Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?

A conversation with a Wheelock researcher, a BU student, and a fourth-grade teacher

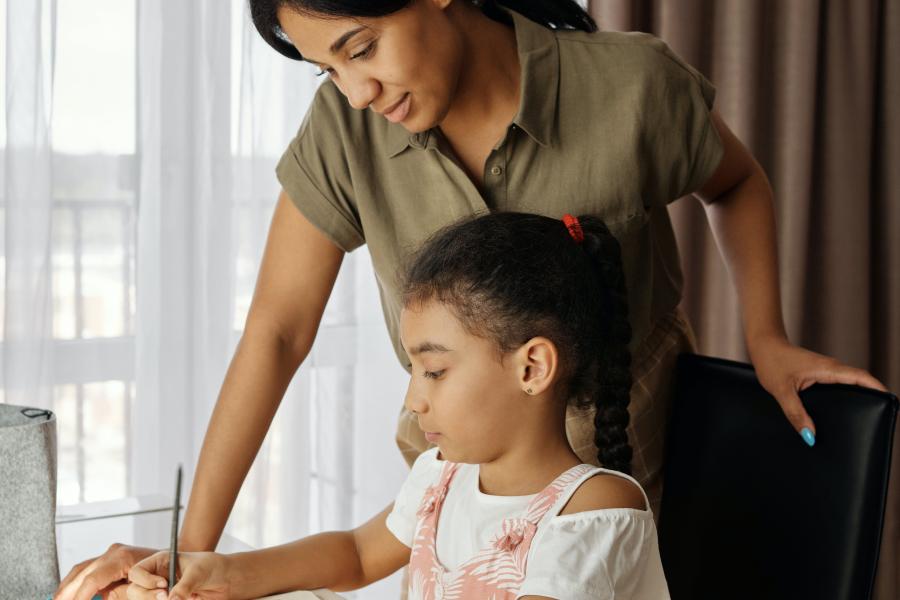
“Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives,” says Wheelock’s Janine Bempechat. “It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.” Photo by iStock/Glenn Cook Photography
Do your homework.
If only it were that simple.
Educators have debated the merits of homework since the late 19th century. In recent years, amid concerns of some parents and teachers that children are being stressed out by too much homework, things have only gotten more fraught.
“Homework is complicated,” says developmental psychologist Janine Bempechat, a Wheelock College of Education & Human Development clinical professor. The author of the essay “ The Case for (Quality) Homework—Why It Improves Learning and How Parents Can Help ” in the winter 2019 issue of Education Next , Bempechat has studied how the debate about homework is influencing teacher preparation, parent and student beliefs about learning, and school policies.
She worries especially about socioeconomically disadvantaged students from low-performing schools who, according to research by Bempechat and others, get little or no homework.
BU Today sat down with Bempechat and Erin Bruce (Wheelock’17,’18), a new fourth-grade teacher at a suburban Boston school, and future teacher freshman Emma Ardizzone (Wheelock) to talk about what quality homework looks like, how it can help children learn, and how schools can equip teachers to design it, evaluate it, and facilitate parents’ role in it.
BU Today: Parents and educators who are against homework in elementary school say there is no research definitively linking it to academic performance for kids in the early grades. You’ve said that they’re missing the point.
Bempechat : I think teachers assign homework in elementary school as a way to help kids develop skills they’ll need when they’re older—to begin to instill a sense of responsibility and to learn planning and organizational skills. That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success. If we greatly reduce or eliminate homework in elementary school, we deprive kids and parents of opportunities to instill these important learning habits and skills.
We do know that beginning in late middle school, and continuing through high school, there is a strong and positive correlation between homework completion and academic success.
That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success.
You talk about the importance of quality homework. What is that?
Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives. It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.

What are your concerns about homework and low-income children?
The argument that some people make—that homework “punishes the poor” because lower-income parents may not be as well-equipped as affluent parents to help their children with homework—is very troubling to me. There are no parents who don’t care about their children’s learning. Parents don’t actually have to help with homework completion in order for kids to do well. They can help in other ways—by helping children organize a study space, providing snacks, being there as a support, helping children work in groups with siblings or friends.
Isn’t the discussion about getting rid of homework happening mostly in affluent communities?
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That’s problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Teachers may not have as high expectations for lower-income children. Schools should bear responsibility for providing supports for kids to be able to get their homework done—after-school clubs, community support, peer group support. It does kids a disservice when our expectations are lower for them.
The conversation around homework is to some extent a social class and social justice issue. If we eliminate homework for all children because affluent children have too much, we’re really doing a disservice to low-income children. They need the challenge, and every student can rise to the challenge with enough supports in place.
What did you learn by studying how education schools are preparing future teachers to handle homework?
My colleague, Margarita Jimenez-Silva, at the University of California, Davis, School of Education, and I interviewed faculty members at education schools, as well as supervising teachers, to find out how students are being prepared. And it seemed that they weren’t. There didn’t seem to be any readings on the research, or conversations on what high-quality homework is and how to design it.
Erin, what kind of training did you get in handling homework?
Bruce : I had phenomenal professors at Wheelock, but homework just didn’t come up. I did lots of student teaching. I’ve been in classrooms where the teachers didn’t assign any homework, and I’ve been in rooms where they assigned hours of homework a night. But I never even considered homework as something that was my decision. I just thought it was something I’d pull out of a book and it’d be done.
I started giving homework on the first night of school this year. My first assignment was to go home and draw a picture of the room where you do your homework. I want to know if it’s at a table and if there are chairs around it and if mom’s cooking dinner while you’re doing homework.
The second night I asked them to talk to a grown-up about how are you going to be able to get your homework done during the week. The kids really enjoyed it. There’s a running joke that I’m teaching life skills.
Friday nights, I read all my kids’ responses to me on their homework from the week and it’s wonderful. They pour their hearts out. It’s like we’re having a conversation on my couch Friday night.
It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Bempechat : I can’t imagine that most new teachers would have the intuition Erin had in designing homework the way she did.
Ardizzone : Conversations with kids about homework, feeling you’re being listened to—that’s such a big part of wanting to do homework….I grew up in Westchester County. It was a pretty demanding school district. My junior year English teacher—I loved her—she would give us feedback, have meetings with all of us. She’d say, “If you have any questions, if you have anything you want to talk about, you can talk to me, here are my office hours.” It felt like she actually cared.
Bempechat : It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Ardizzone : But can’t it lead to parents being overbearing and too involved in their children’s lives as students?
Bempechat : There’s good help and there’s bad help. The bad help is what you’re describing—when parents hover inappropriately, when they micromanage, when they see their children confused and struggling and tell them what to do.
Good help is when parents recognize there’s a struggle going on and instead ask informative questions: “Where do you think you went wrong?” They give hints, or pointers, rather than saying, “You missed this,” or “You didn’t read that.”
Bruce : I hope something comes of this. I hope BU or Wheelock can think of some way to make this a more pressing issue. As a first-year teacher, it was not something I even thought about on the first day of school—until a kid raised his hand and said, “Do we have homework?” It would have been wonderful if I’d had a plan from day one.
Explore Related Topics:
- Share this story
Senior Contributing Editor

Sara Rimer A journalist for more than three decades, Sara Rimer worked at the Miami Herald , Washington Post and, for 26 years, the New York Times , where she was the New England bureau chief, and a national reporter covering education, aging, immigration, and other social justice issues. Her stories on the death penalty’s inequities were nominated for a Pulitzer Prize and cited in the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision outlawing the execution of people with intellectual disabilities. Her journalism honors include Columbia University’s Meyer Berger award for in-depth human interest reporting. She holds a BA degree in American Studies from the University of Michigan. Profile
She can be reached at [email protected] .
Comments & Discussion
Boston University moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (EST) and can only accept comments written in English. Statistics or facts must include a citation or a link to the citation.
There are 81 comments on Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
Insightful! The values about homework in elementary schools are well aligned with my intuition as a parent.
when i finish my work i do my homework and i sometimes forget what to do because i did not get enough sleep
same omg it does not help me it is stressful and if I have it in more than one class I hate it.
Same I think my parent wants to help me but, she doesn’t care if I get bad grades so I just try my best and my grades are great.
I think that last question about Good help from parents is not know to all parents, we do as our parents did or how we best think it can be done, so maybe coaching parents or giving them resources on how to help with homework would be very beneficial for the parent on how to help and for the teacher to have consistency and improve homework results, and of course for the child. I do see how homework helps reaffirm the knowledge obtained in the classroom, I also have the ability to see progress and it is a time I share with my kids
The answer to the headline question is a no-brainer – a more pressing problem is why there is a difference in how students from different cultures succeed. Perfect example is the student population at BU – why is there a majority population of Asian students and only about 3% black students at BU? In fact at some universities there are law suits by Asians to stop discrimination and quotas against admitting Asian students because the real truth is that as a group they are demonstrating better qualifications for admittance, while at the same time there are quotas and reduced requirements for black students to boost their portion of the student population because as a group they do more poorly in meeting admissions standards – and it is not about the Benjamins. The real problem is that in our PC society no one has the gazuntas to explore this issue as it may reveal that all people are not created equal after all. Or is it just environmental cultural differences??????
I get you have a concern about the issue but that is not even what the point of this article is about. If you have an issue please take this to the site we have and only post your opinion about the actual topic
This is not at all what the article is talking about.
This literally has nothing to do with the article brought up. You should really take your opinions somewhere else before you speak about something that doesn’t make sense.
we have the same name
so they have the same name what of it?
lol you tell her
totally agree
What does that have to do with homework, that is not what the article talks about AT ALL.
Yes, I think homework plays an important role in the development of student life. Through homework, students have to face challenges on a daily basis and they try to solve them quickly.I am an intense online tutor at 24x7homeworkhelp and I give homework to my students at that level in which they handle it easily.
More than two-thirds of students said they used alcohol and drugs, primarily marijuana, to cope with stress.
You know what’s funny? I got this assignment to write an argument for homework about homework and this article was really helpful and understandable, and I also agree with this article’s point of view.
I also got the same task as you! I was looking for some good resources and I found this! I really found this article useful and easy to understand, just like you! ^^
i think that homework is the best thing that a child can have on the school because it help them with their thinking and memory.
I am a child myself and i think homework is a terrific pass time because i can’t play video games during the week. It also helps me set goals.
Homework is not harmful ,but it will if there is too much
I feel like, from a minors point of view that we shouldn’t get homework. Not only is the homework stressful, but it takes us away from relaxing and being social. For example, me and my friends was supposed to hang at the mall last week but we had to postpone it since we all had some sort of work to do. Our minds shouldn’t be focused on finishing an assignment that in realty, doesn’t matter. I completely understand that we should have homework. I have to write a paper on the unimportance of homework so thanks.
homework isn’t that bad
Are you a student? if not then i don’t really think you know how much and how severe todays homework really is
i am a student and i do not enjoy homework because i practice my sport 4 out of the five days we have school for 4 hours and that’s not even counting the commute time or the fact i still have to shower and eat dinner when i get home. its draining!
i totally agree with you. these people are such boomers
why just why
they do make a really good point, i think that there should be a limit though. hours and hours of homework can be really stressful, and the extra work isn’t making a difference to our learning, but i do believe homework should be optional and extra credit. that would make it for students to not have the leaning stress of a assignment and if you have a low grade you you can catch up.
Studies show that homework improves student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicates that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” On both standardized tests and grades, students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school.
So how are your measuring student achievement? That’s the real question. The argument that doing homework is simply a tool for teaching responsibility isn’t enough for me. We can teach responsibility in a number of ways. Also the poor argument that parents don’t need to help with homework, and that students can do it on their own, is wishful thinking at best. It completely ignores neurodiverse students. Students in poverty aren’t magically going to find a space to do homework, a friend’s or siblings to help them do it, and snacks to eat. I feel like the author of this piece has never set foot in a classroom of students.
THIS. This article is pathetic coming from a university. So intellectually dishonest, refusing to address the havoc of capitalism and poverty plays on academic success in life. How can they in one sentence use poor kids in an argument and never once address that poor children have access to damn near 0 of the resources affluent kids have? Draw me a picture and let’s talk about feelings lmao what a joke is that gonna put food in their belly so they can have the calories to burn in order to use their brain to study? What about quiet their 7 other siblings that they share a single bedroom with for hours? Is it gonna force the single mom to magically be at home and at work at the same time to cook food while you study and be there to throw an encouraging word?
Also the “parents don’t need to be a parent and be able to guide their kid at all academically they just need to exist in the next room” is wild. Its one thing if a parent straight up is not equipped but to say kids can just figured it out is…. wow coming from an educator What’s next the teacher doesn’t need to teach cause the kid can just follow the packet and figure it out?
Well then get a tutor right? Oh wait you are poor only affluent kids can afford a tutor for their hours of homework a day were they on average have none of the worries a poor child does. Does this address that poor children are more likely to also suffer abuse and mental illness? Like mentioned what about kids that can’t learn or comprehend the forced standardized way? Just let em fail? These children regularly are not in “special education”(some of those are a joke in their own and full of neglect and abuse) programs cause most aren’t even acknowledged as having disabilities or disorders.
But yes all and all those pesky poor kids just aren’t being worked hard enough lol pretty sure poor children’s existence just in childhood is more work, stress, and responsibility alone than an affluent child’s entire life cycle. Love they never once talked about the quality of education in the classroom being so bad between the poor and affluent it can qualify as segregation, just basically blamed poor people for being lazy, good job capitalism for failing us once again!
why the hell?
you should feel bad for saying this, this article can be helpful for people who has to write a essay about it
This is more of a political rant than it is about homework
I know a teacher who has told his students their homework is to find something they are interested in, pursue it and then come share what they learn. The student responses are quite compelling. One girl taught herself German so she could talk to her grandfather. One boy did a research project on Nelson Mandela because the teacher had mentioned him in class. Another boy, a both on the autism spectrum, fixed his family’s computer. The list goes on. This is fourth grade. I think students are highly motivated to learn, when we step aside and encourage them.
The whole point of homework is to give the students a chance to use the material that they have been presented with in class. If they never have the opportunity to use that information, and discover that it is actually useful, it will be in one ear and out the other. As a science teacher, it is critical that the students are challenged to use the material they have been presented with, which gives them the opportunity to actually think about it rather than regurgitate “facts”. Well designed homework forces the student to think conceptually, as opposed to regurgitation, which is never a pretty sight
Wonderful discussion. and yes, homework helps in learning and building skills in students.
not true it just causes kids to stress
Homework can be both beneficial and unuseful, if you will. There are students who are gifted in all subjects in school and ones with disabilities. Why should the students who are gifted get the lucky break, whereas the people who have disabilities suffer? The people who were born with this “gift” go through school with ease whereas people with disabilities struggle with the work given to them. I speak from experience because I am one of those students: the ones with disabilities. Homework doesn’t benefit “us”, it only tears us down and put us in an abyss of confusion and stress and hopelessness because we can’t learn as fast as others. Or we can’t handle the amount of work given whereas the gifted students go through it with ease. It just brings us down and makes us feel lost; because no mater what, it feels like we are destined to fail. It feels like we weren’t “cut out” for success.
homework does help
here is the thing though, if a child is shoved in the face with a whole ton of homework that isn’t really even considered homework it is assignments, it’s not helpful. the teacher should make homework more of a fun learning experience rather than something that is dreaded
This article was wonderful, I am going to ask my teachers about extra, or at all giving homework.
I agree. Especially when you have homework before an exam. Which is distasteful as you’ll need that time to study. It doesn’t make any sense, nor does us doing homework really matters as It’s just facts thrown at us.
Homework is too severe and is just too much for students, schools need to decrease the amount of homework. When teachers assign homework they forget that the students have other classes that give them the same amount of homework each day. Students need to work on social skills and life skills.
I disagree.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning and responsible character traits. And it can give parents an opportunity to see what’s going on at school and let them express positive attitudes toward achievement.
Homework is helpful because homework helps us by teaching us how to learn a specific topic.
As a student myself, I can say that I have almost never gotten the full 9 hours of recommended sleep time, because of homework. (Now I’m writing an essay on it in the middle of the night D=)
I am a 10 year old kid doing a report about “Is homework good or bad” for homework before i was going to do homework is bad but the sources from this site changed my mind!
Homeowkr is god for stusenrs
I agree with hunter because homework can be so stressful especially with this whole covid thing no one has time for homework and every one just wants to get back to there normal lives it is especially stressful when you go on a 2 week vaca 3 weeks into the new school year and and then less then a week after you come back from the vaca you are out for over a month because of covid and you have no way to get the assignment done and turned in
As great as homework is said to be in the is article, I feel like the viewpoint of the students was left out. Every where I go on the internet researching about this topic it almost always has interviews from teachers, professors, and the like. However isn’t that a little biased? Of course teachers are going to be for homework, they’re not the ones that have to stay up past midnight completing the homework from not just one class, but all of them. I just feel like this site is one-sided and you should include what the students of today think of spending four hours every night completing 6-8 classes worth of work.
Are we talking about homework or practice? Those are two very different things and can result in different outcomes.
Homework is a graded assignment. I do not know of research showing the benefits of graded assignments going home.
Practice; however, can be extremely beneficial, especially if there is some sort of feedback (not a grade but feedback). That feedback can come from the teacher, another student or even an automated grading program.
As a former band director, I assigned daily practice. I never once thought it would be appropriate for me to require the students to turn in a recording of their practice for me to grade. Instead, I had in-class assignments/assessments that were graded and directly related to the practice assigned.
I would really like to read articles on “homework” that truly distinguish between the two.
oof i feel bad good luck!
thank you guys for the artical because I have to finish an assingment. yes i did cite it but just thanks
thx for the article guys.
Homework is good
I think homework is helpful AND harmful. Sometimes u can’t get sleep bc of homework but it helps u practice for school too so idk.
I agree with this Article. And does anyone know when this was published. I would like to know.
It was published FEb 19, 2019.
Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college.
i think homework can help kids but at the same time not help kids
This article is so out of touch with majority of homes it would be laughable if it wasn’t so incredibly sad.
There is no value to homework all it does is add stress to already stressed homes. Parents or adults magically having the time or energy to shepherd kids through homework is dome sort of 1950’s fantasy.
What lala land do these teachers live in?
Homework gives noting to the kid
Homework is Bad
homework is bad.
why do kids even have homework?
Comments are closed.
Latest from Bostonia
American academy of arts & sciences welcomes five bu members, com’s newest journalism grad took her time, could boston be the next city to impose congestion pricing, alum has traveled the world to witness total solar eclipses, opening doors: rhonda harrison (eng’98,’04, grs’04), campus reacts and responds to israel-hamas war, reading list: what the pandemic revealed, remembering com’s david anable, cas’ john stone, “intellectual brilliance and brilliant kindness”, one good deed: christine kannler (cas’96, sph’00, camed’00), william fairfield warren society inducts new members, spreading art appreciation, restoring the “black angels” to medical history, in the kitchen with jacques pépin, feedback: readers weigh in on bu’s new president, com’s new expert on misinformation, and what’s really dividing the nation, the gifts of great teaching, sth’s walter fluker honored by roosevelt institute, alum’s debut book is a ramadan story for children, my big idea: covering construction sites with art, former terriers power new professional women’s hockey league.
Duke Study: Homework Helps Students Succeed in School, As Long as There Isn't Too Much
The study, led by professor Harris Cooper, also shows that the positive correlation is much stronger for secondary students than elementary students
- Share this story on facebook
- Share this story on twitter
- Share this story on reddit
- Share this story on linkedin
- Get this story's permalink
- Print this story
It turns out that parents are right to nag: To succeed in school, kids should do their homework.
Duke University researchers have reviewed more than 60 research studies on homework between 1987 and 2003 and concluded that homework does have a positive effect on student achievement.
Harris Cooper, a professor of psychology, said the research synthesis that he led showed the positive correlation was much stronger for secondary students --- those in grades 7 through 12 --- than those in elementary school.
READ MORE: Harris Cooper offers tips for teaching children in the next school year in this USA Today op-ed published Monday.
"With only rare exception, the relationship between the amount of homework students do and their achievement outcomes was found to be positive and statistically significant," the researchers report in a paper that appears in the spring 2006 edition of "Review of Educational Research."
Cooper is the lead author; Jorgianne Civey Robinson, a Ph.D. student in psychology, and Erika Patall, a graduate student in psychology, are co-authors. The research was supported by a grant from the U.S. Department of Education.
While it's clear that homework is a critical part of the learning process, Cooper said the analysis also showed that too much homework can be counter-productive for students at all levels.
"Even for high school students, overloading them with homework is not associated with higher grades," Cooper said.
Cooper said the research is consistent with the "10-minute rule" suggesting the optimum amount of homework that teachers ought to assign. The "10-minute rule," Cooper said, is a commonly accepted practice in which teachers add 10 minutes of homework as students progress one grade. In other words, a fourth-grader would be assigned 40 minutes of homework a night, while a high school senior would be assigned about two hours. For upper high school students, after about two hours' worth, more homework was not associated with higher achievement.
The authors suggest a number of reasons why older students benefit more from homework than younger students. First, the authors note, younger children are less able than older children to tune out distractions in their environment. Younger children also have less effective study habits.
But the reason also could have to do with why elementary teachers assign homework. Perhaps it is used more often to help young students develop better time management and study skills, not to immediately affect their achievement in particular subject areas.
"Kids burn out," Cooper said. "The bottom line really is all kids should be doing homework, but the amount and type should vary according to their developmental level and home circumstances. Homework for young students should be short, lead to success without much struggle, occasionally involve parents and, when possible, use out-of-school activities that kids enjoy, such as their sports teams or high-interest reading."
Cooper pointed out that there are limitations to current research on homework. For instance, little research has been done to assess whether a student's race, socioeconomic status or ability level affects the importance of homework in his or her achievement.
This is Cooper's second synthesis of homework research. His first was published in 1989 and covered nearly 120 studies in the 20 years before 1987. Cooper's recent paper reconfirms many of the findings from the earlier study.
Cooper is the author of "The Battle over Homework: Common Ground for Administrators, Teachers, and Parents" (Corwin Press, 2001).
Link to this page
Copy and paste the URL below to share this page.
- About the Hub
- Announcements
- Faculty Experts Guide
- Subscribe to the newsletter
Explore by Topic
- Arts+Culture
- Politics+Society
- Science+Technology
- Student Life
- University News
- Voices+Opinion
- About Hub at Work
- Gazette Archive
- Benefits+Perks
- Health+Well-Being
- Current Issue
- About the Magazine
- Past Issues
- Support Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Subscribe to the Magazine
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Credit: August de Richelieu
Does homework still have value? A Johns Hopkins education expert weighs in
Joyce epstein, co-director of the center on school, family, and community partnerships, discusses why homework is essential, how to maximize its benefit to learners, and what the 'no-homework' approach gets wrong.
By Vicky Hallett
The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein , co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work," Epstein says.
But after decades of researching how to improve schools, the professor in the Johns Hopkins School of Education remains certain that homework is essential—as long as the teachers have done their homework, too. The National Network of Partnership Schools , which she founded in 1995 to advise schools and districts on ways to improve comprehensive programs of family engagement, has developed hundreds of improved homework ideas through its Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program. For an English class, a student might interview a parent on popular hairstyles from their youth and write about the differences between then and now. Or for science class, a family could identify forms of matter over the dinner table, labeling foods as liquids or solids. These innovative and interactive assignments not only reinforce concepts from the classroom but also foster creativity, spark discussions, and boost student motivation.
"We're not trying to eliminate homework procedures, but expand and enrich them," says Epstein, who is packing this research into a forthcoming book on the purposes and designs of homework. In the meantime, the Hub couldn't wait to ask her some questions:
What kind of homework training do teachers typically get?
Future teachers and administrators really have little formal training on how to design homework before they assign it. This means that most just repeat what their teachers did, or they follow textbook suggestions at the end of units. For example, future teachers are well prepared to teach reading and literacy skills at each grade level, and they continue to learn to improve their teaching of reading in ongoing in-service education. By contrast, most receive little or no training on the purposes and designs of homework in reading or other subjects. It is really important for future teachers to receive systematic training to understand that they have the power, opportunity, and obligation to design homework with a purpose.
Why do students need more interactive homework?
If homework assignments are always the same—10 math problems, six sentences with spelling words—homework can get boring and some kids just stop doing their assignments, especially in the middle and high school years. When we've asked teachers what's the best homework you've ever had or designed, invariably we hear examples of talking with a parent or grandparent or peer to share ideas. To be clear, parents should never be asked to "teach" seventh grade science or any other subject. Rather, teachers set up the homework assignments so that the student is in charge. It's always the student's homework. But a good activity can engage parents in a fun, collaborative way. Our data show that with "good" assignments, more kids finish their work, more kids interact with a family partner, and more parents say, "I learned what's happening in the curriculum." It all works around what the youngsters are learning.
Is family engagement really that important?
At Hopkins, I am part of the Center for Social Organization of Schools , a research center that studies how to improve many aspects of education to help all students do their best in school. One thing my colleagues and I realized was that we needed to look deeply into family and community engagement. There were so few references to this topic when we started that we had to build the field of study. When children go to school, their families "attend" with them whether a teacher can "see" the parents or not. So, family engagement is ever-present in the life of a school.
My daughter's elementary school doesn't assign homework until third grade. What's your take on "no homework" policies?
There are some parents, writers, and commentators who have argued against homework, especially for very young children. They suggest that children should have time to play after school. This, of course is true, but many kindergarten kids are excited to have homework like their older siblings. If they give homework, most teachers of young children make assignments very short—often following an informal rule of 10 minutes per grade level. "No homework" does not guarantee that all students will spend their free time in productive and imaginative play.
Some researchers and critics have consistently misinterpreted research findings. They have argued that homework should be assigned only at the high school level where data point to a strong connection of doing assignments with higher student achievement . However, as we discussed, some students stop doing homework. This leads, statistically, to results showing that doing homework or spending more minutes on homework is linked to higher student achievement. If slow or struggling students are not doing their assignments, they contribute to—or cause—this "result."
Teachers need to design homework that even struggling students want to do because it is interesting. Just about all students at any age level react positively to good assignments and will tell you so.
Did COVID change how schools and parents view homework?
Within 24 hours of the day school doors closed in March 2020, just about every school and district in the country figured out that teachers had to talk to and work with students' parents. This was not the same as homeschooling—teachers were still working hard to provide daily lessons. But if a child was learning at home in the living room, parents were more aware of what they were doing in school. One of the silver linings of COVID was that teachers reported that they gained a better understanding of their students' families. We collected wonderfully creative examples of activities from members of the National Network of Partnership Schools. I'm thinking of one art activity where every child talked with a parent about something that made their family unique. Then they drew their finding on a snowflake and returned it to share in class. In math, students talked with a parent about something the family liked so much that they could represent it 100 times. Conversations about schoolwork at home was the point.
How did you create so many homework activities via the Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program?
We had several projects with educators to help them design interactive assignments, not just "do the next three examples on page 38." Teachers worked in teams to create TIPS activities, and then we turned their work into a standard TIPS format in math, reading/language arts, and science for grades K-8. Any teacher can use or adapt our prototypes to match their curricula.
Overall, we know that if future teachers and practicing educators were prepared to design homework assignments to meet specific purposes—including but not limited to interactive activities—more students would benefit from the important experience of doing their homework. And more parents would, indeed, be partners in education.
Posted in Voices+Opinion
You might also like
News network.
- Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Get Email Updates
- Submit an Announcement
- Submit an Event
- Privacy Statement
- Accessibility
Discover JHU
- About the University
- Schools & Divisions
- Academic Programs
- Plan a Visit
- my.JohnsHopkins.edu
- © 2024 Johns Hopkins University . All rights reserved.
- University Communications
- 3910 Keswick Rd., Suite N2600, Baltimore, MD
- X Facebook LinkedIn YouTube Instagram
The Cult of Homework
America’s devotion to the practice stems in part from the fact that it’s what today’s parents and teachers grew up with themselves.

America has long had a fickle relationship with homework. A century or so ago, progressive reformers argued that it made kids unduly stressed , which later led in some cases to district-level bans on it for all grades under seventh. This anti-homework sentiment faded, though, amid mid-century fears that the U.S. was falling behind the Soviet Union (which led to more homework), only to resurface in the 1960s and ’70s, when a more open culture came to see homework as stifling play and creativity (which led to less). But this didn’t last either: In the ’80s, government researchers blamed America’s schools for its economic troubles and recommended ramping homework up once more.
The 21st century has so far been a homework-heavy era, with American teenagers now averaging about twice as much time spent on homework each day as their predecessors did in the 1990s . Even little kids are asked to bring school home with them. A 2015 study , for instance, found that kindergarteners, who researchers tend to agree shouldn’t have any take-home work, were spending about 25 minutes a night on it.
But not without pushback. As many children, not to mention their parents and teachers, are drained by their daily workload, some schools and districts are rethinking how homework should work—and some teachers are doing away with it entirely. They’re reviewing the research on homework (which, it should be noted, is contested) and concluding that it’s time to revisit the subject.
Read: My daughter’s homework is killing me
Hillsborough, California, an affluent suburb of San Francisco, is one district that has changed its ways. The district, which includes three elementary schools and a middle school, worked with teachers and convened panels of parents in order to come up with a homework policy that would allow students more unscheduled time to spend with their families or to play. In August 2017, it rolled out an updated policy, which emphasized that homework should be “meaningful” and banned due dates that fell on the day after a weekend or a break.
“The first year was a bit bumpy,” says Louann Carlomagno, the district’s superintendent. She says the adjustment was at times hard for the teachers, some of whom had been doing their job in a similar fashion for a quarter of a century. Parents’ expectations were also an issue. Carlomagno says they took some time to “realize that it was okay not to have an hour of homework for a second grader—that was new.”
Most of the way through year two, though, the policy appears to be working more smoothly. “The students do seem to be less stressed based on conversations I’ve had with parents,” Carlomagno says. It also helps that the students performed just as well on the state standardized test last year as they have in the past.
Earlier this year, the district of Somerville, Massachusetts, also rewrote its homework policy, reducing the amount of homework its elementary and middle schoolers may receive. In grades six through eight, for example, homework is capped at an hour a night and can only be assigned two to three nights a week.
Jack Schneider, an education professor at the University of Massachusetts at Lowell whose daughter attends school in Somerville, is generally pleased with the new policy. But, he says, it’s part of a bigger, worrisome pattern. “The origin for this was general parental dissatisfaction, which not surprisingly was coming from a particular demographic,” Schneider says. “Middle-class white parents tend to be more vocal about concerns about homework … They feel entitled enough to voice their opinions.”
Schneider is all for revisiting taken-for-granted practices like homework, but thinks districts need to take care to be inclusive in that process. “I hear approximately zero middle-class white parents talking about how homework done best in grades K through two actually strengthens the connection between home and school for young people and their families,” he says. Because many of these parents already feel connected to their school community, this benefit of homework can seem redundant. “They don’t need it,” Schneider says, “so they’re not advocating for it.”
That doesn’t mean, necessarily, that homework is more vital in low-income districts. In fact, there are different, but just as compelling, reasons it can be burdensome in these communities as well. Allison Wienhold, who teaches high-school Spanish in the small town of Dunkerton, Iowa, has phased out homework assignments over the past three years. Her thinking: Some of her students, she says, have little time for homework because they’re working 30 hours a week or responsible for looking after younger siblings.
As educators reduce or eliminate the homework they assign, it’s worth asking what amount and what kind of homework is best for students. It turns out that there’s some disagreement about this among researchers, who tend to fall in one of two camps.
In the first camp is Harris Cooper, a professor of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University. Cooper conducted a review of the existing research on homework in the mid-2000s , and found that, up to a point, the amount of homework students reported doing correlates with their performance on in-class tests. This correlation, the review found, was stronger for older students than for younger ones.
This conclusion is generally accepted among educators, in part because it’s compatible with “the 10-minute rule,” a rule of thumb popular among teachers suggesting that the proper amount of homework is approximately 10 minutes per night, per grade level—that is, 10 minutes a night for first graders, 20 minutes a night for second graders, and so on, up to two hours a night for high schoolers.
In Cooper’s eyes, homework isn’t overly burdensome for the typical American kid. He points to a 2014 Brookings Institution report that found “little evidence that the homework load has increased for the average student”; onerous amounts of homework, it determined, are indeed out there, but relatively rare. Moreover, the report noted that most parents think their children get the right amount of homework, and that parents who are worried about under-assigning outnumber those who are worried about over-assigning. Cooper says that those latter worries tend to come from a small number of communities with “concerns about being competitive for the most selective colleges and universities.”
According to Alfie Kohn, squarely in camp two, most of the conclusions listed in the previous three paragraphs are questionable. Kohn, the author of The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing , considers homework to be a “reliable extinguisher of curiosity,” and has several complaints with the evidence that Cooper and others cite in favor of it. Kohn notes, among other things, that Cooper’s 2006 meta-analysis doesn’t establish causation, and that its central correlation is based on children’s (potentially unreliable) self-reporting of how much time they spend doing homework. (Kohn’s prolific writing on the subject alleges numerous other methodological faults.)
In fact, other correlations make a compelling case that homework doesn’t help. Some countries whose students regularly outperform American kids on standardized tests, such as Japan and Denmark, send their kids home with less schoolwork , while students from some countries with higher homework loads than the U.S., such as Thailand and Greece, fare worse on tests. (Of course, international comparisons can be fraught because so many factors, in education systems and in societies at large, might shape students’ success.)
Kohn also takes issue with the way achievement is commonly assessed. “If all you want is to cram kids’ heads with facts for tomorrow’s tests that they’re going to forget by next week, yeah, if you give them more time and make them do the cramming at night, that could raise the scores,” he says. “But if you’re interested in kids who know how to think or enjoy learning, then homework isn’t merely ineffective, but counterproductive.”
His concern is, in a way, a philosophical one. “The practice of homework assumes that only academic growth matters, to the point that having kids work on that most of the school day isn’t enough,” Kohn says. What about homework’s effect on quality time spent with family? On long-term information retention? On critical-thinking skills? On social development? On success later in life? On happiness? The research is quiet on these questions.
Another problem is that research tends to focus on homework’s quantity rather than its quality, because the former is much easier to measure than the latter. While experts generally agree that the substance of an assignment matters greatly (and that a lot of homework is uninspiring busywork), there isn’t a catchall rule for what’s best—the answer is often specific to a certain curriculum or even an individual student.
Given that homework’s benefits are so narrowly defined (and even then, contested), it’s a bit surprising that assigning so much of it is often a classroom default, and that more isn’t done to make the homework that is assigned more enriching. A number of things are preserving this state of affairs—things that have little to do with whether homework helps students learn.
Jack Schneider, the Massachusetts parent and professor, thinks it’s important to consider the generational inertia of the practice. “The vast majority of parents of public-school students themselves are graduates of the public education system,” he says. “Therefore, their views of what is legitimate have been shaped already by the system that they would ostensibly be critiquing.” In other words, many parents’ own history with homework might lead them to expect the same for their children, and anything less is often taken as an indicator that a school or a teacher isn’t rigorous enough. (This dovetails with—and complicates—the finding that most parents think their children have the right amount of homework.)
Barbara Stengel, an education professor at Vanderbilt University’s Peabody College, brought up two developments in the educational system that might be keeping homework rote and unexciting. The first is the importance placed in the past few decades on standardized testing, which looms over many public-school classroom decisions and frequently discourages teachers from trying out more creative homework assignments. “They could do it, but they’re afraid to do it, because they’re getting pressure every day about test scores,” Stengel says.
Second, she notes that the profession of teaching, with its relatively low wages and lack of autonomy, struggles to attract and support some of the people who might reimagine homework, as well as other aspects of education. “Part of why we get less interesting homework is because some of the people who would really have pushed the limits of that are no longer in teaching,” she says.
“In general, we have no imagination when it comes to homework,” Stengel says. She wishes teachers had the time and resources to remake homework into something that actually engages students. “If we had kids reading—anything, the sports page, anything that they’re able to read—that’s the best single thing. If we had kids going to the zoo, if we had kids going to parks after school, if we had them doing all of those things, their test scores would improve. But they’re not. They’re going home and doing homework that is not expanding what they think about.”
“Exploratory” is one word Mike Simpson used when describing the types of homework he’d like his students to undertake. Simpson is the head of the Stone Independent School, a tiny private high school in Lancaster, Pennsylvania, that opened in 2017. “We were lucky to start a school a year and a half ago,” Simpson says, “so it’s been easy to say we aren’t going to assign worksheets, we aren’t going assign regurgitative problem sets.” For instance, a half-dozen students recently built a 25-foot trebuchet on campus.
Simpson says he thinks it’s a shame that the things students have to do at home are often the least fulfilling parts of schooling: “When our students can’t make the connection between the work they’re doing at 11 o’clock at night on a Tuesday to the way they want their lives to be, I think we begin to lose the plot.”
When I talked with other teachers who did homework makeovers in their classrooms, I heard few regrets. Brandy Young, a second-grade teacher in Joshua, Texas, stopped assigning take-home packets of worksheets three years ago, and instead started asking her students to do 20 minutes of pleasure reading a night. She says she’s pleased with the results, but she’s noticed something funny. “Some kids,” she says, “really do like homework.” She’s started putting out a bucket of it for students to draw from voluntarily—whether because they want an additional challenge or something to pass the time at home.
Chris Bronke, a high-school English teacher in the Chicago suburb of Downers Grove, told me something similar. This school year, he eliminated homework for his class of freshmen, and now mostly lets students study on their own or in small groups during class time. It’s usually up to them what they work on each day, and Bronke has been impressed by how they’ve managed their time.
In fact, some of them willingly spend time on assignments at home, whether because they’re particularly engaged, because they prefer to do some deeper thinking outside school, or because they needed to spend time in class that day preparing for, say, a biology test the following period. “They’re making meaningful decisions about their time that I don’t think education really ever gives students the experience, nor the practice, of doing,” Bronke said.
The typical prescription offered by those overwhelmed with homework is to assign less of it—to subtract. But perhaps a more useful approach, for many classrooms, would be to create homework only when teachers and students believe it’s actually needed to further the learning that takes place in class—to start with nothing, and add as necessary.
Homework: Facts and Fiction
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 09 November 2021
- Cite this living reference work entry

- Rubén Fernández-Alonso 4 , 5 &
- José Muñiz 6
Part of the book series: Springer International Handbooks of Education ((SIHE))
263 Accesses
4 Citations
Homework is a universal student practice. Despite this universality, the role that homework plays in student academic performance is complex and open to various interpretations. This chapter reviews the current available evidence about the relationships between homework and achievement. We begin by examining the differences between countries and follow that by reviewing the influence of variables related to student homework behavior, teaching practices around assigning homework, and the role of the family in helping with homework. The results indicate that the relationship between time spent on homework and school results is curvilinear, and the best results are seen to be associated with moderate amounts of daily homework. With regard to student homework behavior, there is abundant evidence indicating that the “how” is much more important than the “how much.” Commitment and effort, the emotions prompted by the task, and autonomous working are three key aspects in predicting academic achievement. Effective teaching practice around homework is determined by setting it daily and systematic review. Although family involvement in the educational process is desirable, in the case of homework, direct help has doubtful effects on student achievement.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Bembenutty, H., & White, M. C. (2013). Academic performance and satisfaction with homework completion among college students. Learning and Individual Differences, 24 , 83–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2012.10.013
Article Google Scholar
Borgonovi, F., & Montt, G. (2012). Parental involvement in selected PISA countries and economies . OECD Education Working Papers, 73. OECD Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1787/5k990rk0jsjj-en .
Castro, M., Expósito-Casas, E., López-Martín, E., Lizasoain, L., Navarro-Asencio, E., & Gaviria, J. L. (2015). Parental involvement on student achievement: A meta-analysis. Educational Research Review, 14 , 33–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2015.01.002
Cooper, H. (1989). Homework . Longman. https://doi.org/10.1037/11578-000
Book Google Scholar
Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003. Review of Educational Research, 76 , 1–62. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543076001001
Cooper, H., & Valentine, J. C. (2001). Using research to answer practical questions about homework. Educational Psychologist, 36 (3), 143–153. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15326985EP3603_1
Corno, L. (1996). Homework is a complicated thing. Educational Researcher, 25 (8), 27–30. www.jstor.org/stable/1176489
De Jong, R., Westerhof, K. J., & Creemers, B. P. M. (2000). Homework and student math achievement in junior high schools. Educational Research and Evaluation, 6 (2), 130–157. https://doi.org/10.1076/1380-3611(200006)6:2;1-E;F130
Dettmers, S., Trautwein, U., Lüdtke, M., Kunter, M., & Baumert, J. (2010). Homework works if homework quality is high: Using multilevel modeling to predict the development of achievement in mathematics. Journal of Educational Psychology, 102 , 467–482. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0018453
Dettmers, S., Trautwein, U., & Lüdtke, O. (2009). The relationship between homework time and achievement is not universal: Evidence from multilevel analyses in 40 countries. School Effectiveness and School Improvement, 20 (4), 375–405. https://doi.org/10.1080/09243450902904601
Dettmers, S., Trautwein, U., Lüdtke, O., Goetz, T., Pekrun, R., & Frenzel, A. (2011). Students‘ emotions during homework in mathematics: Testing a theoretical model of antecedents and achievement outcomes. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 36 , 25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2010.10.001
Dumont, H., Trautwein, U., Nagy, G., & Nagengast, B. (2014). Quality of parental homework involvement: Predictors and reciprocal relations with academic functioning in the reading domain. Journal of Educational Psychology, 102 , 144–161. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0034100
Epstein, J. L. (1988). Homework practices, achievements, and behaviors of elementary school students . Center for Research on Elementary and Middle Schools, Johns Hopkins University. Retrieved December 13, 2020, from: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED301322
Epstein, J. L., & Van Voorhis, F. L. (2001). More than minutes: Teachers’ roles in designing homework. Educational Psychologist, 36 (3), 181–193. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15326985EP3603_4
Falch, T., & Rønning, M. (2012). Homework assignment and student achievement in OECD countries . Statistics Norway discussion papers, 711. Statistics Norway. Retrieved April 15, 2020, from: http://hdl.handle.net/10419/192693
Fan, H., Xu, J., Cai, Z., He, J., & Fan, X. (2017). Homework and students’ achievement in math and science: A 30-year meta-analysis, 1986–2015. Educational Research Review, 20 , 35–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2016.11.003
Farrow, S., Tymms, P., & Henderson, B. (1999). Homework and attainment in primary schools. British Educational Research Journal, 25 (3), 323–341. https://doi.org/10.1080/0141192990250304
Fernández-Alonso, R., Álvarez-Díaz, M., Suárez-Álvarez, J., & Muñiz, J. (2017). Students’ achievement and homework assignment strategies. Frontiers in Psychology, 8 , 286. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00286
Fernández-Alonso, R., Álvarez-Díaz, M., Woitschach, P., Suárez-Álvarez, J., & Cuesta, M. (2017). Parental involvement and academic performance: Less control and more communication. Psicothema, 29 , 453–461. https://doi.org/10.7334/psicothema2017.181
Fernández-Alonso, R., Suárez-Álvarez, J., & Muñiz, J. (2015). Adolescents’ homework performance in mathematics and science: Personal factors and teaching practices. Journal of Educational Psychology, 107 (4), 1075–1085. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000032
Fernández-Alonso, R., Suárez-Álvarez, J., & Muñiz, J. (2016). Homework and performance in mathematics: The role of the teacher, the family and the student’s background. Revista de Psicodidáctica, 21 (1), 5–23. https://doi.org/10.1387/RevPsicodidact.13939
Fernández-Alonso, R., Woitschach, P., Álvarez-Díaz, M., González-López, A. M., Cuesta, M., & Muñiz, J. (2019). Homework and academic achievement in Latin America: A multilevel approach. Frontiers in Psychology, 10 , 95. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00095
Flunger, B., Trautwein, U., Nagengast, B., Lüdtke, O., Niggli, A., & Schnyder, I. (2015). The Janus-faced nature of time spent on homework: Using latent profile analyses to predict academic achievement over a school year. Learning and Instruction, 39 , 97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2015.05.008
Flunger, B., Trautwein, U., Nagengast, B., Lüdtke, O., Niggli, A., & Schnyder, I. (2017). A person-centered approach to homework behavior: Students’ characteristics predict their homework learning type. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 48 , 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2016.07.002
Flunger, B., Trautwein, U., Nagengast, B., Lüdtke, O., Niggli, A., & Schnyder, I. (2019). Using multilevel mixture models in educational research: An illustration with homework research. The Journal of Experimental Education. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220973.2019.1652137
Goetz, T., Nett, U. E., Martiny, S. E., Hall, N. C., Pekrun, R., Dettmers, S., & Trautwein, U. (2012). Students’ emotions during homework: Structures, self-concept antecedents, and achievement outcomes. Learning and Individual Differences, 22 , 225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2011.04.006
Gustafsson, J. E. (2013). Causal inference in educational effectiveness research: A comparison of three methods to investigate effects of homework on student achievement. School Effectiveness and School Improvement, 24 (3), 275–295. https://doi.org/10.1080/09243453.2013.806334
Hattie, J. (2009). Visible learning. A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement . Routledge.
Google Scholar
Hill, N. E., & Tyson, D. F. (2009). Parental involvement in middle school: A meta-analytic assessment of the strategies that promote achievement. Developmental Psychology, 45 (3), 740–763. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0015362
Hoover-Dempsey, K. V., Battiato, A. C., Walker, J. M. T., Reed, R. P., DeJong, J. M., & Jones, K. P. (2001). Parental involvement in homework. Educational Psychologist, 36 , 195–210. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15326985EP3603_5
Jerrim, J., Lopez-Agudo, L. A., & Marcenaro-Gutierrez, O. D. (2020). The association between homework and primary school children’s academic achievement. International evidence from PIRLS and TIMSS. European Journal of Education, 00 , 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejed.12374
Kim, S. w., & Hill, N. E. (2015). Including fathers in the picture: A meta-analysis of parental involvement and students’ academic achievement. Journal of Educational Psychology, 107 (4), 919–934. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000023
Kitsantas, A., Cheema, J., & Ware, H. (2011). Mathematics achievement: The role of homework and self-efficacy beliefs. Journal of Advanced Academics, 22 (2), 310–339. https://doi.org/10.1177/1932202X1102200206
Kitsantas, A., & Zimmerman, B. J. (2009). College students homework and academic achievement: The mediating role of self-regulatory beliefs. Metacognition and Learning, 4 (2), 1556–1623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-008-9028-y
Lee, J., & Stankov, L. (2018). Non-cognitive predictors of academic achievement: Evidence from TIMSS and PISA. Learning and Individual Differences, 65 , 50–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2018.05.009
Moroni, S., Dumont, H., Trautwein, U., Niggli, A., & Baeriswyl, F. (2015). The need to distinguish between quantity and quality in research on parental involvement: The example of parental help with homework. Journal of Educational Research, 108 (5), 417–431. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2014.901283
Murillo, F. J. (2003). La investigación sobre eficacia escolar en Iberoamérica. Revisión Internacional sobre el estado del arte [Research on school effectiveness in Latin America. An international review] . Convenio Andrés Bello. Retrieved December 13, 2020, from: http://convenioandresbello.org/cab/educacion/eficacia-escolar-en-iberoamerica/
Núñez, J. C., Suárez, N., Cerezo, R., González-Pienda, J., Rosário, P., Mourão, R., & Valle, A. (2015). Homework and academic achievement across Spanish compulsory education. Educational Psychology, 35 (6), 726–746. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410.2013.817537
Núñez, J. C., Suárez, N., Rosário, P., Vallejo, G., Cerezo, R., & Valle, A. (2015). Teachers’ feedback on homework, homework-related behaviors, and academic achievement. The Journal of Educational Research, 108 , 204–216. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2013.878298
OECD. (2013). PISA 2012 results: What makes schools successful? Resources, policies and practices (volume IV) . OECD Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264201156-en
Paschal, R. A., Weinstein, T., & Walberg, H. J. (1984). The effects of homework on learning: A quantitative synthesis. The Journal of Educational Research, 78 (2), 97–104. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.1984.10885581
Patall, E. A., Cooper, H., & Robinson, J. C. (2008). Parent involvement in homework: A research synthesis. Review of Educational Research, 78 (4), 1039–1101. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654308325185
Pomerantz, E. M., Moorman, E. A., & Litwack, S. D. (2007). The how, whom, and why of parents’ involvement in children’s academic lives: More is not always better. Review of Educational Research, 77 (3), 373–410. https://doi.org/10.3102/003465430305567
Ramdass, D., & Zimmerman, B. J. (2011). Developing self-regulation skills: The important role of homework. Journal of Advanced Academics, 22 , 194–218. https://doi.org/10.1177/1932202X1102200202
Raudenbush, S. W., & Bryk, A. S. (2002). Hierarchical linear models: Applications and data analysis methods . Sage.
Rosário, P., Cunha, J., Nunes, T., Nunes, A. R., Moreira, T., & Núñez, J. C. (2019). “Homework should be…but we do not live in an ideal world”: Mathematics teachers’ perspectives on quality homework and on homework assigned in elementary and middle schools. Frontiers in Psychology, 10 , 224. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00224
Rosário, P., Mourão, R., Baldaque, M., Nunes. T., Núñez, J. C., González-Pienda, J. A., Cerezo, R., & Valle A. (2009). Homework, self-regulated learning and Math achievement. Revista de Psicodidáctica, 14 (2), 179–192. Retrieved December 13, 2020, from: https://ojs.ehu.eus/index.php/psicodidactica/article/view/721
Sammons, P., Hillman, J., & Mortimore, P. (1995). Key characteristics of effective schools: A review of school effectiveness research . Office for Standards in Education. Retrieved December 13, 2020, from: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED389826
Scheerens, J. (2016). Educational effectiveness and ineffectiveness. A critical review of the knowledge base . Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-7459-8
Scheerens, J., Hendriks, M., Luyten, H., Sleegers, P., & Cees, G. (2013). Productive time in education. A review of the effectiveness of teaching time at school, homework and extended time outside school hours . University of Twente. Retrieved April 15, 2020, from: https://research.utwente.nl/en/publications/productive-time-in-education-a-review-of-the-effectiveness-of-tea
Scheerens, J., Witziers, B., & Steen, R. (2013). A meta-analysis of school effectiveness studies. Revista de Educación, 361 , 619–645. https://doi.org/10.4438/1988-592X-RE-2013-361-235
Shell, D. F., Brooks, D. W., Trainin, G., Wilson, K. M., Kauffman, D. F., & Herr, L. M. (2010). The unified learning model . Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-3215-7
Sirin, S. R. (2005). Socioeconomic status and academic achievement: A Meta-Analytic review of research. Review of Educational Research, 75 (3), 417–453. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543075003417
Stoeger, H., & Ziegler, A. (2008). Evaluation of a classroom based training to improve self-regulation in time management tasks during homework activities with fourth graders. Metacognition and Learning, 3 , 207–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-008-9027-z
Tan, C. Y., Lyu, M., & Peng, B. (2019). Academic benefits from parental involvement are stratified by parental socioeconomic status: A Meta-analysis. Parenting , 1–47. https://doi.org/10.1080/15295192.2019.1694836
Tan, C. Y., Peng, B., & Lyu, M. (2019). What types of cultural capital benefit students’ academic achievement at different educational stages? Interrogating the meta-analytic evidence. Educational Research Review , 100289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2019.100289
Trautwein, U. (2007). The homework–achievement relation reconsidered: Differentiating homework time, homework frequency, and homework effort. Learning and Instruction, 17 , 372–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2007.02.009
Trautwein, U., & Köller, O. (2003). The relationship between homework and achievement: Still much of a mystery. Educational Psychology Review, 15 , 115–145. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023460414243
Trautwein, U., Köller, O., Schmitz, B., & Baumert, J. (2002). Do homework assignments enhance achievement? A multilevel analysis in 7th grade mathematics. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 27 , 26–50. https://doi.org/10.1006/ceps.2001.1084
Trautwein, U., & Lüdtke, O. (2007). Students’ self-reported effort and time on homework in six school subjects: Between-student differences and within-student variation. Journal of Educational Psychology, 99 , 432–444. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.99.2.432
Trautwein, U., Niggli, A., Schnyder, I., & Lüdtke, O. (2009). Between-teacher differences in homework assignments and the development of students’ homework effort, homework emotions, and achievement. Journal of Educational Psychology, 101 , 176–189. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.101.1.176
Trautwein, U., Schnyder, I., Niggli, A., Neumann, M., & Lüdtke, O. (2009). Chameleon effects in homework research: The homework–achievement association depends on the measures used and the level of analysis chosen. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 34 , 77–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2008.09.001
UNESCO, & LLECE. (2000). Primer Estudio Internacional Comparativo sobre lenguaje, matemática y factores asociados, para alumnos del tercer y cuarto grado de la educación básica [First international comparative study on language, mathematics and associated factors, for third and fourth grade students of basic education] . UNESCO.
UNESCO-OREALC, & LLECE. (2016). Informe de resultados del Tercer Estudio regional Comparativo y Explicativo. Factores Asociados [Report of the third regional comparative and explanatory study. Effectiveness factors] . UNESCO.
Valle, A., Piñeiro, I., Rodríguez, S., Regueiro, B., Freire, C., & Rosário, P. (2019). Time spent and time management in homework in elementary school students: A person-centered approach. Psicothema, 31 (4), 422–428. https://doi.org/10.7334/psicothema2019.191
Wilder, S. (2014). Effects of parental involvement on academic achievement: A meta-synthesis. Educational Review, 66 (3), 377–397. https://doi.org/10.1080/00131911.2013.780009
Wingard, L., & Forsberg, L. (2009). Parent involvement in children’s homework in American and Swedish dual-earner families. Journal of Pragmatics, 41 , 1576–1595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pragma.2007.09.010
Xu, J. (2013). Why do students have difficulties completing homework? The need for homework management. Journal of Education and Training Studies, 1 (1), 98–105. https://doi.org/10.11114/jets.v1i1.78
Xu, J., & Wu, H. (2013). Self-regulation of homework behavior: Homework management at the secondary school level. The Journal of Educational Research, 106 (1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2012.658457
Xu, J., Yuan, R., Xu, B., & Xu, M. (2014). Modeling students’ time management in math homework. Learning and Individual Differences, 34 , 33–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2014.05.011
Zimmerman, B. J., & Kitsantas, A. (2005). Homework practices and academic achievement: The mediating role of self-efficacy and perceived responsibility beliefs. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 30 , 397–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2005.05.003
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Education, Government of Principado de Asturias, Oviedo, Spain
Rubén Fernández-Alonso
University of Oviedo, Oviedo, Spain
Nebrija University, Madrid, Spain
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rubén Fernández-Alonso .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
University of Oslo, Blindern, Oslo, Norway
Trude Nilsen
IEA Hamburg, Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany
Agnes Stancel-Piątak
University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
Jan-Eric Gustafsson
Section Editor information
CEMO, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway
Ronny Scherer
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Fernández-Alonso, R., Muñiz, J. (2021). Homework: Facts and Fiction. In: Nilsen, T., Stancel-Piątak, A., Gustafsson, JE. (eds) International Handbook of Comparative Large-Scale Studies in Education. Springer International Handbooks of Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-38298-8_40-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-38298-8_40-1
Received : 31 January 2021
Accepted : 03 February 2021
Published : 09 November 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-38298-8
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-38298-8
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Education Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Education
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Your Stories
Evidence Based Living
Bridging the gap between research and real life
- In The Media
- The Learning Center
- Cornell Cooperative Extension
- Youth Development
- Health and Wellness
What we know about homework
I went looking for evidence and found lots of it: there are at least a half dozen systematic reviews about the importance and effectiveness of homework, and all of its nuances. The Center for Public Education and the Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development both provide comprehensive essays that summarize the evidence on homework.
One 2007 analysis published by Duke University researchers in particular caught my attention . It included 50 separate studies on homework research that asked the specific question, “Does homework improve academic achievement?” This study followed an earlier meta-analysis of approximately 100 studies published by the same researchers in 1989. Both reviews conclude that homework does help to improve academic achievement, primarily in the middle and high school. For children in elementary school, the review concludes that while homework can help children develop good study habits, it does not help to improve students’ grades or standardized test scores.
Here are some other interesting take-home messages about homework:
- Students are more likely to complete and learn from homework assignments that have a purpose, for example, reviewing important concepts, improving students’ independence or providing opportunities to explore topics students are interested in.
- Homework assignments are most successful when they are easy enough for students to complete independently, but challenging enough to be interesting.
- Finding appropriate ways to involve parents with their children’s homework leads to improved academic performance.
- Homework provides more academic benefits for older students. For younger students, some homework can help them to establish study habits and routines, but too much homework detracts from family and play activities after school.
- There is strong evidence that homework improves learning for students with learning disabilities, most likely because these students benefit from additional time to practice new skills.
On a personal note, the evidence makes me wonder if my son receives a little too much homework for his age. In first grade, he receives a reading and a math assignment every day, and he often groans about completing them. I certainly plan to discuss the evidence about homework with his teacher at our first conference.
Homework word looks very easy, but for students they know more about it means. From a tutor point of view, Here are some other interesting take-home messages about homework like If a student will take homework help from experts, they will feel free to complete their own homework before deadline. They can feel stress free and can study well. Thanks
Speak Your Mind Cancel reply
A project at…, evidence-based blogs.
- Bandolier Evidence-Based Health Care
- British Psychological Society Research Digest
- Economics in Cooperative Extension
- EPB Exchange
- New Voices for Research
- Research Blogging
- Trust the Evidence
Subscribe by e-mail
Please, insert a valid email.
Thank you, your email will be added to the mailing list once you click on the link in the confirmation email.
Spam protection has stopped this request. Please contact site owner for help.
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Return to top of page
Copyright © 2024 · Magazine Theme on Genesis Framework · WordPress · Log in
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychol
Academic Goals, Student Homework Engagement, and Academic Achievement in Elementary School
Antonio valle.
1 Department of Developmental and Educational Psychology, University of A Coruña, A Coruña, Spain
Bibiana Regueiro
José c. núñez.
2 Department of Psychology, University of Oviedo, Oviedo, Spain
Susana Rodríguez
Isabel piñeiro, pedro rosário.
3 Departmento de Psicologia Aplicada, Universidade do Minho, Braga, Portugal
There seems to be a general consensus in the literature that doing homework is beneficial for students. Thus, the current challenge is to examine the process of doing homework to find which variables may help students to complete the homework assigned. To address this goal, a path analysis model was fit. The model hypothesized that the way students engage in homework is explained by the type of academic goals set, and it explains the amount of time spend on homework, the homework time management, and the amount of homework done. Lastly, the amount of homework done is positively related to academic achievement. The model was fit using a sample of 535 Spanish students from the last three courses of elementary school (aged 9 to 13). Findings show that: (a) academic achievement was positively associated with the amount of homework completed, (b) the amount of homework completed was related to the homework time management, (c) homework time management was associated with the approach to homework, (d) and the approach to homework, like the rest of the variables of the model (except for the time spent on homework), was related to the student's academic motivation (i.e., academic goals).
Introduction
Literature indicates that doing homework regularly is positively associated with students' academic achievement (Zimmerman and Kitsantas, 2005 ). Hence, as expected, the amount of homework done is one of the variables that shows a strong and positive relationship with academic achievement (Cooper et al., 2001 ).
It seems consensual in the literature that doing homework is always beneficial to students, but it is also true that the key for the academic success does not rely on the amount of homework done, but rather on how students engage on homework (Trautwein et al., 2009 ; Núñez et al., 2015c ), and on how homework engagement is related with student motivation (Martin, 2012 ). There is, therefore, a call to analyze the process of homework rather than just the product; that is, to examine the extent to which the quality of the process of doing homework may be relevant to the final outcome.
Trautwein's model of homework
The model by Trautwein et al. ( 2006b ) is rooted in the motivational theories, namely the theory of the expectancy value (Eccles (Parsons) et al., 1983 ; Pintrich and De Groot, 1990 ), and the theory of self-determination (Deci et al., 2002 ), as well as on theories of learning and instruction (Boekaerts, 1999 ). Trautwein and colleagues' model analyzes students' related variables in two blocks, as follows: the motivational (aiming at directing and sustaining the behavior) and the cognitive and behavioral implications (cognitions and behaviors related to the moment of doing homework).These two blocks of variables are rooted in the literature. Motivational variables are related with the theory of expectancy-value by Eccles (Parsons) et al. ( 1983 ), while the variables addressing students' implication are related with the school engagement framework (e.g., Fredricks et al., 2004 ). However, as Eccles and Wang ( 2012 ) stress, both models are interrelated due to the fact that both variables are closely related and show reciprocal relationships.
Student homework engagement: the interplay between cognitive and behavioral components
Engagement is a relatively new construct with great relevance in the field of psychology and instruction (Fredricks et al., 2004 ). Generally considered, engagement has been described as the active implication of the person in an activity (Reeve et al., 2004 ). However, despite the close relation between engagement and motivation, literature clearly differentiates between them (e.g., Martin, 2012 ), stressing engagement as the behavioral manifestation of motivation (Skinner and Pitzer, 2012 ), or arguing that motivation is a precursor of engagement rather than part of it. In sum, motivation relates to the “why” whereas the engagement focuses on the “what” of a particular behavior.
Consistent with this perspective, the current research fitted a model with the variable engagement mediating the relationship between motivation and academic achievement (see Eccles and Wang, 2012 ). Engagement is a complex construct with observational and non-observational aspects (Appleton et al., 2008 ). Some researchers conceptualize engagement with two dimensions—behavior and emotions (e.g., Marks, 2000 )—while others define engagement with four dimensions—academic, behavioral, cognitive, and emotional (e.g., Appleton et al., 2006 ). In the current study, we followed Fredricks' et al. ( 2004 ) conceptualization of engagement as a construct with three dimensions: cognitive (e.g., approaches to learning), behavioral (e.g., student homework behaviors), and emotional (e.g., interest, boredom). For the purpose of the present study, the dimension of emotion was not included in the model (see Figure Figure1 1 ).

General model hypothesized to explain the relationship between academic motivation, student homework engagement, and academic achievement .
Cognitive homework engagement
In the past few decades, a robust body of research has been addressing the relationship between the way students deal with their learning process and academic outcomes (Marton and Säljö, 1976a , b ; Struyven et al., 2006 ; Rosário et al., 2010a , 2013a ). Marton and Säljö ( 1976a , b ) examined how students studied an academic text and found two ways of approaching the task: a surface and a deep approach. The surface approach is characterized by learning the contents aiming at achieving goals that are extrinsic to the learning content. In contrast, the deep approach is characterized by an intrinsic interest in the task and students are likely to be focused on understanding the learning content, relating it to prior knowledge and to the surrounding environment (Entwistle, 2009 ; Rosário et al., 2010b ). The metaphor “surface vs. deep” constitutes an easy to perceive conceptual framework, both in the classroom setting and in other educational settings (i.e., doing homework at home), and has been shown to be a powerful tool for parents, teachers, and students when conceptualizing the ways students approach school tasks (Entwistle, 1991 ; Rosário et al., 2005 ). The core of the concept of approaches to studying (or to learning) is the metacognitive connection between an intention to approach a task and a strategy to implement it (Rosário et al., 2013b ).
The process of doing homework focuses on what students do when completing homework, that is, how they approach their work and how they manage their personal resources and settings while doing homework. It is likely that students' approaches to homework may influence not only the final homework outcome but also the quality of that process. Students who adopt a deep approach are likely to engage their homework with the intention of deepening their understanding of the knowledge learned in class. In this process, students often relate the homework exercises to prior knowledge and monitor their mastery of the content learned. This process involves intrinsic intention to understand the ideas and the use of strategies to build meaning (Cano et al., 2014 ). In contrast, students who approach homework with a surface approach are likely to do homework with extrinsic motivation (e.g., rewards of their parents, fear of upsetting their teacher). Their goals may target finishing homework as soon as and with the less effort possible to be able to do more interesting activities. Students using this approach are more likely to do homework to fulfill an external obligation (e.g., hand in homework in class and get a grade), than for the benefits for learning.
Behavioral homework engagement
Findings from prior research indicate that the more the implication of students in doing their homework the better the academic achievement (Cooper et al., 2006 ). Following Trautwein et al. ( 2006b ), our conceptualization of student homework engagement includes behaviors related with the amount of homework done, time spent on homework, and homework time management (e.g., concentration). In the present investigation, these three variables were included in the model (see Figure Figure1 1 ).
Extant findings on the relationship between the amount of homework done and academic achievement are in need of further clarification. Some authors argue for a strong and positive relationship (e.g., Cooper et al., 2006 ), while others found that this relationship is higher throughout schooling (Cooper et al., 2001 ; Zimmerman and Kitsantas, 2005 ). Authors explained this last finding arguing that the load of homework assigned by teachers vary throughout schooling, and also that the cognitive competencies of students are likely to vary with age (Muhlenbruck et al., 2000 ). More recently, Núñez et al. ( 2015c ) found that the relationship between these two variables varied as a function of the age of the students enrolled. Particularly, this relationship was found to be negative in elementary school, null in junior high school, and positive in high school.
Moreover, the relationship between the amount of homework done and academic achievement relates, among other factors, with the students' age, the quality of the homework assigned, the type of assessment, and the nature of the feedback provided. For example, some students may always complete their homework and get good grades for doing it, which does not mean that these students learn more (Kohn, 2006 ). In fact, more important than the quantity of the homework done, is the quality of that work (Fernández-Alonso et al., 2014 ).
Another variable included in the model was the time spent on homework. Findings on the relationship between time spent on homework and academic achievement are mixed. Some studies found a positive relationship (Cooper et al., 2001 , 2006 ) while others found a null or a negative one (Trautwein et al., 2006b , 2009 ). In 2009, Dettmers, Trautwein and Lüdtke conducted a study with data from the PISA 2003 (Dettmers et al., 2009 ). Findings on the relationship between the number of hours spent on homework and academic achievement in mathematics show that the students in countries with higher grades spend fewer hours doing homework than students in countries with low academic grades. At the student level, findings showed a negative relationship between time spent on homework and academic achievement in 12 out of 40 countries.
The relationship between the amount of homework done, time dedicated to homework, and academic achievement was hypothesized to be mediated by the homework time management. Xu ( 2007 ) was one of the pioneers examining the management of the time spent on homework. Initially, Xu ( 2007 ) did not find a relationship between time management and academic achievement (spend more time on homework is not equal to use efficient strategies for time management). Latter, Xu ( 2010 ) found a positive relationship between students' grade level, organized environment, and homework time management. More recently, Núñez et al. ( 2015c ) found that effective homework time management affects positively the amount of homework done, and, consequently, academic achievement. This relationship is stronger for elementary students when compared with students in high school.
Academic motivation and student homework engagement relationship
Literature has consistently shown that a deep approach to learning is associated positively with the quality of the learning outcomes (Rosário et al., 2013b ; Cano et al., 2014 ; Vallejo et al., 2014 ). The adoption of a deep approach to homework depends on many factors, but students self-set goals and their motives for doing homework are among the most critical motivational variables when students decide to engage in homework.
Literature on achievement motivation highlights academic goals as an important line of research (Ng, 2008 ). In the educational setting, whereas learning goals focus on the comprehension and mastery of the content, performance goals are more focused on achieving a better performance than their colleagues (Pajares et al., 2000 ; Gaudreau, 2012 ).
Extant literature reports a positive relationship between adopting learning goals and the use of cognitive and self-regulation strategies (Elliot et al., 1999 ; Núñez et al., 2013 ). In fact, students who value learning and show an intention to learn and improve their competences are likely to use deep learning strategies (Suárez et al., 2001 ; Valle et al., 2003a , b , 2015d ), which are aimed at understanding the content in depth. Moreover, these learning-goal oriented students are likely to self-regulate their learning process (Valle et al., 2015a ), put on effort to learn, and assume the control of their learning process (Rosário et al., 2016 ). These students persist much longer when they face difficult and challenging tasks than colleagues pursuing performance goals. The former also use more strategies oriented toward the comprehension of content, are more intrinsically motivated, and feel more enthusiasm about academic work. Some researchers also found positive relationships between learning goals and pro-social behavior (e.g., Inglés et al., 2013 ).
Reviewing the differentiation between learning goals and performance goals, Elliot and colleagues (Elliot and Church, 1997 ; Elliot, 1999 ; Elliot et al., 1999 ) proposed a three-dimensional framework for academic goals. In addition to learning goals, performance goals were differentiated as follows: (a) performance-approach goals, focused on achieving competence with regard to others; and (b) performance-avoidance goals, aimed at avoiding incompetence with regard to others. Various studies have provided empirical support for this distinction within performance goals (e.g., Wolters et al., 1996 ; Middleton and Midgley, 1997 ; Skaalvik, 1997 ; Rodríguez et al., 2001 ; Valle et al., 2006 ). Moreover, some authors proposed a similar differentiation for learning goals (Elliot, 1999 ). The rationale was as follows: learning goals are characterized by high engagement in academic tasks, so an avoidance tendency in such goals should reflect avoidance of this engagement. Hence, students who pursue a work avoidance goal are likely to avoid challenging tasks and to put on effort to do well, only doing the bare minimum to complete the task. In general, learning goals are associated with a large amount of positive results in diverse motivational, cognitive, and achievement outcomes, whereas performance goals have been linked to less adaptive outcomes, or even to negative outcomes (Valle et al., 2009 ).
Aims of this study
Several relationships between motivational, cognitive, and behavioral variables involving self-regulated learning in the classroom have recently been studied (Rosário et al., 2013a ). However, there is a lack of knowledge of the relationships between these variables throughout the process of doing homework.
The principal purpose of this work (see Figure Figure1) 1 ) is to analyze how student homework engagement (cognitive and behavioral) mediates motivation and academic performance. This study aims to provide new information about an issue that is taken for granted, but which, as far as we know, lacks empirical data. The question is: to what extent students acknowledge homework as a good way to acquire competence, improve their skills and performance? Our working hypothesis is that student value homework in this regard. Therefore, we hypothesized that the more students are motivated to learn, the more they will be involved (cognitively and behaviorally) in their homework, and the higher their academic achievement.
To address this goal, we developed a path analysis model (see Figure Figure1) 1 ) in which we hypothesized that: (a) the student's motivational level is significantly related to their cognitive homework engagement (i.e., the approach to studying applied to homework), and their behavioral homework engagement (i.e., amount of time spent and homework time management, and amount of homework completed); (b) student's cognitive and behavioral homework engagement are positively associated with academic achievement; and (c) cognitive and behavioral homework engagement are related (the more deep cognitive engagement, the more time spent and time management, and the more amount of homework is done).
Participants
The study enrolled 535 students, aged between 9 and 13 ( M = 10.32, SD = 0.99), of four public schools, from the last three years of the Spanish Elementary Education (4th, 5th, and 6th grade level), of whom 49.3% were boys. By grade, 40.4% ( n = 216) were enrolled in the 4th grade, 35.1% ( n = 188) in the 5th grade, and 24.5% ( n = 131) in the 6th grade.
Learning goals
The level and type of motivation for academic learning was assessed with the Academic Goals Instrument (Núñez et al., 1997 ). Although, this instrument allows differentiating a broad range of academic goals, for the purposes of this work, we only used the subscale of learning goals (i.e., competence and control). The instrument is rated on a 5-point Likert-type scale, with responses ranging from one (not at all interested) to five (absolutely interested in learning and acquiring competence and control in the different subjects). An example item is: “I make an effort in my studies because performing the academic tasks allows me to increase my knowledge.” The reliability of the scale is good (α = 0.87).
Approach to homework
To measure the process of approaching homework, we adapted the Students' Approaches to Learning Inventory (Rosário et al., 2010a , 2013a ), taking into account both the students' age and the homework contexts. This instrument is based on voluminous literature on approaches to learning (e.g., Biggs et al., 2001 ; Rosário et al., 2005 ), and provides information about two ways of approaching homework. For the purpose of this research, we only used the deep approach (e.g., “Before starting homework, I usually decide whether what was taught in class is clear and, if not, I review the lesson before I start”). Students respond to the items on a 5-point Likert-type scale ranging from one (not at all deep approach) to five (completely deep approach). The reliability of the scale is good (α = 0.80).
Time spent on homework, homework time management, and amount of homework completed
To measure these three variables, we used the Homework Survey (e.g., Rosário et al., 2009 ; Núñez et al., 2015a , b ; Valle et al., 2015b , c ). To measure the time spent on homework , students responded to three items (in general, in a typical week, on a typical weekend) with the general formulation, “How much time do you usually spend on homework?,” with the response options 1, <30 min; 2, 30 min to 1 h; 3, 1 h to an hour and a half; 4, 1 h and a half to 2 h; 5, more than 2 h. Homework time management was measured through the responses to three items (in general, in a typical week, on a typical weekend) in which they were asked to indicate how they managed the time normally spent doing homework, using the following scale: 1, I waste it completely (I am constantly distracted by anything); 2, I waste it more than I should; 3, regular; 4, I manage it pretty much; 5, I optimize it completely (I concentrate and until I finish, I don't think about anything else). Finally, the amount of homework completed by students (assigned by teachers) was assessed through responses to an item about the amount of homework usually done, using a 5-point Likert-type scale (1, none; 2, some; 3, one half; 4, almost all; 5, all).
Academic achievement
Assessment of academic achievement was assessed through students' report card grades in Spanish Language, Galician Language, English Language, Knowledge of the Environment, and Mathematics. Average achievement was calculated with the mean grades in these five areas.
Data of the target variables was collected during regular school hours, by research assistants, after obtaining the consent of the school administration and of the teachers and students. Prior to the application of the questionnaires, which took place in a single session, the participants were informed about the goals of the project, and assured that data was confidential and used for research purposes only.
Data analysis
The model was fit with AMOS 18 (Arbuckle, 2009 ). The data were previously analyzed and individual cases presenting a significant number of missing values were eliminated (2.1%), whereas the rest of the missing values were replaced by the mean. Taking into account the analysis of the characteristics of the variables (e.g., skewness and kurtosis in Table Table1), 1 ), we used the maximum likelihood method to fit the model and estimate the values of the parameters.
Means, standard deviations, skewness, kurtosis, and correlation matrix of the target variables .
A series of goodness-of-fit statistics were used to analyze our model. Beyond chi-square (χ 2 ) and its associated probability ( p ), the information provided by the goodness-of-fit index (GFI) and the adjusted goodness-of-fit index (AGFI; Jöreskog and Sörbom, 1983 ); the comparative fit index (CFI) (Bentler, 1990 ); and the root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA; Browne and Cudeck, 1993 ) was used. According to these authors, the model fits well when GFI and AGFI > 0.90, CFI > 0.95, and RMSEA ≤ 0.05.
Descriptive analysis
The relations between the variables included in the model as well as the descriptive statistics are shown in Table Table1. 1 . All the variables were significantly and positively related, except for the time spent on homework, which was only related to the amount of homework done. According to the value of the means of these variables, students in the last years of elementary school: (a) reported a high level of motivation to learn and mastery; (b) used preferentially a deep approach to homework; (c) did the homework assigned by the teachers most of the times; (d) usually spent about an hour a day on homework; (e) reported to manage their study time effectively; and (f) showed a medium-high level of academic achievement.
Evaluation and re-specification of the initial model
The data obtained indicated that the initial model (see Figure Figure1) 1 ) presented a poor fit to the empirical data: χ 2 = 155.80, df = 8, p < 0.001, GFI = 0.917, AGFI = 0.783, TLI = 0.534, CFI = 0.751, RMSEA = 0.186, 90% CI (0.161, 0.212), p < 0.001. Analysis of the modification indexes revealed the need to include three direct effects initially considered as null, and to eliminate a finally null effect (included in the initial model as significant). The strategy adopted to modify the initial model involved including and estimating the model each time a new effect was included. The final model comprised three effects (academic goals on homework time management, on amount of homework done, and on academic achievement) and the elimination of the initially established effect of the approach to studying on the time spent doing homework. The inclusion or elimination of the effects in the model was determined accounting for their statistical and theoretical significance. The final model resulting from these modifications is shown in Figure Figure2, 2 , with an adequate fit to the empirical data: χ 2 = 12.03, df = 6, p = 0.061, GFI = 0.993, AGFI = 0.974, TLI = 0.975, CFI = 0.990, RMSEA = 0.043, 90% CI (0.000, 0.079), p = 0.567.

The results of the fit of the hypothesized model (standardized outcomes): Relations in dashed lines were found to be statistically significant, but this was not established in the initial model .
Assessment of the relationships on the final model
Table Table2 2 presents the data obtained for the relationships considered in the final model (see also Figure Figure2 2 ).
Fit of the hypothesized model (standardized outcomes): final model of student engagement in homework .
The data from Table Table2 2 and Figure Figure2 2 indicates that the majority of the relationships between the variables are consistent with the hypotheses. First, we found a statistically significant association between the learning goals (i.e., competence and control), the approach to homework ( b = 0.50, p < 0.001), two of the variables associated with engagement in homework (the amount of homework done [ b = 0.27, p < 0.001], homework time management [ b = 0.30, p < 0.001]), and academic achievement ( b = 0.34, p < 0.001). These results indicate that the more oriented students are toward learning goals (i.e., competence and control), the deeper the approach to homework, the more homework is completed, the better the homework time management, and the higher the academic achievement.
Second, a statistically significant association between the deep approach and homework time management ( b = 0.30, p < 0.001) and the amount of homework done ( b = 0.09, p < 0.05) was found. These results reflect that the deeper the students' approach to homework, the better the management of the time spent on homework, and the more the homework done. Third, there was a statistically significant association between homework time management, time spent on homework, and the amount of homework done ( b = 0.23, p < 0.001, and b = 0.10, p < 0.01, respectively). These results confirm, as expected, that the more time students spent doing homework and the better students manage their homework time, the more homework they will do. Four, we found a statistically significant relation between the amount of homework done and academic achievement ( b = 0.20, p < 0.001). This indicates that the more homework students complete the better their academic achievement.
In summary, our findings indicate that: (a) academic achievement is positively associated with the amount of homework completed; (b) the amount of homework done is related to homework time management; (c) homework time management is associated with how homework is done (approach to homework); and (d) consistent with the behavior of the variables in the model (except for the time spent on homework), how homework is done (i.e., approach to homework) is explained to a great extent (see total effects in Table Table3) 3 ) by the student's type of academic motivation.
Standardized direct, indirect, and total effects for the final model .
Finally, taking into account both the direct effects (represented in Figure Figure2) 2 ) and the indirect ones (see Table Table3), 3 ), the model explained between 20 and 30% of the variance of the dependent variables (except for the time spent on homework, which is not explained at all): approach to homework (24.7%), time management (26.9%), amount of homework done (24.4%), and academic achievement (21.6%).
Consistent with prior research (e.g., Cooper et al., 2001 ), our findings showed that students' academic achievement in the last years of elementary education is closely related to the amount of homework done. In addition, the present study also confirms the importance of students' effort and commitment to doing homework (Trautwein et al., 2006a , b ), showing that academic achievement is also related with students' desire and interest to learn and improve their skills. Therefore, when teachers assign homework, it is essential to attend to students' typical approach to learning, which is mediated by the motivational profile and by the way students solve the tasks proposed (Hong et al., 2004 ). The results of this investigation suggest that the adoption of learning goals leads to important educational benefits (Meece et al., 2006 ), among which is doing homework.
Importantly, our study shows that the amount of homework done is associated not only with the time spent, but also with the time management. Time spent on homework should not be considered an absolute indicator of the amount of homework done, because students' cognitive skills, motivation, and prior knowledge may significantly affect the time needed to complete the homework assignment (Regueiro et al., 2015 ). For students, managing homework time is a challenge (Corno, 2000 ; Xu, 2008 ), but doing it correctly may have a positive influence on their academic success (Claessens et al., 2007 ), on homework completion (Xu, 2005 ), and on school achievement (Eilam, 2001 ).
Despite, that previous studies reported a positive relationship between the time spent on homework and academic achievement (Cooper et al., 2006 ), the present research shows that time spent on homework is not a relevant predictor of academic achievement. Other studies have also obtained similar results (Trautwein et al., 2009 ; Núñez et al., 2015a ), indicating that time spent on homework is negatively associated to academic achievement, perhaps because spending a lot of time on homework may indicate an inefficient working style and lack of motivation (Núñez et al., 2015a ). Besides, our data indicates that spending more time on homework is positively associated to the amount of homework done.
Although, some studies have found that students who spend more time on homework also tend to report greater commitment to school work (Galloway et al., 2013 ), our findings indicated that spending more time doing homework was not related to a deeper engagement on the task. A possible explanation may be that using a deep approach to school tasks subsumes engaging in homework with the aim of practicing but also to further extend the content learned in class. This approach does not depends on the time spent doing homework, rather on the students' motives for doing homework.
Another important contribution of this study concerns learning-oriented goals—usually associated with positive outcomes in motivational, cognitive, and achievement variables (Pajares et al., 2000 ). Results indicate that the motivation to increase competence and learning is also related to approaching homework deeply and to manage homework efficiently. Consistent with previous findings (Xu, 2005 ), these results provide additional empirical support to time management goals (Pintrich, 2004 ).
There is a robust relationship between learning-oriented goals and a deep approach, and between a deep approach and the amount of homework done. All this indicates that these results are in line with prior research, meaning that the adoption of a deep approach to learning is related with high quality academic achievement (Lindblom-Ylänne and Lonka, 1999 ; Rosário et al., 2013b ).
Educational implications and study limitations
One of the major limitations of this study lies in the type of research design used. We used a cross-sectional design to examine the effects among the variables within a path analysis model. However, to establish a cause-effect relationship a temporal sequence between two variables is needed a requirement that can only be met with longitudinal designs. Future studies should consider address this limitation.
Despite the above limitation, our results can be considered relevant and show important educational implications. It is essential for teachers and school administrators to be sensitized about the effects of teachers' homework follow-up practices on students' homework engagement (Rosário et al., 2015 ), and of these variables in students' school engagement and academic success. Likewise, research on students' learning should be undertaken from the perspective of the learners to understand how students use their knowledge and skills to do homework and to solve problems posed therein. On the other hand, research should examine in-depth the use of learning strategies during homework, as well as how students' motivations at an early age may foster homework completion and increase the quality of school outcomes. For this last purpose, teachers should pay attention not only to the acquisition of curricular content but also to the development of the appropriate thinking skills and self-regulated learning strategies (Rosário et al., 2010b ; Núñez et al., 2013 ). Finally, the amount of homework done and its positive relationship with academic achievement should be considered as a final outcome of a process rooted on a comprehensive and meaningful learning. Students motivated to learn are likely to approach homework deeply and manage homework time efficaciously. As a result, they tend to do more homework and outperform. In sum, is doing homework a good way to acquire competence, improve skills, and outperform? Our data suggest a positive answer.
Author contributions
AV and BR Collect data, data analysis, writing the paper. JN and PR data analysis, writing the paper. SR and IP writing the paper.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was developed through the funding of the research project EDU2013-44062-P, of the State Plan of Scientific and Technical Research and Innovation 2013-2016 (MINECO) and to the financing received by one of the authors in the FPU program of the Ministry of Education, Culture, and Sport.
- Appleton J. J., Christenson S. L., Furlong M. J. (2008). Student engagement with school: critical conceptual and methodological issues of the construct . Psychol. Sch. 45 , 369–386. 10.1002/pits.20303 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Appleton J. J., Christenson S. L., Kim D., Reschly A. L. (2006). Measuring cognitive and psychological engagement: validation of the student engagement instrument . J. Sch. Psychol. 44 , 427–445. 10.1016/j.jsp.2006.04.002 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Arbuckle J. L. (2009). Amos 18.0 User's Guide . Crawfordville, FL: Amos Development Corporation. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bentler P. M. (1990). Comparative fit indexes in structural models . Psychol. Bull. 107 , 238–246. 10.1037/0033-2909.107.2.238 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Biggs J., Kember D., Leung D. Y. (2001). The revised two-actor study process questionnaire: R-SPQ-2F . Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 71 , 133–149. 10.1348/000709901158433 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Boekaerts M. (1999). Self-regulated learning: where are today . Int. J. Educ. Res. 31 , 445–458. 10.1016/S0883-0355(99)00014-2 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Browne M. W., Cudeck R. (1993). Alternative ways of assessing model fit , in Testing Structural Equation Models , eds Bollen K., Long J. (Newbury Park, CA: Sage; ), 136–162. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cano F., García A., Justicia F., García-Berbén A. B. (2014). Enfoques de aprendizaje y comprensión lectora: el papel de las preguntas de los estudiantes y del conocimiento previo [Approaches to learning and reading comprehension: the role of students' questions and of prior knowledge] . Rev. Psicodidáctica 19 , 247–265. 10.1387/RevPsicodidact.10186 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Claessens B. J. C., van Eerde W., Rutte C. G., Roe R. A. (2007). A review of the time management literature . Pers. Rev. 36 , 255–276. 10.1108/00483480710726136 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper H., Jackson K., Nye B., Lindsay J. J. (2001). A model of homework's influence on the performance evaluations of elementary school students . J. Exp. Educ. 69 , 181–200. 10.1080/00220970109600655 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper H., Robinson J. C., Patall E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003 . Rev. Educ. Res. 76 , 1–62. 10.3102/00346543076001001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Corno L. (2000). Looking at homework differently . Element. Sch. J. 100 , 529–548. 10.1086/499654 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Deci E. L., Ryan R. M. (2002). Handbook of Self-Determination Research . New York, NY: University of Rochester Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dettmers S., Trautwein U., Lüdtke O. (2009). The relationship between homework time and achievement is not universal: evidence from multilevel analyses in 40 countries . Sch. Eff. Sch. Improv. 20 , 375–405. 10.1080/09243450902904601 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eccles J., Wang M. T. (2012). Part I Commentary: so what is student engagement anyway? ,in Handbook of Research on Student Engagement , eds Christenson S. L., Reschly A. L., Wylie C. (New York, NY: Springer; ), 133–145. [ Google Scholar ]
- Eccles (Parsons) J., Adler T. F., Futterman R., Goff S. B., Kaczala C. M., Meece J. L., et al. (1983). Expectancies, values, and academic choice: origins and changes , in Achievement and Achievement Motivation , ed Spence J. (San Francisco, CA: Freeman; ), 75–146. [ Google Scholar ]
- Eilam B. (2001). Primary strategies for promoting homework performance . Am. Educ. Res. J. 38 , 691–725. 10.3102/00028312038003691 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elliot A. J. (1999). Approach and avoidance motivation and achievement goals . Educ. Psychol. 34 , 169–189. 10.1207/s15326985ep3403_3 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elliot A. J., Church M. A. (1997). A hierarchical model of approach and avoidance achievement motivation . J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 72 , 218–232. 10.1037/0022-3514.72.1.218 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elliot A. J., McGregor H. A., Gable S. (1999). Achievement goals, study strategies, and exam performance: a mediational analysis . J. Educ. Psychol. 91 , 549–563. 10.1037/0022-0663.91.3.549 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Entwistle N. J. (1991). Approaches to learning and perceptions of the learning environment . High. Educ. 22 , 201–204. 10.1007/BF00132287 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Entwistle N. J. (2009). Teaching for Understanding at University: Deep Approaches and Distinctive Ways of Thinking . Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fernández-Alonso R., Suárez-Álvarez J., Muñiz J. (2014). Tareas escolares en el hogar y rendimiento en matemáticas: una aproximación multinivel con estudiantes de Enseñanza Primaria [Homework and academic performance in mathematics: a multilevel approach with Primary school students] . Rev. Psicol. Educ. 9 , 15–29. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fredricks J. A., Blumenfeld P. C., Paris A. (2004). School engagement: potential of the concept, state of the evidence . Rev. Educ. Res. 74 , 59–109. 10.3102/00346543074001059 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Galloway M., Conner J., Pope D. (2013). Nonacademic effects of homework in privileged, high-performing high schools . J. Exp. Educ. 81 , 490–510. 10.1080/00220973.2012.745469 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gaudreau P. (2012). Goal self-concordance moderates the relationship between achievement goals and indicators of academic adjustment . Learn. Individ. Differ. 22 , 827–832. 10.1016/j.lindif.2012.06.006 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hong E., Milgram R. M., Rowell L. L. (2004). Homework motivation and preference: a learner-centered homework approach . Theory Pract. 43 , 197–203. 10.1207/s15430421tip4303_5 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Inglés C. J., Martínez-González A. E., García-Fernández J. M. (2013). Conducta prosocial y estrategias de aprendizaje en una muestra de estudiantes españoles de Educación Secundaria Obligatoria [Prosocial behavior and learning strategies in a sample of Spanish students of Compulsory Secondary Education] . Eur. J. Educ. Psychol. 6 , 33–53. 10.1989/ejep.v6i1.101 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jöreskog K. G., Sörbom D. (1983). LISREL - 6 User's Reference Guide . Mooresville, IN: Scientifi c Software. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kohn A. (2006). Abusing research: the study of homework and other examples . Phi Delta Kappan 88 , 9–22. 10.1177/003172170608800105 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lindblom-Ylänne S., Lonka K. (1999). Individual ways of interacting with the learning environment - are they related to study success? Learn. Instruct. 9 , 1–18. 10.1016/S0959-4752(98)00025-5 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marks H. (2000). Student engagement in instructional activity: patterns in the elementary, middle, and high school years . Am. Educ. Res. J. 37 , 153–184. 10.3102/00028312037001153 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Martin A. J. (2012). Motivation and engagement: conceptual, operational, and empirical clarity , in Handbook of Research on Student Engagement , eds Christenson S. L., Reschly A. L., Wylie C. (New York, NY: Springer; ), 303–311. [ Google Scholar ]
- Marton F., Säljö R. (1976a). On qualitative differences in learning . I: outcome and process. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 46 , 4–11. 10.1111/j.2044-8279.1976.tb02980.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marton F., Säljö R. (1976b). On qualitative differences in learning . II: outcome as a function of the learner's conception of the task. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 46 , 115–127. 10.1111/j.2044-8279.1976.tb02304.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Meece J. L., Anderman E. M., Anderman L. H. (2006). Classroom goal structure, student motivation, and academic achievement . Annu. Rev. Psychol. 57 , 487–503. 10.1146/annurev.psych.56.091103.070258 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Middleton M., Midgley C. (1997). Avoiding the demonstration of lack of ability: an unexplored aspect of goal theory . J. Educ. Psychol. 89 , 710–718. 10.1037/0022-0663.89.4.710 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Muhlenbruck L., Cooper H., Nye B., Lindsay J. J. (2000). Homework and achievement: explaining the different strengths of relation at the elementary and secondary school levels . Soc. Psychol. Educ. 3 , 295–317. 10.1023/A:1009680513901 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ng C. H. (2008). Multiple-goal learners and their differential patterns of learning . Educ. Psychol. 28 , 439–456. 10.1080/01443410701739470 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Núñez J. C., González-Pienda J. A., González-Pumariega S., García M., Roces C. (1997). Cuestionario Para la Evaluación de Metas Académicas [Academic Goals Assessment Questionnaire] . Department of Psychology, University of Oviedo. [ Google Scholar ]
- Núñez J. C., Suárez N., Cerezo R., González-Pienda J. A., Rosário P., Mourão R., et al. (2015a). Homework and academic achievement across Spanish Compulsory Education . Educ. Psychol. 35 , 726–746. 10.1080/01443410.2013.817537 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Núñez J. C., Suárez N., Rosário P., Vallejo G., Cerezo R., Valle A. (2015b). Teachers' feedback on homework, homework-related behaviors and academic achievement . J. Educ. Res. 108 , 204–216. 10.1080/00220671.2013.878298 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Núñez J. C., Suárez N., Rosário P., Vallejo G., Valle A., Epstein J. L. (2015c). Relationships between parental involvement in homework, student homework behaviors, and academic achievement: differences among elementary, junior high, and high school students . Metacogn. Learn. 10 , 375–406. 10.1007/s11409-015-9135-5 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Núñez J., Rosário P., Vallejo G., González-Pienda J. (2013). A longitudinal assessment of the effectiveness of a school-based mentoring program in middle school . Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 38 , 11–21. 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2012.10.002 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pajares F., Britner S. L., Valiante G. (2000). Relation between achievement goals and self-beliefs of middle school students in writing and science . Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 25 , 406–422. 10.1006/ceps.1999.1027 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pintrich P. R. (2004). A conceptual framework for assessing motivation and self-regulated learning in college students . Educ. Psychol. Rev. 16 , 385–407. 10.1007/s10648-004-0006-x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pintrich P. R., De Groot E. V. (1990). Motivational and self-regulated learning components of classroom performance . J. Educ. Psychol. 82 , 33–40. 10.1037/0022-0663.82.1.33 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reeve J., Jang H., Carrell D., Jeon S., Barch J. (2004). Enhancing students' engagement by increasing teachers' autonomy support . Motiv. Emot. 28 , 147–169. 10.1023/B:MOEM.0000032312.95499.6f [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Regueiro B., Suárez N., Valle A., Núñez J. C., Rosário P. (2015). La motivación e implicación en los deberes escolares a lo largo de la escolaridad obligatoria [Homework motivation and engagement throughout compulsory education] . Rev. Psicodidáctica 20 , 47–63. 10.1387/RevPsicodidact.12641 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rodríguez S., Cabanach R. G., Piñeiro I., Valle A., Núñez J. C., González-Pienda J. A. (2001). Metas de aproximación, metas de evitación y múltiples metas académicas [Approach goals, avoidance goals and multiple academic goals] . Psicothema 13 , 546–550. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosário P., González-Pienda J. A., Pinto R., Ferreira P., Lourenço A., Paiva O. (2010a). Efficacy of the program “Testas's (mis)adventures” to promote the deep approach to learning . Psicothema 22 , 828–834. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosário P., Mourão R., Baldaque M., Nunes T., Núñez J. C., González-Pienda J. A., et al. (2009). Homework, self-regulation of learning and math performance . Rev. Psicodidáctica 14 , 179–192. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosário P., Núñez J. A., Ferrando J. P., Paiva O., Lourenço A., Cerezo R., et al. (2013a). The relationship between approaches to teaching and approaches to studying: a two-level structural equation model for biology achievement in high school . Metacogn. Learn. 8 , 47–77. 10.1007/s11409-013-9095-6 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosário P., Núñez J. C., González-Pienda J. A., Almeida L., Soares S., Rúbio M. (2005). Academic learning from the perspective of Model 3P of J. Biggs . Psicothema 17 , 20–30. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosário P., Núñez J. C., González-Pienda J. A., Valle A., Trigo L., Guimarães C. (2010b). Enhancing self-regulation and approaches to learning in first-year college students: a narrative-based program assessed in the Iberian Peninsula . Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 25 , 411–428. 10.1007/s10212-010-0020-y [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosário P., Núñez J. C., Vallejo G., Cunha J., Azevedo R., Pereira R., et al. (2016). Promoting Gypsy children school engagement: a story-tool project to enhance self-regulated learning . Contemp. Educ. Psychol . [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2015.11.005. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosário P., Núñez J. C., Vallejo G., Cunha J., Nunes T., Suárez N., et al.. (2015). The effects of teachers' homework follow-up practices on students' EFL performance: a randomized-group design . Front. Psychol. 6 : 1528 . 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01528 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosário P., Núñez J., Valle A., González-Pienda J., Lourenço A. (2013b). Grade level, study time, and grade retention and their effects on motivation, self-regulated learning strategies, and mathematics achievement: a structural equation model . Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 28 , 1311–1331. 10.1007/s10212-012-0167-9 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Skaalvik E. (1997). Self- enhancing and self-defeating ego orientation: relations with task and avoidance orientation, achievement, self- perceptions, and anxiety . J. Educ. Psychol. 89 , 71–81. 10.1037/0022-0663.89.1.71 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Skinner E. A., Pitzer J. R. (2012). Developmental dynamics of student engagement, coping, and everyday resilience , in Handbook of Research on Student Engagement , eds Christenson S. L., Reschly A. L., Wylie C. (New York, NY: Springer; ), 21–44. [ Google Scholar ]
- Struyven K., Dochy F., Janssens S., Gielen S. (2006). On the dynamics of students' approaches to learning: the effects of the teaching/learning environment . Learn. Instr. 16 , 279–294. 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2006.07.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Suárez J. M., Cabanach R. G., Valle A. (2001). Multiple-goal pursuit and its relation to cognitive, self-regulatory, and motivational strategies . Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 71 , 561–572. 10.1348/000709901158677 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trautwein U., Lüdtke O., Kastens C., Köller O. (2006a). Effort on homework in grades 5 through 9: development, motivational antecedents, and the association with effort on classwork . Child Dev. 77 , 1094–1111. 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2006.00921.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trautwein U., Ludtke O., Schnyder I., Niggli A. (2006b). Predicting homework effort: support for a domain-specific, multilevel homework model . J. Educ. Psychol. 98 , 438–456. 10.1037/0022-0663.98.2.438 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trautwein U., Schnyder I., Niggli A., Neumann M., Lüdtke O. (2009). Chameleon effects in homework research: the homework-achievement association depends on the measures used and the level of analysis chosen . Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 34 , 77–88. 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2008.09.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valle A., Cabanach R. G., Núñez J. C., González-Pienda J. A., Rodríguez S., Piñeiro I. (2003a). Cognitive, motivational, and volitional dimensions of learning: an empirical test of a hypothetical model . Res. High. Educ. 44 , 557–580. 10.1023/A:1025443325499 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valle A., Cabanach R. G., Núñez J. C., González-Pienda J. A., Rodríguez S., Piñeiro I. (2003b). Multiple goals, motivation and academic learning . Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 73 , 71–87. 10.1348/000709903762869923 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valle A., Cabanach R. G., Rodríguez S., Núñez J. C., González-Pienda J. A. (2006). Metas académicas, estrategias cognitivas y estrategias de autorregulación del estudio [Academic goals, cognitive and self-regulatory strategies] . Psicothema 18 , 166–170. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valle A., Núñez J. C., Cabanach R. G., González-Pienda J. A., Rodríguez S., Rosário P., et al.. (2009). Academic goals and learning quality in higher education students . Span. J. Psychol. 12 , 96–105. 10.1017/S1138741600001517 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valle A., Núñez J. C., Cabanach R., Rodríguez S., Rosário P., Inglés C. (2015a). Motivational profiles as a combination of academic goals in higher education . Educ. Psychol. 35 , 634–650. 10.1080/01443410.2013.819072 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valle A., Pan I., Núñez J. C., Rosário P., Rodríguez S., Regueiro B. (2015b). Deberes escolares y rendimiento académico en Educación Primaria [Homework and academic achievement in Primary Education] . An. Psicol. 31 , 562–569. 10.6018/analesps.31.2.171131 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valle A., Pan I., Regueiro B., Suárez N., Tuero E., Nunes A. R. (2015c). Predicting approach to homework in primary school students . Psicothema 27 , 334–340. 10.7334/psicothema2015.118 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valle A., Regueiro B., Rodríguez S., Piñeiro I., Freire C., Ferradás M., et al. (2015d). Perfiles motivacionales como combinación de expectativas de autoeficacia y metas académicas en estudiantes universitarios [Motivational profiles as a combination of self-efficacy expectations and academic goals in university students] . Eur. J. Educ. Psychol. 8 , 1–8. 10.1016/j.ejeps.2015.10.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vallejo G., Tuero E., Núñez J. C., Rosário P. (2014). Performance evaluation of recent information criteria for selecting multilevel models in behavioral and social sciences . Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 14 , 48–57. 10.1016/S1697-2600(14)70036-5 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wolters C. A., Yu S. L., Pintrich P. R. (1996). The relation between goal orientation and students' motivational beliefs and self- regulated learning . Learn. Individ. Differ. 8 , 211−238. 10.1016/s1041-6080(96)90015-1 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xu J. (2005). Purposes for doing homework reported by middle and high school students . J. Educ. Res. 99 , 46–55. 10.3200/JOER.99.1.46-55 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xu J. (2007). Middle-school homework management: more than just gender and family involvement . Educ. Psychol. 27 , 173–189. 10.1080/01443410601066669 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xu J. (2008). Validation of scores on the Homework Management Scale for high school students . Educ. Psychol. Meas. 68 , 304–324. 10.1177/0013164407301531 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xu J. (2010). Predicting homework time management at the secondary school level: a multilevel analysis . Learn. Individ. Differ. 20 , 34–39. 10.1016/j.lindif.2009.11.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zimmerman B. J., Kitsantas A. (2005). Homework practices and academic achievement: the mediating role of self-efficacy and perceived responsibility beliefs . Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 30 , 397–417. 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2005.05.003 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Is Homework Good for Kids? Here’s What the Research Says
A s kids return to school, debate is heating up once again over how they should spend their time after they leave the classroom for the day.
The no-homework policy of a second-grade teacher in Texas went viral last week , earning praise from parents across the country who lament the heavy workload often assigned to young students. Brandy Young told parents she would not formally assign any homework this year, asking students instead to eat dinner with their families, play outside and go to bed early.
But the question of how much work children should be doing outside of school remains controversial, and plenty of parents take issue with no-homework policies, worried their kids are losing a potential academic advantage. Here’s what you need to know:
For decades, the homework standard has been a “10-minute rule,” which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 minutes of homework each night. High school seniors should complete about two hours of homework each night. The National PTA and the National Education Association both support that guideline.
But some schools have begun to give their youngest students a break. A Massachusetts elementary school has announced a no-homework pilot program for the coming school year, lengthening the school day by two hours to provide more in-class instruction. “We really want kids to go home at 4 o’clock, tired. We want their brain to be tired,” Kelly Elementary School Principal Jackie Glasheen said in an interview with a local TV station . “We want them to enjoy their families. We want them to go to soccer practice or football practice, and we want them to go to bed. And that’s it.”
A New York City public elementary school implemented a similar policy last year, eliminating traditional homework assignments in favor of family time. The change was quickly met with outrage from some parents, though it earned support from other education leaders.
New solutions and approaches to homework differ by community, and these local debates are complicated by the fact that even education experts disagree about what’s best for kids.
The research
The most comprehensive research on homework to date comes from a 2006 meta-analysis by Duke University psychology professor Harris Cooper, who found evidence of a positive correlation between homework and student achievement, meaning students who did homework performed better in school. The correlation was stronger for older students—in seventh through 12th grade—than for those in younger grades, for whom there was a weak relationship between homework and performance.
Cooper’s analysis focused on how homework impacts academic achievement—test scores, for example. His report noted that homework is also thought to improve study habits, attitudes toward school, self-discipline, inquisitiveness and independent problem solving skills. On the other hand, some studies he examined showed that homework can cause physical and emotional fatigue, fuel negative attitudes about learning and limit leisure time for children. At the end of his analysis, Cooper recommended further study of such potential effects of homework.
Despite the weak correlation between homework and performance for young children, Cooper argues that a small amount of homework is useful for all students. Second-graders should not be doing two hours of homework each night, he said, but they also shouldn’t be doing no homework.
Not all education experts agree entirely with Cooper’s assessment.
Cathy Vatterott, an education professor at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, supports the “10-minute rule” as a maximum, but she thinks there is not sufficient proof that homework is helpful for students in elementary school.
“Correlation is not causation,” she said. “Does homework cause achievement, or do high achievers do more homework?”
Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs , thinks there should be more emphasis on improving the quality of homework tasks, and she supports efforts to eliminate homework for younger kids.
“I have no concerns about students not starting homework until fourth grade or fifth grade,” she said, noting that while the debate over homework will undoubtedly continue, she has noticed a trend toward limiting, if not eliminating, homework in elementary school.
The issue has been debated for decades. A TIME cover in 1999 read: “Too much homework! How it’s hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.” The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push for better math and science education in the U.S. The ensuing pressure to be competitive on a global scale, plus the increasingly demanding college admissions process, fueled the practice of assigning homework.
“The complaints are cyclical, and we’re in the part of the cycle now where the concern is for too much,” Cooper said. “You can go back to the 1970s, when you’ll find there were concerns that there was too little, when we were concerned about our global competitiveness.”
Cooper acknowledged that some students really are bringing home too much homework, and their parents are right to be concerned.
“A good way to think about homework is the way you think about medications or dietary supplements,” he said. “If you take too little, they’ll have no effect. If you take too much, they can kill you. If you take the right amount, you’ll get better.”
More Must-Reads from TIME
- The New Face of Doctor Who
- Putin’s Enemies Are Struggling to Unite
- Women Say They Were Pressured Into Long-Term Birth Control
- Scientists Are Finding Out Just How Toxic Your Stuff Is
- Boredom Makes Us Human
- John Mulaney Has What Late Night Needs
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Katie Reilly at [email protected]
share this!
January 18, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
Q&A: Does homework still have value? An education expert weighs in
by Vicky Hallett, Johns Hopkins University

The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein, co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work," Epstein says.
But after decades of researching how to improve schools, the professor in the Johns Hopkins School of Education remains certain that homework is essential—as long as the teachers have done their homework, too. The National Network of Partnership Schools, which she founded in 1995 to advise schools and districts on ways to improve comprehensive programs of family engagement, has developed hundreds of improved homework ideas through its Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program.
For an English class, a student might interview a parent on popular hairstyles from their youth and write about the differences between then and now. Or for science class, a family could identify forms of matter over the dinner table, labeling foods as liquids or solids. These innovative and interactive assignments not only reinforce concepts from the classroom but also foster creativity, spark discussions, and boost student motivation.
"We're not trying to eliminate homework procedures, but expand and enrich them," says Epstein, who is packing this research into a forthcoming book on the purposes and designs of homework. In the meantime, the Hub couldn't wait to ask her some questions.
What kind of homework training do teachers typically get?
Future teachers and administrators really have little formal training on how to design homework before they assign it. This means that most just repeat what their teachers did, or they follow textbook suggestions at the end of units. For example, future teachers are well prepared to teach reading and literacy skills at each grade level, and they continue to learn to improve their teaching of reading in ongoing in-service education.
By contrast, most receive little or no training on the purposes and designs of homework in reading or other subjects. It is really important for future teachers to receive systematic training to understand that they have the power, opportunity, and obligation to design homework with a purpose.
Why do students need more interactive homework?
If homework assignments are always the same—10 math problems, six sentences with spelling words—homework can get boring and some kids just stop doing their assignments, especially in the middle and high school years. When we've asked teachers what's the best homework you've ever had or designed, invariably we hear examples of talking with a parent or grandparent or peer to share ideas.
To be clear, parents should never be asked to "teach" seventh grade science or any other subject. Rather, teachers set up the homework assignments so that the student is in charge. It's always the student's homework. But a good activity can engage parents in a fun, collaborative way.
Our data show that with "good" assignments, more kids finish their work, more kids interact with a family partner, and more parents say, "I learned what's happening in the curriculum." It all works around what the youngsters are learning.
Is family engagement really that important?
At Hopkins, I am part of the Center for Social Organization of Schools, a research center that studies how to improve many aspects of education to help all students do their best in school. One thing my colleagues and I realized was that we needed to look deeply into family and community engagement. There were so few references to this topic when we started that we had to build the field of study. When children go to school, their families "attend" with them whether a teacher can "see" the parents or not. So, family engagement is ever-present in the life of a school.
My daughter's elementary school doesn't assign homework until third grade. What's your take on 'no homework' policies?
There are some parents, writers, and commentators who have argued against homework, especially for very young children. They suggest that children should have time to play after school. This, of course is true, but many kindergarten kids are excited to have homework like their older siblings. If they give homework, most teachers of young children make assignments very short—often following an informal rule of 10 minutes per grade level . "No homework" does not guarantee that all students will spend their free time in productive and imaginative play.
Some researchers and critics have consistently misinterpreted research findings. They have argued that homework should be assigned only at the high school level where data point to a strong connection of doing assignments with higher student achievement. However, as we discussed, some students stop doing homework. This leads, statistically, to results showing that doing homework or spending more minutes on homework is linked to higher student achievement. If slow or struggling students are not doing their assignments, they contribute to—or cause—this "result."
Teachers need to design homework that even struggling students want to do because it is interesting. Just about all students at any age level react positively to good assignments and will tell you so.
Did COVID change how schools and parents view homework?
Within 24 hours of the day school doors closed in March 2020, just about every school and district in the country figured out that teachers had to talk to and work with students' parents. This was not the same as homeschooling—teachers were still working hard to provide daily lessons. But if a child was learning at home in the living room, parents were more aware of what they were doing in school .
One of the silver linings of COVID was that teachers reported that they gained a better understanding of their students' families. We collected wonderfully creative examples of activities from members of the National Network of Partnership Schools. I'm thinking of one art activity where every child talked with a parent about something that made their family unique. Then they drew their finding on a snowflake and returned it to share in class. In math, students talked with a parent about something the family liked so much that they could represent it 100 times. Conversations about schoolwork at home was the point.
How did you create so many homework activities via the Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program?
We had several projects with educators to help them design interactive assignments, not just "do the next three examples on page 38." Teachers worked in teams to create TIPS activities, and then we turned their work into a standard TIPS format in math, reading/language arts, and science for grades K-8. Any teacher can use or adapt our prototypes to match their curricula.
Overall, we know that if future teachers and practicing educators were prepared to design homework assignments to meet specific purposes—including but not limited to interactive activities—more students would benefit from the important experience of doing their homework. And more parents would, indeed, be partners in education.
Provided by Johns Hopkins University
Explore further
Feedback to editors
'Zombie cells' in the sea: Viruses keep the most common marine bacteria in check
6 minutes ago
Researchers use machine-learning modeling tools to improve zinc-finger nuclease editing technology
21 minutes ago

Pottery residue research explores culinary traditions in Germany from the Early Neolithic to the Bronze Age
23 minutes ago
New research shows the true cost of reproduction across the animal kingdom
43 minutes ago
Bacterial proteins shed light on antiviral immunity
57 minutes ago

The observation of a Spin Berry curvature-enhanced orbital Zeeman effect in a kagome metal

Spiny legged 308-million-year-old arachnid discovered in the Mazon Creek locality
Data from MAXI J1820+070 shows Einstein was right about how matter plunges into a black hole

A devastating fire 2,200 years ago preserved a moment of life and war in Iron Age Spain, down to a single gold earring
10 hours ago

Airborne technology brings new hope to map shallow aquifers in Earth's most arid deserts
17 hours ago
Relevant PhysicsForums posts
Physics education is 60 years out of date.
15 hours ago
Is "College Algebra" really just high school "Algebra II"?
May 14, 2024
Plagiarism & ChatGPT: Is Cheating with AI the New Normal?
May 13, 2024
Physics Instructor Minimum Education to Teach Community College
May 11, 2024
Studying "Useful" vs. "Useless" Stuff in School
Apr 30, 2024
Why are Physicists so informal with mathematics?
Apr 29, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

'There's only so far I can take them': Why teachers give up on struggling students who don't do their homework
Sep 27, 2022


Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

What's the point of homework?
Sep 1, 2021

How to help your kids with homework—without doing it for them
Jan 24, 2020

Is homework useful for kids? If so, what age should it start?
Nov 30, 2022

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017
Recommended for you

First-generation medical students face unique challenges and need more targeted support, say researchers
18 hours ago

Investigation reveals varied impact of preschool programs on long-term school success
May 2, 2024

Training of brain processes makes reading more efficient
Apr 18, 2024

Researchers find lower grades given to students with surnames that come later in alphabetical order
Apr 17, 2024

Earth, the sun and a bike wheel: Why your high-school textbook was wrong about the shape of Earth's orbit
Apr 8, 2024

Touchibo, a robot that fosters inclusion in education through touch
Apr 5, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
The New York Times
The learning network | does your homework help you learn.

Does Your Homework Help You Learn?

Questions about issues in the news for students 13 and older.
- See all Student Opinion »
New research suggests that a lot of assigned homework amounts to pointless busy work that doesn’t help students learn, while more thoughtful assignments can help them develop skills and acquire knowledge. How would you characterize the homework you get?
In the Sunday Review article “The Trouble With Homework,” Annie Murphy Paul reviews the research on homework:
The quantity of students’ homework is a lot less important than its quality. And evidence suggests that as of now, homework isn’t making the grade. Although surveys show that the amount of time our children spend on homework has risen over the last three decades, American students are mired in the middle of international academic rankings: 17th in reading, 23rd in science and 31st in math, according to results from the Program for International Student Assessment released last December. In a 2008 survey, one-third of parents polled rated the quality of their children’s homework assignments as fair or poor, and 4 in 10 said they believed that some or a great deal of homework was busywork. A new study, coming in the Economics of Education Review, reports that homework in science, English and history has “little to no impact” on student test scores. (The authors did note a positive effect for math homework.) Enriching children’s classroom learning requires making homework not shorter or longer, but smarter.
She goes on to enumerate some of the aspects of effective independent assignments, like “retrieval practice,” which basically means doing practice tests to reinforce learning and commit it to memory, and “interleaving,” in which problems are not grouped into sets by type, but rather scattered throughout an assignment, which makes the brain work harder to grasp the material.
Students: Tell us how effective you think your homework is. What kinds of assignments seem pointless? Which ones are confusing or frustrating? Which ones are most engaging and interesting? Which ones are you fairly sure help you learn and grow?
Students 13 and older are invited to comment below. Please use only your first name. For privacy policy reasons, we will not publish student comments that include a last name.
Comments are no longer being accepted.
“I see homework as a big part that helps me learn and grow” that’s what I always said up till I was moved to a different math class. My old math teacher made math easy and fun as well as understandable. But when I was moved I got confused easily, I found it boring, and I even found paying attention hard. Then there’s my English class. I love English with all my heart but my teacher makes me feel like I’m in Preschool! She has hand signs for every rule and if we don’t do them we get more homework! She always puts us into groups and so far every group I’ve been placed in I can’t get along in. One group wouldn’t let me talk and when I gave my opion they scolded me and said I was wrong though it was an opion lesson… Another group was lazy and since I ran out of my medicine that helps me focus, I was lost and told them I need their help to help me keep up with what’s going on yet they let me drag along! History was never my strong point from the start even though my dad is a History teacher. But when I got into a certain class I couldn’t stand it! I was miles behind in homework and around every corner was either homework or projects! I asked for help and I got yelled at! I’m sorry but sometimes homework feels like slave work since I don’t get anything out of good grades except a smile and/or a pat on the back and that’s it. Yes homework can be good for you but there is a limit of how much a student can handle before they collaspe underneath all of that work! But I love it when teachers make homework fun or competive (which we normally do now and days)! Cause that’s when I’m having a blast! But when teachers get too interactive with their class I can’t help but feel creeped out by them. (Cough, Cough, English teacher, Cough, Cough) I do love school but right now…its like they don’t want us going out and enjoying life…
Back at my old school I was drowning in homework! I just couldn’t get the chance to sit back and be young! It was just too much! In every class I had homework! Study this, learn that, solve this, and every where in between! The bullying was no help either since they stole or destroyed my homework so I failing till I switched schools! My suggestion to all you kids who don’t like homework….DON’T GO TO [name of school removed]!!!!!!!! Especially if you’re like me and are considered one of the special kids since the teachers don’t flex to your needs!
At my school , we all think that homework helps people learn in so many different ways. You do your homework to get better grades on test scores because some of the homework you get will have some stuff that can be on test. Another reason is that homework can get you better grades if you just hand it in. You can learn from homework. In my opinion.For example, I had to take notes in algebra yesterday for homework and only took 10 minutes it really help a lot the next day because we had a little mini quiz on it !
Doing my homework every night helps me learn because it helps me remember the lesson gone over in class that day. It also makes it easier to follow the next lesson, which is usually an extension from the lesson the day before.
Homework helps me learn because it’s a review of what we learned in class. Sometimes they give too much work though.
I feel like it all depends on if you understand the work. If a teacher taught you a new topic in class and you didn’t understand it, I dont think you would understand it if you did it again. If you understood it, It would help you because you are repeating the problems.
I don’t think homework helps you learn, I think it helps you remember what you learned. Homework is more of a review of what you did in school during the day, rather than a new subject to learn on a whole.
I personally am not a big fan of homework though, I think that some teachers don’t really realize that we have several other classes which also give us homework, and we sometimes end up with a large amount by the end of the day.
But I’m sure that my procrastination has a lot to do with it as well.
Homework definitely helps me learn. By the time i get home from school some subjects become unfamiliar and homework help reinforce what i learned in class. Better students do their homework and teachers recognize that frequently. Repetition of your homework also helps memorize which you could benefit from on tests and other classwork activities.
Depending on the subject or the assigment, homework can either be redundant or effective. Assignments which make you copy straight out of a textbook are redundant. These assignments are redundant because students hardly put all that much effort into it. By copying a textbook, people aren’t focused on the material, because they are just focusing on getting the assigment done. Straight copying is seen as boring or even in some cases ‘annoying’ by students, which translates into them not learning what they need to learn. Assigments where students are interactive and aren’t just being taught the textbook are interesting and that’s when students learn the most. Writing samples when students are asked for their opinion and to have their voice heard are deemed the most interesting. Thus, being because students then have the ability to share what they’ve learned in their own words and also get to apply their knowledge in their own voice.
On the other hand, when homework is done effectively, the end product will be better grades. If a student neglects to do homework, whether interesting or boring, it will show in their grades. Students who do apply their strongest efforts into their homework will ultimately contribute to better grades.
I think that homework is pointless when the teachers give us homework that is for fun and we have to waist our time doing little projects when we can be doing other more important things like studying. I think that most homework is important I just don’t like it when teachers give too much and it becomes over whelming and I can’t have time to study because it would be too late and then I wouldn’t be able to sleep. If anything I think teachers should give us homework but give us one big homework a week and we work on it for the whole week which it would be due on Friday and then get a test grade for it since it was a big homework. If teachers wouldn’t do that I would love if teachers would give us only three days of homework a week and Fridays we would get a test.
Homework is assigned so that students can practice what they have learned in school and see if they can remember what happened in class. Personally, the homework that has been assigned to me lately has been nothing but busy work that I feel is pointless. The truth is most of the modern day students don’t see the value in doing homework but the discipline and the practice for the real world really are fundamental. The most confusing type of homework assignments that we have come with little to no instructions. When teachers give assignments on things that they haven’t covered yet seems pointless to me since it really isn’t evaluating anything at all. Another type of pointless homework would be the ones in which there is so much repetition that it becomes pointless. In my personal life ive been faced with all types of homework. I believe homework is fundamental to the development of the mind and I will keep doing my homework.
I go to an American school in Bogota, Colombia. Recently in my school I have been getting exaggerated amounts of homework, and most of it has no impact on my learning. I say this because the homework I am assigned is just “busywork” and keeps me up until late hours in the night. The homework I am given is also extremely long and not smart, it is just a very basic review of what we did in class that day. Homework like that is a waste of time since if the student is good and pays attention in class he should know all of the material and shouldn’t be forced to demonstrate it through homework. I believe that what should be improved in not the quantity but the quality of the homework we are assigned. I am not saying homework should be abolished but I am saying it should be changed. If a student is overwhelmed with homework his academic development would also be affected. For example if a student has allot of homework he will probably stay up at night doing it. Maybe he will finish his homework around 10 or 11 in the night. The next day he will have to wake up very early and will only get about 5-6 hours of sleep. In order for the teenage brain to develop correctly a kid needs 8 hours of sleep. So. excessive amount of homework leads to a very tired, unmotivated and less active student. In my school I think the only homework assignments that help me learn are the math ones.
Each subject is different and each grade in school requires a different amount of practice. For example, Math is a subject that I believe needs out-of-classroom practice no matter what grade you are in, or what topic you are covering. It is one of the most essential aptitudes one must acquire in order to be successful in life. Language, whether it be english, spanish, or etc, is also a subject that is vital for an accomplished life. I believe that one must practice in order to become and eloquent speaker and writer, but i only think that a small amount of homework should be given, especially once one reaches the ends of high school. A subject that I feel doesn’t need practice outside of school is history. For me, history is more like a gossip story with dates that “should” be remembered than anything else; therefore, I don’t believe that homework would be necessary to enforce a subject like that.
The idea of having to work all night, studying for a billion exams the next day, getting the college applications going, and practicing a sport isn’t something strange for the average senior at CNG. It seems as if the need to excel at everything might just be the COD of many high school students. As college admissions become more competitive, as more and more people take AP exams and admissions tests there is a greater weight on our shoulders. But is it really worth it? I mean, even if everything goes the way we want it to, was it really worth all our time and energy? There are just better things to do with my life. I would prefer to go deeper into the sciences, write of some philosophical tendency I’m being carried into, do more social work, etc. But I need to commit to an organized agenda, learn the Standards I’m supposed to be learning and show my progress through time. These are fancy ways of creating a level playing field so students can be compared. Is this really what learning has become?
Practice makes perfect some might say. There is no arguing about that. Success in those specific tasks, such as doing homework or working on a particular project that requires zero creativity clearly needs those levels of repetitive practice and great memory. But are we supposed to do this the rest of our lives? I don’t think so. Harris Cooper, a professor from Duke University dedicated to homework research states that “even for high school students, overloading them with homework is not associated with higher grades” (Cooper). I’m sorry, so isn’t homework even doing what its supposed to be doing? The counter-productivity of too much homework, especially in such a critical moment as in college application season, makes the whole educational system lose credibility. Are we being trained to do something we aren’t going to really do or even need in the future? What is the real purpose of doing homework when we aren’t truly learning from it?
Don’t get me wrong. I do believe homework is critical in developing certain skills. How were we supposed to learn basic arithmetic operations without those tons of worksheets and problem sets? Yes, homework is a useful tool but only when used consciously. Statistical evidence seems to agree with this: “teachers in many of the nations that outperform the U.S. on student achievement tests–such as Japan, Denmark and the Czech Republic–tend to assign less homework than American teachers, but instructors in low-scoring countries like Greece, Thailand and Iran tend to pile it on” (Wallis). The need to assign homework, to put a million grades in is too antiquated in my opinion. What’s the problem with guiding classes to a true educational experience and leave behind the limitations of grading, of classifying students, of making them lose all interest, worse yet lose passion for learning and generate hatred towards certain areas of knowledge while capturing valuable time that is needed to explore others?
It depends on what type of homework and the time that it takes to finish it. The homework that I get from English, history, science, and math benefit me and my grades a lot. From my three band classes, and P.E. class, I usually do busy work. I love how the school is run… I learn a lot from the class just itself, and from school assemblies, etc. First, I have to learn before I get my grades… meaning, I don’t care what my grades are like until I actually know and understand the material and knowledge that I learned at school. What we learn from school and from homework are is different. We learn more at school and then apply what we learned in our homework. So most of the time we don’t learn anything that much from homework.
Homework assignments should be provided, but once a month. It allows children to have freedom, and actually feel like life is not all about study and going to a prestigious university.
Homework wastes our time, and in recent articles they say that school’s are killing creativity, and now there is an uproar about homework not providing learning material.
What homework should be is a subjet, say history, and children can choose one that interests them, and they could research it for a month. And after the month is up children can present in class, so that means the child knows thoroughly about their topic and can explain well to their friends, and also they will have an opportunity to listen to other peoples’ research.
I wish we didn’t have homework, because the learning network is providing us with a great amount of resources that homework, in a year, can’t accomplish.
40 hours per week, 8 hours a day, is the legal limit of hours an adult can work in California without being payed overtime. An employee must be payed 150% their usual salary for every hour they work past 8 hours a day. I spend between 34 and 39 hours per week at school, not counting homework (aprox. 10-15 hours per week). My suggestion is that any work assigned to students requiring them to spend more than 40 hours a week on academics be graded with a bonus of 50% the student’s grade. This would encourage students to do well in order to have a higher bonus, and would discourage teachers from assigning so much work (since we all how much giving out bonus points pains them!) As for the questions: I think that homework is effective as long as it will help improve a student’s understanding and execution of course material. As a general rule, I don’t think it’s very useful to be assigned more than one assignment in each category of homework to a class (1 chapter to read, 1 exercise, 1 essay). 5 math exercises is 5 too many if I understand the lesson, and 4 too many if it is the teacher’s goal to find out whether or not I do. As a student, I have a limited amount of time and love to divide up into my work. I find work that leaves the thinking up to the student to be the most engaging and helpful to my understanding: the fewer details on how I should do the assignment, the more I work to make it reflect my understanding of the topic.
It is interesting to write your homework in your free time at home. Homework and assignments are important for innovation and elaboration. Take your time in doing your homework because this will help you understand the lesson more.
i think this is the best amendment ever.
Sense at my school , school just started we do not have that much homework. But I’ve hear a lot of people say that towards the middle of the year is when everyone’s backpack’s become really heavy. Teacher’s start giving more than one homework assignment per class. So I think that homework does not help you learn because you do work at school why do you need to do it again at home? I think teacher’s do that because they want to figure out if you are capable to do the same thing at home and also because they just want us to have some type of work to do at home. Once again I do no think that homework helps you learn.
I personally don’t think homework helps a student learn. I feel if you don’t get what the teacher teaches in class then I personally don’t get the homework at all. If I don’t get the subject then I personally to the homework wrong and I’m sure that other people do it wrong too. My teachers all say that they don’t give so much homework and they really don’t, but since they all give about 20-30 minutes of homework each subject, it piles up.I think that homework is effective as long as it will help improve a student’s understanding and execution of course material. I personally don’t think that homework always helps, but it does.
I think that homework is useful sometimes, but not always. Most of the time, it is just the same thing we did in class, and if we didn’t get it then we still won’t get it at home, primarily because our parents have no clue about how to do it either.
i think that homework should not in are school systems because homework is just practice and i know that practice makes perfect but when you got 5 subjects it add to a lot. I also i believe that all homework (practice) is just studying and unless we have i don’t want to take the time for nothing but another school day
1) What kinds of assignments seem pointless?
I don’t believe that any assignments are pointless, because teachers always have a reason for giving homework. However, teachers often give homework where the effort on the part of the student outweighs the teacher’s goal. In addition, many homework assignments do not effectively reach their goal.
2) Which ones are confusing or frustrating?
Assignments are usually not confusing, although sometimes, when given very easy assignments, I do not understand what the point is (which does not mean that the assignments are pointless — the point is simply mysterious to me). I get most frustrated by homework when I receive virtually identical assignments at regular intervals, but never get feedback from the teacher. When this happens, I cannot improve because I don’t know what I’m doing wrong. For example, our French teacher has given us this assignment three times this year: Comment on a predetermined stanza of a Baudelaire poem. The first two stanzas earned me 17 (out of 20) with no corrections other than grammatical mistakes. For the third assignment, I have written a very similar analysis and I expect to get a very similar grade. If there are 20 possible points and I didn’t get all of them, why did the teacher not provide any comments?
3) Which ones are most engaging and interesting?
Honestly, although I understand the value of homework, I do not enjoy doing it (unless it involves creativity, but with no art, music or creative writing classes in high school, this is extremely rare).
Which ones are you fairly sure help you learn and grow?
I believe all homework helps me learn and grow — the question is whether the amount of growth induced by the homework is worth the effort involved.
Yes, some homework are important. Like learning rhetoric at home to be able to talk about it in class. Doing a math problem to make sure the lesson is understood. But is doing ten exercises on a lesson we did not fully go over because the teacher did not manage to end the lesson on time and now needs us to try to figure it out on our own useful? Is doing forty little problems with the same math equation over and over again necessary? I believe it is not. I believe some teachers are using a lot of useless homework because they must think in some way that it will be beneficent one day or another. They are often wrong. Unless a whole class of twenty students decided they want to be physician, i do not understand why learning what is the kind of relation between the Earth and the Moon, over a dozen of exercises, is in anyway useful. Also, a teacher might think they are doing the right thing, making us practice something that is already learned in class, by giving its students five exercises. Sure, it is not a bad idea. But since all the teachers, or most of them, are looking to do the right thing, five teachers that wants you to practice with some homework exercises, becomes twenty-five exercises for the students. Over something they either understood, or not understood. In any case it’s frustrating. If you understand what it is about then you are just wasting your time doing those exercises. If you did not understand it, you are going to spend ten minutes on each question, usually ending by guessing wrong, when all it could have taken was another clear explanation from the teacher. So yes, homework can be useful, and it often is, but not always.
What's Next
US South Carolina
Recently viewed courses
Recently viewed.
Find Your Dream School
This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
COVID-19 Update: To help students through this crisis, The Princeton Review will continue our "Enroll with Confidence" refund policies. For full details, please click here.
Enter your email to unlock an extra $25 off an SAT or ACT program!
By submitting my email address. i certify that i am 13 years of age or older, agree to recieve marketing email messages from the princeton review, and agree to terms of use., homework wars: high school workloads, student stress, and how parents can help.

Studies of typical homework loads vary : In one, a Stanford researcher found that more than two hours of homework a night may be counterproductive. The research , conducted among students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities, found that too much homework resulted in stress, physical health problems and a general lack of balance.
Additionally, the 2014 Brown Center Report on American Education , found that with the exception of nine-year-olds, the amount of homework schools assign has remained relatively unchanged since 1984, meaning even those in charge of the curricula don't see a need for adding more to that workload.
But student experiences don’t always match these results. On our own Student Life in America survey, over 50% of students reported feeling stressed, 25% reported that homework was their biggest source of stress, and on average teens are spending one-third of their study time feeling stressed, anxious, or stuck.
The disparity can be explained in one of the conclusions regarding the Brown Report:
Of the three age groups, 17-year-olds have the most bifurcated distribution of the homework burden. They have the largest percentage of kids with no homework (especially when the homework shirkers are added in) and the largest percentage with more than two hours.
So what does that mean for parents who still endure the homework wars at home?
Read More: Teaching Your Kids How To Deal with School Stress
It means that sometimes kids who are on a rigorous college-prep track, probably are receiving more homework, but the statistics are melding it with the kids who are receiving no homework. And on our survey, 64% of students reported that their parents couldn’t help them with their work. This is where the real homework wars lie—not just the amount, but the ability to successfully complete assignments and feel success.
Parents want to figure out how to help their children manage their homework stress and learn the material.
Our Top 4 Tips for Ending Homework Wars
1. have a routine..
Every parenting advice article you will ever read emphasizes the importance of a routine. There’s a reason for that: it works. A routine helps put order into an often disorderly world. It removes the thinking and arguing and “when should I start?” because that decision has already been made. While routines must be flexible to accommodate soccer practice on Tuesday and volunteer work on Thursday, knowing in general when and where you, or your child, will do homework literally removes half the battle.
2. Have a battle plan.
Overwhelmed students look at a mountain of homework and think “insurmountable.” But parents can look at it with an outsider’s perspective and help them plan. Put in an extra hour Monday when you don’t have soccer. Prepare for the AP Chem test on Friday a little at a time each evening so Thursday doesn’t loom as a scary study night (consistency and repetition will also help lock the information in your brain). Start reading the book for your English report so that it’s underway. Go ahead and write a few sentences, so you don’t have a blank page staring at you. Knowing what the week will look like helps you keep calm and carry on.
3. Don’t be afraid to call in reserves.
You can’t outsource the “battle” but you can outsource the help ! We find that kids just do better having someone other than their parents help them —and sometimes even parents with the best of intentions aren’t equipped to wrestle with complicated physics problem. At The Princeton Review, we specialize in making homework time less stressful. Our tutors are available 24/7 to work one-to-one in an online classroom with a chat feature, interactive whiteboard, and the file sharing tool, where students can share their most challenging assignments.
4. Celebrate victories—and know when to surrender.
Students and parents can review completed assignments together at the end of the night -- acknowledging even small wins helps build a sense of accomplishment. If you’ve been through a particularly tough battle, you’ll also want to reach reach a cease-fire before hitting your bunk. A war ends when one person disengages. At some point, after parents have provided a listening ear, planning, and support, they have to let natural consequences take their course. And taking a step back--and removing any pressure a parent may be inadvertently creating--can be just what’s needed.
Stuck on homework?
Try an online tutoring session with one of our experts, and get homework help in 40+ subjects.
Try a Free Session

Explore Colleges For You
Connect with our featured colleges to find schools that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Career Quiz
Take our short quiz to learn which is the right career for you.

Get Started on Athletic Scholarships & Recruiting!
Join athletes who were discovered, recruited & often received scholarships after connecting with NCSA's 42,000 strong network of coaches.

Best 389 Colleges
165,000 students rate everything from their professors to their campus social scene.
SAT Prep Courses
1400+ course, act prep courses, free sat practice test & events, 1-800-2review, free digital sat prep try our self-paced plus program - for free, get a 14 day trial.
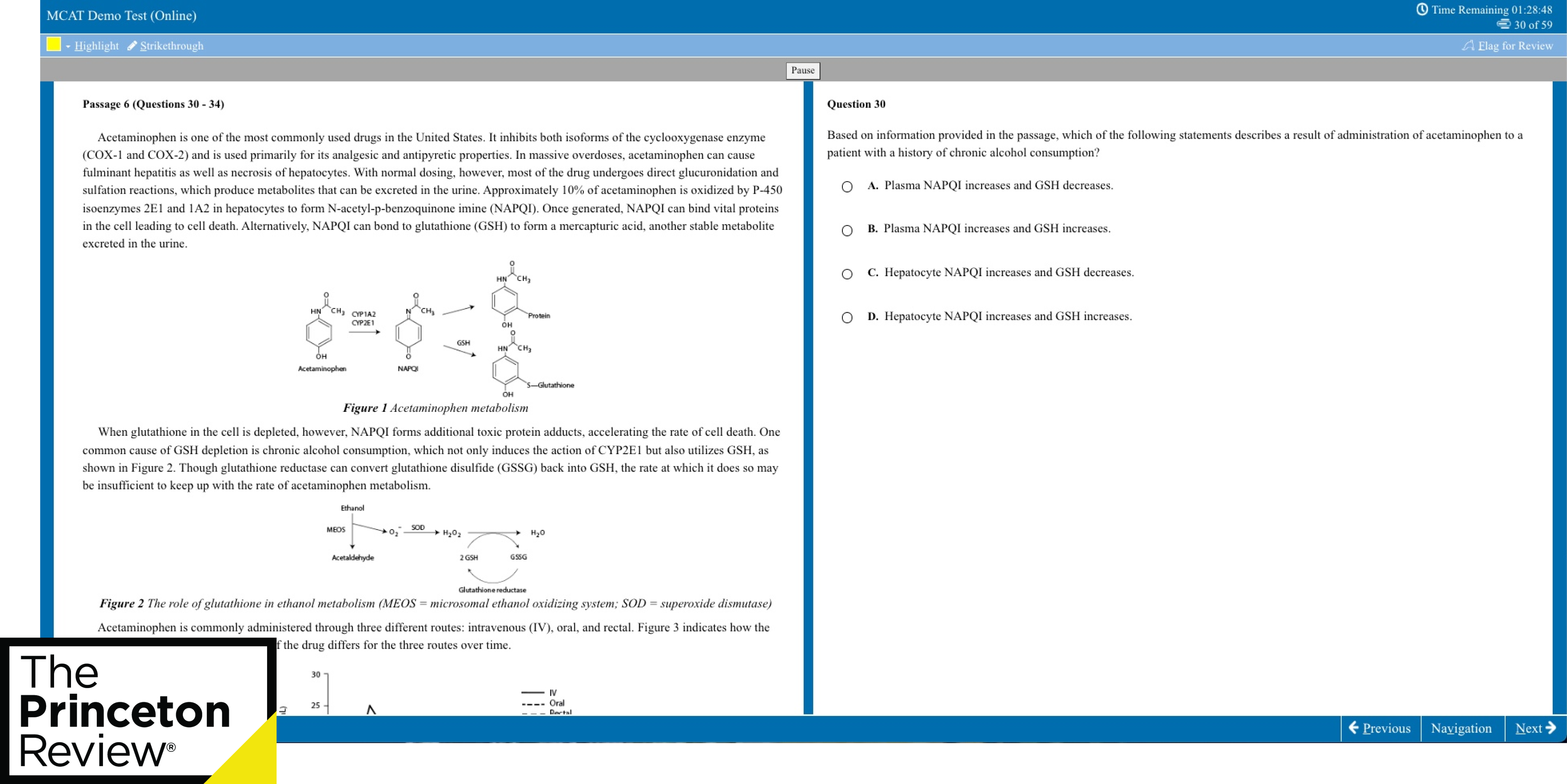
Free MCAT Practice Test
I already know my score.
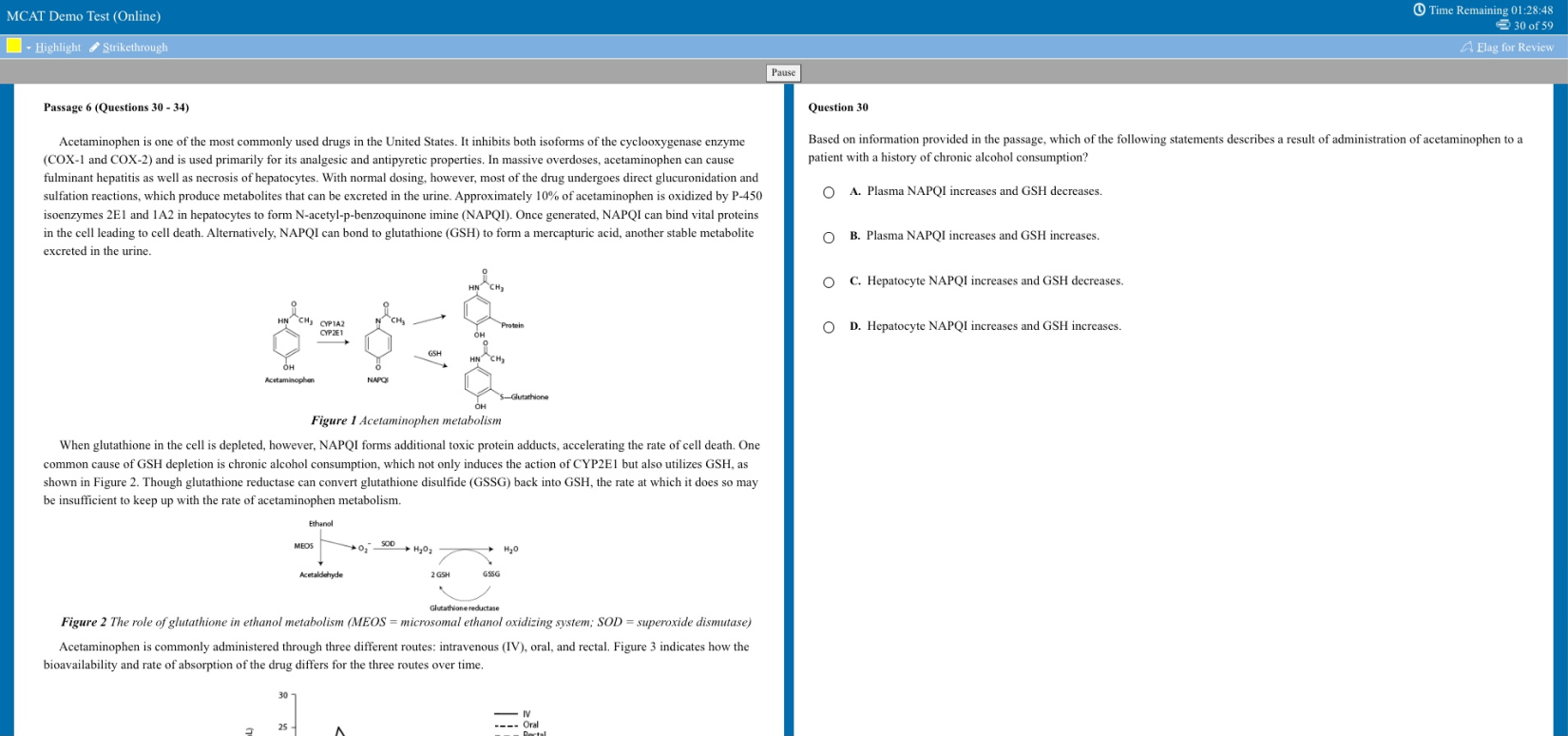
MCAT Self-Paced 14-Day Free Trial
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- Local Offices
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.
Homework: Only Review What You Need to Review
- Share article

A lot of teachers think that if you assign homework, you must review it with students the following day. This makes sense in that it’s important for students to correct and learn from their mistakes.
But what if they didn’t make any mistakes? I realize it’s unlikely every student will have the correct answer for any given question. Yet even if only half the class got it right, what should those students do while you review something they already know how to do? Well, I can tell you what they did in my classroom before I changed my approach: they talked or slept or worked on assignments for other classes.
The root of the problem is the same as what I described in the context of class openers (or Do Nows ): teachers reviewing an assignment without knowing whether students need them to review it. In extreme cases, teachers go over every homework assignment, beginning to end. I’m reminded of my high school math teacher working through problem after problem on the board, oblivious to snoozing and socializing students.
Then there are those teachers who act like disc jockeys by taking audience requests: “What questions would you like me to go over?” And if just one kid requests #3, the teacher reviews #3. Same goes for #4, #5, and so on. I did this until it backfired for a couple of reasons. First, just because Michael needs you to review #3 doesn’t mean Maria and Marcus do, which is why many students don’t pay attention when teachers use the DJ approach. Second, if students want to keep you from moving on to the next activity, all they have to do is request another question. And if you think kids won’t play you like this, think again. Nothing rankled me more than students asking me to go over problems, and then yakking or putting their heads on their desks as I obliged them.
Of course, you can’t look over students’ shoulders while they’re doing homework, so you’ll need to identify in class those homework questions most students need you to review. And here’s a great way to do this:
As you wrap up the class opener, show the answers to homework on your interactive whiteboard or projector screen. Then give students five minutes or so to check their answers and troubleshoot their errors, while you circulate to identify questions worth reviewing as a class (i.e., those most students struggled with)--and identify students to present the correct solutions to the class.
This process not only saves time, but also improves student learning. By working backward from the correct answers, students often figure out where they went wrong, and have a better grasp of the material as a result. And in the end, you’ll have fewer questions to review as a class, and a more captive audience for those questions you do need to review--as captive as any DJ could hope for!
Image provided by GECC, LLC with permission
The opinions expressed in Coach G’s Teaching Tips are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update

The psychological benefits of finishing your homework on time
H omework has long been a staple of the educational experience, often viewed as a tool for reinforcing learning and assessing student understanding. Despite its educational importance, many students struggle with timely completion, facing obstacles such as procrastination, distraction, and a lack of motivation. These challenges can make homework seem like a daunting task. However, the benefits of completing homework on time extend beyond academic achievement. This article aims to explore the psychological benefits associated with timely homework completion, revealing how this practice can enhance mental well-being and foster personal growth.
Enhanced time management skills
One of the key psychological benefits of completing homework on time is the development of robust time management skills. When students regularly meet homework deadlines, they learn to prioritize tasks and manage their time more effectively. This skill is crucial not only in academic settings but also in personal and professional life. Mastering time management can lead to a sense of control over one’s life, which significantly reduces feelings of stress and overwhelm. It’s common to hear students ask, “ Can you write my paper for me ?” as deadlines approach. However, those who have honed their time management skills are more likely to tackle assignments independently and with confidence, knowing they have planned adequately to meet their obligations.
Reduced stress and anxiety
The act of finishing homework on time can significantly alleviate stress and anxiety. Procrastination often leads to a buildup of tasks, which can become overwhelming as deadlines draw near. This not only increases anxiety but also triggers a cycle of stress and poor performance. By completing assignments on time, students can avoid the panic associated with last-minute rushes. The psychological relief that comes from knowing that all tasks are completed and nothing is hanging over one’s head is profound. Regularly experiencing this relief helps students maintain a calmer, more composed mindset, which is conducive to both academic success and general well-being.
Improved self-esteem
Timely completion of homework also plays a critical role in enhancing self-esteem. When students finish their work on time, they receive positive feedback and grades, which reinforces their self-image and confidence in their abilities. This process is vital for building self-efficacy, the belief in one’s capability to execute behaviors necessary to produce specific performance attainments. Achieving daily homework goals provides a continuous stream of small successes, each boosting the student’s self-esteem. Over time, this pattern fosters a more positive self-concept and encourages students to embrace more significant challenges, knowing they have the skills and discipline to succeed.
Better sleep patterns
Regular completion of homework by set deadlines can also lead to improved sleep patterns. When students avoid cramming their studies into late-night hours, they can maintain a healthier sleep schedule. This is crucial because adequate sleep is essential for brain function, emotional regulation, and overall mental health. A consistent sleep pattern prevents sleep deprivation’s cognitive impairments, such as reduced attention, slower processing, and memory issues. Students who manage their homework efficiently tend to go to bed at a reasonable hour, leading to better psychological and physical health outcomes.
Increased academic performance
There is a direct correlation between timely homework completion and academic performance. Students who consistently complete their homework on time often achieve higher grades and gain a deeper understanding of the material. This practice allows for regular study and revision, which enhances learning retention and prepares students for complex topics and exams. Psychologically, the regular accomplishment of set tasks, like homework, enhances mental agility and academic stamina, which is essential for long-term educational success.
Long-term academic and career benefits
Developing good habits in homework completion can yield significant long-term benefits in both academic and professional contexts. Academically, students who are diligent and consistent with their homework are more likely to pursue higher education and succeed in their chosen fields. Professionally, these habits translate into traits valued in the workplace, such as reliability, punctuality, and thoroughness. The psychological advantage of being perceived as dependable and hardworking cannot be overstated, as it opens doors to opportunities and fosters professional growth and stability.
The psychological benefits of completing homework on time are profound and multifaceted. From enhanced time management and reduced stress to improved self-esteem and better sleep patterns, the advantages extend well beyond the classroom. As students cultivate these habits, they not only boost their academic performance but also prepare themselves for future challenges in their academic and professional lives. It’s important for students to recognize these benefits and seek resources that reinforce good study habits, whether through educational tools, supportive peer groups, or essay writing service reviews when necessary. Ultimately, developing the discipline to complete homework on time is an investment in one’s mental health and future success.
- View all journals
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Get the Homework Help You Need
It's okay if you need some homework help. Everybody needs it at times. Be it math homework help or any other type, it's okay to seek out professional help. You can get help at all times. You can see different websites that offer you a great opportunity to get the help you need. You can now always find the best help online and it won't cost you nearly as much as you thought it would. The biggest thing that turns people off from using these types of services is the price. Everybody seems to think that paying for it is ridiculous.
Well, you're going to be so glad that you read this text because we're going to tell you this - my homework help services are really reasonably priced. You won't have to spend a lot of money to get the help you need. Some of our services include personal tutoring services, on-the-spot help, offline help, MATLAB homework help, and beyond. There are many options for different kinds of students and all are extremely beneficial. They also offer individual study services that take the burden off of you in a big way. You can receive offline tutoring in your area so that there are no future issues with the homework at all.
Pick Your Homework Help Web Site Wisely
It's a difficult process - picking which website suits your needs the best. However, it can be done and that's what we want you to do. You will have to conduct your own research before settling on a site that works best for you. You will have to examine third-party sources that review such services, you will have to go through client reviews, there are many elements that you need to take into account before going forward with any of the homework services out there. You'll definitely need to find out whether or not the site is legitimate and the overall quality of the help. You need to ask yourself if everything sounds legit to you.
My Homework Help is On the Way
Hopefully, this encouraged you to seek out the help you needed. The more homework there is, the easier it is to get lost in the shuffle. You need help. Asking your friends for help does not count as homework help. There are other sources out there to help you out!

I’ve witnessed the wonders of the deep sea. Mining could destroy them
World View 25 JUL 23

ChatGPT broke the Turing test — the race is on for new ways to assess AI
News Feature 25 JUL 23

The global fight for critical minerals is costly and damaging
Editorial 19 JUL 23
Pangenomics: prioritize diversity in collaborations
Correspondence 25 JUL 23

Pack up the parachute: why global north–south collaborations need to change
Career Feature 24 JUL 23
Industry: a poor record for whistle-blowers
Correspondence 18 JUL 23
Dementia risk linked to blood-protein imbalance in middle age
News 21 JUL 23
What does ‘brain dead’ really mean? The battle over how science defines the end of life
News Feature 11 JUL 23

Lab mice go wild: making experiments more natural in order to decode the brain
News Feature 14 JUN 23

The pandemic taught me the benefits of flipped homework
In this extract from “Online Education During Covid-19 and Beyond“ by Silvia Puiu and Samuel O. Idowu, Olga Amarie shares what she learned about flipped homework while teaching pandemic-era French lessons
Olga Amarie

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} Rather than restrict the use of AI, embrace the challenge
Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn, leveraging llms to assess soft skills in lifelong learning, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools, a diy guide to starting your own journal.
The pandemic has given rise to an opportunity and a challenge: the need to explore new teaching and learning methods. A unique strategy for enquiry, application and assessment that my students and I refined to navigate these extraordinary times more effectively was teaching and learning from flipped homework. I flipped one portion of my FREN 2001 Intermediate French I course to improve student engagement and motivation.
FREN 2001 Intermediate French I is a course conducted entirely in French, with strolls planned to help students learn the language and explore the cultures of the French-speaking regions.
- An evidence-based approach to flipped learning
- How a flipped classroom model improves learning in online STEM courses
- How to induct students into the flipped-classroom model
Speakers at the Intermediate level can successfully handle various communicative tasks in straightforward social situations. However, their conversation generally remains confined to predictable and concrete exchanges necessary for survival in the target culture. The question arises: How can students progress more rapidly? The flipped classroom concept empowers students to expedite their progress to the advanced level. They can handle topics by combining and recombining known elements before each class. They can practise with native speakers prior to oral exams. They can study grammar modules at home to dedicate their time in class to oral practice.
Students often need help in world language classes owing to vocabulary, grammar and pronunciation limitations. A flipped learning approach allows students to review the new material at their own pace by engaging in online activities. This transforms previously unfamiliar content into something familiar and more easily absorbed. As a result, by the end of the semester, students in a flipped classroom are capable of self-directed learning. They produce paragraph-level language instead of sentence-level language. Their proficiency extends to employing various time frames in oral and written discourse. Moreover, they become adept at comprehending authentic texts such as articles, short stories or native speaker utterances.
The flipped classroom is an innovative educational framework that moves the lecture outside the classroom via technology and moves homework and practice with concepts inside the classroom via learning activities. Students take on a more proactive role in their learning process, developing independent learning skills through presentations, videos, PowerPoint presentations and tutorials done at home. In class, the instructor uses the time to facilitate their discussions and help them apply their knowledge through concrete tasks.
The flipped homework experiment
During the pandemic, my central objective was to tailor homework to students’ unique learning styles, prompting me to investigate the impact of flipped learning. This was when I realised it was necessary to compare the learning environment between a flipped classroom and a traditional conversation-homework classroom.
I wanted to uncover how homework influenced the learning environment, students’ diverse learning styles and students’ engagement. How does the learning environment of a flipped classroom compare with the learning environment of a conversation-homework classroom? Is learning from homework useful, efficient or just busy work?
To address these enquiries, I chose two sections of FREN 2001 Intermediate French I classes during the pandemic to conduct my investigation and help students learn. In one section, I was teaching, as usual, a traditional conversation class followed by assigned activities as homework. In the second section, I opted to flip just the homework and use it predominantly for in-class activities and assessments. My students had to adjust personal learning strategies they had relied on for years to fit this new classroom structure. The outcome was highly encouraging, demonstrating that this adaptation was swift and effective.
In the traditional conversation-homework classroom, students often arrived unprepared for class activities, grappling with producing new vocabulary and grammatical structures. They spent much time completing their homework but they never had the chance to use that material in class because we had more material to cover the next day, which was new and overwhelming. Consequently, students spent significant time on their homework, yet this effort rarely translated into substantial classroom engagement.
After reading about the flipped classroom and attending training sessions and workshops at Georgia Southern University, my teaching methods and strategies changed. I use a highly learner-focused delivery model, fostering personalised engagement with each student. I give clear guidelines for class interaction and, most importantly, I empower learners to take responsibility for their own learning. The focus is on students’ autonomy and accountability for their own learning.
This is how I flipped the homework portion of our course. From the beginning of the semester, I now assign all the activities on the book’s Supersite, with due dates on a course calendar. The dates for the homework are due before the material is covered in class. I encourage students to cultivate a daily practice routine, ingraining the habits necessary for effective learning. I underscore the relevance of these activities to perform in class, whether through quizzes, speaking with their peers or answering open-ended questions. The short quizzes in class are precisely like the activities they practise at home on the Supersite, maintaining consistency.
Make your students feel positive about homework
From a pool of about 20 exercises, I randomly select one for in-class assessment. Class sessions include a five- to 10-minute homework assignment every time. Considering my flipped classroom, two areas are affected: homework and in-class dynamics. Both shape how my students interact with the material, the professor and classroom peers. Interestingly, it appears as though students do not prefer a structured or traditional homework environment; they are pleased by how homework is ultimately handled in the flipped classroom, as evidenced by the Student Ratings of Instruction. Suddenly, students have more time to learn. This freedom positively impacted the students’ attitude towards homework learning activities, affecting how comfortable they were with class participation.
A discernible dichotomy emerges in the dynamics of homework in these two class formats. In the traditional classroom, students frequently complain about completing assigned homework. In the flipped classroom, homework intertwines with active learning, occurring when students are most engaged in the learning process. They match, write, translate, apply, compare, arrange, combine, compose, create, organise, research, choose, record, listen, watch a video and comment on all these good verbs from Bloom’s Taxonomy for Learning Objectives. Students practise repeatedly because the computer allows for unlimited submissions. It is practice; it is learning, not just graded homework for completion. Students see that the homework is accessible in the flipped classroom because the pressure and the stress switch from completing it for a grade to learning from it and using it in class to shine.
In the flipped classroom, students are not penalised for incomplete homework. Some students practise more while others practise less at home, depending on their learning style. From the instructor’s point of view, flipped homework is more manageable and more accurate in measuring student progress and learning. For the flipped classroom, the top priority is not completing homework but a relaxed atmosphere where more learning is happening at the pace that the student needs.
Olga Amarie is professor of French at Georgia Southern University.
This is an adapted extract from Online Education During Covid-19 and Beyond , edited by Silvia Puiu and Samuel O. Idowu, published with permission from Springer.
If you would like advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the Campus newsletter .
Rather than restrict the use of AI, embrace the challenge
Let’s think about assessments and ai in a different way, how students’ genai skills affect assignment instructions, how not to land a job in academia, contextual learning: linking learning to the real world, three steps to unearth the hidden curriculum of networking.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.
Image credit: Claire Scully
New advances in technology are upending education, from the recent debut of new artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots like ChatGPT to the growing accessibility of virtual-reality tools that expand the boundaries of the classroom. For educators, at the heart of it all is the hope that every learner gets an equal chance to develop the skills they need to succeed. But that promise is not without its pitfalls.
“Technology is a game-changer for education – it offers the prospect of universal access to high-quality learning experiences, and it creates fundamentally new ways of teaching,” said Dan Schwartz, dean of Stanford Graduate School of Education (GSE), who is also a professor of educational technology at the GSE and faculty director of the Stanford Accelerator for Learning . “But there are a lot of ways we teach that aren’t great, and a big fear with AI in particular is that we just get more efficient at teaching badly. This is a moment to pay attention, to do things differently.”
For K-12 schools, this year also marks the end of the Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief (ESSER) funding program, which has provided pandemic recovery funds that many districts used to invest in educational software and systems. With these funds running out in September 2024, schools are trying to determine their best use of technology as they face the prospect of diminishing resources.
Here, Schwartz and other Stanford education scholars weigh in on some of the technology trends taking center stage in the classroom this year.
AI in the classroom
In 2023, the big story in technology and education was generative AI, following the introduction of ChatGPT and other chatbots that produce text seemingly written by a human in response to a question or prompt. Educators immediately worried that students would use the chatbot to cheat by trying to pass its writing off as their own. As schools move to adopt policies around students’ use of the tool, many are also beginning to explore potential opportunities – for example, to generate reading assignments or coach students during the writing process.
AI can also help automate tasks like grading and lesson planning, freeing teachers to do the human work that drew them into the profession in the first place, said Victor Lee, an associate professor at the GSE and faculty lead for the AI + Education initiative at the Stanford Accelerator for Learning. “I’m heartened to see some movement toward creating AI tools that make teachers’ lives better – not to replace them, but to give them the time to do the work that only teachers are able to do,” he said. “I hope to see more on that front.”
He also emphasized the need to teach students now to begin questioning and critiquing the development and use of AI. “AI is not going away,” said Lee, who is also director of CRAFT (Classroom-Ready Resources about AI for Teaching), which provides free resources to help teach AI literacy to high school students across subject areas. “We need to teach students how to understand and think critically about this technology.”
Immersive environments
The use of immersive technologies like augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality is also expected to surge in the classroom, especially as new high-profile devices integrating these realities hit the marketplace in 2024.
The educational possibilities now go beyond putting on a headset and experiencing life in a distant location. With new technologies, students can create their own local interactive 360-degree scenarios, using just a cell phone or inexpensive camera and simple online tools.
“This is an area that’s really going to explode over the next couple of years,” said Kristen Pilner Blair, director of research for the Digital Learning initiative at the Stanford Accelerator for Learning, which runs a program exploring the use of virtual field trips to promote learning. “Students can learn about the effects of climate change, say, by virtually experiencing the impact on a particular environment. But they can also become creators, documenting and sharing immersive media that shows the effects where they live.”
Integrating AI into virtual simulations could also soon take the experience to another level, Schwartz said. “If your VR experience brings me to a redwood tree, you could have a window pop up that allows me to ask questions about the tree, and AI can deliver the answers.”
Gamification
Another trend expected to intensify this year is the gamification of learning activities, often featuring dynamic videos with interactive elements to engage and hold students’ attention.
“Gamification is a good motivator, because one key aspect is reward, which is very powerful,” said Schwartz. The downside? Rewards are specific to the activity at hand, which may not extend to learning more generally. “If I get rewarded for doing math in a space-age video game, it doesn’t mean I’m going to be motivated to do math anywhere else.”
Gamification sometimes tries to make “chocolate-covered broccoli,” Schwartz said, by adding art and rewards to make speeded response tasks involving single-answer, factual questions more fun. He hopes to see more creative play patterns that give students points for rethinking an approach or adapting their strategy, rather than only rewarding them for quickly producing a correct response.
Data-gathering and analysis
The growing use of technology in schools is producing massive amounts of data on students’ activities in the classroom and online. “We’re now able to capture moment-to-moment data, every keystroke a kid makes,” said Schwartz – data that can reveal areas of struggle and different learning opportunities, from solving a math problem to approaching a writing assignment.
But outside of research settings, he said, that type of granular data – now owned by tech companies – is more likely used to refine the design of the software than to provide teachers with actionable information.
The promise of personalized learning is being able to generate content aligned with students’ interests and skill levels, and making lessons more accessible for multilingual learners and students with disabilities. Realizing that promise requires that educators can make sense of the data that’s being collected, said Schwartz – and while advances in AI are making it easier to identify patterns and findings, the data also needs to be in a system and form educators can access and analyze for decision-making. Developing a usable infrastructure for that data, Schwartz said, is an important next step.
With the accumulation of student data comes privacy concerns: How is the data being collected? Are there regulations or guidelines around its use in decision-making? What steps are being taken to prevent unauthorized access? In 2023 K-12 schools experienced a rise in cyberattacks, underscoring the need to implement strong systems to safeguard student data.
Technology is “requiring people to check their assumptions about education,” said Schwartz, noting that AI in particular is very efficient at replicating biases and automating the way things have been done in the past, including poor models of instruction. “But it’s also opening up new possibilities for students producing material, and for being able to identify children who are not average so we can customize toward them. It’s an opportunity to think of entirely new ways of teaching – this is the path I hope to see.”
Experience Google AI in even more ways on Android
May 14, 2024
[[read-time]] min read
By building AI right into the Android operating system, we're reimagining how you can interact with your phone.

- Bullet points
- Circle to Search gets smarter, helping students solve physics and math problems directly from their phones and tablets.
- Gemini on Android improves context understanding, allowing users to drag and drop generated images and ask questions about videos and PDFs.
- Gemini Nano with Multimodality coming to Pixel, bringing multimodal capabilities for richer image descriptions and scam alerts during phone calls.
- Android 15 and ecosystem updates coming tomorrow.
- Basic explainer
Google is making Android phones smarter with AI.
Circle to Search can now help students with homework.
Gemini, a new AI assistant, can understand what's on your screen and help you do things.
Android phones will soon be able to alert you to suspected scams during phone calls.
Explore other styles:

We’re at a once-in-a-generation moment where the latest advancements in AI are reinventing what phones can do. With Google AI at the core of Android’s operating system, the billions of people who use Android can now interact with their devices in entirely new ways.
Today, we’re sharing updates that let you experience Google AI on Android.
Circle to Search can now help students with homework
With Circle to Search built directly into the user experience, you can search anything you see on your phone using a simple gesture — without having to stop what you’re doing or switch to a different app. Since launching at Samsung Unpacked , we’ve added new capabilities to Circle to Search, like full-screen translation , and we’ve expanded availability to more Pixel and Samsung devices.
Starting today, Circle to Search can now help students with homework, giving them a deeper understanding, not just an answer — directly from their phones and tablets. When students circle a prompt they’re stuck on, they’ll get step-by-step instructions to solve a range of physics and math 1 word problems without leaving their digital info sheet or syllabus. Later this year, Circle to Search will be able to help solve even more complex problems involving symbolic formulas, diagrams, graphs and more. This is all possible due to our LearnLM effort to enhance our models and products for learning.
Circle to Search is already available on more than 100 million devices today. With plans to bring the experience to more devices, we’re on track to double that by the end of the year.
Gemini will get even better at understanding context to assist you in getting things done
Gemini on Android is a new kind of assistant that uses generative AI to help you be more creative and productive. This experience, which is integrated into Android, is getting even better at understanding the context of what’s on your screen and what app you’re using.
Soon, you’ll be able to bring up Gemini's overlay on top of the app you're in to easily use Gemini in more ways. For example, you can drag and drop generated images into Gmail, Google Messages and other places, or tap “Ask this video” to find specific information in a YouTube video. If you have Gemini Advanced, you’ll also have the option to “Ask this PDF” to quickly get answers without having to scroll through multiple pages. This update will roll out to hundreds of millions of devices over the next few months.
And we’ll continue to improve Gemini to give you more dynamic suggestions related to what’s on your screen.

Full multimodal capabilities coming to Gemini Nano
Android is the first mobile operating system that includes a built-in, on-device foundation model. With Gemini Nano, we’re able to bring experiences to you quickly and keep your information completely private to you. Starting with Pixel later this year, we’ll be introducing our latest model, Gemini Nano with Multimodality. This means your phone will not just be able to process text input but also understand more information in context like sights, sounds and spoken language.
Clearer descriptions with TalkBack
Later this year, Gemini Nano’s multimodal capabilities are coming to TalkBack, helping people who experience blindness or low vision get richer and clearer descriptions of what’s happening in an image. On average, TalkBack users come across 90 unlabeled images per day. This update will help fill in missing information — whether it’s more details about what’s in a photo that family or friends sent or the style and cut of clothes when shopping online. Since Gemini Nano is on-device, these descriptions happen quickly and even work when there's no network connection.
Receive alerts for suspected scams during phone calls
According to a recent report , in a 12-month period, people lost more than $1 trillion to fraud. We’re testing a new feature that uses Gemini Nano to provide real-time alerts during a call if it detects conversation patterns commonly associated with scams. For example, you would receive an alert if a “bank representative” asks you to urgently transfer funds, make a payment with a gift card or requests personal information like card PINs or passwords, which are uncommon bank requests . This protection all happens on-device, so your conversation stays private to you. We’ll share more about this opt-in feature later this year.

More to come on Android
We’re just getting started with how on-device AI can change what your phone can do, and we’ll continue building Google AI into every part of the smartphone experience with Pixel, Samsung and more. If you’re a developer, check out the Android Developers blog to learn how you can build with our latest AI models and tools, like Gemini Nano and Gemini in Android Studio.
Related Article

10 updates coming t…
From Theft Detection Lock to casting on Rivian to Wear OS 5 updates, here’s what’s coming to Android 15 and its device ecosystem.

Here’s a look at everything we announced at Google I/O 2024.
Get more stories from Google in your inbox.
Your information will be used in accordance with Google's privacy policy.
Done. Just one step more.
Check your inbox to confirm your subscription.
You are already subscribed to our newsletter.
You can also subscribe with a different email address .
More Information
Available for some math word problems when opted into Search Labs.
Related stories

New support for AI advancement in Central and Eastern Europe

Bringing Gemini to Google Workspace for Education

8 new accessibility updates across Lookout, Google Maps and more

100 things we announced at I/O 2024

10 updates coming to the Android ecosystem

Android’s theft protection features keep your device and data safe
Let’s stay in touch. Get the latest news from Google in your inbox.
ChatGPT vs. ChatGPT Plus: Is a paid subscription still worth it?

When GPT-4 was OpenAI's most powerful artificial intelligence large language model (LLM), paying for a subscription to ChatGPT Plus -- which costs $20 a month -- made sense. But now that OpenAI announced the availability of GPT-4o, I'm not so sure.
With this latest update, OpenAI revealed an omnimodel that makes GPT-4-level intelligence available for all, so you won't need a Plus subscription to access it. What's more, free users can now access features that were previously reserved for paid subscribers, including GPT Store access to use custom GPT bots; the Memory feature to give their conversations a sense of continuity; uploading photos and documents to discuss them with ChatGPT; browsing the web to give more current context; and advanced data analysis.
Also: 6 ways OpenAI just supercharged ChatGPT for free users
These changes can make it hard to determine who will find free ChatGPT adequate and who should spring for a Plus subscription. As a ChatGPT Plus subscriber, I'll explain below in exactly which cases you should use one or the other. Once GPT-4o is widely available, I'll test it to see how it performs for free users and ChatGPT Plus subscribers and report if any further differences arise.
You should use ChatGPT Plus if...
1. you use chatgpt a lot more than the average user.
With GPT-4o giving free users many of the same capabilities that were only available behind a Plus subscription, the reasons to sign up for a monthly fee have dwindled but are not completely gone. Free ChatGPT users will be limited in the number of messages they can send with GPT-4o, depending on usage and demand; however, OpenAI doesn't specify exactly what that limit is.
Also: Microsoft Copilot vs. Copilot Pro: Is the subscription fee worth it?
OpenAI says ChatGPT will switch automatically to GPT-3.5 when free users reach their limit. ChatGPT Plus subscribers have five times the capacity of free users. Paid users will be able to ask GPT-4o five times as many questions as free users and will still have access to GPT-4 when they exceed their limit. We expect OpenAI will increase the limits for GPT-4o for both free and paid users.
2. You can't wait
OpenAI says it is beginning to roll out GPT-4o to ChatGPT Plus, Team, and ChatGPT free users today, with Enterprise users coming soon. During the Spring Update live stream, OpenAI CTO Mira Murati announced that the new GPT-4o model and the rest of the updates will roll out iteratively to customers over the next few weeks. This means that only a fraction of ChatGPT users currently have access to the new features, with this number increasing shortly.
Also: How to subscribe to ChatGPT Plus (and why you should)
If you don't want to wait until you get the new update in your account to use Plus features as a free subscriber, you can get a Plus subscription now to stave off the excitement. Note that you can cancel the subscription whenever you want.
ChatGPT Plus users also still get early access to new features that OpenAI rolls out, including the new ChatGPT desktop app for macOS. Soon, this early access will include the new Voice Mode that rolls out over the coming weeks. OpenAI also will launch a Windows version of the app later this year.
You should use free ChatGPT if...
1. you don't want to pay a monthly fee.
When GPT-4o is available, ChatGPT users will no longer need a Plus subscription to access most of the features that initially attracted subscribers. OpenAI is making GPT-4o available to all users, whether they are paying or not.
ChatGPT free users will be able to access the multimodal GPT-4o with GPT-4-level intelligence, get responses from the web, use advanced data analysis, upload files and photos to discuss with the chatbot, access custom GPTs in the GPT Store, and have more helpful experience with Memory -- all of which used to be ChatGPT Plus benefits.
Although it's unclear whether free users can generate images natively in GPT-4o (OpenAI did not disclose this during the event), free users will have access to GPT bots in the GPT Store. If DALL-E access remains a Plus feature, free users can still access the DALL-E bot in the GPT Store.
2. You're a casual ChatGPT user
There is no need to upgrade to a ChatGPT Plus membership if you're just a casual user who doesn't reach the usage limits of GPT-4o. The new GPT-4o model is rolling out to ChatGPT free users with usage limits beginning today, but OpenAI hasn't specified this limit. Plus users will have a message limit that is five times greater than that of free users, with Team and Enterprise users getting even higher limits.
Also: ChatGPT vs. Bing Chat vs. Google Bard: Which is the best AI chatbot?
If you're a free user who doesn't use ChatGPT often and stays within the usage limit, you wouldn't get much benefit from a ChatGPT Plus subscription now. I expect OpenAI will amend the subscription benefits or the price as time passes and GPT-4o becomes widely available.
Artificial Intelligence
Copilot pro vs. chatgpt plus: which is ai chatbot is worth your $20 a month, chatgpt vs. copilot: which ai chatbot is better for you, the best business internet service providers.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That's problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
They are less likely to have computers or a quiet place to do homework in peace. "Homework can highlight those inequities," she says. Quantity vs. quality. One point researchers agree on is that for all students, homework quality matters. But too many kids are feeling a lack of engagement with their take-home assignments, many experts say.
A little amount of homework may help elementary school students build study habits. Homework for junior high students appears to reach the point of diminishing returns after about 90 minutes a night. For high school students, the positive line continues to climb until between 90 minutes and 2½ hours of homework a night, after which returns ...
parental support of autonomous homework student behavior relates positively to achievement (Cooper, Jackson, Nye and Lindsay, 2001; as cited in Hatlie 2009 p. 235); and more is not better when it comes to ... Review of Educational Research , 76 (1), 1-62. Corno, L. (1996, November). Homework is a Complicated Thing. Educational Researcher, pp ...
Homework has long been a topic of social research, but rela-tively few studies have focused on the teacher's role in the homework process. Most research examines what students do, and whether and ...
Homework has been in the headlines again recently and continues to be a topic of controversy, with claims that students and families are suffering under the burden of huge amounts of homework. School board members, educators, and parents may wish to turn to the research for answers to their questions about the benefits and drawbacks of homework.
Does homework help? A review of research. Elementary School Journal 1960;60:212-224. ISI. ... Odum ME. A tough assignment for teachers: Getting students to do homework is getting harder. Washington Post 1994 May 2 A1 A10. Google Scholar *Olson M. Homework variables and academic achievement: An integrated study.
It turns out that parents are right to nag: To succeed in school, kids should do their homework. Duke University researchers have reviewed more than 60 research studies on homework between 1987 and 2003 and concluded that homework does have a positive effect on student achievement. Harris Cooper, a professor of psychology, said the research ...
The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein, co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work ...
Cooper conducted a review of the existing research on homework in the mid-2000s, and found that, up to a point, the amount of homework students reported doing correlates with their performance on ...
Homework is a universal student practice. Despite this universality, the role that homework plays in student academic performance is complex and open to various interpretations. This chapter reviews the current available evidence about the relationships between homework and achievement. We begin by examining the differences between countries ...
2001; Lee & Pruitt, 1979). The most common instructional purpose of homework is to provide the student with an opportunity to practice or review material that has already been presented in class (Becker & Epstein, 1982). Preparation assignments introduce material to help students obtain the maximum benefit when the new
Huiyong Fan, Jianzhong Xu, Zhihui Cai, Jinbo He, Xitao Fan Homework and students' achievement in math and science: A 30-year meta-analysis, 1986-2015, Educational Research Review 20 (Feb 2017): 35-54.
Cooper, Robinson, and Patall (2006) issued a strong warning about too much homework. "Even for these older students, too much homework may diminish its effectiveness or even become counterproductive (pg.53)". The Homework Literature Review stated that "excessive homework may impact negatively on student achievement" (2004, p.3).
Both reviews conclude that homework does help to improve academic achievement, primarily in the middle and high school. For children in elementary school, the review concludes that while homework can help children develop good study habits, it does not help to improve students' grades or standardized test scores.
Introduction. Literature indicates that doing homework regularly is positively associated with students' academic achievement (Zimmerman and Kitsantas, 2005).Hence, as expected, the amount of homework done is one of the variables that shows a strong and positive relationship with academic achievement (Cooper et al., 2001). It seems consensual in the literature that doing homework is always ...
For decades, the homework standard has been a "10-minute rule," which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 ...
An education expert weighs in. The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein, co-director of the Center on School ...
Review of Educational Research, 76(1), 1-62. ... Practice assignments do improve scores on class tests at all grade levels. A little amount of homework may help elementary school students build study habits. Homework for junior high students appears to reach the point of diminishing returns after about 90 minutes a night. For high school ...
Better students do their homework and teachers recognize that frequently. Repetition of your homework also helps memorize which you could benefit from on tests and other classwork activities. Alexa S September 14, 2011 · 1:42 pm. Depending on the subject or the assigment, homework can either be redundant or effective.
Studies of typical homework loads vary: In one, a Stanford researcher found that more than two hours of homework a night may be counterproductive.The research, conducted among students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities, found that too much homework resulted in stress, physical health problems and a general lack of balance.
First, just because Michael needs you to review #3 doesn't mean Maria and Marcus do, which is why many students don't pay attention when teachers use the DJ approach. Second, if students want ...
Improved self-esteem. Timely completion of homework also plays a critical role in enhancing self-esteem. When students finish their work on time, they receive positive feedback and grades, which ...
You won't have to spend a lot of money to get the help you need. Some of our services include personal tutoring services, on-the-spot help, offline help, MATLAB homework help, and beyond. There are many options for different kinds of students and all are extremely beneficial. They also offer individual study services that take the burden off of ...
Homework-help websites allow students to post questions and receive answers, and they may also provide access to answers that have already been provided to other students (Lancaster & Cotarian, Citation 2021). Some websites provide both file-sharing and homework-help functions, while others just provide one.
Students practise repeatedly because the computer allows for unlimited submissions. It is practice; it is learning, not just graded homework for completion. Students see that the homework is accessible in the flipped classroom because the pressure and the stress switch from completing it for a grade to learning from it and using it in class to ...
AI can also help automate tasks like grading and lesson planning, freeing teachers to do the human work that drew them into the profession in the first place, said Victor Lee, an associate ...
A new tool called Writable, which uses ChatGPT to help grade student writing assignments, is being offered widely to teachers in grades 3-12.. Why it matters: Teachers have quietly used ChatGPT to grade papers since it first came out — but now schools are sanctioning and encouraging its use. Driving the news: Writable, which is billed as a time-saving tool for teachers, was purchased last ...
Starting today, Circle to Search can now help students with homework, giving them a deeper understanding, not just an answer — directly from their phones and tablets. When students circle a prompt they're stuck on, they'll get step-by-step instructions to solve a range of physics and math 1 word problems without leaving their digital info ...
Apple Vision Pro review: Fascinating, flawed, and needs to fix 5 things; I've tried the top XR headsets. Here's the one most people should buy; ChatGPT vs. ChatGPT Plus: Is the subscription fee ...