An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Patient Cent Res Rev
- v.11(1); Spring 2024
- PMC11000705


Research Frameworks: Critical Components for Reporting Qualitative Health Care Research
Qualitative health care research can provide insights into health care practices that quantitative studies cannot. However, the potential of qualitative research to improve health care is undermined by reporting that does not explain or justify the research questions and design. The vital role of research frameworks for designing and conducting quality research is widely accepted, but despite many articles and books on the topic, confusion persists about what constitutes an adequate underpinning framework, what to call it, and how to use one. This editorial clarifies some of the terminology and reinforces why research frameworks are essential for good-quality reporting of all research, especially qualitative research.
Qualitative research provides valuable insights into health care interactions and decision-making processes – for example, why and how a clinician may ignore prevailing evidence and continue making clinical decisions the way they always have. 1 The perception of qualitative health care research has improved since a 2016 article by Greenhalgh et al. highlighted the higher contributions and citation rates of qualitative research than those of contemporaneous quantitative research. 2 The Greenhalgh et al. article was subsequently supported by an open letter from 76 senior academics spanning 11 countries to the editors of the British Medical Journal . 3 Despite greater recognition and acceptance, qualitative research continues to have an “uneasy relationship with theory,” 4 which contributes to poor reporting.
As an editor for the Journal of Patient-Centered Research and Reviews , as well as Human Resources for Health , I have seen several exemplary qualitative articles with clear and coherent reporting. On the other hand, I have often been concerned by a lack of rigorous reporting, which may reflect and reinforce the outdated perception of qualitative research as the “soft option.” 5 Qualitative research is more than conducting a few semi-structured interviews, transcribing the audio recordings verbatim, coding the transcripts, and developing and reporting themes, including a few quotes. Qualitative research that benefits health care is time-consuming and labor-intensive, requires robust design, and is rooted in theory, along with comprehensive reporting. 6
What Is “Theory”?
So fundamental is theory to qualitative research that I initially toyed with titling this editorial, “ Theory: the missing link in qualitative health care research articles ,” before deeming that focus too broad. As far back as 1967, Merton 6 warned that “the word theory threatens to become meaningless.” While it cannot be overstated that “atheoretical” studies lack the underlying logic that justifies researchers’ design choices, the word theory is so overused that it is difficult to understand what constitutes an adequate theoretical foundation and what to call it.
Theory, as used in the term theoretical foundation , refers to the existing body of knowledge. 7 , 8 The existing body of knowledge consists of more than formal theories , with their explanatory and predictive characteristics, so theory implies more than just theories . Box 1 9 – 12 defines the “building blocks of formal theories.” 9 Theorizing or theory-building starts with concepts at the most concrete, experiential level, becoming progressively more abstract until a higher-level theory is developed that explains the relationships between the building blocks. 9 Grand theories are broad, representing the most abstract level of theorizing. Middle-range and explanatory theories are progressively less abstract, more specific to particular phenomena or cases (middle-range) or variables (explanatory), and testable.
The Building Blocks of Formal Theories 9
The importance of research frameworks.
Researchers may draw on several elements to frame their research. Generally, a framework is regarded as “a set of ideas that you use when you are forming your decisions and judgements” 13 or “a system of rules, ideas, or beliefs that is used to plan or decide something.” 14 Research frameworks may consist of a single formal theory or part thereof, any combination of several theories or relevant constructs from different theories, models (as simplified representations of formal theories), concepts from the literature and researchers’ experiences.
Although Merriam 15 was of the view that every study has a framework, whether explicit or not, there are advantages to using an explicit framework. Research frameworks map “the territory being investigated,” 8 thus helping researchers to be explicit about what informed their research design, from developing research questions and choosing appropriate methods to data analysis and interpretation. Using a framework makes research findings more meaningful 12 and promotes generalizability by situating the study and interpreting data in more general terms than the study itself. 16
Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks
The variation in how the terms theoretical and conceptual frameworks are used may be confusing. Some researchers refer to only theoretical frameworks 17 , 18 or conceptual frameworks, 19 – 21 while others use the terms interchangeably. 7 Other researchers distinguish between the two. For example, Miles, Huberman & Saldana 8 see theoretical frameworks as based on formal theories and conceptual frameworks derived inductively from locally relevant concepts and variables, although they may include theoretical aspects. Conversely, some researchers believe that theoretical frameworks include formal theories and concepts. 18 Others argue that any differences between the two types of frameworks are semantic and, instead, emphasize using a research framework to provide coherence across the research questions, methods and interpretation of the results, irrespective of what that framework is called.
Like Ravitch and Riggan, 22 I regard conceptual frameworks (CFs) as the broader term. Including researchers’ perspectives and experiences in CFs provides valuable sources of originality. Novel perspectives guard against research repeating what has already been stated. 23 The term theoretical framework (TF) may be appropriate where formal published and identifiable theories or parts of such theories are used. 24 However, existing formal theories alone may not provide the current state of relevant concepts essential to understanding the motivation for and logic underlying a study. Some researchers may argue that relevant concepts may be covered in the literature review, but what is the point of literature reviews and prior findings unless authors connect them to the research questions and design? Indeed, Sutton & Straw 25 exclude literature reviews and lists of prior findings as an adequate foundation for a study, along with individual lists of variables or constructs (even when the constructs are defined), predictions or hypotheses, and diagrams that do not propose relationships. One or more of these aspects could be used in a research framework (eg, in a TF), and the literature review could (and should) focus on the theories or parts of theories (constructs), offer some critique of the theory and point out how they intend to use the theory. This would be more meaningful than merely describing the theory as the “background” to the study, without explicitly stating why and how it is being used. Similarly, a CF may include a discussion of the theories being used (basically, a TF) and a literature review of the current understanding of any relevant concepts that are not regarded as formal theory.
It may be helpful for authors to specify whether they are using a theoretical or a conceptual framework, but more importantly, authors should make explicit how they constructed and used their research framework. Some studies start with research frameworks of one type and end up with another type, 8 , 22 underscoring the need for authors to clarify the type of framework used and how it informed their research. Accepting the sheer complexity surrounding research frameworks and lamenting the difficulty of reducing the confusion around these terms, Box 2 26 – 31 and Box 3 offer examples highlighting the fundamental elements of theoretical and conceptual frameworks while acknowledging that they share a common purpose.
Examples of How Theoretical Frameworks May Be Used
Examples of how conceptual frameworks may be used, misconceptions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research’s “uneasy relationship with theory” 4 may be due to several misconceptions. One possible misconception is that qualitative research aims to build theory and thus does not need theoretical grounding. The reality is that all qualitative research methods, not just Grounded Theory studies focused on theory building, may lead to theory construction. 16 Similarly, all types of qualitative research, including Grounded Theory studies, should be guided by research frameworks. 16
Not using a research framework may also be due to misconceptions that qualitative research aims to understand people’s perspectives and experiences without examining them from a particular theoretical perspective or that theoretical foundations may influence researchers’ interpretations of participants’ meanings. In fact, in the same way that participants’ meanings vary, qualitative researchers’ interpretations (as opposed to descriptions) of participants’ meaning-making will differ. 32 , 33 Research frameworks thus provide a frame of reference for “making sense of the data.” 34
Studies informed by well-defined research frameworks can make a world of difference in alleviating misconceptions. Good qualitative reporting requires research frameworks that make explicit the combination of relevant theories, theoretical constructs and concepts that will permeate every aspect of the research. Irrespective of the term used, research frameworks are critical components of reporting not only qualitative but also all types of research.
Acknowledgments
In memory of Martie Sanders: supervisor, mentor, and colleague. My deepest gratitude for your unfailing support and guidance. I feel your loss.
Conflicts of Interest: None.
Use of theoretical and conceptual frameworks in qualitative research
Affiliation.
- 1 University of Leeds, UK.
- PMID: 25059086
- DOI: 10.7748/nr.21.6.34.e1252
Aim: To debate the definition and use of theoretical and conceptual frameworks in qualitative research.
Background: There is a paucity of literature to help the novice researcher to understand what theoretical and conceptual frameworks are and how they should be used. This paper acknowledges the interchangeable usage of these terms and researchers' confusion about the differences between the two. It discusses how researchers have used theoretical and conceptual frameworks and the notion of conceptual models. Detail is given about how one researcher incorporated a conceptual framework throughout a research project, the purpose for doing so and how this led to a resultant conceptual model.
Review methods: Concepts from Abbott (1988) and Witz ( 1992 ) were used to provide a framework for research involving two case study sites. The framework was used to determine research questions and give direction to interviews and discussions to focus the research.
Discussion: Some research methods do not overtly use a theoretical framework or conceptual framework in their design, but this is implicit and underpins the method design, for example in grounded theory. Other qualitative methods use one or the other to frame the design of a research project or to explain the outcomes. An example is given of how a conceptual framework was used throughout a research project.
Conclusion: Theoretical and conceptual frameworks are terms that are regularly used in research but rarely explained. Textbooks should discuss what they are and how they can be used, so novice researchers understand how they can help with research design.
Implications for practice/research: Theoretical and conceptual frameworks need to be more clearly understood by researchers and correct terminology used to ensure clarity for novice researchers.
Keywords: Theoretical framework; case study; case study research.; conceptual framework; conceptual model; qualitative research; research design.
- Nursing Research / organization & administration*
- Qualitative Research*
- Research Design

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
- Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Introduction
Revisiting theoretical frameworks
Revisiting conceptual frameworks, differences between conceptual and theoretical frameworks, examples of theoretical and conceptual frameworks, developing frameworks for your study.
- Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Case studies
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Theoretical and conceptual frameworks are both essential components of research, guiding and structuring the research. Although they are closely related, the conceptual and theoretical framework in any research project serve distinct purposes and have different characteristics. In this section, we provide an overview of the key differences between theoretical and conceptual frameworks.

Theoretical and conceptual frameworks are foundational components of any research study. They each play a crucial role in guiding and structuring the research, from the formation of research questions to the interpretation of results .
While both the theoretical and conceptual framework provides a structure for a study, they serve different functions and can impact the research in distinct ways depending on how they are combined. These differences might seem subtle, but they can significantly impact your research design and outcomes, which is why it is important to think through each one of them.

The theoretical framework describes the broader lens through which the researcher views the topic and guides their overall understanding and approach. It connects the theoretical perspective to the data collection and data analysis strategy and offers a structure for organizing and interpreting the collected data.
On the other hand, the conceptual framework describes in detail and connects specific concepts and variables to illustrate potential relationships between them. It serves as a guide for assessing which aspects of the data are relevant and specifying how the research question is being answered. While the theoretical framework outlines how more abstract-level theories shape the study, the conceptual framework operationalizes the empirical observations that can be connected to theory and broader understanding.
Understanding these differences is crucial when designing and conducting your research study. In this chapter, we will look deeper at the distinctions between these types of frameworks, and how they interplay in qualitative research . We aim to provide you with a solid understanding of both, allowing you to effectively utilize them in your own research.
Theoretical frameworks play a central role in research, serving as the bedrock of any investigation. This section offers a refresher on the essential elements and functions of theoretical frameworks in research.
A theoretical framework refers to existing theory, concepts, and definitions that you use to collect relevant data and offer meaningful empirical findings. Providing an overall orientation or lens, it guides your understanding of the research problem and directs your approach to data collection and analysis .
Your chosen theoretical framework directly influences your research questions and methodological choices . It contains specific theories or sets of assumptions drawn from relevant disciplines—such as sociology, psychology, or economics—that you apply to understand your research topic. These existing models and concepts are tools to help you organize and make sense of your data.
The theoretical framework also plays a key role in crafting your research questions and objectives. By determining the theories that are relevant to your research, the theoretical framework shapes the nature and direction of your study. It's essential to note, however, that the theoretical framework's role in qualitative research is not to predict outcomes. Instead, it offers a broader structure to understand and interpret your data, enabling you to situate your findings within the broader academic discourse in a way that makes your research findings meaningful to you and your research audience.
Conceptual frameworks , though related to theoretical frameworks , serve distinct functions within research. This section reexamines the characteristics and functions of conceptual frameworks to provide a better understanding of their roles in qualitative research .
A conceptual framework, in essence, is a system of concepts, assumptions, and beliefs that supports and informs your research. It outlines the specific variables or concepts you'll examine in your study and proposes relationships between them. It's more detailed and specific than a theoretical framework, acting as a contextualized guide for the collection and interpretation of empirical data.
The main role of a conceptual framework is to illustrate the presumed relationships between the variables or concepts you're investigating. These variables or concepts, which you derive from your theoretical framework, are integral to your research questions , objectives, and hypotheses . The conceptual framework shows how you theorize these concepts are related, providing a visual or narrative model of your research.

A study's own conceptual framework plays a vital role in guiding the data collection process and the subsequent analysis . The conceptual framework specifies which data you need to collect and provides a structure for interpreting and making sense of the collected data. For instance, if your conceptual framework identifies a particular variable as impacting another, your data collection and analysis will be geared towards investigating this relationship.
Rigorous research starts with ATLAS.ti
Turn your data into insights easily and efficiently with our intuitive software. Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti.
Though interconnected, theoretical and conceptual frameworks have distinct roles in research and contribute differently to the research. This section will contrast the two in terms of scope, purpose, their role in the research process, and their relationship to the data analysis strategy and research question .
Scope and purpose of theoretical and conceptual frameworks
Theoretical and conceptual frameworks differ fundamentally in their scope. Theoretical frameworks provide a broad and general view of the research problem, rooted in established theories. They explain phenomena by applying a particular theoretical lens. Conceptual frameworks, on the other hand, offer a more focused view of the specific research problem. They explicitly outline the concrete concepts and variables involved in the study and the relationships between them.
While both frameworks guide the research process, they do so in different ways. Theoretical frameworks guide the overall approach to understanding the research problem by indicating the broader conversation the researcher is contributing to and shaping the research questions.
Conceptual frameworks provide a map for the study, guiding the data collection and interpretation process, including what variables or concepts to explore and how to analyze them.
Study design and data analysis
The two types of frameworks relate differently to the research question and design. The theoretical framework often inspires the research question based on previous theories' predictions or understanding about the phenomena under investigation. A conceptual framework then emerges from the research question, providing a contextualized structure for what exactly the research will explore.
Theoretical and conceptual frameworks also play distinct roles in data analysis. Theoretical frameworks provide the lens for interpreting the data, informing what kinds of themes and patterns might be relevant. Conceptual frameworks, however, present the variables concepts and variables and the relationships among them that will be analyzed. Conceptual frameworks may illustrate concepts and relationships based on previous theory, but they can also include novel concepts or relationships that stem from the particular context being studied.
Finally, the two types of frameworks relate differently to the research question and design. The theoretical framework basically differs from the conceptual framework in that it often inspires the research question based on the theories' predictions about the phenomena under investigation. A conceptual framework, on the other hand, emerges from the research question, providing a structure for investigating it.
Using case studies , we can effectively demonstrate the differences between theoretical and conceptual frameworks. Let’s take a look at some real-world examples that highlight the unique role and function of each framework within a research context.
Consider a study exploring the impact of classroom environments on student learning outcomes. The theoretical framework might be grounded in Piaget's theory of cognitive development, which offers a broad lens for understanding how students learn and process information.
Within this theoretical framework, the researcher formulates the conceptual framework. The conceptual framework identifies specific variables to study such as classroom layout, teacher-student ratio, availability of learning materials, and student performance as the dependent variable. It then outlines the expected relationships between these variables, such as proposing that a lower teacher-student ratio and well-equipped classrooms positively impact student performance.

Another study might aim to understand the factors influencing the job satisfaction of employees in a corporate setting. The theoretical framework could be based on Maslow's hierarchy of needs, interpreting job satisfaction in terms of fulfilling employees' physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization needs.
From this theoretical perspective, the researcher constructs the conceptual framework, identifying specific variables such as salary (physiological needs), job security (safety needs), teamwork (social needs), recognition (esteem needs), and career development opportunities (self-actualization needs). The conceptual framework proposes relationships among these variables and job satisfaction, such as higher salaries and more recognition being related to higher job satisfaction.

After understanding the unique roles and functions of these types of frameworks, you might ask: How do I develop them for my study? It's essential to remember that it's not a question of choosing one over the other, as both frameworks can and often do coexist within the same research project.
The choice of a theoretical and a conceptual framework often depends on the nature of your research question . If your research question is more exploratory and requires a broad understanding of the problem, a theoretical framework can provide a useful lens for interpretation. However, your conceptual framework may end up looking rather different to previous theory as you collect data and discover new concepts or relationships.
Consider the nature of your research problem as well. If you are studying a well-researched problem and there are established theories about it, using a theoretical framework to interpret your findings in light of these theories might be beneficial. But if your study explores a novel problem or aims to understand specific processes or relationships, developing a conceptual framework that maps these specific elements could prove more effective.

Your research methodology could also inform your choice. If your study is more interpretive and aims to understand people's experiences and perceptions, a theoretical framework can outline broader concepts that are relevant to approaching your study. Your conceptual framework can then shed light on the specific concepts that emerged in your data. By carefully thinking through your theoretical and conceptual frameworks, you can effectively utilize both types of frameworks in your research, ensuring a solid foundation for your study.
Turn data into theory with ATLAS.ti
Use our software for every stage of your research project. Trya free trial of ATLAS.ti today.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 4: Theoretical frameworks for qualitative research
Tess Tsindos
Learning outcomes
Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to:
- Describe qualitative frameworks.
- Explain why frameworks are used in qualitative research.
- Identify various frameworks used in qualitative research.
What is a Framework?
A framework is a set of broad concepts or principles used to guide research. As described by Varpio and colleagues 1 , a framework is a logically developed and connected set of concepts and premises – developed from one or more theories – that a researcher uses as a scaffold for their study. The researcher must define any concepts and theories that will provide the grounding for the research and link them through logical connections, and must relate these concepts to the study that is being carried out. In using a particular theory to guide their study, the researcher needs to ensure that the theoretical framework is reflected in the work in which they are engaged.
It is important to acknowledge that the terms ‘theories’ ( see Chapter 3 ), ‘frameworks’ and ‘paradigms’ are sometimes used interchangeably. However, there are differences between these concepts. To complicate matters further, theoretical frameworks and conceptual frameworks are also used. In addition, quantitative and qualitative researchers usually start from different standpoints in terms of theories and frameworks.
A diagram by Varpio and colleagues demonstrates the similarities and differences between theories and frameworks, and how they influence research approaches. 1(p991) The diagram displays the objectivist or deductive approach to research on the left-hand side. Note how the conceptual framework is first finalised before any research is commenced, and it involves the articulation of hypotheses that are to be tested using the data collected. This is often referred to as a top-down approach and/or a general (theory or framework) to a specific (data) approach.
The diagram displays the subjectivist or inductive approach to research on the right-hand side. Note how data is collected first, and through data analysis, a tentative framework is proposed. The framework is then firmed up as new insights are gained from the data analysis. This is referred to as a specific (data) to general (theory and framework) approach .
Why d o w e u se f rameworks?
A framework helps guide the questions used to elicit your data collection. A framework is not prescriptive, but it needs to be suitable for the research question(s), setting and participants. Therefore, the researcher might use different frameworks to guide different research studies.
A framework informs the study’s recruitment and sampling, and informs, guides or structures how data is collected and analysed. For example, a framework concerned with health systems will assist the researcher to analyse the data in a certain way, while a framework concerned with psychological development will have very different ways of approaching the analysis of data. This is due to the differences underpinning the concepts and premises concerned with investigating health systems, compared to the study of psychological development. The framework adopted also guides emerging interpretations of the data and helps in comparing and contrasting data across participants, cases and studies.
Some examples of foundational frameworks used to guide qualitative research in health services and public health:
- The Behaviour Change Wheel 2
- Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) 3
- Theoretical framework of acceptability 4
- Normalization Process Theory 5
- Candidacy Framework 6
- Aboriginal social determinants of health 7(p8)
- Social determinants of health 8
- Social model of health 9,10
- Systems theory 11
- Biopsychosocial model 12
- Discipline-specific models
- Disease-specific frameworks
E xamples of f rameworks
In Table 4.1, citations of published papers are included to demonstrate how the particular framework helps to ‘frame’ the research question and the interpretation of results.
Table 4.1. Frameworks and references
As discussed in Chapter 3, qualitative research is not an absolute science. While not all research may need a framework or theory (particularly descriptive studies, outlined in Chapter 5), the use of a framework or theory can help to position the research questions, research processes and conclusions and implications within the relevant research paradigm. Theories and frameworks also help to bring to focus areas of the research problem that may not have been considered.
- Varpio L, Paradis E, Uijtdehaage S, Young M. The distinctions between theory, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework. Acad Med . 2020;95(7):989-994. doi:10.1097/ACM.0000000000003075
- Michie S, van Stralen MM, West R. The behaviour change wheel: a new method for characterising and designing behaviour change interventions. Implement Sci . 2011;6:42. doi:10.1186/1748-5908-6-42
- CFIR Research Team. Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR). Center for Clinical Management Research. 2023. Accessed February 15, 2023. https://cfirguide.org/
- Sekhon M, Cartwright M, Francis JJ. Acceptability of healthcare interventions: an overview of reviews and development of a theoretical framework. BMC Health Serv Res . 2017;17:88. doi:10.1186/s12913-017-2031-8
- Murray E, Treweek S, Pope C, et al. Normalisation process theory: a framework for developing, evaluating and implementing complex interventions. BMC Med . 2010;8:63. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-8-63
- Tookey S, Renzi C, Waller J, von Wagner C, Whitaker KL. Using the candidacy framework to understand how doctor-patient interactions influence perceived eligibility to seek help for cancer alarm symptoms: a qualitative interview study. BMC Health Serv Res . 2018;18(1):937. doi:10.1186/s12913-018-3730-5
- Lyon P. Aboriginal Health in Aboriginal Hands: Community-Controlled Comprehensive Primary Health Care @ Central Australian Aboriginal Congress; 2016. Accessed February 15, 2023. https://nacchocommunique.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/cphc-congress-final-report.pdf
- Solar O., Irwin A. A Conceptual Framework for Action on the Social Determinants of Health: Social Determinants of Health Discussion Paper 2 (Policy and Practice); 2010. Accessed February 22, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241500852
- Yuill C, Crinson I, Duncan E. Key Concepts in Health Studies . SAGE Publications; 2010.
- Germov J. Imagining health problems as social issues. In: Germov J, ed. Second Opinion: An Introduction to Health Sociology . Oxford University Press; 2014.
- Laszlo A, Krippner S. Systems theories: their origins, foundations, and development. In: Jordan JS, ed. Advances in Psychology . Science Direct; 1998:47-74.
- Engel GL. From biomedical to biopsychosocial: being scientific in the human domain. Psychosomatics . 1997;38(6):521-528. doi:10.1016/S0033-3182(97)71396-3
- Schmidtke KA, Drinkwater KG. A cross-sectional survey assessing the influence of theoretically informed behavioural factors on hand hygiene across seven countries during the COVID-19 pandemic. BMC Public Health . 2021;21:1432. doi:10.1186/s12889-021-11491-4
- Graham-Wisener L, Nelson A, Byrne A, et al. Understanding public attitudes to death talk and advance care planning in Northern Ireland using health behaviour change theory: a qualitative study. BMC Public Health . 2022;22:906. doi:10.1186/s12889-022-13319-1
- Walker R, Quong S, Olivier P, Wu L, Xie J, Boyle J. Empowerment for behaviour change through social connections: a qualitative exploration of women’s preferences in preconception health promotion in the state of Victoria, Australia. BMC Public Health . 2022;22:1642. doi:10.1186/s12889-022-14028-5
- Ayton DR, Barker AL, Morello RT, et al. Barriers and enablers to the implementation of the 6-PACK falls prevention program: a pre-implementation study in hospitals participating in a cluster randomised controlled trial. PLOS ONE . 2017;12(2):e0171932. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0171932
- Pratt R, Xiong S, Kmiecik A, et al. The implementation of a smoking cessation and alcohol abstinence intervention for people experiencing homelessness. BMC Public Health . 2022;22:1260. doi:10.1186/s12889-022-13563-5
- Bossert J, Mahler C, Boltenhagen U, et al. Protocol for the process evaluation of a counselling intervention designed to educate cancer patients on complementary and integrative health care and promote interprofessional collaboration in this area (the CCC-Integrativ study). PLOS ONE . 2022;17(5):e0268091. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0268091
- Lwin KS, Bhandari AKC, Nguyen PT, et al. Factors influencing implementation of health-promoting interventions at workplaces: protocol for a scoping review. PLOS ONE . 2022;17(10):e0275887. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0275887
- Wilhelm AK, Schwedhelm M, Bigelow M, et al. Evaluation of a school-based participatory intervention to improve school environments using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research. BMC Public Health . 2021;21:1615. doi:10.1186/s12889-021-11644-5
- Timm L, Annerstedt KS, Ahlgren JÁ, et al. Application of the Theoretical Framework of Acceptability to assess a telephone-facilitated health coaching intervention for the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes. PLOS ONE . 2022;17(10):e0275576. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0275576
- Laing L, Salema N-E, Jeffries M, et al. Understanding factors that could influence patient acceptability of the use of the PINCER intervention in primary care: a qualitative exploration using the Theoretical Framework of Acceptability. PLOS ONE . 2022;17(10):e0275633. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0275633
- Renko E, Knittle K, Palsola M, Lintunen T, Hankonen N. Acceptability, reach and implementation of a training to enhance teachers’ skills in physical activity promotion. BMC Public Health . 2020;20:1568. doi:10.1186/s12889-020-09653-x
- Alexander SM, Agaba A, Campbell JI, et al. A qualitative study of the acceptability of remote electronic bednet use monitoring in Uganda. BMC Public Health . 2022;22:1010. doi:10.1186/s12889-022-13393
- May C, Rapley T, Mair FS, et al. Normalization Process Theory On-line Users’ Manual, Toolkit and NoMAD instrument. 2015. Accessed February 15, 2023. https://normalization-process-theory.northumbria.ac.uk/
- Davis S. Ready for prime time? Using Normalization Process Theory to evaluate implementation success of personal health records designed for decision making. Front Digit Health . 2020;2:575951. doi:10.3389/fdgth.2020.575951
- Durand M-A, Lamouroux A, Redmond NM, et al. Impact of a health literacy intervention combining general practitioner training and a consumer facing intervention to improve colorectal cancer screening in underserved areas: protocol for a multicentric cluster randomized controlled trial. BMC Public Health . 2021;21:1684. doi:10.1186/s12889-021-11565
- Jones SE, Hamilton S, Bell R, Araújo-Soares V, White M. Acceptability of a cessation intervention for pregnant smokers: a qualitative study guided by Normalization Process Theory. BMC Public Health . 2020;20:1512. doi:10.1186/s12889-020-09608-2
- Ziegler E, Valaitis R, Yost J, Carter N, Risdon C. “Primary care is primary care”: use of Normalization Process Theory to explore the implementation of primary care services for transgender individuals in Ontario. PLOS ONE . 2019;14(4):e0215873. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0215873
- Mackenzie M, Conway E, Hastings A, Munro M, O’Donnell C. Is ‘candidacy’ a useful concept for understanding journeys through public services? A critical interpretive literature synthesis. Soc Policy Adm . 2013;47(7):806-825. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9515.2012.00864.x
- Adeagbo O, Herbst C, Blandford A, et al. Exploring people’s candidacy for mobile health–supported HIV testing and care services in rural KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa: qualitative study. J Med Internet Res . 2019;21(11):e15681. doi:10.2196/15681
- Mackenzie M, Turner F, Platt S, et al. What is the ‘problem’ that outreach work seeks to address and how might it be tackled? Seeking theory in a primary health prevention programme. BMC Health Serv Res . 2011;11:350. doi:10.1186/1472-6963-11-350
- Liberati E, Richards N, Parker J, et al. Qualitative study of candidacy and access to secondary mental health services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Soc Sci Med. 2022;296:114711. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2022.114711
- Pearson O, Schwartzkopff K, Dawson A, et al. Aboriginal community controlled health organisations address health equity through action on the social determinants of health of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples in Australia. BMC Public Health . 2020;20:1859. doi:10.1186/s12889-020-09943-4
- Freeman T, Baum F, Lawless A, et al. Revisiting the ability of Australian primary healthcare services to respond to health inequity. Aust J Prim Health . 2016;22(4):332-338. doi:10.1071/PY14180
- Couzos S. Towards a National Primary Health Care Strategy: Fulfilling Aboriginal Peoples Aspirations to Close the Gap . National Aboriginal Community Controlled Health Organisation. 2009. Accessed February 15, 2023. https://researchonline.jcu.edu.au/35080/
- Napier AD, Ancarno C, Butler B, et al. Culture and health. Lancet . 2014;384(9954):1607-1639. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61603-2
- WHO. COVID-19 and the Social Determinants of Health and Health Equity: Evidence Brief . 2021. Accessed February 15, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240038387
- WHO. Social Determinants of Health . 2023. Accessed February 15, 2023. https://www.who.int/health-topics/social-determinants-of-health#tab=tab_1
- McCrae JS, Robinson JAL, Spain AK, Byers K, Axelrod JL. The Mitigating Toxic Stress study design: approaches to developmental evaluation of pediatric health care innovations addressing social determinants of health and toxic stress. BMC Health Serv Res . 2021;21:71. doi:10.1186/s12913-021-06057-4
- Hosseinpoor AR, Stewart Williams J, Jann B, et al. Social determinants of sex differences in disability among older adults: a multi-country decomposition analysis using the World Health Survey. Int J Equity Health . 2012;11:52. doi:10.1186/1475-9276-11-52
- Kabore A, Afriyie-Gyawu E, Awua J, et al. Social ecological factors affecting substance abuse in Ghana (West Africa) using photovoice. Pan Afr Med J . 2019;34:214. doi:10.11604/pamj.2019.34.214.12851
- Bíró É, Vincze F, Mátyás G, Kósa K. Recursive path model for health literacy: the effect of social support and geographical residence. Front Public Health . 2021;9. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.724995
- Yuan B, Zhang T, Li J. Family support and transport cost: understanding health service among older people from the perspective of social-ecological model. Arch Public Health . 2022;80:173. doi:10.1186/s13690-022-00923-1
- Mahmoodi Z, Karimlou M, Sajjadi H, Dejman M, Vameghi M, Dolatian M. A communicative model of mothers’ lifestyles during pregnancy with low birth weight based on social determinants of health: a path analysis. Oman Med J . 2017 ;32(4):306-314. doi:10.5001/omj.2017.59
- Vella SA, Schweickle MJ, Sutcliffe J, Liddelow C, Swann C. A systems theory of mental health in recreational sport. Int J Environ Res Public Health . 2022;19(21):14244. doi:10.3390/ijerph192114244
- Henning S. The wellness of airline cabin attendants: A systems theory perspective. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure . 2015;4(1):1-11. Accessed February 15, 2023. http://www.ajhtl.com/archive.html
- Sutphin ST, McDonough S, Schrenkel A. The role of formal theory in social work research: formalizing family systems theory. Adv Soc Work . 2013;14(2):501-517. doi:10.18060/7942
- Colla R, Williams P, Oades LG, Camacho-Morles J. “A new hope” for positive psychology: a dynamic systems reconceptualization of hope theory. Front Psychol . 2022;13. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2022.809053
- Engel GL. The need for a new medical model: a challenge for biomedicine. Science. 1977;196(4286):129–136. doi:10.1126/science.847460
- Wade DT, HalliganPW. The biopsychosocial model of illness: a model whose time has come. Clin Rehabi l. 2017;31(8):995–1004. doi:10.1177/0269215517709890
- Ip L, Smith A, Papachristou I, Tolani E. 3 Dimensions for Long Term Conditions – creating a sustainable bio-psycho-social approach to healthcare. J Integr Care . 2019;19(4):5. doi:10.5334/ijic.s3005
- FrameWorks Institute. A Matter of Life and Death: Explaining the Wider Determinants of Health in the UK . FrameWorks Institute; 2022. Accessed February 15, 2023. https://www.frameworksinstitute.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/FWI-30-uk-health-brief-v3a.pdf
- Zemed A, Nigussie Chala K, Azeze Eriku G, Yalew Aschalew A. Health-related quality of life and associated factors among patients with stroke at tertiary level hospitals in Ethiopia. PLOS ONE . 2021;16(3):e0248481. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0248481
- Finch E, Foster M, Cruwys T, et al. Meeting unmet needs following minor stroke: the SUN randomised controlled trial protocol. BMC Health Serv Res . 2019;19:894. doi:10.1186/s12913-019-4746-1
Qualitative Research – a practical guide for health and social care researchers and practitioners Copyright © 2023 by Tess Tsindos is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Cancer Nursing Practice
- Emergency Nurse
- Evidence-Based Nursing
- Learning Disability Practice
- Mental Health Practice
- Nurse Researcher
- Nursing Children and Young People
- Nursing Management
- Nursing Older People
- Nursing Standard
- Primary Health Care
- RCN Nursing Awards
- Nursing Live
- Nursing Careers and Job Fairs
- CPD webinars on-demand
- --> Advanced -->

- Clinical articles
- Expert advice
- Career advice
- Revalidation
Methodology Previous Next
Use of theoretical and conceptual frameworks in qualitative research, helen elise green director of student education, university of leeds, uk.
Aim To debate the definition and use of theoretical and conceptual frameworks in qualitative research.
Background There is a paucity of literature to help the novice researcher to understand what theoretical and conceptual frameworks are and how they should be used. This paper acknowledges the interchangeable usage of these terms and researchers’ confusion about the differences between the two. It discusses how researchers have used theoretical and conceptual frameworks and the notion of conceptual models. Detail is given about how one researcher incorporated a conceptual framework throughout a research project, the purpose for doing so and how this led to a resultant conceptual model.
Review methods Concepts from Abbott ( 1988 ) and Witz ( 1992 ) were used to provide a framework for research involving two case study sites. The framework was used to determine research questions and give direction to interviews and discussions to focus the research.
Discussion Some research methods do not overtly use a theoretical framework or conceptual framework in their design, but this is implicit and underpins the method design, for example in grounded theory. Other qualitative methods use one or the other to frame the design of a research project or to explain the outcomes. An example is given of how a conceptual framework was used throughout a research project.
Conclusion Theoretical and conceptual frameworks are terms that are regularly used in research but rarely explained. Textbooks should discuss what they are and how they can be used, so novice researchers understand how they can help with research design.
Implications for practice/research Theoretical and conceptual frameworks need to be more clearly understood by researchers and correct terminology used to ensure clarity for novice researchers.
Nurse Researcher . 21, 6, 34-38. doi: 10.7748/nr.21.6.34.e1252
This article has been subject to double blind peer review
None declared
Received: 22 May 2013
Accepted: 28 August 2013
Theoretical framework - conceptual framework - case study - conceptual model - qualitative research - research design - case study research.
User not found
Want to read more?
Already have access log in, 3-month trial offer for £5.25/month.
- Unlimited access to all 10 RCNi Journals
- RCNi Learning featuring over 175 modules to easily earn CPD time
- NMC-compliant RCNi Revalidation Portfolio to stay on track with your progress
- Personalised newsletters tailored to your interests
- A customisable dashboard with over 200 topics
Alternatively, you can purchase access to this article for the next seven days. Buy now
Are you a student? Our student subscription has content especially for you. Find out more

25 July 2014 / Vol 21 issue 6
TABLE OF CONTENTS
DIGITAL EDITION
- LATEST ISSUE
- SIGN UP FOR E-ALERT
- WRITE FOR US
- PERMISSIONS
Share article: Use of theoretical and conceptual frameworks in qualitative research
We use cookies on this site to enhance your user experience.
By clicking any link on this page you are giving your consent for us to set cookies.

Research Process Guide
- Step 1 - Identifying and Developing a Topic
- Step 2 - Narrowing Your Topic
- Step 3 - Developing Research Questions
- Step 4 - Conducting a Literature Review
- Step 5 - Choosing a Conceptual or Theoretical Framework
- Step 6 - Determining Research Methodology
- Step 6a - Determining Research Methodology - Quantitative Research Methods
- Step 6b - Determining Research Methodology - Qualitative Design
- Step 7 - Considering Ethical Issues in Research with Human Subjects - Institutional Review Board (IRB)
- Step 8 - Collecting Data
- Step 9 - Analyzing Data
- Step 10 - Interpreting Results
- Step 11 - Writing Up Results
Step 5: Choosing a Conceptual or Theoretical Framework
For all empirical research, you must choose a conceptual or theoretical framework to “frame” or “ground” your study. Theoretical and/or conceptual frameworks are often difficult to understand and challenging to choose which is the right one (s) for your research objective (Hatch, 2002). Truthfully, it is difficult to get a real understanding of what these frameworks are and how you are supposed to find what works for your study. The discussion of your framework is addressed in your Chapter 1, the introduction and then is further explored through in-depth discussion in your Chapter 2 literature review.
“Theory is supposed to help researchers of any persuasion clarify what they are up to and to help them to explain to others what they are up to” (Walcott, 1995, p. 189, as cited in Fallon, 2016). It is important to discuss in the beginning to help researchers “clarify what they are up to” and important at the writing stage to “help explain to others what they are up to” (Fallon, 2016).
What is the difference between the conceptual and the theoretical framework?
Often, the terms theoretical framework and conceptual framework are used interchangeably, which, in this author’s opinion, makes an already difficult to understand idea even more confusing. According to Imenda (2014) and Mensah et al. (2020), there is a very distinct difference between conceptual and theoretical frameworks, not only how they are defined but also, how and when they are used in empirical research.
Imenda (2014) contends that the framework “is the soul of every research project” (p.185). Essentially, it determines how the researcher formulates the research problem, goes about investigating the problem, and what meaning or significance the research lends to the data collected and analyzed investigating the problem.
Very generally, you would use a theoretical framework if you were conducting deductive research as you test a theory or theories. “A theoretical framework comprises the theories expressed by experts in the field into which you plan to research, which you draw upon to provide a theoretical coat hanger for your data analysis and interpretation of results” (Kivunja, 2018, p.45 ). Often this framework is based on established theories like, the Set Theory, evolution, the theory of matter or similar pre-existing generalizations like Newton’s law of motion (Imenda, 2014). A good theoretical framework should be linked to, and possibly emerge from your literature review.
Using a theoretical framework allows you to (Kivunja, 2018):
- Increase the credibility and validity of your research
- Interpret meaning found in data collection
- Evaluate solutions for solving your research problem
According to Mensah et al.(2020) the theoretical framework for your research is not a summary of your own thoughts about your research. Rather, it is a compilation of the thoughts of giants in your field, as they relate to your proposed research, as you understand those theories, and how you will use those theories to understand the data collected.
Additionally, Jabareen (2009) defines a conceptual framework as interlinked concepts that together provide a comprehensive understanding of a phenomenon. “A conceptual framework is the total, logical orientation and associations of anything and everything that forms the underlying thinking, structures, plans and practices and implementation of your entire research project” (Kivunja, 2018, p. 45). You would largely use a conceptual framework when conducting inductive research, as it helps the researcher answer questions that are core to qualitative research, such as the nature of reality, the way things are and how things really work in a real world (Guba & Lincoln, 1994).
Some consideration of the following questions can help define your conceptual framework (Kinvunja, 2018):
- What do you want to do in your research? And why do you want to do it?
- How do you plan to do it?
- What meaning will you make of the data?
- Which worldview will you situate your study in? (i.e. Positivist? Interpretist? Constructivist?)
Examples of conceptual frameworks include the definitions a sociologist uses to describe a culture and the types of data an economist considers when evaluating a country’s industry. The conceptual framework consists of the ideas that are used to define research and evaluate data. Conceptual frameworks are often laid out at the beginning of a paper or an experiment description for a reader to understand the methods used (Mensah et al., 2020).
Writing it up
After choosing your framework is to articulate the theory or concept that grounds your study by defining it and demonstrating the rationale for this particular set of theories or concepts guiding your inquiry. Write up your theoretical perspective sections for your research plan following your choice of worldview/ research paradigm. For a quantitative study you are particularly interested in theory using the procedures for a causal analysis. For qualitative research, you should locate qualitative journal articles that use a priori theory (knowledge that is acquired not through experience) that is modified during the process of research (Creswell & Creswell, 2018). Also, you should generate or develop a theory at the end of your study. For a mixed methods study which uses a transformative (critical theoretical lens) identify how the lens specifically shapes the research process.
Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2 018). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Sage.
Fallon, M. (2016). Writing up quantitative research in the social and behavioral sciences. Sense. https://kean.idm.oclc.org/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&AuthType=cookie,ip,url,cpid&custid=keaninf&db=nlebk&AN=1288374&site=ehost-live&scope=site&ebv=EB&ppid=pp_C1
Guba, E. G., & Lincoln, Y. S. (1994). Competing paradigms in qualitative research. Handbook of Qualitative Research, 2 (163-194), 105.
Hatch, J. A. ( 2002). Doing qualitative research in education settings. SUNY Press.
Imenda, S. (2014). Is there a conceptual difference between theoretical and conceptual frameworks? Journal of Social Sciences, 38 (2), 185-195.
Jabareen, Y. (2009). Building a conceptual framework: Philosophy, definitions, and procedure. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 8 (4), 49-62.
Kivunja, C. ( 2018, December 3). Distinguishing between theory, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework. The International Journal of Higher Education, 7 (6), 44-53. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1198682.pdf
Mensah, R. O., Agyemang, F., Acquah, A., Babah, P. A., & Dontoh, J. (2020). Discourses on conceptual and theoretical frameworks in research: Meaning and implications for researchers. Journal of African Interdisciplinary Studies, 4 (5), 53-64.
- Last Updated: Jun 29, 2023 1:35 PM
- URL: https://libguides.kean.edu/ResearchProcessGuide

- Section 1: Home
- Narrowing Your Topic
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
Defining The Conceptual Framework
Making a conceptual framework, conceptual framework for dmft students, conceptual framework guide, example frameworks, additional framework resources.
- Student Experience Feedback Buttons
- Avoiding Common Mistakes
- Synthesis and Analysis in Writing Support This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Quantitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative & Quantitative Research Support with the ASC This link opens in a new window
- Library Research Consultations This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: Research Process This link opens in a new window
- ASC Guide: Outlining and Annotating This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: Organizing Research & Citations This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: RefWorks This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: Copyright Information This link opens in a new window
What is it?
- The researcher’s understanding/hypothesis/exploration of either an existing framework/model or how existing concepts come together to inform a particular problem. Shows the reader how different elements come together to facilitate research and a clear understanding of results.
- Informs the research questions/methodology (problem statement drives framework drives RQs drives methodology)
- A tool (linked concepts) to help facilitate the understanding of the relationship among concepts or variables in relation to the real-world. Each concept is linked to frame the project in question.
- Falls inside of a larger theoretical framework (theoretical framework = explains the why and how of a particular phenomenon within a particular body of literature).
- Can be a graphic or a narrative – but should always be explained and cited
- Can be made up of theories and concepts
What does it do?
- Explains or predicts the way key concepts/variables will come together to inform the problem/phenomenon
- Gives the study direction/parameters
- Helps the researcher organize ideas and clarify concepts
- Introduces your research and how it will advance your field of practice. A conceptual framework should include concepts applicable to the field of study. These can be in the field or neighboring fields – as long as important details are captured and the framework is relevant to the problem. (alignment)
What should be in it?
- Variables, concepts, theories, and/or parts of other existing frameworks

How to make a conceptual framework
- With a topic in mind, go to the body of literature and start identifying the key concepts used by other studies. Figure out what’s been done by other researchers, and what needs to be done (either find a specific call to action outlined in the literature or make sure your proposed problem has yet to be studied in your specific setting). Use what you find needs to be done to either support a pre-identified problem or craft a general problem for study. Only rely on scholarly sources for this part of your research.
- Begin to pull out variables, concepts, theories, and existing frameworks explained in the relevant literature.
- If you’re building a framework, start thinking about how some of those variables, concepts, theories, and facets of existing frameworks come together to shape your problem. The problem could be a situational condition that requires a scholar-practitioner approach, the result of a practical need, or an opportunity to further an applicational study, project, or research. Remember, if the answer to your specific problem exists, you don’t need to conduct the study.
- The actionable research you’d like to conduct will help shape what you include in your framework. Sketch the flow of your Applied Doctoral Project from start to finish and decide which variables are truly the best fit for your research.
- Create a graphic representation of your framework (this part is optional, but often helps readers understand the flow of your research) Even if you do a graphic, first write out how the variables could influence your Applied Doctoral Project and introduce your methodology. Remember to use APA formatting in separating the sections of your framework to create a clear understanding of the framework for your reader.
- As you move through your study, you may need to revise your framework.
- Note for qualitative/quantitative research: If doing qualitative, make sure your framework doesn’t include arrow lines, which could imply causal or correlational linkages.
- Conceptural and Theoretical Framework for DMFT Students This document is specific to DMFT students working on a conceptual or theoretical framework for their applied project.
- Conceptual Framework Guide Use this guide to determine the guiding framework for your applied dissertation research.
Let’s say I’ve just taken a job as manager of a failing restaurant. Throughout the first week, I notice the few customers they have are leaving unsatisfied. I need to figure out why and turn the establishment into a thriving restaurant. I get permission from the owner to do a study to figure out exactly what we need to do to raise levels of customer satisfaction. Since I have a specific problem and want to make sure my research produces valid results, I go to the literature to find out what others are finding about customer satisfaction in the food service industry. This particular restaurant is vegan focused – and my search of the literature doesn’t say anything specific about how to increase customer service in a vegan atmosphere, so I know this research needs to be done.
I find out there are different types of satisfaction across other genres of the food service industry, and the one I’m interested in is cumulative customer satisfaction. I then decide based on what I’m seeing in the literature that my definition of customer satisfaction is the way perception, evaluation, and psychological reaction to perception and evaluation of both tangible and intangible elements of the dining experience come together to inform customer expectations. Essentially, customer expectations inform customer satisfaction.
I then find across the literature many variables could be significant in determining customer satisfaction. Because the following keep appearing, they are the ones I choose to include in my framework: price, service, branding (branched out to include physical environment and promotion), and taste. I also learn by reading the literature, satisfaction can vary between genders – so I want to make sure to also collect demographic information in my survey. Gender, age, profession, and number of children are a few demographic variables I understand would be helpful to include based on my extensive literature review.
Note: this is a quantitative study. I’m including all variables in this study, and the variables I am testing are my independent variables. Here I’m working to see how each of the independent variables influences (or not) my dependent variable, customer satisfaction. If you are interested in qualitative study, read on for an example of how to make the same framework qualitative in nature.
Also note: when you create your framework, you’ll need to cite each facet of your framework. Tell the reader where you got everything you’re including. Not only is it in compliance with APA formatting, but also it raises your credibility as a researcher. Once you’ve built the narrative around your framework, you may also want to create a visual for your reader.
See below for one example of how to illustrate your framework:

If you’re interested in a qualitative study, be sure to omit arrows and other notations inferring statistical analysis. The only time it would be inappropriate to include a framework in qualitative study is in a grounded theory study, which is not something you’ll do in an applied doctoral study.
A visual example of a qualitative framework is below:

Some additional helpful resources in constructing a conceptual framework for study:
- Problem Statement, Conceptual Framework, and Research Question. McGaghie, W. C.; Bordage, G.; and J. A. Shea (2001). Problem Statement, Conceptual Framework, and Research Question. Retrieved on January 5, 2015 from http://goo.gl/qLIUFg
- Building a Conceptual Framework: Philosophy, Definitions, and Procedure
- https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/conceptual-framework/
- https://www.projectguru.in/developing-conceptual-framework-in-a-research-paper/
Conceptual Framework Research
A conceptual framework is a synthetization of interrelated components and variables which help in solving a real-world problem. It is the final lens used for viewing the deductive resolution of an identified issue (Imenda, 2014). The development of a conceptual framework begins with a deductive assumption that a problem exists, and the application of processes, procedures, functional approach, models, or theory may be used for problem resolution (Zackoff et al., 2019). The application of theory in traditional theoretical research is to understand, explain, and predict phenomena (Swanson, 2013). In applied research the application of theory in problem solving focuses on how theory in conjunction with practice (applied action) and procedures (functional approach) frames vision, thinking, and action towards problem resolution. The inclusion of theory in a conceptual framework is not focused on validation or devaluation of applied theories. A concise way of viewing the conceptual framework is a list of understood fact-based conditions that presents the researcher’s prescribed thinking for solving the identified problem. These conditions provide a methodological rationale of interrelated ideas and approaches for beginning, executing, and defining the outcome of problem resolution efforts (Leshem & Trafford, 2007).
The term conceptual framework and theoretical framework are often and erroneously used interchangeably (Grant & Osanloo, 2014). Just as with traditional research, a theory does not or cannot be expected to explain all phenomenal conditions, a conceptual framework is not a random identification of disparate ideas meant to incase a problem. Instead it is a means of identifying and constructing for the researcher and reader alike an epistemological mindset and a functional worldview approach to the identified problem.
Grant, C., & Osanloo, A. (2014). Understanding, Selecting, and Integrating a Theoretical Framework in Dissertation Research: Creating the Blueprint for Your “House. ” Administrative Issues Journal: Connecting Education, Practice, and Research, 4(2), 12–26
Imenda, S. (2014). Is There a Conceptual Difference between Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks? Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi/Journal of Social Sciences, 38(2), 185.
Leshem, S., & Trafford, V. (2007). Overlooking the conceptual framework. Innovations in Education & Teaching International, 44(1), 93–105. https://doi-org.proxy1.ncu.edu/10.1080/14703290601081407
Swanson, R. (2013). Theory building in applied disciplines . San Francisco: Berrett-Koehler Publishers.
Zackoff, M. W., Real, F. J., Klein, M. D., Abramson, E. L., Li, S.-T. T., & Gusic, M. E. (2019). Enhancing Educational Scholarship Through Conceptual Frameworks: A Challenge and Roadmap for Medical Educators . Academic Pediatrics, 19(2), 135–141. https://doi-org.proxy1.ncu.edu/10.1016/j.acap.2018.08.003
Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Alignment
- Next: Avoiding Common Mistakes >>
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2024 2:48 PM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/c.php?g=1013602

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information
Theoretical vs Conceptual Framework
What they are & how they’re different (with examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | March 2023
If you’re new to academic research, sooner or later you’re bound to run into the terms theoretical framework and conceptual framework . These are closely related but distinctly different things (despite some people using them interchangeably) and it’s important to understand what each means. In this post, we’ll unpack both theoretical and conceptual frameworks in plain language along with practical examples , so that you can approach your research with confidence.
Overview: Theoretical vs Conceptual
What is a theoretical framework, example of a theoretical framework, what is a conceptual framework, example of a conceptual framework.
- Theoretical vs conceptual: which one should I use?
A theoretical framework (also sometimes referred to as a foundation of theory) is essentially a set of concepts, definitions, and propositions that together form a structured, comprehensive view of a specific phenomenon.
In other words, a theoretical framework is a collection of existing theories, models and frameworks that provides a foundation of core knowledge – a “lay of the land”, so to speak, from which you can build a research study. For this reason, it’s usually presented fairly early within the literature review section of a dissertation, thesis or research paper .

Let’s look at an example to make the theoretical framework a little more tangible.
If your research aims involve understanding what factors contributed toward people trusting investment brokers, you’d need to first lay down some theory so that it’s crystal clear what exactly you mean by this. For example, you would need to define what you mean by “trust”, as there are many potential definitions of this concept. The same would be true for any other constructs or variables of interest.
You’d also need to identify what existing theories have to say in relation to your research aim. In this case, you could discuss some of the key literature in relation to organisational trust. A quick search on Google Scholar using some well-considered keywords generally provides a good starting point.
Typically, you’ll present your theoretical framework in written form , although sometimes it will make sense to utilise some visuals to show how different theories relate to each other. Your theoretical framework may revolve around just one major theory , or it could comprise a collection of different interrelated theories and models. In some cases, there will be a lot to cover and in some cases, not. Regardless of size, the theoretical framework is a critical ingredient in any study.
Simply put, the theoretical framework is the core foundation of theory that you’ll build your research upon. As we’ve mentioned many times on the blog, good research is developed by standing on the shoulders of giants . It’s extremely unlikely that your research topic will be completely novel and that there’ll be absolutely no existing theory that relates to it. If that’s the case, the most likely explanation is that you just haven’t reviewed enough literature yet! So, make sure that you take the time to review and digest the seminal sources.
Need a helping hand?
A conceptual framework is typically a visual representation (although it can also be written out) of the expected relationships and connections between various concepts, constructs or variables. In other words, a conceptual framework visualises how the researcher views and organises the various concepts and variables within their study. This is typically based on aspects drawn from the theoretical framework, so there is a relationship between the two.
Quite commonly, conceptual frameworks are used to visualise the potential causal relationships and pathways that the researcher expects to find, based on their understanding of both the theoretical literature and the existing empirical research . Therefore, the conceptual framework is often used to develop research questions and hypotheses .
Let’s look at an example of a conceptual framework to make it a little more tangible. You’ll notice that in this specific conceptual framework, the hypotheses are integrated into the visual, helping to connect the rest of the document to the framework.
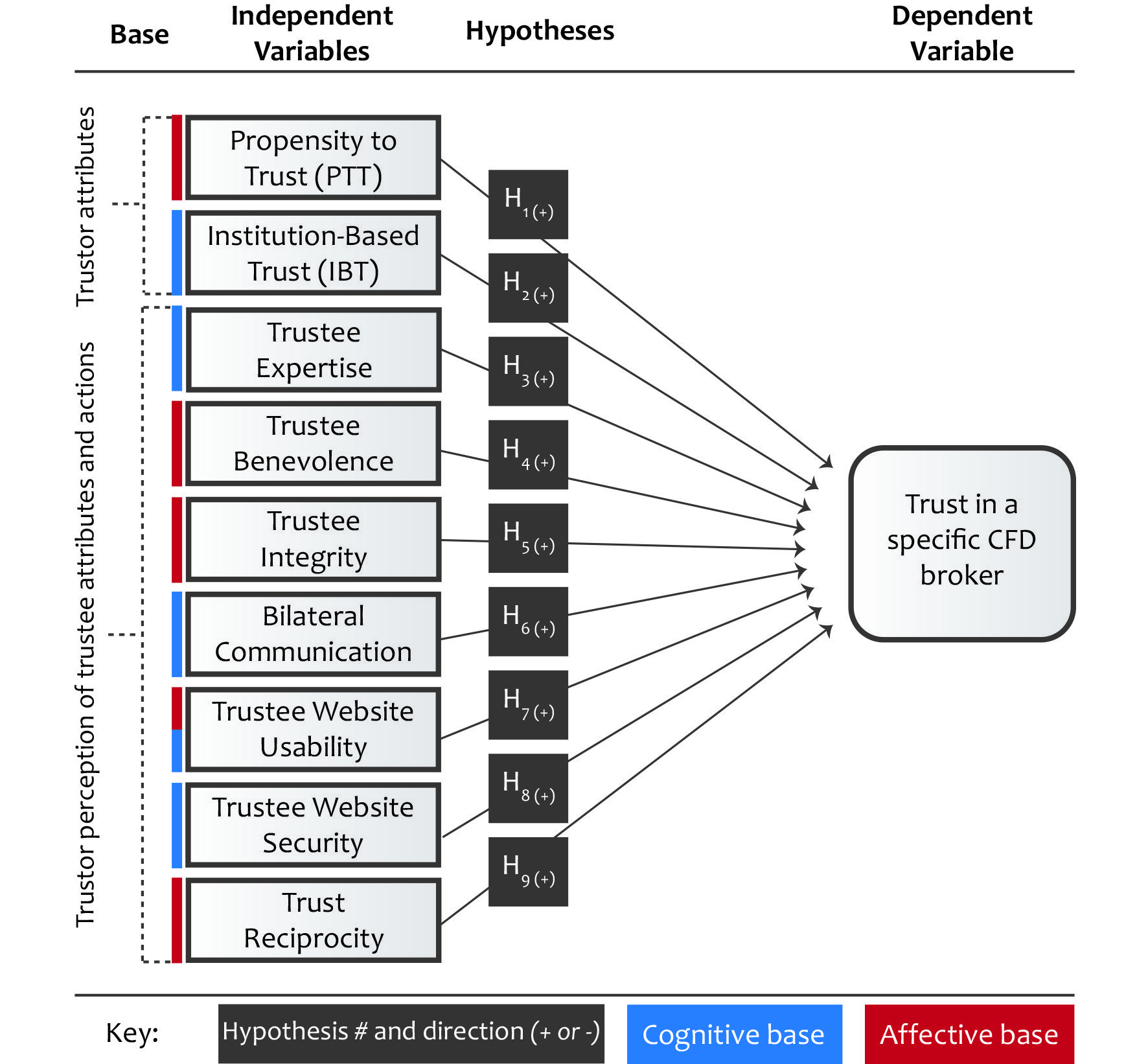
As you can see, conceptual frameworks often make use of different shapes , lines and arrows to visualise the connections and relationships between different components and/or variables. Ultimately, the conceptual framework provides an opportunity for you to make explicit your understanding of how everything is connected . So, be sure to make use of all the visual aids you can – clean design, well-considered colours and concise text are your friends.
Theoretical framework vs conceptual framework
As you can see, the theoretical framework and the conceptual framework are closely related concepts, but they differ in terms of focus and purpose. The theoretical framework is used to lay down a foundation of theory on which your study will be built, whereas the conceptual framework visualises what you anticipate the relationships between concepts, constructs and variables may be, based on your understanding of the existing literature and the specific context and focus of your research. In other words, they’re different tools for different jobs , but they’re neighbours in the toolbox.
Naturally, the theoretical framework and the conceptual framework are not mutually exclusive . In fact, it’s quite likely that you’ll include both in your dissertation or thesis, especially if your research aims involve investigating relationships between variables. Of course, every research project is different and universities differ in terms of their expectations for dissertations and theses, so it’s always a good idea to have a look at past projects to get a feel for what the norms and expectations are at your specific institution.
Want to learn more about research terminology, methods and techniques? Be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach blog . Alternatively, if you’re looking for hands-on help, have a look at our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research process, step by step.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
20 Comments
Thank you for giving a valuable lesson
good thanks!
VERY INSIGHTFUL
thanks for given very interested understand about both theoritical and conceptual framework
I am researching teacher beliefs about inclusive education but not using a theoretical framework just conceptual frame using teacher beliefs, inclusive education and inclusive practices as my concepts
good, fantastic
great! thanks for the clarification. I am planning to use both for my implementation evaluation of EmONC service at primary health care facility level. its theoretical foundation rooted from the principles of implementation science.
This is a good one…now have a better understanding of Theoretical and Conceptual frameworks. Highly grateful
Very educating and fantastic,good to be part of you guys,I appreciate your enlightened concern.
Thanks for shedding light on these two t opics. Much clearer in my head now.
Simple and clear!
The differences between the two topics was well explained, thank you very much!
Thank you great insight
Superb. Thank you so much.
Hello Gradcoach! I’m excited with your fantastic educational videos which mainly focused on all over research process. I’m a student, I kindly ask and need your support. So, if it’s possible please send me the PDF format of all topic provided here, I put my email below, thank you!
I am really grateful I found this website. This is very helpful for an MPA student like myself.
I’m clear with these two terminologies now. Useful information. I appreciate it. Thank you
I’m well inform about these two concepts in research. Thanks
I found this really helpful. It is well explained. Thank you.
very clear and useful. information important at start of research!!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Dr Deborah Gabriel
Using Conceptual Frameworks in Qualitative Research
I previously delivered this presentation to final year undergraduate students about to embark on their dissertation projects – but developed this guide while undertaking my PhD.
You May Also Like

How to write a literature review
Whether you are writing a 2000-word literature review for an undergraduate dissertation or something closer to 10,000-words for a PhD thesis, the process is the same.
I recently delivered this presentation to final year undergraduate students about to embark on their dissertation projects.

Qualitative data analysis
The most important task that you will undertake in your PhD research project is the analysis of data. The integrity and rigour of your research is utterly dependent on getting the analysis right and it will be intensely scrutinised by the external examiners.
29 thoughts on “ Using Conceptual Frameworks in Qualitative Research ”
I only wish I knew as much as you in this area. You have made it very easy to follow and understand. I am starting a project, but just don't know how to get started…very frustrating. You are truely blessed with your gift.
Dear Dawn, my ‘gift’ is my passion for research that contributes to social change, and while research can be complex and challenging – if you pick a topic you are really interested in, you will be highly motivated to overcome any problems that may arise. The key to starting a project is very careful planning from the outset. Ask yourself the question: what are my research aims and objectives? This should then point you towards methodology and determining the most appropriate research methods for your project. Best of Luck!
Dear Dr. Deborah,
I am an Ed.D student and have just started working on my thesis. I have been first struggling with the research question, though I know what I want to work on, there are several factors that arise in the event, that requires one to reframe and rephrase the research question. I am from Singapore, my research interest is in quality assurance in higher education and I am examining it from my institution’s perspective. My research question is “How a quality assurance process transformed an art school to one of a tertiary level, a phenomenological study through staff experience.” As you can see I decided to use phenomenology as a methodology and the method will be interviews of staff. But then I am stuck with so many other questions, first about my research question, next the conceptual framework or theories to support….
Madam, I realy appreciate your constructive idea , you clearly made a good and reasonable differences between inductive research approach and deductive research approach. Big up once again.
Okay I got this.
Thank you. I am refining my thesis proposal and your explanation made clear again how to stay focused, clear and precise.
Thanks so much for explaining the things I could not put into perspective.
Thank you Deborah I also wish l had in-depth on research. My wish is to uproot the carnage on south African roads. This has helped me shape up my research proposal in Professional Development course . Regards
Thanks so much. Your information is very informative and helpful.
Thank you so much. I need to learn a lot from u
precise and useful
Hi Deborah, Thank you for sharing this, I would greatly appreciate if you could elaborate more on Research Paradigm (as stated in slide no 6/10). Transformative Emancipatory Paradigm Interpretive paradigm Critical Paradigm.
Your reply is highly appreciated thanks
Hi Yusuf, glad the slides have been useful for you. I strongly recommend that you read this book as it will provide in-depth overview on the Transformative Emancipatory Paradigm and Critical Paradigm. Essentially, both are concerned with giving voice to marginalised groups and changing the balance of power in research. Truman, C., Mertens, D.M. and Humphries, B. eds., 2000. Research and inequality. Psychology Press.
The Interpretative Research Paradigm is a qualitative approach that aims to understand the world through the subjective experience of individuals. I recommend this book for in-depth reading on the subject:
Schwartz-Shea, P. and Yanow, D., 2013. Interpretive research design: Concepts and processes. Routledge.
Dr. Gabriel,
Thank you so much for providing your thoughts for all to be supported in working through our research. I have been out of the classroom for quite some time and just now beginning work on my dissertation proposal. Your straightforward slides made it very easy for my brain to reengage the material in a more useful way than I ever did in the classroom. I have shared your website with my colleagues who are also working on completing their doctorates.
Additionally, I am hearing about the Transformative Emancipatory Paradigm and Black Feminist Standpoint Theory for the first time from you. I am using Critical Race Theory as one of my theoretical frameworks and it seems these other two aspects will be essential to consider as well. Thank you so much for providing the resources to Yusuf and in turn the rest of us by replying to comments.
Your work is incredibly helpful and valuable, thank you again!
With gratitude,
Molly O. Kennedy
Thanks so much for your comments Molly – I’m glad my posts have been useful for you – good luck with your dissertation!
Hi Deborah, I am currently doing an exploratory research topic on The impact of democracy on state relations in the International System with a case study of the European Union. It looks at using a regional bloc- the EU as a tool for fostering democracy globally. I was wondering if it would be possible to carry out data analysis using only secondary sources (qualitative) given that I live in a non-EU country which limits my use of primary research methods. And If possible I would like to know how this caan be done.
Dear Deborah Thank you for this helpful post – I am currently writing my master thesis and this provide some needed guidance. Best from Switzerland
Hi Deborah, how was ur day? I wish u all the best. Deborah I’m trying to do my MA thesis, and all informations those I got from u, adds something on my knowledge. thanks alot!
Thank you Dr Deborah, completely this article is helped me!
It’s great to read to sharpen the knowledge and your presentation satisfies my thirsty mind. Lot of thanks for your kind efforts to enrich anyone who wants to be served with your contribution.
You’re very welcome – it’s always a pleasure to support enquiring minds in this way!
Hi Deborah Thank you for your nice and helpful post – this will help me and my student also. Best from Bangladesh.
Need help to develop a conceptual frame work for my PhD proposal. I have struggled for two months and has failed to come up with objectives and conceptual frame work. My topic is “COMMUNICATION PATTERNS OF ADULT-CHILDREN RAISED BY SINGLE PARENTS IN THE POST CONFLICT REGION “. The idea is about post war children raised by single parents. I could post details of what I scripted on you mail if accepted. I will be grateful for you help.
Efiti Filliam -Uganda
Hello Deborah. I would love more explanation on creating the conceptual framework itself. I am a PhD student and at the stage where I have to create a conceptual model of my ideas. However, I am having some difficulties achieving this. My study is purely qualitative.
Hi Kelvin, one you have determined the area of enquiry, your aims and objectives for the research, the most appropriate conceptual approach should jump out you. It might be a singular framework or more commonly a combination of complementary approaches. Maybe you can play around with mind maps to help you work through this stage?
I’m so glad I found you. Your explanations are concise and easy to understand.
I am so happy. Thanks for your help and support. I feel like I am in a class room.
Comments are closed.
Understanding the Stigma Experience of Men Living with HIV in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Qualitative Meta-synthesis
- Substantive Review
- Published: 22 May 2024
Cite this article

- Sarah E. Janek ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0002-1213-2791 1 ,
- Sandy Hatoum ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0002-3618-9733 2 ,
- Leila Ledbetter ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5206-8002 3 &
- Michael V. Relf ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4951-8869 1 , 2
55 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Men living with HIV (MLWH) in sub-Saharan Africa experience poor health outcomes and increased AIDS-related deaths due to stigma influencing testing and treatment uptake and adherence. PRISMA 2020 was used to report a meta-synthesis of the stigma experiences of MLWH in SSA. With the help of an expert librarian, a search of six databases was formulated and performed to examine the available qualitative and mixed method studies with qualitative results relevant to the research question. Studies focused on adult men living with HIV, with five studies specifically examining the HIV experience of men who have sex with men. Study themes were synthesized to describe MLWH’s perceived, internalized, anticipated, enacted, and intersectional stigma experiences. Most studies included masculinity as a key theme that affected both testing and treatment adherence upon diagnosis. Future research is needed to better understand subpopulations, such as men who have sex with men living with HIV, and what interventions may be beneficial to mitigate the disparities among MLWH in SSA.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

“It is not an acceptable disease”: A qualitative study of HIV-related stigma and discrimination and impacts on health and wellbeing for people from ethnically diverse backgrounds in Australia
Overcoming hiv stigma a qualitative analysis of hiv cure research and stigma among men who have sex with men living with hiv, understanding hiv-related stigma among women in the southern united states: a literature review.
Kaiser Family Foundation. The global HIV/AIDS epidemic. KFF. 2022. https://www.kff.org/global-health-policy/fact-sheet/the-global-hivaids-epidemic/ . Accessed 13 Nov 2022.
UNAIDS. Fact sheet—latest global and regional statistics on the status of the AIDS epidemic. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). 2022. https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/UNAIDS_FactSheet_en.pdf . Accessed 23 Oct 2022.
West CA, Chang GC, Currie DW, Bray R, Kinchen S, Behel S, McCullough-Sanden R, Low A, Bissek A, Shang JD, Ndongmo CB, Dokubo EK, Balachandra S, Lobognon LR, Dube L, Nuwagaba-Biribonwoha H, Li M, Pasipamire M, Getaneh Y, Lulseged S, Eshetu F, Kingwara L, Zielinski-Gutierrez E, Tlhomola M, Ramphalla P, Kalua T, Auld AF, Williams DB, Remera E, Rwibasira GN, Mugisha V, Malamba SS, Mushi J, Jalloh MF, Mgomella GS, Kirungi WL, Biraro S, Awor AC, Barradas DT, Mugurungi O, Rogers JH, Bronson M, Bodika SM, Ajiboye A, Gaffga N, Moore C, Patel HK, Voetsch AC. Unawareness of HIV infection among men aged 15–59 years in 13 sub-Saharan African countries: findings from the population-based HIV impact assessments, 2015–2019. JAIDS. 2021;87:S97.
PubMed Google Scholar
UNAIDS. Executive summary—in danger: UNAIDS global AIDS update 2022 [Internet]. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). 2022. https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/2022-global-aids-update-summary_en.pdf . Accessed 23 Oct 2022.
UNAIDS. Addressing a blind spot in the response to HIV—reaching out to men and boys. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). 2017. https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/blind_spot_en.pdf . Accessed 23 Oct 2022.
Hatzenbuehler ML, Phelan JC, Link BG. Stigma as a fundamental cause of population health inequalities. Am J Public Health. 2013;103:813–21. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2012.301069 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Relf MV, Holzemer WL, Holt L, Nyblade L, Caiola CE. A review of the state of the science of HIV and stigma: context, conceptualization, measurement, interventions, gaps, and future priorities. J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2021;32:392–407. https://doi.org/10.1097/JNC.0000000000000237 .
Herek GM. AIDS and stigma. Am Behav Sci. 1999;42:1106–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/00027649921954787 .
Article Google Scholar
Earnshaw VA, Smith LR, Chaudoir SR, Amico KR, Copenhaver MM. HIV stigma mechanisms and well-being among PLWH: a test of the HIV stigma framework. AIDS Behav. 2013;17:1785–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-013-0437-9 .
Derlega VJ, Winstead BA, Greene K, Serovich J, Elwood WN. Perceived HIV-related stigma and HIV disclosure to relationship partners after finding out about the seropositive diagnosis. J Health Psychol. 2002;7:415–32. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359105302007004330 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Arinaitwe I, Amutuhaire H, Atwongyeire D, Tusingwire E, Kawungezi PC, Rukundo GZ, Ashaba S. Social support, food insecurity, and HIV stigma among men living with HIV in rural southwestern Uganda: a cross-sectional analysis. HIV AIDS (Auckl). 2021;13:657–66. https://doi.org/10.2147/HIV.S316174 .
Mburu G, Ram M, Siu G, Bitira D, Skovdal M, Holland P. Intersectionality of HIV stigma and masculinity in eastern Uganda: implications for involving men in HIV programmes. BMC Public Health. 2014;14:1061. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-14-1061 .
Sileo KM, Fielding-Miller R, Dworkin SL, Fleming PJ. A scoping review on the role of masculine norms in men’s engagement in the HIV care continuum in sub-Saharan Africa. AIDS Care. 2019;31:1435–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540121.2019.1595509 .
Abara WE, Garba I. HIV epidemic and human rights among men who have sex with men in sub-Saharan Africa: implications for HIV prevention, care, and surveillance. Glob Public Health. 2017;12:469–82. https://doi.org/10.1080/17441692.2015.1094107 .
Joshi K, Lessler J, Olawore O, Loevinsohn G, Bushey S, Tobian AAR, Grabowski MK. Declining HIV incidence in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis of empiric data. J Int AIDS Soc. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1002/jia2.25818 .
Nyato D, Kuringe E, Drake M, Casalini C, Nnko S, Shao A, Komba A, Baral SD, Wambura M, Changalucha J. Participants’ accrual and delivery of HIV prevention interventions among men who have sex with men in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5303-2 .
Hamilton A, Thompson N, Choko AT, Hlongwa M, Jolly P, Korte JE, Conserve DF. HIV self-testing uptake and intervention strategies among men in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review. Front Public Health. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.594298 .
Hlongwa M, Hlongwana K, Makhunga S, Choko AT, Dzinamarira T, Conserve D, Tsai AC. Linkage to HIV care following HIV self-testing among men: systematic review of quantitative and qualitative studies from six countries in sub-Saharan Africa. AIDS Behav. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-022-03800-8 .
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan SE, Chou R, Glanville J, Grimshaw JM, Hróbjartsson A, Lalu MM, Li T, Loder EW, Mayo-Wilson E, McDonald S, McGuinness LA, Stewart LA, Thomas J, Tricco AC, Welch VA, Whiting P, Moher D. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71 .
Turan B, Hatcher AM, Weiser SD, Johnson MO, Rice WS, Turan JM. Framing mechanisms linking HIV-related stigma, adherence to treatment, and health outcomes. Am J Public Health. 2017;107:863–9. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2017.303744 .
McGowan J, Sampson M, Salzwedel DM, Cogo E, Foerster V, Lefebvre C. PRESS peer review of electronic search strategies: 2015 guideline statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;75:40–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2016.01.021 .
UNAIDS. 90-90-90: an ambitious treatment target to help end the AIDS epidemic. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). 2014. https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/90-90-90_en.pdf . Accessed 10 June 2023.
UNAIDS. AIDS by the numbers: AIDS is not over, but it can be. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). 2016. https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/AIDS-by-the-numbers-2016_en.pdf . Accessed 10 June 2023.
Covidence systematic review software. Veritas Health Innovation. 2022. https://www.covidence.org/ . Accessed 8 Mar 2022.
Kmet LM, Lee RC, Cook LS. HTA initiative #13: standard quality assessment criteria for evaluating primary research papers from a variety of fields. Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research. 2004. https://www.ihe.ca/download/standard_quality_assessment_criteria_for_evaluating_primary_research_papers_from_a_variety_of_fields.pdf . Accessed 24 Oct 2022.
Sandelowski M, Barroso J. Handbook for synthesizing qualitative research. New York: Springer Publishing Company; 2007.
Google Scholar
Belay YA, Yitayal M, Atnafu A, Taye FA. Patient experiences and preferences for antiretroviral therapy service provision: implications for differentiated service delivery in Northwest Ethiopia. AIDS Res Ther. 2022;19:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12981-022-00452-5 .
Hlongwa M, Jama NA, Mehlomakulu V, Pass D, Basera W, Nicol E. Barriers and facilitating factors to HIV treatment among men in a high-HIV-burdened district in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa: a qualitative study. Am J Mens Health. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1177/15579883221120987 .
Lofgren SM, Tsui S, Atuyambe L, Ankunda L, Komuhendo R, Wamala N, Sadiq A, Kirumira P, Srishyla D, Flynn A, Pastick KA, Meya DB, Nakasujja N, Porta C. Barriers to HIV care in Uganda and implications for universal test-and-treat: a qualitative study. AIDS Care. 2022;34:597–605. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540121.2021.1946000 .
Mandawa MB, Mahiti GR. Factors contributing to loss to follow-up from HIV care among men living with HIV/AIDS in Kibaha District, Tanzania. HIV AIDS (Auckl). 2022;14:503–16. https://doi.org/10.2147/hiv.S381204 .
Mange T, Henderson N, Lukelelo N. ‘After 25 years of democracy we are still stigmatised and discriminated against’ healthcare experiences of HIV-positive older black gay men in a township in South Africa. J Pract Teach Learn. 2022;9:87–100. https://doi.org/10.1921/jpts.v19i1-2.1674 .
Mathenjwa M, Khidir H, Milford C, Mosery N, Rambally Greener L, Pratt MC, O’Neil K, Harrison A, Bangsberg DR, Safren SA, Smit JA, Psaros C, Matthews LT. Acceptability of an intervention to promote viral suppression and serostatus disclosure for men living with HIV in South Africa: qualitative findings. AIDS Behav. 2022;26:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-021-03278-w .
Muwanguzi PA, Nelson LE, Ngabirano TD, Kiwanuka N, Osingada CP, Sewankambo NK. Linkage to care and treatment among men with reactive HIV self-tests after workplace-based testing in Uganda: a qualitative study. Front Public Health. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.650719 .
Nabikande S, Namutundu J, Nangendo J, Okello T, Agwang W, Tusabe J, Kabwama SN, Katahoire AR. Men’s late presentation for HIV care in Eastern Uganda: the role of masculinity norms. PLoS ONE. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0277534 .
Ndione AG, Procureur F, Senne JN, Cornaglia F, Gueye K, Ndour CT, Lépine A. Sexuality-based stigma and access to care: intersecting perspectives between health care providers and men who have sex with men in HIV care centres in Senegal. Health Policy Plan. 2022;37:587–96. https://doi.org/10.1093/heapol/czac010 .
Rich C, Mavhu W, France NF, Munatsi V, Byrne E, Willis N, Nolan A. Exploring the beliefs, experiences and impacts of HIV-related self-stigma amongst adolescents and young adults living with HIV in Harare, Zimbabwe: a qualitative study. PLoS ONE. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0268498 .
Hendrickson ZM, Naugle DA, Tibbels N, Dosso A, Van Lith LM, Mallalieu EC, Kamara D, Dailly-Ajavon P, Cisse A, Ahanda KS, Thaddeus S, Babalola S, Hoffman CJ. “You take medications, you live normally”: the role of antiretroviral therapy in mitigating men’s perceived threats of HIV in Côte d’Ivoire. AIDS Behav. 2019;23:2600–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-019-02614-5 .
Naugle DA, Tibbels NJ, Hendrickson ZM, Dosso A, Van Lith LM, Mallalieu EC, Kouadio AM, Kra W, Kamara D, Dailly-Ajavon P, Cissé A, Seifert-Ahanda K, Thaddeus S, Babalola S, Hoffman CJ. Bringing fear into focus: the intersections of HIV and masculine gender norms in Côte d’Ivoire. PLoS ONE. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0223414 .
Tibbels NJ, Hendrickson ZM, Naugle DA, Dosso A, Van Lith LM, Mallalieu EC, Kouadio AM, Kra W, Kamara D, Dailly-Ajavon P, Cisse A, Seifert-Ahanda K, Thaddeus S, Babalola S, Hoffmann CJ. Men’s perceptions of HIV care engagement at the facility- and provider-levels: experiences in Cote d’Ivoire. PLoS ONE. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0211385 .
Balogun A, Bissell P, Saddiq M. Negotiating access to the Nigerian healthcare system: the experiences of HIV-positive men who have sex with men. Cult Health Sex. 2020;22:233–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/13691058.2019.1582802 .
Mukumbang FC. Leaving no man behind: how differentiated service delivery models increase men’s engagement in HIV care. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2021;10:129–40. https://doi.org/10.34172/ijhpm.2020.32 .
Ogunbajo A, Kershaw T, Kushwaha S, Boakye F, Wallace-Atiapah N-D, Nelson LE. Barriers, motivators, and facilitators to engagement in HIV care among HIV-infected Ghanaian men who have sex with men (MSM). AIDS Behav. 2018;22:829–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-017-1806-6 .
Okal J, Lango D, Matheka J, Obare F, Ngunu-Gituathi C, Mugambi M, Avina S. “It is always better for a man to know his HIV status”—a qualitative study exploring the context, barriers and facilitators of HIV testing among men in Nairobi, Kenya. PLoS ONE. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0231645 .
Okoror TA, Falade CO, Walker EM, Olorunlana A, Anaele A. Social context surrounding HIV diagnosis and construction of masculinity: a qualitative study of stigma experiences of heterosexual HIV positive men in southwest Nigeria. BMC Public Health. 2016;16:507. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-016-3165-z .
Sileo KM, Reed E, Kizito W, Wagman JA, Stockman JK, Wanyenze RK, Chemusto H, Musoke W, Mukasa B, Kiene SM. Masculinity and engagement in HIV care among male fisherfolk on HIV treatment in Uganda. Cult Health Sex. 2019;21:774–88. https://doi.org/10.1080/13691058.2018.1516299 .
Zissette S, Watt MH, Prose NS, Mntambo N, Moshabela M. “If you don’t take a stand for your life, who will help you?”: men’s engagement in HIV care in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Psychol Men Masc. 2016;17:265–73. https://doi.org/10.1037/men0000025 .
Berner-Rodoreda A, Ngwira E, Alhassan Y, Chione B, Dambe R, Bärnighausen T, Phiri S, Taegtmeyer M, Neuhann F. “Deadly”, “fierce”, “shameful”: notions of antiretroviral therapy, stigma and masculinities intersecting men’s life-course in Blantyre, Malawi. BMC Public Health. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-12314-2 .
Mantell JE, Masvawure TB, Mapingure M, Apollo T, Gwanzura C, Block L, Bennett E, Preko P, Musuka G, Rabkin M. Engaging men in HIV programmes: a qualitative study of male engagement in community-based antiretroviral refill groups in Zimbabwe. J Int AIDS Soc. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/jia2.25403 .
Misra S, Mehta HT, Eschliman EL, Rampa S, Poku OB, Wang W-Q, Ho-Foster AR, Mosepele M, Becker TD, Entaile P, Arscott-Mills T, Opondo PR, Blank MB, Yang LH. Identifying “what matters most” to men in Botswana to promote resistance to HIV-related stigma. Qual Health Res. 2021;31:1680–96. https://doi.org/10.1177/10497323211001361 .
Mooney AC, Gottert A, Khoza N, Rebombo D, Hove J, Suárez AJ, Twine R, MacPhail C, Treves-Kagan S, Kahn K, Pettifor A, Lippman SA. Men’s perceptions of treatment as prevention in South Africa: implications for engagement in HIV care and treatment. AIDS Educ Prev. 2017;29:274–87. https://doi.org/10.1521/aeap.2017.29.3.274 .
Moyo I, Macherera M, Mavhandu-Mudzusi AH. The lived experiences of men who have sex with men when accessing HIV care services in Zimbabwe. Health SA. 2021. https://doi.org/10.4102/hsag.v26i0.1462 .
Meskele M, Khuzwayo N, Taylor M. Mapping the evidence of intimate partner violence among women living with HIV/AIDS in sub-Saharan Africa: a scoping review. BMJ Open. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-041326 .
Tenkorang EY, Asamoah-Boaheng M, Owusu AY. Intimate partner violence (IPV) against HIV-positive women in sub-Saharan Africa: a mixed-method systematic review and meta-analysis. Trauma Violence Abuse. 2021;22:1104–28. https://doi.org/10.1177/1524838020906560 .
Sileo KM, Fielding-Miller R, Dworkin SL, Fleming PJ. What role do masculine norms play in men’s HIV testing in sub-Saharan Africa?: a scoping review. AIDS Behav. 2018;22:2468–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-018-2160-z .
Naanyu V, Ruff J, Goodrich S, Spira T, Bateganya M, Toroitich-Ruto C, Otieno-Nyunya B, Siika AM, Wools-Kaloustian K. Qualitative exploration of perceived benefits of care and barriers influencing HIV care in trans Nzoia, Kenya. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-05236-z .
Makoae LN, Seboni NM, Molosiwa K, Moleko M, Human S, Sukati NA, Holzemer WL. The symptom experience of people living with HIV/AIDS in southern Africa. J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2005;16:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jana.2005.03.005 .
McGuinness LA, Higgins JPT. Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): an R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res Synth Methods. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1411 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
The manuscript was supported by the Fogarty International Center/National Institutes of Health through Award Number R21TW011247 (M. Relf, Contact MPI/L. Nyblade, MPI) and the Duke University Center for AIDS Research (CFAR), an NIH funded program (5P30AI064518). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Research reported in this publication was supported by the Fogarty International Center of the National Institutes for Health under award R21TW012007 and by the Duke Center for AIDS Research, a National Institutes of Health funded program under award number 5P30AI064518. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Nursing, Duke University, 307 Trent Drive, Box 3322, Durham, NC, 27710, USA
Sarah E. Janek & Michael V. Relf
Duke Global Health Institute, Durham, NC, USA
Sandy Hatoum & Michael V. Relf
Medical Center Library, Duke University, Durham, NC, USA
Leila Ledbetter
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors on this paper meet the four criteria for authorship as identified by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors; all authors have contributed to the drafting or been involved in revising it, reviewed the final version of this manuscript before submission, and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. Specifically, using the CRediT taxonomy, the specific contribution of each author is as follows: Conceptualization & Methodology: S. Janek, L. Ledbetter, M. Relf. Formal Analysis: S. Hatoum, S. Janek, M. Relf. Funding Acquisition: M. Relf. Investigation: S. Hatoum, S. Janek, L. Ledbetter, M. Relf. Methodology: S. Janek, L. Ledbetter, M. Relf. Project administration: M. Relf. Supervision: M. Relf. Verification: S. Hatoum, S. Janek, M. Relf. Writing—manuscript draft: S. Janek. Writing—review & editing: S. Hatoum, S. Janek, L. Ledbetter, M. Relf.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Sarah E. Janek or Michael V. Relf .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors report no real or perceived vested interests related to this article that could be construed as a conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Registration The protocol that guided this meta-synthesis was prospectively registered with Prospero (registration ID: CRD42022315871).
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 35 KB)
Rights and permissions.
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Janek, S.E., Hatoum, S., Ledbetter, L. et al. Understanding the Stigma Experience of Men Living with HIV in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Qualitative Meta-synthesis. AIDS Behav (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-024-04329-8
Download citation
Accepted : 20 March 2024
Published : 22 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-024-04329-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Meta-synthesis
- People with HIV
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- Qualitative methodology
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
an example conceptual framework memo that details how a researcher describes their conceptual framework. CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORKS . IN RESEARCH. A conceptual framework lives at the center of an empirical . study. The conceptual framework serves as a guide and ballast to research (Ravitch & Riggan, 2016), functioning as an integrating
Including a conceptual framework in a research study is important, but researchers often opt to include either a conceptual or a theoretical framework. Either may be adequate, but both provide greater insight into the research approach. ... Mertz, N. T. (eds.), Theoretical frameworks in qualitative research (pp. 1-22). Sage. [Google Scholar ...
Developing a conceptual framework in research. Step 1: Choose your research question. Step 2: Select your independent and dependent variables. Step 3: Visualize your cause-and-effect relationship. Step 4: Identify other influencing variables. Frequently asked questions about conceptual models.
Qualitative health care research can provide insights into health care practices that quantitative studies cannot. However, the potential of qualitative research to improve health care is undermined by reporting that does not explain or justify the research questions and design. ... Constructing a conceptual framework would require researchers ...
The purpose of a conceptual framework. A conceptual framework serves multiple functions in a research project. It helps in clarifying the research problem and purpose, assists in refining the research questions, and guides the data collection and analysis process. It's the tool that ties all aspects of the study together, offering a coherent ...
International Journal of Qualitative Methods 2009, 8(4) 51 Redefining conceptual framework Current usage of the terms conceptual framework and theoretical framework are vague and imprecise. In this paper I define conceptual framework as a network, or "a plane," of interlinked concepts that together provide a comprehensive understanding of a phenomenon or phenomena.
Other qualitative methods use one or the other to frame the design of a research project or to explain the outcomes. An example is given of how a conceptual framework was used throughout a research project. Conclusion: Theoretical and conceptual frameworks are terms that are regularly used in research but rarely explained. Textbooks should ...
Theoretical and conceptual frameworks differ fundamentally in their scope. Theoretical frameworks provide a broad and general view of the research problem, rooted in established theories. They explain phenomena by applying a particular theoretical lens. Conceptual frameworks, on the other hand, offer a more focused view of the specific research ...
conceptual and theoretical frameworks. As conceptual defines the key co ncepts, variables, and. relationships in a research study as a roadmap that outlines the researcher's understanding of how ...
A diagram by Varpio and colleagues demonstrates the similarities and differences between theories and frameworks, and how they influence research approaches. 1(p991) The diagram displays the objectivist or deductive approach to research on the left-hand side. Note how the conceptual framework is first finalised before any research is commenced ...
Other qualitative methods use one or the other to frame the design of a research project or to explain the outcomes. An example is given of how a conceptual framework was used throughout a research project. Conclusion Theoretical and conceptual frameworks are terms that are regularly used in research but rarely explained.
Maxwell, J. A. (2005). Qualitative research design: An interactive approach (2nd Ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications. Chapter 3: Conceptual Framework: What Do You Think Is Going On? "Your research problem functions (in combination with your goals) to justify your study, to show people why your research is important (p. 34)."
"A conceptual framework is the total, logical orientation and associations of anything and everything that forms the underlying thinking, structures, plans and practices and implementation of your entire research project" (Kivunja, 2018, p. 45). ... as it helps the researcher answer questions that are core to qualitative research, such as ...
The conceptual framework is an important part of a research. However, there is still a lot of research, especially among students who ignore it. Indeed the conceptual framework has a strategic position and role in research. This article discusses about the conceptual framework in qualitative research. Specifically, it is aimed at providing understanding and practical guidance for students who ...
Conceptual Framework Research. A conceptual framework is a synthetization of interrelated components and variables which help in solving a real-world problem. It is the final lens used for viewing the deductive resolution of an identified issue (Imenda, 2014).
If you're new to academic research, sooner or later you're bound to run into the terms theoretical framework and conceptual framework.These are closely related but distinctly different things (despite some people using them interchangeably) and it's important to understand what each means. In this post, we'll unpack both theoretical and conceptual frameworks in plain language along ...
Using Conceptual Frameworks in Qualitative Research. Deborah Gabriel 14th February 2015. I previously delivered this presentation to final year undergraduate students about to embark on their dissertation projects - but developed this guide while undertaking my PhD. Failed to fetch Error: URL to the PDF file must be on exactly the same domain ...
Behavior analysts in research and clinical practice are interested in an ever-expanding array of topics. They are compelled to explore the social validity of the interventions they propose and the findings they generate. As the field moves in these important directions, qualitative methods are becoming increasingly relevant. Representing a departure from small-n design favored by behavior ...
This research uses qualitative research methods because the focus of this creation is how to find the implementation of minimalist music by knowing the elements of music, including its form and structure. ... motivation, action, and others holistically. The conceptual framework is a method used to explain the relationship or relationship ...
Men living with HIV (MLWH) in sub-Saharan Africa experience poor health outcomes and increased AIDS-related deaths due to stigma influencing testing and treatment uptake and adherence. PRISMA 2020 was used to report a meta-synthesis of the stigma experiences of MLWH in SSA. With the help of an expert librarian, a search of six databases was formulated and performed to examine the available ...
We draw on Moore et al.'s conceptual framework for assessing learning in clinician- and clinical-team-focused ... O'Brien B. C., Harris I. B., Beckman T. J., Reed D. A., Cook D. A. (2014). Standards for reporting qualitative research: A synthesis of recommendations. Academic Medicine: Journal of the Association of American Medical ...