CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free

Controlling Class 12 Business Studies Notes and Questions
Please refer to Controlling Class 12 Business Studies notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Business Studies books for Class 12 . You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 12 Business Studies Controlling Notes and Questions
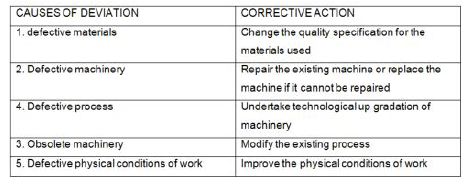
Q. 1. Babita Ltd. is engaged in manufacturing machine components. The target production is 250 units per day per worker. The company had been successfully attaining this target until two months ago. Over the last two months it has been observed that daily production varies between 200-210 units per worker. 1. Name the function of management and identify the step in the process of this function which helped in finding out that the actual production of a worker is less than the set target. 2. To complete the process of the function identified in (a) and to ensure the performance as per set targets, explain what further steps a manager has to take. Ans. 1. The management function is Controlling. “Comparing actual performance with standards” is the step involved in the process of controlling which helped in finding out that the actual production of a worker is less than the set target. 1. A manager has to take the following two further steps to complete the process of controlling: 1. Analysing deviations 2. Taking corrective action Q. 2. Rajeev and Sanjeev are managers in the same organization having different units. While discussing about the function of management, Rajeev says “Planning is looking ahead whereas controlling is looking back.” But Sanjeev says, “Planning is looking back whereas controlling is looked ahead.” Both are giving reasons in favour of their statements. Explain the possible reasons given by both and justify who is correct. Ans. Rajeev who says, “Planning is looking ahead whereas controlling is looking back” must be giving the following reason: Sanjeev who says, “Planning is looking back where as controlling is looking ahead” must be giving the following reasons. Conclusion: Planning and controlling are both backward looking and forward looking functions. Hence, both of them are partially correct. Q. 3. ‘Saurashtra’ is a company involved in the export of indigenous food products like chutneys and pickles.. it has tied up with the small farmers in various states for sourcing of fruits and vegetables. In this way it helps the small farmers to sell their produce at reasonable rates. The company follows a practice where only significant deviations from a budget or plan are brought to the attention of management. The degree of deviations allowed in different categories in the budget are well defined in advance, along with the appropriate levels of managements who will respond to the deviations in question. For example, a deviation of Rs. 20,000 or more in purchase costs will be reported to the concerned department manager. In context of the above case: 1. Identify the principle of management control adopted by the company. State the belief underlying this principle. 2. List any two values that the company wants to communicate to the society. Ans. 1. Management by exception is the principle of management control adopted by the company. It is based on the belief that ‘if you try to control everything, you may end up controlling nothing.’ 2. The two values that the company wants to communicate to the society are: 1. Rural development: 2. Sense of responsibility: Q. 4. Anubhav has set up an export house after completing his masters in fashion designing. As the quality of the garment depends on the quality of raw materials used, he assures that the fabric meets the requirements by conducting a series of tests for the fabrics like shrinkage test, testing colour fastness to washing, colour fastness to light, colour fastness to perspiration etc. through laboratory tests. Later on, at the production areas, fabric inspection is also conducted by stopping the production process. The tests help to detect the deviations and also take corrective action. Moreover, the ensures that complete training about production work was given to every worker at the time of joining his export house. In context of the above case: 1. Identify the function of management being performed by Anubhav by conducting tests to assure for the quality of the garments manufactured in his export house. 2. Briefly explain the term ‘deviations.’ 3. Give any three advantages of giving training to the employees. Ans. 1. Controlling is the function of management being performed by Anubhav by conducting tests to assure for the quality of the garments manufactured in his export house. 2. The term ‘deviations’ refers to the difference between the actual performance and planning performance. If the actual performance is more than the planned performance, it may be said to be positive in nature or vice-versa. 3. The benefits of training of development to an organization are as follows: 1. Training imparts systematic learning to the employees thereby helping to avoid wastage of efforts and money and is considered better than the hit and trial method. 2. It increases the employees’ productivity both in terms of quantity and quality, leading to higher profits. 3. Training increases the morale of the employees and reduces absenteeism and employee turnover. Q. 5. Atul and Ajay are good friends. They decide to set up a digital printing press together as both of them are compute wizards. They plan to offer various types of printed products including labels, manuals, marketing material, memo pads, business order forms, T-shirts, mugs etc. They set standards for every aspect of their work in order to create an efficient working environment. As per the standards, an average person types between 38 and 40 words per minute. Keeping this in mind, they engage two typists Bitto and Raju and assign them work accordingly. Within two days, they realize the output in terms of typing work done by Raju is too less as compared to the desired output. On inspecting, Atul finds out that Raju’s typing speed is between 18 and 20 words per minute only. But Raju exhibits great skills in designing work and is a good human being. Hence, Atul and Ajay decide to retain him for doing creative work and appoint a new typist. In context of the above case: 1. Identify and explain the function of management being discussed here. 2. List the steps involved in the function of management as identified in part (a). Also, quote the liens from the paragraph relating to each step. Ans. 1. Controlling is the function of management being discussed here. 2. The steps involved in the process of controlling which are discussed in the above paragraph are: 1. Setting standards of performance: 2. Measurement of actual performance: 3. Comparison of actual performance with the standards: 4. Analyzing deviations: 5. Taking corrective action: Q. 6. D & D Ltd. is a large manufacturing unit. Recently, the company has conducted the ‘time’ and ‘motion’ studies and concluded that on an average a worker could produce 120 units per day. However, it has been noticed that average daily production of a worker is in the range of 80-90 units. Which function of management is needed to ensure that the actual performance is in accordance with the performance as per ‘time’ and ‘motion ‘studies? State four features of this function of management. Ans. Controlling Features of controlling: 1. Controlling is a goal-oriented function 2. Controlling is a pervasive function 3. Controlling is a continuous process 4. Controlling is both a backward looking as well as forward looking function. Q. 7. ‘A.S. Ltd.’ is a large company engaged in assembly of air-conditioners. Recently the company had conducted the ‘Time’ and ‘Motion’ study and concluded that on an average a worker can assemble ten air-conditioners in a day. The target volume of the company in a day is assembling of 1,000 units of air-conditioners. The company is providing attractive allowances to reduce labour turnover and absenteeism. All the workers are happy. Even then the assembly of air-conditioners per day is i800 units only. To find out the reason the company compared actual performance of each worker and observed through C.C.T.V. that some of the workers were busy is gossiping. 1. Identify the function of management discussed above. 2. State those steps in the process of the function identified which are discussed in the above praragraph. Ans. 1. Controlling 2. Steps discussed in the above paragraph are: 1. Setting performance standards 2. Measurement of actual performance 3. Comparing actual performance with the standards 4. Analyzing deviations for their causes. Q. 8. A company ‘M’ Ltd. is manufacturing mobile phones both for domestic Indian market as well as for export. It has enjoyed a substantial market share and also had a loyal customer following. But latterly it has been experiencing problems because its targets have not been met with regard to sales and customer satisfaction. Also mobile market in India has grown tremendously and new player have come with better technology and pricing. This is causing problems for the company. It is planning to revamp its controlling system and take other steps necessary to rectify the problems it is facing. 1. Identify the benefits the company will derive from a good control system. 2. How can the company relate its planning with control in this line of business to ensure that its plan are actually implemented and targets attained? 3. Give the steps in the control process that the company should follow to remove the problems it is facing. Ans. 1. Explain the importance of controlling. 2. Company can relate its planning with control in this line of business by following measure by implementing an effective controlling system and following a controlling process. 3. Explain steps in the process of controlling system. Q. 9. Alpha Ltd. was manufacturing Auto spare parts. To improve the efficiency of employees the company provided training to their employees by inviting an expert who demonstrated the whole process of manufacturing. The expert quoted that all deviations cannot be controlled, so manager must know which deviation in key areas must be attended urgently as compared to deviation in non-key area. He also suggested that human beings are bound to brake mistakes as manager should not take strict action on every minute mistake of workers, rather he can fix a range of deviation and take action if deviation is above the specified large. 1. Identify the functions of management referred above. 2. Name the two ways of analyzing deviation mentioned above. 3. Name the method of training used by the company. 4. Identify the value being emphasized in above para. Ans. 1. Staffing and controlling 2. (i) critical Point Control (ii) Management by exception 1. Apprenticeship method of training 2. Value of Humanity. Q. 10. A critical point control (CPC) approach is followed by McDonald in the cooking and handling process so that any food safety threat can be prevented, eliminated, or reduced to an acceptable level. Hence, continuous monitoring of activities are undertaken to ensure that the process is right at each critical point control. The main principle followed for cooking at McDonald is “less amount many time” which can ensure the high quality and high fresh level of the food. For instance, if your hamburgers have to be made, a worker cannot cook all the four hamburgers at one time. The time figured out for making one hamburger is one hundred and forty-five seconds. Moreover, nearly all foods in the McDonald have the specific holding time, the holding time for hamburgers is ten minutes and for French fries is seven minutes. If it is not sold within that time it is thrown away. Also, the temperature of the milk sent by t he supplier must b e under 4 0 c, otherwise, it will be returned. In context of the above case: 1. Name the steps involved in the controlling process which is being discussed in the above lines. 2. What do you understand by ‘critical point control’? Explain. 3. How does the controlling function of management help in accomplishing organizational goals and ensure efficient use of resources? Ans. 1. Analyzing deviation and taking corrective action are being discussed in the above lines. 2. Since it may neither be economical nor easy to monitor each and every activity in the organization, there for every organization identifies and states its specific key result area (KRAs) or critical points which require tight control are likely to have a significant effect on the working of the business. Any deviations on these points are attended to urgently by the management. 3. The two points that highlight the importance of the controlling function are listed below: 1. Accomplishing organizational goals: 2. Making efficiently use of resources: Q. 11. Raghav started a take away eating joint in a nearby market. His business was doing well. He ensured that the food was properly cooked, a standard taste was maintained, packing of food was done effectively and the orders were executed on time. But unfortunately he met with an accident and was advised three months bed rest. In his absence, his cousin Rohit took charge of his business. When he resumed his work after three months, he realized that his clientele had dropped. The people were not happy with the services as the quality of food had deteriorated and the delivery time for orders had increased considerably. All this was happening because most of his previous staff had left as Rohit used to adopt a very strict and authoritative approach towards them. In context of the above case: 1. List any two aspects about his business that Raghav was controlling in order to make it successful. 2. Explain briefly any two points to highlight the importance of the controlling function. 3. Name and explain the style of leadership adopted by Rohit. Ans. 1. The two aspects about his business that Raghav was controlling in order to make it successful are listed below: 1. A standard taste was maintained. 2. The orders were executed on time. 1. The two points that highlight the importance of the controlling function are listed below: 1. Judging accuracy of standards: 2. Improving employee motivation: 1. Rohit had adopted an autocratic style of leadership. An autocratic leader expects strict compliance form his subordinates with regard to the orders and instructions given by him. Therefore, it involves only one-way communication. Q. 12. Mr. Nath, a recently appointed production manager of Suntech Ltd. has decided to produce jute bags instead of plastic bags as these are banned by the government. He set a target of producing 1000 jute bags a day. It was reported that the employees were not able to achieve the target. Mr. Nath’s behavior is good towards the employees. His attitude is always positive. So he announced various incentive schemes for the employees like. – installing award or certificate for best performance. – Rewarding an employee for giving valuable suggestions. – Congratulating the employees for good performance. (a) Identify the functions of management highlighted in the above paragraph. (b) State the ‘incentive’ under which the employees are motivated. (c) State any two values which the production manager wants to communicate to the society by his work and behavior. Ans. 1. Controlling and Directing 2. Employee recognition programme (non-monetary incentive) 3. Values: ● Sensitivity to environment ● Good behavior towards employees ● Team work with employees Q. 13. Joseph Bros. was a firm manufacturing jute lamp shades. It uses left over jute pieces from various jute factories to manufacture economical lamp shades which are supplied to various hotels in nearby towns: it employs men and women from nearby villages as workers for creating good lamp shade designs. Joseph Bros., is not able to meet its targets. Namish, the supervisor of the company, was told to analyze the reasons for the poor performance. Namish found following problems and suggested certain solution s in the working of the business. M the number of workers employed was les than what was required for the work. As a result, the existing workers were overburdened. The firm decided to search for new workers and it asked the present employees to introduce candidates or recommend their friends and relatives to the firm. This enabled the firm in “putting people to jobs” and assured attainment of objectives according to plans. 1. Identify the functions of management being performed by the firm in the above situation. 2. Name the concept and its source used by the firm to attract more workers for the firm. 3. State any two values being followed by Jacob Bros. Ans. 1. Staffing and Controlling 2. Recruitment, External Source of Recruitment (Recommendations of employees) 3. Values being followed by Joseph Bros.: 1. Creating employment opportunities. 2. Utilizing resources efficiently by using leftover clothes. Q. 14. A company was manufacturing ‘LED bulbs’ which were in great demand. It was found that the target of producing 300 bulbs a day was not met by the employees. On analysis, it was found that the workers were not at fault. Due to electricity failure and shortage of workers, the company was not able to achieve the set targets and alternative arrangements were needed. To meet the increased demand, the company assessed that approximately 88 additional workers were required out of which 8 would work as heads of different departments and 10 would work as subordinates under each head. The required qualifications and job specifications were also enlisted. It was also decided that necessary relaxation should be given to encourage women, persons from backward and rural areas and persons with special abilities to assume responsible positions in the organization. All efforts were made to match the ability of the applicants with the nature of work. 1. Identify the functions of management discussed above. 2. State the two steps in the process of each function discussed in the above para. 3. List any two values which the company wants to communicate to the society Ans. 1. Staffing and controlling 2. Step in Staffing 1. Estimating manpower requirements: 2. Recruitment: 1. Steps in controlling: 1. Comparison of actual performance with the standards: 2. Analyzing deviations: 3. Taking corrective action: 1. Values which the company wants to communicate to the society: 1. Using environment friendly methods of production. 2. Women empowerment. 3. Upliftment of underprivileged sections of the society. Q. 15. Airtech Ltd. is manufacturing mobile phones both for domestic Indian market as well as for export. It has enjoyed a substantial market share and also had a loyal customer following. But lately it has been experiencing problems because its targets have not been met with regard to sales and customer satisfaction. Also, mobile market in India has grown tremendously and new players have come with better technology and pricing. This is causing problems for the company. It is planning to revamp its controlling system and take other steps necessary to rectify the problems ikt is facing. It also decides to offer its basis models of mobile phones at 50% discount to the poor people. 1. State any two benefits the company with derive from a good control system. 2. How can the company relate its planning with control in this line of business to ensure that its plan are actually implemented and targets attained. 3. Give the steps that the company should follow to remove the problems it is facing. 4. Identify any one value which the company wants to communicate to the society. Ans. 1. Two benefits which the company will derive from a good control system are: 1. Accomplishing organizational goals of increasing market share and customer satisfaction. 2. Making efficient use of resources by controlling wastage and spoilage of resources; and ensuring that each activity is performed according to the predetermined standards. 1. Controlling will improve future planning by providing information to the company derived from past experience that its targets were not met with regard to sales and customer satisfaction. 2. The company should undertake technological up gradation of machinery, and modify the existing process so that cost is reduced and the company can set lower price for its mobile phones to bet its competitors. 3. Value: ● Concern about poor people ● Social responsibility Q. 16. You are the manager of Bharti Chemicals Ltd. it is reported to you that postal expenses have increased by 10% over standard rates and cost of raw materials has increased by 2%. Which of the two deviations will be more critical to you? Ans. Increase in cost of raw materials by 2% is more critical. (Critical Point Control) Q. 17. Surbhi Ltd. produces safety pins on a mass scale. The company’s policy is that at most 25 of the daily production could be defective. Over a three months period, it has been observed that 8% – 10% of the production is defective. The cause of deviation found is defective machinery. What corrective action should be taken by the management? Ans. Repair the existing machine or replace the machine if it cannot be repaired. Q. 18. K & K Co. Ltd. is engaged in manufacturing machine components. The target production is 200 units daily. The company had been successfully attaining this target until two months ago. Over the last few months it has been observed that daily production varies between 150-170 units. Identify the possible causes for the decline in production and the steps to be taken to achieve the desired targets.
Important Notes for NCERT Class 12 Business Studies Chapter Controlling
Meaning & Definition Controlling means ensuring that activities in an organisation are performed as per the plans. Controlling also ensures that an organisation resources are being used effectively and efficiently for the achievement of predetermined goals. It can be defined as comparison of actual performance with the planned performance Importance of Controlling: – 1. Controlling helps in achieving organisational goals: – The controlling function measures progress towards the organisational goals and brings to light/indicates corrective action. 2. Judging accuracy of standards: A good control system enables management to verify whether the standards set are accurate or not. 3. Making efficient use to resources – By the process of control, a manager seeks to reduce wastage of resources. 4. Improves employee’s motivations: A good control system ensures that employees know well in advance what they are expected to do & also the standard of performance. It thus motivates & help them to give better performance. 5. Facilitating Coordination in action: In controlling each department and employee is governed by predetermined standards which are well coordinated with one another. Limitations of Controlling 1. Little Control on external factors: Generally, no enterprise can control external factors such as government policies, technological changes, competitions etc. 2. Resistance from employee – Control is often resisted by employees. They see it as a restriction on their freedom. 3. Costly affair: Control is a costly affair as it involves a lot of expenditure time and efforts. 4. Difficulty in setting quantitative standards: – Control system loses some of its effectiveness, when standards cannot be defined in quantitative terms. In the absence of quantitative standards, comparison with standards becomes difficult. Controlling Process: 1. Setting performance Standards: – Standards are the criteria against which actual performance would be measured. Thus, standards serve as benchmarks. 2. Measurement of Actual performance: Performance should be measured in an objective and reliable manner. Which include personal observation, sample checking. 3. Comparing Actual performance with standard: This step involves comparison of actual performance with the standard. Such comparison will reveal the deviation between actual and desired performance. 4. Analysing Deviations – The deviations from the standards are assessed and analysed to identify the causes of deviations. 5. Taking Corrective Action: – The final step in the controlling process is taking corrective action. No corrective action is required when the deviations are within the acceptable limits.

We hope the above Controlling Class 12 Business Studies are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies
Related Posts

CBSE Class 12 English Lost Spring Summary and Questions

Operators and Expressions Class 11 Computer Science Notes and Questions

The Little Match Girl Summary by Hans Christian Andersen
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Chapter 8 - Controlling
- NCERT Solutions

Class 12 NCERT Solutions Business Studies - Controlling - Free PDF Download
Business Studies are studied worldwide. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies provides students with a plethora of topics offered in a simplified manner. Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 NCERT Solutions is a great platform that provides key terminology, visual representations, and critical analysis. NCERT Solutions Business Studies Chapter 8 is the omnibus a student requires to ace their exams. Students can depend on NCERT Solutions for Class 12th Business Studies for concise summaries. The study material is guaranteed to transform your revision plans for exams.
Related Chapters
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 - Free PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions:
1. An efficient control system helps in
(a) Accomplishes organisational objectives
(b) Boosts employee morale
(c) Judges accuracy of standards
(d) All of the above
Ans: All of the aforementioned objectives can be met with the help of an effective controlling system. Controlling is the process of assessing the progress of current tasks and activities and establishing work standards to achieve the organization's goals. An effective control system assists in keeping a close eye on the progress of the work and taking the necessary corrective actions. It aids in tracking changes in the organization and business environment and, as a result, aids in scrutinizing the accuracy of the standards. Controlling also boosts employee morale by informing them ahead of time of what is expected of them and motivating them to work in accordance with the policies in place.
2. Controlling function of an organisation is
(a) Forward looking
(b) Backward looking
(c) Forward as well as backward looking
(d) None of the above
Ans: Controlling, as an essential component of management, is both forward and backward looking. It is a backward-looking function in the sense that it evaluates completed work and analyzes deviations from established standards. Based on these deviations, it attempts to implement the necessary corrective actions. As a result, it directs future actions and aims to improve future performance. It is also a forward-thinking function in this sense. As a result, we can say that controlling is both a forward and a backward looking function.
3. Management audit is a technique to keep a check on the performance of
(a) Company
(b) Management of the company
(c) Shareholders
(d) Customers
Ans: A management audit is a systematic evaluation of a company's management's overall actions. Its goal is to assess the management's efficiency and effectiveness, as well as to identify areas where it falls short. It reveals performance flaws and aids in the implementation of corrective measures. As a result, a management audit monitors the overall performance of the company's management.
4. Budgetary control requires the preparation of
(a) Training schedule
(b) Budgets
(c) Network diagram
(d) Responsibility centres
Ans: Budgetary control is a managerial control technique that entails creating budgets for each operation of the organization and then comparing the actual results to the budgetary standards. A budget is a quantitative statement that defines the goals to be achieved in a given time period as well as the policies to be followed.
5. Which of the following is not applicable to responsibility accounting?
(a) Investment centre
(b) Accounting centre
(c) Profit centre
(d) Cost centre
Ans: Accounting center is not a component of accountability accounting. Responsibility accounting is a system in which different divisions of an organization are designated as responsibility centers. Each department is given a target to meet, and the department head (manager) is held accountable for meeting it. There are various types of responsibility centers, including cost centers, investment centers, profit centers, and revenue centers.
Short questions:
1. Explain the meaning of controlling.
Ans: Controlling is the function of evaluating and assessing the progress of work. It entails establishing specific criteria or standards for the work and then comparing the actual work to the established standards. It aids in identifying deviations from the set targets and, as a result, in taking the necessary corrective actions. It also ensures that everything goes as per the plan. It also ensures that resources are used fully and efficiently. Controlling is an essential managerial function because it keeps a close eye on the progress of work and thus serves as the foundation for future actions and planning.
2. 'Planning is looking ahead and controlling is looking back'. Comment.
Ans: Planning is forward-thinking, while controlling is backward-thinking. This statement is only partially correct. Planning is a psychological process that involves "thinking and deciding ahead of time" about "what is to be done" and "how it is to be done." It is a mental activity that entails deciding on goals as well as the actions that will be taken to achieve them. Thus, planning is said to be looking ahead because it involves predicting the future. Controlling, on the other hand, entails assessing past performance and comparing it to predetermined standards. Controlling is a backward-looking function in this sense. Both of these statements, however, are only partially correct. Though planning is a forward-thinking concept, it is founded on past actions and experiences. Without looking into the past, it is impossible to plan for the future. Similarly, while controlling involves evaluating past performance, it also aims to improve future performance by implementing necessary corrective actions. As a result, we can say that planning and controlling are both backward and forward looking functions.
3. 'An effort to control everything may end up in controlling nothing'. Explain.
Ans: The statement, 'an effort to control everything may end up controlling nothing,' refers to the 'Management by Exception' principle. It emphasizes the fact that nothing can be effectively controlled. Rather than controlling every deviation in performance, this principle states that an acceptable range of deviations in various activities should be established, and only deviations that exceed the acceptable range should be brought to the attention of managers for control. In other words, only major deviations that exceed the allowable limit should be acknowledged. Assume, for example, that the acceptable range of increase in input cost is set at 3%. In this case, only an increase of more than 3% in input costs (say, 7%) should be brought to the managers' attention. A decrease of less than 3% (say, 1% ) should, on the other hand, be ignored. As a result, instead of attempting to control everything, an effort should be made to control only the major things.
4. Write a short note on budgetary control as a technique of managerial control.
Ans: Budgetary control is a control technique that entails creating plans in the form of budgets. A budget is considered as a financial or quantitative statement that defines the goals to be achieved and the policies to be implemented over a specific time period. The actual results are then compared to the budgetary standards. This comparison aids in identifying deviations and, as a result, guides in the implementation of appropriate corrective measures. Budgets can be created for various divisions of an organization, such as sales, production, and purchasing. However, in order for budgeting to be effective, future estimates must be carefully made. Budgeting also serves as a source of motivation for employees by establishing the benchmarks against which their performance will be measured. As a result, it motivates them to meet their goals. Furthermore, it is used to facilitate coordination among the organization's various divisions/departments. Furthermore, proper budgeting ensures that resources are allocated to different divisions based on their needs. As a result, it aids in the most efficient use of resources.
5. Explain how management audit serves as an effective technique of controlling .
Ans: Management auditing is the comprehensive and constructive evaluation of an organization's management's overall performance. It aims to improve management's overall effectiveness and efficiency. It evaluates all of the functions performed by managers and aids in the identification of deficiencies in work performance. The following factors can be used to assess the effectiveness of management auditing for controlling.
i. Identification of Deficiencies: Management auditing assists in identifying current as well as potential deficiencies in performance. As a result, it aids in the implementation of necessary corrective measures.
ii. Increases Efficiency: Management auditing allows various management activities to be continuously monitored. As a result, it aids in improving management's overall efficiency.
iii. Improves Coordination: As it continuously oversees the work, it improves coordination between employees as well as within the various functions of the organization.
iv. Adapting to Environmental Changes: It assists the organization in appropriately adapting to environmental changes. This is accomplished by ensuring that management policies and strategies are up to date.
Long questions:
1. Explain the various steps involved in the process of control.
Ans: Controlling is a systematic approach to managing and controlling the actions of an organization. The steps involved in the controlling process are as follows.
(i) Establishing Standards: Setting standards entails creating benchmarks against which actual performance will be measured. Standards can be set in both qualitative as well as quantitative terms. Qualitative benchmarks can take the form of improved work coordination, increased goodwill, or increased employee motivation, among other things. For example, to increase employee motivation, a standard can be set in terms of the number of initiatives undertaken. Quantitative benchmarks can take the form of sales targets, units to be produced, or time spent on a specific action, among other things. In a shirt factory, for example, completing 10 pieces per day is a quantitative goal. Creating a performance benchmark Actual performance evaluation When comparing actual performance to standards, Defining and Analyzing Deviation Taking corrective measures The standards that are established should be such that they allow for easy comparison.
(ii) Measuring Real-World Performance: After the standards have been established, the next step is to assess the actual performance of the activities. This can be obtained through a number of methods, including personal observation, sample verification, performance reports, and so on. The checking should be done precisely and reliably so that the correct measurement can be taken for comparison. Measurement can be done both after an activity has been completed and while it is still in progress. For example, before assembling small parts of a larger machine, the parts can be checked. This would allow for continuous monitoring of both the small parts and the final machine.
(iii) Performance Evaluation: Once measured, performance is compared to the established standards. This type of comparison aids in identifying flaws in the work. As a result, it guides managers in taking the necessary steps to improve performance. These comparisons are easier to make when they are in numerical terms. For example, work efficiency in terms of cost incurred can be measured in comparison to the standard cost.
(iv) Deviation Analysis: When comparing actual performance to predetermined standards, every organization encounters deviations. As a result, it is critical to identify the deviations that are within the acceptable range.
It is recommended that deviations in critical areas be addressed first. Managers typically employ 'Critical Point Control' and 'Management by Objectives' to analyze deviations.
Exception'
1.Critical Point Control: An organization cannot monitor all of the management's activities. As a result, this control technique focuses on only the key result areas (KRAs) that affect the entire organization. For example, an increase in input costs would be more significant than an increase in stationary costs.
2.Management by Exception: This management technique is based on the belief that "trying to control everything results in controlling nothing." Only the essential and significant deviations that exceed the acceptable limit should be controlled, according to this. For example, if there is a 6% increase in labor costs while the allowable limit is only 3%, this should be immediately brought to the attention of management. A 2% increase in cost, on the other hand, can be ignored. Once the deviations are identified, the root cause must be identified. Work deviations can be caused by a variety of factors, including infeasible standards, process flaws, underutilization of resources, changes in the business environment, and so on. As a result, it is critical for management to consider the causes of the aforementioned deviations.
(v) Corrective Actions: When deviations exceed the allowable limits, management is required to take corrective action. This is the final step of controlling, and it aims to correct the organization's flaws so that the errors do not reoccur. For example, if the production target is not met on time, appropriate corrective actions, such as training workers or updating machinery, can be taken.
2. Explain the techniques of managerial control.
Ans: Traditional Techniques and Modern Techniques are the two broad categories of managerial control techniques.
Techniques of the Past
Traditional techniques are those that have been used by managers for a long time. The following are examples of traditional managerial control techniques.
i. Personal Observation: This technique involves managers personally observing the work being done. It allows the manager to gather the necessary information while also putting pressure on employees to perform well because they are constantly monitored by their boss. It is, however, a time-consuming process that cannot be used where a variety of functions must be overseen.
ii. Statistical Reports: Data from various statistical analyses, such as averages, ratios, percentages, and so on, can be easily presented in the form of graphs, charts, and tables. This type of presentation allows for easy comparison of performance to standards.
iii. Break-Even Analysis: A study of the relationship between costs, volume, and profits. The amount of sales at which there is no profit or loss is referred to as the break-even point. It is calculated when the total cost incurred equals the total revenue earned. The manager can use this technique to estimate the costs and profits to the organization at various levels of quantity and thus find the level where profit can be maximized.
iv. Budgetary Control: Budgetary control is a technique for planning future operations using budgets. In this context, the term "budget" refers to a quantitative or qualitative statement that outlines the goals that must be met within a specific time frame. These budgets are then used as benchmarks for assessing actual performance. It also presents the time-bound policies that will be used to achieve the objectives. It also facilitates exception management by focusing on activities that deviate significantly from budgeted amounts. However, in order for the technique to be effective, future estimates should be as accurate as possible. Furthermore, budgets should be adaptable to changes in the business environment.
Modern Techniques
As the name implies, modern techniques are new and recent. They are based on managers' new thinking and provide fresh ideas for better managerial control. The following are some of the most recent control techniques.
i. Return on Investment: Return on investment refers to the profits or benefits earned from investments. It is a useful technique for determining whether invested capital is being used effectively and whether reasonable returns are being generated from these investments. Managers can use this technique to compare the performance of different departments or divisions, or to compare current actions to previous year performance.
ii. Ratio Analysis: This technique entails calculating various ratios to analyze financial statements. These ratios are then used to provide effective managerial control. The following are the most commonly used control ratios.
(a) Liquidity Ratio, used to determine a company's short-term solvency.
(b) Solvency Ratio, which is used to determine a company's long-term solvency.
(c) Profitability Ratios, which are used to determine a company's profitability position.
(d) Turnover Ratios, which are used to determine the efficiency of activities based on resource utilization.
iii. Responsibility Accounting: Different divisions of an organization are designated as responsibility centers under this system. Each center's head is in charge of the center's goals and responsibilities. The following are some examples of responsibility centers that can be established.
(a) The Cost Centre is in charge of the organization's expenses.
(b) Revenue Centre, in charge of revenue generated by sales or marketing activities.
(c) Profit Centre, in charge of profits generated after deducting costs and revenues.
(d) Investment Center, which takes into account asset investments.
iv. Management Audit: This is a systematic approach to analyzing and evaluating the overall efficiency of a company's management. Its goal is to assess the management's efficiency and effectiveness in order to identify flaws in overall performance. It serves as an important control system by continuously monitoring the managers' work activities.
v. PERT and CPM: The Programme Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) and the Critical Path Method (CPM) are network-based techniques. It entails breaking down the entire project into various activities and then determining a timeline and cost estimate for each activity and the entire project. Because these techniques deal with time management and resource allocation, they allow for more effective project execution. These techniques are commonly used in shipbuilding, construction projects, and so on.
vi. Management Information System (MIS): An MIS is a computer-based controlling technique that provides managers with timely data and information in order for them to make effective decisions. It processes the organization's massive data and generates useful information for managers. MIS also ensures cost effectiveness in information management by facilitating information collection and dissemination at various levels. Managers can use the aforementioned traditional and modern techniques for effective and efficient organization control.
3. Explain the importance of controlling in an organisation. What are the problems faced by the organisation in implementing an effective control system?
Ans: Controlling is a critical and necessary function of management. Its goal is to manage managerial actions by establishing standards and identifying deviations in actual performance from those standards. It also ensures that resources are used efficiently while corrective actions are taken for deviations. The following are some of the factors that emphasize the significance of control.
(i) Achieving Organizational Goals: Controlling aims to achieve organizational goals by identifying deficiencies and recommending corrective actions. It aids in moving the organization in the right direction in order to achieve the set organizational objectives.
(ii) Evaluating the Standards: Controlling aids in determining the accuracy of the management's standards. A good control system allows the manager to determine whether the standards set are accurate and feasible. It also assists the organization in reviewing and revising standards in response to the changing business environment.
(iii) Optimal Resource Utilization: Constant control and monitoring aid in the efficient and optimum utilization of resources. Because each task is completed to the specified standard, there is less waste and spoilage of resources.
(iv) Employee Motivation: When effective control is exercised, employees are made aware of what is expected of them as well as the standards against which their performance will be measured. This encourages them to work harder to meet the goals they've set for themselves.
(v) Order and Discipline: Effective control contributes to the creation of an atmosphere of order and discipline within the organization. Employee dishonesty and inefficiency in behavior are reduced because they are aware that they are being continuously observed.
(vi) Promoting Coordination: Predetermined standards serve as a foundation for improved coordination across various activities. Controlling promotes coordination among departments by making them aware of their responsibilities and tasks. Controlling ensures that the organization's goals are met while providing unity of direction. As a result, controlling is an important function that all managers must perform. Controlling, on the other hand, has some limitations. The following points highlight the issues that the organization encountered when implementing an effective controlling system.
(i) Complication While Setting Standards: For better control, it is critical to establish quantitative as well as qualitative standards. Controlling, on the other hand, becomes less effective when the standards are defined in qualitative terms. The use of qualitative standards complicates the evaluation of performance and the comparison of actual work to the standards. As a result, it may cause a problem during the control process.
(ii) External Factors: The business environment is constantly changing, and organizations have little control over such external factors. These factors may pose challenges to effective control. Changes in government policies, environmental changes, competition, and so on are examples of such factors.
(iii) Employee Resistance: Controlling can be resisted by employees if it is outside of their comfort zone and freedom. For example, if managers set a specific quantity for production as a standard and the workers find it unrealistic, they can go on strike.
(iv) Expensive Process: Controlling effectively is an expensive endeavor in terms of time, money, and effort. Setting up CCTVs, for example, is very expensive. As a result, it is possible that a small organization will be unable to set up such a system. As a result, managers must ensure that the costs of operating such controlling systems do not outweigh the benefits derived from them.
4. Discuss the relationship between planning and controlling.
Ans: Management's planning and controlling functions are inextricably linked. On the one hand, planning refers to the psychological process of considering and deciding what should be done and how it should be done. That is, planning determines the goals to be achieved and the course of action to be taken. Controlling, on the other hand, refers to the process of managing and evaluating work done in accordance with standards and implementing corrective measures if there are any deficiencies. Planning establishes the standards that serve as the foundation for controlling. The various objectives and policies developed during planning serve as benchmarks against which actual performance is measured. Controlling without planning is a waste of time. There is nothing to control if there are no standards or objectives. That is, if managers do not know what the end goal is, they have no standard against which to judge current performance and deficiencies. Similarly, planning without control is meaningless. Following the formulation of the plans, it is necessary to monitor and evaluate whether the performance is in accordance with the desired plans. Controlling is required for determining whether the plan is being properly implemented, if there are any deficiencies in the work, and if corrective actions are required to achieve the planned goals. Planning cannot be carried out if there is no control. As a result, planning without control is useless. As a result, both planning and controlling can be said to complement one another. Both the concepts of planning as well as controlling are in some ways intertwined because they are both forward and backward looking. Though it is commonly stated that planning is forward-looking and controlling is backward-looking, this is only partially true. Though planning is a forward-thinking concept that deals with making plans and establishing the standards in advance. It is also based on past experiences as well as actions which have been initiated in the controlling function. Thus, planning, in addition to being forward-looking, is also backward-looking. Similarly, while controlling is based on past actions and deals with comparing current actions to predefined standards, it also focuses on taking corrective actions to improve management's future performance. Thus, controlling, in addition to looking back, also looks forward. As a result, while planning is a prerequisite for controlling, controlling is incomplete without planning. Both are inseparable functions that contribute to the achievement of the organization's goals.
Application Type
Following are some behaviours that you and others might engage in on the job. For each item, choose the behaviour that management must keep a check to ensure an efficient control system.
1. Biased performance appraisals
2. Using company’s supplies for personal use
3. Asking a person to violate company’s rules
4. Calling office to take a day off when one is sick
5. Overlooking boss’s error to prove loyalty
6. Claiming credit for someone else’s work
7. Reporting a violation on noticing it
8. Falsifying quality reports
9. Taking longer than necessary to do the job
10. Setting standards in consultation with workers You are also required to suggest to the management how the undesirable behaviour can be controlled.
Ans:
1. To avoid biased appraisals, performance evaluations should be conducted by an expert committee.
2. Because the statements are not expensive, they can be ignored.
3. Immediate and severe disciplinary action should be taken.
4. Mass bunking should be prohibited.
5. A secret suggestion box can be used to gather feedback on the boss for appraisal purposes.
6. Employee performance records must be kept.
7. If it is minor, it can be overlooked.
8. Strict quality control procedures should be followed.
9. A time and motion study will be conducted in order to establish standards.
10. The application of scientific techniques can aid in the establishment of the most feasible and optimal standards.
Case Problem
A company ‘M’ limited is manufacturing mobile phones both for the domestic Indian market as well as for export. It had enjoyed a substantial market share and also had a loyal customer following. But lately it has been experiencing problems because its targets have not been met with regard to sales and customer satisfaction. Also the mobile market in India has grown tremendously and new players have come with better technology and pricing. This is causing problems for the company. It is planning to revamp its controlling system and take other steps necessary to rectify the problems it is facing.
1. Identify the benefits the company will derive from a good control system .
1. Achieving desired outcomes
2. Operational precision.
3. Resource utilization that is efficient and effective.
4. Boosting employee morale.
5. Ensuring the proper flow of orders and the overall system's discipline.
6. Improves individual performance through coordination.
2. How can the company relate its planning with control in this line of business to ensure that its plans are actually implemented and targets attained .
(i) Establishing Standards Setting standards entails creating benchmarks against which actual performance will be measured. If we talk about the standards, they can be set in both qualitative as well as quantitative terms. Creating a performance benchmark Actual performance evaluation When comparing actual performance to standards, Defining and Analyzing Deviation Term for taking corrective action Qualitative benchmarks can take the form of improved work coordination, increased goodwill, or increased employee motivation, among other things.
(ii) Measuring Real-World Performance After the standards have been established, the next step is to assess the actual performance of the activities. This can be gained through a lot of methods such as personal observation, sample verification, performance reports, and so on. The checking should be done precisely and reliably so that the correct measurement can be taken for comparison. Measurement can be done both after an activity has been completed and while it is still in progress.
(iii) Performance Evaluation Once measured, performance is compared to the established standards. This type of comparison aids in identifying flaws in the work. As a result, it guides managers in taking the necessary steps to improve performance. These comparisons are easier to make when they are in numerical terms.
(iv) Deviation Analysis When comparing actual performance to predetermined standards, every organization encounters deviations. As a result, it is critical to identify the deviations that are within the acceptable range. It is recommended that deviations in critical areas be addressed first. Managers typically employ 'Critical Point Control' and 'Management by Exception' to analyze deviations. Once the deviations have been identified, the source of the deviations must be identified. Work deviations can be caused by a variety of factors, including infeasible standards, process flaws, underutilization of resources, changes in the business environment, and so on. As a result, it is critical for management to consider the causes of the aforementioned deviations.
(v) Corrective Actions When deviations exceed the allowable limits, management is required to take corrective action. This is the final step of controlling, and it aims to correct the organization's flaws so that the errors do not reoccur. For example, if the production target is not met on time, appropriate corrective actions, such as training workers or updating machinery, can be taken.
3. Give the steps in the control process that the company should follow to remove the problems it is facing .
1. Establishing performance standards
2. Evaluation of actual performance.
3. Assessment of actual performance in relation to standards.
4. Deviation analysis
5. Implementing corrective measures.
4. What techniques of control can the company use? In all the answers keep in mind the sector of business the company is in.
i. Return on Investment: The gains or benefits earned in relation to the investments made are referred to as return on investment. It is a useful technique for determining whether invested capital is being used effectively and whether reasonable returns are being generated from these investments. Managers can use this technique to compare the performance of different departments or divisions, or to compare current actions to previous year performance.
ii. Responsibility Accounting: Different divisions of an organization are designated as responsibility centers under this system. Each center's head is in charge of the center's goals and responsibilities. The following are some examples of responsibility centers that can be established.
(c) Profit Centre, in charge of profits generated after deducting costs and revenues. W
iii. Management Information System: MIS is a computer-based controlling technique that provides managers with timely data and information in order for them to make effective decisions. It processes the organization's massive data and generates useful information for managers. MIS also ensures cost effectiveness in information management by facilitating information collection and dissemination at various levels.
Downloading the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 Controlling Class 12 Business Studies from the website and app is a free and easy process. It is one of the prime objectives of mastering this chapter. The critical analysis of the chapter provides a strong foundation of knowledge. This NCERT Solutions Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 covers all the student’s doubts about mastering the concepts of acquiring managerial skills and the relationship between controlling and planning. These topics are specifically curated by our subject experts. Exam preparation has never been easier. The study material is guaranteed to enhance your rank in your exams.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapters
Chapter 8 - controlling.
CBSE Business Studies Class 12 Chapter 8 - Controlling is part of the NCERT Business Studies textbook for Class 12 and a primary resource for this topic. NCERT Solutions Class 12th Business Studies Chapter 8 displays structured descriptions highlighted as visual cues to provide a strong grasp of the chapter. The chapter describes the relationship between planning and controlling with emphasis on their factors. It portrays a clear analysis of the managerial skills employed using statistical methodologies.
Our subject matter experts provide the reader with an abundance of information to strengthen the foundation of the subject. The in-depth analysis of the business skills needed in a practical work environment is portrayed strongly in the chapter.
Class 12 Business Studies Chapter-wise NCERT Solution
Download free PDFs of Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies from the links provided below.
NCERT Solutions for Chapter-1 Nature & Significance of management
NCERT Solutions for Chapter-2 Principles of Management
NCERT Solutions for Chapter-3 Business Environment
NCERT Solutions for Chapter-4 Planning
NCERT Solutions for Chapter-5 Organising
NCERT Solutions for Chapter-6 Staffing
NCERT Solutions for Chapter-7 Directing
NCERT Solutions for Chapter-9 Finance and Management
NCERT Solutions for Chapter-10 Financial Market
NCERT Solutions for Chapter-11 Marketing Management
NCERT Solutions for Chapter-12 Consumer Protection
Class 12 Business Studies Chapter Wise Marks Weightage
Check the chapter-wise weightage of Class 12 Business Studies from this table.
This Class 12th Business Studies Chapter 8 has a weightage of 20 marks and is an important topic covered in exams. Basic questions keep repeating in the Board exams from this subject, for which preparing from this study material makes students score better.
Here is more detail about the contents of Chapter 8 Controlling Class 12.
Why are NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 Important?
Class 12 Economics Chapter 8 Controlling NCERT Solutions are prepared by a team of experts who make learning fun.
NCERT Business Studies Class 12 Chapter 8 comes with important terminology, visual cues about the topic, and examples that can be used for simplified revision before exams.
Our brief answers provide a solid foundation of the topic which helps in smooth preparation for exams.
These solutions are composed of key information, graphs, tables, and discussion on specific topics.
For better understanding, the material provides a systematic overview of all the important points.
Students who are appearing for the Class 12 Board Examination this year must give importance to these NCERT Solutions to score well in the exam. They are also advised to go through the entire Class 12 Syllabus and not to keep any topic on hold till the last minute. Students can also refer to the last-minute revision notes for all the Class 12 subjects that we have provided on our website to help you with your preparation. Make sure you keep a peaceful mind and sit for the exam confidently.
Benefits of Using Vedantu for Class 12 Chapter 8 - Controlling
Key Features of NCERT Solutions, These solutions are designed to help students achieve proficiency in their studies. They are crafted by experienced educators who excel in teaching Busniness subject. Some of the features include:
Comprehensive explanations for each exercise and questions, promoting a deeper understanding of the subject.
Clear and structured presentation for easy comprehension.
Accurate answers aligned with the curriculum, boosting students' confidence in their knowledge.
Visual aids like diagrams and illustrations to simplify complex concepts.
Additional tips and insights to enhance students' performance.
Chapter summaries for quick revision.
Online accessibility and downloadable resources for flexible study and revision.
NCERT Solutions play a crucial role in Class 12 exam prep. Start by thoroughly reading the textbook chapter. After that, solve the NCERT questions for Class 12 Chapter 8 Controlling. You can find detailed solutions on Vedantu, aligning with CBSE guidelines. Download the free NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chapter 8 - Controlling to guide your exam preparation with expert-reviewed answers.
Related Links for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter-8
Revision Notes for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter-8
Important Question for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter-8
Other Related Links
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Syllabus
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies
Important Questions for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies
Class 12 Business Studies Previous Year Questions Papers

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Chapter 8 - Controlling
1. What Does the Term ‘Controlling’ Mean?
Controlling is a key concept in learning the terminology of the subject of Business Studies. It is the act of ensuring all organizations perform their planned strategies without hindrance and in the given time constraints. It ensures that the use of resources (both natural and artificial) is done efficiently and effectively for the slated goals of the organization. It is a goal-oriented managerial function. The role of a controlling manager is to compare the actual performance with the planned performance statistics and understand the areas of improvement at all levels.
2. Write a Short Note on the Budgetary Control Used as a Technique of Managerial Control.
Budgetary control is the application of preparing budgets for each activity and operation of the organization. It refers to the goals and objectives of an organization achieved in quantitative terms. The actual results are compared with the planned budgets. The work is assessed and deviations are noted. These are correlated and action plans are developed. The resource requirement of various departments is analyzed and met according to the standards set up by the organization. Therefore, it is used to streamline managerial control.
3. How to easily study and understand Chapter 8 of Class 12 Business Studies?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies on the Vedantu app and the website which are great educational platforms preferred by students, provides an exemplary solution. From solved exercises based on Chapter 8 'Controlling' in a question-answer format including short notes, briefs and MCQs to detailed explanations, these exercises are a very simple and easy method to understand the fundamentals of the chapter making it simpler to learn and remember the concepts.
4. What is 'Management by Exception’?
Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 Controlling explains the various methods and techniques involved in controlling. Controlling means keeping a check on the various functions and analyzing the progress of the work within the set standards. The concept 'Management by Exception' refers to keeping a check on controlling itself as it is not possible to control everything effectively and hence only major variations in the work should be controlled.
5. What are the steps involved in controlling?
Five key steps are involved in the process of controlling which begins with setting the standards of assessment and then measuring the performance to get reliable data which helps in the next step. The next step is comparing the measured performance with the standards set. Further, the data is used to assess deviations in the performance, which if exceeds the limit, must be attended to with the final step of using corrective measures.
6. How to solve Class 12 Chapter 8 case problems of business studies?
Case problems are a method to analyse your comprehension and analytical skills. The problems help evaluate how well you have understood a given topic or a chapter. The NCERT Class 12 Solutions of Business Studies available free of cost also provide a few solved case problems that can be referred to infer how the questions can be answered. Study and understand Chapter 8 properly and keep in mind the essence of the chapter while answering them.
7. Which questions are important in Chapter 8 Business Studies of Class 12?
Chapter 8 Controlling talks about the importance of the controlling process in any organisation. It explains all the types, steps and techniques involved in controlling and what are the outcomes of such processes. The entire chapter is important and carries 20 marks. However, the key points you should learn is the terminology, and procedures and techniques and limitations relating to 'controlling'. These form the base of the chapter and are essential to know.
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Business Studies
Cbse study materials, jee study materials, neet study materials.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 Controlling updated for new academic session 2024-25. Class 12 B St Solutions for chapter 8 are given in simplified format with MCQ, so that every child can understand it easily.
Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 NCERT Solutions
- Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 Solutions
- Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 MCQ
- Study Material English Medium
- NCERT Book Chapter 8 in English
- Study Material Hindi Medium
- NCERT Book Chapter 8 in Hindi
State the meaning of controlling. Controlling refers to the function of evaluating and assessing the progress of the work done. It involves setting a specific criteria or standards for the work and then comparing the actual work with the set standards. It helps in finding the deviations from the set targets and thereby, take the required corrective actions. It ensures that everything goes as per the plans adopted. It also ensures full and efficient utilization of resources. Controlling is an imperative managerial function as it keeps a close check on the progress of work and thereby, forms the basis for future actions and planning.
Name the principle that a manager should consider while dealing with deviations effectively. State any one situation in which an organizations’ control system loses its effectiveness. The principle that a manager should considered while dealing with deviations effectively is management by exception.
State any one situation in which an organizations’ control system loses is effectiveness. An organizations’ control system loses its effectiveness when standards are to be defined in qualitative terms. Standard defined in qualitative terms make measurement of performance and their comparison with standards difficult.
Give any two standards that can be used by a company to evaluate the performance of its Finance & Accounting department. The two standards that can be used by a company to evaluate the performance of its Finance and Accounting department are Capital expenditure and inventories.
Which term is used to indicate the difference between standard performance and actual performance? The term that is used to indicate the difference between standard performance and actual performance is the deviation.
Planning is looking ahead and controlling is looking back. Comment. Planning is looking ahead and controlling is looking back. This statement is partially true. Planning is a psychological process of ‘thinking and deciding in advance’ about ‘what is to be done’ and ‘how it is to be done’. It is a mental activity that includes deciding the goals and also the actions through which they are to be accomplished. Thus, it is said that planning is looking ahead as it involves predicting the future. Controlling on the other hand, involves an assessment of the past performance and evaluating them against the set standards. In this sense, controlling is said to be a backward-looking function. However, both these statements are only partially true. Though planning is a futuristic concept but it is based on past actions and experiences. Planning for future cannot take place without peeping into the past. Similarly, though controlling involves assessment of past performance, it also aims at improving the future performance by taking the required corrective actions. Hence, we can say that planning and controlling are backward looking as well as forward looking functions.
The statement, ‘an effort to control everything may end up in controlling nothing’ is in regard with the principle of ‘Management by Exception’. It stresses on the fact that everything cannot be effectively controlled. According to this principle, rather than controlling each and every deviation in performance, an acceptable limit of deviations in various activities should be set and only those deviations that go beyond the acceptable range should be brought to the notice of the managers for control. In other words, only the major deviations which are beyond permissible limit should be acknowledged. For instance, suppose the acceptable range of increase in the input cost is set at 3 percent. In this case, only a more than 3% increase in the input cost (say 7%) should be brought to the notice of the managers. On the other hand, a less than 3% increase (say 1%) should be neglected. Hence, an effort should be there to control only the major things instead of trying to control everything.
Budgetary control is a technique of controlling that involves preparing plans in the form of budgets. Budget refers to a financial or a quantitative statement that defines the targets to be achieved and the policies to be followed in a specific period of time. The actual performance is then compared with the budgetary standards. This comparison helps in identifying the deviations and thereby, guides in taking appropriate corrective measures. Budget can be prepared for different divisions of the organization such as sales budget, production budget, purchase budget, etc. However, for the budgeting to be effective, future estimates must be made carefully. Budgeting also acts as a source of motivation for the employees by setting the standards against which their performance will be assessed. Thus, it encourages them to achieve the set objectives. In addition, it is also used to facilitate coordination among different divisions/departments of the organization. Moreover, proper budgeting ensures that resources are allocated to different divisions as per their requirements. Thereby, it helps in optimum utilization of the resources.
Management audit refers to the extensive and constructive appraisal of the overall performance of the management of an organization. It aims at improving the overall effectiveness and efficiency of the management. It evaluates all the functions performed by the managers and helps in identifying the deficiencies in the work performance. The effectiveness of management audit for controlling can be judged from the following points:
- Identification of Deficiencies: Management audit helps in recognizing the current as well as probable deficiencies in the performances. Thereby, it helps in taking the necessary corrective measures.
- Improves Efficiency: Through management audit, various activities of the management can be continuously monitored. Thereby, it helps in improving the overall efficiency of the management.
- Enhances Coordination: It improves the coordination between employees as well as within the different functions of the organization as it continuously oversees the work.
- Adapting to Environmental Changes: It helps the organization to adapt to the environmental changes appropriately. This is done by ensuring that the managerial policies and strategies are up-to-date.
Mr. Arfaaz had been heading the production department of Write well Products Ltd., a firm manufacturing stationary items. The firm secured an export order that had to be completed on a priority basis and production targets were defined for all the employees. One of the workers, Mr. Bhanu Prasad, fell short of his daily production target by 10 units for two days consecutively. Mr. Arfaaz approached Ms. Vasundhara, the CEO of the Company, to file a complaint against Mr. Bhanu Prasad and requested her to terminate his services. Explain the principle of management control that Ms. Vasundhara should consider while taking her decision. (Hint: Management by exception). The principle of management control that Ms. Vasundhara should consider while taking her decision is management by exception. It means if a manager tries to control everything, he may end up by controlling nothing. To make control effective and economical, it must focus attention on factors critical to performance. Therefore the manager should pay serious attention to only such cases, which are critical to success. In the above case Mr. Bhanu Prasad, fell short of his daily production target by only 10 units. This is very small deviation and it is not right to terminate him on the basis of this small deviation.
Explain the various steps involved in the process of control. Controlling is a systematic approach of managing and controlling the organizational actions. The following are the steps involved in the controlling process. Setting Standards : Setting up of standards involves developing the benchmarks against which the actual performance is to be measured. The standards can be set in qualitative as well as quantitative terms. Qualitative benchmarks can be in the form of improving coordination in work, higher goodwill or increased motivation level of employees, etc. For example, to improve the motivation level among employees, standard can be set in terms of number of initiatives taken. Quantitative benchmarks can be in the form of sales targets, units to be produced or time to be spent on a particular action, etc. For example, in a shirt factory completing 10 pieces a day is a quantitative target. The standards that are set should be such that they facilitate easy comparison. Measuring Actual Performance : Once the standards are set, the next step is to measure the actual performance of the activities. This may be done through various techniques such as personal observation, checking the sample, performance reports, etc. The checking should be done in an exact and reliable manner so that correct measurement is taken for comparison. Measurement can be done after the completion of an activity as well as while it is in progress. For example, while assembling small parts of a bigger machine, the parts can be checked before assembling. This would ensure the continuous monitoring of the small parts as well as the final machine. Comparing the Performances : Performances once measured are then compared with the set standards. Such a comparison helps in assessing the deviations in the work. Thereby, it guides the managers in taking the necessary steps so as to improve the performances. These comparisons are easier when they are in quantitative terms. For example, efficiency in work in terms of cost incurred can be measured against the standard cost. Analyzing Deviation : Every organization faces deviations when comparing the actual performance with the redeveloped standards. Thus, it is important to find the deviations that are in the permissible range. It is said that deviations in key areas should be attended first. For analyzing the deviations the managers generally use ‘Critical Point Control’ and ‘Management by Exception’ 1. Critical Point Control: An organization cannot keep a check on all the activities of the management. Thus, this technique of controlling aims at focusing on only the key result areas (KRAs) that affect the entire organization. For example, rise in input cost would be more important than rise in stationary cost. 2. Management by Exception: This technique of management is based on the belief that ‘an attempt to control everything results in controlling nothing’. According to this, only the essential and significant deviations that are beyond the acceptable limit should be controlled. For example, if there is a 6 per cent rise in labor cost whereas the permissible limit is just 3 per cent, then, this should be immediately brought into the notice of the management. On the other hand, a 2 percent rise in the cost can be ignored. Once the deviations are recognized, it is necessary to acknowledge the cause for it. There can be a number of elements causing deviations in work such as infeasible standards, deficiencies in process, underutilization of resources, changes in business environment, etc. Thus, it becomes important for the management to take into regard the causes for the concerned deviations. Corrective Measures : When deviations go beyond the admissible limits, there arises a need for the management to take corrective actions. This is the last step of controlling which aims at correcting the deficiencies of the organization so that the errors do not occur again. For example, if the production target was not met duly, appropriate corrective actions such as training the workers or updating the machinery for working, etc. can be taken.
The techniques used for managerial control can be divided into two broad categories namely, Traditional Techniques and Modern Techniques. Traditional Techniques : Techniques which are being used by the managers since long back, are known as traditional techniques. The following are traditional techniques of managerial control. (1) Personal Observation: This technique includes personal observation by the managers to oversee the work being done. It enables the manager to gather the right information and also creates a pressure on the workers to perform well as they are being continuously observed by their supervisor. However, it is a time-consuming process and cannot be used where there are a variety of functions to be overseen. (2) Statistical Reports: Information in the form various statistical analysis such as averages, ratios, percentages, etc. can be easily presented in the form of graphs, charts and tables. Such presentation facilitates easy comparison of the performance with the standards. (3) Break-Even Analysis: It involves a study of relation between costs, volume and profits. Break-Even point refers to that quantity of sales where there is neither profit nor loss. It is determined at the point where total cost incurred is equals the total revenue earned. Through this technique, the manager can estimate the costs and profits to the organization at various levels of quantity and thereby, find the level where profit can be maximized. (4) Budgetary Control: Budgetary control is a technique of planning the future operations in the form of budgets. Here, ‘budget’ refers to a quantitative or qualitative statement which presents the objectives to be achieved in a specified period of time. These budgets are then used as standards for measuring the actual performance. It also presents the time-bounded policies to be used for the attainment of the objectives. It also facilitates management by exception by focusing on the activities which deviate significantly from the set budgets. However, to ensure effectiveness of the technique, estimates about the future should be as accurate as possible. In addition, the budgets should be flexible so as to adapt to the changes in business environment. Modern Techniques : Modern techniques as the name suggests are modern and recent in origin. They are based on the new thinking of the managers and provide refreshing ideas for a better managerial control. Following are the highlighted modern techniques of controlling. (1) Return on Investment: Return on investment refers to the gains or benefits earned in relation to the investments done. It is a useful technique in measuring whether the invested capital is being used effectively and if a reasonable amount of returns are being generated from these investments. Managers can opt for this technique when comparing the performances of different departments or divisions or when comparing the present actions in relation to the previous year performance. (2) Ratio Analysis: This technique involves calculating various ratios in order to analyses the financial statements. These ratios are then used as a tool for effective managerial control. Following are the most commonly used ratios for controlling. a) Liquidity Ratio, for determining the short-term solvency of business. b) Solvency Ratio, for determining the long-term solvency of a business. c) Profitability Ratios, for determining the profitability positions of a business. d) Turnover Ratios, for determining the efficiency of activities based on the utilization of resources. (3) Responsibility Accounting: Under this system, different divisions of an organization are as responsibility centers. The head of each center is responsible for the targets and duties regarding his center. The following are some of the responsibility centers that can be formed. a) Cost Centre, is responsible for the costs incurred by the organization. b) Revenue Centre, responsible for the revenue generated from the sales or marketing activities. c) Profit Centre, responsible for the profits generated considering the costs and revenues. d) Investment Centre, it takes into account the investment made in the form of assets. (4) Management Audit: It refers to a systematic approach for analyzing and appraising the overall efficiency of the management of a company. It aims at reviewing the efficiency and effectiveness of the management in order to identify the deficiencies in the overall performance. It acts as an important control system by continuously monitoring the working activities of the managers. (5) PERT and CPM: Programmed Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) and Critical Path Method (CPM) are techniques that are based on network analysis. It involves dividing the entire project into various activities and then deciding a time line and cost estimate for each activity and for the entire project. As these techniques deal with time scheduling and resource allocation, they enable effective execution of the projects. Such techniques are generally used in shipbuilding, construction projects, etc. (6) Management Information System: MIS is a computer based controlling technique that provides timely data and information to the managers while aiming at effective decision making. It processes the massive data of the organization and generates useful information to the managers. MIS also ensures cost effectiveness in managing information as it facilitates collection and dissemination of information at different levels. The aforementioned traditional and modern techniques can be used by the managers for effective and efficient controlling of the organization.
In what sense the term controlling is used in chapter 8 of 12th B. St.?
Controlling means finding out the deviation between standard performance and actual performance and taking corrective action.
What are the important questions from chapter 8 of 12th B. St.?
Perhaps, The most important question is the interrelationship of planning and controlling.
What should the student remember while studying chapter 8 of 12th Business Studies?
Planning and control are both forward looking and backward looking also. For details please refer to Tiwari Academy notes on the subject.
What are peculiar points to remember in chapter 8 of Class 12 Business Studies?
The techniques of controlling like management audit, PERT and CPM etc. are basically subject taught in senior classes. From examination point of view the steps, importance and limitations of controlling are important.

Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education

myCBSEguide
- Business Studies
- Class 12 Business Studies...
Class 12 Business Studies Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
In this article, we will discuss how to get CBSE class 12 Business Studies Case Study Questions from the myCBSEguide App and our Student Dashboard for free.
For the students appearing for class 12 board exams from the Commerce Stream, Business Studies is a core subject. Business Studies as a subject provides a way of perceiving and interacting with the business ecosystem . It well establishes the interdependence of business on various social, political, legal and economic forces and vice-versa. Business Studies is a purely theoretical and a relevantly easier subject for the Commerce students. Business Studies class 12 exam is a highly scoring subject and it facilitates the students to increase their percentile and excel in academics.
12 Business Studies Paper Design
The exam is divided into 2 parts:
- Part A generally contains questions from Principles and Functions of Management and carries 60 marks.
- Part B comprises questions from Business Finance and Marketing, it carries a total of 40 marks.
The syllabus of class 12 Business Studies comprises 12 chapters that are divided into 2 books
- Principles and Functions of Management
- Business Finance and Marketing
Business Studies Syllabus
CBSE has released the latest class 12 syllabus (2022-23) for Business Studies.
Business Studies Case Study Questions
Case-based questions have always been an integral part of Business Studies class 12 question papers for the past many years. Students are required to focus more on case studies as they require the application of their knowledge of the key business concepts. In the year 2021-22 CBSE introduced a few changes in the question paper pattern to enhance and develop analytical and reasoning skills among students. Sanyam Bhardwaj, controller of examinations, CBSE quoted that case-based questions would be based on real-life situations encountered by the students.
The purpose was to drift from rote learning to competency and situation-based learning. He emphasized the fact that it was the need of the hour to move away from the old system and formulate new policies to enhance the critical reasoning skills of students. Introducing case study questions was a step toward achieving the goals of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
What is a case study question? (Business Studies)
A case study in reference to Business Studies can be thought of as a real-world test of how the implementation works. It is predominantly a report of an organization’s implementation of something such as a practice, a product, a system, or a service. Case studies based on NCERT text form a substantial part of the Business Studies examination. Initially, they were confusing for both students and teachers but now there is a clarity that has made the question paper more student-friendly. A significant weightage has been given to case-based and application-based questions.
Critical and Analytical Thinking
These questions demand critical and analytical thinking on behalf of the students. The best part of these questions is that they provide conceptual hints and keys that point to the right answer. According to the new pattern implemented by CBSE, case-based questions would carry a significant weightage of more than 30% in the Business Studies question paper.
Case Study Passage
As part of these questions, the students would be provided with a comprehensive passage, based on which analytical questions will have to be answered by them. The students would be required to read the passage carefully before attempting the questions. In the coming examination cycle (2022-23), case-based questions have a weightage of around 30%.
Types of Case Study questions in Business Studies
CBSE plans to increase the weightage of such questions in the following years, so as to enhance the intellectual and analytical abilities of the students. Case study questions would be based on various topics and chapters in Business Studies. It is expected from the students to have complete knowledge of the concepts in their syllabus.
They will have to let go of the shortcut techniques and get to read their textbooks with full concentration, especially for solving case-based questions in Business Studies for the passages given are generally lengthy and require an in-depth study. The best part of having these questions is that the question itself projects a hint of its solution.
The questions asked could be :
- Direct and simple-such questions can easily be solved as the answers are either there in the given passage or the student can solve it at ease by reading and analyzing the passage carefully.
- Indirect and application-based- These are the ones that would require the student to have complete knowledge of the topic and could be answered by application of the concepts. The answers to such questions are slightly tricky and not visible in the given passage, though the passage would highlight the concept on which the questions would be asked by CBSE.
Class 12 Business Studies Case Study
Case study questions asked by CBSE were stated to be quite challenging by many students. It prominently focuses on real and present scenarios of the business world. Though the exam, on the whole, was quite direct and its difficulty level was termed out to be moderate. Around 30% of the question paper consisted of case-based questions that required high-order thinking and analytical skills from the students.
Content of Case Study Questions
The concept of case-based questions is not new since CBSE has always included questions based on Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTs) and case-based questions. Though now we will have an increased percentage of such questions in the question paper. The student has to keep in mind that the concept-based questions can be attempted only with the proper understanding of the business concepts.
Benefits Of Case-based Questions
Class 12 Business Studies syllabus comprises two books and CBSE can ask Case study questions from any of them. Students must prepare themselves thoroughly for both the books. They must practice class 12 Business Studies case-based questions from the various options available to them.
- Enhance the intellectual capabilities of the students.
- Provide a complete and deeper understanding of the subject.
- Inculcate analytical reasoning and temperament in students.
- Help students retain knowledge for longer periods of time.
- Would definitely help to discard the concept of rote learning and cramming without understanding the core of the subject.
- The questions would facilitate bringing out the much-awaited change in the prevalent system of education in India that hinders the strengthening of practical learning.
Some Case-Study Questions (Business Studies) Class 12
Here are some case study questions for CBSE class 12 Business Studies. If you wish to get more case study questions and other related study material, download the myCBSEguide App now. You can also access it through our Student Dashboard .
Business Studies Case Study 1
Read the following text and answer the questions: ABLEX Ltd. is a big and well-reputed company. The biggest challenge for the company is managing many employees at the same time. As the company has various departments like human resources, marketing, finance,etc., it is very necessary for the company to maintain unity in different departments. All the employees work hard for the organisation. Despite their different interest, they all perform various activities together so as to achieve the objectives of the company. The career of employees is shown a developmental path through proper training modules and job enrichment. Ajay is a manager who assigns all duties and responsibilities to his employees in the department. He uses all sources to develop proper communication with them and leaves no attempt to motivate them.
- It integrates Group Efforts
- It is a Continuous process
- It ensures Unity of Action
- It is Pervasive
- Top Level Management
- Middle-Level Management
- Lower Level Management
- Supervisory Level Management
- Economic objectives
- Social Objectives
- Organisational Objectives
- Personal Objectives
Answer Key:
- (c) It ensures unity of action
- (b) Middle-level management
- (c) Personal objectives
- (a) Directing
Business Studies Case Study 2
Read the following text and answer the question: Mohan works in a bulb manufacturing company. Each bulb that is manufactured is of standard size and quality. Further, if there is any unrequited type of bulb manufactured then its production is stopped. Last month when the company came to know that 10-watt bulbs were no more liked by customers, their production was stopped. He works in the purchasing department. His job is to purchase the filaments required to make bulbs. This time when he purchases the filament he gets the instruction from the seller that some special care needs to be taken in the first hour of fixing the filaments inside the bulb. Mohan knows this information should be given immediately to the production department before the assembling process starts. However, he finds that his company’s policies only allow him to give the message to his immediate boss who will further pass this message to his boss. The passing of this message will continue until it reaches the desired person in the production department. Based on the passage answer the following questions:
- Method study
- Fatigue study
- Standardization and simplification
- None of these
- Scalar chain
- Departmentalization
- Division of Work
- None of the above
- Organization
- Authority and Responsibility
- All of these
- Division of work
- Scalar Chain
- (b) Fatigue study
- (a) Scalar chain
- (c) Gang plank
- (a) Division of work
Business Studies Case Study 3
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow: Two years ago Radhika completed her degree in food technology. She worked for some time in a company manufacturing chutneys, pickles and murabbas. She was not happy in the company and decided to have her own organic food processing unit for the same. She set the objectives and the targets and formulated an action plan to achieve the same. One of her objectives was to earn 10% profit on the amount invested in the first year. It was decided that raw materials like fruits, vegetables, spices, etc. will be purchased on three months’ credit form farmers cultivating organic crops only. She also decided to follow the steps required for the marketing of the products through her own outlets. She appointed Rakesh as a production manager who decides the exact manner in which the production activities are to be carried out. Rakesh also prepared a statement showing the number of workers that will be required in the factory throughout the year. Radhika informed Mohan about her sales target for different products, area wise for the forthcoming quarter. While working on the production table a penalty of 100 per day for not wearing the caps, gloves and apron was announced.
- Standing Plan
- (a) Objectives
- (c) Procedure
- (b) Programme
Tips to Solve Case Study Questions in Business Studies
Let’s try to comprehend and solve case study questions of class 12 Business Studies. As mentioned earlier, the entire syllabus is divided into 2 books. It is expected from the students to rigorously follow the NCERT book as the language written is quite simple and crisp. The exam in spite of being totally theoretical is quite scoring.
- Read the passage in depth.
- Try to comprehend the situation and focus on the questions asked.
- Generally, the passage given in Business Studies is lengthy but the solutions are brief and simple.
- Can follow a reversal pattern, i.e read the questions before and then search for the answers. You will save time.
- Answer briefly and precisely.
- Focus on solidifying key Business Studies fundamentals for acing any case study. If your concepts are clear, you will hardly face any difficulty in answering them.
- While answering the case study, pick the keywords or any keyline based on which you are withdrawing your conclusion. You need to highlight the reason for your answer.
These simple points if kept in mind will definitely help the student to fetch good marks in case study-based questions in class 12 Business Studies.
WORK HARD, HAVE FUN, AND MAKE HISTORY!
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
1 thought on “Class 12 Business Studies Case Study Questions”
Case study question answer
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Controlling Case Studies for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8
- Last modified on: 2 months ago
- Reading Time: 7 Minutes

Table of Contents
Controlling Case Studies for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8
Here you will find Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies (BST) Chapter 8 Controlling.
Controlling Case Study Questions
Case Study Question 1:
Units and Chapter List:
Unit 1 – Nature and Significance of Management, Principles of Management and Business Environment
Chapter 1: Nature and Significance of Management Case Studies Chapter 2: Principles of Management Case Studies Chapter 3: Business Environment Case Studies
Unit 2 – Planning and Organising
Chapter 4: Planning Case Studies Chapter 5: Organising Case Studies
Unit 3 – Staffing, Directing and Controlling
Chapter 6: Staffing Case Studies Chapter 7: Directing Case Studies Chapter 8: Controlling Case Studies
Unit 4 – Financial Management and Financial Market
Chapter 9: Financial Management Case Studies Chapter 10: Financial Market Case Studies
Unit 5 – Marketing and Consumer Protection
Chapter 11: Marketing Case Studies Chapter 12: Consumer Protection Case Studies
How to Tackle Business Studies Case Studies in Exams
Here’s a tip on how to approach and answer case study questions for Class 12 BST (Business Studies) exams:
1. Understand the Format:
- Case study questions are designed to test your ability to analyze and apply your knowledge to real-world situations.
- These questions are usually longer in length, but your answers should be concise and to the point.
2. Careful Reading:
- Begin by carefully reading the entire case study. Don’t rush; understand the context and details provided.
- Pay attention to any data, statistics, or specific information presented in the case.
3. Examine the Question:
- Before diving into the case study, read the question(s) associated with it. This will help you focus on what to look for while reading the case.
- Identify the key concepts or issues the question is addressing.
4. Highlight Key Information:
- While reading the case, underline or highlight important facts, figures, or statements that seem relevant to the question.
- Make notes if necessary to organize your thoughts.
5. Analyze the Situation:
- Once you have a good grasp of the case and its details, analyze the situation. Consider the cause-and-effect relationships, potential solutions, and any ethical or business principles involved.
6. Structure Your Answer:
- Start your answer with a brief introduction, summarizing the main problem or situation presented in the case.
- Organize your response logically. You can use bullet points or numbered lists for clarity.
- Present your analysis, providing relevant business theories or concepts as appropriate.
- Offer solutions or recommendations based on your analysis. Be clear and concise in your suggestions.
7. Use Simple Language:
- Write your answers in clear and simple language. Avoid unnecessary jargon or complex vocabulary.
- Ensure your answers are easy to understand for the examiner.
8. Practice with Sample Papers:
- Practice case study questions from sample papers and previous year papers to get a feel for the format and types of questions that may be asked.
- Writing practice answers will help you refine your approach.
Remember to practice, and you’ll become more proficient at tackling case study questions effectively.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 – Controlling Class 12 Notes
Controlling Class 12 Revision Notes
In the controlling class 12 notes, we will begin by studying one of the important functions of a manager i.e. Controlling. We will study as to why Controlling is known as a goal-oriented function. Then, we will study the importance of Controlling. Also, we will study the limitation of Controlling. Moreover, we will study the relationship between Planning and Controlling. Planning and controlling are inseparable twins of management. Planning starts the process of management and controlling completes the process. Plans are the base for control and without control, the best plans may go ineffective. Thus, we will understand that planning and controlling are interrelated and, in fact, reinforce each other. Furthermore, we will study the steps involved in the controlling process. The process of control involves setting the performance standards, measurement of actual performance.
Also, it includes comparison of actual performance with standards, analysis of deviations and taking corrective action. Also, we will study the advantages of Critical Point Control and Management by Exception. Then, we will study the various techniques of managerial control. Thus, we will study traditional and modern techniques in detail. In traditional techniques, we will study about Personal observation, Statistical reports, breakeven analysis, and budgetary control. Then, we will study the modern techniques. These consist of Return on investment, Ratio analysis, Responsibility accounting. Also, it includes Management audit, PERT and CPM and Management information system.
Download Toppr app for Android and iOS or signup for free.
Sub-topics under Controlling:
- Meaning of Controlling : In this Sub-topic, we will study one of the important functions of a manager i.e. Controlling. We will study as to why Controlling is known as a goal-oriented function.
- Techniques of Managerial Control : In this Sub-topic, we will study the various techniques of managerial control. Thus, we will study traditional and modern techniques in detail.
- Responsibility Accounting, Management Audit and Pert and CPM : Here, we will study the modern techniques of managerial control i.e. (Responsibility Accounting, Management Audit, PERT and CPM) in detail.
You can download CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 Revision Notes by clicking on the download button below

Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.


CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 13 – Entrepreneurship Development Class 12 Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 12 – Consumer Protection Class 12 Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11 – Marketing Class 12 Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 10 – Financial Markets Class 12 Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 9 – Financial Class 12 Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 7 – Directing Class 12 Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 6 – Staffing Class 12 Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 5 – Organising Class 12 Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 4 – Planning Class 12 Notes
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Bihar Board
SRM University
Pseb 10th result.
- UP Board 10th Result
- UP Board 12th Result
- Punjab Board Result 2024
- MP Board Result 2024
- Rajasthan Board Result 2024
- Karnataka Board Result
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
Controlling Class 12 Notes: CBSE 12th Business Studies Chapter 8, Download PDF
Cbse class 12 controlling notes: here, students can find handwritten class 12 business studies chapter 8 controlling notes. this will guide you in appropriate revision for the upcoming cbse board exam..

Controlling Class 1 2 Notes: This article hands out CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 Controlling Revision Notes along with a PDF download link for the same. Students are advised to check these controlling Class 12 revision notes to understand the concepts present in the chapter in detail and build a strong hold on the preparation. These revision notes on Class 12 Controlling will also add to your knowledge and ensure that you end up answering each question in a perfect manner.
Revision Notes are one of the most important study resources used by teachers as well as students to teach and prepare for the examination. These short and handwritten notes have been prepared by the subject experts in accordance with the updated and revised CBSE Class 12 Business Studies syllabus for students of the current academic session 2023-2024. Also, find attached links to various other important study resources to perform well in the upcoming CBSE Class 12 Board Exam in 2024.
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies MCQs
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Mind Maps
Revision Notes for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 Controlling
What do you mean by Controlling
Controlling means ensuring that activities in an organization are performed as per the plans. Controlling function of a manager is a pervasive function. It is a primary function of every manager. It also ensures that an organization’s resources are being used effectively and efficiently for the achievement of predetermined goals.
- Accomplishing organizational goals
- Judging the accuracy of standards
- Making efficient use of resources
- Improving employee motivation
- Ensuring order and discipline
- Facilitating coordination in action
- Difficulty in setting quantitative standards
- Little control over external factors
- Resistance from employees
- Costly affair
Controlling Process
Step 1:
Setting Performance Standards - Standards are the criteria against which actual performance would be measured. Thus, standards serve as benchmarks towards which an organization strives to work.
Measurement of Actual Performance - There are several techniques for measurement of performance. These include personal observation, sample checking, performance reports, etc. As far as possible, performance should be measured in the same units in which standards are set as this would make their comparison easier.
Comparing Actual Performance with Standards - This step involves a comparison of actual performance with the standard. Such comparison will reveal the deviation between actual and desired results.
Step 4:
Analyzing Deviations - Deviations have to be analyzed to figure out whether they fall under the appropriate range or not. Critical Point Control and Manager by exception are the methods to be used in this case.
Taking Corrective Action - The final step in the controlling process is taking corrective action. No corrective action is required when the deviations are within acceptable limits. However, when the deviations go beyond the acceptable range, especially in important areas, it demands immediate managerial attention so that deviations do not occur again and standards are accomplished.
What is Critical Point Control?
It is neither economical nor easy to keep a check on each and every activity in an organization. Control should, therefore, focus on key result areas (KRAs) that are critical to the success of an organization.
What is management by exception?
Management by exception, which is often referred to as control by exception, is an important principle of management control based on the belief that an attempt to control everything results in controlling nothing.
Also Read :
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Syllabus 2023-2024
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- PSEB 10th Result 2024
- PSEB Class 10th Result 2024
- Punjab Board 10th Result 2024
- pseb.ac.in 10th Result 2024
- Punjab Board Class 10th Result 2024
- ਪੀਐਸਈਬੀ 10ਵੀਂ ਦਾ ਨਤੀਜਾ 2024
- PSEB १०थ रिजल्ट २०२४
- पंजाब बोर्ड १०थ टॉपर्स लिस्ट 2024
- PSEB 10th Topper List 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Study Material
- CBSE Class 12
Latest Education News
Punjab Board 10th Toppers List 2024: अदिति ने 650 अंक लाकर पंजाब बोर्ड 10वीं की परीक्षा में टॉप, जानें कितने हुए पास-फेल
Calcutta High Court LDC Recruitment 2024: Apply Online For Stenographer And Other Posts, Check Eligibility
PSEB 10th Result 2024 Roll Number and Name-wise: Check Punjab Board Matriculation Marks Online
World Liver Day 2024: 15 Important Facts About The Largest Gland Of Human body
Punjab Board 10th Result 2024: PSEB Matric Result Link at pseb.ac.in
PSEB 10th Result 2024 Released: Aditi, Alisha and Karmanpreet got 1st, 2nd and 3rd Position, 97.2% Students Passed and Live Link Tomorrow
Punjab Board 10th Result 2024: When, Where, and How to Check PSEB Matric Results Online and via SMS
T20 World Cup 2024: कौन-कौन से खिलाड़ी भारतीय स्क्वॉड के है प्रबल दावेदार?
Punjab Board Result 2024: Check PSEB 10th, 12th Result Link at pseb.ac.in
pseb.ac.in 10th Result 2024 Declared: 97.2% Pass, List of Official Websites to Check Punjab Board Matriculation Result
PSEB 10th Result 2024 Out: पंजाब बोर्ड मैट्रिक के नतीजे pseb.ac.in पर, इन स्टेप्स से चेक करें नतीजे
World Liver Day 2024: 8 Effective Measures To Prevent Liver Damage
SSC GD Expected Cut Off 2024: State-wise Minimum Passing Marks for Male & Female Candidates
KTET 2024 Application Begins at ktet.kerala.gov.in, Direct Kerala TET April Apply Online Link, Check Registration Process
PSEB 10th Class Result 2024 Out: ਪੰਜਾਬ ਬੋਰਡ ਦਾ 10ਵੀਂ ਦਾ ਨਤੀਜਾ ਜਾਰੀ, pseb.ac.in 'ਤੇ ਕੱਲ੍ਹ ਤੋਂ ਸਿੱਧਾ ਲਿੰਕ ਹੋਵੇਗਾ ਐਕਟਿਵ
PSEB Class 10th Result 2024 Declared: Punjab Board Matriculation Results Online on Official Website pseb.ac.in, How to Check Scorecard
World Liver Day 2024: Quotes, Messages, Liver Cleansing Tips, Liver Functions, Diseases, and More
PSEB 10th Toppers List 2024 Released: Aditi Tops Punjab Board Class 10 Exam, Check Toppers Name, Marks and Percentage Here
भारत का इकलौता अंतरराष्ट्रीय और समुद्री सीमा साझा करने वाला राज्य, जानें
NDA Exam Day Guidelines 2024: Check Do’s and Don’ts, Dress Code at Exam Centre
NCERT Notes for Class 12 business studies Chapter 8 Controlling
Class 12 business studies chapter 8 controlling.
NCERT Notes for Class 12 business studies Chapter 8 Controlling, (business studies) exam are Students are taught thru NCERT books in some state boards and CBSE Schools. As the chapter involves an end, there is an exercise provided to assist students to prepare for evaluation. Students need to clear up those exercises very well because the questions inside the very last asked from those.
Sometimes, students get stuck inside the exercises and are not able to clear up all of the questions. To assist students, solve all of the questions, and maintain their studies without a doubt, we have provided step-by-step NCERT Notes for the students for all classes. These answers will similarly help students in scoring better marks with the assist of properly illustrated Notes as a way to similarly assist the students and answer the questions right.
Controlling is one of the important functions of management. Managerial functions start with planning and ends with controlling. Controlling means ensuring that activities in an organization are performed as per plans. The controlling function finds out how far actual performance deviates from standards, analyses the causes of such deviations and attempts to take corrective actions based on the same. Without proper control even the best plan will not give the desired result. This process helps in formulation of future plans in the light of the problems that were identified and, thus, helps in better planning in the future periods.
Controlling ensures that an organisation’s resources are being used effectively and efficiently for the achievement of predetermined goals. Controlling function of a manager is a pervasive function. It is a primary function of every manager. Managers at all levels of management— top, middle and lower-need to perform controlling functions to keep a control over activities in their areas.
Features of controlling:
- Controlling is a goal-oriented process
- It is a pervasive function
- It is a backward-looking function. Controlling evaluates the past performance on the basis of pre-determined goals.
- Controlling is futuristic also. Controlling process helps in formulation of future plans in the light of the problems that were identified and, thus, helps in better planning in the future periods.
Importance of Controlling
A good control system helps an organisation in the following ways:
Accomplishing organisational goals:
Controlling measures, the actual performance with standards and make corrective action on deviations. Thus, controlling function guides the organization and keeps it on the right track so that the organizational goals might be achieved.
Judging accuracy of standards:
A good control system keeps a careful check on the changes taking place in the organization and in the business environment. This helps to review and revise the standards in the light of such changes.
Making efficient use of resources:
Controlling helps a manager to reduce wastage and spoilage of resources. Controlling ensures each activity is performed in accordance with predetermined standards and norms. This ensures that resources are used in the most effective and efficient manner.
Improving employee motivation:
A good control system ensures that employees know well in advance what they are expected to do and what are the standards of performance on the basis of which they will be evaluated. This will motivate them and helps them to give better performance.
Ensuring order and discipline:
Controlling creates an atmosphere of order and discipline in the organisation. It helps to minimise dishonest behaviour on the part of the employees by keeping a close check on their activities.
Facilitating coordination in action:
Each department and employee is governed by predetermined standards which are well coordinated with one another. This ensures that overall organisational objectives are accomplished.
Limitations of Controlling
Controlling function of management is suffers from the following limitations.
Difficulty in setting quantitative standards:
Controlling will be effective only when standards are fixed in quantitative terms. Control system loses some of its effectiveness when standards cannot be defined in quantitative terms. Employee morale, job satisfaction and human behaviour are such areas where standards can’t be fixed in quantitative terms.
Little control on external factors:
Generally, an enterprise cannot control external factors such as government policies, technological changes, competition etc.
Resistance from employees:
Control is often resisted by employees. They see it as a restriction on their freedom. For instance, employees might object when they are kept under a strict watch with the help of CC TV.
Costly affair:
Control is a costly affair as it involves a lot of expenditure, time and effort. A small enterprise cannot afford to install an expensive control system. It cannot justify the expenses involved. Managers must ensure that the costs of installing and operating a control system should not exceed the benefits derived from it.
Relationship between Planning and Controlling
Planning and controlling are inseparable twins of management. A system of control presupposes the existence of certain standards. These standards of performance which serve as the basis of controlling are provided by planning. Once a plan becomes operational, controlling is necessary to monitor the progress, measure it, discover deviations and initiate corrective actions. Thus, planning without controlling is meaningless. Similarly, controlling is blind without planning. If the standards are not set-in advance, managers have nothing to control. The relation between planning and controlling will be clear from the following points.
- When there is no plan, there is no basis of controlling.
- Future plans are made perfect by correcting the deviations, which are identified through controlling.
- Planning is clearly a prerequisite for controlling.
- Planning means deciding in advance what is to be done, how it is to be done, who should do it etc. Controlling ensures that things are done as per plan.
- It is utterly foolish to think that controlling could be accomplished without planning.
- Planning is basically an intellectual process involving thinking and analysis to discover an appropriate course of action for achieving objectives. Controlling, on the other hand, checks whether decisions have been translated into desired action.
- Planning is prescriptive whereas, controlling is evaluative.
The relationship between planning and controlling is that one helps the other.
- Planning based on facts makes controlling easier and effective
- Controlling improves future planning by providing information derived from past experience.
‘Planning is looking ahead while controlling is looking back’. Comment
Planning is looking ahead while controlling is looking back. However, the statement is only partially correct . Plans are prepared for future and are based on forecasts about future conditions. Therefore, planning involves looking ahead and is called a forward-looking function. On the contrary, controlling is like a postmortem of past activities to find out deviations from the standards. In that sense, controlling is a backward-looking function.
However, controlling is forward looking also because it does not end by comparing the past performance with the standards. It also involves finding the reason for deviation and suggest measures so that these deviations do not occur future. Planning is backward looking also in the sense that it is guided by the past experiences and the corrective actions initiated by the control functions. Thus, planning and controlling are both backward-looking as well as a forward-looking function.
Controlling Process
Controlling is a systematic process involving the following steps.
- Setting performance standards
- Measurement of actual performance
- Comparison of actual performance with standards
- Analysing deviations
- Taking corrective action
Step 1: Setting Performance Standards:
The first step in the controlling process is setting up of performance standards. Standards are the criteria against which actual performance would be measured. Standards can be set in both quantitative as well as qualitative terms. For instance, standards set in terms of cost to be incurred, revenue to be earned, product units to be produced and sold, time to be spent in performing a task, all represents quantitative standards. Sometimes standards may also be set in qualitative terms. Improving goodwill and motivation level of employees are examples of qualitative standards.
Step 2: Measurement of Actual Performance:
Once performance standards are set, the next step is measurement of actual performance. Performance should be measured in an objective and reliable manner. There are several techniques for measurement of performance. These include personal observation, sample checking, performance reports, etc.
Measurement of performance of an employee may require preparation of performance report by his superior. Measurement of a company’s performance may involve calculation of certain ratios like gross profit ratio, net profit ratio, return on investment, etc., at periodic intervals.
Step 3: Comparing Actual Performance with Standards:
This step involves comparison of actual performance with the standard. Such comparison will reveal the deviation between actual and desired results. Comparison becomes easier when standards are set in quantitative terms. For instance, performance of a worker in terms of units produced in a week can be easily measured against the standard output for the week.
Step 4: Analysing Deviations:
Some deviation in performance can be expected in all activities. It is, therefore, important to determine the acceptable range of deviations. All deviations need not be brought to the notice of top management. In this regards, manager should use Critical Point Control(CPC) and Management by Exception (MBE).
Critical Point control (CPC)
It is neither economical nor easy to keep a check on each and every activity in an organization. Control should therefore focus on Key Result Areas (KRS’s). Key areas are those which have impact on whole organisation. For example, in a manufacturing organization, an increase in of 10% in the labour cost may be more worrying than a 20% increase in postal charges.
Management by Exception (MBE)/ Control by Exception
It is one of the important principles of control. This principle implies that only major exceptions (deviations) from the established standard should be reported to the top management. This idea is based on the concept “an attempt to control everything results controlling nothing”. Manager should not waste his time and energy in finding solutions for minor deviations rather he should concentrate on removing deviations of high degree. Deviations within the acceptable range (i.e,minor deviations) are ignored.
For Example, if a garment factory establishes that defects in 100 garments, i.e, 5% defects permissible. If the defect is between 1 to 5%, it need not be reported to the management. If the defects are 6% or more than that it must be reported.
Step 5: Taking Corrective Action:
The final step in the controlling process is taking corrective action. No corrective action is required when the deviations are within acceptable limits. However, when the deviations go beyond the acceptable range, especially in the important areas, it demands immediate managerial attention so that deviations do not occur again and standards are accomplished.
Corrective action might involve:
- Training of employees if the production target could not be met.
- If an important project is running behind schedule, corrective action might involve assigning of additional workers and equipment to the project and permission for overtime work.
- In case the deviation cannot be corrected through managerial action, the standards may have to be revised.

Fig: Controlling process
Techniques of Managerial control
The various techniques of managerial control may be classified as into two broad categories:
Traditional Techniques
Modern techniques.
Traditional techniques are those techniques which have been used by the companies for a long time now. However, these techniques have not become obsolete and re still being used by companies. These include:
- Personal observation
- Statistical reports
- Breakeven analysis
- Budgetary control
Modern techniques of controlling are those which are of recent origin and are comparatively new in management literature. These techniques provide a refreshingly new thinking on the
ways in which various aspects of an organisation can be controlled. These include:
- Return on investment
- Ratio analysis
- Responsibility accounting
Management audit
Pert and cpm.
- Management information system
Personal Observation
This is the most traditional method of control. Personal observation enables the manager to collect firsthand information. It also creates a psychological pressure on the employees to perform well as they are aware that they are being observed personally on their job. However, it is a very time-consuming exercise and cannot effectively be used in all kinds of jobs.
Statistical Reports
Statistical analysis in the form of averages, percentages, ratios, correlation, etc., present useful information to the managers regarding performance of the organisation in various areas. Such information when presented in the form of charts, graphs, tables, etc., enables the managers to read them more easily and allow a comparison to be made with performance in previous periods and also with the benchmarks.
Breakeven Analysis
Breakeven analysis is a technique used by managers to study the relationship between costs, volume and profits. Breakeven point is a point where there is no profit no loss. The sales volume at which there is no profit, no loss is known as breakeven point. With the help of breakeven analysis technique manager can estimate profits at different levels of cost and revenue. Breakeven point is determined by the intersection of Total Revenue and Total Cost curves.

The figure shows that the firm will break even at 500 units of output. At this point, there is no profit no loss. It is beyond this point that the firm will start earning profits.
Breakeven point can be calculated with the help of the following formula:
=Fixed Cost/ Selling price per unit — Variable cost per unit
Advantages of breakeven analysis:.
- Breakeven analysis helps a firm to ascertain profits at different levels of sales.
- By separating fixed cost and variable cost it enables the management to exercise control over variable cost.
- It helps to determine the minimum sales volume at which costa are fully recovered beyond which profit can be earned.
Budgetary Control
Budget is a statement of expected results and expected cost expressed in numerical terms. It helps to know the future results and to achieve these results how much we will have to spend. In budgetary control technique the estimated results are compared with the actual results. The variation between the two indicates inefficiency.
Advantages of budgetary control:
- Budgeting focuses on specific and time-bound targets and thus, helps in attainment of organisational objectives.
- Budgeting is a source of motivation to the employees who know the standards against which their performance will be appraised and thus, enables them to perform better.
- Budgeting helps in optimum utilisation of resources by allocating them according to the requirements of different departments.
- It is used for achieving co-ordination among the different departments.For instance, sales budget cannot be prepared without knowing production programmes and schedules.
- It facilitates management by exception by stressing on those operations which deviate from budgeted standards in a significant way.
However, the effectiveness of budgeting depends on how accurately estimates have been made about future.
Return on Investment
Return on Investment (RoI) is a useful technique which provides the basic yardstick for measuring whether or not invested capital has been used effectively for generating reasonable amount of return. RoI can be used to measure overall performance of an organisation or of its individual departments or divisions. It can be calculated as under.
ROI =Net Income/Sales X Sales/Total Investment
Net Income before or after tax may be used for making comparisons. Total investment includes both working as well as fixed capital invested in business.
According to this technique, RoI can be increased either by increasing sales volume or by reducing total investment without having any reductions in sales volume.
Advantages of ROI to an organization:
- It indicates how effectively resources are being used.
- It focuses attention on profits and relates them to capital invested.
Ratio Analysis
Ratio Analysis refers to analysis of financial statements through computation of ratios. The most commonly used ratios used by organisations can be classified into the following categories:
- Liquidity Ratios: Liquidity ratios are calculated to determine short-term solvency of business. Analysis of current position of liquid funds determines the ability of the business to pay the amount due to its stakeholders.
- Solvency Ratios: Ratios which are calculated to determine the long-term solvency of business are known as solvency ratios. Thus, these ratios determine the ability of a business to service its obligation.
- Profitability Ratios: These ratios are calculated to analyse the profitability position of a business. Such ratios involve analysis of profits in relation to sales or funds or capital employed.
- Turnover Ratios: Turnover ratios are calculated to determine the efficiency of operations based on effective utilisation of resources. Higher turnover means better utilisation of resources.
Responsibility Accounting
Responsibility accounting is a system of accounting in which different sections, divisions and departments of an organisation are set up as ‘Responsibility Centres’. The head of the centre is responsible for achieving the target set for his centre. Responsibility centres may be of the following types:
Cost Centre
A cost center is a location or department within a company. The manager in charge of a cost cente is responsible for its costs but not directly responsible for revenues.
For example, in a manufacturing organisation, production department is classified as cost centre.
Revenue Centre:
A revenue centre is a segment of an organisation which is primarily responsible for generating revenue.
For example, marketing department of an organisation may be classified as a revenue center.
Profit Centre:
A profit centre is a segment of an organisation whose manager is responsible for both revenues and costs.
For example, repair and maintenance department of an organisation may be treated as a profit center if it is allowed to bill other production departments for the services provided to them.
Investment Centre:
An investment centre is responsible not only for profits but also for investments made in the centre in the form of assets. The investment made in each centre is separately ascertained and return on investment is used as a basis for judging the performance of the centre.
This control technique helps to measure the efficiency levels of managers. Management audit refers to systematic appraisal of the overall performance of the management of an organisation. The purpose is to review the efficiency and effectiveness of management and to improve its performance in future periods.
The main advantages of management audit are as follows.
- It helps to locate present and potential deficiencies in the performance of management functions.
- It helps to improve the control system of an organisation by continuously monitoring the performance of management.
- It improves coordination in the functioning of various departments so that they work together effectively towards the achievement of organisational objectives.
- It ensures updating of existing managerial policies and strategies in the light of environmental changes.
Limitations of Management Audit
- There is no standard techniques of management audit.
- Management audit is not compulsory under any law
PERT (Programme Evaluation and Review Technique) and CPM (Critical Path Method) are important network techniques useful in planning and controlling. These techniques are especially useful for planning, scheduling and implementing time bound projects involving performance of a variety of complex, diverse and interrelated activities. The main aim of PERT and CPM is to control the time spent on the completion of a project and the optimum allocation of resources within the cost limit. These techniques deal with time scheduling and
resource allocation for these activities and aims at effective execution of projects within given time schedule and structure of costs.
The steps involved in using PERT/ CPM are as follows:
- The total project is divided into a number of clearly identifiable activities which are then arranged in a logical sequence.
- A network diagram is prepared to show the sequence of activities, the starting point and the termination point of the project.
- Time estimates are prepared for each activity.
- The longest path in the network is identified as the critical path. It represents the sequence of those activities which are important for timely completion of the project and where no delays can be allowed without delaying the entire project.
- Modification of the plan, if necessary.
PERT and CPM are used extensively in areas like ship-building, construction projects, aircraft manu facture, etc.
Management Information System
Management Information System (MIS) is a computer-based information system that provides information and support for effective managerial decision-making. MIS also serves as an important control technique. It provides data and information to the managers at the right time so that appropriate corrective action may be taken in case of deviations from standards.
MIS offers the following advantages to the managers:
- It facilitates collection, management and dissemination of information at different levels of management and across different departments of the organisation.
- It supports planning, decision making and controlling at all levels.
- It improves the quality of information with which a manager works.
- It ensures cost effectiveness in managing information.
- It reduces information overload on the managers as only relevant information is provided to them.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE Class 12 Case Studies In Business Studies – Controlling
CONTROLLING Controlling: Definition Controlling means ensuring that activities in an organisation are performed as per the plans.
Importance of Controlling
- It helps in accomplishing organisational goals by constantly monitoring the performance of the employees and bringing to light the deviations, if any, and taking appropriate corrective action.
- It helps the business managers to judge the objectivity and accuracy of the standards.
- It seeks to make efficient use of resources.
- It seeks to motivate the employees and helps them in giving a better performance.
- It creates an atmosphere of order and discipline in the organisation.
- It facilitates coordination in action by providing direction to all activities within and among departments.
Features of Controlling
- It is a goal-oriented function.
- It is a pervasive function as it is used in the organisations of varying types and sizes.
- It is considered to be a forward looking function as it helps to improve the planning by providing valuable feedback for reviewing and revising the standards.
- It is considered to be a backward looking function as it is like the post mortem of the past activities to ascertain the deviations if any.
- It is not the last function of management as it brings the management cycle back to the planning function.
Steps Involved in the Controlling Process
- Setting performance standards in clear, specific and measurable terms.
- Measurement of actual performance as far as possible in the same units in which standards are set.
- Comparing actual performance with standards to identify deviations if any.
- Analysing deviations through critical point control and management by exception approaches to identify the causes for their occurrence.
- Taking corrective action whenever the deviation occurs beyond the permissible limits so that it does not reoccur in future.
Relationship between Planning and Controlling
- Planning without controlling is useless and controlling without planning is blind.
- Planning provides the basis of controlling by setting the standards in advance. In the absence of these standards, managers will not know what all activities have to be controlled.
- Planning is prescriptive in nature whereas, controlling is evaluative.
- Thus, planning and controlling are interrelated and interdependent. As planning is based on facts, it makes controlling easier and effective whereas controlling helps to improve future planning by providing valuable information derived from the past experiences.
LATEST CBSE QUESTIONS
Question 1. Hina Sweets is a renowned name for quality sweets since 1935. Harsh the owner of Hina Sweets was worried as the sales had declined during the last three months. When he enquired from the Sales Manager, the Sales Manager reported that there were some complaints about the quality of sweets. Therefore Harsh ordered for sample checking of sweets. Identify the step taken by Harsh that is related to one of the functions of management. (CBSE, Delhi 2017) Answer: Measurement of actual performance is the step in controlling process being described.
Question 2. State the steps in the process of controlling. (CBSE, Delhi 2017) Answer: The various steps involved in the controlling process are described below:
- Setting performance standards: The first step in the controlling process involves setting standards in clear, specific and measurable terms. Standards can be set in both quantitative as well as qualitative terms. It is important that standards should be flexible enough to be modified with the changes taking place in the internal and external business environment.
- Measurement of actual performance: The next step relates to the measurement of actual performance. Performance should be measured in an objective and reliable manner. As far as possible, performance should be measured in the same units in which standards are set as this would make their comparison easier. Depending upon the nature of work various techniques for measurement of performance like personal observation, sample checking, performance reports, etc. may be used.
- Comparison of actual performance with standards: This step involves comparison of actual performance with the standard. Such comparison will reveal the deviation and noting deviations if any. If the actual performance is more than planned performance deviations are said to be positive or vice-versa.
- Critical point control: All the deviations may not be significant. Moreover, it may not be either economical nor easy to monitor each and every activity in the organisation. Therefore, every organisation identifies and states its specific key result areas (KRAs) or critical points which require tight control are likely to have a significant effect on the working of the business. Any deviations on these points are attended to urgently by the management. Like if the expenditure on refreshment of workers goes up by 10% it can be ignored but if the production cost goes up by 5% it may call for managerial action.
- Management by exception: Management by exception is the principle of management control which is based on the belief that if you try to control everything, you may end up controlling nothing. Therefore, only significant deviations which go beyond the permissible limits should be brought to the notice of the management. Like the output defects upto 2% may be considered acceptable but if goes up by 5% it may call for managerial action.
- Taking corrective action: This is the final step involved in the controlling process. When the deviations are within acceptable limits no corrective action is required. However, when the deviations go beyond the acceptable range, especially in the important areas, it demands immediate managerial attention so that deviations do not occur again and standards are accomplished. Corrective action might involve training of employees, buying new machinery, increasing supervision and so on.
- Planning is based on facts and makes controlling process easier and adds to the effectiveness.
- Controlling also adds to the effectiveness of planning process by providing valuable feedback based on past experiences.
Question 4. State any five points that highlight the importance of ‘controlling’ function of management. (CBSE, Delhi 2017) Answer: The importance of controlling function of management is described below:
- Accomplishing organisational goals: The controlling function facilitates constant monitoring of the actual performance in comparison to the predetermined standards and brings to light the deviations, if any, and indicates corrective action. All these activities ensure that organisational goals are realised efficiently and effectively.
- Judging accuracy of standards: A good control system enables management to verify whether the standards set are accurate and objective. Moreover, helps to review and revise the standards in light of changes taking place in the organisation or business environment in general.
- Making efficient use of resources: By implementing a good control system a manager seeks to reduce wastage and spoilage of resources. This is because each activity is performed in accordance with predetermined standards and norms rather than hit and trial method.
- Improving employee motivation: An effective control system seeks to provide motivation to the employees as they are made aware well in advance what they are expected to do and what are the standards of performance on the basis of which they will be appraised. This approach helps them to give better performance.
- Ensuring order and discipline: A constant check on the behaviour and work of the employees leads to creation of an atmosphere of order and discipline in the organisation.
Question 5. How does controlling help in “Judging accuracy of standards” and “Ensuring order and discipline” ? (CBSE, Sample Paper, 2017) Answer: Controlling helps in “Judging accuracy of standards” and “Ensuring order and discipline” as explained below:
- Judging accuracy of standards: An efficient control system enables management to determine weather the standards set are accurate and objective. This is because it helps to helps to review and revise the standards in light the changes taking place in the organisation and in the environment.
- Ensuring order and discipline: Controlling helps to minimise dishonest behaviour on the part of the employees by keeping a close check on their activities. Thus, it creates an atmosphere of order and discipline in the organisation.
Question 6. ‘If anything goes wrong with the performance of key activities, the entire organisation suffers. Therefore, the organisation should focus on them.’ Explain the statement with a suitable example. (CBSE, Sample Paper 2015-16) Answer: The given statement refers to the importance of ‘Critical Point Control’ in order to ensure effective performance of key activities in an organisation. Critical Point Control: It may not be either economical nor easy to monitor each and every activity in the organisation. Therefore, every organisation identifies and states its specific Key Result Areas (KRAs) or critical points which require tight control and are likely to have a significant effect on the working of the business. Any deviations on these points are attended to urgently by the management. For example, if in an organisation, the expenditure on stationery goes up by 10%, it can be ignored but if the production cost goes up by 5%, it may call for managerial action.
Question 7. Mr. Nath, a recently appointed production manager of Suntech Ltd., has decided to produce jute bags instead of plastic bags as these are banned by the government. He set a target of producing 1000 jute bags a day. It was reported that the employees were not able to achieve the target. After analysis, he found that employees were demotivated and not putting in their best for achieving the target. Mr. Nath’s behaviour is good towards the employees. His attitude is always positive. So, he announced various incentive schemes for the employees like:
- Installing awards or certificates for best performance
- Rewarding an employee for giving valuable suggestions
- Identify the functions of management highlighted in the above paragraph.
- State the incentive under which the employee are motivated.
- State any two values which the production manager wants to communicate to society by his work and behaviour. (CBSE, Sample Paper 2015)
- The functions of management highlighted in the above paragraph are Controlling and Directing.
- The employees are motivated under Employee recognition programmes which is a non-financial incentive. Employee recognition programmes helps to fulfill the need of due consideration and appreciation of the people working in an organisation. It boosts their self-esteem and motivates them to work with greater zeal and enthusiasm.
- Respect for employees
- Concern for environment
Question 8. A company was manufacturing LED bulbs which were in great demand. It was found that the target of producing 300 bulbs a day was not met by the employees. On analysis, it was found that the workers were not at fault. Due to electricity failure and shortage of workers, the company was not able to achieve the set targets and alternative arrangements were needed. To meet the increased demand, the company assessed that approximately 88 additional workers were required out of which 8 would work as heads of different departments and 10 would work as subordinates under each head. The required qualifications and job specifications were also enlisted. It was also decided that necessary relaxations should be given to encourage women, people from backward and rural areas and people with special abilities to assume responsible positions in the organisations. All efforts were made to match the ability of the applicants with the nature of work.
- Identify the functions of management discussed above.
- State the two steps in the process of each function discussed in the above paragraph.
- List any two values which the company wants to communicate to the society. (CBSE, Delhi 2015)
- The functions of management discussed above are Staffing and Controlling.
- Estimating manpower requirements: The manpower requirements of an organisation are estimated through workload analysis and workforce analysis. The workload analysis helps to determine the number and type of human resource required in the organisation to meet its present and future needs. Whereas workforce analysis seeks to determine the number and type of human resource available within the organisation.
- Recruitment: The process of recruitment involves searching for the prospective candidates and stimulating them to apply for jobs in the organisation. There are two sources of recruitment namely, internal and external. The two steps involved in controlling function are as follows:
- Comparing actual performance with standards to identify deviations if any. “It was found that the target of producing 300 bulbs a day was not met by the employees.”
- Analysing deviations through critical point control and management by exception approach to identify the causes for their occurrence. “On analysis, it was found that the workers were not at fault. Due to electricity failure and shortage of workers, the company was not able to achieve the set targets and alternative arrangements were needed.”
- Taking corrective action, if required “To meet the increased demand, the company assessed that approximately … as subordinate under each head.”
- Women empowerment
Question 9. ‘AS Ltd.’ is a large company engaged in assembling of air-conditioners. Recently the company had conducted the ‘Time’ and ‘Motion’ study and concluded that on an average, a worker can assemble ten air-conditioners in a day. The target volume of the company in a day is assembling of 1,000 units of air-conditioners. The company is providing attractive allowances to reduce labour turnover and absenteeism. All the workers are happy. Even then the assembling of air-conditioners per day is 800 units only. To find out the reason, the company compared actual performance of each worker and observed through CCTV that some of the workers were busy in gossiping.
- Identify the function of management discussed above.
- State the steps in the process of the function identified which are discussed in the above paragraph. (CBSE, 2015)
- The function of management discussed above is Controlling.
- Setting standards of performance: “concluded that on an average, a worker can assemble ten air-conditioners in a day.” “The target volume of the company in a day is assembling of 1,000 units of air-conditioners.”
- Measurement of actual performance: ” Even then the assembling of air-conditioners per day is 800 units only.”
- Comparison of actual performance with the standards: The company compared actual performance of the workers with the planned performance and noted deviation of 200 units.
- Analysing deviations: “To find out the reason, the company compared the actual performance of each worker and observed through CCTV that some of the workers were busy in gossiping.”
Question 10. PQR Ltd. is engaged in manufacturing machine components. The target production is 200 units per day. The company had been successfully attaining this target until two months ago. Over the last two months, it has been observed that daily production varies between 150-170 units.
- Identify the management function to rectify the above situation.
- Briefly state the procedure to be followed so that the actual production may come up to the target production. (CBSE, Delhi 2010)
- The controlling function of management is needed to rectify the above situation.
- Providing training to workers if the workers are not well versed with the production process.
- Improving the work environment if it is not conducive to efficient working.
- Ensuring timely availability of the raw materials and other equipments if they are not made available on time.
- Replacing the machinery if it is defective or has become obsolete.
Question 11. Rajeev and Sanjeev are managers in the same organisation heading different units. While discussing about the functions of management, Rajeev says that ‘Planning is looking ahead whereas controlling is looking back.’ But Sanjeev says, ‘You are wrong because planning is looking back whereas controlling is looking ahead.’ Both are giving reasons in favour of their statements. Explain the possible reasons given by both and justify who is correct. (CBSE, 2009) Answer: Both Rajeev and Sanjeev are correct in their statements as explained below:
- Planning is considered as a forward looking function by Rajeev as plans are made for future.
- Planning may be considered as a backward looking function by Sanjeev because the quality of planning can be improved with the help of valuable information provided by controlling in terms of results achieved.
- Controlling is considered as a backward looking function by Rajeev as it is like the post mortem of the past activities to ascertain the deviations if any.
- Controlling is considered as a forward looking function by Sanjeev as it helps to improve the future performance by providing guidance for taking corrective action so that deviations do not reoccur in future.
Question 12. Kapil & Co. is a large manufacturing unit. Recently the company had conducted time and motion studies and concluded that on an average, a worker could produce 300 units per day. However, it has been noticed that the average daily production per worker is in the range of 200-225 units.
- Name the function of management and identify the steps in the process of this function which helped in finding out that the actual production of a worker is less than the set target.
- To complete the process of the function identified in (1) and to ensure the performance as per time and motion studies, explain what further steps a manager has to take? (CBSE, 2010)
- Setting performance standards in clear, specific and measurable terms. “Recently the company had conducted time and motion studies and concluded that on an average, a worker could produce 300 units per day.”
- Measurement of actual performance as far as possible in the same units in which standards are set. “It has been noticed that the average daily production per worker is in the range of 200-225 units”.
- Comparing actual performance with standards to identify deviations if any. In the given case there is a deviation in output in the range of 25-50 units per worker.
- The workers are not well versed with the production process.
- The working environment is not conducive to efficient working.
- The raw materials and other equipment are not available on time.
- Taking corrective action: The deviations require immediate management attention so that they do not reoccur in future. Therefore, the manager should take appropriate corrective action after analyzing the situation like providing training to workers, improving the work environment, and ensuring timely availability of the raw materials and other equipment.
Question 13. K&K Co. Ltd. is engaged in manufacturing of machine components. The target of production is 200 units daily. The company had been successfully attaining this target until two months ago. Over the last two months it has been observed that daily production varies between 150-170 units. Identify the possible causes for the decline in production and the steps to be taken to achieve the desire targets. (CBSE, 2008) Answer: The possible causes for decline in production are listed below:
- The machinery is defective or has become obsolete.
The deviations require immediate management attention so that- they do not reoccur in future. Therefore, the manager should take appropriate corrective action after analyzing the situation like providing training to workers, improving the work environment, ensuring timely availability of the raw materials and other equipment or replacing the machinery.
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS
Question 1. ‘Taste Buds Ltd.’ is a company known for manufacturing good quality confectionery products. The automated system of production ensures uniformity in production and quality maintenance. The quality assurance team conducts stringent checks at all stages, records and analyses the deviations and takes the necessary corrective actions right from the procurement of raw material to its processing, production and packaging. The company has a well-equipped in¬house quality inspection cell where confectionery products are tested on various parameters of quality by the team of experienced quality staff. In context of the above case:
- Identify and explain the function of management being performed by the quality assurance team of ‘Taste Buds Ltd.’
- Explain the statement, “records and analyses the deviations and takes the necessary corrective actions”.
- Controlling is the function of management being performed by the quality assurance team of ‘Taste Buds Ltd.’ Controlling is the process of ensuring that events conform to plans.
- Comparing the actual performance with the standards: The actual performance is compared with the standards and deviations, if any, are recorded.
- Critical point control: All the deviations may not be significant. Moreover, it may not be either economical nor easy to monitor each and every activity in the organisation. Therefore, every organisation identifies and states its specific key result areas (KRAs) or critical points which require tight control as they are likely to have a significant effect on the working of the business. Any deviations on these points are attended to urgently by the management. Like in the above case, if the expenditure on refreshment of workers goes up by 10% it can be ignored but if the production cost goes up by 5% it may call for managerial action.
- Management by exception: Management by exception is the principle of manage¬ment control which is based on the belief that if you try to control everything, you may end up controlling nothing. Therefore, only significant deviations which go beyond the permissible limits should be brought to the notice of the management. Like in the above case, the output defects upto 2% may be considered acceptable but if it goes up by 5%, it may cal for managerial action.
- Taking corrective action: The last step in controlling process involves taking corrective action whenever the deviation occurs beyond the permissible limits so that they do not reoccur in future. However, the standards may be revised if it is not possible to check deviations through corrective action.
Question 2. Anubhav has set up an export house after completing his masters in fashion designing. As the quality of the garment depends on the quality of raw material used, he assures that the fabric meets the requirements by conducting a series of tests for the fabrics like shrinkage test, testing colour fastness to washing, colour fastness to light, colour fastness to perspiration etc through laboratory tests. Later on, at the production areas, fabric inspection is also conducted by stopping the production process. The tests help to detect the deviations and also take corrective action. Moreover, he ensures that complete training about production work was given to every worker at the time of joining his export house. In context of the above case:
- Identify the function of management being performed by Anubhav by conducting tests to assure for the quality of the garments manufactured in his export house.
- Briefly explain the term ‘deviations.’
- Give any three advantages of giving training to the employees.
- Controlling is the function of management being performed by Anubhav by conducting tests to assure for the quality of the garments manufactured in his export house.
- The term ‘deviations’ refers to the difference between the actual performance and planned performance. If the actual performance is more than the planned performance, it may be said to be positive in nature or vice-versa.
- Training imparts systematic learning to the employees thereby helping to avoid wastage of efforts and money and is considered better than the hit and trial method.
- It increases the employees’ productivity both in terms of quantity and quality, leading to higher profits.
- Training increases the morale of the employees and reduces absenteeism and employee turnover.
Question 3. Raghav started a take away eating joint in a nearby market. His business was doing well. He ensured that the food was properly cooked, a standard taste was maintained, packing of food was done effectively and the orders were executed on time. But unfortunately he met with an accident and was advised three months bed rest. In his absence, his cousin Rohit took charge of his business. When he resumed his work after three months, he realised that his clientele had dropped. The people were not happy with the services as the quality of food had deteriorated and the delivery time for orders had increased considerably. All this was happening because most of his previous staff had left as Rohit used to adopt a very strict and authoritative approach towards them. In context of the above case:
- List any two aspects about his business that Raghav was controlling in order to make it successful.
- Explain briefly any two points to highlight the importance of the controlling function.
- Name and explain the style of leadership adopted by Rohit.
- A standard taste was maintained.
- The orders were executed on time.
- Judging accuracy of standards: The controlling function helps the business managers to judge the objectivity and accuracy of the current standards. It also assists in reviewing and revising the standards keeping in view the forthcoming changes in both the internal and external environment of the business.
- Improving employee motivation: The controlling function seeks to motivate the employees and helps them to give better performance. This is because it makes them aware well in advance about what they are expected to do and what the standards of performance are on the basis of which they will be judged.
- Rohit had adopted an autocratic style of leadership. An autocratic leader expects strict compliance from his subordinates with regard to the orders and instructions given by him. Therefore, it involves only one-way communication.
Question 4. ‘Saurashtra’ is a company involved in the export of indigenous food products like chutneys and pickles. It has tied up with the small farmers in various states for sourcing of fruits and vegetables. In this way it helps the small farmers to sell their produce at reasonable rates. The company follows a practice where only significant deviations from a budget or plan are brought to the attention of management. The degree of deviations allowed in different categories in the budget are well defined in advance, along with the appropriate levels of management who will respond to the deviations in question. For example, a deviation of Rs. 20,000 or more in purchase costs will be reported to the concerned department manager. In context of the above case:
- Identify the principle of management control adopted by the company. State the belief underlying this principle.
- List any two values that the company wants to communicate to the society.
- Management by exception is the principle of management control adopted by the company. It is based on the belief that ‘if you try to control everything, you may end up controlling nothing’.
- Rural development
- Sense of responsibility
Question 5. Shruti has established a small scale factory after completing a course in textile designing. She has tied up with the big home furnishing retail outlets in the city for supplying to them good quality designer home furnishing products like bed covers, cushions etc. She believes that controlling without planning is blind. So, every time she gets an order, she sets the standards in terms of the number of personnel required, the estimated requirements in man-hours per product, the requirements of direct materials for the projected production and the amount of normal overhead expenses required at the projected work-load. She also keeps a close watch on the activities so as to ensure that they conform to plans. Whenever the order size is too large, she hires extra workers by placing a notice on the notice-board of the factory specifying the details of the jobs available. In context of the above case:
- Identify the functions of management being performed by Shruti.
- Do you think Shruti is right in her thinking that, “controlling without planning is blind.” Explain by bringing out the relationship between planning and controlling.
- Name the source of recruitment adopted by Shruti. Also, mention its type.
- The functions of management being performed by Shruti are Controlling and Staffing.
- Yes, Shruti is right in thinking that, ” controlling without planning is blind.” Planning provides the basis of controlling by setting the standards in advance. In the absence of these standards, managers will not know what all activities have to be controlled. Planning is prescriptive in nature whereas controlling is evaluative. Thus, planning and controlling are interrelated and interdependent as planning is based on facts and makes controlling easier and effective whereas controlling helps to improve future planning by providing valuable information derived from the past experiences.
- The source of recruitment adopted by Shruti is Direct Recruitment. It is an external source of recruitment.
Question 6. Vishesh works as an interior designer. He gets a contract to redesign a play school. He employs three painters on the site assuming that an average painter will be able to paint 10 desks in a day. At the end of the first day of their work, Vishesh finds that the painter A, painter B and painter C have painted 12, 14 and 15 desks respectively. On comparing the actual performance with the planned performance, he realises that the standard set by him is too low. Consequently, he decides to review and revise the standard and raise it. In context of the above case:
- Identify the function of management being performed by Vishesh.
- “Planning and controlling are both backward looking as well as forward looking functions.” Explain the statement with reference to the above paragraph.
- Controlling is the function of management being performed by Vishesh.
- It is appropriate to say that, “Planning and controlling are both backward looking as well as forward looking functions” as evident from the above case. Planning is considered as a forward looking function as plans are made for future. “assuming that an average painter will be able to paint 10 desks in a day.” Planning may be considered as a backward looking function because the quality of planning can be improved with the help of valuable information provided by controlling in terms of results achieved. “On comparing the actual performance with the planned performance, he realises that the standard set by him is too low.” Controlling is considered as a backward looking function as it is like the post mortem of the past activities to ascertain the deviations if any. “At the end of the first day of their work, Vishesh finds that the painter A, painter B and painter C have painted 12, 14 and 15 desks respectively.” Controlling is considered as a forward looking function as it helps to improve the future performance by providing guidance for taking corrective action so that deviations do not reoccur in future. “Consequently, he decides to review and revise the standard and raise it.
Question 7. A critical point control (CPC) approach is followed by McDonald in the cooking and handling process so that any food safety threat can be prevented, eliminated, or reduced to an acceptable level. Hence, continuous monitoring of activities are undertaken to ensure that the process is right at each critical point control. The main principle followed for cooking at McDonald is “less amount many time” which can ensure the high quality and high fresh level of the food. For instance, if four hamburgers have to be made, a worker cannot cook all the four hamburgers at one time. The time figured out for making one hamburger is one hundred and forty-five seconds. Moreover, nearly all foods in the McDonald have the specific holding time, the holding time for hamburgers is ten minutes and for french fries is seven minutes. If it is not sold within that time it is thrown away. Also, the temperature of the milk sent by the supplier must be under 4° C, otherwise, it will be returned. In context of the above case:
- Name the steps involved in the controlling process which is being discussed in the above lines.
- What do you understand by ‘critical point control’? Explain.
- How does the controlling function of management help in accomplishing organisational .goals and ensure efficient use of resources?
- Analysing deviation and taking corrective action are being discussed in the above lines.
- Since it may neither be economical nor easy to monitor each and every activity in the organisation, therefore, every organisation identifies ar\d states its specific key result areas (KRAs) or critical points which require tight control are likely to have a significant effect on the working of the business. Any deviations on these points are attended to urgently by the management.
- Accomplishing organisational goals: The controlling function helps in accomplishing organisational goals by constantly monitoring the performance of the employees and bringing to light the deviations, if any, and taking appropriate corrective action.
- Making efficient use of resources: The controlling function enables the managers to work as per predetermined standards. This helps to avoid any ambiguity in business operations and reduce wastage and spoilage of resources in the organisation.
Case Studies in Business Studies Business Studies Case Studies Business Studies Commerce

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
BST Class 12 Case studies: You already know that as per new pattern , questions based on case study can be asked in exam .These type of questions are introduced to check students ability to understand and apply his/her knowledge to given situation . Do not fear the questions based on case study. If you are well prepared and have through understanding of chapter, those questions will not be ...
Part A & B: Principles and Functions of Management & Business Finance and Marketing. Business Studies Class 12 Chapter 1 Case Studies. Business Studies Class 12 Chapter 2 Case Studies. Business Studies Class 12 Chapter 3 Case Studies. Business Studies Class 12 Chapter 4 Case Studies. Business Studies Class 12 Chapter 5 Case Studies.
Class 12 Business Studies Controlling Notes and Questions. Q. 1. Babita Ltd. is engaged in manufacturing machine components. The target production is 250 units per day per worker. The company had been successfully attaining this target until two months ago. Over the last two months it has been observed that daily production varies between 200 ...
Students can download chapter 8 class 12 business studies notes for free from Vedantu. The notes are available in a pdf format. This format makes it easier for students to download the notes without any hassle. Download CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Revision Notes 2023-24 PDF. Also, check CBSE Class 12 Business studies revision notes for other ...
1. Explain the meaning of controlling. Ans: Controlling means ensuring that activities in an organisation are performed as per the plans. Controlling also ensures that an organisations resources are being used effectively and efficiently for the achievement of desired goals. Controlling is, thus a goal oriented function.
Very Short Questions NCERT Business Studies Solutions Class 12 Chapter 8. 1. Explain the meaning of controlling. Controlling is referred to as the process of evaluation of the work that is done. It is all about setting standards for the work and then comparing the actual work that is done with the standard. It ensures that all the activities in ...
This Class 12th Business Studies Chapter 8 has a weightage of 20 marks and is an important topic covered in exams. Basic questions keep repeating in the Board exams from this subject, for which preparing from this study material makes students score better.
on July 15, 2022, 3:17 AM. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 Controlling updated for new academic session 2024-25. Class 12 B St Solutions for chapter 8 are given in simplified format with MCQ, so that every child can understand it easily.
Class: Class 12: Subject: Business Studies: Chapter Number: Ch 8: Chapter Name: Controlling: Book Name: Business Studies Part II Business Finance and Marketing: Book By: NCERT (National Council of Educational Research and Training) Educational Resource Here: NCERT Solutions of Class 12 Business Studies Ch 8 for All Exercise: More Questions ...
12 Business Studies Paper Design. The exam is divided into 2 parts: Part A generally contains questions from Principles and Functions of Management and carries 60 marks. Part B comprises questions from Business Finance and Marketing, it carries a total of 40 marks. The syllabus of class 12 Business Studies comprises 12 chapters that are divided ...
CBSE CLASS 12 BUSINESS STUDIES CHAPTER -8 CONTROLLING REVISION NOTES. CONTROLLING. "Managerial Control implies the measurement of accomplishment against the standard and the correction of deviations to assure attainment of objectives according to plans.". Koontz and O' Donnel. MEANING.
1. Understand the Format: Case study questions are designed to test your ability to analyze and apply your knowledge to real-world situations. These questions are usually longer in length, but your answers should be concise and to the point. 2. Careful Reading: Begin by carefully reading the entire case study.
Business Studies Class 12 Revision Notes Chapter 8 Controlling. NCERT Solutions CBSE Sample Papers Business Studies Class 12 Business Studies. Points to Remember. 1. Controlling It can be defined as comparison of actual performance with the planned performance. According to Ricky W Griffin, "Controlling function leads to goal achievement, an organisation without effective control is not ...
Controlling Class 12 Revision Notes. In the controlling class 12 notes, we will begin by studying one of the important functions of a manager i.e. Controlling. We will study as to why Controlling is known as a goal-oriented function. Then, we will study the importance of Controlling. Also, we will study the limitation of Controlling.
By Tanisha Agarwal. Nov 1, 2023, 17:54 IST. Download PDF for CBSE Class 12 Chapter 8 Controlling Notes. Controlling Class 12 Notes: This article hands out CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 ...
Class 12 business studies Chapter 8 Controlling. Controlling is one of the important functions of management. Managerial functions start with planning and ends with controlling. Controlling means ensuring that activities in an organization are performed as per plans. The controlling function finds out how far actual performance deviates from ...
3. State any one situation in which an organisation's control system loses is effectiveness. A control system is bound to lose its effectiveness whenever the standards cannot be defined in quantitative terms thereby making it difficult to measure deviations happening between actual and standard performance. For example, job satisfaction cannot ...
Question 2. State the steps in the process of controlling. (CBSE, Delhi 2017) Answer: The various steps involved in the controlling process are described below: Setting performance standards: The first step in the controlling process involves setting standards in clear, specific and measurable terms. Standards can be set in both quantitative as ...
Get the MCQs with answers for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 - Controlling. At BYJU'S, students can download the study materials for free.
Management principles are the guidelines for decision-making and behaviour (in present as well as future) for the whole organisation. They are general, broad and flexible in nature. Techniques are sequential in nature, rigid and are like procedures. Scientific principles are rigid, have universal validity and are unchangeable in nature.
In this video you will learn the topic:Case Studies | Chapter-2 | Principles Of Management | Class-12 Business Studies We post video on daily basis related t...