
- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems
- Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books

Scientific Theory Definition and Examples

A scientific theory is a well-established explanation of some aspect of the natural world. Theories come from scientific data and multiple experiments. While it is not possible to prove a theory, a single contrary result using the scientific method can disprove it. In other words, a theory is testable and falsifiable.
Examples of Scientific Theories
There are many scientific theory in different disciplines:
- Astronomy : theory of stellar nucleosynthesis , theory of stellar evolution
- Biology : cell theory, theory of evolution, germ theory, dual inheritance theory
- Chemistry : atomic theory, Bronsted Lowry acid-base theory , kinetic molecular theory of gases , Lewis acid-base theory , molecular theory, valence bond theory
- Geology : climate change theory, plate tectonics theory
- Physics : Big Bang theory, perturbation theory, theory of relativity, quantum field theory
Criteria for a Theory
In order for an explanation of the natural world to be a theory, it meets certain criteria:
- A theory is falsifiable. At some point, a theory withstands testing and experimentation using the scientific method.
- A theory is supported by lots of independent evidence.
- A theory explains existing experimental results and predicts outcomes of new experiments at least as well as other theories.
Difference Between a Scientific Theory and Theory
Usually, a scientific theory is just called a theory. However, a theory in science means something different from the way most people use the word. For example, if frogs rain down from the sky, a person might observe the frogs and say, “I have a theory about why that happened.” While that theory might be an explanation, it is not based on multiple observations and experiments. It might not be testable and falsifiable. It’s not a scientific theory (although it could eventually become one).
Value of Disproven Theories
Even though some theories are incorrect, they often retain value.
For example, Arrhenius acid-base theory does not explain the behavior of chemicals lacking hydrogen that behave as acids. The Bronsted Lowry and Lewis theories do a better job of explaining this behavior. Yet, the Arrhenius theory predicts the behavior of most acids and is easier for people to understand.
Another example is the theory of Newtonian mechanics. The theory of relativity is much more inclusive than Newtonian mechanics, which breaks down in certain frames of reference or at speeds close to the speed of light . But, Newtonian mechanics is much simpler to understand and its equations apply to everyday behavior.
Difference Between a Scientific Theory and a Scientific Law
The scientific method leads to the formulation of both scientific theories and laws . Both theories and laws are falsifiable. Both theories and laws help with making predictions about the natural world. However, there is a key difference.
A theory explains why or how something works, while a law describes what happens without explaining it. Often, you see laws written in the form of equations or formulas.
Theories and laws are related, but theories never become laws or vice versa.
Theory vs Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a proposition that is tested via an experiment. A theory results from many, many tested hypotheses.
Theory vs Fact
Theories depend on facts, but the two words mean different things. A fact is an irrefutable piece of evidence or data. Facts never change. A theory, on the other hand, may be modified or disproven.
Difference Between a Theory and a Model
Both theories and models allow a scientist to form a hypothesis and make predictions about future outcomes. However, a theory both describes and explains, while a model only describes. For example, a model of the solar system shows the arrangement of planets and asteroids in a plane around the Sun, but it does not explain how or why they got into their positions.
- Frigg, Roman (2006). “ Scientific Representation and the Semantic View of Theories .” Theoria . 55 (2): 183–206.
- Halvorson, Hans (2012). “What Scientific Theories Could Not Be.” Philosophy of Science . 79 (2): 183–206. doi: 10.1086/664745
- McComas, William F. (December 30, 2013). The Language of Science Education: An Expanded Glossary of Key Terms and Concepts in Science Teaching and Learning . Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-94-6209-497-0.
- National Academy of Sciences (US) (1999). Science and Creationism: A View from the National Academy of Sciences (2nd ed.). National Academies Press. doi: 10.17226/6024 ISBN 978-0-309-06406-4.
- Suppe, Frederick (1998). “Understanding Scientific Theories: An Assessment of Developments, 1969–1998.” Philosophy of Science . 67: S102–S115. doi: 10.1086/392812
Related Posts
Hypothesis vs. Theory
A hypothesis is either a suggested explanation for an observable phenomenon, or a reasoned prediction of a possible causal correlation among multiple phenomena. In science , a theory is a tested, well-substantiated, unifying explanation for a set of verified, proven factors. A theory is always backed by evidence; a hypothesis is only a suggested possible outcome, and is testable and falsifiable.
Comparison chart
Examples of theory and hypothesis.
Theory: Einstein's theory of relativity is a theory because it has been tested and verified innumerable times, with results consistently verifying Einstein's conclusion. However, simply because Einstein's conclusion has become a theory does not mean testing of this theory has stopped; all science is ongoing. See also the Big Bang theory , germ theory , and climate change .
Hypothesis: One might think that a prisoner who learns a work skill while in prison will be less likely to commit a crime when released. This is a hypothesis, an "educated guess." The scientific method can be used to test this hypothesis, to either prove it is false or prove that it warrants further study. (Note: Simply because a hypothesis is not found to be false does not mean it is true all or even most of the time. If it is consistently true after considerable time and research, it may be on its way to becoming a theory.)
This video further explains the difference between a theory and a hypothesis:
Common Misconception
People often tend to say "theory" when what they're actually talking about is a hypothesis. For instance, "Migraines are caused by drinking coffee after 2 p.m. — well, it's just a theory, not a rule."
This is actually a logically reasoned proposal based on an observation — say 2 instances of drinking coffee after 2 p.m. caused a migraine — but even if this were true, the migraine could have actually been caused by some other factors.
Because this observation is merely a reasoned possibility, it is testable and can be falsified — which makes it a hypothesis, not a theory.
- What is a Scientific Hypothesis? - LiveScience
- Wikipedia:Scientific theory
Related Comparisons

Share this comparison via:
If you read this far, you should follow us:
"Hypothesis vs Theory." Diffen.com. Diffen LLC, n.d. Web. 6 May 2024. < >
Comments: Hypothesis vs Theory
Anonymous comments (2).
October 11, 2013, 1:11pm "In science, a theory is a well-substantiated, unifying explanation for a set of verified, proven hypotheses." But there's no such thing as "proven hypotheses". Hypotheses can be tested/falsified, they can't be "proven". That's just not how science works. Logical deductions based on axioms can be proven, but not scientific hypotheses. On top of that I find it somewhat strange to claim that a theory doesn't have to be testable, if it's built up from hypotheses, which DO have to be testable... — 80.✗.✗.139
May 6, 2014, 11:45pm "Evolution is a theory, not a fact, regarding the origin of living things." this statement is poorly formed because it implies that a thing is a theory until it gets proven and then it is somehow promoted to fact. this is just a misunderstanding of what the words mean, and of how science progresses generally. to say that a theory is inherently dubious because "it isn't a fact" is pretty much a meaningless statement. no expression which qualified as a mere fact could do a very good job of explaining the complicated process by which species have arisen on Earth over the last billion years. in fact, if you claimed that you could come up with such a single fact, now THAT would be dubious! everything we observe in nature supports the theory of evolution, and nothing we observe contradicts it. when you can say this about a theory, it's a pretty fair bet that the theory is correct. — 71.✗.✗.151
- Accuracy vs Precision
- Deductive vs Inductive
- Subjective vs Objective
- Subconscious vs Unconscious mind
- Qualitative vs Quantitative
- Creationism vs Evolution
Edit or create new comparisons in your area of expertise.
Stay connected
© All rights reserved.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.14: Experiments and Hypotheses
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 43806
Now we’ll focus on the methods of scientific inquiry. Science often involves making observations and developing hypotheses. Experiments and further observations are often used to test the hypotheses.
A scientific experiment is a carefully organized procedure in which the scientist intervenes in a system to change something, then observes the result of the change. Scientific inquiry often involves doing experiments, though not always. For example, a scientist studying the mating behaviors of ladybugs might begin with detailed observations of ladybugs mating in their natural habitats. While this research may not be experimental, it is scientific: it involves careful and verifiable observation of the natural world. The same scientist might then treat some of the ladybugs with a hormone hypothesized to trigger mating and observe whether these ladybugs mated sooner or more often than untreated ones. This would qualify as an experiment because the scientist is now making a change in the system and observing the effects.
Forming a Hypothesis
When conducting scientific experiments, researchers develop hypotheses to guide experimental design. A hypothesis is a suggested explanation that is both testable and falsifiable. You must be able to test your hypothesis, and it must be possible to prove your hypothesis true or false.
For example, Michael observes that maple trees lose their leaves in the fall. He might then propose a possible explanation for this observation: “cold weather causes maple trees to lose their leaves in the fall.” This statement is testable. He could grow maple trees in a warm enclosed environment such as a greenhouse and see if their leaves still dropped in the fall. The hypothesis is also falsifiable. If the leaves still dropped in the warm environment, then clearly temperature was not the main factor in causing maple leaves to drop in autumn.
In the Try It below, you can practice recognizing scientific hypotheses. As you consider each statement, try to think as a scientist would: can I test this hypothesis with observations or experiments? Is the statement falsifiable? If the answer to either of these questions is “no,” the statement is not a valid scientific hypothesis.
Practice Questions
Determine whether each following statement is a scientific hypothesis.
- No. This statement is not testable or falsifiable.
- No. This statement is not testable.
- No. This statement is not falsifiable.
- Yes. This statement is testable and falsifiable.
[reveal-answer q=”429550″] Show Answers [/reveal-answer] [hidden-answer a=”429550″]
- d: Yes. This statement is testable and falsifiable. This could be tested with a number of different kinds of observations and experiments, and it is possible to gather evidence that indicates that air pollution is not linked with asthma.
- a: No. This statement is not testable or falsifiable. “Bad thoughts and behaviors” are excessively vague and subjective variables that would be impossible to measure or agree upon in a reliable way. The statement might be “falsifiable” if you came up with a counterexample: a “wicked” place that was not punished by a natural disaster. But some would question whether the people in that place were really wicked, and others would continue to predict that a natural disaster was bound to strike that place at some point. There is no reason to suspect that people’s immoral behavior affects the weather unless you bring up the intervention of a supernatural being, making this idea even harder to test.
[/hidden-answer]
Testing a Vaccine
Let’s examine the scientific process by discussing an actual scientific experiment conducted by researchers at the University of Washington. These researchers investigated whether a vaccine may reduce the incidence of the human papillomavirus (HPV). The experimental process and results were published in an article titled, “ A controlled trial of a human papillomavirus type 16 vaccine .”
Preliminary observations made by the researchers who conducted the HPV experiment are listed below:
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted virus in the United States.
- There are about 40 different types of HPV. A significant number of people that have HPV are unaware of it because many of these viruses cause no symptoms.
- Some types of HPV can cause cervical cancer.
- About 4,000 women a year die of cervical cancer in the United States.
Practice Question
Researchers have developed a potential vaccine against HPV and want to test it. What is the first testable hypothesis that the researchers should study?
- HPV causes cervical cancer.
- People should not have unprotected sex with many partners.
- People who get the vaccine will not get HPV.
- The HPV vaccine will protect people against cancer.
[reveal-answer q=”20917″] Show Answer [/reveal-answer] [hidden-answer a=”20917″]Hypothesis A is not the best choice because this information is already known from previous studies. Hypothesis B is not testable because scientific hypotheses are not value statements; they do not include judgments like “should,” “better than,” etc. Scientific evidence certainly might support this value judgment, but a hypothesis would take a different form: “Having unprotected sex with many partners increases a person’s risk for cervical cancer.” Before the researchers can test if the vaccine protects against cancer (hypothesis D), they want to test if it protects against the virus. This statement will make an excellent hypothesis for the next study. The researchers should first test hypothesis C—whether or not the new vaccine can prevent HPV.[/hidden-answer]
Experimental Design
You’ve successfully identified a hypothesis for the University of Washington’s study on HPV: People who get the HPV vaccine will not get HPV.
The next step is to design an experiment that will test this hypothesis. There are several important factors to consider when designing a scientific experiment. First, scientific experiments must have an experimental group. This is the group that receives the experimental treatment necessary to address the hypothesis.
The experimental group receives the vaccine, but how can we know if the vaccine made a difference? Many things may change HPV infection rates in a group of people over time. To clearly show that the vaccine was effective in helping the experimental group, we need to include in our study an otherwise similar control group that does not get the treatment. We can then compare the two groups and determine if the vaccine made a difference. The control group shows us what happens in the absence of the factor under study.
However, the control group cannot get “nothing.” Instead, the control group often receives a placebo. A placebo is a procedure that has no expected therapeutic effect—such as giving a person a sugar pill or a shot containing only plain saline solution with no drug. Scientific studies have shown that the “placebo effect” can alter experimental results because when individuals are told that they are or are not being treated, this knowledge can alter their actions or their emotions, which can then alter the results of the experiment.
Moreover, if the doctor knows which group a patient is in, this can also influence the results of the experiment. Without saying so directly, the doctor may show—through body language or other subtle cues—his or her views about whether the patient is likely to get well. These errors can then alter the patient’s experience and change the results of the experiment. Therefore, many clinical studies are “double blind.” In these studies, neither the doctor nor the patient knows which group the patient is in until all experimental results have been collected.
Both placebo treatments and double-blind procedures are designed to prevent bias. Bias is any systematic error that makes a particular experimental outcome more or less likely. Errors can happen in any experiment: people make mistakes in measurement, instruments fail, computer glitches can alter data. But most such errors are random and don’t favor one outcome over another. Patients’ belief in a treatment can make it more likely to appear to “work.” Placebos and double-blind procedures are used to level the playing field so that both groups of study subjects are treated equally and share similar beliefs about their treatment.
The scientists who are researching the effectiveness of the HPV vaccine will test their hypothesis by separating 2,392 young women into two groups: the control group and the experimental group. Answer the following questions about these two groups.
- This group is given a placebo.
- This group is deliberately infected with HPV.
- This group is given nothing.
- This group is given the HPV vaccine.
[reveal-answer q=”918962″] Show Answers [/reveal-answer] [hidden-answer a=”918962″]
- a: This group is given a placebo. A placebo will be a shot, just like the HPV vaccine, but it will have no active ingredient. It may change peoples’ thinking or behavior to have such a shot given to them, but it will not stimulate the immune systems of the subjects in the same way as predicted for the vaccine itself.
- d: This group is given the HPV vaccine. The experimental group will receive the HPV vaccine and researchers will then be able to see if it works, when compared to the control group.
Experimental Variables
A variable is a characteristic of a subject (in this case, of a person in the study) that can vary over time or among individuals. Sometimes a variable takes the form of a category, such as male or female; often a variable can be measured precisely, such as body height. Ideally, only one variable is different between the control group and the experimental group in a scientific experiment. Otherwise, the researchers will not be able to determine which variable caused any differences seen in the results. For example, imagine that the people in the control group were, on average, much more sexually active than the people in the experimental group. If, at the end of the experiment, the control group had a higher rate of HPV infection, could you confidently determine why? Maybe the experimental subjects were protected by the vaccine, but maybe they were protected by their low level of sexual contact.
To avoid this situation, experimenters make sure that their subject groups are as similar as possible in all variables except for the variable that is being tested in the experiment. This variable, or factor, will be deliberately changed in the experimental group. The one variable that is different between the two groups is called the independent variable. An independent variable is known or hypothesized to cause some outcome. Imagine an educational researcher investigating the effectiveness of a new teaching strategy in a classroom. The experimental group receives the new teaching strategy, while the control group receives the traditional strategy. It is the teaching strategy that is the independent variable in this scenario. In an experiment, the independent variable is the variable that the scientist deliberately changes or imposes on the subjects.
Dependent variables are known or hypothesized consequences; they are the effects that result from changes or differences in an independent variable. In an experiment, the dependent variables are those that the scientist measures before, during, and particularly at the end of the experiment to see if they have changed as expected. The dependent variable must be stated so that it is clear how it will be observed or measured. Rather than comparing “learning” among students (which is a vague and difficult to measure concept), an educational researcher might choose to compare test scores, which are very specific and easy to measure.
In any real-world example, many, many variables MIGHT affect the outcome of an experiment, yet only one or a few independent variables can be tested. Other variables must be kept as similar as possible between the study groups and are called control variables . For our educational research example, if the control group consisted only of people between the ages of 18 and 20 and the experimental group contained people between the ages of 30 and 35, we would not know if it was the teaching strategy or the students’ ages that played a larger role in the results. To avoid this problem, a good study will be set up so that each group contains students with a similar age profile. In a well-designed educational research study, student age will be a controlled variable, along with other possibly important factors like gender, past educational achievement, and pre-existing knowledge of the subject area.
What is the independent variable in this experiment?
- Sex (all of the subjects will be female)
- Presence or absence of the HPV vaccine
- Presence or absence of HPV (the virus)
[reveal-answer q=”68680″]Show Answer[/reveal-answer] [hidden-answer a=”68680″]Answer b. Presence or absence of the HPV vaccine. This is the variable that is different between the control and the experimental groups. All the subjects in this study are female, so this variable is the same in all groups. In a well-designed study, the two groups will be of similar age. The presence or absence of the virus is what the researchers will measure at the end of the experiment. Ideally the two groups will both be HPV-free at the start of the experiment.
List three control variables other than age.
[practice-area rows=”3″][/practice-area] [reveal-answer q=”903121″]Show Answer[/reveal-answer] [hidden-answer a=”903121″]Some possible control variables would be: general health of the women, sexual activity, lifestyle, diet, socioeconomic status, etc.
What is the dependent variable in this experiment?
- Sex (male or female)
- Rates of HPV infection
- Age (years)
[reveal-answer q=”907103″]Show Answer[/reveal-answer] [hidden-answer a=”907103″]Answer b. Rates of HPV infection. The researchers will measure how many individuals got infected with HPV after a given period of time.[/hidden-answer]
Contributors and Attributions
- Revision and adaptation. Authored by : Shelli Carter and Lumen Learning. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Scientific Inquiry. Provided by : Open Learning Initiative. Located at : https://oli.cmu.edu/jcourse/workbook/activity/page?context=434a5c2680020ca6017c03488572e0f8 . Project : Introduction to Biology (Open + Free). License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Theories, Hypotheses, and Laws: Definitions, examples, and their roles in science
by Anthony Carpi, Ph.D., Anne E. Egger, Ph.D.
Listen to this reading
Did you know that the idea of evolution had been part of Western thought for more than 2,000 years before Charles Darwin was born? Like many theories, the theory of evolution was the result of the work of many different scientists working in different disciplines over a period of time.
A scientific theory is an explanation inferred from multiple lines of evidence for some broad aspect of the natural world and is logical, testable, and predictive.
As new evidence comes to light, or new interpretations of existing data are proposed, theories may be revised and even change; however, they are not tenuous or speculative.
A scientific hypothesis is an inferred explanation of an observation or research finding; while more exploratory in nature than a theory, it is based on existing scientific knowledge.
A scientific law is an expression of a mathematical or descriptive relationship observed in nature.
Imagine yourself shopping in a grocery store with a good friend who happens to be a chemist. Struggling to choose between the many different types of tomatoes in front of you, you pick one up, turn to your friend, and ask her if she thinks the tomato is organic . Your friend simply chuckles and replies, "Of course it's organic!" without even looking at how the fruit was grown. Why the amused reaction? Your friend is highlighting a simple difference in vocabulary. To a chemist, the term organic refers to any compound in which hydrogen is bonded to carbon. Tomatoes (like all plants) are abundant in organic compounds – thus your friend's laughter. In modern agriculture, however, organic has come to mean food items grown or raised without the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, or other additives.
So who is correct? You both are. Both uses of the word are correct, though they mean different things in different contexts. There are, of course, lots of words that have more than one meaning (like bat , for example), but multiple meanings can be especially confusing when two meanings convey very different ideas and are specific to one field of study.
- Scientific theories
The term theory also has two meanings, and this double meaning often leads to confusion. In common language, the term theory generally refers to speculation or a hunch or guess. You might have a theory about why your favorite sports team isn't playing well, or who ate the last cookie from the cookie jar. But these theories do not fit the scientific use of the term. In science, a theory is a well-substantiated and comprehensive set of ideas that explains a phenomenon in nature. A scientific theory is based on large amounts of data and observations that have been collected over time. Scientific theories can be tested and refined by additional research , and they allow scientists to make predictions. Though you may be correct in your hunch, your cookie jar conjecture doesn't fit this more rigorous definition.
All scientific disciplines have well-established, fundamental theories . For example, atomic theory describes the nature of matter and is supported by multiple lines of evidence from the way substances behave and react in the world around us (see our series on Atomic Theory ). Plate tectonic theory describes the large scale movement of the outer layer of the Earth and is supported by evidence from studies about earthquakes , magnetic properties of the rocks that make up the seafloor , and the distribution of volcanoes on Earth (see our series on Plate Tectonic Theory ). The theory of evolution by natural selection , which describes the mechanism by which inherited traits that affect survivability or reproductive success can cause changes in living organisms over generations , is supported by extensive studies of DNA , fossils , and other types of scientific evidence (see our Charles Darwin series for more information). Each of these major theories guides and informs modern research in those fields, integrating a broad, comprehensive set of ideas.
So how are these fundamental theories developed, and why are they considered so well supported? Let's take a closer look at some of the data and research supporting the theory of natural selection to better see how a theory develops.
Comprehension Checkpoint
- The development of a scientific theory: Evolution and natural selection
The theory of evolution by natural selection is sometimes maligned as Charles Darwin 's speculation on the origin of modern life forms. However, evolutionary theory is not speculation. While Darwin is rightly credited with first articulating the theory of natural selection, his ideas built on more than a century of scientific research that came before him, and are supported by over a century and a half of research since.
- The Fixity Notion: Linnaeus

Figure 1: Cover of the 1760 edition of Systema Naturae .
Research about the origins and diversity of life proliferated in the 18th and 19th centuries. Carolus Linnaeus , a Swedish botanist and the father of modern taxonomy (see our module Taxonomy I for more information), was a devout Christian who believed in the concept of Fixity of Species , an idea based on the biblical story of creation. The Fixity of Species concept said that each species is based on an ideal form that has not changed over time. In the early stages of his career, Linnaeus traveled extensively and collected data on the structural similarities and differences between different species of plants. Noting that some very different plants had similar structures, he began to piece together his landmark work, Systema Naturae, in 1735 (Figure 1). In Systema , Linnaeus classified organisms into related groups based on similarities in their physical features. He developed a hierarchical classification system , even drawing relationships between seemingly disparate species (for example, humans, orangutans, and chimpanzees) based on the physical similarities that he observed between these organisms. Linnaeus did not explicitly discuss change in organisms or propose a reason for his hierarchy, but by grouping organisms based on physical characteristics, he suggested that species are related, unintentionally challenging the Fixity notion that each species is created in a unique, ideal form.
- The age of Earth: Leclerc and Hutton
Also in the early 1700s, Georges-Louis Leclerc, a French naturalist, and James Hutton , a Scottish geologist, began to develop new ideas about the age of the Earth. At the time, many people thought of the Earth as 6,000 years old, based on a strict interpretation of the events detailed in the Christian Old Testament by the influential Scottish Archbishop Ussher. By observing other planets and comets in the solar system , Leclerc hypothesized that Earth began as a hot, fiery ball of molten rock, mostly consisting of iron. Using the cooling rate of iron, Leclerc calculated that Earth must therefore be at least 70,000 years old in order to have reached its present temperature.
Hutton approached the same topic from a different perspective, gathering observations of the relationships between different rock formations and the rates of modern geological processes near his home in Scotland. He recognized that the relatively slow processes of erosion and sedimentation could not create all of the exposed rock layers in only a few thousand years (see our module The Rock Cycle ). Based on his extensive collection of data (just one of his many publications ran to 2,138 pages), Hutton suggested that the Earth was far older than human history – hundreds of millions of years old.
While we now know that both Leclerc and Hutton significantly underestimated the age of the Earth (by about 4 billion years), their work shattered long-held beliefs and opened a window into research on how life can change over these very long timescales.
- Fossil studies lead to the development of a theory of evolution: Cuvier
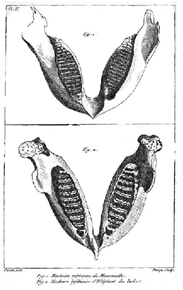
Figure 2: Illustration of an Indian elephant jaw and a mammoth jaw from Cuvier's 1796 paper.
With the age of Earth now extended by Leclerc and Hutton, more researchers began to turn their attention to studying past life. Fossils are the main way to study past life forms, and several key studies on fossils helped in the development of a theory of evolution . In 1795, Georges Cuvier began to work at the National Museum in Paris as a naturalist and anatomist. Through his work, Cuvier became interested in fossils found near Paris, which some claimed were the remains of the elephants that Hannibal rode over the Alps when he invaded Rome in 218 BCE . In studying both the fossils and living species , Cuvier documented different patterns in the dental structure and number of teeth between the fossils and modern elephants (Figure 2) (Horner, 1843). Based on these data , Cuvier hypothesized that the fossil remains were not left by Hannibal, but were from a distinct species of animal that once roamed through Europe and had gone extinct thousands of years earlier: the mammoth. The concept of species extinction had been discussed by a few individuals before Cuvier, but it was in direct opposition to the Fixity of Species concept – if every organism were based on a perfectly adapted, ideal form, how could any cease to exist? That would suggest it was no longer ideal.
While his work provided critical evidence of extinction , a key component of evolution , Cuvier was highly critical of the idea that species could change over time. As a result of his extensive studies of animal anatomy, Cuvier had developed a holistic view of organisms , stating that the
number, direction, and shape of the bones that compose each part of an animal's body are always in a necessary relation to all the other parts, in such a way that ... one can infer the whole from any one of them ...
In other words, Cuvier viewed each part of an organism as a unique, essential component of the whole organism. If one part were to change, he believed, the organism could not survive. His skepticism about the ability of organisms to change led him to criticize the whole idea of evolution , and his prominence in France as a scientist played a large role in discouraging the acceptance of the idea in the scientific community.
- Studies of invertebrates support a theory of change in species: Lamarck
Jean Baptiste Lamarck, a contemporary of Cuvier's at the National Museum in Paris, studied invertebrates like insects and worms. As Lamarck worked through the museum's large collection of invertebrates, he was impressed by the number and variety of organisms . He became convinced that organisms could, in fact, change through time, stating that
... time and favorable conditions are the two principal means which nature has employed in giving existence to all her productions. We know that for her time has no limit, and that consequently she always has it at her disposal.
This was a radical departure from both the fixity concept and Cuvier's ideas, and it built on the long timescale that geologists had recently established. Lamarck proposed that changes that occurred during an organism 's lifetime could be passed on to their offspring, suggesting, for example, that a body builder's muscles would be inherited by their children.
As it turned out, the mechanism by which Lamarck proposed that organisms change over time was wrong, and he is now often referred to disparagingly for his "inheritance of acquired characteristics" idea. Yet despite the fact that some of his ideas were discredited, Lamarck established a support for evolutionary theory that others would build on and improve.
- Rock layers as evidence for evolution: Smith
In the early 1800s, a British geologist and canal surveyor named William Smith added another component to the accumulating evidence for evolution . Smith observed that rock layers exposed in different parts of England bore similarities to one another: These layers (or strata) were arranged in a predictable order, and each layer contained distinct groups of fossils . From this series of observations , he developed a hypothesis that specific groups of animals followed one another in a definite sequence through Earth's history, and this sequence could be seen in the rock layers. Smith's hypothesis was based on his knowledge of geological principles , including the Law of Superposition.
The Law of Superposition states that sediments are deposited in a time sequence, with the oldest sediments deposited first, or at the bottom, and newer layers deposited on top. The concept was first expressed by the Persian scientist Avicenna in the 11th century, but was popularized by the Danish scientist Nicolas Steno in the 17th century. Note that the law does not state how sediments are deposited; it simply describes the relationship between the ages of deposited sediments.

Figure 3: Engraving from William Smith's 1815 monograph on identifying strata by fossils.
Smith backed up his hypothesis with extensive drawings of fossils uncovered during his research (Figure 3), thus allowing other scientists to confirm or dispute his findings. His hypothesis has, in fact, been confirmed by many other scientists and has come to be referred to as the Law of Faunal Succession. His work was critical to the formation of evolutionary theory as it not only confirmed Cuvier's work that organisms have gone extinct , but it also showed that the appearance of life does not date to the birth of the planet. Instead, the fossil record preserves a timeline of the appearance and disappearance of different organisms in the past, and in doing so offers evidence for change in organisms over time.
- The theory of evolution by natural selection: Darwin and Wallace
It was into this world that Charles Darwin entered: Linnaeus had developed a taxonomy of organisms based on their physical relationships, Leclerc and Hutton demonstrated that there was sufficient time in Earth's history for organisms to change, Cuvier showed that species of organisms have gone extinct , Lamarck proposed that organisms change over time, and Smith established a timeline of the appearance and disappearance of different organisms in the geological record .

Figure 4: Title page of the 1859 Murray edition of the Origin of Species by Charles Darwin.
Charles Darwin collected data during his work as a naturalist on the HMS Beagle starting in 1831. He took extensive notes on the geology of the places he visited; he made a major find of fossils of extinct animals in Patagonia and identified an extinct giant ground sloth named Megatherium . He experienced an earthquake in Chile that stranded beds of living mussels above water, where they would be preserved for years to come.
Perhaps most famously, he conducted extensive studies of animals on the Galápagos Islands, noting subtle differences in species of mockingbird, tortoise, and finch that were isolated on different islands with different environmental conditions. These subtle differences made the animals highly adapted to their environments .
This broad spectrum of data led Darwin to propose an idea about how organisms change "by means of natural selection" (Figure 4). But this idea was not based only on his work, it was also based on the accumulation of evidence and ideas of many others before him. Because his proposal encompassed and explained many different lines of evidence and previous work, they formed the basis of a new and robust scientific theory regarding change in organisms – the theory of evolution by natural selection .
Darwin's ideas were grounded in evidence and data so compelling that if he had not conceived them, someone else would have. In fact, someone else did. Between 1858 and 1859, Alfred Russel Wallace , a British naturalist, wrote a series of letters to Darwin that independently proposed natural selection as the means for evolutionary change. The letters were presented to the Linnean Society of London, a prominent scientific society at the time (see our module on Scientific Institutions and Societies ). This long chain of research highlights that theories are not just the work of one individual. At the same time, however, it often takes the insight and creativity of individuals to put together all of the pieces and propose a new theory . Both Darwin and Wallace were experienced naturalists who were familiar with the work of others. While all of the work leading up to 1830 contributed to the theory of evolution , Darwin's and Wallace's theory changed the way that future research was focused by presenting a comprehensive, well-substantiated set of ideas, thus becoming a fundamental theory of biological research.
- Expanding, testing, and refining scientific theories
- Genetics and evolution: Mendel and Dobzhansky
Since Darwin and Wallace first published their ideas, extensive research has tested and expanded the theory of evolution by natural selection . Darwin had no concept of genes or DNA or the mechanism by which characteristics were inherited within a species . A contemporary of Darwin's, the Austrian monk Gregor Mendel , first presented his own landmark study, Experiments in Plant Hybridization, in 1865 in which he provided the basic patterns of genetic inheritance , describing which characteristics (and evolutionary changes) can be passed on in organisms (see our Genetics I module for more information). Still, it wasn't until much later that a "gene" was defined as the heritable unit.
In 1937, the Ukrainian born geneticist Theodosius Dobzhansky published Genetics and the Origin of Species , a seminal work in which he described genes themselves and demonstrated that it is through mutations in genes that change occurs. The work defined evolution as "a change in the frequency of an allele within a gene pool" ( Dobzhansky, 1982 ). These studies and others in the field of genetics have added to Darwin's work, expanding the scope of the theory .
- Evolution under a microscope: Lenski
More recently, Dr. Richard Lenski, a scientist at Michigan State University, isolated a single Escherichia coli bacterium in 1989 as the first step of the longest running experimental test of evolutionary theory to date – a true test meant to replicate evolution and natural selection in the lab.
After the single microbe had multiplied, Lenski isolated the offspring into 12 different strains , each in their own glucose-supplied culture, predicting that the genetic make-up of each strain would change over time to become more adapted to their specific culture as predicted by evolutionary theory . These 12 lines have been nurtured for over 40,000 bacterial generations (luckily bacterial generations are much shorter than human generations) and exposed to different selective pressures such as heat , cold, antibiotics, and infection with other microorganisms. Lenski and colleagues have studied dozens of aspects of evolutionary theory with these genetically isolated populations . In 1999, they published a paper that demonstrated that random genetic mutations were common within the populations and highly diverse across different individual bacteria . However, "pivotal" mutations that are associated with beneficial changes in the group are shared by all descendants in a population and are much rarer than random mutations, as predicted by the theory of evolution by natural selection (Papadopoulos et al., 1999).
- Punctuated equilibrium: Gould and Eldredge
While established scientific theories like evolution have a wealth of research and evidence supporting them, this does not mean that they cannot be refined as new information or new perspectives on existing data become available. For example, in 1972, biologist Stephen Jay Gould and paleontologist Niles Eldredge took a fresh look at the existing data regarding the timing by which evolutionary change takes place. Gould and Eldredge did not set out to challenge the theory of evolution; rather they used it as a guiding principle and asked more specific questions to add detail and nuance to the theory. This is true of all theories in science: they provide a framework for additional research. At the time, many biologists viewed evolution as occurring gradually, causing small incremental changes in organisms at a relatively steady rate. The idea is referred to as phyletic gradualism , and is rooted in the geological concept of uniformitarianism . After reexamining the available data, Gould and Eldredge came to a different explanation, suggesting that evolution consists of long periods of stability that are punctuated by occasional instances of dramatic change – a process they called punctuated equilibrium .
Like Darwin before them, their proposal is rooted in evidence and research on evolutionary change, and has been supported by multiple lines of evidence. In fact, punctuated equilibrium is now considered its own theory in evolutionary biology. Punctuated equilibrium is not as broad of a theory as natural selection . In science, some theories are broad and overarching of many concepts, such as the theory of evolution by natural selection; others focus on concepts at a smaller, or more targeted, scale such as punctuated equilibrium. And punctuated equilibrium does not challenge or weaken the concept of natural selection; rather, it represents a change in our understanding of the timing by which change occurs in organisms , and a theory within a theory. The theory of evolution by natural selection now includes both gradualism and punctuated equilibrium to describe the rate at which change proceeds.
- Hypotheses and laws: Other scientific concepts
One of the challenges in understanding scientific terms like theory is that there is not a precise definition even within the scientific community. Some scientists debate over whether certain proposals merit designation as a hypothesis or theory , and others mistakenly use the terms interchangeably. But there are differences in these terms. A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for an observable phenomenon. Hypotheses , just like theories , are based on observations from research . For example, LeClerc did not hypothesize that Earth had cooled from a molten ball of iron as a random guess; rather, he developed this hypothesis based on his observations of information from meteorites.
A scientist often proposes a hypothesis before research confirms it as a way of predicting the outcome of study to help better define the parameters of the research. LeClerc's hypothesis allowed him to use known parameters (the cooling rate of iron) to do additional work. A key component of a formal scientific hypothesis is that it is testable and falsifiable. For example, when Richard Lenski first isolated his 12 strains of bacteria , he likely hypothesized that random mutations would cause differences to appear within a period of time in the different strains of bacteria. But when a hypothesis is generated in science, a scientist will also make an alternative hypothesis , an explanation that explains a study if the data do not support the original hypothesis. If the different strains of bacteria in Lenski's work did not diverge over the indicated period of time, perhaps the rate of mutation was slower than first thought.
So you might ask, if theories are so well supported, do they eventually become laws? The answer is no – not because they aren't well-supported, but because theories and laws are two very different things. Laws describe phenomena, often mathematically. Theories, however, explain phenomena. For example, in 1687 Isaac Newton proposed a Theory of Gravitation, describing gravity as a force of attraction between two objects. As part of this theory, Newton developed a Law of Universal Gravitation that explains how this force operates. This law states that the force of gravity between two objects is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between those objects. Newton 's Law does not explain why this is true, but it describes how gravity functions (see our Gravity: Newtonian Relationships module for more detail). In 1916, Albert Einstein developed his theory of general relativity to explain the mechanism by which gravity has its effect. Einstein's work challenges Newton's theory, and has been found after extensive testing and research to more accurately describe the phenomenon of gravity. While Einstein's work has replaced Newton's as the dominant explanation of gravity in modern science, Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation is still used as it reasonably (and more simply) describes the force of gravity under many conditions. Similarly, the Law of Faunal Succession developed by William Smith does not explain why organisms follow each other in distinct, predictable ways in the rock layers, but it accurately describes the phenomenon.
Theories, hypotheses , and laws drive scientific progress
Theories, hypotheses , and laws are not simply important components of science, they drive scientific progress. For example, evolutionary biology now stands as a distinct field of science that focuses on the origins and descent of species . Geologists now rely on plate tectonics as a conceptual model and guiding theory when they are studying processes at work in Earth's crust . And physicists refer to atomic theory when they are predicting the existence of subatomic particles yet to be discovered. This does not mean that science is "finished," or that all of the important theories have been discovered already. Like evolution , progress in science happens both gradually and in short, dramatic bursts. Both types of progress are critical for creating a robust knowledge base with data as the foundation and scientific theories giving structure to that knowledge.
Table of Contents
- Theories, hypotheses, and laws drive scientific progress
Activate glossary term highlighting to easily identify key terms within the module. Once highlighted, you can click on these terms to view their definitions.
Activate NGSS annotations to easily identify NGSS standards within the module. Once highlighted, you can click on them to view these standards.
Theory n., plural: theories [ˈθɪɚ.i] Definition: a scientific explanation of a phenomenon based on a concurring set of scientific data from various independent studies
Table of Contents
Theory Definition
In science, a theory is a scientific explanation of a phenomenon. By scientific , it means it is an explanation or expectation based on a body of facts that have been repeatedly confirmed through methodical observations and experiments. For instance, in mathematics, a mathematical theory attempts to describe a particular class of constructs and includes axioms, theorems, examples, etc . In biology, a theory is a widely accepted explanation of a biological phenomenon based on sound evidence from rigorous empirical experiments and scientific observations. An example of a popular biological theory is Charles Darwin’s Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection . This theory attempts to explain evolution where natural selection is one of the vital mechanisms that drive organisms to progressively change over successive generations.
Etymology: from Latin theōria, Greek theōría, meaning “a viewing” or “contemplating”. Compare: hypothesis
Watch this vid about scientific theory:
Theory vs. Hypothesis
The term theory is generally used to imply speculation or assumption that has not been fully verified or has relatively limited proof. However, in science, an unproven idea or mere theoretical speculation is regarded as a hypothesis rather than a scientific theory.
A scientific hypothesis is a tentative explanation for a phenomenon and is yet to be tested through a scientific and methodological experiment. If it is confirmed by repetitive investigations and supports various independent studies, then, the hypothesis will likely be widely accepted by the scientific community, and through time — sans any scientific proof to debunk it — becomes a theory.
Theory vs. Law
Both scientific theories and laws are based on facts and are accepted by the scientific community as the truth. And both are used to make predictions of future events. However, while a scientific theory tells us why and how a phenomenon happens, a scientific law will tell us what to expect in a particular situation, especially through a mathematical equation . (MasterClass, 2020) Therefore, scientific theories and laws are essential in understanding things, particularly to grasp why they happen as they do and to reliably and factually predict results in a given situation or condition .
In biology, we have Mendel’s Laws that can be used as a basis for predicting the genotypes and the phenotypes of the offspring if it conforms to the Mendelian inheritance . Gregor Mendel formulated the Laws of heredity based on the patterns of trait variations, which he noticed when he conducted a series of breeding experiments on garden pea plants. Initially, his principles were not widely accepted until his works were rediscovered and reverified. Now, his principles on heredity are regarded as laws .
Although scientific theories and laws are accepted as scientific facts, they can be disproven when new evidence surfaces.
Mendel’s Laws, for instance, do not apply to some conditions, such as in the case of non-Mendelian inheritance . Codominance , incomplete dominance , and extranuclear inheritance are just some of the many examples of biological inheritance where Mendel’s Laws on heredity do not apply.
- MasterClass. (2020). Theory vs. Law: Basics of the Scientific Method . MasterClass; MasterClass. https://www.masterclass.com/articles/theory-vs-law-basics-of-the-scientific-method#4-examples-of-scientific-theories
Last updated on July 24th, 2022
You will also like...

Darwin and Natural Selection

Examples of Natural Selection
Genetics and Evolution

Water in Plants


Adaptation Tutorial

The Origins of Life
Related articles....

Theory of Neuroscience

A New Theory on the Origin of Animal Multicellularity

Prokaryotic Ancestor of Mitochondria: on the hunt

Nervous System

Why Non-Human Primates Don’t Speak Like Humans
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
AP®︎/College Biology
Course: ap®︎/college biology > unit 7.
- Earth formation
- Beginnings of life
- Origins of life
Hypotheses about the origins of life
- The RNA origin of life
- Origins of life on Earth
Key points:
- The Earth formed roughly 4.5 billion years ago, and life probably began between 3.5 and 3.9 billion years ago.
- The Oparin-Haldane hypothesis suggests that life arose gradually from inorganic molecules, with “building blocks” like amino acids forming first and then combining to make complex polymers.
- The Miller-Urey experiment provided the first evidence that organic molecules needed for life could be formed from inorganic components.
- Some scientists support the RNA world hypothesis , which suggests that the first life was self-replicating RNA. Others favor the metabolism-first hypothesis , placing metabolic networks before DNA or RNA.
- Simple organic compounds might have come to early Earth on meteorites.
Introduction
When did life appear on earth, the earliest fossil evidence of life, how might life have arisen.
- Simple inorganic molecules could have reacted (with energy from lightning or the sun) to form building blocks like amino acids and nucleotides, which could have accumulated in the oceans, making a "primordial soup." 3
- The building blocks could have combined in further reactions, forming larger, more complex molecules (polymers) like proteins and nucleic acids, perhaps in pools at the water's edge.
- The polymers could have assembled into units or structures that were capable of sustaining and replicating themselves. Oparin thought these might have been “colonies” of proteins clustered together to carry out metabolism, while Haldane suggested that macromolecules became enclosed in membranes to make cell-like structures 4 , 5 .
From inorganic compounds to building blocks
Were miller and urey's results meaningful, from building blocks to polymers, what was the nature of the earliest life, the "genes-first" hypothesis, the "metabolism-first" hypothesis, what might early cells have looked like, another possibility: organic molecules from outer space.
- Miller, Urey, and others showed that simple inorganic molecules could combine to form the organic building blocks required for life as we know it.
- Once formed, these building blocks could have come together to form polymers such as proteins or RNA.
- Many scientists favor the RNA world hypothesis, in which RNA, not DNA, was the first genetic molecule of life on Earth. Other ideas include the pre-RNA world hypothesis and the metabolism-first hypothesis.
- Organic compounds could have been delivered to early Earth by meteorites and other celestial objects.
Works cited:
- Harwood, R. (2012). Patterns in palaeontology: The first 3 billion years of evolution. Palaeontology , 2(11), 1-22. Retrieved from http://www.palaeontologyonline.com/articles/2012/patterns-in-palaeontology-the-first-3-billion-years-of-evolution/ .
- Wacey, D., Kilburn, M. R., Saunders, M., Cliff, J., and Brasier, M. D. (2011). Microfossils of sulphur-metabolizing cells in 3.4-billion-year-old rocks of Western Australia. Nature Geoscience , 4 , 698-702. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1238 .
- Primordial soup. (2016, January 20). Retrieved May 22, 2016 from Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Primordial_soup .
- Gordon-Smith, C. (2003). The Oparin-Haldane hypothesis. In Origin of life: Twentieth century landmarks . Retrieved from http://www.simsoup.info/Origin_Landmarks_Oparin_Haldane.html .
- The Oparin-Haldane hypothesis. (2015, June 14). In Structural biochemistry . Retrieved May 22, 2016 from Wikibooks: https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Structural_Biochemistry/The_Oparin-Haldane_Hypothesis .
- Kimball, J. W. (2015, May 17). Miller's experiment. In Kimball's biology pages . Retrieved from http://www.biology-pages.info/A/AbioticSynthesis.html#Miller's_Experiment .
- Earth’s early atmosphere. (Dec 2, 2011). In Astrobiology Magazine . Retrieved from http://www.astrobio.net/topic/solar-system/earth/geology/earths-early-atmosphere/ .
- McCollom, T. M. (2013). Miller-Urey and beyond: What have learned about prebiotic organic synthesis reactions in the past 60 years? Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences , 41_, 207-229. http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-earth-040610-133457 .
- Powner, M. W., Gerland, B., and Sutherland, J. D. (2009). Synthesis of activated pyrimidine ribonucleotides in prebiotically plausible conditions. Nature , 459 , 239-242. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature08013 .
- Lurquin, P. F. (June 5, 2003). Proteins and metabolism first: The iron-sulfur world. In The origins of life and the universe (pp. 110-111). New York, NY: Columbia University Press.
- Ferris, J. P. (2006). Montmorillonite-catalysed formation of RNA oligomers: The possible role of catalysis in the origins of life. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Bio.l Sci ., 361 (1474), 1777–1786. http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2006.1903 .
- Kimball, J. W. (2015, May 17). Assembling polymers. In Kimball's biology pages . Retrieved from
- Montmorillonite. (2016, 28 March). Retrieved May 22, 2016 from Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Montmorillonite .
- Wilkin, D. and Akre, B. (2016, March 23). First organic molecules - Advanced. In CK-12 biology advanced concepts . Retrieved from http://www.ck12.org/book/CK-12-Biology-Advanced-Concepts/section/10.8/ .
- Hollenstein, M. (2015). DNA catalysis: The chemical repertoire of DNAzymes. Molecules , 20 (11), 20777–20804. http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/molecules201119730 .
- Breaker, R. R. and Joyce, G. F. (2014). The expanding view of RNA and DNA function. Chemistry & biology , 21 (9), 1059–1065. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.07.008 .
- Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Raff, M., Roberts, K., and Walter, P. (2002). A pre-RNA world probably predates the RNA world. In Molecular biology of the cell (4th ed.). New York, NY: Garland Science. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26876/#_A1124_ .
- Moran, L. A. (2009, May 15). Metabolism first and the origin of life. In Sandwalk: Strolling with a skeptical biochemist . Retrieved from http://www.simsoup.info/Origin_Landmarks_Oparin_Haldane.html .
- Kimball, J. W. (2015, May 17). The first cell? In Kimball's biology pages . Retrieved from http://www.biology-pages.info/A/AbioticSynthesis.html#TheFirstCell?
- Kimball, J. W. (2015, May 17). Molecules from outer space? In Kimball's biology pages . Retrieved from http://www.biology-pages.info/A/AbioticSynthesis.html#Molecules_from_outer_space? .
- Jeffs, W. (2006, November 30). NASA scientists find primordial organic matter in meteorite. In NASA news . Retrieved from http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/news/releases/2006/J06-103.html .
Additional references:
Want to join the conversation.
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

1.2 The Process of Science
Learning objectives.
- Identify the shared characteristics of the natural sciences
- Understand the process of scientific inquiry
- Compare inductive reasoning with deductive reasoning
- Describe the goals of basic science and applied science
Like geology, physics, and chemistry, biology is a science that gathers knowledge about the natural world. Specifically, biology is the study of life. The discoveries of biology are made by a community of researchers who work individually and together using agreed-on methods. In this sense, biology, like all sciences is a social enterprise like politics or the arts. The methods of science include careful observation, record keeping, logical and mathematical reasoning, experimentation, and submitting conclusions to the scrutiny of others. Science also requires considerable imagination and creativity; a well-designed experiment is commonly described as elegant, or beautiful. Like politics, science has considerable practical implications and some science is dedicated to practical applications, such as the prevention of disease (see Figure 1.15 ). Other science proceeds largely motivated by curiosity. Whatever its goal, there is no doubt that science, including biology, has transformed human existence and will continue to do so.
The Nature of Science
Biology is a science, but what exactly is science? What does the study of biology share with other scientific disciplines? Science (from the Latin scientia, meaning "knowledge") can be defined as knowledge about the natural world.
Science is a very specific way of learning, or knowing, about the world. The history of the past 500 years demonstrates that science is a very powerful way of knowing about the world; it is largely responsible for the technological revolutions that have taken place during this time. There are however, areas of knowledge and human experience that the methods of science cannot be applied to. These include such things as answering purely moral questions, aesthetic questions, or what can be generally categorized as spiritual questions. Science cannot investigate these areas because they are outside the realm of material phenomena, the phenomena of matter and energy, and cannot be observed and measured.
The scientific method is a method of research with defined steps that include experiments and careful observation. The steps of the scientific method will be examined in detail later, but one of the most important aspects of this method is the testing of hypotheses. A hypothesis is a suggested explanation for an event, which can be tested. Hypotheses, or tentative explanations, are generally produced within the context of a scientific theory . A generally accepted scientific theory is thoroughly tested and confirmed explanation for a set of observations or phenomena. Scientific theory is the foundation of scientific knowledge. In addition, in many scientific disciplines (less so in biology) there are scientific laws , often expressed in mathematical formulas, which describe how elements of nature will behave under certain specific conditions. There is not an evolution of hypotheses through theories to laws as if they represented some increase in certainty about the world. Hypotheses are the day-to-day material that scientists work with and they are developed within the context of theories. Laws are concise descriptions of parts of the world that are amenable to formulaic or mathematical description.
Natural Sciences
What would you expect to see in a museum of natural sciences? Frogs? Plants? Dinosaur skeletons? Exhibits about how the brain functions? A planetarium? Gems and minerals? Or maybe all of the above? Science includes such diverse fields as astronomy, biology, computer sciences, geology, logic, physics, chemistry, and mathematics ( Figure 1.16 ). However, those fields of science related to the physical world and its phenomena and processes are considered natural sciences . Thus, a museum of natural sciences might contain any of the items listed above.
There is no complete agreement when it comes to defining what the natural sciences include. For some experts, the natural sciences are astronomy, biology, chemistry, earth science, and physics. Other scholars choose to divide natural sciences into life sciences , which study living things and include biology, and physical sciences , which study nonliving matter and include astronomy, physics, and chemistry. Some disciplines such as biophysics and biochemistry build on two sciences and are interdisciplinary.
Scientific Inquiry
One thing is common to all forms of science: an ultimate goal “to know.” Curiosity and inquiry are the driving forces for the development of science. Scientists seek to understand the world and the way it operates. Two methods of logical thinking are used: inductive reasoning and deductive reasoning.
Inductive reasoning is a form of logical thinking that uses related observations to arrive at a general conclusion. This type of reasoning is common in descriptive science. A life scientist such as a biologist makes observations and records them. These data can be qualitative (descriptive) or quantitative (consisting of numbers), and the raw data can be supplemented with drawings, pictures, photos, or videos. From many observations, the scientist can infer conclusions (inductions) based on evidence. Inductive reasoning involves formulating generalizations inferred from careful observation and the analysis of a large amount of data. Brain studies often work this way. Many brains are observed while people are doing a task. The part of the brain that lights up, indicating activity, is then demonstrated to be the part controlling the response to that task.
Deductive reasoning or deduction is the type of logic used in hypothesis-based science. In deductive reasoning, the pattern of thinking moves in the opposite direction as compared to inductive reasoning. Deductive reasoning is a form of logical thinking that uses a general principle or law to predict specific results. From those general principles, a scientist can deduce and predict the specific results that would be valid as long as the general principles are valid. For example, a prediction would be that if the climate is becoming warmer in a region, the distribution of plants and animals should change. Comparisons have been made between distributions in the past and the present, and the many changes that have been found are consistent with a warming climate. Finding the change in distribution is evidence that the climate change conclusion is a valid one.
Both types of logical thinking are related to the two main pathways of scientific study: descriptive science and hypothesis-based science. Descriptive (or discovery) science aims to observe, explore, and discover, while hypothesis-based science begins with a specific question or problem and a potential answer or solution that can be tested. The boundary between these two forms of study is often blurred, because most scientific endeavors combine both approaches. Observations lead to questions, questions lead to forming a hypothesis as a possible answer to those questions, and then the hypothesis is tested. Thus, descriptive science and hypothesis-based science are in continuous dialogue.
Hypothesis Testing
Biologists study the living world by posing questions about it and seeking science-based responses. This approach is common to other sciences as well and is often referred to as the scientific method. The scientific method was used even in ancient times, but it was first documented by England’s Sir Francis Bacon (1561–1626) ( Figure 1.17 ), who set up inductive methods for scientific inquiry. The scientific method is not exclusively used by biologists but can be applied to almost anything as a logical problem-solving method.
The scientific process typically starts with an observation (often a problem to be solved) that leads to a question. Let’s think about a simple problem that starts with an observation and apply the scientific method to solve the problem. One Monday morning, a student arrives at class and quickly discovers that the classroom is too warm. That is an observation that also describes a problem: the classroom is too warm. The student then asks a question: “Why is the classroom so warm?”
Recall that a hypothesis is a suggested explanation that can be tested. To solve a problem, several hypotheses may be proposed. For example, one hypothesis might be, “The classroom is warm because no one turned on the air conditioning.” But there could be other responses to the question, and therefore other hypotheses may be proposed. A second hypothesis might be, “The classroom is warm because there is a power failure, and so the air conditioning doesn’t work.”
Once a hypothesis has been selected, a prediction may be made. A prediction is similar to a hypothesis but it typically has the format “If . . . then . . . .” For example, the prediction for the first hypothesis might be, “ If the student turns on the air conditioning, then the classroom will no longer be too warm.”
A hypothesis must be testable to ensure that it is valid. For example, a hypothesis that depends on what a bear thinks is not testable, because it can never be known what a bear thinks. It should also be falsifiable , meaning that it can be disproven by experimental results. An example of an unfalsifiable hypothesis is “Botticelli’s Birth of Venus is beautiful.” There is no experiment that might show this statement to be false. To test a hypothesis, a researcher will conduct one or more experiments designed to eliminate one or more of the hypotheses. This is important. A hypothesis can be disproven, or eliminated, but it can never be proven. Science does not deal in proofs like mathematics. If an experiment fails to disprove a hypothesis, then we find support for that explanation, but this is not to say that down the road a better explanation will not be found, or a more carefully designed experiment will be found to falsify the hypothesis.
Each experiment will have one or more variables and one or more controls. A variable is any part of the experiment that can vary or change during the experiment. A control is a part of the experiment that does not change. Look for the variables and controls in the example that follows. As a simple example, an experiment might be conducted to test the hypothesis that phosphate limits the growth of algae in freshwater ponds. A series of artificial ponds are filled with water and half of them are treated by adding phosphate each week, while the other half are treated by adding a salt that is known not to be used by algae. The variable here is the phosphate (or lack of phosphate), the experimental or treatment cases are the ponds with added phosphate and the control ponds are those with something inert added, such as the salt. Just adding something is also a control against the possibility that adding extra matter to the pond has an effect. If the treated ponds show lesser growth of algae, then we have found support for our hypothesis. If they do not, then we reject our hypothesis. Be aware that rejecting one hypothesis does not determine whether or not the other hypotheses can be accepted; it simply eliminates one hypothesis that is not valid ( Figure 1.18 ). Using the scientific method, the hypotheses that are inconsistent with experimental data are rejected.
In recent years a new approach of testing hypotheses has developed as a result of an exponential growth of data deposited in various databases. Using computer algorithms and statistical analyses of data in databases, a new field of so-called "data research" (also referred to as "in silico" research) provides new methods of data analyses and their interpretation. This will increase the demand for specialists in both biology and computer science, a promising career opportunity.
Visual Connection
In the example below, the scientific method is used to solve an everyday problem. Which part in the example below is the hypothesis? Which is the prediction? Based on the results of the experiment, is the hypothesis supported? If it is not supported, propose some alternative hypotheses.
- My toaster doesn’t toast my bread.
- Why doesn’t my toaster work?
- There is something wrong with the electrical outlet.
- If something is wrong with the outlet, my coffeemaker also won’t work when plugged into it.
- I plug my coffeemaker into the outlet.
- My coffeemaker works.
In practice, the scientific method is not as rigid and structured as it might at first appear. Sometimes an experiment leads to conclusions that favor a change in approach; often, an experiment brings entirely new scientific questions to the puzzle. Many times, science does not operate in a linear fashion; instead, scientists continually draw inferences and make generalizations, finding patterns as their research proceeds. Scientific reasoning is more complex than the scientific method alone suggests.
Basic and Applied Science
The scientific community has been debating for the last few decades about the value of different types of science. Is it valuable to pursue science for the sake of simply gaining knowledge, or does scientific knowledge only have worth if we can apply it to solving a specific problem or bettering our lives? This question focuses on the differences between two types of science: basic science and applied science.
Basic science or “pure” science seeks to expand knowledge regardless of the short-term application of that knowledge. It is not focused on developing a product or a service of immediate public or commercial value. The immediate goal of basic science is knowledge for knowledge’s sake, though this does not mean that in the end it may not result in an application.
In contrast, applied science or “technology,” aims to use science to solve real-world problems, making it possible, for example, to improve a crop yield, find a cure for a particular disease, or save animals threatened by a natural disaster. In applied science, the problem is usually defined for the researcher.
Some individuals may perceive applied science as “useful” and basic science as “useless.” A question these people might pose to a scientist advocating knowledge acquisition would be, “What for?” A careful look at the history of science, however, reveals that basic knowledge has resulted in many remarkable applications of great value. Many scientists think that a basic understanding of science is necessary before an application is developed; therefore, applied science relies on the results generated through basic science. Other scientists think that it is time to move on from basic science and instead to find solutions to actual problems. Both approaches are valid. It is true that there are problems that demand immediate attention; however, few solutions would be found without the help of the knowledge generated through basic science.
One example of how basic and applied science can work together to solve practical problems occurred after the discovery of DNA structure led to an understanding of the molecular mechanisms governing DNA replication. Strands of DNA, unique in every human, are found in our cells, where they provide the instructions necessary for life. During DNA replication, new copies of DNA are made, shortly before a cell divides to form new cells. Understanding the mechanisms of DNA replication enabled scientists to develop laboratory techniques that are now used to identify genetic diseases, pinpoint individuals who were at a crime scene, and determine paternity. Without basic science, it is unlikely that applied science could exist.
Another example of the link between basic and applied research is the Human Genome Project, a study in which each human chromosome was analyzed and mapped to determine the precise sequence of DNA subunits and the exact location of each gene. (The gene is the basic unit of heredity represented by a specific DNA segment that codes for a functional molecule.) Other organisms have also been studied as part of this project to gain a better understanding of human chromosomes. The Human Genome Project ( Figure 1.19 ) relied on basic research carried out with non-human organisms and, later, with the human genome. An important end goal eventually became using the data for applied research seeking cures for genetically related diseases.
While research efforts in both basic science and applied science are usually carefully planned, it is important to note that some discoveries are made by serendipity, that is, by means of a fortunate accident or a lucky surprise. Penicillin was discovered when biologist Alexander Fleming accidentally left a petri dish of Staphylococcus bacteria open. An unwanted mold grew, killing the bacteria. The mold turned out to be Penicillium , and a new critically important antibiotic was discovered. In a similar manner, Percy Lavon Julian was an established medicinal chemist working on a way to mass produce compounds with which to manufacture important drugs. He was focused on using soybean oil in the production of progesterone (a hormone important in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy), but it wasn't until water accidentally leaked into a large soybean oil storage tank that he found his method. Immediately recognizing the resulting substance as stigmasterol, a primary ingredient in progesterone and similar drugs, he began the process of replicating and industrializing the process in a manner that has helped millions of people. Even in the highly organized world of science, luck—when combined with an observant, curious mind focused on the types of reasoning discussed above—can lead to unexpected breakthroughs.
Reporting Scientific Work
Whether scientific research is basic science or applied science, scientists must share their findings for other researchers to expand and build upon their discoveries. Communication and collaboration within and between sub disciplines of science are key to the advancement of knowledge in science. For this reason, an important aspect of a scientist’s work is disseminating results and communicating with peers. Scientists can share results by presenting them at a scientific meeting or conference, but this approach can reach only the limited few who are present. Instead, most scientists present their results in peer-reviewed articles that are published in scientific journals. Peer-reviewed articles are scientific papers that are reviewed, usually anonymously by a scientist’s colleagues, or peers. These colleagues are qualified individuals, often experts in the same research area, who judge whether or not the scientist’s work is suitable for publication. The process of peer review helps to ensure that the research described in a scientific paper or grant proposal is original, significant, logical, and thorough. Grant proposals, which are requests for research funding, are also subject to peer review. Scientists publish their work so other scientists can reproduce their experiments under similar or different conditions to expand on the findings.
There are many journals and the popular press that do not use a peer-review system. A large number of online open-access journals, journals with articles available without cost, are now available many of which use rigorous peer-review systems, but some of which do not. Results of any studies published in these forums without peer review are not reliable and should not form the basis for other scientific work. In one exception, journals may allow a researcher to cite a personal communication from another researcher about unpublished results with the cited author’s permission.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/concepts-biology/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Concepts of Biology
- Publication date: Apr 25, 2013
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/concepts-biology/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/concepts-biology/pages/1-2-the-process-of-science
© Jan 8, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
This is the Difference Between a Hypothesis and a Theory
What to Know A hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been done. It is formed so that it can be tested to see if it might be true. A theory is a principle formed to explain the things already shown in data. Because of the rigors of experiment and control, it is much more likely that a theory will be true than a hypothesis.
As anyone who has worked in a laboratory or out in the field can tell you, science is about process: that of observing, making inferences about those observations, and then performing tests to see if the truth value of those inferences holds up. The scientific method is designed to be a rigorous procedure for acquiring knowledge about the world around us.

In scientific reasoning, a hypothesis is constructed before any applicable research has been done. A theory, on the other hand, is supported by evidence: it's a principle formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data.
Toward that end, science employs a particular vocabulary for describing how ideas are proposed, tested, and supported or disproven. And that's where we see the difference between a hypothesis and a theory .
A hypothesis is an assumption, something proposed for the sake of argument so that it can be tested to see if it might be true.
In the scientific method, the hypothesis is constructed before any applicable research has been done, apart from a basic background review. You ask a question, read up on what has been studied before, and then form a hypothesis.
What is a Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is usually tentative, an assumption or suggestion made strictly for the objective of being tested.
When a character which has been lost in a breed, reappears after a great number of generations, the most probable hypothesis is, not that the offspring suddenly takes after an ancestor some hundred generations distant, but that in each successive generation there has been a tendency to reproduce the character in question, which at last, under unknown favourable conditions, gains an ascendancy. Charles Darwin, On the Origin of Species , 1859 According to one widely reported hypothesis , cell-phone transmissions were disrupting the bees' navigational abilities. (Few experts took the cell-phone conjecture seriously; as one scientist said to me, "If that were the case, Dave Hackenberg's hives would have been dead a long time ago.") Elizabeth Kolbert, The New Yorker , 6 Aug. 2007
What is a Theory?
A theory , in contrast, is a principle that has been formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data. It is used in the names of a number of principles accepted in the scientific community, such as the Big Bang Theory . Because of the rigors of experimentation and control, its likelihood as truth is much higher than that of a hypothesis.
It is evident, on our theory , that coasts merely fringed by reefs cannot have subsided to any perceptible amount; and therefore they must, since the growth of their corals, either have remained stationary or have been upheaved. Now, it is remarkable how generally it can be shown, by the presence of upraised organic remains, that the fringed islands have been elevated: and so far, this is indirect evidence in favour of our theory . Charles Darwin, The Voyage of the Beagle , 1839 An example of a fundamental principle in physics, first proposed by Galileo in 1632 and extended by Einstein in 1905, is the following: All observers traveling at constant velocity relative to one another, should witness identical laws of nature. From this principle, Einstein derived his theory of special relativity. Alan Lightman, Harper's , December 2011
Non-Scientific Use
In non-scientific use, however, hypothesis and theory are often used interchangeably to mean simply an idea, speculation, or hunch (though theory is more common in this regard):
The theory of the teacher with all these immigrant kids was that if you spoke English loudly enough they would eventually understand. E. L. Doctorow, Loon Lake , 1979 Chicago is famous for asking questions for which there can be no boilerplate answers. Example: given the probability that the federal tax code, nondairy creamer, Dennis Rodman and the art of mime all came from outer space, name something else that has extraterrestrial origins and defend your hypothesis . John McCormick, Newsweek , 5 Apr. 1999 In his mind's eye, Miller saw his case suddenly taking form: Richard Bailey had Helen Brach killed because she was threatening to sue him over the horses she had purchased. It was, he realized, only a theory , but it was one he felt certain he could, in time, prove. Full of urgency, a man with a mission now that he had a hypothesis to guide him, he issued new orders to his troops: Find out everything you can about Richard Bailey and his crowd. Howard Blum, Vanity Fair , January 1995
And sometimes one term is used as a genus, or a means for defining the other:
Laplace's popular version of his astronomy, the Système du monde , was famous for introducing what came to be known as the nebular hypothesis , the theory that the solar system was formed by the condensation, through gradual cooling, of the gaseous atmosphere (the nebulae) surrounding the sun. Louis Menand, The Metaphysical Club , 2001 Researchers use this information to support the gateway drug theory — the hypothesis that using one intoxicating substance leads to future use of another. Jordy Byrd, The Pacific Northwest Inlander , 6 May 2015 Fox, the business and economics columnist for Time magazine, tells the story of the professors who enabled those abuses under the banner of the financial theory known as the efficient market hypothesis . Paul Krugman, The New York Times Book Review , 9 Aug. 2009
Incorrect Interpretations of "Theory"
Since this casual use does away with the distinctions upheld by the scientific community, hypothesis and theory are prone to being wrongly interpreted even when they are encountered in scientific contexts—or at least, contexts that allude to scientific study without making the critical distinction that scientists employ when weighing hypotheses and theories.
The most common occurrence is when theory is interpreted—and sometimes even gleefully seized upon—to mean something having less truth value than other scientific principles. (The word law applies to principles so firmly established that they are almost never questioned, such as the law of gravity.)
This mistake is one of projection: since we use theory in general use to mean something lightly speculated, then it's implied that scientists must be talking about the same level of uncertainty when they use theory to refer to their well-tested and reasoned principles.
The distinction has come to the forefront particularly on occasions when the content of science curricula in schools has been challenged—notably, when a school board in Georgia put stickers on textbooks stating that evolution was "a theory, not a fact, regarding the origin of living things." As Kenneth R. Miller, a cell biologist at Brown University, has said , a theory "doesn’t mean a hunch or a guess. A theory is a system of explanations that ties together a whole bunch of facts. It not only explains those facts, but predicts what you ought to find from other observations and experiments.”
While theories are never completely infallible, they form the basis of scientific reasoning because, as Miller said "to the best of our ability, we’ve tested them, and they’ve held up."
More Differences Explained
- Epidemic vs. Pandemic
- Diagnosis vs. Prognosis
- Treatment vs. Cure
Word of the Day
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Games & Quizzes

Commonly Confused
'canceled' or 'cancelled', 'virus' vs. 'bacteria', your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, is it 'jail' or 'prison', 'deduction' vs. 'induction' vs. 'abduction', grammar & usage, primary and caucus: what is the difference, words commonly mispronounced, merriam-webster’s great big list of words you love to hate, more commonly misspelled words, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, 12 words for signs of spring, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 13 unusually long english words, 12 star wars words, the words of the week - may 3.
Hypothesis, Model, Theory, and Law
Dorling Kindersley / Getty Images
- Physics Laws, Concepts, and Principles
- Quantum Physics
- Important Physicists
- Thermodynamics
- Cosmology & Astrophysics
- Weather & Climate
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/AZJFaceShot-56a72b155f9b58b7d0e783fa.jpg)
- M.S., Mathematics Education, Indiana University
- B.A., Physics, Wabash College
In common usage, the words hypothesis, model, theory, and law have different interpretations and are at times used without precision, but in science they have very exact meanings.
Perhaps the most difficult and intriguing step is the development of a specific, testable hypothesis. A useful hypothesis enables predictions by applying deductive reasoning, often in the form of mathematical analysis. It is a limited statement regarding the cause and effect in a specific situation, which can be tested by experimentation and observation or by statistical analysis of the probabilities from the data obtained. The outcome of the test hypothesis should be currently unknown, so that the results can provide useful data regarding the validity of the hypothesis.
Sometimes a hypothesis is developed that must wait for new knowledge or technology to be testable. The concept of atoms was proposed by the ancient Greeks , who had no means of testing it. Centuries later, when more knowledge became available, the hypothesis gained support and was eventually accepted by the scientific community, though it has had to be amended many times over the year. Atoms are not indivisible, as the Greeks supposed.
A model is used for situations when it is known that the hypothesis has a limitation on its validity. The Bohr model of the atom , for example, depicts electrons circling the atomic nucleus in a fashion similar to planets in the solar system. This model is useful in determining the energies of the quantum states of the electron in the simple hydrogen atom, but it is by no means represents the true nature of the atom. Scientists (and science students) often use such idealized models to get an initial grasp on analyzing complex situations.
Theory and Law
A scientific theory or law represents a hypothesis (or group of related hypotheses) which has been confirmed through repeated testing, almost always conducted over a span of many years. Generally, a theory is an explanation for a set of related phenomena, like the theory of evolution or the big bang theory .
The word "law" is often invoked in reference to a specific mathematical equation that relates the different elements within a theory. Pascal's Law refers an equation that describes differences in pressure based on height. In the overall theory of universal gravitation developed by Sir Isaac Newton , the key equation that describes the gravitational attraction between two objects is called the law of gravity .
These days, physicists rarely apply the word "law" to their ideas. In part, this is because so many of the previous "laws of nature" were found to be not so much laws as guidelines, that work well within certain parameters but not within others.
Scientific Paradigms
Once a scientific theory is established, it is very hard to get the scientific community to discard it. In physics, the concept of ether as a medium for light wave transmission ran into serious opposition in the late 1800s, but it was not disregarded until the early 1900s, when Albert Einstein proposed alternate explanations for the wave nature of light that did not rely upon a medium for transmission.
The science philosopher Thomas Kuhn developed the term scientific paradigm to explain the working set of theories under which science operates. He did extensive work on the scientific revolutions that take place when one paradigm is overturned in favor of a new set of theories. His work suggests that the very nature of science changes when these paradigms are significantly different. The nature of physics prior to relativity and quantum mechanics is fundamentally different from that after their discovery, just as biology prior to Darwin’s Theory of Evolution is fundamentally different from the biology that followed it. The very nature of the inquiry changes.
One consequence of the scientific method is to try to maintain consistency in the inquiry when these revolutions occur and to avoid attempts to overthrow existing paradigms on ideological grounds.
Occam’s Razor
One principle of note in regards to the scientific method is Occam’s Razor (alternately spelled Ockham's Razor), which is named after the 14th century English logician and Franciscan friar William of Ockham. Occam did not create the concept—the work of Thomas Aquinas and even Aristotle referred to some form of it. The name was first attributed to him (to our knowledge) in the 1800s, indicating that he must have espoused the philosophy enough that his name became associated with it.
The Razor is often stated in Latin as:
entia non sunt multiplicanda praeter necessitatem
or, translated to English:
entities should not be multiplied beyond necessity
Occam's Razor indicates that the most simple explanation that fits the available data is the one which is preferable. Assuming that two hypotheses presented have equal predictive power, the one which makes the fewest assumptions and hypothetical entities takes precedence. This appeal to simplicity has been adopted by most of science, and is invoked in this popular quote by Albert Einstein:
Everything should be made as simple as possible, but not simpler.
It is significant to note that Occam's Razor does not prove that the simpler hypothesis is, indeed, the true explanation of how nature behaves. Scientific principles should be as simple as possible, but that's no proof that nature itself is simple.
However, it is generally the case that when a more complex system is at work there is some element of the evidence which doesn't fit the simpler hypothesis, so Occam's Razor is rarely wrong as it deals only with hypotheses of purely equal predictive power. The predictive power is more important than the simplicity.
Edited by Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph.D.
- Scientific Hypothesis, Model, Theory, and Law
- Theory Definition in Science
- The Basics of Physics in Scientific Study
- A Brief History of Atomic Theory
- Einstein's Theory of Relativity
- What Is a Paradigm Shift?
- Wave Particle Duality and How It Works
- Oversimplification and Exaggeration Fallacies
- Hypothesis Definition (Science)
- Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
- Scientific Method
- Understanding Cosmology and Its Impact
- The History of Gravity
- Tips on Winning the Debate on Evolution
- The Copenhagen Interpretation of Quantum Mechanics
- Geological Thinking: Method of Multiple Working Hypotheses
- Biology Difference Between
- Difference Between Hypothesis And Theory
Difference Between Theory and Hypothesis
Many of them belittle evolution because “it is just a theory.” Gravity, on the other hand, must be real because it is a law. The words “theory,” “facts,” “laws” and “hypothesis” have a very specific meaning in the scientific world that doesn’t quite match the ones we use in everyday language. A hypothesis is a tentative explanation of an observation that can be tested. It acts as a starting point for further explanation. Theory, on the other hand, is an explanation of some aspect of the natural world that’s well-justified by facts, tested hypotheses, and laws. Let us look at more differences between hypothesis and theory given in a tabular column below.
Theory vs Hypothesis
From the above differences, we can infer that a hypothesis might change significantly as the testing occurs. A hypothesis can either be right or wrong. When a hypothesis is tested and proved true, it becomes a theory. At BYJU’S, learn more differences like the difference between asteroid and comet.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Biology related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


COMMENTS
The scientific method. At the core of biology and other sciences lies a problem-solving approach called the scientific method. The scientific method has five basic steps, plus one feedback step: Make an observation. Ask a question. Form a hypothesis, or testable explanation. Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
The term hypothesis means "little theory". A hypothesis is a short statement that can be tested and gives a possible reason for a phenomenon or a possible link between two variables. ... Biology definition: A hypothesis is a supposition or tentative explanation for (a group of) phenomena, (a set of) facts, ...
Theory vs. Hypothesis: Basics of the Scientific Method. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Jun 7, 2021 • 2 min read. Though you may hear the terms "theory" and "hypothesis" used interchangeably, these two scientific terms have drastically different meanings in the world of science.
The Royal Society - On the scope of scientific hypotheses (Apr. 24, 2024) scientific hypothesis, an idea that proposes a tentative explanation about a phenomenon or a narrow set of phenomena observed in the natural world. The two primary features of a scientific hypothesis are falsifiability and testability, which are reflected in an "If ...
A theory is valid as long as there is no evidence to dispute it. Therefore, theories can be disproven. Basically, if evidence accumulates to support a hypothesis, then the hypothesis can become accepted as a good explanation of a phenomenon. One definition of a theory is to say that it's an accepted hypothesis.
Scientific Theories. With repeated testing, some hypotheses may eventually become scientific theories. Keep in mind, a hypothesis is a possible answer to a scientific question. A scientific theory is a broad explanation for events that is widely accepted as true. To become a theory, a hypothesis must be tested over and over again, and it must be supported by a great deal of evidence.
Biology: cell theory, theory of evolution, germ theory, dual inheritance theory; Chemistry: ... A hypothesis is a proposition that is tested via an experiment. A theory results from many, many tested hypotheses. Theory vs Fact. Theories depend on facts, but the two words mean different things. A fact is an irrefutable piece of evidence or data.
A hypothesis is either a suggested explanation for an observable phenomenon, or a reasoned prediction of a possible causal correlation among multiple phenomena. In science, a theory is a tested, well-substantiated, unifying explanation for a set of verified, proven factors. A theory is always backed by evidence; a hypothesis is only a suggested possible outcome, and is testable and falsifiable.
biology textbook: In a previous science course you may have been told that a hypothesis that gains support becomes a theory. This is wrong! Instead a hypothesis that gains support becomes a supported hypothesis—what some may want to call a fact. Regardless of the amount of support that a hypothesis may gain, it can never become a theory.
Meaning. Biology. The study of living things. Observation. Noticing and describing events in an orderly way. Hypothesis. A scientific explanation that can be tested through experimentation or observation. Controlled experiment. An experiment in which only one variable is changed.
A second hypothesis might be, "The classroom is warm because there is a power failure, and so the air conditioning doesn't work." Once one has selected a hypothesis, the student can make a prediction. A prediction is similar to a hypothesis but it typically has the format "If . . . then . . . ."
Biology for Majors II (Lumen) 4: Module 1- Introduction to Biology 4.14: Experiments and Hypotheses ... When conducting scientific experiments, researchers develop hypotheses to guide experimental design. A hypothesis is a suggested explanation that is both testable and falsifiable. You must be able to test your hypothesis, and it must be ...
The escalation hypothesis is a prominent hypothesis in evolutionary biology. In response to the question why species often seem to be well adapted to their biotic environment, it states that enemies are predominant agents of natural selection, and that enduring interactions with enemies brings about long-term evolutionary trends in the ...
A scientific hypothesis is an inferred explanation of an observation or research finding; while more exploratory in nature than a theory, it is based on existing scientific knowledge. ... In fact, punctuated equilibrium is now considered its own theory in evolutionary biology. Punctuated equilibrium is not as broad of a theory as natural ...
Theory vs. Hypothesis. The term theory is generally used to imply speculation or assumption that has not been fully verified or has relatively limited proof. However, in science, an unproven idea or mere theoretical speculation is regarded as a hypothesis rather than a scientific theory.. A scientific hypothesis is a tentative explanation for a phenomenon and is yet to be tested through a ...
The Earth formed roughly 4.5. . billion years ago, and life probably began between 3.5. . and 3.9. . billion years ago. The Oparin-Haldane hypothesis suggests that life arose gradually from inorganic molecules, with "building blocks" like amino acids forming first and then combining to make complex polymers.
A hypothesis is a suggested explanation for an event, which can be tested. Hypotheses, or tentative explanations, are generally produced within the context of a scientific theory. A generally accepted scientific theory is thoroughly tested and confirmed explanation for a set of observations or phenomena.
A hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been done. It is formed so that it can be tested to see if it might be true. A theory is a principle formed to explain the things already shown in data. Because of the rigors of experiment and control, it is much more likely that a theory will be true than a hypothesis.
A scientific theory or law represents a hypothesis (or group of related hypotheses) which has been confirmed through repeated testing, almost always conducted over a span of many years. Generally, a theory is an explanation for a set of related phenomena, like the theory of evolution or the big bang theory . The word "law" is often invoked in ...
A hypothesis is an educated guess based on certain data that acts as a foundation for further investigation. It is based on extensive data. It is based on limited data. A theory is proven and tested scientifically. A hypothesis is not proven scientifically. The results are certain. The results are uncertain. It relies on evidence and verification.
The Red Queen's hypothesis is a hypothesis in evolutionary biology proposed in 1973, that species must constantly adapt, evolve, and proliferate in order to survive while pitted against ever-evolving opposing species.The hypothesis was intended to explain the constant (age-independent) extinction probability as observed in the paleontological record caused by co-evolution between competing ...
Nikki has a master's degree in teaching chemistry and has taught high school chemistry, biology and astronomy. ... The difference between a hypothesis and a theory is the testing. A hypothesis has ...
The mass flow hypothesis was modelled by Ernst Münch in 1930. His simple model consisted of: Two partially permeable membranes containing solutions with different concentrations of ions (one dilute the other concentrated) These two membranes were placed into two chambers containing water and were connected via a passageway.