- Conjunctions
- Prepositions

CASE STUDY in a Sentence Examples: 21 Ways to Use Case Study

Have you ever wondered what a case study actually is? In simple terms, a case study is a research method that involves an in-depth analysis of a specific individual, group, or situation. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject at hand by examining various aspects and contexts.
Case studies are commonly used in academic research, business analyses, and scientific investigations to illustrate theories, showcase real-world scenarios, and draw conclusions based on empirical evidence. By delving deep into a particular case, researchers can uncover valuable insights, identify patterns, and offer practical solutions to complex problems.
Table of Contents
7 Examples Of Case Study Used In a Sentence For Kids
- Case study is like a story we can learn from.
- We can learn different things from a case study .
- Teachers use case studies to help us learn better.
- Case studies can be about animals, people, or places.
- We can ask questions about a case study to understand it better.
- Reading a case study can be fun and interesting.
- We can use our imagination while reading a case study .
14 Sentences with Case Study Examples
- Case study : A group of college students conducted a case study on the impact of social media on mental health among Indian youth.
- The economics professor assigned a case study on the effects of demonetization in India to the students.
- Case study : The management students analyzed a case study on the marketing strategies of popular Indian fashion brands.
- The engineering students presented a case study on the development of renewable energy sources in India.
- Case study : A team of MBA students examined a case study on the growth of e-commerce in the Indian market.
- The biology professor asked the students to review a case study on the outbreak of a disease in a rural Indian village.
- Case study : A group of psychology students analyzed a case study on the prevalence of stress among college students in India.
- The statistics professor provided a case study on data analysis of agricultural productivity in different regions of India to the students.
- Case study : The marketing students worked on a case study to understand consumer behavior towards sustainable fashion in India.
- A case study on the impact of technology on education in rural India was assigned to the education majors.
- The sociology professor discussed a case study on the caste system in India with her students.
- Case study : The finance students analyzed a case study on the financial performance of top companies in India.
- The environmental science class conducted a case study on the effects of pollution on the Ganges River in India.
- Case study : The journalism students examined a case study on the role of media in shaping public opinion during national elections in India.
How To Use Case Study in Sentences?
Case Study is a research method that involves an in-depth analysis of a single individual, group, or event. This method is commonly used in various fields such as psychology, sociology, business, and education.
To use Case Study in a sentence, follow these steps:
Begin by introducing the Case Study topic or subject. For example, “The Case Study examined the impact of social media on teenagers’ mental health.”
Provide a brief overview of the Case Study . For instance, “The Case Study focused on a group of high school students and their usage of social media platforms.”
Include key findings or observations from the Case Study . For example, “The Case Study revealed that prolonged exposure to social media can lead to increased feelings of anxiety and depression among teenagers.”
Conclude your sentence by summarizing the implications or significance of the Case Study . For instance, “Overall, the Case Study highlighted the importance of promoting healthy online behaviors among young people.”
By following these steps, you can effectively incorporate the term Case Study in your writing to convey a detailed analysis of a specific subject or phenomenon.
In conclusion, the use of sentences with case study examples is a powerful way to elucidate real-world applications of theoretical concepts. By providing detailed instances of how a particular theory or approach has been applied in practice, case study sentences bring clarity and concreteness to abstract ideas. They allow readers to connect with the information on a practical level and visualize the impact and outcomes of theoretical knowledge.
Moreover, sentences with case study examples serve as valuable learning tools, offering insights into problem-solving strategies, decision-making processes, and successful implementation of theories in various contexts. Through the detailed examination of specific cases, readers can better understand the complexities and nuances of different situations, leading to a deeper comprehension and appreciation of the subject matter being discussed.
Related Posts

In Front or Infront: Which Is the Correct Spelling?
As an expert blogger with years of experience, I’ve delved… Read More » In Front or Infront: Which Is the Correct Spelling?
Targeted vs. Targetted: Correct Spelling Explained in English (US) Usage
Are you unsure about whether to use “targetted” or “targeted”?… Read More » Targeted vs. Targetted: Correct Spelling Explained in English (US) Usage
As per Request or As per Requested: Understanding the Correct Usage
Having worked in various office environments, I’ve often pondered the… Read More » As per Request or As per Requested: Understanding the Correct Usage

- Get started Get started for free
Figma design
Design and prototype in one place
Collaborate with a digital whiteboard
Translate designs into code
Get the desktop, mobile, and font installer apps
See the latest features and releases
- Prototyping
- Design systems
- Wireframing
- Online whiteboard
- Team meetings
- Strategic planning
- Brainstorming
- Diagramming
- Product development
- Web development
- Design handoff
- Product managers
Organizations
Config 2024
Register to attend in person or online — June 26–27

Creator fund
Build and sell what you love
User groups
Join a local Friends of Figma group
Learn best practices at virtual events
Customer stories
Read about leading product teams
Stories about bringing new ideas to life
Get started
- Developer docs
- Best practices
- Reports & insights
- Resource library
- Help center
What is a use case? How to write one, examples, + template

Designing a product takes more than listing features and goals. Before the first smartphone came out, how would you describe the ways users interact with it? Calling it a cellphone you can browse the web on is a good start, but that doesn’t explain the complexity of its systems. To map out the ways users interact with a system, tool, or product, you need a use case.
Use cases are descriptions of the ways users interact with systems to accomplish tasks or reach goals. Mapping these interactions can improve early planning and ensure a smooth development cycle. To help you work them into project planning, we’ll define a use case, explain how to write one, and share examples.
What is a use case
A use case explains how users interact with a product or system. It outlines the flow of user inputs, establishing successful and failed paths to meeting goals. This allows product teams to better understand what a system does, how it performs, and why errors occur. You can write one out or diagram a use case model for visual thinkers.

Use cases vary in complexity depending on your audience or system. But across the board, your use case should identify a few key components. The most important ones include:
- Actor: anything exhibiting behavior that interacts with a system, such as a single user, a team, or another piece of software
- System: the product or service with defined functionality
- Goal: the purpose or objective users reach with a system’s features
Actors, systems, and goals build the foundation for a use case. When you begin tracking system interactions, a few new elements come into play:
- Stakeholder(s): someone with a stake or interest in a system’s performance
- Primary actor: the actor who initiates a system’s function to reach a goal
- Preconditions: underlying factors required for the use case to happen
- Triggers: events that begin a use case
- Basic flows: use cases where systems work as intended to reach a goal
- Alternate flows: different outcomes based on when and how a system veers off course
Types of use cases
Use cases come in two forms: business and system. A system use case is a detailed look at how users interact with each part of a system. It highlights how unique inputs and contexts cause the system to reach different outcomes. This level of detail highlights how a system’s individual functions work in any scenario.
Business use cases paint a more general picture of how a user might interact with your business to reach their goals. Instead of focusing on technical detail, it’s a cause-and-effect description of different inputs. For example, if you run a code debugging platform, your business use case explains how users enter their code and receive error notices.

Some teams like to write a business use case to outline a system’s processes before development. As developers begin their work, a manager will outline more technical system use cases to follow.
Use scenario vs. use case
Use cases show all the ways a system functions when trying to reach goals, but a scenario only depicts one example. In a scenario, the system can succeed or fail at reaching the user’s goals. Put simply, multiple use scenarios build a use case.
Use case vs. user story
Use cases depict how users interact with a system, and user stories describe features from the user’s perspective. As a result, user stories are much shorter than use cases, typically consisting of brief descriptions teams use as a jumping-off point in development. Additionally, use cases can assist multiple teams in an organization, while user stories help product teams build their tool.
Use case vs. test case
While a use case covers how users and system features work to reach goals, test cases verify if a single feature works correctly. Unlike use cases, test cases look at functionality in isolation.
For example, a test case might involve validating login functionality on an email platform, ensuring users can log in on any browser at any time after creating their account.
How to write a use case
Writing a use case sounds complex, but only requires understanding your system and its users. You can write a use case by following these six steps:
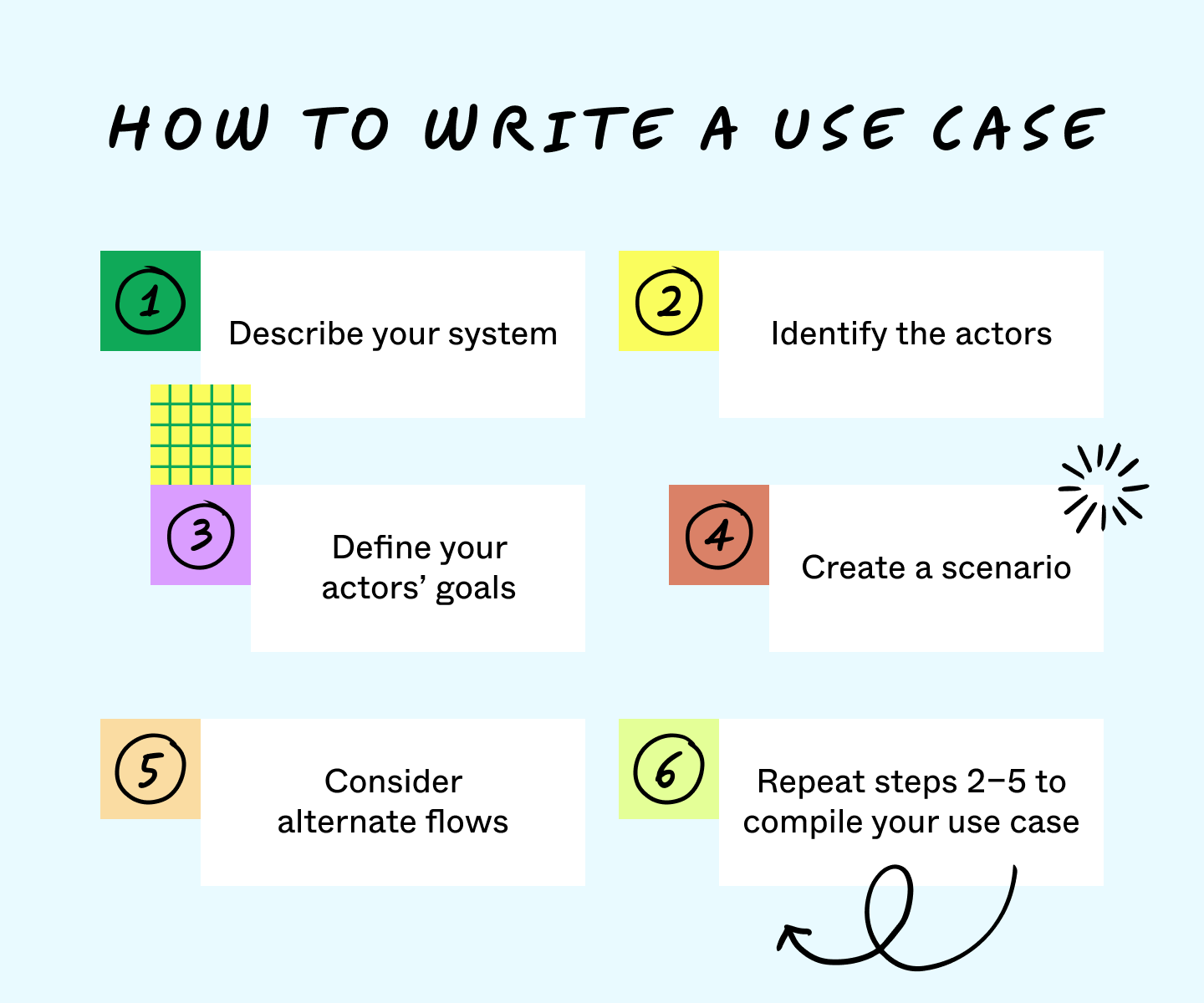
1. Describe your system
Start by describing your system, or the product or service you and your team will build. Focus your description on what your system does for users. In a business use case, you can keep this background general and explain what it accomplishes. For a system use case, give an under-the-hood description of how your product functions.
Define your system by asking:
- What form does it take: product, service, or software?
- What features does it offer?
- What goals can you accomplish with it?
- How does it meet those goals?
- What can you learn about the system from other documents like project charters ?
2. Identify the actors
Actors generally refer to users and customers but can apply to any outside force that engages with your system. Your actor needs well-defined behaviors explaining how and why actors use your system.
Identify actors by asking:
- Are they individuals, teams, hardware, or another system?
- Will primary and secondary actors share the same behavior?
- Will stakeholders take on the role of actors in your use case?
3. Define your actors’ goals
Use cases highlight the outcome actors want from a system. Remember to focus on your actors’ wants over the system’s capabilities to understand why users come to your system. In some cases, customers want to use systems for more than one objective. Listing each of these objectives creates a more robust use case.
4. Create a scenario
In a use case, scenarios are the sequence of actions customers take when using a system and the flow of effects from that interaction. Your basic flows cover scenarios where a system works as intended. A user approaches the system, enters the right inputs, and your system helps them reach their goals.
Start with these successful, basic flows to create a baseline. You can use process mapping techniques to identify potential issues in the next flows.
5. Consider alternate flows
After writing a successful scenario, write alternate flows that lead to different outcomes. Typically, alternate flows involve the misuse of a system that keeps actors from reaching their goals. However, you can also note internal errors that cause a system to break down or unintended ways systems can reach goals.
Alternate flows show how different actors use a system and succeed or fail. They give a more nuanced view of everything your system can do to help you troubleshoot.
6. Repeat steps 2–5 to compile your use case
With enough variation of actors, goals, and scenarios, you can show how your system functions. Compiling these flows together gives you a use case, which can improve development and inform other documents like project status reports .
With simple systems, you can change a few elements to see every potential outcome. However complex systems may have too many elements to see each outcome. In cases like this, you can focus on testing the most common interactions. You can also design systems to prevent untested com
Try Figma’s use case template
Ready to start brainstorming use cases? Try the Figma use case template to break down your systems and find new solutions.
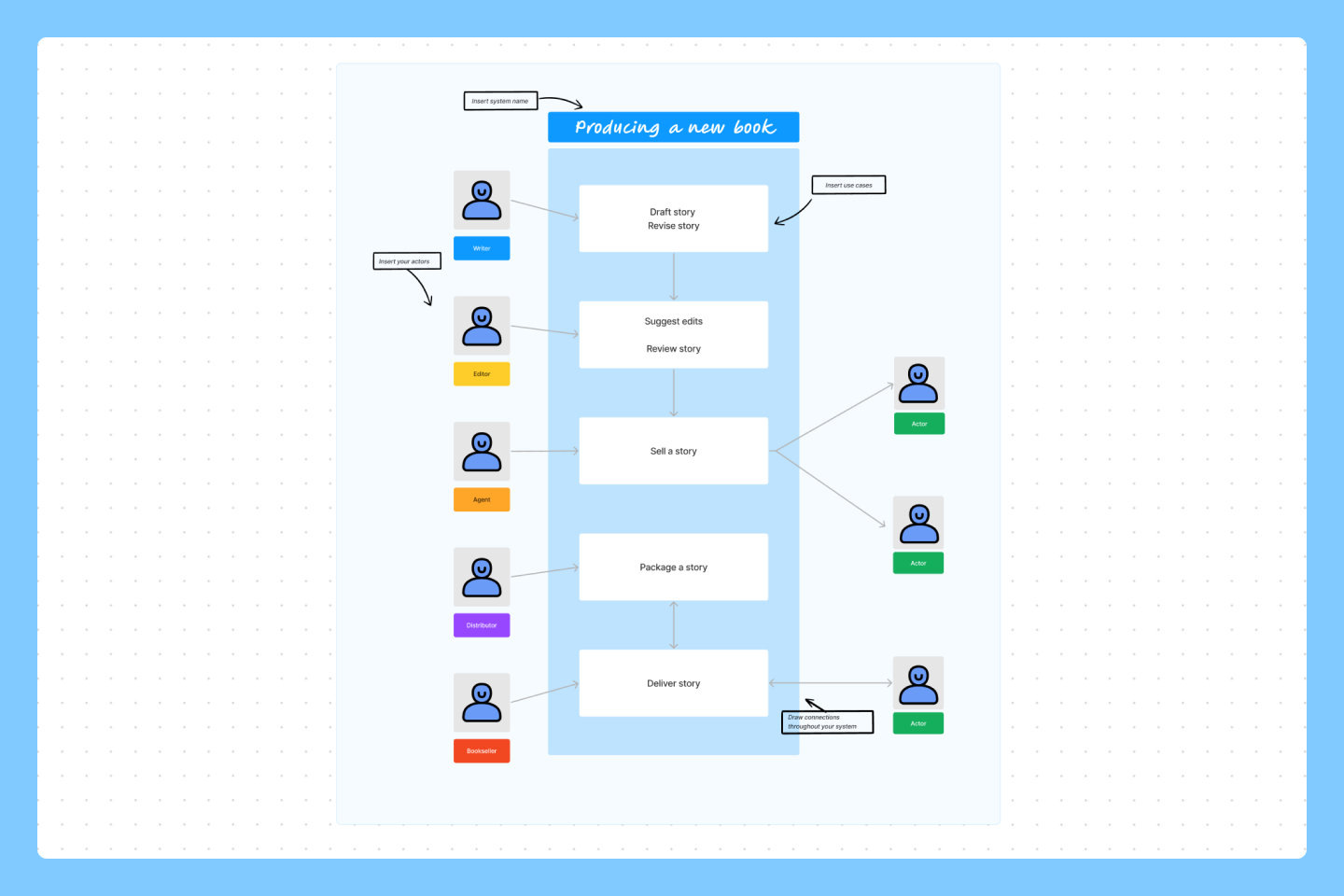
Use case example
Assume you’re a product manager developing a mobile banking app for your company. Your platform needs to streamline user registration and account setup. Here’s a sample use case format based on this app:
Background information:
- System: a mobile banking app
- Primary actor: customers who want to open an account
- Secondary actor: underwriters and automated tools calculating interest rates and maximum principal balances
- Goals: save time on account registration and onboarding
- Stakeholders: the CEO and product VP of your company
- Preconditions: users download the app and meet account requirements
- Triggers: the user chooses to create a new account from the app
- Basic flow: Users download your app and choose to create a new account. The application collects information about the user’s other accounts and credit scores. From there, it automatically shares the accounts they qualify for and their interest rates. The user finds an account that suits their needs and registers.
- Alternate flow 1: Users enter their financial information and the app quickly generates account options. However, each account defaults to the highest interest rate their financial background allows. So, users abandon the app to find a lower rate.
- Alternate flow 2: The onboarding process works as intended, but the app faces compliance issues such as Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements. While the app can provide account options, extra compliance steps slow the process.
- Alternate flow 3: Because the app only looks at other accounts and credit scores, it can’t offer a full range of account options. For example, it can only offer credit cards and lines of credit. So, customers looking for mortgages have to go elsewhere.
Benefits of use cases
In the planning stage, use cases define your project scope, requirements, and roadmap. Teams can also discuss the best user outcomes and design a path to them. With alternate flows, you can also anticipate risks before they hurt a user’s experience. If that isn’t enough reason to pen one, here are a few other benefits of use cases:
- Explains value: Use cases explain a system’s features in plain terms. So, when pitching your plans to stakeholders, a use case makes your system easier to understand.
- Predicts costs: A use case outlines the complexity of a system. More complexity may come with additional features or safeguards. By learning how complex your system is, you can estimate development costs.
- Improves planning: Without a use case, designers and developers focus on what a system does, not how it does it. However, use cases help teams consider all the ways to implement features and safeguards.
- Shares alternative uses: Not all alternative flows in a system lead to failed outcomes. Mapping out different scenarios finds new solutions to old problems or expands your understanding of what a system can accomplish.
Perfect your use cases with FigJam
Use cases go beyond describing what your product can do. They give stakeholders and teams a clear picture of user interactions and successful outcomes. Whether adding a new feature, rapid prototyping , or redesigning a system, your planning should start with writing a use case.
The more insights into actors, interactions, and outcomes, the better—which is why it's important to collaborate on use cases with your team and stakeholders. A shared online whiteboard like FigJam streamlines collaboration between remote teams to help you build out comprehensive use cases. Our gallery of 300+ templates can bring teams together at any stage of development.
Examples of 'case study' in a sentence
Examples from the collins corpus.
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

All ENGLISH words that begin with 'C'
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
What is a use case? Definition, template, and how to write one

For requirements collection and high-level stakeholder communication, product managers need to be able to describe how a consumer will interact with a system or product. This can include a description of the product’s users, how they interact with the product, and what it does.

A great way to visually represent this information is by creating a use case.
In this guide, we’ll define what a use case is, describe the elements therein and what they are designed to do, and walk through how to build a use case step by step.
We’ll also look at some use case examples to show what they look like in practice.
If you’d like to write your own use case while following along with this article, here is a free use case template . To use the template, select File > Make a copy from the top menu bar.
What is a use case?
A use case is a description of how a user interacts with a system or product. Companies build use cases to establish success scenarios, failure scenarios, and any important variants or exceptions.
Many organizations leverage use case modeling tools — such as Miro, LucidChart, and SmartDraw, for some examples — to write or visually represent a use case.
Use cases are frequently employed in software development environments to simplify complicated concepts, but they can be just as important in project management for gathering requirements and defining a project’s scope.
Who creates use cases?
Product management , product development , and product testing domains all use the use case methodology. Product managers and developers employ use cases in a similar manner: as a design tool to specify how the system will react to user activities. However, there are some key differences.
Product managers typically document user-focused use cases whereas developers document product-focused use cases. The user-focused use cases are primarily concerned with the user and their objectives. These are then passed to developers to guide decision-making during the product development process.
Product developers frequently add technical and design elements to provide crucial context. This set of improved use cases gives the development team the insight it needs to start designing, creating, and testing the product and its features.
What is a use case designed to do?
A use case is designed to reveal system demands early on in the process.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
Use cases concentrate on the system’s users rather than the system itself. A user case should be understandable to all stakeholders , not only developers and testers, because they are mostly narrative prose. This includes customers, users, and executives.
During the early planning stages, you should involve whichever roles are best suited to solve the problem at hand. This encourages end users to buy into the solution and reduces surprises once the system is put into place.
Each use case is designed specifically to cover only one application of the system. That said, a key advantage of use case modeling is that it also covers all potential problems. Finding minor requirements early on in the project saves a ton of time by identifying exceptions to a successful scenario.
Finally, after you create a use case, you can use it to guide the creation of many other software development components, such as object models, test case definitions, user documentation, and project planning (cost, complexity, and scheduling estimations).
As a product manager, one of the best justifications for creating use cases is that they serve as genuine connecting points. They should be truly understandable to both business and technical users so that everybody can comment on them.
Business analysts leverage use cases as a communication tool to align people to take a common approach and share a common understanding of what the software aims to accomplish.
A technical product manager, on the other hand, might employ use cases to reach business stakeholders without using tech jargon — talking more about what the system does than how it does it. When you get down to the dirty work of coding, this will really help you accelerate and clarify communication to ensure that you’re building what the business genuinely needs and desires.
Elements of a use case
Let’s break down the components of a typical use case and explain the purpose and objective of each.
Actors are the people or things that interact with your system. An actor could be an individual, a company, a team, or something else entirely. Anything that exists outside of a system and engages in some sort of interaction with it qualifies as an actor.
More great articles from LogRocket:
- How to implement issue management to improve your product
- 8 ways to reduce cycle time and build a better product
- What is a PERT chart and how to make one
- Discover how to use behavioral analytics to create a great product experience
- Explore six tried and true product management frameworks you should know
- Advisory boards aren’t just for executives. Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
The stakeholder who gets the ball rolling with an interaction to achieve a goal using your system is known as the primary actor.
Your system, which some people refer to as a scene, is composed of a number of decisions and interactions made by your actors.
The results of an actor’s interactions with the system are your goals.
Your system may produce several outputs in some circumstances while only producing one in others. Before continuing, consider modifying your method if you encounter any barriers to achieving your goal.
Preconditions
Preconditions are assertions or realities regarding what must occur prior to and following the use case.
Often, software developers are aware of the actions that must come before the next one.
For example, let’s say an online shopper clicks on a product to get a detailed description and customer feedback. The Add to cart button won’t show up until the item is in stock and accessible at the warehouse.
A use case that operates flawlessly and exactly as intended with no exceptions or mistakes in the run is known as the fundamental flow or main success scenario. This frequently serves as a starting point when developing various features.
Knowing how a typical scenario operates can help you write accurate code and come up with alternative flows.
Alternative flows
A deviation from the primary success scenario is known as an alternative path or alternative flow. This typically manifests when a system-level error occurs.
In this section of the use case, you frequently list the most probable or noteworthy exceptions an actor might make. Alternative flows in the e-commerce example might include:
- Adding items to favorites instead of a shopping cart
- Sharing items with friends or family members
- Looking at reviews and comments about a product or service
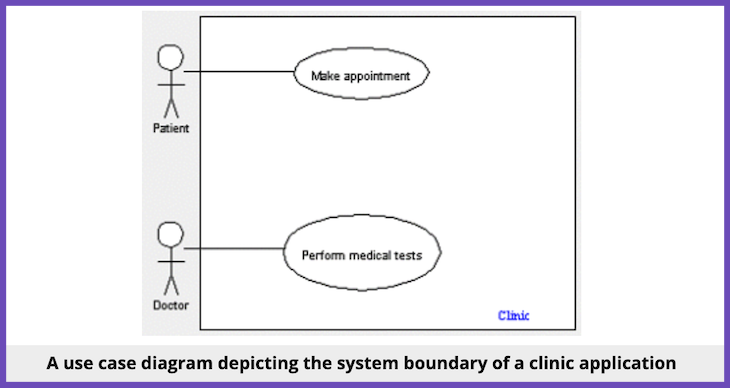
What does a use case diagram look like?
In a use case diagram, stick figures are the most typical way to depict actors .
The use cases/goals you create will be horizontal ovals with a few words of text inside detailing each activity; you can use various colors to indicate different goals.
Associations that depict the connections between components use solid and dotted lines.
Each set of use cases within a system are grouped together by system boundary boxes , which are rectangles.
An example of a use case diagram for a medical clinic application might look something like this:
How to write a use case
To write a use case, complete the following steps:
- Determine the target audience for the product
- Select a user from that list
- Determine what, exactly, the user wants to do with the product and create a separate use case for each action
- Determine the typical flow of events for each use case when the user uses the product
- In the use case description, describe the fundamental course. Give examples of what the user performs and what the system responds with so that the user is aware of both
- Consider alternative courses of action and include them to “expand” the use case once the fundamental process has been presented
- Search for connections between the use cases. Extract these and mark them as typical use cases for courses
- Repeat steps 2–7 for all other users
Use case template
You can use the template below to assist you in writing your own use case:
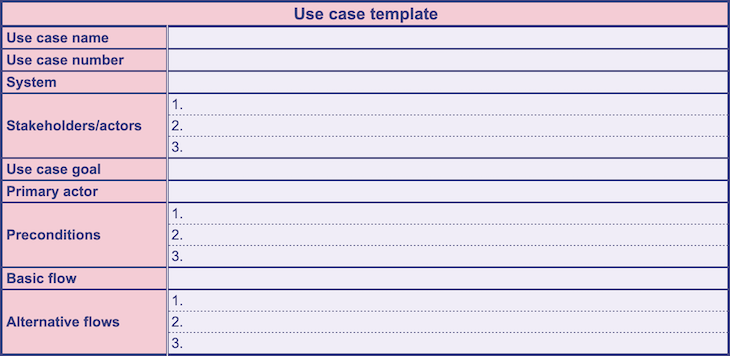
To use this use case template , click here and make a copy by selecting File > Make a copy from the top menu bar.
Use case example
To show how the steps outlined above work in practice, let’s look at an example use case of a housekeeper doing laundry:
- Actors — Residents, housekeeper, etc.
- Primary actor — Housekeeper
- Goals — To do laundry, fold all items, iron clothes if necessary
- Preconditions — It is a Friday and there is laundry in the laundry room
The basic flow for this use case example is as follows:
The housekeeper comes to the laundry room on Friday. They organize the available laundry. After that, they clean and then dry each load. They folds the articles that need folding, then iron and hang the wrinkled items
Alternative flows :
- The housekeeper irons any wrinkled items before putting them on a hanger
- The housekeeper rewashes anything she finds to be still dirty
Use cases help product teams understand a system’s functions from the viewpoint of distinct users. They help stakeholders across the organization visually understand the various flows and how user groups interact with the system.
Use cases also support the development team when generating concepts and assessing the viability of the use cases. Use case definition is a crucial phase in the software development process and is a critical skill for any product manager.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #product strategy

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.
Drive growth with these 7 customer feedback tools
A customer feedback tool is a software solution or platform designed to collect, analyze, and manage feedback from customers.

Leader Spotlight: Motivating teams to hit customer-centric outcomes, with Kristina Bailey
Kristina Bailey discusses the careful balance of knowing the business outcomes you want to achieve while balancing customer outcomes.

Exploring augmented products: Beyond the core offering
Augmented products leverage technology and additional services to provide enhanced functionality, convenience, and value to users.

A guide to acceptance test-driven development (ATDD)
ATDD is an agile methodology involving collaboration to define acceptance criteria before starting any development.

One Reply to "What is a use case? Definition, template, and how to write one"
ok. This was useful
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 6 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.

About These Results
Advanced Search
Login or signup.
Only registered users can use the advanced search. Signup for FREE now, or login if you already have an account.

~~~ We Need YOU ~~~
Popular phrases.
- stress ridden
- pile of paperwork
© 2024 Sentence Stack | Terms | Privacy Cookies -->

How To Use Case Study In a Sentence? Easy Examples
- March 5, 2024

When it comes to understanding a concept or learning a new language, examples play a crucial role in grasping the information effectively. In this article, we will explore the significance of using examples in sentences to enhance comprehension. By providing real-world instances or hypothetical scenarios, example sentences help illustrate the usage of a word or phrase in a particular context.
Utilizing examples in sentences can make learning more engaging and practical. Through examples, learners can see how a word is used in different sentence structures, which aids in solidifying their understanding of vocabulary and grammar rules. Case studies are particularly helpful in showcasing how a word functions in a specific situation, providing a deeper insight into its application.
In the following sections, we will delve into various example sentences with the word “case study,” demonstrating how this approach can facilitate a better understanding of its usage. By exploring these examples, readers will gain a clearer perspective on how to incorporate the word effectively in their own writing or speaking.
Learn To Use Case Study In A Sentence With These Examples
- Have you completed the case study for the marketing campaign?
- Could you analyze the case study of our competitor’s latest product launch?
- Please ensure that the case study is ready for the presentation tomorrow.
- What key insights did you gather from the case study of our sales performance?
- Is it possible to request a copy of the case study for future reference?
- Let’s discuss the findings of the case study during our team meeting.
- Why is the case study report not included in the project files?
- Have you conducted interviews for the case study on employee engagement?
- Can we compare the results of this case study with last year’s data?
- It is crucial to reference the case study when presenting your ideas.
- I need you to analyze the latest case study on consumer behavior in the market.
- How long did it take you to complete the case study on production inefficiencies?
- The case study provides a detailed analysis of supplier relationships.
- Let’s present the case study findings to the client for their feedback.
- Did you find any limitations in the methodology used in the case study ?
- Can we extract some valuable lessons from the case study on project management?
- Have you shared the case study results with the rest of the team?
- Please remember to include the case study references in your report.
- Why do you think the case study results vary from our initial projections?
- Are there any ethical considerations to be aware of when conducting a case study ?
- Let’s gather all the relevant data needed for the case study analysis.
- It is essential to draw actionable insights from the case study findings.
- Could you summarize the key takeaways from the case study on customer satisfaction?
- What are the implications of the case study results on our business strategy?
- Have you reviewed the case study draft for accuracy and completeness?
- Let’s review the case study timeline to ensure we meet the deadline.
- Can you identify any potential biases in the case study methodology?
- Please share your thoughts on the case study approach and methodology used.
- The case study highlights the importance of a customer-centric approach.
- Why was the case study analysis not included in the final report?
- Let’s explore the implications of the case study results on our decision-making process.
- Are there any key learnings you can apply from the case study on supply chain management?
- Would you recommend any changes to the case study methodology for future projects?
- I see great potential in using the case study approach for our upcoming campaign.
- The case study findings provide valuable insights into consumer behavior trends.
- Why do you think the case study results deviate from the industry norms?
- Let’s present the case study data in a clear and concise manner for better understanding.
- Could you outline the steps taken to validate the data in the case study ?
- Have you factored in all variables when analyzing the case study results?
- The case study serves as a roadmap for understanding market dynamics.
- Let’s create a compelling narrative around the case study findings for the presentation.
- Can we leverage the insights gained from the case study to improve our performance?
- It is imperative to consider the context in which the case study was conducted.
- Have you shared the case study methodology with the research team for feedback?
- Let’s integrate the feedback received on the case study draft before finalizing it.
- Could you clarify the methodology used in the case study for better transparency?
- The case study reveals interesting patterns in consumer preferences.
- Why do you think the case study results are not aligning with our expectations?
- Let’s collaborate on analyzing the case study data to draw meaningful conclusions.
- Have you documented all sources used in the case study to ensure credibility and transparency?
Exploring an Example of a Case Study
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth analysis of a specific individual, group, event, or phenomenon. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject and its context, often using multiple data sources and analytical techniques.
Nature of a Case Study
Case studies are typically qualitative in nature, allowing researchers to explore complex issues in real-life contexts. They often involve detailed descriptions, rich narratives, and the use of multiple perspectives to capture the nuances of the case.
Example: Psychological Case Study
An example of a case study could involve a psychological case study examining the effects of childhood trauma on adult mental health. Researchers might select a specific individual who experienced significant trauma during childhood and conduct interviews, psychological assessments, and observations over an extended period.
Analysis and Findings
Through the case study, researchers would analyze the individual’s experiences, coping mechanisms, and psychological outcomes. They may identify patterns, themes, and insights that contribute to our understanding of the long-term effects of childhood trauma and inform therapeutic interventions.
Applications of Case Studies
Case studies are utilized across various disciplines, including psychology, sociology, business, medicine, and education. They provide valuable insights into complex phenomena, inform theory development, and offer practical implications for professional practice.
Business Case Study
In a business context, a case study might involve analyzing a company’s strategic decision-making process or evaluating the implementation of a new marketing campaign. By examining real-world examples, businesses can learn from both successes and failures, informing future strategies and practices.
Exploring the Purpose of Writing a Case Study
Writing a case study serves several important purposes across various fields and disciplines. It allows researchers, scholars, and practitioners to delve deeply into specific topics, phenomena, or individuals, providing detailed insights and contributing to the advancement of knowledge and understanding.
Informing Understanding and Theory
Case studies are valuable for informing understanding and theory development. By examining real-life examples in detail, researchers can identify patterns, relationships, and underlying mechanisms that contribute to theoretical frameworks and conceptual models.
Illustrating Concepts
Case studies serve as powerful illustrations of theoretical concepts and principles. They provide concrete examples that help clarify abstract ideas, making complex theories more accessible and applicable to real-world situations.
Exploring Complexity
Many phenomena are inherently complex, involving multiple factors, interactions, and contexts. Case studies allow researchers to explore this complexity in depth, uncovering the intricacies of a particular case and gaining insights that may not be apparent through other research methods.
Examining Unique Cases
Some cases are unique or rare, offering valuable opportunities for exploration and analysis. Writing a case study enables researchers to document and analyze these unique cases, shedding light on novel phenomena or exceptional circumstances.
Informing Practice and Decision-Making
Case studies are not only valuable for academic research but also for informing practice and decision-making in various fields. They offer practical insights, lessons learned, and best practices that can guide professionals in their work and help them make informed decisions.
Improving Problem-Solving Skills
By analyzing and writing about case studies, individuals develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. They learn to evaluate evidence, identify key issues, and develop effective strategies for addressing complex problems.
How To Use Case Study in a Sentence? Quick Tips
Imagine you are a detective, eager to crack a case wide open. You have your magnifying glass in one hand, a Sherlock Holmes hat perched jauntily on your head, and a mysterious case study in front of you. Just like Sherlock, you need to use your wit and wisdom to dissect the case study properly. Fear not, young sleuth, for we have all the tips and tricks you need to become a master at unraveling case studies.
Tips for using Case Study In Sentences Properly
1. understand the context :.
Just like every crime scene is unique, every case study comes with its own set of circumstances. Before diving in, make sure you grasp the context and purpose of the case study. This will help you frame your sentences accurately.
2. Use Relevant Details :
Avoid vague descriptions that leave your readers scratching their heads. Provide specific details, quotes, and data from the case study to support your arguments. Paint a vivid picture for your audience.

3. Stay Objective :
Remember, you’re a detective, not the judge and jury. Present the facts of the case study objectively and avoid injecting personal bias into your sentences. Let the evidence speak for itself.
4. Draw Comparisons :
Like drawing parallels between different cases can help solve a crime, comparing the case study to real-world examples or theories can strengthen your analysis. Use these comparisons to add depth to your sentences.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
1. overgeneralizing :.
Don’t make sweeping statements based on limited information from the case study. Be precise in your language and back up your claims with solid evidence.
2. Ignoring Counterarguments :
Just as a good defense attorney anticipates the prosecution’s arguments, address potential counterarguments in your sentences. Acknowledging opposing viewpoints shows a nuanced understanding of the case study.
3. Being Repetitive :
Repeating the same information in multiple sentences can make your analysis seem redundant. Mix up your sentence structures and vary your vocabulary to keep your writing engaging.
Examples of Different Contexts
1. business case study :.
“The company’s decision to diversify its product line resulted in a 20% increase in revenue within the first quarter, showcasing the success of their strategic approach.”
2. Legal Case Study :
“The defense attorney cross-examined the witness, highlighting inconsistencies in her testimony and casting doubt on the prosecution’s case.”
3. Medical Case Study :
“The patient’s quick recovery after the experimental treatment suggests promising possibilities for future research in the field of oncology.”
Exceptions to the Rules
1. creative writing :.
In fiction or creative writing, you have more leeway to experiment with sentence structure and narrative style. Let your imagination run wild, but ensure your sentences remain coherent and impactful.
2. Personal Reflection :
When reflecting on a case study from a personal standpoint, you can use a more informal tone and incorporate emotions into your sentences. Just remember to tie your reflections back to the key points of the case study.
Now, dear detective-in-training, armed with these insights, go forth and conquer those case studies with confidence! But before you embark on your next investigation, let’s put your newfound knowledge to the test with a few interactive exercises:
a) Understand the context b) Use vague descriptions c) Stay objective d) Draw comparisons
a) To confuse the readers b) To show a nuanced understanding c) To ignore opposing viewpoints d) To make your sentences repetitive
Happy sleuthing!
More Case Study Sentence Examples
- Can you provide a thorough case study on our most successful marketing campaign?
- Let’s analyze the case study to understand the key factors that led to the project’s success.
- Did you review the latest case study on market trends before making a decision?
- Complete the case study analysis by identifying areas for improvement and implementation.
- In which case study did you find the best strategies for customer retention?
- The case study revealed a significant increase in sales after implementing the new pricing strategy.
- Ensure you include real data and statistics in the case study presentation.
- Could you summarize the main findings from the latest case study presentation?
- To gain better insights, compare the case study results with industry benchmarks.
- We cannot underestimate the importance of conducting a detailed case study before launching a new product.
- I advise you to carefully examine the case study before making any decisions.
- The sales team presented a compelling case study on the effectiveness of the new sales approach.
- Have you explored the case study results to identify potential risks and opportunities?
- Include a section on lessons learned in the case study report for future reference.
- We need to understand the customer behavior patterns outlined in the case study .
- Will you be able to provide a comprehensive case study on supply chain management?
- Let’s brainstorm ways to improve our processes based on the insights from the case study .
- Don’t overlook the recommendations outlined in the case study for process optimization.
- Can you present the case study findings to the management team during the next meeting?
- It’s crucial to validate your assumptions with real data from the case study .
- The case study highlighted the importance of customer feedback in product development.
- How did the team respond to the challenges identified in the case study ?
- Ensure the case study reflects the most recent market trends for accurate analysis.
- The management team requested a detailed case study before approving the budget proposal.
- Do you believe the insights from the case study will help us achieve our sales targets?
- Don’t proceed with the project without conducting a thorough case study to assess risks.
- What were the key takeaways from the latest case study on consumer behavior?
- The case study serves as a valuable tool for understanding our target audience.
- Can you create a visually engaging presentation of the case study findings?
- Remember to cite all sources accurately when referencing information from the case study .
In conclusion, case studies offer valuable insights into real-world scenarios and can be used as powerful educational tools. By examining specific examples, such as *example sentence with case study*, students can gain a deeper understanding of theoretical concepts and their practical applications. Through detailed analysis and critical thinking, case studies help individuals develop problem-solving skills and enhance their learning experience.
Furthermore, case studies are widely used in various fields, from business to healthcare, to explore complex issues and propose viable solutions. For instance, *example sentence with case study* illustrates how a detailed examination of a specific situation can lead to identifying key challenges and implementing effective strategies. By presenting concrete examples, case studies bridge the gap between theory and practice, encouraging active engagement and facilitating a deeper comprehension of the subject matter.
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Add Comment *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post Comment
How to Write a Case Study in 7 Easy Steps (AI Included)

Table of contents

Meredith Sell
One of the most valuable weapons in a content marketer’s arsenal is the case study.
While a blog draws customers to your site and web pages explain your products or services, a case study shows your products or services in action. It makes their impact tangible and relatable, and proves the claims made by your other content.
What’s most important to understand here? Your case studies are for people who are close to making a purchase decision. They might have buying power, they might have influence over those who do. But they are far enough in the scouting process to be weighing different options against each other and seeing how others fared with this or that solution.
Write more in less time with Wortune > Write more in less time with Wortune >

Case studies are helpful because they flesh out your solution for your prospective customers. They show how it worked to solve another customer’s problem. Case studies serve as evidence for the promises you make all over your website.
Simply put, a case study’s purpose is to demonstrate your solution’s practical impact on real customers for prospective customers .
This is not a journal entry for a company achievements scrapbook. This is an outward-facing marketing and sales tool that speaks directly to your prospects in direct, practical terms, showing how another customer in a similar situation found your solution to be exactly what they needed.
The Basic Elements of B2B and B2C Case Studies
Case studies can come in all shapes and sizes—longform reports, condensed one-pagers, blurb-filled infographics, or even videos—but they all involve the same basic elements.
Boiled down, a case study can be described in two words: problem, solution. How you flesh out the problem and solution will depend on your strategy, your audience, and the particular story you’re telling.
Here’s what you’ll want to include:
1. A Descriptive Headline
A quick glance at your case study’s headline should give your audience a clear idea of the takeaway—and whether or not it relates to their situation. This may be the last part of your case study that you write, but it’s the first thing your audience sees and may be the only part that they actually read, so it’s worth spending extra time crafting your headline.
What makes a good case study headline? Specificity.
The headline should sum up your case study’s core takeaway. This could be the specific outcomes your solution led to, the particular action your customer took with your solution, or the unique problem that was solved. Maybe it’s all three. Make sure you mention your customer — either by name or with a concise description of who or what they are.
A simple subject-verb statement starring your customer could suffice:
Elderly residents keep sidewalks clear amid record-breaking blizzard with SnowForce.
Award-winning interior designer saves nonprofit $500K on office redesign.
Channel your inner newscaster as you draft headlines. What’s the most direct, concise way to describe this case?
2. TLDR Section
Too long, didn’t read. You can see those four words as the bane of your existence — or as an opportunity to flex your writing muscles.
For case studies, a TLDR section enables people to grasp the main points without reading every word — and it may entice some to read further.
The concept is simple: In one to three sentences, summarize the main points of the case study. You’ll want to include the problem, the solution, and the outcomes (i.e., beginning, middle, and end).
Housebound adults may face fines if they don’t shovel their sidewalks within the city’s required timeframe, but these elderly adults found the timely help they needed through SnowForce, a snow removal program.
3. Customer Problem
Depending on the length of your case study and the complexity of your customer’s problem, this section could be anywhere from a paragraph to several pages long. It describes the problem your customer was dealing with when they sought out your solution.
Along with the what of the problem, you’ll also want to make clear:
- Why this problem was important and difficult to solve
- How it impacted the customer and/or their business functions
4. Previous Failed Solutions (If Applicable)
Before they came to you, did your customer try multiple solutions, all of which failed? Your case study should mention that.
Your business can decide whether or not to name the failed solutions, but showing that your solution worked where others failed will help your solution stand out. Be sure to get specific on what those other solutions lacked, whether quality customer service, software integrations, understanding of the customer’s industry, or something else relevant to your target audience.
You can write this as its own section or weave it into the “problem” section.
5. Customer Concerns and Limitations in Addressing Their Problem
Did your customer have a tight budget or privacy concerns or a brief time window to work within? These sorts of concerns and limitations are relevant to your target audience, who may have similar restrictions. You can put these details in their own section (if there’s a lot to cover) or make them part of the “problem” or “solution” sections.
6. Company Solution
How did your company solve the customer’s problem, while respecting their concerns and limitations? What steps did you take with the customer to solve their problem? How did this compare to the previous solutions they tried? Did you exceed their expectations? Finish well within their timeframe?
The solution section should answer these questions, leading with the most significant and compelling information.
Be as specific as possible about how you solved their problem — but keep the customer the main character. One trick for doing this? Instead of adopting a first person narrator that refers to your company as “we”, use third person perspective (like a newspaper reporter) and make your customer the acting subject of as many sentences as possible.
What were the outcomes of your company’s solution? Are there any statistics or measurable benefits you can detail here?
The results section is also a great place to include customer quotes describing their happiness with your solution, how effective your solution was, and what they can now do because their problem has been solved.
Just make sure to favor quotes with more concrete information. A few breathless “SnowForce is a godsend”-type quotes are fine, but quotes describing tangible outcomes carry more weight.
8. Conclusion
Sometimes, the results section is enough, but longer case studies are served well by a conclusion that:
- Sums up major takeaways
- Integrates a final customer quote
- Includes a relevant call to action (CTA), if applicable
If you’re writing a one-pager, though, skip the conclusion. The TLDR section covers this and the results section will end your case study in a strong spot. You can always add a quick CTA.
💫 Just like you can use Wordtune's Summarizer tool to pull out key points for the TLDR section, you can also use it to identify major takeaways to cover in the conclusion.

7 Tips for Writing Effective Case Studies
1. choose customer case studies based on your target audience..
Your content marketing department has limited resources — maybe you’re the only resource! So don’t waste your time writing a case study about every happy customer your company has helped. Instead, decide who to write about by focusing on your marketing and sales goals.
Is there a certain corner of the market, a certain “persona” or audience, that your marketing or sales teams are targeting?
If so, what is that audience’s key pain point? Has your company addressed that same issue for another customer already? Were they pleased with the results?
If so, that’s the customer you should write a case study about.
2. Treat your case study like a story.
The main character is your past customer. The audience is your prospective customer. The plot is your past customer’s journey from problem to solution. Your business and solution are mere supporting characters .
Use your storytelling skills to bring the case study to life and entice your target audience. Craft a killer headline and an attention-grabbing hook . Focus on the most compelling details. Show and tell. Answer the why as well as the who , what , when , where , and how .
Even if your case study is only five paragraphs long, your reader should reach the end and feel like they went on a journey.
3. Be as specific as possible.
A vague sentence helps no one. Your prospects have specific problems that need specific solutions. They’ve already waded through too many company websites that make bold, vague claims but never really explain what they do or how they do it. One reason case studies are useful is because they’re not vague — so prioritize specificity.
This means you’ll need to gather specific details in the research stage, ask specific questions when you’re interviewing your customer. Do the hard work up front and the writing process will be much smoother.
4. Focus on your customer’s (and prospective customer’s) perspectives.
The customer is the hero , not you, so make sure the case study keeps the spotlight on them. Your solution is just a way to help them achieve their ultimate goals. When you revise your case study, pay attention to who is doing most of the action—and make sure it’s your customer as much as possible.
5. Stick to the point.
This is typical writing advice, but: only take as much space as you need to tell the story. If it helps, write long and edit down ( Wordtune comes in handy for that editing process!). Don’t waste readers’ time.
6. Break your case study up into scannable sections.
These sections will generally correspond to the basic elements we described earlier, but instead of using generic “problem”, “solution”, and “results” headings, write descriptive headings that are specific to the case study. Match them to the style of your headline — or play around with themes and puns — but make sure they’re understandable at a glance.
💫 Wordtune can help you write headings by summarizing your sections refining them!
7. Make the takeaway crystal clear.
The takeaway is mentioned in the headline, TLDR, and conclusion — and it should be clear in each of those places. If you’re muddy on what the takeaway is, focus on the problem and solution sections. Work on summing up the takeaway in a simple, declarative sentence, and then riff on that sentence in those three places.
A case study is a great tool for showing your prospective customers that your solution works — and it’s right for them. Take the time to craft a vivid, well-structured case study and your sales teams will thank you. Your solution won’t be vague and hypothetical to customers anymore.
Share This Article:

How To Prepare For Studying Abroad (From Someone Who’s Done It)

Strategic Negotiation: How to Ask For A Raise Over Email

Metaphor vs. Simile: What’s the Difference? (+ Examples)
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 9:45 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

Research Writing and Analysis
- NVivo Group and Study Sessions
- SPSS This link opens in a new window
- Statistical Analysis Group sessions
- Using Qualtrics
- Dissertation and Data Analysis Group Sessions
- Defense Schedule - Commons Calendar This link opens in a new window
- Research Process Flow Chart
- Research Alignment Chapter 1 This link opens in a new window
- Step 1: Seek Out Evidence
- Step 2: Explain
- Step 3: The Big Picture
- Step 4: Own It
- Step 5: Illustrate
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review This link opens in a new window
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- How to Synthesize and Analyze
- Synthesis and Analysis Practice
- Synthesis and Analysis Group Sessions
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Quantitative Research Questions
- Qualitative Research Questions
- Trustworthiness of Qualitative Data
- Analysis and Coding Example- Qualitative Data
- Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Dissertation to Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- International Journal of Online Graduate Education (IJOGE) This link opens in a new window
- Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning (JRIT&L) This link opens in a new window
Writing a Case Study

What is a case study?

A Case study is:
- An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology.
- Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research.
- Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event.
- Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
What are the different types of case studies?

Note: These are the primary case studies. As you continue to research and learn
about case studies you will begin to find a robust list of different types.
Who are your case study participants?

What is triangulation ?
Validity and credibility are an essential part of the case study. Therefore, the researcher should include triangulation to ensure trustworthiness while accurately reflecting what the researcher seeks to investigate.

How to write a Case Study?
When developing a case study, there are different ways you could present the information, but remember to include the five parts for your case study.

Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Next: Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS) >>
- Last Updated: May 3, 2024 8:12 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchtools

All You Wanted to Know About How to Write a Case Study

What do you study in your college? If you are a psychology, sociology, or anthropology student, we bet you might be familiar with what a case study is. This research method is used to study a certain person, group, or situation. In this guide from our dissertation writing service , you will learn how to write a case study professionally, from researching to citing sources properly. Also, we will explore different types of case studies and show you examples — so that you won’t have any other questions left.
What Is a Case Study?
A case study is a subcategory of research design which investigates problems and offers solutions. Case studies can range from academic research studies to corporate promotional tools trying to sell an idea—their scope is quite vast.
What Is the Difference Between a Research Paper and a Case Study?
While research papers turn the reader’s attention to a certain problem, case studies go even further. Case study guidelines require students to pay attention to details, examining issues closely and in-depth using different research methods. For example, case studies may be used to examine court cases if you study Law, or a patient's health history if you study Medicine. Case studies are also used in Marketing, which are thorough, empirically supported analysis of a good or service's performance. Well-designed case studies can be valuable for prospective customers as they can identify and solve the potential customers pain point.
Case studies involve a lot of storytelling – they usually examine particular cases for a person or a group of people. This method of research is very helpful, as it is very practical and can give a lot of hands-on information. Most commonly, the length of the case study is about 500-900 words, which is much less than the length of an average research paper.
The structure of a case study is very similar to storytelling. It has a protagonist or main character, which in your case is actually a problem you are trying to solve. You can use the system of 3 Acts to make it a compelling story. It should have an introduction, rising action, a climax where transformation occurs, falling action, and a solution.
Here is a rough formula for you to use in your case study:
Problem (Act I): > Solution (Act II) > Result (Act III) > Conclusion.
Types of Case Studies
The purpose of a case study is to provide detailed reports on an event, an institution, a place, future customers, or pretty much anything. There are a few common types of case study, but the type depends on the topic. The following are the most common domains where case studies are needed:

- Historical case studies are great to learn from. Historical events have a multitude of source info offering different perspectives. There are always modern parallels where these perspectives can be applied, compared, and thoroughly analyzed.
- Problem-oriented case studies are usually used for solving problems. These are often assigned as theoretical situations where you need to immerse yourself in the situation to examine it. Imagine you’re working for a startup and you’ve just noticed a significant flaw in your product’s design. Before taking it to the senior manager, you want to do a comprehensive study on the issue and provide solutions. On a greater scale, problem-oriented case studies are a vital part of relevant socio-economic discussions.
- Cumulative case studies collect information and offer comparisons. In business, case studies are often used to tell people about the value of a product.
- Critical case studies explore the causes and effects of a certain case.
- Illustrative case studies describe certain events, investigating outcomes and lessons learned.
Need a compelling case study? EssayPro has got you covered. Our experts are ready to provide you with detailed, insightful case studies that capture the essence of real-world scenarios. Elevate your academic work with our professional assistance.

Case Study Format
The case study format is typically made up of eight parts:
- Executive Summary. Explain what you will examine in the case study. Write an overview of the field you’re researching. Make a thesis statement and sum up the results of your observation in a maximum of 2 sentences.
- Background. Provide background information and the most relevant facts. Isolate the issues.
- Case Evaluation. Isolate the sections of the study you want to focus on. In it, explain why something is working or is not working.
- Proposed Solutions. Offer realistic ways to solve what isn’t working or how to improve its current condition. Explain why these solutions work by offering testable evidence.
- Conclusion. Summarize the main points from the case evaluations and proposed solutions. 6. Recommendations. Talk about the strategy that you should choose. Explain why this choice is the most appropriate.
- Implementation. Explain how to put the specific strategies into action.
- References. Provide all the citations.
How to Write a Case Study
Let's discover how to write a case study.

Setting Up the Research
When writing a case study, remember that research should always come first. Reading many different sources and analyzing other points of view will help you come up with more creative solutions. You can also conduct an actual interview to thoroughly investigate the customer story that you'll need for your case study. Including all of the necessary research, writing a case study may take some time. The research process involves doing the following:
- Define your objective. Explain the reason why you’re presenting your subject. Figure out where you will feature your case study; whether it is written, on video, shown as an infographic, streamed as a podcast, etc.
- Determine who will be the right candidate for your case study. Get permission, quotes, and other features that will make your case study effective. Get in touch with your candidate to see if they approve of being part of your work. Study that candidate’s situation and note down what caused it.
- Identify which various consequences could result from the situation. Follow these guidelines on how to start a case study: surf the net to find some general information you might find useful.
- Make a list of credible sources and examine them. Seek out important facts and highlight problems. Always write down your ideas and make sure to brainstorm.
- Focus on several key issues – why they exist, and how they impact your research subject. Think of several unique solutions. Draw from class discussions, readings, and personal experience. When writing a case study, focus on the best solution and explore it in depth. After having all your research in place, writing a case study will be easy. You may first want to check the rubric and criteria of your assignment for the correct case study structure.
Read Also: ' WHAT IS A CREDIBLE SOURCES ?'
Although your instructor might be looking at slightly different criteria, every case study rubric essentially has the same standards. Your professor will want you to exhibit 8 different outcomes:
- Correctly identify the concepts, theories, and practices in the discipline.
- Identify the relevant theories and principles associated with the particular study.
- Evaluate legal and ethical principles and apply them to your decision-making.
- Recognize the global importance and contribution of your case.
- Construct a coherent summary and explanation of the study.
- Demonstrate analytical and critical-thinking skills.
- Explain the interrelationships between the environment and nature.
- Integrate theory and practice of the discipline within the analysis.
Need Case Study DONE FAST?
Pick a topic, tell us your requirements and get your paper on time.
Case Study Outline
Let's look at the structure of an outline based on the issue of the alcoholic addiction of 30 people.
Introduction
- Statement of the issue: Alcoholism is a disease rather than a weakness of character.
- Presentation of the problem: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there.
- Explanation of the terms: In the past, alcoholism was commonly referred to as alcohol dependence or alcohol addiction. Alcoholism is now the more severe stage of this addiction in the disorder spectrum.
- Hypotheses: Drinking in excess can lead to the use of other drugs.
- Importance of your story: How the information you present can help people with their addictions.
- Background of the story: Include an explanation of why you chose this topic.
- Presentation of analysis and data: Describe the criteria for choosing 30 candidates, the structure of the interview, and the outcomes.
- Strong argument 1: ex. X% of candidates dealing with anxiety and depression...
- Strong argument 2: ex. X amount of people started drinking by their mid-teens.
- Strong argument 3: ex. X% of respondents’ parents had issues with alcohol.
- Concluding statement: I have researched if alcoholism is a disease and found out that…
- Recommendations: Ways and actions for preventing alcohol use.
Writing a Case Study Draft
After you’ve done your case study research and written the outline, it’s time to focus on the draft. In a draft, you have to develop and write your case study by using: the data which you collected throughout the research, interviews, and the analysis processes that were undertaken. Follow these rules for the draft:

- Your draft should contain at least 4 sections: an introduction; a body where you should include background information, an explanation of why you decided to do this case study, and a presentation of your main findings; a conclusion where you present data; and references.
- In the introduction, you should set the pace very clearly. You can even raise a question or quote someone you interviewed in the research phase. It must provide adequate background information on the topic. The background may include analyses of previous studies on your topic. Include the aim of your case here as well. Think of it as a thesis statement. The aim must describe the purpose of your work—presenting the issues that you want to tackle. Include background information, such as photos or videos you used when doing the research.
- Describe your unique research process, whether it was through interviews, observations, academic journals, etc. The next point includes providing the results of your research. Tell the audience what you found out. Why is this important, and what could be learned from it? Discuss the real implications of the problem and its significance in the world.
- Include quotes and data (such as findings, percentages, and awards). This will add a personal touch and better credibility to the case you present. Explain what results you find during your interviews in regards to the problem and how it developed. Also, write about solutions which have already been proposed by other people who have already written about this case.
- At the end of your case study, you should offer possible solutions, but don’t worry about solving them yourself.
Use Data to Illustrate Key Points in Your Case Study
Even though your case study is a story, it should be based on evidence. Use as much data as possible to illustrate your point. Without the right data, your case study may appear weak and the readers may not be able to relate to your issue as much as they should. Let's see the examples from essay writing service :
With data: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there. Without data: A lot of people suffer from alcoholism in the United States.
Try to include as many credible sources as possible. You may have terms or sources that could be hard for other cultures to understand. If this is the case, you should include them in the appendix or Notes for the Instructor or Professor.
Finalizing the Draft: Checklist
After you finish drafting your case study, polish it up by answering these ‘ask yourself’ questions and think about how to end your case study:
- Check that you follow the correct case study format, also in regards to text formatting.
- Check that your work is consistent with its referencing and citation style.
- Micro-editing — check for grammar and spelling issues.
- Macro-editing — does ‘the big picture’ come across to the reader? Is there enough raw data, such as real-life examples or personal experiences? Have you made your data collection process completely transparent? Does your analysis provide a clear conclusion, allowing for further research and practice?
Problems to avoid:
- Overgeneralization – Do not go into further research that deviates from the main problem.
- Failure to Document Limitations – Just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study, you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis.
- Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications – Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings.
How to Create a Title Page and Cite a Case Study
Let's see how to create an awesome title page.
Your title page depends on the prescribed citation format. The title page should include:
- A title that attracts some attention and describes your study
- The title should have the words “case study” in it
- The title should range between 5-9 words in length
- Your name and contact information
- Your finished paper should be only 500 to 1,500 words in length.With this type of assignment, write effectively and avoid fluff
Here is a template for the APA and MLA format title page:
There are some cases when you need to cite someone else's study in your own one – therefore, you need to master how to cite a case study. A case study is like a research paper when it comes to citations. You can cite it like you cite a book, depending on what style you need.
Citation Example in MLA Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing, 2008. Print.
Citation Example in APA Hill, L., Khanna, T., & Stecker, E. A. (2008). HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing.
Citation Example in Chicago Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies.
Case Study Examples
To give you an idea of a professional case study example, we gathered and linked some below.
Eastman Kodak Case Study
Case Study Example: Audi Trains Mexican Autoworkers in Germany
To conclude, a case study is one of the best methods of getting an overview of what happened to a person, a group, or a situation in practice. It allows you to have an in-depth glance at the real-life problems that businesses, healthcare industry, criminal justice, etc. may face. This insight helps us look at such situations in a different light. This is because we see scenarios that we otherwise would not, without necessarily being there. If you need custom essays , try our research paper writing services .
Get Help Form Qualified Writers
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. If you’re having trouble with your case study, help with essay request - we'll help. EssayPro writers have read and written countless case studies and are experts in endless disciplines. Request essay writing, editing, or proofreading assistance from our custom case study writing service , and all of your worries will be gone.
Don't Know Where to Start?
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. Request ' write my case study ' assistance from our service.
What Is A Case Study?
How to cite a case study in apa, how to write a case study, related articles.
.webp)
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Examples of case study

Word of the Day
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
a unit for measuring the loudness of sound

Varied and diverse (Talking about differences, Part 1)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
{{message}}
There was a problem sending your report.
- How It Works
- Prices & Discounts
Bringing Stories to Your Essay: Introducing a Case Study the Right Way!
Table of contents
Ever found yourself immersed in a story, hanging onto every detail, eager to know what happens next? That, my friend, is the magic of a case study when sprinkled into an essay.
Just as a dash of spice can elevate a dish, a well-placed case study can take your essay from 'meh' to 'marvelous'. It's not just about showcasing real-world examples; it's about making your arguments relatable, tangible, and above all, memorable.
But hold on, before you dive headfirst into weaving in that intriguing case study you found, let’s chat about the art of introducing it. You see, dropping it in without context is like telling a joke without a punchline.
In this post, we'll guide you through the craft of smoothly and effectively introducing a case study into your essay, ensuring it's not just a detour but a meaningful journey for your readers. So, are you ready to give your essay that extra oomph?
Why Use Case Studies in Essays
You know those moments when you're explaining a theory or a concept, and you see those blank stares? Yup, we’ve all been there. That’s where real-world examples come into play. By weaving a case study into your essay, you're essentially turning on a light in a dim room. Suddenly, that complex theory has color, depth, and context. It's no longer just words on paper; it's a story, a lesson, a real-world incident that breathes life into your arguments.
And let's talk about the brownie points. When you toss a well-researched case study into the mix, it's like handing your readers proof that you've rolled up your sleeves and delved deep into your subject. It's a signal: you're not just skimming the surface; you're diving into the depths, bringing out treasures of knowledge.
Lastly, an apt case study is like the secret sauce to winning trust. Readers lean in, believing in your words, connecting with your narrative. It’s not just about flashing your research chops; it’s about creating a bond, engaging them, making them think, "Hey, this writer really knows their stuff!"
In a nutshell? Case studies? They're your essay's best friend.
Choosing the Right Case Study
Before you jump onto the Internet's vast ocean and fish out the first case study that sorta-kinda fits, let’s have a quick heart-to-heart. Not all case studies are created equal. And while it might be tempting to pick that dramatic, headline-grabbing one, it's essential to remember a few golden rules.
Firstly, it's all about alignment. Think of your essay as a puzzle. Every piece, every argument, every citation should fit just right. Your chosen case study? It's that central piece, setting the tone, connecting dots. So, make sure it's directly related to your topic. No square pegs in round holes, okay?
Next, reputation is everything. Dive into journals, accredited institutions, and renowned publications. Trustworthy sources not only boost your essay's credibility but save you from those cringe-worthy moments when someone points out a glaring error or bias in your chosen study.
Quick tip from the pros : Some case studies are like that popular song on the radio - overplayed and heard by everyone. Unless you’re bringing a fresh, unheard angle or a unique perspective to the table, steer clear of the overly popular ones. It's always more impressive to introduce your readers to a gem they haven't encountered before.
Introducing a Case Study: The Art of the Hook
Picture this : You're at a party, and someone starts a story with, "You won't believe what happened to me yesterday!" Chances are, you're all ears. That's the power of a good essay hook . Now, let's bring that energy to your essay!
Starting with a compelling fact or statement is your ticket to gripping your readers. Imagine leading with, "In a village where electricity was once a dream, solar panels changed everything." Instantly, your readers are curious. They want to know more about this village, the change, the story behind it all.
Once you've got their attention, lay down the problem. Paint a picture of the challenges, the obstacles, the scenario before the solution came into play. This sets the stage for your case study. By presenting the problem, you're essentially saying, "Hey, here's a situation. Stick around to see how it unraveled."
Quick Checklist: Crafting That Perfect Hook
- Relevance : Ensure it ties back to your main essay topic.
- Emotion : Strike a chord, whether it's curiosity, empathy, or even surprise.
- Simplicity : Keep it straightforward. No need for jargon or over-the-top language.
- Authenticity : Stay true to the essence of your case study. No embellishing facts!
Remember, the aim is to draw readers in, making them eager to delve into the heart of your case study. With a killer hook, you're not just starting an essay; you're beginning a journey they'll want to join.
MLA Citation: Giving Credit Where It's Due
Alright, let's chat about something we often overlook in our writing excitement: citation. I get it; it may not be the most thrilling part of essay writing, but think of it as the unsung hero, quietly ensuring your work stands tall with authenticity and respect.
First off, why the fuss about proper citation ? Well, citing your sources isn't just about avoiding the scary plagiarism monster. It's about acknowledging the hard work of others. It's a nod to fellow researchers, saying, "Hey, I see your efforts, and they've helped shape mine."
How to cite a case study in MLA format
Author's Last Name, First Name . "Title of the Case Study." Title of the Journal or Publication , vol. number, no. issue number, Year of Publication, page range.
For example: Smith, John. "Solar Power in Remote Villages." Energy Research Journal , vol. 5, no. 2, 2020, pp. 45-59.
If found online: Add the website name, the URL, and the access date at the end.
Smith, John. "Solar Power in Remote Villages." Energy Research Journal , vol. 5, no. 2, 2020, pp. 45-59. ERJ Online, www.erjonline123.com , Accessed 5 June 2022.
Avoid these mistakes
- Forgetting the access date: Especially for online sources, this one's crucial!
- Overlooking the punctuation: Note the periods, commas, and italics. They're all essential in MLA.
Quick Tip : If this feels a tad overwhelming, online citation tools are here to rescue! Platforms like EasyBib or Citation Machine can churn out MLA citations in a snap. Just feed in your source details, and voila!
In the end, think of citations as your essay's backstage crew, working behind the scenes to ensure your masterpiece gets a standing ovation.
Weaving the Case Study into Your Essay Narrative
Alright, so you've got this shiny case study and you’re all set to embed it into your essay. But here's the catch – it's not about just dropping it in; it's about stitching it seamlessly into your narrative fabric.
Make It Relevant : Think of your essay and case study as dance partners. They need to move in harmony. Ensure that your case study doesn't just stand alone; it should back up your arguments, add depth to them, or even offer a contrasting perspective. It’s about making the dance memorable.
Build a Logical Flow : Your readers are on a journey with you. Introduce your case study at a point where it feels natural, leading them from one idea to the next. It’s like following breadcrumbs; one leading to another, ensuring they never get lost in the woods.
Pacing is Key : Imagine watching a movie where the climax is revealed in the first ten minutes. Boring, right? Similarly, don’t spill all the beans about your case study right away. Tease a little, build intrigue, let it unfold gradually, keeping your readers hooked.
In essence, introducing a case study is an art. It’s not about making it fit, but about ensuring it belongs, enriching your essay's narrative and making it truly unforgettable.
Concluding Your Case Study Introduction
As you wrap up the intro to your case study, think of it as putting a bow on a gift. First, make a promise to your readers: assure them that venturing deeper into this case study will shed light, offer insights, or challenge perspectives. Maybe it's a promise of a lesson learned or an innovative solution unveiled. Then, seamlessly pave the way for what's next: your main arguments. Like a skilled guide, hint at the journey ahead, ensuring your readers are not only invested but also eager to embark on the exploration with you.
Final Thoughts & Wrap-up
Introducing a case study in an essay is much like mastering a dance step; at first, it might feel a tad awkward, maybe even a little forced. But with practice? Ah, that’s when the magic happens. Just as dancers become one with the music, with time, you'll find that blending case studies into your essays becomes second nature. The beauty lies in the richness they add, turning plain text into tapestries of real-life stories, insights, and revelations.
But what if you're pressed for time or feeling a tad overwhelmed? Here's a lifesaver: Writers Per Hour offers impeccable custom case study writing services tailored to your needs. They're the backstage crew ensuring your essay shines under the spotlight.
Now, with or without help, here's a challenge for you, dear readers: In your next essay, venture out, find that perfect case study, and weave it in. Experience the transformation it brings. And when you do, remember that every story you tell, every example you cite, adds depth and dimension to your narrative. Ready to give it a whirl?
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Crafted from Scratch for You.
Ensuring Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay
- Top1000 word
- Top5000 word
- Conjunction
- Sentence into pic
Case study in a sentence

- 某某 2016-01-13 联网相关的政策
- desperate (248+29)
- controversial (195+11)
- menu (203+21)
- ratio (290+3)
- membership (166+20)
- bombing (220+22)
- barrel (262+12)
- nerve (248+13)
- etc (182+15)
- cow (165+8)
- sophisticated (242+12)
- myth (152+12)
- proposed (288+42)
- strengthen (279+3)
- publisher (214+11)
- tent (187+25)
- organic (276+13)
- trick (166+13)
- conviction (218+12)
- maintenance (218+13)
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of use case
Examples of use case in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'use case.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
1994, in the meaning defined above
Articles Related to use case

We Added 370 New Words to the...
We Added 370 New Words to the Dictionary for September 2022
Dictionary entries near use case.
use and wont
Cite this Entry
“Use case.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/use%20case. Accessed 11 May. 2024.
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, the words of the week - may 10, a great big list of bread words, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 8 uncommon words related to love, 9 superb owl words, games & quizzes.


COMMENTS
Example sentence: "After the unexpected market crash, the company's finances were a complete basket case, requiring a thorough case study to identify the root causes of their downfall.". 4. "Make A Case For". Meaning: This phrase is used to present arguments or evidence in support of a particular viewpoint or action.
case study. The company's recent history is a case study in bad management. The goal should be to ensure the reader sees themselves in the case study. Hawaii will be a case study for the rest of the nation, said Mikulina. What the San Joaquin Valley does next could be a case study for the rest of the nation.
Examples of CASE STUDY in a sentence, how to use it. 83 examples: In each case study area a large number of in-depth consultations were held with…
To use Case Study in a sentence, follow these steps: Begin by introducing the Case Study topic or subject. For example, "The Case Study examined the impact of social media on teenagers' mental health.". Provide a brief overview of the Case Study. For instance, "The Case Study focused on a group of high school students and their usage of ...
Case-study Sentence Examples. case-study. Meanings. Synonyms. Sentences. The case study was the TV adaptation of Vanity Fair. 5. 1. Examples include ethnography, case-study analysis, discourse analysis.
A use case explains how users interact with a product or system. It outlines the flow of user inputs, establishing successful and failed paths to meeting goals. This allows product teams to better understand what a system does, how it performs, and why errors occur. You can write one out or diagram a use case model for visual thinkers.
We would use example claims as case studies and practise writing refusal letters. The Guardian. ( 2017) So having individual case studies in relation to that were examples of those failures. The Guardian. ( 2018) These case studies represent the very beginning of that work. The Guardian.
A use case is a description of how a user interacts with a system or product. Companies build use cases to establish success scenarios, failure scenarios, and any important variants or exceptions. Many organizations leverage use case modeling tools — such as Miro, LucidChart, and SmartDraw, for some examples — to write or visually represent ...
Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data. Example: Mixed methods case study. For a case study of a wind farm development in a ...
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
A case study is an in-depth analysis of a person or group. A case study allows researchers to investigate a topic in far greater detail than other research methods. The success of private education in Pakistan is used as a case study. It may become a compulsory case study for future students of crisis management.
The meaning of CASE STUDY is an intensive analysis of an individual unit (such as a person or community) stressing developmental factors in relation to environment. How to use case study in a sentence.
Case studies are particularly helpful in showcasing how a word functions in a specific situation, providing a deeper insight into its application. In the following sections, we will delve into various example sentences with the word "case study," demonstrating how this approach can facilitate a better understanding of its usage.
Focus on the most compelling details. Show and tell. Answer the why as well as the who, what, when, where, and how . Even if your case study is only five paragraphs long, your reader should reach the end and feel like they went on a journey. 3. Be as specific as possible. A vague sentence helps no one.
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case ...
A Case study is: An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology. Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research. Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event. Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
Two Main Types of Use Case Studies. Use cases are helpful communication and development tools in many aspects of a business. You'll see them mainly in IT, engineering, software development and systems analysis. ... Summary: The summary is a one or two-sentence explanation about the use case and what project it belongs to. It also includes any ...
Explain what you will examine in the case study. Write an overview of the field you're researching. Make a thesis statement and sum up the results of your observation in a maximum of 2 sentences. Background. Provide background information and the most relevant facts. Isolate the issues.
Examples of case study in a sentence, how to use it. 83 examples: In each case study area a large number of in-depth consultations were held with…
Introducing a Case Study: The Art of the Hook. Picture this: You're at a party, and someone starts a story with, "You won't believe what happened to me yesterday!" Chances are, you're all ears. That's the power of a good essay hook. Now, let's bring that energy to your essay!
218 sentence examples: 1. This is an interesting psychiatric case study of a child with extreme behavioural difficulties. 2. The findings from the case study school may apply to schools elsewhere. 3. More immediately, the case study will represent co
The meaning of USE CASE is a use to which something (such as a proposed product or service) can be put : application. How to use use case in a sentence.
Sentence case is a capitalization style or set of rules describing when to use lowercase and uppercase letters in headings and subheadings. Whether you are writing a research paper, a blog, or a newspaper article, you may have to decide which words need to be capitalized. In English, the standard is to capitalize the first letter of a sentence.
Join us at 6 PM (WAT) this Thursday May 9, 2024, as our distinguish guest will be discussing the topic: GEN-Z ACCOUNTANTS: Redefining Traditional...