Essay on Importance of Sports for Students and Children
500+ words essay on importance of sports.
First of all, Sport refers to an activity involving physical activity and skill . Here, two or more parties compete against each other. Sports are an integral part of human life and there is great importance of sports in all spheres of life. Furthermore, Sports help build the character and personality of a person. It certainly is an excellent tool to keep the body physically fit. Most noteworthy, the benefits of Sports are so many that books can be written. Sports have a massive positive effect on both the mind and body.


Physical Benefits of Sports
First of all, Sports strengthen the heart. Regular Sports certainly make the heart stronger. Hence, Sport is an excellent preventive measure against heart diseases . This certainly increases the life expectancy of individuals. Furthermore, a healthy heart means a healthy blood pressure.
Sports involve physical activity of the body. Due to this physical activity, blood vessels remain clean. Sports reduces the amount of cholesterol and fats in the body. This happens because of the increase of flexibility of the wall of the blood vessels. The flexibility increases due to physical exertion, which is the result of Sports.
Furthermore, the sugar level in blood also gets lower thanks to Sports. The sugar certainly does not accumulate in the blood due to physical activity.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
A person experiences a good quality of breathing because of Sports. Sports strengthen the lungs of the body. Sports certainly escalate the lung capacity and efficiency of the body. Hence, more oxygen enters the blood which is extremely beneficial. Furthermore, there are fewer chances of developing lung diseases due to Sports.
Appropriate body weight is easy to maintain because of sports. A Sports playing person probably does not suffer from obesity or underweight problems. Sports certainly help the body remain fit and slim.
Furthermore, Sports also improves the quality of bones. A person who plays sports will have strong bones even in old age. Several scientific research reports that Sports prevent many diseases. For example, many researchers conclude that Sports prevent the development of cancer.
Other Benefits of Sports
Sport is certainly an excellent tool to build self-confidence . Playing Sports increases confidence to talk properly. A sport certainly improves the skills of communicating with others. Furthermore, the person experiences confidence in sitting, standing, and walking properly. Hence, Sports enriches the social life of an individual.
Sports bring discipline in life. It certainly teaches the values of dedication and patience. Sports also teach people how to handle failure. Furthermore, the importance of following a time schedule is also present in Sports.

Above all, Sports improves the thinking ability of individuals. Sports certainly sharpen the mind. Children who play Sports probably perform better at exams than those who don’t.
Finally, Sports reduces the stress of mind . A Sports playing person would certainly experience less depression. Sports ensure the peace of mind of those playing it. Most noteworthy, Sports brings happiness and joy in the life of individuals.
A sport is an aspect of human life that is of paramount importance. It certainly increases the quality of human life. Sports must be made mandatory in schools. This is because it is as important as education. Everyone must perform at least one Sport activity on a regular basis.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How do Sports clean blood vessels?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Sports clean blood vessels by physical activity. This physical activity certainly reduces the amount of fat and cholesterol.” } }, { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How Sports improves the quality of breathing?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Sports improves the quality of breathing by strengthening the lungs. This certainly results in increasing lung capacity.” } } ] }
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Best Source for Sports Fans
The Importance of Sports: Benefits and Impact on Individuals and Society

Sports play a significant role in society, providing physical and mental benefits to individuals and impacting society as a whole. From improving physical fitness to fostering teamwork and discipline, sports have numerous advantages for people of all ages. In this article, we’ll explore the Importance of Sports and the various benefits of sports , their impact on individuals and society, and how to incorporate sports into daily life.
Introduction
Sports have been an integral part of human culture and history, dating back to ancient civilizations. From the Olympic Games to local community leagues, sports have evolved and diversified over time, encompassing a wide range of activities, such as football, basketball, tennis, swimming, gymnastics, and many more.
While sports are often associated with entertainment, competition, and leisure, they also have numerous physical, mental, and social benefits for individuals and society. In this article, we’ll examine the Importance of Sports and how they contribute to personal and social development.
Physical Benefits of Sports
One of the primary benefits of sports is their impact on physical health. Engaging in regular physical activity can improve various aspects of physical fitness, including cardiovascular health, muscular strength and endurance, weight control, and immune system functioning.
Improving Cardiovascular Health
Sports that involve aerobic exercise, such as running, cycling, or swimming, can improve cardiovascular health by increasing heart rate, blood circulation, and oxygen uptake. Regular aerobic exercise can reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, and other cardiovascular conditions.
Enhancing Muscular Strength and Endurance
Sports that involve resistance training, such as weightlifting, push-ups, or squats, can enhance muscular strength and endurance by stimulating muscle growth and adaptation. Stronger muscles can improve overall body function, prevent injuries, and support daily activities.
Promoting Weight Control
Sports that involve physical activity can help control body weight by burning calories and reducing body fat. Regular exercise can also increase metabolism, which can lead to sustained weight loss and prevent obesity.
Reducing the Risk of Chronic Diseases
Engaging in regular physical activity can reduce the risk of chronic diseases, such as diabetes, cancer, and osteoporosis. Exercise can improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and enhance bone density, among other health benefits.
Boosting Immune System
Sports that involve moderate physical activity can boost the immune system by increasing the production of white blood cells and antibodies that help fight off infections and diseases. Regular exercise can also reduce the risk of infections, such as the common cold, by improving immune function.
Mental Benefits of Sports
In addition to physical benefits, sports also have numerous mental health benefits. Regular physical activity can reduce stress and anxiety, enhance mental health, and improve cognitive functioning.
Reducing Stress and Anxiety
Engaging in physical activity can reduce stress and anxiety by releasing endorphins, natural mood-boosting chemicals in the brain. Exercise can also promote relaxation and improve sleep quality, which can alleviate stress and anxiety.
Enhancing Mental Health
Sports can enhance mental health by reducing the risk of depression and improving self-esteem and confidence. Regular exercise can also provide a sense of purpose and achievement, which can boost mental well-being.
Improving Cognitive Functioning
Sports can improve cognitive functioning by enhancing brain function, memory, and attention. Exercise can also stimulate the growth of new brain cells and improve neuroplasticity, which is the brain’s ability to adapt and change.
Social Benefits of Sports
Sports also have numerous social benefits, including the development of teamwork and collaboration skills, the promotion of leadership skills, the building of confidence and self-esteem, and fostering of cultural exchange and inclusion.
Developing Teamwork and Collaboration Skills
Sports require teamwork and collaboration, which can improve communication, problem-solving, and leadership skills. Working with others towards a common goal can also foster a sense of belonging and connection.
Promoting Leadership Skills
Sports can promote leadership skills by providing opportunities to take on leadership roles, such as team captain or coach. Leading others can enhance decision-making, communication, and motivational skills.
Building Confidence and Self-Esteem
Sports can build confidence and self-esteem by providing opportunities to achieve goals, develop skills, and overcome challenges. Success in sports can also translate into success in other areas of life.
Fostering Cultural Exchange and Inclusion
Sports can foster cultural exchange and inclusion by bringing people from different backgrounds together and promoting understanding and respect. International sports events like the Olympic Games can showcase the diversity and promote global unity.
Economic and Social Impact of Sports
In addition to personal benefits, sports also have economic and social impacts. Sports can generate employment and income, promote tourism and investment, unify communities and foster national identity, and address social issues and promote social justice.
Generating Employment and Income
Sports can generate employment and income by creating jobs in various sectors, such as coaching, administration, media, and hospitality. Sports events can also attract tourists and generate revenue for local businesses.
Promoting Tourism and Investment
Sports can promote tourism and investment by showcasing cities and countries as desirable destinations for sports fans and investors. Sports facilities and infrastructure can also attract investment and boost economic growth.
Unifying Communities and Fostering National Identity
Sports can unify communities and foster national identity by providing a common ground for people to come together and celebrate their shared values and traditions. National sports teams can also promote patriotism and national pride.
Addressing Social Issues and Promoting Social Justice
Sports can address social issues and promote social justice by raising awareness of societal challenges, such as discrimination, inequality, and poverty. Sports events and organizations can also promote social responsibility and philanthropy.
Incorporating Sports into Daily Life
Incorporating sports into daily life can benefit physical, mental, and social well-being. Here are some tips for incorporating sports into daily life:
Choosing an Appropriate Sport or Physical Activity
Choose a sport or physical activity that suits your interests, abilities, and lifestyle. Consider factors such as time, budget, and location when selecting a sport or activity.
Setting Realistic Goals
Set realistic goals for your sports or physical activity. Start small and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts as your fitness level improves.
Staying Consistent
Consistency is key to reaping the benefits of sports and physical activity. Set a regular schedule for your workouts and stick to it, even if it means starting with just a few minutes a day.
Mixing it Up
Mixing up your sports or physical activity routine can help prevent boredom and maintain motivation. Try different sports or activities, or switch up your routine with different types of workouts, such as strength training, yoga, or cardio.
Finding a Support System
Having a support system can help keep you motivated and accountable. Join a sports team or fitness group, or find a workout buddy to exercise with regularly.
In conclusion, sports offer numerous benefits for physical, mental, and social well-being. Regular sports or physical activity can improve cardiovascular health, strengthen muscles and bones, boost immune function, reduce stress and anxiety, enhance mental health and cognitive functioning, promote teamwork and leadership skills, build confidence and self-esteem, foster cultural exchange and inclusion, generate employment and income, promote tourism and investment, unify communities and foster national identity, and address social issues and promote social justice. By incorporating sports into daily life , individuals can reap these benefits and improve their overall health and well-being.

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Importance of Sports

- Updated on
- Oct 7, 2023

Sports are an integral part of life. Sports are exciting activities which are not only fun to play but also promote physical fitness. But do you know the benefits of playing sports both mentally and physically? Well, we have come to your rescue. In this blog, you will read about the importance of sports and how it can help one learn several new qualities. These qualities will help one to be ahead in their life. We will also be discussing more on this topic through essays.
Table of Contents
- 1.1 Physical Benefits
- 1.2 Mental Benefits
- 2 Essay on Importance of Sports in 200 Words
- 3 Essay on Importance of Sports in 300 Words
- 4 Essay on Importance of Sports in 400 Words
Importance of Sports
Sports are essential to every student’s life. Almost every parent believes their child should be involved in sports during their growing years. Moreover, playing sports keeps us fit, healthy and active. Sports teach essential life skills such as discipline, perseverance, teamwork, and time management. Here are all the benefits one gets by playing sports.
Physical Benefits
- By playing sports, one gets to be physically active and at the same time maintain discipline.
- By involving oneself in sports, it reduces the risk of obesity and other chronic health issues.
- Playing sports leads to muscle development, promotes strong bones and lastly reduces the risk of osteoporosis.
Mental Benefits
The benefits of sports are not limited to physical enhancement, they also help in brain functioning and mental activities.
- Playing in team sports, helps one to learn to work together leading to achieving a common goal – leadership skills, teamwork and several other qualities.
- Sports also improve one’s decision-making skills and boost self-confidence.
- Lastly, sports help one to reduce stress, depression and other mental issues.
Also Read: Essay on My Aim in Life
Essay on Importance of Sports in 200 Words
Sports are essential because they promote social, mental, and physical well-being. They are not only a source of amusement but also play a huge role in many facets of life.
To begin with, sports encourage physical fitness. Sports participation helps people maintain a healthy lifestyle by enhancing their stamina, strength, and cardiovascular fitness. The risk of obesity, diabetes, and other lifestyle-related disorders is reduced by regular exercise in sports.
Secondly, sports improve mental health. It encourages self-control, tenacity, and goal-setting. At the same time, athletes gain the ability to manage stress, develop resilience, and cultivate a solid work ethic. While team sports can foster interpersonal, communication, and teamwork skills.
Sports also help to maintain societal harmony. They give people from various backgrounds a place to interact, fostering friendship and harmony. Sporting events frequently foster a sense of belonging and pride among viewers.
Sports in the classroom impart important life lessons including cooperation, initiative, and sportsmanship. For gifted athletes, they can also result in scholarships and educational possibilities.
Also Read: Essay on Waste Management
Essay on Importance of Sports in 300 Words
The development of the body, mind and social structure are all considerably aided by sports in human society. They have a special and complex significance that goes much beyond simple competition or entertainment.
Sports are crucial for physical health in the first place. People who participate in sports and physical activity can keep up a healthy lifestyle. Sporting activity regularly enhances physical endurance, muscular strength, and cardiovascular health. It works well to combat the rising obesity pandemic, lower the likelihood of developing chronic illnesses like diabetes, and improve general health.
Sports are essential for mental health in addition to physical health. Athletes learn to be disciplined, determined, and have a strong work ethic. They get knowledge on how to set and accomplish goals, manage stress, and develop resilience. These life skills learned via sports are transferable to many facets of success on both a personal and professional level.
Sports also encourage social growth. They give people from various backgrounds a place to interact, fostering social cohesiveness and harmony. Sporting activities foster a sense of community by inspiring people to interact, find common ground, and form enduring friendships.
Sports in education provide a distinctive learning opportunity. They impart characteristics like leadership, sportsmanship, and teamwork, which are crucial in both academic and professional environments. Many students find that participating in athletics paves the way for scholarships and other educational opportunities that might not otherwise be possible.
Sports are economically significant as well. They open up positions in the sports sector for everyone from athletes and coaches to event planners and sports medical specialists. Major athletic events can promote local economies, increase income, and create jobs by boosting tourism.
In conclusion, sports are more than just amusement; they are essential to leading a balanced existence. Sports have an enormous value that goes well beyond the pitch or court, making them an essential component of human society.
Essay on Importance of Sports in 400 Words
Sports plays a crucial role in our lives, promoting our physical and mental health as well as our social and economic development. Sports provide entertainment and recreation for both participants and spectators. They offer an escape from daily routines, a source of excitement, and a sense of shared experience.
First off, sports are essential for fostering physical wellness. People can keep up an active lifestyle by participating in sports. It improves muscle strength, total physical endurance, and cardiovascular health. Regular exercise dramatically lowers the risk of lifestyle disorders like diabetes, obesity, and heart problems. These health advantages help people live longer and with higher quality.
Second, engaging in athletics is crucial for mental health. Athletes learn valuable life lessons including self-control, tenacity, and goal-setting. They gain skills for dealing with stress, developing resilience, and upholding a solid work ethic. These mental skills developed via sports are transferable to many facets of life and can promote success and overall well-being.
Additionally, sports encourage social growth and unity. They bridge gaps in class, age, gender, and ethnicity by bringing people together. Sporting occasions foster a sense of belonging and camaraderie, inspiring people to interact, discover similar interests, and form enduring connections. This social component of sport fosters harmony and understanding between various groups.
Sports offer a special educational opportunity. They provide characteristics like leadership, sportsmanship, and teamwork, which are crucial in both academic and professional situations. Sports are given a high priority in the curriculum of many educational institutions, which recognise the benefits they provide for students’ all-around growth.
Sports are economically significant as well. They open up positions in the sports sector for everyone from athletes and coaches to event planners and sports medical specialists. Major athletic events have the potential to increase tourism, fire up local economies, bring in money, and provide jobs.
Sports also support a sense of national identity and pride. International sporting success may bring a nation together by fostering a sense of achievement and patriotism. Athletes serve as ambassadors for their nations, representing the commitment and labour of the populace.
To conclude, sports are more than just amusement; they provide the basis of a full existence. They encourage mental toughness, social harmony, physical fitness, and practical life skills. Sports participation should be promoted as a top priority by everyone—individuals, educational institutions, and governments. Sports are important for reasons that go beyond the physical, contributing to human society as a whole.
Related Articles:
- Essay on Cricket
- Essay on Teacher
- Essay on Covid-19
- Essay on Winter Season
- Essay on Earthquake
Sports teaches one several values. These include discipline, elegance, sacrifice, instills leadership qualities which help people to lead a successful life.
When people participate together in a sport, they know that they competing against each other. This helps them to come together as a team.
As they keep kids physically fit and engaged, sports have a direct link to a healthy physique.
For more information related to such interesting topics, visit our essay-writing page and make sure to follow Leverage Edu .
Malvika Chawla
Malvika is a content writer cum news freak who comes with a strong background in Journalism and has worked with renowned news websites such as News 9 and The Financial Express to name a few. When not writing, she can be found bringing life to the canvasses by painting on them.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
- Milano Cortina 2026
- Brisbane 2032
- Olympic Refuge Foundation
- Olympic Games
- Olympic Channel
- Let's Move
How sport can have a positive impact on mental and physical health
It’s not always easy to start a workout, but research shows that sport and exercise are beneficial not only for your physical health, but your mental well-being, too. Let us help!

Health experts and Olympic athletes agree: Your mental and physical health benefit when you get active and participate in sport – whatever that means for you.
From daily exercise to choosing a sport to practice or play, the body and mind are worked in new and different ways each time you move your body.
On June 23rd every year we come together to celebrate that, as part of Olympic Day.
For the 2020 edition, we connected with Olympians around the world for Olympic Day 2020 at-home workouts – and a reminder: We’re stronger together, especially when we stay active!
And those are still available online to help inspire you today.
Sport benefits: Both the physical and mental
While the physical benefits are numerous (more on that below), the UK's National Health Service (NHS) report that people who take part in regular physical activity have up to a 30 percent lower risk of depression.
Additionally, exercise can help lower anxiety, reduce the risk of illness and increase energy levels. Want better sleep? Work up a good sweat!
Exercise can help you fall asleep faster and sleep for longer, research says.
It was in June 2020 that the IOC partnered with the World Health Organization and United Nations to promote the #HEALTHYTogether campaign , which highlights the benefits of physical activity in the face of the pandemic.
Over 50 at-home workouts are searchable across Olympics.com for you, each which help further the idea that moving and challenging the body can only prove beneficial for your physical and mental well-being.
The athletes' perspective: 'I used this strength to survive'
“If I had sat doing nothing, I would have gone crazy,” says Syria's Sanda Aldass , who fled the trauma of civil war in her country, leaving behind her husband and infant child.
Instead, she had judo - and has been selected for the IOC Refugee Olympic Team Tokyo 2020 for the Games in 2021.
“Running around and doing some exercises filled up my time and also kept me in good mental health,” Sanda said of the impact of sport on her life during nine months spent in a refugee camp in the Netherlands in 2015.
The same power of sport goes for Iranian taekwondo athlete Ali Noghandoost.
"When I had to leave my family and my home in Iran, the first things I packed in my bag were my belt, my dobok, my shoes and my mitt for taekwondo," Noghandoost said . "I took some documents that said I was a champion in Iran and in a national team, so I could prove I was a fighter and continue to train in any city I went to."
"Taekwondo did not only help me physically; mentally, it stopped me from thinking about giving up and that we wouldn’t make it. I used this strength to survive," he added.
Noghandoost has worked as a coach for refugees in Croatia, where he has tried to pass the power of sport on to the next generation.
"When you’re living in a refugee camp, it’s a really hard situation, but when you play sport, you can release any negative energy and feel free. It’s a space – a paradise – for them to be themselves."
A member of the IOC Refugee Olympic Team Rio 2016, Yiech Pur Biel says that the team provided a message of hope for those watching around the world.
"We were ambassadors for a message of hope, that anything is possible," Biel said . "A good thing had come out of our situations. The world understood. I am called a refugee, but you never know when someone else might become a refugee, through war or persecution. We wanted to show that we responded positively. So that made me very happy. Through sport, we can unite and make the world better."
Sport as a tool for much - including mental health
Sport is a powerful tool no matter from what angle you look at it, including mental health. The Olympic Refugee Foundation (ORF) has recently launched two different programs that are aimed at helping young refugees dream of a brighter future - through sport.
One of those programs, Game Connect, is a three-year initiative that was launched in August 2020 and aims to "improve the mental health and psychosocial wellbeing of young refugees by improving their access to safe sport," as explained on Olympics.com last year.
We are "embarking on a three-year project to improve the psychosocial wellbeing and mental health of young refugees, working together with well-trained community-based coaches to deliver a Sport for Protection program and activities," explained Karen Mukiibi of Youth Sport Uganda, which has partnered with the ORF.
Related content

Stay Healthy, Stay Strong, Stay Active with the Olympic Day home workout

Paris 2024 – getting children moving more at school for 30 minutes a day

Daily routine: five things to do - 11 April 2020

Olympic Day Workout | #StayActive with Bryan Clay

Olympic Day Workout | #StayActive with Hong Zhang
You may like.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Importance of Sports Essay for Students in English

Essay on Importance of Sports
Sports are very essential for every human life which keeps them fit and fine and physical strength. It has great importance in each stage of life. It also improves the personality of people. Sports keep our all organs alert and our hearts become stronger by regularly playing some kind of sports. sports has always given priority from old ages and nowadays it has become more fascinating. Due to the physical activity blood pressure also remains healthy, and blood vessels remain clean. Sugar level also reduces and cholesterol comes down by daily activity. Different people have different interests in sports but the action is the same in all sports. Sports are becoming big channels to make more capital/money day by day and the number of people is also increasing. By playing sports even at a young age you can also be better and free from some diseases. By playing sports lung function also improves and becomes healthy because more oxygen is supplied. Sports also improves bone strength even in old age.
Note: ➤ Don't Miss Out: Get Your Free NEET Rank Predictor Instantly!
Significance of Sports in Student’s Life
Just like a diet of healthy nutrients is needed for nourishing the body, playing sports holds a great significance in enhancing our lives, especially for growing children. As a student, one has to face many challenges, and playing sports helps them cope with the exam pressure and prepare them for further challenges by providing them with physical and mental strength.
Children who are indulged in physical activities sustain good values of mutual respect and cooperation. Playing sports teaches them skills such as accountability, leadership, and learning to work with a sense of responsibility and confidence.
Sports help in maintaining Good Health
In today’s era of excessive competition and changing environment, people barely care about our health and have to face its consequences in the later stages of their life. They easily become prey to many life-threatening health issues. Those who are indulged in regular physical activities can easily defend themselves from such diseases. Therefore, playing sports can resolve this concern.
Playing regular sports can help maintain diabetes, improve heart function, and reduce stress and tension in an individual.
Get rid of Excess Weight
Most of the world’s population is obese, and as a result, many other health issues also arise. Hence, playing sports is one of the most recreational and helpful ways of burning calories. All you have to do is follow a healthy diet and play your favourite sport. You can be saved from exhausting workout routines in the gym by playing sports.
Playing your favourite sports and shedding kilos, isn’t it like killing two birds with one stone!
Guard Your Heart
The heart is the most important organ of our body. With changing lifestyles, people are facing heart-related problems these days. The life of heart patients becomes difficult with lots of heavy medications and restrictions. Therefore, people need to indulge in outdoor games. Playing for even 30 minutes a day can do wonders for your life. The heart pumps better, and blood circulation improves whenever we play sports. Heart muscles get stronger, and hence it starts functioning at a better rate.
Enhance Your Immunity
The immune system is the major player of the body in fighting infections. Those who easily catch infections and fall sick frequently can easily get healthier by working on their immune system.
It becomes really difficult to live with poor immunity, take heavy medications frequently, and spend most of your time indoors just to prevent yourself from the effects of changing environments. Getting indulged in regular sports activities can help build your immunity greatly, and the most amazing part with it is that you can do it by just playing your favourite sport.
Impact of Sports on an Individual’s Personality
Playing sports builds your personality and teaches you to live life in a better way. Getting involved in such activities teaches good values, ethics, and skills in your life. The person starts to have a positive outlook towards life and can easily deal with obstacles in their life. Not only this, but it also reduces the stress level in the person as such people start taking challenges with positivity. Their efficiency increases, so they can easily take up challenges confidently.
People can learn lots of important skills through their sports. Every sport teaches us the skills of handling difficult situations, quick- decisions making and problem-solving. By playing sports, one can learn the art of living and managing things and taking leads.
Therefore, if you play sports, you are not just enjoying it; you are also learning many significant life lessons.
Nation’s Pride
All the good values and skills one learns by playing sports can prepare them to conquer any battle-fields. Many eminent sports personalities have brought laurels to our country by proving their mettle on different sports grounds. Some of them are; Sachin Tendulkar, Saina Nehwal, Mary Kom, Sardar Singh, Sania Mirza and many more.
These personalities are inspirations for all those who are passionate about playing sports. Hard work and dedication can help them reach their goals and can become inspirations for others one day.
Common Sports
There are varieties of sports activities you can choose from. Some of the most common sports are; Tennis, Badminton, Volleyball, Cricket, and Basketball.
Learning from Sports:
Sports bring discipline in life. It teaches the way of sitting, talking, walking etc. Without sports in human life it seems too boring, sports activate all the cells and keep the body active, fit and slim. Sports improve thinking ability and reduce the stress of the mind. Those people with not so much interest in sports are less active and also have chances of getting a disease in the early stage of life and also show lethargy in work. Sports should be made mandatory in school, so that at an early age they can know the benefits of sports. People also select their favourite sports players on their more interest in which sports, if we take cricket because in our country India cricket is played more and shown interest by many peoples, many players came but still name like Kapil dev, Sachin Tendulkar, M.S.Dhoni, Virat Kohli will be always favourite for their fans. If we take football players like Messi, Ronaldo and many others, they are an idol for many people who have an interest in football. Sports is generally recognized as a system of activities which are based in athletics such as Olympic games. Sports are always played under government rules which helps to serve fair competition, sports having following criteria like, it should be fair competition, giving no harm to any person, and the winner should be nominated by superior or from the best. In sports like chess improves the mind and thinking capacity. Since from the 21st century, there has been increased in a debate that whether transgender should be able to participate in any sports events.
Benefit of Technology in Sports:
Nowadays technology also plays an important role in sports to judge the fair game for winners. It helps to judge a car racer by seeing properly on the screen, also in cricket like sometimes when it becomes difficult to make the decision again technology is used. In every sport, it has been utilised for fair play and to announce the winners. Research suggests that sports have the capacity to connect youth with positive thinking and provide positive development. For any sportsman, high education is not mandatory but required to be the best sportsman. It is his interest, strength and skills. We have seen in the last two decades women are also showing more interest in sports and for them also proper matches are arranged by the government. Sports give the feeling of living with a positive attitude. sports can be played in both indoor and outdoor, many indoor games like chess, carrom board, helps to improve the thinking power but the sports which are played in outdoor like football, cricket, Rugby, kabaddi etc helps to improve physical strength, thus the person who does more outdoor games should be more fit and slim. 3-4 decades ago the opportunity in sports was not much-showed interest which is shown by the present youth generation. Sports secure life and give a standard lifestyle. The 10 most popular sports played in the World are Soccer, Cricket, Basketball, Hockey, Tennis, Volleyball, Table Tennis and Baseball where Hockey was first played in India and became our national games. There are also some sports which are shown less interest like Kabaddi, Polo, Archery, Weightlifting etc. Swimming is known as the safest sport. So sports should be played by everyone because it helps our body in movement and gives good health. The study has proved that sports have better well controlled many diseases like heart attack, lung function, obesity, and thinking power. Ice hockey, soccer are the games which have the highest paid sportsmen. Also some sports can be played in small places and also some sports require large places. Sports keep us active and energetic, even in some treatment to recover from the disease sports are advised by the doctors. play sports on a regular basis and keep our self-fit, sports should not be neglected but it should be mandatory for everyone.

FAQs on Importance of Sports Essay for Students in English
1. Why Sports are Important?
Any sports makes you physically fit, increase your immune level and even encourage socialism among different people.
2. What are the Common Sports Played in India?
Cricket and Football are major sports played in India.
3. What is the National Sport of India?
Field Hockey has been considered as the national sport of India.Though it has some historical connect as well as popularity too.
4. Which sports are the best for students to become more active?
Sports that require them to move about, such as Football and Basketball can be beneficial. Apart from them, students can also engage in Tennis and Martial Arts can also be good options.
5. How can students manage their study and sports times effectively?
Even when studies seem the most important, engaging in active sports is necessary to maintain overall health. So, students can set aside a few hours everyday in the evening to engage in the sports of their choice. This can help them take rest from studies and work towards maintaining their physical health as well.
6. Which home exercises are equally as effective?
When students do not have time to spare to play extensive sports, then home training can be a beneficial tool. Home-based exercises, such as skipping, running on the treadmill, yoga and pilates can be good substitutes for active sports.

Essay on Importance of Sports
Sports are like a universal language that brings people together, and they play a crucial role in our lives. In this essay, we will explore the importance of sports, their impact on physical and mental health, their contribution to teamwork and personal development, and why they are an essential part of our society.
Defining the Importance of Sports
Sports encompass a wide range of physical activities and games that offer numerous benefits to individuals and communities alike.
Physical Fitness and Health
Participation in sports promotes physical fitness and good health. Regular exercise helps prevent obesity, heart disease, and other health issues.
Mental Health and Well-Being
Sports also have a positive impact on mental health. They reduce stress, boost self-esteem, and improve mood, contributing to overall well-being.
Teamwork and Cooperation
Team sports teach important life skills like teamwork, communication, and cooperation. These skills are valuable in both sports and daily life.
Personal Development and Character Building
Participating in sports helps build character. Athletes learn discipline, perseverance, and the importance of setting and achieving goals.
Social Skills and Friendship
Sports provide opportunities to make new friends and strengthen existing relationships. They foster a sense of belonging and community.
Cultural and Global Unity
Sports have the power to unite people across cultures and nations. Global events like the Olympics promote international cooperation and understanding.
Equal Opportunities
Sports offer equal opportunities for people of all backgrounds. They promote inclusivity and diversity, breaking down barriers.
Role Models and Inspiration
Athletes often become role models who inspire others to pursue their passions, overcome challenges, and achieve greatness.
Educational Benefits
Sports can enhance education by teaching time management, prioritization, and problem-solving, making students better learners.
Expert Opinions on Sports
Experts in sports science and psychology emphasize the physical and psychological benefits of sports participation.
Sports and Community
Sports play a central role in communities. They bring people together, boost local economies, and create a sense of pride.
Sports and Education
Physical education programs in schools introduce children to sports, promoting a healthy lifestyle from a young age.
The Sports Industry
The sports industry provides employment opportunities in areas such as coaching, sports management, and sports medicine.
The Future of Sports
The future of sports holds exciting possibilities, with advancements in technology, accessibility, and opportunities for athletes.
Conclusion of Essay on Importance of Sports
In conclusion, the importance of sports cannot be overstated. They are a powerful force for physical and mental well-being, personal development, and community unity. Sports teach us valuable life skills, promote inclusivity, and inspire us to strive for greatness.
As we embrace the significance of sports in our lives, let us continue to support and encourage participation in sports, whether as athletes or spectators. Sports are more than just games; they are a reflection of our human spirit and our capacity to achieve extraordinary feats. They remind us that, with determination and teamwork, we can overcome challenges and reach new heights, both on and off the field.
Also Check: Simple Guide on How To Write An Essay
Home — Essay Samples — Life — Recreation and Sports — The Importance of Playing Sports

Social, Mental, and Physical Benefits of Sports for Young Adolescents
- Categories: Physical Education Physical Exercise Recreation and Sports
About this sample

Words: 1334 |
Published: Dec 5, 2018
Words: 1334 | Page: 1 | 7 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, social benefits, effects on mental health, effects on physical health.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Education Nursing & Health Life

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 469 words
5 pages / 2430 words
2 pages / 919 words
3 pages / 1325 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Recreation and Sports
Violence has been around forever now. It’s everywhere. So what is violence? Violence is 'the use of physical force so as to injure, abuse, damage, or destroy.' Most will assume there is only one type of violence that people use, [...]
Leisure and recreation are integral aspects of individuals' lives, contributing significantly to their overall well-being. Defined as activities that people engage in for pleasure and relaxation, leisure and recreation play a [...]
Softball is a popular sport that is played by millions of people around the world. It is a variant of baseball that is played on a smaller field and with a larger ball. Softball is a fast-paced and exciting game that requires a [...]
Sports have been an integral part of human society for centuries. From ancient civilizations to modern times, sports have played a crucial role in promoting physical fitness, mental well-being, and social interaction. In [...]
Coyle, J. T. (2004). Use it or lose it - Do effortful mental activities protect against dementia? The New England Journal of Medicine, 352(25), 2571-2572.Einstein, G., & McDaniel, M. (2004). Integrated memory for details and [...]
The Catastrophe theory is a severe version of the inverted U theory. At first, an athlete is under-aroused meaning that they are distracted and not aware of their surroundings. Then they are at optimum level of arousal meaning [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Physical Activity Basics
- Guidelines and Recommendations
- Add Physical Activity as an Older Adult
- Benefits of Physical Activity
- Overcoming Barriers
- Health Benefits of Physical Activity
- Places to Be Physically Active
- Adding Physical Activity as an Adult
- Making Physical Activity Part of a Child's Life
Health Benefits of Physical Activity for Adults
What to know.
A single session of moderate- to vigorous-intensity physical activity provides immediate benefits for your health. Regular physical activity provides important health benefits for chronic disease prevention.
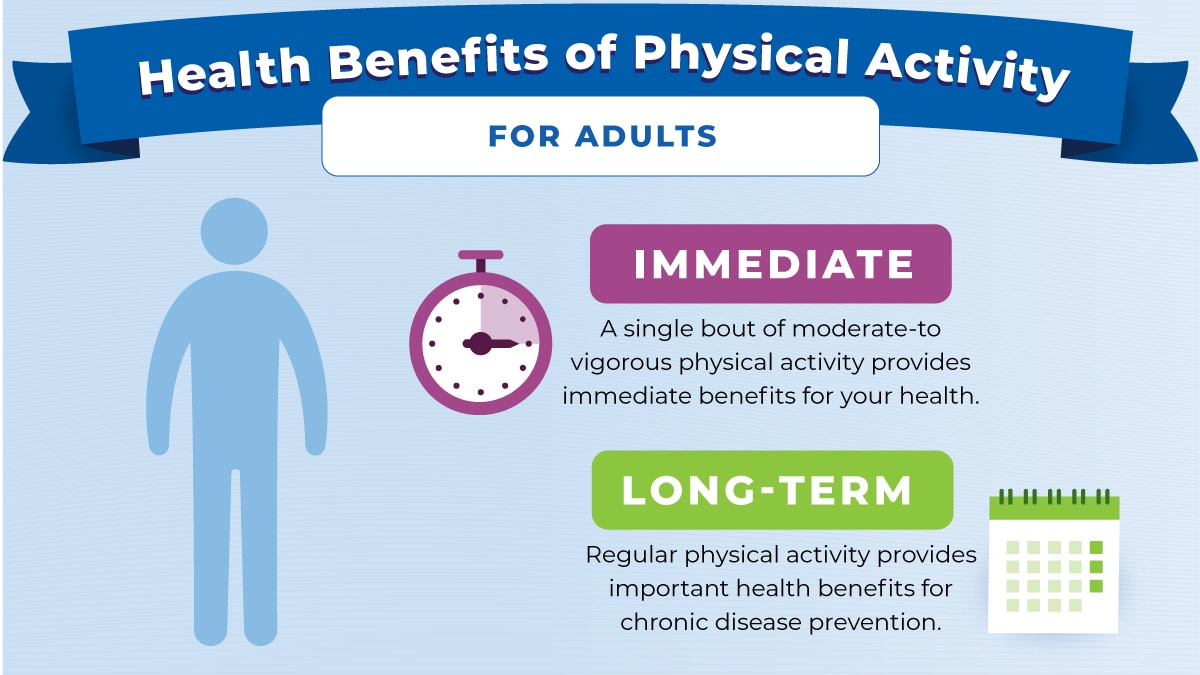
- Sleep: Improves sleep quality
- Less Anxiety: Reduces feelings of anxiety
- Blood Pressure: Reduces blood pressure
- Brain Health: Reduces risks of developing dementia (including Alzheimer's disease) and reduces risk of depression
- Heart Health: Lowers risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes
- Cancer Prevention: Lowers risk of 8 cancers (bladder, breast, colon, endometrium, esophagus, kidney, lung, and stomach)
- Healthy Weight: Reduces risk of weight gain
- Bone Strength: Improves bone health
- Balance and Coordination: Reduces risks of falls
Emerging research suggests physical activity may also help boost immune function 1 2 .
Source: Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans , 2nd edition.
See similar content in Spanish .
- Nieman D, Wentz L. The compelling link between physical activity and the body's defense system. J Sport Health Sci. 2019 May;8(3): 201-17.
- Jones A, Davison G . Exercise, immunity, and illness. Muscle and Exercise Physiology . 2019;317-44.
Regular physical activity is one of the most important things you can do for your health. Learn about the benefits of physical activity and what you can do.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Int Med Res
- v.48(1); 2020 Jan
The increasing importance of sports science and medicine
The notion that exercise has a multitude of benefits, especially for health, has been around for millennia. 1 Physicians’ traditional focus on the prevention of disease and the maintenance of health requires them to find interventions that will help patients, with as few adverse effects and reactions as possible. Only lately has the focus shifted towards acute illnesses and treating patients according to their complaints. 1 In any case, diet and exercise have almost always been part of the regimen emphasised by physicians. 1 Even ancient physicians recognised the importance of these two aspects of care in the formulation of their treatments. 2 This understanding suggests that maintaining health in a preventative manner may be a more appropriate medical approach than treating patients at the doorway of disease.
Most modern diseases can be said to be preventable. 2 Almost half of the mortality rate in the United States can be traced to behavioural causes. 2 The main causes of early death in the country are smoking and diseases attributable to physical inactivity linked to obesity. 2 Physicians should consider returning to an approach of prescribing lifestyle changes before prescribing medication. Prescribing exercise can indeed maximise the health of patients. 1 Clearly, exercise is relatively inexpensive yet massively effective for multiple bodily systems. Exercise can be considered a medication, and physicians should be encouraged to start treating physical activity as a prescription that they can recommend to their patients. As more people are beginning to recognise, the benefits of exercise will usually outweigh the risks, and each person should be able to perform at least a minimum amount of exercise. 2
There is a growing opinion that, in the near future, lack of exercise may be the most important public health problem. 2 Physicians should consider it their duty to modify patients’ lifestyles in ways that lead to the health benefits that science has now confirmed are clear and undeniable. Many conditions, such as depression, osteoarthritis, hypertension, obesity, cancer, and diabetes mellitus have outcomes that are obviously ameliorated by increased physical activity. 3
The United States is in love with sports, with 60% of Americans describing themselves as sports fans. 4 Billions of dollars are generated every year by various US-based sports leagues, such as the National Hockey League, the National Basketball Association, Major League Baseball, and the National Football League. 4 Collegiate sports are a multimillion-dollar business as well. 4 As the earnings increase, so do the investments that these leagues make in the best players. Because of the financial impact of these various sports, it has become a priority for the leagues to keep their players healthy. As such, optimising performance, improving the best players’ availability, and decreasing the risk of injury have become the main thrusts of sports science and sports medicine when tied to high-performance teams. 5
Sports science research can help lead to evidence-based approaches that will allow athletes and active individuals to exercise in optimal ways. There is a continuing gap between current practices in athletics and the latest scientific evidence, compounded by an era of anti-intellectualism and ‘fake news’, as well as a burgeoning disbelief in fact and science. 4 Non-peer-reviewed articles are proliferating, as are so-called ‘predatory’ journals and conferences, which can contribute to the dilution of good science that could be used for the benefit of athletes, active individuals, and indeed, all patients who are trying to exercise more.
Coaches and athletes need to listen more carefully and more often to sports scientists, whose findings can be supported and dispersed by sports medicine physicians. Widespread support for the use of unproven supplements in sports, or wearing specific bracelets or anklets to supposedly improve athletic ability, are but a few of the pseudoscientific practices that coaches and athletes need to discuss further with scientists and physicians. Conversely, those engaged in the science of sports medicine and the provision of health care need to improve their ability to translate terms and ideas that may not be easily understood by those engaged or about to engage in sports and exercise activities.
Knowledge transfer is key, and sports communities all over the world should be able to engage with sports scientists and medical providers more directly. We now have the ability to leverage social media, application software, and other forms of technology to achieve this. Our use of these evolving tools should focus on sports physicians and athletes being proactive, using exercise as prevention, rather than reactive, treating maladies as needed. The idea that ‘exercise is medicine’ should become second nature in the world of primary care and sports medicine. 1
Declaration of conflicting interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
George G.A. Pujalte https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7537-7457
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services

- Virtual Tour
- Staff Directory
- En Español
You are here
Nih research matters.
May 14, 2024
Understanding how exercise affects the body
At a glance.
- A study of endurance training in rats found molecular changes throughout the body that could help explain the beneficial effects of exercise on health.
- Large differences were seen between male and female rats, highlighting the need to include both women and men in exercise studies.

Exercise is one of the most beneficial activities that people can engage in. Regular exercise reduces the risk of heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and other health problems. It can even help people with many mental health conditions feel better.
But exactly how exercise exerts its positive effects hasn’t been well understood. And different people’s bodies can respond very differently to certain types of exercise, such as aerobic exercise or strength training.
Understanding how exercise impacts different organs at the molecular level could help health care providers better personalize exercise recommendations. It might also lead to drug therapies that could stimulate some of the beneficial effects of a workout for people who are physically unable to exercise.
To this end, researchers in the large, NIH-funded Molecular Transducers of Physical Activity Consortium (MoTrPAC) have been studying how endurance exercise and strength training affect both people and animals. The team is examining gene activity, protein alterations, immune cell function, metabolite levels, and numerous other measures of cell and tissue function. The first results, from rat studies of endurance exercise, were published on May 2, 2024, in Nature and several related journals.
Both male and female rats underwent progressive exercise training on a treadmill over an 8-week period. By the end of training, male rats had increased their aerobic capacity by 18%, and females by 16%. Tissue samples were collected from 18 different organs, plus the blood, during the training period and two days after the final bout of exercise. This let the researchers study the longer-term adaptations of the body to exercise.
Changes in gene activity, immune cell function, metabolism, and other cellular processes were seen in all the tissues studied, including those not previously known to be affected by exercise. The types of changes differed from tissue to tissue.
Many of the observed changes hinted at how exercise might protect certain organs against disease. For example, in the small intestines, exercise decreased the activity of certain genes associated with inflammatory bowel disease and reduced signs of inflammation in the gut. In the liver, exercise boosted molecular changes associated with improved tissue health and regeneration.
Some of the effects differed substantially between male and female rats. For example, in male rats, the eight weeks of endurance training reduced the amount of a type of body fat called subcutaneous white adipose tissue (scWAT). The same amount of exercise didn’t reduce the amount of scWAT in female rats. Instead, endurance exercise caused scWAT in female rats to alter its energy usage in ways that are beneficial to health. These and other results highlight the importance of including both women and men in exercise studies.
The researchers also compared gene activity changes in the rat studies with those from human samples taken from previous studies and found substantial overlap. They identified thousands of genes tied to human disease that were affected by endurance exercise. These analyses show how the MoTrPAC results from rats can be used to help guide future research in people.
“This is the first whole-organism map looking at the effects of training in multiple different organs,” says Dr. Steve Carr, a MoTrPAC investigator from the Broad Institute. “The resource produced will be enormously valuable, and has already produced many potentially novel biological insights for further exploration.”
Human trials are expected in the next few years. Information on participating can be found here .
—by Sharon Reynolds
Related Links
- Gut Microbes May Affect Motivation to Exercise
- Exercise-Induced Molecule Reduces Obesity in Mice
- Testing Ways to Encourage Exercise
- Hormone Links Exercise with Cognitive Benefits
- Exercise-Induced Protein May Reverse Age-Related Cognitive Decline
- Getting Active Later in Life Brings Benefits
- Get Active Together: Social Support Can Help Keep You Moving
- Personalized Exercise? How Biology Influences Fitness
- Maintain Your Muscle: Strength Training at Any Age
- Molecular Transducers of Physical Activity Consortium (MoTrPAC)
- Participating in MoTrPAC
References: Temporal dynamics of the multi-omic response to endurance exercise training. MoTrPAC Study Group; Lead Analysts; MoTrPAC Study Group. Nature . 2024 May;629(8010):174-183. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06877-w. Epub 2024 May 1. PMID: 38693412. Sexual dimorphism and the multi-omic response to exercise training in rat subcutaneous white adipose tissue. Many GM, Sanford JA, Sagendorf TJ, Hou Z, Nigro P, Whytock KL, Amar D, Caputo T, Gay NR, Gaul DA, Hirshman MF, Jimenez-Morales D, Lindholm ME, Muehlbauer MJ, Vamvini M, Bergman BC, Fernández FM, Goodyear LJ, Hevener AL, Ortlund EA, Sparks LM, Xia A, Adkins JN, Bodine SC, Newgard CB, Schenk S; MoTrPAC Study Group. Nat Metab . 2024 May 1. doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00959-9. Online ahead of print. PMID: 38693320. The impact of exercise on gene regulation in association with complex trait genetics. Vetr NG, Gay NR; MoTrPAC Study Group; Montgomery SB. Nat Commun . 2024 May 1;15(1):3346. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45966-w. PMID: 38693125.
Funding: NIH’s Office of the Director (OD), National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS), National Institute on Aging (NIA), National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), and National Library of Medicine (NLM); Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation; National Science Foundation (NSF).
Connect with Us
- More Social Media from NIH
- Systematic review update
- Open access
- Published: 21 June 2023
The impact of sports participation on mental health and social outcomes in adults: a systematic review and the ‘Mental Health through Sport’ conceptual model
- Narelle Eather ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6320-4540 1 , 2 ,
- Levi Wade ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4007-5336 1 , 3 ,
- Aurélie Pankowiak ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0178-513X 4 &
- Rochelle Eime ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8614-2813 4 , 5
Systematic Reviews volume 12 , Article number: 102 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
66k Accesses
13 Citations
305 Altmetric
Metrics details
Sport is a subset of physical activity that can be particularly beneficial for short-and-long-term physical and mental health, and social outcomes in adults. This study presents the results of an updated systematic review of the mental health and social outcomes of community and elite-level sport participation for adults. The findings have informed the development of the ‘Mental Health through Sport’ conceptual model for adults.
Nine electronic databases were searched, with studies published between 2012 and March 2020 screened for inclusion. Eligible qualitative and quantitative studies reported on the relationship between sport participation and mental health and/or social outcomes in adult populations. Risk of bias (ROB) was determined using the Quality Assessment Tool (quantitative studies) or Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (qualitative studies).
The search strategy located 8528 articles, of which, 29 involving adults 18–84 years were included for analysis. Data was extracted for demographics, methodology, and study outcomes, and results presented according to study design. The evidence indicates that participation in sport (community and elite) is related to better mental health, including improved psychological well-being (for example, higher self-esteem and life satisfaction) and lower psychological ill-being (for example, reduced levels of depression, anxiety, and stress), and improved social outcomes (for example, improved self-control, pro-social behavior, interpersonal communication, and fostering a sense of belonging). Overall, adults participating in team sport had more favorable health outcomes than those participating in individual sport, and those participating in sports more often generally report the greatest benefits; however, some evidence suggests that adults in elite sport may experience higher levels of psychological distress. Low ROB was observed for qualitative studies, but quantitative studies demonstrated inconsistencies in methodological quality.
Conclusions
The findings of this review confirm that participation in sport of any form (team or individual) is beneficial for improving mental health and social outcomes amongst adults. Team sports, however, may provide more potent and additional benefits for mental and social outcomes across adulthood. This review also provides preliminary evidence for the Mental Health through Sport model, though further experimental and longitudinal evidence is needed to establish the mechanisms responsible for sports effect on mental health and moderators of intervention effects. Additional qualitative work is also required to gain a better understanding of the relationship between specific elements of the sporting environment and mental health and social outcomes in adult participants.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The organizational structure of sport and the performance demands characteristic of sport training and competition provide a unique opportunity for participants to engage in health-enhancing physical activity of varied intensity, duration, and mode; and the opportunity to do so with other people as part of a team and/or club. Participation in individual and team sports have shown to be beneficial to physical, social, psychological, and cognitive health outcomes [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ]. Often, the social and mental health benefits facilitated through participation in sport exceed those achieved through participation in other leisure-time or recreational activities [ 8 , 9 , 10 ]. Notably, these benefits are observed across different sports and sub-populations (including youth, adults, older adults, males, and females) [ 11 ]. However, the evidence regarding sports participation at the elite level is limited, with available research indicating that elite athletes may be more susceptible to mental health problems, potentially due to the intense mental and physical demands placed on elite athletes [ 12 ].
Participation in sport varies across the lifespan, with children representing the largest cohort to engage in organized community sport [ 13 ]. Across adolescence and into young adulthood, dropout from organized sport is common, and especially for females [ 14 , 15 , 16 ], and adults are shifting from organized sports towards leisure and fitness activities, where individual activities (including swimming, walking, and cycling) are the most popular [ 13 , 17 , 18 , 19 ]. Despite the general decline in sport participation with age [ 13 ], the most recent (pre-COVID) global data highlights that a range of organized team sports (such as, basketball, netball volleyball, and tennis) continue to rank highly amongst adult sport participants, with soccer remaining a popular choice across all regions of the world [ 13 ]. It is encouraging many adults continue to participate in sport and physical activities throughout their lives; however, high rates of dropout in youth sport and non-participation amongst adults means that many individuals may be missing the opportunity to reap the potential health benefits associated with participation in sport.
According to the World Health Organization, mental health refers to a state of well-being and effective functioning in which an individual realizes his or her own abilities, is resilient to the stresses of life, and is able to make a positive contribution to his or her community [ 20 ]. Mental health covers three main components, including psychological, emotional and social health [ 21 ]. Further, psychological health has two distinct indicators, psychological well-being (e.g., self-esteem and quality of life) and psychological ill-being (e.g., pre-clinical psychological states such as psychological difficulties and high levels of stress) [ 22 ]. Emotional well-being describes how an individual feels about themselves (including life satisfaction, interest in life, loneliness, and happiness); and social well–being includes an individual’s contribution to, and integration in society [ 23 ].
Mental illnesses are common among adults and incidence rates have remained consistently high over the past 25 years (~ 10% of people affected globally) [ 24 ]. Recent statistics released by the World Health Organization indicate that depression and anxiety are the most common mental disorders, affecting an estimated 264 million people, ranking as one of the main causes of disability worldwide [ 25 , 26 ]. Specific elements of social health, including high levels of isolation and loneliness among adults, are now also considered a serious public health concern due to the strong connections with ill-health [ 27 ]. Participation in sport has shown to positively impact mental and social health status, with a previous systematic review by Eime et al. (2013) indicated that sports participation was associated with lower levels of perceived stress, and improved vitality, social functioning, mental health, and life satisfaction [ 1 ]. Based on their findings, the authors developed a conceptual model (health through sport) depicting the relationship between determinants of adult sports participation and physical, psychological, and social health benefits of participation. In support of Eime’s review findings, Malm and colleagues (2019) recently described how sport aids in preventing or alleviating mental illness, including depressive symptoms and anxiety or stress-related disease [ 7 ]. Andersen (2019) also highlighted that team sports participation is associated with decreased rates of depression and anxiety [ 11 ]. In general, these reviews report stronger effects for sports participation compared to other types of physical activity, and a dose–response relationship between sports participation and mental health outcomes (i.e., higher volume and/or intensity of participation being associated with greater health benefits) when adults participate in sports they enjoy and choose [ 1 , 7 ]. Sport is typically more social than other forms of physical activity, including enhanced social connectedness, social support, peer bonding, and club support, which may provide some explanation as to why sport appears to be especially beneficial to mental and social health [ 28 ].
Thoits (2011) proposed several potential mechanisms through which social relationships and social support improve physical and psychological well-being [ 29 ]; however, these mechanisms have yet to be explored in the context of sports participation at any level in adults. The identification of the mechanisms responsible for such effects may direct future research in this area and help inform future policy and practice in the delivery of sport to enhance mental health and social outcomes amongst adult participants. Therefore, the primary objective of this review was to examine and synthesize all research findings regarding the relationship between sports participation, mental health and social outcomes at the community and elite level in adults. Based on the review findings, the secondary objective was to develop the ‘Mental Health through Sport’ conceptual model.
This review has been registered in the PROSPERO systematic review database and assigned the identifier: CRD42020185412. The conduct and reporting of this systematic review also follows the Preferred Reporting for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [ 30 ] (PRISMA flow diagram and PRISMA Checklist available in supplementary files ). This review is an update of a previous review of the same topic [ 31 ], published in 2012.
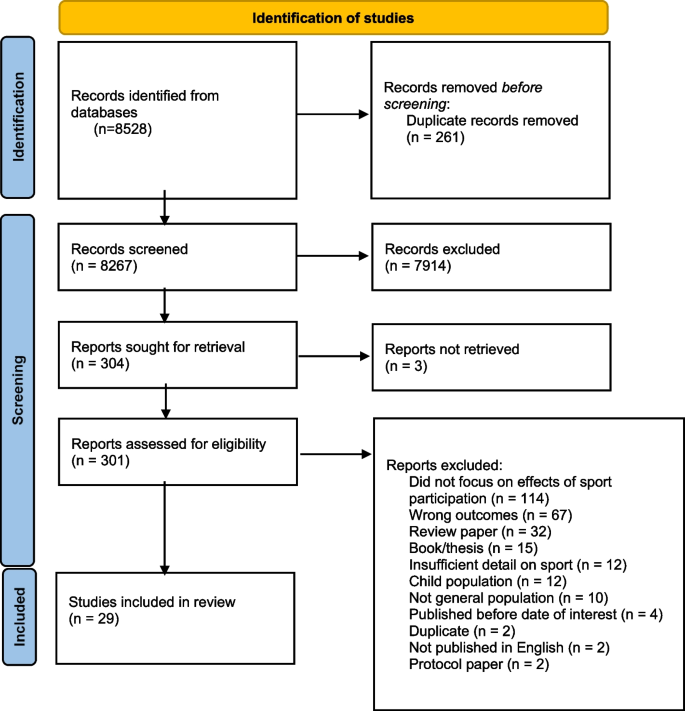
Identification of studies
Nine electronic databases (CINAHL, Cochrane Library, Google Scholar, Informit, Medline, PsychINFO, Psychology and Behavioural Sciences Collection, Scopus, and SPORTDiscus) were systematically searched for relevant records published from 2012 to March 10, 2020. The following key terms were developed by all members of the research team (and guided by previous reviews) and entered into these databases by author LW: sport* AND health AND value OR benefit* OR effect* OR outcome* OR impact* AND psych* OR depress* OR stress OR anxiety OR happiness OR mood OR ‘quality of life’ OR ‘social health’ OR ‘social relation*’ OR well* OR ‘social connect*’ OR ‘social functioning’ OR ‘life satisfac*’ OR ‘mental health’ OR social OR sociolog* OR affect* OR enjoy* OR fun. Where possible, Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) were also used.
Criteria for inclusion/exclusion
The titles of studies identified using this method were screened by LW. Abstract and full text of the articles were reviewed independently by LW and NE. To be included in the current review, each study needed to meet each of the following criteria: (1) published in English from 2012 to 2020; (2) full-text available online; (3) original research or report published in a peer-reviewed journal; (4) provides data on the psychological or social effects of participation in sport (with sport defined as a subset of exercise that can be undertaken individually or as a part of a team, where participants adhere to a common set of rules or expectations, and a defined goal exists); (5) the population of interest were adults (18 years and older) and were apparently healthy. All papers retrieved in the initial search were assessed for eligibility by title and abstract. In cases where a study could not be included or excluded via their title and abstract, the full text of the article was reviewed independently by two of the authors.
Data extraction
For the included studies, the following data was extracted independently by LW and checked by NE using a customized Google Docs spreadsheet: author name, year of publication, country, study design, aim, type of sport (e.g., tennis, hockey, team, individual), study conditions/comparisons, sample size, where participants were recruited from, mean age of participants, measure of sports participation, measure of physical activity, psychological and/or social outcome/s, measure of psychological and/or social outcome/s, statistical method of analysis, changes in physical activity or sports participation, and the psychological and/or social results.
Risk of bias (ROB) assessment
A risk of bias was performed by LW and AP independently using the ‘Quality Assessment Tool for Observational Cohort and Cross-Sectional Studies’ OR the ‘Quality Assessment of Controlled Intervention Studies’ for the included quantitative studies, and the ‘Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) Checklist for the included qualitative studies [ 32 , 33 ]. Any discrepancies in the ROB assessments were discussed between the two reviewers, and a consensus reached.
The search yielded 8528 studies, with a total of 29 studies included in the systematic review (Fig. 1 ). Tables 1 and 2 provide a summary of the included studies. The research included adults from 18 to 84 years old, with most of the evidence coming from studies targeting young adults (18–25 years). Study samples ranged from 14 to 131, 962, with the most reported psychological outcomes being self-rated mental health ( n = 5) and depression ( n = 5). Most studies did not investigate or report the link between a particular sport and a specific mental health or social outcome; instead, the authors’ focused on comparing the impact of sport to physical activity, and/or individual sports compared to team sports. The results of this review are summarized in the following section, with findings presented by study design (cross-sectional, experimental, and longitudinal).
Flow of studies through the review process
Effects of sports participation on psychological well-being, ill-being, and social outcomes
Cross-sectional evidence.
This review included 14 studies reporting on the cross-sectional relationship between sports participation and psychological and/or social outcomes. Sample sizes range from n = 414 to n = 131,962 with a total of n = 239,394 adults included across the cross-sectional studies.
The cross-sectional evidence generally supports that participation in sport, and especially team sports, is associated with greater mental health and psychological wellbeing in adults compared to non-participants [ 36 , 59 ]; and that higher frequency of sports participation and/or sport played at a higher level of competition, are also linked to lower levels of mental distress in adults . This was not the case for one specific study involving ice hockey players aged 35 and over, with Kitchen and Chowhan (2016) Kitchen and Chowhan (2016) reporting no relationship between participation in ice hockey and either mental health, or perceived life stress [ 54 ]. There is also some evidence to support that previous participation in sports (e.g., during childhood or young adulthood) is linked to better mental health outcomes later in life, including improved mental well-being and lower mental distress [ 59 ], even after controlling for age and current physical activity.
Compared to published community data for adults, elite or high-performance adult athletes demonstrated higher levels of body satisfaction, self-esteem, and overall life satisfaction [ 39 ]; and reported reduced tendency to respond to distress with anger and depression. However, rates of psychological distress were higher in the elite sport cohort (compared to community norms), with nearly 1 in 5 athletes reporting ‘high to very high’ distress, and 1 in 3 reporting poor mental health symptoms at a level warranting treatment by a health professional in one study ( n = 749) [ 39 ].
Four studies focused on the associations between physical activity and sports participation and mental health outcomes in older adults. Physical activity was associated with greater quality of life [ 56 ], with the relationship strongest for those participating in sport in middle age, and for those who cycled in later life (> 65) [ 56 ]. Group physical activities (e.g., walking groups) and sports (e.g., golf) were also significantly related to excellent self-rated health, low depressive symptoms, high health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and a high frequency of laughter in males and females [ 60 , 61 ]. No participation or irregular participation in sport was associated with symptoms of mild to severe depression in older adults [ 62 ].
Several cross-sectional studies examined whether the effects of physical activity varied by type (e.g., total physical activity vs. sports participation). In an analysis of 1446 young adults (mean age = 18), total physical activity, moderate-to-vigorous physical activity, and team sport were independently associated with mental health [ 46 ]. Relative to individual physical activity, after adjusting for covariates and moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA), only team sport was significantly associated with improved mental health. Similarly, in a cross-sectional analysis of Australian women, Eime, Harvey, Payne (2014) reported that women who engaged in club and team-based sports (tennis or netball) reported better mental health and life satisfaction than those who engaged in individual types of physical activity [ 47 ]. Interestingly, there was no relationship between the amount of physical activity and either of these outcomes, suggesting that other qualities of sports participation contribute to its relationship to mental health and life satisfaction. There was also some evidence to support a relationship between exercise type (ball sports, aerobic activity, weightlifting, and dancing), and mental health amongst young adults (mean age 22 years) [ 48 ], with ball sports and dancing related to fewer symptoms of depression in students with high stress; and weightlifting related to fewer depressive symptoms in weightlifters exhibiting low stress.
Longitudinal evidence
Eight studies examined the longitudinal relationship between sports participation and either mental health and/or social outcomes. Sample sizes range from n = 113 to n = 1679 with a total of n = 7022 adults included across the longitudinal studies.
Five of the included longitudinal studies focused on the relationship between sports participation in childhood or adolescence and mental health in young adulthood. There is evidence that participation in sport in high-school is protective of future symptoms of anxiety (including panic disorder, generalised anxiety disorder, social phobia, and agoraphobia) [ 42 ]. Specifically, after controlling for covariates (including current physical activity), the number of years of sports participation in high school was shown to be protective of symptoms of panic and agoraphobia in young adulthood, but not protective of symptoms of social phobia or generalized anxiety disorder [ 42 ]. A comparison of individual or team sports participation also revealed that participation in either context was protective of panic disorder symptoms, while only team sport was protective of agoraphobia symptoms, and only individual sport was protective of social phobia symptoms. Furthermore, current and past sports team participation was shown to negatively relate to adult depressive symptoms [ 43 ]; drop out of sport was linked to higher depressive symptoms in adulthood compared to those with maintained participation [ 9 , 22 , 63 ]; and consistent participation in team sports (but not individual sport) in adolescence was linked to higher self-rated mental health, lower perceived stress and depressive symptoms, and lower depression scores in early adulthood [ 53 , 58 ].
Two longitudinal studies [ 35 , 55 ], also investigated the association between team and individual playing context and mental health. Dore and colleagues [ 35 ] reported that compared to individual activities, being active in informal groups (e.g., yoga, running groups) or team sports was associated with better mental health, fewer depressive symptoms and higher social connectedness – and that involvement in team sports was related to better mental health regardless of physical activity volume. Kim and James [ 55 ] discovered that sports participation led to both short and long-term improvements in positive affect and life satisfaction.
A study on social outcomes related to mixed martial-arts (MMA) and Brazilian jiu-jitsu (BJJ) showed that both sports improved practitioners’ self-control and pro-social behavior, with greater improvements seen in the BJJ group [ 62 ]. Notably, while BJJ reduced participants’ reported aggression, there was a slight increase in MMA practitioners, though it is worth mentioning that individuals who sought out MMA had higher levels of baseline aggression.
Experimental evidence
Six of the included studies were experimental or quasi-experimental. Sample sizes ranged from n = 28 to n = 55 with a total of n = 239 adults included across six longitudinal studies. Three studies involved a form of martial arts (such as judo and karate) [ 45 , 51 , 52 ], one involved a variety of team sports (such as netball, soccer, and cricket) [ 34 ], and the remaining two focused on badminton [ 57 ] and handball [ 49 ].
Brinkley and colleagues [ 34 ] reported significant effects on interpersonal communication (but not vitality, social cohesion, quality of life, stress, or interpersonal relationships) for participants ( n = 40) engaging in a 12-week workplace team sports intervention. Also using a 12-week intervention, Hornstrup et al. [ 49 ] reported a significant improvement in mental energy (but not well-being or anxiety) in young women (mean age = 24; n = 28) playing in a handball program. Patterns et al. [ 57 ] showed that in comparison to no exercise, participation in an 8-week badminton or running program had no significant improvement on self-esteem, despite improvements in perceived and actual fitness levels.
Three studies examined the effect of martial arts on the mental health of older adults (mean ages 79 [ 52 ], 64 [ 51 ], and 70 [ 45 ] years). Participation in Karate-Do had positive effects on overall mental health, emotional wellbeing, depression and anxiety when compared to other activities (physical, cognitive, mindfulness) and a control group [ 51 , 52 ]. Ciaccioni et al. [ 45 ] found that a Judo program did not affect either the participants’ mental health or their body satisfaction, citing a small sample size, and the limited length of the intervention as possible contributors to the findings.
Qualitative evidence
Three studies interviewed current or former sports players regarding their experiences with sport. Chinkov and Holt [ 41 ] reported that jiu-jitsu practitioners (mean age 35 years) were more self-confident in their lives outside of the gym, including improved self-confidence in their interactions with others because of their training. McGraw and colleagues [ 37 ] interviewed former and current National Football League (NFL) players and their families about its impact on the emotional and mental health of the players. Most of the players reported that their NFL career provided them with social and emotional benefits, as well as improvements to their self-esteem even after retiring. Though, despite these benefits, almost all the players experienced at least one mental health challenge during their career, including depression, anxiety, or difficulty controlling their temper. Some of the players and their families reported that they felt socially isolated from people outside of the national football league.
Through a series of semi-structured interviews and focus groups, Thorpe, Anders [ 40 ] investigated the impact of an Aboriginal male community sporting team on the health of its players. The players reported they felt a sense of belonging when playing in the team, further noting that the social and community aspects were as important as the physical health benefits. Participating in the club strengthened the cultural identity of the players, enhancing their well-being. The players further noted that participation provided them with enjoyment, stress relief, a sense of purpose, peer support, and improved self-esteem. Though they also noted challenges, including the presence of racism, community conflict, and peer-pressure.
Quality of studies
Full details of our risk of bias (ROB) results are provided in Supplementary Material A . Of the three qualitative studies assessed using the Critical Appraisal Skills Program (CASP), all three were deemed to have utilised and reported appropriate methodological standards on at least 8 of the 10 criteria. Twenty studies were assessed using the Quality Assessment Tool for Observational Cohort and Cross-Sectional Studies, with all studies clearly reporting the research question/s or objective/s and study population. However, only four studies provided a justification for sample size, and less than half of the studies met quality criteria for items 6, 7, 9, or 10 (and items 12 and 13 were largely not applicable). Of concern, only four of the observational or cohort studies were deemed to have used clearly defined, valid, and reliable exposure measures (independent variables) and implemented them consistently across all study participants. Six studies were assessed using the Quality Assessment of Controlled Intervention Studies, with three studies described as a randomized trial (but none of the three reported a suitable method of randomization, concealment of treatment allocation, or blinding to treatment group assignment). Three studies showed evidence that study groups were similar at baseline for important characteristics and an overall drop-out rate from the study < 20%. Four studies reported high adherence to intervention protocols (with two not reporting) and five demonstrated that.study outcomes were assessed using valid and reliable measures and implemented consistently across all study participants. Importantly, researchers did not report or have access to validated instruments for assessing sport participation or physical activity amongst adults, though most studies provided psychometrics for their mental health outcome measure/s. Only one study reported that the sample size was sufficiently powered to detect a difference in the main outcome between groups (with ≥ 80% power) and that all participants were included in the analysis of results (intention-to-treat analysis). In general, the methodological quality of the six randomised studies was deemed low.
Initially, our discussion will focus on the review findings regarding sports participation and well-being, ill-being, and psychological health. However, the heterogeneity and methodological quality of the included research (especially controlled trials) should be considered during the interpretation of our results. Considering our findings, the Mental Health through Sport conceptual model for adults will then be presented and discussed and study limitations outlined.
Sports participation and psychological well-being
In summary, the evidence presented here indicates that for adults, sports participation is associated with better overall mental health [ 36 , 46 , 47 , 59 ], mood [ 56 ], higher life satisfaction [ 39 , 47 ], self-esteem [ 39 ], body satisfaction [ 39 ], HRQoL [ 60 ], self-rated health [ 61 ], and frequency of laughter [ 61 ]. Sports participation has also shown to be predictive of better psychological wellbeing over time [ 35 , 53 ], higher positive affect [ 55 ], and greater life satisfaction [ 55 ]. Furthermore, higher frequency of sports participation and/or sport played at a higher level of competition, have been linked to lower levels of mental distress, higher levels of body satisfaction, self-esteem, and overall life satisfaction in adults [ 39 ].
Despite considerable heterogeneity of sports type, cross-sectional and experimental research indicate that team-based sports participation, compared to individual sports and informal group physical activity, has a more positive effect on mental energy [ 49 ], physical self-perception [ 57 ], and overall psychological health and well-being in adults, regardless of physical activity volume [ 35 , 46 , 47 ]. And, karate-do benefits the subjective well-being of elderly practitioners [ 51 , 52 ]. Qualitative research in this area has queried participants’ experiences of jiu-jitsu, Australian football, and former and current American footballers. Participants in these sports reported that their participation was beneficial for psychological well-being [ 37 , 40 , 41 ], improved self-esteem [ 37 , 40 , 41 ], and enjoyment [ 37 ].
Sports participation and psychological ill-being
Of the included studies, n = 19 examined the relationship between participating in sport and psychological ill-being. In summary, there is consistent evidence that sports participation is related to lower depression scores [ 43 , 48 , 61 , 62 ]. There were mixed findings regarding psychological stress, where participation in childhood (retrospectively assessed) was related to lower stress in young adulthood [ 41 ], but no relationship was identified between recreational hockey in adulthood and stress [ 54 ]. Concerning the potential impact of competing at an elite level, there is evidence of higher stress in elite athletes compared to community norms [ 39 ]. Further, there is qualitative evidence that many current or former national football league players experienced at least one mental health challenge, including depression, anxiety, difficulty controlling their temper, during their career [ 37 ].
Evidence from longitudinal research provided consistent evidence that participating in sport in adolescence is protective of symptoms of depression in young adulthood [ 43 , 53 , 58 , 63 ], and further evidence that participating in young adulthood is related to lower depressive symptoms over time (6 months) [ 35 ]. Participation in adolescence was also protective of manifestations of anxiety (panic disorder and agoraphobia) and stress in young adulthood [ 42 ], though participation in young adulthood was not related to a more general measure of anxiety [ 35 ] nor to changes in negative affect [ 55 ]). The findings from experimental research were mixed. Two studies examined the effect of karate-do on markers of psychological ill-being, demonstrating its capacity to reduce anxiety [ 52 ], with some evidence of its effectiveness on depression [ 51 ]. The other studies examined small-sided team-based games but showed no effect on stress or anxiety [ 34 , 49 ]. Most studies did not differentiate between team and individual sports, though one study found that adolescents who participated in team sports (not individual sports) in secondary school has lower depression scores in young adulthood [ 58 ].
Sports participation and social outcomes
Seven of the included studies examined the relationship between sports participation and social outcomes. However, very few studies examined social outcomes or tested a social outcome as a potential mediator of the relationship between sport and mental health. It should also be noted that this body of evidence comes from a wide range of sport types, including martial arts, professional football, and workplace team-sport, as well as different methodologies. Taken as a whole, the evidence shows that participating in sport is beneficial for several social outcomes, including self-control [ 50 ], pro-social behavior [ 50 ], interpersonal communication [ 34 ], and fostering a sense of belonging [ 40 ]. Further, there is evidence that group activity, for example team sport or informal group activity, is related to higher social connectedness over time, though analyses showed that social connectedness was not a mediator for mental health [ 35 ].
There were conflicting findings regarding social effects at the elite level, with current and former NFL players reporting that they felt socially isolated during their career [ 37 ], whilst another study reported no relationship between participation at the elite level and social dysfunction [ 39 ]. Conversely, interviews with a group of indigenous men revealed that they felt as though participating in an all-indigenous Australian football team provided them with a sense of purpose, and they felt as though the social aspect of the game was as important as the physical benefits it provides [ 40 ].
Mental health through sport conceptual model for adults
The ‘Health through Sport’ model provides a depiction of the determinants and benefits of sports participation [ 31 ]. The model recognises that the physical, mental, and social benefits of sports participation vary by the context of sport (e.g., individual vs. team, organized vs. informal). To identify the elements of sport which contribute to its effect on mental health outcomes, we describe the ‘Mental Health through Sport’ model (Fig. 2 ). The model proposes that the social and physical elements of sport each provide independent, and likely synergistic contributions to its overall influence on mental health.
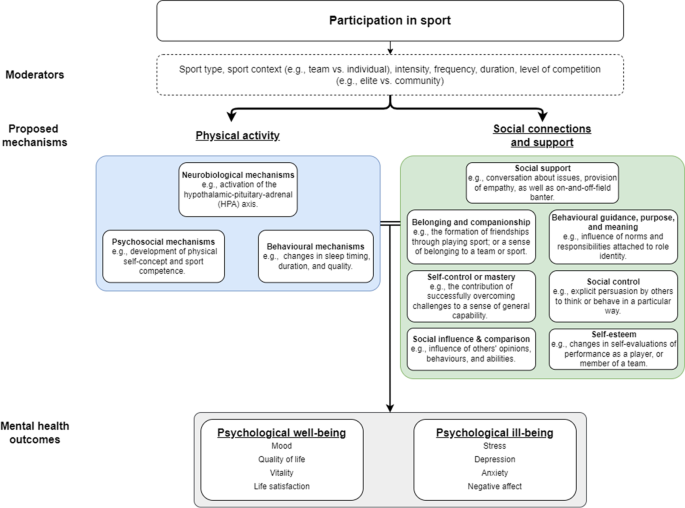
The Mental Health through Sport conceptual model
The model describes two key pathways through which sport may influence mental health: physical activity, and social relationships and support. Several likely moderators of this effect are also provided, including sport type, intensity, frequency, context (team vs. individual), environment (e.g., indoor vs. outdoor), as well as the level of competition (e.g., elite vs. amateur).
The means by which the physical activity component of sport may influence mental health stems from the work of Lubans et al., who propose three key groups of mechanisms: neurobiological, psychosocial, and behavioral [ 64 ]. Processes whereby physical activity may enhance psychological outcomes via changes in the structural and functional composition of the brain are referred to as neurobiological mechanisms [ 65 , 66 ]. Processes whereby physical activity provides opportunities for the development of self-efficacy, opportunity for mastery, changes in self-perceptions, the development of independence, and for interaction with the environment are considered psychosocial mechanisms. Lastly, processes by which physical activity may influence behaviors which ultimately affect psychological health, including changes in sleep duration, self-regulation, and coping skills, are described as behavioral mechanisms.
Playing sport offers the opportunity to form relationships and to develop a social support network, both of which are likely to influence mental health. Thoits [ 29 ] describes 7 key mechanisms by which social relationships and support may influence mental health: social influence/social comparison; social control; role-based purpose and meaning (mattering); self-esteem; sense of control; belonging and companionship; and perceived support availability [ 29 ]. These mechanisms and their presence within a sporting context are elaborated below.
Subjective to the attitudes and behaviors of individuals in a group, social influence and comparison may facilitate protective or harmful effects on mental health. Participants in individual or team sport will be influenced and perhaps steered by the behaviors, expectations, and norms of other players and teams. When individual’s compare their capabilities, attitudes, and values to those of other participants, their own behaviors and subsequent health outcomes may be affected. When others attempt to encourage or discourage an individual to adopt or reject certain health practices, social control is displayed [ 29 ]. This may evolve as strategies between players (or between players and coach) are discussion and implemented. Likewise, teammates may try to motivate each another during a match to work harder, or to engage in specific events or routines off-field (fitness programs, after game celebrations, attending club events) which may impact current and future physical and mental health.
Sport may also provide behavioral guidance, purpose, and meaning to its participants. Role identities (positions within a social structure that come with reciprocal obligations), often formed as a consequence of social ties formed through sport. Particularly in team sports, participants come to understand they form an integral part of the larger whole, and consequently, they hold certain responsibility in ensuring the team’s success. They have a commitment to the team to, train and play, communicate with the team and a potential responsibility to maintain a high level of health, perform to their capacity, and support other players. As a source of behavioral guidance and of purpose and meaning in life, these identities are likely to influence mental health outcomes amongst sport participants.
An individual’s level of self-esteem may be affected by the social relationships and social support provided through sport; with improved perceptions of capability (or value within a team) in the sporting domain likely to have positive impact on global self-esteem and sense of worth [ 64 ]. The unique opportunities provided through participation in sport, also allow individuals to develop new skills, overcome challenges, and develop their sense of self-control or mastery . Working towards and finding creative solutions to challenges in sport facilitates a sense of mastery in participants. This sense of mastery may translate to other areas of life, with individual’s developing the confidence to cope with varied life challenges. For example, developing a sense of mastery regarding capacity to formulate new / creative solutions when taking on an opponent in sport may result in greater confidence to be creative at work. Social relationships and social support provided through sport may also provide participants with a source of belonging and companionship. The development of connections (on and off the field) to others who share common interests, can build a sense of belonging that may mediate improvements in mental health outcomes. Social support is often provided emotionally during expressions of trust and care; instrumentally via tangible assistance; through information such as advice and suggestions; or as appraisal such feedback. All forms of social support provided on and off the field contribute to a more generalised sense of perceived support that may mediate the effect of social interaction on mental health outcomes.
Participation in sport may influence mental health via some combination of the social mechanisms identified by Thoits, and the neurobiological, psychosocial, and behavioral mechanisms stemming from physical activity identified by Lubans [ 29 , 64 ]. The exact mechanisms through which sport may confer psychological benefit is likely to vary between sports, as each sport varies in its physical and social requirements. One must also consider the social effects of sports participation both on and off the field. For instance, membership of a sporting team and/or club may provide a sense of identity and belonging—an effect that persists beyond the immediacy of playing the sport and may have a persistent effect on their psychological health. Furthermore, the potential for team-based activity to provide additional benefit to psychological outcomes may not just be attributable to the differences in social interactions, there are also physiological differences in the requirements for sport both within (team vs. team) and between (team vs. individual) categories that may elicit additional improvements in psychological outcomes. For example, evidence supports that exercise intensity moderates the relationship between physical activity and several psychological outcomes—supporting that sports performed at higher intensity will be more beneficial for psychological health.
Limitations and recommendations
There are several limitations of this review worthy of consideration. Firstly, amongst the included studies there was considerable heterogeneity in study outcomes and study methodology, and self-selection bias (especially in non-experimental studies) is likely to influence study findings and reduce the likelihood that study participants and results are representative of the overall population. Secondly, the predominately observational evidence included in this and Eime’s prior review enabled us to identify the positive relationship between sports participation and social and psychological health (and examine directionality)—but more experimental and longitudinal research is required to determine causality and explore potential mechanisms responsible for the effect of sports participation on participant outcomes. Additional qualitative work would also help researchers gain a better understanding of the relationship between specific elements of the sporting environment and mental health and social outcomes in adult participants. Thirdly, there were no studies identified in the literature where sports participation involved animals (such as equestrian sports) or guns (such as shooting sports). Such studies may present novel and important variables in the assessment of mental health benefits for participants when compared to non-participants or participants in sports not involving animals/guns—further research is needed in this area. Our proposed conceptual model also identifies several pathways through which sport may lead to improvements in mental health—but excludes some potentially negative influences (such as poor coaching behaviors and injury). And our model is not designed to capture all possible mechanisms, creating the likelihood that other mechanisms exist but are not included in this review. Additionally, an interrelationship exits between physical activity, mental health, and social relationships, whereby changes in one area may facilitate changes in the other/s; but for the purpose of this study, we have focused on how the physical and social elements of sport may mediate improvements in psychological outcomes. Consequently, our conceptual model is not all-encompassing, but designed to inform and guide future research investigating the impact of sport participation on mental health.
The findings of this review endorse that participation in sport is beneficial for psychological well-being, indicators of psychological ill-being, and social outcomes in adults. Furthermore, participation in team sports is associated with better psychological and social outcomes compared to individual sports or other physical activities. Our findings support and add to previous review findings [ 1 ]; and have informed the development of our ‘Mental Health through Sport’ conceptual model for adults which presents the potential mechanisms by which participation in sport may affect mental health.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Eime RM, Young JA, Harvey JT, Charity MJ, Payne WR. A systematic review of the psychological and social benefits of participation in sport for adults: informing development of a conceptual model of health through sport. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2013;10:135.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ishihara T, Nakajima T, Yamatsu K, Okita K, Sagawa M, Morita N. Relationship of participation in specific sports to academic performance in adolescents: a 2-year longitudinal study. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020.
Cope E, Bailey R, Pearce G. Why do children take part in, and remain involved in sport?: implications for children’s sport coaches. Int J Coach Sci. 2013;7:55–74.
Google Scholar
Harrison PA, Narayan G. Differences in behavior, psychological factors, and environmental factors associated with participation in school sports and other activities in adolescence. J Sch Health. 2003;73(3):113–20.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Allender S, Cowburn G, Foster C. Understanding particpation in sport and physical activity among children and adults: a review of qualitative studies. Health Educ Res. 2006;21(6):826–35.
Adachi P, Willoughby T. It’s not how much you play, but how much you enjoy the game: The longitudinal associations between adolescents’ self-esteem and the frequency versus enjoyment of involvement in sports. J Youth Adolesc. 2014;43(1):137–45.
Malm C, Jakobsson J, Isaksson A. Physical activity and sports-real health benefits: a review with insight into the public health of Sweden. Sports (Basel, Switzerland). 2019;7(5):127.
PubMed Google Scholar
Mills K, Dudley D, Collins NJ. Do the benefits of participation in sport and exercise outweigh the negatives? An academic review. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2019;33(1):172–87.
Howie EK, Guagliano JM, Milton K, Vella SA, Gomersall SR,Kolbe-Alexander TL, et al. Ten research priorities related to youth sport, physical activity, and health. 2020;17(9):920.
Vella SA, Swann C, Allen MS, Schweickle MJ, Magee CA. Bidirectional associations between sport involvement and mental health in adolescence. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2017;49(4):687–94.
Andersen MH, Ottesen L, Thing LF. The social and psychological health outcomes of team sport participation in adults: An integrative review of research. Scand J Public Health. 2019;47(8):832–50.
Rice SM, Purcell R, De Silva S, Mawren D, McGorry PD, Parker AG. The mental health of elite athletes: a narrative systematic review. Sports medicine (Auckland, NZ). 2016;46(9):1333–53.
Article Google Scholar
Hulteen RM, Smith JJ, Morgan PJ, Barnett LM, Hallal PC, Colyvas K, et al. Global participation in sport and leisure-time physical activities: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prev Med. 2017;95:14–25.
Eime RM, Harvey J, Charity M, Westerbeek H. Longitudinal Trends in Sport Participation and Retention of Women and Girls. Front Sports Act Living. 2020;2:39.
Brooke HL, Corder K, Griffin SJ, van Sluijs EMF. Physical activity maintenance in the transition to adolescence: a longitudinal study of the roles of sport and lifestyle activities in british youth. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(2): e89028.
Coll CVN, Knuth AG, Bastos JP, Hallal PC, Bertoldi AD. Time trends of physical activity among Brazilian adolescents over a 7-year period. J Adolesc Health. 2014;54:209–13.
Klostermann C, Nagel S. Changes in German sport participation: Historical trends in individual sports. Int Rev Sociol Sport. 2012;49:609–34.
Eime RM, Harvey J, Charity M. Sport participation settings: where and “how” do Australians play sport? BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1344.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lim SY, Warner S, Dixon M, Berg B, Kim C, Newhouse-Bailey M. Sport Participation Across National Contexts: A Multilevel Investigation of Individual and Systemic Influences on Adult Sport Participation. Eur Sport Manag Q. 2011;11(3):197–224.
World Health Organisation. Mental Health Action Plan 2013–2020. Geneva: World Health Orgnaisation; 2013.
Keyes C. Bridging Occupational, Organizational and Public Health. Netherlands: Springer Dordrecht; 2014.
Ryff C, Love G, Urry H, Muller D, Rosenkranz M, Friedman E, et al. Psychological well-being and ill-being: Do they have distinct or mirrored biological correlates? Psychother Psychosom. 2006;75:85–95.
Australian Government. Social and emotional wellbeing: Development of a children’s headline indicator information paper. Canberra: Australian Institute of Health and Welfare; 2013.
Global Burden of Disease Injury IP. Collaborators, Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789–858.
World Health Organisation. Mental disorders: Fact sheet 2019 [Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-disorders .
Mental Health [Internet]. 2018 [cited 12 March 2021]. Available from: https://ourworldindata.org/mental-health ' [Online Resource].
Newman MG, Zainal NH. The value of maintaining social connections for mental health in older people. The Lancet Public Health. 2020;5(1):e12–3.
Eime RM, Harvey JT, Brown WJ, Payne WR. Does sports club participation contribute to health-related quality of life? Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42(5):1022–8.
Thoits PA. Mechanisms linking social ties and support to physical and mental health. J Health Soc Behav. 2011;52(2):145–61.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 2021;18(3): e1003583.
Eime RM, Young JA, Harvey JT, Charity MJ, Payne WR. A systematic review of the psychological and social benefits of participation in sport for adults: informing development of a conceptual model of health through sport. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2013;10(1):135.
Critical Appraisal Skills Programme. CASP Qualitative Studies Checklist2019 1/12/2021]. Available from: https://casp-uk.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/CASP-Qualitative-Checklist-2018.pdf .
National Institutes from Health. Quality assessment tool for observational cohort and cross-sectional studies 2014 [Available from: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools .
Brinkley A, McDermott H, Grenfell-Essam R. It’s time to start changing the game: a 12-week workplace team sport intervention study. Sports Med Open. 2017;3(1):30–41.
Doré I, O’Loughlin JL, Schnitzer ME, Datta GD, Fournier L. The longitudinal association between the context of physical activity and mental health in early adulthood. Ment Health Phys Act. 2018;14:121–30.
Marlier M, Van Dyck D, Cardon G, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Babiak K, Willem A. Interrelation of sport participation, physical activity, social capital and mental health in disadvantaged communities: A sem-analysis. PLoS ONE [Internet]. 2015; 10(10):[e0140196 p.]. Available from: http://ezproxy.newcastle.edu.au/login?url=http://ezproxy.newcastle.edu.au/login?url=http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&CSC=Y&NEWS=N&PAGE=fulltext&D=med12&AN=26451731 .
McGraw SA, Deubert CR, Lynch HF, Nozzolillo A, Taylor L, Cohen I. Life on an emotional roller coaster: NFL players and their family members’ perspectives on player mental health. J Clin Sport Psychol. 2018;12(3):404–31.
Mickelsson T. Modern unexplored martial arts – what can mixed martial arts and Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu do for youth development?. Eur J Sport Sci. 2020;20(3):386–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/17461391.2019.1629180 .
Purcell R, Rice S, Butterworth M, Clements M. Rates and Correlates of Mental Health Symptoms in Currently Competing Elite Athletes from the Australian National High-Performance Sports System. Sports Med. 2020.
Thorpe A, Anders W, Rowley K. The community network: an Aboriginal community football club bringing people together. Aust J Prim Health. 2014;20(4):356–64.
Appelqvist-Schmidlechner K, Vaara J, Hakkinen A, Vasankari T, Makinen J, Mantysaari M, et al. Relationships between youth sports participation and mental health in young adulthood among Finnish males. Am J Health Promot. 2018;32(7):1502–9.
Ashdown-Franks G, Sabiston CM, Solomon-Krakus S, O’Loughlin JL. Sport participation in high school and anxiety symptoms in young adulthood. Ment Health Phys Act. 2017;12:19–24.
Brunet J, Sabiston CM, Chaiton M, Barnett TA, O’Loughlin E, Low NC, et al. The association between past and current physical activity and depressive symptoms in young adults: a 10-year prospective study. Ann Epidemiol. 2013;23(1):25–30.
Chinkov AE, Holt NL. Implicit transfer of life skills through participation in Brazilian Jiu-jitsu. J Appl Sport Psychol. 2016;28(2):139–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/10413200.2015.1086447 .
Ciaccioni S, Capranica L, Forte R, Chaabene H, Pesce C, Condello G. Effects of a judo training on functional fitness, anthropometric, and psychological variables in old novice practitioners. J Aging Phys Act. 2019;27(6):831–42.
Doré I, O’Loughlin JL, Beauchamp G, Martineau M, Fournier L. Volume and social context of physical activity in association with mental health, anxiety and depression among youth. Prev Med. 2016;91:344–50.
Eime R, Harvey J, Payne W. Dose-response of women’s health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and life satisfaction to physical activity. J Phys Act Health. 2014;11(2):330–8.
Gerber M, Brand S, Elliot C, Holsboer-Trachsler E, Pühse U. Aerobic exercise, ball sports, dancing, and weight Lifting as moderators of the relationship between Stress and depressive symptoms: an exploratory cross-sectional study with Swiss university students. Percept Mot Skills. 2014;119(3):679–97.
Hornstrup T, Wikman JM, Fristrup B, Póvoas S, Helge EW, Nielsen SH, et al. Fitness and health benefits of team handball training for young untrained women—a cross-disciplinary RCT on physiological adaptations and motivational aspects. J Sport Health Sci. 2018;7(2):139–48.
Mickelsson T. Modern unexplored martial arts–what can mixed martial arts and Brazilian Jiu-Jiutsu do for youth development? Eur J Sport Sci. 2019.
Jansen P, Dahmen-Zimmer K. Effects of cognitive, motor, and karate training on cognitive functioning and emotional well-being of elderly people. Front Psychol. 2012;3:40.
Jansen P, Dahmen-Zimmer K, Kudielka BM, Schulz A. Effects of karate training versus mindfulness training on emotional well-being and cognitive performance in later life. Res Aging. 2017;39(10):1118–44.
Jewett R, Sabiston CM, Brunet J, O’Loughlin EK, Scarapicchia T, O’Loughlin J. School sport participation during adolescence and mental health in early adulthood. J Adolesc Health. 2014;55(5):640–4.
Kitchen P, Chowhan J. Forecheck, backcheck, health check: the benefits of playing recreational ice hockey for adults in Canada. J Sports Sci. 2016;34(21):2121–9.
Kim J, James JD. Sport and happiness: Understanding the relations among sport consumption activities, long-and short-term subjective well-being, and psychological need fulfillment. J Sport Manage. 2019.
Koolhaas CH, Dhana K, Van Rooij FJA, Schoufour JD, Hofman A, Franco OH. Physical activity types and health-related quality of life among middle-aged and elderly adults: the Rotterdam study. J Nutr Health Aging. 2018;22(2):246–53.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Patterson S, Pattison J, Legg H, Gibson AM, Brown N. The impact of badminton on health markers in untrained females. J Sports Sci. 2017;35(11):1098–106.
Sabiston CM, Jewett R, Ashdown-Franks G, Belanger M, Brunet J, O’Loughlin E, et al. Number of years of team and individual sport participation during adolescence and depressive symptoms in early adulthood. J Sport Exerc Psychol. 2016;38(1):105–10.
Sorenson SC, Romano R, Scholefield RM, Martin BE, Gordon JE, Azen SP, et al. Holistic life-span health outcomes among elite intercollegiate student-athletes. J Athl Train. 2014;49(5):684–95.
Stenner B, Mosewich AD, Buckley JD, Buckley ES. Associations between markers of health and playing golf in an Australian population. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2019;5(1).
Tsuji T, Kanamori S, Saito M, Watanabe R, Miyaguni Y, Kondo K. Specific types of sports and exercise group participation and socio-psychological health in older people. J Sports Sci. 2020;38(4):422–9.
Yamakita M, Kanamori S, Kondo N, Kondo K. Correlates of regular participation in sports groups among Japanese older adults: JAGES cross–sectional study. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(10):e0141638.
Howie EK, McVeigh JA, Smith AJ, Straker LM. Organized sport trajectories from childhood to adolescence and health associations. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2016;48(7):1331–9.
Chinkov AE, Holt NL. Implicit transfer of life skills through participation in Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu. J Appl Sport Psychol. 2016;28(2):139–53.
Lubans D, Richards J, Hillman C, Faulkner G, Beauchamp M, Nilsson M, et al. Physical activity for cognitive and mental health in youth: a systematic review of mechanisms. Pediatrics. 2016;138(3):e20161642.
Lin TW, Kuo YM. Exercise benefits brain function: the monoamine connection. Brain Sci. 2013;3(1):39–53.
Dishman RK, O’Connor PJ. Lessons in exercise neurobiology: the case of endorphins. Ment Health Phys Act. 2009;2(1):4–9.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the work of the original systematic review conducted by Eime, R. M., Young, J. A., Harvey, J. T., Charity, M. J., and Payne, W. R. (2013).
No funding associated with this study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Active Living and Learning, University of Newcastle, University Drive, Callaghan, NSW, 2308, Australia
Narelle Eather & Levi Wade
College of Human and Social Futures, School of Education, University of Newcastle, University Drive, Callaghan, NSW, 2308, Australia
Narelle Eather
College of Health, Medicine, and Wellbeing, School of Medicine and Public Health, University of Newcastle, University Drive, Callaghan, NSW, 2308, Australia
Institute for Health and Sport, Victoria University, Ballarat Road, Footscray, VIC, 3011, Australia
Aurélie Pankowiak & Rochelle Eime
School of Science, Psychology and Sport, Federation University Australia, University Drive, Mount Helen, VIC, 3350, Australia
Rochelle Eime
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conducting of this study and reporting the findings. The titles of studies identified were screened by LW, and abstracts and full text articles reviewed independently by LW and NE. For the included studies, data was extracted independently by LW and checked by NE, and the risk of bias assessment was performed by LW and AP independently. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript and agree with the order of presentation of the authors.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Narelle Eather .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: supplementary table a..
Risk of bias.
Additional file 2: Supplementary Table B.
PRISMA Checklist.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Eather, N., Wade, L., Pankowiak, A. et al. The impact of sports participation on mental health and social outcomes in adults: a systematic review and the ‘Mental Health through Sport’ conceptual model. Syst Rev 12 , 102 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-023-02264-8
Download citation
Received : 30 August 2021
Accepted : 31 May 2023
Published : 21 June 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-023-02264-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Experimental
- Observational
- Psychological health
- Mental health
- Social health
Systematic Reviews
ISSN: 2046-4053
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

How Sports Benefit A Student’s Life and Why Is It Important?
Donna paula.
- August 19, 2023
The popularity of sports in schools has been on the rise, with an increasing number of children actively participating in various athletic activities. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in 2020, an encouraging 54.1% of children engaged in sports. This growing trend highlights the importance of fostering discussions about physical well-being in students, as sports play a vital role in promoting their overall health and development.
This article will delve into the reasons behind the surge in sports participation and the significance of prioritizing physical well-being in the lives of young learners.
Why are sports important for students’ lives?
Sports are crucial for students’ lives as they instill discipline, time management, and resilience – essential qualities for academic and professional success. Through rigorous training and commitment, students learn discipline, a valuable skill in balancing studies and extracurriculars. Managing practice sessions, competitions, and academics teaches effective time management.
Moreover, facing challenges, victories, and defeats in sports fosters resilience, preparing students to handle setbacks in their academic and future professional pursuits. These experiences build character, confidence, and teamwork, shaping well-rounded individuals capable of navigating obstacles, adapting to change, and excelling in various spheres of life.
What are the physical health benefits of sports for students?
Sports offer numerous physical health benefits for students. Regular participation improves cardiovascular health, enhances muscular strength and endurance, and promotes flexibility and coordination. Engaging in physical activities helps maintain a healthy weight , reducing the risk of obesity-related issues. It also boosts bone density, reducing the likelihood of osteoporosis later in life.
Sports contribute to better immune function , reducing the occurrence of illnesses. Additionally, students who participate in sports are more likely to adopt a physically active lifestyle, which can lead to long-term health benefits and a decreased risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
How do sports contribute to students’ mental and emotional well-being?
Beyond physical fitness, engaging in sports offers a myriad of psychological benefits that contribute to their overall mental health and emotional resilience.
Positive Impact of Sports on Mental Health and Stress Reduction
Participating in sports positively impacts students’ mental health by releasing endorphins , reducing stress hormones, and promoting a sense of achievement and self-worth. Regular physical activity in sports can alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression, improve mood, and enhance cognitive function. Furthermore, the camaraderie and social support within sports teams foster a sense of belonging and emotional well-being, empowering students to navigate life’s challenges with greater resilience and a positive outlook.
Do sports have an impact on student’s academic performance?

The relationship between sports and academic performance has been a subject of interest among educators and researchers alike. Many studies suggest that sports can positively impact students’ academic achievements , as engagement in physical activities fosters skills and traits that are transferable to the academic realm.
How sports can enhance concentration, discipline, and time management skills
Participating in sports demands focus and concentration, which can improve students’ ability to concentrate during study sessions and exams. The commitment and dedication required in sports instill discipline, enabling students to adhere to study schedules and deadlines. Moreover, managing sports practice and academic commitments cultivates practical time management skills, helping students balance their athletic pursuits and academic responsibilities. These acquired skills and traits contribute to improved academic performance and overall success in their educational journey.
What social skills and personal development opportunities do sports provide for students?

Engaging in team sports and competitive activities can foster a range of interpersonal abilities essential for building solid relationships and navigating social situations effectively.
Exploring the social benefits of sports, such as teamwork, communication, and leadership
Participating in team sports cultivates essential social skills like teamwork, where students learn to collaborate and work cohesively toward a common goal. Effective communication is honed as players interact on and off the field, fostering understanding and cooperation.
Additionally, sports present leadership opportunities, empowering students to take charge, motivate others, and guide their teammates toward success. These social attributes not only enhance the sports experience but also carry over to various aspects of student’s personal and professional lives.
Fostering interpersonal relationships and community engagement through sports
Sports provide a platform for students to build lasting friendships and bonds, creating a sense of belonging and support within their teams. As they compete against other schools or communities, students develop a broader perspective, understanding diverse viewpoints and embracing inclusivity.
Furthermore, sports events and tournaments promote community engagement, bringing together families, friends, and supporters, fostering a collective spirit and a shared passion for sports. These experiences help students appreciate the value of community involvement and contribute to their personal development as empathetic, socially conscious individuals.
How can participating in sports teach students important values and life skills?
The experiences gained in sports, such as perseverance, sportsmanship, and goal setting, play a pivotal role in shaping their character and preparing them for future challenges.
Highlighting the values and life skills learned through sports, such as perseverance, sportsmanship, and goal setting
Sports provide a fertile ground for cultivating important values and life skills. Perseverance is developed as students encounter setbacks and learn to bounce back stronger. Sportsmanship instills respect for opponents and fair play, promoting integrity and empathy. Goal setting teaches students to work with dedication and discipline, fostering a growth mindset and determination to achieve both on and off the field. These invaluable qualities prepare students for success in various aspects of life, laying a strong foundation for personal growth and achievement.
How sports contribute to character development and preparing students for future challenges
Engaging in sports not only enhances physical abilities but also plays a significant role in character development. The challenges and triumphs experienced in sports teach students resilience, teaching them to overcome obstacles with fortitude. Learning to win gracefully and accept defeat with humility nurtures sportsmanship and a sense of fair competition.
Furthermore, the camaraderie and teamwork fostered through sports build social skills and the ability to collaborate effectively. These character-building experiences equip students with the tools needed to face future challenges, instilling confidence and a positive mindset that will serve them well in their academic, professional, and personal endeavors.
How can students balance sports and education effectively?
Balancing sports and education is a common challenge faced by students, as both demand significant time and dedication. Effectively managing these commitments is crucial to ensure academic success while reaping the numerous benefits that sports offer.
Tips and strategies for students to manage their time effectively between sports and academics
- Create a schedule: Develop a well-structured timetable that includes dedicated study hours and sports practice sessions. Organizing tasks in advance helps students allocate time efficiently, preventing last-minute rushes and reducing stress.
- Prioritize tasks: Identify academic assignments and exams that require immediate attention and focus on completing them first. Learning to prioritize helps students manage their time effectively, ensuring they fulfill their academic obligations without compromising their sports commitments.
- Utilize downtime efficiently: Make use of breaks between classes or during travel to review notes or complete quick academic tasks. These pockets of time add up and allow students to stay on top of their studies even during busy sports seasons.
- Communicate with coaches and teachers: Open communication with coaches and teachers is vital. Informing them about academic commitments and sports schedules can lead to better support and flexibility when necessary.
- Set realistic goals: Establish achievable short-term and long-term goals for both academics and sports. Realistic objectives keep students motivated and focused, leading to a more balanced approach.
- Learn time management techniques: Adopt effective time management techniques, such as the Pomodoro Technique, to improve productivity during study sessions and maintain energy levels during sports activities.
- Stay organized: Keep academic materials and sports gear well-organized to save time and reduce distractions when transitioning between sports and study sessions.
- Get enough rest and nutrition: Proper rest and a balanced diet are essential for peak performance in both sports and academics. Adequate sleep and nutrition help students stay alert, focused, and perform at their best in all areas of life.
- Seek support: Reach out to peers, coaches, or academic advisors for support and advice on managing sports and education. Sharing experiences and seeking guidance can be beneficial in finding effective solutions.
The importance of maintaining a healthy balance between sports and other responsibilities
Finding an equilibrium between sports and education is vital for students’ holistic development. While sports contribute to physical fitness, teamwork, and character-building, academic success remains a crucial foundation for future opportunities and career prospects.
Striking a balance ensures that students not only excel in sports but also perform well academically, opening doors to a wider range of possibilities. Furthermore, maintaining a healthy balance teaches students valuable life skills, such as time management, discipline, and adaptability, which are transferable to various aspects of their personal and professional lives. This balance also helps students avoid burnout and excessive stress, promoting overall well-being and fostering a positive outlook toward both their educational and athletic endeavors.
Ultimately, a harmonious blend of sports and education prepares students for future challenges, equipping them with a well-rounded skill set and a strong foundation for success.
What are the long-term benefits of sports in students’ lives?
Participating in sports during their formative years can have a lasting impact on student’s lives, extending far beyond their school days. The skills and values acquired through sports play a significant role in shaping their character and influencing their personal and professional journeys.
How the skills and values acquired through sports continue to benefit students in their personal and professional lives
- Discipline and Time Management: The discipline and time management skills cultivated in sports become ingrained habits that students carry forward into adulthood. Whether it’s meeting work deadlines, balancing family responsibilities, or pursuing personal goals, the ability to manage time efficiently proves invaluable in maintaining a successful and fulfilling life.
- Resilience and Perseverance: Sports often involve facing challenges, setbacks, and failures. Learning to bounce back, stay motivated, and strive for improvement instills resilience and perseverance. These traits enable individuals to navigate the ups and downs of life, tackle obstacles with determination, and ultimately achieve their ambitions.
- Teamwork and Leadership: The teamwork and leadership experiences gained through sports carry over into various aspects of professional life. Working collaboratively, communicating effectively, and motivating others are all vital skills in a team-oriented workplace. For those in leadership positions, the ability to inspire, delegate, and make strategic decisions stems from the foundations laid in their sports endeavors.
- Stress Management and Well-being: Sports offer a healthy outlet for stress relief, promoting mental well-being. Engaging in physical activity as a lifelong practice contributes to better physical health, reducing the risk of chronic illnesses. Regular exercise releases endorphins, fostering a positive mood and overall emotional balance.
- Networking and Social Skills: Participating in sports introduces students to a diverse range of individuals, from teammates to coaches, opponents, and spectators. Building strong interpersonal relationships and networking are essential in both personal and professional life, opening doors to opportunities and connections.
- Healthy Lifestyle: The value of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, learned through sports, remains relevant throughout life. Students who develop a love for physical activity are more likely to continue engaging in exercise and recreational sports as adults, reducing the risk of health issues and promoting longevity.
Participating in sports offers a wealth of long-term benefits that extend well beyond the playing field. For students, the skills and values acquired through sports form a strong foundation for personal and professional growth, fostering resilience, discipline, and teamwork. As parents and students, embracing the opportunities sports provide can pave the way for a healthier, more fulfilling life, promoting overall well-being and a brighter future filled with countless possibilities. Embrace the power of sports, and embark on a journey of holistic development and lasting success.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do sports and fitness affect students’ life.
Sports and fitness positively impact students’ lives by promoting physical health, building discipline, enhancing teamwork, fostering mental well-being, and instilling valuable life skills.
Why sports are important in youth development?

Sports are crucial in youth development as they promote physical fitness, teamwork, discipline, resilience, and social skills, nurturing well-rounded individuals for a successful future.
What is the importance of sports development programs in schools?
Sports development programs in schools are essential as they enhance physical fitness, teach life skills, build teamwork, boost confidence, and cultivate a healthy competitive spirit, contributing to students’ overall growth and success.
How can you encourage youth to participate in sports?
Encourage youth to participate in sports by highlighting the fun, camaraderie, health benefits, and opportunities for personal growth and achievement that sports offer.
Why is physical fitness important to students, and how will it impact your academic performance?
Physical fitness is vital for students as it improves concentration, memory, and cognitive function, leading to better academic performance. Regular exercise also reduces stress, enhances mood, and boosts overall well-being, creating a positive impact on learning and achievement.
About the Author
Latest posts.

Tips for Scuba Diver Beginners

Why You Need to Join a Golf Association

How to Play Pool A Beginners Guide

How Long Are Basketball Games on Average?
Dive deeper.

Activewear to Everyday Wear: How to Perfect the Relaxed Style

Sports: Take Them up with 3 Basic Skills

Sports Stars and the Sharks That Hound for Blood

F1 Pit Crew: The Greatest Secretaries in the World
Quick links.
- Contact Us Today
- Privacy Policy
Get in Touch!

Essay on Benefits of Sports
Students are often asked to write an essay on Benefits of Sports in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Benefits of Sports
Introduction.
Sports play a significant role in our lives. They are more than just games; they teach us important life lessons and have numerous benefits.
Physical Health
Engaging in sports helps maintain a healthy body. It strengthens muscles, improves heart health and boosts the immune system.
Mental Well-being
Sports also enhance mental health. They reduce stress, improve mood and promote better sleep.
Social Skills
Playing sports helps develop social skills. It encourages teamwork, cooperation, and communication with others.
In a nutshell, sports offer numerous benefits. They contribute to our physical health, mental well-being, and social skills.
250 Words Essay on Benefits of Sports
Sport, an integral part of human culture and society, is often viewed purely as a source of entertainment. However, it offers a multitude of benefits that extend well beyond the confines of a playing field or court.
Participation in sports contributes significantly to physical health. It helps maintain a healthy weight, combats health conditions and diseases, and promotes better sleep. Sports also enhance muscular strength, flexibility, and the efficiency of the heart and lungs, all contributing to improved physical health and well-being.
Sports also have a profound impact on mental health. They help reduce stress, anxiety, and depression by releasing endorphins that act as natural mood lifters. Furthermore, the focus and concentration required in sports enhance cognitive abilities, including problem-solving and decision-making skills.
Engaging in sports fosters social skills. Team sports, in particular, promote cooperation, communication, and empathy as individuals work towards a common goal. This interaction nurtures a sense of belonging and helps build strong social networks.
Life Skills
Sports instill valuable life skills. They teach discipline, time management, and responsibility. Additionally, dealing with wins and losses in sports develops resilience and the ability to cope with life’s ups and downs.
In conclusion, sports offer an array of benefits that impact physical health, mental well-being, social skills, and life skills. The multifaceted benefits of sports make them an essential component of a balanced, healthy lifestyle. Therefore, the importance of incorporating sports into daily life cannot be overstated.
500 Words Essay on Benefits of Sports
Sports, often considered a means of entertainment, play a far more significant role in our lives than we usually acknowledge. They are not just about winning medals or achieving personal bests; they are about character building, health enhancement, and fostering social connections. This essay aims to delve into the multifaceted benefits of sports, extending from the individual to societal level.
Physical Health Benefits
Engaging in sports is instrumental in maintaining physical health. Regular physical activity helps to control weight, combat health conditions and diseases, and improve overall bodily functions. It enhances cardiovascular fitness, builds strong bones and muscles, and boosts endurance. For instance, sports like swimming provide a full-body workout, improving heart and lung efficiency, while weight-bearing sports like running can increase bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
Mental Health Benefits
Beyond physical health, sports can significantly influence mental well-being. Participating in sports has been linked to reduced levels of stress, anxiety, and depression. The reason is twofold: the release of endorphins during physical activity that generates feelings of happiness and relaxation, and the sense of accomplishment that comes with achieving a sporting goal. Furthermore, sports can enhance cognitive function, improving concentration, learning, and critical thinking skills.
Social Benefits
Sports also serve as a social platform, fostering a sense of community and belonging. Team sports, in particular, promote cooperation, communication, and understanding, essential skills not just on the field but in everyday life. They cultivate a sense of teamwork, teaching individuals the importance of working together towards a common goal.
Character Development
Character development is another significant benefit of sports. They teach essential life skills such as discipline, responsibility, self-confidence, sacrifice, and accountability. Sports offer a platform for learning how to deal with success and failure. They instill resilience, encouraging individuals to keep striving for their goals despite setbacks.
In conclusion, the benefits of sports are far-reaching and multifaceted. They contribute to the holistic development of an individual, improving physical and mental health, fostering social connections, and shaping character. In a world increasingly dominated by sedentary lifestyles and digital interactions, sports serve as a vital counterpoint, promoting well-being and community. While the competitive aspect of sports often takes the spotlight, the underlying benefits warrant equal, if not more, attention. As such, participation in sports should be encouraged, not just for the love of the game, but for the comprehensive benefits it brings to our lives.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Yoga for Health
- Essay on History of Yoga
- Essay on Hygiene Vital For Our Health
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


COMMENTS
500+ Words Essay on Importance of Sports. First of all, Sport refers to an activity involving physical activity and skill. Here, two or more parties compete against each other. Sports are an integral part of human life and there is great importance of sports in all spheres of life. Furthermore, Sports help build the character and personality of ...
In conclusion, the importance of sports essay explains that sports play a vital role in our lives. It helps us to stay healthy, fit, and active. It teaches us the value of teamwork and encourages us to work hard and never give up. Sports also help us develop discipline, dedication, and commitment, which are essential values for success in life.
Playing Sports: The Importance. Sports have always played a significant role in human society, from ancient civilizations to the modern world. The benefits of participating in sports go beyond physical health and fitness. Engaging in sports activities provides individuals with numerous mental, emotional, and social advantages.
The benefits of sports extend to mental health as well. Participating in sports can help reduce stress, anxiety, and depression. The physical activity stimulates the production of endorphins, the body's natural mood lifters, leading to feelings of happiness and relaxation. Moreover, sports can enhance cognitive functions.
2. Definitions of Physical Activity, Exercise, Training, Sport, and Health. Definitions and terms are based on "Physical activity in the prevention and treatment of disease" (FYSS, www.fyss.se [Swedish] []), World Health Organization (WHO) [] and the US Department of Human Services [].The definition of physical activity in FYSS is: "Physical activity is defined purely physiologically, as ...
This work is an essay about the importance of play and youth sports in child development. Keywords: youth health, movement, play, sports, body. 1. Introduction. This essay article addresses the importance of play and youth sports in child development. We focus mostly on early stages of sport engagement, when play should be the core activity of ...
Additionally, team sports participation during adolescence may lead to better mental health outcomes in adulthood (e.g., less anxiety and depression) for people exposed to adverse childhood experiences. In addition to the physical and mental health benefits, sports can be just plain fun. Physical activity's implications for significant ...
88 percent of parents believe that sports benefit their child's physical health.1 Indeed, participation is one way for youth to get the physical activity they need to be fit and healthy. Participating in physical activity is associated with: Improved bone health21. Improved weight status5,21. Increased cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness5,21.
Here are some other benefits you may get with regular physical activity: Helps you quit smoking and stay tobacco-free. Boosts your energy level so you can get more done. Helps you manage stress and tension. Promotes a positive attitude and outlook. Helps you fall asleep faster and sleep more soundly.
Boosting Immune System. Sports that involve moderate physical activity can boost the immune system by increasing the production of white blood cells and antibodies that help fight off infections and diseases. Regular exercise can also reduce the risk of infections, such as the common cold, by improving immune function.
Also Read: Essay on Waste Management. Essay on Importance of Sports in 300 Words. The development of the body, mind and social structure are all considerably aided by sports in human society. They have a special and complex significance that goes much beyond simple competition or entertainment. Sports are crucial for physical health in the ...
Sport benefits: Both the physical and mental. While the physical benefits are numerous (more on that below), the UK's National Health Service (NHS) report that people who take part in regular physical activity have up to a 30 percent lower risk of depression. Additionally, exercise can help lower anxiety, reduce the risk of illness and increase ...
Engaging in sports is an excellent way to maintain physical health. It helps in the development of muscular strength and enhances body coordination. The physical exertion involved helps in burning calories, improving cardiovascular health, and boosting the immune system. Beyond physical health, sports also contribute to mental well-being.
It has great importance in each stage of life. It also improves the personality of people. Sports keep our all organs alert and our hearts become stronger by regularly playing some kind of sports. sports has always given priority from old ages and nowadays it has become more fascinating. Due to the physical activity blood pressure also remains ...
Essay on Importance of Sports. Sports are like a universal language that brings people together, and they play a crucial role in our lives. In this essay, we will explore the importance of sports, their impact on physical and mental health, their contribution to teamwork and personal development, and why they are an essential part of our society.
Essay on Sports: Sports occupies a vital role in our lives. It keeps us fit, healthy and makes us active. The secret to having a healthy and positive lifestyle is to have a positive mind and body. Sports is one such activity which helps us in maintaining a proper physique and a positive mentality. Apart […]
Effects on Physical Health. Sports also significantly help young adults physically. Overall participating in sports allows for kids to have stronger muscles, increased flexibility, stronger bones, and many more. ... Sports and Its Importance in Society Essay. Sports have been an integral part of human society for centuries. From ancient ...
Healthy Weight: Reduces risk of weight gain. Bone Strength: Improves bone health. Balance and Coordination: Reduces risks of falls. Emerging research suggests physical activity may also help boost immune function 1 2. Source: Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, 2nd edition. See similar content in Spanish.
As such, optimising performance, improving the best players' availability, and decreasing the risk of injury have become the main thrusts of sports science and sports medicine when tied to high-performance teams. 5. Sports science research can help lead to evidence-based approaches that will allow athletes and active individuals to exercise ...
Changes in gene activity, immune cell function, metabolism, and other cellular processes were seen in all the tissues studied, including those not previously known to be affected by exercise. The types of changes differed from tissue to tissue. Many of the observed changes hinted at how exercise might protect certain organs against disease.
Sport is a subset of physical activity that can be particularly beneficial for short-and-long-term physical and mental health, and social outcomes in adults. This study presents the results of an updated systematic review of the mental health and social outcomes of community and elite-level sport participation for adults. The findings have informed the development of the 'Mental Health ...
250 Words Essay on Importance of Physical Exercise The Imperative of Physical Exercise. Physical exercise, often overlooked in the hustle of modern life, is a critical component of overall health and well-being. It serves as a cornerstone for not only physical fitness but also mental and emotional health. Physical Benefits
The importance of maintaining a healthy balance between sports and other responsibilities Finding an equilibrium between sports and education is vital for students' holistic development. While sports contribute to physical fitness, teamwork, and character-building, academic success remains a crucial foundation for future opportunities and ...
The benefits of sports in the development of children is well documented. An Ad Hoc Committee on Sports and Children said the potential benefits from sports to children and adolescents includes the development of healthy physical and social skills, the development of fine motor skills, and both improved health and sport-specific fitness.
Physical Health. Participation in sports contributes significantly to physical health. It helps maintain a healthy weight, combats health conditions and diseases, and promotes better sleep. Sports also enhance muscular strength, flexibility, and the efficiency of the heart and lungs, all contributing to improved physical health and well-being.
If so, you can thank Exercise is Medicine, a global health initiative managed by the American College of Sports Medicine. Created in 2007, the initiative encourages health care providers to assess ...