We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essay Examples >
- Essays Topics >
- Essay on Sugar

Energy Drinks Essay Examples
Type of paper: Essay
Topic: Sugar , Energy , Coffee , Alcohol , Caffeine , Teenagers , Alcoholism , Drinking
Words: 1500
Published: 02/07/2020
ORDER PAPER LIKE THIS
Introduction
A type of beverage consumed to get an instant mental and physical stimulation is referred to as energy drink. Some of the most popular drinks known to give wings to their consumers include Red Bull, Adrenaline Rush, Erektus, Venom and ISO Sprint. In the US, people in quest of quick gratification take to addiction of some form of energy boosters through coffee, tea and highly caffeinated energy drinks. Energy drinks are very popular among young and adults both; especially adolescents and young adults drink the energy beverages at a shocking rate. The easy availability of energy drinks in the market also contributes to its growing popularity and addiction. T. E. Sather states that the advertisement of energy drinks promises that the drinks "will give you a boost of energy"(T. E. Sather) and the energy is delivered through high dosage of concentrated caffeine and other additives. Energy drinks due to its high content of caffeine, sugar and other chemicals have many negative effects which make the need for a solution necessary.
Negative Effects
- The High Content of Caffeine Energy drinks contain a lot of stimulant drugs including caffeine, b vitamins, taurine, glucuronolactone, sugar, artificial sweeteners, inositol, l-carnitine, ginkgo biloba, inositol and ginseng. However, the most alarming is the amount of caffeine used in the drinks. The amount of caffeine used in the energy drinks far outweighs the amount found in tea, coffee and soft drinks like Coca-Cola. Many energy drinks have 2-3 times the amount of caffeine found in a cup of coffee. Sometimes the energy beverages contain more coffee than mentioned on the labels because many supplements such as kola nut, guaranà and yerba mate used in those beverages carry considerable amount of caffeine. Caffeine stimulates the central nervous system of our body and narrows the blood vessels passing through the heart and brain. It results in an increase in heart rate. Therefore, caffeine can lead to serious cardiovascular complications if caffeine infused drink is taken regularly. Caffeine also increases the rate of production of urine and hence drinking beverages that contain higher amount of caffeine can cause dehydration too. Too much caffeine can lead to insomnia, palpitations, tremors, sweating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, chest pains and neurologic symptoms, according to the American College of Emergency Physicians (Bill Radford). - Drink Mixing and Accidents Energy drinks are often used as drink mixers. It has turned into a fashion these days to mix energy drinks with alcoholic beverages to derive an extra stimuli. Dr. Yifrah Kaminer who is a professor of psychiatry and pediatrics has expressed his concern for spiking energy drinks with alcohol stating how this combination is likely to increase the number of alcohol-related injuries. Despite the punch of energy drinks, alcohol will still make the similar impact. So one who has drunk a combination of alcohol and energy drinks might feel that his senses are not numbed and he is alert but in reality he is as impaired as a drunk. So he might remain awake and try driving, but owing to drinking alcohol his motor skill will be impaired, increasing the chances of his making accidents. - Addiction in Youngsters Energy drinks are typically very popular among youngsters in the US with 66% of its consumers hovering between 13 - 35 years of age. Energy drinks are addictive especially for youngsters. The primary market of energy drinks is targeted at teens and college goers. They do not know how to moderately consume energy drink. A nutrition consultant and associate professor of biology at the University of Colorado, Jackie Berning states, "I'm appalled at the amount that these young adults are consumingI've seen them show up at an 8 o'clock class popping three Red Bulls so they could make it through the morning" (Bill Radford). The excessive amount of consumption of energy drinks causes high amount of caffeine in the body and the body gets accustomed to high caffeine levels, leading to addiction over time. If energy drinks are taken with alcohol then caffeine prevents the depressing effect of alcohol and allows a person to drink for a longer period of time. For this reason many young people drink alcohol with energy drinks. Since both alcohol and energy drinks are diuretic, the combined effect of them aggravates the state of dehydration. - Weight Gain Energy drinks are conducive to weight gain and obesity because of the excessive amount of sugar and artificial sweeteners used in them. Normal average person who fights to keep calorie count under check might pile on more weight due to the addiction of drinking energy beverages. Energy drinks may serve the same purpose of junk food in adding extra kilos. Most of the time people resort to energy drinks to combat sleep to remain awake through the night and such dose of high calorie content at the dead of night might boost up the weight gain. - Harmful for People with History of Health Problems Energy drinks could be quite detrimental for people with the health history of liver disease, diabetes, cardiovascular complications, seizures, hyperthyroidism, mood and behavioral disorders and renal disease. Though the caffeine content used in soft drinks is regulated by FDA, there is no such regulation on the use of caffeine in energy drinks. Therefore, the consumption of energy drinks may worsen the state of people with epilepsy and seizure history especially if they consume the drink in sleep deprived state. The high amount of sugar present in energy beverages may exacerbate the condition of people suffering from liver or renal disease and diabetes. - Harmful during Pregnancy Energy drinks are harmful for pregnant women. The main ingredients of any energy drink are augar, vitamin, A, C and E, caffeine, guarana, taurine, ginseng, creatine etc. Sugar is required during pregnancy and hence consumption of moderate quantity of sugar from energy drinks will cause no harm. However, energy drinks are not at all recommended for women going through gestational diabetes during pregnancy. Further, the intake of caffeine or guarana of more than 300 mg per day increases the chances of miscarriage significantly (Carolyn Roy-Bornstein). Any typical bottle of energy drink contains at least 200 mg of caffeine and because of the high caffeine content energy drinks should be avoided during pregnancy.
As of now, there are no age restriction or warning labels placed on energy drinks in the US due to which its side effects impact both young and adults. In the wake of some unfortunate incidents resulting in the death of some youngsters allegedly of energy drink consumption, countries like France and Germany have prohibited the sale of certain energy drinks like Red Bull and others. Some countries including Australia and New Zealand have imposed certain regulations on the manufacturing and sale of energy drinks. They have even restricted the amount of caffeine to be used in the energy beverages. Though the energy drink companies market their products as 'dietary supplements, over a time many reports have brought forth the side effects of consuming energy drinks. Therefore, I think in order to arrest the situation it is important to put restriction on its sale and manufacturing. The caffeine amount should be regulated by FDA. Warning labels, consumption guidelines and age limit of minimum 18 years should be placed on the drinks. Further, these caffeinated beverages should be moderated or banned from school vending machines and cafeterias to restrict consumption of caffeine by teenagers.
Energy drinks used as energy boosters by young and old have many side effects. High amount of caffeine used in energy drinks leads to a lot of many health complications. Mixing the drinks with alcohol compounds its side effects and increases the risk of accidents. These drinks being available in the all places with no age restriction has led to its addiction among children and adolescents. The high amount of sugar in these drinks contributes to weight gain. People with history of health problems might have their condition worsen due to drinking this type of beverage. It is also harmful for women during pregnancy. Taking into account the negative effects of the energy drinks it is the need of the hour to impose some restriction on the sale, manufacturing, caffeine content of the drinks. Also an age limit should be placed to keep teens and adolescents out of harm’s way.
Radford, Bill. Negative Energy? ; Drinks deliver caffeine jolt; just don't overdo, The Gazette, Dec 11, 2006. Freedom Newspapers Inc, Colorado Springs, Retrieved on 3rd June 2013 from <http://search.proquest.com/docview/268278579?accountid=1172> Roy-Bornstein, Carolyn. Just Say No to Energy Drinks, Pediatrics for Parents, Inc. Aug 2011. Retrieved on 3rd June 2013 from <http://search.proquest.com/docview/1017696040?accountid=1172> Sather, T E. The Dangers of Energy Drinks and Supplements, Feb 2013. Retrieved on 3rd June 2013 from <http://search.proquest.com/docview/1326330751?accountid=1172> Energy Drinks Busting Your Health for the Buzz, Pennsylvania Medical Society, September 2008. Retrieved on 3rd June 2013 from <http://newswise.com/articles/view/544512/>

Cite this page
Share with friends using:
Removal Request

Finished papers: 1454
This paper is created by writer with
ID 285254961
If you want your paper to be:
Well-researched, fact-checked, and accurate
Original, fresh, based on current data
Eloquently written and immaculately formatted
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Get your papers done by pros!
Other Pages
Chemistry personal statements, sympathy case studies, steam case studies, butter case studies, nurture case studies, stem case studies, terminology case studies, infusion case studies, crunch case studies, guitar case studies, mirror case studies, music research paper sample, science and faith at odds essay example, research paper on assaults that were not just physical in nature instead cause of social and cultural, example of research summary article review, expanded definition of glycogen essay sample, work ethics critical thinking, good research paper about a study of the effect of aliens on culture, good example of research paper on hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, unconscious mind essay sample, child abuse essay, good example of research paper on life cycle assessment, vulnerable population essays examples, constructions of an enemy essays example, appiahs analysis essay sample, sweatshop essay sample, free essay about growing up online, pro fishing boats case study examples, the liverpool care pathway essay example, power and empowerment in nursing article review examples, good example of case study on aspects of contract and business law, good example of your road map for success by maxwell book review, good essay on abuse of prescription, relationship between contemporary theory and related classical theory course work, free research paper on flu vaccine controversy, lost of connectivity db unit 2 essays example, coco essays, polo ralph lauren essays, andra essays, beevor essays, charnley essays, biosynthetic essays.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
The Effects of Energy Drinks
An energy drink is a beverage comprising stimulating components, normally caffeine. These constituents serve as stimulants that can influence the body’s electrolyte balance by increasing the amount of fluid that comes out as sweat (Wassef et al., 2017). Other symptoms which may arise from consuming large quantities of caffeine include migraines, insomnia, anxiousness, irritability, restlessness, stomach discomfort, irregular heartbeat, and muscular tremor (Sara, 2020). Health problems associated with these drinks are much more severe in people with high blood pressure or heart conditions (Wassef et al., 2017). Health center visits attributable to caffeine’s excessive consumption are frequently accredited to dehydration, seizures, and extremely high blood pressure.
There are laws and regulations which govern the production, distribution, and consumption of food and other products. Industries making such products should therefore be strictly regulated because the high concentration of caffeine puts younger consumers at risk of intoxication. The hazards to people’s health keep increasing as the use of this substance in food and beverages continue rising, and because of such an exponential rise in usage, strict regulation should be considered.
Energy drink firms should not be permitted to sell these beverages to minors because they can cause heart abnormalities and seizures in children. About caffeine from natural sources, most of the stimulants comprise generic drug caffeine. These cumulative sources can cause increased heartbeat and a raise in blood pressure rate (Erdemir, 2016). During and after physical activity, one can still drink mineral water instead of sports drinks, which carry extra calories which lead to obesity and tooth decay. Children are a susceptible group that needs to be protected at all costs.
It should be illegal to sell these drinks to children under the age of sixteen years. It is because they are still young, and they would not be able to regulate consumption, thus resulting in addiction. Furthermore, due to their tender age, the risks are high, and, therefore, relevant authorities should impose an age ban on these products to sixteen years and below.
These drinks should have a warning label and should sensitize and educate people on the risks associated with excessive consumption of such beverages. It should be done in good faith, as it will help save many people from diseases and other health complications. By doing so, the companies would be in a position where they can absolve themselves from any blame should anything go wrong.
Erdemir, U. (2016). Effects of energy and sports drinks on tooth structures and restorative materials. World Journal of Stomatology , 5 (1), 1. Web.
Sara, C. (2020). The cardiovascular effects of energy drinks. Clinical Cardiology and Cardiovascular Interventions , 3 (1), 1-5. Web.
Wassef, B., Kohansieh, M., & Makaryus, A. (2017). Effects of energy drinks on the cardiovascular system. World Journal of Cardiology , 9 (11), 796-806. Web.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, March 3). The Effects of Energy Drinks. https://studycorgi.com/the-effects-of-energy-drinks/
"The Effects of Energy Drinks." StudyCorgi , 3 Mar. 2022, studycorgi.com/the-effects-of-energy-drinks/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) 'The Effects of Energy Drinks'. 3 March.
1. StudyCorgi . "The Effects of Energy Drinks." March 3, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/the-effects-of-energy-drinks/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "The Effects of Energy Drinks." March 3, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/the-effects-of-energy-drinks/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "The Effects of Energy Drinks." March 3, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/the-effects-of-energy-drinks/.
This paper, “The Effects of Energy Drinks”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: March 3, 2022 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
Energy Drinks
Plain water is the best hydrating beverage for most people, but sports and energy drinks are advertised to appeal to those who exercise or need a boost of energy to get through the day.
Though sometimes confused with sports beverages , energy drinks are a different product entirely. They are marketed to increase alertness and energy levels, containing significant amounts of caffeine and as much or more sugar as in soda. Many energy drinks pack about 200 mg of caffeine, the amount in two cups of brewed coffee. Other substances purported to increase energy may be added, like B vitamins and herbs such as ginseng and guarana. Most concerning is a lack of regulation about the safety of these drinks, as well as aggressive marketing tactics geared toward adolescents. [1] The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that in 2007, 1,145 adolescents ages 12 to 17 went to the emergency room for an energy drink-related emergency. In 2011 that number climbed to 1,499. [2]
After water, sugar is the main ingredient in energy drinks. A nutritional comparison shows that a 12-ounce cola drink contains about 39 grams of sugar, 41 grams of sugar in an energy drink. Research has found that consuming high-sugar drinks of any kind can lead to weight gain and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and gout.
Because of the amount of sugar and stimulant ingredients, there is concern that these beverages may not be helpful, and even worse, harmful to adolescents and people with certain health conditions.
Energy Drinks and Health
Sipping a beverage that offers quick energy may appeal to people who feel fatigued or who believe the caffeine can provide an edge when exercising or playing competitive sports. Although statements on the websites of energy drinks warn that these beverages may not be suitable for children, youth are among their largest consumers. An energy drink may be used by adolescents or college students cramming for exams through the night, or by a young athlete before an important game. While it is true that some controlled trials have shown temporary improved alertness and reversal of fatigue after taking energy drinks, as well as enhanced physical performance in young athletes, the majority of studies show an association with negative health effects. These include increased stress, aggressive behaviors like fighting, alcohol/cigarette abuse, increased blood pressure, increased risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes, poor sleep quality, and stomach irritation. [1]
A typical energy drink may contain the following: carbonated water, around 40 grams of sugar (from sucrose and/or glucose), 160 mg or more of caffeine, artificial sweetener , and herbs/substances associated with mental alertness and performance but that lack scientific evidence with controlled trials (taurine, panax ginseng root extract, L-carnitine, L-tartarate, guarana seed extract, B vitamins).
Special concerns with energy drinks:
- Amplified negative health effects in adolescents. Children and teens may experience heightened effects from the high amounts of caffeine, added sugars including high fructose corn syrup, low-calorie sweeteners , and herbal stimulants, partly due to their smaller body size. [3]
- Marketing tactics towards youth. Estimates show more than a 240% increase in U.S. and worldwide sales of energy drinks. It is a $21 billion industry, with marketing campaigns targeting youth and being sold in places that are easily accessed by this age group. [1,4] Youth are exposed to energy drink advertising on children’s websites, computer games, television, supermarkets, and sporting events. [5] Research has shown that adolescents lack maturity in key areas of the brain and are more likely to engage in risk-taking behavior, making them vulnerable to risky behaviors sometimes portrayed in energy drink marketing. Youth are attracted to energy drinks due to effective marketing, influence from peers, and lack of knowledge about their potential harmful effects. [4]
- Negative health outcomes. Emerging evidence has linked energy drink consumption with negative health consequences in youth like risk-seeking behaviors, poor mental health, adverse cardiovascular effects, and metabolic, renal, or dental problems. [1]
- Excessive caffeine. Too much caffeine from any beverage, particularly when several are taken in one day in sensitive individuals, can lead to anxiety, insomnia, heart problems like irregular heartbeat and elevated blood pressure, and in rare cases seizures or cardiac arrest. Some energy drinks may contain as much as 500 mg per can (the amount in 14 cans of cola). [4.6]
- High sugar content. Because of the excessive sugar content in some energy drinks, they carry the same health risks associated with other sugar-sweetened beverages. See Sugary Drinks .
- Dangers with alcohol. A greater danger is introduced if energy drinks are combined with alcohol, a trend largely seen in underage drinkers and associated with binge drinking. Studies suggest that drinking this type of cocktail leads to a greater alcohol intake than if just drinking alcohol alone. This may be because energy drinks increase alertness that masks the signs of inebriation, leading one to believe they can consume even more alcohol. [1] In case reports, high consumption of energy drinks—especially when mixed with alcohol—has been linked to adverse cardiovascular, psychological, and neurologic events, including fatal events. [2]
- Lack of regulation. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not regulate energy drinks but enforces a caffeine limit of 71 mg per 12 ounces of soda; energy drinks typically contain about 120 mg per 12 ounces. However, energy drink manufacturers may choose to classify their product as a supplement to sidestep the caffeine limit. For companies that classify their energy drinks as beverages, the American Beverage Association published voluntary guidelines that advise accurate listings of caffeine content, restriction of marketing to children, and reporting of adverse events to the FDA. However, compliance to these guidelines has been found to be low. [1]
- The International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN) issued a position statement on energy drinks after analyzing their safety and efficacy. (8) They concluded that consuming energy drinks 10-60 minutes before exercise can improve mental focus, alertness, anaerobic performance, and endurance in adults, largely through the effects of caffeine. However, other ingredients in these drinks require more study to demonstrate their safety and effects on performance. ISSN cautioned that higher-calorie energy drinks can lead to weight gain, and that their high glycemic load could negatively affect blood glucose and insulin levels. They discouraged use of energy drinks for children and adolescents unless under careful parental monitoring, and for people with diabetes or cardiovascular disease who could be negatively affected by the stimulant ingredients.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics’ Committee on Nutrition and the Council on Sports Medicine and Fitness encourage pediatric health care providers to discourage the use of and discuss potential health risks of stimulant ingredients in energy drinks with youth and parents, and to limit or avoid sugar-sweetened beverages of any kind in youth due to risk of excessive calorie intake and weight gain, as well as dental erosion. [7]
Bottom Line
Water that is calorie-free and accessible without cost to most people is the beverage of choice taken with and between meals. Energy drinks are a source of caffeine that people may choose as an alternative to coffee or tea. However, they also contain high amounts of sugar, vitamins, and herbs that may not be necessary for the average person. Energy drinks can pose a health risk in vulnerable groups including children, teenagers, pregnant women, and those with medical conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Adults who choose to consume energy drinks should check the label for caffeine content and avoid high consumption (over 200 mg of caffeine per drink); consumption in combination with alcohol should be avoided. [9] Pediatricians should discuss the use of energy drinks with their young patients and parents to ensure that all are aware of the health risks, and if used, are monitored carefully. [7]
Sugary Drinks Sports Drinks
- Al-Shaar L, Vercammen K, Lu C, Richardson S, Tamez M, Mattei J. Health Effects and Public Health Concerns of Energy Drink Consumption in the United States: A Mini-Review. Front Public Health . 2017;5:225.
- Ehlers A, Marakis G, Lampen A, Hirsch-Ernst KI. Risk assessment of energy drinks with focus on cardiovascular parameters and energy drink consumption in Europe. Food and Chemical Toxicology . 2019 Aug 1;130:109-21.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The Buzz on Energy Drinks. https://www.cdc.gov/healthyschools/nutrition/energy.htm Accessed 8/21/19.
- Pound CM, Blair B; Canadian Paediatric Society, Nutrition and Gastroenterology Committee, Ottawa, Ontario. Energy and sports drinks in children and adolescents. Paediatr Child Health . 2017 Oct;22(7):406-410.
- De Sanctis V, Soliman N, Soliman AT, Elsedfy H, Di Maio S, El Kholy M, Fiscina B. Caffeinated energy drink consumption among adolescents and potential health consequences associated with their use: a significant public health hazard. Acta Biomed . 2017 Aug 23;88(2):222-231.
- Wiggers D, Asbridge M, Baskerville NB, Reid JL, Hammond D. Exposure to Caffeinated Energy Drink Marketing and Educational Messages among Youth and Young Adults in Canada. Int J Environ Res Public Health . 2019 Feb 21;16(4).
- Schneider MB, Benjamin HJ. Sports drinks and energy drinks for children and adolescents: Are they appropriate? Pediatrics . 2011;127(6):1182–9.
- Campbell B, Wilborn C, La Bounty P, Taylor L, Nelson MT, Greenwood M, Ziegenfuss TN, Lopez HL, Hoffman JR, Stout JR, Schmitz S, Collins R, Kalman DS, Antonio J, Kreider RB. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: energy drinks. J Int Soc Sports Nutr . 2013 Jan 3;10(1):1.
- van Dam RM, Hu FB, Willett WC. Coffee, Caffeine, and Health. NEJM . 2020 Jul 23; 383:369-378
Last reviewed July 2020
Terms of Use
The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Impact of energy drink versus coffee consumption on periodic repolarization dynamics: an interventional study
Dominik schüttler.
1 Department of Medicine I, University Hospital, LMU Munich, Marchioninistrasse 15, 81377 Munich, Germany
2 German Center for Cardiovascular Research (DZHK), Partner Site Munich, Munich Heart Alliance (MHA), 80802 Munich, Germany
3 Institute of Surgical Research at the Walter-Brendel-Centre of Experimental Medicine, University Hospital, LMU Munich, Marchioninistrasse 27, 81377 Munich, Germany
Wolf-Stephan Rudi
4 University Hospital for Internal Medicine III, Medical University Innsbruck, Innsbruck, Austria
Wolfgang Hamm
Stefan brunner, associated data.
All data sets can be obtained from the corresponding author by request.
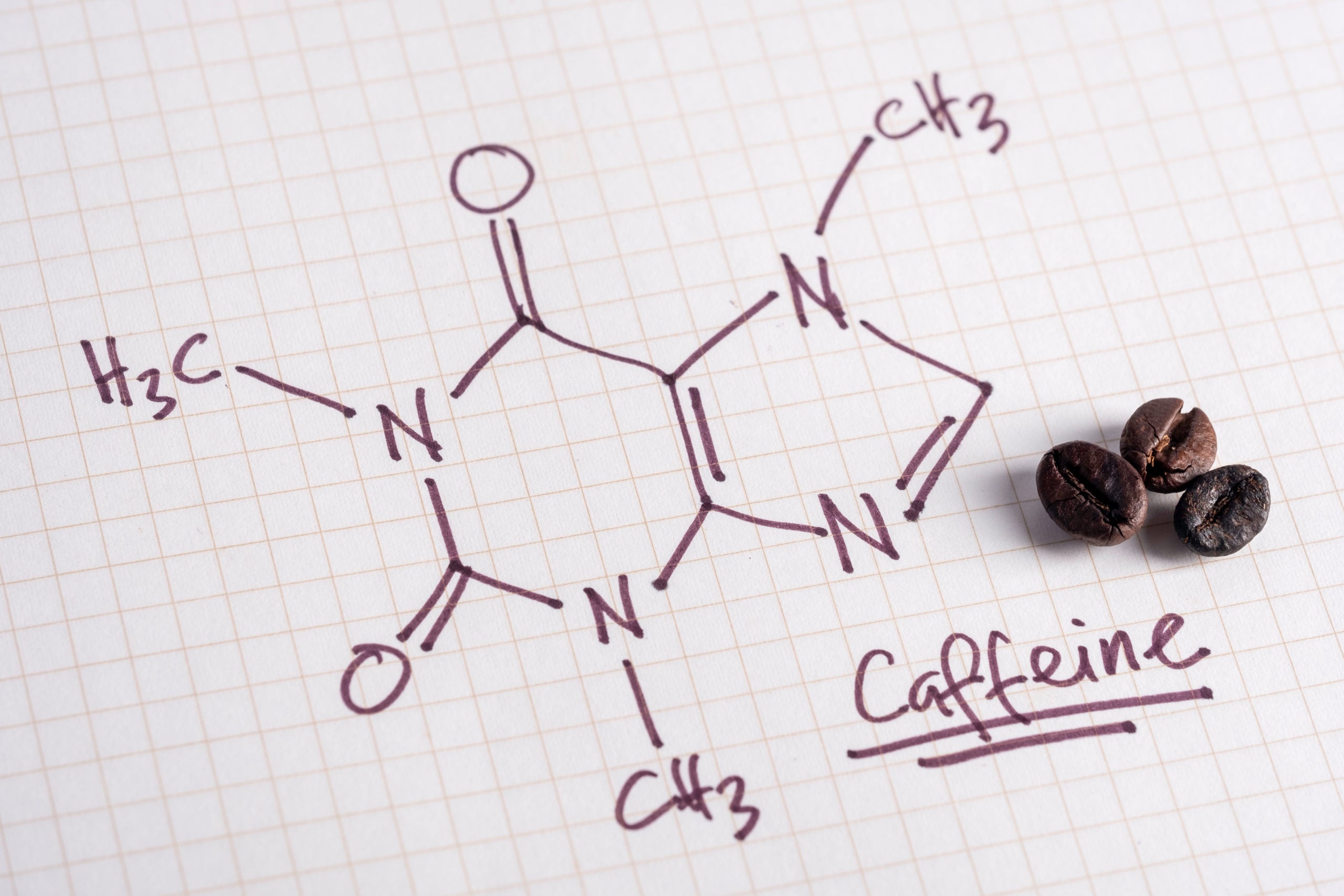
Caffeinated beverages are consumed daily throughout the world. Caffeine consumption has been linked to dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. However, the exact effects are still insufficiently understood.
Sixteen healthy individuals were included in the present non-randomized cross-over interventional study. All study subjects consumed a commercial energy drink (containing 240 mg caffeine), and in a second independent session coffee (containing 240 mg caffeine). High-resolution digital ECGs in Frank-lead configuration were recorded at baseline before consumption, and 45 min after consumption of the respective beverage. Using customized software, we assessed ECG-based biomarker periodic repolarization dynamics (PRD), which mirrors the effect of efferent cardiac sympathetic activity on the ventricular myocardium.
The consumption of energy drinks resulted in an increase in PRD levels (3.64 vs. 5.85 deg 2 ; p < 0.001). In contrast, coffee consumption did not alter PRD levels (3.47 vs 3.16 deg 2 , p = 0.63). The heart rates remained unchanged both after coffee and after energy drink consumption. Spearman analysis showed no significant correlation between PRD changes and heart rate changes ( R = 0.34, p = 0.31 for coffee, R = 0.31, p = 0.24 for energy drink).
Our data suggests that sympathetic activation after consumption of caffeinated beverages is independent from caffeine and might be mediated by other substances.
Trial Number: {"type":"clinical-trial","attrs":{"text":"NCT04886869","term_id":"NCT04886869"}} NCT04886869 , 13 May 2021, retrospectively registered
Introduction
Consumption of caffeinated drinks has a long cultural and social tradition throughout the world making caffeine the most widely used psychoactive and stimulating agent [ 1 ]. Both, deleterious and beneficial health effects have been attributed to caffeine consumption: in the past, major concerns have been raised about potential systemic adverse effects of a long-term consumption of caffeinated beverages including the development of cancer, arrhythmias and other cardiovascular diseases [ 2 , 3 ]. In contrast, a large prospective study showed that coffee consumption—one of the most widely consumed caffeine containing beverages—was inversely associated with total and cause-specific mortality [ 4 ]. However, these contrary research findings should be interpreted with caution, since caffeinated beverages contain many other biologically active substances, and therefore, health effects may not only be related to caffeine [ 3 , 5 ].
From the cardiovascular point of view, caffeinated beverages may contribute to the development of arrhythmias [ 5 , 6 ]. The underlying mechanisms of arrhythmogenesis are not completely understood. One potential mechanism is the caffeine-induced imbalance of the autonomic nervous system (ANS). Various studies intended to support this hypothesis by demonstrating changes of heart rate variability, a measure of the balance of the ANS [ 7 ]. However, results remain still inconclusive.
Periodic repolarization dynamics (PRD) is a novel ECG-based biomarker, which most likely reflects the activity of the sympathetic branch of the ANS on the level of the ventricular myocardium [ 8 ]. It has proven its strong prognostic power in large trials of patients with ischemic and non-ischemic cardiomyopathy [ 8 , 9 ]. Several studies demonstrated its regulation among physiological states which are known to activate the sympathetic nervous system [ 10 – 12 ]. However, the effect of caffeine consumption on PRD levels and on cardiac repolarization instability, is still insufficiently explored. Thus, the aim of the present pilot study was to investigate the effect of consumption of caffeinated beverages on PRD.

Participants
For the present study, 16 healthy individuals (6 females and 10 males) with a mean age of 30.2 ± 7.9 years (standard deviation) were recruited between March and May 2021. Subjects with any previous history of cardiovascular disease or on daily medication were excluded from the study. Table Table1 1 provides further information about baseline characteristics.
Overview of baseline characteristics. Values show mean ± standard deviation
The study protocol was approved by the local ethics committee ( “Ethikkommission der Medizinischen Fakultät der LMU München”, project no. 370–16). Informed consent was obtained from each patient, and the study protocol conforms to the ethical guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Sample size
As there is no data available regarding the effect of caffeine on PRD levels, we estimated sample size by looking at comparable studies which investigated the effect of caffeine on HRV [ 13 , 14 ]. PRD has been proven to be a highly sensitive parameter to monitor sympathetic nervous system on the level of ventricular myocardium [ 8 , 15 ]. Previous studies of our group with similar sample sizes showed robust statistical differences on PRD changes in response to triggers stimulating the sympathetic nervous system [ 10 – 12 ]. We thus assumed that our number of participants would be sufficient to see possible effects.
In this cross-over intervention study, each participant took part in two sessions in a randomized order. There was an interval of at least 48 h between the sessions. In session 1, study participants consumed 750 mL of a commercial energy drink (containing 32 mg caffeine/100 mL (0.03%), 0.4% taurine, 11 g/100 ml sugar according to the manufacturer’s information). In session 2, study participants consumed three cups of coffee (containing 80 mg caffeine/cup according to the manufacturer’s information). Volunteers were urged to consume drinks within 15 min time. In each session, a baseline high-resolution (1000 Hz) digital 20-min ECG (Schiller medilog AR4plus; Schiller AG, Switzerland) was performed in Frank-lead configuration in a resting sitting position, not talking, and quiet surroundings. After baseline recordings, the respective beverage was consumed within 5 min. Caffeine absorption is known to be completed approximately 45 min after intake and blood levels peak around that time [ 16 ]. Therefore, after another resting period of 45 min, a second 20-min high-resolution ECG was recorded. Study participants were required to abstain from caffeine and alcohol consumption 48 h before each session. To exclude volume effects of drinks on PRD changes, we performed an additional experimental session, where study participants drank 750 ml of tap water, and calculated PRD before and after water intake.
All data were collected and analyzed by the study investigators at the Department of Cardiology at the University Hospital Munich (LMU). PRD was calculated out of ECG recordings by a blinded investigator.
Outcome measures
PRD was calculated as described [ 8 ]. In brief, the spatiotemporal properties of each T wave were integrated into a single vector (T°). The angle between two successive vectors (dT°) is plotted over time representing the instantaneous degree of repolarization fluctuations. Typically, an oscillating pattern of the dT° signals can be observed. PRD is calculated by use of wavelet analyses in the low-frequency spectrum (≤ 0.1 Hz).
ECG signals were analyzed using the MATLAB software with established algorithms for calculation of PRD.
Results are expressed as median and corresponding interquartile range (IQR). Statistical analyses were performed with R version 4.0.3. Wilcoxon signed rank test was used to detect differences in PRD levels and heart rates in response to coffee as well as ED consumption ( p < 0.05 estimated as statistical significance). Spearman correlation analysis were performed to test the correlation between changes in heart rate and changes in PRD levels.
After coffee consumption PRD values did not change significantly compared to baseline values ( p = 0.64): PRD at baseline was 3.47 deg 2 (IQR 1.88 deg 2 ) and remained unchanged at 3.16 deg 2 (IQR 1.89 deg 2 ) after coffee consumption (Fig. 1 A). Additionally, mean heart rate did not change when comparing values before and after coffee intake (80.8 bpm (IQR 5.4 bpm) vs. 75.0 bpm (IQR 5.7 bpm); p = 0.15). There was no significant correlation in Spearman analysis between changes in heart rates and changes in PRD levels (Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient R = 0.34, p = 0.31).

Boxplots show changes in PRD levels after coffee consumption (A) and energy drink consumption (B) . Boxes visualize medians with interquartile ranges. Wilcoxon signed rank tests were performed to detect statistical differences ( p < 0.05)
In contrast to coffee consumption, PRD values increased significantly after consumption of energy drinks from 3.64 deg 2 (IQR 1.80 deg 2 ) at baseline to 5.85 deg 2 (IQR 4.40 deg 2 ) ( p < 0.001; Fig. 1 B). Mean heart rate did not change significantly after ED consumption (78.9 bpm (IQR 7.8 bpm) before vs. 80.4 bpm (IQR 9.8 bpm) after intake; p = 0.56) and we did not detect a significant correlation between PRD changes and changes in heart rate (Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient R = 0.31, p = 0.24). Consumption of tap water (750 ml) did not alter PRD levels (2.94 deg 2 (IQR 0.85 deg 2 ) vs. 2.77 deg 2 (IQR 1.1 deg 2 ), p = 0.79).
In our study, we investigated the acute effect of consumption of caffeinated beverages on the sympathetic activity by means of analysis of PRD levels. For this purpose, we have chosen two popular caffeine containing beverages, coffee and energy drinks. We detected a significant increase of PRD levels after consumption of energy drinks indicating enhanced efferent cardiac sympathetic activity. In contrast, we did not observe an effect on PRD levels after coffee consumption. Water consumption did not change PRD levels, excluding an effect on PRD in response to volume intake.
A previous study investigated the effect of energy drink consumption on standard electrocardiographic and blood pressure parameters. The authors described a significant increase of systolic blood pressure after energy drink consumption indicating an activation of the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system [ 7 ]. In another study by this group, the authors compared the effect of energy drinks with another caffeinated beverage. The systolic blood pressure was significantly higher with energy drinks [ 17 ]. A study by Corti et al. detected an increased muscle sympathetic nerve activity after coffee consumption. However, in this study, the sympathetic activity was likewise activated in caffeinated and decaffeinated coffee. Thus, the observed effect was independent from caffeine [ 18 ].
In line with these studies, our findings on changes in PRD levels suggest, that the effect of caffeinated beverages on sympathetic activity-mediated cardiac repolarization instability is independent from caffeine and is mediated by other substances. The ingredients of caffeinated beverages are various. It is well known that energy drinks contain additional energy-boosting substances, such as taurine, guarana, and sugar. These substances may affect the cardiovascular system and may lead to a proarrhythmic substrate via sympathetic activation [ 3 , 5 ]. There are several reports linking an overuse of energy drinks to the occurrence of sudden cardiac deaths [ 5 , 6 ]. This risk may be reflected by the elevated PRD levels after consumption of energy drinks, since PRD is an excellent predictor of mortality and in particular of sudden cardiac deaths in patients with underlying heart diseases [ 8 , 9 ].
A number of considerations are necessary when interpreting our results. With a single ECG recording, we cannot elucidate the temporal relation between caffeine consumption and PRD changes. Further, we did not investigate dose dependent effects of caffeine on PRD levels. In addition, we cannot exclude individual differences of caffeine absorption, since we did not measure blood caffeine levels. Results are limited by the small sample size, further studies investigating the effect of caffeine on PRD, e.g. in combination with HRV-derived parameters might be useful to further support our findings.
In conclusion, our results suggest that sympathetic activity-mediated repolarization instability after consumption of caffeinated beverages is independent from caffeine and might be triggered by other substances.
Authors` contributions
DS collected, analyzed and interpreted data and wrote the original draft. WSR collected data and revised the manuscript for intellectual content. AB revised the manuscript for intellectual content. WH collected, analyzed and interpreted data and revised the manuscript for intellectual content SB was responsible for conceptualization and project administration and revised the manuscript for intellectual content. All author’s read the manuscript and agreed to its submission.
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL. Dominik Schüttler is supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation)—413635475—and the Munich Clinician Scientist Program (MCSP) of the LMU Munich. Funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Declarations
All authors declare no competing interest.
Not applicable.
Research was approved by the local ethics committee (Ethikkommission der Medizinischen Fakultät der LMU München (project no. 370–16)).
All subjects gave written informed consent in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication was obtained from all study volunteers.
Wolfgang Hamm and Stefan Brunner have contributed equally to this study and share authorship.

- < Previous
Home > Honors College > Honors Theses > 323
Honors Theses
Energy drinks and caffeine: the science behind the billion- dollar industry.
Eric Villarreal , University of Mississippi. Sally McDonnell Barksdale Honors College
Date of Award
Document type.
Undergraduate Thesis
Chemistry and Biochemistry
First Advisor
Susan Pedigo
Relational Format
Dissertation/Thesis
Ask any college student how he or she gets through long study sessions, all-nighters, and the always grueling finals week and he or she will most likely reference some caffeine-containing beverage as the antidote, with energy drinks becoming an ever increasing option. The effects, both physiological and psychological, of the ingredients in energy drinks (caffeine and, to a lesser degree, glucose) dictate their usefulness to consumers. A review of the available research literature from http://scholar.google.com using the following keywords: caffeine, energy drink, Red Bull, caffeinated beverage, caffeine drink, energy drink industry, energy drink company, and glucose yielded the references that have been aggregated, synthesized, and summarized in this thesis. Caffeine's ability to improve one's subjective mood, reaction time, memory, and attention has been scientifically verified by the available research literature; in essence, then, caffeine is a legal, low-grade stimulant. The ubiquity of caffeine in everyday life has made its consumption a part of everyday life and a normal means of self-medication. This ubiquity in today's society has also been promoted by the lax regulatory structure regarding the compound — a regulatory structure that has allowed EDs manufacturers to include five times more caffeine in their products than in a can of Coca-Cola. EDs manufacturers have embraced caffeine's stimulatory effects in such an atmosphere of lax regulation and high demand produced by environmental and societal factors to produce high-caffeine, high-sugar products uniquely suited to their target demographic — twenty year olds. However, they also dictate the negative side effects that can harm consumer health over the short or long-term.
Recommended Citation
Villarreal, Eric, "Energy Drinks And Caffeine: The Science Behind The Billion- Dollar Industry" (2014). Honors Theses . 323. https://egrove.olemiss.edu/hon_thesis/323
Accessibility Status
Searchable text
Since August 31, 2019
Included in
Chemistry Commons
To view the content in your browser, please download Adobe Reader or, alternately, you may Download the file to your hard drive.
NOTE: The latest versions of Adobe Reader do not support viewing PDF files within Firefox on Mac OS and if you are using a modern (Intel) Mac, there is no official plugin for viewing PDF files within the browser window.
- Collections
- Disciplines
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
Author Corner
- Submit Thesis
Additional Information
- Request an Accessible Copy
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
88 Energy Drink Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best energy drink topic ideas & essay examples, 🥇 most interesting energy drink topics to write about, 📝 good essay topics on energy drinks, ❓ energy drink research questions.
- New Energy Drink Marketing Strategy The Mission of the company is to be a leader in the manufacturing and marketing of healthy, nutritious beverages in the USA and to satisfy consumers’ needs while at the same time enhancing the individual […]
- Energy Drinks: Benefits and Disadvantages Energy drinks are a relatively new product; the number of sales has been growing since the end of the 20th century. The subject of energy drinks remains debatable as the data available on the effects […] We will write a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts 808 writers online Learn More
- Negative Effects of Caffeine and Energy Drinks It leads to avoidance of making choices and biasness and may result in impaired self-regulation that may affect the social problems of the users.
- New Zealand’s Energy Drinks Industry Marketing Research As a result of increased acceptance of energy drinks, New Zealand has been ranked amongst countries with the highest rate of energy drink consumption.
- Brand Equity for Red Bull and Monster Energy Drinks However, the production process of the Red Bull energy drink is superior to that of Monster energy in terms of ingredients.
- Benefits of Energy Drinks According to Bohlmann et al, energy drinks are being advertised time and then on televisions, radios, and newspapers because of their ability the improvement of metabolism and boost of energy levels of an individual.
- Energy Drink Competition Analysis The short product life cycle in this industry requires an effective research and development strategy to ensure that new products are availed to the market at the opportune time.
- Consumer Behaviour: Soft Energy Drinks Purchase & Consumption However, marketing and availability of products at the convenience of consumers lead to subconscious action of buying the product. Marketing the product also expands the market to another group that was not initially included in […]
- The Master Budget for an Energy Drink Called Blue Camel The master budget or commonly referred to as the financial plan is another common type of budget, which is extremely extensive and wide in coverage.
- “Skinny Boost” Energy Drink Advertisement In modern society, many girls and women could want to achieve a body shape that is of a model, who is usually thin, and their shape is similar to that of the woman in the […]
- Rhetoric of Article on Health Risks Posed by Energy Drinks This is a factual statement which the authors used to illustrate their premise on the consequences of drinking energy drinks to the health of the user.
- Edge Incorporated: Producer of Organic Energy Drink To establish a foundation for discussion, Edge Incorporated specializes in offering new generation energy drinks that not only boost energy levels and have exceptional flavors.
- Energy Drinks: Is It Bad Energy? The concept of energy drinks dates back to the beginning of the 20th century when brands such as Pepsi became popular, and the controversies surrounding the safety of these products started at the time.
- Country Risk and Strategic Planning: AMP Energy Drink This is the first risk in the market as it means that they already have a stronghold and an upper hand in the market.
- Aggression Dependence on Energy Drinks Consumption The main purpose of the proposal research is to conduct the influence of energy drinks based on caffeine on people’s psychological condition, paying significant attention to the arouse of aggression in their behavior.
- Price Influence on Energy Drink Consumption Behavior The goal of the report is to explore the consumption behavior of customers in response to price changes. The understanding of the consumption behavior of customers plays a central role in the marketing of products.
- 5 Hour Energy Drink: Observational Field Research Based on the claims made on the 5 Hour Energy website, the hypothesized characteristics of the people I expect to be buying the product are the age between 14 and 55, male gender prevailing, and […]
- AMP Energy Drink Introduction in India Being the second-most populous country in the world, India poses a huge market size and potential to become a global force in terms of business.
- Energy Drink Product Marketing As far as the objectives regarding the brand in question are concerned, it will be imperative that the introduction of the product into the global market should trigger at least a 10% increase in the […]
- Sports and Energy Drinks Marketing Analysis The study selected the United Kingdom, which has a target market that comprise of the youth, the middle-aged adults, and the old adults.
- The Dangers of Energy Drinks The article, written in the New York Times and dated 1 February 2011, expounds on the dangers of energy drinks to children and presents scientists’ concern about the high content of caffeine in the energy […]
- Competition in Energy Drinks, Sports Drinks & Vitamin Enhanced Beverage The major strategy of the beverage companies has been to diversify and make enormous extension of their brands in the market.
- The Effects of Energy Drinks and Alcohol on Neuropsychological Functioning According to the title of the report, the aim of Curry and Stasio is to identify the effects of energy drinks and alcohol on neuropsychological functioning.
- Cerebro- And Cardio-vascular Responses to Energy Drink in Young Adults: Is There a Gender Effect?
- Health Effects and Public Health Concerns of Energy Drink Consumption in the United States
- Energy Drinks and the Energy Drink Industry Overview
- Analyzing the Marketing Environment Pepsi Energy Drink
- Energy Drink Project for Marketing Management
- How Does The Consumption Of A Particular Energy Drink
- Energy Drink and Reaction Timing
- Comparing Energy Drink and Alternative Beverages
- Energy Drink Market Overview
- Breakfast and Energy Drink Consumption in Secondary School Children
- Energy Drink Age Restriction
- How Red Bull Went Straight to the Top of the Energy Drink Market
- Energy Drink and Alternative Beverages
- Accounting: Generally Accepted Accounting Principles and Energy Drink
- Energy Drink Project for Marketing Management Essay
- Hggh Company’s Expansion Into the Energy Drink Market
- Contact Points for Jones Synergy Energy Drink Campaign & Conclusion
- Energy Drink Company SWOT Analysis
- Energy Drink Market How Long Will It Last
- Red Bull and Energy Drink Industry – Threat of Substitutes
- Miller (2008) Examined the Energy Drink Consumption
- Marketing Plan for Launching Monster Ultra Energy Drink
- Red Bull Worlds Most Popular Energy Drink Brand
- Regulating Energy Drink Sales: Why the Sale of Energy
- Integrated Marketing Communication Plan of Energy Drink
- Recharge and Buy Energy Drink Now
- Monster Energy Drink Target Audience and Company Objectives
- Regression Using Energy Drink Data
- Market Opportunity Factors for Red Bull Energy Drink
- Negative Media Exposure for Red Bull Energy Drink
- McDonalds Energy Drink Research
- Tiger Energy Drink Marketing Plan
- Recharge Your Body With No Fear Energy Drink
- Yuma Puma Energy Drink: The Price Is Heating Up
- Monster Energy Drink Company Financial Ratio Analysis
- New Product Development: How to Launch an Energy Drink
- The Sports Energy Drink Industry Overview
- Redux Beverages LLC and Cocaine Energy Drink
- Sting Energy Drink Idea Screening
- Is the Energy Drink Industry Growing?
- What Is the Future of Energy Drinks?
- How Do Energy Drink Companies Make Money?
- What Is the Main Problem With Energy Drinks?
- Do Energy Drinks Improve Mental Health?
- Are Energy Drinks Safe for Children?
- Who Are the Biggest Consumers of Energy Drinks?
- Can Energy Drinks Be Healthy?
- What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Energy Drinks?
- Do Energy Drinks Have Negative Effects?
- Who Are the Major Players in Energy Drink Industry?
- How Did Energy Drinks Become Popular?
- Why Do Energy Drinks Have a Bad Reputation?
- How Big Is the Energy Drink Industry?
- What Was the First Modern Energy Drink?
- How Do Energy Drinks Affect Your Brain?
- What Country Banned Energy Drinks?
- Do Energy Drinks Replace Food?
- Are Energy Drinks Worse Than Coffee?
- Can Energy Drinks Cause Stress?
- Should Energy Drinks Be Avoided?
- Are Energy Drinks Bad for Your Heart?
- How Are Energy Drinks Different From Other Drinks?
- Do Energy Drinks Affect Blood Vessels?
- Are Energy Drinks Functional Beverages?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, September 26). 88 Energy Drink Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/energy-drink-essay-topics/
"88 Energy Drink Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 26 Sept. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/energy-drink-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2023) '88 Energy Drink Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 26 September.
IvyPanda . 2023. "88 Energy Drink Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." September 26, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/energy-drink-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "88 Energy Drink Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." September 26, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/energy-drink-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "88 Energy Drink Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." September 26, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/energy-drink-essay-topics/.
- Caffeine Paper Topics
- Target Market Topics
- Coca Cola Topics
- Beer Research Ideas
- Coffee Essay Ideas
- Alcohol Essay Titles
- Nestle Topics
- Tea Research Topics
- Water Research Ideas
- Starbucks Topics
- Wine Essay Titles
- Neuropsychology Topics
- Food & Beverage Topics
- Pepsi Topics
- Beverage Questions

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A type of beverage consumed to get an instant mental and physical stimulation is referred to as energy drink. Some of the most popular drinks known to give wings to their consumers include Red Bull, Adrenaline Rush, Erektus, Venom and ISO Sprint. In the US, people in quest of quick gratification take to addiction of some form of energy boosters ...
Abstract. Energy drinks have become products of choice among many consumers around the world. These drinks are marketed as energy boosters to improve performance, especially due to the effects of caffeine, which increases alertness. The history of energy drinks dates back to the early 20th century when Pepsi gained popularity.
The article, written in the New York Times and dated 1 February 2011, expounds on the dangers of energy drinks to children and presents scientists' concern about the high content of caffeine in the energy drinks (Maisto et al, 2010). These scientists question whether these drinks are fit for human consumption, especially teenagers (Nix, 2005).
energy drinks companies is still growing (Kapner, 2008). Thus, we can see other popular companies such as Miller Brewing Co., and Cadbury Schweppes have launched many other different energy drinks on the market (Beverage Spectrum, 2008; Kapner, 2008). In a new turn in the energy drinks race, the producing companies started marketing
Energy drinks affect the nervous and cardiovascular systems; the possible consequences are insomnia, fast heartbeat, headache, accompanied by vomiting, nausea or diarrhea; sometimes, it can cause chest pain (Hammond et al. 23). It can also provoke tachycardia and other cardiac problems; severe cases are seizures and death (Reid et al. 66).
The Effects of Energy Drinks. An energy drink is a beverage comprising stimulating components, normally caffeine. These constituents serve as stimulants that can influence the body's electrolyte balance by increasing the amount of fluid that comes out as sweat (Wassef et al., 2017). Other symptoms which may arise from consuming large ...
Thesis Statement: Energy drinks contain multiple ingredients that are bad for your health. I. INTRODUCTION A. Attention material/Credibility Material: Many people drink energy drinks in order to get them through the day, thinking that by getting a boost of energy it will help then, but it hurts you more than you think.
Consumption of 100mL/day of energy drink was significantly. associated with increased stress in males and females. After making adjustments to the. data to test for those who consumed greater than 250mL/day, the total sample and male participants who consumed greater than 250mL/day had higher anxiety and stress.
2.3 Physiological effects of ingredients in energy drink 12 2.4 Synergetic effect of ingredients in energy drinks 16 2.5 Cardiovascular effect of energy drink on children and adolescent 18 2.6 Consequencess of mixing alcohol with energy drink 19 3 AIM AND TASK 21 4 METHODS 22 5 EMPIRICAL IMPLICATIONS 24 6 DISCUSSION 29
Introduction. Energy drinks (ED) are non-alcoholic beverages marketed to improve energy, stamina, athletic performance, and concentration. Categorized as "functional beverages" alongside sports drinks and nutraceuticals, the ED industry has grown dramatically in the past 20 years, reaching over $9.7 billion in United States (U.S.) sales in 2015, with two brands accounting for nearly 85% of ...
Energy drinks are aggressively marketed in places popular with teens and young adults. Approximately, two thirds of energy drink consumers are 13-35 years old, and boys are two thirds of the market. In the U.S., energy drinks are the second most common dietary supplement used by young people; about 30% consume energy drinks on a regular basis.
ENERGY DRINK CONSUMPTION (WITH AND WITHOUT ALCOHOL) AND ITS RELATIONSHIP TO RISKY BEHAVIOR, RISK AWARENESS, ... permission statements(s) from the owner(s) of each third-party copyrighted matter to be ... ABSTRACT OF THESIS ENERGY DRINK CONSUMPTION (WITH AND WITHOUT ALCOHOL) AND ITS RELATIONSHIP TO RISKY BEHAVIOR, RISK AWARENESS, ...
This is a factual statement which the authors used to illustrate their premise on the consequences of drinking energy drinks to the health of the user. Finally, pathos is applied in the article when the authors explain that the marketing and advertising of energy drinks to children and teens must stop given the danger and health risks they pose ...
Running head: INTERVENTIONS TO REDUCE ENERGY DRINK CONSUMPTION 1 . Exploring the potential for graphic warning labels to reduce intentions to consume energy drinks . Xiaole Zhu . This thesis is submitted in partial fulfilment of the Honours degree of Bachelor of Psychological Science (Honours) School of Psychology . University of Adelaide
After water, sugar is the main ingredient in energy drinks. A nutritional comparison shows that a 12-ounce cola drink contains about 39 grams of sugar, 41 grams of sugar in an energy drink. Research has found that consuming high-sugar drinks of any kind can lead to weight gain and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease ...
Introduction. Consumption of caffeinated drinks has a long cultural and social tradition throughout the world making caffeine the most widely used psychoactive and stimulating agent [].Both, deleterious and beneficial health effects have been attributed to caffeine consumption: in the past, major concerns have been raised about potential systemic adverse effects of a long-term consumption of ...
coffee contains around 100mg of caffeine, tea has 50mg and a can of cola has 30mg. Many energy drinks do not clearly label the exact caffeine content per serving, but. some products contain as ...
Ask any college student how he or she gets through long study sessions, all-nighters, and the always grueling finals week and he or she will most likely reference some caffeine-containing beverage as the antidote, with energy drinks becoming an ever increasing option. The effects, both physiological and psychological, of the ingredients in energy drinks (caffeine and, to a lesser degree ...
Importantly, this study will be guided by a thesis stating as; energy drinks are beneficial to individuals taking them. I will talk about the benefits of energy drinks to individuals' health both physically and mentally. I will also look at the effectiveness of energy drinks to workers in different workplaces (Stone 107-388). Main body
sugar-sweetened soda beverage with one serving of water per day at baseline w as related to a lower incidence of. obesity. A cross-national study of 75 countries found that each 1% rise in soft ...
Here is a breakdown of the thesis statement: 1. Energy drinks contain high levels of caffeine and sugar: - Caffeine is a stimulant that can cause increased heart rate, high blood pressure, and agitation. - Excessive sugar intake can contribute to weight gain, tooth decay, and an increased risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes. 2.
The main purpose of the proposal research is to conduct the influence of energy drinks based on caffeine on people's psychological condition, paying significant attention to the arouse of aggression in their behavior. Price Influence on Energy Drink Consumption Behavior. The goal of the report is to explore the consumption behavior of ...
Thesis Statement Energy Drinks - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.