
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Variations in Fetal Position and Presentation |
During pregnancy, the fetus can be positioned in many different ways inside the mother's uterus. The fetus may be head up or down or facing the mother's back or front. At first, the fetus can move around easily or shift position as the mother moves. Toward the end of the pregnancy the fetus is larger, has less room to move, and stays in one position. How the fetus is positioned has an important effect on delivery and, for certain positions, a cesarean delivery is necessary. There are medical terms that describe precisely how the fetus is positioned, and identifying the fetal position helps doctors to anticipate potential difficulties during labor and delivery.
Presentation refers to the part of the fetus’s body that leads the way out through the birth canal (called the presenting part). Usually, the head leads the way, but sometimes the buttocks (breech presentation), shoulder, or face leads the way.
Position refers to whether the fetus is facing backward (occiput anterior) or forward (occiput posterior). The occiput is a bone at the back of the baby's head. Therefore, facing backward is called occiput anterior (facing the mother’s back and facing down when the mother lies on her back). Facing forward is called occiput posterior (facing toward the mother's pubic bone and facing up when the mother lies on her back).
Lie refers to the angle of the fetus in relation to the mother and the uterus. Up-and-down (with the baby's spine parallel to mother's spine, called longitudinal) is normal, but sometimes the lie is sideways (transverse) or at an angle (oblique).
For these aspects of fetal positioning, the combination that is the most common, safest, and easiest for the mother to deliver is the following:
Head first (called vertex or cephalic presentation)
Facing backward (occiput anterior position)
Spine parallel to mother's spine (longitudinal lie)
Neck bent forward with chin tucked
Arms folded across the chest
If the fetus is in a different position, lie, or presentation, labor may be more difficult, and a normal vaginal delivery may not be possible.
Variations in fetal presentation, position, or lie may occur when
The fetus is too large for the mother's pelvis (fetopelvic disproportion).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains growths such as fibroids .
The fetus has a birth defect .
There is more than one fetus (multiple gestation).

Position and Presentation of the Fetus
Variations in fetal position and presentation.
Some variations in position and presentation that make delivery difficult occur frequently.
Occiput posterior position
In occiput posterior position (sometimes called sunny-side up), the fetus is head first (vertex presentation) but is facing forward (toward the mother's pubic bone—that is, facing up when the mother lies on her back). This is a very common position that is not abnormal, but it makes delivery more difficult than when the fetus is in the occiput anterior position (facing toward the mother's spine—that is facing down when the mother lies on her back).
When a fetus faces up, the neck is often straightened rather than bent,which requires more room for the head to pass through the birth canal. Delivery assisted by a vacuum device or forceps or cesarean delivery may be necessary.
Breech presentation
In breech presentation, the baby's buttocks or sometimes the feet are positioned to deliver first (before the head).
When delivered vaginally, babies that present buttocks first are more at risk of injury or even death than those that present head first.
The reason for the risks to babies in breech presentation is that the baby's hips and buttocks are not as wide as the head. Therefore, when the hips and buttocks pass through the cervix first, the passageway may not be wide enough for the head to pass through. In addition, when the head follows the buttocks, the neck may be bent slightly backwards. The neck being bent backward increases the width required for delivery as compared to when the head is angled forward with the chin tucked, which is the position that is easiest for delivery. Thus, the baby’s body may be delivered and then the head may get caught and not be able to pass through the birth canal. When the baby’s head is caught, this puts pressure on the umbilical cord in the birth canal, so that very little oxygen can reach the baby. Brain damage due to lack of oxygen is more common among breech babies than among those presenting head first.
In a first delivery, these problems may occur more frequently because a woman’s tissues have not been stretched by previous deliveries. Because of risk of injury or even death to the baby, cesarean delivery is preferred when the fetus is in breech presentation, unless the doctor is very experienced with and skilled at delivering breech babies or there is not an adequate facility or equipment to safely perform a cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation is more likely to occur in the following circumstances:
Labor starts too soon (preterm labor).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains abnormal growths such as fibroids .
Other presentations
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.
In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.
Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor. If they do not, a cesarean delivery is usually recommended.
In transverse lie, the fetus lies horizontally across the birth canal and presents shoulder first. A cesarean delivery is done, unless the fetus is the second in a set of twins. In such a case, the fetus may be turned to be delivered through the vagina.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.

- Mammary Glands
- Fallopian Tubes
- Supporting Ligaments
- Reproductive System
- Gametogenesis
- Placental Development
- Maternal Adaptations
- Menstrual Cycle
- Antenatal Care
- Small for Gestational Age
- Large for Gestational Age
- RBC Isoimmunisation
- Prematurity
- Prolonged Pregnancy
- Multiple Pregnancy
- Miscarriage
- Recurrent Miscarriage
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
- Breech Presentation
- Abnormal lie, Malpresentation and Malposition
- Oligohydramnios
- Polyhydramnios
- Placenta Praevia
- Placental Abruption
- Pre-Eclampsia
- Gestational Diabetes
- Headaches in Pregnancy
- Haematological
- Obstetric Cholestasis
- Thyroid Disease in Pregnancy
- Epilepsy in Pregnancy
- Induction of Labour
- Operative Vaginal Delivery
- Prelabour Rupture of Membranes
- Caesarean Section
- Shoulder Dystocia
- Cord Prolapse
- Uterine Rupture
- Amniotic Fluid Embolism
- Primary PPH
- Secondary PPH
- Psychiatric Disease
- Postpartum Contraception
- Breastfeeding Problems
- Primary Dysmenorrhoea
- Amenorrhoea and Oligomenorrhoea
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
- Endometriosis
- Endometrial Cancer
- Adenomyosis
- Cervical Polyps
- Cervical Ectropion
- Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia + Cervical Screening
- Cervical Cancer
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Ovarian Cysts & Tumours
- Urinary Incontinence
- Genitourinary Prolapses
- Bartholin's Cyst
- Lichen Sclerosus
- Vulval Carcinoma
- Introduction to Infertility
- Female Factor Infertility
- Male Factor Infertility
- Female Genital Mutilation
- Barrier Contraception
- Combined Hormonal
- Progesterone Only Hormonal
- Intrauterine System & Device
- Emergency Contraception
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- Genital Warts
- Genital Herpes
- Trichomonas Vaginalis
- Bacterial Vaginosis
- Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
- Obstetric History
- Gynaecological History
- Sexual History
- Obstetric Examination
- Speculum Examination
- Bimanual Examination
- Amniocentesis
- Chorionic Villus Sampling
- Hysterectomy
- Endometrial Ablation
- Tension-Free Vaginal Tape
- Contraceptive Implant
- Fitting an IUS or IUD
Abnormal Fetal lie, Malpresentation and Malposition
Original Author(s): Anna Mcclune Last updated: 1st December 2018 Revisions: 12
- 1 Definitions
- 2 Risk Factors
- 3.2 Presentation
- 3.3 Position
- 4 Investigations
- 5.1 Abnormal Fetal Lie
- 5.2 Malpresentation
- 5.3 Malposition
The lie, presentation and position of a fetus are important during labour and delivery.
In this article, we will look at the risk factors, examination and management of abnormal fetal lie, malpresentation and malposition.
Definitions
- Longitudinal, transverse or oblique
- Cephalic vertex presentation is the most common and is considered the safest
- Other presentations include breech, shoulder, face and brow
- Usually the fetal head engages in the occipito-anterior position (the fetal occiput facing anteriorly) – this is ideal for birth
- Other positions include occipito-posterior and occipito-transverse.
Note: Breech presentation is the most common malpresentation, and is covered in detail here .
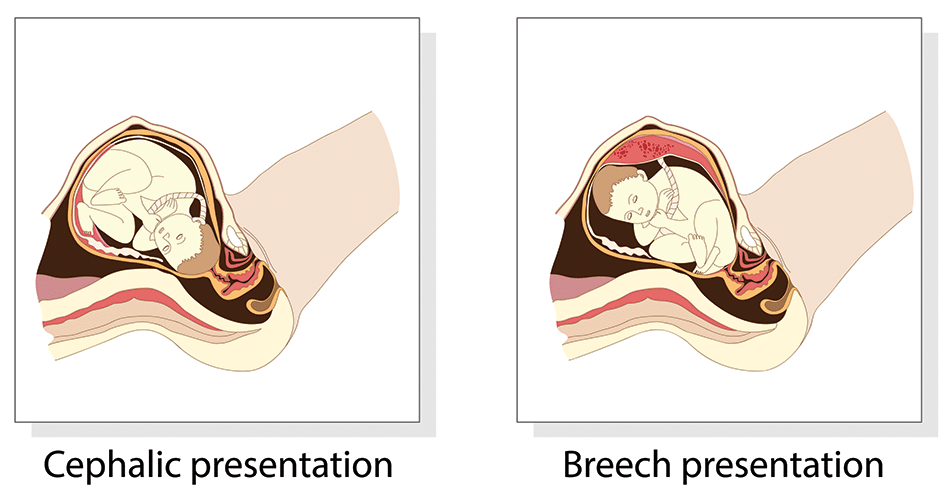
Fig 1 – The two most common fetal presentations: cephalic and breech.
Risk Factors
The risk factors for abnormal fetal lie, malpresentation and malposition include:
- Multiple pregnancy
- Uterine abnormalities (e.g fibroids, partial septate uterus)
- Fetal abnormalities
- Placenta praevia
- Primiparity
Identifying Fetal Lie, Presentation and Position
The fetal lie and presentation can usually be identified via abdominal examination. The fetal position is ascertained by vaginal examination.
For more information on the obstetric examination, see here .
- Face the patient’s head
- Place your hands on either side of the uterus and gently apply pressure; one side will feel fuller and firmer – this is the back, and fetal limbs may feel ‘knobbly’ on the opposite side
Presentation
- Palpate the lower uterus (above the symphysis pubis) with the fingers of both hands; the head feels hard and round (cephalic) and the bottom feels soft and triangular (breech)
- You may be able to gently push the fetal head from side to side
The fetal lie and presentation may not be possible to identify if the mother has a high BMI, if she has not emptied her bladder, if the fetus is small or if there is polyhydramnios .
During labour, vaginal examination is used to assess the position of the fetal head (in a cephalic vertex presentation). The landmarks of the fetal head, including the anterior and posterior fontanelles, indicate the position.
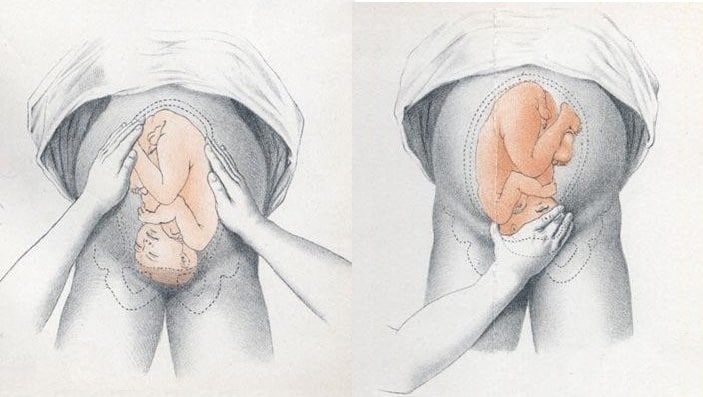
Fig 2 – Assessing fetal lie and presentation.
Investigations
Any suspected abnormal fetal lie or malpresentation should be confirmed by an ultrasound scan . This could also demonstrate predisposing uterine or fetal abnormalities.
Abnormal Fetal Lie
If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted – ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation.
ECV is the manipulation of the fetus to a cephalic presentation through the maternal abdomen.
It has an approximate success rate of 50% in primiparous women and 60% in multiparous women. Only 8% of breech presentations will spontaneously revert to cephalic in primiparous women over 36 weeks gestation.
Complications of ECV are rare but include fetal distress , premature rupture of membranes, antepartum haemorrhage (APH) and placental abruption. The risk of an emergency caesarean section (C-section) within 24 hours is around 1 in 200.
ECV is contraindicated in women with a recent APH, ruptured membranes, uterine abnormalities or a previous C-section .
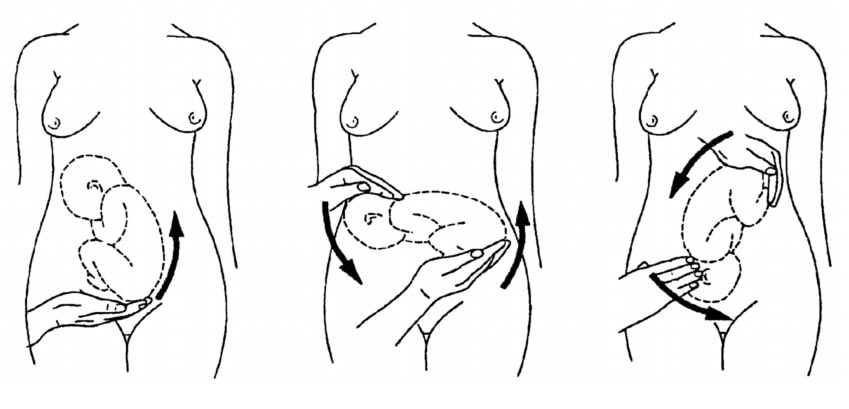
Fig 3 – External cephalic version.
Malpresentation
The management of malpresentation is dependent on the presentation.
- Breech – attempt ECV before labour, vaginal breech delivery or C-section
- Brow – a C-section is necessary
- If the chin is anterior (mento-anterior) a normal labour is possible; however, it is likely to be prolonged and there is an increased risk of a C-section being required
- If the chin is posterior (mento-posterior) then a C-section is necessary
- Shoulder – a C-section is necessary
Malposition
90% of malpositions spontaneously rotate to occipito-anterior as labour progresses. If the fetal head does not rotate, rotation and operative vaginal delivery can be attempted. Alternatively a C-section can be performed.
- Usually the fetal head engages in the occipito-anterior position (the fetal occiput facing anteriorly) - this is ideal for birth
If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted - ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation.
- Breech - attempt ECV before labour, vaginal breech delivery or C-section
Found an error? Is our article missing some key information? Make the changes yourself here!
Once you've finished editing, click 'Submit for Review', and your changes will be reviewed by our team before publishing on the site.
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site and to show you relevant advertising. To find out more, read our privacy policy .
Privacy Overview
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Delivery, face and brow presentation.
Julija Makajeva ; Mohsina Ashraf .
Affiliations
Last Update: January 9, 2023 .
- Continuing Education Activity
Face and brow presentation is a malpresentation during labor when the presenting part is either the face or, in the case of brow presentation, it is the area between the orbital ridge and the anterior fontanelle. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of these two presentations and explains the role of the interprofessional team in managing delivery safely for both the mother and the baby.
- Describe the mechanism of labor in the face and brow presentation.
- Summarize potential maternal and fetal complications during the face and brow presentations.
- Review different management approaches for the face and brow presentation.
- Outline some interprofessional strategies that will improve patient outcomes in delivery cases with face and brow presentation issues.
- Introduction
The term presentation describes the leading part of the fetus or the anatomical structure closest to the maternal pelvic inlet during labor. The presentation can roughly be divided into the following classifications: cephalic, breech, shoulder, and compound. Cephalic presentation is the most common and can be further subclassified as vertex, sinciput, brow, face, and chin. The most common presentation in term labor is the vertex, where the fetal neck is flexed to the chin, minimizing the head circumference.
Face presentation – an abnormal form of cephalic presentation where the presenting part is mentum. This typically occurs because of hyperextension of the neck and the occiput touching the fetal back. Incidence of face presentation is rare, accounting for approximately 1 in 600 of all presentations. [1] [2] [3]
In brow presentation, the neck is not extended as much as in face presentation, and the leading part is the area between the anterior fontanelle and the orbital ridges. Brow presentation is considered the rarest of all malpresentation with a prevalence of 1 in 500 to 1 in 4000 deliveries. [3]
Both face and brow presentations occur due to extension of the fetal neck instead of flexion; therefore, conditions that would lead to hyperextension or prevent flexion of the fetal neck can all contribute to face or brow presentation. These risk factors may be related to either the mother or the fetus. Maternal risk factors are preterm delivery, contracted maternal pelvis, platypelloid pelvis, multiparity, previous cesarean section, black race. Fetal risk factors include anencephaly, multiple loops of cord around the neck, masses of the neck, macrosomia, polyhydramnios. [2] [4] [5]
These malpresentations are usually diagnosed during the second stage of labor when performing a digital examination. It is possible to palpate orbital ridges, nose, malar eminences, mentum, mouth, gums, and chin in face presentation. Based on the position of the chin, face presentation can be further divided into mentum anterior, posterior, or transverse. In brow presentation, anterior fontanelle and face can be palpated except for the mouth and the chin. Brow presentation can then be further described based on the position of the anterior fontanelle as frontal anterior, posterior, or transverse.
Diagnosing the exact presentation can be challenging, and face presentation may be misdiagnosed as frank breech. To avoid any confusion, a bedside ultrasound scan can be performed. [6] The ultrasound imaging can show a reduced angle between the occiput and the spine or, the chin is separated from the chest. However, ultrasound does not provide much predicting value in the outcome of the labor. [7]
- Anatomy and Physiology
Before discussing the mechanism of labor in the face or brow presentation, it is crucial to highlight some anatomical landmarks and their measurements.
Planes and Diameters of the Pelvis
The three most important planes in the female pelvis are the pelvic inlet, mid pelvis, and pelvic outlet.
Four diameters can describe the pelvic inlet: anteroposterior, transverse, and two obliques. Furthermore, based on the different landmarks on the pelvic inlet, there are three different anteroposterior diameters, named conjugates: true conjugate, obstetrical conjugate, and diagonal conjugate. Only the latter can be measured directly during the obstetric examination. The shortest of these three diameters is obstetrical conjugate, which measures approximately 10.5 cm and is a distance between the sacral promontory and 1 cm below the upper border of the symphysis pubis. This measurement is clinically significant as the fetal head must pass through this diameter during the engagement phase. The transverse diameter measures about 13.5cm and is the widest distance between the innominate line on both sides.
The shortest distance in the mid pelvis is the interspinous diameter and usually is only about 10 cm.
Fetal Skull Diameters
There are six distinguished longitudinal fetal skull diameters:
- Suboccipito-bregmatic: from the center of anterior fontanelle (bregma) to the occipital protuberance, measuring 9.5 cm. This is the presenting diameter in vertex presentation.
- Suboccipito-frontal: from the anterior part of bregma to the occipital protuberance, measuring 10 cm
- Occipito-frontal: from the root of the nose to the most prominent part of the occiput, measuring 11.5cm
- Submento-bregmatic: from the center of the bregma to the angle of the mandible, measuring 9.5 cm. This is the presenting diameter in face presentation where the neck is hyperextended.
- Submento-vertical: from the midpoint between fontanelles and the angle of the mandible, measuring 11.5cm
- Occipito-mental: from the midpoint between fontanelles and the tip of the chin, measuring 13.5 cm. It is the presenting diameter in brow presentation.
Cardinal Movements of Normal Labor
- Neck flexion
- Internal rotation
- Extension (delivers head)
- External rotation (Restitution)
- Expulsion (delivery of anterior and posterior shoulders)
Some of the key movements are not possible in the face or brow presentations.
Based on the information provided above, it is obvious that labor will be arrested in brow presentation unless it spontaneously changes to face or vertex, as the occipito-mental diameter of the fetal head is significantly wider than the smallest diameter of the female pelvis. Face presentation can, however, be delivered vaginally, and further mechanisms of face delivery will be explained in later sections.
- Indications
As mentioned previously, spontaneous vaginal delivery can be successful in face presentation. However, the main indication for vaginal delivery in such circumstances would be a maternal choice. It is crucial to have a thorough conversation with a mother, explaining the risks and benefits of vaginal delivery with face presentation and a cesarean section. Informed consent and creating a rapport with the mother is an essential aspect of safe and successful labor.
- Contraindications
Vaginal delivery of face presentation is contraindicated if the mentum is lying posteriorly or is in a transverse position. In such a scenario, the fetal brow is pressing against the maternal symphysis pubis, and the short fetal neck, which is already maximally extended, cannot span the surface of the maternal sacrum. In this position, the diameter of the head is larger than the maternal pelvis, and it cannot descend through the birth canal. Therefore the cesarean section is recommended as the safest mode of delivery for mentum posterior face presentations.
Attempts to manually convert face presentation to vertex, manual or forceps rotation of the persistent posterior chin to anterior are contraindicated as they can be dangerous.
Persistent brow presentation itself is a contraindication for vaginal delivery unless the fetus is significantly small or the maternal pelvis is large.
Continuous electronic fetal heart rate monitoring is recommended for face and brow presentations, as heart rate abnormalities are common in these scenarios. One study found that only 14% of the cases with face presentation had no abnormal traces on the cardiotocograph. [8] It is advised to use external transducer devices to prevent damage to the eyes. When internal monitoring is inevitable, it is suggested to place monitoring devices on bony parts carefully.
People who are usually involved in the delivery of face/ brow presentation are:
- Experienced midwife, preferably looking after laboring woman 1:1
- Senior obstetrician
- Neonatal team - in case of need for resuscitation
- Anesthetic team - to provide necessary pain control (e.g., epidural)
- Theatre team - in case of failure to progress and an emergency cesarean section will be required.
- Preparation
No specific preparation is required for face or brow presentation. However, it is essential to discuss the labor options with the mother and birthing partner and inform members of the neonatal, anesthetic, and theatre co-ordinating teams.
- Technique or Treatment
Mechanism of Labor in Face Presentation
During contractions, the pressure exerted by the fundus of the uterus on the fetus and pressure of amniotic fluid initiate descent. During this descent, the fetal neck extends instead of flexing. The internal rotation determines the outcome of delivery, if the fetal chin rotates posteriorly, vaginal delivery would not be possible, and cesarean section is permitted. The approach towards mentum-posterior delivery should be individualized, as the cases are rare. Expectant management is acceptable in multiparous women with small fetuses, as a spontaneous mentum-anterior rotation can occur. However, there should be a low threshold for cesarean section in primigravida women or women with large fetuses.
When the fetal chin is rotated towards maternal symphysis pubis as described as mentum-anterior; in these cases further descend through the vaginal canal continues with approximately 73% cases deliver spontaneously. [9] Fetal mentum presses on the maternal symphysis pubis, and the head is delivered by flexion. The occiput is pointing towards the maternal back, and external rotation happens. Shoulders are delivered in the same manner as in vertex delivery.
Mechanism of Labor in Brow Presentation
As this presentation is considered unstable, it is usually converted into a face or an occiput presentation. Due to the cephalic diameter being wider than the maternal pelvis, the fetal head cannot engage; thus, brow delivery cannot take place. Unless the fetus is small or the pelvis is very wide, the prognosis for vaginal delivery is poor. With persistent brow presentation, a cesarean section is required for safe delivery.
- Complications
As the cesarean section is becoming a more accessible mode of delivery in malpresentations, the incidence of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality during face presentation has dropped significantly. [10]
However, there are still some complications associated with the nature of labor in face presentation. Due to the fetal head position, it is more challenging for the head to engage in the birth canal and descend, resulting in prolonged labor.
Prolonged labor itself can provoke foetal distress and arrhythmias. If the labor arrests or signs of fetal distress appear on CTG, the recommended next step in management is an emergency cesarean section, which in itself carries a myriad of operative and post-operative complications.
Finally, due to the nature of the fetal position and prolonged duration of labor in face presentation, neonates develop significant edema of the skull and face. Swelling of the fetal airway may also be present, resulting in respiratory distress after birth and possible intubation.
- Clinical Significance
During vertex presentation, the fetal head flexes, bringing the chin to the chest, forming the smallest possible fetal head diameter, measuring approximately 9.5cm. With face and brow presentation, the neck hyperextends, resulting in greater cephalic diameters. As a result, the fetal head will engage later, and labor will progress more slowly. Failure to progress in labor is also more common in both presentations compared to vertex presentation.
Furthermore, when the fetal chin is in a posterior position, this prevents further flexion of the fetal neck, as browns are pressing on the symphysis pubis. As a result, descend through the birth canal is impossible. Such presentation is considered undeliverable vaginally and requires an emergency cesarean section.
Manual attempts to change face presentation to vertex, manual or forceps rotation to mentum anterior are considered dangerous and are discouraged.
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
A multidisciplinary team of healthcare experts supports the woman and her child during labor and the perinatal period. For a face or brow presentation to be appropriately diagnosed, an experienced midwife and obstetrician must be involved in the vaginal examination and labor monitoring. As fetal anomalies, such as anencephaly or goiter, can contribute to face presentation, sonographers experienced in antenatal scanning should also be involved in the care. It is advised to inform the anesthetic and neonatal teams in advance of the possible need for emergency cesarean section and resuscitation of the neonate. [11] [12]
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Julija Makajeva declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Mohsina Ashraf declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Makajeva J, Ashraf M. Delivery, Face and Brow Presentation. [Updated 2023 Jan 9]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Sonographic diagnosis of fetal head deflexion and the risk of cesarean delivery. [Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020] Sonographic diagnosis of fetal head deflexion and the risk of cesarean delivery. Bellussi F, Livi A, Cataneo I, Salsi G, Lenzi J, Pilu G. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020 Nov; 2(4):100217. Epub 2020 Aug 18.
- Review Sonographic evaluation of the fetal head position and attitude during labor. [Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022] Review Sonographic evaluation of the fetal head position and attitude during labor. Ghi T, Dall'Asta A. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Jul 6; . Epub 2022 Jul 6.
- Stages of Labor. [StatPearls. 2024] Stages of Labor. Hutchison J, Mahdy H, Hutchison J. StatPearls. 2024 Jan
- Leopold Maneuvers. [StatPearls. 2024] Leopold Maneuvers. Superville SS, Siccardi MA. StatPearls. 2024 Jan
- Review Labor with abnormal presentation and position. [Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. ...] Review Labor with abnormal presentation and position. Stitely ML, Gherman RB. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2005 Jun; 32(2):165-79.
Recent Activity
- Delivery, Face and Brow Presentation - StatPearls Delivery, Face and Brow Presentation - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Variations in Fetal Position and Presentation |
During pregnancy, the fetus can be positioned in many different ways inside the mother's uterus. The fetus may be head up or down or facing the mother's back or front. At first, the fetus can move around easily or shift position as the mother moves. Toward the end of the pregnancy the fetus is larger, has less room to move, and stays in one position. How the fetus is positioned has an important effect on delivery and, for certain positions, a cesarean delivery is necessary. There are medical terms that describe precisely how the fetus is positioned, and identifying the fetal position helps doctors to anticipate potential difficulties during labor and delivery.
Presentation refers to the part of the fetus’s body that leads the way out through the birth canal (called the presenting part). Usually, the head leads the way, but sometimes the buttocks (breech presentation), shoulder, or face leads the way.
Position refers to whether the fetus is facing backward (occiput anterior) or forward (occiput posterior). The occiput is a bone at the back of the baby's head. Therefore, facing backward is called occiput anterior (facing the mother’s back and facing down when the mother lies on her back). Facing forward is called occiput posterior (facing toward the mother's pubic bone and facing up when the mother lies on her back).
Lie refers to the angle of the fetus in relation to the mother and the uterus. Up-and-down (with the baby's spine parallel to mother's spine, called longitudinal) is normal, but sometimes the lie is sideways (transverse) or at an angle (oblique).
For these aspects of fetal positioning, the combination that is the most common, safest, and easiest for the mother to deliver is the following:
Head first (called vertex or cephalic presentation)
Facing backward (occiput anterior position)
Spine parallel to mother's spine (longitudinal lie)
Neck bent forward with chin tucked
Arms folded across the chest
If the fetus is in a different position, lie, or presentation, labor may be more difficult, and a normal vaginal delivery may not be possible.
Variations in fetal presentation, position, or lie may occur when
The fetus is too large for the mother's pelvis (fetopelvic disproportion).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains growths such as fibroids .
The fetus has a birth defect .
There is more than one fetus (multiple gestation).

Position and Presentation of the Fetus
Variations in fetal position and presentation.
Some variations in position and presentation that make delivery difficult occur frequently.
Occiput posterior position
In occiput posterior position (sometimes called sunny-side up), the fetus is head first (vertex presentation) but is facing forward (toward the mother's pubic bone—that is, facing up when the mother lies on her back). This is a very common position that is not abnormal, but it makes delivery more difficult than when the fetus is in the occiput anterior position (facing toward the mother's spine—that is facing down when the mother lies on her back).
When a fetus faces up, the neck is often straightened rather than bent,which requires more room for the head to pass through the birth canal. Delivery assisted by a vacuum device or forceps or cesarean delivery may be necessary.
Breech presentation
In breech presentation, the baby's buttocks or sometimes the feet are positioned to deliver first (before the head).
When delivered vaginally, babies that present buttocks first are more at risk of injury or even death than those that present head first.
The reason for the risks to babies in breech presentation is that the baby's hips and buttocks are not as wide as the head. Therefore, when the hips and buttocks pass through the cervix first, the passageway may not be wide enough for the head to pass through. In addition, when the head follows the buttocks, the neck may be bent slightly backwards. The neck being bent backward increases the width required for delivery as compared to when the head is angled forward with the chin tucked, which is the position that is easiest for delivery. Thus, the baby’s body may be delivered and then the head may get caught and not be able to pass through the birth canal. When the baby’s head is caught, this puts pressure on the umbilical cord in the birth canal, so that very little oxygen can reach the baby. Brain damage due to lack of oxygen is more common among breech babies than among those presenting head first.
In a first delivery, these problems may occur more frequently because a woman’s tissues have not been stretched by previous deliveries. Because of risk of injury or even death to the baby, cesarean delivery is preferred when the fetus is in breech presentation, unless the doctor is very experienced with and skilled at delivering breech babies or there is not an adequate facility or equipment to safely perform a cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation is more likely to occur in the following circumstances:
Labor starts too soon (preterm labor).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains abnormal growths such as fibroids .
Other presentations
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.
In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.
Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor. If they do not, a cesarean delivery is usually recommended.
In transverse lie, the fetus lies horizontally across the birth canal and presents shoulder first. A cesarean delivery is done, unless the fetus is the second in a set of twins. In such a case, the fetus may be turned to be delivered through the vagina.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Labour and Delivery Care Module: 8. Abnormal Presentations and Multiple Pregnancies
Study session 8 abnormal presentations and multiple pregnancies, introduction.
In previous study sessions of this module, you have been introduced to the definitions, signs, symptoms and stages of normal labour, and about the ‘normal’ vertex presentation of the fetus during delivery. In this study session, you will learn about the most common abnormal presentations (breech, shoulder, face or brow), their diagnostic criteria and the required actions you need to take to prevent complications developing during labour. Taking prompt action may save the life of the mother and her baby if the delivery becomes obstructed because the baby is in an abnormal presentation. We will also tell you about twin births and the complications that may result if the two babies become ‘locked’ together, preventing either of them from being born.
Learning Outcomes for Study Session 8
After studying this session, you should be able to:
8.1 Define and use correctly all of the key words printed in bold . (SAQs 8.1 and 8.2)
8.2 Describe how you would identify a fetus in the vertex presentation and distinguish this from common malpresentations and malpositions. (SAQs 8.1 and 8.2)
8.3 Describe the causes and complications for the fetus and the mother of fetal malpresentation during full term labour. (SAQ 8.3)
8.4 Describe how you would identify a multiple pregnancy and the complications that may arise. (SAQ 8.4)
8.5 Explain when and how you would refer a woman in labour due to abnormal fetal presentation or multiple pregnancy. (SAQ 8.4)
8.1 Normal and abnormal presentations
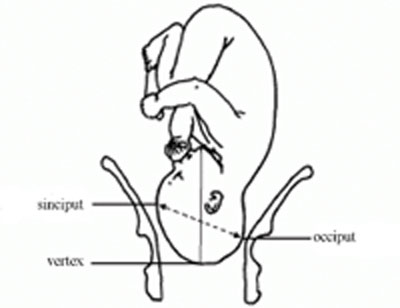
8.1.1 vertex presentation.
In about 95% of deliveries, the part of the fetus which arrives first at the mother’s pelvic brim is the highest part of the fetal head, which is called the vertex (Figure 8.1). This presentation is called the vertex presentation . Notice that the baby’s chin is tucked down towards its chest, so that the vertex is the leading part entering the mother’s pelvis. The baby’s head is said to be ‘well-flexed’ in this position.
During early pregnancy, the baby is the other way up — with its bottom pointing down towards the mother’s cervix — which is called the breech presentation . This is because during its early development, the head of the fetus is bigger than its buttocks; so in the majority of cases, the head occupies the widest cavity, i.e. the fundus (rounded top) of the uterus. As the fetus grows larger, the buttocks become bigger than the head and the baby spontaneously reverses its position, so its buttocks occupy the fundus. In short, in early pregnancy, the majority of fetuses are in the breech presentation and later in pregnancy most of them make a spontaneous transition to the vertex presentation.
8.1.2 Malpresentations
You will learn about obstructed labour in Study Session 9.
When the baby presents itself in the mother’s pelvis in any position other than the vertex presentation, this is termed an abnormal presentation, or m alpresentation . The reason for referring to this as ‘abnormal’ is because it is associated with a much higher risk of obstruction and other birth complications than the vertex presentation. The most common types of malpresentation are termed breech, shoulder, face or brow. We will discuss each of these in turn later. Notice that the baby can be ‘head-down’ but in an abnormal presentation, as in face or brow presentations, when the baby’s face or forehead (brow) is the presenting part.
8.1.3 Malposition
Although it may not be so easy for you to identify this, the baby can also be in an abnormal position even when it is in the vertex presentation. In a normal delivery, when the baby’s head has engaged in the mother’s pelvis, the back of the baby’s skull (the occiput ) points towards the front of the mother’s pelvis (the pubic symphysis ), where the two pubic bones are fused together. This orientation of the fetal skull is called the occipito-anterior position (Figure 8.2a). If the occiput (back) of the fetal skull is towards the mother’s back, this occipito-posterior position (Figure 8.2b) is a vertex malposition , because it is more difficult for the baby to be born in this orientation. The good thing is that more than 90% of babies in vertex malpositions undergo rotation to the occipito-anterior position and are delivered normally.
You learned the directional positions: anterior/in front of and posterior/behind or in the back of, in the Antenatal Care Module, Part 1, Study Session 3.
Note that the fetal skull can also be tilted to the left or to the right in either the occipito-anterior or occipito-posterior positions.

8.2 Causes and consequences of malpresentations and malpositions
In the majority of individual cases it may not be possible to identify what caused the baby to be in an abnormal presentation or position during delivery. However, the general conditions that are thought to increase the risk of malpresentation or malposition are listed below:
Multiple pregnancy is the subject of Section 8.7 of this study session. You learned about placenta previa in the Antenatal Care Module, Study Session 21.
- Abnormally increased or decreased amount of amniotic fluid
- A tumour (abnormal tissue growth) in the uterus preventing the spontaneous inversion of the fetus from breech to vertex presentation during late pregnancy
- Abnormal shape of the pelvis
- Laxity (slackness) of muscular layer in the walls of the uterus
- Multiple pregnancy (more than one baby in the uterus)
- Placenta previa (placenta partly or completely covering the cervical opening).
If the baby presents at the dilating cervix in an abnormal presentation or malposition, it will more difficult (and may be impossible) for it to complete the seven cardinal movements that you learned about in Study Sessions 3 and 5. As a result, birth is more difficult and there is an increased risk of complications, including:
You learned about PROM in Study Session 17 of the Antenatal Care Module, Part 2.
- Premature rupture of the fetal membranes (PROM)
- Premature labour
- Slow, erratic, short-lived contractions
- Uncoordinated and extremely painful contractions, with slow or no progress of labour
- Prolonged and obstructed labour, leading to a ruptured uterus (see Study Sessions 9 and 10 of this Module)
- Postpartum haemorrhage (see Study Session 11)
- Fetal and maternal distress, which may lead to the death of the baby and/or the mother.
With these complications in mind, we now turn your attention to the commonest types of malpresentation and how to recognise them.
8.3 Breech presentation
In a b reech presentation , the fetus lies with its buttocks in the lower part of the uterus, and its buttocks and/or the feet are the presenting parts during delivery. Breech presentation occurs on average in 3–4% of deliveries after 34 weeks of pregnancy.
When is the breech position the normal position for the fetus?
During early pregnancy the baby’s bottom points down towards the mother’s cervix, and its head (the largest part of the fetus at this stage of development) occupies the fundus (rounded top) of the uterus, which is the widest part of the uterine cavity.
8.3.1 Causes of breech presentation
You can see a transverse lie in Figure 8.7 later in this study session.
In the majority of cases there is no obvious reason why the fetus should present by the breech at full term. In practice, what is commonly observed is the association of breech presentation at delivery with a transverse lie earlier in the pregnancy, i.e. the fetus lies sideways across the mother’s abdomen, facing a sideways implanted placenta. It is thought that when the placenta is in front of the baby’s face, it may obstruct the normal process of inversion, when the baby turns head-down as it gets bigger during the pregnancy. As a result, the fetus turns in the other direction and ends in the breech presentation. Some other circumstances that are thought to favour a breech presentation during labour include:
- Premature labour, beginning before the baby undergoes spontanous inversion from breech to vertex presentation
- Multiple pregnancy, preventing the normal inversion of one or both babies
- Polyhydramnios: excessive amount of amniotic fluid, which makes it more difficult for the fetal head to ‘engage’ with the mother’s cervix (polyhydramnios is pronounced ‘poll-ee-hy-dram-nee-oss’. Hydrocephaly is pronounced ‘hy-droh-keff-all-ee’)
- Hydrocephaly (‘water on the brain’) i.e. an abnormally large fetal head due to excessive accumulation of fluid around the brain
- Placenta praevia
- Breech delivery in the previous pregnancy
- Abnormal formation of the uterus.
8.3.2 Diagnosis of breech presentation
On abdominal palpation the fetal head is found above the mother’s umbilicus as a hard, smooth, rounded mass, which gently ‘ballots’ (can be rocked) between your hands.
Why do you think a mass that ‘ballots’ high up in the abdomen is a sign of breech presentation? (You learned about this in Study Session 11 of the Antenatal Care Module.)
The baby’s head can ‘rock’ a little bit because of the flexibility of the baby’s neck, so if there is a rounded, ballotable mass above the mother’s umbilicus it is very likely to be the baby’s head. If the baby was ‘bottom-up’ (vertex presentation) the whole of its back will move of you try to rock the fetal parts at the fundus (Figure 8.3).
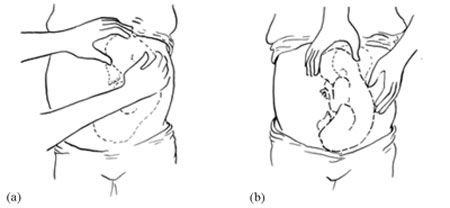
Once the fetus has engaged and labour has begun, the breech baby’s buttocks can be felt as soft and irregular on vaginal examination. They feel very different to the relatively hard rounded mass of the fetal skull in a vertex presentation. When the fetal membranes rupture, the buttocks and/or feet can be felt more clearly. The baby’s anus may be felt and fresh thick, dark meconium may be seen on your examining finger. If the baby’s legs are extended, you may be able to feel the external genitalia and even tell the sex of the baby before it is born.
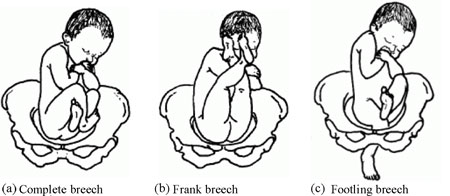
8.3.3 Types of breech presentation
There are three types of breech presentation, as illustrated in Figure 8.4. They are:
- Complete breech is characterised by flexion of the legs at both hips and knee joints, so the legs are bent underneath the baby.
- Frank breech is the commonest type of breech presentation, and is characterised by flexion at the hip joints and extension at the knee joints, so both the baby’s legs point straight upwards.
- Footling breech is when one or both legs are extended at the hip and knee joint and the baby presents ‘foot first’.
8.3.4 Risks of breech presentation
Regardless of the type of breech presentation, there are significant associated risks to the baby. They include:
- The fetal head gets stuck (arrested) before delivery
- Labour becomes obstructed when the fetus is disproportionately large for the size of the maternal pelvis
- Cord prolapse may occur, i.e. the umbilical cord is pushed out ahead of the baby and may get compressed against the wall of the cervix or vagina
- Premature separation of the placenta (placental abruption)
- Birth injury to the baby, e.g. fracture of the arms or legs, nerve damage, trauma to the internal organs, spinal cord damage, etc.
A breech birth may also result in trauma to the mother’s birth canal or external genitalia through being overstretched by the poorly fitting fetal parts.
Cord prolapse in a normal (vertex) presentation was illustrated in Study Session 17 of the Antenatal Care Module, and placental abruption was covered in Study Session 21.
What will be the effect on the baby if it gets stuck, the labour is obstructed, the cord prolapses, or placental abruption occurs?
The result will be hypoxia , i.e. it will be deprived of oxygen, and may suffer permanent brain damage or die.
You learned about the causes and consequences of hypoxia in the Antenatal Care Module.
8.4 Face presentation
Face presentation occurs when the baby’s neck is so completely extended (bent backwards) that the occiput at the back of the fetal skull touches the baby’s own spine (see Figure 8.5). In this position, the baby’s face will present to you during delivery.
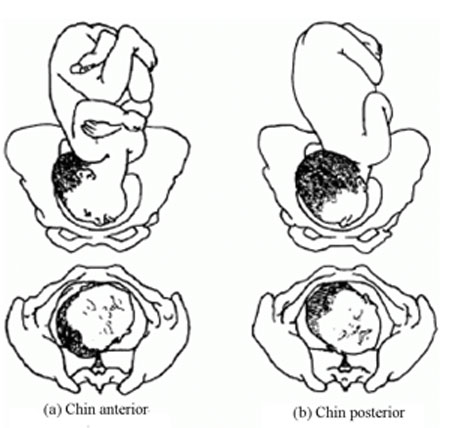
Refer the mother if a baby in the chin posterior face presentation does not rotate and the labour is prolonged.
The incidence of face presentation is about 1 in 500 pregnancies in full term labours. In Figure 8.5, you can see how flexed the head is at the neck. Babies who present in the ‘chin posterior’ position (on the right in Figure 8.5) usually rotate spontaneously during labour, and assume the ‘chin anterior’ position, which makes it easier for them to be born. However, they are unlikely to be delivered vaginally if they fail to undergo spontaneous rotation to the chin anterior position, because the baby’s chin usually gets stuck against the mother’s sacrum (the bony prominence at the back of her pelvis). A baby in this position will have to be delivered by caesarean surgery.
8.4.1 Causes of face presentation
The causes of face presentation are similar to those already described for breech births:
- Laxity (slackness) of the uterus after many previous full-term pregnancies
- Multiple pregnancy
- Polyhydramnios (excessive amniotic fluid)
- Congenital abnormality of the fetus (e.g. anencephaly, which means no or incomplete skull bones)
- Abnormal shape of the mother’s pelvis.
8.4.2 Diagnosis of face presentation
Face presentation may not be easily detected by abdominal palpation, especially if the chin is in the posterior position. On abdominal examination, you may feel irregular shapes, formed because the fetal spine is curved in an ‘S’ shape. However, on vaginal examination, you can detect face presentation because:
- The presenting part will be high, soft and irregular.
- When the cervix is sufficiently dilated, you may be able to feel parts of the face, such as the orbital ridges above the eyes, the nose or mouth, gums, or bony chin.
- If the membranes are ruptured, the baby may suck your examining finger!
But as labour progresses, the baby’s face becomes o edematous (swollen with fluid), making it more difficult to distinguish from the soft shape you will feel in a breech presentation.
8.4.3 Complications of face presentation
Complications for the fetus include:
- Obstructed labour and ruptured uterus
- Cord prolapse
- Facial bruising
- Cerebral haemorrhage (bleeding inside the fetal skull).
8.5 Brow presentation

In brow presentation , the baby’s head is only partially extended at the neck (compare this with face presentation), so its brow (forehead) is the presenting part (Figure 8.6). This presentation is rare, with an incidence of 1 in 1000 deliveries at full term.
8.5.1 Possible causes of brow presentation
You have seen all of these factors before, as causes of other malpresentations:
- Lax uterus due to repeated full term pregnancy
- Polyhydramnios
8.5.2 Diagnosis of brow presentation
Brow presentation is not usually detected before the onset of labour, except by very experienced birth attendants. On abdominal examination, the head is high in the mother’s abdomen, appears unduly large and does not descend into the pelvis, despite good uterine contractions. On vaginal examination, the presenting part is high and may be difficult to reach. You may be able to feel the root of the nose, eyes, but not the mouth, tip of the nose or chin. You may also feel the anterior fontanel, but a large caput (swelling) towards the front of the fetal skull may mask this landmark if the woman has been in labour for some hours.
Recall the appearance of a normal caput over the posterior fontanel shown in Figure 4.4 earlier in this Module.
8.5.3 Complications of brow presentation
The complications of brow presentation are much the same as for other malpresentations:
- Cerebral haemorrhage.
Which are you more likely to encounter — face or brow presentations?
Face presentation, which occurs in 1 in 500 full term labours. Brow presentation is more rare, at 1 in 1,000 full term labours.
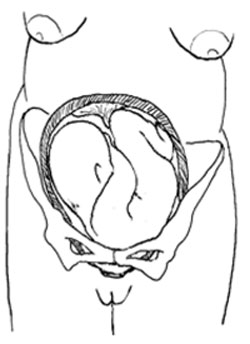
8.6 Shoulder presentation
Shoulder presentation is rare at full term, but may occur when the fetus lies transversely across the uterus (Figure 8.7), if it stopped part-way through spontaneous inversion from breech to vertex, or it may lie transversely from early pregnancy. If the baby lies facing upwards, its back may be the presenting part; if facing downwards its hand may emerge through the cervix. A baby in the transverse position cannot be born through the vagina and the labour will be obstructed. Refer babies in shoulder presentation urgently.
8.6.1 Causes of shoulder presentation
Causes of shoulder presentation could be maternal or fetal factors.
Maternal factors include:
- Lax abdominal and uterine muscles: most often after several previous pregnancies
- Uterine abnormality
- Contracted (abnormally narrow) pelvis.
Fetal factors include:
- Preterm labour
- Placenta previa.
What do ‘placenta previa’ and ‘polyhydramnios’ indicate?
Placenta previa is when the placenta is partly or completely covering the cervical opening. Polyhydramnios is an excess of amniotic fluid. They are both potential causes of malpresentation.
8.6.2 Diagnosis of shoulder presentation
On abdominal palpation, the uterus appears broader and the height of the fundus is less than expected for the period of gestation, because the fundus is not occupied by either the baby’s head or buttocks. You can usually feel the head on one side of the mother’s abdomen. On vaginal examination, in early labour, the presenting part may not be felt, but when the labour is well progressed, you may feel the baby’s ribs. When the shoulder enters the pelvic brim, the baby’s arm may prolapse and become visible outside the vagina.
8.6.3 Complications of shoulder presentation
Complications include:
- Trauma to a prolapsed arm
- Fetal hypoxia and death.
Remember that a shoulder presentation means the baby cannot be born through the vagina; if you detect it in a woman who is already in labour, refer her urgently to a higher health facility.
8.7 Multiple pregnancy
In this section, we turn to the subject of multiple pregnancy , when there is more than one fetus in the uterus. More than 95% of multiple pregnancies are twins (two fetuses), but there can also be triplets (three fetuses), quadruplets (four fetuses), quintuplets (five fetuses), and other higher order multiples with a declining chance of occurrence. The spontaneous occurrence of twins varies by country : it is lowest in East Asia n countries like Japan and China (1 out of 1000 pregnancies are fraternal or non-identical twins), and highest in black Africans , particularly in Nigeria , where 1 in 20 pr egnancies are fraternal twins. In general, compared to single babies, multiple pregnancies are highly associated with early pregnancy loss and high perinatal mortality, mainly due to prematurity.
8.7.1 Types of twin pregnancy
Twins may be identical (monozygotic) or non-identical and fraternal (dizigotic). Monozygotic twins develop from a single fertilised ovum (the zygote), so they are always the same sex and they share the same placenta . By contrast, dizygotic twins develop from two different zygotes, so they can have the same or different sex, and they have separate placenta s . Figure 8.8 shows the types of twin pregnancy and the processes by which they are formed.
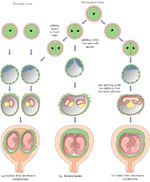
8.7.2 Diagnosis of twin pregnancy
On abdominal examination you may notice that:
- The size of the uterus is larger than the expected for the period for gestation.
- The uterus looks round and broad, and fetal movement may be seen over a large area. (The shape of the uterus at term in a singleton pregnancy in the vertex presentation appears heart-shaped rounder at the top and narrower at the bottom.)
- Two heads can be felt.
- Two fetal heart beats may be heard if two people listen at the same time, and they can detect at least 10 beats different (Figure 8.6).
- Ultrasound examination can make an absolute diagnosis of twin pregnancy.

8.7.3 Consequences of twin pregnancy
Women who are pregnant with twins are more prone to suffer with the minor disorders of pregnancy, like morning sickness, nausea and heartburn. Twin pregnancy is one cause of hyperemesis gravidarum (persistent, severe nausea and vomiting). Mothers of twins are also more at risk of developing iron and folate-deficiency anaemia during pregnancy.
Can you suggest why anaemia is a greater risk in multiple pregnancies?
The mother has to supply the nutrients to feed two (or more) babies; if she is not getting enough iron and folate in her diet, or through supplements, she will become anaemic.
Other complications include the following:
- Pregnancy-related hypertensive disorders like pre-eclampsia and eclampsia are more common in twin pregnancies.
- Pressure symptoms may occur in late pregnancy due to the increased weight and size of the uterus.
- Labour often occurs spontaneously before term, with p remature delivery or premature rupture of membranes (PROM) .
- Respiratory deficit ( shortness of breath, because of fast growing uterus) is another common problem.
Twin babies may be small in comparison to their gestational age and more prone to the complications associated with low birth weight (increased vulnerability to infection, losing heat, difficulty breastfeeding).
You will learn about low birth weight babies in detail in the Postnatal Care Module.
- Malpresentation is more common in twin pregnancies, and they may also be ‘locked’ at the neck with one twin in the vertex presentation and the other in breech. The risks associated with malpresentations already described also apply: prolapsed cord, poor uterine contraction, prolonged or obstructed labour, postpartum haemorrhage, and fetal hypoxia and death.
- Conjoined twins (fused twins, joined at the head, chest, or abdomen, or through the back) may also rarely occur.
8.8 Management of women with malpresentation or multiple pregnancy
As you have seen in this study session, any presentation other than vertex has its own dangers for the mother and baby. For this reason, all women who develop abnormal presentation or multiple pregnancy should ideally have skilled care by senior health professionals in a health facility where there is a comprehensive emergency obstetric service. Early detection and referral of a woman in any of these situations can save her life and that of her baby.
What can you do to reduce the risks arising from malpresentation or multiple pregnancy in women in your care?
During focused antenatal care of the pregnant women in your community, at every visit after 36 weeks of gestation you should check for the presence of abnormal fetal presentation. If you detect abnormal presentation or multiple pregnancy, you should refer the woman before the onset of labour.
Summary of Study Session 8
In Study Session 8, you learned that:
- During early pregnancy, babies are naturally in the breech position, but in 95% of cases they spontaneously reverse into the vertex presentation before labour begins.
- Malpresentation or malposition of the fetus at full term increases the risk of obstructed labour and other birth complications.
- Common causes of malpresentations/malpositions include: excess amniotic fluid, abnormal shape and size of the pelvis; uterine tumour; placenta praevia; slackness of uterine muscles (after many previous pregnancies); or multiple pregnancy.
- Common complications include: premature rupture of membranes, premature labour, prolonged/obstructed labour; ruptured uterus; postpartum haemorrhage; fetal and maternal distress which may lead to death.
- Vertex malposition is when the fetal head is in the occipito-posterior position — i.e. the back of the fetal skull is towards the mother’s back instead of pointing towards the front of the mother’s pelvis. 90% of vertex malpositions rotate and deliver normally.
- Breech presentation (complete, frank or footling) is when the baby’s buttocks present during labour. It occurs in 3–4% of labours after 34 weeks of pregnancy and may lead to obstructed labour, cord prolapse, hypoxia, premature separation of the placenta, birth injury to the baby or to the birth canal.
- Face presentation is when the fetal head is bent so far backwards that the face presents during labour. It occurs in about 1 in 500 full term labours. ‘Chin posterior’ face presentations usually rotate spontaneously to the ‘chin anterior’ position and deliver normally. If rotation does not occur, a caesarean delivery is likely to be necessary.
- Brow presentation is when the baby’s forehead is the presenting part. It occurs in about 1 in 1000 full term labours and is difficult to detect before the onset of labour. Caesarean delivery is likely to be necessary.
- Shoulder presentation occurs when the fetal lie during labour is transverse. Once labour is well progressed, vaginal examination may feel the baby’s ribs, and an arm may sometimes prolapse. Caesarean delivery is always required unless a doctor or midwife can turn the baby head-down.
- Multiple pregnancies are always at high risk of malpresentation. Mothers need greater antenatal care, and twins are more prone to complications associated with low birth weight and prematurity.
- Any presentation other than vertex after 34 weeks of gestation is considered as high risk to the mother and to her baby. Do not attempt to turn a malpresenting or malpositioned baby! Refer the mother for emergency obstetric care.
Self-Assessment Questions (SAQs) for Study Session 8
Now that you have completed this study session, you can assess how well you have achieved its Learning Outcomes by answering the following questions. Write your answers in your Study Diary and discuss them with your Tutor at the next Study Support Meeting. You can check your answers with the Notes on the Self-Assessment Questions at the end of this Module.
SAQ 8.1 (tests Learning Outcomes 8.1, 8.2 and 8.4)
Which of the following definitions are true and which are false? Write down the correct definition for any which you think are false.
A Fundus — the ‘rounded top’ and widest cavity of the uterus.
B Complete breech — where the legs are bent at both hips and knee joints and are folded underneath the baby.
C Frank breech — where the breech is so difficult to treat that you have to be very frank and open with the mother about the difficulties she will face in the birth.
D Footling breech — when one or both legs are extended so that the baby presents ‘foot first’.
E Hypoxia — the baby gets too much oxygen.
F Multiple pregnancy — when a mother has had many babies previously.
G Monozygotic twins — develop from a single fertilised ovum (the zygote). They can be different sexes but they share the same placenta.
H Dizygotic twins — develop from two zygotes. They have separate placentas, and can be of the same sex or different sexes.
A is true. The fundus is the ‘rounded top’ and widest cavity of the uterus.
B is true. Complete breech is where the legs are bent at both hips and knee joints and are folded underneath the baby.
C is false . A frank breech is the most common type of breech presentation and is when the baby’s legs point straight upwards (see Figure 8.4).
D is true. A footling breech is when one or both legs are extended so that the baby presents ‘foot first’.
E is false . Hypoxia is when the baby is deprived of oxygen and risks permanent brain damage or death.
F is false. Multiple pregnancy is when there is more than one fetus in the uterus.
G is false. Monozygotic twins develop from a single fertilised ovum (the zygote), and they are always the same sex , as well as sharing the same placenta.
H is true. Dizygotic twins develop from two zygotes, have separate placentas, and can be of the same or different sexes.
SAQ 8.2 (tests Learning Outcomes 8.1 and 8.2)
What are the main differences between normal and abnormal fetal presentations? Use the correct medical terms in bold in your explanation.
In a normal presentation, the vertex (the highest part of the fetal head) arrives first at the mother’s pelvic brim, with the occiput (the back of the baby’s skull) pointing towards the front of the mother’s pelvis (the pubic symphysis ).
Abnormal presentations are when there is either a vertex malposition (the occiput of the fetal skull points towards the mother’s back instead towards of the pubic symphysis), or a malpresentation (when anything other than the vertex is presenting): e.g. breech presentation (buttocks first); face presentation (face first); brow presentation (forehead first); and shoulder presentation (transverse fetal).
SAQ 8.3 (tests Learning Outcomes 8.3 and 8.5)
- a. List the common complications of malpresentations or malposition of the fetus at full term.
- b. What action should you take if you identify that the fetus is presenting abnormally and labour has not yet begun?
- c. What should you not attempt to do?
- a. The common complications of malpresentation or malposition of the fetus at full term include: premature rupture of membranes, premature labour, prolonged/obstructed labour; ruptured uterus; postpartum haemorrhage; fetal and maternal distress which may lead to death.
- b. You should refer the mother to a higher health facility – she may need emergency obstetric care.
- c. You should not attempt to turn the baby by hand. This should only be attempted by a specially trained doctor or midwife and should only be done at a health facility.
SAQ 8.4 (tests Learning Outcomes 8.4 and 8.5)
A pregnant woman moves into your village who is already at 37 weeks gestation. You haven’t seen her before. She tells you that she gave birth to twins three years ago and wants to know if she is having twins again this time.
- a. How would you check this?
- b. If you diagnose twins, what would you do to reduce the risks during labour and delivery?
- Is the uterus larger than expected for the period of gestation?
- What is its shape – is it round (indicative of twins) or heart-shaped (as in a singleton pregnancy)?
- Can you feel more than one head?
- Can you hear two fetal heartbeats (two people listening at the same time) with at least 10 beats difference?
- If there is access to a higher health facility, and you are still not sure, try and get the woman to it for an ultrasound scan.
- Be extra careful to check that the mother is not anaemic.
- Encourage her to rest and put her feet up to reduce the risk of increased blood pressure or swelling in her legs and feet.
- Be alert to the increased risk of pre-eclampsia.
- Expect her to go into labour before term, and be ready to get her to the health facility before she goes into labour, going with her if at all possible.
- Get in early touch with that health facility to warn them to expect a referral from you.
- Make sure that transport is ready to take her to a health facility when needed.
Except for third party materials and/or otherwise stated (see terms and conditions ) the content in OpenLearn is released for use under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Sharealike 2.0 licence . In short this allows you to use the content throughout the world without payment for non-commercial purposes in accordance with the Creative Commons non commercial sharealike licence. Please read this licence in full along with OpenLearn terms and conditions before making use of the content.
When using the content you must attribute us (The Open University) (the OU) and any identified author in accordance with the terms of the Creative Commons Licence.
The Acknowledgements section is used to list, amongst other things, third party (Proprietary), licensed content which is not subject to Creative Commons licensing. Proprietary content must be used (retained) intact and in context to the content at all times. The Acknowledgements section is also used to bring to your attention any other Special Restrictions which may apply to the content. For example there may be times when the Creative Commons Non-Commercial Sharealike licence does not apply to any of the content even if owned by us (the OU). In these stances, unless stated otherwise, the content may be used for personal and non-commercial use. We have also identified as Proprietary other material included in the content which is not subject to Creative Commons Licence. These are: OU logos, trading names and may extend to certain photographic and video images and sound recordings and any other material as may be brought to your attention.
Unauthorised use of any of the content may constitute a breach of the terms and conditions and/or intellectual property laws.
We reserve the right to alter, amend or bring to an end any terms and conditions provided here without notice.
All rights falling outside the terms of the Creative Commons licence are retained or controlled by The Open University.
Head of Intellectual Property, The Open University
- GP practice services
- Health advice
- Health research
- Medical professionals
Health topics
Advice and clinical information on a wide variety of healthcare topics.
All health topics
Latest features
Allergies, blood & immune system
Bones, joints and muscles
Brain and nerves
Chest and lungs
Children's health
Cosmetic surgery
Digestive health
Ear, nose and throat
General health & lifestyle
Heart health and blood vessels
Kidney & urinary tract
Men's health
Mental health
Oral and dental care
Senior health
Sexual health
Signs and symptoms
Skin, nail and hair health
Travel and vaccinations
Treatment and medication
Women's health
Healthy living
Expert insight and opinion on nutrition, physical and mental health.
Exercise and physical activity
Healthy eating
Healthy relationships
Managing harmful habits
Mental wellbeing
Relaxation and sleep
Managing conditions
From ACE inhibitors for high blood pressure, to steroids for eczema, find out what options are available, how they work and the possible side effects.
Featured conditions
ADHD in children
Crohn's disease
Endometriosis
Fibromyalgia
Gastroenteritis
Irritable bowel syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Scarlet fever
Tonsillitis
Vaginal thrush
Health conditions A-Z
Medicine information
Information and fact sheets for patients and professionals. Find out side effects, medicine names, dosages and uses.
All medicines A-Z
Allergy medicines
Analgesics and pain medication
Anti-inflammatory medicines
Breathing treatment and respiratory care
Cancer treatment and drugs
Contraceptive medicines
Diabetes medicines
ENT and mouth care
Eye care medicine
Gastrointestinal treatment
Genitourinary medicine
Heart disease treatment and prevention
Hormonal imbalance treatment
Hormone deficiency treatment
Immunosuppressive drugs
Infection treatment medicine
Kidney conditions treatments
Muscle, bone and joint pain treatment
Nausea medicine and vomiting treatment
Nervous system drugs
Reproductive health
Skin conditions treatments
Substance abuse treatment
Vaccines and immunisation
Vitamin and mineral supplements
Tests & investigations
Information and guidance about tests and an easy, fast and accurate symptom checker.
About tests & investigations
Symptom checker
Blood tests
BMI calculator
Pregnancy due date calculator
General signs and symptoms
Patient health questionnaire
Generalised anxiety disorder assessment
Medical professional hub
Information and tools written by clinicians for medical professionals, and training resources provided by FourteenFish.
Content for medical professionals
FourteenFish training
- Professional articles
Evidence-based professional reference pages authored by our clinical team for the use of medical professionals.
View all professional articles A-Z
Actinic keratosis
Bronchiolitis
Molluscum contagiosum
Obesity in adults
Osmolality, osmolarity, and fluid homeostasis
Recurrent abdominal pain in children
Medical tools and resources
Clinical tools for medical professional use.
All medical tools and resources
Malpresentations and malpositions
Peer reviewed by Dr Laurence Knott Last updated by Dr Colin Tidy, MRCGP Last updated 22 Jun 2021
Meets Patient’s editorial guidelines
Medical Professionals
Professional Reference articles are designed for health professionals to use. They are written by UK doctors and based on research evidence, UK and European Guidelines. You may find one of our health articles more useful.
In this article :
Malpresentation, malposition.
Usually the fetal head engages in the occipito-anterior position (more often left occipito-anterior (LOA) rather than right) and then undergoes a short rotation to be directly occipito-anterior in the mid-cavity. Malpositions are abnormal positions of the vertex of the fetal head relative to the maternal pelvis. Malpresentations are all presentations of the fetus other than vertex.
Obstetrics - the pelvis and head

Continue reading below
Predisposing factors to malpresentation include:
Prematurity.
Multiple pregnancy.
Abnormalities of the uterus - eg, fibroids.
Partial septate uterus.
Abnormal fetus.
Placenta praevia.
Primiparity.
Breech presentation
See the separate Breech Presentations article for more detailed discussion.
Breech presentation is the most common malpresentation, with the majority discovered before labour. Breech presentation is much more common in premature labour.
Approximately one third are diagnosed during labour when the fetus can be directly palpated through the cervix.
After 37 weeks, external cephalic version can be attempted whereby an attempt is made to turn the baby manually by manipulating the pregnant mother's abdomen. This reduces the risk of non-cephalic delivery 1 .
Maternal postural techniques have also been tried but there is insufficient evidence to support these 2 .
Many women who have a breech presentation can deliver vaginally. Factors which make this less likely to be successful include 3 :
Hyperextended neck on ultrasound.
High estimated fetal weight (more than 3.8 kg).
Low estimated weight (less than tenth centile).
Footling presentation.
Evidence of antenatal fetal compromise.
Transverse lie 4
When the fetus is positioned with the head on one side of the pelvis and the buttocks in the other (transverse lie), vaginal delivery is impossible.
This requires caesarean section unless it converts or is converted late in pregnancy. The surgeon may be able to rotate the fetus through the wall of the uterus once the abdominal wall has been opened. Otherwise, a transverse uterine incision is needed to gain access to a fetal pole.
Internal podalic version is no longer attempted.
Transverse lie is associated with a risk of cord prolapse of up to 20%.
Occipito-posterior position
This is the most common malposition where the head initially engages normally but then the occiput rotates posteriorly rather than anteriorly. 5.2% of deliveries are persistent occipito-posterior 5 .
The occipito-posterior position results from a poorly flexed vertex. The anterior fontanelle (four radiating sutures) is felt anteriorly. The posterior fontanelle (three radiating sutures) may also be palpable posteriorly.
It may occur because of a flat sacrum, poorly flexed head or weak uterine contractions which may not push the head down into the pelvis with sufficient strength to produce correct rotation.
As occipito-posterior-position pregnancies often result in a long labour, close maternal and fetal monitoring are required. An epidural is often recommended and it is essential that adequate fluids be given to the mother.
The mother may get the urge to push before full dilatation but this must be discouraged. If the head comes into a face-to-pubis position then vaginal delivery is possible as long as there is a reasonable pelvic size. Otherwise, forceps or caesarean section may be required.
Occipito-transverse position
The head initially engages correctly but fails to rotate and remains in a transverse position.
Alternatives for delivery include manual rotation of fetal head using Kielland's forceps, or delivery using vacuum extraction. This is inappropriate if there is any fetal acidosis because of the risk of cerebral haemorrhage.
Therefore, there must be provision for a failure of forceps delivery to be changed immediately to a caesarean. The trial of forceps is therefore often performed in theatre. Some centres prefer to manage by caesarean section without trial of forceps.
Face presentations
Face presents for delivery if there is complete extension of the fetal head.
Face presentation occurs in 1 in 1,000 deliveries 5 .
With adequate pelvic size, and rotation of the head to the mento-anterior position, vaginal delivery should be achieved after a long labour.
Backwards rotation of the head to a mento-posterior position requires a caesarean section.
Brow positions
The fetal head stays between full extension and full flexion so that the biggest diameter (the mento-vertex) presents.
Brow presentation occurs in 0.14% of deliveries 5 .
Brow presentation is usually only diagnosed once labour is well established.
The anterior fontanelle and super orbital ridges are palpable on vaginal examination.
Unless the head flexes, a vaginal delivery is not possible, and a caesarean section is required.
Further reading and references
- Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R, West HM ; External cephalic version for breech presentation at term. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 1;(4):CD000083. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000083.pub3.
- Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R ; Cephalic version by postural management for breech presentation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Oct 17;10:CD000051. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000051.pub2.
- Management of Breech Presentation ; Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (Mar 2017)
- Szaboova R, Sankaran S, Harding K, et al ; PLD.23 Management of transverse and unstable lie at term. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2014 Jun;99 Suppl 1:A112-3. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2014-306576.324.
- Gardberg M, Leonova Y, Laakkonen E ; Malpresentations - impact on mode of delivery. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2011 May;90(5):540-2. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0412.2011.01105.x.
Article history
The information on this page is written and peer reviewed by qualified clinicians.
Next review due: 21 Jun 2026
22 jun 2021 | latest version.
Last updated by
Peer reviewed by

Feeling unwell?
Assess your symptoms online for free
Need to talk? Call 1800 882 436. It's a free call with a maternal child health nurse. *call charges may apply from your mobile
Is it an emergency? Dial 000 If you need urgent medical help, call triple zero immediately.
Share via email
There is a total of 5 error s on this form, details are below.
- Please enter your name
- Please enter your email
- Your email is invalid. Please check and try again
- Please enter recipient's email
- Recipient's email is invalid. Please check and try again
- Agree to Terms required
Error: This is required
Error: Not a valid value
Malpresentation
8-minute read
If you feel your waters break and you have been told that your baby is not in a head-first position, seek medical help immediately .
- Malpresentation is when your baby is not facing head-first down the birth canal as birth approaches.
- The most common type of malpresentation is breech — when your baby’s bottom or feet are facing downwards.
- A procedure called external cephalic version can sometimes turn a breech baby into a head-first position at 36 weeks.
- Most babies with malpresentation are born by caesarean, but you may be able to have a vaginal birth if your baby is breech.
- There is a serious risk of cord prolapse if your waters break and your baby is not head-first.
What are presentation and malpresentation?
‘Presentation’ describes how your baby is facing down the birth canal. The ‘presenting part’ is the part of your baby’s body that is against the cervix .
The ideal presentation is head-first, with the crown (top) of the baby’s head against the cervix, with the chin tucked into the baby’s chest. This is called ‘vertex presentation’.
If your baby is in any other position, it’s called ‘malpresentation’. Malpresentation can mean your baby’s face, brow, buttocks, foot, back, shoulder, arms or legs or the umbilical cord are against the cervix.
It’s safest for your baby’s head to come out first. If any other body part goes down the birth canal first, the risks to you and your baby may be higher. Malpresentation increases the chance that you will have a more complex vaginal birth or a caesarean.
If my baby is not head-first, what position could they be in?
Malpresentation is caused by your baby’s position (‘lie’). There are different types of malpresentation.
Breech presentation
This is when your baby is lying with their bottom or feet facing down. Sometimes one foot may enter the birth canal first (called a ‘footling presentation’).
Breech presentation is the most common type of malpresentation.
Face presentation
This is when your baby is head-first but stretching their neck, with their face against the cervix.
Transverse lie
This is when your baby is lying sideways. Their back, shoulders, arms or legs may be the first to enter the birth canal.
Oblique lie
This is when your baby is lying diagonally. No particular part of their body is against the cervix.

Unstable lie
This is when your baby continually changes their position after 36 weeks of pregnancy.
Cord presentation
This is when the umbilical cord is against the cervix, between your baby and the birth canal. It can happen in any situation where your baby’s presenting part is not sitting snugly in your pelvis. It can become an emergency if it leads to cord prolapse (when the cord is born before your baby, potentially reducing placental blood flow to your baby).
What is malposition?
If your baby is lying head-first, the best position for labour is when their face is towards your back.
If your baby is facing the front of your body (posterior position) or facing your side (transverse position) this is called malposition. Transverse position is not the same as transverse lie. A transverse position means your labour may take a bit longer and you might feel more pain in your back. Often your baby will move into a better position before or during labour.
Why might my baby be in the wrong position?
Malpresentation may be caused by:
- a low-lying placenta
- too much or too little amniotic fluid
- many previous pregnancies, making the muscles of the uterus less stable
- carrying twins or more
Often no cause is found.
Is it likely that my baby will be in the wrong position?
Many babies are in a breech position during pregnancy. They usually turn head-first as pregnancy progresses, and more than 9 in 10 babies in Australia have a vertex presentation (ideal presentation, head-first) at birth.
You are more likely to have a malpresentation if:
- this is your first baby
- you are over 40 years old
- you've had a previous breech baby
- you go into labour prematurely
How is malpresentation diagnosed?
Malpresentation is normally diagnosed when your doctor or midwife examines you, from 36 weeks of pregnancy. If it’s not clear, it can be confirmed with an ultrasound.
Can my baby’s position be changed?
If you are 36 weeks pregnant , it may be possible to gently turn your baby into a head-first position. This is done by an obstetrician using a technique called external cephalic version (ECV).
Some people try different postures or acupuncture to correct malpresentation, but there isn’t reliable evidence that either of these work.
Will I need a caesarean if my baby has a malpresentation?
Most babies with a malpresentation close to birth are born by caesarean . You may be able to have a vaginal birth with a breech baby, but you will need to go to a hospital that can offer you and your baby specialised care.
If your baby is breech, an elective (planned) caesarean is safer for your baby than a vaginal birth in the short term. However, in the longer term their health will be similar, on average, regardless of how they were born.
A vaginal birth is safer for you than an elective caesarean. However, about 4 in 10 people planning a vaginal breech birth end up needing an emergency caesarean . If this happens to you, the risk of complications will be higher.
Your doctor can talk to you about your options. Whether it’s safe for you to try a vaginal birth will depend on many factors. These include how big your baby is, the position of your baby, the structure of your pelvis and whether you’ve had a caesarean in the past.
What are the risks if I have my baby when it’s not head-first?
If your waters break when your baby is not head-first, there is a risk of cord prolapse. This is an emergency.
Vaginal breech birth
Risks to your baby can include:
- Erb’s palsy
- fractures, dislocations or other injuries
- bleeding in your baby’s brain
- low Apgar scores
- their head getting stuck – this is an emergency
Risks to you include:
- blood loss or blood clots
- infection in the wound
- problems with the anaesthetic
- damage to other organs nearby, such as your bladder
- a higher chance of problems in future pregnancies
- a longer recovery time than after a vaginal birth
Risks to your baby include:
- trouble with breathing — this is temporary
- getting a small cut during the surgery
Will I have a malpresentation in my future pregnancies?
If you had a malpresentation in one pregnancy, you have a higher chance of it happening again, but it won’t necessarily happen in future pregnancies. If you’re worried, it may help to talk to your doctor or midwife so they can explain what happened.

Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call . Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content .
Last reviewed: July 2022
Related pages
Labour complications.
- Interventions during labour
- Giving birth - stages of labour
Breech pregnancy
Search our site for.
- Caesarean Section
- Foetal Version
Need more information?
Top results
When a baby is positioned bottom-down late in pregnancy, this is called the breech position. Find out about 3 main types and safe birthing options.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website

Breech Presentation at the End of your Pregnancy
Breech presentation occurs when your baby is lying bottom first or feet first in the uterus (womb) rather than the usual head first position. In early pregnancy, a breech position is very common.
Read more on RANZCOG - Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists website

Breech presentation and turning the baby
In preparation for a safe birth, your health team will need to turn your baby if it is in a bottom first ‘breech’ position.
Read more on WA Health website

External Cephalic Version for Breech Presentation - Pregnancy and the first five years
This information brochure provides information about an External Cephalic Version (ECV) for breech presentation
Read more on NSW Health website

Presentation and position of baby through pregnancy and at birth
Presentation and position refer to where your baby’s head and body is in relation to your birth canal. Learn why it’s important for labour and birth.
Even if you’re healthy and well prepared for childbirth, there’s always a chance of unexpected problems. Learn more about labour complications.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Call us and speak to a Maternal Child Health Nurse for personal advice and guidance.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Government Accredited with over 140 information partners
We are a government-funded service, providing quality, approved health information and advice

Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
© 2024 Healthdirect Australia Limited
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.

An expert resource for medical professionals Provided FREE as a service to women’s health
The Global Library of Women’s Medicine EXPERT – RELIABLE - FREE Over 20,000 resources for health professionals
The Alliance for Global Women’s Medicine A worldwide fellowship of health professionals working together to promote, advocate for and enhance the Welfare of Women everywhere

An Educational Platform for FIGO
The Global Library of Women’s Medicine Clinical guidance and resourses
A vast range of expert online resources. A FREE and entirely CHARITABLE site to support women’s healthcare professionals
The Global Academy of Women’s Medicine Teaching, research and Diplomates Association
- Expert clinical guidance
- Safer motherhood
- Skills videos
- Clinical films
- Special textbooks
- Ambassadors
- Can you help us?
- Introduction
- Definitions
- Complications
- External Cephalic Version
- Management of Labor And Delivery
- Cesarean Delivery
- Perinatal Outcome
- Practice Recommendations
- Study Assessment – Optional
- Your Feedback
This chapter should be cited as follows: Okemo J, Gulavi E, et al , Glob. libr. women's med ., ISSN: 1756-2228; DOI 10.3843/GLOWM.414593
The Continuous Textbook of Women’s Medicine Series – Obstetrics Module
Common obstetric conditions
Volume Editor: Professor Sikolia Wanyonyi , Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi, Kenya

Abnormal Lie/Presentation
First published: February 2021
Study Assessment Option
By completing 4 multiple-choice questions (randomly selected) after studying this chapter readers can qualify for Continuing Professional Development awards from FIGO plus a Study Completion Certificate from GLOWM See end of chapter for details
INTRODUCTION
The mechanism of labor and delivery, as well as the safety and efficacy, is determined by the specifics of the fetal and maternal pelvic relationship at the onset of labor. Normal labor occurs when regular and painful contractions cause progressive cervical dilatation and effacement, accompanied by descent and expulsion of the fetus. Abnormal labor involves any pattern deviating from that observed in the majority of women who have a spontaneous vaginal delivery and includes:
- Protraction disorders (slower than normal progress);
- Arrest disorders (complete cessation of progress).
Among the causes of abnormal labor is the disproportion between the presenting part of the fetus and the maternal pelvis, which rather than being a true disparity between fetal size and maternal pelvic dimensions, is usually due to a malposition or malpresentation of the fetus.
This chapter reviews how to define, diagnose, and manage the clinical impact of abnormalities of fetal lie and malpresentation with the most commonly occurring being the breech-presenting fetus.
DEFINITIONS
At the onset of labor, the position of the fetus in relation to the birth canal is critical to the route of delivery and, thus, should be determined early. Important relationships include fetal lie, presentation, attitude, and position .
Fetal lie describes the relationship of the fetal long axis to that of the mother. In more than 99% of labors at term, the fetal lie is longitudinal . A transverse lie is less frequent when the fetal and maternal axes may cross at a 90 ° angle, and predisposing factors include multiparity, placenta previa, hydramnios, and uterine anomalies. Occasionally, the fetal and maternal axes may cross at a 45 ° angle, forming an oblique lie .
Fetal presentation
The presenting part is the portion of the fetal body that is either foremost within the birth canal or in closest proximity to it. Thus, in longitudinal lie, the presenting part is either the fetal head or the breech, creating cephalic and breech presentations , respectively. The shoulder is the presenting part when the fetus lies with the long axis transversely.
Commonly the baby lies longitudinally with cephalic presentation. However, in some instances, a fetus may be in breech where the fetal buttocks are the presenting part. Breech fetuses are also referred to as malpresentations. Fetuses that are in a transverse lie may present the fetal back (or shoulders, as in the acromial presentation), small parts (arms and legs), or the umbilical cord (as in a funic presentation) to the pelvic inlet. When the fetal long axis is at an angle to the bony inlet, and no palpable fetal part generally is presenting, the fetus is likely in oblique lie. This lie usually is transitory and occurs during fetal conversion between other lies during labor.
The point of direction is the most dependent portion of the presenting part. In cephalic presentation in a well-flexed fetus, the occiput is the point of direction.
The fetal position refers to the location of the point of direction with reference to the four quadrants of the maternal outlet as viewed by the examiner. Thus, position may be right or left as well as anterior or posterior.
Unstable lie
Refers to the frequent changing of fetal lie and presentation in late pregnancy (usually refers to pregnancies >37 weeks).
Fetal position
Fetal position refers to the relationship of an arbitrarily chosen portion of the fetal presenting part to the right or left side of the birth canal. With each presentation there may be two positions – right or left. The fetal occiput, chin (mentum) and sacrum are the determining points in vertex, face, and breech presentations. Thus:
- left and right occipital presentations
- left and right mental presentations
- left and right sacral presentations.
Fetal attitude
The fetus instinctively forms an ovoid mass that corresponds to the shape of the uterine cavity towards the third trimester, a characteristic posture described as attitude or habitus. The fetus becomes folded upon itself to create a convex back, the head is flexed, and the chin is almost in contact with the chest. The thighs are flexed over the abdomen and the legs are bent at the knees. The arms are usually parallel to the sides or lie across the chest while the umbilical cord fills the space between the extremities. This posture is as a result of fetal growth and accommodation to the uterine cavity. It is possible that the fetal head can become progressively extended from the vertex to face presentation resulting in a change of fetal attitude from convex (flexed) to concave (extended) contour of the vertebral column.
The categories of frank, complete, and incomplete breech presentations differ in their varying relations between the lower extremities and buttocks (Figure 1). With a frank breech, lower extremities are flexed at the hips and extended at the knees, and thus the feet lie close to the head. With a complete breech, both hips are flexed, and one or both knees are also flexed. With an incomplete breech, one or both hips are extended. As a result, one or both feet or knees lie below the breech, such that a foot or knee is lowermost in the birth canal. A footling breech is an incomplete breech with one or both feet below the breech.
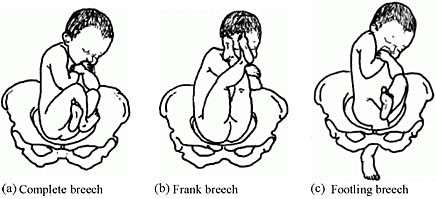
Types of breech presentation. Reproduced from WHO 2006, 1 with permission.
The relative incidence of differing fetal and pelvic relations varies with diagnostic and clinical approaches to care.
About 1 in 25 fetuses are breech at the onset of labor and about 1 in 100 are transverse or oblique, also referred to as non-axial. 2
With increasing gestational age, the prevalence of breech presentation decreases. In early pregnancy the fetus is highly mobile within a relatively large volume of amniotic fluid, therefore it is a common finding. The incidence of breech presentation is 20–25% of fetuses at <28 weeks, but only 7–16% at 32 weeks, and only 3–4% at term. 2 , 3
Face and brow presentation are uncommon. Their prevalence compared with other types of malpresentations are shown below. 4
- Occiput posterior – 1/19 deliveries;
- Breech – 1/33 deliveries;
- Face – 1/600–1/800 deliveries;
- Brow – 1/500–1/4000 deliveries;
- Transverse lie – 1/833 deliveries;
- Compound – 1/1500 deliveries.
Transverse lie is often unstable and fetuses in this lie early in pregnancy later convert to a cephalic or breech presentation.
The fetus has a relatively larger head than body during most of the late second and early third trimester, it therefore tends to spend much of its time in breech presentation or in a non-axial lie as it rotates back and forth between cephalic and breech presentations. The relatively large volume of amniotic fluid present facilitates this dynamic presentation.
Abnormal fetal lie is frequently seen in multifetal gestation, especially with the second twin. In women of grand parity, in whom relaxation of the abdominal and uterine musculature tends to occur, a transverse lie may be encountered. Prematurity and macrosomia are also predisposing factors. Distortion of the uterine cavity shape, such as that seen with leiomyomas, prior uterine surgery, or developmental anomalies (Mullerian fusion defects), predisposes to both abnormalities in fetal lie and malpresentations. The location of the placenta also plays a contributing role with fundal and cornual implantation being seen more frequently in breech presentation. Placenta previa is a well-described affiliate for both transverse lie and breech presentation.
Fetuses with congenital anomalies also present with abnormalities in either presentation or lie. It is possibly as a cause (i.e. fitting the uterine cavity optimally) or effect (the fetus with a neuromuscular condition that prevents the normal turning mechanism). The finding of an abnormal lie or malpresentation requires a thorough search for fetal abnormalities. Such abnormalities could include chromosomal (autosomal trisomy) and structural abnormalities (hydrocephalus), as well as syndromes of multiple effects (fetal alcohol syndrome).
In most cases, breech presentation appears to be as a chance occurrence; however, up to 15% may be owing to fetal, maternal, or placental abnormalities. It is commonly thought that a fetus with normal anatomy, activity, amniotic fluid volume, and placental location adopts the cephalic presentation near term because this position is the best fit for the intrauterine space, but if any of these variables is abnormal, then breech presentation is more likely.
Factors associated with breech presentation are shown in Table 1.
Risk factors for breech presentation.
Spontaneous version may occur at any time before delivery, even after 40 weeks of gestation. A prospective longitudinal study using serial ultrasound examinations reported the likelihood of spontaneous version to cephalic presentation after 36 weeks was 25%. 5
In population-based registries, the frequency of breech presentation in a second pregnancy was approximately 2% if the first pregnancy was not a breech presentation and approximately 9% if the first pregnancy was a breech presentation. After two consecutive pregnancies with breech presentation at delivery, the risk of another breech presentation was approximately 25% and this rose to 40% after three consecutive breech deliveries. 6 , 7
In addition, parents who themselves were delivered at term from breech presentation were twice as likely to have their offspring in breech presentation as parents who were delivered in cephalic presentation. This suggests a possible heritable component to fetal presentation. 8
Leopold’s maneuvers
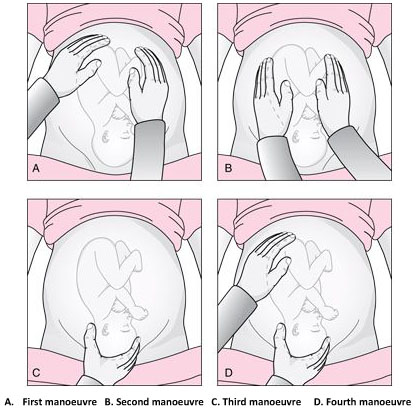
The Leopold’s maneuvers: palpation of fetus in left occiput anterior position. Reproduced from World Health Organization, 2006, 1 with permission.
Abdominal examination can be conducted systematically employing the four maneuvers described by Leopold in 1894. 9 , 10 In obese patients, in polyhydramnios patients or those with anterior placenta, these maneuvers are difficult to perform and interpret.
The first maneuver is to assess the uterine fundus. This allows the identification of fetal lie and determination of which fetal pole, cephalic or podalic – occupies the fundus. In breech presentation, there is a sensation of a large, nodular mass, whereas the head feels hard and round and is more mobile.
The second maneuver is accomplished as the palms are placed on either side of the maternal abdomen, and gentle but deep pressure is exerted. On one side, a hard, resistant structure is felt – the back. On the other, numerous small, irregular, mobile parts are felt – the fetal extremities. By noting whether the back is directed anteriorly, transversely, or posteriorly, fetal orientation can be determined.
The third maneuver aids confirmation of fetal presentation. The thumb and fingers of one hand grasp the lower portion of the maternal abdomen just above the symphysis pubis. If the presenting part is not engaged, a movable mass will be felt, usually the head. The differentiation between head and breech is made as in the first maneuver.
The fourth maneuver helps determine the degree of descent. The examiner faces the mother’s feet, and the fingertips of both hands are positioned on either side of the presenting part. They exert inward pressure and then slide caudad along the axis of the pelvic inlet. In many instances, when the head has descended into the pelvis, the anterior shoulder or the space created by the neck may be differentiated readily from the hard head.
According to Lyndon-Rochelle et al ., 11 experienced clinicians have accurately identified fetal malpresentation using Leopold maneuvers with a high sensitivity 88%, specificity 94%, positive-predictive value 74%, and negative-predictive value 97%.
Vaginal examination
Prelabor diagnosis of fetal presentation is difficult as the presenting part cannot be palpated through a closed cervix. Once labor begins and the cervix dilates, and palpation through vaginal examination is possible. Vertex presentations and their positions are recognized by palpation of the various fetal sutures and fontanels, while face and breech presentations are identified by palpation of facial features or the fetal sacrum and perineum, respectively.
Sonography and radiology
Sonography is the gold standard for identifying fetal presentation. This can be done during antenatal period or intrapartum. In obese women or in women with muscular abdominal walls this is especially important. Compared with digital examinations, sonography for fetal head position determination during second stage labor is more accurate. 12 , 13
COMPLICATIONS
Adverse outcomes in malpresented fetuses are multifactorial. They could be due to either underlying conditions associated with breech presentation (e.g., congenital anomalies, intrauterine growth restriction, preterm birth) or trauma during delivery.
Neonates who were breech in utero are more at risk for mild deformations (e.g., frontal bossing, prominent occiput, upward slant and low-set ears), torticollis, and developmental dysplasia of the hip.
Other obstetric complications include prolapse of the umbilical cord, intrauterine infection, maldevelopment as a result of oligohydramnios, asphyxia, and birth trauma and all are concerns.
Birth trauma especially to the head and cervical spine, is a significant risk to both term and preterm infants who present breech. In cephalic presenting fetuses, the labor process prepares the head for delivery by causing molding which helps the fetus to adapt to the birth canal. Conversely, the after-coming head of the breech fetus must descend and deliver rapidly and without significant change in shape. Therefore, small alterations in the dimensions or shape of the maternal bony pelvis or the attitude of the fetal head may have grave consequences. This process poses greater risk to the preterm infant because of the relative size of the fetal head and body. Trauma to the head is not eliminated by cesarean section; both intracranial and cervical spine trauma may result from entrapment in either the uterine or abdominal incisions.
In resource-limited countries where ultrasound imaging, urgent cesarean delivery, and neonatal intensive care are not readily available, the maternal and perinatal mortality/morbidity associated with transverse lie in labor can be high. Uterine rupture from prolonged labor in a transverse lie is a major reason for maternal/perinatal mortality and morbidity.
EXTERNAL CEPHALIC VERSION
External cephalic version (ECV) is the manual rotation of the fetus from a non-cephalic to a cephalic presentation by manipulation through the maternal abdomen (Figure 3).
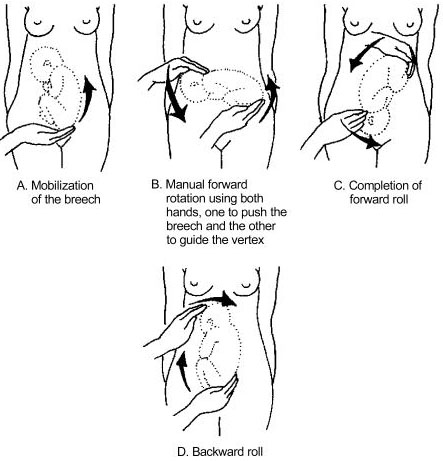
External version of breech presentation . Reproduced from WHO 2003 , 14 with permission .
This procedure is usually performed as an elective procedure in women who are not in labor at or near term to improve their chances of having a vaginal cephalic birth. ECV reduces the risk of non-cephalic presentation at birth by approximately 60% (relative risk [RR] 0.42, 95% CI 0.29–0.61) and reduces the risk of cesarean delivery by approximately 40% (RR 0.57, 95% CI 0.40–0.82). 7
In a 2008 systematic review of 84 studies including almost 13,000 version attempts at term, the pooled success rate was 58%. 15
A subsequent large series of 2614 ECV attempts over 18 years reported a success rate of 49% and provided more details): 16
- The success rate was 40% in nulliparous women and 64% in parous women.
- After successful ECV, 97% of fetuses remained cephalic at birth, 86% of which were delivered vaginally.
- Spontaneous version to a cephalic presentation occurred after 4.3% of failed attempts, and 2.2% of successfully vertexed cases reverted to breech.
Factors associated with lower ECV success rates include nulliparity, anterior placenta, lateral or cornual placenta, decreased amniotic fluid volume, low birth weight, obesity, posteriorly located fetal spine, frank breech presentation, ruptured membranes.
The following factors should be considered while managing malpresentations: type of malpresentation, gestational age at diagnosis, availability of skilled personnel, institutional resources and protocols and patient factors and preferences.
Breech presentation
According to a term breech trial, 17 planned cesarean delivery carries a reduced perinatal mortality and early neonatal morbidity for babies with breech presentation at term compared to vaginal breech delivery. When planning a breech vaginal birth, appropriate patient selection and skilled personnel in breech delivery are key in achieving good neonatal outcomes. In appropriately selected patients and skilled personnel in vaginal breech deliveries, perinatal mortality is between 0.8 and 1.7/1000 for planned vaginal breech birth and between 0 and 0.8/1000 for planned cesarean section. 18 , 19 The choice of the route of delivery should therefore be made considering the availability of skilled personnel in conducting breech vaginal delivery; providing competent newborn care; conducting rapid cesarean delivery should need arise and performing ECV if desired; availability of resources for continuous intrapartum fetal heart rate and labor monitoring; patient clinical features, preferences and values; and institutional policies, protocols and resources.
Four approaches to the management of breech presentation are shown in Figure 4: 8
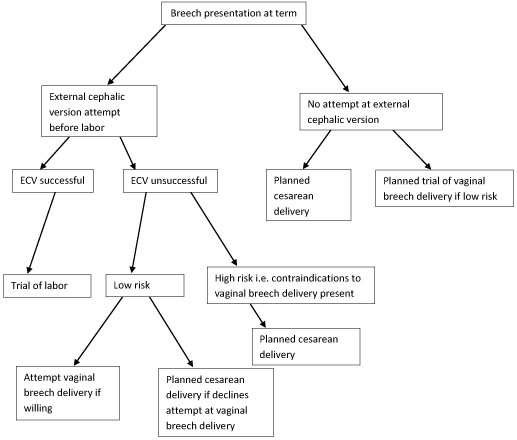
Management of breech presentation. ECV, external cephalic version.
The options available are:
- Attempting external cephalic version (ECV) before labor with a trial of labor if successful and conducting cesarean delivery if unsuccessful.
- Footling or kneeling breech presentation;
- Fetal macrosomia;
- Fetal growth restriction;
- Hyperextended fetal neck in labor;
- Previous cesarean delivery;
- Unavailability of skilled personnel in breech delivery;
- Other contraindications to vaginal delivery like placenta previa, cord prolapse;
- Fetal anomaly that may interfere with vaginal delivery like hydrocephalus.
- Planned cesarean delivery without an attempt at ECV.
- Planned trial of vaginal breech delivery in patients with favorable clinical characteristics for vaginal delivery without an attempt at ECV.
All the four approaches should be discussed in detail with the patient, and in light of all the considerations highlighted above, a safe plan of care agreed upon by both the patient and the clinician in good time.
Transverse and oblique lie
If a diagnosis of transverse/oblique fetal lie is made before onset of labor and there are no contraindications to vaginal birth or ECV, ECV can be attempted at 37 weeks' gestation. If the malpresentation recurs, further attempts at ECV can be made at 38–39 weeks with induction of labor if successful.
ECV can also be attempted in early labor with intact fetal membranes and no contraindications to vaginal birth.
If ECV is declined or is unsuccessful, then planned cesarean section should be arranged after 39 weeks' gestation.
MANAGEMENT OF LABOR AND DELIVERY
Skills to conduct vaginal breech delivery are very important as there are women who may opt for planned vaginal breech birth and even among those who choose planned cesarean delivery, about 10% may go into labor and end up with a vaginal breech delivery. 17 Some implications of cesarean delivery such as need for repeat cesarean deliveries, placental attachment disorders and uterine rupture make vaginal birth more desirable to some individuals. In addition, vaginal birth has advantages such as affordability, quicker recovery, shorter hospital stay, less complications and is more favorable for resource poor settings.
In appropriately selected women, planned vaginal breech birth is not associated with any significant long-term neurological morbidity. Regardless of planned mode of birth, cerebral palsy occurs in approximately 1.5/1,000 breech births, and abnormal neurological development occurs in approximately 3/100. 18 Careful patient selection is very important for good outcomes and it is generally agreed that women who choose to undergo a trial of labor and vaginal breech delivery should be at low risk of complications from vaginal breech delivery. Some contraindications to vaginal breech delivery have been highlighted above.
Women with breech presentation near term, pre- or early-labor ultrasound should be performed to assess type of breech presentation, flexion of the fetal head and fetal growth. If a woman presents in labor and ultrasound is unavailable and has not recently been performed, cesarean section is recommended. Vaginal breech deliveries should only take place in a facility with ability and resources readily available for emergency cesarean delivery should the need arise.
Induction of labor may be considered in carefully selected low-risk women. Augmentation of labor is controversial as poor progress of labor may be a sign of cephalo-pelvic disproportion, however, it may be considered in the event of weak contractions. A cesarean delivery should be performed if there is poor progress of labor despite adequate contractions. Labor analgesia including epidural can be used as needed.
Vaginal breech delivery should be conducted in a facility that is able to carry out continuous electronic fetal heart rate monitoring sufficient personnel to monitor the progress of labor. From the term breech trial, 17 the commonest indications for cesarean section are poor progress of labor (50%) and fetal distress (29%). There is an increased risk of cord compression which causes variable decelerations. Since the fetal head is at the fundus where contractions begin, the incidence of early decelerations arising from head compression is also higher. Due to the irregular contour of the presenting part which presents a high risk of cord prolapse, immediate vaginal examination should be undertaken if membranes rupture to rule out cord prolapse. The frequency of cord prolapse is 1% with frank breech and more than 10% in footling breech. 8
Fetal blood sampling from the buttocks is not recommended. A passive second stage of up to 90 minutes before active pushing is acceptable to allow the breech to descend well into the pelvis. Once active pushing commences, delivery should be accomplished or imminent within 60 minutes. 18
During planned vaginal breech birth, a skilled clinician experienced in vaginal breech birth should supervise the first stage of labor and be present for the active second stage of labor and delivery. Staff required for rapid cesarean section and skilled neonatal resuscitation should be in-hospital during the active second stage of labor.
The optimum maternal position in second stage has not been extensively studied. Episiotomy should be undertaken as needed and only after the fetal anus is visible at the vulva. Breech extraction of the fetus should be avoided. The baby should be allowed to deliver spontaneously with maternal effort only and without any manipulations at least until the level of the umbilicus. A loop of the cord is then pulled to avoid cord compression. After this point, suprapubic pressure can be applied to facilitate flexion of the fetal head and descent.
Delay of arm delivery can be managed by sweeping them across the face and downwards towards in front of the chest or by holding the fetus at the hips or bony pelvis and performing a 180° rotation to deliver the first arm and shoulder and then in the opposite direction so that the other arm and shoulder can be delivered i.e., Lovset’s maneuver (Figure 5).
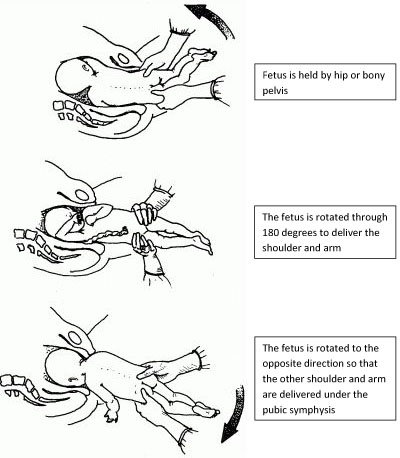
Lovset’s maneuver. Reproduced from WHO 2006 , 1 with permission .
The fetal head can deliver spontaneously or by the following maneuvers:
- Turning the body to the floor with application of suprapubic pressure to flex the head and neck.
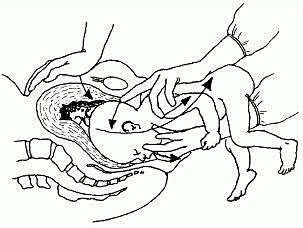
Mauriceau-smellie-veit maneuver . Reproduced from WHO 2003, 14 with permission.
- By use of Piper’s forceps.
- Burns-Marshall maneuver where the baby’s legs and trunk are allowed to hang until the nape of the neck is visible at the mother’s perineum so that its weight exerts gentle downwards and backwards traction to promote flexion of the head. The fetal trunk is then swept in a wide arc over the maternal abdomen by grasping both the feet and maintaining gentle traction; the aftercoming head is slowly born in this process.
If the above methods fail to deliver the fetal head, symphysiotomy and zavanelli maneuver with cesarean section can be attempted. Duhrssen incisions where 1–3 full length incisions are made on an incompletely dilated cervix at the 6, 2 and 10 o’clock positions can be done especially in preterm.
Face presentation
The diagnosis of face presentation is made during vaginal examination where the presenting portion of the fetus is the fetal face between the orbital ridges and the chin. At diagnosis, 60% of all face presentations are mentum anterior, 26% are mentum posterior and 15% are mentum transverse. Since the submentobregmatic (face presentation) and suboccipitobregmatic (vertex presentation) have the same diameter of 9.5 cm, most face presentations can have a successful vaginal birth and not necessarily require cesarean section delivery. 6 The position of a fetus in face presentation helps in guiding the management plan. Over 75% of mentum anterior presentations will have a successful vaginal delivery, whereas it is impossible to have a vaginal birth in mentum posterior position unless it converts spontaneously to mentum anterior position. In mentum posterior position the neck is maximally extended and cannot extend further to deliver beneath the symphysis pubis (Figure 7).
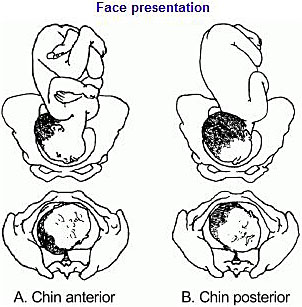
Face presentation. Reproduced from WHO 2003, 14 with permission.
As in breech management, face presentation also requires continuous fetal heart rate monitoring, since abnormalities of fetal heart rate are more common. 5 , 6 In one study , 20 only 14% of pregnancies had normal tracings, 29% developed variable decelerations and 24% had late decelerations. Internal fetal heart rate monitoring with an electrode is not recommended, as it may cause facial and ophthalmic injuries if incorrectly placed. Labor augmentation and cesarean sections are performed as per standard obstetric indications. Vacuum and midforceps delivery should be avoided, but an outlet forceps delivery can be attempted. Attempts to manually convert the face to vertex or to rotate a posterior position to a more favorable anterior mentum position are rarely successful and are associated with high fetal morbidity and mortality, and maternal morbidity, including cord prolapse, uterine rupture, and fetal cervical spine injury with neurological impairment.
Brow presentation
The diagnosis of brow presentation is made during vaginal examination in second stage of labor where the presenting portion of the fetal head is between the orbital ridge and the anterior fontanel.
Brow presentation may be encountered early in labor, but is usually a transitional state and converts to a vertex presentation after the fetal neck flexes. Occasionally, further extension may occur resulting in a face presentation. The majority of brow presentations diagnosed early in labor convert to a more favorable presentation and deliver vaginally. Once brow presentation is confirmed, continuous fetal heart rate monitoring is necessary and labor progress should be monitored closely in order to pick any signs of abnormal labor. Since the brow diameter is large (13.5 cm), persistent brow presentation usually results in prolonged or arrested labor requiring a cesarean delivery. Labor augmentation and instrumental deliveries are therefore not recommended.
CESAREAN DELIVERY
This is an option for women with breech presentation at term to choose cesarean section as their preferred mode of delivery, for those with unsuccessful ECV who do not want to attempt vaginal breech delivery, have contraindications for vaginal breech delivery or in the event that there is no available skilled personnel to safely conduct a vaginal breech delivery. Women should be given enough and accurate information about pros and cons for both planned cesarean section and planned vaginal delivery to help them make an informed decision.
Since the publication of the term breech trial, 17 , 19 there has been a dramatic global shift from selective to planned cesarean delivery for women with breech presentation at term. This study revealed that planned cesarean section carried a reduced perinatal mortality and early neonatal morbidity for babies with breech presentation at term compared to planned vaginal birth (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.19–0.56). The cesarean delivery rate for breech presentation is now about 70% in European countries, 95% in the United States and within 2 months of the study’s publication, there was a 50–80% increase in rates of cesarean section for breech presentation in The Netherlands.
A planned cesarean delivery should be scheduled at term between 39–41 weeks' gestation to allow maximum time for spontaneous cephalic version and minimize the risk of neonatal respiratory problems. 8 Physical exam and ultrasound should be performed immediately prior to the surgery to confirm the fetal presentation. A detailed consent should be obtained prior to surgery and should include both short- and long-term complications of cesarean section and the alternatives of care that are available. The abdominal and uterine incisions should be sufficiently large to facilitate easy delivery. Thereafter, extraction of the fetus is similar to what is detailed above for vaginal delivery.
Cesarean section for face presentation is indicated for persistent mentum posterior position, mentum transverse and some mentum anterior positions where there is standard indication for cesarean section.
Persistent brow presentation usually necessitates cesarean delivery due to the large presenting diameter that causes arrest or protracted labor.
Transverse/oblique lie
Cesarean section is indicated for patients who present in active labor, in those who decline ECV, following an unsuccessful ECV or in those with contraindications to vaginal birth.
For dorsosuperior (back up) transverse lie, a low transverse incision is made on the uterus and an attempt to grasp the fetal feet with footling breech extraction is made. If this does not succeed, a vertical incision is made to convert the hysterotomy into an inverted T incision.
Dorsoinferior (back down) transverse lie is more difficult to deliver since the fetal feet are hard to grasp. An attempt at intraabdominal version to cephalic or breech presentation can be done if membranes are intact before the uterine incision is made. Another option is to make a vertical uterine incision; however, the disadvantage of this is the risk of uterine rupture in subsequent pregnancies.
PERINATAL OUTCOME
Availability of skilled neonatal care at delivery is important for good perinatal outcomes to facilitate resuscitation if needed for all fetal malpresentations. 8 All newborns born from fetal malpresentations require a thorough examination to check for possible injuries resulting from birth or as the cause of the malpresentation.
Neonates who were in face presentation often have facial edema and bruising/ecchymosis from vaginal examinations that usually resolve within 24–48 hours of life and low Apgar scores. Trauma during labor may cause tracheal and laryngeal edema immediately after delivery, which can result in neonatal respiratory distress and difficulties in resuscitative efforts.
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
- Diagnosis of unstable lie is made when a varying fetal lie is found on repeated clinical examination in the last month of pregnancy.
- Consider external version to correct lie if not longitudinal.
- Consider ultrasound to exclude mechanical cause.
- Inform woman of need for prompt admission to hospital if membranes rupture or when labor starts.
- If spontaneous rupture of membranes occurs, perform vaginal examination to exclude the presence of a cord or malpresentation.
- If the lie is not longitudinal in labor and cannot be corrected perform cesarean section.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Author(s) statement awaited.
Publishers’ note: We are constantly trying to update and enhance chapters in this Series. So if you have any constructive comments about this chapter please provide them to us by selecting the "Your Feedback" link in the left-hand column.
Online Study Assessment Option All readers who are qualified doctors or allied medical professionals can now automatically receive 2 Continuing Professional Development credits from FIGO plus a Study Completion Certificate from GLOWM for successfully answering 4 multiple choice questions (randomly selected) based on the study of this chapter. Medical students can receive the Study Completion Certificate only.
(To find out more about FIGO’s Continuing Professional Development awards programme CLICK HERE )
I wish to proceed with Study Assessment for this chapter
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience from our website. By using the website or clicking OK we will assume you are happy to receive all cookies from us.

- Pregnancy Week By Week
- Ovulation Calculator
Malpresentation and Malposition of the Fetus
A malpresentation or malposition of the fetus is when the fetus is in any abnormal position, other than vertex (head down) with the occiput anterior or posterior.
The following are considered malpresentations or malpositions:
Unstable lie
- Transverse presentation
- Oblique presentation
Face presentation
Brow presentation
Shoulder presentation
High head at term
- Prolapsed arm
The cause of a malpresentation can often not be clearly identified but it can be associated with the following:
- Preterm pregnancy
- Uterine anomalies
- Pelvic tumors eg f ibroids
- Placenta previa
- Grandmultiparty
- Contracted maternal pelvis
- Multiple gestation
- Too much amniotic fluyid (polyhydramnios)
- Short umbilical cord
- Fetal anomalies (e.g. anencephaly, hydro-cephalus)
- Abnormal fetal motor ability
There is an increased risk of neonatal and maternal complications associated with a malpresentation including neonatal and maternal trauma. If delivery is indicated, doing a cesarean delivery can significantly decrease the risk of complications.
Transverse lie
Oblique lie
In most cases of a normal vertex (head down) presentation, the baby's head is flexed with the chin close to the baby's chest. In these cases, the presenting part is the occiput, the posterior part of the baby's head. If the baby's head is more but not completekly extended then the baby's brow presents towards the vagina. A brow presentation is rare, maybe happening in about 1 in 2,000 births, more likely in pwomen with their second or subsequent births. A baby with a brow presentation can only deliver vaginally if the head flexes or extends.
Prolapsed arm
Our attorneys at Pediatric Malpractice Guide prioritize the health and well-being of our team and the community during this time. We are fully operational and equipped to work remotely to avoid any disruption in our ability to serve your needs. We continue to be available by phone and online to answer questions and provide free consultations. Please feel free to contact us 24/7.
Pediatric Malpractice & Birth Injury Resource Center Presented by Fronzuto Law Group
Recent news, abnormal birth presentation & position.
Published: March 14, 2021
Need Your Specific Questions Answered?
We're here to discuss your child's unique case anytime.
When a Baby is in the Wrong Position or Wrong Direction before Delivery
Two important considerations for a woman nearing the end of her pregnancy are the presentation and position of her baby. Fundamentally, the way that the fetus enters the birth canal and the direction that the fetus faces have a significant effect on labor and delivery. Abnormal position or presentation may mean that the pregnant woman is in for a long and difficult vaginal delivery or a C-section delivery . Regardless of the situation, doctors and healthcare providers must be at the ready to act whenever necessary. Even before birth occurs, proper assessments, planning, and a prepared action plan that can be modified if circumstances change are critical for the mother’s and baby’s protection.
Fetal Presentation vs. Position
First and foremost, it is important to understand the distinction between presentation and position when it comes to childbirth. A fetus exits the birth canal with one part of the body or another. This is known as the presentation. On the other hand, the direction in which the fetus is facing in the womb is its position. For instance, is the fetus facing toward the front or the mother’s body or her back? Both of these are key when determining the appropriate course of action prior to and during labor and delivery, as well as the right delivery method to protect the mother’s and child’s safety.
What is Considered Normal Position and Presentation and what is Abnormal?
The safest position for a fetus ready to deliver is facing the mother’s front of the body and the safest presentation is headfirst through the birth canal. When a fetus is headed down the birth canal feet, face, or shoulders first, the presentation is considered abnormal. Likewise, if the fetus is facing the mother’s back, the fetus’s position is considered abnormal. The least difficult delivery position and presentation is facing the mother’s back and proceeding down the birth canal headfirst, with the highest point of the head, or vertex, leading down the canal. Ideally, the fetus is also situated facing slightly right or left, with a tucked chin and arms crossing the chest. All other positions and presentations are considered abnormal.
When the Baby is Face Forward
When facing the wrong direction, the fetus’s face may be forced forward as it moves through the curvature of the mother’s pelvis and the vaginal canal. Thus, the headfirst presentation may be right, but the face forward position creates enhanced tension and pressure on the fetus’s stretched out neck, with the chin jutting far forward. Known as occiput posterior, this position typically requires instrument-assisted delivery with forceps or vacuum extractor , or surgical intervention by C-section. If a baby cannot be safely delivered with birth-assistance tools, a cesarean may be the only way to birth the fetus in this position.
Still another unsafe situation occurs when the fetus’s brow is angled first down the birth canal. In these cases, the neck can also be stretched like face forward presentation, as the chin is pressed upward. This may be the result of a misshapen pelvis, weak uterine muscles, multiple prior pregnancies, or polyhydramnios.
Meaning of Breech Presentation
Another abnormal presentation, breech births, are buttocks or feet first deliveries. In early pregnancy, a fetus is breech because the head is larger than the rest of the body and fits better into the largest and topmost part of the uterus. As the fetus’s body fills out in later pregnancy and in preparation for birth, it should right itself facing downward.
A breech birth increases the likelihood of serious injuries. If not addressed properly, the baby may suffer harm on the way out of the birth canal, but also before or after the baby is born. The delivery goes quickly and smoothly most often when the fetus’s head, the largest part of its body, makes its way through the birth canal first. As the birth canal widens to accommodate the size of the head, then the smaller remainder of the body can seamlessly follow under ordinary circumstances. Conversely, the larger head can become wedged in the birth canal when the smaller buttocks and feet go first. This situation is highly dangerous, as it may create enhanced pressure on the umbilical cord when the baby’s head gets stuck in the birth canal. A decrease in oxygen flow soon follows, placing the infant’s brain and their very life in jeopardy, as an oxygen-deprived brain can lead to brain damage and even fatality.
If the Shoulder gets Stuck behind the Pelvic Bone
Even if the fetus is in the right position and presentation, a baby’s shoulder can get stuck against the pelvic bone while traveling through the birth canal. This condition is called shoulder dystocia . While the baby’s head is delivering, the stuck shoulder then stretches the neck, risking major injury to the child. Not only that, but the delivery is stalled, and the fetus’s oxygen supply may be cut off , a common cause of brain damage.
Risk Factors for Abnormal Delivery Presentation
Although causes for a baby’s abnormal position or presentation in the womb are often unknown, some risk factors for abnormal presentation or position include:
- Too little or too much amniotic fluid
- A misshapen pelvis
- Uterine tumors
- Weak uterine muscles
- Placenta previa
- Pregnancy involving multiples (twins, triplets, or more)
Notably, some types of delivery presentations have particular, identified possible causes. For instance, beech presentation has been associated with fetal birth defects , premature labor , and abnormalities affecting the uterus, including fibroids. Breech presentation may likewise be caused by multiple fetuses, excess amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios), water on the baby’s brain ( hydrocephalus ), and placenta previa. In addition, a presenting with a transverse lie may be caused by weak uterine muscles, an abnormal uterus or narrow pelvis. Like other abnormal presentations, preterm labor, polyhydramnios, prior pregnancies, and placenta previa may also play a role in shoulder presentation. Additionally, shoulder dystocia occurs most often with large fetuses, long labors, quick labors, maternal obesity, and maternal diabetes .
Lastly, not all risks create both abnormal position and presentation. For instance, the fetus facing the mother’s front may occur even though the fetus is vertex down the canal. In other words, risk factors may create either an unusually positioned baby or an outside of the norm presentation before the baby is delivered. In both scenarios, it is essential for doctors to assess and properly determine which way the baby is set to leave the canal and whether their face is toward the mother’s spine or her abdomen.
How can they Tell which way your Baby is Positioned?
Since complications from abnormal presentation and position are life threatening, the first preventative practice is to assess each patient for risk factors, by checking the patient’s medical history for prior pregnancies, placenta previa, obesity, and diabetes. A physical exam, sonogram, or other prenatal tests may detect abnormalities in the shape of the uterus, position of the placenta, the amount of amniotic fluid, or a narrow pelvis, especially if a fetus appears large in later weeks of pregnancy. Ensuring that conditions like diabetes and obesity are treated is also important. In addition, through physical exam, sonogram, genetic testing, and other prenatal tests, birth assistants and medical personnel can assess whether the fetus has hydrocephalus or other conditions that affect fetal position or presentation. Further, rigorously checking for abnormal presentation or position starting in late term, around 36 weeks, at each doctor visit is crucial.
How do Doctors Handle Abnormal Birth Presentation?
If detected, a birthing mother may need a full spectrum care for emergency delivery by c-section, if necessary. Depending on the case, some deliveries are best handled by specialists who regularly perform complicated deliveries. In addition, physicians must be informed and experienced with various labor and delivery techniques and testing methods, including the mastery of birth assistance instruments, fetal monitoring, and advanced manipulation techniques to shift the fetal position.
When deciding the best course of action, it depends on the type of abnormality. For example, if the baby is breech, this requires repositioning if possible. On the other hand, if the fetus is face forward, it may reposition naturally or may not, in which case further action may be necessary. If possible, an experienced doctor may try to reposition the baby in utero or refer the patient to someone who can. They may also recommend the patient do specific exercises to try to turn the baby prior to the birth itself. Patients must be monitored carefully to ensure they are doing the exercises safely and that the unborn child is doing well. Assessing and timing of the next step is critical. In other positions, the physician and assisting personnel must be prepared for instrument delivery, cesarean section, and other appropriate medical interventions based on the baby’s position and presentation.
When dealing with a breech presentation, a mother has better chances of vaginal birth if the breech presentation is known before delivery, when a doctor can attempt to turn the fetus around in the womb. Also, if discovered early, a physician can take steps to prevent premature labor by the administration of medication. If unable to right the fetus’s presentation, the baby may have to be delivered by c-section to prevent brain damage or death. In the case of brow presentation, if the fetus does not re-adjust naturally, an obstetrician may resort to a c-section delivery. Similarly, if the fetus’s shoulder is first down the birth canal but the body is horizontal, a c-section generally results. If the fetus is transverse lying, the patient should be prepared for cesarean delivery and preparations made. Moreover, there are multiple ways to address shoulder dystocia, including specially-designed maneuvers and other methods. For instance, a doctor may cut the vaginal opening to widen it, known as an episiotomy, and try to maneuver the baby out. However, errors and inexperience with this risks damage to the arm or shoulder nerves or a broken arm or collarbone. Even after cutting and maneuvering, a c-section may still be necessary.
What can Happen in Delivery if the Baby is Abnormally Situated?
Once labor starts and the fetus is abnormally situated, complications may arise, such as premature membranes breaking , weak or extremely painful contractions, entering labor too soon, excessively long labor, uterine rupture, fetal distress , excessive bleeding after birth, and other dangerous complications, all of which risk the lives and overall health of the mother and the newborn. If such complications do occur, time is of the essence and can even save the infant or mother’s life. The reality is that after care for the mother and baby for bleeding, oxygen, and repairs to any injuries suffered during delivery must be immediate. Failure to act in a timely manner can cost someone their life; it equally amounts to medical malpractice. Still more, failing to detect the abnormal position or presentation before labor may be the clearest example of malpractice and the source of serious birth injuries or wrongful death for the mother or her child.
Ultimately, any missteps along the way can lead to devastating results, permanent neurological damage, cerebral palsy and conditions resulting from brain injury, hemorrhaging, or prove fatal. All medical professionals must perform their duties so as not to cause unnecessary injury or death to patients, nor to cause the unnecessary pain and suffering inevitably resulting from these events. Being unprepared, undereducated, overtired, or inexperienced is unacceptable, plain and simple. It may also be cause for liability.
If Someone Mishandled Your Fetal Abnormal Positioning, You Have Rights
If you would like to discuss a situation in which mismanagement of an abnormal birth position or presentation caused harm to you or someone you love, contact us now at 866-708-8617 for a free consultation. An attorney with extensive experience achieving compensation on behalf of those injured during birth throughout New Jersey, and consulting on these cases nationwide, is standing by to assist you.
- Abnormal Position and Presentation of the Fetus, Merck Manual
- Labour and Delivery Care Module: 8. Abnormal Presentations and Multiple Pregnancies
Categories: Birth Injury Factors
Get specialized advice about your situation
Free Case Evaluation
- Full Name *
- Describe your case *
Get your specific questions answered by completing our contact form
How do i know if my child has a pediatric malpractice case, how can i get help to pay for my child's medical bills, how long do i have to file a pediatric malpractice claim, get in touch..
- First Name *
- Last Name *
- Your Message *
A Trigger Tool to Detect Harm in Pediatric Inpatient Settings
Research published in the Journal Pediatrics found that 45 percent of pediatric patient medical errors resulting in harm were most likely preventable.
read full article here →

Face Presentation and Birth Injury
Normally, children are born head-first with the chin tucked towards the chest (vertex presentation). In a face presentation, the chin is not tucked and the neck is hyperextended. This can inhibit the engagement of the head and complicate the labor process. In some cases, a baby in face presentation can be delivered vaginally, but in other cases vaginal delivery is difficult and dangerous. Face presentation increases the risk of facial edema, skull molding, breathing problems (due to tracheal and laryngeal trauma), prolonged labor, fetal distress, spinal cord injuries, permanent brain damage, and neonatal death. Usually, medical staff conduct a vaginal examination to determine the position of the baby. If they suspect an abnormal presentation, they can confirm with an ultrasound and take action to properly handle the delivery of a baby in the face presentation. This includes additional monitoring and in some cases requires a C-Section. Because ventilation issues are more common in babies with face presentation, staff should be ready to intubate immediately after delivery (1).
Risk factors and causes of face presentation
Conditions that may increase the likelihood of a face presentation include the following (1, 2, 3, 4):
- Prematurity
- Very low birth weight
- Fetal macrosomia (large baby)
- Cephalopelvic disproportion, or CPD (a mismatch in size between the mother’s pelvis and the baby’s head)
- Anencephaly (a birth defect in which the baby is missing part of the brain and skull)
- Severe hydrocephalus with enlargement of the head
- Anterior neck mass
- Multiple nuchal cords (umbilical cord wrapped around baby’s neck more than once)
- Maternal pelvis abnormalities
- Maternal obesity
- Multiparity (the mother has previously given birth)
- Polyhydramnios (too much amniotic fluid)
- Previous cesarean delivery
Diagnosing face presentation
Face presentation is diagnosed late in the first or second stage of labor by vaginal examination. The distinctive facial features of the chin, mouth, nose, and cheekbones can be felt. Face presentation is sometimes confused with breech presentation (because both are characterized by soft tissues with an orifice), which is why it is imperative that a very skilled physician be present during any potentially risky delivery or malpresentation . Diagnosis can be confirmed by an ultrasound, which reveals a deflexed/hyperextended neck (1).
Face presentation and delivery
There are three types of face presentation:
- Mentum anterior (MA) . In this position, the chin is facing the front of the mother, and will be the presenting part of the face. Babies in mentum anterior position are usually delivered vaginally, although in some cases a C-section may be necessary.
- Mentum posterior (MP) . In this position, the chin is facing the mother’s back. The baby’s head, neck, and shoulders enter the pelvis at the same time, and the pelvis is usually not large enough to accommodate this (however, the baby may spontaneously rotate into mentum anterior position) . Typically, a C-section is indicated, but there are certain circumstances under which vaginal delivery may be attempted (e.g. the mother is multiparous, the infant in face presentation is relatively small compared to her other children, fetal monitoring is reassuring, and the baby is progressing in labor). Regardless, the medical team should be prepared to perform a prompt C-section if there are any complications.
- Mentum transverse (MT) . In this position, the baby’s chin is facing the side of the birth canal. Doctors may recommend a trial of labor under certain circumstances, but they should promptly proceed to a C-section if there are issues. If labor is progressing and the fetal heart monitor is reassuring when face presentation is present, physician intervention may not be necessary since many MP and MT positions convert to MA. Oxytocin (Pitocin) augmentation may be used in a face presentation with a normal fetus and abnormally slow progress, as long as fetal heart rate patterns remain reassuring (although there are certain risks associated with this drug, including uterine tachysystole ). Of course, in any face presentation, if progress in dilation and descent ceases despite adequate contractions, delivery must occur by C-section.
There is an increased risk of trauma to the baby when the face presents first, and the physician should not internally manipulate (try to rotate) the baby. In addition, the physician must not use vacuum extractors or manual extraction (grasping the baby with hands) to pull the baby from the uterine cavity. Furthermore, midforceps ( forcep extraction when the baby’s station is above +2 cm, but the head is engaged) should never be used. Outlet forceps should only be used by experienced physicians who understand the circumstances under which this is appropriate (1).
Abnormalities of the fetal heart rate occur more frequently with face presentation. In one study, 59% of infants in face presentation had variable heart decelerations, and 24% had late decelerations. Of the babies who were born live, 37% had 1-minute Apgar scores lower than 7, and 13% had 5-minute Apgar scores lower than 7. The majority of the low 5-minute Apgar scores were babies that had been in mentum posterior position (5).
For these reasons, it is crucial that babies are continuously monitored during labor, ideally with an external heart monitoring device. An internal device may cause facial or eye injuries if improperly placed. If internal monitoring is needed, the electrode should be cautiously placed over a bony structure such as the forehead, jaw or cheekbone to minimize the risk of trauma (1).
It is always critical that doctors obtain a mother’s informed consent , which means discussing delivery options (vaginal, C-section, enhanced with oxytocin, etc.) with her and explaining the potential risks and benefits of each. Failure to do so constitutes negligence.
Complications and side effects of face presentation
Complications associated with face presentation include the following:
- Prolonged labor
- Facial trauma
- Facial edema (fluid build up in the face, often caused by trauma)
- Skull molding (abnormal head shape that results from pressure on the baby’s head during childbirth)
- Respiratory distress /difficulty in ventilation due to airway trauma and edema
- Spinal cord injury
- Abnormal fetal heart rate patterns
- Low Apgar score
A baby may be at increased risk of complications if forceps or oxytocin are used during labor. Forceps can cause traumatic injury to the head, and oxytocin can deprive a baby of oxygen due to uterine tachysystole/hyperstimulation (strong, frequent contractions). Hyperstimulation increases pressure on the blood vessels in the womb, which can deprive the baby of oxygen-rich blood.
Trauma to the head and decreased oxygenation can cause permanent brain damage, such as hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) and cerebral palsy (CP) , as well as fetal deaths.
Our team is here to help.
Call ABC Law Centers today to secure your child’s care and reclaim their future.
Standards of care, medical malpractice, and face presentation
Informed consent must be given during all medical procedures. This means that when a mother has a baby with face presentation, she must be given the option of a C-section versus a vaginal birth. One of the reasons a mother may opt for a C-section is to avoid the extensive facial bruising/trauma that is common in babies with face presentation. In addition to thoroughly explaining the risks and benefits of each type of delivery method, the physician must explain and obtain consent from the mother if forceps or oxytocin are used.
Because there are many complications associated with face presentation, it is essential that the baby be closely monitored and that delivery is handled by a physician with experience in this area. Furthermore, the physician must quickly proceed to a C-section delivery if there are any signs of fetal distress , labor is not progressing, or the baby fails to convert (rotate) to MA position. In addition, once a face presentation is diagnosed, the physician must check for pelvic adequacy. When the pelvis is inadequate (contracted/small), a C-section is recommended (1).
Since respiratory problems can occur in babies with face presentation, equipment and staff to perform intubation of the baby (placement of a breathing tube) should be readily available at the time of delivery.
Failure to follow any of these standards of care is negligence. If this negligence results in injury to the baby, it is medical malpractice .
Trusted birth injury attorneys
If your baby has HIE, cerebral palsy, periventricular leukomalacia (PVL), developmental delays , a seizure disorder , or any other birth injury , we may be able to help. Unlike other firms, the attorneys at ABC Law Centers (Reiter & Walsh, P.C.) focus solely on birth injury cases and have been helping children throughout the nation since 1997. During your free legal consultation, our attorneys will discuss your case with you, determine if negligence caused your loved one’s injuries, identify the negligent party, and discuss your legal options with you. Moreover, you pay nothing throughout the entire legal process unless we win or favorably settle your case.
“Reiter and Walsh goes above and beyond the norm in getting their clients the best possible results. Each client is treated with respect and compassion, and they are truly sensitive to what it means to help a family whose child has been injured.” -Client review from 11/23/2015
- Free Case Review
- Available 24/7
- No Fee Unless We Win
Featured Videos
Testimonial from keziah’s family, posterior position, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (hie).
Featured Testimonial
What Our Clients Say…
After the traumatic birth of my son, I was left confused, afraid, and seeking answers. We needed someone we could trust and depend on . ABC Law Centers was just that.
Helpful resources
More about our firm.
- Meet our birth injury attorneys
- Meet our in-house medical staff
- Verdicts and settlements
- Testimonials
- Julien, S., Lockwood, C. J., & Barss, V. A. (2014). Face and brow presentations in labor. Up to date.
- Duff, P. (1981). Diagnosis and management of face presentation. Obstetrics and gynecology, 57(1), 105-112.
- S. BHAL NJ DAVIES T. CHUNG, P. (1998). A population study of face and brow presentation. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 18(3), 231-235.
- Shaffer, B. L., Cheng, Y. W., Vargas, J. E., Laros Jr, R. K., & Caughey, A. B. (2006). Face presentation: predictors and delivery route. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology, 194(5), e10-e12.
- Benedetti, T. J., Lowensohn, R. I., & Truscott, A. M. (1980). Face presentation at term. Obstetrics and gynecology, 55(2), 199-202.
The above information is intended to be an educational resource. It is not meant to be, and should not be interpreted as, medical advice.
Over $350 Million Recovered
In Verdicts, Settlements, & Judgements
$4.75 Million
$3.9 Million
$5.85 Million
Awards & Memberships
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
malpresentation
Medical Definition of malpresentation
Dictionary entries near malpresentation.
malpractice
malrotation
Cite this Entry
“Malpresentation.” Merriam-Webster.com Medical Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/malpresentation. Accessed 20 May. 2024.
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, the words of the week - may 17, birds say the darndest things, a great big list of bread words, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), games & quizzes.

A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs)
- Data and Statistics on FASDs
- FASD Resources
- Stories: Living with FASDs
- FASDs: Online Trainings and Resources
About Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs)
- FASDs are a group of conditions that can occur in a person who was exposed to alcohol before birth.
- FASDs can have lifelong effects, including problems with behavior and learning as well as physical problems.

Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) are a group of conditions that can occur in a person exposed to alcohol before birth. These conditions can affect each person in different ways and can range from mild to severe. People with FASDs can have lifelong effects, including problems with behavior and learning as well as physical problems. FASDs are preventable if a developing baby is not exposed to alcohol.
Signs and symptoms
A person with an FASD might have:
Behavioral issues
- Hyperactive behavior
- Difficulty with attention
- Poor reasoning and judgment skills
Learning challenges
- Poor memory
- Learning disabilities
- Speech and language delays
- Intellectual disability or low IQ
- Difficulty in school (especially with math)
Physical problems
- Low body weight
- Poor coordination
- Problems with the heart, kidneys, or bones
- Shorter-than-average height
- Vision or hearing problems
- Small head size
- Sleep and sucking problems as a baby
- Abnormal facial features, such as a smooth ridge between the nose and upper lip (this ridge is called the philtrum)
FASDs can occur when a person is exposed to alcohol before birth. Alcohol in the mother's blood passes to the baby through the umbilical cord.
There is no known safe amount of alcohol during pregnancy or when trying to get pregnant. There is also no safe time to drink during pregnancy. Alcohol can cause problems for a developing baby throughout pregnancy, including before a woman knows she's pregnant. All types of alcohol are equally harmful, including all wines and beer.
Reducing risk
To prevent FASDs, a woman should avoid alcohol if she is pregnant or might be pregnant. This is because a woman could get pregnant and not know for up to 4 to 6 weeks.
It is never too late to stop alcohol use during pregnancy. Because brain growth takes place throughout pregnancy, stopping alcohol use will improve the baby's health and well-being.
Different FASD diagnoses are based on particular symptoms and include:
Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS): FAS represents the most involved end of the FASD spectrum. People with FAS have central nervous system (CNS) problems, minor facial features, and growth problems. People with FAS can have problems with learning, memory, attention span, communication, vision, or hearing. They might have a mix of these problems. People with FAS often have a hard time in school and trouble getting along with others.
Alcohol-related neurodevelopmental disorder (ARND): People with ARND might have intellectual disabilities and problems with behavior and learning. They might do poorly in school and have difficulties with math, memory, attention, judgment, and poor impulse control.
Alcohol-related birth defects (ARBD): People with ARBD might have problems with the heart, kidneys, or bones or with hearing. They might have a mix of these.
Neurobehavioral disorder associated with prenatal alcohol exposure (ND-PAE): A child or youth with ND-PAE will have problems in three areas: (1) thinking and memory, where the child may have trouble planning or may forget material he or she has already learned, (2) behavior problems, such as severe tantrums, mood issues (for example, irritability), and difficulty shifting attention from one task to another, and (3) trouble with day-to-day living, which can include problems with bathing, dressing for the weather, and playing with other children. In addition, to be diagnosed with ND-PAE, the mother of the child must have consumed more than minimal levels of alcohol before the child's birth (defined as more than 13 alcoholic drinks per month of pregnancy or more than 2 alcoholic drinks in one sitting).
Areas evaluated for FASD diagnoses
The term FASDs is not meant for use as a clinical diagnosis. If your child is diagnosed with an FASD, the diagnosis will be for a specific condition under the umbrella of FASDs, as listed above.
Diagnosing FASDs can be hard because there is no medical test, like a blood test, for these conditions. And other disorders, such as ADHD (attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder) and Williams syndrome, have some symptoms like FAS.
To diagnose FASDs, healthcare providers look for:
- Prenatal alcohol exposure, although confirmation is not required for diagnosis
- Central nervous system problems (e.g., small head size, problems with attention and hyperactivity, poor coordination)
- Lower-than-average height, weight, or both
- Abnormal facial features (e.g., smooth ridge between nose and upper lip)
If you're concerned
If you think there could be a problem, ask your healthcare provider for a referral to a specialist (someone who knows about FASDs). Specialists could be a developmental pediatrician, child psychologist, or clinical geneticist. In some cities, there are clinics whose staff members have special training in diagnosing and treating children with FASDs. To find healthcare providers and clinics in your area visit the National and State Resource Directory from FASD United (formerly NOFAS).
At the same time as you ask your healthcare provider for a referral to a specialist, call your state or territory's early intervention program. Request a free evaluation to find out if your child can get services to help. This is sometimes called a Child Find evaluation. You do not need to wait for a healthcare provider's referral or a medical diagnosis to make this call.
Where to call for a free evaluation from the state depends on your child's age:
Younger than 3 years old: Call your state or territory's early intervention program . Say, "I have concerns about my child's development. I would like to have my child evaluated to find out if they are eligible for early intervention services."
3 years old or olde r : Contact your local public school system. Even if your child is not old enough for kindergarten or enrolled in a public school, call your local elementary school or board of education. Ask to speak with someone who can help you have your child evaluated.
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) are a group of conditions that can occur in a person who was exposed to alcohol before birth. FASDs are preventable if a baby is not exposed to alcohol before birth.
For Everyone
Health care providers.
At revered Black school, Biden leans into faith and tells grads he hears voices of dissent

ATLANTA – President Joe Biden on Sunday warned graduates at one of the country's most revered African American academic institutions of "extremist forces aligned against the meaning and message of Morehouse" College in a commencement address that sought to lay out the stakes of the 2024 election.
"Graduates, this is what we're up against," Biden said during a 27-minute speech that leaned heavily into themes of faith and democracy in an appeal to Black voters. "They peddle a fiction, a character about what being a man is about − tough talk, abusing power, bigotry. Their idea of being a man is toxic."
"But that's not you. It's not us," he said.
Biden's remarks to the 414 graduates at Morehouse , an all-male historically Black college in Atlanta, came as he is struggling to unite Black voters , particularly Black men, around his candidacy. Many Morehouse students and faculty criticized Biden's participation when it was announced because of his support for Israel's war in Gaza.
"In a democracy, we debate dissent about America's role in the world. I want to say this very clearly: I support peaceful, nonviolent protest," Biden said on Sunday in response to the complaints. "Your voices should be heard. I promise you, I hear them."
Prep for the polls: See who is running for president and compare where they stand on key issues in our Voter Guide
No major disruptions, but peaceful protests target Biden
Although there were no major disruptions during Biden's speech, a few students walked out when Biden received an honorary Morehouse degree. More than a dozen graduates and at least three faculty members wore keffiyehs, while one student entered the ceremony draped in a Palestinian flag.
As Biden delivered his address, at least one female faculty member stood in the opposite direction, her fist raised, in a sign of protest.
Biden, wearing a maroon gown at the outdoor ceremony, said his administration is "working around the clock for more than just one cease-fire," but also to "bring the region together." He reiterated his support for a two-state solution in which Israelis and Palestinians live in peace.
"This is one of the hardest, most complicated problems in the world. There's nothing easy about it," Biden said. "I know it angers and frustrates many of you, including my family, but most of all, I know it breaks your heart. It breaks mine as well."
Biden added that leadership is about "fighting through the most intractable problems" to "find a solution by doing what you believe is right, even when it's hard and lonely."
About a mile away, pro-Palestinian protesters held a rally organized under the banner of "Say No to Genocide Joe Speaking at Morehouse." Morehouse's valedictorian also raised Israel's war in Gaza during his remarks before Biden took the lectern.
"It is my stance as a Morehouse man – nay as a human being – to call for an immediate and the permanent cease-fire in the Gaza Strip," graduating senior DeAngelo Jeremiah Fletcher said, with Biden sitting just steps behind him. Biden applauded in response.
Biden touts record with Black voters
Polling shows Biden is vastly underperforming his 2020 performance among Black voters, a reliably Democratic constituency, as some drift to Donald Trump, the former president and presumptive Republican nominee.
A New York Times/Siena College poll of six battleground states, including Georgia, found Biden has support from 60% of Black voters and Trump, while Trump is backed by 20% of Black voters. Biden won Black voters in the 2020 election by a 87%-12% margin, according to exit polls.
Ahead of Biden's arrival, Anwar Karim, a sophomore studying film at Morehouse and a member of Atlanta University Center Students for Justice in Palestine, told USA TODAY he was disappointed in his school’s choice of commencement speaker. He also decried Morehouse’s decision to award Biden an honorary degree, which is typically awarded to the school’s commencement speaker after a faculty vote.
“Morehouse College is dedicated to producing men of consequence who lead lives of service and leadership, and I just have to beg the question, when it comes to Biden, what is an example of his leadership?” Karim said Friday.
Biden commits to showing 'democracy is still the way'
In his speech, Biden touted his presidency as one that has delivered to Black Americans, pointing to efforts to invest in Black families and communities, cut child poverty, expand work opportunities, reduce prescription drug prices and cut student loan debt. He called out the "poison of white supremacy" and "systemic racism."
He said he is committed to "show that democracy, democracy, democracy is still the way," even in the face of inequality for Black Americans.
"What is democracy if Black men are being killed in the street? What is democracy if the trail of broken promises still leave Black communities behind?" Biden said. "What is democracy if you have to be ten times better than anyone else to get a fair shot? Most of all, what does it mean, as you've heard before, to be a Black man who loves his country even if it doesn't love him back in equal measure?"
Biden railed against new voting restrictions in Georgia and the "constant attacks on Black election workers." He also said those who stormed the U.S. Capitol on Jan. 6, 2021 "are called patriots by some," a clear reference to Trump.
“Not in my house," Biden said.
In the days leading up to his Morehouse visit, the White House focused on Black outreach. Biden met on Thursday with plaintiffs of the landmark Brown v. Board of Education Supreme Court decision, on the 70th anniversary of the dismantling of the "separate but equal" precedent. On Friday, Biden met with leaders of the "Divine Nine" HBCU sororities and fraternities.
More: In a nod to history, Biden meets with Brown v. Board of Education families
In Atlanta on Saturday, Biden spoke to Morehouse alumni and others at a campaign event at Mary Mac's Tea Room. "The fact is, this election, lots at stake, lots at stake. It's not about me. It's about the alternative as well," Biden said. "My opponent's not a good loser, but he is a loser."
Introducing Biden, Morehouse President David Thomas said, "No administration in history, since the inception of historically Black colleges and universities, has invested more in our institutions than the Biden administration."
"And if you look at his policies, it is very clear that those investments are not charity," Thomas said.
Biden, 81, closed his remarks with a reference to his age, a liability that has hung over his reelection. When he started his political career, Biden said he was told he was "too young." Now he hears he's "too old."
"Whether you're young or old, I know what endures: The strength and wisdom of faith endures. And my challenge to you is to still keep the faith as long as you can," Biden said. "Together we're capable of building a democracy worthy of our dreams."
State Government websites value user privacy. To learn more, view our full privacy policy .
Secure websites use HTTPS certificates. A lock icon or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the official website.

2024 SUN Bucks Webinar Presentation for Community Stakeholders
2024 SUN Bucks Webinar Presentation for Community Stakeholders.pdf

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Compound presentation means that a fetal hand is coming out with the fetal head. This is a problem because: The amount of baby that must come through the birth canal at one time is increased. There is increased risk of mechanical injury to the arm and shoulder, including fractures, nerve injuries and soft tissue injury.
Toward the end of pregnancy, the fetus moves into position for delivery. Normally, the presentation is vertex (head first), and the position is occiput anterior (facing toward the pregnant patient's spine) with the face and body angled to one side and the neck flexed. Abnormal presentations include face, brow, breech, and shoulder.
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.. In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.. Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor.
Abnormal Fetal Lie. If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted - ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation. ECV is the manipulation of the fetus to a cephalic presentation through the maternal abdomen. It has an approximate success rate of 50% in primiparous women and 60% in multiparous women.
The term presentation describes the leading part of the fetus or the anatomical structure closest to the maternal pelvic inlet during labor. The presentation can roughly be divided into the following classifications: cephalic, breech, shoulder, and compound. Cephalic presentation is the most common and can be further subclassified as vertex, sinciput, brow, face, and chin. The most common ...
Occiput or cephalic anterior: This is the best fetal position for childbirth. It means the fetus is head down, facing the birth parent's spine (facing backward). Its chin is tucked towards its chest. The fetus will also be slightly off-center, with the back of its head facing the right or left. This is called left occiput anterior or right ...
The Trusted Provider of Medical Information since 1899
8.1 Normal and abnormal presentations 8.1.1 Vertex presentation. In about 95% of deliveries, the part of the fetus which arrives first at the mother's pelvic brim is the highest part of the fetal head, which is called the vertex (Figure 8.1).This presentation is called the vertex presentation.Notice that the baby's chin is tucked down towards its chest, so that the vertex is the leading ...
Malpresentation. Malposition. Usually the fetal head engages in the occipito-anterior position (more often left occipito-anterior (LOA) rather than right) and then undergoes a short rotation to be directly occipito-anterior in the mid-cavity. Malpositions are abnormal positions of the vertex of the fetal head relative to the maternal pelvis.
Causes and Treatments Failure to Progress (Prolonged Labor) Abnormal Presentation. Umbilical Cord. Umbilical Cord Compression. 7 min read. A pregnancy that has progressed without any apparent ...
When abnormal presentation or lie occurs in a twin gestation, management includes a greater range of options. The conversion of a backup transverse second twin, either by internal or external version at the time of delivery, is an option for the experienced clinician. ... She likely has heard, at least peripherally, that a breech baby means a ...
Summary. Labor and delivery can be complicated by multiple factors: prolonged stages of labor can lead to active-phase labor arrest, obstructed labor can occur due to mechanical reasons (e.g., fetal malpresentation ), abnormal rupture of membranes can increase the risk of chorioamnionitis and neonatal sepsis, and umbilical cord complications ...
This means the labor does not progress as fast as it should. This could happen with a big baby, a baby in a breech position (buttocks down), or other abnormal presentation, or with a uterus that ...
Malpresentation can mean your baby's face, brow, buttocks, foot, back, shoulder, arms or legs or the umbilical cord are against the cervix. It's safest for your baby's head to come out first. If any other body part goes down the birth canal first, the risks to you and your baby may be higher. Malpresentation increases the chance that you ...
The incidence of breech presentation is 20-25% of fetuses at <28 weeks, but only 7-16% at 32 weeks, and only 3-4% at term. 2, 3. Face and brow presentation are uncommon. Their prevalence compared with other types of malpresentations are shown below. 4. Occiput posterior - 1/19 deliveries;
Abnormal fetal motor ability; There is an increased risk of neonatal and maternal complications associated with a malpresentation including neonatal and maternal trauma. If delivery is indicated, doing a cesarean delivery can significantly decrease the risk of complications. Unstable lie Breech Transverse lie Oblique lie Face presentation
In these cases, abnormal presentations may place the baby at risk of experiencing umbilical cord problems and/or a birth trauma (1). Types of abnormal fetal positions and presentations include the following. We'll cover each in more detail on this page. ... Limb presentation during childbirth means that the part of the baby's body that ...
Abnormal position or presentation may mean that the pregnant woman is in for a long and difficult vaginal delivery or a C-section delivery. Regardless of the situation, doctors and healthcare providers must be at the ready to act whenever necessary. Even before birth occurs, proper assessments, planning, and a prepared action plan that can be ...
A normal fetal lie is an ideal position for labor and baby delivery in which the baby is head-down with the chin tucked into its chest. The back of the head is positioned so that it is ready to enter the pelvis. The fetus faces the mother's back, called cephalic presentation, and the babies mostly settle in this position by 32 to 36 weeks of ...
An abnormal position or presentation also means that the pregnant woman is in for a difficult or long vaginal delivery or a cesarean delivery. Regardless of the situation and position, doctors and healthcare providers must be prepared to act whenever necessary. ... The abnormal presentations incorporate face and brow, followed by breech and ...
Informed consent must be given during all medical procedures. This means that when a mother has a baby with face presentation, she must be given the option of a C-section versus a vaginal birth. One of the reasons a mother may opt for a C-section is to avoid the extensive facial bruising/trauma that is common in babies with face presentation.
The meaning of MALPRESENTATION is abnormal presentation of the fetus at birth.
abnormal presentation: Any part of the baby that presents to the birth canal other than the crown of its head (cephalic presentation). Examples Breech, brow, face, and shoulder presentations
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Explore Topics ... Abnormal facial features, such as a smooth ridge between the nose and upper lip (this ridge is called the philtrum)
As Biden delivered his address, at least one female faculty member stood in the opposite direction, her fist raised, in a sign of protest. Biden, wearing a maroon gown at the outdoor ceremony ...
OpenAi Chief Technology Officer Mira Murati introduced the company's product upgrades on stage and in a live-stream presentation on Monday. ... using text and "vision," meaning it can view ...
Secure websites use HTTPS certificates. A lock icon or https:// means you've safely connected to the official website. Utility Menu. NCDHHS COVID-19; NC.GOV; AGENCIES; JOBS; Main menu. ... 2024 SUN Bucks Webinar Presentation for Community Stakeholders. 2024 SUN Bucks Webinar Presentation for Community Stakeholders.pdf. PDF • 1.34 MB - May ...
Join us on May 21st, Tuesday, at 12 pm for a research lunch seminar with Mellon Sawyer Postdoctoral Fellow Nichole Nomura. Her presentation is titled "Effortful Reading: Word Embeddings and Meaning-making Strategies for Analogies". She will talk about how we read word embedding. Her project grows out of a literary-critical desire to interpret, rather than assess, word embeddings.