- Communications
- Computer Science
- Criminal Justice
- Environmental Management
- Forensic Psychology
- Healthcare Admin
- Human Resources
- Project Management
- Social work
- Special Education
- Sports Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Adult Education
- Business Intelligence
- Early Childhood Education
- Educational Technology
- Homeland Security
- Information Systems Security
- Information Technology
- International Business
- Management Information Systems
- Nonprofit Management
- School Counseling
- Academic Publishing Guide
- Building a Graduate School Resume or CV
- Choosing Between a Thesis or Non-thesis Master's Degree
- Expert Guide to Studying Abroad
- FAQ: Online Master's Degrees
- Grad School Guide Book
- Graduate School for Students with Disabilities
- Green Graduate Degrees
- How to Be a Successful Grad Student
- How to Choose the Right Graduate Program
- How to Get a Master's Degree in an Unrelated Field
- How to Transfer College Credits in Grad School
- How to Write a Winning Personal Statement
- Inside Graduate Admissions
- Ivy League Grad Schools
- Master's Degrees for Veterans
- Master's Degree for Women
- Mental Health in Grad School
- Progressive LGBTQ Graduate Degrees
- Should You Apply for a Graduate School Assistantship?
- Surviving Grad School with a Family
- Taking a Gap Year Before Grad School
- Women in STEM Graduate Resources
- Writing a Successful Statement of Purpose
- Alternative Ways to Pay for School
- The Best Part-Time Jobs During Grad School
- Company Funded Graduate School
- FAFSA For Grad Students
- Financial Aid Resources
- Graduate Student Loans
- Paying for Your Master's Degree
- Paying Off Student Loans
- Paying for Your PhD
- Fellowship Opportunities
- LGBTQ Scholarships
- MBA Scholarships
- Scholarship Resources
- Scholarships for Veterans
- Scholarships for Women
- Crushing the GRE Guidebook
- GMAT Guidebook
- Guide to the LSAT
- MCAT Prep for Medical School
- Study Guide: Exam Resources
- TOEFL Prep for Non-Native English Speakers
- Financial Aid PhD Scholarships and Financial Aid

PAYING FOR YOUR PHD Expert Tips, Scholarships Opportunities and Resources for Financing an Advanced Degree
The average yearly tuition for a PhD program is slightly above $16,000, which means students will invest about $80,000 in tuition fees alone for a five-year program. Add in fees, cost-of-living, travel expenses and the figure can easily surpass six figures. Yet, it is possible to fund a PhD program without breaking the bank and going into debt.
Featured Online Schools
- PhD Cost Breakdown
- PhD Financial Aid Options
- Expert Spotlight: Lawrence Burns, PhD
- Earning Outlook for Phd Students
- Most Lucrative PhD Careers
- Expert Spotlight: Darren Pierre, PhD
- PhD: By The Numbers
- Additional Financial Aid Resources
PHD COST BREAKDOWN
The value of a college education should not be understated, but neither should its actual cost. Earning a doctoral degree can be an expensive proposition. According to the latest data from the National Center for Education Statistics, the average tuition and fees for a graduate program of study was $16,435 in 2012-2013. The table below outlines the 2012-2013 graduate tuition and fees by academic institution.
- All Institutions $16,435
- Public $10,408
- Private Non-Profit $23,698
- Private For-Profit $14,418
Source: National Center for Education Statistics
A rough calculation of the number of years it takes to complete a doctoral program, multiplied by the average 2012-2013 tuition and fees from the NCES, reveals the following total cost figures by academic field of study.
A five- to six-figure education is something to take seriously as there are debt implications after leaving finishing a PhD program. Graduating doctoral students in 2013 left school with an average debt of just over $15,000, according to the National Science Foundation. By field, students in the Social Sciences, Education and Humanities graduate with the highest levels of student debt:
- Education: $26,566
- Social Sciences: $26,222
- Humanities: $21,485
Conversely, the science and technology fields graduate students with the lowest debt figures:
- Physical Sciences: $6,342
- Engineering: $7,031
- Life Sciences: $11,905
- Physical Sciences 78.2%
- Engineering 75.1%
- Life Sciences 67.2%
- Humanities 48.4%
- Social Sciences 46.5%
- Education 44.1%
Source: National Science Foundation, Survey of Earned Doctorates, 2013
While these figures may seem alarming, a deeper dive into survey data from the National Science Foundation actually paints a more positive picture. Overall, more than 62 percent of all doctoral recipients graduate from school without a single dollar of debt.
Prospective students can use the table below to get a better sense of the percentage of students who take on debt at incremental levels in each field of academic study. A majority of students graduate with $10,000 or less in debt after finishing their doctoral degree.
PhD Cost Factors
The total cost of earning a doctoral degree is variable because of the sheer number of different factors involved. Tuition is not the only cost to consider when thinking about applying to a PhD program.
Typically, students pay full tuition rates during their first three years of doctoral study and receive reduced tuition rates for the remainder of the program. However, the actual cost of tuition does vary and may be dependent on the student’s actual degree program.
Graduate students pay a range of fees, with the most common including:
- Health Services (access to health facilities on campus)
- Health Insurance (personal health insurance)
- Student Activity (subsidizes athletics and other clubs)
- Student Recreation (access to recreational facilities on campus)
Some programs estimate students should be prepared to pay between $3,000 and $4,500 per academic year in student fees and health insurance costs.
Students with a master’s degree or coursework in a similar graduate program may be able to transfer credits into their doctoral program. That can lower the total number of credits required to graduate, which can lower the total cost of the degree. However, some institutions do limit the amount of tuition credits that can be applied for graduate work done in a related field at other institutions.
Whether or not the student has an assistantship does not affect the cost of textbooks and other academic materials. Books are a revolving charge, one a student should plan upon each semester or quarter.
Housing, utilities and food are considered indirect expenses students incur during their education. PhD students should plan on anywhere from $12,000 to $25,000 and up for living expenses each year. Again, this figure is highly variable based on the location of the university and the cost-of-living in that area.
Owning a car means additional budgeting for insurance, car payments and gas. Additionally, students may need to travel for conferences and research. Without funding from a graduate student association or grant program, the student will have to cover these costs individually.
PhD students with children may have to account for childcare costs. Purchasing a new computer and other supplies may also be required. This type of budgeting will vary from individual to individual, program to program.
Most PhD programs allow students to progress at their own pace, requiring them to complete and defend their dissertation within a certain time period (e.g. six years). However, the time it takes to complete a dissertation depends on the student, area of study, research, etc. This can impact cost of attending a doctoral program.
Example Cost of Attendance
A student’s budget should include the total cost of attendance—that is both direct (tuition and fees) and indirect costs (e.g. housing). This budget is the starting point for determining the student’s financial need, how much financial aid they require, and if they can afford to attend a doctoral program. Below is a sample five-year total cost of attendance chart based on an in-state tuition program, with a budget that assumes fixed costs for fees and indirect costs, such as housing. It also does not take into account assistantships and tuition waivers for assistants.
Based on a figure that’s slightly below the 2012-2013 average graduate tuition cost, the total cost of attendance can still produce sticker shock. An average student in a program that charges $12,000 per year in tuition could have to pay between $30,000 and $45,000 year in total costs.
PhD FINANCIAL AID OPTIONS
Prospective PhD candidates have an abundance of financial aid options to help fund their graduate studies. Typically, students are fully funded by a combination of sources, including scholarships, fellowships, research assistantships, teaching assistantships, or student loans.
It is important for students to note that most sources of aid are awarded by individual academic programs, so they should follow-up with their department for up-to-date information.
Below is a high-level overview of the common types of graduate financial aid.
Prospective PhD candidates can turn to a variety of funding sources, including scholarships, grants, and fellowships to support their education financially. As discussed, most students use a combination of one or more of these funding sources to finance their degree program and research.
PhD students can apply for a variety of scholarships that award students with funds that can be used to help cover the cost of tuition, books and other fees.
Grants are similar to scholarships and are academic-based awards that can be used to augment other sources of financial aid.
Fellowships are a different type of funding that may encompass a scholarship or grant and can be used to fund research, study and teaching in the US and internationally. Many fellowships provide full tuition and a yearly stipend to students.
A PhD should never be an end in itself but rather a means to an end. The path to a PhD is an arduous one and should never be undertaken without serious thought to what it will bring the student. That said, there is money available for graduate study in most fields, and a student in the humanities should be very careful to apply to appropriate programs which fund their grad students.
- Engineering
- Physical Sciences
The SMART program is designed to support graduate students studying in STEM disciplines and offers a range of other benefits, including supplies and health insurance allowances and employment placement services with the DoD after graduation.
The National Defense Science and Engineering Graduate Fellowship is a three-year graduate fellowship that is designed to support doctoral students across fifteen engineering disciplines.
This three-year fellowship program supports the research efforts of doctoral students in STEM-related fields of study and allows them to pursue their work at any accredited graduate program in the country.
Renewable award for graduate students enrolled in a full-time APA-accredited doctoral program of study in psychology. Underrepresented, minority students are encouraged to apply.
This fellowship is open to female scholars and is designed to help offset the doctoral student’s living expenses during her final year of working on a dissertation.
This fellowship is a single-year of funding that is designed to support the doctoral research of a student working in child psychology.
The Javits Fellowship is provided on a needs- and competitive-basis to graduate students pursing graduate degrees in the humanities, social sciences, and the arts.
Two fellowships are awarded to support doctoral students who plan to study at the American School of Classical Studies in Athens, Greece for a year.
The Richard M. Weaver Scholarship is open to graduate student members of the Intercollegiate Studies Institute and supports the academic work of scholars pursuing teaching careers at the college level.
The AICPA fellowship is designed for minority students pursuing or planning to pursue a doctorate in accounting.
Five scholarships are available to provide financial assistance to graduate students pursuing studies in accounting and plan on earning CPA licensure.
This fellowship provides financial support to female scholars conducting research and economic analysis into natural resource, food, or agricultural issues.
This renewable, four-year fellowship is designed to support a scholar’s work in the field of stewardship science: nuclear science, high density physics, and materials under extreme conditions and hydrodynamics.
This multi-year fellowship supports doctoral research in several fields, ranging from chemistry to geology, materials science to physics and connects fellows with NPSC employer partners.
The NWRI fellowship program is open to full-time doctoral students conducting water-based research in areas such as water quality, water treatment and technologies, water supplies and water resources.
Really think about your reasons for getting a PhD. Critically exam the support systems you have in place to get you through the journey: 50 percent of doctoral students suffer from depression. Utilize services like the counseling center on your college/university campuses to help you respond to the stressors that may occur with the transition.
ASSISTANTSHIPS, FELLOWSHIPS AND LOANS
Graduate assistantships.
Graduate assistantships are a form of academic appointment and are provided by individual departments. Competitive in nature, they are typically awarded on the basis of the student’s academic accomplishments and potential in the graduate program of study. Most programs provide appointments for one year at time and students receive a tuition credit or waiver and monthly stipend. There are three types of assistantships: Teaching Assistantships, Assistant Lecturers, and Research Assistants.
Teaching assistants perform a range of support duties for faculty members at a university, including grading papers and teaching classes.
Lecturers may serve as instructors in the academic department where they are studying.
Research assistants conduct and assist faculty members with research projects in the student’s area of interest.
Fellowships
Fellowships are short-term funding opportunities (typically 9- to 12 months) provided to students in the form of tuition credits and/or stipends. They support a student’s graduate study in their field of choice, may assist them in their research, or gain professional training in an area of interest. Fellowships are competitive and are available in two types: University-based and External.
Individual schools, colleges, and departments at a university (e.g. College of Science, Department of English) may have endowed fellowships. Students are either nominated for an award by their department or may be open to an application process.
External fellowships are funded by foundations, government agencies and other groups and provide opportunities to study both in the US and abroad. For example, the Department of Defense offers the National Defense Science & Engineering Graduate Fellowship to engineering students studying in one of sixteen engineering specialties.
Corporations
Many companies and businesses have created scholarship, fellowship, and tuition reimbursement programs for their employees. Depending on the company, there may be a possibility it supports the graduate school efforts of its employees. Speak to the Human Resources department to learn more about the potential funding avenues available.
Graduate students may borrow funds from the federal government under two loan programs: William D. Ford Federal Direct Loan Program and the Federal Perkins Loan Program.
Private financial institutions, including banks and credit unions, offer unsecured educational loans to graduate students. These loans must be repaid with interest. The interest rates, loan amount, and repayment terms are based on the credit worthiness of the borrower.
Federal work study provides students with demonstrated financial need part-time job opportunities that allow them to earn income while they are in graduate school. The program focuses on placing students in community service situations related to the student’s academic course of study. A majority of jobs are on-campus, but some schools may have some off-campus jobs with nonprofit agencies and other groups. It is important to note that some universities may not allow students to use their federal work study for tuition, but other related expenses (e.g. books, fees).
EXPERT SPOTLIGHT: Lawrence Burns, PhD
What should a future phd student consider when selecting a program of study .
Speaking in the humanities, a student is best advised, I think, to select the faculty member with whom he or she wishes to study rather than simply a program. This faculty member becomes the student’s mentor, a relationship that lasts well beyond graduate school years. Because the mentor becomes the student’s primary reference, his or her standing in the field can and does have an impact on pre- and post-doctoral grants a student might win as well as on the student’s success on the academic job market.
It is a delicate balance though, because one must also look at programs that have standing in a particular field and at institutions that can afford to fund their PhD students throughout their graduate years.
Much is made about the saturation of PhD graduates and not enough positions — both in academic and the private sector. Should that dissuade a student from pursuing a PhD?
Yes, of course. Again, a PhD is not something that comes easily, and it should not be pursued without a reason for it. On the other hand, for students who are committed to their fields, and for whom that field is a career choice, the PhD is still the only way into the university job market.
There is a catch-22 in the world of post-graduate education. Research universities need to turn out research, and researchers often depend on their grad students to assist them–in all fields–and departments on their PhD candidates to teach many undergraduate courses. PhD students are thus recruited regardless of the job market for the PhD holders.
The challenges in funding the PhD for me were less about how am I going to pay for this degree, but making the adjustment from being a full-time salaried employee to now, taking a significant pay cut to serve as a graduate assistant.
EARNING OUTLOOK FOR PHD STUDENTS
Potential career earnings should be a significant part of the discussion when considering whether or not to pursue a doctoral degree. Completing an advanced program of study could increase an individual’s earning potential with their current or future employers.
Research from the Bureau of Labor Statistics reveals a direct correlation between educational attainment and career success—both in employment opportunities and annual salaries. Doctoral degree holders are some of the highest paid professionals in the country. The table below outlines the difference in earnings by degree level in 2014.
source: Bureau of Labor Statistics, Earnings and Unemployment by Educational Attainment
- Industry or Business $97,700
- Government $82,000
- Nonprofit Organizations $72,500
- Other $70,000
- Academia $60,000
Source: National Science Foundation, Survey of Earned Doctorates
In turn, prospective students should consider how their sacrifice of time and money will pay off when they embark in their careers. Some professional fields have a higher return on investment than others. A majority of PhD candidates endeavor to become tenured-track faculty members, but they should realize that academia is one of the lowest paying sectors for individuals with a doctoral degree.
A review of National Science Foundation survey information shows that the best paying professional areas for PhD graduates include Industry and Business—with an average salary of $97,700. At the bottom of the list? Academia.
MOST LUCRATIVE PHD CAREERS
So, which PhD degrees pay the best?
According to the NSF, business, economics, and engineering are consistently among the best earning academic fields regardless of industry. The following tables outline the highest paying academic fields by professional area of work after graduation.
- Business Management and Administration $110,000
- Economics $82,000
- Engineering $79,000
- Health Sciences $70,000
- Education $60,000
- Business Management and Administration $135,000
- Economics $115,000
- Mathematics and Computer Information Sciences $115,000
- Geosciences $110,000
- Engineering $98,000
- Economics $112,500
- Business Management and Administration $96,590
- Engineering $96,500
- Mathematics and Computer Information Sciences $95,300
- Health Sciences $94,000
- Business Management and Administration $105,000
- Economics $100,000
- Mathematics and Computer Information Sciences $100,000
- Health Sciences $98,000
At the occupational level, 2012 employment research from the Bureau of Labor Statistics revealed the best paying doctoral career was Physicist ($109,600), followed by Astronomers ($105,410), and Engineering Professors ($94,130).
Overall, the top 10 most lucrative PhD careers include the following:
- 1 Physicists $109,600
- 2 Astronomers $105,410
- 3 Engineering Professors $94,130
- 4 Economics Professors $90,870
- 5 Health Specialties Professors: $90,210
- 6 Agricultural Sciences Professors $86,260
- 7 Biochemists and Biophysicists $84,940
- 8 Forestry and Conservation Science Professors $84,090
- 9 Physics Professors $80,720
- 10 Medical Scientists $79,930
EXPERT SPOTLIGHT: Darren Pierre, PhD
How has earning a phd impacted you personally and professionally.
Personally, the PhD was an incredibly introspective process. I believe for many, they go into the PhD thinking one thing, and come out transformed by the experience. I learned and grew personally in how I harness my self-worth, I grew professionally in my ability to humble myself and authentically listen to the feedback given about my work.
Professionally, I move with a greater level of confidence, I have more insight into my own potential in ways I could have never imagined, and all of that propelled me to write my book, The Invitation to Love.
Through your own experience, what are the biggest mistakes prospective PhD students make when choosing and/or funding their PhD?
The biggest mistake that perspective students make is doing the degree for the wrong reason. If you are doing the degree for any other reason that self-motivated factors, you will falter. Doing the PhD to cover areas of insecurity, or low self-worth; doing the PhD for the prestige or title sake, those reasons will have you floundering and faltering when the psychological stressors being to weigh heavy.
Did you create a roadmap--financially or academically--to stay on track to completing your PhD?
Absolutely, you have to have a plan and work that plan. Each Sunday, I would develop the week's action plan, I would carve out everything from when I was doing assignments/research to when I would work out, everything was on a schedule so that even when the fog of the process set in, I had headlights (my schedule) that allowed me to drive consistently when the road ahead was hard to see.
PHD: BY THE NUMBERS
Doctoral education in the U.S. is a varied and broad system, one that has been growing in popularity. In the 2013-2014 academic year, more than 178,000 doctoral degrees were conferred to students nationally, according to data from the National Center for Education Statistics.
- Doctoral Education Continues to Grow
- Engineering and Physical Sciences Dominate
- STEM Fields are the Most Popular
- Only Half of Students Earn a PhD in the Same Academic Field as their Master’s Degree
- Doctoral Degrees are an Investment in Time
- Primary Source of Funding Varies by Program
In its survey of earned doctorates, the National Science Foundation learned the number of doctoral recipients increased by nearly 30 percent between 2003 and 2013.
The most popular academic areas of study were Engineering and the Physical Sciences.
- Engineering 69.80%
- Physical Sciences 59.30%
- Health Sciences 53.60%
- Life Sciences 44.60%
- Other 38.90%
- Social Sciences 19.90%
- Humanities 9.10%
- Education -25.70%
Within the engineering and physical sciences disciplines, multiple sub-fields have been experiencing explosive interest and enrollments, with some programs (e.g. physics, materials science engineering) growing by more than 70 percent between 2003 and 2013.
- Other engineering 127.5%
- Materials science engineering 86.5%
- Aerospace, aeronautical, and astronautical engineering 74.5%
- Mechanical engineering 70.5%
- Electrical, electronics, and communication engineering 53.6%
- Chemical engineering 46.0%
- Computer and information sciences 119.1%
- Mathematics 83.0%
- Physics and astronomy 76.7%
- Geosciences 28.8%
- Chemistry 22.0%
According to NSF, the science, technology, engineering and mathematics fields are the most popular doctoral areas of study.
- Life Sciences 23.3%
- Physical Sciences 17.6%
- Engineering 17.0%
- Social Sciences 15.9%
- Humanities 10.7%
- Education 9.4%
Interestingly, slightly more than 56 percent of graduate students continue into a doctoral program in the same field as their master’s degree. Rates are highest in the humanities, engineering, and social sciences fields.
- Humanities 67.6%
- Engineering 65.7%
- Social Sciences 65.6%
- Education 61.5%
- All Fields 56.1%
- Physical Sciences 53.4%
- Life Sciences 35.5%
It requires approximately 7.5 years of study for the average graduate student to complete a doctoral degree after enrolling in graduate school. Education takes the longest — more than 11 years, while the physical sciences and engineering fields only require 6.5 to 6.6 years of study to complete.
- Education 11.7
- Humanities 9.2
- Social Sciences 7.7
- All Fields 7.5
- Life Sciences 6.9
- Engineering 6.6
- Physical Sciences 6.5
According to the NSF, the most common source of funding for doctoral students are teaching and research assistantships. The table below details the primary source of funding for students by academic area of study.
- Life Sciences Fellowships/ Grants
- Physical Sciences Research Assistantships
- Social Sciences Teaching Assistantships
- Engineering Research Assistantships
- Education Own Resources
- Humanities Teaching Assistantships
- All Fields Research Assistantships
The following table includes a breakout of the primary funding source by major field of study, according the National Science Foundation.
Source: http://www.nsf.gov/statistics/sed/2013/data-tables.cfm
ADDITIONAL FINANCIAL AID RESOURCES
The ultimate financial goal of any PhD student should be to complete their program successfully and move into a professional career with as little debt as possible. The resources below are available to help students locate scholarships and other funding sources that can help make that goal a reality.
Unigo offers a selection of financial assistance resources for graduate students, including a scholarship directory, a scholarship match tool, educational information on student loans and funding options, and more.
Scholarships.com is a website that provides a selection of financial aid information, including a searchable scholarship directory, insights into funding trends, financial aid calculators, and information about grants and fellowships.
Peterson’s is an educational resource site that includes a searchable scholarship database, articles and advice columns, and a catalog of graduate school profiles.
FinAid.org is an educational resource site that focuses on financial aid and offers information about student loans, federal financial aid, financing a doctoral education, and includes a scholarship search option.
An office of the U.S. Department of Education, Federal Student Aid is the country’s largest provider of financial aid. Graduate students can learn about and pally for loans, grants, and work-study funds to pay for their doctoral education.
FastWeb is a financial aid-focused website that offers a searchable scholarship directory that allows students to focus their search to their major area of study, work experience, and personal and professional activities.
Chegg is an online educational portal that not only offers used textbooks, but a scholarship database as well.
- PhD Degree Funding
Harvard guarantees full financial support to PhD students—including tuition, health fees, and basic living expenses—for a minimum of five years.
- Dissertation
- Fellowships
- Maximizing Your Degree
- Before You Arrive
- First Weeks at Harvard
- Harvard Speak
- Pre-Arrival Resources for New International Students
- Alumni Council
- Student Engagement
- Applying to Degree Programs
- Applying to the Visiting Students Program
- Admissions Policies
- Cost of Attendance
- Express Interest
- Campus Safety
- Commencement
- Diversity & Inclusion Fellows
- Student Affinity Groups
- Recruitment and Outreach
- Find Your Financial Aid Officer
- Master's Degree Funding
- Federal Student Aid
- Other Sources of Support
- Financial Wellness
- Consumer Information
- Life Sciences
- Policies (Student Handbook)
- Student Center
- Title IX and Gender Equity
Harvard's financial support package is typically for the first four years of study and the completion year, using a tiered tuition structure that reduces tuition over time as students progress through their degree programs. This multiyear funding package includes a combination of tuition grants, stipends, traineeships, teaching fellowships, research assistantships, and other academic appointments. In addition, Harvard Griffin GSAS students are particularly successful in securing grants, fellowships , and other sources of external funding as part of their professional development.
The standard funding package includes:
- grant toward tuition and fees—paid in full for years 1 through 4, plus the dissertation completion year, with a partially subsidized dental plan option available
- living expense stipend during years 1 and 2
- a combination of stipend, teaching fellowships, and/or research assistantships during years 3 and 4
- if noted in your Notice of Financial Support, summer research funding following the first four academic years from Harvard Griffin GSAS or faculty grants
- stipend and/or research support during the completion year.
In some programs, the timing and structure of living expense support may vary from this pattern. For example, students in the sciences typically receive full funding until they complete their degrees.
Financial Aid
Share this page, explore events.
Find Education Scholarships for PhD Students
Every little bit helps, get a head start funding your doctoral degree using the U.S. News scholarship database. Apply for money now.
- Clear Filters
Elevar Scholars Program
California State University, Fullerton
What You'll Need
- Application Form
- Recommendation
- Demonstrated Financial Need
- Merit-based Aid
Description
Funded by the CSU and Giles T. Brown Endowment for Graduate Studies through the Cal State Fullerton Philanthropic Foundation, this program seeks to increase the diversity of students completing graduate degree programs, encourage further study in doctoral programs and promote consideration of university faculty careers. If provides fellowships to economically disadvantaged CSUF students who have overcome educational disadvantages or hardships. The fellowships are intended to minimize students’ debt burden, allowing them to complete their program more quickly and commence doctoral study.
Fletcher Jones Fellowship
University of California, Irvine
- Need-based Aid
The Fletcher Jones Fellowship is a highly prestigious award, made available through funding from the Fletcher Jones Foundation. It is competitively awarded to an outstanding doctoral student who has advanced to candidacy and demonstrates financial need. The award of a one-year fellowship of approximately $22,290, to be used as a stipend, is intended to assist with doctoral degree completion.
Chancellor's Club Fellowship
Chancellor’s Club Fellowships recognize our most academically superior doctoral and MFA students — those who exhibit outstanding promise as scholars, researchers, and public leaders. Nominated students must be first-generation college students, with neither parent having received a four-year degree. Nominations are made by Associate Deans for scholars in their respective schools.
Miguel Velez Scholarship
The Miguel Velez Scholarship provides financial support to graduate students who demonstrate outstanding past academic achievement as well as future promise, have financial need, and are citizens and residents of a Latin American country. Preference is given to citizens of Colombia.
James Harvey Scholar
The James Harvey Scholar award provides financial support to graduate students who demonstrate outstanding past academic achievement as well as future promise, have financial need, and are completing a publishable thesis or dissertation on homosexuality or the life or works of James Harvey.
Otto W. Shaler Scholarship
The Otto W. Shaler Scholarship provides financial support to international graduate students who have financial need, and who demonstrate outstanding past academic achievement as well as future promise. Each school may submit no more than two applications for this award.
Brython Davis Fellowship
Overview: The Brython Davis Fellowship provides financial support to students who demonstrate outstanding past academic achievement as well as future promise, have financial need, are U.S. citizens, and are the child of a service member or veteran of the U.S. Navy or Marine Corps.
La Verne Noyes Fellowship
The La Verne Noyes Fellowship provides financial support to graduate students who demonstrate outstanding past academic achievement as well as future promise, have financial need, are U.S. citizens, and are descendants of World War I U.S. Army or Navy veterans.
Barbara Bell Blake Nursing Scholarship
Purdue University, Northwest
Need Based: Please note: This specialty scholarship requires a separate application. Even if you've already applied for a PNW admissions scholarship, you need to submit a separate application to be eligible.
Intel SWE Scholarship (Graduate)
Society of Women Engineers (SWE)
SWE Scholarships support those who identify as a female/woman and are pursuing an ABET-accredited bachelor or graduate student program in preparation for careers in engineering, engineering technology and computer science in the United States. US Citizenship required. Minimum GPA: 3.0. Class: Graduate (Masters, Doctoral) Major: CprE, CS, EE.
Google PhD fellowship program
Google PhD Fellowships directly support graduate students as they pursue their PhD, as well as connect them to a Google Research Mentor.
Nurturing and maintaining strong relations with the academic community is a top priority at Google. The Google PhD Fellowship Program was created to recognize outstanding graduate students doing exceptional and innovative research in areas relevant to computer science and related fields. Fellowships support promising PhD candidates of all backgrounds who seek to influence the future of technology. Google’s mission is to foster inclusive research communities and encourage people of diverse backgrounds to apply. We currently offer fellowships in Africa, Australia, Canada, East Asia, Europe, India, Latin America, New Zealand, Southeast Asia and the United States.
Quick links
- Copy link ×
Program details
Application status, how to apply, research areas of focus, review criteria, award recipients.
Applications are currently closed.
Decisions for the 2024 application cycle will be announced via email in July 2024. Please check back in 2025 for details on future application cycles.
- Launch March 27, 2024
- Deadline May 8, 2024
- Winner selected by July 31, 2024
The details of each Fellowship vary by region. Please see our FAQ for eligibility requirements and application instructions.
PhD students must be nominated by their university. Applications should be submitted by an official representative of the university during the application window. Please see the FAQ for more information.
Australia and New Zealand
Canada and the United States
PhD students in Japan, Korea and Taiwan must be nominated by their university. After the university's nomination is completed, either an official representative of the university or the nominated students can submit applications during the application window. Please see the FAQ for more information.
India and Southeast Asia
PhD students apply directly during the application window. Please see the FAQ for more information.
Latin America
The 2024 application cycle is postponed. Please check back in 2025 for details on future application cycles.
Google PhD Fellowship students are a select group recognized by Google researchers and their institutions as some of the most promising young academics in the world. The Fellowships are awarded to students who represent the future of research in the fields listed below. Note that region-specific research areas will be listed in application forms during the application window.
Algorithms and Theory
Distributed Systems and Parallel Computing
Health and Bioscience
Human-Computer Interaction and Visualization
Machine Intelligence
Machine Perception
Natural Language Processing
Quantum Computing
Security, Privacy and Abuse Prevention
Software Engineering
Software Systems
Speech Processing
Applications are evaluated on the strength of the research proposal, research impact, student academic achievements, and leadership potential. Research proposals are evaluated for innovative concepts that are relevant to Google’s research areas, as well as aspects of robustness and potential impact to the field. Proposals should include the direction and any plans of where your work is going in addition to a comprehensive description of the research you are pursuing.
In Canada and the United States, East Asia and Latin America, essay responses are evaluated in addition to application materials to determine an overall recommendation.
What does the Google PhD Fellowship include?
Students receive named Fellowships which include a monetary award. The funds are given directly to the university to be distributed to cover the student’s expenses and stipend as appropriate. In addition, the student will be matched with a Google Research Mentor. There is no employee relationship between the student and Google as a result of receiving the fellowship. The award does not preclude future eligibility for internships or employment opportunities at Google, nor does it increase the chances of obtaining them. If students wish to apply for a job at Google, they are welcome to apply for jobs and go through the same hiring process as any other person.
- Up to 3 year Fellowship
- US $12K to cover stipend and other research related activities, travel expenses including overseas travel
- Google Research Mentor
- 1 year Fellowship
- AUD $15K to cover stipend and other research related activities, travel expenses including overseas travel
- Up to 2 year Fellowship (effective from 2024 for new recipients)
- Full tuition and fees (enrollment fees, health insurance, books) plus a stipend to be used for living expenses, travel and personal equipment
- US $10K to cover stipend and other research related activities, travel expenses including overseas travel
- Yearly bursary towards stipend / salary, health care, social benefits, tuition and fees, conference travel and personal computing equipment. The bursary varies by country.
Early-stage PhD students
- Up to 4 year Fellowship
- US $50K to cover stipend and other research related activities, travel expenses including overseas travel
Late-stage PhD students
- US $10K to recognise research contributions, cover stipend and other research related activities, travel expenses including overseas travel
- US $15K per year to cover stipend and other research related activities, travel expenses including overseas travel
Southeast Asia
- US $10K per year for up to 3 years (or up to graduation, whichever is earlier) to cover stipend and other research related activities, travel expenses including overseas travel
Is my university eligible for the PhD Fellowship Program?
Africa, Australia/New Zealand , Canada, East Asia, Europe and the United States : universities must be an accredited research institution that awards research degrees to PhD students in computer science (or an adjacent field).
India, Latin America and Southeast Asia : applications are open to universities/institutes in India, Latin America (excluding Cuba), and in eligible Southeast Asian countries/regions (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam).
Restrictions : All award payments and recipients will be reviewed for compliance with relevant US and international laws, regulations and policies. Google reserves the right to withhold funding that may violate laws, regulations or our policies.
What are the eligibility requirements for students?
All regions
- Students must remain enrolled full-time in the PhD program for the duration of the Fellowship or forfeit the award.
- Google employees, and their spouses, children, and members of their household are not eligible.
- Students that are already supported by a comparable industry award are not eligible. Government or non-profit organization funding is exempt.
- Past awardees from the PhD Fellowship program are not eligible to apply again.
- Grant of the Fellowship does not mean admission to a PhD program. The awardee must separately apply and be accepted to a PhD program in computer science (or an adjacent field) at an eligible institution.
- Grant of the Fellowship will be subject to the rules and guidelines applicable in the institution where the awardee registers for the PhD program.
Nominated students in Africa, Australia and New Zealand, Canada and the United States, East Asia and Europe.
Universities should only nominate students that meet the following requirements:
- Africa: Incoming PhD students are eligible to apply, but the Fellowship award shall be contingent on the awardee registering for a full-time PhD program in computer science (or an adjacent field) within the academic award year of the Fellowship award, or the award shall be forfeited.
- Australia and New Zealand : early-stage students enrolled in the first or second year of their PhD (no requirement for completion of graduate coursework by the academic award year).
- Canada and the United States : students who have completed graduate coursework in their PhD by the academic award year when the Fellowship begins.
- East Asia: students who have completed most of graduate coursework in their PhD by the academic award year when the Fellowship begins. Students should have sufficient time for research projects after receiving a fellowship.
- Europe: Students enrolled at any stage of their PhD are eligible to apply.
Direct applicant students in India, Latin America and Southeast Asia
- Latin America : incoming or early stage-students enrolled in the first or second year of their PhD (no requirement for completion of graduate coursework by the academic award year).
What should be included in an application? What language should the application be in?
All application materials should be submitted in English.
For each student nomination, the university will be asked to submit the following material in a single, flat (not portfolio) PDF file:
- Student CV with links to website and publications (if available)
- Short (1-page) resume/CV of the student's primary PhD program advisor
- Available transcripts (mark sheets) starting from first year/semester of Bachelor's degree to date
- Research proposal (maximum 3 pages, excluding references)
- 2-3 letters of recommendation from those familiar with the nominee''s work (at least one from the thesis advisor for current PhD students)
- Student essay response (350-word limit) to: What impact would receiving this Fellowship have on your education? Describe any circumstances affecting your need for a Fellowship and what educational goals this Fellowship will enable you to accomplish.
- Transcripts of current and previous academic records
- 1-2 letters of recommendation from those familiar with the nominee's work (at least one from the thesis advisor)
Canada, East Asia, the United States
- Cover sheet signed by the Department Chair confirming the student passes eligibility requirements. (See FAQ "What are the eligibility requirements for students?")
- Short (1-page) CV of the student's primary advisor
- 2-3 letters of recommendation from those familiar with the nominee's work (at least one from the thesis advisor)
- Research / dissertation proposal (maximum 3 pages, excluding references)
- Student essay response (350-word limit) to: Describe the desired impact your research will make on the field and society, and why this is important to you. Include any personal, educational and/or professional experiences that have motivated your research interests.
- Student essay response (350-word limit) to: Describe an example of your leadership experience in which you have positively influenced others, helped resolve disputes or contributed to group efforts over time. (A leadership role can mean more than just a title. It can mean being a mentor to others, acting as the person in charge of a specific task, or taking the lead role in organizing an event or project. Think about what you accomplished and what you learned from the experience. What were your responsibilities? Did you lead a team? How did your experience change your perspective on leading others? Did you help to resolve an important dispute at your school, church, in your community or an organization? And your leadership role doesn’t necessarily have to be limited to school activities. For example, do you help out or take care of your family?)
Students will need the following documents in a single, flat (not portfolio) PDF file in order to complete an application (in English only):
- Student applicant’s resume with links to website and publications (if available)
- Short (one-page) resume/CV of the student applicant's primary PhD program advisor
- 2-3 letters of recommendation from those familiar with the applicant's work (at least one from the thesis advisor for current PhD students)
- Applicant's essay response (350-word limit) to: Describe the desired impact your research will make on the field and society, and why this is important to you. Include any personal, educational and/or professional experiences that have motivated your research interests.
- Applicant's essay response (350-word limit) to: What are your long-term goals for your pathway in computing research, and how would receiving the Google PhD Fellowship help you progress toward those goals in the short-term?
How do I apply for the PhD Fellowship Program? Who should submit the applications? Can students apply directly for a Fellowship?
Check the eligibility and application requirements in your region before applying. Submission forms are available on this page when the application period begins.
India, Latin America and Southeast Asia: students may apply directly during the application period.
Africa, Australia, Canada, East Asia, Europe, New Zealand, and the United States : students cannot apply directly to the program; they must be nominated by an eligible university during the application period.
How many students may each university nominate?
India, Latin America and Southeast Asia : applications are open directly to students with no limit to the number of students that can apply from a university.
Australia and New Zealand : universities may nominate up to two eligible students.
Canada and the United States : Universities may nominate up to four eligible students. We encourage nominating students with diverse backgrounds especially those from historically marginalized groups in the field of computing. If more than two students are nominated then we strongly encourage additional nominees who self-identify as a woman, Black / African descent, Hispanic / Latino / Latinx, Indigenous, and/or a person with a disability.
Africa, East Asia and Europe : Universities may nominate up to three eligible students. We encourage nominating students with diverse backgrounds especially those from historically marginalized groups in the field of computing. If more than two students are nominated then we strongly encourage the additional nominee who self-identifies as a woman.
*Applications are evaluated on merit. Please see FAQ for details on how applications are evaluated.
How are applications evaluated?
In Canada and the United State, East Asia and Latin America, essay responses are evaluated in addition to application materials to determine an overall recommendation.
A nominee's status as a member of a historically marginalized group is not considered in the selection of award recipients.
Research should align with Google AI Principles .
Incomplete proposals will not be considered.
How are Google PhD Fellowships given?
Any monetary awards will be paid directly to the Fellow's university for distribution. No overhead should be assessed against them.
What are the intellectual property implications of a Google PhD Fellowship?
Fellowship recipients are not subject to intellectual property restrictions unless they complete an internship at Google. If that is the case, they are subject to the same intellectual property restrictions as any other Google intern.
Will the Fellowship recipients become employees of Google?
No, Fellowship recipients do not become employees of Google due to receiving the award. The award does not preclude future eligibility for internships or employment opportunities at Google, nor does it increase the chances of obtaining them. If they are interested in working at Google, they are welcome to apply for jobs and go through the same hiring process as any other person.
Can Fellowship recipients also be considered for other Google scholarships?
Yes, Fellowship recipients are eligible for these scholarships .
After award notification, when do the Google PhD Fellowships begin?
After Google PhD Fellowship recipients are notified, the Fellowship is effective starting the following school year.
What is the program application time period?
Applications for the 2024 program will open in March 2024 and close in May 2024 for all regions. Refer to the main Google PhD Fellowship Program page for each region’s application details.
A global awards announcement will be made in September on the Google Research Blog publicly announcing all award recipients.
How can I ask additional questions?
Due to the volume of emails we receive, we may not be able to respond to questions where the answer is available on the website. If your question has not been answered by a FAQ, email:
Africa: [email protected]
Australia and New Zealand: [email protected]
Canada and the United States: [email protected]
East Asia: [email protected]
Europe: [email protected]
India: [email protected]
Latin America: [email protected]
Southeast Asia: [email protected]
See past PhD Fellowship recipients.
Discover our collection of tools and resources
Browse our library of open source projects, public datasets, APIs and more to find the tools you need to tackle your next challenge or fuel your next breakthrough.


The Savvy Scientist
Experiences of a London PhD student and beyond
How To Get A Fully Funded PhD Scholarship

It may come as a surprise, but when you’re applying for a PhD the difficult part isn’t always getting offered a place at the university. I found this out the hard way!
Instead, securing the funding to support your research can often be the biggest barrier to starting a PhD. Securing a fully funded PhD scholarship can be a great means of funding your research because it offers you lots of academic freedom.
It took me several tries (see my applications timeline and PhD application failures ), but after a few years I was eventually able to secure a fully funded PhD scholarship at my first-choice university.
Now I want to help guide you through how to get a fully funded PhD scholarship for yourself.
Is it Hard to Get a Fully Funded PhD Scholarship?
There are a lot of different types of PhD funding. In fact I’ve written a full post about the PhD funding landscape which you can read here .
Any PhD funding is better than none, yet there is a hierarchy and scholarships sit at the top:

Scholarships and fellowships are typically the most prestigious types of PhD funding and usually come with the highest PhD stipends, therefore they can be tough to secure. As a side note if you’re interested in learning more about how much PhD students typically earn, check out my post here .
PhD scholarships and fellowships are pretty similar (and roughly interchangeable), so to keep things simple I’ll just refer to them both as scholarships going forward.
Project-specific funding comes about when a supervisor is awarded a grant by a funding body and uses this money to employ researchers and carry out the research as outlined in the grant application. If you go with this type of project there are usually restrictions on how much you can change the PhD topic.
Similarly to bursaries, PhD scholarships and fellowships are awarded to the individual student rather than a specific project grant. You therefore have far more academic freedom and scope to tailor a project to your own interests, without having to worry about whether it fits the theme of a certain grant.
Since scholarships are the most lucrative they are usually the most difficult type of PhD funding to get. Your CV and application will therefore need to be stronger than when applying for project-specific funding.
My Journey to Securing a PhD Scholarship
It took me several years to secure PhD funding:

Over this period I decided to work as a research assistant at a few different universities. Firstly this was so that I had a job and was earning money. Secondly, it was relevant experience which would help boost my chances of success when reapplying for a PhD.
It turned out that this work experience would be a big part of how I secured my PhD scholarship. Later in this post I’ll be mentioning papers I authored and prizes I played a part in winning and I want to make it clear that I didn’t do all of this as an undergraduate.
In fact, I did none of it as an undergraduate!
Outstanding undergraduate students may already have names of papers, patents, prizes or something else to show research prowess, but that wasn’t me.
If you’re struggling with securing PhD funding, getting a job as a research assistant in the meantime can be a great idea. Along with building up your research credentials it can also help you to understand whether you’d enjoy a career in research prior to committing to a PhD.
How I Got a PhD Scholarship at Imperial
When I was looking for PhD projects at Imperial I got in contact with a potential PhD supervisor who had advertised a PhD online and we discussed different funding routes.
Before applying for the scholarship I eventually got, there were a few other potential funding options on the table:
- Project-specific funding already in place. This is what initially got me chatting with the supervisor. I had previously learned my lesson that seeing a project advertised online doesn’t mean it is automatically funded!
- An in-progress grant application to a research council which would have funded my PhD. We did also eventually get this grant.
- The prestigious President’s PhD scholarships which funds 50 projects per year at Imperial. I did apply for this but was unsuccessful with the application and didn’t make the short list. This scholarship was more prestigious than the one I eventually won.
During these discussions I got told about the possibility of applying for another scholarship, which was the one I went on to get awarded. This highlights the value of having several applications on the go for different funding pots.
Had I not engaged directly with a supervisor who was within the university I would have never found out about the scholarship, since as far as I know it wasn’t ever advertised online.
Applying for the PhD Scholarship
The first I heard about the PhD scholarship was when I got told that the department was considering putting me forward for it. It turned out that the scholarship would fund one PhD across the entire university, and each department could only put forward one student to apply.
Just one PhD project across the whole university! Even just getting selected to represent the department would be tough.
This all sounded extremely intimidating to me. We’ll shortly come onto things you can do to boost your chances of success.
Here is what I had to provide for the application:
- A copy of the standard university online application: form, CV, personal statement, undergraduate transcript
- PhD scholarship proposal
- Two references
- A statement from the Supervisor / Head of department in support of the scholarship application
How Long Does it Take to Get a PhD Scholarship?
Here is the timeline to me securing my scholarship, from finding a PhD advert through to getting the all important scholarship offer.
- Mid December 2015 – I found an advert for a fully funded PhD project.
- 4th January 2016 – I emailed the potential supervisor with my CV and a cover letter attached, saying that I was interested in the project.
- 15th January – Response from the supervisor: “You have a very strong cv and I think you should apply for a PhD scholarship, have you considered this? Have a look at the details for the President’s scholarship. With a first class degree and several papers I would say you have a strong chance of winning one.”
- 18th January – First chat with supervisor on the phone. We discussed how I had already applied for a PhD in the past (got the place but no funding) with someone who turned out to be a close collaborator of his. We decided this person would be my second supervisor if we got funding.
- 25th January – Supervisor sent me a PhD scholarship project proposal that he and the co-supervisor wanted to propose to me. Yes, they basically wrote it for me. Yes I got lucky.
- 26th January – Received feedback on my personal statement from the supervisor, and got pushed to submit the online application.
- 9th February – First I heard about the scholarship . Since I had been in contact for a few weeks and they had my CV, the supervisor had been speaking about me to support staff. I got told that the department wanted to put me forward for the scholarship: I would be the department’s top choice. Eek!
- 12th February – Deadline to submit the scholarship application. Because I’d already been applying for other funding, this mostly just needed the statement of support from my supervisor and finalisation of the PhD proposal.
- 10th March – Unofficial email from supervisor saying we were successful
- 11th March – Official email notifying me that I’d be awarded the PhD scholarship :

I got the PhD scholarship and was elated! 🎉
From initially speaking to the potential supervisor to getting the scholarship took about 9 weeks. From finding out about the scholarship to getting it took just over 4 weeks.
I certainly don’t expect I was the smartest person to be put forward, even just from the department let alone the whole university. My application included my mediocre A level results (AABC) and not-so-committed marks in the first couple of years of my undergraduate degree.
Even so, I was successful. Let’s now dive into what you can do to get your own PhD scholarship.
How to Get Your Own Fully Funded PhD Scholarship
Step 1: identify available scholarships.
To find potential PhD scholarships I suggest looking on the university website and searching online for funding relevant to your domain. For instance Google has its own PhD fellowships .
The best thing you can do is start chatting with potential supervisors. They will know the funding landscape at that specific university very well and will have a good idea of the best routes for PhD funding.
Also, having a supervisor such as mine who was willing to help so much with the application is incredibly useful to boost your chances of success. It is also a very good indicator that they will be supportive throughout your PhD.
I remember when I was first cold emailing potential supervisors: most replied but some never even acknowledged my message: a good sign that maybe they wouldn’t be the best supervisors to work with…
With all PhD funding it is really important to check your eligibility. There are sometimes some limitations to be aware of, for instance:
- Nationality / Citizenship. Some funding is not available to overseas students. Thankfully this isn’t usually the case with scholarships since they aim to attract the best students.
- Background, including undergraduate marks. There are sometimes minimum requirements for the grade you achieved during your prior degree(s). Of course to get a scholarship you’re competing against other students so we’ll shortly come onto how to stand out.
Step 2: Put Together an Outstanding Application
The bits of your scholarship application you can control usually revolve around:
- Your CV – showcasing why you’re a good choice (see my full post on writing a CV here and examples of other researchers’ CVs here )
- Personal statement – your motivation for wanting to start a PhD
- PhD scholarship proposal – what you would like to spend the scholarship money on
I won’t go into depth now on the actual writing of the application, but let me know if you’d like a separate post about how to compose the personal statement and scholarship proposal.
Generally in order to put yourself in a good position make sure to:
- Give yourself as much time as possible
- Incorporate feedback from your potential PhD supervisor(s)
- Be ready to pester your referees to make sure they submit your references on time
Right, now let’s move onto what you can do to bolster your application in order to give yourself the best chances of winning a PhD scholarship.
How to Improve Your Chances of Securing a Fully Funded PhD Scholarship
Imagine you’re in the position of awarding PhD funding. How do you decide which candidate to pick?
A good starting point would be looking at how much research experience candidates have and what outcomes they achieved. If someone already has a track-record of conducting research it takes away some of the risks during a PhD and is reassuring for funders that they’ll probably do a good job during the PhD.
The more research experience you can evidence in your application, the far stronger you’ll make the PhD scholarship application.
Some of the main traits that the scholarship committee could be looking for in a PhD student include:
- Research competence
- Enthusiasm for research & outreach
- Academic potential and a thirst for knowledge
- Technical knowledge
- Interpersonal skills
Let’s look at what you can do to evidence each of the above.
Demonstrating Research Competence
1. undergraduate research projects.
Hopefully during your degree(s) you’ve had some research experience. Perhaps this is what got you thinking about starting a PhD.
Being able to use this experience to illustrate your interest, experience and competence in research is extremely beneficial in your funding application. Bonus points if you submitted your work to a journal or conference, as we’ll come onto in a moment.
Examples of undergrad projects could be:
- Individual projects e.g. final year project as part of your degree
- Group projects as part of your degree
- UROP outside of term time
Experience working on your own is great for demonstrating independence while group projects can be useful for showing that you can work in a team. Both are useful but being able to work on your own is definitely the more important of the two.
In your application be sure to focus on what you did, what was novel about it and any interesting experimental or analytical techniques you used: especially if they could be applied to the PhD.
Here is what I had on my CV when I applied for my PhD scholarship:
UNIVERSITY RESEARCH PROJECTS Fourth year project: Optimal design of orthoses for treatment of intermittent claudication Conducted motion analysis capture of human joints to test effectiveness of commercially- available orthoses with EMG technology and muscle activation data Analysed test results, concluding in recommending the most appropriate orthoses for individual participants Progressed validation of a physical artificial leg model and OpenSim software model Third year project: 3-D printing of multi-scale porous biocement scaffolds for ligament attachment Prototyped novel magnesium calcium phosphate biocement scaffolds to investigate 3-D printing parameters for optimum implant integration Analysed parts under SEM to verify multi-scale porosity and XRD for detecting phase changes and composition Conducted a statistical analysis of variance study in sample porosity using optical microscopy and deduced the optimum printing parameters to maximise porosity Wrote a technical report and presented results during an oral presentation and viva Part of my CV at the time I applied for the fully funded PhD scholarship
2. Peer-Reviewed Publications
It is often said that papers are the currency of academia. The advantage of having papers starts with your PhD application.
It’s important to say that you don’t need to have papers to get offered a PhD position. You might not need them to get offered funding via a bursary or CDT, unless it is very competitive. But having any papers published will greatly enhance your chance of being offered a PhD scholarship because it’s so much more competitive.
For more on papers see my publishing series here .
How Many Publications Did I Have When I Applied for My PhD Scholarship?
When I was awarded my PhD scholarship I had on my CV:
- 1 x accepted journal paper
- 3 x abstracts from conferences published in the supplementary sections of journals
- 1 x paper under review at a journal (and clearly described as such)
Of these, I was the first author of just one of the published abstracts.
Just being part of the team showed that I was participating in projects which helped the research community.
Publication Tips to Get a PhD Scholarship:
- If you’re interested in a PhD and are offered the chance to get involved with some research which could result in a publication, do it. It will massively help. Even if it doesn’t end up being published any extra research experience is helpful.
- With the rise of arXiv it is now more easy to share early work and protocols. Sure, it isn’t the same as getting something accepted to a peer-reviewed journal or conference but it if you don’t yet have a complete paper ready to go through peer review, you could use arXiv to demonstrate that you’re working on research outputs.
- Already got publications? Here is a direct quote from my PhD supervisor, a professor at Imperia l: “I would also add the quartile and impact factor of the journals (the people reviewing will be non expert in your field). You can get the journal quartile rankings here http://www.scimagojr.com/index.php . Anaesthesia and Journal of Colloid and Interface Science [where I had some of my stuff accepted] are both Q1 and Impact factors of 3.5 and 3.4 respectively which is excellent and should be highlighted.”
3. Attending & Presenting at Conferences
As well as journal articles, another way researchers share their work is by presenting work at conferences. They’re an important part of academia and you’ll undoubtedly attend conferences as a PhD student.
A low stakes way of boosting your prospects of securing a fully funded PhD scholarship are by attending conferences, workshops, symposiums or other meeting points for research. If you’re attending conferences prior to applying for a PhD it can show that you have more than a passing interest in research.
Attending a conference is good for many reasons:
- Learn about potential PhD topics
- Meet current PhD students and ask advice for getting started
- Network with potential PhD supervisors
- Add it to your CV / application and it is something relevant to discuss in a PhD interview
Bonus points if you’re going to a conference which is relevant to your PhD research area. If your CV is looking a little thin I’d suggest highlighting any and every conference you’ve attended. Even small scale research symposiums at a university can be a good way to show that you broadly know how research gets presented.
Going to conferences is great but even better is submitting research to one and ideally presenting it yourself. The cherry on the top is if you, or the person from your group presenting the work, win a prize:

It is particularly useful when accepted abstracts get published as proceedings in a journal. This means that:
- You get a publication out of it
- People not at the conference can see your work, either for PhD interviews or citing it
I wouldn’t worry too much about the prestige of a conference. Showing that you have any experience attending one is great.
I also wouldn’t worry about posters vs oral presentations. Again, experience with either is fantastic.
Conferences on my CV when applying for my PhD scholarship
When I applied for my scholarship funding I’d been to a few different conferences and had some work accepted.
I was very fortunate that when I was applying for a PhD my CV looked like this, with three prizes from conferences:
Burton, M., Heyman, J., Clark, J. , Owens, D. (2015) Ventilation problems in a shared airway: the effect of the compression of the endotracheal tube during tonsillectomy. Unpublished poster presentation at: All-Wales Airway Group , 15 May 2015, Newport, Wales. [Poster presented by co-author and awarded first prize ] Clark, J. , Short, A., Chawathe, M., Francis, J., Saxena, N., Bogod, D., Girotra V (2014) Development of a realistic epidural simulator – a translational research project. Anaesthesia ; s4 69: 1-9. [Presented by co-author at AAGBI Annual Congress 2014 and awarded first prize in Original Research category] Hamlyn, V.G., Bruynseels, D., Clark, J. , Hall, J.E., Collis, R.E. (2014) Assessment and training on a new epidural simulator. International Journal of Obstetric Anesthesia 2014; S34 23: 44. [Presented by co-author at OAA Obstetric Anaesthesia 2014 and awarded first prize in Training poster category] My CV when applying the PhD scholarship I got awarded
It’s important to highlight that I didn’t present any of the work myself.
I was first author for one of them but since it was an anaesthetics conference we figured it would be better for an anaesthetist to present…
Always be truthful with who actually presented, especially if there was a prize involved. Even if you aren’t the presenter, it is easy to see how someone associated with prize-winning work sounds like a good bet to the scholarship committee.
4. Other Research Competence
This could be things such as:
- A year in industry or other work experience. Bonus points if is is a research-orientated environment. Don’t just think R&D for a pharmaceutical company, this could include computational modelling for a car company or analysis in a finance company.
- For data science / AI / ML people: entering Kaggle competitions . Bonus points for doing well.
- Volunteering on a citizen science project.
I didn’t have any of this stuff on my CV when applying for the scholarship.
Demonstrating Enthusiasm for Research & Outreach
Beyond typical research outputs, it can go in your favour if you can show your eagerness to communicate research to others.
- Setting up a research paper reading group at your university
- Starting a podcast and discussing new research or interviewing researchers
- Traditional outreach: exhibiting science to the public, probably through your undergrad university
- Creating YouTube videos
- Writing articles, for instance on LinkedIn or medium.com
- Starting a science website or blog
- Explaining research on Twitter, Instagram, TikTok or anywhere else
All of these show:
- You are the type of individual to go above and beyond to help others to understand research. Funding bodies are starting to care more and more about public engagement.
- Communication skills.
- That you can probably do a decent job at distilling complicated topics into something which is easy to understand. This is a very useful skill.
The handy thing with a lot of these is that you don’t need access to a lab or even to still be affiliated with a university. You can do as much or a little of them as you want.
I’ve written a whole post about STEM volunteering opportunities which I suggest you check out for some ideas for how you could demonstrate enthusiasm for research and outreach:
STEM Volunteering Opportunities in the UK
Any amount is better than none, especially if your CV is otherwise looking a little thin.
What outreach did I have on my CV when applying for my scholarship?
All I had done was manage an academic department’s blog. I actually didn’t start the website you’re reading this on until I was already working towards my PhD.
However, if I had not already had my research assistant experience I certainly would have considered starting something earlier to boost my application.
Demonstrating Academic Potential
Moving on from research, the committee will broadly want to judge your academic potential. Are you a committed student? Can you do well when you apply yourself to a topic? Do you have certain experience which could stand out?
Useful things to have on your CV include:
- Decent grades. Having good grades in relevant modules/units to your potential PhD topic and in research projects throughout your degree help. An impressive overall percentage for the degree (eg 85%) is even better. Me? I just scraped a 1st with 70.5%, see more details in the blue box below.
- Dean’s list, for being one of the top students during your undergraduate degree
- Academic prizes for doing well in certain topics
- Exchange schemes to other universities. Regrettably you get bonus points if it is a big name university, not least because this suggests that it must have been competitive to secure.
- For programmers: sharing coding projects on GitHub, GitLab etc. Bonus points if they’re popular open source projects.
Do You Need Good Grades to Get a PhD Scholarship?
In order to have a competitive application for a fully funded PhD scholarship you will need to have a minimum of a 2.1 overall for your undergraduate degree. However, you certainly don’t need to be top of your class, or having outstanding grades all the way back to school.
My marks? GCSEs: 7A*s, 3As, 1B A-levels: AABC. Which wouldn’t be enough to get into Imperial as an undergrad! Undergrad degree: 1st class. But only just, with my final average at 70.5%. My transcript showed modules with 48% and 54%. Yes, really. The scholarship committee will have seen those grades if they looked closely.
As you can see, I didn’t have a blemish-free stellar track record. However, thankfully, there are plenty of things you can do about it!
Demonstrating Technical Knowledge
Distinct from academic potential is your technical knowledge.
What’s the difference?
- Academic potential is about how you can apply yourself to any topic and do well.
- Technical knowledge relates specifically to your chosen PhD field or topic.
Thankfully, being an expert in your field certainly isn’t a requirement when you’re starting a PhD. I’d go as far as to say that PhD supervisors and funding committees are much more keen to find someone with academic potential and a willingness to learn.
How much technical knowledge do you need?
You do generally need to have at least some knowledge of the field.
For instance, a friend of mine studied human physiology for undergrad and wanted to move into neuroscience for her PhD. Without any technical knowledge in this area she couldn’t convince the committee that she would be able to confidently complete the PhD so she got rejected. Don’t worry, she did go on to get a PhD but in something which she could demonstrate a little more technical know-how in.
If you want to do start a PhD project which falls within the broad category of your undergrad degree, you’re fine. For instance, want to do a project which would be defined as a chemical engineering project and you have a degree in chemical engineering? You’re fine. Usually there is a good amount of latitude too: in this example if you alternatively had a degree in a chemistry or another engineering sub discipline you may also be fine.
You do not need to specifically know lots about your PhD area of focus before you start. Of course, the more specific technical knowledge you can demonstrate certainly won’t hurt your chances, especially for a PhD scholarship.
The exception to all of this are CDTs where you get a year of training to bring non-specialists up to speed in a discipline different to their undergrad.
Demonstrating Interpersonal Skills
Sure, your PhD will involve a lot of lone working but you will also have to interact with other people. Therefore, demonstrating interpersonal skills is a great asset for PhD scholarship applications.
Interpersonal skills include:
- Team work . From basics such as being courteous and respectful to other lab users through to working well with others on joint projects, so things like delegating and splitting tasks up.
- Communication skills. Getting comfortable presenting to a broad audience and discussing ideas with others. In particular showing that you can deal with people from other disciplines and speaking a common language.
- Showing initiative and initiating collaborations . This can involve networking and a motivation to seek out people with complimentary skills to achieve more impactful research projects.
These could be demonstrated by undergraduate projects, work experience, volunteering or even things like sports. Basically try to add in examples of any time you’ve worked with other people.
Do You Need to Tick Every Box to Get a Fully Funded PhD Scholarship?
No, not necessarily. There are loads of ways to impress the committee. For instance, I hadn’t really done any outreach.
When I first sent my CV to my PhD supervisor he immediately highlighted two things which would stand out to the scholarship committee:
- Being named on publications in reputable journals
- Being associated with some prizes at conferences, even though I wasn’t the presenter
I would highly suggest that if you get the opportunity to work on research which could result in a publication, take the opportunity!! Publications are really a golden ticket to a PhD, so do as much as you can to get your name on them.
Don’t be disheartened if you don’t already have experience in lots of these areas, instead focus on ways to gain experience to bolster your CV and boost your chances. This could be either through taking a job temporarily as a researcher (like I did) or proactively doing things outside of work to show your suitability, such as submitting a review article or starting a reading group.
My Top Tips for Getting a PhD Scholarship
For those currently at university:
- Try to get involved with some research and if possible try to present that research somewhere. Saying that you’ve presented at a conference makes you sound like a fully fledged PhD student before you’ve even started. Even better would be to get your name on a paper accepted to a peer-reviewed journal.
For everyone:
- Work with a potential supervisor to perfect your application. Often for scholarships you’ll have to name a supervisor should you get the award. The supervisor should be a great resource for improving your application to give you the best chance of success. If the supervisor doesn’t seem interested in helping you, I’d suggest that they’re probably not someone you want to be working with for the next 3-4 years of your life during a PhD.
- If your CV is looking a little light, consider adding to it with some things you can do in your free time such as research communication: writing articles online, informational YouTube videos etc.
Summary: How To Get A Fully Funded PhD Scholarship
In your application and interview try to demonstrate:
Providing as much evidence as you can include for each of these topics will put you in the best possible position for securing a fully funded PhD scholarship.
If you’d like personalised help with your PhD application I am now starting to offer a small number of one-to-one sessions. Please contact me to find out more or click here to book a call.
Best of luck with your PhD funding applications. I hope this post has given you some pointers to increase your chances of securing a fully funded PhD scholarship. If you think I’ve missed anything, please do let me know.
Make sure to subscribe for access to the resource library and to get notified about new content:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
Related Posts

PhD Salary UK: How Much Do PhD Students Get Paid Compared to Graduates?
5th February 2024 5th February 2024

How to Find PhD Funding in the UK
2nd January 2018 30th January 2024
2 Comments on “How To Get A Fully Funded PhD Scholarship”
A holder of a Master of science education degree in wood science and technology I need help to get a full funded phd programme. Currently am teaching in one of the school in Zimbabwe. Also assist on what programme is do i embark on for PHD
Hi Qhubani thanks for your comment. It sounds like you’re on a great path and are picking up useful experience. I would suggest starting to reach out to potential PhD supervisors. They will be best placed people to give you specific advice about PhD programmes relevant to you. See my post about finding supervisors . Best wishes! Jeff
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
2024 Fully Funded Online PhD Programs [Doctorate Guide]
If the cost of an advanced degree has discouraged you from furthering your education, fully funded online PhD programs may be the answer.

These doctoral programs provide students with the opportunity to enhance their knowledge and skills in their field without paying high out-of-pocket expenses. They typically cover your tuition and may also pay for fees, living expenses, and course materials.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Schools offer affordable PhD programs in many specializations, so students can pursue their goals no matter their area of interest. Earning a free doctorate degree online could help you grow your career prospects and become an expert in your field.
Universities Offering Fully Funded PhD Degree Program Online
Methodology: The following school list is in alphabetical order. To be included, a college or university must be regionally accredited and offer fully funded PhD programs online or in a hybrid format.
Boston University
Boston University typically offers free tuition, a stipend, and a health insurance credit to eligible PhD students. Students have 5 years to complete a PhD program. Funding details are based on the specific program. Programs include Behavioral Neuroscience, Astronomy, and Theological Studies. Most programs are available online and on campus.
Boston University is accredited by the New England Commission of Higher Education.
Brown University
PhD students at Brown University may be eligible for financial support, including free tuition, a stipend, and medical assistance. Brown requires participation in a teaching assistantship, fellowship, or research assistantship to be eligible for these benefits. These benefits are available for 5 to 6 years. Programs include Anthropology, Political Science, and Physics.
Brown University is accredited by the New England Commission of Higher Education.
Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University works with students to make getting a hybrid PhD more affordable. Those who have earned a master’s through Johns Hopkins may be eligible for free tuition and a stipend for 3 years, while transfer students may be eligible for 4 years. Programs include International Policy and Regions of the world.
Johns Hopkins University is accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education.

New York University
New York University PhD students may be eligible for funding, including full tuition, stipends, and health insurance credits. Aid is typically available for up to 5 years. NYU currently offers a PhD in Hebrew and Judaic Studies, with the option to add a History degree.
New York University is accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education.
Northwestern University
PhD students at Northwestern University usually receive total funding for at least 5 years. Students who wish to earn more can take on teaching or research assistant roles. Courses are in quarter semesters and are offered 4 times each year. Northwestern offers over 60 PhDs, including Music and Linguistics.
Northwestern University is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission.
Temple University
Temple University offers full tuition remission and a stipend to all eligible PhD students. Programs require participation in research or teaching assistant projects for up to 20 hours each week to receive this funding. The funding is renewable for up to 5 years. Programs include Business Administration, Statistics, and Decision Neuroscience.
Temple University is accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education.
University at Buffalo
The University at Buffalo’s PhD Excellence Initiative helps highly qualified students earn a fully-funded PhD Students work as a research or teaching assistant in exchange for a yearly stipend. UB offers multiple PhD programs online including Nursing and Information Science. All courses are completed online with synchronous and asynchronous coursework.
The University at Buffalo is accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education.
University of Michigan
The University of Michigan provides several opportunities to fun joint PhD programs in Social Work and Social Science. Students work as teaching or research assistants and receive tuition, a stipend, and healthcare. Students are eligible for up to 5 years and may not work over 10 hours per week outside of university commitments.
The University of Michigan is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission of the North Central Association of Colleges and Schools.
Vanderbilt University
Vanderbilt University offers the opportunity to earn a PhD in Nursing. The school offers full tuition and a stipend for up to 4 years of the program. Most of the program is online with a short residency required each semester. The program begins each fall and follows a semester schedule.
Vanderbilt University is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.
Yale University
PhD students at Yale University may have tuition covered along with a 12 month stipend. These services are available for up to 5 years. There is also the possibility of funding for an additional year. Programs include Environmental Science and Comparative Literature.
Yale University is accredited by the New England Commission of Higher Education.
Fully Funded Online PhD Programs

Earning a fully funded PhD online sounds like it’s too good to be true, but it’s a realistic possibility if you’re prepared to invest time and effort into the application process and your studies.
Most colleges and universities require students to hold a minimum of a bachelor’s degree to enroll in a PhD program. Others will only accept students who have earned a master’s degree in a relevant field. Professional experience may also help strengthen your application.
If you’re admitted to a fully funded online PhD program, you’ll have the chance to earn your degree without taking out excessive loans. Many of these doctoral degree programs pay for most or all of the costs of attendance—including tuition, fees, and living expenses.
In exchange for this funding, some programs employ students as teaching or research assistants. In these roles, PhD candidates provide support to current faculty and balance this work with their own classes and research.
An online PhD may help prepare you for a career with desirable employers, such as:
- Colleges and universities
- Research labs
- Government agencies
- Private businesses
- Healthcare facilities
These organizations hire graduates of PhD programs to work in prominent roles, including analysts, researchers, policy developers, and engineers. If you’re currently working in your field of choice, a PhD may also help you advance into a position as an executive or administrator.
Many graduates of these programs also work in higher education as professors, academic deans, and presidents. A PhD helps you build a foundation of knowledge that allows you to conduct research and teach upcoming undergraduate and graduate students.
PhD Careers & Salaries

You can earn a PhD in a wide range of fields, and the degree you complete will determine what career paths are available. Many job paths for PhDs offer healthy salaries and opportunities for advancement.
Students often enroll in PhD programs because they want to enter academia. Universities typically require that college professors have a PhD and are capable of conducting advanced research and publishing articles and books related to their work.
A PhD is also an asset if you hope to build a career in science or technology. These specialized fields involve the sophisticated skills and technical knowledge that a PhD program typically provides.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics , these are some of the most common careers for graduates of PhD programs, depending on their specialty.
In addition to paying above-average salaries, many of these careers are also expected to experience accelerated growth. For instance, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the projected growth rate for epidemiologists over the next ten years is 26%.
The growth rates for computer and information research scientists (21%), medical scientists (17%), and postsecondary teachers (12%) over this period are also much higher than the average rate for all occupations.
How to Get a Fully Funded PhD Program Online

Gaining admission to a fully funded PhD program can be more challenging than enrolling in bachelor’s or master’s degree programs. Here are some tips to consider:
- Consider STEM programs . PhDs in science, technology, engineering, and math often offer full funding to students. You may have more schools to choose from if you complete a STEM degree.
- Check accreditation status . It’s strategic to avoid any online PhD program that isn’t accredited. A lack of accreditation could indicate that the program is of low quality or will not properly prepare you for the professional world.
- Apply for fellowships or assistantships . International students may qualify for fellowships that pay for tuition and provide a stipend. Many fully funded programs require students to participate in an assistantship focused on teaching or research.
- Fine-tune your application . Most fully funded PhDs only accept a few students for each academic year, and they base their admissions on your application materials. It’s beneficial to look closely at each program’s requirements and adhere to them as closely as possible.
When you research fully funded PhDs, be wary of any program that makes exaggerated promises or cannot provide job placement or graduation data for recent students.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fully Funded Online Doctoral Programs
Prospective PhD students may struggle to decide whether a fully funded program is the right path. Fully funded online doctoral programs offer a variety of benefits and drawbacks, including:
When deciding whether a fully funded online PhD is a good fit for you, you might consider your learning style, preferences, and goals.
Admissions Requirements

Fully funded PhD programs are usually selective, so it’s important to carefully follow their application process. Admissions requirements for online PhD programs for working professionals may include:
- Test scores . While it’s not always required, some schools have you submit current scores from the GRE or other standardized tests.
- Transcripts . Request official transcripts from schools you previously attended, including undergraduate and graduate programs.
- Statement of purpose . You can describe your motivation for pursuing a PhD, why you selected this particular program, and your specific research interests.
- Recommendations . You can ask former professors or supervisors to explain why you would excel in an online PhD program.
- CV . It’s beneficial to list all relevant professional, publishing, and volunteer experience.
Some universities also require students to participate in a virtual interview or provide a portfolio that demonstrates the strength of their past work.
Fully Funded PhD Programs Online Accreditation

When selecting an online PhD program, it’s vital to determine whether it has regional accreditation . Some online schools offer degrees with little to no academic value, but a regionally accredited institution must meet certain standards of excellence.
Attending a program that has met the high bar of a regional accrediting board usually provides you with a better educational experience that includes the most current practices and theories in the field. For this reason, most employers only accept PhDs from accredited schools.
If you end up changing programs before graduating, it’s generally easier to transfer credits from programs with regional accreditation.
How Much Does a PhD Cost?

The cost of PhD program tuition varies widely based on the school you attend. Rates generally range from $500 to $2,000 per credit hour. In addition, students often have to pay for materials and fees on top of their base tuition.
A PhD program could range between 60 and 120 required credits, so the total cost of tuition and fees could easily reach top dollar. A fully funded PhD reduces or removes much of this cost by allowing students to complete their degrees without paying tuition.
What Does Fully Funded Mean?

Fully funded means that a PhD student doesn’t pay any of the costs of attending a doctoral program. This generally includes all tuition and fees required for full-time enrollment in the program. In many cases, the university covers these costs. Students may also receive funding from private businesses or sponsors.
To ensure that students can focus solely on their studies during the program, a fully funded PhD may also include a stipend to cover living expenses and housing. Some colleges require students to complete teaching or research assistantships to receive their funding.
What Is Funded in Fully Funded Doctorate Programs?

A fully funded PhD program essentially covers the costs associated with attending school. This typically includes:
- Full-time tuition for the duration of the program
- Fees required by the university
- Living and housing expenses
- School-provided health insurance
This funding is usually only provided for 3 to 5 years of study. This helps ensure that students complete their programs in a timely manner. If a fully funded PhD doesn’t completely address the cost of a student’s degree, the school may also offer additional financial opportunities. Scholarships, grants, and loans are possible avenues to fill the gaps in funding.
What Can You Get a PhD in?

There are PhD programs available for practically every field. Popular doctoral specializations include:
- Educational administration and leadership
- Physical therapy
- Electrical engineering
Although there are PhD programs available for each of these disciplines, some may be more suitable for online study. A PhD program that involves hands-on learning or lab work may not be as ideal for an online format.
Some online PhD programs that require in-person components allow students to participate in fieldwork in their communities. Other disciplines that focus primarily on research and writing can more easily be completed online.
What Are Some of the Highest Paying PhDs?
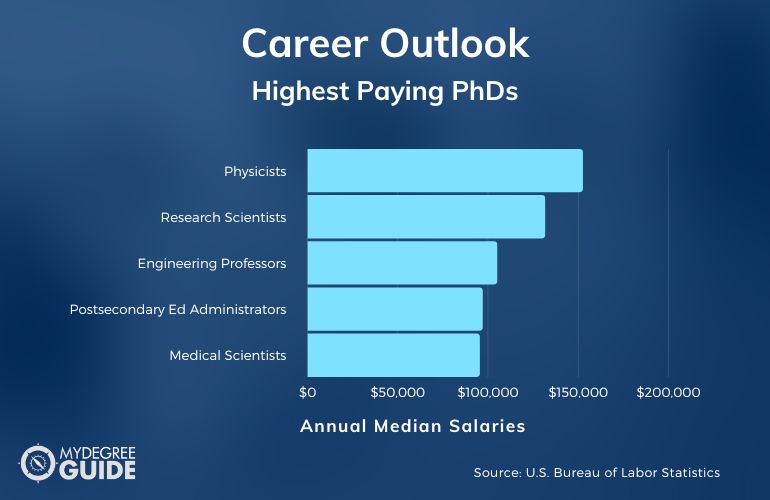
Your future earnings ultimately depend on your employer, geographic location, and professional experience, but some PhDs tend to have better pay than others.
Many of the highest paying PhDs are related to science. For example, medical scientists earn median annual salaries of $95,310, physicists make a median of $152,430, and the median for computer and information research scientists is $131,490 (Bureau of Labor Statistics). Postsecondary education administrators also have competitive salaries, with median earnings of $96,910 per year.
Depending on their specific field and whether they have tenure, college professors may earn salaries above six figures. For example, $104,940 is the median salary for engineering professors.
What’s the Difference Between a Doctorate vs. PhD Degree?
People sometimes use the terms doctorate and PhD interchangeably, but there are differences between them.
All PhD programs are doctorates, but not all doctorates are PhDs.
Getting Your Fully Funded PhD Online

Earning a fully funded PhD online can open doors to new career opportunities that are professionally and personally rewarding, all without draining your financial resources.
This type of PhD may cover your tuition, fees, and expenses, allowing you to graduate with very little debt. Because they offer low-cost or no-cost degrees, universities with fully funded PhDs tend to enroll a small number of students with proven skills and experience in the field.
Once you decide that you want to earn a fully funded degree, you can begin by researching accredited universities that offer free PhD programs online.


Studentships and doctoral training
Get a studentship to fund your doctorate.
UKRI studentships offer funding for doctoral research. They also offer you access to training, networking and development opportunities to help you build a research and innovation career.
Our expectations for research organisations, supervisors and students are set out in the statement of expectations for doctoral training .
You could get:
- a minimum stipend of £19,237 per year for your living costs, which is paid to you in regular instalments
- support for your tuition fees (minimum £4,786 per year)
The stipend is usually non-taxable and does not need to be paid back. Some research organisations may offer more if you study in London, or they or one of their collaborators might decide to top up the payment. This will be outlined in the studentship advert from the research organisation.
We normally pay the support for tuition fees directly to your research organisation.
The levels given here are for the academic year 2024 to 2025. UKRI’s approach to doctoral stipend and fee levels will be reviewed through the new deal for postgraduate research .
Additional support for your doctoral studies
As a UKRI-funded doctoral student, you may be able to access additional funding to cover the cost of other related training and development opportunities.
This could include:
- conference attendance
- language training
- overseas research visits
- internships or placements with a non-academic partner
The availability of support will depend on the research organisation and the training grants they have on offer. You should contact the research organisation you are interested in applying to, to find out what you could get.
Extra support if you have a disability
If you have a disability, you may be entitled to a Disabled Students’ Allowance (DSA) on top of your studentship.
You should speak to your research organisation’s disability advisor to assess your needs. They can help put the right support in place, including a DSA application if necessary. You cannot claim DSA directly from UKRI.
DSA helps to cover the cost of any additional support that a person studying for a doctorate might need as a result of a disability, mental health problem or specific learning difficulty.
The allowance covers:
- non-medical personal assistance
- specialist equipment
- extra travel costs
- general expenses
Find out more about DSA in our framework .
If you are a research organisation you can download claim forms and guidance for DSA .
Who can apply
Any prospective doctoral student wishing to study at a UK research organisation, including prospective international students, can apply for a UKRI studentship.
All UKRI-funded doctoral students will be eligible for the full award, both the stipend to support living costs, and home-level fees at the UK research organisation rate.
How to find opportunities
Many UK research organisations offer some form of studentship funding from UKRI. These opportunities will depend on the subject you want to study and will normally be advertised by the research organisations.
Research organisations may have additional opportunities that do not involve UKRI. UKRI supports around 20% of all UK-based postgraduate researchers. You should speak to the research organisation you are interested in to find out what studentships are available.
You could also consider using a specialist website like FindaPhD to look for opportunities.
When to apply
Research organisations set their own deadlines for applications.
Many open for applications early in the academic year and close in January or February. This is not a hard and fast rule. It is important that you check the deadlines for the research organisation where you want to study.
How to apply
You cannot apply to UKRI for a studentship. You must contact the research organisation you are interested in studying with and use their application process.
For doctoral students who are already studying with a studentship, there are opportunities to get additional funding to support placements that are separate from your doctorate. Find training and development opportunities .
Last updated: 14 February 2024
This is the website for UKRI: our seven research councils, Research England and Innovate UK. Let us know if you have feedback or would like to help improve our online products and services .

- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to secondary sidebar
- Skip to footer
career-advice.jobs.ac.uk
PhD Funding – A Checklist of Possible Sources

There are probably more funding opportunities for your PhD than you think. It is worth making sure you have investigated them all.
Funding bodies support PhD students in different ways. Some pay course fees only, some include a stipend (maintenance costs) or travel expenses, and others offer a one-off award to ease the financial burden of academic study.
Each funding body will have its own criteria for eligibility. At PhD level full funding will tend to be awarded on academic merit, but there are also some that take into account financial background and other criteria such as gender (such as in the case of the British Federation of Women Graduates).
Research Councils
The seven Research Councils invest in the region of £380 million into doctorate research every year. However, funding is made available through the participating universities rather than the research councils themselves. Universities set up Doctoral Training Partnerships (DTPs) or Centres for Doctoral Training (CDTs) in order to receive funding.
It is then up to the universities to decide who to award studentships to – usually based on academic merit following a competitive application process.
Eligibility criteria and award amounts are standardised and you will find many other funded PhDs referring to research council rates when defining their own. Research council studentships include fees and a minimum stipend per annum which is paid tax-free.
The seven Research Councils include:
Arts and Humanities Research Council (AHRC)
Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)
Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC)
Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC)
Medical Research Council (MRC)
Natural Environment Research Council (NERC)
Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC)
The above organisations have been grouped together with Innovate UK and Research England in 2018, and the umbrella organisation is called UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) .
UKRI’s key objectives include providing funding for the training of new researchers.
Academic institutions
Universities, colleges and research institutes also fund their own studentships, and these are typically listed on the institution’s own website alongside its research council-funded studentships. Some will offer fees only, while others may offer a stipend as well. Amounts may vary although many use the research council rates as a benchmark.
Commercial and charitable organisations
A number of non-academic organisations help fund research at PhD level in collaboration with the university hosting the study. CASE (Cooperative Awards in Science and Engineering) studentships are for four-year PhDs. These are part-funded by a non-academic ‘co-operating body’ such as a UK industrial firm, public sector organisation or charity. Students spend at least three months of the PhD working in-situ at the co-operating body which makes a financial contribution to both the student and the project. Students often find these to be good avenues for finding full-time work at the end of their placement, and will have gained valuable hands-on work experience. There are also CASE-Plus studentships where students spend a further year working full-time on the premises of the co-operating body as an employee following the PhD.
A number of charitable organisations, foundations and trusts can help fund PhDs:
The Wellcome Trust
Cancer Research UK
The British Academy
The British Federation of Women Graduates
The Institution of Civil Engineers
Institution of Engineering & Technology
Institution of Mechanical Engineers
Royal Geographical Society
Carnegie Trust for the Universities of Scotland
Leverhulme Trust
Action Medical Research
The Grundy Educational Trust .
Self-funding
If you are having difficulty in getting funding from the above sources, you may be able to fund your own way through a PhD. You may be eligible for Professional and Career development loans. It is wise to review the specific application criteria to ensure that you are eligible.
A further option is to study part-time while working. This could however place additional demands on your time and financial situation. Be aware that if you have managed to access some funding elsewhere, you may be prohibited from working during your PhD as part of the stipulations of the award.
The jobs.ac.uk website lists some excellent PhD opportunities as well as a wide range of jobs – do take a look at them!
For more PhD tips:
Your PhD Journey – Top Tips
What Can You Do With a PhD?
PhD Application Tips
What is a PhD and Why Should YOU do one?
What did you think of our article? - please rate
Share this article
Henrietta Nagy
Henrietta Nagy is a seasoned portfolio worker with over 10 years’ experience in the UK education sector. Henrietta writes educational content, designs academic courses, delivers university lectures, mentors entrepreneurs, and provides career development coaching. One of Henrietta's recent organisational clients is the Oxford University where she has facilitated over 100 hours of learning events. With 9 years of higher education studies internationally (including an MBA), she has worked with CEOs, academics, scholars, managers, women entrepreneurs, academic administrators and other consultants.
Reader Interactions
You may also like:.
10th October 2019 at 12:12 pm
I am a PHD Scholar at Wollegga University, Ethiopia.I need a Research Grant. Would you please help me?
3rd December 2019 at 9:21 am
I am conflict management PhD candidate in South Africa I need funding. My area of focus is Terrorism in Nigeria. Any advice
4th September 2020 at 8:57 pm
I was offered PhD opportunities at Universities of Cape Town, Queen Margaret and Winchester but could not find funding. My area of specialization is health systems management planning and poli
11th September 2020 at 3:25 pm
I am DBA scholar at University of Northampton researching on industrial actions. I need a research grant. Please assist.
4th December 2020 at 5:11 pm
I am looking for an admission to study PhD Medical Imaging or PhD Nuclear Medicine Technology with finding or grants. Kindly specifically help.
6th August 2022 at 6:45 am
I am a PhD scholar in one of the Federal Universities of Technology in Nigeria. I seriously need a funding to allow me carry out a thorough research on Microplastics pollution in coastal areas of Southwestern part of Nigeria. Thanking you for your timely response. Olanipekun Oluwafunmilayo (Mrs)
5th January 2021 at 9:00 am
I am South African and I have been admitted for a PhD programme at the University of Worcester, UK. However, I am struggling to get funding. Please assist where you can.
18th October 2021 at 12:03 pm
I am due to go into my final year of my Professional doctorate in education, and need funding just for this one year. My research is into COVID and the impact upon young children. Please, can anyone guide me towards any potential sources of funding for this one year?
27th January 2022 at 1:42 pm
I have been admitted for a PhD programme at the University College London in 2022 fall, but I find it difficult to get funding as a non-European international student. Any advice! Many thanks in advance.
5th March 2022 at 1:32 pm
Hello, I am a Chinese student. If I am admitted to a PhD programme of Newcastle University in 2022 fall, but I have not applied for CSC, and the program I applied for is not a full prize program, what other subsidies can I apply for?Any advice! Thank you very much in advance!
10th June 2022 at 6:13 am
I am interested in fully funded PhD, I am a master student in de Montfort university presently.
22nd June 2022 at 5:13 pm
My name is Esther, a Nigerian. I am looking for a PHD in Gender studies and Food Economics, please i will appreciate your kind assistance.
31st January 2023 at 2:57 am
I am a Nigerian and will be taking a Ph. D in UK or any European country soon. Please can you share useful information on how to get external funding for my Ph. D in Urban and Regional Planning with specialty in Landscaping and Transportation. Your impactful feedbacks will be highly appreciated.
7th October 2023 at 4:31 pm
My name is Jingrong, a Chinese student. I am a PhD student in the University of Bristol presently, my research is based on the remanufacturing operations. I am interested in some related funding.
13th August 2022 at 5:50 pm
My name is Bulea Christopher, I am seeking to do PhD in Organizational leadership and management. I shall be grateful.
19th October 2022 at 1:31 pm
I am Nigeria and will be taking a Ph. D in UK soon. Please can you share useful information on how to get external funding for my Ph. D in renewable energy system of technology. Your impactful feedbacks will be highly appreciated. Thanks
31st October 2022 at 8:58 am
My name is Nkomo Dalubuhle from Zimbabwe lm looking for a PHD in curriculum studies in education
18th November 2022 at 3:51 am
I am from Pakistan and want to apply for PhD programme at the University of Staffordshire UK. However, I am struggling to get funding. Please assist where you can.
21st October 2023 at 3:56 pm
I am master’s in special education from pakistan.i required fully funded uni of this field.
14th March 2024 at 8:01 am
I’m a Tunisian student who has been accepted into a PhD program at Newcastle University for 2024, specializing in Agriculture and Rural Development, as well as a master’s degree program at the University of East Anglia, focusing on Rural Development. Unfortunately, I haven’t been able to secure funding for either program. Do you have any advice on what steps I can take or where I can apply for funding? Thank you in advance!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Please enter an answer in digits: fourteen − 13 =
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Log in
- Site search
PhD studentships
If you're looking to get PhD funding for a specific research project or field of study, Doctoral studentships can provide you with either a partially or fully-funded PhD
Who awards PhD studentships?
PhD studentships are most commonly awarded by the UK's seven Research Councils in the form of Research Council grants , with research funding overseen by UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) .
Individual UK universities also offer scholarships and bursaries to PhD students, while many professional bodies fund Doctoral research in collaboration with these academic institutions.
For instance, research awards are offered by the following engineering organisations:
- Institution of Civil Engineers (ICE) - QUEST scholarships
- Institution of Mechanical Engineers (IMechE)
- The Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET)
- Royal Academy of Engineering (RAEng)
Additionally, CASE studentships (formerly known as Cooperative Awards in Science and Engineering) can be part-funded by any non-academic body in partnership with the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) . These four-year PhDs require the student to work at the organisation for at least three months.
You can also apply for funded PhD opportunities through many charities, foundations and trusts, including:
- Action Medical Research
- Alzheimer's Society
- British Federation of Women Graduates (BFWG)
- British Heart Foundation (BHF)
- Cancer Research UK
- Diabetes UK
- Rosetrees Trust - PhD Plus
- The Leverhulme Trust
- Wellcome Trust
Before you start applying for a funded PhD, it's always a good idea to discuss this with a prospective supervisor first, as they're often able to provide tips on maximising the likelihood of receiving financial support.
How much can I receive?
Many PhD studentships, including those offered by universities, professional bodies, or charities, foundations and trusts, provide three years' funding paid at a similar rate to the Research Council grant:
- Fees-only studentship - These cover a student's tuition fees, plus any associated project and training costs (a minimum of £4,786 per year in 2024/25).
- Full studentship - These add a non-repayable, tax-free maintenance grant known as a 'stipend'. In 2024/25, this is worth a minimum of £19,237 and it can be used towards living costs - see UKRI - Find studentships and Doctoral training .
For example, a University of Manchester School of Social Sciences PhD studentship includes tuition fees for three-and-a-half years and a maintenance grant of £18,622 (2023/24 rate) per year for living expenses, plus associated research costs - such as fieldwork and attending conferences - from the Research Training Support Grant.
However, you should be aware that some PhD studentship recipients are required to teach undergraduates. While this provides an excellent opportunity to gain vital employability skills, it can also be hugely time-consuming. You must be satisfied that tutoring won't negatively affect the quality of your research before accepting your place.
Is my programme eligible for a PhD studentship?
PhD studentships can start at any time of the year, but most begin in September, October or January.
Certain types of PhD, for example professional Doctorates, may not be eligible for a PhD studentship. The same applies to part-time or distance learning options.
Am I eligible?
PhD studentships typically demand that applicants have a Bachelors degree at 2:1 or above, plus a relevant Masters degree or professional experience at that level of study.
Those who already possess a PhD are often ineligible, while some PhD studentships are limited to students fitting certain criteria - for example, those from a disadvantaged background, from a certain country or of a certain ethnicity.
If you're a European Union (EU) national, you'll need to have settled or pre-settled status under the government's EU Settlement Scheme to be eligible for student finance in this country - and this includes PhD studentships.
How do I apply for a PhD studentship?
The application process can be lengthy, and competition is fierce.
Some PhD students will be automatically considered for financial support once they've been accepted by an institution, but many are required to make separate PhD funding applications. These are usually made directly to the university - even for those studentships from Research Councils, professional bodies, or charities, foundations and trusts.
You'll typically be asked for your PhD application form, a research proposal , a cover letter and your references. After the institution has reviewed your application, you may be invited to interview.
Throughout this process, the university will scrutinise what you'll bring to the institution. Applicants at Liverpool John Moores University (LJMU), for example, are judged on:
- the quality of their research project and how it connects with research currently being undertaken at the institution
- how appropriate the supervisory team is
- their calibre, academic qualifications and academic/research experience
- whether the research can contribute towards the Research Excellence Framework (REF), meaning that interdisciplinary research will be preferred.
How do I increase my chances of getting a PhD studentship?
You can improve your chances of success by:
- asking a friend or family member to proofread your application
- carefully choosing your referees, ensuring that they'll speak positively of you
- discussing your draft application with a relevant academic
- explaining how your work will be unique and innovative
- following the funding body's guidance regarding word counts and formatting.
What other PhD funding is available?
If you're unsuccessful with your PhD studentship application, you could consider:
- crowdfunding
- employer sponsorship
- PhD loans .
Find out more
- Explore 5 routes to getting a Doctorate .
- Read about 5 challenges faced by PhD students .
- Consider what to do next after completing a PhD .
How would you rate this page?
On a scale where 1 is dislike and 5 is like
- Dislike 1 unhappy-very
- Like 5 happy-very
Thank you for rating the page
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Education and learning
- Student finance
Funding for postgraduate study
You can get funding for postgraduate study through loans, studentships, bursaries and grants - you might also get help from your employer.
You can now apply for funding for the 2023 to 2024 academic year.
Search for postgraduate funding on the Scholarship Search website or Prospects website .
Postgraduate Master’s Loan
If you’re starting a master’s degree, you could get a Postgraduate Master’s Loan to help with course fees and living costs. You can get up to:
- £12,167 if your course starts on or after 1 August 2023
- £11,836 if your course started between 1 August 2022 and 31 July 2023
- £11,570 if your course started between 1 August 2021 and 31 July 2022
Postgraduate Doctoral Loan
If you’re starting a doctoral degree, you could get a Postgraduate Doctoral Loan to help with course fees and living costs. You can get up to:
- £28,673 if your course starts on or after 1 August 2023
- £27,892 if your course started between 1 August 2022 and 31 July 2023
- £27,265 if your course started between 1 August 2021 and 31 July 2022
It is not based on your income or your family’s and it’s paid directly to you.
Studentships
Studentships are postgraduate positions that have funding attached for fees, living expenses or both. They’re mainly funded by UK Research and Innovation .
Teacher training, social work, medical and healthcare courses
You can apply for funding for:
- Initial Teacher Training
- social work - through a social work bursary
- some medical or healthcare courses - through an NHS bursary
- most medical or healthcare courses - through a student loan
Graduate-entry medical students can also get support from Student Finance England for fees charged over £3,465.
Charities and trusts
Charities and trusts sometimes provide grants, often for students from poorer backgrounds or those who’ve achieved academic excellence. Find out more at your local library in these publications:
- the Educational Grants Directory
- the Charities Digest
- the Grants Register
- the Directory of Grant Making Trusts
You can also use the Family Action grant search .
Learned societies
Societies sometimes offer funding for postgraduate or postdoctoral research. They include:
- the British Academy (for humanities and social sciences - postdoctorate only)
- the Royal Academy of Engineering (for engineering)
- the Royal Society (for science - postdoctorate only)
You might be able to get funding from:
- an individual - sometimes people donate awards to help postgraduates (these are usually offered through your university or college)
- your employer - they might sponsor you if the course is relevant to your job
- a Disabled Students’ Allowance
- the Student Awards Agency for Scotland if you’re from Scotland
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .
Sweden and the Netherlands: 16 fully-funded PhD positions

Are you looking for exciting PhD positions at esteemed universities in Sweden and the Netherlands ?
Over 16 fully-funded multiple doctoral scholarships in diverse fields are available at various universities in Sweden and the Netherlands for the year 2024. These fellowships provide funding for doctoral researchers to conduct their research projects at universities, research institutions, and other organizations in these countries. These PhD positions are funded by prestigious sources including the MSCA doctoral program and other funding programs.
For detailed information on specific doctoral positions, please visit the provided links to explore corresponding PhD scholarships, which include specific requirements and application procedures.
PhD positions available in Swedish universities:
1. Computational condensed matter physics, Linköping University
2. Urban Freight Management, Chalmers University of Technology
3. eDNA environmental monitoring, Sveriges lantbruksuniversitet
4. Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), Luleå University of Technology
5. Medical Science - Regional differences in gestational duration, University of Gothenburg
6. Computational Sciences within the national Data-Driven Life Sciences program, Umeå universitet
7. Computational biology of infection, Lunds universitet
PhD positions available in Dutch/Netherlands universities:
8. Donders Centre of Neuroscience - Motor Disorder Rehabilitation, Radboud University
9. Human-aligned Video-AI, University of Amsterdam (UvA)
10. Multivariate Dependence Modelling and Statistical Machine Learning Algorithms for Patient Risk Profiling, Delft University of Technology (TU Delft)
11. Computational Cognitive Neuroscience at the Predictive Brain Lab, Radboud University
12. Atmospheric Sciences - Unraveling the mesoscale organisation of shallow convective clouds for better climate projection, Wageningen University & Research
13. Dynamic On-Body and In-Body Compression Systems, University of Twente (UT)
14. Modelling Micropollutant Removal using Charge-Mosaic Nanofiltration Membranes, University of Twente (UT)
15. Economic Life Cycle Costing and Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Hydropower, University of Twente (UT)
16. Environmental Life Cycle Assessment of Hydropower, University of Twente (UT)
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 24 May 2024
What steps to take when funding starts to run out
- Neil Savage 0
Neil Savage is a science and technology journalist in Lowell, Massachusetts.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

Bridge-funding programmes can provide researchers with enough money to sustain their work until they have secured a bigger grant. Credit: Getty
Zhen Jiang had spent several years studying molecules that regulate insulin signalling and glucose transport, and his results were urging him in a new research direction, focused on inflammation in obesity and how it relates to tissue damage. After five years, his first grant from the US National Institutes of Health (NIH) was running out, so he applied for new funds to follow the leads he’d uncovered.
But reviewers scored his grant application too low to qualify for funding, and suddenly Jiang, a biochemist at Boston University’s Chobanian and Avedisian School of Medicine in Massachusetts, found himself without the funds he needed to keep his laboratory, of three people, running. “We depend on grant support, and if you don’t have money, a school can let you go.” A stressful situation to be in, he says.
Trying to work out what to do, he turned to the programme officer at the NIH. The officer noted that his score was close to being accepted, and suggested he apply for an NIH bridge grant, which would give him US$350,000, allowing him to gather more data and strengthen his next, larger, grant application. He also received some funding from his university, which he says was crucial to keep the lab going. After 6 months of accumulating data, he reapplied to the NIH and won a 3-year grant of about $415,000 per year to study inflammation in liver tissue, then a second 4-year grant for more than $500,000 per year to apply his work to the heart.

NIH pay rise for postdocs and PhD students could have US ripple effect
“This kind of bridge fund is so necessary for a lab,” Jiang says, even though the amount was tens of thousands of dollars less than one year’s worth of standard funding, which can be around $500,000 per year. It does mean, however, that researchers need to make sacrifices. “You have to cut your cost,” he says. “That’s the only way to do it.” He was forced to lay off one member of his lab and take on more of the work himself.
Jiang, who had worked as a physician in Jiangxi, China, before switching to research, knew that he’d have to fight for funding in this line of work. “This is always a competitive field. The money’s always not enough,” he says. “You have to work very hard in order to find something new and convince your funder into supporting you. It’s a tough business.”
Ahead of the game
The problem of maintaining enough support to keep lines of research going is a continuing one for academics, with the major government funding bodies regularly awarding money to only one-quarter — or less — of the proposals that they receive. The funding gaps lead to stress for researchers, who might have to curtail a line of enquiry, lay off support staff or postdocs and even potentially lose their position.
Statistics show that the problem hasn’t changed much in years, although budgets might now be spread thinner. Over the past two decades, the percentage of successful applications for NIH research grants has hovered at around 20% (see go.nature.com/4bghwbi ). Although the gross amount of those grants has increased, the NIH’s spending power has remained relatively constant; the average NIH grant size was $247,000 in 1998 and in 2022, it was $288,000 in 1998 dollars (see go.nature.com/3uh4mup ). And although the funding has stayed the same, the money has to go further, because the NIH approved an 8% pay raise for postdoctoral researchers earlier this year.
The NIH, which is the world’s largest funder of biomedical research, gave out just shy of 59,000 awards in 2023, a total of $34.9 billion.

Around only one-quarter of grant proposals that are submitted to major funding bodies are successful. Credit: Adapted from Getty
The US National Science Foundation (NSF), meanwhile, handed out more than 11,000 awards in the 2020–21 fiscal year, the latest year for which statistics are available. Applicants had a success rate of 26%. The situation in the United Kingdom is similar; the UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) funding agency gave out £3.1 billion (US$3.9 billion) in the 2022–23 fiscal year, with a success rate of 27%.
The success rate for Horizon Europe, a European Union funding scheme with €95.5 billion (US$103.6 billion) to give out between 2021 and 2027, is even lower. As of 2022, applicants had a success rate of 16% for 5,509 grants, up from 12% in the final year of Horizon 2020 (the EU’s previous funding scheme that ran from 2014 to 2020). The European Commission says that 71% of high-quality proposals don’t get funded (see go.nature.com/3yuzhp4 ). Germany is the leading European country in research expenditures, and the German Research Foundation (DFG) had around €3.9 billion to work with in 2022. It funded 26.5% of applications, including humanities and social sciences.
Boom and bust
Post-pandemic spikes in inflation have caused researchers to run out of grant money quickly, especially in the United Kingdom, where prices have soared much more rapidly than in the United States. Researchers estimate their costs when applying for a grant, says Bryony Butland, a former programme director at UKRI and now director of research and innovation at Queen Mary University of London, but thanks to inflation, those estimates don’t hold over four or five years of funding. “You’re in the middle of spending it, and suddenly you find that goods prices, things that you want to do, consumables have all gone up,” she says.
The uncertainty in funding can be hard on researchers, says Stuart Buck, a lawyer based in Houston, Texas. Buck runs the Good Science Project, which is searching for more sustainable ways to fund research. He says he spoke to a principal investigator with several postdoctoral students at a leading university, who told him that because of the 20% success rate, he applies for multiple grants at one time. One year the researcher applied for ten five-year grants, and not one was funded, Buck says. The next year, three applications that he resubmitted were successful.

US postdocs on strike: how will demands for higher wages be met?
Aside from the stress that this kind of boom-and-bust cycle creates for researchers, Buck says, it also introduces uncertainty. “It’s hard to have long-term planning for who to offer multi-year positions to when you’re not sure whether your funding might double one year because you got two grants, or it might be cut in half one year because you lost one of your grants.” And time spent submitting proposals is time not spent doing research. “We want people who are trained scientists to be able to focus on science and not just worry about having to hustle for money,” Buck says.
Toll on trainees
The loss of grants can also take a toll on trainee researchers’ careers. Wei Yang Tham, an economist at the Laboratory for Innovation Science at Harvard University in Boston, Massachusetts, and his colleagues compared data from a group of NIH grants with data from the US census and tax records to look at what effect lapses in funding had on people working in labs with a single grant (see go.nature.com/4br9fli ). After a grant ran out, personnel in these labs were 40% more likely than others to disappear from the tax records, he found, meaning that they probably became unemployed. A lot of those people, many of whom had gone to the United States to study, end up leaving the country, Tham says. The largest effects are not on the faculty members, but on postdocs, graduate students and non-research staff such as project managers. Those who do stay, Tham and his colleagues found, earn on average 20% less five years later than do their continuously funded peers.
Bridging the gap
To avoid such problems, many institutions have programmes that provide labs with bridge funding, which can be used to tide over labs for a relatively short period of time while a larger package of money is sought from a research funder. A portion of research grants are intended to pay for the indirect costs of an academic lab, including fees for building maintenance, student services and utilities, which are distributed among the academic department, the school it’s in or the university as a whole. University administrators might be able to use some of that funding to provide a cushion for researchers whose money runs low.
Bridge-funding programmes are important both to make sure that a university can treat its employees well and to ensure the continuity of the science, says Deborah Thomas, a geographer and interim associate vice-chancellor for research at the University of North Carolina at Charlotte. Labs would prefer not to lose their graduate students, postdocs and research scientists, and then have to look for new staff members when funding is restored. “If you have to let that person go, then you have to rehire, there’s a lot of time involved in that. Plus, you lose knowledge,” she says.
Allan Jacobson, a molecular biologist at the University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School in Worcester, agrees. “We’ve put so much into these people and see them as assets,” he says. “Just because they have a bit of a funding problem doesn’t mean you should let them sink. It’s in the department’s interest to keep everybody happy and functional.”
Jacobson, who spent 30 years as chair of the department of microbiology and physiological systems at the Chan Medical School, negotiated funding from the school to develop what he called a rejuvenation programme. If faculty members were struggling to get grants, he would offer them multi-year in-house ‘sabbaticals’, with funding for supplies and technical help, to work with another researcher at the medical school and learn something new that could bolster their own research.
Jacobson says there can be other creative ways to drum up research support. That includes considering whether research that is struggling to get funding might have some commercial potential, and if so turning to the university’s commercialization office, which can sometimes provide “fairly sizeable grants”, he says. That can then be used for the translation of that research into a product. For instance, one researcher in his department whose funding was on the edge had done work which showed promise as a treatment for an eye disease. The department helped him to team up with a researcher in ophthalmology to develop a mouse model for the study, and the commercialization department helped to license the technology.

How philanthropy can nurture your research
Funding policies and support structures differ across countries. For example, some researchers at German universities have access to bridge funding. Postdocs whose positions are expiring can apply for funding from the DFG to set up their own groups, through the Emmy Noether Programme. At the University of Potsdam in Germany, applicants to the programme who are waiting for a decision and whose applications look promising can receive up to six months of bridge funds, says Barbara Höhle, a linguist and vice-president for research at the university.
Tenured and tenure-track faculty members in Germany, by contrast, don’t have to look to funding agencies to pay their salaries. They have salaries and a budget guaranteed by the universities, which are publicly funded, and agency funding goes towards the implicit cost of hiring researchers. “It’s more the employees in the projects that can be affected by these gaps,” Höhle says. The downside for aspiring researchers, she says, is that universities don’t have much room to increase the number of faculty members.
Planning helps
Researchers can keep their projects going when their laboratory income drops by planning ahead, Jacobson says. It’s a good idea to apply for several grants with different expiration dates, so that money doesn’t run completely dry. And careful budgeting can allow faculty members to save some of their grant in a rainy-day fund; the NIH allows one-time ‘no-cost extensions’ using unspent funds to complete or phase out a project for up to 12 months. Jacobson has twice had a grant expire with no replacement, and was able to survive for a few months until the next grant came along thanks to both of these strategies, he says. “It’s easy to lose funding,” he says. “Most divisions of the NIH are funding 10–12% of approvable grants. It’s a rough world out there.”
The University of Houston in Texas holds grant-writing workshops for its faculty members, says Claudia Neuhauser, a mathematician and the university’s interim vice-chancellor for research. For those who might be funded by, for example, the NIH, but whose research might also appeal to the grants office at the US Department of Defense, the university introduces them to proposal-writing companies that can provide researchers with insights on how to tailor their grant applications for each agency. “Helping somebody make that transition so they can expand the types of grants they can apply for, that’s obviously important,” she says. The university also provides bridge funding of up to $100,000 that faculty members can apply for if their proposal has received a high enough score from the funding agency, which means there’s a good chance it could win funding after a revision.
“We do push team science at the moment quite strongly because there are many more opportunities where you can apply as a team,” Neuhauser says. Collaborating with other scientists can lead to larger grants that are funded for longer and that often include funding for shared equipment.
Some researchers might think that they can improve their odds of success by making the costs in their proposals as low as possible. Butland cautions against this. Not only might the researchers run out of money sooner that way, but they’re also misleading funding agencies about the true costs of research. “We need to try and not underprice ourselves, which then just feeds that underfunding of the system as well,” she says.
New funding opportunities
There is new hope for UK researchers. After being cut out of the EU’s Horizon Europe funding programme by Brexit, the country rejoined it in January this year. Therefore, UK scientists can once again apply to it and to Copernicus, a component of the EU’s space programme.
Butland worries about the effects of the low success rates. “You can be spending a lot of time putting in a research application and actually never winning anything,” she says. “There is a point at which running a full competitive process doesn’t make any sense. It’s a lot of bureaucracy and burden on people.”
But competitive funding is a fact of life in science, she concedes. So researchers whose grants are nearing an end should try to expand their horizons when it comes to looking for funding sources, Butland says. UK researchers shouldn’t just stick with the research council they’re used to, and scientists in the United states can look to other NIH institutes and even other funding agencies. “Maybe another part of the funding landscape actually would find your work really interesting,” she says. “You just need to think about it a little bit differently, speak a slightly different language, but relate to their challenges and opportunities in a way that maybe you haven’t thought about before.”
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-01570-y
Related Articles

I had my white colleagues walk in a Black student’s shoes for a day
Career Q&A 28 MAY 24

Changemakers — Nature’s new series celebrates champions of inclusion in science
Editorial 28 MAY 24

Researcher parents are paying a high price for conference travel — here’s how to fix it
Career Column 27 MAY 24

Brazil’s plummeting graduate enrolments hint at declining interest in academic science careers
Career News 21 MAY 24

US halts funding to controversial virus-hunting group: what researchers think
News 16 MAY 24

A DARPA-like agency could boost EU innovation — but cannot come at the expense of existing schemes
Editorial 14 MAY 24
Lack of effective intercultural communication is hobbling academia — fix it for research equity
Correspondence 21 MAY 24

Harassment of scientists is surging — institutions aren’t sure how to help
News Feature 21 MAY 24
Assistant, Associate or Full Professor
The McLaughlin Research Institute and Touro University – Montana campus invite applications for open rank faculty positions.
McLaughlin Research Institute
Postdoctoral Associate- Neuroscience
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Call for applications- junior and senior scientists
The BORDEAUX INSTITUTE OF ONCOLOGY (BRIC U1312, https://www.bricbordeaux.com/) is seeking to recruit new junior and senior researchers
Bordeaux (Ville), Gironde (FR)
INSERM - U1312 BRIC
Postdoctoral Scholar - Organic Synthesis
Memphis, Tennessee
The University of Tennessee Health Science Center (UTHSC)
Postdoctoral Scholar - Chemical Biology
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Main navigation
- News & Stories
- Get Involved
Putting the “fun” in fundraising for 35 years

- Add to calendar
- Tweet Widget
The Défi Canderel, the fundraiser that has never taken itself very seriously, turned 35 this year. The Montreal event brings together scientists, the corporate community and cancer survivors, replete in some of the least practical running gear. Since 1989, it has used its infectious fun to raise over $25 million for both the Rosalind and Morris Goodman Cancer Institute (GCI) and Institut du cancer de Montréal (ICM).

An outbreak of Défi fever takes over numerous Montreal offices every year. An example at this year’s event: 15 colleagues wearing matching shiny nylon tracksuits in '80s shades of electric blue, fuchsia and purple. Also on-site was a normally mild-mannered scientist who coaxes tumours onto microchips but looked more like a parody of a used-car salesman, save for the headband that matched his garish suit. It was in that outfit that he took part in the event’s run, four laps around McGill’s Percival Molson Memorial Stadium, this year’s venue.
Ground zero for the Défi can be traced to Jonathan Wener. As many now know, he turned personal tragedy into what has become a vital funding pipeline for cancer research.
In 1989, his wife Susan Wener (BEd’75) was diagnosed with colon cancer at the age of 36 and he asked her doctor what he could do to make a difference.
“If you want to do something that has value,” he remembers the doctor saying. “Get some money into the hands of researchers, so we can find a cure.”
Wener has always been a natural fundraiser. Growing up, his father raised money for summer camps, his mother for the Jewish community. “As a child, when you see your parents doing it with enthusiasm you get infected by it.”
In the last few decades, he has broken previous fundraising totals as he spearheaded campaigns for the Jewish General Hospital and Concordia University. Around half of his day is spent on Canderel business—he runs one of the country’s biggest real estate firms—the other half on philanthropic work.

Back in 1989, Wener had many corporate connections and some ideas for his Défi Canderel project.
“We wanted to show the public that business had a heart,” he recalls. He also contacted the McGill- and Université de Montréal-affiliated cancer research institutes, and both were happy to become beneficiaries. He wanted it to be a fun run, not a race.
A few images in his head from those early days include wheelbarrows being pushed during the run for people to throw coins and dollar bills into; the late H. Heward Stikeman (BA’35, BCL’38, LLD) being pulled in a Roman chariot by five Stikeman Elliott lawyers; and costumes that ranged from billiard tables to buildings.
Director Morag Park, who joined what is now the GCI during that inaugural year of the Défi, was struck by the madness of the event. She recalls seeing businessmen in tutus, as she and her team did the run dressed up as members of the band The Cure. “It was wild and inspiring.”
The event has grown from a $100,000-a-year fundraiser to one that has more recently been bringing in $2 million from each run. This year’s goal was an ambitious $3 million.
Those funds, says Park, have made a difference in the type of research that can be pursued, her centre’s recruitment efforts and the shot in the arm it gives young scientists.
When asked what accounts for the Défi’s longevity, Park says, “Two words: Jonathan Wener.” She says the larger-than-life force is not just a person who can create an offbeat and engaged event, but someone who inherently knows what cancer research requires.
“He has always believed that the researchers should make the decisions as to what is needed,” she says of the no-strings-attached money for graduate students and postdocs that her centre receives.
“This allows us to recruit the best trainees and to put on the table—year one—a studentship.” Thanks to the Défi runs, the GCI has offered 165 studentships and 55 fellowships in the last three and a half decades.
Park describes a more intangible benefit for the emerging researcher. “This feeling that somebody believes in you is very important at that point in your career. It says you are worth the effort and that Jonathan Wener and the whole business community are stepping up to support you. It continues to give me goosebumps.”

Another grateful recipient, Sheri McDowell (BSc’17, PhD’22), who is currently completing a postdoc at the University of Geneva in the Agora Cancer Research Center, points out that Canderel grants offer a boost to trainees from out of the country. “These trainees may not be able to apply for funding that’s based on nationality, whereas with Canderel, anyone can apply.”

“I get so much energy from you every year. I don’t care how much pressure I was under before I got here today; the energy when I walked into this area from all of you was amazing.”
He will thank lots of people and eventually mention his recent brush with cancer. A malignant tumour on his kidney had been removed this past December. Earlier in our interview, there is nothing resembling self-pity, as he mentions his luck and gratitude for it having been discovered early.

Part of “Team Wenes” is on stage, including two of the Wener grandchildren who go door to door selling cookies for cancer research. “So, the inculcation I got from my parents,” Jonathan says proudly in the interview, “has worked with my grandchildren.”
Wener is optimistic about his succession. “Susan and I have dedicated a huge part of our lives to cancer and we hope it will continue for decades to come.”

A man in his mid-70s, with 35 successful editions of the Défi behind him, is looking to the future. With his family and his community, he has built a lasting legacy for the benefit of all.
Department and University Information
University advancement.
- Share on twitter
- Share on facebook
Australia rethinks age limit for post-PhD work visas
Lower work rights cut-off would have excluded most doctoral graduates, critics warned.
- Share on linkedin
- Share on mail

In a rare piece of good news for Australia’s beleaguered international education industry, the federal government has reversed its decision to deny post-study work rights to foreign research degree students aged over 35.
The Department of Home Affairs has revealed that overseas graduates of PhD and research master’s programmes will be exempt from an adjustment to the age limit on temporary graduate visas (TGVs), to come into force in July.
While the new cut-off will apply to graduates of taught master’s, bachelor’s, associate degree and vocational programmes, higher research degree recipients will maintain their eligibility for TGVs until they turn 50.
When it announced the lower age limit in its December migration strategy , the government said it was “repositioning the visa as a product for early career professionals who can contribute to the Australian economy over a longer period”.
Critics warned that the new rule would exclude the high-skilled foreigners the government said it wanted to retain. The Group of Eight said around half of the PhD students enrolled with its universities were international, and 40 per cent of overseas doctoral graduates were in their 30s or older.
The lowering of the age limit was also framed as a way of addressing a discrepancy between TGVs and permanent residency, which has an age cutoff of 45. This mismatch left many older graduates in immigration limbo, the government argued.
UNSW Sydney legal student Sonia Qadir, part of a group of foreign doctoral candidates campaigning against the change, said enquiries with the government had failed to unearth any reasons for its plan to replace the five-year discrepancy with one that was twice as long.
Ms Qadir, who expects to complete her PhD this year, said many international doctoral candidates hoped to stay on in Australia for work experience if not permanent residency. “Once you’ve had…experience, your research is going to be much more useful. It’s going to be much more interesting; much more rigorous.
“It’s just the nature of this degree that it’s going to usually be done by people who are a little older. It’s quite likely that you’re going to be in your early to mid-30s when you begin, and some people are even starting in their 40s. We’ve been advocating on those lines for a few months, and we’re really happy to see that those efforts have borne fruit.”
Having worked as a human rights lawyer in her native Pakistan, Ms Qadir plans a new career as an academic. “It’s really useful to have…international experience in academia to be competitive in the job market internationally. I’ve also built my life…during the trajectory of my PhD in Australia. I have built an intellectual community as well.”
The new rules entitle higher research degree graduates to stay in Australia for up to another three years, with an extra year or two available to those from India, Hong Kong and the UK. The government has also maintained the 50-year cut-off for Hong Kong and British passport holders irrespective of the level of their qualifications.
Foreigners dominate PhD enrolments in many science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) disciplines, constituting 65 per cent of doctoral candidates in engineering and 63 per cent in information technology, according to the latest available Department of Education statistics.
Register to continue
Why register?
- Registration is free and only takes a moment
- Once registered, you can read 3 articles a month
- Sign up for our newsletter
Or subscribe for unlimited access to:
- Unlimited access to news, views, insights & reviews
- Digital editions
- Digital access to THE’s university and college rankings analysis
Already registered or a current subscriber? Login
Related articles

Visa chaos ‘turning students off Australia’
Delays and baffling rejections are leaving their mark, analyst warns

Australia cuts post-study work visas by two years
Representative groups broadly welcome focus on quality and integrity, but proposed changes to migration points test will be pivotal

US parents flex power in campus confrontations
While administrators, faculty, students and police get main attention in protests, those paying the bills – especially in wealthier families – pursue more decisive roles


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tip 3 - Be really organised. Some of the most boring and obvious advice for a PhD funding search also happens to be some of the most effective. First of all, make a list of the different funding options you might apply for. Include details of the amounts they offer, their specific eligibility criteria and, most importantly, their deadlines.
PhD and Doctorate Scholarships. Grants and scholarships are financial aid recipients don't need to pay back. In general, grants are need-based while scholarships are based on character or merit. For graduate students, particularly PhD and doctoral candidates, scholarships are often career specific. In contrast, undergraduate scholarships are ...
Interest rates are currently set at 7.05% for the 2023-24 year. Direct PLUS Loans don't award a set amount. Instead, you can borrow up to the full cost of your Masters programme, minus any other forms of financial support you are receiving for it. Interest rates are set at 8.05% for the 2023-24 year.
You may be able to get a PhD loan of up to £27,892 for a UK doctorate. Our guide explains eligibility, applications and repayments. A range of scholarships may be available to help you fund a PhD. Our guide explains the different types of award with tips for making a successful funding application.
The average yearly tuition for a PhD program is slightly above $16,000, which means students will invest about $80,000 in tuition fees alone for a five-year program. Add in fees, cost-of-living, travel expenses and the figure can easily surpass six figures. Yet, it is possible to fund a PhD program without breaking the bank and going into debt.
Students enrolled in the economics Ph.D. program at Emory University typically receive full funding, according to the Georgia university's website. The stipend provided to students is $36,376 per ...
Even though there's no right or wrong way to go about funding a PhD, it does pay to be realistic and well-informed, so make sure you do your research first to find the best way for you. Crowdfunding, employer funding and postgraduate loans are just some of the popular ways to help fund PhD studies, in addition to studentships and research ...
Harvard's financial support package is typically for the first four years of study and the completion year, using a tiered tuition structure that reduces tuition over time as students progress through their degree programs. This multiyear funding package includes a combination of tuition grants, stipends, traineeships, teaching fellowships, research assistantships, and other academic appointments.
Find Education Scholarships for PhD Students. Every little bit helps, get a head start funding your doctoral degree using the U.S. News scholarship database. Apply for money now. 206 results. Sort by:
Search our free database of more than 2,800 funding awardsfor graduate study and professional development. Get Started. Funding database, expert advice, and application tips for academic and professional fellowships and fully funded PhD and fully funded Master's programs.
In the UK, being a self-funded PhD student can be an expensive undertaking, with an annual tuition bill of approximately £3,000 to £6,000 (about US$3,800-7,670) for domestic students and up to £18,000 ($23,000) for international students for the first three years. In the US, the price tag for a PhD is even higher, ranging from US$28,000 to ...
All PhD students at Columbia University get full funding. Columbia has particularly strong programs in medicine and sciences, as well as public administration and policy. Boston College's Department of Psychology offers a four- to five-year, full-time, fully-funded, research-oriented doctoral program. Students admitted Duke University's PhD ...
The Google PhD Fellowship Program was created to recognize outstanding graduate students doing exceptional and innovative research in areas relevant to computer science and related fields. Fellowships support promising PhD candidates of all backgrounds who seek to influence the future of technology. Google's mission is to foster inclusive ...
A PhD stipend is a regular payment for living costs. It functions a bit like an annual salary, but is usually paid tax-free. It's rare for a separate funding package to be referred to in this way, but full scholarships and studentships include a stipend. A PhD bursary is money paid to a student during a degree.
How to Get Your Own Fully Funded PhD Scholarship Step 1: Identify Available Scholarships. To find potential PhD scholarships I suggest looking on the university website and searching online for funding relevant to your domain. For instance Google has its own PhD fellowships. The best thing you can do is start chatting with potential supervisors.
Fully funded means that a PhD student doesn't pay any of the costs of attending a doctoral program. This generally includes all tuition and fees required for full-time enrollment in the program. In many cases, the university covers these costs. Students may also receive funding from private businesses or sponsors.
Our expectations for research organisations, supervisors and students are set out in the statement of expectations for doctoral training. You could get: a minimum stipend of £19,237 per year for your living costs, which is paid to you in regular instalments. support for your tuition fees (minimum £4,786 per year)
PhD Scholarships - A Guide for 2023. Written by Mark Bennett. One type of PhD fundining is a scholarship which can be won from your university or from an independent organisation such as a charity, trust or research foundation. This guide will help you understand how different types of scholarship work and what you need to apply for them.
The seven Research Councils invest in the region of £380 million into doctorate research every year. However, funding is made available through the participating universities rather than the research councils themselves. Universities set up Doctoral Training Partnerships (DTPs) or Centres for Doctoral Training (CDTs) in order to receive funding.
Full studentship - These add a non-repayable, tax-free maintenance grant known as a 'stipend'. In 2024/25, this is worth a minimum of £19,237 and it can be used towards living costs - see UKRI - Find studentships and Doctoral training. For example, a University of Manchester School of Social Sciences PhD studentship includes tuition fees for ...
Starting this week, principal investigators (PIs) seeking funding from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will be required to include a plan describing how they will mentor the graduate students and postdoctoral researchers involved in the project as part of their application. PIs who receive funding will also be required to certify ...
Postgraduate Doctoral Loan. If you're starting a doctoral degree, you could get a Postgraduate Doctoral Loan to help with course fees and living costs. You can get up to: £28,673 if your course ...
Are you looking for exciting PhD positions at esteemed universities in Sweden and the Netherlands?. Over 16 fully-funded multiple doctoral scholarships in diverse fields are available at various universities in Sweden and the Netherlands for the year 2024. These fellowships provide funding for doctoral researchers to conduct their research projects at universities, research institutions, and ...
The success rate for Horizon Europe, a European Union funding scheme with €95.5 billion (US$103.6 billion) to give out between 2021 and 2027, is even lower. As of 2022, applicants had a success ...
A Simple Introduction to PhD Funding. Written by Mark Bennett. Funding for PhD study is a little more complicated than it is for other degrees. There are lots of different ways a student can be funded and your situation may also change during the 3-4 years (or more) it takes to complete a doctorate. This short guide is here to introduce PhD ...
Another grateful recipient, Sheri McDowell (BSc'17, PhD'22), who is currently completing a postdoc at the University of Geneva in the Agora Cancer Research Center, points out that Canderel grants offer a boost to trainees from out of the country. "These trainees may not be able to apply for funding that's based on nationality, whereas ...
In a rare piece of good news for Australia's beleaguered international education industry, the federal government has reversed its decision to deny post-study work rights to foreign research degree students aged over 35. The Department of Home Affairs has revealed that overseas graduates of PhD and research master's programmes will be exempt from an adjustment to the age limit on temporary ...
The Alternative Guide to Postgraduate Funding was created by two PhD students who secured over £50,000 in charity grants towards their studies between them. As well as offering practical tips for identifying suitable organisations and making successful applications, the Alternative Guide runs a database of more than 1,000 charities.