a picture on the board that begins with that letter sound. The object is to get five of your game tokens in a row on the board. Can we talk about how perfect this game is for an intervention group or kindergarten small reading lesson?! What I love even more is that the letter cards feature the letter in both uppercase and lowercase, so students are seeing both forms every time they play. Sequence Letters is a game that every primary teacher needs to add to their classrooms!
SEQUENCE FOR KIDS

Sequence for Kids is another version in the Sequence games line-up. This is a great critical thinking game for students who cannot yet read, and it makes the perfect indoor recess game for strategy skills! At first, the initial concept of the game seems TOO easy: Students simply place a token on the picture on the board that matches the picture on their card. When a player gets four tokens in a row, he or she wins. Don’t let this game fool you! There is a lot of thinking-rich strategy skills involved when playing this game. You see, in addition to the picture cards, there are also unicorn and dragon cards. A unicorn card allows you to place your game token anywhere on the board. A dragon card allows you to remove an opponent’s game token. Now, you’ve got a game that involves some “if this…then that” thinking! Which, my friends, are the games I love for kids! You can find Sequence for Kids below:
Brain-Freeze

If you don’t own Brain-Freeze , RUN and get it! It is not only engaging, fun, and child-friendly, but it is the perfect strategy game for young students ages 5 and up. Brain-Freeze reminds me of a cooler version of Guess Who for kids. It also builds mental skills such as memory, deductive-reasoning, and strategy skills. It received multiple awards for children and only takes about 15 minutes to play. That amount of playing time makes it an ideal game to place in a literacy center or math center for kindergarten, first-grade, and second-grade students. To play, one child chooses a sweet treat off of the “menu” and circles characteristics of the treat on their game board. The other child guesses and asks questions about what the sweet treat is, just like in the game, Guess Who? Using a dry-erase marker, the player who is guessing crosses out and eliminates different choices based on the clues and the answers the first player gives. The object is to correctly guess the sweet treat the first player secretly chose at the beginning of the game. This game is also wonderful for asking questions and using inference skills! Find it here:

Let’s move on to some more challenging games. These next few games are great for second-grade and up. On the Dot is a challenging puzzle game that requires focus, creative thinking, and an ability to look at things from new perspectives. It’s a true brainteaser that students will love! To play, students choose two transparent cards. The cards have colored dots on them. The student must rotate, flip, turn, or overlap the cards in order to get the dots on both cards to match up. This game is great for building and practicing logical thinking, spatial reasoning, and problem-solving. With 60 different puzzles to match up, On the Dot is a game that can stay in your bins for a long time!
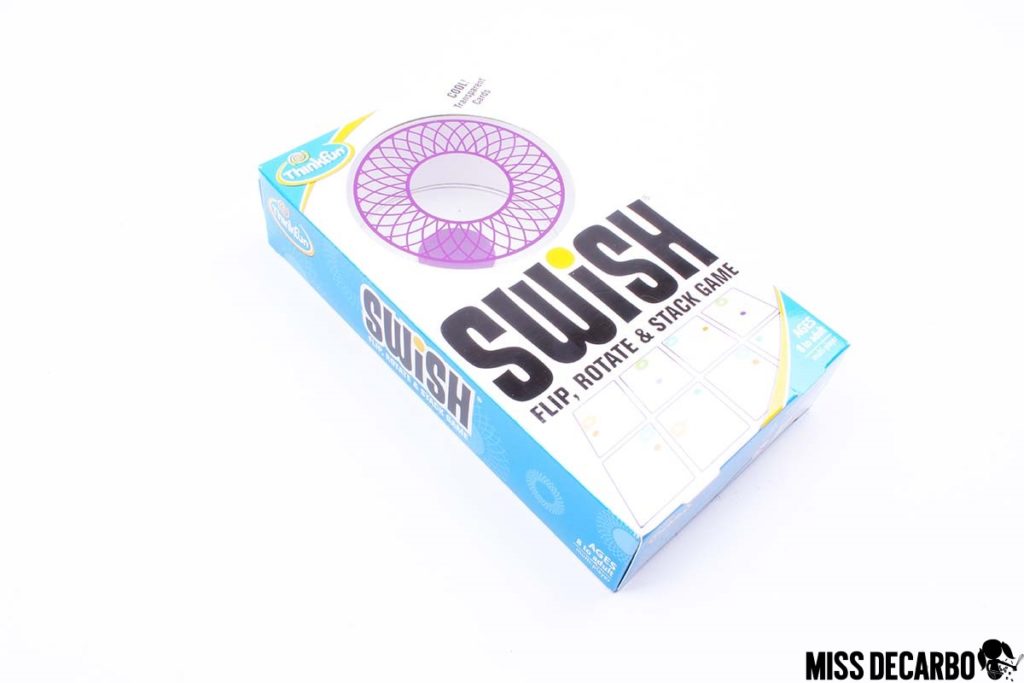

Swish is a game designed for ages 8 and up. It reminds me of On the Dot with transparent cards and colored hoops, or circles. Players take turns stacking and matching up the colored cards. When a match is made, the player keeps both cards. The player with the most matches wins. After playing this game a few times, I decided the Swish Junior game would be the best version to start with in the primary classroom. The pace would go faster and kindergarten and first-grade students would feel more confident and successful. In the Junior version (ages 5+), players layer or stack two or more transparent cards to make a match. The cards have shapes on them in various colors and sizes, making it a much better game for primary students! The Junior version would be great for building spatial reasoning skills and promoting shape recognition. You can find the Swish Junior version below:
For my last critical thinking game, I can’t get enough of my Brainamin games! In this post, I’ll feature the CVC-e and long vowel edition , but I also have a Brainamin Short Vowel Bundle and a B rainamin Vowel Teams Bundle available, too. This is one of the best games to add to a morning tub or literacy center, and it’s certainly fun to use as a small group warm-up game! If you have students who are struggling with decoding and phonics skills, these games also make a nice change of pace for an intervention group. To play, students flip over two cards: a word card, and a picture card. The students will scan the cards and find the matching word and picture, as shown below:
There is only one match, so the students must think fast and be the first person to find it. The student who finds the match first gets to keep both cards in his or her pile. The student who has the most matches in his or her pile at the end of the game wins. (You can also just play for fun and not keep “score” using the matches.) Let’s play again. Can you find the matching word and picture in the cards shown below?
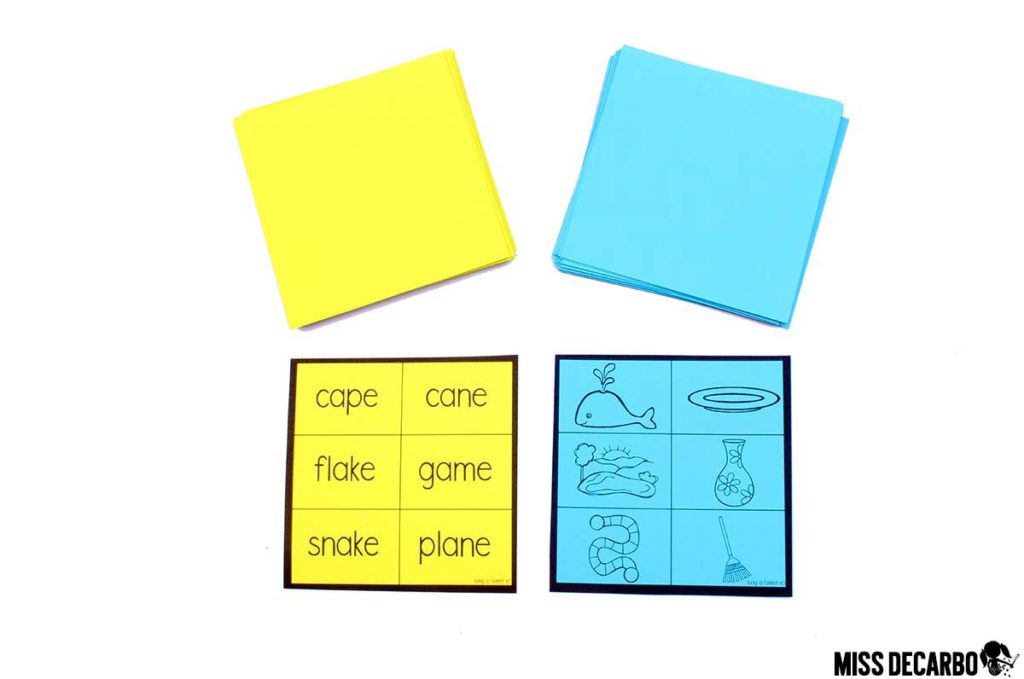
SO fun, right?! What I love MOST about Brainamin is that you can play with a group of students, or with just two students. In fact, students can even play against themselves as an independent game as they race to find the matches among the deck of cards. Brainamin not only improves phonics skills but it also works on visual discrimination skills, critical thinking skills, deductive reasoning, decoding, and fluency for word recall. You can find the different Brainamin bundles and games that I have available by below:
- Brainamin Short Vowels (cvc words)
- Brainamin Long Vowels (cvc-e words)
- Brainamin Vowel Teams
- …more to come in the future!
Try Brainamin for FREE!
You can learn more about critical thinking AND get a FREE Brainamin Short A game pack in a blog post I wrote by clicking HERE or on the blog post image below:

I hope you enjoyed learning about these seven games for critical thinking in the primary classroom! I know they will add fun, play, and lots of great thinking skills into your classroom routine. In order to save this post for later or share it with a colleague, feel free to use the image below to PIN IT on Pinterest !

Similar Posts

easy Grab and go teacher pd: Popcorn and a podcast
Continuous professional development is important, but it is SO difficult to find the time to fit teacher pd opportunities into schedules that are already overbooked. As…

5 Simple Ideas for a Brain-Friendly Classroom
Today I would like to share five simple ideas to make your classroom more brain-friendly! I am a HUGE advocate of educational research. I believe that reading…

independent brain bins for the classroom
What are independent brain bins? Brain bins are what I like to call morning tubs! These little bins are filled with STEM materials and toys that…

The Tricky Triangle Game: Boost Thinking Skills!
Do you use partner math games and centers in your classroom? I do! I love watching my first graders interact with one another while they play their…

Using Thinking Stems In The Primary Classroom
Hello Teacher Friends! Today I would love to tell you about how I use thinking stems in my classroom! Thinking stems are simply a way to…

Is Your Teaching Brain-Friendly? 4 Tips for Instructional Success
One day, I walked into my classroom and found this pink, painted….thing….sitting on my desk. I remember staring at it for a few seconds. What is…
One Comment
Loved all the games which you have shared with us. Perfect way to engage kids in such fun games for long hours which helps to nurture their overall growth. In this world of technology. where kids are inclined more towards playing online or video games, which affects their physical as well as mental growth. I think it the responsibility of parents to involve kids in games or activities which helps to improve their overall development. Saved your entire list of games to incorporate these in regular kids play. Thanks for sharing such an awesome list of games with us.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Lost your password?
Don't have an account yet? Sign up
Educationise
10 Innovative Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking in the Classroom
Are you looking for innovative ways to promote critical thinking skills in your classroom? As an educator, you know the importance of developing strong critical thinking skills in your students. In today’s complex and ever-changing world, critical thinking is a vital skill that can make the difference between success and failure.
Critical Thinking Lessons and Activities
Now you may be wondering how to promote critical thinking in the classroom or how to develop critical thinking skills in the students. Well, to help you out, we’ve put together 10 surprising strategies to promote critical thinking skills in your classroom, complete with real-world examples and actionable strategies.
Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking in the Classroom
These strategies are designed to promote active learning, inquiry-based learning, and Bloom’s Taxonomy levels of analysis, evaluation, and interpretation. Here they are:
1. Collaborative Learning
Collaborative learning is an effective way to promote critical thinking skills in your classroom. By encouraging your students to work together to solve complex problems, you can help them develop skills in analysis, evaluation, and interpretation.
For example, you could divide your students into small groups and give them a problem to solve. Each group can then present their solution to the class and the class can evaluate and critique each solution. This not only encourages critical thinking, but it also promotes teamwork and communication skills.
If you are looking for examples of critical thinking in the classroom, then read our article 11 activities that promote critical thinking skills in the classroom .
2. Questioning
Asking open-ended questions is another effective way to promote critical thinking skills in your classroom. Open-ended questions encourage your students to think deeply about a topic and consider different perspectives.
Read our article: 10 Best Educational Games for Kids That will Shape Their Future
For example, if you’re teaching a lesson on climate change, you could ask your students questions such as “What are the causes of climate change?” and “What are the potential consequences of climate change?” These questions encourage your students to analyze information and think critically about the topic.
3. Active Listening
Encouraging active listening is another way to promote critical thinking skills in your classroom. When students actively listen to each other, they consider different perspectives and analyze information more deeply.
Think Like a Detective – A Kid’s Guide to Critical Thinking
For example, you could ask your students to work in pairs and have each student share their opinion on a topic. The other student must actively listen and ask follow-up questions to better understand their partner’s perspective. This activity promotes critical thinking skills such as analysis, evaluation, and interpretation.
4. Case Studies
Using case studies is another effective way to promote critical thinking skills in your classroom. Case studies allow your students to apply critical thinking skills to real-world situations.
For example, if you’re teaching a lesson on business ethics , you could present a case study on a company that faced an ethical dilemma. Your students can then analyze the case study and identify potential solutions. This activity promotes critical thinking skills such as analysis, evaluation, and interpretation.
Organizing debates is another effective way to promote critical thinking skills in your classroom. Debates encourage your students to analyze and evaluate different viewpoints on a topic.
For example, if you’re teaching a lesson on gun control, you could organize a debate where half of the class argues for gun control and the other half argues against it. This activity promotes critical thinking skills such as analysis, evaluation, and interpretation.
Read our article: Engaging STEM Activities for Elementary, Middle and High School Students
6. Mind Mapping
Using mind mapping is another effective way to promote critical thinking skills in your classroom. Mind mapping allows your students to organize and analyze complex information.
For example, if you’re teaching a lesson on the solar system, you could have your students create a mind map of the different planets and their characteristics. This activity promotes critical thinking skills such as analysis, evaluation, and interpretation.
7. Gamification
Using game-based learning is another effective way to promote critical thinking skills in your classroom. Game-based learning engages your students and promotes critical thinking skills such as problem-solving, analysis, and evaluation.
For example, you could use an online game that requires your students to solve math problems. This activity promotes critical thinking skills such as problem-solving, analysis, and evaluation.
8. Problem-Based Learning
Using problem-based learning is another effective way to promote critical thinking skills in your classroom. Problem-based learning requires your students to solve real-world problems using critical thinking skills such as analysis, evaluation, and interpretation.
For example, you could present your students with a real-world problem, such as designing a sustainable community. Your students can then work in groups to research and propose solutions to the problem. This activity promotes critical thinking skills such as problem-solving, analysis, evaluation, and interpretation.
9. Reflection
Encouraging reflection is another way to promote critical thinking skills in your classroom. When students reflect on their learning experiences, they can identify areas where they need to improve and develop critical thinking skills.
For example, you could have your students keep a learning journal where they reflect on their learning experiences and identify areas where they need to improve. This activity promotes critical thinking skills such as analysis, evaluation, and interpretation.
10. Real-World Applications
Using real-world applications is another effective way to promote critical thinking skills in your classroom. When students can see how the skills they are learning can be applied in the real world, they are more motivated to learn and develop critical thinking skills.
For example, if you’re teaching a lesson on fractions, you could show your students how fractions are used in cooking recipes. This activity promotes critical thinking skills such as analysis, evaluation, and interpretation.
In conclusion, critical thinking skills are essential for success in today’s complex and ever-changing world. As an educator, you can promote critical thinking skills in your classroom by using these 10 surprising ways. Collaborative learning, questioning, active listening, case studies, debates, mind mapping, gamification, problem-based learning, reflection, and real-world applications are all effective ways to promote critical thinking skills. By incorporating these strategies into your teaching, you can help your students develop the critical thinking skills they need to succeed in the 21st century.
Share this:
One thought on “ 10 innovative strategies for promoting critical thinking in the classroom ”.
- Pingback: Engaging Problem-Solving Activities That Spark Student Interest - Educationise
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Discover more from educationise.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Site Search

10 Team-Building Games That Promote Critical Thinking

Preparing students for ongoing learning success needs to incorporate curriculum and extra-curriculum activities. The team at TeachThought have compiled their list of games to promote better peer-to-peer learning in the classroom.
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
- Order Tracking
- Create an Account

200+ Award-Winning Educational Textbooks, Activity Books, & Printable eBooks!
- Compare Products
Reading, Writing, Math, Science, Social Studies
- Search by Book Series
- Algebra I & II Gr. 7-12+
- Algebra Magic Tricks Gr. 2-12+
- Algebra Word Problems Gr. 7-12+
- Balance Benders Gr. 2-12+
- Balance Math & More! Gr. 2-12+
- Basics of Critical Thinking Gr. 4-7
- Brain Stretchers Gr. 5-12+
- Building Thinking Skills Gr. Toddler-12+
- Building Writing Skills Gr. 3-7
- Bundles - Critical Thinking Gr. PreK-9
- Bundles - Language Arts Gr. K-8
- Bundles - Mathematics Gr. PreK-9
- Bundles - Multi-Subject Curriculum Gr. PreK-12+
- Bundles - Test Prep Gr. Toddler-12+
- Can You Find Me? Gr. PreK-1
- Complete the Picture Math Gr. 1-3
- Cornell Critical Thinking Tests Gr. 5-12+
- Cranium Crackers Gr. 3-12+
- Creative Problem Solving Gr. PreK-2
- Critical Thinking Activities to Improve Writing Gr. 4-12+
- Critical Thinking Coloring Gr. PreK-2
- Critical Thinking Detective Gr. 3-12+
- Critical Thinking Tests Gr. PreK-6
- Critical Thinking for Reading Comprehension Gr. 1-5
- Critical Thinking in United States History Gr. 6-12+
- CrossNumber Math Puzzles Gr. 4-10
- Crypt-O-Words Gr. 2-7
- Crypto Mind Benders Gr. 3-12+
- Daily Mind Builders Gr. 5-12+
- Dare to Compare Math Gr. 2-7
- Developing Critical Thinking through Science Gr. 1-8
- Dr. DooRiddles Gr. PreK-12+
- Dr. Funster's Gr. 2-12+
- Editor in Chief Gr. 2-12+
- Fun-Time Phonics! Gr. PreK-2
- Half 'n Half Animals Gr. K-4
- Hands-On Thinking Skills Gr. K-1
- Inference Jones Gr. 1-6
- James Madison Gr. 10-12+
- Jumbles Gr. 3-5
- Language Mechanic Gr. 4-7
- Language Smarts Gr. 1-4
- Mastering Logic & Math Problem Solving Gr. 6-9
- Math Analogies Gr. K-9
- Math Detective Gr. 3-8
- Math Games Gr. 3-8
- Math Mind Benders Gr. 5-12+
- Math Ties Gr. 4-8
- Math Word Problems Gr. 4-10
- Mathematical Reasoning Gr. Toddler-11
- Middle School Science Gr. 6-8
- Mind Benders Gr. PreK-12+
- Mind Building Math Gr. K-1
- Mind Building Reading Gr. K-1
- Novel Thinking Gr. 3-6
- OLSAT® Test Prep Gr. PreK-K
- Organizing Thinking Gr. 2-8
- Pattern Explorer Gr. 3-9
- Practical Critical Thinking Gr. 8-12+
- Punctuation Puzzler Gr. 3-8
- Reading Detective Gr. 3-12+
- Red Herring Mysteries Gr. 4-12+
- Red Herrings Science Mysteries Gr. 4-9
- Science Detective Gr. 3-6
- Science Mind Benders Gr. PreK-3
- Science Vocabulary Crossword Puzzles Gr. 4-6
- Sciencewise Gr. 4-12+
- Scratch Your Brain Gr. 2-12+
- Sentence Diagramming Gr. 3-12+
- Smarty Pants Puzzles Gr. 3-12+
- Snailopolis Gr. K-4
- Something's Fishy at Lake Iwannafisha Gr. 5-9
- Teaching Technology Gr. 3-12+
- Tell Me a Story Gr. PreK-1
- Think Analogies Gr. 3-12+
- Think and Write Gr. 3-8
- Think-A-Grams Gr. 4-12+
- Thinking About Time Gr. 3-6
- Thinking Connections Gr. 4-12+
- Thinking Directionally Gr. 2-6
- Thinking Skills & Key Concepts Gr. PreK-2
- Thinking Skills for Tests Gr. PreK-5
- U.S. History Detective Gr. 8-12+
- Understanding Fractions Gr. 2-6
- Visual Perceptual Skill Building Gr. PreK-3
- Vocabulary Riddles Gr. 4-8
- Vocabulary Smarts Gr. 2-5
- Vocabulary Virtuoso Gr. 2-12+
- What Would You Do? Gr. 2-12+
- Who Is This Kid? Colleges Want to Know! Gr. 9-12+
- Word Explorer Gr. 6-8
- Word Roots Gr. 3-12+
- World History Detective Gr. 6-12+
- Writing Detective Gr. 3-6
- You Decide! Gr. 6-12+
- Special of the Month
- Sign Up for our Best Offers
- Bundles = Greatest Savings!
- Sign Up for Free Puzzles
- Sign Up for Free Activities
- Toddler (Ages 0-3)
- PreK (Ages 3-5)
- Kindergarten (Ages 5-6)
- 1st Grade (Ages 6-7)
- 2nd Grade (Ages 7-8)
- 3rd Grade (Ages 8-9)
- 4th Grade (Ages 9-10)
- 5th Grade (Ages 10-11)
- 6th Grade (Ages 11-12)
- 7th Grade (Ages 12-13)
- 8th Grade (Ages 13-14)
- 9th Grade (Ages 14-15)
- 10th Grade (Ages 15-16)
- 11th Grade (Ages 16-17)
- 12th Grade (Ages 17-18)
- 12th+ Grade (Ages 18+)
- Test Prep Directory
- Test Prep Bundles
- Test Prep Guides
- Preschool Academics
- Store Locator
- Submit Feedback/Request
- Sales Alerts Sign-Up
- Technical Support
- Mission & History
- Articles & Advice
- Testimonials
- Our Guarantee
- New Products
- Free Activities
- Libros en Español
How To Promote Critical Thinking In Your Classroom
Promoting Thinking
November 25, 2006, by The Critical Thinking Co. Staff
Modeling of critical thinking skills by instructors is crucial for teaching critical thinking successfully. By making your own thought processes explicit in class - explaining your reasoning, evaluating evidence for a claim, probing the credibility of a source, or even describing what has puzzled or confused you - you provide a powerful example to students, particularly if you invite them to join in; e.g., "Can you see where we're headed with this?" "I can't think of other explanations; can you?" "This idea/principle struck me as difficult or confusing at first, but here's how I figured it out." You can encourage students to emulate this by using them in demonstrations, asking them to "think out loud" in order for classmates to observe how they reason through a problem.
Develop the habit of asking questions that require students to think critically, and tell students that you really expect them to give answers! In particular, Socratic questioning encourages students to develop and clarify their thinking: e.g., "Would your answer hold in all cases?" "How would you respond to a counter-example or counter-argument?" "Explain how you arrived at that answer?"
This is another skill that students can learn from your example, and can use in working with each other. Providing regular opportunities for pair or small group discussions after major points or demonstrations during lectures is also important: this allows students to process the new material, connect it to previously learned topics, and practice asking questions that promote further critical thinking. Obviously, conveying genuine respect for student input is essential. Communicating the message that you value and support student contributions and efforts to think critically increases confidence, and motivates students to continue building their thinking skills. An essential component of this process is the creation of a climate where students feel comfortable with exploring the process of reasoning through a problem without being "punished" for getting the wrong answer.
Researchers have found consistently that interaction among students, in the form of well-structured group discussions plays a central role in stimulating critical thinking. Discussing course material and its applications allows students to formulate and test hypotheses, practice asking thought-provoking questions, hear other perspectives, analyze claims, evaluate evidence, and explain and justify their reasoning. As they become more sophisticated and fluent in thinking critically, students can observe and critique each others' reasoning skills.
- Submit A Post
- EdTech Trainers and Consultants
- Your Campus EdTech
- Your EdTech Product
- Your Feedback
- Your Love for Us
- EdTech Product Reviews
ETR Resources
- Mission/Vision
- Testimonials
- Our Clients
- Press Release
Critical Thinking Activities Recommended for Teachers to Implement in the Classroom
Someone with critical thinking skills is being able to understand the logical connections between ideas, identify, construct and evaluate arguments, detect inconsistencies and common mistakes in reasoning.
This skill is developed among students by engaging them in activities that require them to process questions and come out with solutions for the same helping them to develop this skill.
In order to help students develop this skill and come out with uncommon thoughts, it is important for educators to understand the role they play in developing critical thinking is different than the role they are typically playing. For students to be engaged in critical thinking, the educator needs to act as a facilitator to allow for discussion and encourage a wider and open thought process, as well as to encourage understanding of the different perception of every individual that comes with thinking critically. Also engaged in this skill, it is important to understand that students do not always end with a right answer, but instead sometimes ends in more questions or differing evaluations of the topic.
Below are some activities recommended for teachers that they can implement in the classroom to help students develop critical thinking skill and prepare them for a better future.
1. If You Build it…
This team-building game is flexible. You simply have to divide students into teams and give them equal amounts of a certain material, like pipe cleaners, blocks, or even dried spaghetti and marshmallows.
Then, give them something to construct. The challenge can be variable (think: Which team can build the tallest, structurally-sound castle? Which team can build a castle the fastest?).
You can recycle this activity throughout the year by adapting the challenge or materials to specific content areas. Apart from critical thinking students also learn to collaborate and to work in groups.
2. Think–Pair–Share
In this activity first asks students to consider a question on their own, and then provide them an opportunity to discuss it in pairs, and finally together with the whole class. The success of such activities depends on the nature of the questions posed. This activity works ideally with questions to encourage deeper thinking, problem-solving, and/or critical analysis. The group discussions are critical as they allow students to articulate their thought processes.
Re-group as a whole class and solicit responses from some or all of the pairs.
Advantages of the think-pair-share include the engagement of all students in the classroom (particularly the opportunity to give voice to quieter students who might have difficulty sharing in a larger group), quick feedback for the instructor (e.g., the revelation of student misconceptions), encouragement and support for higher levels of thinking of the students.
3. The Worst Case Scenario
Construct a scenario in which students would need to work together and solve problems to succeed, like being stranded on a deserted island or getting lost at sea/jungle/town. Ask them to work together and come out with a solution that ensures everyone arrives safely. You might ask them to come up with a list of 10 must-have items that would help them most, or a creative passage to safety. Encourage them to vote everyone must agree to the final solution.
4. Go for Gold
This game is similar to the “If you build it” game: Teams have a common objective, but instead of each one having the same materials, they have access to a whole cache of materials. For instance, the goal might be to create a contraption with pipes, rubber tubing and pieces of cardboard that can carry a marble from point A to point B in a certain number of steps, using only gravity.
5. Keep it Real
This open-ended concept is simple and serves as an excellent segue into problem-based learning. Challenge students to identify and cooperatively solve a real problem in their schools or communities. You may set the parameters, including a time limit, materials and physical boundaries.
6. Gap Fill In
Students are shown a picture, projected in the front of the room, if possible. At the top of their paper, students should write: “What is happening in this picture?” At the bottom of the page, they should answer with what they believe is happening in the photo simply in 1-2 sentences or according to the age/grade this activity is being done with.
In the middle of the page students write down all of the steps they took to arrive at that answer. Students are encouraged to write down the evidence they see that supports their conclusion.
This activity not only uses evidence, but supports Meta cognition skills by asking what prior knowledge brought you to your conclusion. This is a good activity to Bell Work or “Do Now.”
7. Fishbowl
Set up an inner circle and an outer circle in your classroom. Students should not be sitting in this setup yet, but rather in their regular classroom seats. The class should be presented with a question or a statement and allowed to reflect individually for a few minutes.
During this reflection period, count the class off into small groups by 3s, 4s, or 5s.
Students should now transition to the fishbowl setup. In the numbered groups, have students facilitate a conversation while others on the outside observe without comment. (For example, a teacher may have all 1s go to the fishbowl, while the rest of the class sits in the outer ring.)
Once the inner group has discussed for a bit, have the outer group evaluate two things: Their process is they actually listened to one another and their content from knowing whether they are providing evidence or just opinions.
8. Big Paper – Building a Silent Conversation
Writing (or drawing) and silence are used as tools to slow down thinking and allow for silent reflection, unfiltered. By using silence and writing, students can focus on other viewpoints. This activity uses a driving question, markers, and Big Paper. Students work in pairs or threes to have a conversation on the Big Paper. Students can write at will, but it must be done in silence after a reflection on the driving question. This strategy is great for introverts, and provides a readymade visual record of thought for later.
9. Barometer—Taking a Stand on Controversial Issues
When posed with a thought-provoking prompt, students line themselves up along a U-shaped continuum representing where they stand on that issue. The sides of the U are opposite extremes, with the middle being neutral. The teacher starts a discussion by giving equal opportunity for individuals in each area of the continuum to speak about their stand. The students use “I” statements when stating their opinion.
10. Journal Data Goals
Last but not the least, Students must be asked to maintain journals and update them on a regular basis. This can be done in the form of a blog as well. By doing so students become their own progress monitors and can assess the growth within oneself.
Latest EdTech News To Your Inbox
Stay connected.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
- Description Generator
Child Report Generator
- Marking and Grading Assistant
- Lesson Plans
- Lesson Plan Power Points
Email & Message Reply Generator
- Story Writer
Question Generator
- Multi Choice Generator
- Long Form Question Generator
- All Articles
- Digital Literacy Blog
- Digital Divide & Equity in Education
- Culturally Responsive Teaching
- Feedback Strategies for Student Success
- Growth Mindset Blog
- English Language
- English Literature
- Religious Studies
- Phonics and Reading
- Get Started in Seconds
Subject Description Generator
How to promote critical thinking in the classroom.
A comprehensive guide for educators on enhancing critical thinking skills among students through innovative classroom techniques.
Empower Your Students with Critical Thinking Skills
In the evolving landscape of education, fostering critical thinking in the classroom has become paramount. As educators, it's essential to cultivate an environment where students can analyze information critically, engage in meaningful debate, and approach problems with a solution-oriented mindset. This article explores practical strategies to enhance critical thinking skills, leveraging the power of inquiry-based learning and open-ended questioning.
Asking open-ended questions is a cornerstone of promoting critical thinking. By challenging students with questions that require more than a yes or no answer, educators can stimulate deeper thought and encourage students to explore multiple perspectives. Integrating these questions into lesson plans can transform the classroom into a dynamic space for intellectual exploration.
Debate is another powerful tool in the critical thinking arsenal. Structured debates on relevant topics not only sharpen students' argumentation skills but also teach them to consider and respect different viewpoints. This form of student-centered learning fosters a sense of ownership over the learning process, making education a collaborative and engaging experience.
Inquiry-based learning activities are designed to put students in the driver's seat of their educational journey. By posing questions, problems, or scenarios, teachers can guide students through a process of discovery that encourages critical analysis and independent thought. This approach not only boosts critical thinking but also aligns with the natural curiosity and creativity of learners.
Utilizing AI teaching assistants, like those offered by Planit Teachers, can further enhance critical thinking in the classroom. These innovative platforms provide tools such as Lesson Plan Generators and AI Marking Assistants, which free up valuable time for educators to focus on developing student-centered learning experiences that promote critical thinking.
Transform Your Grading with AI Teacher Marking
Revolutionize your grading process with our advanced AI Teacher Marking tool. Our AI algorithms can efficiently grade a variety of assignments, providing detailed feedback and insights.
AI Teacher Marking doesnt just grade; it provides constructive criticism, pinpoints errors, identifies model answers, and references the mark scheme for a holistic evaluation.
By automating the grading process, AI Teacher Marking frees up valuable time for educators, allowing them to focus more on student engagement and personalized teaching.
AI Teacher Marking revolutionizes workflow efficiency for educators. The tool's capability to quickly process and grade student submissions in bulk significantly reduces the time spent on manual marking.
Beyond just grading, AI Teacher Marking offers deep analytical insights into student performance. It provides educators with detailed reports highlighting class trends, common misconceptions, and areas needing more focus.
Revolutionize Your Teaching with AI-Powered Lesson Plans
Welcome to the future of education! Planit Teachers brings you AI-powered lesson plans, tailored for any subject and age group. Just describe your topic and age group, and our advanced AI will craft a bespoke, unique lesson plan designed specifically for your needs.
Our AI-driven lesson plans are not just about convenience, they're about quality. Each plan is meticulously crafted to ensure it meets the highest educational standards. Plus, with our AI's ability to learn and adapt, your lesson plans will only get better over time.
But that's not all! With each lesson plan, you'll also receive a comprehensive list of resources to aid your teaching. And the best part? You can save your plan to your account, edit it as you see fit, and even generate a PDF for offline use or printing.
Innovative Long Form Question Generator
Transform the way you create quizzes with our state-of-the-art Long Form Question Generator. Designed for educators, this revolutionary tool crafts unlimited, expertly written questions tailored to any topic or age group, all powered by advanced AI.
Experience the freedom to customize your quizzes to align perfectly with your educational goals. Our generator allows for unparalleled customization of topics, difficulty levels, and more, enabling you to craft the perfect questions for your students in mere minutes.
Elevate your teaching and engage your students like never before. Save time, enhance learning, and ensure your quizzes are always fresh and relevant. Our Long Form Question Generator is your ultimate partner in creating dynamic, impactful educational content.
End of term reports are a time consuming and stressful task for any teacher. We've built a tool to help you save time and effort when writing reports. Simply describe the child and we'll generate a report for you. You can then edit the report to make it perfect and download it as a PDF. Your report can be tailored using tone, length and complexity settings.
Get back control of your free time using our Child Report Generator. Instant report generation for any child. Happy, angry, concerned and comedic reports generated instantly to your exact specifications.
Crafting quizzes and question sheets for your class is a problem of the past with our Question Generator. Simply describe the topic and age group and we'll do the rest, crafting you a bespoke and totally unique set of questions built exactly for your needs.
With your new quiz, you'll also get a list of resources to help as well as the ability to save your quiz to your account and edit it later. You can then generate a PDF from your quiz, download it for offline use and print for your class.
Get back control of your free time using our Question Generator. Instant quiz and question generation for any topic and age group.
When teaching English, Teachers often need to spend time crafting complex subject, landscape, setting and character descriptions. With our Subject Description Generator, you can instantly generate a description for any subject, landscape, setting or character. Simply describe the subject, landscape, setting or character and we'll do the rest, crafting you a bespoke and totally unique description built exactly for your needs.
We even tailor the description to your exact specifications, allowing you to choose the length, complexity and tone of the description. We then craft the wording to perfectly match your age group and child level.
Multiple Choice Question Generator
Say goodbye to the hassle of creating quizzes manually. Our innovative Multiple Choice Question Generator empowers teachers to generate unlimited questions with 4 multiple choice answers on any topic for any age group, all powered by AI.
Tailor your quizzes to perfectly match your teaching needs. With the ability to customize topics, difficulty levels, and more, you can create the ideal quiz for your class in minutes. Plus, save your quizzes for future use, edit them as needed, and even generate PDFs for easy sharing and printing.
Reclaim your free time and enhance your teaching with quizzes that engage and challenge your students. Our Multiple Choice Question Generator is the ultimate tool for instant, hassle-free quiz creation for any subject and age group.
AI-powered instant replies for emails and messages. Everyone knows that teachers already have enough on their plate, so we've built a tool to help you save time and effort when replying to emails and messages from parents, students and colleagues. Simply describe the topic of the email and we'll generate a reply for you. You can then edit the reply to make it perfect and send it off. If it totally misses the mark, you can instantly regenerate a new reply and try again.
Get back control of your free time using our Email, Message, Class Dojo Reply Generator. Instant message generation for any usage.
Related Articles
- 10 Innovative Ways to Engage Students in Virtual Learning - Planit Teachers
- The Power of Gamification in Education - Boost Student Engagement
- Innovative Approaches to Assessing Student Learning - Planit Teachers
- The Science of Effective Learning Strategies | Planit Teachers
- Empowering Students Through Project-Based Learning
- 10 Creative Ways to Engage Students in Virtual Learning - Planit Teachers
- Innovative Assessment Strategies: Moving Beyond Traditional Testing - Planit Teachers
- The Science of Motivation: Strategies to Inspire Student Success - Planit Teachers
- The Art of Inquiry-Based Learning: Fostering Curiosity and Critical Inquiry in the Classroom
- The Impact of Outdoor Education: Fostering Exploration and Environmental Awareness
- The Magic of Mind Mapping: Boosting Creativity and Critical Thinking in Students
- The Power of Peer Collaboration: Fostering Student Engagement
- Empowering Teachers: Tools and Resources for Effective Lesson Planning - Planit Teachers
- The Benefits of Project-Based Learning: Engaging Students Through Real-World Experiences
- The Art of Questioning: Enhancing Critical Thinking Through Inquiry-Based Learning - Planit Teachers
- The Art of Effective Feedback: Strategies for Providing Constructive Criticism - Planit Teachers
- Creative Ways to Engage Students in Online Learning - Planit Teachers
- The Science of Learning: Understanding How Students Learn Best
- The Art of Effective Feedback: Strategies for Providing Constructive Criticism
- The Evolution of Lesson Planning: From Paper to AI-Powered Platforms
These languages are provided via eTranslation, the European Commission's machine translation service.
- slovenščina
- Azerbaijani

STEAM Essentials: Creative Learning in the Classroom (Barcelona, Spain)
This is an engaging Erasmus+ program designed for teachers seeking to enhance their skills in STEAM education. This program focuses on the fundamental concepts of each STEAM discipline and how they can be integrated for interdisciplinary learning. Teachers will explore the latest research and best practices in the field to create dynamic and innovative lesson plans.
Description
- The STEAM Essentials course is an engaging Erasmus+ program designed for teachers seeking t o enhance their skills in STEAM education (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics). This course aims to empower educators with practical tools and strategies to promote creative learning experiences in the classroom.
- Through interactive workshops and collaborative projects, participants will gain hands-on experience in designing STEAM-based activities that foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills. The course also covers the use of technology and digital tools to enhance STEAM learning, as well as how arts and creativity can inspire students' imagination.
- The course will dive into project-based learning (PBL) methodologies, demonstrating how educators can design and implement STEAM projects that encourage teamwork, communication, and problem-solving. Teachers will discover how to nurture a growth mindset in their students, instilling a passion for lifelong learning and adaptability in an ever-changing world.
- Course Program
- Pre-registration
- Course Category: School Innovation
- Related Courses: 21st Century Skills for Teachers , The 4Cs in Education: Creativity, Collaboration, Communication and Critical Thinking , Entrepreneurship Education: Fostering Creativity and Innovation
- You can also directly contact us by email: [email protected]
Learning objectives
- Understanding STEAM Principles: Participants will gain a comprehensive understanding of the core principles of STEAM education and its interdisciplinary nature, recognising the significance of integrating Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics in the teaching and learning process.
- Designing STEAM Lesson Plans: Teachers will learn how to design and implement engaging STEAM-based lesson plans and activities that promote creativity, critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration among students.
- Integrating Arts and Creativity: Educators will explore methods for integrating arts and creativity into STEM subjects, fostering students' imagination and self-expression, and making learning enjoyable and meaningful.
- Utilising Technology in STEAM Education: Participants will discover how to leverage technology and digital tools to enhance STEAM learning experiences, incorporating innovative digital resources into their teaching practices.
- Implementing Project-Based Learning: Teachers will learn how to apply project-based learning (PBL) methodologies to design and facilitate STEAM projects that encourage teamwork, communication, and independent exploration of subjects.
Methodology & assessment
Certification details.
- Certificate of Attendance: includes the name of the participant and the trainer, the location, the dates, learning hours and competences acquired.
- Learning Agreement(s)
- Europass Mobility Document(s)
Pricing, packages and other information
- Price: 400 Euro
- Package contents: Course
Additional information
- Language: English
- Target audience ISCED: Primary education (ISCED 1) Lower secondary education (ISCED 2) Upper secondary education (ISCED 3)
- Target audience type: Teacher Head Teacher / Principal Teacher Educator
- Learning time: 25 hours or more
Upcoming sessions

Vocational subjects
Key competences, more courses by this organiser.

Game Based Learning and Gamification (Barcelona, Spain)
Next upcoming session 03.06.2024 - 07.06.2024
Digital Tools for Innovative Teaching (Barcelona, Spain)

Interpersonal and Intrapersonal Skills for Teachers (Barcelona, Spain)
Doncic's 36 points spur Mavericks to NBA Finals with 124-103 toppling of Timberwolves in Game 5
Luka doncic had a 20-point first quarter on his way to 36 points for his high this postseason, and the dallas mavericks beat the minnesota timberwolves 124-103 to breeze through the western conference finals in five games.

MINNEAPOLIS (AP) — Luka Doncic was in his element, hitting shots from everywhere on the court, hushing the crowd and flashing those sly smiles as the Dallas Mavericks delivered a knockout performance.
Now one of the global sport's young superstars gets his first trip to the NBA Finals.
Doncic had a 20-point first quarter on his way to 36 points for his high this postseason, and the Mavericks beat the Minnesota Timberwolves 124-103 on Thursday night to breeze through the Western Conference finals in five games.
“He let his teammates know that it’s time and they’ve got to take it up a notch,” coach Jason Kidd said. “He sent the invites out, and they all came.”
Kyrie Irving also scored 36 points for the Mavericks, who built a 29-point halftime lead on 61% shooting to deflate the once-energized crowd before most fans got up for their first snack break. The Mavs went up by 36 in the third quarter, consistently keeping the Timberwolves offense all out of whack.
“I just had that utmost confidence when I was going to sleep last night and went to shootaround this morning," Irving said, “just feeling like we were going to play one of our best games.”
The Mavs, the No. 5 seed in the West, have a full week to rest before the NBA Finals begin in Boston on June 6 for the franchise's first appearance since winning the championship in 2011 when Kidd was playing for them. The Celtics will have had 10 days between games after sweeping Indiana in the Eastern Conference finals.
Anthony Edwards scored 28 points and Karl-Anthony Towns had 28 points and 12 rebounds for the third-seeded Wolves, who met their match with the defense-smashing duo of Doncic and Irving after stifling Phoenix in a first-round sweep and then dethroning defending champion Denver in a seven-game series.
“We never clicked all together as a team in this series, not even one game,” Edwards said. “The last two series, we were all clicking at one time, making shots and stuff. It wasn’t clicking at one time here.”
Irving improved to 15-1 in his career in closeout games in the playoffs .
Doncic set a defiant tone by starting 4 for 4, hitting rainbows from 28 and 31 feet as he turned to talk trash to the courtside fans with each swish.
“That gets me going," Doncic said. "Everybody knows that by now.”
He drained a 32-footer later in a first quarter as the Mavs closed on a 17-1 spurt, a run they pushed to 28-5 over a nine-minute stretch.
“I thought I set a good-enough screen, and I turned around and he's shooting from half court,” center Daniel Gafford said.
This was Doncic’s second 20-point quarter in his postseason career, following a 21-point fourth quarter in the Western Conference finals loss to Golden State in 2022. He was voted the MVP of the series.
Doncic, who shot 14 for 22 and grabbed 10 rebounds, and his savvy sidekick Irving, who has a championship ring from 2016 with Cleveland, were the superior stars in the series as this Wolves team found its first taste of a sustained postseason run to be a bitter — but perhaps ultimately beneficial — one.
“You can’t skip any steps. The West is going to be a monster next year as it continues to be every year. There was a lot of things we did well this year,” Wolvers coach Chris Finch said. “I’m super proud of our guys. Just building another layer of foundation to try to get where we want to go.”
Though he familiarly and persistently waved his arms at the officials almost every time a whistle didn’t go his way, the 25-year-old Doncic played with an unshakeable confidence and unflappable joy from start to finish. As he was taunted by the fans with a “Flopper!” chant when he shot free throws in the third quarter, Doncic smiled and mockingly mouthed the words along with them.
The Mavs got 7-foot-1 rookie Dereck Lively II back from the sprained neck that kept him out of the previous game, restoring the complete rim protection duo with Gafford that helped them disrupt Rudy Gobert in the post and just about everyone else who tried to attack the basket. Gafford had 11 points and nine rebounds, and Lively added nine points and eight rebounds.
Edwards, though he hit the 25-point mark for the 15th time in 27 career playoff games, had trouble finding his rhythm amid all the double-teams. The Wolves, for all their progress this season, were reminded they don’t yet have a championship offense despite his dynamic skills and clutch mentality.
They had several wince-inducing possessions in the decisive first half, with the coaches struggling to find a group that could play in sync together.
As the final seconds of the second quarter ticked away, Edwards drove to the lane and kicked the ball to the corner to Kyle Anderson, who swung it back to Towns on the wing and failed to find a look he liked. He passed back to Anderson, who tried to move closer and had the shot clock expire on him.
P.J. Washington, who had 12 points, flexed his arms in celebration of yet another stifling defensive sequence by the Mavs.
“They won the series. They earned the series. They deserve the series. Congrats to them and their entire staff. They were led by two world-class players that played at a world-class level,” Finch said.
AP NBA: https://apnews.com/hub/NBA

East Texas lineman dies while working to restore power outages

Human remains found in Tyler identified as missing 44 year old

Reports of significant wind damage to homes, marina, trees in Coffee City, Bullard areas

Gregg County law enforcement officials seen entering medical office of accused murderer’s son

3 East Texas locations among national Red Lobster closures
Latest news.

Federal prosecutor in Arkansas stepped down while being investigated, report says

Walmart's strong first quarter driven by consumers seeking bargains with inflation still an issue

Sheriff faces questions from Arkansas lawmakers over Netflix series filmed at county jail

Arkansas cannot prevent 2 teachers from discussing critical race theory in classroom, judge rules

Pelicans host the Kings for play-in game

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Read our article: 10 Innovative Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking in the Classroom. 5. Save the Egg. Make groups of three or four in the class. Ask them to drop an egg from a certain height and think of creative ideas to save the egg from breaking.
The following team-building games can promote cooperation and communication, help establish a positive classroom environment and — most importantly — provide a fun, much-needed reprieve from routine. See also Team-Building Games For The First Day Of School. 10 Team-Building Games That Promote Collaborative Critical Thinking
Students grappled with ideas and their beliefs and employed deep critical-thinking skills to develop arguments for their claims. Embedding critical-thinking skills in curriculum that students care ...
26. Compare/contrast. Compare and contrast are important critical thinking strategies. Students can create a Venn diagram to show similarities or differences, or they could write a good old-fashioned compare/contrast essay about the characters of Romeo and Juliet. 27. Pick a word, find a related word.
Check out these critical thinking activities, adapted from Critical Thinking in the Classroom , a book with over 100 practical tools and strategies for teaching critical thinking in K-12 classrooms. Four Corners. In this activity, students move to a corner of the classroom based on their responses to a question with four answer choices.
Little Alchemy 2. Flex alchemical muscles in amusing, discovery-based puzzler. Bottom Line: This amusing puzzle game encourages creativity, perseverance, and systems thinking, and with creative integration it can build interest in math, science, history, and literature. Grades: 6-12. Price:
Other Critical Thinking Activities. Jigsaw—Developing Community and Disseminating Knowledge: Learners take on the role of "experts" or "specialists" of a particular topic. Then a panel of experts is assembled to get the larger picture. K-W-L Charts—Assessing What We Know/What We Still Want to Learn: Charts to document "What I Know ...
This arrangement will help you and your students more clearly understand and identify the specific critical-thinking skills they are using. For each thinking skill in this book, there are two kinds of activities: (1) those that you, as the teacher, will lead, and (2) student reproducibles for indepen-dent work.
By promoting critical thinking in the classroom, educators can foster intellectual curiosity, enhance problem-solving abilities, and prepare students for success in an ever-evolving world. This article explores effective strategies and engaging activities to promote critical thinking among students. 1. Ask Thought-Provoking Questions.
Critical thinking is a key skill that goes far beyond the four walls of a classroom. It equips students to better understand and interact with the world around them. Here are some reasons why fostering critical thinking is important: Making Informed Decisions: Critical thinking enables students to evaluate the pros and cons of a situation ...
Here are 10 fun classroom activities that promote critical thinking: 1. Problem-Solving Scenarios: Provide students with real-life scenarios and ask them to come up with solutions. This activity encourages students to think critically and creatively to solve problems. 2.
Teach Reasoning Skills. Reasoning skills are another key component of critical thinking, involving the abilities to think logically, evaluate evidence, identify assumptions, and analyze arguments. Students who learn how to use reasoning skills will be better equipped to make informed decisions, form and defend opinions, and solve problems.
Debates. This is one of those classic critical thinking activities that really prepares kids for the real world. Assign a topic (or let them choose one). Then give kids time to do some research to find good sources that support their point of view. Finally, let the debate begin!
8. Desert Island Survival Game . This classic game is sure to inspire student engagement, as they use their critical thinking skills to survive being stranded on a desert island. Students have to watch out for ideological assumptions and question ideas in order to determine the appropriate items to bring. Learn More: ED Foundations. 9.
Teachers, for example, can use role-playing games in the classroom to help students inhabit different perspectives and understand them as part of larger, holistic systems of thought, explains Matthew Farber, a former teacher and assistant professor at the University of Northern Colorado who studies the intersection of game-based learning and SEL. This system of thinking can become a good entry ...
Sequence Letters is a game designed for ages 4-7, making it the perfect literacy and word work center for the kindergarten and first-grade classroom. To play, students name the letter on their card, say the sound for that letter, and then match it to a picture on the board that begins with that letter sound.
If you are looking for examples of critical thinking in the classroom, then read our article 11 activities that promote critical thinking skills in the classroom. Critical Thinking Lessons and Activities. 2. Questioning. Asking open-ended questions is another effective way to promote critical thinking skills in your classroom.
The team at TeachThought have compiled their list of games to promote better peer-to-peer learning in the classroom. Collaborative game-playing in the classroom teaches cooperation and communication among students, and complements structured textbook learning. TeachThought lists 10 games to accelerate students' critical thinking.
Cornell Critical Thinking Tests Gr. 5-12+ Cranium Crackers Gr. 3-12+ Creative Problem Solving Gr. PreK-2 ; Critical Thinking Activities to Improve Writing Gr. 4-12+ Critical Thinking Coloring Gr. PreK-2 ; Critical Thinking Detective
8. Big Paper - Building a Silent Conversation. Writing (or drawing) and silence are used as tools to slow down thinking and allow for silent reflection, unfiltered. By using silence and writing, students can focus on other viewpoints. This activity uses a driving question, markers, and Big Paper.
These games encourage movement, helping students to expend energy and improve their physical fitness. Hot Potato: Pass an object (the "potato") around a circle while music plays. When the music stops, the person holding the potato is out. Encourages quick thinking and awareness. Duck, Duck, Goose: Children sit in a circle, and one person ...
This article explores practical strategies to enhance critical thinking skills, leveraging the power of inquiry-based learning and open-ended questioning. Asking open-ended questions is a cornerstone of promoting critical thinking. By challenging students with questions that require more than a yes or no answer, educators can stimulate deeper ...
Critical thinking in the classroom is a common term used by educators. Critical thinking has been called "the art of thinking about thinking" (Ruggiero, V.R., 2012) with the intent to improve one's thinking. The challenge, of course, is to create learning environments that promote critical thinking both in the classroom and beyond.
Collaborative learning and peer-to-peer teaching activities can greatly enhance student learning and engagement in the classroom. This work evaluates the implementation of an additional required class period dedicated to collaborative problem solving activities. A two-semester integrative upper-level anatomy and physiology course (Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 and 2) was revised for the 2022 ...
Project-Based Learning (PBL) is an educational methodology that offers numerous benefits for students by fostering collaboration, critical thinking, and the practical application of knowledge. If you're interested in adopting PBL in your classroom, here are some practical tips and step-by-step strategies to help you implement it effectively: 1.
This course aims to empower educators with practical tools and strategies to promote creative learning experiences in the classroom. Through interactive workshops and collaborative projects, participants will gain hands-on experience in designing STEAM-based activities that foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
DALLAS (AP) — Dallas Stars defenseman Chris Tanev will be a game-time decision for Game 5 of the Western Conference Final on Friday night after taking a shot of his right foot in the previous game. Coach Pete DeBoer said at the morning skate Friday that he was optimistic that Tanev could play. Tanev got hurt in the second period of Game 4 on ...
FORT WORTH, Texas (AP) — Brody Malone is officially back. The two-time national champion surged to the lead at the U.S. men's gymnastics championships on Thursday, posting an all-around total of 85.950 to build a significant lead over Fred Richard and Donnell Whittenburg. The 24-year-old Malone — a member of the 2020 Olympic team and a two ...
BOTTOM LINE: The Dallas Stars visit the Edmonton Oilers in the third round of the NHL Playoffs with a 2-1 lead in the series. The teams meet Monday for the seventh time this season. The Stars won 5-3 in the last meeting. Jason Robertson led the Stars with three goals. Edmonton has a 49-27-6 record overall and a 32-11-5 record in home games.
Now one of the global sport's young superstars gets his first trip to the NBA Finals. Doncic had a 20-point first quarter on his way to 36 points for his high this postseason, and the Mavericks beat the Minnesota Timberwolves 124-103 on Thursday night to breeze through the Western Conference finals in five games.